Differentiated Product Project: Tessellation
|
|
|
- Marion Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Brianna Myers and Adriana Pena Doctor Loughmiller SPED April 2013 Differentiated Product Project: Tessellation Definition: Tessellation (or Tilling)- is when you cover a surface with a pattern of flat shapes so that there are no overlaps or gaps. Intended Grade Levels: 6 th, 7 th, or 8 th Grade TEKS: 6.8 Expressions, equations, and relationships. The student applies mathematical process standards to use geometry to represent relationships and solve problems. 7.9 Expressions, equations, and relationships. The student applies mathematical process standards to solve geometric problems Two-dimensional shapes. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop transformational geometry concepts. Levels of Learning: Kinesthetic Learner-This activity will satisfy students who are this type of smart; they can be hands-on making the tessellation. Vocabulary: Visual Learner-The students who prefer images, pictures, and colors will enjoy this activity because of the different colored patterns that are involved to make the tessellations. Logical Learner-This activity is perfect for students who enjoy dealing with patterns and connections consisting of mathematical content such as, tessellation, transformation, rotation, translation, concave, convex, basic shapes, and in-depth shapes. Linguistic Learner-The students who are this type of smart will be able to use their strengths because of the written and verbal part of this activity. Intrapersonal Learner-Students get to work in a group to make the tessellation. Interpersonal Learner-Students get to work individually when doing the reflection. Tessellation (or Tilling)- is when you cover a surface with a pattern of flat shapes so that there are no overlaps or gaps. Examples: rotating or translating a figure. Transformations ways of moving a figure. Rotation-a figure moves in a circular path around a point. Translation-a figure moves up, down, left, right, or diagonally by sliding it.
2 2 Concave-the curving in or hollowed inward. Convex-the curving out or bulging outward. Basic Shapes-common geometric figures. Examples: triangle, square, rectangle, and trapezoid. In-Depth Shapes-uncommon/unique geometric figures. Instructions: Lowest Level-tessellating four basic geometry shapes Average Level-tessellating two basic shapes and one in-depth shape Highest Level-tessellating at least three basic shapes and at least three in-depth shapes The Lowest-level group will get a 7-inch square that has instructions on it for how to make the shape and then they will translate the shape as much as they can on half a sheet of poster board. The Average-level group will get a 6-inch square and will have to cut out two basic shapes on the right side of the square and one in-depth shape on the left side of the square. Then they will rotate this shape as many times as they can on the poster board. The Highest-level group will get a 5-inch square and will have to cut out at least two basic shapes and one in-depth shape on the right side of the square. Then cut out at least two in-depth shapes and one basic shape on the bottom side of the square. Then the student will translate the shape as much as they can on half a sheet of poster board. Modifications: This tessellation assignment is something all levels of students can do, but in order for each group level to succeed at the assignment, modifications need to be taken into consideration. The idea we had in mind was to have three different tables focusing on different complex or simple tessellation. The idea is to key our modifications as discrete as possible, we do not want any group of children to feel insecure or discouraged about what they are capable of and what they may be too complex for them. When the Lowest group switches to work on the Average or Highest group activity, their modifications will consist of patterns already formulated and they will have to tessellate the figures onto the poster board, whereas the Average and Highest group would have to cut the shapes and draw the patterns before they could answer any further question about the assignment. The modifications/instructions will take place for each group no matter what tessellation they did. Follow Up Activity/Next Day: The Lowest-level learners will answer multiple-choice questions to reflect on the project. The Average-level learners will have a word bank of the vocabulary words that will help them write a reflection on the project. The Highest-level learners will write a description of what they learned from doing this activity, as well as using the vocabulary they learned.
3 3 7-Inch Square Tessellation Project Materials needed: One 7-Inch Instruction Square A pencil Scissors Tape Half of a White Poster Board Markers or Color Pencils Instructions: You will get a 7-inch square that has instructions on it for how to make the shape Next you will trace the shape on the lower right side of the poster board Then trace the shape again to the left of it and again After that trace the shape on top, so that the shapes look like a puzzle (also known as, a tessellation) Finally color each shape a different color Yay you created a tessellation by moving (also known as, transforming) the shape up, down, left, and right by sliding it (also known as, translation)!
4 End Result of a 7-Inch Tessellation 4
5 5 6-Inch Square Tessellation Project Materials needed: One 6-Inch Square A pencil Scissors Tape Half of a White Poster Board Markers or Color Pencils Instructions: Draw with your pencil and cut out two basic shapes (ex: triangles, squares, rectangles, and rhombuses) on the right side of the 6-inch square Take the shapes you cut out and place them exactly how you cut them, but this time have them sticking out of the top of the square (this object is convex) Then tape the convex objects on top, so the right side would have the concave of the shapes and the top side would have convex of the two basic shapes Next trace and cut out one in-depth shape on the left side of the square Then take the shape you cut out and place it exactly how you cut it, but this time have it convex at the bottom of the square Next you will put and trace the your unique geometric shape on the top left corner of the white poster board Then they will rotate this shape to the right and trace it again and continue this as many times as they can on the poster board Finally color each figure a different color from the one next to it Yay you created a tessellation by moving (transforming) the geometric figure through rotation!
6 End Result of a 6-Inch Tessellation 6
7 7 5-Inch Square Tessellation Project Materials needed: One 5-Inch Square A pencil Scissors Tape Half of a White Poster Board Markers or Color Pencils Vocabulary: Tessellation (or Tilling)- is when you cover a surface with a pattern of flat shapes so that there are no overlaps or gaps. Examples: rotating or translating a figure. Transformations ways of moving a figure. Rotation-a figure moves in a circular path around a point. Translation-a figure moves up, down, left, right, or diagonally by sliding it. Concave-the curving in or hollowed inward. Convex-the curving out or bulging outward. Basic Shapes-common geometric figures. Examples: triangle, square, rectangle, and trapezoid. In-Depth Shapes-uncommon/unique geometric figures. Instructions: Draw with your pencil and cut out at least two basic shapes and one in-depth shape on the right side of the 5-inch square Take the shapes you cut out and place them exactly how you cut them, but this time put them so they are convex on the left side of the square Then tape the convex objects on the left side, so the right side would be concave and the left side would be, the opposite, convex Next trace and cut out at least two in-depth shapes and one basic shape on the bottom side of the square Then take the shape you cut out and place it exactly how you cut it, but this time have it convex at the top of the square Next you will put and trace the your unique geometric shape on the top right corner of the white poster board Then they will translate this shape left, right, up, and down as many times as you can to create a unique geometric tessellation Finally color each figure a different color from the one next to it Yay you created a tessellation by transforming the unique geometric figure through translation!
