Maximizing an interpolating quadratic
|
|
|
- Blaze May
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Week 11: Monday, Apr 9 Maximizing an interpolating quadratic Suppose that a function f is evaluated on a reasonably fine, uniform mesh {x i } n i=0 with spacing h = x i+1 x i. How can we find any local maxima inside the mesh interval (x 0, x n )? A natural first approximation is to simply find local maxima in the discrete sequence {f(x i )} n i=0. I would usually do that by looking for a place where differences between adjacent points change from positive to negative (the discrete analog of looking for a critical point where the derivative changes from positive to negative): % [idx] = find local max( fi ) % % Based on samples fi of a function on a uniform mesh over % an interval, find the indices of mesh points where there % are discrete local maxima. function [idx] = find local max(fi ) d fi = fi (2:end) fi(1:end 1); idx = find( d fi :end 1) > 0 & d fi(2:end) <= 0 ); idx = idx+1; Unfortunately, unless we use a rather fine mesh, this method is unlikely to give us more than a couple digits of accuracy. A simple method of improving the accuracy of the result is to fit a polynomial interpolant to the data near the discrete local maximum, and use a maximum of the interpolating polynomial as an estimate for the local maximum of f. The simplest variant of this is to fit a quadratic; let s look in a little detail at how this works. Suppose x j is an interior mesh point where f has a discrete local maximum. We would like to find a corrected estimate of the local maximum, x = x j + z, by maximizing a quadratic interpolant through x j 1, x j, and
2 x j+1. In terms of the correction z, the interpolation conditions are p(0) = f(x j + 0) = f(x j ) p(h) = f(x j + h) = f(x j+1 ) p( h) = f(x j h) = f(x j 1 ) In a homework exercise, we saw how to differentiate a polynomial interpolant written in the Newton basis. For variety, let s now write things in terms of the Lagrange polynomials for {0, h, h}: p(z) = p(0) (h2 z 2 ) + p(h) p( h) z(z + h) + z(z h) 2 ( ) 2 p(h) p( h) = p(0) + z + 1 ( ) p(h) 2p(0) + p( h) z 2. 2 Note that this last expression is just p(z) expressed in Taylor series form: where p(z) = p(0) + p (0)z p (0)z 2. p p(h) p( h) (0) = p[h, h] =, p p(h) 2p(0) + p( h) (0) = 2p[h, 0, h] =. Therefore, the maximum z for p satisfies z = p (0) p (0), p(z ) = p(0) p (0) 2 2p (0). It s worth comparing this maximization to what we would do if we took x j as an initial guess at the maximum and did one step of Newton iteration to improve our guess: x new = x j f (x j ) f (x j ) The correction z looks just like what we would compute in one Newton step, but with the approximations f (x j ) p (0) and f (x j ) p (0)!
3 Two ways to numerical differentiation One way to approximate derivatives is by interpolation. If we can use interpolation to estimate function values, why not use it to estimate derivatives as well? The basic procedure here is: Interpolate f at some nodes x 0,..., x n. Differentiate the interpolating polynomial in order to approximate derivatives of f. Usually, one is interested in the derivative at one of the node points. In general, if the interpolation points x 0,..., x n all lie within an interval of length h, and if f has enough continuous derivatives in that interval, we have p (k) (x j ) = O(h n+1 k ). The error analysis is relatively straightforward, and is in the book; but I did not drag you through the algebra in class, and do not intend to do so here. This, therefore, is one way of thinking about numerical differentiation. Another way to get to the same end is to manipulate Taylor series. For example, in the previous section we derived the centered difference approximations by differentiating a quadratic interpolant: f f(x + h) f(x h) (x), f f(x + h) 2f(0) + f(x h) (x). We could have also said we have f(x), f(x + h), and f(x h); what linear combination of these values best approximates f (x) (or f (x))? That is, we somehow want to choose coefficients a +, a 0, a so that we get a good approximation of f (x) of the form f (x) ˆf (x) a 0 f(x) + a + f(x + h) + a f(x h). Note that we can Taylor expand the terms in ˆf (x) about x to get ˆf (x) = (a 0 + a + + a )f(x) + h(a + a )f (x) + h2 2 (a + + a )f (x) + h3 6 (a + a )f (x) + O(h 4 )
4 We can adjust the three coefficients to match the first three terms in this series with the the (trivial) Taylor series for f (x) by solving the linear system This gives us or (a 0 + a + + a ) = 0 h(a + a ) = 1 2 (a + + a ) = 0. a 0 = 0, a ± = ± 1 ˆf (x) = f(x + h) f(x h) = f (x) + O( ) Let s walk through the same exercise for computing the second derivative. We want a formula of the form ˆf (x) = b 0 f(x) + b + f(x + h) + b f(x h), and Taylor expanding each term in the right hand side about zero gives ˆf (x) = (b 0 + b + + b )f(x) + h(b + b )f (x) + h2 2 (b + + b )f (x) + h3 6 (b + b )f (x) + O(h 4 ) Setting the first three terms in this series to match f (x), we get the equations which has the solution (b 0 + b + + b ) = 0 h(b + b ) = 0 2 (b + + b ) = 1, b 0 = 2, b ± = 1.
5 Notice that because b + b, we also automatically get that and so h 3 6 (b + b )f (x) = 0, ˆf (x) f (x) = O( ), which is one better order of accuracy than we might have expected from looking too uncautiously at the bound based on the derivation via polynomial interpolation.
