Comparative Analysis of IEEE Standards in Wireless Networking
|
|
|
- Adrian Underwood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IJECT Vo l. 4, Is s u e Sp l - 2, Ja n - Ma r c h 2013 ISSN : (Online) ISSN : (Print) Comparative Analysis of IEEE Standards in Wireless Networking 1 Vandana Jindal, 2 Anil Kumar Verma, 3 Seema Bawa Thapar Univ., Patiala, Punjab, India Abstract Communication among devices in a network takes place according to some set of rules and procedures called protocols. Various protocols have been established by IEEE to suit the varied requirements of range, devices in the networks, cost, security and fidelity of data..all these protocols are covered under various IEEE 802 standards which have evolved over time keeping in view the requirements described above. Among the plethora of standards, standards governs the communication between wireless networks. Keywords IEEE, IEEE , BSS, IBSS, ESS, PLCP, PMD. I. Introduction Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an organization of engineers, scientists and students who are involved in developing standards for computer and electronics industry. It was founded in 1884 and came into existence as IEEE in 1963 merging American Institute of Electrical Engineers (AIEE) and Institute of Radio Engineers (IRE). These standards provide advantages like interoperability, low product cost etc. IEEE 802 standards are divided into 22 parts namely Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth/ZigBee, and WiMax Certification etc. Table 1: IEEE 802 Standards IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE e IEEE Bridging (networking) and network management Logical link layer Ethernet (CSMA/CD) Token bus (disbanded) Defines a MAC layer for a token ring (inactive) Metropolitan Area Networks (disbanded) Broadband LAN using coaxial cable (disbanded) Fiber optic TAG (disbanded) Integrated Services LAN (disbanded) Interoperable LAN Security (disbanded) Wireless LAN and mesh (Wi-Fi certification) Demand Priority (disbanded) Not used Cable modems (disbanded) Wireless PAN Blue-tooth certification ZigBee Certification Broadband Wireless Access (WiMax Certification) (Mobile) Broadband Wireless Access Resilient Packet Ring IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE IEEE Radio regulatory TAG Co-existence TAG Mobile Broadband Wireless Access Media Independent Handoff Wireless Regional Area Network It comprises a family of networking standards ranging from (physical layer specifications of technologies) Ethernet to wireless. All the specifications use the Ethernet protocol and Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA) for path sharing. The original modulation used in was phase-shift keying (PSK). However, other schemes, such as complementary code keying (CCK), are used in some of the newer specifications. The newer modulation methods provide higher data speed and reduced vulnerability to interference. II. Wireless Networking It is a technology which allows computers to communicate amongst themselves without cables but requires certain protocols. This technology employs the IEEE standards which provide us the technique in creating networks where network wiring is not possible. A. Types of Wireless Networks 1. Wireless PAN Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) connect devices which are within a person s reach. It is based on IEEE standard. The technologies used are: Bluetooth, Infrared data association, Wi-Fi. 2. Wireless LAN Wireless Local Area Network links two or more devices over a short distance using wireless methods. It is based on IEEE standards marketed under the name of Wi-Fi. The technologies used are spread spectrum or Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). 3. Wireless Mesh Network It is a wireless network made up of radio nodes arranged in a mesh topology. It consists of mesh clients (laptops/cell phones), routers and gateways. It is based on IEEE , , , cellular technologies or combinations of one or more types. More than 70 routing protocols may be used for routing the packets in a mesh network. 4. Wireless MAN Wireless Metropolitan Area Network consists of many WLANs. It is based on IEEE standard. The technologies used for this purpose are Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI), and Switched Multi megabit Data Service (SMDS). International Journal of Electronics & Communication Technology 95
2 IJECT Vo l. 4, Is s u e Sp l - 2, Ja n - Ma r c h 2013 ISSN : (Online) ISSN : (Print) 5. Wireless WAN Wireless Wide Area Network covers large areas like between cities or towns. The technologies used are LTE, WiMAX, UMTS, CDMA, cellular digital packet data (CDPD) etc. It is based on IEEE standard. 1. IEEE Wireless LAN Architecture 6. Mobile Devices Network Services rendered by the telephone dept. to phones which are mobile (not fixed) The wireless networking hardware uses the technology that deals with radio frequencies and data transmission. The most widely used standard is given by IEEE. This is a standard which defines all aspects of Radio Frequency Wireless Networking. III. Protocols A network protocol tells us about the rules and conventions for communication to take place between network devices or specify interactions between the communicating entities. Protocols have the techniques for devices to identify and establish connections between them. They also determine how the data is to be sent and received. Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) is a specification for a set of communication protocols to standardize the way that wireless devices, such as cellular telephones and radio transceivers, can be used for Internet access, including , the World Wide Web, newsgroups, and instant messaging family has a long list of over-the-air modulation techniques that use the same basic protocols came into existence in It is thus said to be the first wireless networking standard. After this, many standards came into existence like b, g, and n etc. Of all these, b was the first most widely accepted standard followed by others. The standards (c-f, h, j) are actually the service amendments and extensions or corrections to the previous specifications. A ( legacy) IEEE (legacy mode) [1, 3, 4, 5, 6] is actually the original version of the IEEE wireless networking. It used infrared rays for data transmission at the speed of 1-2 Mbps. It also employed frequency hopping or direct-sequence spread spectrum (DSSS). DSSS version of legacy was quickly replaced by b amendment in 1999 whose transfer rate rose up to 11Mbps.The architecture resides in the Data Link Media Access Control (MAC) sub layer and the physical layer in the OSI reference model. It is the original version of IEEE wireless networking standard which was released in 1997, defining Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/ CA) as medium access method. The technologies (physical layer) specified by this standard were: Diffuse infra red operating. Frequency hopping spread spectrum (@ 1 or 