Recent Advances in MSC/PATRAN Pre-Processing Software Allows Modeling of Complex Automotive Lamp Designs
|
|
|
- Cynthia Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Recent Advances in MSC/PATRAN Pre-Processing Software Allows Modeling of Complex Automotive Lamp Designs William I. Moore, Eric S. Donovan and Christopher R. Powers Delphi Interior and Lighting Systems Anderson, IN ABSTRACT Advances in automotive lamp designs have resulted in a more compact, aerodynamic packaging and the use of less expensive plastic materials for the lens and housing. The smaller packaging and lower melting point of plastics have increased the need for a predictive tool for simulating the lamp temperature rise under operating conditions. The modeling of lamps requires sophisticated analysis tools incorporating computational fluid dynamics and specular radiation. These tools use a finite element method to solve a system of non-linear equations for velocity, pressure and temperature. In addition to the non-linearity, the complex parabolic shape of the lamp reflector and lens requires very powerful mesh generation capability in order to produce an adequately refined mesh. The lamp modeling is performed in two stages. First the model is generated by importing CAD data from Pro/ENGINEER or Unigraphics into the MSC/PATRAN preprocessor. The surfaces are then meshed with triangular elements which are used as a seed for creating the air volume and lamp solid wall tetrahedral element meshes. The use of the new MSC/PATRAN hybrid tetrahedral mesher has enabled the creation of very complex 3D element meshes to represent fluid volumes with several hundred thousand elements. MSC/PATRAN has become a common pre/post-processor for many analysis codes because of the open CAE environment, advanced meshing capability, ease of applying loads and boundary conditions and effective post-processing capability for displaying results. 1
2 1. INTRODUCTION The introduction of plastic materials in automotive lamp design, which have low melt temperatures relative to glass, and the requirement of a more aerodynamic shape to the lamp body have increased the need for accurately predicting lamp operating temperatures. Predicting lamp temperatures requires a sophisticated computational fluid dynamic (CFD) code with the capability to model combined surface radiation and natural convection effects. The Adina-F CFD code was chosen for the lamp thermal analysis program because of the coupled specular surface radiation and fluid flow analysis capabilities [1]. Since the CFD code is not typically designed to specialize in importing and meshing geometry, a dedicated pre-processor code for these tasks is highly desirable. Because many lamps are designed using Unigraphics [2] and Pro/ENGINEER [3] the preprocessor must have a strong interface with these computer aided design (CAD) programs and to be able to import the math data geometry in a highly reliable and clean manner. Powerful three dimensional (3D) mesh generation capability is also required due to the complex parabolic shape of the lamp reflector and the need to model details such as the bulb, shield, lens and lamp internal air volume -- as well as other internal lamp features as required. Because of the difficulties involved in creating a structured brick mesh for the lamp geometry, an unstructured mesh is used with 4 node tetrahedral elements to represent the 3D regions of the model. Another reason for using an unstructured mesh is the improved performance of the Adina-F code under rapid flow conditions with the tetrahedral elements. Using an unstructured mesh requires much less time for geometry preparation and meshing, so that design alternatives can be analyzed faster with more emphasis on evaluating results and making recommendations to the designer. In addition to the advanced geometry importation and meshing capability available in the pre-processor, the ability to analyze results using the post-processor is also desirable. MSC/PATRAN [4] was used due to its CAD and CFD analysis software interface and due to the pre- and postprocessing requirements of the lamp thermal analysis program. The following sections describe the lamp thermal analysis process in detail. Section 2 discusses the importation of geometry into the MSC/PATRAN database and the meshing technique. A triangular surface mesh is applied to the surfaces from which the 3D tetrahedral mesh is generated to represent the lamp air volume and solid wall. Separate lamp components such as bulbs are imported from an existing database file using the database import feature. Finally, loads and boundary conditions are applied, and the model is translated into an Adina-F analysis input file. Section 3 presents the results of a thermal analysis of a production headlamp using the MSC/PATRAN post-processor. The predicted lamp temperatures are compared with measurements obtained using an infrared thermal imaging camera. 2
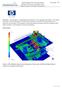
3 Signal are stamped metal, and the bulbs are gasfilled glass envelopes. Depending on the complexity, lamps may include inner lens, bezels, internal moveable reflectors, etc. Low Beam High Beam High Beam Signal Math Data Preparation Low Beam Parabolic Reflector Reflector Figure 1. Headlamp Geometry for FEA Model Section 4 demonstrates the successful benchmarking of the lamp thermal analysis method using enhancements in MSC/PATRAN. 2. PROBLEM DEFINITION As the automotive industry looks to build sleeker and more attractive cars, automotive engineers are faced with larger and more complex problems to solve. A trend in automotive styling is to update the exterior lighting components on a car line in the years between major body styling updates. The updated design is typically more complex than the original. Given this design complexity, the analyst must determine the level of detail to be incorporated into the finite element model. A typical automotive headlamp consists of a lens adhesively bonded to a reflector, one or more bulbs, and a bulb shield (see Fig. 1). The lens and reflector are generally made of plastic or composite materials. Bulb shields Initially the analyst simplifies the geometry for meshing. When performing a thermal analysis, features that are unnecessary or irrelevant to temperature profiles are discarded (e.g., vent holes, screw bosses, attachment mechanisms, lock towers, etc.). Once these features are removed, the major task of mating the lens and housing surfaces is addressed (see Fig. 2). The inherent problem is that the data is designed with a gap between the housing and lens to account for the adhesive; however, for meshing purposes enclosed volumes must be created to represent the inside and outside surfaces of the lamp. Therefore, the inner surfaces of the housing are matched with the inner surfaces of the lens. The same methodology Housing Design Gap Figure 2. Lens and Housing Seal Channel Lens Design Gap applies to the lamp s outer surfaces as well (see Fig. 3). 3
