Spline Collocation Method for Solving Three Dimensional Parabolic Equations
|
|
|
- Ethan Lester
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spline Collocation Method for Solving Three Dimensional Parabolic Equations Dr A.K.Pathak H.O.D,H&S.S. Department S.T.B.S.College Of Diploma Engg. Surat, India an Dr. H.D.Doctor Prof. & H.O.D,Mathematics Department Veer Narmad South Gujarat Uni. Surat, India Abstract The present work describes spline collocation approximation for solving Heat Conduction In Rectangular problem. The mathematical problem gives rise to solve a linear partial differential equation which is of three dimensional parabolic type. The method involves the solution of algebraic linear equation which can be written in the matrix form is main advantage. The solution are obtained by this method compared with analytic solution to demonstrate the justification and simplicity of the spline approximation converge to analytic solution. Keywords: Spline Collocation Method, Partial Differential Equation.. INTRODUCTION: Two common questions are encountered while the numerical solution to the problem is obtained. The first is about its acceptance whether it is sufficiently close to the true solution or not. If one has an analytic solution then this can be answered very clearly but in either case it is not so easy. One has to be careful while concluding that a particular numerical solution is acceptable when an analytic solution is not available. Normally a method is selected which requires a minimum number of steps, consuming the shortest computational time and yet one that does not produce an excessive errors.. SPLINE COLLOCATION METHOD: For solving linear and nonlinear differential equation with the help of the numerical methods required much computational work and time. Bickley [968] Suggested the method of spline function containing truncated power polynomials to solve a linear boundary value problem Ahlberg et al [967] used cardinal splines for solving differential equations. Doctor et al [983,984] have shown that the method of spline collocation is quite useful for the solution of physical phenomena which give rise to linear parabolic one dimensional partial differential equation. The method demonstrates the use of spline function. Spline functions are piecewise polynomial and their successive derivatives are continuous. They were used for data interpolation initially. In 967, Blue [969] suggested the use of spline function for the solution of B.V.P. y = f(x,y,y ) (.) with boundary conditions G [Y(0),Y (0)] G [Y(),y ()] (.) The following recurrence relations were used. S ( x i- )+4s ( x i )+s ( x i+ ) = 6/ h (f( x i- )-f( x i )+f( x i+ ) (.3) 50
2 . Spline Formula To Solve Parabolic Partial Differential Equation With Three Space Variables The general form of linear parabolic partial differential equation with three space variables is of the form u = R (u + u u ) ; 0 < x < a,0 < y < b,0 < z < c (..) t xx yy + yy With Dirichlite condition prescribed on the boundaries x=0,y=0,z=0. We should divide the region 0 x a 0, y b,0 z c in to L,M and N sub-intervals of width Dx, Dy, Dz respectively such that L D x = a, MDy = b, and NDz = c. Let us denote the points of subdivisions by x i : i = 0,,,..., L, y j : j = 0,,,...,M, z k : k = 0,,,..., N. Let us u i, k, p denotes the values of u at the (i,k) th Mesh point at the time pd t.for simplicity, let us take cubic region with equal sides and D x = Dy = Dz = h (say) and L=M=N. Approximate the function u at time pdt by cubic spline S(x).Discretizing the left side of equation (..) by forward difference formula and replacing right hand side by three times of the second " derivative. i.e. 3s ( x i, k ) at p th level we get (u i, p+ + 4u i, k,p+ + u = (+ 8r) u ) i+, k,p+ i-, k,p + (4-36r) u i, k,p + (+ 8r) u i+, k,p i,k=,,n- (..) Where r = R Dt / h.these set of (N-) x (N-) x (N-) equations in (N-) x (N-) x (N-) unknowns can be solved by any well- known method. The above set of simultaneous equations gives a square matrix. The above equation (..) is known as cubic spline explicit formula to solve equation (..). For this explicit method maximum possible value of r, for stability and convergence of this method, maximum possible value of r is r /6. In Implicit method, he finite difference replacement of equation (...) is (u i, k,p+ - ui, k, p ) 3 = R [ ( s" i, k, p + s" i, k, p+ )] (..3) Dt Where s" i, k, p and s" i, k,p+ denote the second derivatives of s(x) at x = x" i, k, p at the time interval p and p+ respectively. we get (- 9r)ui,k, p+ + (4 + 8r)ui, k,p+ + ( - 9r) ui+, k,p+ (..4) = (+ 9r)u + (4-8r) u + (+ 9r)u i-, k,p i, k,p Where r = R Dt / h and i,k=,,3,..,n- Above relation known as cubic spline implicit formula to solve equation (...). Like explicit scheme we get (N-) x (N-) x (N-) equation in (N-) x (N-) x (N-) unknowns. These simultaneous equations with square matrix can be solved any standard method. In both methods once the value of u are known at (p+) th level, we can proceed to compute the next level (p+) by same techniques described as above. i+, k,p 3. HEAT CONDUCTION IN THIN RECTANGULAR VOLUME: Consider a flow of heat in a rectangular volume with sides of length axes x,y,z (figure(3.)) D x, Dy, Dz along the co-ordinate 5
3 R N z S M Dz y P(x,y,z) Q Dx L Dy O x Fig(3.) Rectangular element of solid The amount of heat entering the element through the face PQRS in time Dt is - k( D y D z )( u / x ) x D t in the element through the approximate face is - k( DyDz)( u / x) x+ Dx Dt Where is the thermal conductivity of the material and u(x,y,z,t) is the temperature function. The negative signs are taken because the heat flows in the direction of decreasing temperature. Hence the quantity of heat remaining in the solid as a result of entry through the PQRS and exit through the opposite face is - k{( u / x) x+ Dy - ( u / x) x} DyDzDt (3.) = { u / x ) Dx} DyDzDt Up to a first approximation. Similarly, the corresponding differences in the heat entering and heaving through the nearing two pairs of opposite face are k{( u / y ) DyDxDtDz and k{( u / y ) DzDxDyDt (3.) Hence the total heat retained by the solid in time Dt is the sum of (3. ) and (3.) which is equal to the heat required to the heat required to raise the temperature to raise the temperature of the element by D u.thus we have k( u / x + u / y + u / z ) DxDyDzDt = ( rdxdydz) sdu Where r is density and s be the specific heat of the solid. Dividing by Dt 0, weget DxDyDzs and limit as u / t = R ( u / x + u / x + u / x ); R = k / sr (3.3) Above equation (3.3) is the heat equation in three space variables. Also it is known as parabolic partial differential equation with three space variables x,y,z and time variable t. Solution of above equation (3.3) gives the temperature distribution in the rectangular volume. Consider the edges of rectangular volume of side are kept at temperature zero and faces are perfectly insulated. Hence the flow of heat in the volume governed by the equation (3.3) with boundary conditions U(x,0,z,t)=0, u(x,y,0,t)=0, u(0,y,z,t)=0 (3.4) 5