8 End Result of a 5-Inch Tessellation 8
Lesson 10. Unit 3. Creating Designs. Transformational Designs. Reflection
 Lesson 10 Transformational Designs Creating Designs M.C. Escher was an artist that made remarkable pieces of art using geometric transformations. He was first inspired by the patterns in mosaic tiles.
Lesson 10 Transformational Designs Creating Designs M.C. Escher was an artist that made remarkable pieces of art using geometric transformations. He was first inspired by the patterns in mosaic tiles.
Name. Criteria for grading. Total Points Earned. What to do to Create your own Tessellation
 What to do to Create your own Tessellation Name 1. Begin by creating a template using at least 1 of the nibbling methods. You may start with any size rectangular piece of cardstock. Use tape to assemble
What to do to Create your own Tessellation Name 1. Begin by creating a template using at least 1 of the nibbling methods. You may start with any size rectangular piece of cardstock. Use tape to assemble
TESSELLATION PROJECT DIRECTIONS
 TESSELLATION PROJECT DIRECTIONS You are to create your own tessellation masterpiece. Your tessellation will be created based on specific criteria. You MUST follow the guidelines given in order to receive
TESSELLATION PROJECT DIRECTIONS You are to create your own tessellation masterpiece. Your tessellation will be created based on specific criteria. You MUST follow the guidelines given in order to receive
TESSELLATION PROJECT DIRECTIONS
 TESSELLATION PROJECT DIRECTIONS You are to create a tessellation portfolio. In addition to your portfolio, you will be making your own tessellation masterpiece. Your tessellation will be created based
TESSELLATION PROJECT DIRECTIONS You are to create a tessellation portfolio. In addition to your portfolio, you will be making your own tessellation masterpiece. Your tessellation will be created based
Investigate and compare 2-dimensional shapes *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m30563 1 Investigate and compare 2-dimensional shapes * Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 MATHEMATICS
OpenStax-CNX module: m30563 1 Investigate and compare 2-dimensional shapes * Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 MATHEMATICS
Lesson 4. Objective: Compare and classify quadrilaterals. Lesson Suggested Lesson Structure. Multiply by 4 (8 minutes)
 Lesson 4 3 7 Lesson 4 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (7 minutes) (31 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Lesson 4 3 7 Lesson 4 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (7 minutes) (31 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Quadrilaterals Mini- Lesson
 Quadrilaterals Mini- Lesson Students investigate and compare the characteristics of quadrilaterals. This activity helps students to: Identify the characteristics (equal side length, equal angle, lines
Quadrilaterals Mini- Lesson Students investigate and compare the characteristics of quadrilaterals. This activity helps students to: Identify the characteristics (equal side length, equal angle, lines
Getting Ready to Teach Unit 6
 Getting Ready to Teach Unit 6 Learning Path in the Common Core Standards In this unit, students study the attributes of triangles, quadrilaterals, and other polygons. They find perimeter and area of various
Getting Ready to Teach Unit 6 Learning Path in the Common Core Standards In this unit, students study the attributes of triangles, quadrilaterals, and other polygons. They find perimeter and area of various
Pattern tessellates the plane Template with modifications turned in Appearance and Neatness Creativity/Originality/Difficulty
 Name: Date: Hour: A tessellation is a repeated polygon and/or combinations of polygons on a two dimensional plane. Each tessellated tile fits perfectly next to its adjacent twin. A true tessellation could
Name: Date: Hour: A tessellation is a repeated polygon and/or combinations of polygons on a two dimensional plane. Each tessellated tile fits perfectly next to its adjacent twin. A true tessellation could
Foundations of Math II Unit 2: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane
 Foundations of Math II Unit 2: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Academics High School Mathematics 2.1 Warm Up 1. Draw the image of stick-man m when translated using arrow p. What motion will take
Foundations of Math II Unit 2: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Academics High School Mathematics 2.1 Warm Up 1. Draw the image of stick-man m when translated using arrow p. What motion will take
Principles and Standards for School Mathematics. Content Standards. Process Standards. Emphasis across the Grades. Principles
 1 Navigating through Geometry Grades 3-5 Principles and Standards for School Mathematics Presented by Dr. Karol L. Yeatts Navigations Writer Navigating through Algebra Grades 3-5 Navigating through Number
1 Navigating through Geometry Grades 3-5 Principles and Standards for School Mathematics Presented by Dr. Karol L. Yeatts Navigations Writer Navigating through Algebra Grades 3-5 Navigating through Number
NCTM Strands. NCTM Strands. NCTM Strands. Geometry. Number and Operations Algebra Geometry Measurement Data Analysis & Probability
 NCTM Strands NCTM Strands Number and Operations Algebra Measurement Data Analysis & Probability NCTM Strands Number and Operations Algebra Measurement Data Analysis & Probability Strand 3 and properties
NCTM Strands NCTM Strands Number and Operations Algebra Measurement Data Analysis & Probability NCTM Strands Number and Operations Algebra Measurement Data Analysis & Probability Strand 3 and properties
Camden County HS Honors Math II Summer Tessellation Project 2018
 Camden County HS Honors Math II Summer Tessellation Project 2018 Maurits Cornelis Escher, born in Leeuwarden, Holland in 1898 created unique and fascinating works or art that explore and exhibit an array
Camden County HS Honors Math II Summer Tessellation Project 2018 Maurits Cornelis Escher, born in Leeuwarden, Holland in 1898 created unique and fascinating works or art that explore and exhibit an array
4 Mathematics Curriculum. Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1. Topic B: Angle Measurement... 4.B.1
 New York State Common Core 4 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1
New York State Common Core 4 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1
Geometry. Students at Dommerich Elementary helped design and construct a mosaic to show parts of their community and local plants and animals.