2 Mbps). Direct sequence spread spectrum (@ 1 or 2 Mbps). Fig. 1: Architecture of IEEE Its architecture includes many components and services providing station mobility. (i). Wireless LAN Station The station (STA) is the basic component of the wireless network which may be a laptop PC, handheld device or an access point and can be either mobile or stationary. A station always supports the protocol and a connection to the wireless media. The hardware and software of a network interface card (NIC) supports functionality. (ii). Basic Service Set (BSS) It has a group of many stations. The various topologies included in WLAN are: Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS) [1]: It is also referred to as an ad hoc network. This topology has stations connected through wireless media. In an IBSS it is not necessary that every mobile station can communicate with every other station. Only the ones which are in the close proximity (range) to each other are able to communicate amongst themselves. No relay functions are present in IBSS so the stations are required to be within range of each other. Infrastructure basic Service Set (IBSS): It is a BSS with an Access Point (AP).The station does not communicate directly but through the access point. All the frames are relayed between the stations by the access point. Distributed System: The communication takes place between two access points. The frames from the station are sent to their respective access points from where they are exchanged/ forwarded to that access point having the intended station. Extended Coverage via an Extended Service Set (ESS): An extended service set is a set of infrastructure BSS s, where the access points communicate amongst themselves forwarding the traffic from one BSS to another, facilitating the movement of stations between BSS s. The communication amongst the access points takes place with the help of distributed system. 2. Services standards clearly define the stations services like security, data delivery, de-authorization, privacy, association, disassociation, re-association, distribution and integration etc. 96 International Journal of Electronics & Communication Technology
3 ISSN : (Online) ISSN : (Print) Fig. 2: MAC Layers in IEEE Standard (i) Media Access Control: the following functionalities are provided Reliable data delivery for the upper layers over the wireless PHY media. Provides a controlled access method to the shared wireless media i.e. CSMA/CA. Provide security and privacy. (ii). Physical Layer (PHY): The physical layer is the interface between the MAC and the wireless media where frames are transmitted and received. The PHY layer provides three different techniques for transferring of data. These are: Spread Spectrum, Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS), Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Infra Red (IR). Spread Spectrum: A technique which employs more bandwidth for reliability thus reducing the impact of interference on the media. FHSS: A method of transmitting radio signals by rapidly switching a carrier among different frequency channels, using a pseudo random sequence known to each transmitter and receiver. DSSS: It spreads a signal over a longer frequency band by multiplexing it with a signature code to minimize local interference and background noise. IR: The IR PHY uses infra red light to transmit binary data using a specific modulation technique address mobility, security, reliability, dynamic nature of wireless LANs etc. B a It is an extension of standards. It is believed that it came into existence after b. Actually it was created at the same time but due to its high cost it made its place more in the business world rather than homes. It uses 5GHz frequency spectrum, supporting nearly 54Mbps of bandwidth. Higher the frequency, more the difficulty faced by the signals in penetrating through walls and other solid objects. 1. Architecture of a Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM): The IEEE a standard specifies an OFDM physical layer (PHY) splitting into information across 52 different sub carriers transmitting the data at different speeds like 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48 or 54 Mbps. It is a method that allows transmitting the high data rates over extremely hostile channels at a comparable low complexity. OFDM s spread spectrum technique distributes the data over a large number of carriers that are spread apart at precise frequencies. This spacing provides the orthogonality in this technique which prevents the demodulators from seeing IJECT Vo l. 4, Is s u e Sp l - 2, Ja n - Ma r c h 2013 frequencies other than their own. Primary goal of the OFDM PHY is to transmit MAC protocol data units (MACDUs). OFDM PHY is divided into 2 elements: Physical layer Convergence Protocol (PLCP): The PLCP [2] sublayer communicates with the data link layer (MAC). Its main work is to collect PLCP Service Data Units (PSDUs). The MAC layer communicates with the PLCP with certain commands through a Service Access Point (SAP). On receiving the commands the PLCP prepares MAC protocol data units (MPDUs) for transmission. The dependence of the MAC layer on the Physical Medium Dependent (PMD) sub layer is reduced by mapping MPDUs into a frame format suitable for transmission by the PMD. The PLCP also delivers incoming frames from the wireless medium to the MAC layer. Physical Medium Dependent (PMD): The PMD sub layer provides transmission and reception of physical layer data units between two stations via the wireless medium. To provide this service, the PMD interfaces with the wireless medium and provides modulation and demodulation of the frame transmissions. The PLCP and PMD sub layers communicate via commands through a SAP to govern transmission and reception functions. Fast maximum speed. Less interference Auto configuration Highest cost Shorter range signal so gets obstructed. It uses OFDM based air interface. OFDM is a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. It is similar to coded OFDM (COFDM) and discrete multi-tone modulation (DMT) and is a frequency division multiplexing (FDM) scheme used as a digital multi-carrier modulation method. C b IEEE b is an amendment to IEEE specification. It uses CSMA/CA media access method. IEEE b is a direct extension of Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS). It uses Complementary Code keying (CCK) as its modulation technique. CCK is a modulation scheme which helps in achieving data rate higher than 2Mbps at the expense of shorter distance. Lowest cost Signal range good. Not easily obstructed. Slowest maximum speed. Home appliances may interface on the unregulated frequency band. D g The g specification is a standard for wireless local area networks (WLANs) that offers transmission over relatively short distances at up to 54 megabits per second (Mbps), compared with the 11 Mbps with the earlier b standard. Networks employing g operate at radio frequencies between 2.4GHz and GHz, the same band as b. But the g specification employs orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) (the modulation scheme used in a, to obtain higher data speed). This feature makes b and g devices compatible within a single network. Modification of an b access point to g compliance usually involves only a International Journal of Electronics & Communication Technology 97
