The Internet and Optical Networking at the IETF
|
|
|
- Bruno Stone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Internet and Optical Networking at the IETF COIN 2002 Scott Bradner Harvard University coin Syllabus u a short technical history of the Internet u Internet architectures u the IETF u the IETF Sub-IP area u IETF & optical networks coin
2 Why History u important to know where the Internet people are coming from u specifically packets vs. circuits u effects IETF view of optical nets coin Fundamental Goal of Internet Protocols u multiplexed utilization of existing networks different administrative boundaries different network types multiplexing via packets networks interconnected with packet switches called gateways (now called routers) note: international in scope u did not want to build a new global network too expensive too limiting coin
3 Internet Protocols Design Philosophy u ordered set of 2nd-level goals 1/ survivability in the face of failure 2/ support multiple types of communications service 3/ accommodate a variety of network types 4/ permit distributed management of resources 5/ cost effective 6/ low effort to attach a host 7/ account for use of resources u note: no performance (QoS) or security goals u not all goals have been met management & accounting functions are limited coin Packets! u basic decision: use packets not circuits Kleinrock s work showed packet switching to be a more efficient switching method u packet (a.k.a. datagram) self contained, same format end-to-end not link dependent coin Dest Addr Src Addr payload handled independently of preceding or following packets contains destination and source internetwork address may contain processing hints (e.g. QoS tag) no delivery guarantees net may drop, duplicate, or deliver out of order reliability (where needed) is done at higher levels 3
4 End Node Function u assumption: end nodes do more than one thing at a time not all with the same other end multiple concurrent sessions on each end node e.g., a WWW session is actually multiple sessions to multiple servers u i.e., multiplex at packet level not single circuit not even a few VCs (e.g., ATM) coin Routing u sub parts of the network are connected together by computers that forward packets toward destination these computers are called routers u routers use destination address in packet to make forwarding decision u routers exchange reachability information with other routers to build tables of next hops toward specific local networks exchange of reachability information done with routing protocol coin
5 A Quote the lesson of the Internet is that efficiency is not the primary consideration. Ability to grow and adapt to changing requirements is the primary consideration. This makes simplicity and uniformity very precious indeed. Bob Braden coin End-to-End Argument u 1981 paper by Saltzer, Reed & Clark u smart networks do not help adding functions into network can be redundant since actual function is end-to-end e.g. encryption, data reliability also harder to change with new technology also see Lampson Hints for Computer System Design u e2e argument projected to mean no per-session knowledge or state in the network but some soft-state (auto refreshed) may be OK network should be transparent to end-to-end applications coin
6 IP as a Common Bearer Service Layer 4 Applications Electronic Mail Video Server Audio Server Remote Login Teleconferencing Fax Information Browsing Financial Services Image Server Interactive Education Layer 3 Middleware Services File Systems Security Privacy Name Servers Storage Repositories Service Directories Electronic Money Multisite Coordination Layer 2 Transport Services and Representation Standarards (fax, video, text, and so on) Open Bearer Service Interface Layer 1 ODN Bearer Servive Network Technology Substrate LANs Point-to-Point Circuits Frame Relay ATM Direct Broadcast Satellite coin Wireless Dial-up SMDS Modems FIGURE 2.1 A four-layer model for the Open Data Network From: Realizing the Information Future Architecture of the Internet u history of nets that created the Internet u traffic engineering coin
7 1973: ARPANET HAWAII! PDP-15" 360/75" SIGMA-7" XEROX! PNWC! 316" SRI! UCSB! 316" PDP-11" 360/65" IBM" 1800" UCSD! AMES! " AMES! RAND! 316" STANFORD! B6700" MICHO" B10" USC-ISI! TINKER! 316" UNIVAC" 418 III" UTAH! PDP-11" ETAC! SDC! USC! DOCB! GWC! CASE! UCLA! CARNEGIE! PDP-11" PDP-11" ABERDEEN! 316" WBS! PDP-15" ARPA! ILLINOIS! MITRE! CCA! HARVARD! SLAC! PDP-1" BBN! H-316" DELVOIR! 316" BBN! PDP-1" 360/67" TSP" MIT! H-645" LINCOLN! RADC! TX-2" 360/91" DDP-516" 360/44" 360/145" coin ARPA NETWORK, LOGICAL MAP, JANUARY 1973" 1990: NSFNet T1 network CA*n et Palo Alto, CA Seattle, WA CA*n et Ithaca, Ann Arbor, NY MI Boulder, CO Pittsburgh, PA Salt Lk Cty, Lincoln, NE Champaign, UT IL Princeton, NJ College Pk, MD CERN San Diego, CA Atlanta, GA Houston, TX coin
8 2002: Current Internet Architecture coin you are here Traditional ISP Architecture u multiple POPs u interconnected with backbone links not full mesh coin
9 Traditional ISP Arch.: with MPLS coin Alternate ISP Architecture circuit cloud coin
10 Core Circuits u multiple options for technology for core circuits frame relay ATM MPLS SONET/SDH optical u (full) mesh connections between ISP POPs core routers are L3 adjacent note that customer routers not connected to core coin Circuits u IP ISPs use circuits to connect POP core routers together u can redirect circuit path to do traffic engineering u currently few or no QoS-specific sub-pipes u others see MPLS as a way to do other types of circuits Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) application-specific circuits (e.g. phone calls) coin
11 The IETF u The Internet Engineering Task Force u standards development for the Internet u since 1986 u international most recent meeting - last week in Yokohama u individuals not organizations u no defined membership u scale: about 2,000 attendees in Yokohama thousands more on mailing lists (from 100s of companies) u under umbrella of the Internet Society (ISOC) coin The IETF Organization u most work done on mailing lists u 3 times a year face-to-face meetings u individuals or groups request BOFs exploratory meeting - may lead to working group u working groups for specific projects about 135 working groups restrictive charters with milestones working groups closed when their work is done u working groups gathered together into Areas each area has 1 or 2 Area Directors - managers coin
