Application Description
|
|
|
- Lee York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USER S GUIDE FOR SDB GUI (SDB-J) Modifications by Janice Sylvestre Based on NWS Document THE NWS SIMPLIFIED DAM-BREAK FLOOD FORECASTING MODEL 1 By Danny L. Fread, Janice M. Lewis, and Stephen M. Wiele This document contains portions of the NWS SMPDBK document 1 which includes a description of the input and output variables. It contains corrections to the original documentation in addition to a description of the enhancements to the model (renamed SDB to distinguish it from the NWS model). Application Description The National Weather Service (NWS) developed a simplified procedure for predicting downstream flooding information produced by a dam failure. This procedure, known as the Simplified Dam Break (SMPDBK) Flood Forecasting Model, produces information needed for delineating areas endangered by dam-break floodwaters while substantially reducing the amount of time, data, and technical expertise required in employing more highly sophisticated unsteady flow routing models such as the NWS FLDWAV model. With a minimal amount of data, The NWS SMPDBK model can be used to predict the dam-break flood-wave peak flows, peak flood elevations, and peak travel times at selected downstream points. This capacity for providing results quickly and efficiently makes the NWS SMPDBK model a useful forecasting tool in a dam failure emergency when warning response time is short and data are sparse. The NWS SMPDBK model is also useful for pre-event dam failure analysis by emergency management personnel engaged in preparing disaster contingency plans when the use of other flood routing models is precluded by limited resources. The NWS SMPDBK model retains the critical deterministic components of the numerical NWS DAMBRK model by approximating the downstream channel as a prism, including the effects of the off-channel (dead) storage where appropriate; concerning itself with only the peak flows, maximum water surface elevations and travel times; neglecting the effects of backwater from downstream bridges and dams; and utilizing dimensionless peak-flow routing graphs developed using the NWS DAMBRK model (which has been replaced by the NWS FLDWAV model). The applicability of the NWS SMPDBK model is further enhanced by its minimal data requirements. Three steps make up the procedure used in the NWS SMPDBK model, These are: (1) calculation of the peak outflow at the dam using the temporal and geometrical description of the breach and the reservoir volume; (2) approximation of the channel downstream of the dam as a prismatic channel; and (3) calculation of dimensionless peak-flow routing parameters used with families of dimensionless routing curves to determine the peak flow at specified cross sections downstream of the dam. A detailed description of these steps is in the original NWS SMPDBK paper 1. The RiverMechanics.net Group (RM) has enhanced the NWS SMPDBK GUI by adding the ability to export an NWS FLDWAV input data file. This feature allows the FLDWAV model to be used as easily as NWS SMPDBK while removing NWS SMPDBK s limitations including backwater effects caused by natural or man-made channel constrictions, the presence of which can substantially reduce NWS SMPDBK s accuracy. SDB GUI Users Guide 05 February 2019 Page 1 of 7
2 Development History NWS SMPDBK vs. SDB-J The original NWS SMPDBK model was developed in 1983 and the last major NWS revision was in In 2003, NWS replaced the awkward Fortran-based interactive component of NWS SMPDBK with a JAVA Tool (NWS SMPDBK GUI) which improved data input and the graphical output display. The hydraulic component in the FORTRAN application was unchanged. The NWS SMPDBK GUI was never officially released. The last beta release was in In 2009, the RiverMechanics.net group enhanced NWS SMPDBK GUI and renamed the application since it is no not affiliated with NWS. The FORTRAN component (hydraulic algorithms) is SDB, and the JAVA GUI component is SDB-J (Version 1.00). Since the source code in SDB is identical the code in NWS SMPDBK, the hydraulic results in the two models produced the same results. The changes in the SDB-J output display better reflected the content of the output table. In 2018, SDB-J Version underwent extensive testing using over 100 datasets. The changes made to this version (2.0.0) may result in slight changes in the output when compared to the previous version. This is due to corrections made as stated in the SDB-J Release Notes. SDB-J Version (2019) is more robust than any version of the SMPDBK model since its development. Features in SDB-J The following enhancements have been made to SDB-J: Input GUI The SMPDBK GUI allows the user to enter the data in a simpler, easier way. A debug option (JNK) has been added to SDB-J to allow the user to see hydraulic information printed at each iteration. Error Checking Error checking is done to the input parameters in SDB-J to reduce computational problems. Metric Option The input and output may now be displayed in metric units. The input parameters (in metric units) are converted to English units for computations. Although the computations are done in English units, all output information, including debug information, is displayed in metric units. Graphical Output Display A graphical representation of the water surface profile is displayed in SDB-J along with an average symmetrical cross sectional view which includes the peak water surface and flood depth of each cross section. Export FLDWAVE File SDB-J will export a FLDWAVE text file with a.fwd extension which can be run by the FLDWAVE model. System Information Operating Systems Windows 2000, XP, Vista, Windows Windows processor can be 32-bit or 64-bit. Linux Fedora 27 with 64 bit processor. Language Java 1.8+ Default Directory C:\RiverMechanics\SDB-J for Windows or ~/RiverMechanics/SDB-J for Linux SDB GUI Users Guide 05 February 2019 Page 2 of 7
3 Windows Installation Instructions The installation package for SDB-J Version (sdbjinstall exe) can be downloaded from the RiverMechanics.net website. When executed, the Install Shield will copy the files in Tables 1 & 2 into the RiverMechanics\SDB-J folder. The user has the option to change the path. If the path is changed, the sdb-j.bat file must be manually modified to reflect the new path location. A shortcut (SDB GUI 2019) is placed on the desktop. The user must have JAVA installed on their computer in order to run the SDB GUI. Linux Installation Instructions To install SDB-J Version 2-0-0, do the following: 1. Download the sdbjlinuxinstallation zip file from the RiverMechanics.net website. 2. Unzip the sdbjlinuxinstallation zip file which contains the.sh installation shell script file. 3. Open a terminal session, and change to the directory containing the.sh file. 4. Type. sdbjlinuxinstall sh (Note: there is a space after the dot). 5. SDB-J will be installed in the root folder ~/RiverMechanics/. All the files in Tables 1 and 2 will be copied to the SDB-J folder. If the root folder is changed, it must be created prior to running the shell script. 6. A SDB-J icon will be placed on the desktop. 7. To run the program, double-click on the icon. A Untrusted Application Launcher message will pop up. Select the Trust and Launch option, and the SDB GUI image will appear on the desktop. The SDB GUI will also open. Table 1. Files within the Installation Package (Common to Both Windows & Linux) sdbgui.jar Java archive file for SDB-J application sdbgui.ico SDB-J icon SDB GUI User s Guide.pdf this file SDB GUI Release Notes pdf release notes for SDB and SDB-J SDB Input Summary.pdf updated Input/Output summary which was extracted from the NWS SMPDBK paper (smpdbk.pdf) smpdbk.pdf the last NWS SMPDBK documentation teton.dat sample input data set lib folder containing jars for graphics (collections.jar & jcchart450j.jar) Table 2. Additional Files within the Windows Installation Package sdbjinstall exe Installation program sdb-x32.exe Fortran executable for SDB application (32-bit) sdb-x64.exe Fortran executable for SDB application (64-bit) sdbgui.bat batch file to execute SDB-J Table 3. Additional Files within the Linux Installation Package sdbjlinuxinstall zip Compressed file containing common files (.zip) and installation program (.sh) SDB GUI Linux Installation Instructions.pdf instructions for Linux installation document sdbjlinuxinstall sh Shell script to install SDB-J sdb-j-linux-installation.zip Contains files common to Windows & Linux and the SDB executable sdb-lx Fortran executable for SDB application SDB GUI Users Guide 05 February 2019 Page 3 of 7
