Working with the BCC Z Space I Filter
|
|
|
- Jordan Matthews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Working with the BCC Z Space I Filter Normally, if you create an effect with multiple DVE layers, each layer is rendered separately. The layer that is topmost in the timeline overlaps all other layers, no matter how the layers move or rotate. The Z Space Þlters allow you to create effects using multiple DVE layers ( Z planes ) and/or sphere layers which can interact and intersect in 3D space. In a Z Space effect, each plane or sphere s apparent depth, or position on the Z axis, determines how the plane interacts with other planes and spheres. The plane closest to the viewer in Z space covers planes and spheres that are farther away, regardless of the order in the timeline. Normal DVE planes DVE planes in Z Space Viewing Selected Planes The View menu sets which portion of the effect displays. Choose Effect to view the entire effect. The other View menu choices vary depending on the Z Space Þlter. In Z-Space I, you can choose Plane 1, Plane 2, Plane 3 or Background to view only the corresponding plane. If View is set to a Plane which does not have a source layer assigned to it, the Effect Preview monitor displays a transparent layer. Container Parameter Group The Z Space Þlters use a container to group and arrange Z planes and spheres in 3D space. When you add planes and spheres to a container, you can animate each plane and sphere independently (using the Plane and Sphere parameters), then apply parameters and animations globally to all the planes and spheres within the container (using the Container parameters). The container preserves the spatial relationship between the objects within it as you reposition and rotate the container. The illustration at right shows three Z planes in a 3D container. Each plane is scaled and positioned independently. When you scale or rotate the container, all three planes scale and rotate as well, yet the spatial relationship between the three tracks remains constant.
2 Container rotated Container rotated and stretched You can still adjust any individual Z plane by making changes to the corresponding group of Plane parameters. In the example at right, Plane 2 (the facade) is tumbled forward. You can control which planes are in the container using the Link menu in each Plane parameter group. You can also choose whether the background plane is inside the container using the Link menu in the Background parameter group. Scale X Container and Scale Y Container adjust the size of the container along the X and Y axis respectively. These parameters are scaled as percentages of the container s original width and height. Thus, a Scale X setting of 200 produces a container twice as wide as the original. Select the Lock Scale checkbox to keep these values in proportion, or deselect this option to adjust the Scale X and Y independently. Position XY Container sets the horizontal and vertical location of the container. Position Z Container sets the apparent depth of the container. Decreasing negative values move the container closer to the viewer; increasing positive values move the container away. Very low Position Z values move the container behind the viewer, making it invisible. Tumble Container, Spin Container, and Rotate Container move the container around the X, Y, and Z axis, respectively. Tumble, Spin, and Rotate can animate over values greater than 360 to make the container undergo more than one full revolution. Container tumbled Container spun Container rotated
3 When the Lock Pivot to Position checkbox is selected, the container tumbles, spins, and rotates around its own center. If this option is deselected, you can set an external pivot point around which to tumble, spin, or rotate the container. Container rotated around center Rotate= 45 Rotate=0 Rotate=45 Container rotated around independent pivot point in lower left corner Rotate= 45 Rotate=0 Rotate=45 Pivot XY Container and Pivot Z Container set the X, Y, and Z coordinates of the pivot point. If Lock Pivot to Position is selected, moving the pivot point has no affect. The Motion Blur menu enables motion blur and controls the smoothness of the blur. Off turns motion blur off. The remaining options, Rough, Medium, Smooth, and Smoothest, produce motion blur of varying degrees of smoothness. Increasing smoothness produces a higher quality blur but increases rendering and preview times proportionately. Motion Blur=Rough Motion Blur=Smoothest Motion Blur is very processor intensive. You might want to turn motion blur off then enable it just before rendering. You can also work in Draft Mode in your host application to speed your previews.
4 Shutter Angle refers to the workings of a conventional Þlm camera. Normally, the shutter is open to 180, meaning that the shutter is open for half of each frame. Increasing the angle opens the shutter longer, creating a wider blur. Decreasing the angle produces a thinner blur. Shutter Angle=180 Shutter Angle=300 Shadows Parameter Group Parameters in this section enable you to add true 3D cast shadows to the Z Space effect. These shadows are more realistic than simple drop shadows because the cast shadows change as the objects casting or receiving the shadows are transformed. In the following examples, notice that the shadow falls differently on the background plane as the plane rotates in 3D space. Each plane has a Shadows control that determines whether that plane casts and receives shadows. For example, if you want a track to cast shadows on all other planes, but do not want the track shadowed by other planes, you can set the track to cast but not receive shadows. The Shadows menu turns shadows on and off and adjusts the quality of the shadows. Off turns off the shadows. The remaining three choices turn on shadows and provide three different rendering algorithms. Faster #1 and Faster #2 render shadows more quickly but a lower quality. Experiment with these two settings to Þnd the algorithm that looks better for your effect. Better increases rendering time, but produces a better-looking shadow. If Shadow Softness is 0, Faster #1, Faster #2, and Better all produce the same quality. For more information on Shadow Softness, see the next page.
5 Shadow Intensity controls the opacity of the shadows. A Shadow Intensity value of 100 creates completely opaque shadows, and a Shadow Intensity value of 0 makes the shadows completely transparent. Shadow Color sets the color of the shadows. Shadow Elevation sets the elevation of the synthetic light source used to produce shadows. A high elevation value produces a shadow that falls directly behind the plane casting the shadow. Decrease Shadow Elevation to offset the shadow farther from the plane casting the shadow. Negative Shadow Elevation values cause the plane to cast a shadow in front of itself in Z space so that the plane is partially covered by its own shadow. Shadow Elevation=60 Shadow Elevation=25 Shadow Direction sets the angle between the beam of light and the horizontal axis. The plane casts a shadow in the direction opposite that of the of the light beam. For example, if the light hits the plane from the right, the plane casts a shadow to the left. Shadow Direction= 135 Shadow Direction= 45 Shadow Softness controls the softness of the shadow edges. A setting of 0 produces a sharply deþned shadow with hard edges. Increasing Shadow Softness produces shadows with softer edges.