12 IETF Areas u Applications Area u General Area u Internet Area u Operations and Management Area u Routing Area u Security Area u Sub-IP Area u Transport Area coin IETF Standards Process u rough consensus and running code rough consensus required not unanimity interoperable implementations needed to advance standard u multi-stage standards process Proposed Standard: good idea, no known problems Draft Standard: multiple interoperable implementations Standard: market acceptance coin
13 Above and below u traditionally the IETF has been: above the wire and below the application not (often) defining user interfaces not defining physical wire types u while doing IP over foo foo has been types of networks Ethernet, Token Ring, ATM, SONET/SDH,... but foo has been changing coin IP over trails, circuits, paths,... u what looks like wires to IP may not be physical wires may instead be something where paths can be configured where a path looks like a wire to IP e.g. ATM VCs & optical networks might also be routed datagrams another layer down e.g. IPsec tunnels u and then there is MPLS a progressively more important foo coin
14 A New Area u a systematic approach to sub-ip issues would be nice but exact scope is not clear u IESG created a temporary area for sub-ip like what was done for IPng u to be short lived (1-2 years) 2 current ADs were appointed to run the area coin Non-Objectives u the IETF is not expanding into standards for physical or virtual circuit technologies no new circuit switch architecture from IETF e.g., the IETF is not working on optical switches leave them to others u need to communicate with other standards organizations on what we are actually doing u significant overlap with some other SDOs OIF, ITU-T, etc coin
15 Area Work u Layer 2.5 protocol: MPLS u protocols that monitor, manage or effect logical circuit technology e.g. IP Over Optical, Traffic Engineering, Common Control and Management Protocols u protocols that create logical circuits over IP e.g. Provider Provisioned VPNs u protocols that interface to forwarding hardware General Switch Management Protocol coin IETF Optical Work u technologies for Internet service providers (ISPs) not necessarily anyone else - but may be useful to others u i.e, IETF works on technology for the Internet (including private IP networks), the technology may be useful for networks not carrying IP but it s not a design goal u ways to control optical networks from IP point of view based on IETF traffic engineering technologies i.e., intelligent IP-based control plane for optical networks coin
16 IETF Sub-IP Basic Architecture u for all sub-ip network types not just pure optical nets u two main components topology discovery control signaling u development work being done in IETF ccamp working group coin Topology Discovery u run link-state routing protocol e.g., OSPF or IS-IS u report on L2 links OSPF & IS-IS normally report on L3 links u add link parameters e.g., bandwidth, type of link, restoration functions u can support link bundling multiple parallel L2 links treated as one bundle characteristics are an aggregate of link characteristics coin
17 Control Signaling u used to establish paths through sub-ip network u uses labels to identify paths coin Traffic Engineering u aim: combat congestion at a reasonable cost networks w/o congestion are not a problem other than speed of light issues u decide paths through network rather than letting routing do its thing paths could be in infrastructure: ATM PVCs, Frame relay PVCs, optical (SONET, Ethernet & other) paths could be IP-ish: MPLS u note - tail circuits a common congestion point but can not be traffic engineered around u same issue with servers coin
18 MPLS u Multiprotocol Label Switching u basic functions: direct packets in a way that routing would not have but not required feature enable packet forwarding based on things other than IP destination address simplify network core (e.g., no routing needed) aggregate traffic with some common characteristics can provide traffic matrix data apply QoS to specific traffic group coin MPLS, contd. u not really routing (was in IETF routing area) u circuit-based path setup u original purposes: traffic engineering & forwarding speed u moving into QoS circuit per QoS class -> circuit per flow u some treating MPLS like packet-based ATM coin
19 GMPLS u generalized MPLS u assumes sub-ip links can be controlled with tags extension of MPLS concepts u routing algorithms do not need to be standardized used to compute explicit routes - not hop-by-hop routing u can do link bundling for scaling parallel links between switches can be treated as a bundle u data and control planes do not need to be the same coin The Internet & Optical Networks u to the Internet a lambda switched optical network is another link layer not an end-to-end circuit u could be a point-to-point link between routers u different case for optical packet switched networks lots of that at this conference not tomorrow but I d like to install some before I retire coin
20 IP Packets & Link-Level Frames u IP end-to-end an IP connection may go over multiple link types Ethernet, DSL, wireless, token ring, POS, TDM etc u can not assume single e2e link technology one of ATM s problems not the last networking technology need to maintain the isolation that layering provides u the IP packet format can not be changed to support just one link type (or even multiple link types) this has been proposed for wireless and some other links coin Summary u the Internet is a switched packet inter-network coin rides above L2 networks including switched ones u optical networks are key L2 support networks including switched L2 frame optical networks u e2e circuits are not the Internet e.g., switched lambdas can be very useful to support data services but not Internet u COIN + PS 2002 is showing us the future and it is exciting 20
21 coin
The Internet: Philosophy & Technology. The Network That Was There
 The Internet: Philosophy & Technology Scott Bradner Harvard University Feb 4 2002 bu 2/4/02-1 The Network That Was There the Phone Net from The Phone Company (TPC) circuit-based assumed simple & predictable
The Internet: Philosophy & Technology Scott Bradner Harvard University Feb 4 2002 bu 2/4/02-1 The Network That Was There the Phone Net from The Phone Company (TPC) circuit-based assumed simple & predictable
Plans to Re-Organize Sub-IP Technologies in the IETF
 Plans to Re-Organize Sub-IP Technologies in the IETF Dan Romascanu Avaya Inc. Bert Wijnen Lucent Technologies Scott Bradner Harvard University David Harrington Enterasys Networks Motivation IEEE 802 develops
Plans to Re-Organize Sub-IP Technologies in the IETF Dan Romascanu Avaya Inc. Bert Wijnen Lucent Technologies Scott Bradner Harvard University David Harrington Enterasys Networks Motivation IEEE 802 develops
Computer-to-Computer Networks (cont.)