4 Input GUI A description of the SDB input parameters is in the SDB Input Summary document. The user may populate the Input component of SDB-J (Figure 1) by entering the input data manually into the GUI (File New) or by loading an existing SDB text file (File Open) created using the SDB Input Summary document or created and saved previously using SDB-J. All parameters with an asterisk (*) in addition to at least two cross sections must be entered before the file can be saved. Error checking exists to ensure that real numbers are entered when appropriate. The TAB key may be used to navigate between parameters. When entering new cross sections, the user must hit the Add Section button first. Each cross section must have at least two levels. All cross sections must have the same number of levels. Cross sections can be read-in in any order; they will be sorted automatically. The arrow, TAB, and ENTER keys may be used to navigate between the cross section values. The TAB key is used to navigate between the parameters. When viewing of editing an existing cross section, select the cross section in the Cross Section List section. Although the input can be saved to a file with or without an extension, it is recommended that a.dat extension be used. Error checking is done prior to saving the file to ensure that SDB can be run without input errors. Figure 1. SDB-J Input GUI Running SDB If an input file exists, the user can run SDB manually or by using the SDB-J Run Option. To run SDB manually, double-click on the executable file (sdb-x64.exe or sdb-x32.exe for Windows-based computers or sdb-lx for linux-based computers) located in the RiverMechanics/SDB-J folder. The user will be prompted for the input SDB GUI Users Guide 05 February 2019 Page 4 of 7
5 and output file names. Although the output file name does not require a specific extension, it is recommended that a.out extension be used. The output file can be viewed with a text editor or using SDB-J. If no input file has been loaded into the input GUI, the Run Option of SDB-J (Run Run SDB Model) will prompt the user for input and output file names (Figure 2). If an input file is loaded into the Input GUI, the loaded file will be used for input, and the users will be prompted for the output filename. Error checking is done prior to running SDB. Errors and warnings will guide the user to correct the data so that a successful run is made. If SDB runs successfully, the output display manager will be shown. Figure 2. SDB-J Input GUI Run Menu The user may view an output file that was run previously by clicking Run View SDB Ouptut. Note: If SDB-J was not installed in the default directory, the SDB path may need to be set (Run Set Path to SDB) prior to running the SDB model. Output GUI The SDB Output Display Manager will show the contents of the hydraulic summary table in the output text file visually as follows: Figure 3. SDB Model Graphic SDB Model Graphic Tab This tab (Figure 3) shows a graphical representation of the dam and the downstream routing reach are shown: Pool level before failure Channel invert and peak water surface profiles. A symmetrical cross section at each river location showing the maximum depth and the flood stage. To see additional cross sections, select the appropriate river location in the Cross Section pull-down window. Output Data Table Tab This tab (Figure 4) shows the summary table from the output text file which contains the maximum discharge and water surface profiles in addition to the times of flooding and de-flooding. Peak Water Surface Profile Chart Tab This tab (Figure 5) shows a graphical representation of the maximum water surface and the channel invert profiles. Peak Discharge Profile Chart Tab - This tab (Figure 6) shows a graphical representation of the peak discharge profile. SDB-J Users Guide 04 February 2019 Page 5 of 7
6 SDB Output Text Tab This tab (Figure 7) shows the contents of the output text file generated by SDB. Figure 4. Output Data Table Figure 5. Peak Water Surface Table Figure 6. Peak Discharge Table Figure 7. SDB Output Text Exporting FLDWAVE File SDB-J will export a FLDWAVE text file (File Export FLDWAVE File) with a.fwd extension which can be run by the FLDWAVE model (Figure 1). The following assumptions have been made regarding FLDWAVE parameters. After a successful run of the FLDWAVE model with the file exported from SDB-J, these parameters should be modified. TEH (DG 7) The run period is 1.5 times the time to peak of the downstream water level. This parameter may need to be increased to allow the falling limb of the downstream hydrograph to be reached. DXM (DG 19) The distance interval is computed using the equation DXM = c t where c is the distance interval divided by the difference between the times to the peak water level at adjacent cross SDB-J Users Guide 04 February 2019 Page 6 of 7
7 sections, and t is the time of failure in hours (TFH)/20. The DXM values are usually much smaller than they need to be. The values should be adjusted according to the recommendations in the FLDWAVE output. SAR (DG 26) vs HSAR (DG 27) The Surface Area Elevation table consist of two points. This table may not adequately represent the volume of the reservoir. Preferably, the actual table should be used. If the table does not exist, it can be created by generating a table of values that result in the outflow volume matching the reservoir volume. The outflow volume is computed in FLDWAVE and shown in the output file when JNK 4. The base flow volume should be subtracted from the outflow volume before comparing it to the reservoir volume. HDD (DG 28) The height of the dam is set equal to the pool level. If piping failure is the failure mode or if the pool level is above the dam crest, HDD should be set back to the actual top of dam elevation. CLL (DG 28) The crest length is set equal to 3 times the height of the dam. It should be reset to the actual crest length. If piping failure is modeled as overtopping failure, the crest length should be set to the length of the dam at the pool level. QTD (DG 28) The turbine flow is equal to the initial inflow hydrograph value. ST1 (DG 58) The inflow hydrograph is a steady-state value equal to 1% of the peak flow. This value may be decreased if a minimum base flow is desired. Also, if the routing reach is complex and the time of failure is short, the base flow may need to be increased for stability reasons. T1 (DG 59) The time period for the inflow hydrograph goes from 0 to TEH. Running FLDWAVE provides instantaneous results (hydrographs, profiles, and rating curves) along the routing reach that are not available in SDB-J. REFERENCE 1 Fread, Danny L., Lewis, Janice M., and Wiele, Stephen M. 1991, The NWS Simplified Dam-Break Flood Forecasting Model, Hydrology Laboratory, National Weather Service, Silver Spring, MD. SDB-J Users Guide 04 February 2019 Page 7 of 7
