Chapter 4 Review. 1. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter. 2. Draw a graph for the following task table.
|
|
|
- Jeremy Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 hapter Review 1. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter.. raw a graph for the following task table. Task Time Prerequisites Start 0 None 1 5,, I, inish. a. List the vertices of the following graph and give their earlieststart time. b. etermine the minimum project time. 5 Start 0 J 5 inish 1 6 I
2 hapter raphs and Their pplications. omplete the task table for the following graph. Start inish Task Time Prerequisites Start 0 inish 5. Use your graph from xercise. a. Recopy it and label each vertex with its ST. b. etermine the critical path and the minimum project time.
3 hapter Review 6. Task Time Prerequisites Start 0 6 None 9 None 8 None 5, 10 5, 7 I 8 inish 7. a. raw a graph using the information in the table. b. Label each vertex with its earliest-start time. c. etermine the minimum project time. d. etermine the critical path(s). a. Is this graph connected? xplain why or why not. b. Is this graph complete? xplain why or why not. c. Name two vertices that are adjacent to vertex. d. Name a path from to of length. e. What is the degree of vertex? f. etermine an adjacency matrix for the graph.
4 hapter raphs and Their pplications 8. a. raw a K 5 graph. Label the vertices,,,, and I. b. eg() =?. c. oes the graph have an uler circuit? xplain. 9. Try to construct a graph with five vertices that is not connected so that two of the vertices have degree and two of the vertices have degree. No loops or multiple edges may be used. 10. Tell whether the following graphs have an uler circuit, an uler path, or neither. xplain your answers. a. b. 11. onstruct a graph for each of the following. a. V = {,,,, } = {,,,, } b
5 hapter Review 5 1. ollowing is a multigraph that represents the downtown area of a small city. The local post office has decided that the mail drop boxes, which are located at the intersection of each street, must be monitored twice daily. a. Is it possible to find a circuit that begins and ends at the same intersection and visits each drop box exactly once? b. If not, is there a path that begins at one drop box, visits each drop box exactly once, and ends at a different drop box? c. If either route exists, copy the figure onto your paper and darken the edges of your proposed route. 1. Use the graph in xercise 1. a. Is it possible for the local street inspector to begin at an intersection and inspect each street exactly once? b. Is it possible for the inspector to finish her route at the same intersection from which she began? xplain why or why not. 1. ind an adjacency matrix for the following digraph.
6 6 hapter raphs and Their pplications 15. onsider the following set of preference schedules a. Represent this election with a cumulative preference tournament. b. Is there a ondorcet winner? xplain why or why not. c. ind several amiltonian paths for your graph. d. Show how to use a amiltonian path to construct a pairwise voting scheme (see xercise, Lesson 1., page 0) that results in winning the election. 16. raw a connected graph with four vertices that has a amiltonian circuit but no uler circuits or paths. 17. In scheduling the final exam for summer school at entral igh, six different tests must be scheduled. The following table shows the exams that are needed for seven different students. Students xams (M) Math () rt (S) Science () istory () rench (R) Reading a. raw a graph that models which exams have students in common with other exams. b. What is the minimum number of time slots needed to schedule the six exams? 0
7 hapter Review The ederal ommunications ommission () is in charge of assigning frequencies to radio stations so that broadcasts from one station do not interfere with broadcasts from other stations. Suppose the needs to assign frequencies to eight stations. The following table shows which stations cannot share frequencies. Station annot Share with,,,,,,,,,,,,,, a. Model this situation with a graph. b. ind the minimum number of frequencies needed by the. 19. onsider the following digraph. a. oes it have a directed uler circuit? xplain why or why not. If it does, list one. b. oes it have a directed uler path? xplain why or why not. If it does, list one.
8 8 hapter raphs and Their pplications 0. a. Represent the following map with a graph. b. olor your graph. c. What is the minimum number of colors needed to color the map? KY V TN N S MS L L ibliography iggs, N. L.,. K. Lloyd, and R. J. Wilson raph Theory Oxford: larendon Press. usch, The New ritical Path Method. hicago: Probus. havey, arrah rawing Pictures with One Line. (istomp Module 1). Lexington, M: OMP, Inc. OMP, Inc. 01. or ll Practical Purposes: Mathematical Literacy in Today s World. 9th ed. New York: W.. reeman. opes, W.,. Sloyer, R. Stark, and W. Sacco raph Theory: uler s Rich Legacy. Providence, RI: Janson. ozzens, Margaret., and R. Porter Mathematics and Its pplications. Lexington, M:.. eath and ompany. ozzens, Margaret., and R. Porter Problem Solving Using raphs. (imp Module 6). Lexington, M: OMP, Inc.
9 hapter Review 9 ossey, John,. Otto, L. Spence, and. Vanden ynden iscrete Mathematics. 5th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson. rancis, Richard L The Mathematicians oloring ook. (imp Module #10). Lexington, M: OMP, Inc. Kenney, Margaret J., ed iscrete Mathematics across the urriculum, K Yearbook of the National ouncil of Teachers of Mathematics. Reston, V: NTM. Malkevitch, J., and W. Meyer raphs, Models, and inite Mathematics. nglewood liffs, NJ: Prentice all. Tannenbaum, P., and R. rnold. 01. xcursions in Modern Mathematics. 8th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson. Wilson, Robin. 00. our olors Suffice. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Chapter 5 Review. 1. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter.