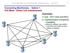 Computer-to-Computer Networks (cont.) 1 Connecting Mainframes - Option 1: Full Mesh / Direct Link Infrastructure Downsides: 1) cost - O(n 2 ) links and NICs 2) implementation complexity / scalability [
Computer-to-Computer Networks (cont.) 1 Connecting Mainframes - Option 1: Full Mesh / Direct Link Infrastructure Downsides: 1) cost - O(n 2 ) links and NICs 2) implementation complexity / scalability [
Chapter 1 Communication
 Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services Network Architecture and Services Telegraph Networks & Message Switching Telephone Networks and Circuit Switching Computer Networks & Packet Switching Future
Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services Network Architecture and Services Telegraph Networks & Message Switching Telephone Networks and Circuit Switching Computer Networks & Packet Switching Future
Introduction. Computer Networks: Introduction 1
 Introduction Computer Networks: Introduction 1 Network Definitions and Classification Preliminary definitions and network terminology Sample application paradigms Classifying networks by transmission technology
Introduction Computer Networks: Introduction 1 Network Definitions and Classification Preliminary definitions and network terminology Sample application paradigms Classifying networks by transmission technology
CS155b: E-Commerce. Lecture 3: Jan 16, How Does the Internet Work? Acknowledgements: S. Bradner and R. Wang
 CS155b: E-Commerce Lecture 3: Jan 16, 2001 How Does the Internet Work? Acknowledgements: S. Bradner and R. Wang Internet Protocols Design Philosophy ordered set of goals 1. multiplexed utilization of existing
CS155b: E-Commerce Lecture 3: Jan 16, 2001 How Does the Internet Work? Acknowledgements: S. Bradner and R. Wang Internet Protocols Design Philosophy ordered set of goals 1. multiplexed utilization of existing
L2: Introduction to Communication Networks: Internet. Outline
 EECS 3213 Fall 2014 L2: Introduction to Communication Networks: Internet Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline ARPANET A connectionless datagram network Internet A connectionless/connection-oriented
EECS 3213 Fall 2014 L2: Introduction to Communication Networks: Internet Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline ARPANET A connectionless datagram network Internet A connectionless/connection-oriented
Introduction. Computer Networks Term B10
 Introduction Computer Networks Term B10 Introduction Outline Preliminary Definitions Internet Components Network Application Paradigms Classifying networks by transmission technology by size/scale by topology
Introduction Computer Networks Term B10 Introduction Outline Preliminary Definitions Internet Components Network Application Paradigms Classifying networks by transmission technology by size/scale by topology
CS4514 Computer Networks
 CS4514 Computer Networks Term B07 Professor Bob Kinicki Networks: Introduction 1 Course Objectives Networks: Introduction 2 Course Objectives 1. To develop an understanding of modern network architectures
CS4514 Computer Networks Term B07 Professor Bob Kinicki Networks: Introduction 1 Course Objectives Networks: Introduction 2 Course Objectives 1. To develop an understanding of modern network architectures
MPLS Multi-protocol label switching Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Torino)
 MPLS Multi-protocol label switching Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Torino) http://staff.polito.it/mario.baldi MPLS - 1 From MPLS Forum Documents MPLS is the enabling technology
MPLS Multi-protocol label switching Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Torino) http://staff.polito.it/mario.baldi MPLS - 1 From MPLS Forum Documents MPLS is the enabling technology
Correction to BBN Report No. 1822
 7818 Network Working Group RFC # 270 NIC "7818 Categories: B.l Updates: none Obsoletes: none A. McKenzie BBN 1 January 1972 Correction to BBN In the process of generating RFC # 271 we have discovered a
7818 Network Working Group RFC # 270 NIC "7818 Categories: B.l Updates: none Obsoletes: none A. McKenzie BBN 1 January 1972 Correction to BBN In the process of generating RFC # 271 we have discovered a
Multi Protocol Label Switching
 MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Network Management and QoS Provisioning - 1 MPLS: introduction
MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Network Management and QoS Provisioning - 1 MPLS: introduction
MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching
 MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Computer Networks Design and Management - 1 MPLS: introduction
MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Computer Networks Design and Management - 1 MPLS: introduction
Network Architecture. TOC Architecture
 Network Architecture Introduction Layering Example Internet Layers First Look Layering Step by Step Downside of Layering Interconnecting Networks The Internet TOC Architecture Introduction Issues: Inter-operability
Network Architecture Introduction Layering Example Internet Layers First Look Layering Step by Step Downside of Layering Interconnecting Networks The Internet TOC Architecture Introduction Issues: Inter-operability
Core Networks Evolution
 Core Networks Evolution Prof. Daniel Kofman daniel.kofman@enst.fr Telecom Paris - ENST Content Any Service, Any Time, Everywhere, Everyone Towards the triple play and beyond Main trends in Core Networks
Core Networks Evolution Prof. Daniel Kofman daniel.kofman@enst.fr Telecom Paris - ENST Content Any Service, Any Time, Everywhere, Everyone Towards the triple play and beyond Main trends in Core Networks
MPLS Multi-protocol label switching Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Torino)
 MPLS Multi-protocol label switching Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Torino) http://staff.polito.it/mario.baldi MPLS - 1 MPLS - 2 Copyright notice This set of transparencies,
MPLS Multi-protocol label switching Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Torino) http://staff.polito.it/mario.baldi MPLS - 1 MPLS - 2 Copyright notice This set of transparencies,
Hands-On Metro Ethernet Carrier Class Networks
 Hands-On Carrier Class Networks Course Description Carriers have offered connectivity services based on traditional TDM, Frame Relay and ATM for many years. However customers now use Ethernet as the interface
Hands-On Carrier Class Networks Course Description Carriers have offered connectivity services based on traditional TDM, Frame Relay and ATM for many years. However customers now use Ethernet as the interface
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Last Updated: December 14, 2011 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Last Updated: December 14, 2011 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one
Data Networks. Lecture 1: Introduction. September 4, 2008
 Data Networks Lecture 1: Introduction September 4, 2008 Slide 1 Learning Objectives Fundamental aspects of network Design and Analysis: Architecture: layering, topology design, switching mechanisms Protocols:
Data Networks Lecture 1: Introduction September 4, 2008 Slide 1 Learning Objectives Fundamental aspects of network Design and Analysis: Architecture: layering, topology design, switching mechanisms Protocols:
Introduction to Networking
 Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
MPLS etc.. MPLS is not alone TEST. 26 April 2016 AN. Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC PBB-TE VPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS GMPLS SR RSVP-TE OSPF-TE PCEP
 Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC VPLS PBB-TE MPLS etc.. MPLS is not alone LDP MPLS-TE LABEL MP-BGP LSP TAG H-VPLS 26 April 2016 AN TEST GMPLS SR T-MPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS OSPF-TE PCEP Multi-Protocol
Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC VPLS PBB-TE MPLS etc.. MPLS is not alone LDP MPLS-TE LABEL MP-BGP LSP TAG H-VPLS 26 April 2016 AN TEST GMPLS SR T-MPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS OSPF-TE PCEP Multi-Protocol
1.264 Lecture 23. Telecom Enterprise networks MANs, WANs
 1.264 Lecture 23 Telecom Enterprise networks MANs, WANs Enterprise networks Connections within enterprise External connections Remote offices Employees Customers Business partners, supply chain partners
