University of Sioux Falls. MATH 303 Foundations of Geometry
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Taylor
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Sioux Falls MATH 303 Foundations of Geometry Concepts addressed: Geometry Texts Cited: Hvidsten, Michael, Exploring Geometry, New York: McGraw-Hill, Kay, David, College Geometry: A Discovery Approach, 2 nd edition, Boston: Addison Wesley Longman, Solve problems using relationships of parts of geometric figures (e.g., medians of triangles, inscribed angles in circles). Angles (see Hvidsten section 2.1 and Kay sections ) In angle measure, 180 is equivalent to 2π radians. Supplementary angles have measures that sum to 180. Complementary angles have measures that sum to 90. Vertical angles formed by two intersecting lines are congruent, and thus have the same measure. Every angle can be bisected, forming two congruent angles, each with half the measure of the original. Trisection of an angle by purely geometric methods is not possible in general. Triangles (see Hvidsten sections and Kay sections 1.1, 3.1, 3.4) In Euclidean geometry, the angle sum of a triangle is 180. (The generalization of this theorem to neutral geometry is the Saccheri-Legendre Theorem, which states that the angle sum of a triangle cannot be greater than 180.) The Exterior Angle Theorem states that an exterior angle of a triangle will have a measure greater than each of the two opposite interior angles. From the diagram below, this would mean that m D > m A and m D > m B. B A C D
2 In an isosceles triangle, the base angles are congruent. A median of a triangle is a segment joining a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side. The three medians of a triangle intersect concurrently at a point called the centroid, as illustrated below. The centroid is the triangle s center of mass, when the interior of the triangle is viewed as a planar lamina with uniform density. The circumcenter of a triangle is the point equidistant from all three of its vertices, as shown below. The circumcenter also turns out to be the concurrent intersection of the perpendicular bisectors of the three sides of the triangle. Notice from the second diagram that the circumcenter is not necessarily located in the interior of the triangle.
3 The incenter of a triangle is the concurrent intersection of the bisectors of the three vertex angles. The largest circle that can be inscribed in the triangle has as its center the triangle s incenter. The orthocenter of a triangle is the concurrent intersection of the three altitudes of the triangle. Again, note that the orthocenter is not necessarily located in the interior of the triangle. Circles (see Hvidsten section 2.6 and Kay section 3.8, 4.5) Given any three noncolinear points in the plane, there exists a unique circle on which they are incident. A chord is a segment whose endpoints lie on a circle. A diameter is a chord that passes through the center of the circle. The center of the circle is the midpoint of every diameter.
4 An angle whose vertex is located at the center of a circle is called a central angle. An angle whose vertex lies on the circle (and whose sides pass through the interior of the circle) is called an inscribed angle. The arc whose endpoints are the endpoints of a chord or the points at which the sides of an angle intersect the circle is called an intercepted or subtended arc. In a circle of radius r, a central angle of T radians intercepts an arc of length rt. The measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of the central angle that 1 subtends the same arc. In the diagram below, m COD = m CBD. 2 The perpendicular bisector of any chord of a circle passes through the center. The converse is also true: a line passing through the center of a circle that is perpendicular to a chord will also bisect that chord. Two chords have equal length if and only if they are equidistant from the center of the circle. A tangent to a circle is a line that intersects the circle at exactly one point. A radius and a tangent that intersect at the point of tangency will always be perpendicular to each other. In the diagram below, this would imply that OA PA and OB PB. For every point P external to a circle c, there exist exactly two tangents to c passing through P. In this context, P is called a pole. If A and B are the points of tangency for the two tangent lines, then PA PB.
5 Polygons (see Kay section 4.4) The angle sum (in degrees) of any convex n-gon is 180(n 2). This elementary theorem is easily verified geometrically by subdividing the n-gon into n 2 triangles (by inserting segments that connect nonadjacent vertices). 2. Solve problems using relationships among 2-dimensional geometric figures (e.g., congruence, similarity). Congruence Among Triangles (see Hvidsten section 2.2 and Kay sections 3.1, 3.3, 3.6) Two triangles are congruent if they meet any (and consequently all) of the following criteria: SAS, SSS, ASA, and AAS. (Note that AAA and SSA are not congruence criteria!) If the two triangles are known to be right triangles, then one pair of corresponding angles (one A ) is already known to be congruent. Similarity Among Triangles (see Hvidsten section 2.5 and Kay section 4.3) Similar planar figures (including triangles) have congruent corresponding angles. All corresponding lengths associated with similar planar figures (including side lengths, diagonal lengths, etc.) are proportional.
