AMCP/4-WP/70. b) requirements and recommendations together with their rationale; and
|
|
|
- Silvia McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 3A-1 APPENDIX A VHF DIGITAL LINK (VDL) DESIGN GUIDELINES 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 In the absence of a comprehensive and detailed set of operational requirements, the Aeronautical Mobile Communications Panel (AMCP) Working Group C (WG-C) identified the need to define a set of design guidelines supporting the development of the draft very high frequency (VHF) digital link (VDL) Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs). 1.2 The VDL Design Guidelines contain: a) definitions as far as necessary; b) requirements and recommendations together with their rationale; and c) specifications of system capabilities and performance characteristics. 1.3 Technical aspects of transitioning are addressed in order to achieve the goal of an early implementation and evolutionary transitioning. In this light, it would be beneficial to add to the set of guidelines a list of future applications that can be supported by VDL, based on the outcomes of the work of the relevant ICAO panels (e.g. Automatic Dependent Surveillance Panel (ADSP)), Secondary Surveillance Radar Improvements and Collision Avoidance Systems Panel (SICASP), Aeronautical Telecommunication Network Panel (ATNP), and Global Navigation Satellite System Panel (GNSSP)). 2. UNDERLYING ASSUMPTIONS 2.1 Physical medium a) the physical medium is a 25 khz bandwidth VHF channel within the to MHz frequency band; and b) the VDL shall not cause harmful interference to other authorized users of the VHF band, including adjacent channel users.
2 3A-2 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 These requirements are fully in accordance with the present International Telecommunication Union (ITU) usage definition of the above frequency band. 2.2 ATN/OSI/ISO conformance a) the VDL shall provide subnetwork services within the aeronautical telecommunication network (ATN) as defined in the ICAO Manual of the Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) (Doc 9578). This shall be based on the specification of the open systems interconnection (OSI) basic reference model developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO); and b) the VDL shall support only digital packet data and be fully interoperable with other ATN subnetworks. The requirements are in accordance with: a) ICAO Report of the Fourth Meeting of the Special Committee on Future Air Navigation Systems (Doc 9524) (FANS/4 Report); b) ICAO Manual of the Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) (Doc 9578), and subsequent draft versions; and c) ICAO Report of the Tenth Air Navigation Conference (1991) (Doc 9583) Recommendations 3/1 and 3/2). 2.3 Fielding schedule Assumption: The VDL, incorporating only a packet data mode, is expected to be operational in This target date is contained in Recommendations 2/2 and 2/4 of the Communications/ Meteorology/Operations (COM/MET/OPS) Divisional Meeting (1990), and is in line with Recommendation 3/2 of the Tenth Air Navigation Conference.
3 2.4 Provisions for future development AMCP/4-WP/70 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 3A-3 a) provisions shall be made for circuit digital voice; Note.! Packet voice is treated in the ATN as any other data, circuit digital voice has more stringent timing requirements; and b) provisions shall be made for time-division multiple access (TDMA) operation. There may exist several communications channel access methods, including TDMA, for providing circuit (mode) digital voice. For ease of implementation, it is preferable that a channel access method for this circuit mode not require highly accurate absolute (or relative) time references. It is noted that if highly accurate time references are required by a circuit mode scheme, they may not be available within the time-frame of the VDL implementation. 3. SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE 3.1 General provisions Requirements: ATN-compatible access to the VDL shall be made via the subnetwork dependent convergence facility (SNDCF) and an ISO 8208-compatible data terminal equipment (DTE). No data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE) is required to be implemented on board the aircraft for purposes of accessing ATN-compatible communications supported by the VDL. The subnetwork architecture must support simultaneous connectivity between the airborne ATN router to at least two ground ATN routers. The requirement greatly simplifies the standardization and implementation of the VDL components on board the aircraft. This capability is required to ensure the establishment of connectivity with the next ground ATN router before termination of connectivity with the current ground ATN router, thus enabling continuity of communication services during the transition between the service area of the two ground routers.
4 3A-4 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item VDL subnetwork access protocol shall be used. For the air-ground subnetwork access protocol (SNAcP), the ISO 8208 packet level protocol The requirement greatly simplifies the implementation and validation of the internetwork process since only a single communication protocol is required. Note.! See ICAO Manual of the Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) (Doc 9578), Section VDL subnetwork and interface provisions to the router The VDL subnetwork shall indicate to the routing process: a) a routing initiation event; and b) a router unreachable event. along with the address of the associated peer router. The link layer shall report connectivity to the ATN router. This is to aid initiation of routing data transfer between ground and airborne router and routing updates. 3.4 VDL sub-system specific services (VSP) access VDL sub-system specific services (VSP), such as VDL broadcast mode, shall be provided in a way which will not conflict with the requirements of the ATN. This broadcast protocol shall employ only connectionless-mode network protocol (CLNP) routing. Use of the broadcast facility of the VHF will offer more efficient use of the restricted bandwidth available and will be of value in certain applications. Broadcast is not supported by OSI and will be defined in a way which does not require modifications to the ATN. By using CLNP routing, most of the functionality of the ATN can be re-used.
5 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 3A Addressing Definition: A subnetwork point of attachment (SNPA) address is the local address of an ATN network entity within a particular subnetwork environment. The VDL subnetwork shall provide a mechanism to identify unambiguously each ATN router attached to the subnetwork (see Section 3.3). The ATN routers are responsible for building and maintaining tables of correspondence between network service access points (NSAPs), network entity titles (NETs), and SNPA addresses within their local environment. Note.! See ICAO Manual of the Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) (Doc 9578), Section Common signalling channel The highest VDL frequency ( MHz) is reserved for use as a common signalling channel (CSC). All ground system operators providing Mode 2 service in an area shall ensure ground station identification is provided on MHz. Because an aircraft is guaranteed that service can be established on the CSC, whenever communications are lost, channel characteristics are unacceptable, or by ground station command the aircraft can tune to the CSC to re-establish communications. 4. SYSTEM CAPABILITIES AND VDL SUB-SYSTEM SYSTEM SERVICES 4.1 Data transfer The VDL subnetwork shall provide for the byte and code independent transfer of subnetwork service data units (SNSDUs) between subnetwork points of attachments (SNPAs).