4 The next task is to break out sections that represent probable high temperature regions (hot spots). These are typically the areas directly above (+z) and in front (-x) of the bulbs. The hot spot of the housing is defined by generating a circle in xy-plane with its center at the filament centroid and then projecting the circle in the +z direction to the inner and outer surfaces of the housing. The hot spot of the lens is defined by generating a circle in yz-plane with its center at the filament centroid and then projecting the circle in the -x direction to the inner and outer surfaces of the lens. Figures 4 and 5 show examples of the housing and lens respectively. Lens and housing surfaces are broken or recreated around this projected circle to allow for a fine mesh in the hot spot locations. The data is then separated into groups prior to importing the geometry into MSC/PATRAN. Projection Circle x z y Filament Centroid Inner & Outer Hot Spots The method used to import the data into MSC/PATRAN depends upon the CAD system of origin. Due to issues with solid modeling, math data created in Pro/ENGINEER is exported in an IGES[6] format then imported into MSC/PATRAN using the IGES translator. However, Unigraphics data is brought directly into MSC/PATRAN. After the CAD data has been imported, an Edit/Surface/EdgeMatch is performed on the geometry in order to prepare the surfaces for meshing. Meshing The geometric surfaces including the high and low beam bulbs, bulb shield, reflector, and lens are meshed using triangular elements in preparation for generating solid tetrahedral elements for the lamp inner air volume. A fine mesh is first applied to regions where high temperature gradients are expected. Then a relatively coarse mesh is applied to the remaining surfaces using smooth transitioning from smaller to larger elements. Typically, an element edge length of 2 mm is Projection Axis Housing Gap Closure Lens Figure 4. Housing Hot Spot Geometry Creation x z y Filament Centroid Inner & Outer Hot Spots Projection Circle Projection Axis Figure 5. Lens Hot Spot Geometry Creation Figure 3. Matching Lens and Housing Inner and Outer Surfaces used in the hot spots and lengths of 7 to 15 4
5 mm are used for the remaining portions of Inner Bezel the Reflector model where specific temperature Lens predictions are not of interest. The main reason for using variable mesh density is model size constraints. Surface radiation Bulb analysis is very CPU intensive requiring large amounts of RAM and hard Bulb Shield disk space. Software and hardware limitations impose a limit on the maximum allowable Housing number of surface radiation elements which can be solved. Currently, Figure 6. Solid Mesh Showing Components of this limit Complex is 2.1 Gbytes, Headlamp or System about 15,000 in Low - 20,000 surface Beam Cavity elements. The next step involves equivalencing all nodes. Because the outer lamp shell must be completely enclose the lamp air volume, all nodes must be equivalenced and any gaps closed. This process is repeated for all surface meshes in the model, both inner and outer. After all surfaces have been meshed the element normals are oriented in the outward direction from the volume to meshed. MSC/PATRAN s Hybrid mesher is used to generate the tetrahedral mesh while the State Machine mesher is used for diagnostic work. The lamp 3D air volume mesh poses the most difficult meshing problem due to the number of entities inside the enclosed air volume (e.g., bulbs, bulb shield, reflectors, etc.). Figure 6 is a cutaway section through the low beam cavity which shows the reflector, bulb, and bulb shield. The State Machine, MSC/PATRAN r1.4 algorithm, has diagnostics for determining the causes of mesh failure such as self intersections, problems with element normals, or duplicate elements. Several attempts are often required to resolve the surface element problems before the volume can be successfully meshed. The new Hybrid tetrahedral mesher, available with MSC/PATRAN version 7.5, is used to create the solid tetrahedral mesh representing air inside the lamp. Figure 7 is a crosssection of a simple headlamp to be analyzed showing the air volume mesh in the low beam cavity with a 2 mm global element edge length for the high beam bulb and a 7 mm edge length for the lamp air volume. Lamp Internal Air Mesh High Beam Bulb The hybrid mesher produces a smooth element transition from the fine 2 mm bulb elements to the larger 7 to 15 mm lamp surface elements. Smooth transitioning and high quality tetrahedral elements are extremely important for CFD analysis. Material Properties Lamp Wall Mesh Figure 7. Lamp Air Volume Solid Mesh Showing Section Through Low Beam Cavity Material properties are assigned to all 3D element groups. A viscous incompressible flow model with temperature dependent properties is assigned to the air element group while thermal conductivities are 5
6 assigned to the lamp wall, lens, and shield groups. Loads & Boundary Conditions As in any problem involving heat transfer, many loads and boundary conditions must be specified, including: Temperature Dependent Air Properties - Density, Viscosity, Thermal Conductivity Solid Lamp Wall Conductivity Bulb and Lamp Outer Surface Emissivity Aluminized Surface Reflectivity Lens Transmissivity Boundary Convection and Radiation to Environment Fixed Velocity and Initial Temperature Bulb Heat Loads was to run a thermal analysis of the bulb to verify the accuracy of the bulb model. The results for the predicted and measured high beam bulb temperatures are shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9 respectively. The predicted temperature was 830 F while the thermal camera temperature measurement was 777 F. Successfully correlating the bulb thermal model was a very important step in accurately modeling the headlamp temperature ANALYSIS RESULTS In order to test the accuracy of the lamp thermal model, an actual headlamp design was selected and modeled. The purpose of the analysis was to verify the accuracy of the lamp thermal model temperature predictions by comparing them to actual test data. The first step in the analysis process 830 Deg.F Figure 9. Bulb Temperature Measurement Next, a thermal model of the full headlamp was run. The headlamp thermal analysis temperature prediction is shown below in Figure 10. The maximum predicted lens outer surface temperature of 198 F for the high beam compartment showed outstanding agreement with the thermal camera temperature measurement of 195 F (see Fig. 11). Figure 8. Predicted Bulb Temperature 6
7 Deg.F Figure 11. Measured Lens Temperature The temperature distribution also exhibits nearly complete agreement with the thermal camera image (compare Figures 10 and 11). The predicted maximum temperature of 175 F for the signal compartment was slightly below the measured value of 189 F. The lamp internal air flow pattern is shown in Figure 12 exhibiting the phenomenon of a counter rotating vortex with high velocity air above the bulb and a relatively stagnant layer of air below. Figure 10. Predicted Lens Temperature Table 1 which shows a very satisfactory correlation. Table 1 Location Predicted ( F) Bulb High Beam Lens Signal Lens Measure d ( F) The high accuracy of the lamp temperature predictions indicates that the mesh refinement was sufficient to accurately capture the primary effects of radiation and natural convection. Using high quality elements improved the stability and convergence of the analysis as well as the accuracy. Figure 12. Lamp Internal Air Velocity 4.0 DISCUSSION A comparison between the predicted and measured temperatures is summarized in In the surface radiation model, very large amounts of memory were required to obtain a solution. The memory requirements increased as the square of the number of surface radiation elements and could have easily exceeded the available computer memory. Therefore, in order to reduce the number of surface radiation elements and 7
8 reduce the required memory, a somewhat coarse global element edge length was used in low temperature gradient regions while a finer element edge length was used in regions where high thermal and velocity gradients exist. meshing and building the model, and more time is available for evaluating new conceptual designs and solving existing design problems. Advances in the MSC/PATRAN hybrid mesher capability have reduced the time required to generate large, complex 3D meshes. Using an HPJ210 workstation with 512 Mbytes of RAM, the tetrahedral mesher generated 200,000 elements in less than fifteen minutes which is an improvement over the hybrid mesher performance in previous versions. 5.0 CONCLUSIONS The results of the headlamp thermal analysis have demonstrated that complex geometries with coupled fluid flow and surface radiation can be accurately modeled using state of the art CFD codes and pre-processing software with powerful meshing capability. Using MSC/PATRAN with the Adina-F analysis preference provides the necessary flexibility in meshing, in applying loads and boundary conditions, and in analyzing the results. The ability to import lamp design geometry from Unigraphics and other standard CAD formats and to create high quality triangular surface and 3D tetrahedral meshes makes MSC/PATRAN an acceptable tool for preprocessing. These meshing capabilities result in a significant reduction in the analysis cycle time. Enhancements to MSC/PATRAN, such as importing one database into another database while not losing material properties and loads and boundary conditions, have also resulted in time savings. Now, less effort is spent in 8