THE NWS SIMPLIFIED DAM-BREAK FLOOD FORECASTING MODEL
 THE NWS SIMPLIFIED DAM-BREAK FLOOD FORECASTING MODEL by Jonathan N. Wetmore and Danny L. Fread 1 (Revised 12/18/91) by Danny L. Fread, Janice M. Lewis 2, and Stephen M. Wiele 2 SYNOPSIS The National Weather
THE NWS SIMPLIFIED DAM-BREAK FLOOD FORECASTING MODEL by Jonathan N. Wetmore and Danny L. Fread 1 (Revised 12/18/91) by Danny L. Fread, Janice M. Lewis 2, and Stephen M. Wiele 2 SYNOPSIS The National Weather
Prof. B.S. Thandaveswara. The computation of a flood wave resulting from a dam break basically involves two
 41.4 Routing The computation of a flood wave resulting from a dam break basically involves two problems, which may be considered jointly or seperately: 1. Determination of the outflow hydrograph from the
41.4 Routing The computation of a flood wave resulting from a dam break basically involves two problems, which may be considered jointly or seperately: 1. Determination of the outflow hydrograph from the
Cross Sections, Profiles, and Rating Curves. Viewing Results From The River System Schematic. Viewing Data Contained in an HEC-DSS File
 C H A P T E R 9 Viewing Results After the model has finished the steady or unsteady flow computations the user can begin to view the output. Output is available in a graphical and tabular format. The current
C H A P T E R 9 Viewing Results After the model has finished the steady or unsteady flow computations the user can begin to view the output. Output is available in a graphical and tabular format. The current
WMS 8.4 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
Introducion to Hydrologic Engineering Centers River Analysis System (HEC- RAS) Neena Isaac Scientist D CWPRS, Pune -24
 Introducion to Hydrologic Engineering Centers River Analysis System (HEC- RAS) Neena Isaac Scientist D CWPRS, Pune -24 One dimensional river models (1-D models) Assumptions Flow is one dimensional Streamline
Introducion to Hydrologic Engineering Centers River Analysis System (HEC- RAS) Neena Isaac Scientist D CWPRS, Pune -24 One dimensional river models (1-D models) Assumptions Flow is one dimensional Streamline
Watershed Modeling HEC-HMS Interface
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to set up a basic HEC-HMS model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-HMS model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to set up a basic HEC-HMS model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-HMS model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic
WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS
 Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS CE 412/512 Spring 2017 Introduction The intent of this exercise is to introduce you to the structure and some of the functions of the HEC-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS),
Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS CE 412/512 Spring 2017 Introduction The intent of this exercise is to introduce you to the structure and some of the functions of the HEC-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS),
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS Objectives Define a conceptual schematic of the roadway, invert, and downstream
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS Objectives Define a conceptual schematic of the roadway, invert, and downstream
Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to perform unsteady sediment transport simulations in SRH-2D.
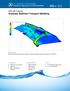 SMS v. 12.2 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to perform unsteady sediment transport simulations in SRH-2D. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial SRH-2D SRH-2D Sediment Transport
SMS v. 12.2 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to perform unsteady sediment transport simulations in SRH-2D. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial SRH-2D SRH-2D Sediment Transport
RESCDAM DEVELOPMENT OF RESCUE ACTIONS BASED ON DAM BREAK FLOOD ANALYSI A PREVENTION PROJECT UNDER THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITY ACTION PROGRAMME
 RESCDAM DEVELOPMENT OF RESCUE ACTIONS BASED ON DAM BREAK FLOOD ANALYSI A PREVENTION PROJECT UNDER THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITY ACTION PROGRAMME 1-DIMENSIONAL FLOW SIMULATIONS FOR THE KYRKÖSJÄRVI DAM BREAK HAZARD
RESCDAM DEVELOPMENT OF RESCUE ACTIONS BASED ON DAM BREAK FLOOD ANALYSI A PREVENTION PROJECT UNDER THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITY ACTION PROGRAMME 1-DIMENSIONAL FLOW SIMULATIONS FOR THE KYRKÖSJÄRVI DAM BREAK HAZARD
HECRAS 2D: Are you ready for the revolution in the world of hydraulic modeling?
 HECRAS 2D: Are you ready for the revolution in the world of hydraulic modeling? Rishab Mahajan, Emily Campbell and Matt Bardol March 8, 2017 Outline Reasons for hydraulic modeling 1D Modeling 2D Modeling-
HECRAS 2D: Are you ready for the revolution in the world of hydraulic modeling? Rishab Mahajan, Emily Campbell and Matt Bardol March 8, 2017 Outline Reasons for hydraulic modeling 1D Modeling 2D Modeling-
SRH-2D Additional Boundary Conditions
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial SRH-2D Additional Boundary Conditions Objectives Learn techniques for using various additional boundary conditions with the Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial SRH-2D Additional Boundary Conditions Objectives Learn techniques for using various additional boundary conditions with the Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional
IBM iaccess (Java) Setup Guide for Foxtrot RPA
 IBM iaccess (Java) Setup Guide for Foxtrot RPA Revised 03/31/17 Setup Steps - IBM iaccess is a Java application which requires these specific setup steps before it can be automated using Foxtrot RPA: 1.
IBM iaccess (Java) Setup Guide for Foxtrot RPA Revised 03/31/17 Setup Steps - IBM iaccess is a Java application which requires these specific setup steps before it can be automated using Foxtrot RPA: 1.
Watershed Modeling Rational Method Interface. Learn how to model urban areas using WMS' rational method interface
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to model urban areas using WMS' rational method interface Objectives Learn how to model urban areas using the Rational method, including how to compute rainfall intensity,
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to model urban areas using WMS' rational method interface Objectives Learn how to model urban areas using the Rational method, including how to compute rainfall intensity,
Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
 v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives Learn how to define a basic MODRAT model using the hydrologic schematic tree in WMS by building a tree and defining
v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives Learn how to define a basic MODRAT model using the hydrologic schematic tree in WMS by building a tree and defining
UNDERSTAND HOW TO SET UP AND RUN A HYDRAULIC MODEL IN HEC-RAS CREATE A FLOOD INUNDATION MAP IN ARCGIS.