4 Where 0 x, y, z Let initial temperature distribution in the volume be u( x, y, z,0) = sin Pxsin Pysin Pz (3.5) Where 0 x, y, z The given Problem with boundary and initial conditions described as above is solved by explicit and implicit method. 4. SPLINE SOLUTION WITH EXPLICIT METHOD We shall determine the solution of equation (3.3) satisfying the initial and boundary conditions defined by the equation (3.4) and (3.5) respectively, using the explicit formula given by equation(3.3) as follows For that let h=/0 R = 0.00 and D t =0.00 which gives r= r=.08 and 4-36r = Substituting the value of +8r,4-36r with initial and boundary condition in equation (3.3) gives following result For p=0, k= and j= i= + 4u + u 0.74 u 0,,,,,,,,, = Since u0,,, = 0 4u,,, + u,,, = 0.74 u,,, + 4u,,, + u 3,,, = u,,, + 4u3,,, + u,,, = i= i= etc. Proceeding in this way for I,k =,3,,9 We get 9x9x9 equations in 9x9x9 unknowns, which can be solved by any standard method once the values of p=0 are obtained, the results for p=,.. are obtained by same process discussed as above. Due to symmetry of the solution the result obtained for 0 z 0.5,0 y 0.5,0 x 0. 5 at t=0.00 and t=0.003 Hear the result for z=0.5, y=0. at t=0.00 are given in table I and plotted in fig. 4. SPLINE SOLUTION WITH IMPLICIT METHOD: Using implicit formula given by equation(..4)the solution of equation (3.3) satisfying boundary and initial conditions For p=0, k=,j= i= (4.08)u,,, + (0.99)u,,, = i= (0.99)u,, + (4.08)u,,, + (0.99) u3,,, = i=3 (0.99)u,,, + (4.08)u3,,, + (0.99) u 4,,, = Similarly in this way we get 9x9x9 simultaneous equations we get the temperature distribution in rectangular volume at time t=0.00 Proceeding in the same way we get the temperature in the volume at t=0.00,0.003 etc. Result for z=0.5, y=0. at t=0.003 are given in table 6. and plotted in fig RESULT TABLE 5. Temperature Distribution In Rectangular Volume U At t=0.003, z=0.5 X,Y
5 TABLE 5. Temperature Distribution In Rectangular Volume U At t=0.003, z=0.5 X,Y TABLE 5.3 Error Analysis Of Temperature Distribution Rectangular Volume U at t=0.003,z=0.5 y=0. X UEXT UEXT -UE X0-6 UEXT - UI X Fig (5.) Temperature Distribution In Rectangular Volume through cubic spline explicit method (at z=0.5,y=0.) 54
6 Fig(5.) Temperature Distribution In Rectangular Volume through cubic spline implicit method (at z=0.5,y=0.) 6. CONCLUTION: Fig(5.3)Error Analysis (at t=0.003,z=0.5,y=0.) The solution of equation (3.3) obtained by spline explicit and implicit as well as explicit methods are compared with the exact solutions in table 5.3. Fig. 5.3 indicates the error analysis which compares the exact solutions with spline solutions obtained by both explicit as well as implicit method. From the fig. 5.3 and table 5.3 it is clear that spline solutions are quite reliable up to five digits of decimal places. 7. REFERENCES: [].Ahlberg J H, Nilson E N And Wals J N, The Theory of Spline And Their Application. Academic Press, N.Y,967. [].Berdyshev V I, Subbopim J N,Numerical Methods of Approximation of functions (Russian). Sverdlovsk. Ural.Publ.House, 979,8pp [3].Bhatt R V: An Extended Study Of The Spline Collocation Approach To Partial Differential Equations, Thesis, South Gujarat University, Surat, 005. [4].Bickley W G -Piecewise Cubic Interpolation and Two point Boundary Value Problem. Comp. J,, 968,06. 55
7 [5].Blue J L - Spline Function Methods for linear Boundary Value problem. Communications of the ACM., No.6, 969, 37. [6].Bruch J C And G Zyvoloski: Transient Two-Dimensional Heat Conduction Problems Solved by the Finite Element Method, International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 8, 974, PP [7].Clough R W: The Finite Element Method in Plane Stress Analysis J.Struct. Div., ASCE, Proc.d conf. Electronic Computation, 960,pp [8].Cook R D: Concepts and Applications of Finite Element Techniques for Fluid Flow, Butterworths, London, 976. [9].Courant R: Variational Methods for the Solution of Problems of Equilibrium and Vibration Bull. Am. Math. Soc., vol. 49, 943,pp-43. [0].Doctor H D And Kalathia,N L - Spline Collocation in the Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids. Presented at the Annual conf. of National Academic of science [].Doctor H D And Kalthia N L - Spline Approximation of Boundary Value Problems. Presented at Annual Conf.of Indian math.soc, 49, 983. [].Doctor H D, And Kalathia N L -Spline Approximations of Boundary Value Problems Presented at Annual conf. of Indian Mathematical Society, 49, 983. [3].Doctor H D, Bulsari A B And Kalathia N L -Spline Collocation Approach to Boundary Value Problems. Int. J. Numer.Fluids, 4,6, 984,5. [4].Doctor H D, Bulsari A B And Kalthia N L - Spline Collocation Approach To Boundary Value Problems. Int. J. Number, Floids., 4, 6, 984,5. [5].Dr. Grewal B S:- Numerical Methods In Engineering And Science, Fifth ed, Khanna Publishers, 005. [6].Fyfe D J -The Use Of Cubic Splines In Solutions Of Two Point Boundary Value Problems, Com.P.J.,, 969,88-9. [7].Pathak A K and Doctor H D, Comparative Study of Collocation Method- Spline, Finite Difference and Finite Element Method for Solving Partial Differential Equation Presented at Conf. of Gujarat Science Congress, 00. [8].Reddy J N : An Introduction To The Finite Element Method. Mc Graw-Hill International Editions, New York, 984. [9].Sastry S S - Introductory Methods of Numerical Analysis. Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited. New Delhi,005. AUTHOR S BIOGRAPHY: Dr.Anant K Pathak: He is working as H.O.D. of Humanities and Social Science Department in S.T.B.S. College of Diploma Engineering. He has published 3 papers in international journal and in national journal.he has presented 3 papers in national conference and in International conference. He has 9 years of teaching experience. 56
Solve Non-Linear Parabolic Partial Differential Equation by Spline Collocation Method
 Solve Non-Linear Parabolic Partial Differential Equation by Spline Collocation Method P.B. Choksi 1 and A.K. Pathak 2 1 Research Scholar, Rai University,Ahemdabad. Email:pinalchoksey@gmail.com 2 H.O.D.
Solve Non-Linear Parabolic Partial Differential Equation by Spline Collocation Method P.B. Choksi 1 and A.K. Pathak 2 1 Research Scholar, Rai University,Ahemdabad. Email:pinalchoksey@gmail.com 2 H.O.D.