 DM_Final.qxp:DM.qxp // 8: AM Page 89 Chapter Review. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter.. Is the following graph planar or nonplanar? If it is planar, redraw it
DM_Final.qxp:DM.qxp // 8: AM Page 89 Chapter Review. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter.. Is the following graph planar or nonplanar? If it is planar, redraw it
Lesson 4.2. Critical Paths
 Lesson. ritical Paths It is relatively easy to find the shortest time needed to complete a project if the project consists of only a few activities. ut as the tasks increase in number, the problem becomes
Lesson. ritical Paths It is relatively easy to find the shortest time needed to complete a project if the project consists of only a few activities. ut as the tasks increase in number, the problem becomes
MATH 103: Contemporary Mathematics Study Guide for Chapter 6: Hamilton Circuits and the TSP
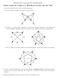 MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
SAMPLE. Networks. A view of Königsberg as it was in Euler s day.
 ack to Menu >>> How are graphs used to represent networks? H P T R 10 Networks How do we analyse the information contained in graphs? How do we use graphs to represent everyday situations? 10.1 Graph theory
ack to Menu >>> How are graphs used to represent networks? H P T R 10 Networks How do we analyse the information contained in graphs? How do we use graphs to represent everyday situations? 10.1 Graph theory
11-5 Networks. Königsberg Bridge Problem
 Section 11-5 Networks 1 11-5 Networks In the 1700s, the people of Königsberg, Germany (now Kaliningrad in Russia), used to enjoy walking over the bridges of the Pregel River. There were three landmasses
Section 11-5 Networks 1 11-5 Networks In the 1700s, the people of Königsberg, Germany (now Kaliningrad in Russia), used to enjoy walking over the bridges of the Pregel River. There were three landmasses
Chapter 4 Answers. Lesson 4.1. Chapter 4 Answers 1
 Chapter 4 Answers Lesson 4.1 1. 2. 3. 4. Chapter 4 Answers 1 5. Answers vary. Sample answer: a. A: 2, none; B: 4, A; C: 3, B; D: 7, C; E: 5, A; F: 10, E; G: 8, A; H: 3, A; I: 4, D, F, G, and H b. c. In
Chapter 4 Answers Lesson 4.1 1. 2. 3. 4. Chapter 4 Answers 1 5. Answers vary. Sample answer: a. A: 2, none; B: 4, A; C: 3, B; D: 7, C; E: 5, A; F: 10, E; G: 8, A; H: 3, A; I: 4, D, F, G, and H b. c. In
Math 100 Homework 4 B A C E
 Math 100 Homework 4 Part 1 1. nswer the following questions for this graph. (a) Write the vertex set. (b) Write the edge set. (c) Is this graph connected? (d) List the degree of each vertex. (e) oes the
Math 100 Homework 4 Part 1 1. nswer the following questions for this graph. (a) Write the vertex set. (b) Write the edge set. (c) Is this graph connected? (d) List the degree of each vertex. (e) oes the
Graphs. Reading Assignment. Mandatory: Chapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2. Peeking into Computer Science. Jalal Kawash 2010
 Graphs Mandatory: hapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2 Reading ssignment 2 Graphs bstraction of ata 3 t the end of this section, you will be able to: 1.efine directed and undirected graphs 2.Use graphs to model
Graphs Mandatory: hapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2 Reading ssignment 2 Graphs bstraction of ata 3 t the end of this section, you will be able to: 1.efine directed and undirected graphs 2.Use graphs to model
SAMPLE. MODULE 5 Undirected graphs
 H P T R MOUL Undirected graphs How do we represent a graph by a diagram and by a matrix representation? How do we define each of the following: graph subgraph vertex edge (node) loop isolated vertex bipartite
H P T R MOUL Undirected graphs How do we represent a graph by a diagram and by a matrix representation? How do we define each of the following: graph subgraph vertex edge (node) loop isolated vertex bipartite
Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4
 MATH 11008: Graph Theory Terminology Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4 Routing problem: A routing problem is concerned with finding ways to route the delivery of good and/or services to an assortment of destinations.
MATH 11008: Graph Theory Terminology Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4 Routing problem: A routing problem is concerned with finding ways to route the delivery of good and/or services to an assortment of destinations.
Graphs And Algorithms
 Graphs nd lgorithms Mandatory: hapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2 Reading ssignment 2 1 Graphs bstraction of ata 3 t the end of this section, you will be able to: 1. efine directed and undirected graphs 2. Use
Graphs nd lgorithms Mandatory: hapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2 Reading ssignment 2 1 Graphs bstraction of ata 3 t the end of this section, you will be able to: 1. efine directed and undirected graphs 2. Use
Angle Bisectors of Triangles
 6 What You ll Learn You ll learn to identify and use angle bisectors in triangles. ngle isectors of Triangles ecall that the bisector of an angle is a ray that separates the angle into two congruent angles.
6 What You ll Learn You ll learn to identify and use angle bisectors in triangles. ngle isectors of Triangles ecall that the bisector of an angle is a ray that separates the angle into two congruent angles.
NUMB3RS Activity: Sinks & Sources. Episode: Hot Shot
 NUM3RS ctivity Teacher Page 1 pisode: Hot Shot NUM3RS ctivity: Sinks & Sources pisode: Hot Shot Topic: irected graphs Grade Level: 9-12 Objective: Investigate paths and flow in directed graphs Time: 30
NUM3RS ctivity Teacher Page 1 pisode: Hot Shot NUM3RS ctivity: Sinks & Sources pisode: Hot Shot Topic: irected graphs Grade Level: 9-12 Objective: Investigate paths and flow in directed graphs Time: 30
Lesson 5.5. Minimum Spanning Trees. Explore This
 Lesson. St harles ounty Minimum Spanning Trees s in many of the previous lessons, this lesson focuses on optimization. Problems and applications here center on two types of problems: finding ways of connecting
Lesson. St harles ounty Minimum Spanning Trees s in many of the previous lessons, this lesson focuses on optimization. Problems and applications here center on two types of problems: finding ways of connecting
a) Graph 2 and Graph 3 b) Graph 2 and Graph 4 c) Graph 1 and Graph 4 d) Graph 1 and Graph 3 e) Graph 3 and Graph 4 f) None of the above
 Mathematics 105: Math as a Liberal Art. Final Exam. Name Instructor: Ramin Naimi Spring 2008 Close book. Closed notes. No Calculators. NO CELL PHONES! Please turn off your cell phones and put them away.
Mathematics 105: Math as a Liberal Art. Final Exam. Name Instructor: Ramin Naimi Spring 2008 Close book. Closed notes. No Calculators. NO CELL PHONES! Please turn off your cell phones and put them away.