6 Shadow Softness=15 Shadow Softness=50 When the Lights Cast Shadows checkbox is selected, the positioning of the Z planes affects how applied light hits the planes. For example, suppose there are two Z planes in an effect, one on top of the other. If Lights Cast Shadows is selected, a light source positioned above both planes lights the top plane and perhaps part of the bottom plane, but the top plane obstructs some of the light falling on the bottom plane. This creates a more natural lighting effect. If this option is deselected, the light falls on both planes, and the top plane does not act as an obstruction. Lights Cast Shadows on Lights Cast Shadows off Plane 1, 2, and 3 Parameter Groups These parameters apply geometric transformations to the corresponding Z plane. The Plane menu sets which layer in the timeline is used as the source for the corresponding Z plane. Choose None to remove the plane from the effect. The Link menu determines how the plane is grouped with the other elements of the effect. Free places the plane outside the container. In Container places the plane inside the container. In Layer 1 links the plane to Plane 1. This link functions like a second container that can be also nested inside the main container. Thus, any changes made to Plane 1 also affect any Z planes whose Link menus are set to In Layer 1. Scale X and Scale Y adjust the size of the plane along the X and Y axis respectively. These parameters are scaled as percentages of the plane s original width and height. Thus, a Scale X setting of 200 produces a plane twice as wide as the original plane. Select the Lock to Scale X checkbox to keep the X and Y Scale values in proportion.
7 Opacity scales the opacity of the Z plane. When Opacity is 100, the plane is completely opaque. As Opacity decreases, the plane becomes increasingly transparent, and at value of 0, the plane is completely transparent. Position XY sets the X and Y coordinates of the center point of the plane. Position Z adjusts the apparent depth of the plane. Decreasing negative values move the plane closer to the viewer, while increasing positive values move the plane farther from the viewer. Very low Position Z values move the plane behind the viewer, making it invisible. Tumble, Spin, and Rotate move the plane around the X, Y, and Z axis, respectively. You can animate over values greater than 360 to make the plane complete more than one full revolution. When the Lock Pivot to Position checkbox is selected, the plane tumbles, spins, and rotates around its own center. If this option is deselected, you can set an external pivot point around which to tumble, spin, or rotate the plane. Pivot XY and Pivot Z set the X, Y, and Z coordinates of the pivot point. If Lock Pivot to Position is selected, moving the pivot point has no affect. The Crop controls crop the edges of the plane. The X and Y position controls set the upper left and lower right corners of a rectangle that deþnes the borders of the cropped area. The Shadows menu determines whether the plane casts and/or receives shadows. Cast Only causes the plane to cast shadows on other objects but not to receive them. Receive Only causes the plane to receive shadows cast by other objects but not to cast any. Cast and Receive causes the plane to both cast and receive shadows. Off causes the plane to neither cast nor receive shadows. The Lights menu determines which of the two spotlights light the plane. Choose Light 1 Only, Light 2 Only, Lights 1 and 2, or Off. You must select the appropriate Spotlight On checkbox above the Spotlight parameter groups apply the corresponding spotlight. Deselect this option to leave the object unlit. Ambient Light adjusts the brightness of the plane. The default setting of 100 does not add or subtract ambient light from the image. Decreasing this setting darkens the plane before any other light is applied. Ambient light illuminates or darkens the plane evenly, and is unaffected by any other lighting parameters. Background Parameter Group These parameters adjust the corresponding Background plane. Background planes are similar to Z planes but have fewer controls. The Background menu determines which layer in the timeline is used as the background plane. Choose None to eliminate the background from the effect. The Link menu controls how the background plane is grouped with the other elements. Background places the background plane outside of the main container, and causes the background plane s size to remain the same regardless of its depth. This allows you to position the background plane as far away in Z space as you need without adjusting the scale of the plane.
8 Free places the background plane outside of the main container. In Container places the background plane inside the main container. In Layer 1 links the background plane to Z Plane 1. This link functions like a second container that can be nested inside the main container. Any changes made to Plane 1 also affect any background planes whose Link Background menus are set to In Layer 1. Scale Background scales the size of the background plane along the X and Y axis. This parameter is scaled as percentages of the plane s original width and height. Thus, a Scale Background setting of 200 produces a plane twice as wide as the original plane. Opacity Background scales the opacity of the background plane. When Opacity Background is 100, the plane is completely opaque. As Opacity Background decreases, the plane is increasingly transparent, and at value of 0, the plane is completely transparent. Position XY Background sets the X and Y coordinates of the center point of the plane. Position Z Background sets the apparent depth of the plane. Decreasing negative values move the plane closer to the viewer; increasing positive values move the plane away. Very low Position Z values move the plane behind the viewer, making it invisible. The Crop controls crop the edges of the background. The X and Y position controls set the upper left and lower right corners of a rectangle that deþnes the borders of the cropped area. The Shadows menu sets whether the background casts and/or receives shadows. Cast Only causes the plane to cast shadows on other planes but not to receive them. Receive Only causes the plane to receive shadows cast by other planes but not to cast any of its own. Cast and Receive causes the plane to both cast and receive shadows. Off causes the plane to neither cast nor receive shadows. The Lights menu determines which of the two spotlights affect the background. Choose Light 1 Only, Light 2 Only, Lights 1 and 2, or Off. Ambient Light Background adjusts the brightness of the plane. The default setting of 100 does not add or subtract ambient light from the source image. Decreasing this setting makes the plane darker before the other light is applied. Ambient light illuminates or darkens the plane evenly, and is unaffected by any other lighting parameters. Spotlight 1 and Spotlight 2 Parameter Groups Select the Spotlight On checkbox to turn on the corresponding light source. Deselect this option to turn off the light. Source X and Source Y set the horizontal and vertical location of the light source. Source Z sets the apparent depth of the light source. Decreasing negative values move the source closer to the viewer, while increasing positive values move the source farther away.
9 Target X and Target Y set the horizontal and vertical location of the point on the image plane at which the spotlight is aimed. Width Spotlight controls the width (in degrees) of the beam of light. Changing the Width Spotlight is analogous to altering the placement of a physical spotlight within its enclosure. Intensity Spotlight sets the intensity of the light. Color Spotlight sets the color of the light. Falloff Spotlight controls the softness of the edges of the lit region. Increase Falloff to soften the transition between the lit and unlit regions. The Apply Mode menu controls how the light is composited with the effect.for descriptions of all the possible Apply Modes, see Apply Modes on page 611. Apply Mix Spotlight controls the mix of the speciþed Apply Mode with the Normal apply mode. If the Apply Mode is Normal, Apply Mix has no affect. If Apply Mix is 0, Apply Mode has no affect. Increase Apply Mix to blend the Apply Mode setting with the Normal apply mode.
