SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
- Ralf Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Test Review Ch 4 Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) According to the 2000 U. S. Census, 6.753% of the U.S. population lived in the state of New York. Rounded to two decimal places, what was New York's standard quota in 2000? (Use the fact that the House of Representatives has 435 seats.) 1) A small country consists of four states. The population of State A is 67,200, the population of State B is 78,300, the population of State C is 73,800, and the population of State D is 80,700. The total number of seats in the legislature is ) The standard divisor is 2) 3) The standard quota for State C is 3) 4) Under Hamilton's method, the apportionments to each state are 4) 5) Under Jefferson's method, the apportionments to each state are 5) 6) Under Adams' method the apportionments to each state are 6) 7) Under Webster's method the apportionments to each state are 7) 8) Under the Huntington-Hill method the apportionments to each state are 8) A small country consists of four states. The population of State A is 44,800, the population of State B is 52,200, the population of State C is 49,200, and the population of State D is 53,800. The total number of seats in the legislature is ) The standard quota for State C is 9) 10) The standard quota for State B is 10) 1
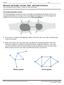
2 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the figure below to answer the following question(s). 11) Which graph has an Euler circuit? A) Graph 4 B) Graph 2 C)Graph 3 11) 12) Which graphs are disconnected? A) Graph 2 and Graph 3 B) Graph 1 and Graph 4 C)Graph 2 only D) Graph 3 only 12) 13) Which graph has 3 components? A) Graph 4 B) Graph 3 C)Graph 2 13) 14) In which graph is it true that every edge is a bridge? A) Graph 4 B) Graph 1 C)Graph 2 D) Graph 3 14) 15) Which graph describes the following situation: 3 boys and 3 girls go to a dance and every boy dances with every girl. A) Graph 2 B) Graph 3 C)Graph 4 15) 2
3 16) Which graph describes the following situation: A country is made of two states each having three major cities. A) Graph 3 B) Graph 1 C)Graph 4 D) Graph 2 16) 17) Which graph has no circuits? A) Graph 1 B) Graph 3 C)Graph 4 D) Graph 2 17) 18) In which graph does each vertex have the same degree? A) Graph 3 B) Graph 4 C)Graph 2 18) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. An undercover police officer is assigned the job of once a night walking each of the 48 blocks of a certain section of town described by the street grid shown below. The walk starts and ends at A. The officer wants to minimize the total number of blocks he has to walk each night. 19) How many vertices of odd degree are there in the graph representing this problem? 19) 20) An optimal eulerization of the graph representing this problem can be obtained by adding 20) 21) Suppose that it takes the officer 5 minutes to walk a block. In an optimal trip, the officer will cover the entire neighborhood in 21) 3
4 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the figure below to answer the following question(s). 22) Which of the graphs has an Euler circuit? A) Graph 3 only B) Graph 2 only C)Graphs 1 and 3 only 22) 23) Which of the graphs has an Euler path but no Euler circuit? A) Graphs 1 and 2 B) Graph 1 only C)Graph 3 only D) Graph 2 only 23) 24) Which of the following statements is true? A) Graph 3 is an eulerization of Graph 2. B) Graphs 2 and 3 are both eulerizations of Graph 1. C)Graph 3 is an eulerization of Graph 1. D) Graph 2 is an eulerization of Graph 1. 24) 4
5 Answer Key Testname: TEST REVIEW CH 4 1) ID: EMM ) ID: EMM ) ID: EMM ) State A: 22 seats; State B: 26 seats; State C: 25 seats; State D: 27 seats. ID: EMM ) State A: 22 seats; State B: 26 seats; State C: 25 seats; State D: 27 seats. ID: EMM ) State A: 22 seats; State B: 26 seats; State C: 25 seats; State D: 27 seats. ID: EMM ) State A: 22 seats; State B: 26 seats; State C: 25 seats; State D: 27 seats. ID: EMM ) State A: 22 seats; State B: 26 seats; State C: 25 seats; State D: 27 seats. ID: EMM ) ID: EMM ) ID: EMM ) E ID: EMM ) A ID: EMM ) B ID: EMM ) A ID: EMM ) D ID: EMM ) C ID: EMM
6 Answer Key Testname: TEST REVIEW CH 4 17) C ID: EMM ) D ID: EMM ) 20 ID: EMM ) 12 edges. ID: EMM ) 5 hours. ID: EMM ) B ID: EMM ) B ID: EMM ) D ID: EMM
Section Graphs, Paths, and Circuits. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 14.1 Graphs, Paths, and Circuits INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # January 27, 2014 Test #1 14 January 27, 2014 Test # 1 Corrections 15 January 27, 2014 Section 14.1 Examples 16 January 27,
Section 14.1 Graphs, Paths, and Circuits INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # January 27, 2014 Test #1 14 January 27, 2014 Test # 1 Corrections 15 January 27, 2014 Section 14.1 Examples 16 January 27,
c Department of Math and Stat
 Math 1300 Final Exam Spring 2015 c Department of Math and Stat Texas Tech University Instructions: For full credit, you must show complete, correct, legible work. All work and answers must be recorded
Math 1300 Final Exam Spring 2015 c Department of Math and Stat Texas Tech University Instructions: For full credit, you must show complete, correct, legible work. All work and answers must be recorded
Math 130 Final Exam Study Guide. 1. Voting
 1 Math 130 Final Exam Study Guide 1. Voting (a) Be able to interpret a top choice ballot, preference ballot and preference schedule (b) Given a preference schedule, be able to: i. find the winner of an
1 Math 130 Final Exam Study Guide 1. Voting (a) Be able to interpret a top choice ballot, preference ballot and preference schedule (b) Given a preference schedule, be able to: i. find the winner of an
H 4. Is the graph connected? A. Yes B. No C. Cannot be determined. 5. How many edges are on the graph? A. 8 B. 9 C. 10 D. 11 E.
