Regional Group Nordic GRID DISTURBANCE AND FAULT STATISTICS
|
|
|
- Bertina Sibyl Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Regional Group Nordic GRID DISTURBANCE AND FAULT STATISTICS
2 Table contents Table contents Page 1 INTRODUCTION Contact persons Guidelines the statistics Voltage levels in the ENTSO-E Nordic network Scope and limitations the statistics SUMMARY Summary for Denmark Summary for Finland Summary for Iceland Summary for Norway Summary for Sweden DISTURBANCES Annual number disturbances during the period Disturbances divided according to month Disturbances divided according to cause ENERGY NOT SUPPLIED (ENS) Energy not supplied (ENS) divided according to voltage level Energy not supplied (ENS) and total consumption Energy not supplied (ENS) divided according to month Energy not supplied (ENS) divided according to cause Energy not supplied (ENS) divided according to component FAULTS IN POWER SYSTEM COMPONENTS Overview all faults Faults in overhead lines Faults in cables Faults in power transformers Faults in instrument transformers Faults in circuit breakers Faults in control equipment Faults in compensation devices OUTAGES Coverage the outage statistics Outages in power system units Duration in different power system units Cumulative duration in some power system units Reliability trend for some power system units REFERENCES Appendix 1: The calculation energy not supplied Appendix 2: Contact persons in the Nordic countries
3 TABLE OF CONTENTS Appendix 3: Contact persons for the distribution network statistics
4 1 Introduction This report is an overview the Danish, Finnish, Icelandic, Norwegian and Swedish transmission grid disturbance statistics for the year. Although Iceland does not belong to the ENTSO-E Regional Group Nordic, it is included in this report. Also the disturbance data the whole Denmark is included in this report although only the grid eastern Denmark belongs to the synchronous Nordic grid. The report is made according to ENTSO-E Nordic guidelines for disturbance statistics [1] and it includes the faults causing disturbances in the kv grids. Transmission System Operators providing the statistical data are Energinet.dk in Denmark, Fingrid Oyj in Finland, Landsnet in Iceland, Statnett SF in Norway and Svenska Kraftnät in Sweden. ENTSO-E Nordic Guidelines for the Classification Grid Disturbances [1] were prepared by Nordel 1 during the years and have been used since Therefore, most charts include data for the ten-year period In those cases where older data has been available, even longer periods have been used. The statistics can be found at ENTSO-E website The guidelines and disturbance statistics were in the Scandinavian language until In 2007, however, the guidelines were translated into English and the report for 2006 was the first set statistics to be written in English. The structure these statistics is similar to the 2006 statistics. Although this summary originates from the Nordic co-operation that has aimed to use the combined experience from the five countries regarding the design and operation their respective power systems, other ENTSO-E countries are encouraged to participate in the statistics as well. The material in the statistics covers the main systems and associated network devices with the 100 kv voltage level as the minimum. Control equipment and installations for reactive compensation are also included in the statistics. Despite common guidelines, there are very slight differences in interpretations between different countries and companies. These differences may have a minor effect on the statistical material and are considered being little significance. Nevertheless, users should partly because these differences, but also because the different countries or transmission and power companies maintenance and general policies use the appropriate published average values. Values that concern control equipment and unspecified faults or causes should be used with wider margins than other values. 1 Nordel was the predecessor ENTSO-E Regional Group Nordic until. 4
5 The total number HVDC disturbances is too low to make relevant statistics for the Nordic countries. For the time being, the report does not include HVDC fault statistics either. However, there is parallel reporting to CIGRE that makes a worldwide HVDC statistics every second year. The publications CIGRE can be found at In Chapter 2, the statistics are summarised, covering the consequences disturbances in the form energy not supplied (ENS) and covering the total number disturbances in the Nordic power system. In addition, each Transmission System Operator has presented the most important issues the year. In Chapter 3 disturbances are discussed. The focus is on the analysis and allocation the causes disturbances. The division disturbances during the year for each country is presented; for example, the consequences the disturbances in the form energy not supplied. Chapter 4 presents tables and figures energy not supplied for each country. In Chapter 5 faults in different components are discussed. A summary all the faults is followed by the presentation more detailed statistics. Chapter 6 covers in the various power system units. This part the statistics starts from the year There are no common disturbance statistics for voltage levels lower than 100 kv. Appendix 3 presents the relevant contact persons for these statistics. 1.1 Contact persons Each country is represented by at least one contact person, responsible for his/her country s statistical information. The relevant contact person can provide additional information concerning ENTSO-E Nordic disturbance statistics. The relevant contact information is given in Appendix Guidelines the statistics The scope and definitions ENTSO-E Nordic disturbance statistics are presented in more detail in ENTSO-E Nordic Guidelines for the Classification Grid Disturbances [1]. 5
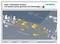
6 1.3 Voltage levels in the ENTSO-E Nordic network The Nordic main grid is in Figure 1 [5]. Voltage levels the network in the Nordic countries are presented in Table 1.1. In the statistics, voltage levels are grouped according to the table. Figure 1 The Nordic main grid. 6
7 Table 1.1 Voltage levels in the ENTSO-E Nordic network Nominal voltage Statistical Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden level voltage U N P U N P U N P U N P U N P kv U (kv) kv % kv % kv % kv % kv % U statistical (designated) voltage, U N nominal voltage P Percentage the grid at the respective nominal voltage level for each statistical voltage. The following tables use the 132, 220 and 400 kv values to represent the nominal voltages, in accordance with Table Scope and limitations the statistics Table 1.2 presents the coverage the statistics in each country. The percentage the grid is estimated according to the length lines included in the statistics material. Table 1.2 Percentage national networks included in the statistics Voltage level Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden 400 kv 100% 100% - 100% 100% 220 kv 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 132 kv 100% 99% 100% 100% 99% The network statistics each country, except Iceland, cover data from several grid owners and the representation their statistics is not fully consistent. Finland: The data includes approximately 99% Finnish 110 kv lines and approximately 90% 110/20 kv transformers. Iceland: The network statistics cover the whole 220kV and 132kV transmission grid. There is only one transmission company in Iceland. Norway: A large part the 132 kv network is resonant earthed but is combined with a solid earthed network in these statistics. 7
8 2 Summary In, the energy not supplied (ENS) due to faults in the Nordic main grid was quite high. ENS was 6.24 GWh, which is more than during any other year since The ten-year annual average energy not supplied during the 2000 period in the ENTSO-E Nordic area was 7.72 GWh. The corresponding average value for each country is presented in brackets in the following paragraphs. The following paragraphs also present the number disturbances for each country as well as the number disturbances that caused energy not supplied in. The corresponding annual averages are from the periods 2000 and 2002, respectively. In addition, the most important issues in defined by each Transmission System Operator are also presented in the summaries. 2.1 Summary for Denmark In Denmark, the energy not supplied for the year was 12.7 MWh (10-year average 959 MWh). The number grid disturbances was 52 (10-year average 77). In, four those 52 disturbances caused ENS. Approximately customers were interrupted during these four grid disturbances. On average four disturbances per year caused ENS during On the 4th March, a 150 kv power transformer tripped due to icing on a pressure switch. This fault resulted in 0.7 MWh ENS. On the 28th May, a 150 kv power transformer tripped due to high pressure. Further investigation showed a blocked drain on a tap changer. This fault resulted in 11.5 MWh ENS (power flow from 60 kv to 150 kv grid due to a large amount wind power). 2.2 Summary for Finland For Finland, the energy not supplied in was 509 MWh (10-year average 200 MWh). The number grid disturbances was 386 (10-year average 282) and 77 them caused ENS. On average 55 disturbances per year caused ENS in In, 30% ENS occurred due to operation and maintenance and 30% ENS occurred due to external influences. Most the disturbances were caused by lightning and occurred during the summer months. The percentage unknown disturbances went down to 48% in from 58% in Almost all the unknown disturbances occurred in 110 kv lines. 8
9 72% ENS was caused by only five disturbances. The highest amount ENS (115 MWh) in a single disturbance was caused by a passenger hoist collision to power lines, which also resulted in one person being injured. 2.3 Summary for Iceland For Iceland, the energy not supplied in was 562 MWh (10-year average 756 MWh). The total number disturbances was 17 (10-year average 40), which 9 led to ENS. On average there have been 25 disturbances per year that caused ENS in In Iceland, over 75% ENS occurred in January. Two the disturbances in January were relatively significant. On the 23rd January, a suspension lock on the 132 kv radial line MJ1 broke, causing a conductor to fall to the earth. That same day the transmission line GE1 (serial in front MJ1) tripped owing to icing during the outage the MJ1 line. Energy not supplied as a result these disturbances totalled 416 MWh. In October, a widespread disturbance occurred in the eastern Iceland. The disturbance was caused by icing and lasted for a relatively long period, but resulted in rather low ENS. 2.4 Summary for Norway For Norway, the energy not supplied for was 1156 MWh (10-year average 2358 MWh). The number grid disturbances was 237 (10-year average 331), which is less than during any other year since Of these 237 disturbances 80 led to ENS. On average, there have been 100 disturbances per year that caused ENS in In, the two biggest contributors to ENS were faults on technical equipment and faults with unknown cause. They caused together 2/3 the total ENS. 2.5 Summary for Sweden In Sweden, the energy not supplied in was 4001 MWh (10-year average 3451 MWh). The total number disturbances was 555 (10-year average 585) and 146 those caused ENS. On average there have been 133 disturbances per year that have caused ENS in The amount ENS consists many disturbances; no single significant incidents occurred. 9
10 3 Disturbances This chapter includes an overview disturbances in the ENTSO-E Nordic countries. In addition, Chapter 3 presents the connection between disturbances, energy not supplied, fault causes and division during the year, together with the development the number disturbances over the ten-year period It is important to note the difference between a disturbance and a fault. A disturbance may consist a single fault but it can also contain many faults, typically consisting an initial fault followed by some secondary faults. Definition a grid disturbance: Outages, forced or unintended disconnection or failed reconnection as a result faults in the power grid [1, 2]. 3.1 Annual number disturbances during the period 2000 The number disturbances during the year in the Nordic main grid was 1247, which is slightly lower than the 10-year average The number grid disturbances cannot be used directly for comparative purposes between countries, because big differences between external conditions in the transmission networks ENTSO-E Nordic countries. Table 3.1 presents the sum disturbances during the year for the complete kv grid in each respective country. Figure 3.1 shows the development the number disturbances in each respective country during the period Table 3.1 grid disturbances in Year Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden disturbances