NUMB3RS Activity: Location! Location! Location! Episode: "Bones of Contention"
 NUMRS ctivity Teacher Page Episode: "ones of ontention NUMRS ctivity: Location! Location! Location! Episode: "ones of ontention" Topic: Voronoi Diagrams Grade Level: 8 - Objectives: Understand the basic
NUMRS ctivity Teacher Page Episode: "ones of ontention NUMRS ctivity: Location! Location! Location! Episode: "ones of ontention" Topic: Voronoi Diagrams Grade Level: 8 - Objectives: Understand the basic
1-1 Skills Practice. Points, Lines, and Planes. Lesson 1-1. Refer to the figure. 1. Name a line that contains point e. n G
 M T RIO 1-1 Skills ractice 1. ame a line that contains point e. 2. ame a point contained in line n. p n q e 3. What is another name for line p? 4. ame the plane containing lines n and p. raw and label
M T RIO 1-1 Skills ractice 1. ame a line that contains point e. 2. ame a point contained in line n. p n q e 3. What is another name for line p? 4. ame the plane containing lines n and p. raw and label
Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around
 1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
Examples of Tasks from Course 1, Unit 4
 Examples of Tasks from Course 1, Unit 4 What Solutions are Available? Lesson 1: page 258, Modeling Task 1; page 260, Modeling Task 4; page 261, Organizing Task 1; page 271, Modeling Task 2; page 272, Modeling
Examples of Tasks from Course 1, Unit 4 What Solutions are Available? Lesson 1: page 258, Modeling Task 1; page 260, Modeling Task 4; page 261, Organizing Task 1; page 271, Modeling Task 2; page 272, Modeling
The Oberwolfach Problem in Graph Theory
 The Oberwolfach Problem in Graph Theory Andrea Zentz Andrea Zentz graduated Magna Cum Laude from Ball State in May with a major in Mathematics Education. She plans to work as a teacher while eventually
The Oberwolfach Problem in Graph Theory Andrea Zentz Andrea Zentz graduated Magna Cum Laude from Ball State in May with a major in Mathematics Education. She plans to work as a teacher while eventually
Sec 7.1 EST Graphs Networks & Graphs
 Sec 7.1 ST raphs Networks & raphs Name: These graphs are models to find the RLIST TIM any particular job can STRT. What do you think is meant in a team by the following statement? You are only as fast
Sec 7.1 ST raphs Networks & raphs Name: These graphs are models to find the RLIST TIM any particular job can STRT. What do you think is meant in a team by the following statement? You are only as fast
Altitudes and Perpendicular Bisectors
 6 2 hat ou ll Learn ou ll learn to identify and construct s and perpendicular bisectors in triangles. ltitudes and erpendicular isectors In geometry, an of a triangle is a perpendicular segment with one
6 2 hat ou ll Learn ou ll learn to identify and construct s and perpendicular bisectors in triangles. ltitudes and erpendicular isectors In geometry, an of a triangle is a perpendicular segment with one
llj EXERCISES 938 CHAPTER 15 Graph Theory 11. For Exercises 1-6, determine how many vertices and how many edges each graph has. 13.
 938 HAPTR 15 Graph Theory 15.1 XRISS or xercises 1-6, determine how many vertices and how many edges each graph has. 13. 1. 2. (a) (b) 3. 4. 14. (al (b) s. 15. (a) L. (b) 7.-10. or xercises 7-10, refer
938 HAPTR 15 Graph Theory 15.1 XRISS or xercises 1-6, determine how many vertices and how many edges each graph has. 13. 1. 2. (a) (b) 3. 4. 14. (al (b) s. 15. (a) L. (b) 7.-10. or xercises 7-10, refer
Honors ICM- Graph Theory Unit 7 Homework Packet Homework Day 1
 Honors ICM- Graph Theory Unit 7 Homework Packet Homework Day 1 Name Period: 6. Construct a graph with three critical paths. 7. Determine the minimum project time and the critical path for the following
Honors ICM- Graph Theory Unit 7 Homework Packet Homework Day 1 Name Period: 6. Construct a graph with three critical paths. 7. Determine the minimum project time and the critical path for the following
Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around
 1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
Undirected graphs and networks
 Gen. Maths h. 1(1) Page 1 Thursday, ecember 0, 1999 1:10 PM Undirected graphs and networks 1 V co covverage rea of study Units 1 & Geometry In this chapter 1 Vertices and edges 1 Planar graphs 1 ulerian
Gen. Maths h. 1(1) Page 1 Thursday, ecember 0, 1999 1:10 PM Undirected graphs and networks 1 V co covverage rea of study Units 1 & Geometry In this chapter 1 Vertices and edges 1 Planar graphs 1 ulerian
Lesson 5.2. The Traveling Salesperson Problem. Explore This
 Lesson 5.2 The Traveling alesperson Problem In Lesson 4.5, you explored circuits that visited each vertex of your graph exactly once (Hamiltonian circuits). In this lesson, you will extend your thinking
Lesson 5.2 The Traveling alesperson Problem In Lesson 4.5, you explored circuits that visited each vertex of your graph exactly once (Hamiltonian circuits). In this lesson, you will extend your thinking
Brief History. Graph Theory. What is a graph? Types of graphs Directed graph: a graph that has edges with specific directions
 Brief History Graph Theory What is a graph? It all began in 1736 when Leonhard Euler gave a proof that not all seven bridges over the Pregolya River could all be walked over once and end up where you started.
Brief History Graph Theory What is a graph? It all began in 1736 when Leonhard Euler gave a proof that not all seven bridges over the Pregolya River could all be walked over once and end up where you started.
Practice Exam #3, Math 100, Professor Wilson. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Exam #3, Math 100, Professor Wilson MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A tree is A) any graph that is connected and every
Practice Exam #3, Math 100, Professor Wilson MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A tree is A) any graph that is connected and every
Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal. ESSENTIAL QUESTION What can you conclude about the angles formed by parallel lines that are cut by a transversal?