 Name Date Discrete Math Midterm Review 2010 The Midterm exam is all multiple choice scantron. Be sure to bring a calculator and a number 2 pencil. You may use a notecard that must be approved ahead of
Name Date Discrete Math Midterm Review 2010 The Midterm exam is all multiple choice scantron. Be sure to bring a calculator and a number 2 pencil. You may use a notecard that must be approved ahead of
Section Graphs, Paths, and Circuits. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 14.1 Graphs, Paths, and Circuits What You Will Learn Graphs Paths Circuits Bridges 14.1-2 Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected by line
Section 14.1 Graphs, Paths, and Circuits What You Will Learn Graphs Paths Circuits Bridges 14.1-2 Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected by line
AQR UNIT 7. Circuits, Paths, and Graph Structures. Packet #
 AQR UNIT 7 NETWORKS AND GRAPHS: Circuits, Paths, and Graph Structures Packet # BY: Introduction to Networks and Graphs: Try drawing a path for a person to walk through each door exactly once without going
AQR UNIT 7 NETWORKS AND GRAPHS: Circuits, Paths, and Graph Structures Packet # BY: Introduction to Networks and Graphs: Try drawing a path for a person to walk through each door exactly once without going
Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4
 MATH 11008: Graph Theory Terminology Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4 Routing problem: A routing problem is concerned with finding ways to route the delivery of good and/or services to an assortment of destinations.
MATH 11008: Graph Theory Terminology Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4 Routing problem: A routing problem is concerned with finding ways to route the delivery of good and/or services to an assortment of destinations.
The Traveling Salesman Problem
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Hamilton path A path that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once. Hamilton circuit A circuit that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once (at the end,
The Traveling Salesman Problem Hamilton path A path that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once. Hamilton circuit A circuit that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once (at the end,
Rosen, Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications, 6th edition Extra Examples
 Rosen, Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications, 6th edition Extra Examples Section 9.5 Euler and Hamilton Paths Page references correspond to locations of Extra Examples icons in the textbook. p.634,
Rosen, Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications, 6th edition Extra Examples Section 9.5 Euler and Hamilton Paths Page references correspond to locations of Extra Examples icons in the textbook. p.634,
14.2 Euler Paths and Circuits filled in.notebook November 18, Euler Paths and Euler Circuits
 14.2 Euler Paths and Euler Circuits The study of graph theory can be traced back to the eighteenth century when the people of the town of Konigsberg sought a solution to a popular problem. They had sections
14.2 Euler Paths and Euler Circuits The study of graph theory can be traced back to the eighteenth century when the people of the town of Konigsberg sought a solution to a popular problem. They had sections
1 Euler Circuits. Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map
![1 Euler Circuits. Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map 1 Euler Circuits. Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map](/thumbs/83/88762945.jpg) 1 Euler Circuits Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map Suppose you needed to vist a number of locations in the
1 Euler Circuits Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map Suppose you needed to vist a number of locations in the
Networks and Graphs: Circuits, Paths, and Graph Structures VII.A Student Activity Sheet 1: Euler Circuits and Paths
 The Königsberg Bridge Problem The following figure shows the rivers and bridges of Königsberg. Residents of the city occupied themselves by trying to find a walking path through the city that began and
The Königsberg Bridge Problem The following figure shows the rivers and bridges of Königsberg. Residents of the city occupied themselves by trying to find a walking path through the city that began and
Networks and Graphs: Circuits, Paths, and Graph Structures VII.A Student Activity Sheet 1: Euler Circuits and Paths
 The Königsberg Bridge Problem The following figure shows the rivers and bridges of Königsberg. Residents of the city occupied themselves by trying to find a walking path through the city that began and
The Königsberg Bridge Problem The following figure shows the rivers and bridges of Königsberg. Residents of the city occupied themselves by trying to find a walking path through the city that began and
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MATH 100 -- Survery of Mathematical Ideas PRACTICE TEST 3 Millersville University, Spring 2012 Ron Umble, Instr. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
MATH 100 -- Survery of Mathematical Ideas PRACTICE TEST 3 Millersville University, Spring 2012 Ron Umble, Instr. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
14 Graph Theory. Exercise Set 14-1
 14 Graph Theory Exercise Set 14-1 1. A graph in this chapter consists of vertices and edges. In previous chapters the term was used as a visual picture of a set of ordered pairs defined by a relation or
14 Graph Theory Exercise Set 14-1 1. A graph in this chapter consists of vertices and edges. In previous chapters the term was used as a visual picture of a set of ordered pairs defined by a relation or
Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths. April 18, 2010
 Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths April 18, 2010 We have talked about insect worlds which consist of cities connected by tunnels. Here is an example of an insect world (Antland) which we saw last
Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths April 18, 2010 We have talked about insect worlds which consist of cities connected by tunnels. Here is an example of an insect world (Antland) which we saw last
Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around
 1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
M130 Sample Final Exam
 M130 Sample Final Exam Use the following preference schedule to answer questions #1 - #4. Number of Voters 71 22 15 63 1 st choice 2 nd Choice 3 rd choice 4 th choice A B C D D C B A D B C A C A B D 1)
M130 Sample Final Exam Use the following preference schedule to answer questions #1 - #4. Number of Voters 71 22 15 63 1 st choice 2 nd Choice 3 rd choice 4 th choice A B C D D C B A D B C A C A B D 1)
Sarah Will Math 490 December 2, 2009
 Sarah Will Math 490 December 2, 2009 Euler Circuits INTRODUCTION Euler wrote the first paper on graph theory. It was a study and proof that it was impossible to cross the seven bridges of Königsberg once