1.264 Lecture 23 Telecom Enterprise networks MANs, WANs Enterprise networks Connections within enterprise External connections Remote offices Employees Customers Business partners, supply chain partners
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one MPLS VPN-based service provider
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one MPLS VPN-based service provider
Next Generation Networks MultiService Network Design. Dr. Ben Tang
 Next Generation Networks MultiService Network Design Dr. Ben Tang April 23, 2008 Operators face difficult network planning and design questions Can your current planning methods handle the complexity of
Next Generation Networks MultiService Network Design Dr. Ben Tang April 23, 2008 Operators face difficult network planning and design questions Can your current planning methods handle the complexity of
An IETF Insider View
 An IETF Insider View TranSwitch April 15, 2002 Scott Bradner sob@harvard.edu ts - 1 u missing u next gen signaling ts - 2 Topics u work being done in IETF working groups u that seemed possibly related
An IETF Insider View TranSwitch April 15, 2002 Scott Bradner sob@harvard.edu ts - 1 u missing u next gen signaling ts - 2 Topics u work being done in IETF working groups u that seemed possibly related
Router Router Microprocessor controlled traffic direction home router DSL modem Computer Enterprise routers Core routers
 Router Router is a Microprocessor controlled device that forwards data packets across the computer network. It is used to connect two or more data lines from different net works. The function of the router
Router Router is a Microprocessor controlled device that forwards data packets across the computer network. It is used to connect two or more data lines from different net works. The function of the router
Module 1. Introduction. Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 1 Introduction Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur Introduction In this module we shall highlight some of the basic aspects of computer networks in two lessons. In lesson 1.1 we shall start with the historical
Module 1 Introduction Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur Introduction In this module we shall highlight some of the basic aspects of computer networks in two lessons. In lesson 1.1 we shall start with the historical
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers Feature History Release 11.1CT 12.1(3)T 12.1(5)T 12.0(14)ST 12.0(21)ST 12.0(22)S Modification The document introduced MPLS and was titled Tag Switching
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers Feature History Release 11.1CT 12.1(3)T 12.1(5)T 12.0(14)ST 12.0(21)ST 12.0(22)S Modification The document introduced MPLS and was titled Tag Switching
Digital Communication Networks
 Digital Communication Networks MIT PROFESSIONAL INSTITUTE, 6.20s July 25-29, 2005 Professor Muriel Medard, MIT Professor, MIT Slide 1 Digital Communication Networks Introduction Slide 2 Course syllabus
Digital Communication Networks MIT PROFESSIONAL INSTITUTE, 6.20s July 25-29, 2005 Professor Muriel Medard, MIT Professor, MIT Slide 1 Digital Communication Networks Introduction Slide 2 Course syllabus
Virtualization of networks
 Virtualization of networks Virtualization of resources: powerful abstraction in systems engineering Computing examples: Virtual memory, virtual devices Virtual machines: e.g., Java IBM VM OS from 1960
Virtualization of networks Virtualization of resources: powerful abstraction in systems engineering Computing examples: Virtual memory, virtual devices Virtual machines: e.g., Java IBM VM OS from 1960
Chapter 1 Introduction. COSC 3213 Summer 2003
 Chapter 1 Introduction COSC 3213 Summer 2003 5/7/2003 Course Objectives Introduce communication networks and understand how different components work including the underlying technology including hardware
Chapter 1 Introduction COSC 3213 Summer 2003 5/7/2003 Course Objectives Introduce communication networks and understand how different components work including the underlying technology including hardware
Part 1: Introduction. Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview
 Part 1: Introduction Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview Get context Get overview, feel of the Internet Application layer protocols and addressing Network layer / Routing Link layer / Example
Part 1: Introduction Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview Get context Get overview, feel of the Internet Application layer protocols and addressing Network layer / Routing Link layer / Example
Network Architecture
 Unit 7 Network Architecture Acknowledgments: These slides were originally developed by Prof. Jean Walrand for EE122. The past and current EE122 instructors including Kevin Fall, Abhay Parekh, Shyam Parekh,
Unit 7 Network Architecture Acknowledgments: These slides were originally developed by Prof. Jean Walrand for EE122. The past and current EE122 instructors including Kevin Fall, Abhay Parekh, Shyam Parekh,
Network Protocols and Architectures
 Network Protocols and Architectures Introduction 1 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view Millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end-systems PC s workstations, servers PDA s, phones, toasters
Network Protocols and Architectures Introduction 1 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view Millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end-systems PC s workstations, servers PDA s, phones, toasters
GMPLS Overview Generalized MPLS
 GMPLS Overview Generalized MPLS Hanyang Univ ( jijung@hanyang.ac.kr ) Outline GMPLS Overview Draft-ietf-ccamp-gmpls-architecture-00.txt GMPLS IGP Extension Draft-ietf-ccamp-ospf-gmpls-extensions-00.txt
GMPLS Overview Generalized MPLS Hanyang Univ ( jijung@hanyang.ac.kr ) Outline GMPLS Overview Draft-ietf-ccamp-gmpls-architecture-00.txt GMPLS IGP Extension Draft-ietf-ccamp-ospf-gmpls-extensions-00.txt
voice-enabling.book Page 72 Friday, August 23, :19 AM
 voice-enabling.book Page 72 Friday, August 23, 2002 11:19 AM voice-enabling.book Page 73 Friday, August 23, 2002 11:19 AM C H A P T E R 4 Offering Bundled and Data Services Chapter 2, VoIP Network Architectures:
voice-enabling.book Page 72 Friday, August 23, 2002 11:19 AM voice-enabling.book Page 73 Friday, August 23, 2002 11:19 AM C H A P T E R 4 Offering Bundled and Data Services Chapter 2, VoIP Network Architectures:
and Networks Data Communications Second Edition Tata McGraw Hill Education Private Limited Managing Director SoftExcel Services Limited, Mumbai
 Data Communications and Networks Second Edition ACHYUT S GODBOLE Managing Director SoftExcel Services Limited, Mumbai ATUL KAHATE Senior Consultant Oracle Financial Services Software Limited, Pune Tata
Data Communications and Networks Second Edition ACHYUT S GODBOLE Managing Director SoftExcel Services Limited, Mumbai ATUL KAHATE Senior Consultant Oracle Financial Services Software Limited, Pune Tata
Virtual Link Layer : Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace
 Virtual Link Layer 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia 3 Lectures left HW #2
Virtual Link Layer 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia 3 Lectures left HW #2
Mission Critical MPLS in Utilities
 Mission Critical MPLS in Utilities The Technology to Support Evolving Networks Application Note February 2017 Mission Critical MPLS in Utilities The Technology to Support Evolving Networks Abstract This
Mission Critical MPLS in Utilities The Technology to Support Evolving Networks Application Note February 2017 Mission Critical MPLS in Utilities The Technology to Support Evolving Networks Abstract This
Techniques and Protocols for Improving Network Availability
 Techniques and Protocols for Improving Network Availability Don Troshynski dtroshynski@avici.com February 26th, 2004 Outline of Talk The Problem Common Convergence Solutions An Advanced Solution: RAPID
Techniques and Protocols for Improving Network Availability Don Troshynski dtroshynski@avici.com February 26th, 2004 Outline of Talk The Problem Common Convergence Solutions An Advanced Solution: RAPID
Lecture 3 Protocol Stacks and Layering
 Lecture 3 Protocol Stacks and ing Hui Zhang School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University 15-441 Networking, Fall 2007 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~srini/15-441/f07/ 1 What is a Communication Network?