4 IJECT Vo l. 4, Is s u e Sp l - 2, Ja n - Ma r c h 2013 ISSN : (Online) ISSN : (Print) firmware upgrade. Fast maximum speed. Signal range is good and not easily obstructed. Costs more than b Appliances may interfere on the unregulated signal frequency. E e The wireless community faces some constraints like standards, bandwidth, link errors, power, security, mobility and roaming etc., in contrast to the wired counterparts. With increasing demand of support for real time applications like the Voice over WLAN and streaming multimedia, there is a compelling need for Quality of Service (QoS) in present day WLANs. IEEE MAC has become a defacto standard for WLANs, but there are many inherent QoS limitations in the base standard, as it was basically developed for data services. The IEEE Task Group E (TGe), ratified a QoS extension to the base standard namely IEEE e. The IEEE e standard provides many mechanisms for QoS support at the MAC layer level. However, even the service differentiation provided in IEEE e is not enough to meet the QoS requirements of time bounded multimedia traffic at high load. It adds QoS features and multimedia support to the existing IEEE b and IEEE a wireless standards, while maintaining full backward compatibility with these standards. The amendment was incorporated into the published IEEE standard. F n n systems employ MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) which defines multiple transmit and receive radios each with its own antenna that combine to deliver multiple streams of data between stations on the same channel. By digitally controlling simultaneous transmissions and reception, n stations can effectively multiply the data rate by the number of simultaneous spatial streams they support n defines up to 4 spatial streams. The Wi-Fi Alliance n Draft 2 certification requires that systems support at least 2 spatial streams. Spatial multiplexing can increase the burst transmission rate up to 4 times. Fastest maximum speed Best signal range. More resistant to signal interference from outside sources. Totally backward compatible Many new laptops come with in-built adaptors for n and can also be added via an interface like USB. Features of earlier standards like Radio Management, Wireless Multi media, Intrusion Detection etc. are supposed to work better with g. Standard not yet finalized. Costs more than g. Use of multiple signals may greatly interfere with nearly b/g based networks. Fig. 3: Non-Overlapping Channels for 2.4 GHz WLAN b uses a DSSS and both g and a use OFDM g clients using OFDM enjoy better performance at the same ranges as b clients do. When g clients are operating at the b rates (11, 5.5, 2, and 1Mbps), they re actually using the same modulation b does. Fig. 3 shows the 14 different channels (each 22Mhz wide) that the FCC released in the 2.4GHz range. Fig. 4: 14 (each 22Mhz wide) that the FCC released in the 2.4GHz Range IEEE divided the 2.4GHz ISM band into 14 channels, but local regulatory agencies (FCC) designate which channels are allowed. For e.g. channels 1 through 11 in the US. Each channel in the 2.4 GHz ISM band is 22 MHz wide with 5 MHz separation, resulting in overlap with channels before or after a defined channel. Therefore, a separation of 5 channels is needed to ensure unique non overlapping channels. Given the FCC example of 11 channels, the maximum of non overlapping frequencies are channels 1, 6, and 11. IV. Conclusion A firm hold is required on the composition of WiFi wireless LAN technologies. Wi-Fi is designed for medium-range data transfers, and most versions of work up to about feet away from the access point indoors, and about 1,000 feet away outdoors and with the increase in distance between the computer/laptop and the access point, the speed and the quality deteriorates drastically. It also doesn t help when there is an interference from microwaves or cordless phones which use the same frequency that g and b use: 2.4 GHz. Another disadvantage for WiFi products is their security system. The Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is the common wireless encryption standard which is easily broken even when configured accurately. To counteract this problem, however, Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) has been established. Many new standards are also in the pipeline like: IEEE aa, ac, ad, ae, af, ah, ai etc. The updating of the standard is the responsibility of the task group. 98 International Journal of Electronics & Communication Technology
5 ISSN : (Online) ISSN : (Print) IJECT Vo l. 4, Is s u e Sp l - 2, Ja n - Ma r c h 2013 Table: Depicting 802 stds. & their characteristics Standard a b g e n Transmission OFDM DSSS DSSS/ OFDM QoS TDMA MIMO SDM Spectrum (GHz) / 5 2.4/5 Data Rate in 1-11 (DSSS) Mbps 6-54(OFDM) No. of Channels overlapping Upto Interference HyperLAN II Microwave, Cordless Phones,Bluetooth, HomeRF, Light Bulbs! Security WEP/WPA WEP/WPA WEP/WPA Enhancement to that added higher data rate modes to the DSSS (Direct Extends the Sequence Spread Specifies a PHY maximum data rate Spectrum) already that operates in the of WLAN devices defined in the 5 GHz U-NII band that operate in the original in the US - initially 2.4 GHz band, in a standard, AND fashion that permits Basics of Boosted data since expanded interoperation with physical speed to 11 Mbps, to additional b devices, and logical 22 MHz frequencies, Uses OFDM, networking Bandwidth yields Uses Orthogonal Operates at up to concepts 3 non-overlaping FDM, 54 megabits per channels in the Enhanced data speed second (Mbps), with frequency range to 54 Mbps, fall-back speeds of Ratified after b that include the b GHz, speeds. Beacons at 1 Mbps, falls back to 5.5, 2, or 1 Mbps from 11 Mbps max. Enhancement to that includes quality of service (QoS) features, Facilitates prioritization of data, voice, and video transmissions Higher-speed standards -- under development, Several competing and non-compatible technologies; often called pre-n, Top speeds claimed of 108, 240, and 350+ MHz, Competing proposals come from the groups, EWC, TGn Sync, and WWiSE and are all variations based MIMO. References [1] IEEE Working Group ( ). IEEE , Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical layer (PHY) specifications. [2] [Online] Available: [3] "Official IEEE working group project timelines, Sept. 19, 2009 [4] "Wi-Fi CERTIFIED n: longer-range, Faster Throughput, Multimedia-Grade Wi-Fi networks, September [5] "802.11n Delivers Better Range, Wi-Fi Planet, [6] IEEE Working Group ( ). IEEE , Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical layer (PHY) specifications. Vandana Jindal, B.Tech, MCA, M.Phil. is an Assistant Professor and Head of Department of Computer Science at D.A.V College, Bathinda and a Doctoral student in the Department of Computer Science, Thapar University, Patiala. Since January 2009, she has been associated with Thapar University and has been working on Wireless Sensor Networks. Apart from WSNs, her research interests include Database Management Systems. She is a member of IEEE and IEI. International Journal of Electronics & Communication Technology 99