6 3. Solve problems using relationships among 3-dimensional geometric figures (e.g., congruence, similarity). (see Kay sections ) Note that formulas for volume and surface area of common three-dimensional objects are provided within the Praxis exam. The only notable omission may be the surface area of a right circular cylinder (with the ends included). This formula is Similarity among three-dimensional figures is analogous to the case for twodimensional figures. Shape and angles will be the same, while lengths will be scaled proportionally. Do note, however, that if two figures are geometrically similar with corresponding lengths proportional with a scaling factor of l, then the surface areas will be scaled by a factor of l 2, and the volumes will be scaled by a factor of l 3. Example: Suppose two right circular cones are geometrically similar, one with height 5 cm and with a base of radius 2 cm, the other with height 15 cm. The latter cone will then have a base of radius 6 cm. Furthermore, the larger cone will have a surface area 9 times that of the smaller cone (9 = 3 2 ), and will have a volume 27 times that of the smaller cone (27 = 3 3 ). Also note that the faces and other selected parts of three-dimensional figures are themselves two-dimensional figures (right triangles, trapezoids, etc.), and thus subject to the properties listed elsewhere on this sheet. Culminating Example: Here is a problem that incorporates principles from several parts of this review sheet. In the diagram below, suppose that BC is a diameter of a circle of radius 4. Suppose further that BC OD and OG BF, and that BJ = 1. Find the length of OI.
7 Solution: Since BFC intercepts a semicircle, BFC must be a right angle. We also note that since OG BF, OG must bisect the chord BF. Since BJ = 1, we may conclude that BF = 2. Therefore, BFC is a right triangle for which one leg has length 2 and the hypotenuse has length 8 (twice the radius). The third side, FC, must have length 2 15, using the Pythagorean Theorem. We now observe that IOC is similar to BFC, as both are right triangles (we re given BC OD ) and both share a common angle, OCI. The leg OC, which is given to have length 4, corresponds to the leg FC from BFC. Hence we may set up and solve the proportion: BF = FC IO OC 2 IO = IO =. 15
SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal)
 1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties
 Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Postulates, Theorems, and Corollaries. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 10 Similarity
 Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
MANHATTAN HUNTER SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY CURRICULUM
 COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
Unit Number of Days Dates. 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/ Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9
 8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
Theorems & Postulates Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 30-60 -90 Triangle In a 30-60 -90 triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is two times the length of the shorter leg, and the length of the longer leg is the length
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 30-60 -90 Triangle In a 30-60 -90 triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is two times the length of the shorter leg, and the length of the longer leg is the length
Geometry. Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section.
 Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Madison County Schools Suggested Geometry Pacing Guide,
 Madison County Schools Suggested Geometry Pacing Guide, 2016 2017 Domain Abbreviation Congruence G-CO Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry G-SRT Modeling with Geometry *G-MG Geometric Measurement
Madison County Schools Suggested Geometry Pacing Guide, 2016 2017 Domain Abbreviation Congruence G-CO Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry G-SRT Modeling with Geometry *G-MG Geometric Measurement
DEFINITIONS. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle.
 DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
Geometry. Geometry. Domain Cluster Standard. Congruence (G CO)
 Domain Cluster Standard 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Domain Cluster Standard 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Course: Geometry PAP Prosper ISD Course Map Grade Level: Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block Days. Unit Title
 Unit Title Unit 1: Geometric Structure Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block 1 st 9 weeks Description of What Students will Focus on on the terms and statements that are the basis for geometry. able to use terms
Unit Title Unit 1: Geometric Structure Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block 1 st 9 weeks Description of What Students will Focus on on the terms and statements that are the basis for geometry. able to use terms
Perimeter. Area. Surface Area. Volume. Circle (circumference) C = 2πr. Square. Rectangle. Triangle. Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh
 Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Pearson Mathematics Geometry Common Core 2015
 A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Common Core 2015 to the Common Core State Standards for Bid Category 13-040-10 A Correlation of Pearson, Common Core Pearson Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment
A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Common Core 2015 to the Common Core State Standards for Bid Category 13-040-10 A Correlation of Pearson, Common Core Pearson Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide
 Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Geometry 2015 correlated to the New York Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Geometry
 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Geometry 2015 correlated to the New York Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Geometry Standards for Mathematical Practice SMP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Geometry 2015 correlated to the New York Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Geometry Standards for Mathematical Practice SMP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere
MADISON ACADEMY GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE
 MADISON ACADEMY GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE 2018-2019 Standards (ACT included) ALCOS#1 Know the precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined
MADISON ACADEMY GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE 2018-2019 Standards (ACT included) ALCOS#1 Know the precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined
Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards. Geometry. Table of Contents. Geometry 1 Statistics and Probability 8
 Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards Geometry Table of Contents Geometry 1 Statistics and Probability 8 Geometry Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions
Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards Geometry Table of Contents Geometry 1 Statistics and Probability 8 Geometry Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions
Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments
 Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments Concept 9 Parallel Lines and Triangles (Section 3.5) ANGLE Classifications Acute: Obtuse: Right: SIDE Classifications Scalene: Isosceles:
Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments Concept 9 Parallel Lines and Triangles (Section 3.5) ANGLE Classifications Acute: Obtuse: Right: SIDE Classifications Scalene: Isosceles:
If B is the If two angles are
 If If B is between A and C, then 1 2 If P is in the interior of RST, then If B is the If two angles are midpoint of AC, vertical, then then 3 4 If angles are adjacent, then If angles are a linear pair,
If If B is between A and C, then 1 2 If P is in the interior of RST, then If B is the If two angles are midpoint of AC, vertical, then then 3 4 If angles are adjacent, then If angles are a linear pair,
Geometry Practice Questions Semester 1
 Geometry Practice Questions Semester 1 MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1 - Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line,
Geometry Practice Questions Semester 1 MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1 - Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line,
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
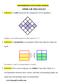 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
Geometry Rules. Triangles:
 Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Test #1: Chapters 1, 2, 3 Test #2: Chapters 4, 7, 9 Test #3: Chapters 5, 6, 8 Test #4: Chapters 10, 11, 12
 Progress Assessments When the standards in each grouping are taught completely the students should take the assessment. Each assessment should be given within 3 days of completing the assigned chapters.
Progress Assessments When the standards in each grouping are taught completely the students should take the assessment. Each assessment should be given within 3 days of completing the assigned chapters.
Standards to Topics. Common Core State Standards 2010 Geometry
 Standards to Topics G-CO.01 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Standards to Topics G-CO.01 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Test Blueprint Dysart Math Geometry #2 Comp. AZ-HS.G-CO CONGRUENCE. 27.9% on Test. # on AP. # on Test. % on Test
 Blueprint AZ-HS.G-CO CONGRUENCE Page 1 27.9 AZ-HS.G-CO.A.1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line,
Blueprint AZ-HS.G-CO CONGRUENCE Page 1 27.9 AZ-HS.G-CO.A.1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line,
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with
 Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
YEAR AT A GLANCE Student Learning Outcomes by Marking Period
 2014-2015 Term 1 Overarching/general themes: Tools to Build and Analyze Points, Lines and Angles Dates Textual References To Demonstrate Proficiency by the End of the Term Students Will : Marking Period
2014-2015 Term 1 Overarching/general themes: Tools to Build and Analyze Points, Lines and Angles Dates Textual References To Demonstrate Proficiency by the End of the Term Students Will : Marking Period
Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist
 3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
GEOMETRY Curriculum Overview
 GEOMETRY Curriculum Overview Semester 1 Semester 2 Unit 1 ( 5 1/2 Weeks) Unit 2 Unit 3 (2 Weeks) Unit 4 (1 1/2 Weeks) Unit 5 (Semester Break Divides Unit) Unit 6 ( 2 Weeks) Unit 7 (7 Weeks) Lines and Angles,
GEOMETRY Curriculum Overview Semester 1 Semester 2 Unit 1 ( 5 1/2 Weeks) Unit 2 Unit 3 (2 Weeks) Unit 4 (1 1/2 Weeks) Unit 5 (Semester Break Divides Unit) Unit 6 ( 2 Weeks) Unit 7 (7 Weeks) Lines and Angles,
2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? Formula: Area of a Trapezoid. 3 Centroid. 4 Midsegment of a triangle
 1 Formula: Area of a Trapezoid 2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? 3 Centroid 4 Midsegment of a triangle 5 Slope formula 6 Point Slope Form of Linear Equation *can
1 Formula: Area of a Trapezoid 2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? 3 Centroid 4 Midsegment of a triangle 5 Slope formula 6 Point Slope Form of Linear Equation *can
Given a rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, or regular polygon, describe the rotations and reflections that carry it onto itself.