Numerical Analysis Fall. Numerical Differentiation
 Numerical Analysis 5 Fall Numerical Differentiation Differentiation The mathematical definition of a derivative begins with a difference approimation: and as is allowed to approach zero, the difference
Numerical Analysis 5 Fall Numerical Differentiation Differentiation The mathematical definition of a derivative begins with a difference approimation: and as is allowed to approach zero, the difference
Today s class. Roots of equation Finish up incremental search Open methods. Numerical Methods, Fall 2011 Lecture 5. Prof. Jinbo Bi CSE, UConn
 Today s class Roots of equation Finish up incremental search Open methods 1 False Position Method Although the interval [a,b] where the root becomes iteratively closer with the false position method, unlike
Today s class Roots of equation Finish up incremental search Open methods 1 False Position Method Although the interval [a,b] where the root becomes iteratively closer with the false position method, unlike
Handout 4 - Interpolation Examples
 Handout 4 - Interpolation Examples Middle East Technical University Example 1: Obtaining the n th Degree Newton s Interpolating Polynomial Passing through (n+1) Data Points Obtain the 4 th degree Newton
Handout 4 - Interpolation Examples Middle East Technical University Example 1: Obtaining the n th Degree Newton s Interpolating Polynomial Passing through (n+1) Data Points Obtain the 4 th degree Newton
Numerical Integration
 Numerical Integration Numerical Integration is the process of computing the value of a definite integral, when the values of the integrand function, are given at some tabular points. As in the case of
Numerical Integration Numerical Integration is the process of computing the value of a definite integral, when the values of the integrand function, are given at some tabular points. As in the case of
Lesson 13: Exploring Factored Form
 Opening Activity Below is a graph of the equation y = 6(x 3)(x + 2). It is also the graph of: y = 3(2x 6)(x + 2) y = 2(3x 9)(x + 2) y = 2(x 3)(3x + 6) y = 3(x 3)(2x + 4) y = (3x 9)(2x + 4) y = (2x 6)(3x
Opening Activity Below is a graph of the equation y = 6(x 3)(x + 2). It is also the graph of: y = 3(2x 6)(x + 2) y = 2(3x 9)(x + 2) y = 2(x 3)(3x + 6) y = 3(x 3)(2x + 4) y = (3x 9)(2x + 4) y = (2x 6)(3x
Natasha S. Sharma, PhD
 Revisiting the function evaluation problem Most functions cannot be evaluated exactly: 2 x, e x, ln x, trigonometric functions since by using a computer we are limited to the use of elementary arithmetic
Revisiting the function evaluation problem Most functions cannot be evaluated exactly: 2 x, e x, ln x, trigonometric functions since by using a computer we are limited to the use of elementary arithmetic
February 2017 (1/20) 2 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation 2.2 (Natural) Cubic Splines. MA378/531 Numerical Analysis II ( NA2 )
 f f f f f (/2).9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2. S Knots.7.6.5.4.3.2. 5 5.2.8.6.4.2 S Knots.2 5 5.9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2..9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2. S Knots 5 5 S Knots 5 5 5 5.35.3.25.2.5..5 5 5.6.5.4.3.2. 5 5 4 x 3 3.5 3 2.5 2.5.5 5
f f f f f (/2).9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2. S Knots.7.6.5.4.3.2. 5 5.2.8.6.4.2 S Knots.2 5 5.9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2..9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2. S Knots 5 5 S Knots 5 5 5 5.35.3.25.2.5..5 5 5.6.5.4.3.2. 5 5 4 x 3 3.5 3 2.5 2.5.5 5
SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS
 SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS Widely used in the mathematical modeling of real world phenomena. We introduce some numerical methods for their solution. For better intuition, we examine systems of two
SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS Widely used in the mathematical modeling of real world phenomena. We introduce some numerical methods for their solution. For better intuition, we examine systems of two
February 23 Math 2335 sec 51 Spring 2016
 February 23 Math 2335 sec 51 Spring 2016 Section 4.1: Polynomial Interpolation Interpolation is the process of finding a curve or evaluating a function whose curve passes through a known set of points.
February 23 Math 2335 sec 51 Spring 2016 Section 4.1: Polynomial Interpolation Interpolation is the process of finding a curve or evaluating a function whose curve passes through a known set of points.
Lecture VIII. Global Approximation Methods: I
 Lecture VIII Global Approximation Methods: I Gianluca Violante New York University Quantitative Macroeconomics G. Violante, Global Methods p. 1 /29 Global function approximation Global methods: function
Lecture VIII Global Approximation Methods: I Gianluca Violante New York University Quantitative Macroeconomics G. Violante, Global Methods p. 1 /29 Global function approximation Global methods: function
Lecture 9. Curve fitting. Interpolation. Lecture in Numerical Methods from 28. April 2015 UVT. Lecture 9. Numerical. Interpolation his o
 Curve fitting. Lecture in Methods from 28. April 2015 to ity Interpolation FIGURE A S Splines Piecewise relat UVT Agenda of today s lecture 1 Interpolation Idea 2 3 4 5 6 Splines Piecewise Interpolation
Curve fitting. Lecture in Methods from 28. April 2015 to ity Interpolation FIGURE A S Splines Piecewise relat UVT Agenda of today s lecture 1 Interpolation Idea 2 3 4 5 6 Splines Piecewise Interpolation
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems
 1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
Chapter 5. Radicals. Lesson 1: More Exponent Practice. Lesson 2: Square Root Functions. Lesson 3: Solving Radical Equations
 Chapter 5 Radicals Lesson 1: More Exponent Practice Lesson 2: Square Root Functions Lesson 3: Solving Radical Equations Lesson 4: Simplifying Radicals Lesson 5: Simplifying Cube Roots This assignment is
Chapter 5 Radicals Lesson 1: More Exponent Practice Lesson 2: Square Root Functions Lesson 3: Solving Radical Equations Lesson 4: Simplifying Radicals Lesson 5: Simplifying Cube Roots This assignment is
Quadratic Functions Dr. Laura J. Pyzdrowski
 1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory A quadratic function in the variable x is a polynomial where the highest power of x is 2. We will explore the domains, ranges, and graphs of quadratic
1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory A quadratic function in the variable x is a polynomial where the highest power of x is 2. We will explore the domains, ranges, and graphs of quadratic
f( x ), or a solution to the equation f( x) 0. You are already familiar with ways of solving
 The Bisection Method and Newton s Method. If f( x ) a function, then a number r for which f( r) 0 is called a zero or a root of the function f( x ), or a solution to the equation f( x) 0. You are already
The Bisection Method and Newton s Method. If f( x ) a function, then a number r for which f( r) 0 is called a zero or a root of the function f( x ), or a solution to the equation f( x) 0. You are already
Reals 1. Floating-point numbers and their properties. Pitfalls of numeric computation. Horner's method. Bisection. Newton's method.