 ? LSSON 7.1 Parallel Lines ut by a Transversal SSNTIL QUSTION What can you conclude about the angles formed by parallel lines that are cut by a transversal? xpressions, equations, and relationships Use
? LSSON 7.1 Parallel Lines ut by a Transversal SSNTIL QUSTION What can you conclude about the angles formed by parallel lines that are cut by a transversal? xpressions, equations, and relationships Use
Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around
 Euler Paths and Circuits Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around 5.1 Street-Routing Problem Our story begins in the 1700s in the medieval town of Königsberg, in Eastern Europe. At the time, Königsberg
Euler Paths and Circuits Chapter 5: The Mathematics of Getting Around 5.1 Street-Routing Problem Our story begins in the 1700s in the medieval town of Königsberg, in Eastern Europe. At the time, Königsberg
Grade 7/8 Math Circles March 7, 2012 Introduction to Graph Theory
 1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics entre for Education in Mathematics and omputing Grade 7/8 Math ircles March 7, 2012 Introduction to Graph Theory What is graph theory? Graph theory is the
1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics entre for Education in Mathematics and omputing Grade 7/8 Math ircles March 7, 2012 Introduction to Graph Theory What is graph theory? Graph theory is the
Math Fall 2011 Exam 3 Solutions - December 8, 2011
 Math 365 - all 2011 xam 3 Solutions - ecember 8, 2011 NM: STUNT I: This is a closed-book and closed-note examination. alculators are not allowed. Please show all your work. Use only the paper provided.
Math 365 - all 2011 xam 3 Solutions - ecember 8, 2011 NM: STUNT I: This is a closed-book and closed-note examination. alculators are not allowed. Please show all your work. Use only the paper provided.
Math 110 Graph Theory II: Circuits and Paths
 Math 110 Graph Theory II: Circuits and Paths For Next Time. Read Section 6.1 Circuit Training (p. 386ff) for more background on this material. Review the definition of a graph. Make sure you understand
Math 110 Graph Theory II: Circuits and Paths For Next Time. Read Section 6.1 Circuit Training (p. 386ff) for more background on this material. Review the definition of a graph. Make sure you understand
14.2 Euler Paths and Circuits filled in.notebook November 18, Euler Paths and Euler Circuits
 14.2 Euler Paths and Euler Circuits The study of graph theory can be traced back to the eighteenth century when the people of the town of Konigsberg sought a solution to a popular problem. They had sections
14.2 Euler Paths and Euler Circuits The study of graph theory can be traced back to the eighteenth century when the people of the town of Konigsberg sought a solution to a popular problem. They had sections
QUESTIONS FROM 2017 VCAA EXAMS ON PROBABILITY
 2017 MATHMETH EXAM 2 Question 3 (19 marks) QUESTIONS FROM 2017 VCAA EXAMS ON PROBABILITY The time Jennifer spends on her homework each day varies, but she does some homework every day. The continuous random
2017 MATHMETH EXAM 2 Question 3 (19 marks) QUESTIONS FROM 2017 VCAA EXAMS ON PROBABILITY The time Jennifer spends on her homework each day varies, but she does some homework every day. The continuous random
5.2 ASA Triangle Congruence
 Name lass ate 5.2 S Triangle ongruence ssential question: What does the S Triangle ongruence Theorem tell you about triangles? xplore 1 rawing Triangles Given Two ngles and a Side You have seen that two
Name lass ate 5.2 S Triangle ongruence ssential question: What does the S Triangle ongruence Theorem tell you about triangles? xplore 1 rawing Triangles Given Two ngles and a Side You have seen that two
Essential Question How can you describe angle pair relationships and use these descriptions to find angle measures?
 1.6 escribing Pairs of ngles OMMON OR Learning Standard HSG-O..1 ssential Question How can you describe angle pair relationships and use these descriptions to find angle measures? Finding ngle Measures
1.6 escribing Pairs of ngles OMMON OR Learning Standard HSG-O..1 ssential Question How can you describe angle pair relationships and use these descriptions to find angle measures? Finding ngle Measures
Unit graph theory UNIT 4
 Unit graph theory UNIT 4 Concept Characteristics What is a Graph Really? Get in groups of three and discuss what you think a graph really is. Come up with three statements that describe the characteristics
Unit graph theory UNIT 4 Concept Characteristics What is a Graph Really? Get in groups of three and discuss what you think a graph really is. Come up with three statements that describe the characteristics
Using Euler s Theorem
 Using Euler s Theorem Suppose that a connected, planar graph has 249 vertices and 57 faces. How many edges does it have? A: 106 B: 194 C: 304 D: 306 E: We don t have enough information Using Euler s Theorem
Using Euler s Theorem Suppose that a connected, planar graph has 249 vertices and 57 faces. How many edges does it have? A: 106 B: 194 C: 304 D: 306 E: We don t have enough information Using Euler s Theorem
The University of Sydney MATH 2009
 The University of Sydney MTH 009 GRPH THORY Tutorial 10 Solutions 004 1. In a tournament, the score of a vertex is its out-degree, and the score sequence is a list of all the scores in non-decreasing order.
The University of Sydney MTH 009 GRPH THORY Tutorial 10 Solutions 004 1. In a tournament, the score of a vertex is its out-degree, and the score sequence is a list of all the scores in non-decreasing order.
An Early Problem in Graph Theory. Clicker Question 1. Konigsberg and the River Pregel
 raphs Topic " Hopefully, you've played around a bit with The Oracle of acon at Virginia and discovered how few steps are necessary to link just about anybody who has ever been in a movie to Kevin acon,
raphs Topic " Hopefully, you've played around a bit with The Oracle of acon at Virginia and discovered how few steps are necessary to link just about anybody who has ever been in a movie to Kevin acon,
Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1
 Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1 Finite Math A Chapter 8 The Mathematics of Scheduling Chapter 8: The Mathematics of Scheduling Pd 2 & 6 Pd 4 & 7 Lesson Homework Tues Wed 8.1, 8.2 The Basic Elements
Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1 Finite Math A Chapter 8 The Mathematics of Scheduling Chapter 8: The Mathematics of Scheduling Pd 2 & 6 Pd 4 & 7 Lesson Homework Tues Wed 8.1, 8.2 The Basic Elements
Foundations of Discrete Mathematics
 Foundations of Discrete Mathematics Chapters 9 By Dr. Dalia M. Gil, Ph.D. Graphs Graphs are discrete structures consisting of vertices and edges that connect these vertices. Graphs A graph is a pair (V,
Foundations of Discrete Mathematics Chapters 9 By Dr. Dalia M. Gil, Ph.D. Graphs Graphs are discrete structures consisting of vertices and edges that connect these vertices. Graphs A graph is a pair (V,
Sec 2. Euler Circuits, cont.