Working with the BCC Z Space II Filter
 Working with the BCC Z Space II Filter Normally, if you create an effect with multiple DVE layers, each layer is rendered separately. The layer that is topmost in the timeline overlaps all other layers,
Working with the BCC Z Space II Filter Normally, if you create an effect with multiple DVE layers, each layer is rendered separately. The layer that is topmost in the timeline overlaps all other layers,
Working with the BCC Bump Map Generator
 Working with the BCC Bump Map Generator Bump mapping is used to create three dimensional detail on an image based on the luminance information in the image. The luminance value of each pixel of the image
Working with the BCC Bump Map Generator Bump mapping is used to create three dimensional detail on an image based on the luminance information in the image. The luminance value of each pixel of the image
Working with the BCC Brick Generator
 Working with the BCC Brick Generator Brick is a versatile generator of tiled surfaces with realistic texture and lighting controls. The bricks can act as a Þlter on a layer or generate a brick surface
Working with the BCC Brick Generator Brick is a versatile generator of tiled surfaces with realistic texture and lighting controls. The bricks can act as a Þlter on a layer or generate a brick surface
BCC Sphere Transition
 BCC Sphere Transition The Sphere Transition shape models the source image onto a sphere. Unlike the Sphere filter, the Sphere Transition filter allows you to animate Perspective, which is useful in creating
BCC Sphere Transition The Sphere Transition shape models the source image onto a sphere. Unlike the Sphere filter, the Sphere Transition filter allows you to animate Perspective, which is useful in creating
Working with the BCC 3D Image Shatter Filter
 Working with the BCC 3D Image Shatter Filter 3D Image Shatter shatters the image in 3D space and disperses the image fragments. The Þlter provides a variety of explosion, velocity, and gravity parameters
Working with the BCC 3D Image Shatter Filter 3D Image Shatter shatters the image in 3D space and disperses the image fragments. The Þlter provides a variety of explosion, velocity, and gravity parameters
Working with the BCC 2D Particles Filter
 Working with the BCC 2D Particles Filter 2D Particles breaks the source image into particles and disperses them in 2D space. This Þlter also provides a variety of explosion, velocity, and gravity controls
Working with the BCC 2D Particles Filter 2D Particles breaks the source image into particles and disperses them in 2D space. This Þlter also provides a variety of explosion, velocity, and gravity controls
BCC 3D Extruded Image Shatter Filter
 BCC 3D Extruded Image Shatter Filter 3D Extruded Image Shatter shatters the image in 3D space and disperses the image fragments. Unlike the 3D Image Shatter filter, this filter allows you to create threedimensional
BCC 3D Extruded Image Shatter Filter 3D Extruded Image Shatter shatters the image in 3D space and disperses the image fragments. Unlike the 3D Image Shatter filter, this filter allows you to create threedimensional
Working with the BCC Particle System Generator
 Working with the BCC Particle System Generator BCC Particle System is an auto-animated particle generator that provides in-depth control over individual particles as well as the overall shape and movement
Working with the BCC Particle System Generator BCC Particle System is an auto-animated particle generator that provides in-depth control over individual particles as well as the overall shape and movement
BCC Comet Generator Source XY Source Z Destination XY Destination Z Completion Time
 BCC Comet Generator Comet creates an auto-animated comet that streaks across the screen. The comet is compromised of particles whose sizes, shapes, and colors can be adjusted. You can also set the length
BCC Comet Generator Comet creates an auto-animated comet that streaks across the screen. The comet is compromised of particles whose sizes, shapes, and colors can be adjusted. You can also set the length
BCC Particle System Generator
 BCC Particle System Generator BCC Particle System is an auto-animated particle generator that provides in-depth control over individual particles as well as the overall shape and movement of the system.
BCC Particle System Generator BCC Particle System is an auto-animated particle generator that provides in-depth control over individual particles as well as the overall shape and movement of the system.
Avid FX Tutorials. Understanding the Tutorial Exercises
 Avid FX Tutorials Understanding the Tutorial Exercises The following tutorial exercises provide step-by-step instructions for creating various kinds of effects, while exploring many aspects of the Avid
Avid FX Tutorials Understanding the Tutorial Exercises The following tutorial exercises provide step-by-step instructions for creating various kinds of effects, while exploring many aspects of the Avid
BCC Textured Wipe Animation menu Manual Auto Pct. Done Percent Done
 BCC Textured Wipe The BCC Textured Wipe creates is a non-geometric wipe using the Influence layer and the Texture settings. By default, the Influence is generated from the luminance of the outgoing clip
BCC Textured Wipe The BCC Textured Wipe creates is a non-geometric wipe using the Influence layer and the Texture settings. By default, the Influence is generated from the luminance of the outgoing clip
BCC Rays Ripply Filter
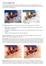 BCC Rays Ripply Filter The BCC Rays Ripply filter combines a light rays effect with a rippled light effect. The resulting light is generated from a selected channel in the source image and spreads from
BCC Rays Ripply Filter The BCC Rays Ripply filter combines a light rays effect with a rippled light effect. The resulting light is generated from a selected channel in the source image and spreads from
BCC Linear Wipe. When the Invert Wipe Checkbox is selected, the alpha channel created by the wipe inverts.
 BCC Linear Wipe BCC Linear Wipe is similar to a Horizontal wipe. However, it offers a variety parameters for you to customize. This filter is similar to the BCC Rectangular Wipe filter, but wipes in a
BCC Linear Wipe BCC Linear Wipe is similar to a Horizontal wipe. However, it offers a variety parameters for you to customize. This filter is similar to the BCC Rectangular Wipe filter, but wipes in a
BCC Multi Stretch Wipe
 BCC Multi Stretch Wipe The BCC Multi Stretch Wipe is a radial wipe with three additional stretch controls named Taffy Stretch. The Taffy Stretch parameters do not significantly impact render times. The
BCC Multi Stretch Wipe The BCC Multi Stretch Wipe is a radial wipe with three additional stretch controls named Taffy Stretch. The Taffy Stretch parameters do not significantly impact render times. The
3D Space is one of the most rewarding areas
 Lesson 8 206 3D Space Add a new dimension to your animations. In This Lesson 207 enabling layers for 3D 208 moving and rotating layers in 3D space 210 multiplaning effects 212 3D motion paths 213 multiple
Lesson 8 206 3D Space Add a new dimension to your animations. In This Lesson 207 enabling layers for 3D 208 moving and rotating layers in 3D space 210 multiplaning effects 212 3D motion paths 213 multiple
Working with the BCC Lens Flare and BCC Lens Flare Advanced
 Working with the BCC Lens Flare and BCC Lens Flare Advanced The BCC Lens Flare filter simulates a lens flare that is, streaks and spots of light on film caused by light bouncing inside of a camera lens.
Working with the BCC Lens Flare and BCC Lens Flare Advanced The BCC Lens Flare filter simulates a lens flare that is, streaks and spots of light on film caused by light bouncing inside of a camera lens.