 Reals 1 13 Reals Floating-point numbers and their properties. Pitfalls of numeric computation. Horner's method. Bisection. Newton's method. 13.1 Floating-point numbers Real numbers, those declared to be
Reals 1 13 Reals Floating-point numbers and their properties. Pitfalls of numeric computation. Horner's method. Bisection. Newton's method. 13.1 Floating-point numbers Real numbers, those declared to be
APPM/MATH Problem Set 4 Solutions
 APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
Today. Golden section, discussion of error Newton s method. Newton s method, steepest descent, conjugate gradient
 Optimization Last time Root finding: definition, motivation Algorithms: Bisection, false position, secant, Newton-Raphson Convergence & tradeoffs Example applications of Newton s method Root finding in
Optimization Last time Root finding: definition, motivation Algorithms: Bisection, false position, secant, Newton-Raphson Convergence & tradeoffs Example applications of Newton s method Root finding in
x 6 + λ 2 x 6 = for the curve y = 1 2 x3 gives f(1, 1 2 ) = λ actually has another solution besides λ = 1 2 = However, the equation λ
 Math 0 Prelim I Solutions Spring 010 1. Let f(x, y) = x3 y for (x, y) (0, 0). x 6 + y (4 pts) (a) Show that the cubic curves y = x 3 are level curves of the function f. Solution. Substituting y = x 3 in
Math 0 Prelim I Solutions Spring 010 1. Let f(x, y) = x3 y for (x, y) (0, 0). x 6 + y (4 pts) (a) Show that the cubic curves y = x 3 are level curves of the function f. Solution. Substituting y = x 3 in
Algebra 1. Standard 11 Operations of Expressions. Categories Combining Expressions Multiply Expressions Multiple Operations Function Knowledge
 Algebra 1 Standard 11 Operations of Expressions Categories Combining Expressions Multiply Expressions Multiple Operations Function Knowledge Summative Assessment Date: Wednesday, February 13 th Page 1
Algebra 1 Standard 11 Operations of Expressions Categories Combining Expressions Multiply Expressions Multiple Operations Function Knowledge Summative Assessment Date: Wednesday, February 13 th Page 1
Math Homework 3
 Math 0 - Homework 3 Due: Friday Feb. in class. Write on your paper the lab section you have registered for.. Staple the sheets together.. Solve exercise 8. of the textbook : Consider the following data:
Math 0 - Homework 3 Due: Friday Feb. in class. Write on your paper the lab section you have registered for.. Staple the sheets together.. Solve exercise 8. of the textbook : Consider the following data:
Computer Simulations
 Computer Simulations A practical approach to simulation Semra Gündüç gunduc@ankara.edu.tr Ankara University Faculty of Engineering, Department of Computer Engineering 2014-2015 Spring Term Ankara University
Computer Simulations A practical approach to simulation Semra Gündüç gunduc@ankara.edu.tr Ankara University Faculty of Engineering, Department of Computer Engineering 2014-2015 Spring Term Ankara University
PowerPoints organized by Dr. Michael R. Gustafson II, Duke University
 Part 5 Chapter 19 Numerical Differentiation PowerPoints organized by Dr. Michael R. Gustafson II, Duke University All images copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Part 5 Chapter 19 Numerical Differentiation PowerPoints organized by Dr. Michael R. Gustafson II, Duke University All images copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Review Initial Value Problems Euler s Method Summary
 THE EULER METHOD P.V. Johnson School of Mathematics Semester 1 2008 OUTLINE 1 REVIEW 2 INITIAL VALUE PROBLEMS The Problem Posing a Problem 3 EULER S METHOD Method Errors 4 SUMMARY OUTLINE 1 REVIEW 2 INITIAL
THE EULER METHOD P.V. Johnson School of Mathematics Semester 1 2008 OUTLINE 1 REVIEW 2 INITIAL VALUE PROBLEMS The Problem Posing a Problem 3 EULER S METHOD Method Errors 4 SUMMARY OUTLINE 1 REVIEW 2 INITIAL
COURSE: NUMERICAL ANALYSIS. LESSON: Methods for Solving Non-Linear Equations
 COURSE: NUMERICAL ANALYSIS LESSON: Methods for Solving Non-Linear Equations Lesson Developer: RAJNI ARORA COLLEGE/DEPARTMENT: Department of Mathematics, University of Delhi Page No. 1 Contents 1. LEARNING
COURSE: NUMERICAL ANALYSIS LESSON: Methods for Solving Non-Linear Equations Lesson Developer: RAJNI ARORA COLLEGE/DEPARTMENT: Department of Mathematics, University of Delhi Page No. 1 Contents 1. LEARNING
Math 3316, Fall 2016 Due Nov. 3, 2016
 Math 3316, Fall 2016 Due Nov. 3, 2016 Project 3 Polynomial Interpolation The first two sections of this project will be checked in lab the week of Oct. 24-26 this completion grade will count for 10% of
Math 3316, Fall 2016 Due Nov. 3, 2016 Project 3 Polynomial Interpolation The first two sections of this project will be checked in lab the week of Oct. 24-26 this completion grade will count for 10% of
x n x n stepnumber k order r error constant C r+1 1/2 5/12 3/8 251/720 abs. stab. interval (α,0) /11-3/10
 MATH 573 LECTURE NOTES 77 13.8. Predictor-corrector methods. We consider the Adams methods, obtained from the formula xn+1 xn+1 y(x n+1 y(x n ) = y (x)dx = f(x,y(x))dx x n x n by replacing f by an interpolating
MATH 573 LECTURE NOTES 77 13.8. Predictor-corrector methods. We consider the Adams methods, obtained from the formula xn+1 xn+1 y(x n+1 y(x n ) = y (x)dx = f(x,y(x))dx x n x n by replacing f by an interpolating
The Bisection Method versus Newton s Method in Maple (Classic Version for Windows)
 The Bisection Method versus (Classic Version for Windows) Author: Barbara Forrest Contact: baforres@uwaterloo.ca Copyrighted/NOT FOR RESALE version 1.1 Contents 1 Objectives for this Lab i 2 Approximate
The Bisection Method versus (Classic Version for Windows) Author: Barbara Forrest Contact: baforres@uwaterloo.ca Copyrighted/NOT FOR RESALE version 1.1 Contents 1 Objectives for this Lab i 2 Approximate
Objectives. Materials
 Activity 13 Objectives Understand what a slope field represents in terms of Create a slope field for a given differential equation Materials TI-84 Plus / TI-83 Plus Graph paper Introduction One of the
Activity 13 Objectives Understand what a slope field represents in terms of Create a slope field for a given differential equation Materials TI-84 Plus / TI-83 Plus Graph paper Introduction One of the
specified or may be difficult to handle, we often have a tabulated data
 Interpolation Introduction In many practical situations, for a function which either may not be explicitly specified or may be difficult to handle, we often have a tabulated data where and for In such
Interpolation Introduction In many practical situations, for a function which either may not be explicitly specified or may be difficult to handle, we often have a tabulated data where and for In such
(1) Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14)z = a + 2
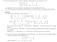 (1 Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, x + 2y 3z = 4 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14z = a + 2 (a Classify the system of equations depending on the values of