6 IJECT Vo l. 4, Is s u e Sp l - 2, Ja n - Ma r c h 2013 ISSN : (Online) ISSN : (Print) A K Verma is currently working as Assistant Professor in the department of Computer Science and Engineering at Thapar University, Patiala in Punjab (INDIA). He received his B.S. and M.S. in 1991 and 2001 respectively, majoring in Computer Science and Engineering. He has worked as Lecturer at M.M.M. Engg. College,Gorakhpur from 1991 to From 1996 he is associated with the Thapar University. He has been a visiting faculty to many institutions. He has published over 100 papers in referred journals and conferences (India and Abroad). He is member of various program committees for different International/National Conferences and is on the review board of various journals. He is a senior member (ACM), MIEEE, LMCSI (Mumbai), GMAIMA (New Delhi). He is a certified software quality auditor by MoCIT, Govt. of India. His main areas of interests are: Bioinformatics, database management systems and Computer Networks. His research interests include wireless networks, routing algorithms, securing ad hoc networks and design/develop applications for other fields based on IT. Seema Bawa holds M.Tech (Computer Science) degree from IIT Kharagpur and Ph.D. from Thapar Institute of Engineering & Technology, Patiala. She is currently Professor and Dean of Students affairs (DOSA). Her areas of interest include Parallel and distributed computing, Grid computing, VLSI Testing and network management. Prof. Bawa is member of IEEE, ACM, Computer society of India and VLSI Society of India. 100 International Journal of Electronics & Communication Technology
Wireless technology Principles of Security
 Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment:
 Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
IEEE Romel Rudyard J. Lucentales, ECE 5
 IEEE 802.11 Romel Rudyard J. Lucentales, ECE 5 IEEE 802.11 a set of standards for wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication developed by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee (IEEE 802)
IEEE 802.11 Romel Rudyard J. Lucentales, ECE 5 IEEE 802.11 a set of standards for wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication developed by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee (IEEE 802)
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 8 High-Speed WLANs and WLAN Security Objectives Describe how IEEE 802.11a networks function and how they differ from 802.11 networks Outline how 802.11g
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 8 High-Speed WLANs and WLAN Security Objectives Describe how IEEE 802.11a networks function and how they differ from 802.11 networks Outline how 802.11g
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer. Computer Networks: Wireless LANs
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
Wireless Standards a, b/g/n, and ac The family explained
 Wireless Standards 802.11a, 802.11b/g/n, and 802.11ac The 802.11 family explained by Bradley Mitchell Updated December 09, 2017 Home and business owners looking to buy networking gear face an array of
Wireless Standards 802.11a, 802.11b/g/n, and 802.11ac The 802.11 family explained by Bradley Mitchell Updated December 09, 2017 Home and business owners looking to buy networking gear face an array of
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Wireless LAN. Access Point. Provides network connectivity over wireless media
 LAN Technologies 802.11 Wireless LAN Network connectivity to the legacy wired LAN Access Point Desktop with PCI 802.11 LAN card Laptop with PCMCIA 802.11 LAN card Provides network connectivity over wireless
LAN Technologies 802.11 Wireless LAN Network connectivity to the legacy wired LAN Access Point Desktop with PCI 802.11 LAN card Laptop with PCMCIA 802.11 LAN card Provides network connectivity over wireless
WIRELESS LANS. By: M. Habibullah Pagarkar Mandar Gori Rajesh Jaiswal
 WIRELESS LANS By: M. Habibullah Pagarkar Mandar Gori Rajesh Jaiswal Introduction Why wireless? World will become fully mobile Increase in wireless devices usage Wireless will succeed; integrates into many
WIRELESS LANS By: M. Habibullah Pagarkar Mandar Gori Rajesh Jaiswal Introduction Why wireless? World will become fully mobile Increase in wireless devices usage Wireless will succeed; integrates into many
Wireless Networks. Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas. Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov.
 Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Wireless LANs. The Protocol Stack The Physical Layer The MAC Sublayer Protocol The Frame Structure Services 802.
 Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
WNC-0300USB. 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL
 WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560. Wireless Technologies. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth 7/3/2014.
 Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Chapter 3: Overview 802 Standard
 Chapter 3: Overview 802 Standard IEEE - Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers What is the IEEE? international non-profit, professional organization for the advancement of technology related
Chapter 3: Overview 802 Standard IEEE - Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers What is the IEEE? international non-profit, professional organization for the advancement of technology related
Lecture 23 Overview. Last Lecture. This Lecture. Next Lecture ADSL, ATM. Wireless Technologies (1) Source: chapters 6.2, 15
 Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Wireless Local Area Networks. Networks: Wireless LANs 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Chapter 7. Basic Wireless Concepts and Configuration. Part I
 Chapter 7 Basic Wireless Concepts and Configuration Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 7-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
Chapter 7 Basic Wireless Concepts and Configuration Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 7-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
EE 597: Wireless Networks (Spring 12)
 EE 597: Wireless Networks (Spring 12) Intro to Cellular and WiFi Networks Bhaskar Krishnamachari= Acknowledgement These slides were prepared by Dr. Kyuho Son, kyuhoson@usc.edu, visiting scholar at USC.
EE 597: Wireless Networks (Spring 12) Intro to Cellular and WiFi Networks Bhaskar Krishnamachari= Acknowledgement These slides were prepared by Dr. Kyuho Son, kyuhoson@usc.edu, visiting scholar at USC.