11 disturbances Grid disturbances Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 3.1 grid disturbances in each Nordic country during the period Disturbances divided according to month Figure 3.2 presents the percentage distribution grid disturbances according to month in different countries in the year. Figure 3.3 shows the ten-year average distribution disturbances during the period
12 % disturbances % disturbances Distribution grid disturbances according to month ) 1) Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 3.2 Percentage distribution grid disturbances according to month in each country in. 1) For Iceland, the high percentage disturbances in January and October was caused by bad weather. Average distribution grid disturbances according to month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 3.3 Average percentage distribution grid disturbances according to month for the period
13 Table 3.2 and Table 3.3 present the numerical values behind Figure 3.2 and Figure 3.3. The numbers in the tables are sums all the disturbances in the kv networks. For all countries, except Iceland, the number disturbances is usually greatest during the summer period. This is caused by lightning strikes during the summer. Table 3.2 Percentage distribution grid disturbances per month for each country in Country Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Nordic Table 3.3 Percentage division grid disturbances during the years 2000 Country Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Nordic Disturbances divided according to cause There are some minor scale differences in the definitions fault causes and disturbances between countries. Some countries use up to 40 different options and others differentiate between initiating and underlying causes. The exact definitions are listed in Section in the guidelines [1]. ENTSO-E Nordic s statistics use seven different options for fault causes and list the initiating cause the event as the starting point. An overview the causes grid disturbances and energy not supplied in each country is presented in Table 3.4. Each country or company that participates in the ENTSO-E Nordic s statistics has its own more detailed way gathering data according to fault cause. ENTSO-E Nordic s guidelines [1] describe how each fault cause relates to ENTSO-E Nordic s cause allocation. 13
14 Table 3.4 Grouping grid disturbances and energy not supplied (ENS) by cause Cause Country Percentage distribution disturbances Percentage distribution ENS 1) Lightning Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden environmental causes Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden External influences Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Operation and maintenance Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Technical equipment Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Unknown Denmark Finland 2) Iceland Norway Sweden ) Calculation energy not supplied varies between different countries and is presented in Appendix 1. 2) Most the Finnish unknown disturbances probably have other natural phenomenon or external influence as their cause. 14
15 % disturbances In Figure 3.4, disturbances for all voltage levels are identified in terms the initial fault. Distribution grid disturbances according to cause ) Lightning environmental cause External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Unknown Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 3.4 Percentage distribution grid disturbances according to cause in. 1) For Iceland, the high percentage disturbances in the category other environmental cause results mainly from bad weather in January and October. A large number disturbances with unknown cause probably have their real cause in the categories other environmental cause and lightning. 15
16 4 Energy not supplied (ENS) This chapter presents an overview energy not supplied in the ENTSO-E Nordic countries. One should notice that the amount energy not supplied is always an estimation. The accuracy the estimation varies between companies in different countries and so does the calculation method for energy not supplied, as can be seen in Appendix 1. Definition energy not supplied: The estimated energy which would have been supplied to end users if no interruption and no transmission restrictions had occurred [1, 2]. 4.1 Energy not supplied (ENS) divided according to voltage level Table 4.1 shows the amount energy not supplied in the five countries and its division according to voltage level. Table 4.1 Energy not supplied (ENS) according to the voltage level the initiating fault Country ENS ENS divided into different voltage levels during the period 2000 MWh (%) 132 kv 220 kv 400 kv 2) Denmark 12,7 3) 5,2 0,0 94,8 0,0 Finland 508,9 94,3 4,1 0,3 1,3 Iceland 562,5 42,6 57,4 0,0 0,0 Norway 1156,0 41,4 32,7 6,8 19,2 Sweden 4001,1 51,6 8,0 30,4 9,9 Nordic 6241,2 43,0 19,3 27,4 10,3 1) The high values for the 400 kv share energy not supplied in Denmark and Sweden are the result a major disturbance in southern Sweden on the 23rd September in ) The category other contains energy not supplied from system faults, auxiliary equipment, lower voltage level networks and the connections to foreign countries, etc. 3) The further explanation for the low ENS in Denmark compared with other countries can be found in Appendix 1, where the different calculation methods ENS are discussed. In Figure 4.1 and Figure 4.2, energy not supplied is summarised according to the different voltage levels for the year and for the period 2000, respectively. Voltage level refers to the initiating fault the respective disturbance. 16
17 ENS divided into different voltage levels in 100 % 90 % 80 % 70 % 60 % 50 % 40 % 400 kv 220 kv 132 kv 30 % 20 % 10 % 0 % Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Nordic Figure 4.1 Energy not supplied (ENS) in terms the voltage level the initiating fault in. ENS divided into different voltage levels during the period % 90 % 1) 80 % 70 % 60 % 50 % 40 % 400 kv 220 kv 132 kv 30 % 20 % 10 % 0 % Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Nordic Figure 4.2 Energy not supplied (ENS) in terms the voltage level the initiating fault during the period ) The large amount energy not supplied at 400 kv grid in Denmark is a consequence the big disturbance in southern Sweden and Zealand on the 23rd September in That disturbance caused 88% the total amount energy not supplied at the 400 kv level during that year. 17
18 ENS / consumption (ppm) 4.2 Energy not supplied (ENS) and total consumption Table 4.2 shows the energy not supplied in relation to the total consumption energy in each respective country and its division according to installation. Table 4.2 Energy not supplied (ENS) according to installation Country Total consumption ENS ENS / consumption ENS divided according to installation during the period 2000 (%) GWh MWh Ppm Ppm Overhead Sta line Cable tions Denmark ,7 0,4 27,8 11,7 0,0 4,6 83,6 Finland ,9 6,3 2,6 44,1 0,0 43,5 12,4 Iceland ,5 33,4 71,9 40,0 1,1 44,1 14,8 Norway ,0 7,0 18,7 34,7 0,5 41,8 23,0 Sweden ,1 28,9 23,6 15,8 9,1 65,7 9,4 Nordic ,2 14,4 19,6 24,2 4,3 48,1 23,4 Ppm (parts per million) is ENS as a proportional value the consumed energy, which is calculated: ENS (MWh) 10 6 / consumption (MWh). Figure 4.3 presents the development energy not supplied during the period One should note that there is a considerable difference from year to year, which depends on occasional events, such as storms. These events have a significant effect on each country s yearly statistics. ENS in relation to the total consumption 250 1) 200 2) Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 4.3 Energy not supplied (ENS) / consumption (ppm). 18
19 % ENS 1) The large amount energy not supplied in Denmark is a consequence the major disturbance in southern Sweden on the 23rd September in 2003 that caused the whole Zealand to lose its power. 2) An unusual number disturbances, which had an influence on the power intensive industry, caused the high value energy not supplied in Iceland during Energy not supplied (ENS) divided according to month Figure 4.4 presents the distribution energy not supplied according to month in the respective countries. Distribution ENS according to month ) 2) Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 4.4 Percentage distribution energy not supplied (ENS) according to month in. 1) In Iceland, the high value ENS in January was mainly caused by two relatively significant disturbances on the 23rd January. 2) In Denmark, only four disturbances led to ENS in. 19
20 % ENS 4.4 Energy not supplied (ENS) divided according to cause Figure 4.5 presents the distribution energy not supplied according to cause in different countries. Distribution ENS according to cause ) 2) Lightning environmental cause External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Unknown Figure 4.5 Percentage distribution energy not supplied (ENS) according to the cause the primary fault in. 1) For Iceland, the high value ENS in the category other environmental cause was due to bad weather in January. 2) The major ENS contribution in Denmark was caused by a blocked drain. 20
21 4.5 Energy not supplied (ENS) divided according to component Table 4.3 shows the amount energy not supplied in and the annual average for the period Table 4.4 shows the distribution energy not supplied according to component. Table 4.3 Energy not supplied (ENS) in and the annual average for the period 2001 Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Nordic Time period ENS (MWh)
22 Table 4.4 Percentage distribution energy not supplied in terms component Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Nordic Fault location Overhead line 0,0 0,4 73,1 47,2 90,9 40,7 42,2 31,6 2,8 14,4 23,8 20,8 Cable 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 1,2 0,0 0,5 0,5 9,7 0,3 4,7 Sum line faults 0,0 0,4 73,1 47,2 90,9 41,9 42,2 32,1 3,4 24,1 24,1 25,5 Power transformer 96,9 0,7 1,2 2,0 0,0 0,2 0,4 0,7 4,8 10,4 3,4 5,1 Instrument transformer 0,0 0,0 0,0 4,9 0,0 0,0 1,6 3,9 1,0 2,5 0,9 2,4 Circuit breaker 0,0 3,5 0,0 3,6 0,0 3,9 6,8 1,7 0,0 1,6 1,3 2,2 Disconnector 0,0 0,2 11,9 3,9 0,0 13,6 0,2 4,7 0,1 35,7 1,0 19,2 Surge arrester and spark gap 0,0 0,0 0,0 3,1 0,0 0,0 3,9 2,6 0,5 0,2 1,0 0,9 Busbar 0,0 0,2 0,0 3,6 0,0 8,6 1,9 1,7 0,2 1,5 0,5 2,1 Control equipment 3,1 11,4 13,7 22,7 9,1 12,1 38,6 28,7 2,1 4,0 10,4 13,1 Common ancillary equipment 0,0 0,0 0,0 1,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,1 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,1 substation faults 0,0 0,0 0,1 1,0 0,0 0,0 4,3 2,1 87,5 13,8 56,9 6,9 Sum substation faults 100,0 16,0 26,9 45,7 9,1 38,4 57,8 46,2 96,1 69,7 75,6 52,1 Shunt capacitor 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 3,9 0,0 0,0 0,0 1,0 0,0 0,9 Series capacitor 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 Reactor 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 SVC and statcom 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 Synchronous compensator 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 Sum compensation faults 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 3,9 0,0 0,0 0,0 1,0 0,0 0,9 System fault 0,0 83,6 0,0 0,0 0,0 15,8 0,0 7,1 0,5 0,7 0,3 15,3 Faults in adjoining statistical area 0,0 0,0 0,0 7,1 0,0 0,0 0,0 14,6 0,0 4,5 0,0 6,3 Unknown 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 Sum other faults 0,0 83,7 0,0 7,1 0,0 15,8 0,0 21,7 0,5 5,2 0,3 21,6 One should notice that some countries register the total number energy not supplied in a disturbance in terms the initiating fault, which can give the wrong picture. 22