 G- CO.1 Identify Definitions Standard 1 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, or line segment, based on the undefined
G- CO.1 Identify Definitions Standard 1 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, or line segment, based on the undefined
Common Core Specifications for Geometry
 1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Geometry Indiana Standards Worktext Correlations
 Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
GEOMETRY is the study of points in space
 CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
Mathematics Standards for High School Geometry
 Mathematics Standards for High School Geometry Geometry is a course required for graduation and course is aligned with the College and Career Ready Standards for Mathematics in High School. Throughout
Mathematics Standards for High School Geometry Geometry is a course required for graduation and course is aligned with the College and Career Ready Standards for Mathematics in High School. Throughout
Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist
 3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
Geometry. Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 G.CO.2. Common Core Institute
 Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
added to equal quantities, their sum is equal. Same holds for congruence.
 Mr. Cheung s Geometry Cheat Sheet Theorem List Version 6.0 Updated 3/14/14 (The following is to be used as a guideline. The rest you need to look up on your own, but hopefully this will help. The original
Mr. Cheung s Geometry Cheat Sheet Theorem List Version 6.0 Updated 3/14/14 (The following is to be used as a guideline. The rest you need to look up on your own, but hopefully this will help. The original
Ganado Unified School District Geometry
 Ganado Unified School District Geometry PACING Guide SY 2016-2017 Timeline & Resources 1st Quarter Unit 1 AZ & ELA Standards Essential Question Learning Goal Vocabulary CC.9-12.G.CO. Transformations and
Ganado Unified School District Geometry PACING Guide SY 2016-2017 Timeline & Resources 1st Quarter Unit 1 AZ & ELA Standards Essential Question Learning Goal Vocabulary CC.9-12.G.CO. Transformations and
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS
 NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
Geometry Geometry Grade Grade Grade
 Grade Grade Grade 6.G.1 Find the area of right triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the
Grade Grade Grade 6.G.1 Find the area of right triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the
Unit 1: Tools of Geometry
 Unit 1: Tools of Geometry Geometry CP Pacing Guide First Nine Weeks Tennessee State Math Standards Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel G.CO.A.1 line, and line segment,
Unit 1: Tools of Geometry Geometry CP Pacing Guide First Nine Weeks Tennessee State Math Standards Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel G.CO.A.1 line, and line segment,
Plane Geometry. Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2011
 lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM ACCELERATED GEOMETRY (June 2014)
 UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
Geometry Common Core State Standard (CCSS) Math
 = ntroduced R=Reinforced/Reviewed HGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY MATH STANDARDS 1 2 3 4 Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line,
= ntroduced R=Reinforced/Reviewed HGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY MATH STANDARDS 1 2 3 4 Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line,
Geometry Curriculum Map
 Geometry Curriculum Map Unit 1 st Quarter Content/Vocabulary Assessment AZ Standards Addressed Essentials of Geometry 1. What are points, lines, and planes? 1. Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 1. Observation
Geometry Curriculum Map Unit 1 st Quarter Content/Vocabulary Assessment AZ Standards Addressed Essentials of Geometry 1. What are points, lines, and planes? 1. Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 1. Observation
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12
 West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12 Unit 1: Basics of Geometry Content Area: Mathematics Course & Grade Level: Basic Geometry, 9 12 Summary and Rationale This unit
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12 Unit 1: Basics of Geometry Content Area: Mathematics Course & Grade Level: Basic Geometry, 9 12 Summary and Rationale This unit
KCAS or Common Core Standards
 Unit Title Tools of Geometry Length of Unit 4 Essential Questions/Learning Targets/Student Objectives 1-1 Make Nets & Drawings of 3-D Figures 1-2 Understand Basic Terms & Postulates 1-3 Find & Compare