BCC Rays Streaky Filter
 BCC Rays Streaky Filter The BCC Rays Streaky filter produces a light that contains streaks. The resulting light is generated from a chosen channel in the source image, and spreads from a source point in
BCC Rays Streaky Filter The BCC Rays Streaky filter produces a light that contains streaks. The resulting light is generated from a chosen channel in the source image, and spreads from a source point in
BCC Optical Stabilizer Filter
 BCC Optical Stabilizer Filter The Optical Stabilizer filter allows you to stabilize shaky video footage. The Optical Stabilizer uses optical flow technology to analyze a specified region and then adjusts
BCC Optical Stabilizer Filter The Optical Stabilizer filter allows you to stabilize shaky video footage. The Optical Stabilizer uses optical flow technology to analyze a specified region and then adjusts
BCC Extruded EPS Applying the BCC Extruded EPS filter in Adobe After Effects Comp size Solid layer BCC6 3D Objects category watch folder
 BCC Extruded EPS quick links ; Applying the filter, Presets, Render Options, AE Lights and Camera, Extrusion, Materials, Transformations, Built-in Light, Built-in Camera, Deformers Applying the BCC Extruded
BCC Extruded EPS quick links ; Applying the filter, Presets, Render Options, AE Lights and Camera, Extrusion, Materials, Transformations, Built-in Light, Built-in Camera, Deformers Applying the BCC Extruded
bcc pan and zoom filter description:
 bcc pan and zoom filter description: the bcc pan and zoom filter was designed to automate the work of documentary style pan and zoom effects, where a large still image file is moved along the x and y axis
bcc pan and zoom filter description: the bcc pan and zoom filter was designed to automate the work of documentary style pan and zoom effects, where a large still image file is moved along the x and y axis
Transforming Objects and Components
 4 Transforming Objects and Components Arrow selection Lasso selection Paint selection Move Rotate Scale Universal Manipulator Soft Modification Show Manipulator Last tool used Figure 4.1 Maya s manipulation
4 Transforming Objects and Components Arrow selection Lasso selection Paint selection Move Rotate Scale Universal Manipulator Soft Modification Show Manipulator Last tool used Figure 4.1 Maya s manipulation
Texture Mapping. Images from 3D Creative Magazine
 Texture Mapping Images from 3D Creative Magazine Contents Introduction Definitions Light And Colour Surface Attributes Surface Attributes: Colour Surface Attributes: Shininess Surface Attributes: Specularity
Texture Mapping Images from 3D Creative Magazine Contents Introduction Definitions Light And Colour Surface Attributes Surface Attributes: Colour Surface Attributes: Shininess Surface Attributes: Specularity
User's Guide Low Poly OBJ Importer v1.0
 User's Guide Low Poly OBJ Importer v1.0 Chapter 1 How It Works 1 Chapter 2 Quick Start 2 Chapter 3 Main Interface 3 Import 3 Object/SubObject Selector 4 Fill Options 5 Stroke Options 7 Global Options 8
User's Guide Low Poly OBJ Importer v1.0 Chapter 1 How It Works 1 Chapter 2 Quick Start 2 Chapter 3 Main Interface 3 Import 3 Object/SubObject Selector 4 Fill Options 5 Stroke Options 7 Global Options 8
Volume Rendering. Computer Animation and Visualisation Lecture 9. Taku Komura. Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics
 Volume Rendering Computer Animation and Visualisation Lecture 9 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Volume Rendering 1 Volume Data Usually, a data uniformly distributed
Volume Rendering Computer Animation and Visualisation Lecture 9 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Volume Rendering 1 Volume Data Usually, a data uniformly distributed
Announcements. Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) Computer Graphics
 Announcements Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) 1 Advanced Ray Tracing (Recursive) Ray Tracing Antialiasing Motion Blur Distribution Ray Tracing Ray Tracing and Radiosity Assumptions Simple shading
Announcements Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) 1 Advanced Ray Tracing (Recursive) Ray Tracing Antialiasing Motion Blur Distribution Ray Tracing Ray Tracing and Radiosity Assumptions Simple shading
Think about film & lighting
 Quiz 3: Textures Camera and Lighting for Animation Hand back Quiz 2 Amy Gooch CS 395: Intro to Animation Summer 2004 Think about film & lighting Reality! Cameras & Viewpoint Lighting in animation Same
Quiz 3: Textures Camera and Lighting for Animation Hand back Quiz 2 Amy Gooch CS 395: Intro to Animation Summer 2004 Think about film & lighting Reality! Cameras & Viewpoint Lighting in animation Same
Applying the BCC Extruded EPS filter in Final Cut Pro - In a new project add a slug to the timeline.
 BCC Extruded EPS quick links ; Applying the filter, Presets, Render Options, Extrusion, Materials, Transformations, Built-in Light, Built-in Camera, Deformers Applying the BCC Extruded EPS filter in Final
BCC Extruded EPS quick links ; Applying the filter, Presets, Render Options, Extrusion, Materials, Transformations, Built-in Light, Built-in Camera, Deformers Applying the BCC Extruded EPS filter in Final
Shadow Techniques. Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation
 Shadow Techniques Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation sim.dietrich@nvidia.com Lighting & Shadows The shadowing solution you choose can greatly influence the engine decisions you make This talk will outline
Shadow Techniques Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation sim.dietrich@nvidia.com Lighting & Shadows The shadowing solution you choose can greatly influence the engine decisions you make This talk will outline
Chapter 9. 3D DVE and Titling. User s Guide 377
 Chapter 9 3D DVE and Titling User s Guide 377 Chapter 9 3D DVE and Titling In This Chapter... This chapter describes how to create and edit 3D DVEs and titles. Combining the flexibility of 3D animation
Chapter 9 3D DVE and Titling User s Guide 377 Chapter 9 3D DVE and Titling In This Chapter... This chapter describes how to create and edit 3D DVEs and titles. Combining the flexibility of 3D animation
Easy View Manual Nicolaudie-Sunlite
 1989-2004 Nicolaudie-Sunlite Table of Contents Part I Preface Part II 3D Visualizer 1 2... 2 1 First steps Menu... 2 Toolbar... 3 Mouse move... 4... 5 2 3D stage Your first stage... 5... 7 3 Stage settings
1989-2004 Nicolaudie-Sunlite Table of Contents Part I Preface Part II 3D Visualizer 1 2... 2 1 First steps Menu... 2 Toolbar... 3 Mouse move... 4... 5 2 3D stage Your first stage... 5... 7 3 Stage settings
A Quick Introduction to POV-Ray
 A Quick Introduction to POV-Ray POV-Ray, the Persistence of Vision ray tracer, is open source software available from www.povray.org. This is good, highly functional software that you might enjoy playing
A Quick Introduction to POV-Ray POV-Ray, the Persistence of Vision ray tracer, is open source software available from www.povray.org. This is good, highly functional software that you might enjoy playing
ADOBE 9A After Effects(R) CS3 ACE. Download Full Version :
 ADOBE 9A0-068 After Effects(R) CS3 ACE Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/9a0-068 D. Increase the Maximum RAM Cache Size to 100%. Question: 71 For a presentation, you want
ADOBE 9A0-068 After Effects(R) CS3 ACE Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/9a0-068 D. Increase the Maximum RAM Cache Size to 100%. Question: 71 For a presentation, you want
The Wireframe Update Buttons. The Frontface and Backface Buttons. The Project Designer 265
 The Wireframe Update Buttons The speed at which objects can be manipulated in the Project Designer viewport depends in part on the complexity of the object being moved. An object that is made up of many
The Wireframe Update Buttons The speed at which objects can be manipulated in the Project Designer viewport depends in part on the complexity of the object being moved. An object that is made up of many
Lesson 11. Polygonal Spaceship
 11 Polygonal Spaceship In this lesson, you will build and texture map a polygonal spaceship. Starting with a polygonal cube, you will extrude facets until you have a completed ship. You will then be able
11 Polygonal Spaceship In this lesson, you will build and texture map a polygonal spaceship. Starting with a polygonal cube, you will extrude facets until you have a completed ship. You will then be able
Advanced Rendering CHAPTER. Render Window. Learning Objectives. Image Pane
 CHAPTER Advanced Rendering Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Make advanced rendering settings. Set the resolution for a rendering. Save a rendering to an image file.