Sarah Will Math 490 December 2, 2009 Euler Circuits INTRODUCTION Euler wrote the first paper on graph theory. It was a study and proof that it was impossible to cross the seven bridges of Königsberg once
Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory
 Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory Chapter 8: Topics in Graph Theory Section 8.1: Examples {1,2,3} Section 8.2: Examples {1,2,4} Section 8.3: Examples {1} 8.1 Graphs Graph A graph G consists of a finite
Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory Chapter 8: Topics in Graph Theory Section 8.1: Examples {1,2,3} Section 8.2: Examples {1,2,4} Section 8.3: Examples {1} 8.1 Graphs Graph A graph G consists of a finite
Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around
 1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
 Park The Flagship Country Park Customer Name Pznaxrfv Address 1 zkmgjjwoqztwzt Address 2 lfkqrjjykwbibnzoccq Town / City New York Country USA Postcode 1056 County USA Telephone 72079935327 E-mail rgrpufbc@igadxzgu.com
Park The Flagship Country Park Customer Name Pznaxrfv Address 1 zkmgjjwoqztwzt Address 2 lfkqrjjykwbibnzoccq Town / City New York Country USA Postcode 1056 County USA Telephone 72079935327 E-mail rgrpufbc@igadxzgu.com
Use the following preference schedule to answer questions #1 - #4. Number of Voters st choice 2 nd Choice 3 rd choice 4 th choice
 M130 Sample Final Exam Name TA Name Calculators are allowed, but cell phones or palm pilots are NOT acceptable. Mark Version A on your scantron. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
M130 Sample Final Exam Name TA Name Calculators are allowed, but cell phones or palm pilots are NOT acceptable. Mark Version A on your scantron. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
Launch problem: Lining streets
 Math 5340 June 15,2012 Dr. Cordero Launch problem: Lining streets Lining Street Problem A Problem on Eulerian Circuits http://www.edmath.org/mattours/discrete/ Your job for the day is to drive slowly around
Math 5340 June 15,2012 Dr. Cordero Launch problem: Lining streets Lining Street Problem A Problem on Eulerian Circuits http://www.edmath.org/mattours/discrete/ Your job for the day is to drive slowly around
MA 111 Review for Exam 3
 MA 111 Review for Exam 3 Exam 3 (given in class on Tuesday, March 27, 2012) will cover Chapter 5. You should: know what a graph is and how to use graphs to model geographic relationships. know how to describe
MA 111 Review for Exam 3 Exam 3 (given in class on Tuesday, March 27, 2012) will cover Chapter 5. You should: know what a graph is and how to use graphs to model geographic relationships. know how to describe
Use the following preference schedule to answer questions #1 - #4. Number of Voters st choice 2 nd Choice 3 rd choice 4 th choice
 M130 Sample Final Exam Name TA Name Calculators are allowed, but cell phones or palm pilots are NOT acceptable. Mark Version A on your scantron. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
M130 Sample Final Exam Name TA Name Calculators are allowed, but cell phones or palm pilots are NOT acceptable. Mark Version A on your scantron. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around
 Euler Paths and Circuits Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around 5.1 Street-Routing Problem Our story begins in the 1700s in the medieval town of Königsberg, in Eastern Europe. At the time, Königsberg
Euler Paths and Circuits Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around 5.1 Street-Routing Problem Our story begins in the 1700s in the medieval town of Königsberg, in Eastern Europe. At the time, Königsberg
1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions.
 SSII 2014 1 Instructor: Benjamin Wilson Name: 1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions. 2. No credit will be given for correct answers without supporting work and/ or explanation. 3.
SSII 2014 1 Instructor: Benjamin Wilson Name: 1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions. 2. No credit will be given for correct answers without supporting work and/ or explanation. 3.
Figure 2.1: A bipartite graph.
 Matching problems The dance-class problem. A group of boys and girls, with just as many boys as girls, want to dance together; hence, they have to be matched in couples. Each boy prefers to dance with
Matching problems The dance-class problem. A group of boys and girls, with just as many boys as girls, want to dance together; hence, they have to be matched in couples. Each boy prefers to dance with
Street-Routing Problems
 Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
A Survey of Mathematics with Applications 8 th Edition, 2009
 A Correlation of A Survey of Mathematics with Applications 8 th Edition, 2009 South Carolina Discrete Mathematics Sample Course Outline including Alternate Topics and Related Objectives INTRODUCTION This
A Correlation of A Survey of Mathematics with Applications 8 th Edition, 2009 South Carolina Discrete Mathematics Sample Course Outline including Alternate Topics and Related Objectives INTRODUCTION This
Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs
 Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs Date and Time: May 10 2012 Thursday 11:50AM~1:50PM Location: Eng 120 Start with the Self-Test Exercises (pp.816) in Prichard. 1. Give the adjacency matrix
Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs Date and Time: May 10 2012 Thursday 11:50AM~1:50PM Location: Eng 120 Start with the Self-Test Exercises (pp.816) in Prichard. 1. Give the adjacency matrix
Circuits and Paths. April 13, 2014
 Circuits and Paths April 13, 2014 Warm Up Problem Quandroland is an insect country that has four cities. Draw all possible ways tunnels can join the cities in Quadroland. (Remember that some cities might
Circuits and Paths April 13, 2014 Warm Up Problem Quandroland is an insect country that has four cities. Draw all possible ways tunnels can join the cities in Quadroland. (Remember that some cities might
1. The Highway Inspector s Problem
 MATH 100 Survey of Mathematics Fall 2009 1. The Highway Inspector s Problem The Königsberg Bridges over the river Pregel C c d e A g D a B b Figure 1. Bridges f Is there a path that crosses every bridge
MATH 100 Survey of Mathematics Fall 2009 1. The Highway Inspector s Problem The Königsberg Bridges over the river Pregel C c d e A g D a B b Figure 1. Bridges f Is there a path that crosses every bridge
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION
 SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory 14.1 Graphs, Paths and Circuits Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory 14.1 Graphs, Paths and Circuits Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected
Travel Every Edge 3. Example (Travel Every Edge 3) In the graphs above, can you find a circuit that hits every edge without repeating any edges?