 Geometry Describing and analyzing two-dimensional shapes Students at Dommerich Elementary helped design and construct a mosaic to show parts of their community and local plants and animals. 479 Make a
Geometry Describing and analyzing two-dimensional shapes Students at Dommerich Elementary helped design and construct a mosaic to show parts of their community and local plants and animals. 479 Make a
Geometry Vocabulary. acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees
 Geometry Vocabulary acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees angle-the turn or bend between two intersecting lines, line segments, rays, or planes angle bisector-an angle bisector is a ray that
Geometry Vocabulary acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees angle-the turn or bend between two intersecting lines, line segments, rays, or planes angle bisector-an angle bisector is a ray that
"Unpacking the Standards" 4th Grade Student Friendly "I Can" Statements I Can Statements I can explain why, when and how I got my answer.
 0406.1.1 4th Grade I can explain why, when and how I got my answer. 0406.1.2 I can identify the range of an appropriate estimate. I can identify the range of over-estimates. I can identify the range of
0406.1.1 4th Grade I can explain why, when and how I got my answer. 0406.1.2 I can identify the range of an appropriate estimate. I can identify the range of over-estimates. I can identify the range of
Math Polygons
 Math 310 9.2 Polygons Curve & Connected Idea The idea of a curve is something you could draw on paper without lifting your pencil. The idea of connected is that a set can t be split into two disjoint sets.
Math 310 9.2 Polygons Curve & Connected Idea The idea of a curve is something you could draw on paper without lifting your pencil. The idea of connected is that a set can t be split into two disjoint sets.
The Grade 3 Common Core State Standards for Geometry specify that students should
 Students in third grade describe, analyze, and compare properties of two-dimensional shapes. They compare and classify shapes by their sides and angles, and they use these classifications to define shapes.
Students in third grade describe, analyze, and compare properties of two-dimensional shapes. They compare and classify shapes by their sides and angles, and they use these classifications to define shapes.
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning. Two-Dimensional Figures Important Book
 Geometry and Spatial Reasoning Activity: TEKS: Two-Dimensional Figures Important Book (4.8) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student identifies and describes attributes of geometric figures using formal
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning Activity: TEKS: Two-Dimensional Figures Important Book (4.8) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student identifies and describes attributes of geometric figures using formal
and Transitional Comprehensive Curriculum. Grade 6 Mathematics Unit 6: Geometry, Perimeter, Area, and Measurement
 Grade 6 Mathematics Unit 6: Geometry, Perimeter, Area, and Measurement Time Frame: Approximately five weeks Unit Description This unit focuses on measurement and the application of perimeter and area concepts
Grade 6 Mathematics Unit 6: Geometry, Perimeter, Area, and Measurement Time Frame: Approximately five weeks Unit Description This unit focuses on measurement and the application of perimeter and area concepts
2D Shapes, Scaling, and Tessellations
 2D Shapes, Scaling, and Tessellations Name(s): Sarah Hunter Title of lesson: How do different shapes fit together? Date of lesson: Week 2, Day 5 Length of lesson: 50 Minutes (1 Class Period) Description
2D Shapes, Scaling, and Tessellations Name(s): Sarah Hunter Title of lesson: How do different shapes fit together? Date of lesson: Week 2, Day 5 Length of lesson: 50 Minutes (1 Class Period) Description
Tessellations. A tessellation is a repeating pattern of polygons that covers a plane with no gaps or overlaps. What transformations do you see?
 Tessellations A tessellation is a repeating pattern of polygons that covers a plane with no gaps or overlaps. What transformations do you see? Typically the shapes making up a tessellation are polygons
Tessellations A tessellation is a repeating pattern of polygons that covers a plane with no gaps or overlaps. What transformations do you see? Typically the shapes making up a tessellation are polygons
UNIT PLAN. Big Idea/Theme: Polygons can be identified, classified, and described.
 UNIT PLAN Grade Level: 5 Unit #: 11 Unit Name Geometry Polygons Time: 15 lessons, 18 days Big Idea/Theme: Polygons can be identified, classified, and described. Culminating Assessment: (requirements of
UNIT PLAN Grade Level: 5 Unit #: 11 Unit Name Geometry Polygons Time: 15 lessons, 18 days Big Idea/Theme: Polygons can be identified, classified, and described. Culminating Assessment: (requirements of
Geometry Sixth Grade
 Standard 6-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of shape, location, and movement within a coordinate system; similarity, complementary, and supplementary
Standard 6-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of shape, location, and movement within a coordinate system; similarity, complementary, and supplementary
Geometry. Standardized Practice Have students try the following problem.