Wireless Technologies
 Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
802 Wireless Access Techniques Overview
 802 Wireless Access Techniques Overview Markku Renfors Institute of Communications Engineering Tampere University of Technology TLT-6556 15.2.2007/MR 1 Wireless Access Techniques WLAN,, Wireless Local
802 Wireless Access Techniques Overview Markku Renfors Institute of Communications Engineering Tampere University of Technology TLT-6556 15.2.2007/MR 1 Wireless Access Techniques WLAN,, Wireless Local
Wireless Networking based on Chapter 15 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers
 Wireless Networking 802.11 based on Chapter 15 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers topics Standards Technical Concepts Implementation Troubleshooting 802.11 timeline source: Anandtech
Wireless Networking 802.11 based on Chapter 15 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers topics Standards Technical Concepts Implementation Troubleshooting 802.11 timeline source: Anandtech
Naveen Kumar. 1 Wi-Fi Technology
 Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
Architecture. Copyright :I1996 IEEE. All rights reserved. This contains parts from an unapproved draft, subject to change
 802.11 Architecture Copyright :I1996 IEEE. All rights reserved. This contains parts from an unapproved draft, subject to change What is unique about wireless? Difficult media - interference and noise -
802.11 Architecture Copyright :I1996 IEEE. All rights reserved. This contains parts from an unapproved draft, subject to change What is unique about wireless? Difficult media - interference and noise -
04/11/2011. Wireless LANs. CSE 3213 Fall November Overview
 Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8
 MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8 Michael L. Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University November 2017 The Multiple Access Problem How can multiple mobiles access (communicate with) the same
MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8 Michael L. Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University November 2017 The Multiple Access Problem How can multiple mobiles access (communicate with) the same
Unit title: Mobile Technology: Device Connectivity (SCQF level 5) Outcome 1
 1 Outcome 1 A description of mobile device internet connectivity using two current Wi-Fi methods. A description of mobile device internet connectivity using two current GSM mobile telephony methods. A
1 Outcome 1 A description of mobile device internet connectivity using two current Wi-Fi methods. A description of mobile device internet connectivity using two current GSM mobile telephony methods. A
Lecture Objectives. Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs. Agenda (1) Agenda (2) Wireless Spectrum (1)
 Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs Discuss the impact of the wireless environment on networks Explain the concept of spread spectrum,
Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs Discuss the impact of the wireless environment on networks Explain the concept of spread spectrum,
Overview of Wireless LANs
 Wireless LANs Chapter 17 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Overview of Wireless LANs use wireless transmission medium issues of high prices, low data rates, occupational safety concerns, & licensing requirements
Wireless LANs Chapter 17 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Overview of Wireless LANs use wireless transmission medium issues of high prices, low data rates, occupational safety concerns, & licensing requirements
IEEE Overview (2)
 Wireless LANs December 2011 March 2012 IEEE 802.11 Overview (2) รศ. ดร. อน นต ผลเพ ม Assoc. Prof. Anan Phonphoem, Ph.D. anan.p@ku.ac.th Intelligent Wireless Network Group (IWING Lab) http://iwing.cpe.ku.ac.th
Wireless LANs December 2011 March 2012 IEEE 802.11 Overview (2) รศ. ดร. อน นต ผลเพ ม Assoc. Prof. Anan Phonphoem, Ph.D. anan.p@ku.ac.th Intelligent Wireless Network Group (IWING Lab) http://iwing.cpe.ku.ac.th
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs
 Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wireless Transmission for LAN Radio Frequency Transmission (RF) Infrared Transmission 2 1
Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wireless Transmission for LAN Radio Frequency Transmission (RF) Infrared Transmission 2 1
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN)
 Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN) Mobile Communication and Mobile Computing Prof. Dr. Alexander Schill http://www.rn.inf.tu-dresden.de
Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN) Mobile Communication and Mobile Computing Prof. Dr. Alexander Schill http://www.rn.inf.tu-dresden.de
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs
 Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h, i, n z) Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Comparison Prof. Jó Ueyama courtesy
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h, i, n z) Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Comparison Prof. Jó Ueyama courtesy
02/21/08 TDC Branch Offices. Headquarters SOHO. Hot Spots. Home. Wireless LAN. Customer Sites. Convention Centers. Hotel
 TDC 363 Introductions to LANs Lecture 7 Wireless LAN 1 Outline WLAN Markets and Business Cases WLAN Standards WLAN Physical Layer WLAN MAC Layer WLAN Security WLAN Design and Deployment 2 The Mobile Environment
TDC 363 Introductions to LANs Lecture 7 Wireless LAN 1 Outline WLAN Markets and Business Cases WLAN Standards WLAN Physical Layer WLAN MAC Layer WLAN Security WLAN Design and Deployment 2 The Mobile Environment
Learning Objectives. Introduction. Advantages of WLAN. Information Technology. Mobile Computing. Module: Wireless Local Area Network: IEEE 802.
 Information Technology Mobile Computing Module: Wireless Local Area Network: IEEE 802.11 Learning Objectives Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network Advantages of WLAN Types of WLAN IEEE 802.11 standards
Information Technology Mobile Computing Module: Wireless Local Area Network: IEEE 802.11 Learning Objectives Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network Advantages of WLAN Types of WLAN IEEE 802.11 standards
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371
 Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
Overview of IEEE Networks. Timo Smura
 Overview of IEEE 802.11 Networks Timo Smura 24.03.2004 Outline Introduction IEEE 802.11 standards Protocol model Network topologies 802.11 MAC layer 802.11 PHY layers Interoperability: Wi-Fi Alliance 3GPP
Overview of IEEE 802.11 Networks Timo Smura 24.03.2004 Outline Introduction IEEE 802.11 standards Protocol model Network topologies 802.11 MAC layer 802.11 PHY layers Interoperability: Wi-Fi Alliance 3GPP
This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to successfully survey, install, and administer enterprise Wi-Fi networks.
 Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to successfully survey, install, and administer enterprise Wi-Fi networks. Course
Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to successfully survey, install, and administer enterprise Wi-Fi networks. Course
Wireless Terms. Uses a Chipping Sequence to Provide Reliable Higher Speed Data Communications Than FHSS
 How to Set Up a Secure Home Wireless Network What you don t know about setting up a home wireless network can hurt you. 2008 APCUG Convention Session Tom Jones, P.E., RCDD-NTS CQS-CWLSS AGENDA Some Terms
How to Set Up a Secure Home Wireless Network What you don t know about setting up a home wireless network can hurt you. 2008 APCUG Convention Session Tom Jones, P.E., RCDD-NTS CQS-CWLSS AGENDA Some Terms
A Study Wireless Communication Domain
 A Study Wireless Communication Domain Sangram Routray 1, Sanjib k. Nayak 2 Lalit M. Satapathy 1 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engg. KIST,Bhubaneswar 2 Department of Computer science and
A Study Wireless Communication Domain Sangram Routray 1, Sanjib k. Nayak 2 Lalit M. Satapathy 1 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engg. KIST,Bhubaneswar 2 Department of Computer science and
1. INTRODUCTION. Wi-Fi 1
 Wi-Fi 1 1. INTRODUCTION Wi-Fi, or Wireless Fidelity, is freedom: it allows you to connect to the Internet from your home, a bed in a hotel room or at a conference room at work without wires. How? Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi 1 1. INTRODUCTION Wi-Fi, or Wireless Fidelity, is freedom: it allows you to connect to the Internet from your home, a bed in a hotel room or at a conference room at work without wires. How? Wi-Fi
Wireless Technologies: Wi-Fi
 SHORT < RANGE > LONG Wireless Technologies: Wi-Fi Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Marquette University A presentation in the Senior Design Project (SDP) course in the OPUS
SHORT < RANGE > LONG Wireless Technologies: Wi-Fi Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Marquette University A presentation in the Senior Design Project (SDP) course in the OPUS
Computer Networks. Wireless LANs
 Computer Networks Wireless LANs Mobile Communication Technology according to IEEE (examples) Local wireless networks WLAN 802.11 Personal wireless nw WPAN 802.15 WiFi 802.11a 802.11b 802.11h 802.11i/e/
Computer Networks Wireless LANs Mobile Communication Technology according to IEEE (examples) Local wireless networks WLAN 802.11 Personal wireless nw WPAN 802.15 WiFi 802.11a 802.11b 802.11h 802.11i/e/
Feature. What exactly is WLAN? More reading:
 The WLAN Roadmap Wireless Local Area Networking (WLAN) is a simple concept, but one that entails a wide, sometimes confusing, variety of standards, implementations, and future plans for development. This
The WLAN Roadmap Wireless Local Area Networking (WLAN) is a simple concept, but one that entails a wide, sometimes confusing, variety of standards, implementations, and future plans for development. This
IT220 Network Standards & Protocols. Unit 6: Chapter 6 Wireless LANs
 IT220 Network Standards & Protocols Unit 6: Chapter 6 Wireless LANs 2 Objectives Identify the major needs and stakeholders for computer networks and network applications. Identify the classifications of
IT220 Network Standards & Protocols Unit 6: Chapter 6 Wireless LANs 2 Objectives Identify the major needs and stakeholders for computer networks and network applications. Identify the classifications of
Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 7: Wireless LAN
 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 7: Wireless LAN [Schiller, Section 7.3] [Reader, Part 6] [Optional: "IEEE 802.11n Development: History, Process, and Technology", Perahia, IEEE Communications
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 7: Wireless LAN [Schiller, Section 7.3] [Reader, Part 6] [Optional: "IEEE 802.11n Development: History, Process, and Technology", Perahia, IEEE Communications
Data Communication. Introduction of Communication. Data Communication. Elements of Data Communication (Communication Model)
 Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
Wireless LAN -Architecture
 Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
Advanced Computer Networks WLAN
 Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2014 1 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Outlook Medium Access COPE Short Range Wireless Networks:
Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2014 1 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Outlook Medium Access COPE Short Range Wireless Networks:
WLAN a-z 2010/02/15. (C) Herbert Haas
 WLAN 802.11a-z (C) Herbert Haas 2010/02/15 Wireless Products WLAN is integrated E. g. Intel Centrino chipsets Increasing data rates Towards Fast Ethernet speeds and more Today strong native security solutions
WLAN 802.11a-z (C) Herbert Haas 2010/02/15 Wireless Products WLAN is integrated E. g. Intel Centrino chipsets Increasing data rates Towards Fast Ethernet speeds and more Today strong native security solutions
Overview : Computer Networking. Spectrum Use Comments. Spectrum Allocation in US Link layer challenges and WiFi WiFi
 Overview 15-441 15-441: Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 21: Wireless Justine Sherry Peter Steenkiste Fall 2017 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f17 Link layer challenges and WiFi WiFi Basic WiFi design Some
Overview 15-441 15-441: Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 21: Wireless Justine Sherry Peter Steenkiste Fall 2017 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f17 Link layer challenges and WiFi WiFi Basic WiFi design Some
Wireless Communication
 Wireless Communication Hwajung Lee Key Reference: Prof. Jong-Moon Chung s Lecture Notes at Yonsei University Wireless Communications Bluetooth Wi-Fi Mobile Communications LTE LTE-Advanced WLAN WLAN (Wireless
Wireless Communication Hwajung Lee Key Reference: Prof. Jong-Moon Chung s Lecture Notes at Yonsei University Wireless Communications Bluetooth Wi-Fi Mobile Communications LTE LTE-Advanced WLAN WLAN (Wireless
WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK
 1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS
 3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
Topics for Today. More on Ethernet. Wireless LANs Readings. Topology and Wiring Switched Ethernet Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet. 4.3 to 4.
 Topics for Today More on Ethernet Topology and Wiring Switched Ethernet Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet Wireless LANs Readings 4.3 to 4.4 1 Original Ethernet Wiring Heavy coaxial cable, called thicknet,
Topics for Today More on Ethernet Topology and Wiring Switched Ethernet Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet Wireless LANs Readings 4.3 to 4.4 1 Original Ethernet Wiring Heavy coaxial cable, called thicknet,
Discovering Computers Chapter 9 Communications and Networks
 Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 9 Communications and Networks Chapter 9 Objectives Discuss the components required for successful communications Identify various sending and receiving devices Describe
Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 9 Communications and Networks Chapter 9 Objectives Discuss the components required for successful communications Identify various sending and receiving devices Describe
Alternate PHYs