 CE 412/512, Spring 2017 HW9: Introduction to HEC-RAS and Floodplain Mapping Due: end of class, print and hand in. HEC-RAS is a Hydrologic Modeling System that is designed to describe the physical properties
CE 412/512, Spring 2017 HW9: Introduction to HEC-RAS and Floodplain Mapping Due: end of class, print and hand in. HEC-RAS is a Hydrologic Modeling System that is designed to describe the physical properties
PRACTICAL UNIT 1 exercise task
 Practical Unit 1 1 1 PRACTICAL UNIT 1 exercise task Developing a hydraulic model with HEC RAS using schematic river geometry data In the course of practical unit 1 we prepare the input for the execution
Practical Unit 1 1 1 PRACTICAL UNIT 1 exercise task Developing a hydraulic model with HEC RAS using schematic river geometry data In the course of practical unit 1 we prepare the input for the execution
Linear Routing: Floodrouting. HEC-RAS Introduction. Brays Bayou. Uniform Open Channel Flow. v = 1 n R2/3. S S.I. units
 Linear Routing: Floodrouting HEC-RAS Introduction Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Robert Pitt University of Alabama April 26, 2004 Two (2) types of floodrouting of a hydrograph Linear Muskingum Reservoir
Linear Routing: Floodrouting HEC-RAS Introduction Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Robert Pitt University of Alabama April 26, 2004 Two (2) types of floodrouting of a hydrograph Linear Muskingum Reservoir
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station Analysis Setup a simple HY-12 pump station storm drain model in the WMS interface with pump and pipe information Objectives Using the HY-12
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station Analysis Setup a simple HY-12 pump station storm drain model in the WMS interface with pump and pipe information Objectives Using the HY-12
Day 1. HEC-RAS 1-D Training. Rob Keller and Mark Forest. Break (9:45 am to 10:00 am) Lunch (12:00 pm to 1:00 pm)
 Day 1 HEC-RAS 1-D Training Rob Keller and Mark Forest Introductions and Course Objectives (8:00 am to 8:15 am) Introductions: Class and Content Module 1 Open Channel Hydraulics (8:15 am to 9:45 am) Lecture
Day 1 HEC-RAS 1-D Training Rob Keller and Mark Forest Introductions and Course Objectives (8:00 am to 8:15 am) Introductions: Class and Content Module 1 Open Channel Hydraulics (8:15 am to 9:45 am) Lecture
SMS v Simulations. SRH-2D Tutorial. Time. Requirements. Prerequisites. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will demonstrate the process of creating a new SRH-2D simulation from an existing simulation. This workflow is very useful when adding new features
SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will demonstrate the process of creating a new SRH-2D simulation from an existing simulation. This workflow is very useful when adding new features
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling SWMM Modeling Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
Advanced 1D/2D Modeling Using HEC-RAS
 Advanced 1D/2D Modeling Using HEC-RAS Davis, California Objectives This is an advanced course in applying computer program HEC-RAS. The course provides participants with the knowledge to effectively use
Advanced 1D/2D Modeling Using HEC-RAS Davis, California Objectives This is an advanced course in applying computer program HEC-RAS. The course provides participants with the knowledge to effectively use
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling SWMM Modeling Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network information
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network information
Required: 486DX-33, 8MB RAM, HDD w. 20 MB free, VGA, Win95. Recommended: Pentium 60, 16 MB RAM, SVGA, Win95 or NT
 Evaluation Form Evaluator Information Name: Jeff Hagan Date: Feb. 17, 2000 Software Information Title of Software: Purpose: Publisher: CulvertMaster Culvert Hydraulic Design Haestad Methods, Inc. Version:
Evaluation Form Evaluator Information Name: Jeff Hagan Date: Feb. 17, 2000 Software Information Title of Software: Purpose: Publisher: CulvertMaster Culvert Hydraulic Design Haestad Methods, Inc. Version:
WMS 9.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Stream Flow Integrate stream flow with your GSSHA overland flow model
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Integrate stream flow with your GSSHA overland flow model Objectives Learn how to add hydraulic channel routing to your GSSHA model and how to define channel properties. Learn how
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Integrate stream flow with your GSSHA overland flow model Objectives Learn how to add hydraulic channel routing to your GSSHA model and how to define channel properties. Learn how
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling HEC-1 Interface Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-1 model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic parameters
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-1 model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic parameters
Agenda. Background Connecting to model Running the model Viewing results Running what if scenarios
 Agenda Background Connecting to model Running the model Viewing results Running what if scenarios Background Don Pedro Reservoir Temperature model Danish Hydraulic Institute (DHI) MIKE software 3 dimensional
Agenda Background Connecting to model Running the model Viewing results Running what if scenarios Background Don Pedro Reservoir Temperature model Danish Hydraulic Institute (DHI) MIKE software 3 dimensional
Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
H y d r o C A D. Owner's Manual
 H y d r o C A D Stormwater Modeling System Version 8 Owner's Manual Copyright 2006 HydroCAD Software Solutions LLC. All rights reserved. HydroCAD is a registered trademark of HydroCAD Software Solutions
H y d r o C A D Stormwater Modeling System Version 8 Owner's Manual Copyright 2006 HydroCAD Software Solutions LLC. All rights reserved. HydroCAD is a registered trademark of HydroCAD Software Solutions
CEE3430 Engineering Hydrology
 CEE3430 Engineering Hydrology Homework 8. Step by Step Guidance for using HEC HMS to solve homework problems 1. Solve Part 1, problem 3 above using HEC-HMS. The standard lag referred to in the inputs (and
CEE3430 Engineering Hydrology Homework 8. Step by Step Guidance for using HEC HMS to solve homework problems 1. Solve Part 1, problem 3 above using HEC-HMS. The standard lag referred to in the inputs (and
This tutorial introduces the HEC-RAS model and how it can be used to generate files for use with the HEC-RAS software.
 v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial introduces the model and how it can be used to generate files for use with the software. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements 5.0 Mesh Module
v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial introduces the model and how it can be used to generate files for use with the software. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements 5.0 Mesh Module
ENV3104 Hydraulics II 2017 Assignment 1. Gradually Varied Flow Profiles and Numerical Solution of the Kinematic Equations:
 ENV3104 Hydraulics II 2017 Assignment 1 Assignment 1 Gradually Varied Flow Profiles and Numerical Solution of the Kinematic Equations: Examiner: Jahangir Alam Due Date: 27 Apr 2017 Weighting: 1% Objectives
ENV3104 Hydraulics II 2017 Assignment 1 Assignment 1 Gradually Varied Flow Profiles and Numerical Solution of the Kinematic Equations: Examiner: Jahangir Alam Due Date: 27 Apr 2017 Weighting: 1% Objectives
MEMORANDUM. Corona Subdivision XP Storm Evaluation. Date: March 5, Curt Bates, City of Petaluma. David S. Smith, P.E., WEST Consultants, Inc.
 MEMORANDUM Project: Corona Subdivision XP Storm Evaluation Subject: Results Summary Date: March 5, 2013 To: Curt Bates, City of Petaluma No. C056132 EXP. 12/31/14 From: David S. Smith, P.E., WEST Consultants,
MEMORANDUM Project: Corona Subdivision XP Storm Evaluation Subject: Results Summary Date: March 5, 2013 To: Curt Bates, City of Petaluma No. C056132 EXP. 12/31/14 From: David S. Smith, P.E., WEST Consultants,
Using HEC-RAS and HEC-GeoRAS for River Modeling Adapted by E. Maurer, using an exercise by V. Merwade, Purdue Univ.