CHAPTER Advanced Rendering Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Make advanced rendering settings. Set the resolution for a rendering. Save a rendering to an image file.
Chapter 6- Lighting and Cameras
 Lighting Types and Settings When you create a scene in Blender, you start with a few basic elements that will include a camera, but may or may not include a light. Remember that what the camera sees is
Lighting Types and Settings When you create a scene in Blender, you start with a few basic elements that will include a camera, but may or may not include a light. Remember that what the camera sees is
12 APPLYING EFFECTS. Lesson overview
 12 APPLYING EFFECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use various effects like Pathfinder, Distort & Transform, Offset Path, and Drop Shadow effects. Use Warp effects
12 APPLYING EFFECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use various effects like Pathfinder, Distort & Transform, Offset Path, and Drop Shadow effects. Use Warp effects
Creative Web Designer Course
 Creative Web Designer Course Photoshop 1. Getting to Know the Work Area Starting to work in Adobe Photoshop Using the tools Setting tool properties Undoing actions in Photoshop More about panels and panel
Creative Web Designer Course Photoshop 1. Getting to Know the Work Area Starting to work in Adobe Photoshop Using the tools Setting tool properties Undoing actions in Photoshop More about panels and panel
Using Boris Continuum Complete with Apple Motion
 Using Boris Continuum Complete with Apple Motion 1 Installing in Apple Motion...............................................2 Technical Support...................................................... 2 Supported
Using Boris Continuum Complete with Apple Motion 1 Installing in Apple Motion...............................................2 Technical Support...................................................... 2 Supported
Chapter 6 Formatting Graphic Objects
 Impress Guide Chapter 6 OpenOffice.org Copyright This document is Copyright 2007 by its contributors as listed in the section titled Authors. You can distribute it and/or modify it under the terms of either
Impress Guide Chapter 6 OpenOffice.org Copyright This document is Copyright 2007 by its contributors as listed in the section titled Authors. You can distribute it and/or modify it under the terms of either
Transforming Objects in Inkscape Transform Menu. Move
 Transforming Objects in Inkscape Transform Menu Many of the tools for transforming objects are located in the Transform menu. (You can open the menu in Object > Transform, or by clicking SHIFT+CTRL+M.)
Transforming Objects in Inkscape Transform Menu Many of the tools for transforming objects are located in the Transform menu. (You can open the menu in Object > Transform, or by clicking SHIFT+CTRL+M.)
12 APPLYING EFFECTS. Lesson overview
 12 APPLYING EFFECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use various effects, such as Pathfinder, Scribble, and Drop Shadow. Use Warp effects to distort type. Create three-dimensional
12 APPLYING EFFECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use various effects, such as Pathfinder, Scribble, and Drop Shadow. Use Warp effects to distort type. Create three-dimensional
Adobe Premiere Pro CC 2018
 Course Outline Adobe Premiere Pro CC 2018 1 TOURING ADOBE PREMIERE PRO CC Performing nonlinear editing in Premiere Pro Expanding the workflow Touring the Premiere Pro interface Keyboard shortcuts 2 SETTING
Course Outline Adobe Premiere Pro CC 2018 1 TOURING ADOBE PREMIERE PRO CC Performing nonlinear editing in Premiere Pro Expanding the workflow Touring the Premiere Pro interface Keyboard shortcuts 2 SETTING
CTvox Quick Start Guide
 CTvox Quick Start Guide For Software Version 3.0 CTvox Quick Start Guide (for Software Version 3.0) Page 1 Contents Version history... 3 Introduction... 4 Loading a dataset... 5 Navigating the scene...
CTvox Quick Start Guide For Software Version 3.0 CTvox Quick Start Guide (for Software Version 3.0) Page 1 Contents Version history... 3 Introduction... 4 Loading a dataset... 5 Navigating the scene...
ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CS3
 ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CS3 Chapter 2 Creating Text and Gradients Chapter 2 1 Creating type Create and Format Text Create text anywhere Select the Type Tool Click the artboard and start typing or click and drag
ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CS3 Chapter 2 Creating Text and Gradients Chapter 2 1 Creating type Create and Format Text Create text anywhere Select the Type Tool Click the artboard and start typing or click and drag
Glass Gambit: Chess set and shader presets for DAZ Studio
 Glass Gambit: Chess set and shader presets for DAZ Studio This product includes a beautiful glass chess set, 70 faceted glass shader presets and a 360 degree prop with 5 material files. Some people find
Glass Gambit: Chess set and shader presets for DAZ Studio This product includes a beautiful glass chess set, 70 faceted glass shader presets and a 360 degree prop with 5 material files. Some people find
I have a meeting with Peter Lee and Bob Cosgrove on Wednesday to discuss the future of the cluster. Computer Graphics
 Announcements Assignment 4 will be out later today Problem Set 3 is due today or tomorrow by 9am in my mail box (4 th floor NSH) How are the machines working out? I have a meeting with Peter Lee and Bob
Announcements Assignment 4 will be out later today Problem Set 3 is due today or tomorrow by 9am in my mail box (4 th floor NSH) How are the machines working out? I have a meeting with Peter Lee and Bob
GIMP WEB 2.0 ICONS. GIMP is all about IT (Images and Text) OPEN GIMP
 GIMP WEB 2.0 ICONS Web 2.0 Banners: Download E-Book WEB 2.0 ICONS: DOWNLOAD E-BOOK OPEN GIMP GIMP is all about IT (Images and Text) Step 1: To begin a new GIMP project, from the Menu Bar, select File New.