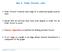 Sec 2. uler ircuits, cont. uler ircuits traverse each edge of a connected graph exactly once. Recall that all vertices must have even degree in order for an uler ircuit to exist. leury s lgorithm is a
Sec 2. uler ircuits, cont. uler ircuits traverse each edge of a connected graph exactly once. Recall that all vertices must have even degree in order for an uler ircuit to exist. leury s lgorithm is a
EXERCISES Practice and Problem Solving
 XI ractice and roblem olving or more practice, see xtra ractice. ractice by xample xample (page 224) In each diagram, the red and blue triangles are congruent. Identify their common side or angle.. K 2.
XI ractice and roblem olving or more practice, see xtra ractice. ractice by xample xample (page 224) In each diagram, the red and blue triangles are congruent. Identify their common side or angle.. K 2.
7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles
 Name lass Date 7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles Essential Question: What are the special relationships among angles and sides in isosceles and equilateral triangles? Resource Locker Explore G.6.D
Name lass Date 7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles Essential Question: What are the special relationships among angles and sides in isosceles and equilateral triangles? Resource Locker Explore G.6.D
Euler and Hamilton circuits. Euler paths and circuits
 1 7 16 2013. uler and Hamilton circuits uler paths and circuits o The Seven ridges of Konigsberg In the early 1700 s, Konigsberg was the capital of ast Prussia. Konigsberg was later renamed Kaliningrad
1 7 16 2013. uler and Hamilton circuits uler paths and circuits o The Seven ridges of Konigsberg In the early 1700 s, Konigsberg was the capital of ast Prussia. Konigsberg was later renamed Kaliningrad
Week 11: Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs; Trees. 21 and 23 November, 2018
 (1/22) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 11: Eulerian and amiltonian graphs; Trees http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ amilton s Icosian Game (Library or the Royal Irish Academy) 21 and 23 November,
(1/22) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 11: Eulerian and amiltonian graphs; Trees http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ amilton s Icosian Game (Library or the Royal Irish Academy) 21 and 23 November,
MHS Practice Examination
 MHS Practice Examination Exam #2 563-504 MATHEMATICS CULTURAL, SOCIAL AND TECHNICAL OPTION SEC V CST Student Question Booklet Parts A, B and C This resource can be used for FREE by any teacher or student
MHS Practice Examination Exam #2 563-504 MATHEMATICS CULTURAL, SOCIAL AND TECHNICAL OPTION SEC V CST Student Question Booklet Parts A, B and C This resource can be used for FREE by any teacher or student
Possibilities of Voting
 Possibilities of Voting MATH 100, Survey of Mathematical Ideas J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2018 Introduction When choosing between just two alternatives, the results of voting are
Possibilities of Voting MATH 100, Survey of Mathematical Ideas J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2018 Introduction When choosing between just two alternatives, the results of voting are
ASA Triangle Congruence
 Locker LSSON 5.2 S Triangle ongruence Texas Math Standards The student is expected to: G.6. Prove two triangles are congruent by applying the Side-ngle-Side, ngle-side-ngle, Side-Side-Side, ngle-ngle-side,
Locker LSSON 5.2 S Triangle ongruence Texas Math Standards The student is expected to: G.6. Prove two triangles are congruent by applying the Side-ngle-Side, ngle-side-ngle, Side-Side-Side, ngle-ngle-side,
Graph Theory(Due with the Final Exam)
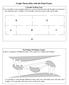 Graph Theory(ue with the Final Exam) Possible Walking Tour.. Is it possible to start someplace(either in a room or outside) and walk through every doorway once and only once? Explain. If it is possible,
Graph Theory(ue with the Final Exam) Possible Walking Tour.. Is it possible to start someplace(either in a room or outside) and walk through every doorway once and only once? Explain. If it is possible,
Angle Theorems for Triangles 8.8.D
 ? LSSON 7.2 ngle Theorems for Triangles SSNTIL QUSTION xpressions, equations, and relationships 8.8. Use informal arguments to establish facts about the angle sum and exterior angle of triangles, What
? LSSON 7.2 ngle Theorems for Triangles SSNTIL QUSTION xpressions, equations, and relationships 8.8. Use informal arguments to establish facts about the angle sum and exterior angle of triangles, What
Unit 7 Day 2 Section Vocabulary & Graphical Representations Euler Circuits and Paths
 Unit 7 Day 2 Section 4.3-4.5 Vocabulary & Graphical Representations Euler Circuits and Paths 1 Warm Up ~ Day 2 List the tasks and earliest start times in a table, as in exercise #1. Determine the minimum
Unit 7 Day 2 Section 4.3-4.5 Vocabulary & Graphical Representations Euler Circuits and Paths 1 Warm Up ~ Day 2 List the tasks and earliest start times in a table, as in exercise #1. Determine the minimum
Finite Mathematical Structures A
 MS 301.2 (Spring, 2010) stie rkin inite Mathematical Structures xam 1: Thursday, ebruary 25, 2010 R TS INSTRUTIONS RULLY. o not start the exam until told to do so. Make certain that you have all 5 pages
MS 301.2 (Spring, 2010) stie rkin inite Mathematical Structures xam 1: Thursday, ebruary 25, 2010 R TS INSTRUTIONS RULLY. o not start the exam until told to do so. Make certain that you have all 5 pages
Determining Similarity. Which isosceles triangle does not belong? I noticed that the. corresponding angles in. measurements.