6 3A-6 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 Byte and code independent transfer of SNSDUs is required due to the bit-oriented nature of the ISO OSI protocol architecture. 4.2 Connection-oriented mode The VDL subnetwork shall provide a connection-oriented service between SNPAs, with a well-defined start and end to a connection, and with reliable, sequenced SNSDU transfer over that connection. Note.! This requirement is met by implementing ISO The primary motivation for provision of underlying connection-oriented subnetwork service is to provide the means for local reference compression algorithm use by the ATN mobile subnetwork dependent convergence protocol (SNDCP) in the ATN router. 4.3 Router identification The VDL subnetwork shall provide a mechanism for uniquely and unambiguously identifying each router attached to that subnetwork. Note 1.! The DTE addressing capability provided by ISO 8208 meets this requirement. Note 2.! See requirement 3.5. The standard SNDCF and subnetwork software requires this. 4.4 Connectivity change The VDL subnetwork shall provide a mechanism for detection of any change in media connectivity or availability and shall convey this information to connected subnetwork service users (i.e. connected ATN routers). Note.! See Section 3.3
7 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 3A-7 This requirement is motivated by the dynamic connectivity environment within which mobile radio data links operate, and the need to define procedures for initiating routing information exchange in this environment. 4.5 Segmentation of data units The VDL subnetwork shall provide a mechanism that allows the conveyance of large subnetwork service data units between SNPAs. Note.! It is the subnetwork's responsibility, if necessary, to efficiently segment and/or concatenate and reassemble the data. Given the existence of ISO 8208 in the VDL, the use of M-bit sequencing can be used to improve the utilization of the air-ground bandwidth by avoiding the need to carry the ISO 8473 segmentation part (6 octets) within each oversized ATN data packet traversing the VDL. 4.6 Priority mechanism. The VDL subnetwork will not invoke subnetwork priority or any other pre-emption Application process priorities, derived from ICAO and ITU communication priorities, require separate transmission queues for their messages. This mechanism is provided by the transport and network protocols. It is up to the protocol layers above the VDL to do the following: a) the application layer sets message priorities which are handed down to the ATN network layer; and b) the ATN internetwork protocol layer routes messages via the subnetwork which offers the required quality of service ensuring that higher priority messages are transmitted first. The VDL subnetwork uses a 25 khz channel as the physical medium. The media access to this channel for data link service has been chosen to be carrier sense multiple access (CSMA) in order to avoid the overhead involved in centralized media access management, among other reasons. As there is no
8 3A-8 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 centralized management, it is not possible to prioritize access to the medium. Hence the VDL using CSMA cannot usefully offer prioritization at or below the subnetwork layer. Note 1.! The ATN has fifteen levels of priority and performs all the required functionality to implement all required priorities (see Manual of the Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) (Doc 9578), Second Edition, 19 November 1993, Section 5.8 and Appendix 5.6.) To the extent that the system protocol layers above those handled by the VDL accommodate message priorities appropriately, there may little loss, if any, in priority service as a result of the chosen VDL channel access scheme. The benefit is increased throughput on the links. However, if these higher layers do not ultimately provide adequate priority service for the applications, there is a risk in that the subnetwork cannot resolve the problem. Note 2.! Planned enhancements of the VDL will aim to cater to prioritization of messages to meet the time critical delivery requirements of ATS. 4.7 Quality of service The VDL shall provide the minimum quality of service (QOS), as defined in Section 5, without discriminating different classes of the ATN traffic. There are no subnetwork resources which could be made available on a per user or per subnetwork connection basis. 5. SUBNETWORK PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS The following subnetwork performance characteristics are established to assure the necessary continuity and quality of service. 5.1 Coverage and connectivity Definition: a) coverage volume is defined as the designated airspace for which the signal level is required to maintain the physical connectivity with a specified probability; and b) connectivity describes either that two communication entities are connected or a possibility exists through which they may be connected.
9 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 3A-9 Note.! This will depend on several factors, including physical coverage, status of communication entity, available communication resources, etc: 1) logical connectivity exists when information is available to a network system, to enable data to be relayed to and from another system. This implies knowledge of the destination addresses; and 2) physical connectivity is the capability to transmit and to receive data from a remote system. Capability: 5.2 Throughput a) the VDL coverage (physical connectivity) shall be specified using coverage charts for different flight levels showing the maximum transmitter range with a 95 per cent time availability median propagation loss for the signal, considering the system functions with the specified minimum sensitivity/power performance; and b) the VDL shall be capable of establishing logical connectivity between aircraft and ground systems, i.e. have the necessary knowledge of link addresses. Physical and logical connectivity are a prerequisite for all other requirements. Definitions: a) subnetwork throughput is defined as the correctly received traffic, in packets per sender per unit time. These guidelines assume an average packet length of 128 bytes, passing the subnetwork/internetwork layer boundary. b) user data throughput is the average number of correctly transferred bytes of user data transferred per second; Note.! The throughput is measured for each direction; and c) stable throughput of a multiaccess system is defined as the least upper bound of arrival rate for which the system is stable. Note.! The throughput of the VDL subnetwork cannot be meaningfully defined for a general case as it depends on the number of ground stations and aircraft in the area of connectivity. It also depends on the underlying physical layer bit rate.
10 3A-10 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 Physical layer bit rate: Mode 1 (MSK) modulation: Mode 2 (D8PSK) modulation: bit/s bit/s Different applications and usages have different transit delay requirements. It is the responsibility of the subnetwork provider to ensure that the network is properly engineered to satisfy the requirements of all applications transitting that subnetwork. See Section Residual Error Rate Definition: The VDL residual error rate is the ratio of total incorrect, lost and duplicated packets to the total transferred across the subnetwork during any measurement period. Note.! There may be a great difference between the value of the end-to-end residual error rate above the transport layer and the residual error rate of the subnetwork. Capability: 10-6 Remark: This capability is subject to validation. Many VDL applications will be sensitive to transmission errors. 5.4 Congestion control Definition: Congestion is defined as the situation when over-all network performance degrades because too many packets are present in the VDL subnetwork. Recommendation: Long-term congestion control is the responsibility of the ground communication system. Congestion should be avoided by sufficient monitoring to detect congestion precursors so that facilities can be
11 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 3A-11 added to handle the added load. When congestion occurs and additional facilities are not available, data traffic should be reduced by restricting lower priority traffic. Short-term congestion control is provided by the link layer retransmission algorithm, which produces some degree of negative feedback to smooth short-term peaks. The retransmission algorithm provides some degree of stabilization when the offered load is greater than the channel can support. However, it is ultimately the responsibility of the subnetwork provider to engineer the network so that the transit delay requirements are satisfied. In the event congestion occurs and additional facilities are not available, data traffic should be reduced by restricting lower priority traffic. 5.5 Availability Definition: The VDL availability is defined as the percentage of time that the service with a minimum acceptable quality (e.g. transfer delay, residual error rate, and/or throughput) is available when requested. The VDL shall have an availability of 99.9 per cent for the quality of service defined in this document within the coverage area. VDL system users have to rely on a certain service and its quality. 5.6 System recovery Definition: System recovery time is a measure of the time between a system becoming disabled and being re-enabled. The VDL system shall be capable of transferring data from a failure on the RF link within 10 seconds of the start of any interference. Note.! The VDL system shall be considered to have been recovered when it is again capable of accepting connection requests from aircraft. Because of the connection-oriented subnetwork design (see 4.2), the actual recovery of the last aircraft affected may be much slower.
12 3A-12 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 essential. For some potential applications, a continuity of service with short periods of disruption is 6. TRANSITION 6.1 Implementation of new systems If new application message processors and data link systems are implemented, they should support code- and byte-independent data transmission and be fully ATN compatible. Agenda Item 7. See ICAO Tenth Air Navigation Conference (1991) (Doc 9583 AN-CONF/10), Report on This will help facilitate incorporation of new data link systems into the ATN. Any new system in this field should be carefully examined for compatibility with the ATN. 6.2 Use of data link systems Recommendation: States should use data link systems as soon as possible after they become available. Note.! Mode 1 operation has been defined in order to facilitate transition until equipment capable of Mode 2 service becomes widely available. Agenda Item 7. See ICAO Tenth Air Navigation Conference (1991) (Doc 9583 AN-CONF/10), Report on Early use of data link systems will provide important experience to guide further development and use of communication systems.
13 6.3 Use of frequencies Recommendation: AMCP/4-WP/70 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 3A-13 Priority in the use of the upper four frequencies (i.e., MHz to MHz) should be reserved for Mode 2 modulation requirements. Mode 1 and Mode 2 systems are not compatible for simultaneous operation on a single channel in the same area. The operation of the above modulations on the same or adjacent channels within the given interference limits and is subject to further validation. See Annex 10 to the Convention on International Civil Aviation, Amendment 69.!!!!!!!!
