Chapter 3: The Parabola
|
|
|
- Alfred Hill
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 3: The Parabola SSMth1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Mr. Migo M. Mendoza
2 Chapter 3: The Parabola Lecture 7: Introduction to Parabola Lecture 8: Converting General Form of a Parabola to Its Standard Form and Vice-Versa Lecture 9: The Graph of Parabola with Vertex at the Origin Lecture 10: The Graph of Parabola with Vertex at (h, k) Lecture 11: The Parabola and the Tangent Line Lecture 12: Some Applications of Parabola
3 TED Ed Video Number 3: The Math Behind Michael Jordan s Legendary Hang Time by Andy Peterson and Zack Patterson
4 Lecture 7: Introduction to Parabola SSMth1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Mr. Migo M. Mendoza
5 A Short Recap From our previous lesson about conic section, how does a parabola formed?
6 A Short Recap A parabola is graph of what kind of function?
7 Classroom Task Number 4: Using the figure on the next slide, give your own definition of a parabola.
8 Parabola to You: Look at Me, How Do You Define Me?
9 The Definition of Parabola A parabola is the set of all points in a plane equidistant from a fixed point and a fixed line.
10 The Focus and the Directrix The fixed point is called the focus and the fixed line is called the directrix.
11 The Graph of the Parabola
12 Something to think about What do you think are the roles of the focus and the directrix in the graph of a parabola?
13 Type 1: Parabola Opening Upward Whenever the directrix is below the focus, then the parabola opens upward.
14 Type 2: Parabola Opening Downward Whenever the directrix is above the focus, then the parabola opens downward.
15 Type 3: Parabola Opening to the Right Whenever the directrix is on the left side of the focus, then the parabola opens to the right.
16 Type 4: Parabola Opening to the Left Whenever the directrix is on the right side of the focus, then the parabola opens to the left.
17 The Vertex and the Axis of Symmetry The vertex of the parabola is the midpoint of the perpendicular segment from the focus to the directrix, while the line that passes through the vertex and focus is the axis of symmetry.
18 The Graph of the Parabola
19 Something to think about What condition will guarantee that the vertex is exactly the midpoint of the perpendicular segment from focus to the directrix?
20 Parabola to You: Look at Me, How Do You Define Me?
21 Something to think about When we say an image/ an object is symmetric, what do we mean by that?
22 The Graph of the Parabola
23 The Latus Rectum The line segment through the focus perpendicular to the axis of symmetry is called the latus rectum whose length is 4c.
24 Did you know? The word latus rectum (singular, plural: latera recta) came from a Latin word latus which means line or side and rectum which means straight. So, the its English translation is straight line or straight side.
25 The Graph of the Parabola
26 Something to think about What do you think is the relationship of latus rectum to the directrix?
27 Something to think about Why is it called a "latus rectum"? What do you think its purpose?
28 The Focal Length The focal length is the undirected distance between the vertex and focus in this case c.
29 The Graph of the Parabola
30 Classroom Task Number 5: Derive the formula of the Parabola Opening to the Right having the Vertex at the Origin
31 The Definition of Parabola A parabola is the set of all points in a plane equidistant from a fixed point and a fixed line.
32 Parabola Opening to the Right having the Vertex at the Origin (0, 0)
33 Our Equation: Using the definition, we will use the equation below to derive the formula: d 1 d 2
34 Formula of the Parabola Opening to the Right having the Vertex at the Origin Formula of the Parabola Opening to the Right having the Vertex at the Origin: 2 y 4cx
35 Classroom Task Number 6: Derive the formula of the Parabola Opening Upward having the Vertex at the Origin
36 The Definition of Parabola A parabola is the set of all points in a plane equidistant from a fixed point and a fixed line.