 Introduction Using HEC-RAS and HEC-GeoRAS for River Modeling Adapted by E. Maurer, using an exercise by V. Merwade, Purdue Univ. This tutorial uses the output from HEC_GeoRAS from a prior exercise as input
Introduction Using HEC-RAS and HEC-GeoRAS for River Modeling Adapted by E. Maurer, using an exercise by V. Merwade, Purdue Univ. This tutorial uses the output from HEC_GeoRAS from a prior exercise as input
WMS 9.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and bank
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and bank
This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional (SRH-2D) simulation. Requirements
 v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
solidthinking Compose Installation Guide
 Installation Guide This document describes the installation procedure for Compose 2017.3 on Windows and Linux platforms. Main Installer for Windows To execute the installation, double-click Compose_2017.3_Win64.exe.
Installation Guide This document describes the installation procedure for Compose 2017.3 on Windows and Linux platforms. Main Installer for Windows To execute the installation, double-click Compose_2017.3_Win64.exe.
SMS v Culvert Structures. SRH-2D Tutorial. Prerequisites. Requirements. Time. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.0 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of modeling culverts in SRH-2D. The Working with Simulations tutorial should have been completed before attempting this one.
SMS v. 12.0 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of modeling culverts in SRH-2D. The Working with Simulations tutorial should have been completed before attempting this one.
WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and
Storm Drain Modeling Defining HY-12 Storm Drain Networks with Shapefiles and LandXML files
 WMS 10.1 Tutorial v. 10.1 Storm Drain Modeling Defining HY-12 Storm Drain Networks with Shapefiles and LandXML files Set up an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using common file types such
WMS 10.1 Tutorial v. 10.1 Storm Drain Modeling Defining HY-12 Storm Drain Networks with Shapefiles and LandXML files Set up an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using common file types such
Introduction to Bentley PondPack
 Introduction to Bentley PondPack CE 365K Hydraulic Engineering Design Prepared by Cassandra Fagan and David Maidment Spring 2015 Contents Goals of the Tutorial... 1 Procedure... 1 (1) Opening Bentley PondPack...
Introduction to Bentley PondPack CE 365K Hydraulic Engineering Design Prepared by Cassandra Fagan and David Maidment Spring 2015 Contents Goals of the Tutorial... 1 Procedure... 1 (1) Opening Bentley PondPack...
ISIS Free & ISIS Professional Quick Start Guide
 ISIS Free & ISIS Professional Cost effective, integrated modelling solutions Think saving, think ISIS, think Halcrow This quick start guide enables first time users to quickly understand how to use ISIS
ISIS Free & ISIS Professional Cost effective, integrated modelling solutions Think saving, think ISIS, think Halcrow This quick start guide enables first time users to quickly understand how to use ISIS
Prepared for CIVE 401 Hydraulic Engineering By Kennard Lai, Patrick Ndolo Goy & Dr. Pierre Julien Fall 2015
 Prepared for CIVE 401 Hydraulic Engineering By Kennard Lai, Patrick Ndolo Goy & Dr. Pierre Julien Fall 2015 Contents Introduction General Philosophy Overview of Capabilities Applications Computational
Prepared for CIVE 401 Hydraulic Engineering By Kennard Lai, Patrick Ndolo Goy & Dr. Pierre Julien Fall 2015 Contents Introduction General Philosophy Overview of Capabilities Applications Computational
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows users how to define a basic MODRAT model using
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows users how to define a basic MODRAT model using
TUFLOW 1D/2D SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM. 1 Introduction. 2 Background Data
 SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM TUFLOW 1D/2D 1 Introduction This tutorial describes the generation of a 1D TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. It is recommended that the TUFLOW 2D tutorial be done before
SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM TUFLOW 1D/2D 1 Introduction This tutorial describes the generation of a 1D TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. It is recommended that the TUFLOW 2D tutorial be done before
HEC-RAS 3.0 January, 2001 Release Notes
 HEC-RAS 3.0 January, 2001 Release Notes A new version of HEC-RAS (3.0) has been released with significant new features over the previous version (2.21). Version 3.0 includes unsteady flow routing capabilities,
HEC-RAS 3.0 January, 2001 Release Notes A new version of HEC-RAS (3.0) has been released with significant new features over the previous version (2.21). Version 3.0 includes unsteady flow routing capabilities,
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Rational Design
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to design storm drain inlets, pipes, and other components of a storm drain system using FHWA's HY-12 storm drain analysis software and the WMS interface Objectives Define
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to design storm drain inlets, pipes, and other components of a storm drain system using FHWA's HY-12 storm drain analysis software and the WMS interface Objectives Define
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools Objectives Experiment with the various floodplain delineation options
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools Objectives Experiment with the various floodplain delineation options
Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional (SRH-2D) simulation.