Spline Solutions to Dengue Disease Transmission Model
 VNSGU JOURNAL OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Vol.6. No. 1 Jul 2018 28-35 ISSN : 0975-5446 Accepted in : Oct 2017 Spline Solutions to Dengue Disease Transmission Model SHAH Keyuri J. Teaching Assistant Applied
VNSGU JOURNAL OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Vol.6. No. 1 Jul 2018 28-35 ISSN : 0975-5446 Accepted in : Oct 2017 Spline Solutions to Dengue Disease Transmission Model SHAH Keyuri J. Teaching Assistant Applied
A Quintic Spline method for fourth order singularly perturbed Boundary Value Problem of Reaction-Diffusion type
 A Quintic Spline method for fourth order singularly perturbed Boundary Value Problem of Reaction-Diffusion type Jigisha U. Pandya and Harish D. Doctor Asst. Prof., Department of Mathematics, Sarvajanik
A Quintic Spline method for fourth order singularly perturbed Boundary Value Problem of Reaction-Diffusion type Jigisha U. Pandya and Harish D. Doctor Asst. Prof., Department of Mathematics, Sarvajanik
Lacunary Interpolation Using Quartic B-Spline
 General Letters in Mathematic, Vol. 2, No. 3, June 2017, pp. 129-137 e-issn 2519-9277, p-issn 2519-9269 Available online at http:\\ www.refaad.com Lacunary Interpolation Using Quartic B-Spline 1 Karwan
General Letters in Mathematic, Vol. 2, No. 3, June 2017, pp. 129-137 e-issn 2519-9277, p-issn 2519-9269 Available online at http:\\ www.refaad.com Lacunary Interpolation Using Quartic B-Spline 1 Karwan
(Part - 1) P. Sam Johnson. April 14, Numerical Solution of. Ordinary Differential Equations. (Part - 1) Sam Johnson. NIT Karnataka.
 P. April 14, 2015 1/51 Overview We discuss the following important methods of solving ordinary differential equations of first / second order. Picard s method of successive approximations (Method of successive
P. April 14, 2015 1/51 Overview We discuss the following important methods of solving ordinary differential equations of first / second order. Picard s method of successive approximations (Method of successive
99 International Journal of Engineering, Science and Mathematics
 Journal Homepage: Applications of cubic splines in the numerical solution of polynomials Najmuddin Ahmad 1 and Khan Farah Deeba 2 Department of Mathematics Integral University Lucknow Abstract: In this
Journal Homepage: Applications of cubic splines in the numerical solution of polynomials Najmuddin Ahmad 1 and Khan Farah Deeba 2 Department of Mathematics Integral University Lucknow Abstract: In this
course outline basic principles of numerical analysis, intro FEM
 idealization, equilibrium, solutions, interpretation of results types of numerical engineering problems continuous vs discrete systems direct stiffness approach differential & variational formulation introduction
idealization, equilibrium, solutions, interpretation of results types of numerical engineering problems continuous vs discrete systems direct stiffness approach differential & variational formulation introduction
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems
 1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
Module 1: Introduction to Finite Difference Method and Fundamentals of CFD Lecture 6:
 file:///d:/chitra/nptel_phase2/mechanical/cfd/lecture6/6_1.htm 1 of 1 6/20/2012 12:24 PM The Lecture deals with: ADI Method file:///d:/chitra/nptel_phase2/mechanical/cfd/lecture6/6_2.htm 1 of 2 6/20/2012
file:///d:/chitra/nptel_phase2/mechanical/cfd/lecture6/6_1.htm 1 of 1 6/20/2012 12:24 PM The Lecture deals with: ADI Method file:///d:/chitra/nptel_phase2/mechanical/cfd/lecture6/6_2.htm 1 of 2 6/20/2012
Deficient Quartic Spline Interpolation
 International Journal of Computational Science and Mathematics. ISSN 0974-3189 Volume 3, Number 2 (2011), pp. 227-236 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Deficient Quartic
International Journal of Computational Science and Mathematics. ISSN 0974-3189 Volume 3, Number 2 (2011), pp. 227-236 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Deficient Quartic
AS 5850 Finite Element Analysis
 AS 5850 Finite Element Analysis INTRODUCTION Prof. IIT Madras Goal of engineering computations Perform analysis and design of physical systems and processes subjected to imposed conditions (or loads) and
AS 5850 Finite Element Analysis INTRODUCTION Prof. IIT Madras Goal of engineering computations Perform analysis and design of physical systems and processes subjected to imposed conditions (or loads) and
INTERPOLATION BY QUARTIC SPLINE
 INTERPOLATION BY QUARTIC SPLINE K.K.Nigam 1, Y.P. Dubey 2, Brajendra Tiwari 3, Anil Shukla 4 1 Mathematics Deptt., LNCT Jabalpur, MP, (India) 2 Sarswati Institution of Engg. & Technology, Jabalpur MP,
INTERPOLATION BY QUARTIC SPLINE K.K.Nigam 1, Y.P. Dubey 2, Brajendra Tiwari 3, Anil Shukla 4 1 Mathematics Deptt., LNCT Jabalpur, MP, (India) 2 Sarswati Institution of Engg. & Technology, Jabalpur MP,
Cubic Spline Interpolation with New Conditions on M 0 and M n
 Cubic Spline Interpolation with New Conditions on M 0 and M n 1 Parcha Kalyani and P.S. Rama Chandra Rao 2 1,2 Kakatiya Institute of Technology and Sciences, Warangal-506009-India Abstract In this communication,
Cubic Spline Interpolation with New Conditions on M 0 and M n 1 Parcha Kalyani and P.S. Rama Chandra Rao 2 1,2 Kakatiya Institute of Technology and Sciences, Warangal-506009-India Abstract In this communication,
MODELING MIXED BOUNDARY PROBLEMS WITH THE COMPLEX VARIABLE BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHOD (CVBEM) USING MATLAB AND MATHEMATICA
 A. N. Johnson et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 3, No. 3 (2015) 269 278 MODELING MIXED BOUNDARY PROBLEMS WITH THE COMPLEX VARIABLE BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHOD (CVBEM) USING MATLAB AND MATHEMATICA
A. N. Johnson et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 3, No. 3 (2015) 269 278 MODELING MIXED BOUNDARY PROBLEMS WITH THE COMPLEX VARIABLE BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHOD (CVBEM) USING MATLAB AND MATHEMATICA
Friday, 11 January 13. Interpolation
 Interpolation Interpolation Interpolation is not a branch of mathematic but a collection of techniques useful for solving computer graphics problems Basically an interpolant is a way of changing one number
Interpolation Interpolation Interpolation is not a branch of mathematic but a collection of techniques useful for solving computer graphics problems Basically an interpolant is a way of changing one number
Convergence of C 2 Deficient Quartic Spline Interpolation
 Advances in Computational Sciences and Technology ISSN 0973-6107 Volume 10, Number 4 (2017) pp. 519-527 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Convergence of C 2 Deficient Quartic Spline
Advances in Computational Sciences and Technology ISSN 0973-6107 Volume 10, Number 4 (2017) pp. 519-527 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Convergence of C 2 Deficient Quartic Spline
1, 2
 A QUARTIC LEGENDRE SPLINE COLLOCATION METHOD TO SOLVE FREDHOLM INTEGRO DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION B. M. Pya 1, D. C. Joshi 2 1 Asst. Prof., Dept.of Applied Mathematics, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel Institute of
A QUARTIC LEGENDRE SPLINE COLLOCATION METHOD TO SOLVE FREDHOLM INTEGRO DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION B. M. Pya 1, D. C. Joshi 2 1 Asst. Prof., Dept.of Applied Mathematics, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel Institute of
A numerical grid and grid less (Mesh less) techniques for the solution of 2D Laplace equation
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2014, 5(1):150-155 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC A numerical grid and grid less (Mesh less) techniques for
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2014, 5(1):150-155 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC A numerical grid and grid less (Mesh less) techniques for
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 24