Unit Title Tools of Geometry Length of Unit 4 Essential Questions/Learning Targets/Student Objectives 1-1 Make Nets & Drawings of 3-D Figures 1-2 Understand Basic Terms & Postulates 1-3 Find & Compare
Killingly Public Schools. Grades Draft Sept. 2002
 Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Geometry CP Pen Argyl Area High School 2018
 Geometry emphasizes the development of logical thinking as it relates to geometric problems. Topics include using the correct language and notations of geometry, developing inductive and deductive reasoning,
Geometry emphasizes the development of logical thinking as it relates to geometric problems. Topics include using the correct language and notations of geometry, developing inductive and deductive reasoning,
CURRICULUM GUIDE. Honors Geometry
 CURRICULUM GUIDE Honors Geometry This level of Geometry is approached at an accelerated pace. Topics of postulates, theorems and proofs are discussed both traditionally and with a discovery approach. The
CURRICULUM GUIDE Honors Geometry This level of Geometry is approached at an accelerated pace. Topics of postulates, theorems and proofs are discussed both traditionally and with a discovery approach. The
Correlation of Discovering Geometry 5th Edition to Florida State Standards
 Correlation of 5th Edition to Florida State s MAFS content is listed under three headings: Introduced (I), Developed (D), and Applied (A). Developed standards are the focus of the lesson, and are being
Correlation of 5th Edition to Florida State s MAFS content is listed under three headings: Introduced (I), Developed (D), and Applied (A). Developed standards are the focus of the lesson, and are being
Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology Program of Studies TJ Math 1
 Course Description: This course is designed for students who have successfully completed the standards for Honors Algebra I. Students will study geometric topics in depth, with a focus on building critical
Course Description: This course is designed for students who have successfully completed the standards for Honors Algebra I. Students will study geometric topics in depth, with a focus on building critical
Achievement Level Descriptors Geometry
 Achievement Level Descriptors Geometry ALD Stard Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Policy MAFS Students at this level demonstrate a below satisfactory level of success with the challenging Students at this
Achievement Level Descriptors Geometry ALD Stard Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Policy MAFS Students at this level demonstrate a below satisfactory level of success with the challenging Students at this
Grade 9, 10 or 11- Geometry
 Grade 9, 10 or 11- Geometry Strands 1. Congruence, Proof, and Constructions 2. Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry 3. Extending to Three Dimensions 4. Connecting Algebra and Geometry through Coordinates
Grade 9, 10 or 11- Geometry Strands 1. Congruence, Proof, and Constructions 2. Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry 3. Extending to Three Dimensions 4. Connecting Algebra and Geometry through Coordinates
Appendix. Correlation to the High School Geometry Standards of the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
 Appendix Correlation to the High School Geometry Standards of the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics The correlation shows how the activities in Exploring Geometry with The Geometer s Sketchpad
Appendix Correlation to the High School Geometry Standards of the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics The correlation shows how the activities in Exploring Geometry with The Geometer s Sketchpad
, Geometry, Quarter 1
 2017.18, Geometry, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical Proficiency 1.
2017.18, Geometry, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical Proficiency 1.
Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never
 1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
Suggested List of Mathematical Language. Geometry
 Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Geometry GEOMETRY. Congruence
 Geometry Geometry builds on Algebra I concepts and increases students knowledge of shapes and their properties through geometry-based applications, many of which are observable in aspects of everyday life.
Geometry Geometry builds on Algebra I concepts and increases students knowledge of shapes and their properties through geometry-based applications, many of which are observable in aspects of everyday life.