 1 Students need a basic understanding of angles to learn the properties of twodimensional shapes. In this lesson, students use models to represent, measure, and classify angles. Objective Recognize types
1 Students need a basic understanding of angles to learn the properties of twodimensional shapes. In this lesson, students use models to represent, measure, and classify angles. Objective Recognize types
Lesson 5 Post-Visit Circling the Bases
 Lesson 5 Post-Visit Circling the Bases Objective: Students will be able to: Review types and measurements of angles. Review types of polygons. Review formulas for perimeter and area. Time Required: 1 class
Lesson 5 Post-Visit Circling the Bases Objective: Students will be able to: Review types and measurements of angles. Review types of polygons. Review formulas for perimeter and area. Time Required: 1 class
Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes
 Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes Day 1: Area of Square, Rectangles, and Parallelograms Day 2: Area of Triangles Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Day 3: Quiz over Area of those
Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes Day 1: Area of Square, Rectangles, and Parallelograms Day 2: Area of Triangles Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Day 3: Quiz over Area of those
SHAPE AND STRUCTURE. Shape and Structure. An explanation of Mathematical terminology
 Shape and Structure An explanation of Mathematical terminology 2005 1 POINT A dot Dots join to make lines LINE A line is 1 dimensional (length) A line is a series of points touching each other and extending
Shape and Structure An explanation of Mathematical terminology 2005 1 POINT A dot Dots join to make lines LINE A line is 1 dimensional (length) A line is a series of points touching each other and extending
Objective: Combine shapes to create a composite shape; create a new shape from composite shapes.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 2 8 Lesson 6 Objective: Combine shapes to create a composite shape; create a new shape Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 2 8 Lesson 6 Objective: Combine shapes to create a composite shape; create a new shape Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 2016/2017 INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT
 HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 2016/2017 INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Third Grade Quarter 4 Unit 10: Geometry and Measurement Word Problems Approximately 40 Days Begin around March 27 th This 40-day final unit
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 2016/2017 INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Third Grade Quarter 4 Unit 10: Geometry and Measurement Word Problems Approximately 40 Days Begin around March 27 th This 40-day final unit
TESSELATIONS. BIG IDEA: Students will create a representational tessellation composition in the style of M.C. Escher ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS:
 TESSELATIONS BIG IDEA: Students will create a representational tessellation composition in the style of M.C. Escher ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: Why might M.C. Escher think like a mathematician? What is the relationship
TESSELATIONS BIG IDEA: Students will create a representational tessellation composition in the style of M.C. Escher ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: Why might M.C. Escher think like a mathematician? What is the relationship
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations
 Translations, Reflections, and Rotations This photo shows a classic optical illusion called the Necker Cube. It's an example of an impossible object. Optical illusions are often helpful to scientists who
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations This photo shows a classic optical illusion called the Necker Cube. It's an example of an impossible object. Optical illusions are often helpful to scientists who
Warning! Construction Zone: Building Solids from Nets
 Brief Overview: Warning! Construction Zone: Building Solids from Nets In this unit the students will be examining and defining attributes of solids and their nets. The students will be expected to have
Brief Overview: Warning! Construction Zone: Building Solids from Nets In this unit the students will be examining and defining attributes of solids and their nets. The students will be expected to have
Creating Escher-Style Tessellations
 Creating Escher-Style Tessellations Focus on After this lesson, you will be able to... create tessellations from combinations of regular and irregular polygons describe the tessellations in terms of the
Creating Escher-Style Tessellations Focus on After this lesson, you will be able to... create tessellations from combinations of regular and irregular polygons describe the tessellations in terms of the
Prime Time (Factors and Multiples)
 CONFIDENCE LEVEL: Prime Time Knowledge Map for 6 th Grade Math Prime Time (Factors and Multiples). A factor is a whole numbers that is multiplied by another whole number to get a product. (Ex: x 5 = ;
CONFIDENCE LEVEL: Prime Time Knowledge Map for 6 th Grade Math Prime Time (Factors and Multiples). A factor is a whole numbers that is multiplied by another whole number to get a product. (Ex: x 5 = ;
GEOMETRY CIRCLING THE BASES PRE-VISIT - A DIAMOND FILLED WITH SHAPES
 PRE-VISIT - A DIAMOND FILLED WITH SHAPES OBJECTIVE: Students will be able to: Define the term polygon. Recognize different polygons evident in baseball. Draw and identify different polygons. TIME REQUIRED:
PRE-VISIT - A DIAMOND FILLED WITH SHAPES OBJECTIVE: Students will be able to: Define the term polygon. Recognize different polygons evident in baseball. Draw and identify different polygons. TIME REQUIRED:
Focus of this Unit: Connections to Subsequent Learning: Approximate Time Frame: 4-6 weeks Connections to Previous Learning:
 Approximate Time Frame: 4-6 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: In Grade 8, students are introduced to the concepts of congruence and similarity through the use of physical models and dynamic geometry
Approximate Time Frame: 4-6 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: In Grade 8, students are introduced to the concepts of congruence and similarity through the use of physical models and dynamic geometry
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Tiling the Plane
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: Tiling the Plane Let s look at tiling patterns and think about area. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Tilings Which pattern doesn t belong? 1 1.2: More Red, Green, or Blue? m.openup.org//6-1-1-2
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Tiling the Plane Let s look at tiling patterns and think about area. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Tilings Which pattern doesn t belong? 1 1.2: More Red, Green, or Blue? m.openup.org//6-1-1-2
6 Polygons and. Quadrilaterals CHAPTER. Chapter Outline.
 www.ck12.org CHAPTER 6 Polygons and Quadrilaterals Chapter Outline 6.1 ANGLES IN POLYGONS 6.2 PROPERTIES OF PARALLELOGRAMS 6.3 PROVING QUADRILATERALS ARE PARALLELOGRAMS 6.4 RECTANGLES, RHOMBUSES AND SQUARES
www.ck12.org CHAPTER 6 Polygons and Quadrilaterals Chapter Outline 6.1 ANGLES IN POLYGONS 6.2 PROPERTIES OF PARALLELOGRAMS 6.3 PROVING QUADRILATERALS ARE PARALLELOGRAMS 6.4 RECTANGLES, RHOMBUSES AND SQUARES
Minnesota 4 th Grade 2007 Math Strands & Standards
 Minnesota 4 th Grade 2007 Math Strands & Standards Number & Operation Algebra Geometry & Measurement Demonstrate mastery of multiplication and division basic facts; multiply multi-digit numbers; solve
Minnesota 4 th Grade 2007 Math Strands & Standards Number & Operation Algebra Geometry & Measurement Demonstrate mastery of multiplication and division basic facts; multiply multi-digit numbers; solve
Main Idea: classify polygons and determine which polygons can form a tessellation.