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 24 So in today s class, we will look at quadrilateral elements; and we will
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 24 So in today s class, we will look at quadrilateral elements; and we will
MATLAB. Advanced Mathematics and Mechanics Applications Using. Third Edition. David Halpern University of Alabama CHAPMAN & HALL/CRC
 Advanced Mathematics and Mechanics Applications Using MATLAB Third Edition Howard B. Wilson University of Alabama Louis H. Turcotte Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology David Halpern University of Alabama
Advanced Mathematics and Mechanics Applications Using MATLAB Third Edition Howard B. Wilson University of Alabama Louis H. Turcotte Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology David Halpern University of Alabama
Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation
 Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation For functions of one variable, y = f (x), the rate of change of the dependent variable can dy be found unambiguously by differentiation: f x. In this chapter we explore
Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation For functions of one variable, y = f (x), the rate of change of the dependent variable can dy be found unambiguously by differentiation: f x. In this chapter we explore
QUIZ 4 (CHAPTER 17) SOLUTIONS MATH 252 FALL 2008 KUNIYUKI SCORED OUT OF 125 POINTS MULTIPLIED BY % POSSIBLE
 QUIZ 4 (CHAPTER 17) SOLUTIONS MATH 5 FALL 8 KUNIYUKI SCORED OUT OF 15 POINTS MULTIPLIED BY.84 15% POSSIBLE 1) Reverse the order of integration, and evaluate the resulting double integral: 16 y dx dy. Give
QUIZ 4 (CHAPTER 17) SOLUTIONS MATH 5 FALL 8 KUNIYUKI SCORED OUT OF 15 POINTS MULTIPLIED BY.84 15% POSSIBLE 1) Reverse the order of integration, and evaluate the resulting double integral: 16 y dx dy. Give
STATIC FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF N1 TYPE VEHICLE CHASSIS MEMBERS FOR BENDING PERFORMANCE
 STATIC FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF N1 TYPE VEHICLE CHASSIS MEMBERS FOR BENDING PERFORMANCE 1 CHINMAY POTDAR, 2 AMEY PISE, 3 AISHWARYA DUBEY, 4 SUSHRUT JADHAV 1, 3 TATA Technologies Limited,
STATIC FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS AND VALIDATION OF N1 TYPE VEHICLE CHASSIS MEMBERS FOR BENDING PERFORMANCE 1 CHINMAY POTDAR, 2 AMEY PISE, 3 AISHWARYA DUBEY, 4 SUSHRUT JADHAV 1, 3 TATA Technologies Limited,
A Modified Spline Interpolation Method for Function Reconstruction from Its Zero-Crossings
 Scientific Papers, University of Latvia, 2010. Vol. 756 Computer Science and Information Technologies 207 220 P. A Modified Spline Interpolation Method for Function Reconstruction from Its Zero-Crossings
Scientific Papers, University of Latvia, 2010. Vol. 756 Computer Science and Information Technologies 207 220 P. A Modified Spline Interpolation Method for Function Reconstruction from Its Zero-Crossings
Using Modified Euler Method (MEM) for the Solution of some First Order Differential Equations with Initial Value Problems (IVPs).
 Using Modified Euler Method (MEM) for the Solution of some First Order Differential Equations with Initial Value Problems (IVPs). D.I. Lanlege, Ph.D. * ; U.M. Garba, B.Sc.; and A. Aluebho, B.Sc. Department
Using Modified Euler Method (MEM) for the Solution of some First Order Differential Equations with Initial Value Problems (IVPs). D.I. Lanlege, Ph.D. * ; U.M. Garba, B.Sc.; and A. Aluebho, B.Sc. Department
Contents. MATH 32B-2 (18W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables. 1 Homework 1 - Solutions 3. 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 13
 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Homework - Solutions 3 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 3 3 Homework 3 - Solutions 9 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus
MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Homework - Solutions 3 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 3 3 Homework 3 - Solutions 9 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus
Asymptotic Error Analysis
 Asymptotic Error Analysis Brian Wetton Mathematics Department, UBC www.math.ubc.ca/ wetton PIMS YRC, June 3, 2014 Outline Overview Some History Romberg Integration Cubic Splines - Periodic Case More History:
Asymptotic Error Analysis Brian Wetton Mathematics Department, UBC www.math.ubc.ca/ wetton PIMS YRC, June 3, 2014 Outline Overview Some History Romberg Integration Cubic Splines - Periodic Case More History:
Fully discrete Finite Element Approximations of Semilinear Parabolic Equations in a Nonconvex Polygon
 Fully discrete Finite Element Approximations of Semilinear Parabolic Equations in a Nonconvex Polygon Tamal Pramanick 1,a) 1 Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati, Guwahati
Fully discrete Finite Element Approximations of Semilinear Parabolic Equations in a Nonconvex Polygon Tamal Pramanick 1,a) 1 Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati, Guwahati
Table for Third-Degree Spline Interpolation Using Equi-Spaced Knots. By W. D. Hoskins
 MATHEMATICS OF COMPUTATION, VOLUME 25, NUMBER 116, OCTOBER, 1971 Table for Third-Degree Spline Interpolation Using Equi-Spaced Knots By W. D. Hoskins Abstract. A table is given for the calculation of the
MATHEMATICS OF COMPUTATION, VOLUME 25, NUMBER 116, OCTOBER, 1971 Table for Third-Degree Spline Interpolation Using Equi-Spaced Knots By W. D. Hoskins Abstract. A table is given for the calculation of the
f xx (x, y) = 6 + 6x f xy (x, y) = 0 f yy (x, y) = y In general, the quantity that we re interested in is
 1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
CS 450 Numerical Analysis. Chapter 7: Interpolation
 Lecture slides based on the textbook Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey by Michael T. Heath, copyright c 2018 by the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics. http://www.siam.org/books/cl80
Lecture slides based on the textbook Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey by Michael T. Heath, copyright c 2018 by the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics. http://www.siam.org/books/cl80
Physics I : Oscillations and Waves Prof. S Bharadwaj Department of Physics & Meteorology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Physics I : Oscillations and Waves Prof. S Bharadwaj Department of Physics & Meteorology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 20 Diffraction - I We have been discussing interference, the
Physics I : Oscillations and Waves Prof. S Bharadwaj Department of Physics & Meteorology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 20 Diffraction - I We have been discussing interference, the
Natural Quartic Spline
 Natural Quartic Spline Rafael E Banchs INTRODUCTION This report describes the natural quartic spline algorithm developed for the enhanced solution of the Time Harmonic Field Electric Logging problem As
Natural Quartic Spline Rafael E Banchs INTRODUCTION This report describes the natural quartic spline algorithm developed for the enhanced solution of the Time Harmonic Field Electric Logging problem As
Finite Element Method. Chapter 7. Practical considerations in FEM modeling
 Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
13.1. Functions of Several Variables. Introduction to Functions of Several Variables. Functions of Several Variables. Objectives. Example 1 Solution
 13 Functions of Several Variables 13.1 Introduction to Functions of Several Variables Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Understand
13 Functions of Several Variables 13.1 Introduction to Functions of Several Variables Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Understand
Math 265 Exam 3 Solutions
 C Roettger, Fall 16 Math 265 Exam 3 Solutions Problem 1 Let D be the region inside the circle r 5 sin θ but outside the cardioid r 2 + sin θ. Find the area of D. Note that r and θ denote polar coordinates.