GIMP WEB 2.0 ICONS Web 2.0 Banners: Download E-Book WEB 2.0 ICONS: DOWNLOAD E-BOOK OPEN GIMP GIMP is all about IT (Images and Text) Step 1: To begin a new GIMP project, from the Menu Bar, select File New.
Images from 3D Creative Magazine. 3D Modelling Systems
 Images from 3D Creative Magazine 3D Modelling Systems Contents Reference & Accuracy 3D Primitives Transforms Move (Translate) Rotate Scale Mirror Align 3D Booleans Deforms Bend Taper Skew Twist Squash
Images from 3D Creative Magazine 3D Modelling Systems Contents Reference & Accuracy 3D Primitives Transforms Move (Translate) Rotate Scale Mirror Align 3D Booleans Deforms Bend Taper Skew Twist Squash
Raytracing. COSC 4328/5327 Scott A. King
 Raytracing COSC 4328/5327 Scott A. King Basic Ray Casting Method pixels in screen Shoot ray p from the eye through the pixel. Find closest ray-object intersection. Get color at intersection Basic Ray Casting
Raytracing COSC 4328/5327 Scott A. King Basic Ray Casting Method pixels in screen Shoot ray p from the eye through the pixel. Find closest ray-object intersection. Get color at intersection Basic Ray Casting
Computer Graphics. Shadows
 Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shadows Taku Komura Today Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow texture Shadow volume Shadow map Soft shadows Why Shadows? Shadows tell us about the relative locations
Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shadows Taku Komura Today Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow texture Shadow volume Shadow map Soft shadows Why Shadows? Shadows tell us about the relative locations
An object in 3D space
 An object in 3D space An object's viewpoint Every Alice object has a viewpoint. The viewpoint of an object is determined by: The position of the object in 3D space. The orientation of the object relative
An object in 3D space An object's viewpoint Every Alice object has a viewpoint. The viewpoint of an object is determined by: The position of the object in 3D space. The orientation of the object relative
LIGHTING - 1. Note. Lights. Ambient occlusion
 Note LIGHTING - 1 The creation and use of lights varies greatly between the default Blender renderer and the Cycles renderer. This section refers only to simple lighting in the default renderer. Lights
Note LIGHTING - 1 The creation and use of lights varies greatly between the default Blender renderer and the Cycles renderer. This section refers only to simple lighting in the default renderer. Lights
Computer Graphics. Ray Tracing. Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College
 Computer Graphics Ray Tracing Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College Ray Tracing Example Created by Anto Matkovic Ray Tracing Example Ray Tracing Example Ray Tracing Most light rays do not reach
Computer Graphics Ray Tracing Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College Ray Tracing Example Created by Anto Matkovic Ray Tracing Example Ray Tracing Example Ray Tracing Most light rays do not reach
Illumination & Shading: Part 1
 Illumination & Shading: Part 1 Light Sources Empirical Illumination Shading Local vs Global Illumination Lecture 10 Comp 236 Spring 2005 Computer Graphics Jargon: Illumination Models Illumination - the
Illumination & Shading: Part 1 Light Sources Empirical Illumination Shading Local vs Global Illumination Lecture 10 Comp 236 Spring 2005 Computer Graphics Jargon: Illumination Models Illumination - the
INFS 2150 Introduction to Web Development
 INFS 2150 Introduction to Web Development 4. Graphics and Images Objectives Create a figure box Add a background image Add a border to an element Create rounded borders Create a graphic border Create a
INFS 2150 Introduction to Web Development 4. Graphics and Images Objectives Create a figure box Add a background image Add a border to an element Create rounded borders Create a graphic border Create a
INFS 2150 Introduction to Web Development
 Objectives INFS 2150 Introduction to Web Development 4. Graphics and Images Create a figure box Add a background image Add a border to an element Create rounded borders Create a graphic border Create a
Objectives INFS 2150 Introduction to Web Development 4. Graphics and Images Create a figure box Add a background image Add a border to an element Create rounded borders Create a graphic border Create a
All forms of EM waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s This speed is constant in air as well
 Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Previously... contour or image rendering in 2D
 Volume Rendering Visualisation Lecture 10 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Volume Rendering 1 Previously... contour or image rendering in 2D 2D Contour line
Volume Rendering Visualisation Lecture 10 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Volume Rendering 1 Previously... contour or image rendering in 2D 2D Contour line
Written by Catherine Adams, Jeanine Brennan and Anne Renehan. Copyright 2003 by Boris FX, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the U. S. A.