23 5 Faults in power system components Faults in a component imply that it may not perform its function properly. Faults can have many causes, for example, manufacturing defects or insufficient maintenance by the user. In this chapter, the fault statistics in different grid components are presented. One should take note both the causes and consequences the fault when analysing the fault frequencies different devices. For example, overhead lines normally have more faults than cables. On the other hand, cables normally have considerably longer repair times than overhead lines. Definition a component fault: The inability a component to perform its required function [3]. First an overview all faults registered in the component groups used in the ENTSO-E Nordic statistics is given. More detailed statistics relating to each specific component group are then presented. Ten-year average values have been calculated for most components. For overhead lines, even a longer period has been used due to their long lifetime. In the calculation averages, the annual variation in the number components has been taken into consideration. The averages are therefore calculated on the basis the number components with the number faults for each time period. This chapter also presents fault trend curves for some components. The trend curves show the variation in the fault frequencies consecutive 5-year periods. These curves are divided into kv and 132 kv voltage levels for all the components except for cables, which are not divided. Readers who need more detailed data should use the national statistics. 5.1 Overview all faults Table 5.1 presents the number faults and disturbances during. For Iceland, the fault statistics cover data from Landsnet, the only transmission company in Iceland. For the other four countries, the Transmission System Operators collect data from several grid owners and the representation their statistics is not fully consistent. Table 5.1 faults and grid disturbances in Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden faults in disturbances in Fault/disturbance ratio in 1,02 1,06 1,41 1,16 1,00 The average fault/disturbance ratio during ,16 1,13 1,26 1,31 1,12 23
24 5.1.1 Overview faults divided according to voltage level The division faults and energy not supplied in terms voltage level and country is presented in Table 5.2. In addition, the table shows the line length and the number power transformers in order to give a view the grid size in each country. One should note that the number faults includes all faults, not just faults in lines and power transformers. Table 5.2 Faults in different countries in terms voltage level Voltage Country power transformers Size the grid faults ENS 2) (MWh) Length 2000 lines in km 1) (annual average) 2000 (annual average) Denmark ,2 0,0 329,1 Finland ,9 0,0 0,5 400 kv Iceland Norway ,1 0,0 148,1 Sweden ,6 13,1 1050,8 Denmark ,6 0,0 0,0 Finland ,9 50,3 8,2 220 kv Iceland ,1 51,2 438,3 Norway ,4 137,8 783,4 Sweden ,1 862,2 277,5 Denmark ,8 12,7 50,0 Finland ,6 458,6 189,4 132 kv Iceland ,7 511,3 324,9 Norway ,2 1018,2 1064,3 Sweden ,0 3125,8 1780,5 1) Length lines is the sum the length cables and overhead lines. 2) Calculation energy not supplied (ENS) varies between countries. Table 5.3 shows the number faults classified according to the component groups used in the ENTSO-E Nordic statistics for each respective country. One should note that not all countries have every type equipment in their network, for example, SVCs or statcom installations. The distribution the number components can also vary from country to country, so one should be careful when comparing countries. Note that faults that begin outside the ENTSO-E Nordic statistics voltage range (typically from networks with voltages lower than 100 kv) but that nevertheless have an influence on the ENTSO-E Nordic statistic area are included in the statistics. 24
25 Table 5.3 Percentage division faults according to component Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Nordic Fault location Overhead line 60,4 60,9 74,3 73,9 54,2 39,6 43,3 39,1 38,4 55,0 51,7 54,1 Cable 9,4 2,7 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,6 1,1 0,8 0,7 0,5 0,9 0,6 Sum line faults 69,8 63,6 74,3 73,9 54,2 40,2 44,4 39,9 39,1 55,5 52,6 54,7 Power transformer 7,5 3,8 2,2 0,9 4,2 3,1 3,6 1,8 7,5 5,7 5,0 3,4 Instrument transformer 1,9 0,7 0,2 0,4 0,0 0,4 1,5 1,8 1,1 0,9 0,9 1,0 Circuit breaker 7,5 5,7 0,5 1,3 0,0 6,3 2,5 3,3 1,3 3,6 1,5 3,2 Disconnector 0,0 1,5 0,7 0,6 0,0 0,2 2,5 1,5 0,9 0,7 1,1 0,9 Surge arresters and spark gap 1,9 0,6 0,2 0,2 0,0 0,4 0,7 1,1 0,9 0,3 0,7 0,5 Busbar 0,0 0,5 0,0 0,4 0,0 0,8 2,2 1,2 0,5 1,0 0,7 0,9 Control equipment 1) 5,7 13,1 14,7 12,1 20,8 26,2 18,2 30,2 3,4 11,3 10,4 17,4 Common ancillary equipment 0,0 0,3 0,0 0,2 0,0 0,0 1,1 1,0 0,4 0,8 0,4 0,7 substation faults 0,0 2,3 2,5 1,2 4,2 7,8 20,0 5,5 36,4 5,5 20,4 4,5 Sum substation faults 24,5 28,4 21,1 17,4 29,2 45,1 52,4 47,5 52,4 29,7 41,2 32,7 Shunt capacitor 0,0 0,1 0,0 0,8 8,3 1,9 0,0 1,2 0,2 0,7 0,2 0,9 Series capacitor 0,0 0,0 2,0 0,6 0,0 0,2 0,0 0,0 0,5 1,1 0,8 0,6 Reactor 1,9 1,7 0,0 0,4 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,5 1,6 1,0 0,8 0,7 SVC and statcom 0,0 0,1 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 3,3 1,2 1,8 1,1 1,4 0,8 Synchronous compensator 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,8 0,5 0,4 0,2 0,4 Sum compensation faults 1,9 1,9 2,0 1,8 8,3 2,1 3,3 3,6 4,7 4,3 3,5 3,4 System fault 0,0 2,5 0,2 0,1 8,3 12,0 0,0 1,7 1,6 3,4 0,9 2,5 Faults in adjoining statistical area 3,8 3,5 2,5 3,9 0,0 0,0 0,0 7,4 2,2 4,3 1,8 4,9 Unknown 0,0 0,1 0,0 3,0 0,0 0,6 0,0 0,0 0,0 2,8 0,0 1,8 Sum other faults 3,8 6,1 2,7 7,0 8,3 12,6 0,0 9,1 3,8 10,5 2,7 9,2 1) The category control equipment includes also protection. 25
26 faults per 100 km/year 5.2 Faults in overhead lines Overhead lines constitute a very large part the Nordic transmission grid. Therefore, the tables in this section show the division faults in as well as the average values for the period Faults divided by cause during the period 1996 are also given. Along with the tables, the annual division faults during the period 2000 is presented graphically for all voltage levels. Figure 5.4 and Figure 5.5 present the trend faults for overhead lines. With the help the trend curve, it may be possible to determine the trend faults also in the future kv overhead lines Table 5.4 Division faults according to cause for 400 kv overhead lines Country Line km faults faults per 100 km 1996 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 1996 (%) environmental causes External influences Operation and maintenance Unknown 1- phase faults Technical equipment Permanent faults Denmark ,33 0,35 19,0 58,6 8,6 5,2 5,2 1,7 1,7 50,0 5,2 Finland ,13 0,25 78,5 5,6 1,4 3,5 2,8 2,8 5,6 58,3 8,3 Norway ,60 1,08 24,8 67,3 0,3 0,3 1,9 2,2 3,3 65,1 7,9 Sweden ,26 0,35 54,1 19,4 1,7 2,5 2,5 1,1 18,8 81,8 8,3 Nordic ,28 0,43 45,6 35,7 1,6 2,0 2,5 1,7 10,9 71,4 8,0 400 kv overhead line 2,50 2,00 1,50 1,00 0,50 0, Denmark Finland Norway Sweden Figure 5.1 Annual division faults during the period
27 faults per 100km/year kv overhead lines Table 5.5 Division faults according to cause for 220 kv overhead lines Country Line km faults faults per 100 km 1996 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 1996 (%) environmental causes External influences Operation and maintenance Unknown 1- phase faults Technical equipment Permanent faults Denmark ,00 0,48 57,1 14,3 14,3 0,0 0,0 0,0 14,3 85,7 0,0 Finland ,46 0,78 47,2 3,0 2,2 0,4 0,4 0,7 46,1 71,2 2,6 Iceland ,00 0,40 29,7 51,4 0,0 0,0 18,9 0,0 0,0 56,8 24,3 Norway ,61 0,71 55,6 32,1 1,1 0,4 2,3 2,8 5,8 58,4 12,5 Sweden ,89 0,88 71,5 4,3 3,7 3,9 2,8 0,4 13,5 56,2 7,9 Nordic ,62 0,76 59,4 16,5 2,3 1,7 2,5 1,4 16,2 60,1 9,1 1,60 1,40 1,20 1,00 0,80 0,60 0,40 0, kv overhead line 0, Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 5.2 Annual division faults during the period
28 faults per 100 km/year kv overhead lines Table 5.6 Division faults according to cause for 132 kv overhead lines Country Line km faults faults per 100 km 1996 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 1996 (%) environmental causes External influences Operation and maintenance Unknown 1- phase faults Technical equipment Permanent faults Denmark ,76 1,09 23,7 45,9 17,1 2,2 1,3 2,7 7,1 47,3 5,1 Finland ,71 1,92 41,8 6,2 1,7 1,2 0,4 0,8 48,0 76,2 2,8 Iceland ,02 1,36 3,0 86,3 3,4 0,9 6,0 0,0 0,4 42,9 12,4 Norway ,65 1,07 55,9 29,2 2,9 1,0 6,3 3,5 1,4 21,6 16,7 Sweden ,01 2,24 63,7 5,1 2,6 1,9 2,4 1,8 22,5 40,7 5,3 Nordic ,16 1,70 51,3 14,1 3,3 1,5 2,4 1,7 25,7 49,5 6,5 1) The Norwegian grid includes a resonant earthed system, which has an effect on the low number single-phase earth faults in Norway. 5,00 4,50 4,00 3,50 3,00 2,50 2,00 1,50 1,00 0, kv overhead line 0, Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 5.3 Annual division faults during the period
29 faults per 100 km/year faults per 100 km/year Fault trend for kv overhead lines 1,20 1,00 0,80 0,60 0,40 0,20 0, year period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 5.4 Fault trend for overhead lines at voltage level kv. 3,50 Fault trend for 132 kv overhead lines 3,00 2,50 2,00 1,50 1,00 0,50 0, year period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 5.5 Fault trend for overhead lines at voltage level 132 kv. 29
30 Figure 5.4 and Figure 5.5 present faults divided by line length at different voltage levels. The trend curve is proportioned to line length in order to get comparable results between countries. 5.3 Faults in cables The tables in this section present faults in cables at each respective voltage level, with fault division for the year and for the period In addition, the division faults according to cause is given for the whole ten-year period. The annual division faults during the period 2000 is presented graphically for 132 kv cables. Figure 5.7 presents the trend faults for cables. With due caution, the trend curve can be used to estimate the likely fault frequencies in the future kv cables Table 5.7 Division faults according to cause for 400 kv cables Country Line km faults faults per 100 km 2000 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 2000 (%) Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Unknown Denmark ,00 0,24 0,0 0,0 0,0 25,0 25,0 25,0 25,0 Norway ,00 1,62 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 50,0 25,0 25,0 Sweden 8 0 0,00 0,00 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 Nordic ,58 0,41 0,0 0,0 0,0 12,5 37,5 25,0 25, kv cables Table 5.8 Division faults according to cause for 220 kv cables Country Line km environmental cause External influence faults faults per 100 km 2000 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 2000 (%) environmental cause External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Unknown Norway ,22 0,09 0,0 33,3 0,0 33,3 0,0 0,0 33,3 Sweden ,00 0,75 0,0 0,0 0,0 11,1 77,8 0,0 11,1 Nordic ,15 0,26 0,0 8,3 0,0 16,7 58,3 0,0 16,7 30
31 faults per 100 km/year kv cables Table 5.9 Division faults according to cause for 132 kv cables Country Line km faults faults per 100 km 2000 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 2000 (%) environmental cause External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Unknown Denmark ,68 0,38 0,0 0,0 26,3 15,8 42,1 10,5 5,3 Finland ,00 0,00 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 Iceland ,00 0,75 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 100,0 0,0 0,0 Norway 1) ,00 1,36 0,0 0,0 11,5 19,2 53,8 11,5 3,8 Sweden ,94 0,97 0,0 0,0 20,8 12,5 33,3 16,7 16,7 Nordic ,64 0,69 0,0 0,0 18,1 15,3 45,8 12,5 8,3 1) Cables in Norway include resonant earthed cables. 5,00 4, kv cable 4,00 3,50 3,00 2,50 2,00 1,50 1,00 0,50 0, Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 5.6 Annual division faults during the period
32 faults per 100 km/year Fault trend for cables 1,40 1,20 1,00 0,80 0,60 0,40 0,20 0, year period Denmark Norway Sweden Figure 5.7 Fault trend for cables at all voltage level. Figure 5.7 presents the fault trend for Denmark, Norway and Sweden only due to the low number cables in Finland and Iceland. 5.4 Faults in power transformers The tables in this section present the division faults for the year and for the period 2000 in power transformers at each respective voltage level. The division faults according to cause during the ten-year period is also presented. The annual division faults during the period 2000 is presented graphically for all voltage levels. Figure 5.11 and Figure 5.12 present the trend faults for power transformers, which also allows the trend to be estimated in the future. For power transformers the rated voltage the winding with the highest voltage is stated [1, Section 6.2]. Each transformer is counted only once. 32