Lecture 3 Protocol Stacks and ing Hui Zhang School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University 15-441 Networking, Fall 2007 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~srini/15-441/f07/ 1 What is a Communication Network?
Network Working Group Request for Comment: 597 NIC: December 1973
 Network Working Group N. Neigus Request for Comment: 597 J. Feinler NIC: 20826 12 December 1973 Host Status Attached are the latest network maps -- geographic and logical -- and a list of Hosts connected
Network Working Group N. Neigus Request for Comment: 597 J. Feinler NIC: 20826 12 December 1973 Host Status Attached are the latest network maps -- geographic and logical -- and a list of Hosts connected
Metro Ethernet Design and Engineering for CO
 Hands-On Metro Ethernet Design and Engineering for CO Designing Carrier Networks that Deliver Metro Ethernet Services Course Description Carriers have offered connectivity services based on traditional
Hands-On Metro Ethernet Design and Engineering for CO Designing Carrier Networks that Deliver Metro Ethernet Services Course Description Carriers have offered connectivity services based on traditional
NIC # RFC # August 1972 Categories: F, G.3 Updates: RFC #370 Obsoletes: None
 Network Working Group Ellen Westheimer NIC # 11118 BBN RFC # 376 8 August 1972 Categories: F, G.3 Updates: RFC #370 Obsoletes: None NETWORK HOST STATUS This RFC reports on the status of most Network Hosts
Network Working Group Ellen Westheimer NIC # 11118 BBN RFC # 376 8 August 1972 Categories: F, G.3 Updates: RFC #370 Obsoletes: None NETWORK HOST STATUS This RFC reports on the status of most Network Hosts
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Feature History Release 12.0(14)ST 12.0(16)ST 12.2(8)T 12.0(21)ST 12.0(22)S 12.0(23)S Modification This feature was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(14)ST. Support
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Feature History Release 12.0(14)ST 12.0(16)ST 12.2(8)T 12.0(21)ST 12.0(22)S 12.0(23)S Modification This feature was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(14)ST. Support
Virtualization. Stefan Schmid - 1
 Virtualization Stefan Schmid - 1 Virtualization and Benefits What is virtualization? An abstraction Used where and (dis)advantages? Java virtual machine, virtual memory, VPN, abstraction = simpler and
Virtualization Stefan Schmid - 1 Virtualization and Benefits What is virtualization? An abstraction Used where and (dis)advantages? Java virtual machine, virtual memory, VPN, abstraction = simpler and
Need For Protocol Architecture
 Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
for Metropolitan Area Networks MPLS No. 106 Technology White Paper Abstract
 No. 106 Technology White Paper Page: 1 of 7 MPLS for Metropolitan Area Networks Abstract The demand for bandwidth in Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) and the increased availability of fiber has created
No. 106 Technology White Paper Page: 1 of 7 MPLS for Metropolitan Area Networks Abstract The demand for bandwidth in Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) and the increased availability of fiber has created
Pseudo Wire Emulation Edge to Edge (PWE3) and Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS)
 Pseudo Wire Emulation Edge to Edge (PWE3) and Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) Course Description Network transport service providers and their users are seeking to rationalize their networks by migrating
Pseudo Wire Emulation Edge to Edge (PWE3) and Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) Course Description Network transport service providers and their users are seeking to rationalize their networks by migrating
Internet. 1) Internet basic technology (overview) 3) Quality of Service (QoS) aspects
 Internet 1) Internet basic technology (overview) 2) Mobility aspects 3) Quality of Service (QoS) aspects Relevant information: these slides (overview) course textbook (Part H) www.ietf.org (details) IP
Internet 1) Internet basic technology (overview) 2) Mobility aspects 3) Quality of Service (QoS) aspects Relevant information: these slides (overview) course textbook (Part H) www.ietf.org (details) IP
 Http://www.passcert.com Exam : 642-889 Title : Implementing Cisco Service Provider Next-Generation Egde Network Services Version : DEMO 1 / 6 1.Which type of VPN requires a full mesh of virtual circuits
Http://www.passcert.com Exam : 642-889 Title : Implementing Cisco Service Provider Next-Generation Egde Network Services Version : DEMO 1 / 6 1.Which type of VPN requires a full mesh of virtual circuits
BW Protection. 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 BW Protection 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Cisco MPLS - Traffic Engineering for VPNs Amrit Hanspal Sr. Product Manager MPLS & QoS Internet Technologies Division 2 Agenda MPLS Fundamentals
BW Protection 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Cisco MPLS - Traffic Engineering for VPNs Amrit Hanspal Sr. Product Manager MPLS & QoS Internet Technologies Division 2 Agenda MPLS Fundamentals
RAJIV GANDHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 RAJIV GANDHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: COMPUTER NETWORKS SUBJECT CODE: CST52 UNIT-I 2 MARKS 1. What is Network? 2.
RAJIV GANDHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: COMPUTER NETWORKS SUBJECT CODE: CST52 UNIT-I 2 MARKS 1. What is Network? 2.