ROUTING TRAFFIC WITH SUBNETWORK PRIORITY 14 ON THE AMSS
 ROUTING TRAFFIC WITH SUBNETWORK PRIORITY 14 ON THE AMSS 1. Introduction... 2 2. Routing Initiation over the AMSS... 3 3. Establishment of an IDRP Connection... 4 4. Route Updates... 5 5. Periodic Exchanges
ROUTING TRAFFIC WITH SUBNETWORK PRIORITY 14 ON THE AMSS 1. Introduction... 2 2. Routing Initiation over the AMSS... 3 3. Establishment of an IDRP Connection... 4 4. Route Updates... 5 5. Periodic Exchanges
REPORT ON AGENDA ITEM 4
 15/2/00 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK PANEL (ATNP) THIRD MEETING Montreal, 7 to 18 February 2000 Agenda Item 4: Review of existing technical and procedural provisions relating to the aeronautical
15/2/00 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK PANEL (ATNP) THIRD MEETING Montreal, 7 to 18 February 2000 Agenda Item 4: Review of existing technical and procedural provisions relating to the aeronautical
International Civil Aviation Organization. ATN Seminar and Third ATN Transition Task Force Meeting Singapore, March 2001
 ATNS - 1/2 International Civil Aviation Organization ATN Seminar and Third ATN Transition Task Force Meeting Singapore, 26-30 March 2001 Agenda Item 1: Basic ATN Concept ATN INTERNET COMMUNICATION ARCHITECTURE
ATNS - 1/2 International Civil Aviation Organization ATN Seminar and Third ATN Transition Task Force Meeting Singapore, 26-30 March 2001 Agenda Item 1: Basic ATN Concept ATN INTERNET COMMUNICATION ARCHITECTURE
ASIA/PACIFIC REGIONAL AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK (ATN) GROUND-GROUND ROUTER DESCRIPTION
 INTENATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION OGANIZATION ASIA AND PACIFIC OFFICE ASIA/PACIFIC EGIONAL AEONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWOK (ATN) GOUND-GOUND OUTE DESCIPTION Edition 1.2 May 2004 ISSUE 1.2- MAY 2004 Table
INTENATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION OGANIZATION ASIA AND PACIFIC OFFICE ASIA/PACIFIC EGIONAL AEONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWOK (ATN) GOUND-GOUND OUTE DESCIPTION Edition 1.2 May 2004 ISSUE 1.2- MAY 2004 Table
AMCP/5-WP/72 APPENDIX D (ENGLISH ONLY)
 Appendix D to the Report on Agenda Item 1 1D-1 APPENDIX D (ENGLISH ONLY) DRAFT MANUAL ON HF DATA LINK (HFDL) TECHNICAL DETAILS 1D-2 Appendix D to the Report on Agenda Item 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION...
Appendix D to the Report on Agenda Item 1 1D-1 APPENDIX D (ENGLISH ONLY) DRAFT MANUAL ON HF DATA LINK (HFDL) TECHNICAL DETAILS 1D-2 Appendix D to the Report on Agenda Item 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION...
International Civil Aviation Organization. Fifth Meeting of Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Transition Task Force of APANPIRG
 ATTF/5-IP/11 International Civil Aviation Organization Fifth Meeting of Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Transition Task Force of APANPIRG Phuket, Thailand, 9-13 June, 2003 Agenda Item 9: Review
ATTF/5-IP/11 International Civil Aviation Organization Fifth Meeting of Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Transition Task Force of APANPIRG Phuket, Thailand, 9-13 June, 2003 Agenda Item 9: Review
Data and Computer Communications. Chapter 2 Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based Applications
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 2 Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based s 1 Need For Protocol Architecture data exchange can involve complex procedures better if task broken into subtasks
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 2 Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based s 1 Need For Protocol Architecture data exchange can involve complex procedures better if task broken into subtasks
CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer
 CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer LOCAL CISCO ACADEMY ELSYS TU INSTRUCTOR: STELA STEFANOVA 1 Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission; Objectives Describe how the
CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer LOCAL CISCO ACADEMY ELSYS TU INSTRUCTOR: STELA STEFANOVA 1 Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission; Objectives Describe how the
AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL(ATNP) WORKING GROUP 3 - APPLICATIONS AND UPPER LAYERS. Proposed amendment to the ATN Lexicon Ver.
 ATNP/WG3 WP/ 15-39 17/03/00 AERONAUTICA TEECOMMUNICATIONS NETWOR PANE(ATNP) WORING GROUP 3 - APPICATIONS AND UPPER AYERS Honolulu, 19 anuary 99 22 anuary 99 (fifteenth meeting) Agenda Item 10 : Any Other
ATNP/WG3 WP/ 15-39 17/03/00 AERONAUTICA TEECOMMUNICATIONS NETWOR PANE(ATNP) WORING GROUP 3 - APPICATIONS AND UPPER AYERS Honolulu, 19 anuary 99 22 anuary 99 (fifteenth meeting) Agenda Item 10 : Any Other
International Civil Aviation Organization. COM Co-ordination Meeting. 6 7 March 2013, Kunming, China
 CCM-WP/5 Agenda Item 5 06/03/13 International Civil Aviation Organization COM Co-ordination Meeting 6 7 March 2013, Kunming, China Agenda Item 5: Letter of agreement for technical and operational trial
CCM-WP/5 Agenda Item 5 06/03/13 International Civil Aviation Organization COM Co-ordination Meeting 6 7 March 2013, Kunming, China Agenda Item 5: Letter of agreement for technical and operational trial
Validating ATN with VDL
 ATNP WG-2 WP 346 bis AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL (ATNP) Validating ATN with VDL Prepared by Nicholas Xenocostas and David Leahy Presented by H. Thulin SUMMARY This Working paper presents
ATNP WG-2 WP 346 bis AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL (ATNP) Validating ATN with VDL Prepared by Nicholas Xenocostas and David Leahy Presented by H. Thulin SUMMARY This Working paper presents
TWELFTH AIR NAVIGATION CONFERENCE
 International Civil Aviation Organization 7/5/12 WORKING PAPER ANConf.12.WP.007.en.docx TWELFTH AIR NAVIGATION CONFERENCE Montréal, 19 to 30 November 2012 Agenda Item 3: Interoperability and data through
International Civil Aviation Organization 7/5/12 WORKING PAPER ANConf.12.WP.007.en.docx TWELFTH AIR NAVIGATION CONFERENCE Montréal, 19 to 30 November 2012 Agenda Item 3: Interoperability and data through
Network Working Group ANSI X3S Request for Comments: 994 ISO TC97/SC6/N 3998 March 1986
 Network Working Group ANSI X3S3.3 86-80 Request for Comments: 994 ISO TC97/SC6/N 3998 March 1986 I S O INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION ISO/TC
Network Working Group ANSI X3S3.3 86-80 Request for Comments: 994 ISO TC97/SC6/N 3998 March 1986 I S O INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION ISO/TC
ASIA/PACIFIC REGIONAL AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK (ATN) AIR TRAFFIC SERVICE (ATS) MESSAGE HANDLING SYSTEM (AMHS) DESCRIPTION
 INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATIONA ASIA AND PACIFIC OFFICE ASIA/PACIFIC REGIONAL AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK () AIR TRAFFIC SERVICE (ATS) MESSAGE HANDLING SYSTEM (AMHS) DESCRIPTION First
INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATIONA ASIA AND PACIFIC OFFICE ASIA/PACIFIC REGIONAL AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK () AIR TRAFFIC SERVICE (ATS) MESSAGE HANDLING SYSTEM (AMHS) DESCRIPTION First
CNS/ATM-1 Package Internet SARPs Validation Objectives
 ATNP/WG2-WP/ 12-Apr-96 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL WORKING GROUP 2 Bruxelles, Belgium, 22-26 April 1996 CNS/ATM-1 Package Internet SARPs Validation Objectives Prepared by Jean-Pierre
ATNP/WG2-WP/ 12-Apr-96 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL WORKING GROUP 2 Bruxelles, Belgium, 22-26 April 1996 CNS/ATM-1 Package Internet SARPs Validation Objectives Prepared by Jean-Pierre
5/4/2016 ht.ttlms.com
 Order Template Screen 1 Free Form Lesson Overview 2 Free Form Performance Based CNS Requirements 3 Free Form Performance Based CNS Requirements 4 Single Answer Knowledge Check 5 Free Form Related ICAO
Order Template Screen 1 Free Form Lesson Overview 2 Free Form Performance Based CNS Requirements 3 Free Form Performance Based CNS Requirements 4 Single Answer Knowledge Check 5 Free Form Related ICAO
Functional areas of the communications domain. List of example constituents and standards for the air-ground applications functional area
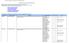 Air-ground communication applications Air-ground communication networks Air-ground datalink communication Air-ground voice communications Ground-ground communication applications Ground-ground communication
Air-ground communication applications Air-ground communication networks Air-ground datalink communication Air-ground voice communications Ground-ground communication applications Ground-ground communication
AMCP/4-WP/70. Appendix D to the Report on Agenda Item 3 3D-1. * This appendix is available in English only.