Index COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Symbols & Numerics
 Symbols & Numerics. (dot) character, point representation, 37 symbol, perpendicular lines, 54 // (double forward slash) symbol, parallel lines, 54, 60 : (colon) character, ratio of quantity representation
Symbols & Numerics. (dot) character, point representation, 37 symbol, perpendicular lines, 54 // (double forward slash) symbol, parallel lines, 54, 60 : (colon) character, ratio of quantity representation
GEOMETRY CURRICULUM MAP
 2017-2018 MATHEMATICS GEOMETRY CURRICULUM MAP Department of Curriculum and Instruction RCCSD Congruence Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions Prove geometric theorems Common Core Major Emphasis
2017-2018 MATHEMATICS GEOMETRY CURRICULUM MAP Department of Curriculum and Instruction RCCSD Congruence Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions Prove geometric theorems Common Core Major Emphasis
Geometry/Pre AP Geometry Common Core Standards
 1st Nine Weeks Transformations Transformations *Rotations *Dilation (of figures and lines) *Translation *Flip G.CO.1 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle,
1st Nine Weeks Transformations Transformations *Rotations *Dilation (of figures and lines) *Translation *Flip G.CO.1 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle,
Sequence of Geometry Modules Aligned with the Standards
 Sequence of Geometry Modules Aligned with the Standards Module 1: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Module 2: Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry Module 3: Extending to Three Dimensions Module 4: Connecting
Sequence of Geometry Modules Aligned with the Standards Module 1: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Module 2: Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry Module 3: Extending to Three Dimensions Module 4: Connecting
Pearson Mathematics Geometry
 A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
HS Geometry Mathematics CC
 Course Description This course involves the integration of logical reasoning and spatial visualization skills. It includes a study of deductive proofs and applications from Algebra, an intense study of
Course Description This course involves the integration of logical reasoning and spatial visualization skills. It includes a study of deductive proofs and applications from Algebra, an intense study of
Geometry SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2
 SEMESTER 1 Geometry 1. Geometry Basics 2. Coordinate Geometry a) Transformations, e.g., T(x + a, y + b) 3. Angles 4. Triangles a) Circumcenter 5. Construction a) Copy a segment, angle b) Bisect a segment,
SEMESTER 1 Geometry 1. Geometry Basics 2. Coordinate Geometry a) Transformations, e.g., T(x + a, y + b) 3. Angles 4. Triangles a) Circumcenter 5. Construction a) Copy a segment, angle b) Bisect a segment,
Mathematics Geometry
 Common Core Correlations Mathematics Geometry Please note the following abbreviations found in this document: A=Activity L=Lesson AP=Activity Practice EA=Embedded Assessment GR=Getting Ready BENCHMARK
Common Core Correlations Mathematics Geometry Please note the following abbreviations found in this document: A=Activity L=Lesson AP=Activity Practice EA=Embedded Assessment GR=Getting Ready BENCHMARK
Geometry. Given a rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, or regular polygon, describe the rotations and reflections that carry it onto itself.
 Common Core State for Mathematics High School Following is a correlation of Pearson s Prentice Hall Common Core Geometry 2012 to Common Core State for High School Mathematics. Geometry Congruence G-CO
Common Core State for Mathematics High School Following is a correlation of Pearson s Prentice Hall Common Core Geometry 2012 to Common Core State for High School Mathematics. Geometry Congruence G-CO
Angles. Classification Acute Right Obtuse. Complementary s 2 s whose sum is 90 Supplementary s 2 s whose sum is 180. Angle Addition Postulate
 ngles Classification cute Right Obtuse Complementary s 2 s whose sum is 90 Supplementary s 2 s whose sum is 180 ngle ddition Postulate If the exterior sides of two adj s lie in a line, they are supplementary
ngles Classification cute Right Obtuse Complementary s 2 s whose sum is 90 Supplementary s 2 s whose sum is 180 ngle ddition Postulate If the exterior sides of two adj s lie in a line, they are supplementary
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
2003/2010 ACOS MATHEMATICS CONTENT CORRELATION GEOMETRY 2003 ACOS 2010 ACOS
 CURRENT ALABAMA CONTENT PLACEMENT G.1 Determine the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a second line through a given point. G.2 Justify theorems related to pairs of angles, including angles
CURRENT ALABAMA CONTENT PLACEMENT G.1 Determine the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a second line through a given point. G.2 Justify theorems related to pairs of angles, including angles
GEOMETRY CCR MATH STANDARDS
 CONGRUENCE, PROOF, AND CONSTRUCTIONS M.GHS. M.GHS. M.GHS. GEOMETRY CCR MATH STANDARDS Mathematical Habits of Mind. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them.. Use appropriate tools strategically..