(1 Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, x + 2y 3z = 4 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14z = a + 2 (a Classify the system of equations depending on the values of
2.1 Quadraticsnts.notebook. September 10, 2018
 1 A quadratic function is a polynomial function of second degree. The graph of a quadratic function is called a parabola. 2 Standard Form: Intercept Form: Vertex Form: f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k vertex: (h, k)
1 A quadratic function is a polynomial function of second degree. The graph of a quadratic function is called a parabola. 2 Standard Form: Intercept Form: Vertex Form: f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k vertex: (h, k)
5.5 Newton s Approximation Method
 498CHAPTER 5. USING DERIVATIVES TO ANALYZE FUNCTIONS; FURTHER APPLICATIONS 4 3 y = x 4 3 f(x) = x cosx y = cosx 3 3 x = cosx x cosx = 0 Figure 5.: Figure showing the existence of a solution of x = cos
498CHAPTER 5. USING DERIVATIVES TO ANALYZE FUNCTIONS; FURTHER APPLICATIONS 4 3 y = x 4 3 f(x) = x cosx y = cosx 3 3 x = cosx x cosx = 0 Figure 5.: Figure showing the existence of a solution of x = cos
Handout 2 - Root Finding using MATLAB
 Handout 2 - Root Finding using MATLAB Middle East Technical University MATLAB has couple of built-in root finding functions. In this handout we ll have a look at fzero, roots and solve functions. It is
Handout 2 - Root Finding using MATLAB Middle East Technical University MATLAB has couple of built-in root finding functions. In this handout we ll have a look at fzero, roots and solve functions. It is
Subtraction Understand Subtraction on a Number Line Using a number line let s demonstrate the subtraction process using the problem 7 5.
 Objective 1 Subtraction Understand Subtraction on a Number Line Using a number line let s demonstrate the subtraction process using the problem 7 5. -7-6 -5-4 -3-2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Using the number line
Objective 1 Subtraction Understand Subtraction on a Number Line Using a number line let s demonstrate the subtraction process using the problem 7 5. -7-6 -5-4 -3-2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Using the number line
Optimizations and Lagrange Multiplier Method
 Introduction Applications Goal and Objectives Reflection Questions Once an objective of any real world application is well specified as a function of its control variables, which may subject to a certain
Introduction Applications Goal and Objectives Reflection Questions Once an objective of any real world application is well specified as a function of its control variables, which may subject to a certain
Linear and quadratic Taylor polynomials for functions of several variables.
 ams/econ 11b supplementary notes ucsc Linear quadratic Taylor polynomials for functions of several variables. c 016, Yonatan Katznelson Finding the extreme (minimum or maximum) values of a function, is
ams/econ 11b supplementary notes ucsc Linear quadratic Taylor polynomials for functions of several variables. c 016, Yonatan Katznelson Finding the extreme (minimum or maximum) values of a function, is
A Short SVM (Support Vector Machine) Tutorial
 A Short SVM (Support Vector Machine) Tutorial j.p.lewis CGIT Lab / IMSC U. Southern California version 0.zz dec 004 This tutorial assumes you are familiar with linear algebra and equality-constrained optimization/lagrange
A Short SVM (Support Vector Machine) Tutorial j.p.lewis CGIT Lab / IMSC U. Southern California version 0.zz dec 004 This tutorial assumes you are familiar with linear algebra and equality-constrained optimization/lagrange
3.9 LINEAR APPROXIMATION AND THE DERIVATIVE
 158 Chapter Three SHORT-CUTS TO DIFFERENTIATION 39 LINEAR APPROXIMATION AND THE DERIVATIVE The Tangent Line Approximation When we zoom in on the graph of a differentiable function, it looks like a straight
158 Chapter Three SHORT-CUTS TO DIFFERENTIATION 39 LINEAR APPROXIMATION AND THE DERIVATIVE The Tangent Line Approximation When we zoom in on the graph of a differentiable function, it looks like a straight
MA 323 Geometric Modelling Course Notes: Day 10 Higher Order Polynomial Curves
 MA 323 Geometric Modelling Course Notes: Day 10 Higher Order Polynomial Curves David L. Finn December 14th, 2004 Yesterday, we introduced quintic Hermite curves as a higher order variant of cubic Hermite
MA 323 Geometric Modelling Course Notes: Day 10 Higher Order Polynomial Curves David L. Finn December 14th, 2004 Yesterday, we introduced quintic Hermite curves as a higher order variant of cubic Hermite
Optimal Control Techniques for Dynamic Walking
 Optimal Control Techniques for Dynamic Walking Optimization in Robotics & Biomechanics IWR, University of Heidelberg Presentation partly based on slides by Sebastian Sager, Moritz Diehl and Peter Riede
Optimal Control Techniques for Dynamic Walking Optimization in Robotics & Biomechanics IWR, University of Heidelberg Presentation partly based on slides by Sebastian Sager, Moritz Diehl and Peter Riede
College Algebra Extra Credit Worksheet
 College Algebra Extra Credit Worksheet Fall 011 Math W1003 (3) Corrin Clarkson Due: Thursday, October 0 th, 011 1 Instructions Each section of this extra credit work sheet is broken into three parts. The
College Algebra Extra Credit Worksheet Fall 011 Math W1003 (3) Corrin Clarkson Due: Thursday, October 0 th, 011 1 Instructions Each section of this extra credit work sheet is broken into three parts. The
MATH 51: MATLAB HOMEWORK 3
 MATH 5: MATLAB HOMEWORK Experimental data generally suffers from imprecision, though frequently one can predict how data should behave by graphing results collected from experiments. For instance, suppose
MATH 5: MATLAB HOMEWORK Experimental data generally suffers from imprecision, though frequently one can predict how data should behave by graphing results collected from experiments. For instance, suppose
Introduction to optimization methods and line search
 Introduction to optimization methods and line search Jussi Hakanen Post-doctoral researcher jussi.hakanen@jyu.fi How to find optimal solutions? Trial and error widely used in practice, not efficient and
Introduction to optimization methods and line search Jussi Hakanen Post-doctoral researcher jussi.hakanen@jyu.fi How to find optimal solutions? Trial and error widely used in practice, not efficient and
Lesson 19. Opening Discussion
 Opening Discussion 1. Think about the forms of the quadratic equations you ve written throughout this module. We have gone from vertex form to standard form and from factored form to standard form. Draw
Opening Discussion 1. Think about the forms of the quadratic equations you ve written throughout this module. We have gone from vertex form to standard form and from factored form to standard form. Draw
MAT128A: Numerical Analysis Lecture One: Course Logistics and What is Numerical Analysis?