9 REFERENCES 1. Adina Theory and Modeling Guide, Report ARD 97-8, Adina R&D,Inc., Watertown, MA, Unigraphics Version 13.0, Electronic Data Systems Corp., Cypress, CA, Pro/ENGINEER, Parametric Technology Corp., Waltham, MA 4. MSC/PATRAN Version 7.5, The MacNeal-Schwendler Corporation, Los Angeles, CA, CGS, Corporate Graphics System, Version 4.4.3, IGES, International Graphics Exchange Specification Version 5.2, November
Using the Discrete Ordinates Radiation Model
 Tutorial 6. Using the Discrete Ordinates Radiation Model Introduction This tutorial illustrates the set up and solution of flow and thermal modelling of a headlamp. The discrete ordinates (DO) radiation
Tutorial 6. Using the Discrete Ordinates Radiation Model Introduction This tutorial illustrates the set up and solution of flow and thermal modelling of a headlamp. The discrete ordinates (DO) radiation
How TMG Uses Elements and Nodes
 Simulation: TMG Thermal Analysis User's Guide How TMG Uses Elements and Nodes Defining Boundary Conditions on Elements You create a TMG thermal model in exactly the same way that you create any finite
Simulation: TMG Thermal Analysis User's Guide How TMG Uses Elements and Nodes Defining Boundary Conditions on Elements You create a TMG thermal model in exactly the same way that you create any finite
Abstract. Die Geometry. Introduction. Mesh Partitioning Technique for Coextrusion Simulation
 OPTIMIZATION OF A PROFILE COEXTRUSION DIE USING A THREE-DIMENSIONAL FLOW SIMULATION SOFTWARE Kim Ryckebosh 1 and Mahesh Gupta 2, 3 1. Deceuninck nv, BE-8830 Hooglede-Gits, Belgium 2. Michigan Technological
OPTIMIZATION OF A PROFILE COEXTRUSION DIE USING A THREE-DIMENSIONAL FLOW SIMULATION SOFTWARE Kim Ryckebosh 1 and Mahesh Gupta 2, 3 1. Deceuninck nv, BE-8830 Hooglede-Gits, Belgium 2. Michigan Technological
Using MSC.Nastran for Explicit FEM Simulations
 3. LS-DYNA Anwenderforum, Bamberg 2004 CAE / IT III Using MSC.Nastran for Explicit FEM Simulations Patrick Doelfs, Dr. Ingo Neubauer MSC.Software GmbH, D-81829 München, Patrick.Doelfs@mscsoftware.com Abstract:
3. LS-DYNA Anwenderforum, Bamberg 2004 CAE / IT III Using MSC.Nastran for Explicit FEM Simulations Patrick Doelfs, Dr. Ingo Neubauer MSC.Software GmbH, D-81829 München, Patrick.Doelfs@mscsoftware.com Abstract:
Program: Advanced Certificate Program
 Program: Advanced Certificate Program Course: CFD-Vehicle Aerodynamics Directorate of Training and Lifelong Learning #470-P, Peenya Industrial Area, 4th Phase Peenya, Bengaluru 560 058 www.msruas.ac.in
Program: Advanced Certificate Program Course: CFD-Vehicle Aerodynamics Directorate of Training and Lifelong Learning #470-P, Peenya Industrial Area, 4th Phase Peenya, Bengaluru 560 058 www.msruas.ac.in
Autodesk Moldflow Insight AMI The Mold
 Autodesk Moldflow Insight 2012 AMI The Mold Revision 1, 22 March 2012. This document contains Autodesk and third-party software license agreements/notices and/or additional terms and conditions for licensed
Autodesk Moldflow Insight 2012 AMI The Mold Revision 1, 22 March 2012. This document contains Autodesk and third-party software license agreements/notices and/or additional terms and conditions for licensed
NX Advanced FEM. fact sheet
 Advanced FEM fact sheet www.ugs.com Summary Advanced FEM is a comprehensive multi-cad finite element modeling and results visualization product that is designed to meet the needs of experienced CAE analysts.
Advanced FEM fact sheet www.ugs.com Summary Advanced FEM is a comprehensive multi-cad finite element modeling and results visualization product that is designed to meet the needs of experienced CAE analysts.
METHOD IMPROVEMENTS IN THERMAL ANALYSIS OF MACH 10 LEADING EDGES
 METHOD IMPROVEMENTS IN THERMAL ANALYSIS OF MACH 10 LEADING EDGES Ruth M. Amundsen National Aeronautics and Space Administration Langley Research Center Hampton VA 23681-2199 ABSTRACT Several improvements
METHOD IMPROVEMENTS IN THERMAL ANALYSIS OF MACH 10 LEADING EDGES Ruth M. Amundsen National Aeronautics and Space Administration Langley Research Center Hampton VA 23681-2199 ABSTRACT Several improvements
Free Convection Cookbook for StarCCM+
 ME 448/548 February 28, 2012 Free Convection Cookbook for StarCCM+ Gerald Recktenwald gerry@me.pdx.edu 1 Overview Figure 1 depicts a two-dimensional fluid domain bounded by a cylinder of diameter D. Inside
ME 448/548 February 28, 2012 Free Convection Cookbook for StarCCM+ Gerald Recktenwald gerry@me.pdx.edu 1 Overview Figure 1 depicts a two-dimensional fluid domain bounded by a cylinder of diameter D. Inside
Vehicle thermal safety with THESEUS-FE. Author: Dr. Daniel Koester
 Author: Dr. Daniel Koester Date: September 4, 2014 Workflow for Underhood Simulations ANSA or other CAD/meshing software CAD cleanup and meshing: either CAD geometry description or NASTRAN-style FE meshes
Author: Dr. Daniel Koester Date: September 4, 2014 Workflow for Underhood Simulations ANSA or other CAD/meshing software CAD cleanup and meshing: either CAD geometry description or NASTRAN-style FE meshes
NX Advanced FEM. Benefits
 Advanced FEM fact sheet Siemens PLM Software www.siemens.com/plm Summary Advanced FEM software is a comprehensive multi-cad finite element modeling and results visualization product that is designed to
Advanced FEM fact sheet Siemens PLM Software www.siemens.com/plm Summary Advanced FEM software is a comprehensive multi-cad finite element modeling and results visualization product that is designed to
Validation of an Unstructured Overset Mesh Method for CFD Analysis of Store Separation D. Snyder presented by R. Fitzsimmons
 Validation of an Unstructured Overset Mesh Method for CFD Analysis of Store Separation D. Snyder presented by R. Fitzsimmons Stores Separation Introduction Flight Test Expensive, high-risk, sometimes catastrophic
Validation of an Unstructured Overset Mesh Method for CFD Analysis of Store Separation D. Snyder presented by R. Fitzsimmons Stores Separation Introduction Flight Test Expensive, high-risk, sometimes catastrophic
Autodesk Moldflow Insight AMI Cool Analysis Products
 Autodesk Moldflow Insight 2012 AMI Cool Analysis Products Revision 1, 22 March 2012. This document contains Autodesk and third-party software license agreements/notices and/or additional terms and conditions
Autodesk Moldflow Insight 2012 AMI Cool Analysis Products Revision 1, 22 March 2012. This document contains Autodesk and third-party software license agreements/notices and/or additional terms and conditions
LucidShape MacroFocal Surfaces
 WHITE PAPER LucidShape MacroFocal Surfaces Paper #007-2 Author Peter Sommer Synopsys Abstract State-of-the-art lighting systems in motor vehicles require new geometries to achieve the required lighting
WHITE PAPER LucidShape MacroFocal Surfaces Paper #007-2 Author Peter Sommer Synopsys Abstract State-of-the-art lighting systems in motor vehicles require new geometries to achieve the required lighting
Driven Cavity Example
 BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
Impact of STAR-CCM+ v7.0 in the Automotive Industry Frederick J. Ross, CD-adapco Director, Ground Transportation