37 Parabola Opening Upward having the Vertex at the Origin (0, 0)
38 Our Equation: Using the definition, we will use the equation below to derive the formula: d 1 d 2
39 Formula of the Parabola Opening Upward having the Vertex at the Origin Formula of the Parabola Opening Upward having the Vertex at the Origin 2 x 4cy
40 Performance Task 6: Using the definition of the parabola, its parts and its graph, derive the formulae for the following: o Parabola Opening Downward having the Vertex at the Origin; and o Parabola Opening to the Left having the Vertex at the Origin.
41 Lecture 8: Converting General Form to Standard Form of a Parabola SSMth1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Mr. Migo M. Mendoza
42 Learning Expectations: This section presents how to convert form of a parabola to its standard form and viceversa.
43 The General and Standard Equations of the Parabola Vertex General Form Standard Form (0, 0) (h, k) 0 2 F Dx y cx y F Ey x y 4cx 2 x 4cy 2 x 4cy F Ey Dx y ) ( 4 ) ( 2 h x c k y ) ( 4 ) ( 2 h x c k y 0 2 F Ey Dx x ) ( 4 ) ( 2 k y c h x ) ( 4 ) ( 2 k y c h x
44 Example 21: Convert the general equations to standard form: y 2 12 x 2y x 2 12 x y 16 0
45 Final Answer: The standard forms of the given general equations are: ( 2 y 1) 12( x 2) 1 ( x 3) 2 ( y 2 2)
46 Example 22: Convert the standard equations to general form: ( 2 y 3) 7( x 8) 2 ( x 2) 8( y 5)
47 Final Answer: The general forms of the given standard equations are: y 2 7 x 6 y 65 0 x 2 4x 8 y 44 0
48 Performance Task 7: Please download, print and answer the Let s Practice 7. Kindly work independently.
49 Lecture 9: The Graph of the Parabola with Vertex at the Origin SSMth1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Mr. Migo M. Mendoza
50 The Parts of the Graph of the Parabola with Vertex at the Origin Standard Equation Focus Directrix Axis of Symmetry Endpoints of Latus Rectum Graph y 2 4cx (c, 0) x = -c x-axis E 1 (c, 2c) E 2 (c, -2c) Opening to the Right 2 y 4cx (-c, 0) x = c x-axis E 1 (-c, 2c) E 2 (-c, -2c) Opening to the Left x 2 4cy (0, c) y = -c y-axis E 1 (2c, c) E 2 (-2c, c) Opening Upward 2 x 4cy (0, -c) y = c y-axis E 1 (2c, -c) E 2 (-2c, -c) Opening Downward
51 Classroom Task Number 8: To understand where the coordinates of each part of the graph of the parabola with vertex at the origin V (0, 0) derived from, show it to the class using the graph of the parabola opening upward.
52 Example 22: Sketch and discuss: 2 x 8y
53 Supply the Table: Vertex: Focus: Axis of Symmetry: Directrix: Length of Latus Rectum: Endpoints of Latus Rectum:
54
55 Example 23: Find the equation of the parabola with vertex at (0, 0) and focus at ( 0, 3 4).
56 Supply the Table: Vertex: Focus: Axis of Symmetry: Directrix: Length of Latus Rectum: Endpoints of Latus Rectum:
57
58 Performance Task 8: Please download, print and answer the Let s Practice 8. Kindly work independently.
59 Lecture 10: The Graph of the Parabola with Vertex at (h, k) SSMth1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Mr. Migo M. Mendoza
60 The Parts of the Graph of the Parabola with Vertex at the (h, k) Standard Equation Focus Directrix Axis of Symmetry Endpoints of Latus Rectum Graph ( y k) ( y k) 2 ( x h) ( x h) c( x h) 4c( x h) 4c( y k) 4c( y k) (h+c, k) x = h-c y = k (h-c, k) x = h+c y = k E 1 (h+c, k+2c) E 2 (h+c, k-2c) E 1 (h-c, k+2c) E 2 (h-c, k-2c) (h, k+c) y = k-c x = h E 1 (h+2c, k+c) E 2 (h-2c, k+c) (h, k-c) y = k+c x = h E 1 (h+2c, k-c) E 2 (h-2c, k-c) Opening to the Right Opening to the Left Opening Upward Opening Downward
61 Classroom Task Number 9: To understand where the coordinates of each part of the graph of the parabola with vertex at V (h, k) derived from, show it to the class using the graph of the parabola opening to the right.