 A whitepaper by Ayman Mukaddam 2018, LLC Page 1 of 12 Contents Modern 802.11 Amendments... 3 Traditional PHYs Review (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz PHYs)... 3 802.11ad Directional Multi-Gigabit - DMG PHY... 4 Frequency
A whitepaper by Ayman Mukaddam 2018, LLC Page 1 of 12 Contents Modern 802.11 Amendments... 3 Traditional PHYs Review (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz PHYs)... 3 802.11ad Directional Multi-Gigabit - DMG PHY... 4 Frequency
3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE
 3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE 802.11 WCOM, WLAN, 1 References [1] J. Schiller, Mobile Communications, 2nd Ed., Pearson, 2003. [2] Martin Sauter, "From GSM to LTE", chapter 6, Wiley, 2011. [3] wiki to
3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE 802.11 WCOM, WLAN, 1 References [1] J. Schiller, Mobile Communications, 2nd Ed., Pearson, 2003. [2] Martin Sauter, "From GSM to LTE", chapter 6, Wiley, 2011. [3] wiki to
Data and Computer Communications. Chapter 13 Wireless LANs
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
NT1210 Introduction to Networking. Unit 6: Chapter 6, Wireless LANs
 NT1210 Introduction to Networking Unit 6: Chapter 6, Wireless LANs Objectives Identify the major needs and stakeholders for computer networks and network applications. Identify the classifications of networks
NT1210 Introduction to Networking Unit 6: Chapter 6, Wireless LANs Objectives Identify the major needs and stakeholders for computer networks and network applications. Identify the classifications of networks
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks. Csci 4211 David H.C. Du
 Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Csci 4211 David H.C. Du Wireless LAN IEEE 802.11 a, b, g IEEE 802.15 Buletooth Hidden Terminal Effect Hidden Terminal Problem Hidden terminals A, C cannot hear each
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Csci 4211 David H.C. Du Wireless LAN IEEE 802.11 a, b, g IEEE 802.15 Buletooth Hidden Terminal Effect Hidden Terminal Problem Hidden terminals A, C cannot hear each
CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks
 King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Engineering CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks Dr. Ridha OUNI rouni@ksu.edu.sa LMS web site References Text book
King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Engineering CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks Dr. Ridha OUNI rouni@ksu.edu.sa LMS web site References Text book
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei 1393
 Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 1 PLCP, Packet Format 2 PHY Layer Characteristics and Data Rates Area Concept Layers and Functions (PLCP and PMD Sublayers) Antennas DSSS in IEEE 802.11b
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 1 PLCP, Packet Format 2 PHY Layer Characteristics and Data Rates Area Concept Layers and Functions (PLCP and PMD Sublayers) Antennas DSSS in IEEE 802.11b
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Wireless Networks
 802.11 Wireless Networks Presentation for North Central Regional Meeting October 19, 2010 Tom Jones, PE, RCDD / NTS Field Sales Engineer, D-Link Agenda Brief History of Wireless Networks 802.11b, 802.11g
802.11 Wireless Networks Presentation for North Central Regional Meeting October 19, 2010 Tom Jones, PE, RCDD / NTS Field Sales Engineer, D-Link Agenda Brief History of Wireless Networks 802.11b, 802.11g
Wi-Fi. Metro Part 1. Metropolitan based Wi- Friend or Foe?
 Metro Part 1 Wi-Fi Friend or Foe? The number of municipalities getting into the Wi-Fi game has more than tripled in the past two years. Worried yet? Part 1 in a two-part series. By Christopher Skarica,
Metro Part 1 Wi-Fi Friend or Foe? The number of municipalities getting into the Wi-Fi game has more than tripled in the past two years. Worried yet? Part 1 in a two-part series. By Christopher Skarica,
 Wireless Networking WiFi Standards 802.11a 5GHz 54MB 802.11b 2.4 GHz 11MB 802.11g 2.4GHz 52MB 802.11n 2.4/5GHz 108MB 802.11b The 802.11b standard has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s, and uses
Wireless Networking WiFi Standards 802.11a 5GHz 54MB 802.11b 2.4 GHz 11MB 802.11g 2.4GHz 52MB 802.11n 2.4/5GHz 108MB 802.11b The 802.11b standard has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s, and uses
6.9 Summary. 11/20/2013 Wireless and Mobile Networks (SSL) 6-1. Characteristics of selected wireless link standards a, g point-to-point
 Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Wireless Networking. Chapter The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
OPNET based Performance Evaluation of WIMAX Network with WIMAX Management using Different QoS
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 6, June 2014, pg.862
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 6, June 2014, pg.862
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition. Chapter 8 Wireless Networking
 Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 8 Wireless Networking Objectives Explain how nodes exchange wireless signals Identify potential obstacles to successful wireless transmission and their repercussions,
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 8 Wireless Networking Objectives Explain how nodes exchange wireless signals Identify potential obstacles to successful wireless transmission and their repercussions,
It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers.
 1 Communications It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers. Numerous applications depend on communication systems: E-mail Instant messaging (IM) Internet
1 Communications It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers. Numerous applications depend on communication systems: E-mail Instant messaging (IM) Internet
Overview of Wi-Fi. Dr. Srikanth Subramanian CKO, Nanocell Networks Wi-Fi A Wireless Success Story
 Overview of Wi-Fi Dr. Srikanth Subramanian CKO, Nanocell Networks www.nanocellnetworks.com Wi-Fi A Wireless Success Story Wi-Fi present in all laptops/aps Wi-Fi Traffic trends Source: Cisco percentage
Overview of Wi-Fi Dr. Srikanth Subramanian CKO, Nanocell Networks www.nanocellnetworks.com Wi-Fi A Wireless Success Story Wi-Fi present in all laptops/aps Wi-Fi Traffic trends Source: Cisco percentage
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 3: Wireless LANs and IEEE 802.11 Part I Now we study a significant new area of wireless communications over the past 10 years Wireless
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 3: Wireless LANs and IEEE 802.11 Part I Now we study a significant new area of wireless communications over the past 10 years Wireless
Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology
 Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology Mobile Communication Entails transmission of data to and from handheld devices Two or more communicating devices
Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology Mobile Communication Entails transmission of data to and from handheld devices Two or more communicating devices
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE standards
 HW Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802.11 standards WLAN Standard (IEEE 802.11) The IEEE 802.11 is a family of standards that governs the operations and functions of WLANs.
HW Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802.11 standards WLAN Standard (IEEE 802.11) The IEEE 802.11 is a family of standards that governs the operations and functions of WLANs.