 Impact of STAR-CCM+ v7.0 in the Automotive Industry Frederick J. Ross, CD-adapco Director, Ground Transportation Vehicle Simulation Components Vehicle Aerodynamics Design Studies Aeroacoustics Water/Dirt
Impact of STAR-CCM+ v7.0 in the Automotive Industry Frederick J. Ross, CD-adapco Director, Ground Transportation Vehicle Simulation Components Vehicle Aerodynamics Design Studies Aeroacoustics Water/Dirt
Coupled Analysis of FSI
 Coupled Analysis of FSI Qin Yin Fan Oct. 11, 2008 Important Key Words Fluid Structure Interface = FSI Computational Fluid Dynamics = CFD Pressure Displacement Analysis = PDA Thermal Stress Analysis = TSA
Coupled Analysis of FSI Qin Yin Fan Oct. 11, 2008 Important Key Words Fluid Structure Interface = FSI Computational Fluid Dynamics = CFD Pressure Displacement Analysis = PDA Thermal Stress Analysis = TSA
International Power, Electronics and Materials Engineering Conference (IPEMEC 2015)
 International Power, Electronics and Materials Engineering Conference (IPEMEC 2015) Numerical Simulation of the Influence of Intake Grille Shape on the Aerodynamic Performance of a Passenger Car Longwei
International Power, Electronics and Materials Engineering Conference (IPEMEC 2015) Numerical Simulation of the Influence of Intake Grille Shape on the Aerodynamic Performance of a Passenger Car Longwei
CFD Simulation of Air Flow and Thermal Behavior of Electronics Assembly within Plastic Enclosure for Outdoor Environments
 Keywords: CFD Simulation, Computational Fluid Dynamics, CFD conjugate heat transfer, CFD natural convection, CFD PCB simulation, CFD electronics enclosures, CFD ASICS, thermal predictions of electronic
Keywords: CFD Simulation, Computational Fluid Dynamics, CFD conjugate heat transfer, CFD natural convection, CFD PCB simulation, CFD electronics enclosures, CFD ASICS, thermal predictions of electronic
CFD Analysis for the Cooling Vent in Automobile
 International Journal for Ignited Minds (IJIMIINDS) CFD Analysis for the Cooling Vent in Automobile Vijay Kumar M a, Dr. Basawaraj b & Dr. B R Shridhar c a Asst Prof, Department of Mechanical, S.E.A.C.E.T,
International Journal for Ignited Minds (IJIMIINDS) CFD Analysis for the Cooling Vent in Automobile Vijay Kumar M a, Dr. Basawaraj b & Dr. B R Shridhar c a Asst Prof, Department of Mechanical, S.E.A.C.E.T,
Applications of ICFD solver by LS-DYNA in Automotive Fields to Solve Fluid-Solid-Interaction (FSI) Problems
 Applications of ICFD solver by LS-DYNA in Automotive Fields to Solve Fluid-Solid-Interaction (FSI) Problems George Wang(1 ), Facundo del Pin(2), Inaki Caldichoury (2), Prince Rodriguez(3), Jason Tippie
Applications of ICFD solver by LS-DYNA in Automotive Fields to Solve Fluid-Solid-Interaction (FSI) Problems George Wang(1 ), Facundo del Pin(2), Inaki Caldichoury (2), Prince Rodriguez(3), Jason Tippie
Solid Conduction Tutorial
 SECTION 1 1 SECTION 1 The following is a list of files that will be needed for this tutorial. They can be found in the Solid_Conduction folder. Exhaust-hanger.tdf Exhaust-hanger.ntl 1.0.1 Overview The
SECTION 1 1 SECTION 1 The following is a list of files that will be needed for this tutorial. They can be found in the Solid_Conduction folder. Exhaust-hanger.tdf Exhaust-hanger.ntl 1.0.1 Overview The
Femap Thermal & Flow V11
 Femap Thermal & Flow V11 by Carl J. Poplawsky presented to Femap Symposium Ann Arbor, MI. date June 4th, 2015 MAYA Company Overview OEM Foundation Siemens PLM Partner 30+ years Software Developer Femap
Femap Thermal & Flow V11 by Carl J. Poplawsky presented to Femap Symposium Ann Arbor, MI. date June 4th, 2015 MAYA Company Overview OEM Foundation Siemens PLM Partner 30+ years Software Developer Femap
CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 ME 475: Computer-Aided Design of Structures 1-1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Analysis versus Design 1.2 Basic Steps in Analysis 1.3 What is the Finite Element Method? 1.4 Geometrical Representation, Discretization
ME 475: Computer-Aided Design of Structures 1-1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Analysis versus Design 1.2 Basic Steps in Analysis 1.3 What is the Finite Element Method? 1.4 Geometrical Representation, Discretization
midas NFX 2017R1 Release Note
 Total Solution for True Analysis-driven Design midas NFX 2017R1 Release Note 1 midas NFX R E L E A S E N O T E 2 0 1 7 R 1 Major Improvements Midas NFX is an integrated finite element analysis program
Total Solution for True Analysis-driven Design midas NFX 2017R1 Release Note 1 midas NFX R E L E A S E N O T E 2 0 1 7 R 1 Major Improvements Midas NFX is an integrated finite element analysis program
Module 3 Mesh Generation
 Module 3 Mesh Generation 1 Lecture 3.1 Introduction 2 Mesh Generation Strategy Mesh generation is an important pre-processing step in CFD of turbomachinery, quite analogous to the development of solid
Module 3 Mesh Generation 1 Lecture 3.1 Introduction 2 Mesh Generation Strategy Mesh generation is an important pre-processing step in CFD of turbomachinery, quite analogous to the development of solid
Element Order: Element order refers to the interpolation of an element s nodal results to the interior of the element. This determines how results can
 TIPS www.ansys.belcan.com 鲁班人 (http://www.lubanren.com/weblog/) Picking an Element Type For Structural Analysis: by Paul Dufour Picking an element type from the large library of elements in ANSYS can be
TIPS www.ansys.belcan.com 鲁班人 (http://www.lubanren.com/weblog/) Picking an Element Type For Structural Analysis: by Paul Dufour Picking an element type from the large library of elements in ANSYS can be
Problem description. Problem 65: Free convection in a lightbulb. Filament (Tungsten): Globe (Glass): = FSI boundary. Gas (Argon):
 Problem description This tutorial demonstrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid flow and heat transfer in a lightbulb using the Thermal Fluid-Structure Interaction (TFSI) features of ADINA. The
Problem description This tutorial demonstrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid flow and heat transfer in a lightbulb using the Thermal Fluid-Structure Interaction (TFSI) features of ADINA. The
CDA Workshop Physical & Numerical Hydraulic Modelling. STAR-CCM+ Presentation
 CDA Workshop Physical & Numerical Hydraulic Modelling STAR-CCM+ Presentation ENGINEERING SIMULATION CFD FEA Mission Increase the competitiveness of companies through optimization of their product development
CDA Workshop Physical & Numerical Hydraulic Modelling STAR-CCM+ Presentation ENGINEERING SIMULATION CFD FEA Mission Increase the competitiveness of companies through optimization of their product development
Coupled Simulation of the Fluid Flow and Conjugate Heat Transfer in Press Hardening Processes
 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Metal Forming Coupled Simulation of the Fluid Flow and Conjugate Heat Transfer in Press Hardening Processes Uli Göhner 1), Bruno Boll 1), Inaki Caldichouri
13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Metal Forming Coupled Simulation of the Fluid Flow and Conjugate Heat Transfer in Press Hardening Processes Uli Göhner 1), Bruno Boll 1), Inaki Caldichouri
MANUFACTURING OPTIMIZING COMPONENT DESIGN
 82 39 OPTIMIZING COMPONENT DESIGN MANUFACTURING SIMULATION OF LASER WELDING SHORTENS DESIGN CYCLE AND OPTIMIZES COMPONENT DESIGN AT OWENS CORNING JOHN KIRKLEY interviews BYRON BEMIS of Owens Corning It
82 39 OPTIMIZING COMPONENT DESIGN MANUFACTURING SIMULATION OF LASER WELDING SHORTENS DESIGN CYCLE AND OPTIMIZES COMPONENT DESIGN AT OWENS CORNING JOHN KIRKLEY interviews BYRON BEMIS of Owens Corning It
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS USED IN THE DESIGN OF WATERBLAST TOOLING
 2015 WJTA-IMCA Conference and Expo November 2-4 New Orleans, Louisiana Paper COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS USED IN THE DESIGN OF WATERBLAST TOOLING J. Schneider StoneAge, Inc. Durango, Colorado, U.S.A.