 3.2 etermining Similarity O evelop strategies to determine if two shapes are similar. YOU WI N a ruler a protractor RN OUT the Math ia-wen and Sam are sorting isosceles triangles to solve a puzzle in a
3.2 etermining Similarity O evelop strategies to determine if two shapes are similar. YOU WI N a ruler a protractor RN OUT the Math ia-wen and Sam are sorting isosceles triangles to solve a puzzle in a
Subtraction Understand Subtraction on a Number Line Using a number line let s demonstrate the subtraction process using the problem 7 5.
 Objective 1 Subtraction Understand Subtraction on a Number Line Using a number line let s demonstrate the subtraction process using the problem 7 5. -7-6 -5-4 -3-2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Using the number line
Objective 1 Subtraction Understand Subtraction on a Number Line Using a number line let s demonstrate the subtraction process using the problem 7 5. -7-6 -5-4 -3-2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Using the number line
Database Design. 1-2 Data vs. Information. Copyright 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
 Database Design 1-2 Objectives This lesson covers the following objectives: Distinguish between data and information, and provide examples of each Describe and give an example of how data becomes information
Database Design 1-2 Objectives This lesson covers the following objectives: Distinguish between data and information, and provide examples of each Describe and give an example of how data becomes information
of Nebraska - Lincoln
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2008 De Bruijn Cycles Val Adams University of Nebraska
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2008 De Bruijn Cycles Val Adams University of Nebraska
What could be the name of the plane represented by the top of the box?
 hapter 02 Test Name: ate: 1 Use the figure below. What could be the name of the plane represented by the top of the box? E F I 2 Use the figure below. re points,, and E collinear or noncollinear? noncollinear
hapter 02 Test Name: ate: 1 Use the figure below. What could be the name of the plane represented by the top of the box? E F I 2 Use the figure below. re points,, and E collinear or noncollinear? noncollinear
Unit 7 Day 1. Task Graphs and Critical Paths
 Unit 7 Day 1 Task Graphs and ritical Paths Remember that ollege Tour ctivity is due at the beginning of class tomorrow!! Notes Day 1 Task Graphs and ritical Paths GRPH PPLITIONS How does a building contractor
Unit 7 Day 1 Task Graphs and ritical Paths Remember that ollege Tour ctivity is due at the beginning of class tomorrow!! Notes Day 1 Task Graphs and ritical Paths GRPH PPLITIONS How does a building contractor
1.6 Start Thinking. 1.6 Warm Up. 1.6 Cumulative Review Warm Up
 .6 Start Thinking In Section.5, you learned that a straight angle is an angle with a measure of 0. Imagine the straight angle you are measuring is the x-axis of a coordinate plane and the origin is the
.6 Start Thinking In Section.5, you learned that a straight angle is an angle with a measure of 0. Imagine the straight angle you are measuring is the x-axis of a coordinate plane and the origin is the
6 segment from vertex A to BC. . Label the endpoint D. is an altitude of ABC. 4 b. Construct the altitudes to the other two sides of ABC.
 6. Medians and ltitudes of Triangles ssential uestion What conjectures can you make about the medians and altitudes of a triangle? inding roperties of the Medians of a Triangle Work with a partner. Use
6. Medians and ltitudes of Triangles ssential uestion What conjectures can you make about the medians and altitudes of a triangle? inding roperties of the Medians of a Triangle Work with a partner. Use
Math 167 Review 1 (c) Janice Epstein
 Math 167 Review 1 (c) Janice Epstein HAPTER 1 URBAN SERVIES A graph is a collection of one or more points (vertices). The vertices may be connected by edges. Two vertices are adjacent if they are connected
Math 167 Review 1 (c) Janice Epstein HAPTER 1 URBAN SERVIES A graph is a collection of one or more points (vertices). The vertices may be connected by edges. Two vertices are adjacent if they are connected
Varying Applications (examples)
 Graph Theory Varying Applications (examples) Computer networks Distinguish between two chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures Solve shortest path problems between cities
Graph Theory Varying Applications (examples) Computer networks Distinguish between two chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures Solve shortest path problems between cities
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Name ate hapter 6 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Write an equation of the line passing through point P that is perpendicular to the given line. 1. P(5, ), y = x + 6. P(4, ), y = 6x 3 3. P( 1, ),
Name ate hapter 6 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Write an equation of the line passing through point P that is perpendicular to the given line. 1. P(5, ), y = x + 6. P(4, ), y = 6x 3 3. P( 1, ),
Launch problem: Lining streets
 Math 5340 June 15,2012 Dr. Cordero Launch problem: Lining streets Lining Street Problem A Problem on Eulerian Circuits http://www.edmath.org/mattours/discrete/ Your job for the day is to drive slowly around
Math 5340 June 15,2012 Dr. Cordero Launch problem: Lining streets Lining Street Problem A Problem on Eulerian Circuits http://www.edmath.org/mattours/discrete/ Your job for the day is to drive slowly around
Shape Up. SETTING THE STAGE Children sort figures according to basic attributes.
 Shape Up MA.C.1.1.1.2.1,.2,.3, and.4; MA.C.3.1.1.2.1 and.3 LESSON FOCUS Building models/diagrams to represent quantities between zero and one. COMPANION ANCHORS LESSONS Recognizing Shapes; Building Shapes;
Shape Up MA.C.1.1.1.2.1,.2,.3, and.4; MA.C.3.1.1.2.1 and.3 LESSON FOCUS Building models/diagrams to represent quantities between zero and one. COMPANION ANCHORS LESSONS Recognizing Shapes; Building Shapes;
Congruence and Similarity in Triangles. INVESTIGATE the Math. as shown in Colin s design. Explain how you know they are similar.