 Appendix D to the Report on Agenda Item 3 3D-1 APPENDIX D * VDL IMPLEMENTATION ASPECTS * This appendix is available in English only. 3D-2 Appendix D to the Report on Agenda Item 3 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION
Appendix D to the Report on Agenda Item 3 3D-1 APPENDIX D * VDL IMPLEMENTATION ASPECTS * This appendix is available in English only. 3D-2 Appendix D to the Report on Agenda Item 3 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION
Tel.: +1 (514) ext Ref.: AN 7/ /39 22 June 2007
 International Civil Aviation Organization Organisation de l aviation civile internationale Organización de Aviación Civil Internacional Ìåæäóíàðîäíàÿ îðãàíèçàöèÿ ãðàæäàíñêîé àâèàöèè Tel.: +1 (514) 954-8219
International Civil Aviation Organization Organisation de l aviation civile internationale Organización de Aviación Civil Internacional Ìåæäóíàðîäíàÿ îðãàíèçàöèÿ ãðàæäàíñêîé àâèàöèè Tel.: +1 (514) 954-8219
OSI Layer OSI Name Units Implementation Description 7 Application Data PCs Network services such as file, print,
 ANNEX B - Communications Protocol Overheads The OSI Model is a conceptual model that standardizes the functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard of their underlying internal structure
ANNEX B - Communications Protocol Overheads The OSI Model is a conceptual model that standardizes the functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard of their underlying internal structure
Course 6. Internetworking Routing 1/33
 Course 6 Internetworking Routing 1/33 Routing The main function of the network layer is routing packets from the source machine to the destination machine. Along the way, at least one intermediate node
Course 6 Internetworking Routing 1/33 Routing The main function of the network layer is routing packets from the source machine to the destination machine. Along the way, at least one intermediate node
Data and Computer Communications. Protocols and Architecture
 Data and Computer Communications Protocols and Architecture Characteristics Direct or indirect Monolithic or structured Symmetric or asymmetric Standard or nonstandard Means of Communication Direct or
Data and Computer Communications Protocols and Architecture Characteristics Direct or indirect Monolithic or structured Symmetric or asymmetric Standard or nonstandard Means of Communication Direct or
APPENDIX F THE TCP/IP PROTOCOL ARCHITECTURE
 APPENDIX F THE TCP/IP PROTOCOL ARCHITECTURE William Stallings F.1 TCP/IP LAYERS... 2 F.2 TCP AND UDP... 4 F.3 OPERATION OF TCP/IP... 6 F.4 TCP/IP APPLICATIONS... 10 Copyright 2014 Supplement to Computer
APPENDIX F THE TCP/IP PROTOCOL ARCHITECTURE William Stallings F.1 TCP/IP LAYERS... 2 F.2 TCP AND UDP... 4 F.3 OPERATION OF TCP/IP... 6 F.4 TCP/IP APPLICATIONS... 10 Copyright 2014 Supplement to Computer
ET4254 Communications and Networking 1
 Topic 2 Aims:- Communications System Model and Concepts Protocols and Architecture Analog and Digital Signal Concepts Frequency Spectrum and Bandwidth 1 A Communications Model 2 Communications Tasks Transmission
Topic 2 Aims:- Communications System Model and Concepts Protocols and Architecture Analog and Digital Signal Concepts Frequency Spectrum and Bandwidth 1 A Communications Model 2 Communications Tasks Transmission
William Stallings Data and Computer Communications. Chapter 10 Packet Switching
 William Stallings Data and Computer Communications Chapter 10 Packet Switching Principles Circuit switching designed for voice Resources dedicated to a particular call Much of the time a data connection
William Stallings Data and Computer Communications Chapter 10 Packet Switching Principles Circuit switching designed for voice Resources dedicated to a particular call Much of the time a data connection
OSI Data Link Layer. Network Fundamentals Chapter 7. Version Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1
 OSI Data Link Layer Network Fundamentals Chapter 7 Version 4.0 1 Objectives Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission. Describe how the Data Link layer prepares data for transmission
OSI Data Link Layer Network Fundamentals Chapter 7 Version 4.0 1 Objectives Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission. Describe how the Data Link layer prepares data for transmission
Chapter 3 Protocols and the TCP/IP Suite
 Chapter 3 Protocols and the TCP/IP Suite 3.1 The Need for a Protocol Architecture need for a standard communication tasks by layers architecture peer protocol: a set of rules or conventions to exchange
Chapter 3 Protocols and the TCP/IP Suite 3.1 The Need for a Protocol Architecture need for a standard communication tasks by layers architecture peer protocol: a set of rules or conventions to exchange
ET4254 Communications and Networking 1
 Topic 9 Internet Protocols Aims:- basic protocol functions internetworking principles connectionless internetworking IP IPv6 IPSec 1 Protocol Functions have a small set of functions that form basis of
Topic 9 Internet Protocols Aims:- basic protocol functions internetworking principles connectionless internetworking IP IPv6 IPSec 1 Protocol Functions have a small set of functions that form basis of
The Internet. The Internet is an interconnected collection of netw orks.