 10 8: Polygons and Tesselations Main Idea: classify polygons and determine which polygons can form a tessellation. Vocabulary: polygon A simple closed figure in a plane formed by three or more line segments
10 8: Polygons and Tesselations Main Idea: classify polygons and determine which polygons can form a tessellation. Vocabulary: polygon A simple closed figure in a plane formed by three or more line segments
HEARTLANDS ACADEMY LESSON STUDY SERIES RESEARCH LESSON 2 GEOMETRICAL REASONING
 HEARTLANDS ACADEMY LESSON STUDY SERIES 2015-2016 RESEARCH LESSON 2 GEOMETRICAL REASONING Spatial intuition or spatial perception is an enormously powerful tool and that is why geometry is actually such
HEARTLANDS ACADEMY LESSON STUDY SERIES 2015-2016 RESEARCH LESSON 2 GEOMETRICAL REASONING Spatial intuition or spatial perception is an enormously powerful tool and that is why geometry is actually such
Nets and Drawings for Visualizing Geometry. Unit 1 Lesson 1
 Nets and Drawings for Visualizing Geometry Unit 1 Lesson 1 Students will be able to: Represent three-dimensional figures using nets. Make isometric and orthographic drawings. Key Vocabulary: Net Isometric
Nets and Drawings for Visualizing Geometry Unit 1 Lesson 1 Students will be able to: Represent three-dimensional figures using nets. Make isometric and orthographic drawings. Key Vocabulary: Net Isometric
Instructional Alignment Chart
 CLUSTER HEADING: STANDARD: N/A CLUSTER HEADING: Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). STANDARD: K.G.3 Identify shapes as
CLUSTER HEADING: STANDARD: N/A CLUSTER HEADING: Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). STANDARD: K.G.3 Identify shapes as
Roswell Independent School District Grade Level Targets Summer 2010
 1 NM Standards Children s Progress Core Standards Target: Possesses a working knowledge of the base ten number system, including ones and tens. Q1 Counts, sketches and represents some numbers. Q2 Counts,
1 NM Standards Children s Progress Core Standards Target: Possesses a working knowledge of the base ten number system, including ones and tens. Q1 Counts, sketches and represents some numbers. Q2 Counts,
PERSPECTIVES ON GEOMETRY PRE-ASSESSMENT ANSWER SHEET (GEO )
 PERSPECTIVES ON GEOMETRY PRE-ASSESSMENT ANSWER SHEET (GEO.11.02.2) Name Date Site TURN IN BOTH TEST AND ANSWER SHEET TO YOUR INSTRUCTOR WHEN DONE. 1. 18. I. 2. 19. 3. 20. 4. 21. 5. 22. 6. 23. 7. 24. 8.
PERSPECTIVES ON GEOMETRY PRE-ASSESSMENT ANSWER SHEET (GEO.11.02.2) Name Date Site TURN IN BOTH TEST AND ANSWER SHEET TO YOUR INSTRUCTOR WHEN DONE. 1. 18. I. 2. 19. 3. 20. 4. 21. 5. 22. 6. 23. 7. 24. 8.
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6
 acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
Pop! Rockets. Rocket Activity. Students design, construct, and launch paper rockets.
 Rocket Activity Pop! Rockets Students design, construct, and launch paper rockets. A rocket with a triangular cross section is made from three rocket-shaped strips of card-stock paper and launched with
Rocket Activity Pop! Rockets Students design, construct, and launch paper rockets. A rocket with a triangular cross section is made from three rocket-shaped strips of card-stock paper and launched with
TESSELLATIONS #1. All the shapes are regular (equal length sides). The side length of each shape is the same as any other shape.
 TESSELLATIONS #1 Arrange for students to work in pairs during this lesson. Each pair of students needs unlined paper and two tessellation sets, one red and one blue. Ask students in each pair to share
TESSELLATIONS #1 Arrange for students to work in pairs during this lesson. Each pair of students needs unlined paper and two tessellation sets, one red and one blue. Ask students in each pair to share
Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction
 Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction AR.Math.Content.1.OA.A.1 Use addition and subtraction within 20 to solve word problems involving situations
Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction AR.Math.Content.1.OA.A.1 Use addition and subtraction within 20 to solve word problems involving situations
Go to Grade 5 Everyday Mathematics Sample Lesson
 McGraw-Hill makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy of any information contained in this McGraw-Hill Material, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular
McGraw-Hill makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy of any information contained in this McGraw-Hill Material, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular
G2-1 Lines Pages 70 71
 G2-1 Lines Pages 70 71 CURRICULUM REQUIREMENT AB: required BC: required MB: required ON: required Goals Students will identify straight and curved lines and sides, and open and closed lines. PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
G2-1 Lines Pages 70 71 CURRICULUM REQUIREMENT AB: required BC: required MB: required ON: required Goals Students will identify straight and curved lines and sides, and open and closed lines. PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
2D Shapes. Sub Strand Two Dimensional Space 1. Booragul Public School NSW Syllabus for the Australian Curriculum Measurement and Geometry ~ 1 ~
 Booragul Public School NSW Syllabus for the Australian Curriculum Measurement and Geometry Sub Strand Two Dimensional Space 1 Outcome Teaching and Learning Activities Notes/ Future Directions/Evaluation
Booragul Public School NSW Syllabus for the Australian Curriculum Measurement and Geometry Sub Strand Two Dimensional Space 1 Outcome Teaching and Learning Activities Notes/ Future Directions/Evaluation
HPISD Curriculum: Grade 4 TAG Math
 Unit Overview HPISD Curriculum: Grade 4 TAG Math Title Estimated Duration 9 Weeks Geometry and Measurement 8 weeks 1 2 3 4 Properties/attributes of polygons, triangles, quadrilaterals Area and perimeter
Unit Overview HPISD Curriculum: Grade 4 TAG Math Title Estimated Duration 9 Weeks Geometry and Measurement 8 weeks 1 2 3 4 Properties/attributes of polygons, triangles, quadrilaterals Area and perimeter
15.4. PROBLEM SOLVING Three- Dimensional Solids? Are You Ready? Lesson Opener Making Connections. Resources. Essential Question
 5.4 PROBLEM SOLVING Three- Dimensional Solids? Essential Question How can making a model help you identify and describe attributes of three-dimensional solids? How can making a model help you identify
5.4 PROBLEM SOLVING Three- Dimensional Solids? Essential Question How can making a model help you identify and describe attributes of three-dimensional solids? How can making a model help you identify
Grade 1 Mathematics Curriculum Map