33 faults per 100 devices/year kv power transformers Table 5.10 Division faults according to cause for 400 kv power transformers Country devices faults faults per 100 devices 2000 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 2000 (%) environmental cause External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Unknown Denmark ,35 3,56 12,5 12,5 0,0 12,5 12,5 0,0 50,0 Finland ,65 2,05 0,0 22,2 0,0 22,2 33,3 11,1 11,1 Norway ,13 1,13 0,0 0,0 0,0 14,3 57,1 0,0 28,6 Sweden ,17 1,13 0,0 0,0 0,0 60,0 20,0 20,0 0,0 Nordic ,63 1,56 2,9 8,8 0,0 29,4 29,4 8,8 20,6 1) The high number faults in Denmark was caused by a transformer that inflicted three out the seven faults registered during the period ,00 9,00 8,00 7,00 6,00 5,00 4,00 3,00 2,00 1, kv power transformer 0, Denmark Finland Norway Sweden Figure 5.8 Annual division faults during the period
34 faults per 100 devices/year kv power transformers Table 5.11 Division faults according to cause for 220 kv power transformers Country devices faults faults per 100 devices 2000 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 2000 (%) environmental cause External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Unknown Denmark 2 0 0,00 0,00 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 Finland ,00 1,31 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 100,0 Iceland ,13 3,82 0,0 0,0 0,0 10,0 80,0 0,0 10,0 Norway ,11 1,29 5,7 2,9 2,9 25,7 42,9 17,1 2,9 Sweden ,94 3,46 33,3 5,1 10,3 20,5 17,9 2,6 10,3 Nordic ,33 2,00 17,2 3,4 5,7 20,7 34,5 8,0 10,3 14, kv power transformer 12,00 10,00 8,00 6,00 4,00 2,00 0, Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 5.9 Annual division faults during the period
35 faults per 100 devices/year kv power transformers Table 5.12 Division faults according to cause for 132 kv power transformers Country devices faults faults per 100 devices 2000 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 2000 (%) environmental cause External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Unknown Denmark ,26 1,15 3,8 7,7 3,8 34,6 23,1 3,8 23,1 Finland ,76 0,47 0,0 5,9 23,5 11,8 23,5 0,0 35,3 Iceland ,00 0,93 0,0 0,0 0,0 50,0 25,0 0,0 25,0 Norway ,69 0,51 2,8 11,1 5,6 19,4 38,9 16,7 5,6 Sweden 1) ,61 5,23 18,4 2,8 3,4 16,9 27,5 12,2 18,7 Nordic ,83 2,07 15,1 4,0 4,5 18,4 28,0 11,4 18,6 1) The high number faults shown for Sweden during the period was caused by misinterpretation ENTSO-E Nordic s guidelines [1]. The old data is not corrected for Table 5.12, Figure 5.10 or Figure , kv power transformer 10,00 8,00 6,00 4,00 2,00 0, Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 5.10 Annual division faults during the period
36 faults per 100 devices/year faults per 100 devices/year 6,00 Fault trend for kv power transformers 5,00 4,00 3,00 2,00 1,00 0, year period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 5.11 Fault trend for power transformers at voltage level kv. 8,00 Fault trend for 132 kv power transformers 7,00 6,00 5,00 4,00 3,00 2,00 1,00 0, year period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 5.12 Fault trend for power transformers at voltage level 132 kv. 36
37 5.5 Faults in instrument transformers The tables in this section present the faults in instrument transformers for the year and for the period 2000 at each respective voltage level. In addition, the division faults according to cause during the ten-year period is presented. Figure 5.13 and Figure 5.14 present the trend faults for instrument transformers. Both current and voltage transformers are included among instrument transformers. A 3-phase instrument transformer is treated as one unit. If a single-phase transformer is installed, it is also treated as a single unit kv instrument transformers Table 5.13 Division faults according to cause for 400 kv instrument transformers Country devices faults faults per 100 devices 2000 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 2000 (%) Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Unknown Denmark ,00 0,00 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 Finland ,00 0,00 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 Norway ,00 0,12 0,0 10,0 0,0 10,0 30,0 40,0 10,0 Sweden ,00 0,11 8,3 0,0 0,0 16,7 66,7 0,0 8,3 Nordic ,00 0,08 4,5 4,5 0,0 13,6 50,0 18,2 9, kv instrument transformers Table 5.14 Division faults according to cause for 220 kv instrument transformers Country devices environmental cause External influence faults faults per 100 devices 2000 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 2000 (%) environmental cause External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Unknown Denmark ,00 0,00 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 Finland ,00 0,00 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 Iceland ,00 0,03 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 100,0 0,0 0,0 Norway ,04 0,08 9,1 9,1 0,0 0,0 63,6 9,1 9,1 Sweden ,09 0,08 0,0 0,0 0,0 10,0 90,0 0,0 0,0 Nordic ,04 0,07 6,1 6,1 0,0 3,0 72,7 6,1 6,1 37
38 faults per 100 devices/year kv instrument transformers Table 5.15 Division faults according to cause for 132 kv instrument transformers Country devices faults faults per 100 devices 2000 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 2000 (%) environmental cause External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Unknown Denmark ,02 0,02 0,0 16,7 0,0 16,7 50,0 0,0 16,7 Finland ,06 0,07 20,0 0,0 10,0 0,0 60,0 10,0 0,0 Iceland ,00 0,02 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 100,0 0,0 0,0 Norway ,04 0,06 13,0 0,0 0,0 8,7 47,8 15,2 15,2 Sweden ,10 0,06 20,0 0,0 0,0 8,6 60,0 2,9 8,6 Nordic ,05 0,05 15,3 1,0 1,0 8,2 54,1 9,2 11,2 0,16 Fault trend for kv instrument transformers 0,14 0,12 0,10 0,08 0,06 0,04 0,02 0, year period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 5.13 Fault trend for instrument transformers at voltage level kv. 38
39 faults per 100 devices/year 0,14 Fault trend for 132 kv instrument transformers 0,12 0,10 0,08 0,06 0,04 0,02 0, year period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 5.14 Fault trend for instrument transformers at voltage level 132 kv. 5.6 Faults in circuit breakers The tables in this section present circuit breaker faults for the year and for the period 2000 at each respective voltage level. The division faults according to cause during the ten-year period is also presented. Figure 5.15 and Figure 5.15 present the trend faults for circuit breakers. One should note that a significant part the faults are caused by shunt reactor circuit breakers, which usually operate very ten compared with other circuit breakers. Disturbances caused by erroneous circuit breaker operations are registered as faults in circuit breakers, with operation and maintenance as their cause. 39
40 kv circuit breakers Table 5.16 Division faults according to cause for 400 kv circuit breakers Country devices faults faults per 100 devices 2000 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 2000 (%) Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Unknown Denmark ,67 0,77 0,0 10,0 10,0 20,0 50,0 10,0 0,0 Finland ,00 0,31 0,0 0,0 16,7 16,7 66,7 0,0 0,0 Norway ,15 1,01 0,0 0,0 0,0 28,0 56,0 4,0 12,0 Sweden 1) ,10 2,00 0,0 2,4 0,0 3,6 75,9 12,0 6,0 Nordic ,82 1,26 0,0 2,4 1,6 10,5 69,4 9,7 6,5 1) For Sweden, the breaker failures at the 400 kv level most ten occurred in breakers used to switch the reactors. This is the reason for the high number circuit breaker faults in Sweden, because a reactor breaker is operated significantly more ten than a line breaker kv circuit breakers Table 5.17 Division faults according to cause for 220 kv circuit breakers Country devices environmental cause External influence faults faults per 100 devices 2000 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 2000 (%) environmental cause External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Unknown Denmark 2 0 0,00 0,00 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 Finland ,94 0,64 0,0 0,0 0,0 0,0 83,3 16,7 0,0 Iceland ,00 3,75 0,0 8,0 0,0 8,0 72,0 0,0 12,0 Norway ,41 0,73 0,0 0,0 0,0 35,3 54,9 2,0 7,8 Sweden ,49 0,50 5,0 0,0 0,0 20,0 70,0 0,0 5,0 Nordic ,53 0,81 1,0 2,0 0,0 23,5 63,7 2,0 7,8 40
41 faults per 100 devices/year kv circuit breakers Table 5.18 Division faults according to cause for 132 kv circuit breakers Country devices faults faults per 100 devices 2000 Lightning Faults divided by cause during the period 2000 (%) environmental cause External influence Operation and maintenance Technical equipment Unknown Denmark ,37 0,55 0,0 2,3 0,0 36,4 54,5 6,8 0,0 Finland ,00 0,20 25,9 7,4 0,0 22,2 37,0 3,7 3,7 Iceland ,00 0,66 0,0 0,0 0,0 12,5 75,0 0,0 12,5 Norway ,05 0,32 3,1 0,0 0,0 52,3 38,5 1,5 4,6 Sweden ,00 0,84 24,6 2,3 2,3 18,5 41,5 2,3 8,5 Nordic ,05 0,47 15,0 2,2 1,1 29,6 43,4 2,9 5,8 8,00 Fault trend for kv circuit breakers 7,00 6,00 5,00 4,00 3,00 2,00 1,00 0, year period Denmark Finland Iceland Norway Sweden Figure 5.15 Fault trend for circuit breakers at voltage level kv. 1) The explanation for the remarkable improvement on the fault trend Iceland is that most the disturbances on circuit breakers up to 2003 in the 220 kv network were in one substation. These breakers caused problems due to gas leaks and were repaired in In addition to this, two new substations were installed with total 18 circuit breakers (from 56 breakers to 74 breakers total). 41
GUIDELINES FOR THE CLASSIFICATION OF GRID DISTURBANCES ABOVE 100 kv
 GUIDELINES FOR THE CLASSIFICATION OF GRID DISTURBANCES ABOVE 100 kv 13.04.2017 1 INTRODUCTION... 4 2 PURPOSE OF THE GUIDELINES... 4 3 SCOPE AND LIMITATIONS OF THE STATISTICS... 5 4 DEFINITIONS... 6 4.1
GUIDELINES FOR THE CLASSIFICATION OF GRID DISTURBANCES ABOVE 100 kv 13.04.2017 1 INTRODUCTION... 4 2 PURPOSE OF THE GUIDELINES... 4 3 SCOPE AND LIMITATIONS OF THE STATISTICS... 5 4 DEFINITIONS... 6 4.1
Denmarks Cable Policy
 Denmarks Cable Policy Landsnet Annual meeting 2014 March 20th 2014 Jens Møller Birkebæk Director, International Affairs 1 About Energinet.dk 3 Interconnector capacity 3 Agenda Danish Cable Policy 1. Political
Denmarks Cable Policy Landsnet Annual meeting 2014 March 20th 2014 Jens Møller Birkebæk Director, International Affairs 1 About Energinet.dk 3 Interconnector capacity 3 Agenda Danish Cable Policy 1. Political
Nigerian Telecommunications Sector
 Nigerian Telecommunications Sector SUMMARY REPORT: Q4 and full year 2015 NATIONAL BUREAU OF STATISTICS 26th April 2016 Telecommunications Data The telecommunications data used in this report were obtained
Nigerian Telecommunications Sector SUMMARY REPORT: Q4 and full year 2015 NATIONAL BUREAU OF STATISTICS 26th April 2016 Telecommunications Data The telecommunications data used in this report were obtained
On Line Diagnostics for Condition Based and Reliability Centered Maintenance
 1 On Line Diagnostics for Condition Based and Reliability Centered Maintenance Carl Öhlen* STRI Abstract-- Maintenance is required for almost all equipment in order to guarantee its performance, prevent
1 On Line Diagnostics for Condition Based and Reliability Centered Maintenance Carl Öhlen* STRI Abstract-- Maintenance is required for almost all equipment in order to guarantee its performance, prevent
Questions for national reference groups
 Common Harmonised Nordic Retail Market - Message format, content and interface Questions for national reference groups August 2013 Prerequisites for the BRS This document is assuming a supplier centric
Common Harmonised Nordic Retail Market - Message format, content and interface Questions for national reference groups August 2013 Prerequisites for the BRS This document is assuming a supplier centric
Nigerian Telecommunications (Services) Sector Report Q2 2016
 Nigerian Telecommunications (Services) Sector Report Q2 2016 01 SEPTEMBER 2016 Telecommunications Data The telecommunications data used in this report were obtained from the National Bureau of Statistics
Nigerian Telecommunications (Services) Sector Report Q2 2016 01 SEPTEMBER 2016 Telecommunications Data The telecommunications data used in this report were obtained from the National Bureau of Statistics
Hybrid STATCOM / SVC Workgroup 15 th May 2014
 Hybrid STATCOM / SVC Workgroup 15 th May 2014 Place your chosen image here. The four corners must just cover the arrow tips. For covers, the three pictures should be the same size and in a straight line.