C Roettger, Fall 16 Math 265 Exam 3 Solutions Problem 1 Let D be the region inside the circle r 5 sin θ but outside the cardioid r 2 + sin θ. Find the area of D. Note that r and θ denote polar coordinates.
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING DESIGN (BFF2612)
 COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING DESIGN (BFF2612) BASIC MATHEMATICAL CONCEPTS IN CAED by Dr. Mohd Nizar Mhd Razali Faculty of Manufacturing Engineering mnizar@ump.edu.my COORDINATE SYSTEM y+ y+ z+ z+ x+ RIGHT
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING DESIGN (BFF2612) BASIC MATHEMATICAL CONCEPTS IN CAED by Dr. Mohd Nizar Mhd Razali Faculty of Manufacturing Engineering mnizar@ump.edu.my COORDINATE SYSTEM y+ y+ z+ z+ x+ RIGHT
Math 213 Exam 2. Each question is followed by a space to write your answer. Please write your answer neatly in the space provided.
 Math 213 Exam 2 Name: Section: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may be used other than a onepage cheat
Math 213 Exam 2 Name: Section: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may be used other than a onepage cheat
Discrete Cubic Interpolatory Splines
 Publ RIMS, Kyoto Univ. 28 (1992), 825-832 Discrete Cubic Interpolatory Splines By Manjulata SHRIVASTAVA* Abstract In the present paper, existence, uniqueness and convergence properties of a discrete cubic
Publ RIMS, Kyoto Univ. 28 (1992), 825-832 Discrete Cubic Interpolatory Splines By Manjulata SHRIVASTAVA* Abstract In the present paper, existence, uniqueness and convergence properties of a discrete cubic
Module 1: Introduction to Finite Difference Method and Fundamentals of CFD Lecture 13: The Lecture deals with:
 The Lecture deals with: Some more Suggestions for Improvement of Discretization Schemes Some Non-Trivial Problems with Discretized Equations file:///d /chitra/nptel_phase2/mechanical/cfd/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/20/2012
The Lecture deals with: Some more Suggestions for Improvement of Discretization Schemes Some Non-Trivial Problems with Discretized Equations file:///d /chitra/nptel_phase2/mechanical/cfd/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/20/2012
Video 11.1 Vijay Kumar. Property of University of Pennsylvania, Vijay Kumar
 Video 11.1 Vijay Kumar 1 Smooth three dimensional trajectories START INT. POSITION INT. POSITION GOAL Applications Trajectory generation in robotics Planning trajectories for quad rotors 2 Motion Planning
Video 11.1 Vijay Kumar 1 Smooth three dimensional trajectories START INT. POSITION INT. POSITION GOAL Applications Trajectory generation in robotics Planning trajectories for quad rotors 2 Motion Planning
Method of Finite Elements I
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Held by Prof. Dr. E. Chatzi, Dr. P. Steffen Assistants: Adrian Egger (HIL E 13.3), Harry Mylonas (HIL H33.1), Konstantinos Tatsis (HIL H33.1) Lectures homepage:
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Held by Prof. Dr. E. Chatzi, Dr. P. Steffen Assistants: Adrian Egger (HIL E 13.3), Harry Mylonas (HIL H33.1), Konstantinos Tatsis (HIL H33.1) Lectures homepage:
Numerical and theoretical analysis of shock waves interaction and reflection
 Fluid Structure Interaction and Moving Boundary Problems IV 299 Numerical and theoretical analysis of shock waves interaction and reflection K. Alhussan Space Research Institute, King Abdulaziz City for
Fluid Structure Interaction and Moving Boundary Problems IV 299 Numerical and theoretical analysis of shock waves interaction and reflection K. Alhussan Space Research Institute, King Abdulaziz City for
Partial Differential Equations
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Partial Differential Equations Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Motivation various dynamic effects and physical processes are described
Simulation in Computer Graphics Partial Differential Equations Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Motivation various dynamic effects and physical processes are described
Analysis of Distortion Parameters of Eight node Serendipity Element on the Elements Performance
 Analysis of Distortion Parameters of Eight node Serendipity Element on the Elements Performance Vishal Jagota & A. P. S. Sethi Department of Mechanical Engineering, Shoolini University, Solan (HP), India
Analysis of Distortion Parameters of Eight node Serendipity Element on the Elements Performance Vishal Jagota & A. P. S. Sethi Department of Mechanical Engineering, Shoolini University, Solan (HP), India
Simulation of rotation and scaling algorithm for numerically modelled structures
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of rotation and scaling algorithm for numerically modelled structures To cite this article: S K Ruhit et al 2018 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of rotation and scaling algorithm for numerically modelled structures To cite this article: S K Ruhit et al 2018 IOP
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis
 Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
Parameterization of triangular meshes
 Parameterization of triangular meshes Michael S. Floater November 10, 2009 Triangular meshes are often used to represent surfaces, at least initially, one reason being that meshes are relatively easy to
Parameterization of triangular meshes Michael S. Floater November 10, 2009 Triangular meshes are often used to represent surfaces, at least initially, one reason being that meshes are relatively easy to
CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 ME 475: Computer-Aided Design of Structures 1-1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Analysis versus Design 1.2 Basic Steps in Analysis 1.3 What is the Finite Element Method? 1.4 Geometrical Representation, Discretization
ME 475: Computer-Aided Design of Structures 1-1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Analysis versus Design 1.2 Basic Steps in Analysis 1.3 What is the Finite Element Method? 1.4 Geometrical Representation, Discretization
A Comparison of Some Numerical Methods for the Advection-Diffusion Equation
 Res Lett Inf Math Sci, 26, Vol1, pp49-62 Available online at http://iimsmasseyacnz/research/letters/ 49 A Comparison of Some Numerical Methods for the Advection-Diffusion Equation M Thongmoon 1 & R McKibbin
Res Lett Inf Math Sci, 26, Vol1, pp49-62 Available online at http://iimsmasseyacnz/research/letters/ 49 A Comparison of Some Numerical Methods for the Advection-Diffusion Equation M Thongmoon 1 & R McKibbin
An introduction to interpolation and splines
 An introduction to interpolation and splines Kenneth H. Carpenter, EECE KSU November 22, 1999 revised November 20, 2001, April 24, 2002, April 14, 2004 1 Introduction Suppose one wishes to draw a curve
An introduction to interpolation and splines Kenneth H. Carpenter, EECE KSU November 22, 1999 revised November 20, 2001, April 24, 2002, April 14, 2004 1 Introduction Suppose one wishes to draw a curve
Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two
 Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Thursday, February 28, class time. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration: sections 13.3,
Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Thursday, February 28, class time. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration: sections 13.3,
Nodal Integration Technique in Meshless Method
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Feb. 2014), PP 18-26 Nodal Integration Technique in Meshless Method Ahmed MJIDILA
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Feb. 2014), PP 18-26 Nodal Integration Technique in Meshless Method Ahmed MJIDILA
THE STUDY OF NEW APPROACHES IN CUBIC SPLINE INTERPOLATION FOR AUTO MOBILE DATA
 Journal of Science and Arts Year 17, No. 3(4), pp. 41-46, 217 ORIGINAL PAPER THE STUDY OF NEW APPROACHES IN CUBIC SPLINE INTERPOLATION FOR AUTO MOBILE DATA NAJMUDDIN AHMAD 1, KHAN FARAH DEEBA 1 Manuscript
Journal of Science and Arts Year 17, No. 3(4), pp. 41-46, 217 ORIGINAL PAPER THE STUDY OF NEW APPROACHES IN CUBIC SPLINE INTERPOLATION FOR AUTO MOBILE DATA NAJMUDDIN AHMAD 1, KHAN FARAH DEEBA 1 Manuscript
Section 17.7: Surface Integrals. 1 Objectives. 2 Assignments. 3 Maple Commands. 4 Lecture. 4.1 Riemann definition
 ection 17.7: urface Integrals 1 Objectives 1. Compute surface integrals of function of three variables. Assignments 1. Read ection 17.7. Problems: 5,7,11,1 3. Challenge: 17,3 4. Read ection 17.4 3 Maple
ection 17.7: urface Integrals 1 Objectives 1. Compute surface integrals of function of three variables. Assignments 1. Read ection 17.7. Problems: 5,7,11,1 3. Challenge: 17,3 4. Read ection 17.4 3 Maple
Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 8 Boston Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow E. Kaufman
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 8 Boston Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow E. Kaufman
Module 2: Single Step Methods Lecture 4: The Euler Method. The Lecture Contains: The Euler Method. Euler's Method (Analytical Interpretations)
 The Lecture Contains: The Euler Method Euler's Method (Analytical Interpretations) An Analytical Example file:///g /Numerical_solutions/lecture4/4_1.htm[8/26/2011 11:14:40 AM] We shall now describe methods
The Lecture Contains: The Euler Method Euler's Method (Analytical Interpretations) An Analytical Example file:///g /Numerical_solutions/lecture4/4_1.htm[8/26/2011 11:14:40 AM] We shall now describe methods
Knot Insertion and Reparametrization of Interval B-spline Curves
 International Journal of Video&Image Processing and Network Security IJVIPNS-IJENS Vol:14 No:05 1 Knot Insertion and Reparametrization of Interval B-spline Curves O. Ismail, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
International Journal of Video&Image Processing and Network Security IJVIPNS-IJENS Vol:14 No:05 1 Knot Insertion and Reparametrization of Interval B-spline Curves O. Ismail, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
A NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF ONE DIMENSIONAL HEAT EQUATION USING CUBIC B-SPLINE BASIS FUNCTIONS
 A NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF ONE DIMENSIONAL HEAT EQUATION USING CUBIC B-SPLINE BASIS FUNCTIONS 1 SHARANJEET DHAWAN, 2 SHEO KUMAR 1 Department of mathematics 2 Dr. B.R.Ambedkar National Institute of Technology,
A NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF ONE DIMENSIONAL HEAT EQUATION USING CUBIC B-SPLINE BASIS FUNCTIONS 1 SHARANJEET DHAWAN, 2 SHEO KUMAR 1 Department of mathematics 2 Dr. B.R.Ambedkar National Institute of Technology,
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV. Exam I (Friday, April 29) will cover sections
 REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
Optimizations and Lagrange Multiplier Method
 Introduction Applications Goal and Objectives Reflection Questions Once an objective of any real world application is well specified as a function of its control variables, which may subject to a certain
Introduction Applications Goal and Objectives Reflection Questions Once an objective of any real world application is well specified as a function of its control variables, which may subject to a certain
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements
 Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
MODELLING-Representing space and time in a numerical model
 MODELLING-Representing space and time in a numerical model Simulation parameters When setting up any simulation, whether computer-based or to be computed manually, it is important to identify the parameters
MODELLING-Representing space and time in a numerical model Simulation parameters When setting up any simulation, whether computer-based or to be computed manually, it is important to identify the parameters
27. Tangent Planes & Approximations
 27. Tangent Planes & Approximations If z = f(x, y) is a differentiable surface in R 3 and (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is a point on this surface, then it is possible to construct a plane passing through this point,
27. Tangent Planes & Approximations If z = f(x, y) is a differentiable surface in R 3 and (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is a point on this surface, then it is possible to construct a plane passing through this point,
Approximations for Linear Tenth-order Boundary Value Problems through Polynomial and Non-polynomial Cubic Spline Techniques
 Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 52 4): 389 396 2015) Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 0377-2969 print), 2306-1448 online) Pakistan Academy of Sciences Research Article Approximations
Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 52 4): 389 396 2015) Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 0377-2969 print), 2306-1448 online) Pakistan Academy of Sciences Research Article Approximations
Ordinary differential equations solving methods
 Radim Hošek, A07237 radhost@students.zcu.cz Ordinary differential equations solving methods Problem: y = y2 (1) y = x y (2) y = sin ( + y 2 ) (3) Where it is possible we try to solve the equations analytically,
Radim Hošek, A07237 radhost@students.zcu.cz Ordinary differential equations solving methods Problem: y = y2 (1) y = x y (2) y = sin ( + y 2 ) (3) Where it is possible we try to solve the equations analytically,
Generalizations of the Distance and Dependent Function in Extenics to 2D, 3D, and n D
 Volume 3 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS July, 01 Generalizations of the Distance and Dependent Function in Extenics to D, 3D, and n D Florentin Smarandache University of New Mexico, Mathematics and Science Department,
Volume 3 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS July, 01 Generalizations of the Distance and Dependent Function in Extenics to D, 3D, and n D Florentin Smarandache University of New Mexico, Mathematics and Science Department,
(Refer Slide Time: 00:02:24 min)
 CAD / CAM Prof. Dr. P. V. Madhusudhan Rao Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. # 9 Parametric Surfaces II So these days, we are discussing the subject