Design Principles : Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace
 Design Principles 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia No Paper Review for today
Design Principles 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia No Paper Review for today
Session 3 Networks I
 15.561 Information Technology Essentials Session 3 Networks I Copyright 2005 Thomas Malone, Chris Dellarocas, Stuart Madnick Acknowledgments: Slides marked SM are adapted from Stuart Madnick, MIT. Slides
15.561 Information Technology Essentials Session 3 Networks I Copyright 2005 Thomas Malone, Chris Dellarocas, Stuart Madnick Acknowledgments: Slides marked SM are adapted from Stuart Madnick, MIT. Slides
Developing Standards for Metro Ethernet Networks
 Developing Standards for Metro Ethernet s Stephen Haddock shaddock@extremenetworks.com Chief Technology Officer Agenda Metro Ethernet s Metro Ethernet Forum Services Model and Definitions Traffic Management
Developing Standards for Metro Ethernet s Stephen Haddock shaddock@extremenetworks.com Chief Technology Officer Agenda Metro Ethernet s Metro Ethernet Forum Services Model and Definitions Traffic Management
Internet Design Principles and Architecture
 Internet Design Principles and Architecture Venkat Padmanabhan Microsoft Research 2 April 2001 Venkat Padmanabhan 1 Lecture Outline A brief history of the Internet How is the Internet different from the
Internet Design Principles and Architecture Venkat Padmanabhan Microsoft Research 2 April 2001 Venkat Padmanabhan 1 Lecture Outline A brief history of the Internet How is the Internet different from the
MAN/WAN Interconnection Options for SBC. Vish Ramamurti George Young
 MAN/WAN Interconnection Options for SBC Vish Ramamurti George Young 1 MAN/WAN interconnection Customer Premises Transparent LAN service Router Router Private Net NxDS1 Building Closet DSU DSU To ISP POP
MAN/WAN Interconnection Options for SBC Vish Ramamurti George Young 1 MAN/WAN interconnection Customer Premises Transparent LAN service Router Router Private Net NxDS1 Building Closet DSU DSU To ISP POP
Typical Network Uses
 Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF
 LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF MODULE 07 - MPLS BASED LAYER 2 SERVICES 1 by Xantaro MPLS BASED LAYER 2 VPNS USING MPLS FOR POINT-TO-POINT LAYER 2 SERVICES 2 by Xantaro Why are Layer-2
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF MODULE 07 - MPLS BASED LAYER 2 SERVICES 1 by Xantaro MPLS BASED LAYER 2 VPNS USING MPLS FOR POINT-TO-POINT LAYER 2 SERVICES 2 by Xantaro Why are Layer-2
MPLS etc.. 9 May 2017 AN
 MPLS etc.. 9 May 2017 AN Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC VPLS PBB-TE LDP MPLS-TE LABEL MP-BGP MPLS is not alone LSP TAG H-VPLS GMPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS RSVP-TE SR OSPF-TE T-MPLS PCEP Multi-Protocol
MPLS etc.. 9 May 2017 AN Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC VPLS PBB-TE LDP MPLS-TE LABEL MP-BGP MPLS is not alone LSP TAG H-VPLS GMPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS RSVP-TE SR OSPF-TE T-MPLS PCEP Multi-Protocol
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers This document describes commands for configuring and monitoring Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) functionality on Cisco routers and switches. This
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers This document describes commands for configuring and monitoring Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) functionality on Cisco routers and switches. This
Mobile Communications. Ad-hoc and Mesh Networks
 Ad-hoc+mesh-net 1 Mobile Communications Ad-hoc and Mesh Networks Manuel P. Ricardo Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto Ad-hoc+mesh-net 2 What is an ad-hoc network? What are differences between
Ad-hoc+mesh-net 1 Mobile Communications Ad-hoc and Mesh Networks Manuel P. Ricardo Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto Ad-hoc+mesh-net 2 What is an ad-hoc network? What are differences between
Virtual Link Layer : Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace
 Virtual Link Layer 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia 3 Lectures left HW #2
Virtual Link Layer 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia 3 Lectures left HW #2
Week 2 / Paper 1. The Design Philosophy of the DARPA Internet Protocols
 Week 2 / Paper 1 The Design Philosophy of the DARPA Internet Protocols David D. Clark ACM CCR, Vol. 18, No. 4, August 1988 Main point Many papers describe how the Internet Protocols work But why do they
Week 2 / Paper 1 The Design Philosophy of the DARPA Internet Protocols David D. Clark ACM CCR, Vol. 18, No. 4, August 1988 Main point Many papers describe how the Internet Protocols work But why do they
0 TCP/IP overview. 0.1 The Internet
 0521841445 - / Essentials: A Lab-Based Approach 0 / overview From these assumptions comes the fundamental structure of the Internet: a packet switched communications facility in which a number of distinguishable
0521841445 - / Essentials: A Lab-Based Approach 0 / overview From these assumptions comes the fundamental structure of the Internet: a packet switched communications facility in which a number of distinguishable
Computer Networks
 15-441 Computer s Lecture 3 Professor Hui Zhang Wean Hall 7126 hzhang@cs.cmu.edu 1 Review of Lecture 1 How long does it take to move 1GB data from campus to your home? 56Kbps modem 2Mbps DSL Other possibilities?
15-441 Computer s Lecture 3 Professor Hui Zhang Wean Hall 7126 hzhang@cs.cmu.edu 1 Review of Lecture 1 How long does it take to move 1GB data from campus to your home? 56Kbps modem 2Mbps DSL Other possibilities?