 7.1 ongruence and Similarity in Triangles YOU WILL N dynamic geometry software, or ruler and protractor GOL Investigate the relationships between corresponding sides and angles in pairs of congruent and
7.1 ongruence and Similarity in Triangles YOU WILL N dynamic geometry software, or ruler and protractor GOL Investigate the relationships between corresponding sides and angles in pairs of congruent and
Majority and Friendship Paradoxes
 Majority and Friendship Paradoxes Majority Paradox Example: Small town is considering a bond initiative in an upcoming election. Some residents are in favor, some are against. Consider a poll asking the
Majority and Friendship Paradoxes Majority Paradox Example: Small town is considering a bond initiative in an upcoming election. Some residents are in favor, some are against. Consider a poll asking the
7.4 Showing Triangles are
 7. howing riangles are imilar: and oal how that two triangles are similar using the and imilarity heorems. ey ords similar polygons p. he triangles in the avajo rug look similar. o show that they are similar,
7. howing riangles are imilar: and oal how that two triangles are similar using the and imilarity heorems. ey ords similar polygons p. he triangles in the avajo rug look similar. o show that they are similar,
1. a graph G = (V (G), E(G)) consists of a set V (G) of vertices, and a set E(G) of edges (edges are pairs of elements of V (G))
 10 Graphs 10.1 Graphs and Graph Models 1. a graph G = (V (G), E(G)) consists of a set V (G) of vertices, and a set E(G) of edges (edges are pairs of elements of V (G)) 2. an edge is present, say e = {u,
10 Graphs 10.1 Graphs and Graph Models 1. a graph G = (V (G), E(G)) consists of a set V (G) of vertices, and a set E(G) of edges (edges are pairs of elements of V (G)) 2. an edge is present, say e = {u,
1-5. Skills Practice. Angle Relationships. Lesson 1-5. ALGEBRA For Exercises 9 10, use the figure at the right.
 M IO kills ractice ngle elationships or xercises 6, use the figure at the right. ame an angle or angle pair that satisfies each condition.. ame two acute vertical angles. 2. ame two obtuse vertical angles.
M IO kills ractice ngle elationships or xercises 6, use the figure at the right. ame an angle or angle pair that satisfies each condition.. ame two acute vertical angles. 2. ame two obtuse vertical angles.
EXERCISES Practice and Problem Solving
 XI ractice and roblem olving For more practice, see xtra ractice. ractice by xample lgebra Find the value of x in each parallelogram. xample (page 95. 5.. 0. 56 5. 80 6. 6 xample (page 95 lgebra Find the
XI ractice and roblem olving For more practice, see xtra ractice. ractice by xample lgebra Find the value of x in each parallelogram. xample (page 95. 5.. 0. 56 5. 80 6. 6 xample (page 95 lgebra Find the
Problems for Breakfast
 Problems for Breakfast Shaking Hands Seven people in a room start shaking hands. Six of them shake exactly two people s hands. How many people might the seventh person shake hands with? Soccer Schedules
Problems for Breakfast Shaking Hands Seven people in a room start shaking hands. Six of them shake exactly two people s hands. How many people might the seventh person shake hands with? Soccer Schedules
Graph Coloring. Margaret M. Fleck. 3 May This lecture discusses the graph coloring problem (section 9.8 of Rosen).
 Graph Coloring Margaret M. Fleck 3 May 2010 This lecture discusses the graph coloring problem (section 9.8 of Rosen). 1 Announcements Makeup quiz last day of classes (at the start of class). Your room
Graph Coloring Margaret M. Fleck 3 May 2010 This lecture discusses the graph coloring problem (section 9.8 of Rosen). 1 Announcements Makeup quiz last day of classes (at the start of class). Your room
Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Note 13. An Introduction to Graphs
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Note 13 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite to writing a
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Note 13 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite to writing a
Grade 7/8 Math Circles Graph Theory - Solutions October 13/14, 2015
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Graph Theory - Solutions October 13/14, 2015 The Seven Bridges of Königsberg In
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Graph Theory - Solutions October 13/14, 2015 The Seven Bridges of Königsberg In
Solutions to Assignment 5
 Solutions to ssignment 5. We have captured several people whom we suspect are part of a spy ring. They are identified as,,,, E, F, and G. fter interrogation, admits to having met the other six. admits
Solutions to ssignment 5. We have captured several people whom we suspect are part of a spy ring. They are identified as,,,, E, F, and G. fter interrogation, admits to having met the other six. admits
2. Find the measure of AC. 4. Find the measure of BD. 6. Find the measure of AB.
 7.3 Start Thinking xamine the diagram and determine if there appears to be enough information to conclude that the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. If there is not enough information, give an example
7.3 Start Thinking xamine the diagram and determine if there appears to be enough information to conclude that the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. If there is not enough information, give an example
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MATH 100 -- Survery of Mathematical Ideas PRACTICE TEST 3 Millersville University, Spring 2012 Ron Umble, Instr. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
MATH 100 -- Survery of Mathematical Ideas PRACTICE TEST 3 Millersville University, Spring 2012 Ron Umble, Instr. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Excursions in Modern Mathematics Sixth Edition. Chapter 5 Euler Circuits. The Circuit Comes to Town. Peter Tannenbaum
 Excursions in Modern Mathematics Sixth Edition Chapter 5 Peter Tannenbaum The Circuit Comes to Town 1 2 Outline/learning Objectives Outline/learning Objectives (cont.) To identify and model Euler circuit
Excursions in Modern Mathematics Sixth Edition Chapter 5 Peter Tannenbaum The Circuit Comes to Town 1 2 Outline/learning Objectives Outline/learning Objectives (cont.) To identify and model Euler circuit
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Name ate hapter 8 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Tell whether the ratios form a proportion. 1. 16, 4 12 2. 5 45, 6 81. 12 16, 96 100 4. 15 75, 24 100 5. 17 2, 68 128 6. 65 156, 105 252 Find the scale
Name ate hapter 8 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Tell whether the ratios form a proportion. 1. 16, 4 12 2. 5 45, 6 81. 12 16, 96 100 4. 15 75, 24 100 5. 17 2, 68 128 6. 65 156, 105 252 Find the scale
1. Right angles. 2. Parallel lines
 Math 3329-Uniform Geometries Lecture 03 Euclid defines a right angle as follows 1. Right angles When a straight line set up on a straight line makes the adjacent angles equal to one another, each of the
Math 3329-Uniform Geometries Lecture 03 Euclid defines a right angle as follows 1. Right angles When a straight line set up on a straight line makes the adjacent angles equal to one another, each of the
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 1. The network in the diagram above shows the distances, in metres, between 10 wildlife observation points. The observation points are to be linked by footpaths, to form a network along the arcs indicated,
1. The network in the diagram above shows the distances, in metres, between 10 wildlife observation points. The observation points are to be linked by footpaths, to form a network along the arcs indicated,
Mathematics 504 CST. Mid-Year Examination January Question/Answer Booklet. Student's Name FOR TEACHER USE ONLY. Part A /24.