Hybrid STATCOM / SVC Workgroup 15 th May 2014 Place your chosen image here. The four corners must just cover the arrow tips. For covers, the three pictures should be the same size and in a straight line.
Nigerian Telecommunications (Services) Sector Report Q3 2016
 Nigerian Telecommunications (Services) Sector Report Q3 2016 24 NOVEMBER 2016 Telecommunications Data The telecommunications data used in this report were obtained from the National Bureau of Statistics
Nigerian Telecommunications (Services) Sector Report Q3 2016 24 NOVEMBER 2016 Telecommunications Data The telecommunications data used in this report were obtained from the National Bureau of Statistics
NETS SQSS Review of Requirement of Onshore Connection Facilities for Offshore Wind Farm Connections (GSR014) Working Group Report
 NETS SQSS Review of Requirement of Onshore Connection Facilities for Offshore Wind Farm Connections (GSR014) Working Group Report January 2014 Executive Summary This document summarises the results of
NETS SQSS Review of Requirement of Onshore Connection Facilities for Offshore Wind Farm Connections (GSR014) Working Group Report January 2014 Executive Summary This document summarises the results of
Smart Grid - Annual Report
 STATE OF MICHIGAN Case No.: U-18255 Page: 1 of 48 BEFORE THE MICHIGAN PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION In the matter of the Application of ) DTE GAS COMPANY ) for authority to increase its rates, amend ) Case
STATE OF MICHIGAN Case No.: U-18255 Page: 1 of 48 BEFORE THE MICHIGAN PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION In the matter of the Application of ) DTE GAS COMPANY ) for authority to increase its rates, amend ) Case
Power Transmission Division Link between power generation and distribution
 Power Transmission Division Link between power generation and distribution Seite 4 High Voltage Substations Schemes, Devices and Types of AIS Installation Content Link between power generation and distribution
Power Transmission Division Link between power generation and distribution Seite 4 High Voltage Substations Schemes, Devices and Types of AIS Installation Content Link between power generation and distribution
Main Components of a Static Var Compensator (SVC)
 Exercise 1 Main Components of a Static Var Compensator (SVC) EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the simplified diagram of an SVC. You will also be familiar
Exercise 1 Main Components of a Static Var Compensator (SVC) EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the simplified diagram of an SVC. You will also be familiar
p. 1 p. 9 p. 26 p. 56 p. 62 p. 68
 The Challenges and Opportunities Faced by Utilities using Modern Protection and Control Systems - Paper Unavailable Trends in Protection and Substation Automation Systems and Feed-backs from CIGRE Activities
The Challenges and Opportunities Faced by Utilities using Modern Protection and Control Systems - Paper Unavailable Trends in Protection and Substation Automation Systems and Feed-backs from CIGRE Activities
Third SafeSeaNet Data Quality quarterly report (October, November and December 2009)
 Third SafeSeaNet Data Quality quarterly report (October, November and December 2009) Lisbon, 25 January 2010 Ref: C.2.2/QR3/2010 1. Introduction The purpose of the quarterly report is to present measurable
Third SafeSeaNet Data Quality quarterly report (October, November and December 2009) Lisbon, 25 January 2010 Ref: C.2.2/QR3/2010 1. Introduction The purpose of the quarterly report is to present measurable
European Developments
 European Developments Place your chosen image here. The four corners must just cover the arrow tips. For covers, the three pictures should be the same size and in a straight line. Transmission Workgroup
European Developments Place your chosen image here. The four corners must just cover the arrow tips. For covers, the three pictures should be the same size and in a straight line. Transmission Workgroup
Evaluation of different solutions of faulted phase earthing technique for an earth fault current limitation
 24th International Conference & Exhibition on Electricity Distribution (CIRED) 12-15 June 2017 Session 3: Operation, control and protection Evaluation of different solutions of faulted phase earthing technique
24th International Conference & Exhibition on Electricity Distribution (CIRED) 12-15 June 2017 Session 3: Operation, control and protection Evaluation of different solutions of faulted phase earthing technique
RCP2 Portfolio Overview Document
 RCP2 Portfolio Overview Document Portfolio: Expenditure Class: Base Capex Expenditure Category: Grid Replacement & Refurbishment As at date: 15 November 2013 Expenditure Forecast Real 2012/13 NZ$ (m) 2015-2016
RCP2 Portfolio Overview Document Portfolio: Expenditure Class: Base Capex Expenditure Category: Grid Replacement & Refurbishment As at date: 15 November 2013 Expenditure Forecast Real 2012/13 NZ$ (m) 2015-2016
Study Committee SC A3
 Prepared by Dagmar Kopejtkova in August 2010 Study Committee SC A3 Study Committee A3 HV Equipment Theory, design, construction and application of HV equipment components, equipment and equipment systems
Prepared by Dagmar Kopejtkova in August 2010 Study Committee SC A3 Study Committee A3 HV Equipment Theory, design, construction and application of HV equipment components, equipment and equipment systems
DAS LRS Monthly Service Report
 DAS LRS Monthly Service Report Customer Service Manager : Diploma Aggregation Service : Daniel Ward Project/document reference : DAS LRS 2010-12 Issue : 1.0 Issue date : 17 th January 2011 Reporting Period
DAS LRS Monthly Service Report Customer Service Manager : Diploma Aggregation Service : Daniel Ward Project/document reference : DAS LRS 2010-12 Issue : 1.0 Issue date : 17 th January 2011 Reporting Period
Implementation Status & Results Montenegro Energy Community of South East Europe APL 3 - Montenegro Project (P106899)
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Implementation Status & Results Montenegro Energy Community of South East Europe APL 3 - Montenegro Project (P106899) Operation Name: Energy Community
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Implementation Status & Results Montenegro Energy Community of South East Europe APL 3 - Montenegro Project (P106899) Operation Name: Energy Community
software.sci.utah.edu (Select Visitors)
 software.sci.utah.edu (Select Visitors) Web Log Analysis Yearly Report 2002 Report Range: 02/01/2002 00:00:0-12/31/2002 23:59:59 www.webtrends.com Table of Contents Top Visitors...3 Top Visitors Over Time...5
software.sci.utah.edu (Select Visitors) Web Log Analysis Yearly Report 2002 Report Range: 02/01/2002 00:00:0-12/31/2002 23:59:59 www.webtrends.com Table of Contents Top Visitors...3 Top Visitors Over Time...5
Call for Papers GCC POWER 2011 GCC Cigre s Leading Electric Power Conference & Exhibition In the Gulf Region
 Call for Papers GCC POWER 2011 GCC Cigre s Leading Electric Power Conference & Exhibition In the Gulf Region Kuwait - November 2011 GCC Cigre, is pleased to announce its 7 th International Conference GCC
Call for Papers GCC POWER 2011 GCC Cigre s Leading Electric Power Conference & Exhibition In the Gulf Region Kuwait - November 2011 GCC Cigre, is pleased to announce its 7 th International Conference GCC
Work to establish standard ENTSOE STAKEHOLDER COMMITTEE 1
 Work to establish standard EN50549-1 EN50549-2 EN50549-10 2017-03-14 ENTSOE STAKEHOLDER COMMITTEE 1 SOMMAIRE Summary Key points TC8X / WG31 01 Schedule1 TC8X / approach1 02 03 Next steps 04 Others considerations1
Work to establish standard EN50549-1 EN50549-2 EN50549-10 2017-03-14 ENTSOE STAKEHOLDER COMMITTEE 1 SOMMAIRE Summary Key points TC8X / WG31 01 Schedule1 TC8X / approach1 02 03 Next steps 04 Others considerations1
ENTSO-E connection network codes Implementation guidance documents. Joint DSO response paper
 ENTSO-E connection network codes Implementation guidance documents Joint DSO response paper August 2016 Dépôt légal: D/2016/12.105/45 Questionnaire Rate-of-change- of- frequency withstand capability (RoCoF)
ENTSO-E connection network codes Implementation guidance documents Joint DSO response paper August 2016 Dépôt légal: D/2016/12.105/45 Questionnaire Rate-of-change- of- frequency withstand capability (RoCoF)
Implementation Guide. afrr capacity market. Version: 0.8
 Implementation Guide afrr capacity market Business process: afrr capacity market Version: 0.8 Status: Draft Date: 28.06.2018 1 Revision History Version Release Date Changed by Comments 0.8 Draft A 28.06.2018
Implementation Guide afrr capacity market Business process: afrr capacity market Version: 0.8 Status: Draft Date: 28.06.2018 1 Revision History Version Release Date Changed by Comments 0.8 Draft A 28.06.2018
Analysis of System Protection Misoperations
 Analysis of System Protection Misoperations December 2015 Table of Contents Preface... ii Executive Summary...1 Introduction...2 Chapter 1 Misoperation Data Analysis...4 Misoperation Data Reported...4
Analysis of System Protection Misoperations December 2015 Table of Contents Preface... ii Executive Summary...1 Introduction...2 Chapter 1 Misoperation Data Analysis...4 Misoperation Data Reported...4
Telecommunication Markets in the Nordic Countries. - Per
 Telecommunication Markets in the Nordic Countries - Per 3.2.20 - About the Nordstat database Established 2007 A descriptive database A selected number of variables that is comparable between the Nordic
Telecommunication Markets in the Nordic Countries - Per 3.2.20 - About the Nordstat database Established 2007 A descriptive database A selected number of variables that is comparable between the Nordic
High and Medium Voltage Substation Design, Testing and Maintenance. KSA, Jeddah, Holiday Inn Jeddah Gateway Hotel.
 Training Course : High and Medium Voltage Substation Design, Testing and Maintenance Training Course For One Week In KSA, Jeddah, Holiday Inn Jeddah Gateway Hotel Which Be Held As Under Details : Tel.
Training Course : High and Medium Voltage Substation Design, Testing and Maintenance Training Course For One Week In KSA, Jeddah, Holiday Inn Jeddah Gateway Hotel Which Be Held As Under Details : Tel.
NIA Progress Report. Programme Summary. 31 July Electricity North West/NIA Programme Summary/31 July 2016 Page 1 of 10
 NIA Progress Report Programme Summary 31 July 2017 Electricity rth West/NIA Programme Summary/31 July 2016 Page 1 of 10 VERSION HISTORY Version Date Author Status Comments V1.0 4 July 2017 L Eyquem Draft
NIA Progress Report Programme Summary 31 July 2017 Electricity rth West/NIA Programme Summary/31 July 2016 Page 1 of 10 VERSION HISTORY Version Date Author Status Comments V1.0 4 July 2017 L Eyquem Draft
Airside Congestion. Airside Congestion
 Airside Congestion Amedeo R. Odoni T. Wilson Professor Aeronautics and Astronautics Civil and Environmental Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Objectives Airside Congestion _ Introduce fundamental
Airside Congestion Amedeo R. Odoni T. Wilson Professor Aeronautics and Astronautics Civil and Environmental Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Objectives Airside Congestion _ Introduce fundamental
I.A.C. - Italian Activity Contest.