Securizarea Calculatoarelor și a Rețelelor 32. Tehnologia MPLS VPN
 Platformă de e-learning și curriculă e-content pentru învățământul superior tehnic Securizarea Calculatoarelor și a Rețelelor 32. Tehnologia MPLS VPN MPLS VPN 5-ian-2010 What this lecture is about: IP
Platformă de e-learning și curriculă e-content pentru învățământul superior tehnic Securizarea Calculatoarelor și a Rețelelor 32. Tehnologia MPLS VPN MPLS VPN 5-ian-2010 What this lecture is about: IP
Name of Course : E1-E2 CFA. Chapter 14. Topic : NG SDH & MSPP
 Name of Course : E1-E2 CFA Chapter 14 Topic : NG SDH & MSPP Date of Creation : 28.03.2011 NGN SDH and MSPP 1. Introduction: Innovation, the lifeline to survival in the telecommunication market, has spurred
Name of Course : E1-E2 CFA Chapter 14 Topic : NG SDH & MSPP Date of Creation : 28.03.2011 NGN SDH and MSPP 1. Introduction: Innovation, the lifeline to survival in the telecommunication market, has spurred
Free4Torrent. Free and valid exam torrent helps you to pass the exam with high score
 Free4Torrent http://www.free4torrent.com Free and valid exam torrent helps you to pass the exam with high score Exam : 642-889 Title : Implementing Cisco Service Provider Next-Generation Egde Network Services
Free4Torrent http://www.free4torrent.com Free and valid exam torrent helps you to pass the exam with high score Exam : 642-889 Title : Implementing Cisco Service Provider Next-Generation Egde Network Services
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 1133 Merit Computer Network November 1989
 Network Working Group Request for Comments: 1133 J. Yu H-W. Braun Merit Computer Network November 1989 Status of this Memo Routing between the NSFNET and the DDN This document is a case study of the implementation
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 1133 J. Yu H-W. Braun Merit Computer Network November 1989 Status of this Memo Routing between the NSFNET and the DDN This document is a case study of the implementation
Lecture 2: Layering & End-to-End
 Lecture 2: Layering & End-to-End CSE 222A: Computer Communication Networks Alex C. Snoeren Thanks: Mike Freedman & Amin Vahdat Lecture 2 Overview Layering Application interface Transport services Discussion
Lecture 2: Layering & End-to-End CSE 222A: Computer Communication Networks Alex C. Snoeren Thanks: Mike Freedman & Amin Vahdat Lecture 2 Overview Layering Application interface Transport services Discussion
Design Considerations : Computer Networking. Outline. Challenge 1: Address Formats. Challenge. How to determine split of functionality
 Design Considerations 15-744: Computer Networking L-2 Design Considerations How to determine split of functionality Across protocol layers Across network nodes Assigned Reading [SRC84] End-to-end Arguments
Design Considerations 15-744: Computer Networking L-2 Design Considerations How to determine split of functionality Across protocol layers Across network nodes Assigned Reading [SRC84] End-to-end Arguments
Configuring Virtual Private LAN Services
 Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
EECS 228a Lecture 1 Overview: Networks. Jean Walrand
 EECS 228a Lecture 1 Overview: Networks Jean Walrand www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~wlr Fall 2002 Course Information Instructor: Jean Walrand n Office Hours: M-Tu 1:00-2:00 Time/Place: MW 2:00-3:30 in 285 Cory
EECS 228a Lecture 1 Overview: Networks Jean Walrand www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~wlr Fall 2002 Course Information Instructor: Jean Walrand n Office Hours: M-Tu 1:00-2:00 Time/Place: MW 2:00-3:30 in 285 Cory
MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB
 First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
Computer Network Architectures and Multimedia. Guy Leduc. Chapter 2 MPLS networks. Chapter 2: MPLS
 Computer Network Architectures and Multimedia Guy Leduc Chapter 2 MPLS networks Chapter based on Section 5.5 of Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley,
Computer Network Architectures and Multimedia Guy Leduc Chapter 2 MPLS networks Chapter based on Section 5.5 of Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley,
The Internet and the World Wide Web
 Technology Briefing The Internet and the World Wide Web TB5-1 Learning Objectives TB5-2 Learning Objectives TB5-3 How Did the Internet Get Started? Internet derived from internetworking 1960s U.S. Defense
Technology Briefing The Internet and the World Wide Web TB5-1 Learning Objectives TB5-2 Learning Objectives TB5-3 How Did the Internet Get Started? Internet derived from internetworking 1960s U.S. Defense
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
 CHAPTER 19 Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) Virtual private network is defined as customer connectivity deployed on a shared infrastructure with the same policies as a private network. The shared infrastructure
CHAPTER 19 Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) Virtual private network is defined as customer connectivity deployed on a shared infrastructure with the same policies as a private network. The shared infrastructure
Networking Applications
 Networking Dr. Ayman A. Abdel-Hamid College of Computing and Information Technology Arab Academy for Science & Technology and Maritime Transport 1 Outline Internet Layers Internet Data Packet transmission
Networking Dr. Ayman A. Abdel-Hamid College of Computing and Information Technology Arab Academy for Science & Technology and Maritime Transport 1 Outline Internet Layers Internet Data Packet transmission
Need For Protocol Architecture
 Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
THE MPLS JOURNEY FROM CONNECTIVITY TO FULL SERVICE NETWORKS. Sangeeta Anand Vice President Product Management Cisco Systems.
 THE MPLS JOURNEY FROM CONNECTIVITY TO FULL SERVICE NETWORKS Sangeeta Anand Vice President Product Management Cisco Systems October 20, 2003 1 Agenda Introducing the Full Service Network The MPLS Journey
THE MPLS JOURNEY FROM CONNECTIVITY TO FULL SERVICE NETWORKS Sangeeta Anand Vice President Product Management Cisco Systems October 20, 2003 1 Agenda Introducing the Full Service Network The MPLS Journey
COMP9332 Network Routing & Switching
 COMP9332 Network Routing & Switching Switching in IP Networks with MPLS http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs9332 1 Lecture Overview This lecture introduces the concept of switching, which allows faster processing
COMP9332 Network Routing & Switching Switching in IP Networks with MPLS http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs9332 1 Lecture Overview This lecture introduces the concept of switching, which allows faster processing
IT114 NETWORK+ Learning Unit 1 Objectives: 1, 2 Time In-Class Time Out-Of-Class Hours 2-3. Lectures: Course Introduction and Overview
 IT114 NETWORK+ Course Objectives Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Identify the devices and elements of computer networks; 2. Diagram network models using the appropriate
IT114 NETWORK+ Course Objectives Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Identify the devices and elements of computer networks; 2. Diagram network models using the appropriate
Optimizing Ethernet Access Network for Internet Protocol Multi-Service Architecture
 1 Optimizing Ethernet Access Network for Internet Protocol Multi-Service Architecture Author: Mikael Forsten TeliaSonera Sonera Carrier Networks Supervisor: Docent Timo O. Korhonen Instructor: M.Sc Jari