 563-504 Mathematics 504 CST Mid-Year Examination January 2011 Question/Answer Booklet Student's Name Group Date FOR TEACHER USE ONLY Part A /24 Part B /16 Part C /60 Total /100 Question/Answer Booklet
563-504 Mathematics 504 CST Mid-Year Examination January 2011 Question/Answer Booklet Student's Name Group Date FOR TEACHER USE ONLY Part A /24 Part B /16 Part C /60 Total /100 Question/Answer Booklet
MA 111 Review for Exam 3
 MA 111 Review for Exam 3 Exam 3 (given in class on Tuesday, March 27, 2012) will cover Chapter 5. You should: know what a graph is and how to use graphs to model geographic relationships. know how to describe
MA 111 Review for Exam 3 Exam 3 (given in class on Tuesday, March 27, 2012) will cover Chapter 5. You should: know what a graph is and how to use graphs to model geographic relationships. know how to describe
15.2 Angles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals
 Name lass ate 15.2 ngles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals Essential Question: What can you conclude about the angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle? Resource Locker Explore Investigating Inscribed
Name lass ate 15.2 ngles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals Essential Question: What can you conclude about the angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle? Resource Locker Explore Investigating Inscribed
A region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that is divided up by the network.
 Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Answers to Chapter 4. Exercise 4A. b vertex U V W X Y Z valency There are more than 2 nodes of odd degree so the. vertex A B C D E F
 nswers to hapter xercise 1 a vertex valency 2 2 There are nodes with odd valency so the graph is neither ulerian nor Semi-ulerian. vertex J K valency 2 There are precisely 2 nodes of odd degree ( and )
nswers to hapter xercise 1 a vertex valency 2 2 There are nodes with odd valency so the graph is neither ulerian nor Semi-ulerian. vertex J K valency 2 There are precisely 2 nodes of odd degree ( and )
9.4 Conditions for Rectangles, Rhombuses, and Squares
 Name lass ate 9.4 onditions for Rectangles, Rhombuses, and Squares ssential Question: ow can you use given conditions to show that a quadrilateral is a rectangle, a rhombus, or a square? Resource Locker
Name lass ate 9.4 onditions for Rectangles, Rhombuses, and Squares ssential Question: ow can you use given conditions to show that a quadrilateral is a rectangle, a rhombus, or a square? Resource Locker
Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory
 Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory Chapter 8: Topics in Graph Theory Section 8.1: Examples {1,2,3} Section 8.2: Examples {1,2,4} Section 8.3: Examples {1} 8.1 Graphs Graph A graph G consists of a finite
Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory Chapter 8: Topics in Graph Theory Section 8.1: Examples {1,2,3} Section 8.2: Examples {1,2,4} Section 8.3: Examples {1} 8.1 Graphs Graph A graph G consists of a finite
13.4 Classify Quadrilaterals
 ? Name 13.4 lassify Quadrilaterals Essential Question How can you sort and classify quadrilaterals? Geometry and Measurement 4.6. MTHEMTIL PROESSES 4.1., 4.1.E Unlock the Problem quadrilateral is a polygon
? Name 13.4 lassify Quadrilaterals Essential Question How can you sort and classify quadrilaterals? Geometry and Measurement 4.6. MTHEMTIL PROESSES 4.1., 4.1.E Unlock the Problem quadrilateral is a polygon
G5-20 Introduction to Slides
 WORKBOOK 5:2 PAGE 317 G5-20 Introduction to Slides GOALS Students will slide a dot on a grid. PRIOR KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED Ability to count Distinguish between right and left VOCABULARY slide For this lesson,
WORKBOOK 5:2 PAGE 317 G5-20 Introduction to Slides GOALS Students will slide a dot on a grid. PRIOR KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED Ability to count Distinguish between right and left VOCABULARY slide For this lesson,
LATIN SQUARES AND THEIR APPLICATION TO THE FEASIBLE SET FOR ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS
 LATIN SQUARES AND THEIR APPLICATION TO THE FEASIBLE SET FOR ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS TIMOTHY L. VIS Abstract. A significant problem in finite optimization is the assignment problem. In essence, the assignment
LATIN SQUARES AND THEIR APPLICATION TO THE FEASIBLE SET FOR ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS TIMOTHY L. VIS Abstract. A significant problem in finite optimization is the assignment problem. In essence, the assignment
Week 11: Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs; Trees. 15 and 17 November, 2017
 (1/22) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 11: Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs; Trees http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/~niall/ma284/ 15 and 17 November, 2017 Hamilton s Icosian Game (Library or the Royal Irish
(1/22) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 11: Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs; Trees http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/~niall/ma284/ 15 and 17 November, 2017 Hamilton s Icosian Game (Library or the Royal Irish
Essential Question How can you use congruent triangles to make an indirect measurement?
 5.7 Using ongruent riangles ssential uestion How can you use congruent triangles to make an indirect measurement? easuring the Width of a iver IIUI H OI O OH o be proficient in math, you need to listen
5.7 Using ongruent riangles ssential uestion How can you use congruent triangles to make an indirect measurement? easuring the Width of a iver IIUI H OI O OH o be proficient in math, you need to listen
A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit.
 Math 167 Review of Chapter 2 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 2 BUSINESS EFFICENCY A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian
Math 167 Review of Chapter 2 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 2 BUSINESS EFFICENCY A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian
1. A model for spherical/elliptic geometry
 Math 3329-Uniform Geometries Lecture 13 Let s take an overview of what we know. 1. A model for spherical/elliptic geometry Hilbert s axiom system goes with Euclidean geometry. This is the same geometry
Math 3329-Uniform Geometries Lecture 13 Let s take an overview of what we know. 1. A model for spherical/elliptic geometry Hilbert s axiom system goes with Euclidean geometry. This is the same geometry