2015 WJTA-IMCA Conference and Expo November 2-4 New Orleans, Louisiana Paper COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS USED IN THE DESIGN OF WATERBLAST TOOLING J. Schneider StoneAge, Inc. Durango, Colorado, U.S.A.
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems
 1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
3. Preprocessing of ABAQUS/CAE
 3.1 Create new model database 3. Preprocessing of ABAQUS/CAE A finite element analysis in ABAQUS/CAE starts from create new model database in the toolbar. Then save it with a name user defined. To build
3.1 Create new model database 3. Preprocessing of ABAQUS/CAE A finite element analysis in ABAQUS/CAE starts from create new model database in the toolbar. Then save it with a name user defined. To build
The Role of CFD in Real Life Designs
 white paper The Role of CFD in Real Life Designs insight SUMMARY This paper relates two heat sinks, a medical suction device, a household oven, and an industrial control valve as examples that illustrate
white paper The Role of CFD in Real Life Designs insight SUMMARY This paper relates two heat sinks, a medical suction device, a household oven, and an industrial control valve as examples that illustrate
Geometric Modeling. Introduction
 Geometric Modeling Introduction Geometric modeling is as important to CAD as governing equilibrium equations to classical engineering fields as mechanics and thermal fluids. intelligent decision on the
Geometric Modeling Introduction Geometric modeling is as important to CAD as governing equilibrium equations to classical engineering fields as mechanics and thermal fluids. intelligent decision on the
Automotive Thermal Management for Full Vehicles
 Automotive Thermal Management for Full Vehicles Concerning the thermal behavior of automotive vehicles it is pursued to accomplish simulations for the full complexity of a vehicle's geometry and transport
Automotive Thermal Management for Full Vehicles Concerning the thermal behavior of automotive vehicles it is pursued to accomplish simulations for the full complexity of a vehicle's geometry and transport
Tutorial 2. Modeling Periodic Flow and Heat Transfer
 Tutorial 2. Modeling Periodic Flow and Heat Transfer Introduction: Many industrial applications, such as steam generation in a boiler or air cooling in the coil of an air conditioner, can be modeled as
Tutorial 2. Modeling Periodic Flow and Heat Transfer Introduction: Many industrial applications, such as steam generation in a boiler or air cooling in the coil of an air conditioner, can be modeled as
Experimental Data Confirms CFD Models of Mixer Performance
 The Problem Over the years, manufacturers of mixing systems have presented computational fluid dynamics (CFD) calculations to claim that their technology can achieve adequate mixing in water storage tanks
The Problem Over the years, manufacturers of mixing systems have presented computational fluid dynamics (CFD) calculations to claim that their technology can achieve adequate mixing in water storage tanks
CFD Modeling of a Radiator Axial Fan for Air Flow Distribution
 CFD Modeling of a Radiator Axial Fan for Air Flow Distribution S. Jain, and Y. Deshpande Abstract The fluid mechanics principle is used extensively in designing axial flow fans and their associated equipment.
CFD Modeling of a Radiator Axial Fan for Air Flow Distribution S. Jain, and Y. Deshpande Abstract The fluid mechanics principle is used extensively in designing axial flow fans and their associated equipment.
Tutorial 1. Introduction to Using FLUENT: Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow
 Tutorial 1. Introduction to Using FLUENT: Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Introduction This tutorial illustrates the setup and solution of the two-dimensional turbulent fluid flow and heat
Tutorial 1. Introduction to Using FLUENT: Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Introduction This tutorial illustrates the setup and solution of the two-dimensional turbulent fluid flow and heat
Lab 9: FLUENT: Transient Natural Convection Between Concentric Cylinders
 Lab 9: FLUENT: Transient Natural Convection Between Concentric Cylinders Objective: The objective of this laboratory is to introduce how to use FLUENT to solve both transient and natural convection problems.
Lab 9: FLUENT: Transient Natural Convection Between Concentric Cylinders Objective: The objective of this laboratory is to introduce how to use FLUENT to solve both transient and natural convection problems.
Recent Approaches of CAD / CAE Product Development. Tools, Innovations, Collaborative Engineering.
 Recent Approaches of CAD / CAE Product Development. Tools, Innovations, Collaborative Engineering. Author: Dr.-Ing. Peter Binde Abstract: In this paper, the latest approaches in the field of CAD-CAE product
Recent Approaches of CAD / CAE Product Development. Tools, Innovations, Collaborative Engineering. Author: Dr.-Ing. Peter Binde Abstract: In this paper, the latest approaches in the field of CAD-CAE product
Introduction to ANSYS CFX
 Workshop 03 Fluid flow around the NACA0012 Airfoil 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS CFX 2015 ANSYS, Inc. March 13, 2015 1 Release 16.0 Workshop Description: The flow simulated is an external aerodynamics
Workshop 03 Fluid flow around the NACA0012 Airfoil 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS CFX 2015 ANSYS, Inc. March 13, 2015 1 Release 16.0 Workshop Description: The flow simulated is an external aerodynamics
Computational Fluid Dynamics PRODUCT SHEET
 TM 2014 Computational Fluid Dynamics PRODUCT SHEET 1 Breaking Limitations The Challenge of Traditional CFD In the traditional mesh-based approach, the reliability highly depends on the quality of the mesh,
TM 2014 Computational Fluid Dynamics PRODUCT SHEET 1 Breaking Limitations The Challenge of Traditional CFD In the traditional mesh-based approach, the reliability highly depends on the quality of the mesh,
Aerodynamic Study of a Realistic Car W. TOUGERON
 Aerodynamic Study of a Realistic Car W. TOUGERON Tougeron CFD Engineer 2016 Abstract This document presents an aerodynamic CFD study of a realistic car geometry. The aim is to demonstrate the efficiency
Aerodynamic Study of a Realistic Car W. TOUGERON Tougeron CFD Engineer 2016 Abstract This document presents an aerodynamic CFD study of a realistic car geometry. The aim is to demonstrate the efficiency
New Technologies in CST STUDIO SUITE CST COMPUTER SIMULATION TECHNOLOGY
 New Technologies in CST STUDIO SUITE 2016 Outline Design Tools & Modeling Antenna Magus Filter Designer 2D/3D Modeling 3D EM Solver Technology Cable / Circuit / PCB Systems Multiphysics CST Design Tools
New Technologies in CST STUDIO SUITE 2016 Outline Design Tools & Modeling Antenna Magus Filter Designer 2D/3D Modeling 3D EM Solver Technology Cable / Circuit / PCB Systems Multiphysics CST Design Tools
USAGE OF ANSA S AUTOMATED VOLUME MESHING-METHODS IN THE RAPID PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS OF DIESEL ENGINES
 USAGE OF ANSA S AUTOMATED VOLUME MESHING-METHODS IN THE RAPID PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS OF DIESEL ENGINES Günther Pessl *, Dr. Robert Ehart, Gerwin Bumberger BMW Motoren GmbH, Austria KEYWORDS - ANSA,
USAGE OF ANSA S AUTOMATED VOLUME MESHING-METHODS IN THE RAPID PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS OF DIESEL ENGINES Günther Pessl *, Dr. Robert Ehart, Gerwin Bumberger BMW Motoren GmbH, Austria KEYWORDS - ANSA,
Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 413 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Spring 2015 (Dr.
 Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 413 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Spring 2015 (Dr. Sert) COMSOL 1 Tutorial 2 Problem Definition Hot combustion gases of a
Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 413 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Spring 2015 (Dr. Sert) COMSOL 1 Tutorial 2 Problem Definition Hot combustion gases of a
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING. Part-1
 COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
Computational Simulation of the Wind-force on Metal Meshes
 16 th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference Crown Plaza, Gold Coast, Australia 2-7 December 2007 Computational Simulation of the Wind-force on Metal Meshes Ahmad Sharifian & David R. Buttsworth Faculty
16 th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference Crown Plaza, Gold Coast, Australia 2-7 December 2007 Computational Simulation of the Wind-force on Metal Meshes Ahmad Sharifian & David R. Buttsworth Faculty
Applications of ICFD /SPH Solvers by LS-DYNA to Solve Water Splashing Impact to Automobile Body. Abstract
 Applications of ICFD /SPH Solvers by LS-DYNA to Solve Water Splashing Impact to Automobile Body George Wang (1 ), Kevin Gardner (3), Eric DeHoff (1), Facundo del Pin (2), Inaki Caldichoury (2), Edouard
Applications of ICFD /SPH Solvers by LS-DYNA to Solve Water Splashing Impact to Automobile Body George Wang (1 ), Kevin Gardner (3), Eric DeHoff (1), Facundo del Pin (2), Inaki Caldichoury (2), Edouard
Introduction to ANSYS DesignModeler
 Lecture 5 Modeling 14. 5 Release Introduction to ANSYS DesignModeler 2012 ANSYS, Inc. November 20, 2012 1 Release 14.5 Preprocessing Workflow Geometry Creation OR Geometry Import Geometry Operations Meshing
Lecture 5 Modeling 14. 5 Release Introduction to ANSYS DesignModeler 2012 ANSYS, Inc. November 20, 2012 1 Release 14.5 Preprocessing Workflow Geometry Creation OR Geometry Import Geometry Operations Meshing
Finite Element Analysis and Optimization of I.C. Engine Piston Using RADIOSS and OptiStruct
 Finite Element Analysis and Optimization of I.C. Engine Piston Using RADIOSS and OptiStruct Vivek Zolekar Student M. Tech. Mechanical (CAD/CAM) SGGSIE&T Nanded - 431 606 Dr. L.N. Wankhade Professor Department
Finite Element Analysis and Optimization of I.C. Engine Piston Using RADIOSS and OptiStruct Vivek Zolekar Student M. Tech. Mechanical (CAD/CAM) SGGSIE&T Nanded - 431 606 Dr. L.N. Wankhade Professor Department
Thermal Coupling Method Between SPH Particles and Solid Elements in LS-DYNA
 Thermal Coupling Method Between SPH Particles and Solid Elements in LS-DYNA INTRODUCTION: Jingxiao Xu, Jason Wang LSTC Heat transfer is very important in many industrial and geophysical problems. Many
Thermal Coupling Method Between SPH Particles and Solid Elements in LS-DYNA INTRODUCTION: Jingxiao Xu, Jason Wang LSTC Heat transfer is very important in many industrial and geophysical problems. Many
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Simulation in Air Duct Channels Using STAR CCM+
 Available onlinewww.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2017,4 (3): 216-220 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Simulation in Air Duct
Available onlinewww.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2017,4 (3): 216-220 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Simulation in Air Duct
Calculate a solution using the pressure-based coupled solver.
 Tutorial 19. Modeling Cavitation Introduction This tutorial examines the pressure-driven cavitating flow of water through a sharpedged orifice. This is a typical configuration in fuel injectors, and brings
Tutorial 19. Modeling Cavitation Introduction This tutorial examines the pressure-driven cavitating flow of water through a sharpedged orifice. This is a typical configuration in fuel injectors, and brings
PREDICTION OF E-COAT VOIDS AND PUDDLES DURING AUTOMOTIVE PAINTING USING ANSA
 Session H3.6 PREDICTION OF E-COAT VOIDS AND PUDDLES DURING AUTOMOTIVE PAINTING USING ANSA 1 Prasad Dev Hanumalagutti, 1 Yu-Ning Liu, 2 Ramu Mothukuri * 1 Research and Advanced Engineering, Ford Motor Company,
Session H3.6 PREDICTION OF E-COAT VOIDS AND PUDDLES DURING AUTOMOTIVE PAINTING USING ANSA 1 Prasad Dev Hanumalagutti, 1 Yu-Ning Liu, 2 Ramu Mothukuri * 1 Research and Advanced Engineering, Ford Motor Company,
Simcenter 3D Engineering Desktop
 Simcenter 3D Engineering Desktop Integrating geometry and FE modeling to streamline the product development process Benefits Speed simulation processes by up to 70 percent Increase product quality by rapidly
Simcenter 3D Engineering Desktop Integrating geometry and FE modeling to streamline the product development process Benefits Speed simulation processes by up to 70 percent Increase product quality by rapidly
Structured Grid Generation for Turbo Machinery Applications using Topology Templates
 Structured Grid Generation for Turbo Machinery Applications using Topology Templates January 13th 2011 Martin Spel martin.spel@rtech.fr page 1 Agenda: R.Tech activities Grid Generation Techniques Structured
Structured Grid Generation for Turbo Machinery Applications using Topology Templates January 13th 2011 Martin Spel martin.spel@rtech.fr page 1 Agenda: R.Tech activities Grid Generation Techniques Structured
Study Of Overloading Effects, In A Refrigerated Display Case
 Study Of Overloading Effects, In A Refrigerated Display Case Sandeep Palaksha Senior CAE Engineer HUSSMANN Basavanagudi Bangalore 04, India p.sandeep@hussmann.com Narasimhamurthy CAE Engineer HUSSMANN
Study Of Overloading Effects, In A Refrigerated Display Case Sandeep Palaksha Senior CAE Engineer HUSSMANN Basavanagudi Bangalore 04, India p.sandeep@hussmann.com Narasimhamurthy CAE Engineer HUSSMANN
CFD DATA TRANSFER TO STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS. W. Scott Taylor. Sverdrup Technology, Inc. 620 Discovery Drive Huntsville, Alabama ABSTRACT
 CFD DATA TRANSFER TO STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS W. Scott Taylor Sverdrup Technology, Inc. 620 Discovery Drive Huntsville, Alabama 35806 ABSTRACT This paper describes the development of a procedure to transfer
CFD DATA TRANSFER TO STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS W. Scott Taylor Sverdrup Technology, Inc. 620 Discovery Drive Huntsville, Alabama 35806 ABSTRACT This paper describes the development of a procedure to transfer
Building the Finite Element Model of a Space Satellite
 Exercise 4 Building the Finite Element Model of a Space Satellite 30000 20000 Objectives: mesh & MPC s on a Space Satellite. Perform Model and Element Verification. Learn how to control mesh parameters
Exercise 4 Building the Finite Element Model of a Space Satellite 30000 20000 Objectives: mesh & MPC s on a Space Satellite. Perform Model and Element Verification. Learn how to control mesh parameters
Mesh Morphing and the Adjoint Solver in ANSYS R14.0. Simon Pereira Laz Foley
 Mesh Morphing and the Adjoint Solver in ANSYS R14.0 Simon Pereira Laz Foley 1 Agenda Fluent Morphing-Optimization Feature RBF Morph with ANSYS DesignXplorer Adjoint Solver What does an adjoint solver do,
Mesh Morphing and the Adjoint Solver in ANSYS R14.0 Simon Pereira Laz Foley 1 Agenda Fluent Morphing-Optimization Feature RBF Morph with ANSYS DesignXplorer Adjoint Solver What does an adjoint solver do,
Advanced Training Lighting Design With LucidShape
 Advanced Training Lighting Design With LucidShape 1: Topics FF reflectors with MF and PS systems Low/high beam headlamps, Signal lamps Multi filament sources Projector Type Headlamps with PCS (Poly Curve
Advanced Training Lighting Design With LucidShape 1: Topics FF reflectors with MF and PS systems Low/high beam headlamps, Signal lamps Multi filament sources Projector Type Headlamps with PCS (Poly Curve