 v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
Updated on November 10, 2017
 CIVE 7397 Unsteady flows in Rivers and Pipe Networks/Stormwater Management and Modeling / Optimization in Water Resources Engineering Updated on November 10, 2017 Tutorial on using HEC-GeoRAS 10.1 (or
CIVE 7397 Unsteady flows in Rivers and Pipe Networks/Stormwater Management and Modeling / Optimization in Water Resources Engineering Updated on November 10, 2017 Tutorial on using HEC-GeoRAS 10.1 (or
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event
 Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event F-1P - Designing with a Pond Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook This workbook is
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event F-1P - Designing with a Pond Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook This workbook is
Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox Learn how to design inlet grates, detention basins, channels, and riprap using the FHWA Hydraulic Toolbox
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox Learn how to design inlet grates, detention basins, channels, and riprap using the FHWA Hydraulic Toolbox
Getting started with Hydra Modeller
 Getting started with Hydra Modeller Download Installation Hydra Modeller Basics Logging in Installing a template Building a network manually Importing a pre-defined network Setting GIS Layers Managing
Getting started with Hydra Modeller Download Installation Hydra Modeller Basics Logging in Installing a template Building a network manually Importing a pre-defined network Setting GIS Layers Managing
v TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics SMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
Numerical Hydraulics
 ETHZ, Fall 2017 Numerical Hydraulics Assignment 3 Comparison of two numerical solutions of river flow: use of Finite Elements (HEC-RAS) and Finite Volumes (BASEMENT) 1 Introduction In the course, two different
ETHZ, Fall 2017 Numerical Hydraulics Assignment 3 Comparison of two numerical solutions of river flow: use of Finite Elements (HEC-RAS) and Finite Volumes (BASEMENT) 1 Introduction In the course, two different
ISIS 1D. Quick Start Guide. Cost effective, integrated software solutions ch2mhill.com/isis
 ISIS 1D Quick Start Guide Cost effective, integrated software solutions 0845 094 7990 ch2mhill.com/isis softwaresupport@ch2m.com Table of Contents Overview... 3 1. Starting ISIS and Basic Concepts... 3
ISIS 1D Quick Start Guide Cost effective, integrated software solutions 0845 094 7990 ch2mhill.com/isis softwaresupport@ch2m.com Table of Contents Overview... 3 1. Starting ISIS and Basic Concepts... 3
River Analysis System HEC-RAS
 Hydrologic Engineering Center River Analysis System HEC-RAS Release Notes Version 4.0.0 March 2008 Approved for Public Release Distribution Unlimited 1 Introduction Version 4.0.0 of the River Analysis
Hydrologic Engineering Center River Analysis System HEC-RAS Release Notes Version 4.0.0 March 2008 Approved for Public Release Distribution Unlimited 1 Introduction Version 4.0.0 of the River Analysis
v SMS Tutorials SRH-2D Prerequisites Requirements SRH-2D Model Map Module Mesh Module Data files Time
 v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation using SMS version 11.2 or later. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial
v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation using SMS version 11.2 or later. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial
Manage and Generate Reports
 Report Manager, page 1 Generate Reports, page 3 Trust Self-Signed Certificate for Live Data Reports, page 4 Report Viewer, page 4 Save an Existing Stock Report, page 7 Import Reports, page 7 Export Reports,
Report Manager, page 1 Generate Reports, page 3 Trust Self-Signed Certificate for Live Data Reports, page 4 Report Viewer, page 4 Save an Existing Stock Report, page 7 Import Reports, page 7 Export Reports,
Files to Contents. User Guide March 11, 2008
 Files 8.3.0 to 8.4.1 User Guide March 11, 2008 Contents Managing files File properties Opening a file or folder Creating a new folder Copying a file or folder Deleting a file or folder Renaming of a file
Files 8.3.0 to 8.4.1 User Guide March 11, 2008 Contents Managing files File properties Opening a file or folder Creating a new folder Copying a file or folder Deleting a file or folder Renaming of a file
National Fire Incident Reporting System (NFIRS 5.0) Configuration Tool User's Guide
 National Fire Incident Reporting System (NFIRS 5.0) Configuration Tool User's Guide NFIRS 5.0 Software Version 5.3 Prepared for: FEMA Round Hill, VA 20142 Prepared by: Verizon Federal Incorporated P.O.
National Fire Incident Reporting System (NFIRS 5.0) Configuration Tool User's Guide NFIRS 5.0 Software Version 5.3 Prepared for: FEMA Round Hill, VA 20142 Prepared by: Verizon Federal Incorporated P.O.
R. Reports Menu: 8. Batch Detail Report
 R. Reports Menu: 8. Batch Detail Report Table of Contents Batch Detail Report... 3 The Transaction Options tab... 3 The Output tab... 5 The Accounts tab... 6 The More Accounts tab... 8 Click on R. Reports
R. Reports Menu: 8. Batch Detail Report Table of Contents Batch Detail Report... 3 The Transaction Options tab... 3 The Output tab... 5 The Accounts tab... 6 The More Accounts tab... 8 Click on R. Reports
Sabre Customer Virtual Private Network Launcher (SCVPNLauncher)
 Sabre Customer Virtual Private Network Launcher (SCVPNLauncher) User s Guide Sabre Travel Network This document provides detailed information for the install/uninstall, operation, configuration and troubleshooting
Sabre Customer Virtual Private Network Launcher (SCVPNLauncher) User s Guide Sabre Travel Network This document provides detailed information for the install/uninstall, operation, configuration and troubleshooting
PCSWMM 2002 EXTRAN Block PAT AVENUE Storm Drainage Design
 PCSWMM 2002 EXTRAN Block PAT AVENUE Storm Drainage Design A Hello World Example Prepared by Dr. Robert Pitt and Jason Kirby, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Alabama August 20, 2002 Introduction
PCSWMM 2002 EXTRAN Block PAT AVENUE Storm Drainage Design A Hello World Example Prepared by Dr. Robert Pitt and Jason Kirby, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Alabama August 20, 2002 Introduction
2-D Hydraulic Modeling Theory & Practice
 2-D Hydraulic Modeling Theory & Practice Author: Maged A. Aboelata, PhD, PE, CFM Presenter: Heather Zhao, PE, CFM October 2017 Presentation Outline * 1-D vs. 2-D modeling * Theory of 2-D simulation * Commonly
2-D Hydraulic Modeling Theory & Practice Author: Maged A. Aboelata, PhD, PE, CFM Presenter: Heather Zhao, PE, CFM October 2017 Presentation Outline * 1-D vs. 2-D modeling * Theory of 2-D simulation * Commonly
v Prerequisite Tutorials GSSHA Modeling Basics Stream Flow GSSHA WMS Basics Creating Feature Objects and Mapping their Attributes to the 2D Grid
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
SMS v Weir Flow. SRH-2D Tutorial. Prerequisites. Requirements. Time. Objectives
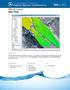 SMS v. 12.2 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of using a weir boundary condition (BC) within SRH-2D to model an overflow weir near a bridge structure. The Simulations tutorial
SMS v. 12.2 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of using a weir boundary condition (BC) within SRH-2D to model an overflow weir near a bridge structure. The Simulations tutorial
Efficiency and Accuracy of Importing HEC RAS Datafiles into PCSWMM and SWMM5
 5 Efficiency and Accuracy of Importing HEC RAS Datafiles into PCSWMM and SWMM5 Karen Finney, Rob James, William James and Tiehong Xiao An advantage of USEPA s SWMM5 is its capability to dynamically model
5 Efficiency and Accuracy of Importing HEC RAS Datafiles into PCSWMM and SWMM5 Karen Finney, Rob James, William James and Tiehong Xiao An advantage of USEPA s SWMM5 is its capability to dynamically model
INTRODUCTION TO HEC-RAS
 INTRODUCTION TO HEC-RAS HEC- RAS stands for Hydrologic Engineering Center s River Analysis System By U.S. Army Corps of Engineers One dimensional analysis of : 1. Steady flow 2. Unsteady flow 3. Sediment
INTRODUCTION TO HEC-RAS HEC- RAS stands for Hydrologic Engineering Center s River Analysis System By U.S. Army Corps of Engineers One dimensional analysis of : 1. Steady flow 2. Unsteady flow 3. Sediment
WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows you how to define a basic MODRAT model using
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows you how to define a basic MODRAT model using
JPdfBookmarks Manual. by Flaviano Petrocchi
 JPdfBookmarks Manual by Flaviano Petrocchi JPdfBookmarks Manual 1 Introduction 3 Installation and Uninstallation 4 Linux Instructions 4 Debian Instructions 6 Windows Instructions 6 Universal Archive Instructions
JPdfBookmarks Manual by Flaviano Petrocchi JPdfBookmarks Manual 1 Introduction 3 Installation and Uninstallation 4 Linux Instructions 4 Debian Instructions 6 Windows Instructions 6 Universal Archive Instructions
Automating Hydraulic Analysis v 1.0.