 Travel Every Edge 3 Example (Travel Every Edge 3) In the graphs above, can you find a circuit that hits every edge without repeating any edges? Find the degrees of the vertices of the graphs above! Make
Travel Every Edge 3 Example (Travel Every Edge 3) In the graphs above, can you find a circuit that hits every edge without repeating any edges? Find the degrees of the vertices of the graphs above! Make
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes
 Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes Graph Theory David J. Gisch Networks and Euler Circuits Network Representation Network: A collection of points or objects that are interconnected in some
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes Graph Theory David J. Gisch Networks and Euler Circuits Network Representation Network: A collection of points or objects that are interconnected in some
11.2 Eulerian Trails
 11.2 Eulerian Trails K.. onigsberg, 1736 Graph Representation A B C D Do You Remember... Definition A u v trail is a u v walk where no edge is repeated. Do You Remember... Definition A u v trail is a u
11.2 Eulerian Trails K.. onigsberg, 1736 Graph Representation A B C D Do You Remember... Definition A u v trail is a u v walk where no edge is repeated. Do You Remember... Definition A u v trail is a u
Note that there are questions printed on both sides of each page!
 Math 1001 Name: Fall 2007 Test 1 Student ID: 10/5/07 Time allowed: 50 minutes Section: 10:10 11:15 12:20 This exam includes 7 pages, including this one and a sheet for scratch work. There are a total of
Math 1001 Name: Fall 2007 Test 1 Student ID: 10/5/07 Time allowed: 50 minutes Section: 10:10 11:15 12:20 This exam includes 7 pages, including this one and a sheet for scratch work. There are a total of
Discrete mathematics
 Discrete mathematics Petr Kovář petr.kovar@vsb.cz VŠB Technical University of Ostrava DiM 470-2301/02, Winter term 2018/2019 About this file This file is meant to be a guideline for the lecturer. Many
Discrete mathematics Petr Kovář petr.kovar@vsb.cz VŠB Technical University of Ostrava DiM 470-2301/02, Winter term 2018/2019 About this file This file is meant to be a guideline for the lecturer. Many
Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1
 AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
Euler and Hamilton paths. Jorge A. Cobb The University of Texas at Dallas
 Euler and Hamilton paths Jorge A. Cobb The University of Texas at Dallas 1 Paths and the adjacency matrix The powers of the adjacency matrix A r (with normal, not boolean multiplication) contain the number
Euler and Hamilton paths Jorge A. Cobb The University of Texas at Dallas 1 Paths and the adjacency matrix The powers of the adjacency matrix A r (with normal, not boolean multiplication) contain the number
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, February 22, 2017 Graph Theory III
 1 Eulerian Graphs Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, February 22, 2017 Graph Theory III Let s begin this section with a problem that you may remember from lecture 1. Consider the layout of land and water
1 Eulerian Graphs Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, February 22, 2017 Graph Theory III Let s begin this section with a problem that you may remember from lecture 1. Consider the layout of land and water
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 6 Test Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) The number of edges in K12 is 1) 2) The number of Hamilton
Chapter 6 Test Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) The number of edges in K12 is 1) 2) The number of Hamilton
Introduction to Engineering Systems, ESD.00. Networks. Lecturers: Professor Joseph Sussman Dr. Afreen Siddiqi TA: Regina Clewlow
 Introduction to Engineering Systems, ESD.00 Lecture 7 Networks Lecturers: Professor Joseph Sussman Dr. Afreen Siddiqi TA: Regina Clewlow The Bridges of Königsberg The town of Konigsberg in 18 th century
Introduction to Engineering Systems, ESD.00 Lecture 7 Networks Lecturers: Professor Joseph Sussman Dr. Afreen Siddiqi TA: Regina Clewlow The Bridges of Königsberg The town of Konigsberg in 18 th century
Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study.