 1 st Unit 1A: Extend the Counting Underst Place Value *1.NBT.1 is repeated in Units 2, 4, 5, each time extending the skill. The skill focused on in this unit is bolded in the Scope S.L.O. 1.NBT.1 Count
1 st Unit 1A: Extend the Counting Underst Place Value *1.NBT.1 is repeated in Units 2, 4, 5, each time extending the skill. The skill focused on in this unit is bolded in the Scope S.L.O. 1.NBT.1 Count
Lesson 2 Pre-Visit A Diamond Filled with Shapes
 Lesson 2 Pre-Visit A Diamond Filled with Shapes Objective: Students will be able to: Define the term polygon. Recognize different polygons evident in baseball. Draw and identify different polygons. Time
Lesson 2 Pre-Visit A Diamond Filled with Shapes Objective: Students will be able to: Define the term polygon. Recognize different polygons evident in baseball. Draw and identify different polygons. Time
CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE
 School: Cumberland County Elementary School CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE Subject: Math Grade: Third Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: Weeks
School: Cumberland County Elementary School CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE Subject: Math Grade: Third Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: Weeks
Geometry Lesson Polyhedron Nets. National Standards
 Geometry Lesson Polyhedron Nets National Standards Instructional programs for Algebra grades 6 th -8 th should enable all students to: Precisely describe, classify, and understand relationships among types
Geometry Lesson Polyhedron Nets National Standards Instructional programs for Algebra grades 6 th -8 th should enable all students to: Precisely describe, classify, and understand relationships among types
Polyhedron Nets. National Standards (NCTM) 21 st Century Skills. Middle School
 Polyhedron Nets Middle School National Standards (NCTM) 21 st Century Skills Instructional programs from prekindergarten through grade 12 in Geometry should enable each and every student to Analyze characteristics
Polyhedron Nets Middle School National Standards (NCTM) 21 st Century Skills Instructional programs from prekindergarten through grade 12 in Geometry should enable each and every student to Analyze characteristics
Next Generation Math Standards----Grade 3 Cognitive Complexity/Depth of Knowledge Rating: Low, Moderate, High
 Next Generation Math Standards----Grade 3 Cognitive Complexity/Depth of Knowledge Rating: Low,, BIG IDEAS (3) BIG IDEA 1: Develop understandings of multiplication and division and strategies for basic
Next Generation Math Standards----Grade 3 Cognitive Complexity/Depth of Knowledge Rating: Low,, BIG IDEAS (3) BIG IDEA 1: Develop understandings of multiplication and division and strategies for basic
Geometry Unit 1: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane. Guided Notes
 Geometry Unit 1: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Guided Notes Standard: MGSE9 12.G.CO.1 Know precise definitions Essential Question: What are the undefined terms essential to any study of geometry?
Geometry Unit 1: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Guided Notes Standard: MGSE9 12.G.CO.1 Know precise definitions Essential Question: What are the undefined terms essential to any study of geometry?
Course Number: Course Title: Geometry
 Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
Anoka Hennepin K-12 Curriculum plan
 Anoka Hennepin K-12 Curriculum plan Department: Elementary Math Unit Title: Packages and Polygons (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Triangles and Beyond (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Everyday Math: Volume
Anoka Hennepin K-12 Curriculum plan Department: Elementary Math Unit Title: Packages and Polygons (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Triangles and Beyond (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Everyday Math: Volume
For many years, geometry in the elementary schools was confined to
 SHOW 118 PROGRAM SYNOPSIS Segment 1 (1:39) MATHMAN: RECTANGLES Mathman is told to eat only the rectangles that appear on his video game board. He notes that rectangles must have four right angles (and
SHOW 118 PROGRAM SYNOPSIS Segment 1 (1:39) MATHMAN: RECTANGLES Mathman is told to eat only the rectangles that appear on his video game board. He notes that rectangles must have four right angles (and
Recalling Quadrilaterals
 Recalling Quadrilaterals Play Area Lesson 23-1 Recalling Quadrilaterals Learning Targets: Define and classify quadrilaterals based on their properties. Use properties of quadrilaterals to determine missing
Recalling Quadrilaterals Play Area Lesson 23-1 Recalling Quadrilaterals Learning Targets: Define and classify quadrilaterals based on their properties. Use properties of quadrilaterals to determine missing
Title: Identifying, Classifying, and Creating Quadrilaterals - Qualifying Quadrilaterals
 Title: Identifying, Classifying, and Creating Quadrilaterals - Qualifying Quadrilaterals Brief Overview: Through problem solving, oral and written communication, higher-order thinking and a variety of
Title: Identifying, Classifying, and Creating Quadrilaterals - Qualifying Quadrilaterals Brief Overview: Through problem solving, oral and written communication, higher-order thinking and a variety of
6.5 Symmetries of Quadrilaterals A Develop Understanding Task
 6.5 Symmetries of Quadrilaterals A Develop Understanding Task A line that reflects a figure onto itself is called a line of symmetry. A figure that can be carried onto itself by a rotation is said to have
6.5 Symmetries of Quadrilaterals A Develop Understanding Task A line that reflects a figure onto itself is called a line of symmetry. A figure that can be carried onto itself by a rotation is said to have
Is the triangle a right triangle? Who is Pythagoras? CPM Materials modified by Mr. Deyo. IM 8 Ch How Can I Find Lengths In Three Dimensions
 Common Core Standard: 8.G.7 Is the triangle a right triangle? Who is Pythagoras? CPM Materials modified by Mr. Deyo Title: IM8 Ch. 9.2.6 How Can I Find The Lengths in 3 Dimensions? Date: Learning Target
Common Core Standard: 8.G.7 Is the triangle a right triangle? Who is Pythagoras? CPM Materials modified by Mr. Deyo Title: IM8 Ch. 9.2.6 How Can I Find The Lengths in 3 Dimensions? Date: Learning Target
MD5-26 Stacking Blocks Pages
 MD5-26 Stacking Blocks Pages 115 116 STANDARDS 5.MD.C.4 Goals Students will find the number of cubes in a rectangular stack and develop the formula length width height for the number of cubes in a stack.
MD5-26 Stacking Blocks Pages 115 116 STANDARDS 5.MD.C.4 Goals Students will find the number of cubes in a rectangular stack and develop the formula length width height for the number of cubes in a stack.