 2011 Automating Hydraulic Analysis v 1.0. Basic tutorial and introduction Automating Hydraulic Analysis (AHYDRA) is a freeware application that automates some specific features of HEC RAS or other hydraulic
2011 Automating Hydraulic Analysis v 1.0. Basic tutorial and introduction Automating Hydraulic Analysis (AHYDRA) is a freeware application that automates some specific features of HEC RAS or other hydraulic
v TUFLOW FV SMS 12.2 Tutorial Time Requirements Prerequisites Objectives
 SMS 12.2 Tutorial v. 12.2 Objectives is an engine for performing 2D and 3D hydrodynamic simulations. The model solves the Non-linear Shallow Water Equations (NLSWE) on a flexible mesh using a finite-volume
SMS 12.2 Tutorial v. 12.2 Objectives is an engine for performing 2D and 3D hydrodynamic simulations. The model solves the Non-linear Shallow Water Equations (NLSWE) on a flexible mesh using a finite-volume
CHAPTER 7 FLOOD HYDRAULICS & HYDROLOGIC VIVEK VERMA
 CHAPTER 7 FLOOD HYDRAULICS & HYDROLOGIC VIVEK VERMA CONTENTS 1. Flow Classification 2. Chezy s and Manning Equation 3. Specific Energy 4. Surface Water Profiles 5. Hydraulic Jump 6. HEC-RAS 7. HEC-HMS
CHAPTER 7 FLOOD HYDRAULICS & HYDROLOGIC VIVEK VERMA CONTENTS 1. Flow Classification 2. Chezy s and Manning Equation 3. Specific Energy 4. Surface Water Profiles 5. Hydraulic Jump 6. HEC-RAS 7. HEC-HMS
Running Java Programs
 Running Java Programs Written by: Keith Fenske, http://www.psc-consulting.ca/fenske/ First version: Thursday, 10 January 2008 Document revised: Saturday, 13 February 2010 Copyright 2008, 2010 by Keith
Running Java Programs Written by: Keith Fenske, http://www.psc-consulting.ca/fenske/ First version: Thursday, 10 January 2008 Document revised: Saturday, 13 February 2010 Copyright 2008, 2010 by Keith
v TUFLOW 1D/2D SMS 11.2 Tutorial Time minutes Prerequisites TUFLOW 2D Tutorial
 v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a 1D TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. It is strongly recommended that the TUFLOW 2D tutorial be completed before doing
v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a 1D TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. It is strongly recommended that the TUFLOW 2D tutorial be completed before doing
SAP GUI 7.30 for Windows Computer
 SAP GUI 7.30 for Windows Computer Student and Faculty Installation Instructions Table of Contents Caution:... 2 System Requirements:... 2 System Memory (RAM) requirements:... 2 Disk Space requirements:...
SAP GUI 7.30 for Windows Computer Student and Faculty Installation Instructions Table of Contents Caution:... 2 System Requirements:... 2 System Memory (RAM) requirements:... 2 Disk Space requirements:...
v Basic FESWMS Analysis SMS 11.2 Tutorial Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements FESWMS Fst2dh Mesh Module
 v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This lesson teaches how to prepare a mesh for a FESWMS simulation. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements FESWMS Fst2dh Mesh Module Time 15-30 minutes Page 1
v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This lesson teaches how to prepare a mesh for a FESWMS simulation. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements FESWMS Fst2dh Mesh Module Time 15-30 minutes Page 1
Flood Inundation Mapping using HEC-RAS
 Flood Inundation Mapping using HEC-RAS Goodell, C. 1 ; Warren, C. 2 WEST Consultants, 2601 25 th St SE, Suite 450, Salem, OR 97302. Abstract Flood inundation mapping is an important tool for municipal
Flood Inundation Mapping using HEC-RAS Goodell, C. 1 ; Warren, C. 2 WEST Consultants, 2601 25 th St SE, Suite 450, Salem, OR 97302. Abstract Flood inundation mapping is an important tool for municipal
HEC-RAS. A Tutorial (Model Development of a Small Flume)
 HEC-RAS A Tutorial (Model Development of a Small Flume) HEC-RAS Hydraulic Engineering Center:River Analysis System 1-D step backwater model Utilizes energy equation to compute water surface elevation for
HEC-RAS A Tutorial (Model Development of a Small Flume) HEC-RAS Hydraulic Engineering Center:River Analysis System 1-D step backwater model Utilizes energy equation to compute water surface elevation for
Building a new model in wspg2010
 Building a new model in wspg2010 The Water Surface Profile Gradient 2010 (wspg2010 by XP Software) model is a hydraulic analysis system that computes and plots uniform and non-uniform steady flow water
Building a new model in wspg2010 The Water Surface Profile Gradient 2010 (wspg2010 by XP Software) model is a hydraulic analysis system that computes and plots uniform and non-uniform steady flow water
Part 3: Setup of Client PC
 Version 2.2, January 16, 2013 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Requirements of Client PC... 3 1.2 Flow Chart of Client PC Setup... 4 2. Setting of Windows OS... 5 2.1 Setting to Display File Type Extension
Version 2.2, January 16, 2013 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Requirements of Client PC... 3 1.2 Flow Chart of Client PC Setup... 4 2. Setting of Windows OS... 5 2.1 Setting to Display File Type Extension
SMS v Culvert Structures with HY-8. Prerequisites. Requirements. Time. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Culvert Structures with HY-8 Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of modeling culverts in SRH-2D coupled with the Federal Highway Administrations HY-8 culvert analysis
SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Culvert Structures with HY-8 Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of modeling culverts in SRH-2D coupled with the Federal Highway Administrations HY-8 culvert analysis
This loads a preset standard set of data appropriate for Malaysian modeling projects.