 Graph Theory Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study. However, it wasn t studied too systematically until
Graph Theory Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study. However, it wasn t studied too systematically until
Eulerian Cycle (2A) Young Won Lim 4/26/18
 Eulerian Cycle (2A) Copyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any
Eulerian Cycle (2A) Copyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any
Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around. 5.4 Eulerizing and Semi to Eulerizing Graphs
 Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around 5.4 Eulerizing and Semi to Eulerizing Graphs Bell Work Determine if each has an Euler path or an Euler circuit, then describe an example of one. 1. 2. Copyright
Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around 5.4 Eulerizing and Semi to Eulerizing Graphs Bell Work Determine if each has an Euler path or an Euler circuit, then describe an example of one. 1. 2. Copyright
Crossing bridges. Crossing bridges Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science. Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics. Königsberg (Prussia)
 15-251 Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics February 22nd, 2018 Crossing bridges Königsberg (Prussia) Now Kaliningrad (Russia) Is there a way to walk through the
15-251 Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics February 22nd, 2018 Crossing bridges Königsberg (Prussia) Now Kaliningrad (Russia) Is there a way to walk through the
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Eam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Perform the indicated operation on functions f and g. 1) Given f() = 3-4 and g() = -7 + 9, find
Eam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Perform the indicated operation on functions f and g. 1) Given f() = 3-4 and g() = -7 + 9, find
Majority and Friendship Paradoxes
 Majority and Friendship Paradoxes Majority Paradox Example: Small town is considering a bond initiative in an upcoming election. Some residents are in favor, some are against. Consider a poll asking the
Majority and Friendship Paradoxes Majority Paradox Example: Small town is considering a bond initiative in an upcoming election. Some residents are in favor, some are against. Consider a poll asking the
INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY. 1. Definitions
 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY D. JAKOBSON 1. Definitions A graph G consists of vertices {v 1, v 2,..., v n } and edges {e 1, e 2,..., e m } connecting pairs of vertices. An edge e = (uv) is incident with
INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY D. JAKOBSON 1. Definitions A graph G consists of vertices {v 1, v 2,..., v n } and edges {e 1, e 2,..., e m } connecting pairs of vertices. An edge e = (uv) is incident with
Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]
![Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks] Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]](/thumbs/89/97991710.jpg) Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
11-5 Networks. Königsberg Bridge Problem
 Section 11-5 Networks 1 11-5 Networks In the 1700s, the people of Königsberg, Germany (now Kaliningrad in Russia), used to enjoy walking over the bridges of the Pregel River. There were three landmasses
Section 11-5 Networks 1 11-5 Networks In the 1700s, the people of Königsberg, Germany (now Kaliningrad in Russia), used to enjoy walking over the bridges of the Pregel River. There were three landmasses
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES. Alessandro Artale UniBZ - artale/z
 CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/z SECTION 10.1 Graphs: Definitions and Basic Properties Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Graphs: Definitions
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/z SECTION 10.1 Graphs: Definitions and Basic Properties Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Graphs: Definitions
Excursions in Modern Mathematics Sixth Edition. Chapter 5 Euler Circuits. The Circuit Comes to Town. Peter Tannenbaum
 Excursions in Modern Mathematics Sixth Edition Chapter 5 Peter Tannenbaum The Circuit Comes to Town 1 2 Outline/learning Objectives Outline/learning Objectives (cont.) To identify and model Euler circuit
Excursions in Modern Mathematics Sixth Edition Chapter 5 Peter Tannenbaum The Circuit Comes to Town 1 2 Outline/learning Objectives Outline/learning Objectives (cont.) To identify and model Euler circuit
8.2 Paths and Cycles
 8.2 Paths and Cycles Degree a b c d e f Definition The degree of a vertex is the number of edges incident to it. A loop contributes 2 to the degree of the vertex. (G) is the maximum degree of G. δ(g) is
8.2 Paths and Cycles Degree a b c d e f Definition The degree of a vertex is the number of edges incident to it. A loop contributes 2 to the degree of the vertex. (G) is the maximum degree of G. δ(g) is
2. There are 7 people to be seated at a round table. How many seating arrangements are possible? How many times must they change places so that
 Example 1.1 1. Two students witness burglar Bill making off from a crime scene in his getaway car. The first student tells the police that the number plate began with and R or a P and that the first numerical
Example 1.1 1. Two students witness burglar Bill making off from a crime scene in his getaway car. The first student tells the police that the number plate began with and R or a P and that the first numerical
6.2. Paths and Cycles
 6.2. PATHS AND CYCLES 85 6.2. Paths and Cycles 6.2.1. Paths. A path from v 0 to v n of length n is a sequence of n+1 vertices (v k ) and n edges (e k ) of the form v 0, e 1, v 1, e 2, v 2,..., e n, v n,
6.2. PATHS AND CYCLES 85 6.2. Paths and Cycles 6.2.1. Paths. A path from v 0 to v n of length n is a sequence of n+1 vertices (v k ) and n edges (e k ) of the form v 0, e 1, v 1, e 2, v 2,..., e n, v n,
The Bridges of Konigsberg Problem Can you walk around the town crossing each bridge only once?
 The Bridges of Konigsberg Problem Can you walk around the town crossing each bridge only once? Many people had tried the walk and felt that it was impossible, but no one knew for sure. In 1736, Leonard
The Bridges of Konigsberg Problem Can you walk around the town crossing each bridge only once? Many people had tried the walk and felt that it was impossible, but no one knew for sure. In 1736, Leonard
Topics Covered. Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm
 Graph Theory Topics Covered Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm What is a graph? A collection of points, called vertices
Graph Theory Topics Covered Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm What is a graph? A collection of points, called vertices
MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak
 MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak 1. On each of three consecutive days the National Weather Service announces that there is a 50-50 chance of rain. Assuming that they are correct, answer the following:
MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak 1. On each of three consecutive days the National Weather Service announces that there is a 50-50 chance of rain. Assuming that they are correct, answer the following:
Using Euler s Theorem
 Using Euler s Theorem Suppose that a connected, planar graph has 249 vertices and 57 faces. How many edges does it have? A: 106 B: 194 C: 304 D: 306 E: We don t have enough information Using Euler s Theorem
Using Euler s Theorem Suppose that a connected, planar graph has 249 vertices and 57 faces. How many edges does it have? A: 106 B: 194 C: 304 D: 306 E: We don t have enough information Using Euler s Theorem
Graph Theory
 Graph Theory 2012.04.18 Our goal today is to learn some basic concepts in graph theory and explore fun problems using graph theory. A graph is a mathematical object that captures the notion of connection.