62 Example 24: Reduce the general equation y 2 4x 6y 11 0 standard form. Determine the vertex, focus, directrix, axis of symmetry, length of latus rectum and its endpoints and sketch the graph.
63 Supply the Table: Vertex: Focus: Axis of Symmetry: Directrix: Length of Latus Rectum: Endpoints of Latus Rectum:
64
65 Example 25: Find the general equation of the parabola with vertex at (3, 6) and focus at (3, 4). Sketch the graph.
66
67 Final Answer: Thus, general equation of the parabola is x 2 6x 8 y 37 0.
68 Example 26: Find the general equation of the parabola with vertex at (2, 1) and directrix x = 5. Sketch the graph.
69
70 Final Answer: Thus, general equation of the parabola is y 2 12 x 2 y 23 0.
71 Performance Task 9: Please download, print and answer the Let s Practice 9. Kindly work independently.
72 Lecture 11: The Parabola and the Tangent Line SSMth1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Mr. Migo M. Mendoza
73 Learning Expectations: This section illustrates the tangent line to a parabola and a line that pass through two points of the parabola.
74 A Review: Aside from what we have discussed about the introduction to parabola, what is another way of writing the general equation of a parabola?
75 The General Equation of a Parabola The General Equation of a Parabola is: Ax 2 Bx C 0
76 Did you know? A quadratic equation denoted by Ax Bx C 0, contains one and only one solution if B 4AC
77 The Parabola and the Tangent Line
78 Example 27: Find the equation of the tangent line to y 2 12 x at the point (-3, 6).
79 Something to think about Based on our previous discussion about a line tangent to the circle, what relationship exists between the tangent line, the point of tangency PT (- 3, 6) and the equation of the parabola 2 y 12 x.
80 What we knew: We can use our prior knowledge about our lesson about tangent to a circle. That is, if a line is tangent to a parabola, then they shared a common point which is the point of tangency denoted by PT (-3, 6). This common point is one of the infinitely many points of the tangent line and the parabola, y 2 12 x which can make both of their equations true once substituted.
81 Something to think about Since we all knew that the point PT (-3, 6) is one of the infinitely many points of the tangent line, it is associated with linear equations, and we were asked to look for its equation, which among the five forms of linear equations can we use in determining its equation?
82 What we know: We can use the point slope form to determine the equation of the tangent line denoted by: y y m x x 1 1 where x 1 is -3 and y 1 is 6.
83 Something to think about Since the value of slope denoted by m is unknown, what can we do to find its value to finally complete the equation of the tangent line?
84 Something to think about What method can we use to simplify: mx 3m x?
85 Something to think about How to simplify mx 3m 6 2 using square of trinomial?
86 Something to think about mx 3m x To simplify, we can use FOIL method given 2 three terms denoted by: 2 2 a b c 2ab 2ac 2bc
87 Something to think about What idea/ theorem can we use to ensure that we can only have one value of slope denoted by m?
88 To Ensure We Can Have One and Only One Slope: A quadratic equation denoted by Ax Bx C 0, contains one and only one solution if B 4AC
89 Final Answer: Thus, the tangent line is x y 3 0.
90 Example 28: Find the points of intersection between the parabola y 2 4x 8y 16 0 and the line x y 4 0. Sketch the graph.
91 Take Note: These points of intersection we are about to compute are two of infinitely many points of both the parabola and the line. Moreover, they are solutions that will make the two equations true. When we say we are to find the points of intersection, it is same as to say we are to find the solutions to the given equations. To determine these two points of intersection, it is more convenient to use substitution method.
92 Final Answer: Thus, the points of intersection are (-4, 0) and (0, 4).
93 Performance Task 10: Please download, print and answer the Let s Practice 10. Kindly work independently.
94 Classroom Task 10: Please prepare a five-minute presentation about the applications of ellipse in the real-world by family. The presentation can be in a form of a family report, skit, video presentation, etc. This will be presented on our next meeting.