 2 Boris Title Toolkit User Guide Version 1.0 The material contained herein is protected by copyrights. Permission to use materials may be granted upon written request and proper credit. Contact information
2 Boris Title Toolkit User Guide Version 1.0 The material contained herein is protected by copyrights. Permission to use materials may be granted upon written request and proper credit. Contact information
How to work with text
 How to work with text Adobe Flash Professional lets you add text to a Flash application in two formats: You can add Text Layout Framework (TLF) text. You can add Classic text. Using the Text Layout Framework
How to work with text Adobe Flash Professional lets you add text to a Flash application in two formats: You can add Text Layout Framework (TLF) text. You can add Classic text. Using the Text Layout Framework
Consider a partially transparent object that is illuminated with two lights, one visible from each side of the object. Start with a ray from the eye
 Ray Tracing What was the rendering equation? Motivate & list the terms. Relate the rendering equation to forward ray tracing. Why is forward ray tracing not good for image formation? What is the difference
Ray Tracing What was the rendering equation? Motivate & list the terms. Relate the rendering equation to forward ray tracing. Why is forward ray tracing not good for image formation? What is the difference
Chapter 5. Transforming Shapes
 Chapter 5 Transforming Shapes It is difficult to walk through daily life without being able to see geometric transformations in your surroundings. Notice how the leaves of plants, for example, are almost
Chapter 5 Transforming Shapes It is difficult to walk through daily life without being able to see geometric transformations in your surroundings. Notice how the leaves of plants, for example, are almost
How to draw and create shapes
 Adobe Flash Professional Guide How to draw and create shapes You can add artwork to your Adobe Flash Professional documents in two ways: You can import images or draw original artwork in Flash by using
Adobe Flash Professional Guide How to draw and create shapes You can add artwork to your Adobe Flash Professional documents in two ways: You can import images or draw original artwork in Flash by using
Computer Graphics. Si Lu. Fall uter_graphics.htm 11/22/2017
 Computer Graphics Si Lu Fall 2017 http://web.cecs.pdx.edu/~lusi/cs447/cs447_547_comp uter_graphics.htm 11/22/2017 Last time o Splines 2 Today o Raytracing o Final Exam: 14:00-15:30, Novermber 29, 2017
Computer Graphics Si Lu Fall 2017 http://web.cecs.pdx.edu/~lusi/cs447/cs447_547_comp uter_graphics.htm 11/22/2017 Last time o Splines 2 Today o Raytracing o Final Exam: 14:00-15:30, Novermber 29, 2017
Ambient Occlusion Pass
 Ambient Occlusion Pass (Soft Shadows in the Nooks and Crannies to Replicate Photorealistic Lighting) In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for an Ambient Occlusion
Ambient Occlusion Pass (Soft Shadows in the Nooks and Crannies to Replicate Photorealistic Lighting) In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for an Ambient Occlusion
4 TRANSFORMING OBJECTS
 4 TRANSFORMING OBJECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Add, edit, rename, and reorder artboards in an existing document. Navigate artboards. Select individual objects,
4 TRANSFORMING OBJECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Add, edit, rename, and reorder artboards in an existing document. Navigate artboards. Select individual objects,
Work with Shapes. Concepts CHAPTER. Concepts, page 3-1 Procedures, page 3-5
 3 CHAPTER Revised: November 15, 2011 Concepts, page 3-1, page 3-5 Concepts The Shapes Tool is Versatile, page 3-2 Guidelines for Shapes, page 3-2 Visual Density Transparent, Translucent, or Opaque?, page
3 CHAPTER Revised: November 15, 2011 Concepts, page 3-1, page 3-5 Concepts The Shapes Tool is Versatile, page 3-2 Guidelines for Shapes, page 3-2 Visual Density Transparent, Translucent, or Opaque?, page
CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007
 Visible Surface Detection CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 Visible Surface Detection Visible surface detection or hidden surface removal. Realistic scenes: closer objects occludes the
Visible Surface Detection CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 Visible Surface Detection Visible surface detection or hidden surface removal. Realistic scenes: closer objects occludes the
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS
 COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS SESSION 15 RAY TRACING 1 Announcements Programming Assignment 3 out today - overview @ end of the class Ray Tracing 2 Lecture Overview Review of last class Ray Tracing 3 Local
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS SESSION 15 RAY TRACING 1 Announcements Programming Assignment 3 out today - overview @ end of the class Ray Tracing 2 Lecture Overview Review of last class Ray Tracing 3 Local
Topics and things to know about them:
 Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Quick Start Tutorial
 Tutorial Tutorial: Build an Apple Welcome to Design 3D CX 7. This is a quick tutorial to get you started. In this tutorial you ll learn how to import an Adobe Illustrator file, Lathe it into a 3D object,
Tutorial Tutorial: Build an Apple Welcome to Design 3D CX 7. This is a quick tutorial to get you started. In this tutorial you ll learn how to import an Adobe Illustrator file, Lathe it into a 3D object,
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics. Spring Shading
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Shading Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and then color it using a fixed color. We get something like But we rather
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Shading Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and then color it using a fixed color. We get something like But we rather
Lighting. To do. Course Outline. This Lecture. Continue to work on ray programming assignment Start thinking about final project
 To do Continue to work on ray programming assignment Start thinking about final project Lighting Course Outline 3D Graphics Pipeline Modeling (Creating 3D Geometry) Mesh; modeling; sampling; Interaction
To do Continue to work on ray programming assignment Start thinking about final project Lighting Course Outline 3D Graphics Pipeline Modeling (Creating 3D Geometry) Mesh; modeling; sampling; Interaction
Lecture Outlines Chapter 26
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 11/18/2013 2 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Objectives: After completing this module, you should be able to: Explain and discuss with diagrams, reflection and refraction of light
Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 11/18/2013 2 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Objectives: After completing this module, you should be able to: Explain and discuss with diagrams, reflection and refraction of light
Shading I Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008
 Shading I 1 Objectives Learn to shade objects ==> images appear threedimensional Introduce types of light-material interactions Build simple reflection model Phong model Can be used with real time graphics
Shading I 1 Objectives Learn to shade objects ==> images appear threedimensional Introduce types of light-material interactions Build simple reflection model Phong model Can be used with real time graphics
You ve learned a lot in the previous 11 lessons.
 280 Excerpt from After Effects Apprentice, 2nd Edition. Copyright 2009 Trish and Chris Meyer. Final Project Using 3D space plus effects to create a show s opening title. In This Lesson 281 creating elements;
280 Excerpt from After Effects Apprentice, 2nd Edition. Copyright 2009 Trish and Chris Meyer. Final Project Using 3D space plus effects to create a show s opening title. In This Lesson 281 creating elements;
EECS 487: Interactive Computer Graphics
 Ray Tracing EECS 487: Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 29: Distributed Ray Tracing Introduction and context ray casting Recursive ray tracing shadows reflection refraction Ray tracing implementation
Ray Tracing EECS 487: Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 29: Distributed Ray Tracing Introduction and context ray casting Recursive ray tracing shadows reflection refraction Ray tracing implementation
9 Using Appearance Attributes, Styles, and Effects
 9 Using Appearance Attributes, Styles, and Effects You can alter the look of an object without changing its structure using appearance attributes fills, strokes, effects, transparency, blending modes,
9 Using Appearance Attributes, Styles, and Effects You can alter the look of an object without changing its structure using appearance attributes fills, strokes, effects, transparency, blending modes,
4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb?
 1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
SNC2D PHYSICS 4/27/2013. LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L Light Rays & Reflection (P ) Light Rays & Reflection. The Ray Model of Light
 SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L Light Rays & Reflection (P.402-409) Light Rays & Reflection A driver adjusts her rearview mirror. The mirror allows her to see the cars behind her. Mirrors help
SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L Light Rays & Reflection (P.402-409) Light Rays & Reflection A driver adjusts her rearview mirror. The mirror allows her to see the cars behind her. Mirrors help
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing. Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19
 Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
Effects, part 5. Particle Playground (PB only) Overview of Particle Playground workflow
 1 Adobe After Effects 5.0 This PDF file contains documentation for the Particle Playground effect, which is in the Simulation effect category. Particle Playground (PB only) Use this effect to create animations
1 Adobe After Effects 5.0 This PDF file contains documentation for the Particle Playground effect, which is in the Simulation effect category. Particle Playground (PB only) Use this effect to create animations
User Guide. MLT FX Tracker.