 XP Software On-Site Detention (OSD) Example Step 1 Open xpswmm2010 program Or from Start menu select Programs XPS - then select xpswmm2010 Select Create From Template Save file, e.g. Filename.xp The program
XP Software On-Site Detention (OSD) Example Step 1 Open xpswmm2010 program Or from Start menu select Programs XPS - then select xpswmm2010 Select Create From Template Save file, e.g. Filename.xp The program
Ducks on the Pond: Stormwater Management Basin Analysis Using AutoCAD Civil 3D and Autodesk SSA
 Ducks on the Pond: Stormwater Management Basin Analysis Using AutoCAD Civil 3D and Autodesk Josh Kehs, P.E. Autodesk, Inc. CI4541 Learning Objectives At the end of this class, you will be able to: Model
Ducks on the Pond: Stormwater Management Basin Analysis Using AutoCAD Civil 3D and Autodesk Josh Kehs, P.E. Autodesk, Inc. CI4541 Learning Objectives At the end of this class, you will be able to: Model
Video Performance Evaluation Resource. Quick Start Guide
 Video Performance Evaluation Resource Quick Start Guide November 25, 2002 Table of Contents 1 Welcome to ViPER... 3 1.1 Welcome to the ViPER Documentation... 3 2 Setting Up ViPER... 3 2.1 Preparing for
Video Performance Evaluation Resource Quick Start Guide November 25, 2002 Table of Contents 1 Welcome to ViPER... 3 1.1 Welcome to the ViPER Documentation... 3 2 Setting Up ViPER... 3 2.1 Preparing for
Objectives This tutorial will introduce how to prepare and run a basic ADH model using the SMS interface.
 v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will introduce how to prepare and run a basic ADH model using the SMS interface. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements ADH Mesh Module Scatter
v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will introduce how to prepare and run a basic ADH model using the SMS interface. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements ADH Mesh Module Scatter
HEC-RAS 2D Flood Modelling Tutorial
 HEC-RAS 2D Flood Modelling Tutorial Civil Site Design and HECRAS 2D Flood Modelling HECRAS version 5 and later includes functionality to analyse water flows moving across a surface. this is known as 2D
HEC-RAS 2D Flood Modelling Tutorial Civil Site Design and HECRAS 2D Flood Modelling HECRAS version 5 and later includes functionality to analyse water flows moving across a surface. this is known as 2D
Instructions for Installing FlowMaster & CulvertMaster Using Bentley Student Services Hydraulics and Hydrology Spring 2016
 Instructions for Installing FlowMaster & CulvertMaster Using Bentley Student Services Hydraulics and Hydrology Spring 2016 Contents Instructions for Installing FlowMaster & CulvertMaster Using Bentley
Instructions for Installing FlowMaster & CulvertMaster Using Bentley Student Services Hydraulics and Hydrology Spring 2016 Contents Instructions for Installing FlowMaster & CulvertMaster Using Bentley
3M Molecular Detection System Software Upgrade/Installation Instructions
 User Manual Supplement Number: TB.342837.03 Effective Date: March 2018 Supersedes: TB.342837.02 Technology Platform: 3M Molecular Detection System Originating Location: St. Paul, MN 3M Molecular Detection
User Manual Supplement Number: TB.342837.03 Effective Date: March 2018 Supersedes: TB.342837.02 Technology Platform: 3M Molecular Detection System Originating Location: St. Paul, MN 3M Molecular Detection
v Basic FESWMS Analysis SMS Tutorials Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial instructs on how to prepare a mesh for a FESWMS simulation. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements FESWMS Fst2dh Mesh Module Time 15 30 minutes
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial instructs on how to prepare a mesh for a FESWMS simulation. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements FESWMS Fst2dh Mesh Module Time 15 30 minutes
Office 2016 Excel Basics 25 Video/Class Project #37 Excel Basics 25: Power Query (Get & Transform Data) to Convert Bad Data into Proper Data Set
 Office 2016 Excel Basics 25 Video/Class Project #37 Excel Basics 25: Power Query (Get & Transform Data) to Convert Bad Data into Proper Data Set Goal in video # 25: Learn about how to use the Get & Transform
Office 2016 Excel Basics 25 Video/Class Project #37 Excel Basics 25: Power Query (Get & Transform Data) to Convert Bad Data into Proper Data Set Goal in video # 25: Learn about how to use the Get & Transform
LiveNX Upgrade Guide from v5.2.0 to v5.2.1
 LIVEACTION, INC. LiveNX Upgrade Guide from v5.2.0 to v5.2.1 UPGRADE LiveAction, Inc. 3500 Copyright WEST BAYSHORE 2016 LiveAction, ROAD Inc. All rights reserved. LiveAction, LiveNX, LiveUX, the LiveAction
LIVEACTION, INC. LiveNX Upgrade Guide from v5.2.0 to v5.2.1 UPGRADE LiveAction, Inc. 3500 Copyright WEST BAYSHORE 2016 LiveAction, ROAD Inc. All rights reserved. LiveAction, LiveNX, LiveUX, the LiveAction
JGuiB User s Guide. JGuiB Development Team. Version 3.0 ( )
 JGuiB User s Guide a GUI-based pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling assistant tool for BOOMER Version 3.0 (2007-06-28) JGuiB Development Team Tech Support: jguib.taiwan@gmail.com - 2 - Table of
JGuiB User s Guide a GUI-based pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling assistant tool for BOOMER Version 3.0 (2007-06-28) JGuiB Development Team Tech Support: jguib.taiwan@gmail.com - 2 - Table of
GETTING STARTED WITH HAZUS- MH 2.1
 GETTING STARTED WITH HAZUS- MH 2.1 SYSTEM AND SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS In order for Hazus- MH to run properly, your system must meet certain minimum requirements. figure 1 provides guidance for supported
GETTING STARTED WITH HAZUS- MH 2.1 SYSTEM AND SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS In order for Hazus- MH to run properly, your system must meet certain minimum requirements. figure 1 provides guidance for supported
Modeling Detention Ponds Malaysian Example (v2009)
 Modeling Detention Ponds Malaysian Example (v2009) This tutorial demonstrates the usability of xpswmm and xpstorm for simulating detention basins in urban areas. This fictitious example includes the use
Modeling Detention Ponds Malaysian Example (v2009) This tutorial demonstrates the usability of xpswmm and xpstorm for simulating detention basins in urban areas. This fictitious example includes the use
i2b2 Workbench Developer s Guide: Eclipse Neon & i2b2 Source Code
 i2b2 Workbench Developer s Guide: Eclipse Neon & i2b2 Source Code About this guide Informatics for Integrating Biology and the Bedside (i2b2) began as one of the sponsored initiatives of the NIH Roadmap
i2b2 Workbench Developer s Guide: Eclipse Neon & i2b2 Source Code About this guide Informatics for Integrating Biology and the Bedside (i2b2) began as one of the sponsored initiatives of the NIH Roadmap
Code Check TM Software Requirements Specification
 Code Check TM Software Requirements Specification Author: Richard McKenna Debugging Enterprises TM Based on IEEE Std 830 TM -1998 (R2009) document format Copyright 2017 Debugging Enterprises No part of
Code Check TM Software Requirements Specification Author: Richard McKenna Debugging Enterprises TM Based on IEEE Std 830 TM -1998 (R2009) document format Copyright 2017 Debugging Enterprises No part of