 I.A.C. - Italian Activity Contest. RULES FOR 2017 I.A.C. EDITION. Scope: Main goal of the I.A.C. - Italian Activity Contest is to promote, encourage and support the use of the HAM bands from 50 MHz to
I.A.C. - Italian Activity Contest. RULES FOR 2017 I.A.C. EDITION. Scope: Main goal of the I.A.C. - Italian Activity Contest is to promote, encourage and support the use of the HAM bands from 50 MHz to
Small Generator Interconnection System Impact Study Report. Completed For Q0047
 Small Generator Interconnection Completed For Q0047 Proposed Interconnection PacifiCorp s Existing Goshen Rigby 69 kv Line March 7, 2005 1.0 Description of the Generation Facility Q0047 ( Interconnection
Small Generator Interconnection Completed For Q0047 Proposed Interconnection PacifiCorp s Existing Goshen Rigby 69 kv Line March 7, 2005 1.0 Description of the Generation Facility Q0047 ( Interconnection
Design, Control and Application of Modular Multilevel Converters for HVDC Transmission Systems by Kamran Sharifabadi, Lennart Harnefors, Hans-Peter
 1 Design, Control and Application of Modular Multilevel Converters for HVDC Transmission Systems by Kamran Sharifabadi, Lennart Harnefors, Hans-Peter Nee, Staffan Norrga, Remus Teodorescu ISBN-10: 1118851560
1 Design, Control and Application of Modular Multilevel Converters for HVDC Transmission Systems by Kamran Sharifabadi, Lennart Harnefors, Hans-Peter Nee, Staffan Norrga, Remus Teodorescu ISBN-10: 1118851560
MODELING OF SIMULTANEOUS FAULT TO RELIABILITY ENHANCEMENT IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
 MODELING OF SIMULTANEOUS FAULT TO RELIABILITY ENHANCEMENT IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM Nemat DEHGHANI Antti SUPPONEN Sami REPO Tampere University of Technology (TUT) TUT- Finland TUT- Finland Finland antti.supponen@tut.fi
MODELING OF SIMULTANEOUS FAULT TO RELIABILITY ENHANCEMENT IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM Nemat DEHGHANI Antti SUPPONEN Sami REPO Tampere University of Technology (TUT) TUT- Finland TUT- Finland Finland antti.supponen@tut.fi
National Load Despatch Centre Power System Operation Corporation
 Module on Procedure for Data Collection National Load Despatch Centre Power System Operation Corporation Background Algorithms/ Processes AC Load flow and transmission losses Slack bus determination- Average
Module on Procedure for Data Collection National Load Despatch Centre Power System Operation Corporation Background Algorithms/ Processes AC Load flow and transmission losses Slack bus determination- Average
Approval...6. Current Revision...7. Introduction... 8 About PJM Manuals... 8 About This Manual... 8 Using This Manual...9
 PJM Manual 07: PJM Protection Standards Revision: 3 Effective Date: May 24, 2018 Prepared by System Planning Division Transmission Planning Department PJM 2018 Table of Contents Table of Contents Approval...6
PJM Manual 07: PJM Protection Standards Revision: 3 Effective Date: May 24, 2018 Prepared by System Planning Division Transmission Planning Department PJM 2018 Table of Contents Table of Contents Approval...6
Equipment protection
 Equipment protection Serie K Risk of electrical surges Equipment protection 5.000.000 ightning strikes per day 61% Electrical damages caused by surges 30k verage current of a lightning strike ightning
Equipment protection Serie K Risk of electrical surges Equipment protection 5.000.000 ightning strikes per day 61% Electrical damages caused by surges 30k verage current of a lightning strike ightning
Siemens FuseSaver New half-cycle circuit breaker for rural smart grids to minimize operating costs of feeder and spur lines
 Siemens FuseSaver New half-cycle circuit breaker for rural smart grids to minimize operating costs of feeder and spur lines Authors: Dr. Brett Watson, Siemens Ltd., PO Box 4833, Loganholme, QLD 4129, Australia
Siemens FuseSaver New half-cycle circuit breaker for rural smart grids to minimize operating costs of feeder and spur lines Authors: Dr. Brett Watson, Siemens Ltd., PO Box 4833, Loganholme, QLD 4129, Australia
ABB Surge Arresters Contribution to Power Quality Line Side Protection
 James Taylor, Technology Support Manager / Principal Specialist May 2013 ABB Surge Arresters Contribution to Power Quality Line Side Protection May 6, 2013 Slide 1 Availability of electric power supply
James Taylor, Technology Support Manager / Principal Specialist May 2013 ABB Surge Arresters Contribution to Power Quality Line Side Protection May 6, 2013 Slide 1 Availability of electric power supply
Midwest ISO Overview - ATC Customer Meeting. February 26, 2009
 Midwest ISO Overview - ATC Customer Meeting February 26, 2009 Agenda Overview January 2009 Dashboard Module E RAR Timeline Questions 2 Overview January was characterized by seasonal cold temperatures,
Midwest ISO Overview - ATC Customer Meeting February 26, 2009 Agenda Overview January 2009 Dashboard Module E RAR Timeline Questions 2 Overview January was characterized by seasonal cold temperatures,
State of Reliability Report 2013
 State of Reliability Report 2013 Jessica Bian, Director of Performance Analysis Reliability Assessment and Performance Analysis (RAPA), NERC Risk Issues Steering Committee Meeting, July 11-12, 2013 State
State of Reliability Report 2013 Jessica Bian, Director of Performance Analysis Reliability Assessment and Performance Analysis (RAPA), NERC Risk Issues Steering Committee Meeting, July 11-12, 2013 State
WEB-BASED CUSTOMER INTERRUPTION MONITORING USING DMS SYSTEM DATABASE
 WEB-BASED CUSTOMER INTERRUPTION MONITORING USING DMS SYSTEM DATABASE K. Kivikko, S. Antila, A. Mäkinen and P. Järventausta Tampere University of Technology, Institute of Power Engineering Abstract This
WEB-BASED CUSTOMER INTERRUPTION MONITORING USING DMS SYSTEM DATABASE K. Kivikko, S. Antila, A. Mäkinen and P. Järventausta Tampere University of Technology, Institute of Power Engineering Abstract This
Application of overvoltage protection to the Peruvian Power System
 Application of overvoltage protection to the Peruvian Power System Presented to Western Protective Relay Conference 2008 Spokane, Washington, USA Prepared by Yofre Jacome, and Francisco Torres, COES SINAC
Application of overvoltage protection to the Peruvian Power System Presented to Western Protective Relay Conference 2008 Spokane, Washington, USA Prepared by Yofre Jacome, and Francisco Torres, COES SINAC
Cirprotec Technical Article No. 5
 Lightning and surge protection in waste water purification plants (WWTPs and DWTPs) Cirprotec Technical Article No. 5 2010 CIRPROTEC All rights reserved 2012 CIRPROTEC All rights reserved Cirprotec Technica
Lightning and surge protection in waste water purification plants (WWTPs and DWTPs) Cirprotec Technical Article No. 5 2010 CIRPROTEC All rights reserved 2012 CIRPROTEC All rights reserved Cirprotec Technica
Network Configuration Document Selection for New Substations Framework
 Network Configuration Document Selection for New Substations Current version: 20/06/2018 EXTERNAL USE Page 1 of 14 Table of contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Purpose... 3 1.2 Scope... 3 1.3 References...
Network Configuration Document Selection for New Substations Current version: 20/06/2018 EXTERNAL USE Page 1 of 14 Table of contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Purpose... 3 1.2 Scope... 3 1.3 References...
SCI - software.sci.utah.edu (Select Visitors)
 SCI - software.sci.utah.edu (Select Visitors) Web Log Analysis Yearly Report 2004 Report Range: 01/01/2004 00:00:00-12/31/2004 23:59:59 www.webtrends.com Table of Contents Top Visitors...3 Top Visitors
SCI - software.sci.utah.edu (Select Visitors) Web Log Analysis Yearly Report 2004 Report Range: 01/01/2004 00:00:00-12/31/2004 23:59:59 www.webtrends.com Table of Contents Top Visitors...3 Top Visitors
4.1.1 Generator Owner Transmission Owner that owns synchronous condenser(s)
 A. Introduction 1. Title: Verification and Data Reporting of Generator Real and Reactive Power Capability and Synchronous Condenser Reactive Power Capability 2. Number: MOD-025-2 3. Purpose: To ensure
A. Introduction 1. Title: Verification and Data Reporting of Generator Real and Reactive Power Capability and Synchronous Condenser Reactive Power Capability 2. Number: MOD-025-2 3. Purpose: To ensure
COMPACT SUBSTATION WITH 34.5kV GIS (GAS-INSULATED SWITCHGEAR. Cleverson Shindi Takiguchi S&C Electric Europe LTd. Cape Town/WC South Africa
 COMPACT SUBSTATION WITH 34.5kV GIS (GAS-INSULATED SWITCHGEAR Cleverson Shindi Takiguchi S&C Electric Europe LTd. Cape Town/WC South Africa Alexandre Taijun Ohara S&C Electric Company Curitiba/PR Brazil
COMPACT SUBSTATION WITH 34.5kV GIS (GAS-INSULATED SWITCHGEAR Cleverson Shindi Takiguchi S&C Electric Europe LTd. Cape Town/WC South Africa Alexandre Taijun Ohara S&C Electric Company Curitiba/PR Brazil
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 10, 2015 ISSN (online):
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 10, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Comparison of Shunt Facts Devices for the Improvement of Transient Stability of Two Machine
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 10, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Comparison of Shunt Facts Devices for the Improvement of Transient Stability of Two Machine
Markets Gateway Roadmap
 Markets Gateway Roadmap As of April 17, 2018 www.pjm.com Background Markets Gateway allows users to submit information and obtain data needed to conduct business in the Day-Ahead, Regulation and Synchronized
Markets Gateway Roadmap As of April 17, 2018 www.pjm.com Background Markets Gateway allows users to submit information and obtain data needed to conduct business in the Day-Ahead, Regulation and Synchronized
STCP 04-3 Issue 005 Real Time Data Provision
 STCP 04-3 Issue 005 Real Time Data Provision STC Procedure Document Authorisation Party Name of Party Representative Signature Date National Grid Electricity Transmission plc SP Transmission plc Scottish
STCP 04-3 Issue 005 Real Time Data Provision STC Procedure Document Authorisation Party Name of Party Representative Signature Date National Grid Electricity Transmission plc SP Transmission plc Scottish
National Grid UK Electricity Transmission plc NATIONAL SAFETY INSTRUCTION
 National Grid UK Electricity Transmission plc NATIONAL SAFETY INSTRUCTION NSI 0 NATIONAL SAFETY INSTRUCTION INDEX Copyright National Grid plc 2016, all rights reserved. No part of this publication may
National Grid UK Electricity Transmission plc NATIONAL SAFETY INSTRUCTION NSI 0 NATIONAL SAFETY INSTRUCTION INDEX Copyright National Grid plc 2016, all rights reserved. No part of this publication may
Purpose of High Voltage Circuit Switchers
 Purpose of High Voltage Circuit Switchers Vertical interrupter circuit switcher without integral disconnect switch (Figure 2) Three-phase Interruption and Protection Circuit switchers have been developed
Purpose of High Voltage Circuit Switchers Vertical interrupter circuit switcher without integral disconnect switch (Figure 2) Three-phase Interruption and Protection Circuit switchers have been developed
Final Report. Mini Project TET Group nr 7 - Project nr 4. Students: Hans Lavoll Halvorson, NTNU
 Final Report Mini Project TET4190 28.10.2010 Optimal Distance for connection of offshore wind farm with AC cable with SVC or STATCOM To increase the distance compensation technologies such as SVC and STATCOM
Final Report Mini Project TET4190 28.10.2010 Optimal Distance for connection of offshore wind farm with AC cable with SVC or STATCOM To increase the distance compensation technologies such as SVC and STATCOM
REPORT ON TELECOMMUNICATIONS SERVICE QUALITY WINDSTREAM FLORIDA, INC.