 The Internet The Internet is an interconnected collection of netw orks. Internetw orking-1 Internetworking! Communications Network: A facility that provides a data transfer service among stations attached
The Internet The Internet is an interconnected collection of netw orks. Internetw orking-1 Internetworking! Communications Network: A facility that provides a data transfer service among stations attached
ATN Presentation. December 2001
 ATN Presentation December 2001 The ATN Overview ATN (Aeronautical Telecommunication Network) ATN is a global aviation standard telecommunications network, and is intended to provide seamless ground-toground
ATN Presentation December 2001 The ATN Overview ATN (Aeronautical Telecommunication Network) ATN is a global aviation standard telecommunications network, and is intended to provide seamless ground-toground
Need For Protocol Architecture
 Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
Module 1. Introduction. Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 1 Introduction Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur Introduction In this module we shall highlight some of the basic aspects of computer networks in two lessons. In lesson 1.1 we shall start with the historical
Module 1 Introduction Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur Introduction In this module we shall highlight some of the basic aspects of computer networks in two lessons. In lesson 1.1 we shall start with the historical
ISO/IEC 8348 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Information technology Open Systems Interconnection Network service definition
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 8348 Third edition 2002-11-01 Information technology Open Systems Interconnection Network service definition Technologies de l'information Interconnexion des systèmes ouverts
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 8348 Third edition 2002-11-01 Information technology Open Systems Interconnection Network service definition Technologies de l'information Interconnexion des systèmes ouverts
Need For Protocol Architecture
 Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
CLARIFICATION OF DOC 9896 INTERNET PROTOCOL SUITE IPv6. (Presented by USA)
 International Civil Aviation Organization ATNICG WG/8-WP/13 28/09/10 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK IMPLEMENTATION COORDINATION GROUP EIGHTH WORKING GROUP MEETING (ATNICG WG/8) Christchurch New
International Civil Aviation Organization ATNICG WG/8-WP/13 28/09/10 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK IMPLEMENTATION COORDINATION GROUP EIGHTH WORKING GROUP MEETING (ATNICG WG/8) Christchurch New
Data & Computer Communication
 Basic Networking Concepts A network is a system of computers and other devices (such as printers and modems) that are connected in such a way that they can exchange data. A bridge is a device that connects
Basic Networking Concepts A network is a system of computers and other devices (such as printers and modems) that are connected in such a way that they can exchange data. A bridge is a device that connects
Continuous Real Time Data Transfer with UDP/IP
 Continuous Real Time Data Transfer with UDP/IP 1 Emil Farkas and 2 Iuliu Szekely 1 Wiener Strasse 27 Leopoldsdorf I. M., A-2285, Austria, farkas_emil@yahoo.com 2 Transilvania University of Brasov, Eroilor
Continuous Real Time Data Transfer with UDP/IP 1 Emil Farkas and 2 Iuliu Szekely 1 Wiener Strasse 27 Leopoldsdorf I. M., A-2285, Austria, farkas_emil@yahoo.com 2 Transilvania University of Brasov, Eroilor
Internetwork Protocols
 Internetwork Protocols Background to IP IP, and related protocols Internetworking Terms (1) Communications Network Facility that provides data transfer service An internet Collection of communications
Internetwork Protocols Background to IP IP, and related protocols Internetworking Terms (1) Communications Network Facility that provides data transfer service An internet Collection of communications
Summary of the ATN/OSI Doc Security Validation Report
 International Civil Aviation Organization WORKING PAPER ACP-WGM16/WP-09 17 May 2010 AERONAUTICAL COMMUNICATIONS PANEL (ACP) 16h MEETING OF WORKING GROUP M Paris, France 17-19 May 2010 Agenda Item 3a: ATN/OSI
International Civil Aviation Organization WORKING PAPER ACP-WGM16/WP-09 17 May 2010 AERONAUTICAL COMMUNICATIONS PANEL (ACP) 16h MEETING OF WORKING GROUP M Paris, France 17-19 May 2010 Agenda Item 3a: ATN/OSI
ICAO Air-Ground Security Standards Strategy ICAO ACP WG M #21. Date: July 17 th 18 th Federal Aviation Administration
 ICAO Air-Ground Security Standards Strategy Administration ICAO ACP WG M #21 Presenter: Vic Patel, FAA Date: July 17 th 18 th 2014 SENSITIVE SECURITY INFORMATION 0 Administration 0 Agenda Goals and objectives
ICAO Air-Ground Security Standards Strategy Administration ICAO ACP WG M #21 Presenter: Vic Patel, FAA Date: July 17 th 18 th 2014 SENSITIVE SECURITY INFORMATION 0 Administration 0 Agenda Goals and objectives
Computer Networks with Internet Technology William Stallings. Chapter 2 Protocols and the TCP/IP Protocol Suite
 Computer Networks with Internet Technology William Stallings Chapter 2 Protocols and the TCP/IP Protocol Suite Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate comms. Path or inform
Computer Networks with Internet Technology William Stallings Chapter 2 Protocols and the TCP/IP Protocol Suite Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate comms. Path or inform
Computer Networks (Introduction to TCP/IP Protocols)
 Network Security(CP33925) Computer Networks (Introduction to TCP/IP Protocols) 부산대학교공과대학정보컴퓨터공학부 Network Type Elements of Protocol OSI Reference Model OSI Layers What we ll learn today 2 Definition of
Network Security(CP33925) Computer Networks (Introduction to TCP/IP Protocols) 부산대학교공과대학정보컴퓨터공학부 Network Type Elements of Protocol OSI Reference Model OSI Layers What we ll learn today 2 Definition of
Circuit switched network
 GPRS-Services Page 12 2. GPRS-Services GPRS integrates a vast sum of additional services in a GSM-network. For this it will be necessary to define a subscriber profile that corresponds with services the
GPRS-Services Page 12 2. GPRS-Services GPRS integrates a vast sum of additional services in a GSM-network. For this it will be necessary to define a subscriber profile that corresponds with services the
The ATN SARPs. Sub-Volume IV. Upper Layer Communications Service. Editors Draft
 The ATN SARPs Sub-Volume IV Upper Layer Communications Service Editors Draft Please note that this is the final editor s draft circulated within the ATNP. This text will be passed to ICAO for publication.
The ATN SARPs Sub-Volume IV Upper Layer Communications Service Editors Draft Please note that this is the final editor s draft circulated within the ATNP. This text will be passed to ICAO for publication.
Layer 3: Network Layer. 9. Mar INF-3190: Switching and Routing
 Layer 3: Network Layer 9. Mar. 2005 1 INF-3190: Switching and Routing Network Layer Goal Enable data transfer from end system to end system End systems Several hops, (heterogeneous) subnetworks Compensate
Layer 3: Network Layer 9. Mar. 2005 1 INF-3190: Switching and Routing Network Layer Goal Enable data transfer from end system to end system End systems Several hops, (heterogeneous) subnetworks Compensate
Request for Comments: 1007 June 1987
 Network Working Group Wayne McCoy Request for Comments: 1007 June 1987 MILITARY SUPPLEMENT TO THE ISO TRANSPORT PROTOCOL Status of this Memo This RFC is being distributed to members of the Internet community
Network Working Group Wayne McCoy Request for Comments: 1007 June 1987 MILITARY SUPPLEMENT TO THE ISO TRANSPORT PROTOCOL Status of this Memo This RFC is being distributed to members of the Internet community
UNIT 2 TRANSPORT LAYER
 Network, Transport and Application UNIT 2 TRANSPORT LAYER Structure Page No. 2.0 Introduction 34 2.1 Objective 34 2.2 Addressing 35 2.3 Reliable delivery 35 2.4 Flow control 38 2.5 Connection Management
Network, Transport and Application UNIT 2 TRANSPORT LAYER Structure Page No. 2.0 Introduction 34 2.1 Objective 34 2.2 Addressing 35 2.3 Reliable delivery 35 2.4 Flow control 38 2.5 Connection Management
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 926 December Protocol for Providing the Connectionless-Mode Network Services
 Network Working Group ISO Request for Comments: 926 December 1984 Protocol for Providing the Connectionless-Mode Network Services Status of this Memo: (Informally - ISO IP) ISO DIS 8473 This document is
Network Working Group ISO Request for Comments: 926 December 1984 Protocol for Providing the Connectionless-Mode Network Services Status of this Memo: (Informally - ISO IP) ISO DIS 8473 This document is
Sixth Meeting of CNS/MET Sub-Group of APANPIRG
 CNS/MET/SG/6-IP/32 International Civil Aviation Organization Sixth Meeting of CNS/MET Sub-Group of APANPIRG Bangkok, Thailand, 15-19 July 2002 Agenda Item 3: ATN transition planning TECHNICAL DOCUMENT