CAD / CAM Prof. Dr. P. V. Madhusudhan Rao Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. # 9 Parametric Surfaces II So these days, we are discussing the subject
Estimation of Flow Field & Drag for Aerofoil Wing
 Estimation of Flow Field & Drag for Aerofoil Wing Mahantesh. HM 1, Prof. Anand. SN 2 P.G. Student, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, East Point College of Engineering, Bangalore, Karnataka, India 1 Associate
Estimation of Flow Field & Drag for Aerofoil Wing Mahantesh. HM 1, Prof. Anand. SN 2 P.G. Student, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, East Point College of Engineering, Bangalore, Karnataka, India 1 Associate
Approximation of 3D-Parametric Functions by Bicubic B-spline Functions
 International Journal of Mathematical Modelling & Computations Vol. 02, No. 03, 2012, 211-220 Approximation of 3D-Parametric Functions by Bicubic B-spline Functions M. Amirfakhrian a, a Department of Mathematics,
International Journal of Mathematical Modelling & Computations Vol. 02, No. 03, 2012, 211-220 Approximation of 3D-Parametric Functions by Bicubic B-spline Functions M. Amirfakhrian a, a Department of Mathematics,
LASer Cavity Analysis and Design
 The unique combination of simulation tools for LASer Cavity Analysis and Design During the last 15 years LASCAD has become industry-leading so ware for LASer Cavity Analysis and Design. The feedback from
The unique combination of simulation tools for LASer Cavity Analysis and Design During the last 15 years LASCAD has become industry-leading so ware for LASer Cavity Analysis and Design. The feedback from
Reparametrization of Interval Curves on Rectangular Domain
 International Journal of Video&Image Processing and Network Security IJVIPNS-IJENS Vol:15 No:05 1 Reparametrization of Interval Curves on Rectangular Domain O. Ismail, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract The
International Journal of Video&Image Processing and Network Security IJVIPNS-IJENS Vol:15 No:05 1 Reparametrization of Interval Curves on Rectangular Domain O. Ismail, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract The
Generalizations of the Distance and Dependent Function in Extenics to 2D, 3D, and n-d
 Generalizations of the Distance and Dependent Function in Extenics to D, 3D, and n-d Florentin Smarandache University of New Mexico Mathematics and Science Department 705 Gurey Ave. Gallup, NM 87301, USA
Generalizations of the Distance and Dependent Function in Extenics to D, 3D, and n-d Florentin Smarandache University of New Mexico Mathematics and Science Department 705 Gurey Ave. Gallup, NM 87301, USA
Deccan Education Society s
 Deccan Education Society s FERGUSSON COLLEGE, PUNE (AUTONOMOUS) SYLLABUS UNDER AUTONOMY SECOND YEAR B.Sc.(COMPUTER SCIENCE) MATHEMATICS SEMESTER III w.e.f. Academic Year 2017-2018 Deccan Education Society
Deccan Education Society s FERGUSSON COLLEGE, PUNE (AUTONOMOUS) SYLLABUS UNDER AUTONOMY SECOND YEAR B.Sc.(COMPUTER SCIENCE) MATHEMATICS SEMESTER III w.e.f. Academic Year 2017-2018 Deccan Education Society
ADAPTIVE APPROACH IN NONLINEAR CURVE DESIGN PROBLEM. Simo Virtanen Rakenteiden Mekaniikka, Vol. 30 Nro 1, 1997, s
 ADAPTIVE APPROACH IN NONLINEAR CURVE DESIGN PROBLEM Simo Virtanen Rakenteiden Mekaniikka, Vol. 30 Nro 1, 1997, s. 14-24 ABSTRACT In recent years considerable interest has been shown in the development
ADAPTIVE APPROACH IN NONLINEAR CURVE DESIGN PROBLEM Simo Virtanen Rakenteiden Mekaniikka, Vol. 30 Nro 1, 1997, s. 14-24 ABSTRACT In recent years considerable interest has been shown in the development
 Set No. 1 IV B.Tech. I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2010 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
Set No. 1 IV B.Tech. I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2010 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
Investigation of a Robust Method for Connecting Dissimilar 3D Finite Element Models. David M. Trujillo 1. December 2005
 Investigation of a Robust Method for Connecting Dissimilar 3D Finite Element Models by David M. Trujillo 1 December 2005 1 Consultant, TRUCOMP, Fountain Valley, California trucomp@earthlink.net Abstract
Investigation of a Robust Method for Connecting Dissimilar 3D Finite Element Models by David M. Trujillo 1 December 2005 1 Consultant, TRUCOMP, Fountain Valley, California trucomp@earthlink.net Abstract
Curve Representation ME761A Instructor in Charge Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Kanpur
 Curve Representation ME761A Instructor in Charge Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Kanpur Email: jrkumar@iitk.ac.in Curve representation 1. Wireframe models There are three types
Curve Representation ME761A Instructor in Charge Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Kanpur Email: jrkumar@iitk.ac.in Curve representation 1. Wireframe models There are three types
Wavelet-Galerkin Solutions of One and Two Dimensional Partial Differential Equations
 VOL 3, NO0 Oct, 202 ISSN 2079-8407 2009-202 CIS Journal All rights reserved http://wwwcisjournalorg Wavelet-Galerkin Solutions of One and Two Dimensional Partial Differential Equations Sabina, 2 Vinod
VOL 3, NO0 Oct, 202 ISSN 2079-8407 2009-202 CIS Journal All rights reserved http://wwwcisjournalorg Wavelet-Galerkin Solutions of One and Two Dimensional Partial Differential Equations Sabina, 2 Vinod
Finite Element Analysis of Von Mises Stresses & Deformation at Tip of Cutting Tool
 Finite Element Analysis of Von Mises Stresses & Deformation at Tip of Cutting Tool Maheshwari N Patil Shreepad Sarange Dr.D.Y.Patil Institute of Engineering & Technology, Ambi Dr.D.Y.Patil College of Engineering,Lohegaon
Finite Element Analysis of Von Mises Stresses & Deformation at Tip of Cutting Tool Maheshwari N Patil Shreepad Sarange Dr.D.Y.Patil Institute of Engineering & Technology, Ambi Dr.D.Y.Patil College of Engineering,Lohegaon
An explicit feature control approach in structural topology optimization
 th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimisation 07 th -2 th, June 205, Sydney Australia An explicit feature control approach in structural topology optimization Weisheng Zhang, Xu Guo
th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimisation 07 th -2 th, June 205, Sydney Australia An explicit feature control approach in structural topology optimization Weisheng Zhang, Xu Guo
Module 3: Stand Up Conics
 MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 36
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 In last class, we have derived element equations for two d elasticity problems
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 In last class, we have derived element equations for two d elasticity problems
Modeling Skills Thermal Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University
 Introduction Modeling Skills Thermal Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University Most finite element analysis tasks involve utilizing commercial software, for which you do not have the source code. Thus, you need