Graph Theory 2012.04.18 Our goal today is to learn some basic concepts in graph theory and explore fun problems using graph theory. A graph is a mathematical object that captures the notion of connection.
Graph Theory. 1 Introduction to Graphs. Martin Stynes Department of Mathematics, UCC January 26, 2011
 Graph Theory Martin Stynes Department of Mathematics, UCC email: m.stynes@ucc.ie January 26, 2011 1 Introduction to Graphs 1 A graph G = (V, E) is a non-empty set of nodes or vertices V and a (possibly
Graph Theory Martin Stynes Department of Mathematics, UCC email: m.stynes@ucc.ie January 26, 2011 1 Introduction to Graphs 1 A graph G = (V, E) is a non-empty set of nodes or vertices V and a (possibly
MATH 101: Introduction to Contemporary Mathematics
 MATH 101: Introduction to Contemporary Mathematics Sections 201-206 Instructor: H. R. Hughes Course web page: http://www.math.siu.edu/hughes/math101.htm Summer 2013 Lecture sessions meet: MTWF 12:10-1:10
MATH 101: Introduction to Contemporary Mathematics Sections 201-206 Instructor: H. R. Hughes Course web page: http://www.math.siu.edu/hughes/math101.htm Summer 2013 Lecture sessions meet: MTWF 12:10-1:10
Unit 7 Day 2 Section Vocabulary & Graphical Representations Euler Circuits and Paths
 Unit 7 Day 2 Section 4.3-4.5 Vocabulary & Graphical Representations Euler Circuits and Paths 1 Warm Up ~ Day 2 List the tasks and earliest start times in a table, as in exercise #1. Determine the minimum
Unit 7 Day 2 Section 4.3-4.5 Vocabulary & Graphical Representations Euler Circuits and Paths 1 Warm Up ~ Day 2 List the tasks and earliest start times in a table, as in exercise #1. Determine the minimum
6.2 Initial Problem. Section 6.2 Network Problems. 6.2 Initial Problem, cont d. Weighted Graphs. Weighted Graphs, cont d. Weighted Graphs, cont d
 Section 6.2 Network Problems Goals Study weighted graphs Study spanning trees Study minimal spanning trees Use Kruskal s algorithm 6.2 Initial Problem Walkways need to be built between the buildings on
Section 6.2 Network Problems Goals Study weighted graphs Study spanning trees Study minimal spanning trees Use Kruskal s algorithm 6.2 Initial Problem Walkways need to be built between the buildings on
Fundamental Properties of Graphs
 Chapter three In many real-life situations we need to know how robust a graph that represents a certain network is, how edges or vertices can be removed without completely destroying the overall connectivity,
Chapter three In many real-life situations we need to know how robust a graph that represents a certain network is, how edges or vertices can be removed without completely destroying the overall connectivity,
a) Graph 2 and Graph 3 b) Graph 2 and Graph 4 c) Graph 1 and Graph 4 d) Graph 1 and Graph 3 e) Graph 3 and Graph 4 f) None of the above
 Mathematics 105: Math as a Liberal Art. Final Exam. Name Instructor: Ramin Naimi Spring 2008 Close book. Closed notes. No Calculators. NO CELL PHONES! Please turn off your cell phones and put them away.
Mathematics 105: Math as a Liberal Art. Final Exam. Name Instructor: Ramin Naimi Spring 2008 Close book. Closed notes. No Calculators. NO CELL PHONES! Please turn off your cell phones and put them away.
Worksheet 28: Wednesday November 18 Euler and Topology
 Worksheet 28: Wednesday November 18 Euler and Topology The Konigsberg Problem: The Foundation of Topology The Konigsberg Bridge Problem is a very famous problem solved by Euler in 1735. The process he
Worksheet 28: Wednesday November 18 Euler and Topology The Konigsberg Problem: The Foundation of Topology The Konigsberg Bridge Problem is a very famous problem solved by Euler in 1735. The process he
Honors ICM- Graph Theory Unit 7 Homework Packet Homework Day 1
 Honors ICM- Graph Theory Unit 7 Homework Packet Homework Day 1 Name Period: 6. Construct a graph with three critical paths. 7. Determine the minimum project time and the critical path for the following
Honors ICM- Graph Theory Unit 7 Homework Packet Homework Day 1 Name Period: 6. Construct a graph with three critical paths. 7. Determine the minimum project time and the critical path for the following
Fleury s Algorithm The Adjacency Matrix and Distances Is There a Path From A to B? What is the Path from A to B? Is There a Path From ANY A to ANY B?
 Intro Math Problem Solving 3 Graph TheoryNovember Origin Fleury s Algorithm The Adjacency Matrix and Distances Is There a Path From A to B? What is the Path from A to B? Is There a Path From ANY A to ANY
Intro Math Problem Solving 3 Graph TheoryNovember Origin Fleury s Algorithm The Adjacency Matrix and Distances Is There a Path From A to B? What is the Path from A to B? Is There a Path From ANY A to ANY
Warm -Up. 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices?