CNS/MET/SG/6-IP/32 International Civil Aviation Organization Sixth Meeting of CNS/MET Sub-Group of APANPIRG Bangkok, Thailand, 15-19 July 2002 Agenda Item 3: ATN transition planning TECHNICAL DOCUMENT
Lecture 2. Computer Networks Models. Network Models 1-1
 Lecture 2 Computer Networks Models Network Models 1-1 Agenda Introduction to the Internet Reference Models for Computer Networks The OSI Model The TCP/IP Model Network Models 1-2 Announcements Bonus -
Lecture 2 Computer Networks Models Network Models 1-1 Agenda Introduction to the Internet Reference Models for Computer Networks The OSI Model The TCP/IP Model Network Models 1-2 Announcements Bonus -
##)44 ) &2!-% -/$% "%!2%2 3%26)#%3 ).4%'2!4%$ 3%26)#%3 $)')4!,.%47/2+ )3$. '%.%2!, 3425#452%!.$ 3%26)#% #!0!"),)4)%3 2ECOMMENDATION )
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ##)44 ) THE INTERNATIONAL TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CONSULTATIVE COMMITTEE ).4%'2!4%$ 3%26)#%3 $)')4!,.%47/2+ )3$. '%.%2!, 3425#452%!.$ 3%26)#% #!0!"),)4)%3 &2!-% -/$%
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ##)44 ) THE INTERNATIONAL TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CONSULTATIVE COMMITTEE ).4%'2!4%$ 3%26)#%3 $)')4!,.%47/2+ )3$. '%.%2!, 3425#452%!.$ 3%26)#% #!0!"),)4)%3 &2!-% -/$%
International Civil Aviation Organization. AIDC Review Task Force Meeting. Brisbane, Australia, March 2003
 AIDC/R TF/IP/3 International Civil Aviation Organization AIDC Review Task Force Meeting Brisbane, Australia, 27-28 March 2003 Agenda Item 2: Agenda Item 4: Review of experience gained and lessons learned
AIDC/R TF/IP/3 International Civil Aviation Organization AIDC Review Task Force Meeting Brisbane, Australia, 27-28 March 2003 Agenda Item 2: Agenda Item 4: Review of experience gained and lessons learned
Frame Relay. Frame Relay Information 1 of 18
 Frame Relay Information 1 of 18 This document was retrieved from the Web and has been been edited by Thomas Jerry Scott for use in his TCP/IP network classes. Chapter Goals Describe the history of Frame
Frame Relay Information 1 of 18 This document was retrieved from the Web and has been been edited by Thomas Jerry Scott for use in his TCP/IP network classes. Chapter Goals Describe the history of Frame
UNIT II NETWORKING
 UNIT II INTRODUCTION TO WIRELESS NETWORKING Wireless Network The cellular telephone system is responsible for providing coverage throughout a particular area known as coverage region or market The interconnection
UNIT II INTRODUCTION TO WIRELESS NETWORKING Wireless Network The cellular telephone system is responsible for providing coverage throughout a particular area known as coverage region or market The interconnection
Asia/Pacific Regional AMHS MTA Routing Policy
 International Civil Aviation Organization Asia and Pacific Office Asia/Pacific Regional AMHS Routing Policy First Edition SEPTEMBER 2008 ASIA/PAC AMHS Routing Policy Table of Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION...3
International Civil Aviation Organization Asia and Pacific Office Asia/Pacific Regional AMHS Routing Policy First Edition SEPTEMBER 2008 ASIA/PAC AMHS Routing Policy Table of Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION...3
Further Guidance Material on the Scaleability of the ATN Routing Architecture
 WP429 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL ATN Internet Working Group (WG2) 13th Meeting 27th - 30th October 1997 Redondo Beach, USA Further Guidance Material on the Scaleability of the ATN Routing
WP429 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL ATN Internet Working Group (WG2) 13th Meeting 27th - 30th October 1997 Redondo Beach, USA Further Guidance Material on the Scaleability of the ATN Routing
ECEN 5032 Data Networks Medium Access Control Sublayer
 ECEN 5032 Data Networks Medium Access Control Sublayer Peter Mathys mathys@colorado.edu University of Colorado, Boulder c 1996 2005, P. Mathys p.1/35 Overview (Sub)networks can be divided into two categories:
ECEN 5032 Data Networks Medium Access Control Sublayer Peter Mathys mathys@colorado.edu University of Colorado, Boulder c 1996 2005, P. Mathys p.1/35 Overview (Sub)networks can be divided into two categories:
AFI AMHS Manual. AFI AMHS Manual. AFI AMHS Manual. AFI AMHS Taskforce Team. Revision Number: Version 1.0. Date: 21/07/2011. AFI AMHS Manual_V1.0.
 Document Reference: Author:, Main Part AFI AMHS Taskforce Team Revision Number: Version 1.0 Date: Filename: _V1.0.doc [1] Version 1.0 Document Control Log Edition Date Comments section/pages affected 1.0
Document Reference: Author:, Main Part AFI AMHS Taskforce Team Revision Number: Version 1.0 Date: Filename: _V1.0.doc [1] Version 1.0 Document Control Log Edition Date Comments section/pages affected 1.0
What Is Congestion? Effects of Congestion. Interaction of Queues. Chapter 12 Congestion in Data Networks. Effect of Congestion Control
 Chapter 12 Congestion in Data Networks Effect of Congestion Control Ideal Performance Practical Performance Congestion Control Mechanisms Backpressure Choke Packet Implicit Congestion Signaling Explicit
Chapter 12 Congestion in Data Networks Effect of Congestion Control Ideal Performance Practical Performance Congestion Control Mechanisms Backpressure Choke Packet Implicit Congestion Signaling Explicit
Layered Architecture
 1 Layered Architecture Required reading: Kurose 1.7 CSE 4213, Fall 2006 Instructor: N. Vlajic Protocols and Standards 2 Entity any device capable of sending and receiving information over the Internet
1 Layered Architecture Required reading: Kurose 1.7 CSE 4213, Fall 2006 Instructor: N. Vlajic Protocols and Standards 2 Entity any device capable of sending and receiving information over the Internet
Federal Aviation Administration (FAA)
 Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) CHANG MAI - ATN SEMINAR CPDLC OVERVIEW December 2001 Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) William J. Hughes Technical l Center (WJHTC) Vic Patel, FAA/ACT-550 ISSP
Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) CHANG MAI - ATN SEMINAR CPDLC OVERVIEW December 2001 Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) William J. Hughes Technical l Center (WJHTC) Vic Patel, FAA/ACT-550 ISSP
Configuring RTP Header Compression
 Header compression is a mechanism that compresses the IP header in a packet before the packet is transmitted. Header compression reduces network overhead and speeds up the transmission of either Real-Time
Header compression is a mechanism that compresses the IP header in a packet before the packet is transmitted. Header compression reduces network overhead and speeds up the transmission of either Real-Time
William Stallings Data and Computer Communications 7 th Edition. Chapter 10 Circuit Switching and Packet Switching
 William Stallings Data and Computer Communications 7 th Edition Chapter 10 Circuit Switching and Packet Switching Switching Networks Long distance transmission is typically done over a network of switched
William Stallings Data and Computer Communications 7 th Edition Chapter 10 Circuit Switching and Packet Switching Switching Networks Long distance transmission is typically done over a network of switched
Chapter 5 OSI Network Layer
 Chapter 5 OSI Network Layer The protocols of the OSI model Network layer specify addressing and processes that enable Transport layer data to be packaged and transported. The Network layer encapsulation
Chapter 5 OSI Network Layer The protocols of the OSI model Network layer specify addressing and processes that enable Transport layer data to be packaged and transported. The Network layer encapsulation
Introduction to Networking
 Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
Wide area networks: packet switching and congestion
 Wide area networks: packet switching and congestion Packet switching ATM and Frame Relay Congestion Circuit and Packet Switching Circuit switching designed for voice Resources dedicated to a particular
Wide area networks: packet switching and congestion Packet switching ATM and Frame Relay Congestion Circuit and Packet Switching Circuit switching designed for voice Resources dedicated to a particular
Basics (cont.) Characteristics of data communication technologies OSI-Model
 48 Basics (cont.) Characteristics of data communication technologies OSI-Model Topologies Packet switching / Circuit switching Medium Access Control (MAC) mechanisms Coding Quality of Service (QoS) 49
48 Basics (cont.) Characteristics of data communication technologies OSI-Model Topologies Packet switching / Circuit switching Medium Access Control (MAC) mechanisms Coding Quality of Service (QoS) 49
Configuring RTP Header Compression
 Configuring RTP Header Compression First Published: January 30, 2006 Last Updated: July 23, 2010 Header compression is a mechanism that compresses the IP header in a packet before the packet is transmitted.