 REPORT ON TELECOMMUNICATIONS SERVICE QUALITY For WINDSTREAM FLORIDA, INC. Alachua, Brooker, High Springs, Melrose, and Waldo s February 4 March 14, 2008 Division of Service, Safety & Consumer Assistance
REPORT ON TELECOMMUNICATIONS SERVICE QUALITY For WINDSTREAM FLORIDA, INC. Alachua, Brooker, High Springs, Melrose, and Waldo s February 4 March 14, 2008 Division of Service, Safety & Consumer Assistance
Title Substations - Base Safety & Operating Standards. Reference Number POP 07 - (RIC Standard: EP SP)
 Discipline Engineering Standard - NSW Category Electrical Title Reference Number POP 07 - (RIC Standard: EP 99 00 00 04 SP) Document Control Status Date Prepared Reviewed Endorsed Approved Mar 05 Standards
Discipline Engineering Standard - NSW Category Electrical Title Reference Number POP 07 - (RIC Standard: EP 99 00 00 04 SP) Document Control Status Date Prepared Reviewed Endorsed Approved Mar 05 Standards
Effects of PROC EXPAND Data Interpolation on Time Series Modeling When the Data are Volatile or Complex
 Effects of PROC EXPAND Data Interpolation on Time Series Modeling When the Data are Volatile or Complex Keiko I. Powers, Ph.D., J. D. Power and Associates, Westlake Village, CA ABSTRACT Discrete time series
Effects of PROC EXPAND Data Interpolation on Time Series Modeling When the Data are Volatile or Complex Keiko I. Powers, Ph.D., J. D. Power and Associates, Westlake Village, CA ABSTRACT Discrete time series
How It All Stacks Up - or - Bar Charts with Plotly. ISC1057 Janet Peterson and John Burkardt Computational Thinking Fall Semester 2016
 * How It All Stacks Up - or - Bar Charts with Plotly ISC1057 Janet Peterson and John Burkardt Computational Thinking Fall Semester 2016 In a game of poker, players bet by tossing chips into the center
* How It All Stacks Up - or - Bar Charts with Plotly ISC1057 Janet Peterson and John Burkardt Computational Thinking Fall Semester 2016 In a game of poker, players bet by tossing chips into the center
ereliability Tracker Software Leader User Guide
 ereliability Tracker Software Leader User Guide Revision Date: 10/15/2014 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Log-in/Create an Account... 2 Types of Users and Permissions... 2 Functions... 3 Home... 3
ereliability Tracker Software Leader User Guide Revision Date: 10/15/2014 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Log-in/Create an Account... 2 Types of Users and Permissions... 2 Functions... 3 Home... 3
DTRV-EP. COMPLEX DIGITAL PROTECTION FOR 120 kv / MEDIUM VOLTAGE TRANSFORMERS. Application field
 DTRV-EP COMPLEX DIGITAL PROTECTION FOR 120 kv / MEDIUM VOLTAGE TRANSFORMERS Application field The DTRV type of complex transformer protection is designed to protect 120 kv / medium voltage transformers,
DTRV-EP COMPLEX DIGITAL PROTECTION FOR 120 kv / MEDIUM VOLTAGE TRANSFORMERS Application field The DTRV type of complex transformer protection is designed to protect 120 kv / medium voltage transformers,
San Joaquin County Emergency Medical Services Agency
 San Joaquin County Emergency Medical Services Agency http://www.sjgov.org/ems Memorandum TO: All Interested Parties FROM: Rick Jones, EMS Analyst DATE: January, 19 Mailing Address PO Box French Camp, CA
San Joaquin County Emergency Medical Services Agency http://www.sjgov.org/ems Memorandum TO: All Interested Parties FROM: Rick Jones, EMS Analyst DATE: January, 19 Mailing Address PO Box French Camp, CA
Testing of Real Time Power System Control Software
 Testing of Real Time Power System Control Software Transpower s Pole 3 Project Presentation to Special Interest Group of ANZTB 7 October 2013 Richard Sherry 1 Summary 1. What does the HVDC Control System
Testing of Real Time Power System Control Software Transpower s Pole 3 Project Presentation to Special Interest Group of ANZTB 7 October 2013 Richard Sherry 1 Summary 1. What does the HVDC Control System
MV Network Switchgear, Protection and Control
 MV Network Switchgear, Protection and Control Ravinder Negi Manager, Services Execution INDIA Schneider Electric, New Delhi. Agenda An Overview MV Network Basic Definitions Circuit breaker Switchgear Control
MV Network Switchgear, Protection and Control Ravinder Negi Manager, Services Execution INDIA Schneider Electric, New Delhi. Agenda An Overview MV Network Basic Definitions Circuit breaker Switchgear Control
RELIABILITY AS A SERVICE FOR BUSINESS. by MidEnterprises, LLC
 RELIABILITY AS A SERVICE FOR BUSINESS by MidEnterprises, LLC THE OPPORTUNITY Less than 30% of commercial facilities have a reliable back-up power supply Only10-15% of those having existing installations
RELIABILITY AS A SERVICE FOR BUSINESS by MidEnterprises, LLC THE OPPORTUNITY Less than 30% of commercial facilities have a reliable back-up power supply Only10-15% of those having existing installations
Demand Estimation Sub Committee Ad-hoc Work Plan
 Demand Estimation Sub Committee Ad-hoc Work Plan Background The DESC Ad-hoc Work Plan was established in 2012 to capture any issues and ideas which arise during the year that DESC decide they may like
Demand Estimation Sub Committee Ad-hoc Work Plan Background The DESC Ad-hoc Work Plan was established in 2012 to capture any issues and ideas which arise during the year that DESC decide they may like
CIMA Asia. Interactive Timetable Live Online
 CIMA Asia Interactive Timetable 2017 2018 Live Online Version 1 Information last updated 09 October 2017 Please note: Information and dates in this timetable are subject to change. CIMA Cert BA Course
CIMA Asia Interactive Timetable 2017 2018 Live Online Version 1 Information last updated 09 October 2017 Please note: Information and dates in this timetable are subject to change. CIMA Cert BA Course
1.2 Characteristics of Function Graphs
 1.2 Characteristics of Function Graphs Essential Question: What are some of the attributes of a function, and how are they related to the function s graph? Resource Locker Explore Identifying Attributes
1.2 Characteristics of Function Graphs Essential Question: What are some of the attributes of a function, and how are they related to the function s graph? Resource Locker Explore Identifying Attributes
IMS INTERFACE MARKET PROCEDURE NETWORK OPERATORS AND AEMO
 IMS INTERFACE MARKET PROCEDURE NETWORK OPERATORS AND AEMO PREPARED BY: System Management (WA) DOCUMENT REF: SO_OP_WA_3805 VERSION: 1.0 EFFECTIVE DATE: 13/10/2017 STATUS: FINAL Approved for distribution
IMS INTERFACE MARKET PROCEDURE NETWORK OPERATORS AND AEMO PREPARED BY: System Management (WA) DOCUMENT REF: SO_OP_WA_3805 VERSION: 1.0 EFFECTIVE DATE: 13/10/2017 STATUS: FINAL Approved for distribution
UK EPR GDA PROJECT. Name/Initials Date 30/06/2011 Name/Initials Date 30/06/2011. Resolution Plan Revision History
 RP unique number: Page GI-UKEPR-RP-01-RP 0 30/06/2011 1 of 5 Approved for EDF by: A. PETIT Approved for AREVA by: C. WOOLDRIDGE Name/Initials Date 30/06/2011 Name/Initials Date 30/06/2011 Resolution Plan
RP unique number: Page GI-UKEPR-RP-01-RP 0 30/06/2011 1 of 5 Approved for EDF by: A. PETIT Approved for AREVA by: C. WOOLDRIDGE Name/Initials Date 30/06/2011 Name/Initials Date 30/06/2011 Resolution Plan
Table 1: Operators Authorized to Provide Public Fixed Domestic Telecommunications Services as at 2010
 2. Fixed Telephony Market Data As at December 2010, there were eight (8) operators authorized to provide fixed domestic telecommunications services to the public over wired or wireless facilities. These
2. Fixed Telephony Market Data As at December 2010, there were eight (8) operators authorized to provide fixed domestic telecommunications services to the public over wired or wireless facilities. These
Overvoltage Protection
 Overvoltage Protection OVR Range FRSOX 0100 03 GB ABB Lightning Protection Group 1 Main causes of transient overvoltages The solution: ABB OVR Surge Protective Device Range Lightning strike A lightning
Overvoltage Protection OVR Range FRSOX 0100 03 GB ABB Lightning Protection Group 1 Main causes of transient overvoltages The solution: ABB OVR Surge Protective Device Range Lightning strike A lightning
ABB static var compensator stabilizes Namibian grid voltage
 Power ABB static var compensator stabilizes Namibian grid voltage factor! Rolf Grünbaum, Mikael Halonen, Staffan Rudin The spectacular dune landscapes of Namibia are a key factor in the country s booming
Power ABB static var compensator stabilizes Namibian grid voltage factor! Rolf Grünbaum, Mikael Halonen, Staffan Rudin The spectacular dune landscapes of Namibia are a key factor in the country s booming
AN579 Application note
 Application note Protection concepts in telecommunications equipment Introduction The goal of a telecommunication network (see Figure 1) is to permit data exchange (speech or digital) between two or more
Application note Protection concepts in telecommunications equipment Introduction The goal of a telecommunication network (see Figure 1) is to permit data exchange (speech or digital) between two or more
Asset Criticality Framework
 Asset Risk Management Asset Criticality Framework October 2018 1 Contents 1. Introduction...2 2. Overview of criticality...3 2.1 Criticality bands...4 3. The Asset Criticality Framework...5 3.1 Criticality
Asset Risk Management Asset Criticality Framework October 2018 1 Contents 1. Introduction...2 2. Overview of criticality...3 2.1 Criticality bands...4 3. The Asset Criticality Framework...5 3.1 Criticality
ASSET RISK MANAGEMENT Criticality Framework
 ASSET RISK MANAGEMENT Criticality Framework 15 C O P Y R I G H T 2013 T R A N S P O W E R N E W Z E A L A N D L I M I T E D. A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D Preface This document has been prepared to
ASSET RISK MANAGEMENT Criticality Framework 15 C O P Y R I G H T 2013 T R A N S P O W E R N E W Z E A L A N D L I M I T E D. A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D Preface This document has been prepared to
This is a preview - click here to buy the full publication TECHNICAL REPORT
 TECHNICAL REPORT IEC TR 62066 First edition 2002-06 Surge overvoltages and surge protection in low-voltage a.c. power systems General basic information Surtensions de choc et protection contre la foudre
TECHNICAL REPORT IEC TR 62066 First edition 2002-06 Surge overvoltages and surge protection in low-voltage a.c. power systems General basic information Surtensions de choc et protection contre la foudre
SP Energy Networks Business Plan
 SP Energy Networks 2015 2023 Business Plan Updated March 2014 Annex 132kV Substation Plant Strategy SP Energy Networks 29 March 2014 March 2014 Issue Date Issue No. Document Owner Amendment Details 17th
SP Energy Networks 2015 2023 Business Plan Updated March 2014 Annex 132kV Substation Plant Strategy SP Energy Networks 29 March 2014 March 2014 Issue Date Issue No. Document Owner Amendment Details 17th
Power System Operating Incident Report Trip of Calvale No.2 275kV busbar and Calvale-Halys 8810 and 8811 transmission lines on 30 March 2014