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE METERING SITUATIONS UNDER ABNORMAL CONFIGURATIONS
 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE METERING SITUATIONS UNDER ABNORMAL CONFIGURATIONS Dr W. Malalasekera Version 3.0 August 2013 1 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE METERING SITUATIONS UNDER ABNORMAL CONFIGURATIONS Dr W. Malalasekera Version 3.0 August 2013 1 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE
Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial
 Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Solidification of a Casting Problem Specification Problem Description Prepare for a Thermal Analysis Input Geometry Define Materials Generate
Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Solidification of a Casting Problem Specification Problem Description Prepare for a Thermal Analysis Input Geometry Define Materials Generate
In this problem, we will demonstrate the following topics:
 Z Periodic boundary condition 1 1 0.001 Periodic boundary condition 2 Y v V cos t, V 1 0 0 The second Stokes problem is 2D fluid flow above a plate that moves horizontally in a harmonic manner, schematically
Z Periodic boundary condition 1 1 0.001 Periodic boundary condition 2 Y v V cos t, V 1 0 0 The second Stokes problem is 2D fluid flow above a plate that moves horizontally in a harmonic manner, schematically
GEOMETRY MODELING & GRID GENERATION
 GEOMETRY MODELING & GRID GENERATION Dr.D.Prakash Senior Assistant Professor School of Mechanical Engineering SASTRA University, Thanjavur OBJECTIVE The objectives of this discussion are to relate experiences
GEOMETRY MODELING & GRID GENERATION Dr.D.Prakash Senior Assistant Professor School of Mechanical Engineering SASTRA University, Thanjavur OBJECTIVE The objectives of this discussion are to relate experiences
Vehicle Cabin Noise from Turbulence Induced by Side-View Mirrors. Hua-Dong Yao, 2018/8/29 Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden
 Vehicle Cabin Noise from Turbulence Induced by Side-View Mirrors Hua-Dong Yao, 2018/8/29 Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden An Important Cabin Noise Source Turbulence As the development of quiet
Vehicle Cabin Noise from Turbulence Induced by Side-View Mirrors Hua-Dong Yao, 2018/8/29 Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden An Important Cabin Noise Source Turbulence As the development of quiet
Speed and Accuracy of CFD: Achieving Both Successfully ANSYS UK S.A.Silvester
 Speed and Accuracy of CFD: Achieving Both Successfully ANSYS UK S.A.Silvester 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Content ANSYS CFD Introduction ANSYS, the company Simulation
Speed and Accuracy of CFD: Achieving Both Successfully ANSYS UK S.A.Silvester 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Content ANSYS CFD Introduction ANSYS, the company Simulation
Influence of mesh quality and density on numerical calculation of heat exchanger with undulation in herringbone pattern
 Influence of mesh quality and density on numerical calculation of heat exchanger with undulation in herringbone pattern Václav Dvořák, Jan Novosád Abstract Research of devices for heat recovery is currently
Influence of mesh quality and density on numerical calculation of heat exchanger with undulation in herringbone pattern Václav Dvořák, Jan Novosád Abstract Research of devices for heat recovery is currently
Section 8.3: Examining and Repairing the Input Geometry. Section 8.5: Examining the Cartesian Grid for Leakages
 Chapter 8. Wrapping Boundaries TGrid allows you to create a good quality boundary mesh using a bad quality surface mesh as input. This can be done using the wrapper utility in TGrid. The following sections
Chapter 8. Wrapping Boundaries TGrid allows you to create a good quality boundary mesh using a bad quality surface mesh as input. This can be done using the wrapper utility in TGrid. The following sections
Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 8 Boston Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow E. Kaufman
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 8 Boston Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow E. Kaufman
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016
 FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
Introduction to Solid Modeling Parametric Modeling. Mechanical Engineering Dept.
 Introduction to Solid Modeling Parametric Modeling 1 Why draw 3D Models? 3D models are easier to interpret. Simulation under real-life conditions. Less expensive than building a physical model. 3D models
Introduction to Solid Modeling Parametric Modeling 1 Why draw 3D Models? 3D models are easier to interpret. Simulation under real-life conditions. Less expensive than building a physical model. 3D models
Aero-Vibro Acoustics For Wind Noise Application. David Roche and Ashok Khondge ANSYS, Inc.
 Aero-Vibro Acoustics For Wind Noise Application David Roche and Ashok Khondge ANSYS, Inc. Outline 1. Wind Noise 2. Problem Description 3. Simulation Methodology 4. Results 5. Summary Thursday, October
Aero-Vibro Acoustics For Wind Noise Application David Roche and Ashok Khondge ANSYS, Inc. Outline 1. Wind Noise 2. Problem Description 3. Simulation Methodology 4. Results 5. Summary Thursday, October
McNair Scholars Research Journal
 McNair Scholars Research Journal Volume 2 Article 1 2015 Benchmarking of Computational Models against Experimental Data for Velocity Profile Effects on CFD Analysis of Adiabatic Film-Cooling Effectiveness
McNair Scholars Research Journal Volume 2 Article 1 2015 Benchmarking of Computational Models against Experimental Data for Velocity Profile Effects on CFD Analysis of Adiabatic Film-Cooling Effectiveness
Thermal Analysis using Imported CAD Geometry
 Exercise 5 Thermal Analysis using Imported CAD Geometry Objective: In this exercise you will complete a thermal analysis of a model created from imported CAD geometry. PATRAN 312 Exercises - Version 7.5
Exercise 5 Thermal Analysis using Imported CAD Geometry Objective: In this exercise you will complete a thermal analysis of a model created from imported CAD geometry. PATRAN 312 Exercises - Version 7.5
Accuracy Analysis of Charged Particle Trajectory CAE Software
 www.integratedsoft.com Accuracy Analysis of Charged Particle Trajectory CAE Software Content Executive Summary... 3 Overview of Charged Particle Beam Analysis... 3 Types of Field Distribution... 4 Simulating
www.integratedsoft.com Accuracy Analysis of Charged Particle Trajectory CAE Software Content Executive Summary... 3 Overview of Charged Particle Beam Analysis... 3 Types of Field Distribution... 4 Simulating
NX Advanced Simulation: FE modeling and simulation
 Advanced Simulation: FE modeling and simulation NX CAE Benefits Speed simulation processes by up to 70 percent Increase product quality by rapidly simulating design trade-off studies Lower overall product
Advanced Simulation: FE modeling and simulation NX CAE Benefits Speed simulation processes by up to 70 percent Increase product quality by rapidly simulating design trade-off studies Lower overall product
LaBS: a CFD tool based on the Lattice Boltzmann method. E. Tannoury, D. Ricot, B. Gaston
 LaBS: a CFD tool based on the Lattice Boltzmann method E. Tannoury, D. Ricot, B. Gaston Impact of HPC on automotive engineering applications Alain Prost, 1989 Lewis Hamilton, 2008 Impact of HPC on automotive
LaBS: a CFD tool based on the Lattice Boltzmann method E. Tannoury, D. Ricot, B. Gaston Impact of HPC on automotive engineering applications Alain Prost, 1989 Lewis Hamilton, 2008 Impact of HPC on automotive
The part to be analyzed is the bracket from the tutorial of Chapter 3.
 Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2007 COSMOSWorks Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the COSMOSWorks finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response of a component
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2007 COSMOSWorks Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the COSMOSWorks finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response of a component
Pressure Losses Analysis in Air Duct Flow Using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
 International Academic Institute for Science and Technology International Academic Journal of Science and Engineering Vol. 3, No. 9, 2016, pp. 55-70. ISSN 2454-3896 International Academic Journal of Science
International Academic Institute for Science and Technology International Academic Journal of Science and Engineering Vol. 3, No. 9, 2016, pp. 55-70. ISSN 2454-3896 International Academic Journal of Science
Thermal Design and Management of Servers
 White Paper Thermal Design and Management of Servers Thermal Design and Management of Servers P.1 Overview With the exponential growth of knowledge development, data needs to be stored, processed and secured
White Paper Thermal Design and Management of Servers Thermal Design and Management of Servers P.1 Overview With the exponential growth of knowledge development, data needs to be stored, processed and secured
Using ANSYS and CFX to Model Aluminum Reduction Cell since1984 and Beyond. Dr. Marc Dupuis
 Using ANSYS and CFX to Model Aluminum Reduction Cell since1984 and Beyond Dr. Marc Dupuis 1980-84, 2D potroom ventilation model Physical model 1980-84, 2D potroom ventilation model Experimental results
Using ANSYS and CFX to Model Aluminum Reduction Cell since1984 and Beyond Dr. Marc Dupuis 1980-84, 2D potroom ventilation model Physical model 1980-84, 2D potroom ventilation model Experimental results
System Level Cooling, Fatigue, and Durability. Co-Simulation. Stuart A. Walker, Ph.D.
 System Level Cooling, Fatigue, and Durability Analysis via Multiphysics Co-Simulation Stuart A. Walker, Ph.D. swalker@altair.com Outline Motivation Presentation of process Presentation of tools Presentation
System Level Cooling, Fatigue, and Durability Analysis via Multiphysics Co-Simulation Stuart A. Walker, Ph.D. swalker@altair.com Outline Motivation Presentation of process Presentation of tools Presentation
Estimation of Flow Field & Drag for Aerofoil Wing
 Estimation of Flow Field & Drag for Aerofoil Wing Mahantesh. HM 1, Prof. Anand. SN 2 P.G. Student, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, East Point College of Engineering, Bangalore, Karnataka, India 1 Associate
Estimation of Flow Field & Drag for Aerofoil Wing Mahantesh. HM 1, Prof. Anand. SN 2 P.G. Student, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, East Point College of Engineering, Bangalore, Karnataka, India 1 Associate
SolidWorks. An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs
 An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs prepared by Prof. D. Xue University of Calgary SolidWorks - a solid modeling CAD tool. COSMOSWorks - a design analysis system fully integrated
An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs prepared by Prof. D. Xue University of Calgary SolidWorks - a solid modeling CAD tool. COSMOSWorks - a design analysis system fully integrated
Metafor FE Software. 2. Operator split. 4. Rezoning methods 5. Contact with friction
 ALE simulations ua sus using Metafor eao 1. Introduction 2. Operator split 3. Convection schemes 4. Rezoning methods 5. Contact with friction 1 Introduction EULERIAN FORMALISM Undistorted mesh Ideal for
ALE simulations ua sus using Metafor eao 1. Introduction 2. Operator split 3. Convection schemes 4. Rezoning methods 5. Contact with friction 1 Introduction EULERIAN FORMALISM Undistorted mesh Ideal for
True 3D CAE visualization of filling imbalance in geometry-balanced runners
 True 3D CAE visualization of filling imbalance in geometry-balanced runners C.C. Chien, * C.C. Chiang, W. H. Yang, Vito Tsai and David C.Hsu CoreTech System Co.,Ltd., HsinChu, Taiwan, ROC Abstract The
True 3D CAE visualization of filling imbalance in geometry-balanced runners C.C. Chien, * C.C. Chiang, W. H. Yang, Vito Tsai and David C.Hsu CoreTech System Co.,Ltd., HsinChu, Taiwan, ROC Abstract The
NEi FEA. IRONCAD Advanced FEA. IRONCAD Advanced FEA. NEi FEA
 2011 Overview has been designed as a universal, adaptive and user-friendly graphical user interface for geometrical modeling, data input and visualization of results for all types of numerical simulation
2011 Overview has been designed as a universal, adaptive and user-friendly graphical user interface for geometrical modeling, data input and visualization of results for all types of numerical simulation
Realize Your Product Promise. Icepak
 Realize Your Product Promise Icepak ANSYS Icepak delivers powerful technology for electronics thermal management. Simulating high-performance electronics cooling readily solves challenges in this rapidly
Realize Your Product Promise Icepak ANSYS Icepak delivers powerful technology for electronics thermal management. Simulating high-performance electronics cooling readily solves challenges in this rapidly
A New Way for Multi-piece and Multi-hit Fragment Impact Simulation Using LS-DYNA
 9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Impact Analysis (1) A New Way for Multi-piece and Multi-hit Fragment Impact Simulation Using LS-DYNA Xudong Xin Karagozian and Case 255 N. Hollywood Way, Suite
9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Impact Analysis (1) A New Way for Multi-piece and Multi-hit Fragment Impact Simulation Using LS-DYNA Xudong Xin Karagozian and Case 255 N. Hollywood Way, Suite
Simulation of Automotive Fuel Tank Sloshing using Radioss
 Simulation of Automotive Fuel Tank Sloshing using Radioss Prashant V. Kulkarni CAE Analyst Tata Motors. Pimpri, Pune - 411018, India Sanjay S. Patil Senior Manager Tata Motors. Pimpri, Pune - 411018, India
Simulation of Automotive Fuel Tank Sloshing using Radioss Prashant V. Kulkarni CAE Analyst Tata Motors. Pimpri, Pune - 411018, India Sanjay S. Patil Senior Manager Tata Motors. Pimpri, Pune - 411018, India
HPC Computer Aided CINECA
 HPC Computer Aided Engineering @ CINECA Raffaele Ponzini Ph.D. CINECA SuperComputing Applications and Innovation Department SCAI 16-18 June 2014 Segrate (MI), Italy Outline Open-source CAD and Meshing
HPC Computer Aided Engineering @ CINECA Raffaele Ponzini Ph.D. CINECA SuperComputing Applications and Innovation Department SCAI 16-18 June 2014 Segrate (MI), Italy Outline Open-source CAD and Meshing
2008 International ANSYS Conference
 2008 International ANSYS Conference Simulation Driven Product Development using ANSYS Technology Padmesh Mandloi Rahul Kumar Samir Kadam 2008 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2008 International ANSYS Conference Simulation Driven Product Development using ANSYS Technology Padmesh Mandloi Rahul Kumar Samir Kadam 2008 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
BURN-IN OVEN MODELING USING COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD)
 BURN-IN OVEN MODELING USING COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) Jefferson S. Talledo ATD-P Technology Business Group Intel Technology Philippines, Inc., Gateway Business Park, Gen. Trias, Cavite jefferson.s.talledo@intel.com
BURN-IN OVEN MODELING USING COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) Jefferson S. Talledo ATD-P Technology Business Group Intel Technology Philippines, Inc., Gateway Business Park, Gen. Trias, Cavite jefferson.s.talledo@intel.com
LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA.
 12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference FSI/ALE(1) LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA Part 1 Facundo Del
12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference FSI/ALE(1) LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA Part 1 Facundo Del
LOCAL STRESS ANALYSIS OF STIFFENED SHELLS USING MSC/NASTRAN S SHELL AND BEAM p-elements
 LOCAL STRESS ANALYSIS OF STIFFENED SHELLS USING MSC/NASTRAN S SHELL AND BEAM p-elements Sanjay Patel, Claus Hoff, Mark Gwillim The MacNeal-Schwendler Corporation Abstract In large finite element models
LOCAL STRESS ANALYSIS OF STIFFENED SHELLS USING MSC/NASTRAN S SHELL AND BEAM p-elements Sanjay Patel, Claus Hoff, Mark Gwillim The MacNeal-Schwendler Corporation Abstract In large finite element models