 MAT128A: Numerical Analysis Lecture One: Course Logistics and What is Numerical Analysis? September 26, 2018 Lecture 1 September 26, 2018 1 / 19 Course Logistics My contact information: James Bremer Email:
MAT128A: Numerical Analysis Lecture One: Course Logistics and What is Numerical Analysis? September 26, 2018 Lecture 1 September 26, 2018 1 / 19 Course Logistics My contact information: James Bremer Email:
Math 4 quiz review October 27, 2016 Polynomial functions: review page 1 Quadratic and Polynomial functions: Quiz review
 October 27, 2016 Polynomial functions: review page 1 Quadratic and Polynomial functions: Quiz review Topic outline Quadratic functions Quadratic function formulas: you should be able to convert between
October 27, 2016 Polynomial functions: review page 1 Quadratic and Polynomial functions: Quiz review Topic outline Quadratic functions Quadratic function formulas: you should be able to convert between
4.3, Math 1410 Name: And now for something completely different... Well, not really.
 4.3, Math 1410 Name: And now for something completely different... Well, not really. How derivatives affect the shape of a graph. Please allow me to offer some explanation as to why the first couple parts
4.3, Math 1410 Name: And now for something completely different... Well, not really. How derivatives affect the shape of a graph. Please allow me to offer some explanation as to why the first couple parts
Polynomial Approximation and Interpolation Chapter 4
 4.4 LAGRANGE POLYNOMIALS The direct fit polynomial presented in Section 4.3, while quite straightforward in principle, has several disadvantages. It requires a considerable amount of effort to solve the
4.4 LAGRANGE POLYNOMIALS The direct fit polynomial presented in Section 4.3, while quite straightforward in principle, has several disadvantages. It requires a considerable amount of effort to solve the
Introduction to Algorithms / Algorithms I Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Approximation algorithms Date: 11/18/14
 600.363 Introduction to Algorithms / 600.463 Algorithms I Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Approximation algorithms Date: 11/18/14 23.1 Introduction We spent last week proving that for certain problems,
600.363 Introduction to Algorithms / 600.463 Algorithms I Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Approximation algorithms Date: 11/18/14 23.1 Introduction We spent last week proving that for certain problems,
ME 261: Numerical Analysis Lecture-12: Numerical Interpolation
 1 ME 261: Numerical Analysis Lecture-12: Numerical Interpolation Md. Tanver Hossain Department of Mechanical Engineering, BUET http://tantusher.buet.ac.bd 2 Inverse Interpolation Problem : Given a table
1 ME 261: Numerical Analysis Lecture-12: Numerical Interpolation Md. Tanver Hossain Department of Mechanical Engineering, BUET http://tantusher.buet.ac.bd 2 Inverse Interpolation Problem : Given a table
Kai Hormann, N. Sukumar. Generalized Barycentric Coordinates in Computer Graphics and Computational Mechanics
 Kai Hormann, N. Sukumar Generalized Barycentric Coordinates in Computer Graphics and Computational Mechanics Contents Chapter 1 Multi-Sided Patches via Barycentric Coordinates 1 Scott Schaefer 1.1 INTRODUCTION
Kai Hormann, N. Sukumar Generalized Barycentric Coordinates in Computer Graphics and Computational Mechanics Contents Chapter 1 Multi-Sided Patches via Barycentric Coordinates 1 Scott Schaefer 1.1 INTRODUCTION
Natural Numbers and Integers. Big Ideas in Numerical Methods. Overflow. Real Numbers 29/07/2011. Taking some ideas from NM course a little further
 Natural Numbers and Integers Big Ideas in Numerical Methods MEI Conference 2011 Natural numbers can be in the range [0, 2 32 1]. These are known in computing as unsigned int. Numbers in the range [ (2
Natural Numbers and Integers Big Ideas in Numerical Methods MEI Conference 2011 Natural numbers can be in the range [0, 2 32 1]. These are known in computing as unsigned int. Numbers in the range [ (2
1. Practice the use of the C ++ repetition constructs of for, while, and do-while. 2. Use computer-generated random numbers.
 1 Purpose This lab illustrates the use of looping structures by introducing a class of programming problems called numerical algorithms. 1. Practice the use of the C ++ repetition constructs of for, while,
1 Purpose This lab illustrates the use of looping structures by introducing a class of programming problems called numerical algorithms. 1. Practice the use of the C ++ repetition constructs of for, while,
4.3 Finding Local Extreme Values: First and Second Derivatives
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 2914: Calculus I Dr. Marcel B. Finan 4.3 Finding Local Extreme Values: First and Second Derivatives Recall that a function f(x) is said to be increasing (respectively decreasing)
Arkansas Tech University MATH 2914: Calculus I Dr. Marcel B. Finan 4.3 Finding Local Extreme Values: First and Second Derivatives Recall that a function f(x) is said to be increasing (respectively decreasing)
Evaluating the polynomial at a point
 Evaluating the polynomial at a point Recall that we have a data structure for each piecewise polynomial (linear, quadratic, cubic and cubic Hermite). We have a routine that sets evenly spaced interpolation
Evaluating the polynomial at a point Recall that we have a data structure for each piecewise polynomial (linear, quadratic, cubic and cubic Hermite). We have a routine that sets evenly spaced interpolation
Appendix A Using a Graphing Calculator. Section 4: The CALCULATE Menu
 Appendix A Using a Graphing Calculator Section 4: The CALCULATE Menu The CALC menu provides access to many features that will be regularly used in the class. value returns a single y value when the user
Appendix A Using a Graphing Calculator Section 4: The CALCULATE Menu The CALC menu provides access to many features that will be regularly used in the class. value returns a single y value when the user
The goal is the definition of points with numbers and primitives with equations or functions. The definition of points with numbers requires a
 The goal is the definition of points with numbers and primitives with equations or functions. The definition of points with numbers requires a coordinate system and then the measuring of the point with
The goal is the definition of points with numbers and primitives with equations or functions. The definition of points with numbers requires a coordinate system and then the measuring of the point with
The simplest quadratic function we can have is y = x 2, sketched below.