 User Guide MLT FX Tracker www.s.a.m.com Information and Notices Information and Notices Copyright and Disclaimer Copyright protection claimed includes all forms and matters of copyrightable material and
User Guide MLT FX Tracker www.s.a.m.com Information and Notices Information and Notices Copyright and Disclaimer Copyright protection claimed includes all forms and matters of copyrightable material and
The process of making a selection is fundamental to all Photoshop
 102640 ch15.1.qxp 3/10/07 11:23 AM Page 303 Making Selections The process of making a selection is fundamental to all Photoshop documents. A selection isolates an area of an image so that you can apply
102640 ch15.1.qxp 3/10/07 11:23 AM Page 303 Making Selections The process of making a selection is fundamental to all Photoshop documents. A selection isolates an area of an image so that you can apply
Motion Graphics Pack for Avid Media Composer Adrenaline
 Motion Graphics Pack for Avid Media Composer Adrenaline Boris Motion Graphics Pack is a bundle of Boris RED and CONTINUUM Complete AVX. Boris RED adds motion graphic features that are not available inside
Motion Graphics Pack for Avid Media Composer Adrenaline Boris Motion Graphics Pack is a bundle of Boris RED and CONTINUUM Complete AVX. Boris RED adds motion graphic features that are not available inside
How to create shapes. Drawing basic shapes. Adobe Photoshop Elements 8 guide
 How to create shapes With the shape tools in Adobe Photoshop Elements, you can draw perfect geometric shapes, regardless of your artistic ability or illustration experience. The first step to drawing shapes
How to create shapes With the shape tools in Adobe Photoshop Elements, you can draw perfect geometric shapes, regardless of your artistic ability or illustration experience. The first step to drawing shapes
Ray Tracing. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15. Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch ]
![Ray Tracing. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15. Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch ] Ray Tracing. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15. Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch ]](/thumbs/78/78594982.jpg) CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15 Ray Tracing Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch. 13.2-13.3] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Local Illumination Object illuminations
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15 Ray Tracing Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch. 13.2-13.3] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Local Illumination Object illuminations
Radeon ProRender add-in for SOLIDWORKS. User Guide v1.1
 Radeon ProRender add-in for SOLIDWORKS User Guide v1.1 This document is a user and setup guide with tips and tricks on how to render photorealistic images in real-time, apply decals and create animations.
Radeon ProRender add-in for SOLIDWORKS User Guide v1.1 This document is a user and setup guide with tips and tricks on how to render photorealistic images in real-time, apply decals and create animations.
Education and Training CUFMEM14A. Exercise 2. Create, Manipulate and Incorporate 2D Graphics
 Education and Training CUFMEM14A Exercise 2 Create, Manipulate and Incorporate 2D Graphics Menu Exercise 2 Exercise 2a: Scarecrow Exercise - Painting and Drawing Tools... 3 Exercise 2b: Scarecrow Exercise
Education and Training CUFMEM14A Exercise 2 Create, Manipulate and Incorporate 2D Graphics Menu Exercise 2 Exercise 2a: Scarecrow Exercise - Painting and Drawing Tools... 3 Exercise 2b: Scarecrow Exercise
ART 268 3D Computer Graphics Texture Mapping and Rendering. Texture Mapping
 ART 268 3D Computer Graphics Texture Mapping and Rendering Texture Mapping Is the way in which a material is wrapped around an object. The default method is UVW mapping (see below). When you drag a material
ART 268 3D Computer Graphics Texture Mapping and Rendering Texture Mapping Is the way in which a material is wrapped around an object. The default method is UVW mapping (see below). When you drag a material
Multimedia Technology CHAPTER 4. Video and Animation
 CHAPTER 4 Video and Animation - Both video and animation give us a sense of motion. They exploit some properties of human eye s ability of viewing pictures. - Motion video is the element of multimedia
CHAPTER 4 Video and Animation - Both video and animation give us a sense of motion. They exploit some properties of human eye s ability of viewing pictures. - Motion video is the element of multimedia
Drawing shapes and lines
 Fine F Fi i Handmade H d d Ch Chocolates l Hours Mon Sat 10am 6pm In this demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CS6, you will be introduced to new and exciting application features, like gradients on a stroke
Fine F Fi i Handmade H d d Ch Chocolates l Hours Mon Sat 10am 6pm In this demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CS6, you will be introduced to new and exciting application features, like gradients on a stroke
Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007
 Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007 Programming For this assignment you will write a simple ray tracer. It will be written in C++ without
Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007 Programming For this assignment you will write a simple ray tracer. It will be written in C++ without
Chapter 5. Projections and Rendering
 Chapter 5 Projections and Rendering Topics: Perspective Projections The rendering pipeline In order to view manipulate and view a graphics object we must find ways of storing it a computer-compatible way.
Chapter 5 Projections and Rendering Topics: Perspective Projections The rendering pipeline In order to view manipulate and view a graphics object we must find ways of storing it a computer-compatible way.
A simple OpenGL animation Due: Wednesday, January 27 at 4pm
 CMSC 23700 Winter 2010 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 1 January 12 A simple OpenGL animation Due: Wednesday, January 27 at 4pm 1 Summary This project is the first part of a three-part project.
CMSC 23700 Winter 2010 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 1 January 12 A simple OpenGL animation Due: Wednesday, January 27 at 4pm 1 Summary This project is the first part of a three-part project.
Advances in MicroStation 3D
 MW1HC515 Advances in MicroStation 3D Hands-on class sponsored by the Bentley Institute Presenter: Sam Hendrick, Senior MicroStation Product Consultant Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton,
MW1HC515 Advances in MicroStation 3D Hands-on class sponsored by the Bentley Institute Presenter: Sam Hendrick, Senior MicroStation Product Consultant Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton,
I N T R O D U C T I O N T O C O M P U T E R G R A P H I C S
 3D Viewing: the Synthetic Camera Programmer s reference model for specifying 3D view projection parameters to the computer General synthetic camera (e.g., PHIGS Camera, Computer Graphics: Principles and
3D Viewing: the Synthetic Camera Programmer s reference model for specifying 3D view projection parameters to the computer General synthetic camera (e.g., PHIGS Camera, Computer Graphics: Principles and
Scheme Extensions Aa thru Lz
 Chapter 2. Scheme Extensions Aa thru Lz Topic: Ignore Scheme is a public domain programming language, based on the LISP language, that uses an interpreter to run commands. ACIS provides extensions (written
Chapter 2. Scheme Extensions Aa thru Lz Topic: Ignore Scheme is a public domain programming language, based on the LISP language, that uses an interpreter to run commands. ACIS provides extensions (written