DRAFT. Wireless Networking. Introduction
 Introduction Wireless Networking The IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN Standard Wireless Networking Bluetooth, WiMAX, RFID, and Mobile Communications Wireless LAN Security DRAFT Introduction So far, we have been
Introduction Wireless Networking The IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN Standard Wireless Networking Bluetooth, WiMAX, RFID, and Mobile Communications Wireless LAN Security DRAFT Introduction So far, we have been
Wireless Networks. CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: , Kurose and Ross
 Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Wireless Local Area Network (IEEE )
 Wireless Local Area Network (IEEE 802.11) -IEEE 802.11 Specifies a single Medium Access Control (MAC) sublayer and 3 Physical Layer Specifications. Stations can operate in two configurations : Ad-hoc mode
Wireless Local Area Network (IEEE 802.11) -IEEE 802.11 Specifies a single Medium Access Control (MAC) sublayer and 3 Physical Layer Specifications. Stations can operate in two configurations : Ad-hoc mode
Data Communications. Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs
 Data Communications Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs Wireless Networks Several different types of communications networks are using unguided media. These networks are generally referred to as wireless
Data Communications Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs Wireless Networks Several different types of communications networks are using unguided media. These networks are generally referred to as wireless
IEEE Wireless LANs Part I: Basics
 IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs Part I: Basics Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this
IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs Part I: Basics Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this
INTRODUCTION DATA COMMUNICATION TELECOMMUNICATIONS SYSTEM COMPONENTS 1/28/2015. Satish Chandra satish0402.weebly.com
 INTRODUCTION DATA COMMUNICATION Satish Chandra satish0402.weebly.com The term telecommunication means communication at a distance. The word data refers to information presented in whatever form is agreed
INTRODUCTION DATA COMMUNICATION Satish Chandra satish0402.weebly.com The term telecommunication means communication at a distance. The word data refers to information presented in whatever form is agreed
Network Media and Layer 1 Functionality
 Network Media and Layer 1 Functionality BSAD 146 Dave Novak Dean, Chapter 3, pp 93-124 Objectives Introduction to transmission media Basic cabling Coaxial Twisted pair Optical fiber Basic wireless (NIC)
Network Media and Layer 1 Functionality BSAD 146 Dave Novak Dean, Chapter 3, pp 93-124 Objectives Introduction to transmission media Basic cabling Coaxial Twisted pair Optical fiber Basic wireless (NIC)
CSMC 417. Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala Ashok Agrawala. Fall 2018 CMSC417 Set 1 1
 CSMC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2018 Ashok Agrawala Fall 2018 CMSC417 Set 1 1 The Medium Access Control Sublayer November 18 Nov 6, 2018 2 Wireless Networking Technologies November 18
CSMC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2018 Ashok Agrawala Fall 2018 CMSC417 Set 1 1 The Medium Access Control Sublayer November 18 Nov 6, 2018 2 Wireless Networking Technologies November 18
Mobile and Sensor Systems
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Wi-Fi Scanner. Glossary. LizardSystems
 Wi-Fi Scanner Glossary LizardSystems 2 Table of Contents 802 6 802.11 6 802.11a 6 802.11b 6 802.11d 6 802.11e 6 802.11g 6 802.11h 6 802.11i 6 802.11j 6 802.11n 7 802.1X 7 802.3 7 A 8 Ad-Hoc mode 8 AES
Wi-Fi Scanner Glossary LizardSystems 2 Table of Contents 802 6 802.11 6 802.11a 6 802.11b 6 802.11d 6 802.11e 6 802.11g 6 802.11h 6 802.11i 6 802.11j 6 802.11n 7 802.1X 7 802.3 7 A 8 Ad-Hoc mode 8 AES
Mobile Computing IEEE Standard 9/11/12. CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2012
 Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2012 IEEE IEEE (Ins4tute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) established the 802.11 Group in 1990. Specifica4ons for standard ra4fied in 1997. Ini4al speeds were
Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2012 IEEE IEEE (Ins4tute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) established the 802.11 Group in 1990. Specifica4ons for standard ra4fied in 1997. Ini4al speeds were
EC Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank
 EC 6802 - Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank UNIT I PART A 1. Find out the capacity of a single IS-95 cell that uses QPSK modulation and convolutional coding 3 db < Sr < 9 db, and bandwidth
EC 6802 - Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank UNIT I PART A 1. Find out the capacity of a single IS-95 cell that uses QPSK modulation and convolutional coding 3 db < Sr < 9 db, and bandwidth
Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-2
 Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Investigation of WLAN
 Investigation of WLAN Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 ABBREVIATIONS...II 1 Introduction...3 2 IEEE 802.11...3 2.1 Architecture...3 2.2 MAC layer...4 2.3 PHY layer...9 2.4 Mobility in IEEE 802.11...12
Investigation of WLAN Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 ABBREVIATIONS...II 1 Introduction...3 2 IEEE 802.11...3 2.1 Architecture...3 2.2 MAC layer...4 2.3 PHY layer...9 2.4 Mobility in IEEE 802.11...12
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part I
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part I Raj Jain Professor of CSE Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-08/
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part I Raj Jain Professor of CSE Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-08/
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing. Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology
 CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part II WiFi vs 802.11 IEEE 802.11 Features Hidden Node
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part II WiFi vs 802.11 IEEE 802.11 Features Hidden Node
Wireless Router at Home
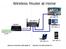 Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wi-Fi Technology, Standards,and Evolution. Dr. Srikanth Subramanian CKO, Nanocell Networks
 Wi-Fi Technology, Standards,and Evolution Dr. Srikanth Subramanian CKO, Nanocell Networks www.nanocellnetworks.com percentage Wi-Fi A Wireless Success Story Wi-Fi present in all laptops/aps Wi-Fi Traffic
Wi-Fi Technology, Standards,and Evolution Dr. Srikanth Subramanian CKO, Nanocell Networks www.nanocellnetworks.com percentage Wi-Fi A Wireless Success Story Wi-Fi present in all laptops/aps Wi-Fi Traffic
CCNA 1 Capítulo 8 OSI Physical Layer. 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 CCNA 1 Capítulo 8 OSI Physical Layer 1 Physical Layer Protocols & Services There are three basic forms of network media on which data is represented: Copper cable Fiber Wireless 2 Physical Layer Protocols
CCNA 1 Capítulo 8 OSI Physical Layer 1 Physical Layer Protocols & Services There are three basic forms of network media on which data is represented: Copper cable Fiber Wireless 2 Physical Layer Protocols
VISUAL SUMMARY COMMUNICATION CHANNELS COMMUNICATIONS. Communications and Networks
 Rev.Confirming Pages VISUAL SUMMARY Communications and Networks COMMUNICATIONS COMMUNICATION CHANNELS Communications is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers.
Rev.Confirming Pages VISUAL SUMMARY Communications and Networks COMMUNICATIONS COMMUNICATION CHANNELS Communications is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers.