 Name: LESSON 6-8 COMPLETING THE SQUARE AND SHIFTING PARABOLAS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Date: Parabolas, and graphs more generall, can be moved horizontall and verticall b simple manipulations of their equations.
Name: LESSON 6-8 COMPLETING THE SQUARE AND SHIFTING PARABOLAS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Date: Parabolas, and graphs more generall, can be moved horizontall and verticall b simple manipulations of their equations.
An introduction to plotting data
 An introduction to plotting data Eric D. Black California Institute of Technology February 25, 2014 1 Introduction Plotting data is one of the essential skills every scientist must have. We use it on a
An introduction to plotting data Eric D. Black California Institute of Technology February 25, 2014 1 Introduction Plotting data is one of the essential skills every scientist must have. We use it on a
30. Constrained Optimization
 30. Constrained Optimization The graph of z = f(x, y) is represented by a surface in R 3. Normally, x and y are chosen independently of one another so that one may roam over the entire surface of f (within
30. Constrained Optimization The graph of z = f(x, y) is represented by a surface in R 3. Normally, x and y are chosen independently of one another so that one may roam over the entire surface of f (within
Fall CSCI 420: Computer Graphics. 4.2 Splines. Hao Li.
 Fall 2014 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 4.2 Splines Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Roller coaster Next programming assignment involves creating a 3D roller coaster animation We must model the 3D curve
Fall 2014 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 4.2 Splines Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Roller coaster Next programming assignment involves creating a 3D roller coaster animation We must model the 3D curve
Limits and Derivatives (Review of Math 249 or 251)
 Chapter 3 Limits and Derivatives (Review of Math 249 or 251) 3.1 Overview This is the first of two chapters reviewing material from calculus; its and derivatives are discussed in this chapter, and integrals
Chapter 3 Limits and Derivatives (Review of Math 249 or 251) 3.1 Overview This is the first of two chapters reviewing material from calculus; its and derivatives are discussed in this chapter, and integrals
8 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation
 Applied Math Notes by R. J. LeVeque 8 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation 8. Pitfalls of high order interpolation Suppose we know the value of a function at several points on an interval and we wish to
Applied Math Notes by R. J. LeVeque 8 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation 8. Pitfalls of high order interpolation Suppose we know the value of a function at several points on an interval and we wish to
Interpolation. TANA09 Lecture 7. Error analysis for linear interpolation. Linear Interpolation. Suppose we have a table x x 1 x 2...
 TANA9 Lecture 7 Interpolation Suppose we have a table x x x... x n+ Interpolation Introduction. Polynomials. Error estimates. Runge s phenomena. Application - Equation solving. Spline functions and interpolation.
TANA9 Lecture 7 Interpolation Suppose we have a table x x x... x n+ Interpolation Introduction. Polynomials. Error estimates. Runge s phenomena. Application - Equation solving. Spline functions and interpolation.
Contents. Hilary Term. Summary of Numerical Analysis for this term. Sources of error in numerical calculation. Solving Problems
 Contents Hilary Term 1 Root Finding 4 11 Bracketing and Bisection 5 111 Finding the root numerically 5 112 Pseudo BRACKET code 7 113 Drawbacks 8 114 Tips for success with Bracketing & Bisection 9 115 Virtues
Contents Hilary Term 1 Root Finding 4 11 Bracketing and Bisection 5 111 Finding the root numerically 5 112 Pseudo BRACKET code 7 113 Drawbacks 8 114 Tips for success with Bracketing & Bisection 9 115 Virtues
Generalised Mean Averaging Interpolation by Discrete Cubic Splines
 Publ. RIMS, Kyoto Univ. 30 (1994), 89-95 Generalised Mean Averaging Interpolation by Discrete Cubic Splines By Manjulata SHRIVASTAVA* Abstract The aim of this work is to introduce for a discrete function,
Publ. RIMS, Kyoto Univ. 30 (1994), 89-95 Generalised Mean Averaging Interpolation by Discrete Cubic Splines By Manjulata SHRIVASTAVA* Abstract The aim of this work is to introduce for a discrete function,
UNIT 1: NUMBER LINES, INTERVALS, AND SETS
 ALGEBRA II CURRICULUM OUTLINE 2011-2012 OVERVIEW: 1. Numbers, Lines, Intervals and Sets 2. Algebraic Manipulation: Rational Expressions and Exponents 3. Radicals and Radical Equations 4. Function Basics
ALGEBRA II CURRICULUM OUTLINE 2011-2012 OVERVIEW: 1. Numbers, Lines, Intervals and Sets 2. Algebraic Manipulation: Rational Expressions and Exponents 3. Radicals and Radical Equations 4. Function Basics
/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Approximation algorithms Date: 11/27/18
 601.433/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Approximation algorithms Date: 11/27/18 22.1 Introduction We spent the last two lectures proving that for certain problems, we can
601.433/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Approximation algorithms Date: 11/27/18 22.1 Introduction We spent the last two lectures proving that for certain problems, we can
Interpolation and Splines
 Interpolation and Splines Anna Gryboś October 23, 27 1 Problem setting Many of physical phenomenona are described by the functions that we don t know exactly. Often we can calculate or measure the values
Interpolation and Splines Anna Gryboś October 23, 27 1 Problem setting Many of physical phenomenona are described by the functions that we don t know exactly. Often we can calculate or measure the values
Exam in Calculus. Wednesday June 1st First Year at The TEK-NAT Faculty and Health Faculty
 Exam in Calculus Wednesday June 1st 211 First Year at The TEK-NAT Faculty and Health Faculty The present exam consists of 7 numbered pages with a total of 12 exercises. It is allowed to use books, notes,
Exam in Calculus Wednesday June 1st 211 First Year at The TEK-NAT Faculty and Health Faculty The present exam consists of 7 numbered pages with a total of 12 exercises. It is allowed to use books, notes,
February 8 th February 12 th. Unit 6: Polynomials & Introduction to Quadratics
 Algebra I February 8 th February 12 th Unit 6: Polynomials & Introduction to Quadratics Jump Start 1) Use the elimination method to solve the system of equations below. x + y = 2 3x + y = 8 2) Solve: 13
Algebra I February 8 th February 12 th Unit 6: Polynomials & Introduction to Quadratics Jump Start 1) Use the elimination method to solve the system of equations below. x + y = 2 3x + y = 8 2) Solve: 13
a) y = x 3 + 3x 2 2 b) = UNIT 4 CURVE SKETCHING 4.1 INCREASING AND DECREASING FUNCTIONS
 UNIT 4 CURVE SKETCHING 4.1 INCREASING AND DECREASING FUNCTIONS We read graphs as we read sentences: left to right. Plainly speaking, as we scan the function from left to right, the function is said to
UNIT 4 CURVE SKETCHING 4.1 INCREASING AND DECREASING FUNCTIONS We read graphs as we read sentences: left to right. Plainly speaking, as we scan the function from left to right, the function is said to
Polynomial Functions Graphing Investigation Unit 3 Part B Day 1. Graph 1: y = (x 1) Graph 2: y = (x 1)(x + 2) Graph 3: y =(x 1)(x + 2)(x 3)
 Part I: Polynomial Functions when a = 1 Directions: Polynomial Functions Graphing Investigation Unit 3 Part B Day 1 1. For each set of factors, graph the zeros first, then use your calculator to determine
Part I: Polynomial Functions when a = 1 Directions: Polynomial Functions Graphing Investigation Unit 3 Part B Day 1 1. For each set of factors, graph the zeros first, then use your calculator to determine