CONGRUENCE, PROOF, AND CONSTRUCTIONS M.GHS. M.GHS. M.GHS. GEOMETRY CCR MATH STANDARDS Mathematical Habits of Mind. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them.. Use appropriate tools strategically..
Segment Addition Postulate: If B is BETWEEN A and C, then AB + BC = AC. If AB + BC = AC, then B is BETWEEN A and C.
 Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
Chapter 6. Sir Migo Mendoza
 Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
U4 Polygon Notes January 11, 2017 Unit 4: Polygons
 Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
Honors Geometry Pacing Guide Honors Geometry Pacing First Nine Weeks
 Unit Topic To recognize points, lines and planes. To be able to recognize and measure segments and angles. To classify angles and name the parts of a degree To recognize collinearity and betweenness of
Unit Topic To recognize points, lines and planes. To be able to recognize and measure segments and angles. To classify angles and name the parts of a degree To recognize collinearity and betweenness of
Geometry I Can Statements I can describe the undefined terms: point, line, and distance along a line in a plane I can describe the undefined terms:
 Geometry I Can Statements I can describe the undefined terms: point, line, and distance along a line in a plane I can describe the undefined terms: point, line, and distance along a line in a plane I can
Geometry I Can Statements I can describe the undefined terms: point, line, and distance along a line in a plane I can describe the undefined terms: point, line, and distance along a line in a plane I can
GEOMETRY. Changes to the original 2010 COS is in red. If it is red and crossed out, it has been moved to another course.
 The Geometry course builds on Algebra I concepts and increases students knowledge of shapes and their properties through geometry-based applications, many of which are observable in aspects of everyday
The Geometry course builds on Algebra I concepts and increases students knowledge of shapes and their properties through geometry-based applications, many of which are observable in aspects of everyday
MATHia Unit MATHia Workspace Overview TEKS
 1 Tools of Geometry Lines, Rays, Segments, and Angles Distances on the Coordinate Plane Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Angle Properties Naming Lines, Rays, Segments, and Angles Working with Measures
1 Tools of Geometry Lines, Rays, Segments, and Angles Distances on the Coordinate Plane Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Angle Properties Naming Lines, Rays, Segments, and Angles Working with Measures
terms, postulates, and notation segment and angle measurement basic constructions
 SEPTEMBER 2008 OCTOBER 2008 geometry terms, postulates, and notation understand how to calculate segment and angle measurements understand how to do basic constructions with a compass and straight edge
SEPTEMBER 2008 OCTOBER 2008 geometry terms, postulates, and notation understand how to calculate segment and angle measurements understand how to do basic constructions with a compass and straight edge
Mathematics High School Geometry
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Standards to Topics. Louisiana Student Standards for Mathematics Geometry
 Standards to Topics GM.G-CO.A.01 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and
Standards to Topics GM.G-CO.A.01 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 Math 121 Fall 2017 - Practice Exam - Chapters 5 & 6 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The simplified form of the ratio 6 inches to 1 foot is 6:1. 2. The triple (20,21,29) is a Pythagorean
Math 121 Fall 2017 - Practice Exam - Chapters 5 & 6 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The simplified form of the ratio 6 inches to 1 foot is 6:1. 2. The triple (20,21,29) is a Pythagorean
Geometry. Geometry. No Louisiana Connectors written for this standard.
 GM: G-CO.A.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a
GM: G-CO.A.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a
Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles
 Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles Angle Vocabulary Complementary- two angles whose sum is 90 degrees. Supplementary- two angles whose sum is 180 degrees. Congruent angles- two or more angles with
Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles Angle Vocabulary Complementary- two angles whose sum is 90 degrees. Supplementary- two angles whose sum is 180 degrees. Congruent angles- two or more angles with
Geometry A Year-at-a-Glance Year-at-a-Glance
 Year-at-a-Glance 2018-2019 Year-at-a-Glance FIRST SEMESTER SECOND SEMESTER Unit 1 Foundations of Geometry Unit 2 Circles Unit 3 Equations of Lines and Angle-Pairs Unit 4 Congruence Unit 5 Triangles 1st
Year-at-a-Glance 2018-2019 Year-at-a-Glance FIRST SEMESTER SECOND SEMESTER Unit 1 Foundations of Geometry Unit 2 Circles Unit 3 Equations of Lines and Angle-Pairs Unit 4 Congruence Unit 5 Triangles 1st
Pre-AP Geometry Year-at-a-Glance Year-at-a-Glance
 Pre-AP Geometry Year-at-a-Glance 2018-2019 Year-at-a-Glance FIRST SEMESTER SECOND SEMESTER Unit 1 Foundations of Geometry Unit 2 Equations of Lines, Angle-Pairs, Triangles Unit 3 Right Triangles, Polygons,
Pre-AP Geometry Year-at-a-Glance 2018-2019 Year-at-a-Glance FIRST SEMESTER SECOND SEMESTER Unit 1 Foundations of Geometry Unit 2 Equations of Lines, Angle-Pairs, Triangles Unit 3 Right Triangles, Polygons,
Common Core Cluster. Experiment with transformations in the plane. Unpacking What does this standard mean that a student will know and be able to do?
 Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Curriki Geometry Glossary
 Curriki Geometry Glossary The following terms are used throughout the Curriki Geometry projects and represent the core vocabulary and concepts that students should know to meet Common Core State Standards.
Curriki Geometry Glossary The following terms are used throughout the Curriki Geometry projects and represent the core vocabulary and concepts that students should know to meet Common Core State Standards.
G.CO.2 G.CO.3 G.CO.4 G.CO.5 G.CO.6
 Standard G.CO.1 G.CO.2 G.CO.3 G.CO.4 G.CO.5 G.CO.6 Jackson County Core Curriculum Collaborative (JC4) Geometry Learning Targets in Student Friendly Language I can define the following terms precisely in
Standard G.CO.1 G.CO.2 G.CO.3 G.CO.4 G.CO.5 G.CO.6 Jackson County Core Curriculum Collaborative (JC4) Geometry Learning Targets in Student Friendly Language I can define the following terms precisely in
The School District of Palm Beach County GEOMETRY HONORS Unit A: Essentials of Geometry
 MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1 MAFS.912.G-CO.4.12 MAFS.912.G-GPE.2.7 MAFS.912.G-MG.1.1 Unit A: Essentials of Mathematics Florida Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line
MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1 MAFS.912.G-CO.4.12 MAFS.912.G-GPE.2.7 MAFS.912.G-MG.1.1 Unit A: Essentials of Mathematics Florida Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line
Chapter 6.1 Medians. Geometry
 Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Curriculum Scope & Sequence
 BOE APPROVED 3/27/12 REVISED 9/25/12 Curriculum Scope & Sequence Subject/Grade Level: MATHEMATICS/HIGH SCHOOL Course: GEOMETRY CP/HONORS *The goals and standards addressed are the same for both levels
BOE APPROVED 3/27/12 REVISED 9/25/12 Curriculum Scope & Sequence Subject/Grade Level: MATHEMATICS/HIGH SCHOOL Course: GEOMETRY CP/HONORS *The goals and standards addressed are the same for both levels
Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips
 & present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
& present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
Northern York County School District Curriculum
 Course Name Keystone Geometry (1.03 / 1.06 / 1.10) Grade Level Grade 10 Northern York County School District Curriculum Module Instructional Procedures Module 1: Geometric Properties and Reasoning Course
Course Name Keystone Geometry (1.03 / 1.06 / 1.10) Grade Level Grade 10 Northern York County School District Curriculum Module Instructional Procedures Module 1: Geometric Properties and Reasoning Course
Ref: GIS Math G 9 C.D
 Ref: GIS Math G 9 C.D. 2015-2016 2011-2012 SUBJECT : Math TITLE OF COURSE : Geometry GRADE LEVEL : 9 DURATION : ONE YEAR NUMBER OF CREDITS : 1.25 Goals: Congruence G-CO Experiment with transformations
Ref: GIS Math G 9 C.D. 2015-2016 2011-2012 SUBJECT : Math TITLE OF COURSE : Geometry GRADE LEVEL : 9 DURATION : ONE YEAR NUMBER OF CREDITS : 1.25 Goals: Congruence G-CO Experiment with transformations
Russell County Pacing Guide
 August Experiment with transformations in the plane. 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance
August Experiment with transformations in the plane. 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance
Geometry Definitions and Theorems. Chapter 9. Definitions and Important Terms & Facts
 Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