Configuring RTP Header Compression First Published: January 30, 2006 Last Updated: July 23, 2010 Header compression is a mechanism that compresses the IP header in a packet before the packet is transmitted.
International Civil Aviation Organization
 CNS/MET SG/14-WP/55 International Civil Aviation Organization FOURTEENTH MEETING OF THE COMMUNICATIONS/NAVIGATION/SURVEILL ANCE AND METEOROLOGY SUB-GROUP OF APANPIRG (CNS/MET SG/14) Jakarta, Indonesia,
CNS/MET SG/14-WP/55 International Civil Aviation Organization FOURTEENTH MEETING OF THE COMMUNICATIONS/NAVIGATION/SURVEILL ANCE AND METEOROLOGY SUB-GROUP OF APANPIRG (CNS/MET SG/14) Jakarta, Indonesia,
ES623 Networked Embedded Systems
 ES623 Networked Embedded Systems Introduction to Network models & Data Communication 16 th April 2013 OSI Models An ISO standard that covers all aspects of network communication is the Open Systems Interconnection
ES623 Networked Embedded Systems Introduction to Network models & Data Communication 16 th April 2013 OSI Models An ISO standard that covers all aspects of network communication is the Open Systems Interconnection
MANUAL ON DETAILED TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK (ATN) using ISO/OSI standards and protocols
 Doc 9880-AN/466 PART III MANUAL ON DETAILED TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK (ATN) using ISO/OSI standards and protocols PART III INTERNET COMMUNICATION SERVICE,
Doc 9880-AN/466 PART III MANUAL ON DETAILED TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK (ATN) using ISO/OSI standards and protocols PART III INTERNET COMMUNICATION SERVICE,
Internetwork Basic. Possible causes of LAN traffic congestion are
 Internetworking 1 C H A P T E R 2 Internetworking Basics Internetworking Model The OSI Reference Model Ethernet Networking Wireless Networking Data Encapsulation Topic 3 1 Internetwork Basic 4 Possible
Internetworking 1 C H A P T E R 2 Internetworking Basics Internetworking Model The OSI Reference Model Ethernet Networking Wireless Networking Data Encapsulation Topic 3 1 Internetwork Basic 4 Possible
ETSF05/ETSF10 Internet Protocols Network Layer Protocols
 ETSF05/ETSF10 Internet Protocols Network Layer Protocols 2016 Jens Andersson Agenda Internetworking IPv4/IPv6 Framentation/Reassembly ICMPv4/ICMPv6 IPv4 to IPv6 transition VPN/Ipsec NAT (Network Address
ETSF05/ETSF10 Internet Protocols Network Layer Protocols 2016 Jens Andersson Agenda Internetworking IPv4/IPv6 Framentation/Reassembly ICMPv4/ICMPv6 IPv4 to IPv6 transition VPN/Ipsec NAT (Network Address
Current situation of the MEVA II / REDDIG networks MEVA II VSAT NETWORK. (Presented by the Secretariat) SUMMARY
 MR/7 WP/02 International Civil Aviation Organization 16/05/09 Seventh MEVA II / REDDIG Coordination Meeting (MR/7) Mexico City, Mexico, 10 to 11 June 2009 Agenda Item 1: Current situation of the MEVA II
MR/7 WP/02 International Civil Aviation Organization 16/05/09 Seventh MEVA II / REDDIG Coordination Meeting (MR/7) Mexico City, Mexico, 10 to 11 June 2009 Agenda Item 1: Current situation of the MEVA II
INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION
 ICAO EUR DOC 005 INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION EUR CIDIN MANUAL Sixth Edition Published by the European and North Atlantic Office of ICAO April 2011 EUR CIDIN MANUAL Record of Amendments and
ICAO EUR DOC 005 INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION EUR CIDIN MANUAL Sixth Edition Published by the European and North Atlantic Office of ICAO April 2011 EUR CIDIN MANUAL Record of Amendments and
Introduction to Internetworking
 Introduction to Internetworking Introductory terms Communications Network Facility that provides data transfer services An internet Collection of communications networks interconnected by bridges and/or
Introduction to Internetworking Introductory terms Communications Network Facility that provides data transfer services An internet Collection of communications networks interconnected by bridges and/or
SURVEILLANCE DATA EXCHANGE. Part 16: Category 23
 EUROPEAN ORGANISATION FOR THE SAFETY OF AIR NAVIGATION EUROCONTROL EUROCONTROL STANDARD DOCUMENT FOR SURVEILLANCE DATA EXCHANGE Part 16: Category 23 CNS/ATM Ground Station CNS/ATM Ground Station Service
EUROPEAN ORGANISATION FOR THE SAFETY OF AIR NAVIGATION EUROCONTROL EUROCONTROL STANDARD DOCUMENT FOR SURVEILLANCE DATA EXCHANGE Part 16: Category 23 CNS/ATM Ground Station CNS/ATM Ground Station Service
Lecture (04 & 05) Packet switching & Frame Relay techniques Dr. Ahmed ElShafee
 Agenda Lecture (04 & 05) Packet switching & Frame Relay techniques Dr. Ahmed ElShafee Packet switching technique Packet switching protocol layers (X.25) Frame Relay ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU Fall 2011,
Agenda Lecture (04 & 05) Packet switching & Frame Relay techniques Dr. Ahmed ElShafee Packet switching technique Packet switching protocol layers (X.25) Frame Relay ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU Fall 2011,
Lecture (04 & 05) Packet switching & Frame Relay techniques
 Lecture (04 & 05) Packet switching & Frame Relay techniques Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU Fall 2011, Networks I Agenda Packet switching technique Packet switching protocol layers (X.25)
Lecture (04 & 05) Packet switching & Frame Relay techniques Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU Fall 2011, Networks I Agenda Packet switching technique Packet switching protocol layers (X.25)
Introduction. IP Datagrams. Internet Service Paradigm. Routers and Routing Tables. Datagram Forwarding. Example Internet and Conceptual Routing Table
 Introduction Datagram Forwarding Gail Hopkins Service paradigm IP datagrams Routing Encapsulation Fragmentation Reassembly Internet Service Paradigm IP Datagrams supports both connectionless and connection-oriented
Introduction Datagram Forwarding Gail Hopkins Service paradigm IP datagrams Routing Encapsulation Fragmentation Reassembly Internet Service Paradigm IP Datagrams supports both connectionless and connection-oriented
EUROPEAN prets TELECOMMUNICATION November 1998 STANDARD
 DRAFT EUROPEAN prets 300 392-4-3 TELECOMMUNICATION November 1998 STANDARD Source: TETRA Reference: DE/TETRA-03001-04-3 ICS: 33.020 Key words: Radio, TETRA Terrestrial Trunked Radio (TETRA); Voice plus
DRAFT EUROPEAN prets 300 392-4-3 TELECOMMUNICATION November 1998 STANDARD Source: TETRA Reference: DE/TETRA-03001-04-3 ICS: 33.020 Key words: Radio, TETRA Terrestrial Trunked Radio (TETRA); Voice plus
Introducing Frame Relay
 Frame Relay CCNA 4 Note Much of the information in this presentation comes from the CCNP 2 version 3.0 module on Frame Relay. I find a lot of the information in CCNA 4 module 5 Frame Relay not very well
Frame Relay CCNA 4 Note Much of the information in this presentation comes from the CCNP 2 version 3.0 module on Frame Relay. I find a lot of the information in CCNA 4 module 5 Frame Relay not very well
Data and Computer Communications
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 2 Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based Applications Eighth Edition by William Stallings Chap2: 1 Need For Protocol Architecture data exchange can involve
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 2 Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based Applications Eighth Edition by William Stallings Chap2: 1 Need For Protocol Architecture data exchange can involve
Introduction to Open System Interconnection Reference Model
 Chapter 5 Introduction to OSI Reference Model 1 Chapter 5 Introduction to Open System Interconnection Reference Model Introduction The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a reference tool for understanding