AREA OF POLYGONS
 AREA OF POLYGONS 5.3.1 5.3.4 Area is the number of non-overlapping square units needed to cover the interior region of a twodimensional figure or the surface area of a three-dimensional figure. For example,
AREA OF POLYGONS 5.3.1 5.3.4 Area is the number of non-overlapping square units needed to cover the interior region of a twodimensional figure or the surface area of a three-dimensional figure. For example,
Sample Quilt Word Board
 Sample Quilt Word Board See next page for further details Geo Jammin By DeSign 2000, 2003 www.beaconlearningcenter.com Rev. 11.05.03 Lesson 2, Duo Dancing, 1 For this unit design a repeating pattern to
Sample Quilt Word Board See next page for further details Geo Jammin By DeSign 2000, 2003 www.beaconlearningcenter.com Rev. 11.05.03 Lesson 2, Duo Dancing, 1 For this unit design a repeating pattern to
6. 5 Symmetries of Quadrilaterals
 2 CC BY fdecomite 6. Symmetries of Quadrilaterals A Develop Understanding Task A line that reflects a figure onto itself is called a line of symmetry. A figure that can be carried onto itself by a rotation
2 CC BY fdecomite 6. Symmetries of Quadrilaterals A Develop Understanding Task A line that reflects a figure onto itself is called a line of symmetry. A figure that can be carried onto itself by a rotation
heptagon; not regular; hexagon; not regular; quadrilateral; convex concave regular; convex
 10 1 Naming Polygons A polygon is a plane figure formed by a finite number of segments. In a convex polygon, all of the diagonals lie in the interior. A regular polygon is a convex polygon that is both
10 1 Naming Polygons A polygon is a plane figure formed by a finite number of segments. In a convex polygon, all of the diagonals lie in the interior. A regular polygon is a convex polygon that is both
Describe Triangles. About the Math Professional Development 12.7 LESSON AT A GLANCE
 12.7 LESSON Describe Triangles FOUS OHERENE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANE F R Focus: ommon ore State Standards 3.G.A.1 Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses, rectangles, and others)
12.7 LESSON Describe Triangles FOUS OHERENE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANE F R Focus: ommon ore State Standards 3.G.A.1 Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses, rectangles, and others)
UNIT 4: LENGTH, AREA, AND VOLUME WEEK 16: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 4: LENGTH, AREA, AND VOLUME WEEK 16: Student Packet 16.1 Circles: Area Establish the area formula for a circle. Apply the area formula for a circle to realistic problems. Demonstrate
Name Period Date UNIT 4: LENGTH, AREA, AND VOLUME WEEK 16: Student Packet 16.1 Circles: Area Establish the area formula for a circle. Apply the area formula for a circle to realistic problems. Demonstrate
Middle School Geometry. Session 3
 Middle School Geometry Session 3 Topic Transformational Geometry: Tessellations Activity Name Sums of the Measures of Angles of Triangles Do Congruent Triangles Tessellate? Do Congruent Quadrilaterals
Middle School Geometry Session 3 Topic Transformational Geometry: Tessellations Activity Name Sums of the Measures of Angles of Triangles Do Congruent Triangles Tessellate? Do Congruent Quadrilaterals
Number and Operations - Fractions
 NF.1.3c Number and Operations - Fractions NF.1.3 NF.1.2b NF.1.2a Understand Fractions February 3 - February 20 NF.1.2 NF.1.1 Math! Lessons Develop understanding of fractions as numbers. Understand a fraction
NF.1.3c Number and Operations - Fractions NF.1.3 NF.1.2b NF.1.2a Understand Fractions February 3 - February 20 NF.1.2 NF.1.1 Math! Lessons Develop understanding of fractions as numbers. Understand a fraction
A VERTICAL LOOK AT KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCEDURES GEOMETRY
 A VERTICAL LOOK AT KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCEDURES GEOMETRY Revised TEKS (2012): Building to Geometry Coordinate and Transformational Geometry A Vertical Look at Key Concepts and Procedures Derive and use
A VERTICAL LOOK AT KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCEDURES GEOMETRY Revised TEKS (2012): Building to Geometry Coordinate and Transformational Geometry A Vertical Look at Key Concepts and Procedures Derive and use
Does a group of parallel line segments need to be the same length?
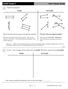 1 Parallel Line Segments Parallel t Parallel What is the same about the groups of parallel line segments? They are always the same distance apart. They do not intersect each other. If you extend the line
1 Parallel Line Segments Parallel t Parallel What is the same about the groups of parallel line segments? They are always the same distance apart. They do not intersect each other. If you extend the line
Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention Building Blocks of Geometry
 8-1 Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention Building Blocks of Geometry A point is an exact location. A line is a straight path that extends without end in opposite directions. A plane is a flat surface that
8-1 Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention Building Blocks of Geometry A point is an exact location. A line is a straight path that extends without end in opposite directions. A plane is a flat surface that
Constructing Symmetrical Shapes
 1 Constructing Symmetrical Shapes 1 Construct 2-D shapes with one line of symmetry A line of symmetry may be horizontal or vertical 2 a) Use symmetry to complete the picture b) Describe the method you
1 Constructing Symmetrical Shapes 1 Construct 2-D shapes with one line of symmetry A line of symmetry may be horizontal or vertical 2 a) Use symmetry to complete the picture b) Describe the method you
Rocket Activity Pop! Rockets
 Rocket Activity Pop! Rockets Objective Students design, construct, and launch paper rockets. Description A rocket with a triangular cross section is made from three rocket-shaped strips of card-stock paper
Rocket Activity Pop! Rockets Objective Students design, construct, and launch paper rockets. Description A rocket with a triangular cross section is made from three rocket-shaped strips of card-stock paper
M8WSB-C07.qxd 4/4/08 7:00 PM Page NEL
 8 NEL GOAL Chapter 7 Tessellations You will be able to use angle measurements to identify regular and irregular polygons that might tessellate identify and describe translations, reflections, or rotations
8 NEL GOAL Chapter 7 Tessellations You will be able to use angle measurements to identify regular and irregular polygons that might tessellate identify and describe translations, reflections, or rotations
The Math Learning Center PO Box 12929, Salem, Oregon Math Learning Center
 Resource Overview Quantile Measure: Skill or Concept: 560Q Use manipulatives, pictorial representations, and appropriate vocabulary (e.g., face, edge, vertex, and base) to identify and compare properties
Resource Overview Quantile Measure: Skill or Concept: 560Q Use manipulatives, pictorial representations, and appropriate vocabulary (e.g., face, edge, vertex, and base) to identify and compare properties
Explore Solids
 1212.1 Explore Solids Surface Area and Volume of Solids 12.2 Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.3 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones 12.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders 12.5 Volume of Pyramids and
1212.1 Explore Solids Surface Area and Volume of Solids 12.2 Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.3 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones 12.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders 12.5 Volume of Pyramids and
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
AREA Judo Math Inc.