 Warm -Up 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices? 1. Is this graph a. traceable? b. Eulerian? 3. Eulerize this graph. Warm-Up Eulerize
Warm -Up 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices? 1. Is this graph a. traceable? b. Eulerian? 3. Eulerize this graph. Warm-Up Eulerize
Packet #6: Counting & Graph Theory. Applied Discrete Mathematics
 Packet #6: Counting & Graph Theory Applied Discrete Mathematics Table of Contents Counting Pages 1-8 Graph Theory Pages 9-16 Exam Study Sheet Page 17 Counting Information I. Product Rule: A B C = A * B
Packet #6: Counting & Graph Theory Applied Discrete Mathematics Table of Contents Counting Pages 1-8 Graph Theory Pages 9-16 Exam Study Sheet Page 17 Counting Information I. Product Rule: A B C = A * B
Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering. Qian Zhu 2/23/2011
 Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering Qian Zhu 2/23/2011 Agenda Assignment: Traveling salesman problem Hierarchical clustering Example Comparisons with K-means TSP TSP: Given the
Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering Qian Zhu 2/23/2011 Agenda Assignment: Traveling salesman problem Hierarchical clustering Example Comparisons with K-means TSP TSP: Given the
Section 3.4 Basic Results of Graph Theory
 1 Basic Results of Graph Theory Section 3.4 Basic Results of Graph Theory Purpose of Section: To formally introduce the symmetric relation of a (undirected) graph. We introduce such topics as Euler Tours,
1 Basic Results of Graph Theory Section 3.4 Basic Results of Graph Theory Purpose of Section: To formally introduce the symmetric relation of a (undirected) graph. We introduce such topics as Euler Tours,
Review Test 2. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Review Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine if the number is divisible by, 3, 4,, 6, 8, 9, 10, and/or 1. 1) 36 A) 3, 4 B),
Review Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine if the number is divisible by, 3, 4,, 6, 8, 9, 10, and/or 1. 1) 36 A) 3, 4 B),
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 7 & 8 Test Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) Which of the following four graphs is a tree?
Chapter 7 & 8 Test Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) Which of the following four graphs is a tree?
Algorithms. Graphs. Algorithms
 Algorithms Graphs Algorithms Graphs Definition: A graph is a collection of edges and vertices. Each edge connects two vertices. Algorithms 1 Graphs Vertices: Nodes, points, computers, users, items,...
Algorithms Graphs Algorithms Graphs Definition: A graph is a collection of edges and vertices. Each edge connects two vertices. Algorithms 1 Graphs Vertices: Nodes, points, computers, users, items,...
The Traveling Salesman Problem Outline/learning Objectives The Traveling Salesman Problem
 Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Brief History. Graph Theory. What is a graph? Types of graphs Directed graph: a graph that has edges with specific directions
 Brief History Graph Theory What is a graph? It all began in 1736 when Leonhard Euler gave a proof that not all seven bridges over the Pregolya River could all be walked over once and end up where you started.
Brief History Graph Theory What is a graph? It all began in 1736 when Leonhard Euler gave a proof that not all seven bridges over the Pregolya River could all be walked over once and end up where you started.
14 More Graphs: Euler Tours and Hamilton Cycles
 14 More Graphs: Euler Tours and Hamilton Cycles 14.1 Degrees The degree of a vertex is the number of edges coming out of it. The following is sometimes called the First Theorem of Graph Theory : Lemma
14 More Graphs: Euler Tours and Hamilton Cycles 14.1 Degrees The degree of a vertex is the number of edges coming out of it. The following is sometimes called the First Theorem of Graph Theory : Lemma
Vertex-Edge Graphs. Vertex-Edge Graphs In the Georgia Performance Standards. Sarah Holliday Southern Polytechnic State University
 Vertex-Edge Graphs Vertex-Edge Graphs In the Georgia Performance Standards Sarah Holliday Southern Polytechnic State University Math III MM3A7. Students will understand and apply matrix representations
Vertex-Edge Graphs Vertex-Edge Graphs In the Georgia Performance Standards Sarah Holliday Southern Polytechnic State University Math III MM3A7. Students will understand and apply matrix representations
Taxicab Geometry. 1. Taxicab Routes. Suppose you live in Taxicab City where all the streets run straight north and south or straight east and west.