 Power System Operating Incident Report Trip of Calvale No.2 275kV busbar and Calvale-Halys 8810 and 8811 transmission lines on 30 March 2014 PREPARED BY: Systems Capability DATE: 6 June 2014 STATUS: FINAL
Power System Operating Incident Report Trip of Calvale No.2 275kV busbar and Calvale-Halys 8810 and 8811 transmission lines on 30 March 2014 PREPARED BY: Systems Capability DATE: 6 June 2014 STATUS: FINAL
Central Power Research Institute, Medipally PO, Uppal, Hyderabad, Telangana. Discipline Electrical Testing Issue Date
 Last Amended on 31.07.2015 Page 1 of 11 I. SWITCHGEAR EQUIPMENT 1. High Voltage switchgear & control gear and AB switches Ratings upto 1200 kv system Switching Impulse Voltage (Dry & Wet) Power Frequency
Last Amended on 31.07.2015 Page 1 of 11 I. SWITCHGEAR EQUIPMENT 1. High Voltage switchgear & control gear and AB switches Ratings upto 1200 kv system Switching Impulse Voltage (Dry & Wet) Power Frequency
IMS INTERFACE MARKET PROCEDURE NETWORK OPERATORS AND AEMO
 IMS INTERFACE MARKET PROCEDURE NETWORK OPERATORS AND AEMO PREPARED BY: System Management (WA) DOCUMENT REF: SO_OP_WA_3805 VERSION: 1.0 EFFECTIVE DATE: 13/10/2017 STATUS: DRAFT FOR CONSULTATION Approved
IMS INTERFACE MARKET PROCEDURE NETWORK OPERATORS AND AEMO PREPARED BY: System Management (WA) DOCUMENT REF: SO_OP_WA_3805 VERSION: 1.0 EFFECTIVE DATE: 13/10/2017 STATUS: DRAFT FOR CONSULTATION Approved
Japan s Measures against Spam
 June 22, 2, 2006 Japan s Measures against Spam Yoshichika Imaizumi Telecommunications Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC), Japan Characteristics of spam in Japan 1.. Media 2004
June 22, 2, 2006 Japan s Measures against Spam Yoshichika Imaizumi Telecommunications Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC), Japan Characteristics of spam in Japan 1.. Media 2004
Externally Gapped Line Arresters Smart Solution for Stable Power Supply
 Smart Solution for Stable Power Supply Metal-oxide surge arresters with external series gaps improve the reliability of transmission systems, and help eliminate not only lightning damages of transmission
Smart Solution for Stable Power Supply Metal-oxide surge arresters with external series gaps improve the reliability of transmission systems, and help eliminate not only lightning damages of transmission
User Guide for the WegenerNet Data Portal
 User Guide for the WegenerNet Data Portal (v9/18feb2010) The WegenerNet Data Portal provides access to measurement data from the climate stations as well as detailed information about the project. Quality-checked
User Guide for the WegenerNet Data Portal (v9/18feb2010) The WegenerNet Data Portal provides access to measurement data from the climate stations as well as detailed information about the project. Quality-checked
INTERTANKO Vetting seminar 24 th October 2017
 INTERTANKO Vetting seminar 24 th October 2017 SIRE Developments VIQ 7 New VIQ being developed Structure will remain the same with 13 chapters. Reduction in the number of questions, net approx. 70 decrease.
INTERTANKO Vetting seminar 24 th October 2017 SIRE Developments VIQ 7 New VIQ being developed Structure will remain the same with 13 chapters. Reduction in the number of questions, net approx. 70 decrease.
This annex is valid from: to Replaces annex dated: Location(s) where activities are performed under accreditation
 Location(s) where activities are performed under accreditation Head Office Utrechtseweg 310, Building no. R11 6812 AR Arnhem The Netherlands Location Abbreviation/ location code Utrechtseweg 310, Building
Location(s) where activities are performed under accreditation Head Office Utrechtseweg 310, Building no. R11 6812 AR Arnhem The Netherlands Location Abbreviation/ location code Utrechtseweg 310, Building
Externally Gapped Line Arresters Smart Solution for Stable Power Supply
 Smart Solution for Stable Power Supply Metal-oxide surge arresters with external series gaps improve the reliability of transmission systems, and help eliminate not only lightning damages of transmission
Smart Solution for Stable Power Supply Metal-oxide surge arresters with external series gaps improve the reliability of transmission systems, and help eliminate not only lightning damages of transmission
Distribution Management System Open++ Opera v.3.3. User Manual
 Distribution Management System Open++ Opera v.3.3 User Manual 1MRS 751464-MUM Issued: 31.12.1999 Version: D/29.8.2003 Program Revision: 3.3D We reserve the right to change data without prior notice. User
Distribution Management System Open++ Opera v.3.3 User Manual 1MRS 751464-MUM Issued: 31.12.1999 Version: D/29.8.2003 Program Revision: 3.3D We reserve the right to change data without prior notice. User
All King County Summary Report
 September, 2016 MTD MARKET UPDATE Data Current Through: September, 2016 18,000 16,000 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 0 Active, Pending, & Months Supply of Inventory 15,438 14,537 6.6 6.7
September, 2016 MTD MARKET UPDATE Data Current Through: September, 2016 18,000 16,000 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 0 Active, Pending, & Months Supply of Inventory 15,438 14,537 6.6 6.7
Quantum Chargers Enhanced AC Line Transient Immunity
 Introduction Quantum Chargers Enhanced AC Line Transient Immunity By: Nasser Kutkut, PhD, DBA Advanced Charging Technologies Inc. This white paper outlines the most common AC power quality disturbances
Introduction Quantum Chargers Enhanced AC Line Transient Immunity By: Nasser Kutkut, PhD, DBA Advanced Charging Technologies Inc. This white paper outlines the most common AC power quality disturbances
Schedule 2e. Schedule 2E Additional Terms for Carrier Ethernet Services Eng Lang v page 1 of 11
 1. SERVICE DESCRIPTION The Interoute E-CERTUS and E-AGILIS Services offer Carrier Ethernet Services between Interoute Demarcation Points on the Interoute Network and/ or on the Customer s Premises. The
1. SERVICE DESCRIPTION The Interoute E-CERTUS and E-AGILIS Services offer Carrier Ethernet Services between Interoute Demarcation Points on the Interoute Network and/ or on the Customer s Premises. The
ISE Cyber Security UCITS Index (HUR)
 ISE Cyber Security UCITS Index (HUR) Why Cybersecurity is important Data breaches have become almost commonplace in the last few years Cybersecurity focuses on protecting computers, networks, programs,
ISE Cyber Security UCITS Index (HUR) Why Cybersecurity is important Data breaches have become almost commonplace in the last few years Cybersecurity focuses on protecting computers, networks, programs,
AUTOMATION OF POWER DISTRIBUTION USING SCADA
 1 2 ABSTRACT In every substation certain measurements, supervision, control, operation and protection functions are necessary. Traditionally these functions were performed manually by system operator from
1 2 ABSTRACT In every substation certain measurements, supervision, control, operation and protection functions are necessary. Traditionally these functions were performed manually by system operator from
1. Project Description
 Page No: 1 of 16 1. Project Description 1.1 Introduction This document outlines protection, monitoring and control requirements for the shared network assets associated with establishment of Tarrone Terminal
Page No: 1 of 16 1. Project Description 1.1 Introduction This document outlines protection, monitoring and control requirements for the shared network assets associated with establishment of Tarrone Terminal
Annex B. International price comparisons and development of the prices in the retail market for mobile phone services in Iceland
 Annex B International price comparisons and development of the prices in the retail market for mobile phone services in Iceland 5 February 2007 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 METHODOLOGY...3 2 INTERNATIONAL PRICE
Annex B International price comparisons and development of the prices in the retail market for mobile phone services in Iceland 5 February 2007 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 METHODOLOGY...3 2 INTERNATIONAL PRICE
July 30, Q2 Quarterly Report on Progress in Processing Interconnection Requests; Docket No. ER
 California Independent System Operator Corporation The Honorable Kimberly D. Bose Secretary Federal Energy Regulatory Commission 888 First Street, N.E. Washington, D.C. 20426 July 30, 2010 Re: Q2 Quarterly
California Independent System Operator Corporation The Honorable Kimberly D. Bose Secretary Federal Energy Regulatory Commission 888 First Street, N.E. Washington, D.C. 20426 July 30, 2010 Re: Q2 Quarterly
Statistical Methods in Trending. Ron Spivey RETIRED Associate Director Global Complaints Tending Alcon Laboratories
 Statistical Methods in Trending Ron Spivey RETIRED Associate Director Global Complaints Tending Alcon Laboratories What s In It For You? Basic Statistics in Complaint Trending Basic Complaint Trending
Statistical Methods in Trending Ron Spivey RETIRED Associate Director Global Complaints Tending Alcon Laboratories What s In It For You? Basic Statistics in Complaint Trending Basic Complaint Trending
ELG4125: System Protection
 ELG4125: System Protection System Protection Any power system is prone to 'faults', (also called short-circuits), which occur mostly as a result of insulation failure and sometimes due to external causes.
ELG4125: System Protection System Protection Any power system is prone to 'faults', (also called short-circuits), which occur mostly as a result of insulation failure and sometimes due to external causes.
CFD, IEC STANDARDS AND TESTING LABORATORIES: JOINING THE PIECES FOR HIGHER QUALITY HV EQUIPMENT. Cognitor Consultancy, Research and Training Ltd.
 CFD, IEC STANDARDS AND TESTING LABORATORIES: JOINING THE PIECES FOR HIGHER QUALITY HV EQUIPMENT. Author name: Sergio Feitoza Costa Affiliation: Cognitor Consultancy, Research and Training Ltd. Summary:
CFD, IEC STANDARDS AND TESTING LABORATORIES: JOINING THE PIECES FOR HIGHER QUALITY HV EQUIPMENT. Author name: Sergio Feitoza Costa Affiliation: Cognitor Consultancy, Research and Training Ltd. Summary:
Tracking the Internet s BGP Table
 Tracking the Internet s BGP Table Geoff Huston Telstra December 2000 Methodology! The BGP table monitor uses a router at the boundary of AS1221 which has a default-free ebgp routing table 1. Capture the
Tracking the Internet s BGP Table Geoff Huston Telstra December 2000 Methodology! The BGP table monitor uses a router at the boundary of AS1221 which has a default-free ebgp routing table 1. Capture the
NFX MARKET DATA FEED INTERFACE SPECIFICATIONS. NFX Market Data Feed
 NFX Market Data Feed Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 PURPOSE... 3 1.2 ARCHITECTURE... 3 2 SESSION CHARACTERISTICS... 4 2.1 REAL-TIME PRODUCTION DATA... 4 2.2 PRE-LAUNCH TEST DATA... 4 2.3 TRANSMISSION
NFX Market Data Feed Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 PURPOSE... 3 1.2 ARCHITECTURE... 3 2 SESSION CHARACTERISTICS... 4 2.1 REAL-TIME PRODUCTION DATA... 4 2.2 PRE-LAUNCH TEST DATA... 4 2.3 TRANSMISSION