6. Find the equation of the plane that passes through the point (-1,2,1) and contains the line x = y = z.
 Week 1 Worksheet Sections from Thomas 13 th edition: 12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 13.1 1. A plane is a set of points that satisfies an equation of the form c 1 x + c 2 y + c 3 z = c 4. (a) Find any three distinct
Week 1 Worksheet Sections from Thomas 13 th edition: 12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 13.1 1. A plane is a set of points that satisfies an equation of the form c 1 x + c 2 y + c 3 z = c 4. (a) Find any three distinct
Consider functions such that then satisfies these properties: So is represented by the cubic polynomials on on and on.
 1 of 9 3/1/2006 2:28 PM ne previo Next: Trigonometric Interpolation Up: Spline Interpolation Previous: Piecewise Linear Case Cubic Splines A piece-wise technique which is very popular. Recall the philosophy
1 of 9 3/1/2006 2:28 PM ne previo Next: Trigonometric Interpolation Up: Spline Interpolation Previous: Piecewise Linear Case Cubic Splines A piece-wise technique which is very popular. Recall the philosophy
Module 4 : Solving Linear Algebraic Equations Section 11 Appendix C: Steepest Descent / Gradient Search Method
 Module 4 : Solving Linear Algebraic Equations Section 11 Appendix C: Steepest Descent / Gradient Search Method 11 Appendix C: Steepest Descent / Gradient Search Method In the module on Problem Discretization
Module 4 : Solving Linear Algebraic Equations Section 11 Appendix C: Steepest Descent / Gradient Search Method 11 Appendix C: Steepest Descent / Gradient Search Method In the module on Problem Discretization
Tangent line problems
 You will find lots of practice problems and homework problems that simply ask you to differentiate. The following examples are to illustrate some of the types of tangent line problems that you may come
You will find lots of practice problems and homework problems that simply ask you to differentiate. The following examples are to illustrate some of the types of tangent line problems that you may come
MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS. MEI conference University of Hertfordshire June C3 COURSEWORK
 MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS MEI conference University of Hertfordshire June 29 2009 C3 COURSEWORK What is this coursework designed to do and how do we prepare students for it? Presenter: Val Hanrahan The
MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS MEI conference University of Hertfordshire June 29 2009 C3 COURSEWORK What is this coursework designed to do and how do we prepare students for it? Presenter: Val Hanrahan The
GEOMETRY APPLICATIONS
 GEOMETRY APPLICATIONS Chapter 3: Parallel & Perpendicular Lines Name: Teacher: Pd: 0 Table of Contents DAY 1: (Ch. 3-1 & 3-2) SWBAT: Identify parallel, perpendicular, and skew lines. Identify the angles
GEOMETRY APPLICATIONS Chapter 3: Parallel & Perpendicular Lines Name: Teacher: Pd: 0 Table of Contents DAY 1: (Ch. 3-1 & 3-2) SWBAT: Identify parallel, perpendicular, and skew lines. Identify the angles
3.7. Vertex and tangent
 3.7. Vertex and tangent Example 1. At the right we have drawn the graph of the cubic polynomial f(x) = x 2 (3 x). Notice how the structure of the graph matches the form of the algebraic expression. The
3.7. Vertex and tangent Example 1. At the right we have drawn the graph of the cubic polynomial f(x) = x 2 (3 x). Notice how the structure of the graph matches the form of the algebraic expression. The
1 Trajectories. Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733. Figure 1: Robot control system.
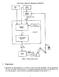 Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
Unit 1 Algebraic Functions and Graphs
 Algebra 2 Unit 1 Algebraic Functions and Graphs Name: Unit 1 Day 1: Function Notation Today we are: Using Function Notation We are successful when: We can Use function notation to evaluate a function This
Algebra 2 Unit 1 Algebraic Functions and Graphs Name: Unit 1 Day 1: Function Notation Today we are: Using Function Notation We are successful when: We can Use function notation to evaluate a function This
an interpolating polynomial P (x) for f(x) Issues: how to find, represent, compute P (x); errors?