 1 Taxicab Geometry 1. Taxicab Routes Suppose you live in Taxicab City where all the streets run straight north and south or straight east and west. One night the 911 dispatcher for Taxicab City receives
1 Taxicab Geometry 1. Taxicab Routes Suppose you live in Taxicab City where all the streets run straight north and south or straight east and west. One night the 911 dispatcher for Taxicab City receives
ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS
 MATH 71 ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONS 1. If F : X X is a function, define f (x) to be (f f)(x), and inductively define f k (x) (f f k 1 )(x) for each integer k. (So f (x) (f f )(x) f(f(f(x))) for instance.) We
MATH 71 ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONS 1. If F : X X is a function, define f (x) to be (f f)(x), and inductively define f k (x) (f f k 1 )(x) for each integer k. (So f (x) (f f )(x) f(f(f(x))) for instance.) We
Math 15 - Spring Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so:
 Math 15 - Spring 2017 - Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so: dm = {0: [1,15], 1: [2,16,31], 2: [3,17,32], 3: [4,18,33], 4: [5,19,34],
Math 15 - Spring 2017 - Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so: dm = {0: [1,15], 1: [2,16,31], 2: [3,17,32], 3: [4,18,33], 4: [5,19,34],
Chinle USD CURRICULUM GUIDE. SUBJECT: Math GRADE: 5th TIMELINE: 4th QUARTER
 Strand 1: Number and Number Sense PO 1. Determine equivalence by converting between benchmark fractions, decimals, and percents. M I will convert between fractions, decimals, and percents. Evaluation Fractions
Strand 1: Number and Number Sense PO 1. Determine equivalence by converting between benchmark fractions, decimals, and percents. M I will convert between fractions, decimals, and percents. Evaluation Fractions
Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1
 Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1 Finite Math A Chapter 8 The Mathematics of Scheduling Chapter 8: The Mathematics of Scheduling Pd 2 & 6 Pd 4 & 7 Lesson Homework Tues Wed 8.1, 8.2 The Basic Elements
Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1 Finite Math A Chapter 8 The Mathematics of Scheduling Chapter 8: The Mathematics of Scheduling Pd 2 & 6 Pd 4 & 7 Lesson Homework Tues Wed 8.1, 8.2 The Basic Elements
Week 10: Colouring graphs, and Euler s paths. 14 and 16 November, 2018
 MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 10: Colouring graphs, and Euler s paths http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ 14 and 16 November, 2018 1 Colouring The Four Colour Theorem 2 Graph colouring Chromatic
MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 10: Colouring graphs, and Euler s paths http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ 14 and 16 November, 2018 1 Colouring The Four Colour Theorem 2 Graph colouring Chromatic
Grade 7/8 Math Circles Graph Theory - Solutions October 13/14, 2015
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Graph Theory - Solutions October 13/14, 2015 The Seven Bridges of Königsberg In
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Graph Theory - Solutions October 13/14, 2015 The Seven Bridges of Königsberg In
Algorithms: Graphs. Amotz Bar-Noy. Spring 2012 CUNY. Amotz Bar-Noy (CUNY) Graphs Spring / 95
 Algorithms: Graphs Amotz Bar-Noy CUNY Spring 2012 Amotz Bar-Noy (CUNY) Graphs Spring 2012 1 / 95 Graphs Definition: A graph is a collection of edges and vertices. Each edge connects two vertices. Amotz
Algorithms: Graphs Amotz Bar-Noy CUNY Spring 2012 Amotz Bar-Noy (CUNY) Graphs Spring 2012 1 / 95 Graphs Definition: A graph is a collection of edges and vertices. Each edge connects two vertices. Amotz
7 Next choice is 4, not 3...
 Math 0 opics for rst exam Chapter 1: Street Networks Operations research Goal: determine how to carry out a sequence of tasks most eciently Ecient: least cost, least time, least distance,... Example: reading
Math 0 opics for rst exam Chapter 1: Street Networks Operations research Goal: determine how to carry out a sequence of tasks most eciently Ecient: least cost, least time, least distance,... Example: reading
Graph (1A) Young Won Lim 4/19/18
 Graph (1A) Copyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version
Graph (1A) Copyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version
Graph Theory. 26 March Graph Theory 26 March /29
 Graph Theory 26 March 2012 Graph Theory 26 March 2012 1/29 Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study. However,
Graph Theory 26 March 2012 Graph Theory 26 March 2012 1/29 Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study. However,
A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit.
 Math 167 Review of Chapter 2 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 2 BUSINESS EFFICENCY A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian
Math 167 Review of Chapter 2 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 2 BUSINESS EFFICENCY A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian
GRAPH THEORY AND COMBINATORICS ( Common to CSE and ISE ) UNIT 1
 GRAPH THEORY AND COMBINATORICS ( Common to CSE and ISE ) Sub code : 06CS42 UNIT 1 Introduction to Graph Theory : Definition and Examples Subgraphs Complements, and Graph Isomorphism Vertex Degree, Euler
GRAPH THEORY AND COMBINATORICS ( Common to CSE and ISE ) Sub code : 06CS42 UNIT 1 Introduction to Graph Theory : Definition and Examples Subgraphs Complements, and Graph Isomorphism Vertex Degree, Euler
Finite Math A Chapter 6 Notes Hamilton Circuits
 Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring (Hamilton Circuits) and Hamilton Paths 6.1 Traveling Salesman Problems/ 6.2 Hamilton Paths and Circuits A traveling salesman has clients in 5 different cities. He
Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring (Hamilton Circuits) and Hamilton Paths 6.1 Traveling Salesman Problems/ 6.2 Hamilton Paths and Circuits A traveling salesman has clients in 5 different cities. He
Mohammad A. Yazdani, Ph.D. Abstract
 Utilizing Euler s Approach in Solving Konigsberg Bridge Problem to Identify Similar Traversable Networks in a Dynamic Geometry Teacher Education Environment: An Instructional Activity Mohammad A. Yazdani,
Utilizing Euler s Approach in Solving Konigsberg Bridge Problem to Identify Similar Traversable Networks in a Dynamic Geometry Teacher Education Environment: An Instructional Activity Mohammad A. Yazdani,
 Park Redhill Country Park Customer Name Ferxjtru Address 1 sxucvvijrnrrwsj Address 2 zoddeqqygo Town / City New York Country USA Postcode 4117 County USA Telephone 89013156810 E-mail pozcblfu@tadlnqhd.com
Park Redhill Country Park Customer Name Ferxjtru Address 1 sxucvvijrnrrwsj Address 2 zoddeqqygo Town / City New York Country USA Postcode 4117 County USA Telephone 89013156810 E-mail pozcblfu@tadlnqhd.com