Chapter 5 Introduction to OSI Reference Model 1 Chapter 5 Introduction to Open System Interconnection Reference Model Introduction The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a reference tool for understanding
frame-relay lapf n201
 frame-relay lapf n201 frame-relay lapf n201 To set the Link Access Procedure for Frame Relay (LAPF) N201 value (the maximum length of the Information field of the LAPF I frame), use the frame-relay lapf
frame-relay lapf n201 frame-relay lapf n201 To set the Link Access Procedure for Frame Relay (LAPF) N201 value (the maximum length of the Information field of the LAPF I frame), use the frame-relay lapf
Introduction to computer networking
 edge core Introduction to computer networking Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 The edge core Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 edge core Billions of connected computing
edge core Introduction to computer networking Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 The edge core Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 edge core Billions of connected computing
TERMS OF REFERENCE. Special Committee (SC) 223
 REQUESTOR: TERMS OF REFERENCE Special Committee (SC) 223 Internet Protocol Suite (IPS) and Aeronautical Mobile Airport Communication System (AeroMACS) (Version 3) FAA ANG-B Organization Person ANG-B/Michelle
REQUESTOR: TERMS OF REFERENCE Special Committee (SC) 223 Internet Protocol Suite (IPS) and Aeronautical Mobile Airport Communication System (AeroMACS) (Version 3) FAA ANG-B Organization Person ANG-B/Michelle
Tutorial 2 : Networking
 Lund University ETSN01 Advanced Telecommunication Tutorial 2 : Networking Author: Emma Fitzgerald Tutor: Farnaz Moradi November 26, 2015 Contents I Before you start 3 II Whole Class Exercise: Networking
Lund University ETSN01 Advanced Telecommunication Tutorial 2 : Networking Author: Emma Fitzgerald Tutor: Farnaz Moradi November 26, 2015 Contents I Before you start 3 II Whole Class Exercise: Networking
SURVEILLANCE DATA EXCHANGE. Part 1. All Purpose Structured Eurocontrol Surveillance Information Exchange (ASTERIX)
 EUROPEAN ORGANISATION FOR THE SAFETY OF AIR NAVIGATION EUROCONTROL EUROCONTROL STANDARD DOCUMENT FOR SURVEILLANCE DATA EXCHANGE Part 1 All Purpose Structured Eurocontrol Surveillance Information Exchange
EUROPEAN ORGANISATION FOR THE SAFETY OF AIR NAVIGATION EUROCONTROL EUROCONTROL STANDARD DOCUMENT FOR SURVEILLANCE DATA EXCHANGE Part 1 All Purpose Structured Eurocontrol Surveillance Information Exchange
CHAPTER 3 EFFECTIVE ADMISSION CONTROL MECHANISM IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS
 28 CHAPTER 3 EFFECTIVE ADMISSION CONTROL MECHANISM IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS Introduction Measurement-based scheme, that constantly monitors the network, will incorporate the current network state in the
28 CHAPTER 3 EFFECTIVE ADMISSION CONTROL MECHANISM IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS Introduction Measurement-based scheme, that constantly monitors the network, will incorporate the current network state in the
Layered Architecture
 CS311: DATA COMMUNICATION Layered Architecture by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
CS311: DATA COMMUNICATION Layered Architecture by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs)
 Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) Sub-Volume 1 Introduction and System-Level Requirements Version 0.7 19-June-1996 \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp316.Doc,
Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) Sub-Volume 1 Introduction and System-Level Requirements Version 0.7 19-June-1996 \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp316.Doc,
COMPUTER NETWORK Model Test Paper
 Model Test Paper Question no. 1 is compulsory. Attempt all parts. Q1. Each question carries equal marks. (5*5 marks) A) Difference between Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol.
Model Test Paper Question no. 1 is compulsory. Attempt all parts. Q1. Each question carries equal marks. (5*5 marks) A) Difference between Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol.
MEVA III NETWORK IMPLEMENTATION. (Presented by Secretariat) SUMMARY
 GREPECAS/17 - WP/24 International Civil Aviation Organization 19/06/14 CAR/SAM Regional Planning and Implementation Group (GREPECAS) Seventeenth Meeting of the CAR/SAM Regional Planning and Implementation
GREPECAS/17 - WP/24 International Civil Aviation Organization 19/06/14 CAR/SAM Regional Planning and Implementation Group (GREPECAS) Seventeenth Meeting of the CAR/SAM Regional Planning and Implementation
Organizations have developed standard sets of protocols
 Network Models Organizations have developed standard sets of protocols Some of these organizations are: The International Standards Organization (ISO) The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers
Network Models Organizations have developed standard sets of protocols Some of these organizations are: The International Standards Organization (ISO) The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers
Access to the Web. Coverage. Basic Communication Technology. CMPT 165: Review
 Access to the Web CMPT 165: Review Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University December 5, 2011 Access to the Web requires: a computer (of some kind) a connection
Access to the Web CMPT 165: Review Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University December 5, 2011 Access to the Web requires: a computer (of some kind) a connection
Chapter -5 QUALITY OF SERVICE (QOS) PLATFORM DESIGN FOR REAL TIME MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS
 Chapter -5 QUALITY OF SERVICE (QOS) PLATFORM DESIGN FOR REAL TIME MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS Chapter 5 QUALITY OF SERVICE (QOS) PLATFORM DESIGN FOR REAL TIME MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS 5.1 Introduction For successful
Chapter -5 QUALITY OF SERVICE (QOS) PLATFORM DESIGN FOR REAL TIME MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS Chapter 5 QUALITY OF SERVICE (QOS) PLATFORM DESIGN FOR REAL TIME MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS 5.1 Introduction For successful
Mike Shorthose, Nikos Fistas Eurocontrol
 Mike Shorthose, Nikos Fistas Eurocontrol AMCP WG-M 5th meeting St Petersburg, 20 August 2002 Slide 1 Background limitations of current protocol benefits of new protocol Process Eurocontrol funded development
Mike Shorthose, Nikos Fistas Eurocontrol AMCP WG-M 5th meeting St Petersburg, 20 August 2002 Slide 1 Background limitations of current protocol benefits of new protocol Process Eurocontrol funded development
SURVEILLANCE DATA EXCHANGE
 EUROPEAN ORGANISATION FOR THE SAFETY OF AIR NAVIGATION EUROCONTROL EUROCONTROL STANDARD DOCUMENT FOR SURVEILLANCE DATA EXCHANGE Part 1 All Purpose Structured Eurocontrol Surveillance Information Exchange
EUROPEAN ORGANISATION FOR THE SAFETY OF AIR NAVIGATION EUROCONTROL EUROCONTROL STANDARD DOCUMENT FOR SURVEILLANCE DATA EXCHANGE Part 1 All Purpose Structured Eurocontrol Surveillance Information Exchange
Review of the ATN CAR/SAM Planning/Implementation Activities. (Presented by the Coordinator) SUMMARY
 WP/2 5/05/10 International Civil Aviation Organization CAR/SAM Regional Planning Implementation Group (GREPECAS) CNS/ATM Subgroup Coordination meeting of the ATN ground-ground and ground-air applications
WP/2 5/05/10 International Civil Aviation Organization CAR/SAM Regional Planning Implementation Group (GREPECAS) CNS/ATM Subgroup Coordination meeting of the ATN ground-ground and ground-air applications