 INTERPOLATION Background Polynomial Approximation Problem: given f(x) C[a, b], find P n (x) = a 0 + a 1 x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n with P n (x) close to f(x) for x [a, b]. Motivations: f(x) might be difficult
INTERPOLATION Background Polynomial Approximation Problem: given f(x) C[a, b], find P n (x) = a 0 + a 1 x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n with P n (x) close to f(x) for x [a, b]. Motivations: f(x) might be difficult
MATH Lagrange multipliers in 3 variables Fall 2016
 MATH 20550 Lagrange multipliers in 3 variables Fall 2016 1. The one constraint they The problem is to find the extrema of a function f(x, y, z) subject to the constraint g(x, y, z) = c. The book gives
MATH 20550 Lagrange multipliers in 3 variables Fall 2016 1. The one constraint they The problem is to find the extrema of a function f(x, y, z) subject to the constraint g(x, y, z) = c. The book gives
CS321 Introduction To Numerical Methods
 CS3 Introduction To Numerical Methods Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington KY 456-46 - - Table of Contents Errors and Number Representations 3 Error Types
CS3 Introduction To Numerical Methods Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington KY 456-46 - - Table of Contents Errors and Number Representations 3 Error Types
Vertex Cover Approximations
 CS124 Lecture 20 Heuristics can be useful in practice, but sometimes we would like to have guarantees. Approximation algorithms give guarantees. It is worth keeping in mind that sometimes approximation
CS124 Lecture 20 Heuristics can be useful in practice, but sometimes we would like to have guarantees. Approximation algorithms give guarantees. It is worth keeping in mind that sometimes approximation
Section 3.2 Properties of a Function s Graph
 Section 3. Properties of a Function s Graph Objectives Find the intercepts of a function given its formula. Given the graph of a function, identify the domain and range of the function. Approximate relative
Section 3. Properties of a Function s Graph Objectives Find the intercepts of a function given its formula. Given the graph of a function, identify the domain and range of the function. Approximate relative
99 International Journal of Engineering, Science and Mathematics
 Journal Homepage: Applications of cubic splines in the numerical solution of polynomials Najmuddin Ahmad 1 and Khan Farah Deeba 2 Department of Mathematics Integral University Lucknow Abstract: In this
Journal Homepage: Applications of cubic splines in the numerical solution of polynomials Najmuddin Ahmad 1 and Khan Farah Deeba 2 Department of Mathematics Integral University Lucknow Abstract: In this
The following information is for reviewing the material since Exam 3:
 Outcomes List for Math 121 Calculus I Fall 2010-2011 General Information: The purpose of this Outcomes List is to give you a concrete summary of the material you should know, and the skills you should
Outcomes List for Math 121 Calculus I Fall 2010-2011 General Information: The purpose of this Outcomes List is to give you a concrete summary of the material you should know, and the skills you should
lecture 10: B-Splines
 9 lecture : -Splines -Splines: a basis for splines Throughout our discussion of standard polynomial interpolation, we viewed P n as a linear space of dimension n +, and then expressed the unique interpolating
9 lecture : -Splines -Splines: a basis for splines Throughout our discussion of standard polynomial interpolation, we viewed P n as a linear space of dimension n +, and then expressed the unique interpolating
Unit #3: Quadratic Functions Lesson #13: The Almighty Parabola. Day #1
 Algebra I Unit #3: Quadratic Functions Lesson #13: The Almighty Parabola Name Period Date Day #1 There are some important features about the graphs of quadratic functions we are going to explore over the
Algebra I Unit #3: Quadratic Functions Lesson #13: The Almighty Parabola Name Period Date Day #1 There are some important features about the graphs of quadratic functions we are going to explore over the
Lesson 11 Rational Functions
 Lesson 11 Rational Functions In this lesson, you will embark on a study of rational functions. These may be unlike any function you have ever seen. Rational functions look different because they are in
Lesson 11 Rational Functions In this lesson, you will embark on a study of rational functions. These may be unlike any function you have ever seen. Rational functions look different because they are in
A-SSE.1.1, A-SSE.1.2-
 Putnam County Schools Curriculum Map Algebra 1 2016-2017 Module: 4 Quadratic and Exponential Functions Instructional Window: January 9-February 17 Assessment Window: February 20 March 3 MAFS Standards
Putnam County Schools Curriculum Map Algebra 1 2016-2017 Module: 4 Quadratic and Exponential Functions Instructional Window: January 9-February 17 Assessment Window: February 20 March 3 MAFS Standards
What is Multigrid? They have been extended to solve a wide variety of other problems, linear and nonlinear.
 AMSC 600/CMSC 760 Fall 2007 Solution of Sparse Linear Systems Multigrid, Part 1 Dianne P. O Leary c 2006, 2007 What is Multigrid? Originally, multigrid algorithms were proposed as an iterative method to
AMSC 600/CMSC 760 Fall 2007 Solution of Sparse Linear Systems Multigrid, Part 1 Dianne P. O Leary c 2006, 2007 What is Multigrid? Originally, multigrid algorithms were proposed as an iterative method to
Solution Methods Numerical Algorithms
 Solution Methods Numerical Algorithms Evelien van der Hurk DTU Managment Engineering Class Exercises From Last Time 2 DTU Management Engineering 42111: Static and Dynamic Optimization (6) 09/10/2017 Class
Solution Methods Numerical Algorithms Evelien van der Hurk DTU Managment Engineering Class Exercises From Last Time 2 DTU Management Engineering 42111: Static and Dynamic Optimization (6) 09/10/2017 Class
Final Exam Review Algebra Semester 1
 Final Exam Review Algebra 015-016 Semester 1 Name: Module 1 Find the inverse of each function. 1. f x 10 4x. g x 15x 10 Use compositions to check if the two functions are inverses. 3. s x 7 x and t(x)
Final Exam Review Algebra 015-016 Semester 1 Name: Module 1 Find the inverse of each function. 1. f x 10 4x. g x 15x 10 Use compositions to check if the two functions are inverses. 3. s x 7 x and t(x)
In this course we will need a set of techniques to represent curves and surfaces in 2-d and 3-d. Some reasons for this include
 Parametric Curves and Surfaces In this course we will need a set of techniques to represent curves and surfaces in 2-d and 3-d. Some reasons for this include Describing curves in space that objects move
Parametric Curves and Surfaces In this course we will need a set of techniques to represent curves and surfaces in 2-d and 3-d. Some reasons for this include Describing curves in space that objects move
3.2 - Interpolation and Lagrange Polynomials
 3. - Interpolation and Lagrange Polynomials. Polynomial Interpolation: Problem: Givenn pairs of data points x i, y i,wherey i fx i, i 0,,...,n for some function fx, we want to find a polynomial P x of
3. - Interpolation and Lagrange Polynomials. Polynomial Interpolation: Problem: Givenn pairs of data points x i, y i,wherey i fx i, i 0,,...,n for some function fx, we want to find a polynomial P x of
Chapter One. Numerical Algorithms
 Chapter One Numerical Algorithms The word algorithm derives from the name of the Persian mathematician (Abu Ja far Muhammad ibn Musa) Al- Khwarizmi who lived from about 790 CE to about 840 CE. He wrote
Chapter One Numerical Algorithms The word algorithm derives from the name of the Persian mathematician (Abu Ja far Muhammad ibn Musa) Al- Khwarizmi who lived from about 790 CE to about 840 CE. He wrote