Introduction Modeling Skills Thermal Analysis J.E. Akin, Rice University Most finite element analysis tasks involve utilizing commercial software, for which you do not have the source code. Thus, you need
Parameterization. Michael S. Floater. November 10, 2011
 Parameterization Michael S. Floater November 10, 2011 Triangular meshes are often used to represent surfaces, at least initially, one reason being that meshes are relatively easy to generate from point
Parameterization Michael S. Floater November 10, 2011 Triangular meshes are often used to represent surfaces, at least initially, one reason being that meshes are relatively easy to generate from point
Interpolation and Splines
 Interpolation and Splines Anna Gryboś October 23, 27 1 Problem setting Many of physical phenomenona are described by the functions that we don t know exactly. Often we can calculate or measure the values
Interpolation and Splines Anna Gryboś October 23, 27 1 Problem setting Many of physical phenomenona are described by the functions that we don t know exactly. Often we can calculate or measure the values
FOURTH ORDER COMPACT FORMULATION OF STEADY NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS ON NON-UNIFORM GRIDS
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET Volume 9 Issue 10 October 2018 pp. 179 189 Article ID: IJMET_09_10_11 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtypeijmet&vtype9&itype10
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET Volume 9 Issue 10 October 2018 pp. 179 189 Article ID: IJMET_09_10_11 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtypeijmet&vtype9&itype10
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction GTU Paper Analysis (New Syllabus) Sr. No. Questions 26/10/16 11/05/16 09/05/16 08/12/15 Theory 1. What is graphic standard? Explain different CAD standards. 2. Write Bresenham s
Chapter 1 Introduction GTU Paper Analysis (New Syllabus) Sr. No. Questions 26/10/16 11/05/16 09/05/16 08/12/15 Theory 1. What is graphic standard? Explain different CAD standards. 2. Write Bresenham s
3D Modeling Parametric Curves & Surfaces. Shandong University Spring 2013
 3D Modeling Parametric Curves & Surfaces Shandong University Spring 2013 3D Object Representations Raw data Point cloud Range image Polygon soup Surfaces Mesh Subdivision Parametric Implicit Solids Voxels
3D Modeling Parametric Curves & Surfaces Shandong University Spring 2013 3D Object Representations Raw data Point cloud Range image Polygon soup Surfaces Mesh Subdivision Parametric Implicit Solids Voxels
APPM/MATH Problem Set 4 Solutions
 APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
Math Analysis Chapter 1 Notes: Functions and Graphs
 Math Analysis Chapter 1 Notes: Functions and Graphs Day 6: Section 1-1 Graphs Points and Ordered Pairs The Rectangular Coordinate System (aka: The Cartesian coordinate system) Practice: Label each on the
Math Analysis Chapter 1 Notes: Functions and Graphs Day 6: Section 1-1 Graphs Points and Ordered Pairs The Rectangular Coordinate System (aka: The Cartesian coordinate system) Practice: Label each on the
Grade 9 Math Terminology
 Unit 1 Basic Skills Review BEDMAS a way of remembering order of operations: Brackets, Exponents, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction Collect like terms gather all like terms and simplify as
Unit 1 Basic Skills Review BEDMAS a way of remembering order of operations: Brackets, Exponents, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction Collect like terms gather all like terms and simplify as
Module 4 : Solving Linear Algebraic Equations Section 11 Appendix C: Steepest Descent / Gradient Search Method
 Module 4 : Solving Linear Algebraic Equations Section 11 Appendix C: Steepest Descent / Gradient Search Method 11 Appendix C: Steepest Descent / Gradient Search Method In the module on Problem Discretization
Module 4 : Solving Linear Algebraic Equations Section 11 Appendix C: Steepest Descent / Gradient Search Method 11 Appendix C: Steepest Descent / Gradient Search Method In the module on Problem Discretization
Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 413 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Spring 2015 (Dr.
 Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 413 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Spring 2015 (Dr. Sert) COMSOL 1 Tutorial 2 Problem Definition Hot combustion gases of a
Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 413 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Spring 2015 (Dr. Sert) COMSOL 1 Tutorial 2 Problem Definition Hot combustion gases of a
Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates
 Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates P. Sam Johnson April 10, 2017 P. Sam Johnson (NIT Karnataka) Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates April 10, 2017 1 / 28 Overview We use triple integrals
Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates P. Sam Johnson April 10, 2017 P. Sam Johnson (NIT Karnataka) Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates April 10, 2017 1 / 28 Overview We use triple integrals
f xx + f yy = F (x, y)
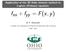 Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
WHAT YOU SHOULD LEARN
 GRAPHS OF EQUATIONS WHAT YOU SHOULD LEARN Sketch graphs of equations. Find x- and y-intercepts of graphs of equations. Use symmetry to sketch graphs of equations. Find equations of and sketch graphs of
GRAPHS OF EQUATIONS WHAT YOU SHOULD LEARN Sketch graphs of equations. Find x- and y-intercepts of graphs of equations. Use symmetry to sketch graphs of equations. Find equations of and sketch graphs of
The Rectangular Coordinate System and Equations of Lines. College Algebra
 The Rectangular Coordinate System and Equations of Lines College Algebra Cartesian Coordinate System A grid system based on a two-dimensional plane with perpendicular axes: horizontal axis is the x-axis
The Rectangular Coordinate System and Equations of Lines College Algebra Cartesian Coordinate System A grid system based on a two-dimensional plane with perpendicular axes: horizontal axis is the x-axis
Quadratic Functions Dr. Laura J. Pyzdrowski
 1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory A quadratic function in the variable x is a polynomial where the highest power of x is 2. We will explore the domains, ranges, and graphs of quadratic
1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory A quadratic function in the variable x is a polynomial where the highest power of x is 2. We will explore the domains, ranges, and graphs of quadratic
Lecture 3.2 Methods for Structured Mesh Generation
 Lecture 3.2 Methods for Structured Mesh Generation 1 There are several methods to develop the structured meshes: Algebraic methods, Interpolation methods, and methods based on solving partial differential
Lecture 3.2 Methods for Structured Mesh Generation 1 There are several methods to develop the structured meshes: Algebraic methods, Interpolation methods, and methods based on solving partial differential