1 Optimizing Ethernet Access Network for Internet Protocol Multi-Service Architecture Author: Mikael Forsten TeliaSonera Sonera Carrier Networks Supervisor: Docent Timo O. Korhonen Instructor: M.Sc Jari
Multiprotocol Label Switching Overview
 This chapter describes the Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) distribution protocol. MPLS is a high-performance packet forwarding technology that integrates the performance and traffic management capabilities
This chapter describes the Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) distribution protocol. MPLS is a high-performance packet forwarding technology that integrates the performance and traffic management capabilities
GÉANT perspective of Virtual Networks and Implementation
 GÉANT perspective of Virtual Networks and Implementation NORDUnet 2002 Conference Copenhagen 15th of April 2002 Agnès Pouélé, Network Engineer DANTE GÉANT perspective of Virtual Networks and implementation
GÉANT perspective of Virtual Networks and Implementation NORDUnet 2002 Conference Copenhagen 15th of April 2002 Agnès Pouélé, Network Engineer DANTE GÉANT perspective of Virtual Networks and implementation
Company Overview. Network Overview
 Company Overview InfiniComm is an imaginary Internet Service Provider (ISP) in the United States that owns its fiber transmission facilities as well as a Layer 2 switching infrastructure (ATM) across the
Company Overview InfiniComm is an imaginary Internet Service Provider (ISP) in the United States that owns its fiber transmission facilities as well as a Layer 2 switching infrastructure (ATM) across the
MPLS VPN. 5 ian 2010
 MPLS VPN 5 ian 2010 What this lecture is about: IP CEF MPLS architecture What is MPLS? MPLS labels Packet forwarding in MPLS MPLS VPNs 3 IP CEF & MPLS Overview How does a router forward packets? Process
MPLS VPN 5 ian 2010 What this lecture is about: IP CEF MPLS architecture What is MPLS? MPLS labels Packet forwarding in MPLS MPLS VPNs 3 IP CEF & MPLS Overview How does a router forward packets? Process
A Two-Level Architecture for Internet Signaling
 A Two-Level Architecture for Internet Signaling Bob Braden USC Information Sciences Institute IETF 54 July 15, 2002 Braden@isi.edu NSIS IETF 54 July 2002 1 A Two-Level Architecture for Signaling draft-braden-2level-signaling-00.txt,
A Two-Level Architecture for Internet Signaling Bob Braden USC Information Sciences Institute IETF 54 July 15, 2002 Braden@isi.edu NSIS IETF 54 July 2002 1 A Two-Level Architecture for Signaling draft-braden-2level-signaling-00.txt,
The internet What is it??
 The internet What is it?? The internet is a global system of interconnected computer network that use the standard internet protocol suit (TCP/IP) to serve billions of users word wide. In other word it
The internet What is it?? The internet is a global system of interconnected computer network that use the standard internet protocol suit (TCP/IP) to serve billions of users word wide. In other word it
L1: Introduction to Communication Networks. Outline
 SC/CSE 3213 Winter 2014 L1: Introduction to Communication Networks Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline Course texts, mark breakdown, topics Telegraph A connectionless message-switching network
SC/CSE 3213 Winter 2014 L1: Introduction to Communication Networks Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline Course texts, mark breakdown, topics Telegraph A connectionless message-switching network
CS 268: Internet Architecture & E2E Arguments. Today s Agenda. Scott Shenker and Ion Stoica (Fall, 2010) Design goals.
 CS 268: Internet Architecture & E2E Arguments Scott Shenker and Ion Stoica (Fall, 2010) 1 Today s Agenda Design goals Layering (review) End-to-end arguments (review) 2 1 Internet Design Goals Goals 0 Connect
CS 268: Internet Architecture & E2E Arguments Scott Shenker and Ion Stoica (Fall, 2010) 1 Today s Agenda Design goals Layering (review) End-to-end arguments (review) 2 1 Internet Design Goals Goals 0 Connect
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS
 BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS INTRODUCTION ATM stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode ATM is a flexible high bandwidth, low delay network technology that is: Capable of handling voice, video and data
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS INTRODUCTION ATM stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode ATM is a flexible high bandwidth, low delay network technology that is: Capable of handling voice, video and data
Overview of Networks
 CMPT765/408 08-1 Overview of Networks Qianping Gu 1 Overview of Networks This note is mainly based on Chapters 1-2 of High Performance of Communication Networks by J. Walrand and P. Pravin, 2nd ed, and
CMPT765/408 08-1 Overview of Networks Qianping Gu 1 Overview of Networks This note is mainly based on Chapters 1-2 of High Performance of Communication Networks by J. Walrand and P. Pravin, 2nd ed, and
CS589: Advanced Computer Networks
 CS589: Advanced Computer Networks Instructor - Z. Morley Mao (zmao@umich.edu, 4629 CSE) Lecture time: TuTh, 10:30-12:30 PM Location: 1018 DOW Office hour: - TuTh 1-2PM - email for appointment Z. Morley
CS589: Advanced Computer Networks Instructor - Z. Morley Mao (zmao@umich.edu, 4629 CSE) Lecture time: TuTh, 10:30-12:30 PM Location: 1018 DOW Office hour: - TuTh 1-2PM - email for appointment Z. Morley
Facilitator. Introduction to IT Networking for Facilities Managers. Class Logistics
 Introduction to IT Networking for Facilities Managers APPA Institute for Facilities Management Dallas, TX January 16, 2017 Facilitator J. Craig Klimczak, D.V.M., M.S. Chief Information Officer Community
Introduction to IT Networking for Facilities Managers APPA Institute for Facilities Management Dallas, TX January 16, 2017 Facilitator J. Craig Klimczak, D.V.M., M.S. Chief Information Officer Community
TOC: Switching & Forwarding
 TOC: Switching & Forwarding Why? Switching Techniques Switch Characteristics Switch Examples Switch Architectures Summary Why? Direct vs. Switched Networks: Single link Switches Direct Network Limitations:
TOC: Switching & Forwarding Why? Switching Techniques Switch Characteristics Switch Examples Switch Architectures Summary Why? Direct vs. Switched Networks: Single link Switches Direct Network Limitations:
Communication Networks - 3 general areas: data communications, networking, protocols
 Communication Networks - Overview CSE 3213 Fall 2011 1 7 September 2011 Course Content 3 general areas: data communications, networking, protocols 1. Data communications: basic concepts of digital communications
Communication Networks - Overview CSE 3213 Fall 2011 1 7 September 2011 Course Content 3 general areas: data communications, networking, protocols 1. Data communications: basic concepts of digital communications
IPv6: An Introduction
 Outline IPv6: An Introduction Dheeraj Sanghi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur dheeraj@iitk.ac.in http://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/dheeraj Problems with
Outline IPv6: An Introduction Dheeraj Sanghi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur dheeraj@iitk.ac.in http://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/dheeraj Problems with