 AREA 2013 Judo Math Inc. 6 th grade Problem Solving Discipline: Black Belt Training Order of Mastery: Area 1. Area of triangles by composition 2. Area of quadrilaterals by decomposing 3. Draw polygons
AREA 2013 Judo Math Inc. 6 th grade Problem Solving Discipline: Black Belt Training Order of Mastery: Area 1. Area of triangles by composition 2. Area of quadrilaterals by decomposing 3. Draw polygons
3 Identify shapes as two-dimensional (lying in a plane, flat ) or three-dimensional ( solid ).
 Geometry Kindergarten Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1 Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes,
Geometry Kindergarten Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1 Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes,
Mrs. Daniel s Geometry Vocab List
 Mrs. Daniel s Geometry Vocab List Geometry Definition: a branch of mathematics concerned with questions of shape, size, relative position of figures, and the properties of space. Refectional Symmetry Definition:
Mrs. Daniel s Geometry Vocab List Geometry Definition: a branch of mathematics concerned with questions of shape, size, relative position of figures, and the properties of space. Refectional Symmetry Definition:
SESSION FIVE CIRCUMFERENCE AND AREA OF A CIRCLE
 SESSION FIVE CIRCUMFERENCE AND AREA OF A CIRCLE Outcomes Participants will be familiarized with different kinds of compasses to trace circles Learn or remember some of the principal parts of a circle:
SESSION FIVE CIRCUMFERENCE AND AREA OF A CIRCLE Outcomes Participants will be familiarized with different kinds of compasses to trace circles Learn or remember some of the principal parts of a circle:
6th Grade ~ Conceptual Foundations for Unit of Study 8 Geometry DRAFT 6/30/11 Geometry (Spatial Sense & Reasoning) 1. Shapes, Solids and Properties
 Geometry is the only CCSSM Domain that consistently appears in every grade level K-12. At all grade levels, geometry content goals can be summarized into four main geometric ideas: 1. Shapes, Solids and
Geometry is the only CCSSM Domain that consistently appears in every grade level K-12. At all grade levels, geometry content goals can be summarized into four main geometric ideas: 1. Shapes, Solids and
CCBC Math 081 Geometry Section 2.2
 2.2 Geometry Geometry is the study of shapes and their mathematical properties. In this section, we will learn to calculate the perimeter, area, and volume of a few basic geometric shapes. Perimeter We
2.2 Geometry Geometry is the study of shapes and their mathematical properties. In this section, we will learn to calculate the perimeter, area, and volume of a few basic geometric shapes. Perimeter We
Unit 1, Lesson 11: Polygons
 Unit 1, Lesson 11: Polygons Lesson Goals Understand and explain that one can find the area of any polygon by decomposing and rearranging it into rectangles and triangles. Understand the defining characteristics
Unit 1, Lesson 11: Polygons Lesson Goals Understand and explain that one can find the area of any polygon by decomposing and rearranging it into rectangles and triangles. Understand the defining characteristics
2nd Grade. 2D Shapes - Part 1 Angles and Sides. Slide 1 / 117 Slide 2 / 117. Slide 3 / 117. Slide 4 / 117. Slide 6 / 117.
 Slide 1 / 117 Slide 2 / 117 2nd Grade Geometry Presentation 1 2015-11-30 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 117 Table of ontents Presentation 1 2 Shapes - Sides and ngles - Part 1 2 Shapes - Part 2 Lab: 2 Shapes
Slide 1 / 117 Slide 2 / 117 2nd Grade Geometry Presentation 1 2015-11-30 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 117 Table of ontents Presentation 1 2 Shapes - Sides and ngles - Part 1 2 Shapes - Part 2 Lab: 2 Shapes
MCC5.G.3 Understand that attributes belonging to a category of two-dimensional figures also belong to all subcategories of that categories.
 Fifth Grade Mathematics Unit 6 CONSTRUCTING TASK: Property Lists of Quadrilaterals Adapted from Van De Walle, Teaching Student-Centered Math pg. 207 The purpose of this task is for students to become familiar
Fifth Grade Mathematics Unit 6 CONSTRUCTING TASK: Property Lists of Quadrilaterals Adapted from Van De Walle, Teaching Student-Centered Math pg. 207 The purpose of this task is for students to become familiar
The National Strategies Secondary Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9
 Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9 183 As outcomes, Year 8 pupils should, for example: Understand a proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 and of a quadrilateral is 360, and that the exterior
Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9 183 As outcomes, Year 8 pupils should, for example: Understand a proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 and of a quadrilateral is 360, and that the exterior
4 th Grade MCA3 Standards, Benchmarks, Test Specifications & Sampler Questions
 4 th Grade MCA3 Standards, Benchmarks, Test Specifications & Sampler Questions Standard No. Benchmark (4 th Grade) Sampler Item Demonstrate fluency with multiplication and division facts. 4.1.1.1 Factors
4 th Grade MCA3 Standards, Benchmarks, Test Specifications & Sampler Questions Standard No. Benchmark (4 th Grade) Sampler Item Demonstrate fluency with multiplication and division facts. 4.1.1.1 Factors
For full credit, show all work. Study all geometry vocabulary words from your chapter packet.
 Accelerated Review 9: Geometric Relationships Name: For full credit, show all work. Study all geometry vocabulary words from your chapter packet. Caleb drew a quadrilateral on his paper. Which of the following
Accelerated Review 9: Geometric Relationships Name: For full credit, show all work. Study all geometry vocabulary words from your chapter packet. Caleb drew a quadrilateral on his paper. Which of the following