95 Lecture 12: Some Applications of Parabola SSMth1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Mr. Migo M. Mendoza
96 Parabolas in Real Life: Arch Bridges; Microphones; Suspension Car Headlights; Bridges; Mirror in Radar Equipment; Reflecting Telescope; Solar Furnaces; Television; and Search Lights; Radio Antennas.
97 Example 29: How high is the parabolic arch of span 20 feet and height of 16 feet, at a distance 5 feet from the center?
98 Unlocking Terms in the Given Problem: To help us easily solve the given problem, we shall unlock the following terms: 1. PARABOLIC ARCH 2. SPAN What do you know about these?
99 Parabolic Arch It is usually a curved part of a structure that is over an opening and that supports a wall or other weight above the opening.
100 The Span The span is the distance from the end of the thumb to the end of the little finger of a spread hand.
101 The Parabolic Arc:
102 Something to think about How do you understand the problem?
103 Our Understanding of the Problem: We can deduce from the problem that the height of the parabolic arch from the center of its span is 16 feet. However, the problem is asking us to find the height of the parabola when the distance, denoted by span, is 5 feet away from the center.
104 Our Strategy in Solving the Problem: As we have observed, a parabolic arch is modeled by a parabola opens downward with its vertex as the maximum value. Thus, to solve the given problem, we will use the equation of the parabola opens downward graphed on the Cartesian Coordinate Plane, where the x-axis serves as its span while the y-axis is the its height.
105 Our Representations: Let: x-axis be the span of the parabolic arch with 20 feet width y-axis be the height of the parabolic arch with 16 feet height
106 Our Task: Our Task: To find the height (y) when the width or the span (x) is 5 feet away from the center. Thus: 5 feet, y
107 Please Take Note: The y-axis doesn t only represent the height of our parabolic arch. But, by definition, it also serves as the axis of symmetry which divides our parabolic arch into two congruent parts. Hence, our span in the x-axis is also divided into two, resulting to 10 feet each side from the center. Thus, we will have S 1 (-10, 0) and S 2 (10, 0) to denote the endpoints of the span of our parabolic arc.
108 Please Take Note: Remember, when the parabola is opening downward the highest/ maximum point of it is its vertex. Thus, the vertex is V (0, 16) since the height denoted by y-axis is 16 feet and the span denoted by x-axis is zero. Moreover, its vertex is of the form V (h, k), to find the height of the parabolic arch when the distance is 5 feet away from the center, we will use the equation of a parabola opening downward with vertex at V (h, k): x h 2 4c y k
109 Something to think about As we can observed, to find the height of the parabolic arch when its span is 5 feet away from its center, denoted by y, we need to find first the its focal length denoted by c. What will be your strategy? What will you do to find the focal length?
110 Helpful Illustration:
111 Final Answer The height is 12 feet.
112 Example 30: The cable of a suspension bridge has supporting towers which are 70 feet high and 500 feet apart. If the lowest point of the cable is 20 feet above the floor of the bridge, find the length of a supporting rod 80 feet from the center of the span.
113 The Suspension Bridge:
114 Helpful Illustration:
115 Final Answer: Thus, the length of the supporting rod is feet.
116 Example 31: A truck has to pass under an overhead parabolic arch bridge which has a span of 20 meters and is 16 meters high. If the tank is 14 meters wide, is placed in the truck with its sides vertical, and the top of the tank is 7.5 meters above the street level, what is the smallest clearance from the top of the tank so that the truck can pass under the bridge?
117 The Overhead Parabolic Arch Bridge/ Tunnel:
118 Helpful Illustration:
119 Final Answer: Thus, the clearance is 0.66 meters.
120 Example 32: The cross section of a large parabolic microphone can be molded by the equation 2 y 116 x. What is the length of the feedhorn?
121 The Large Parabolic Microphone
122 The Large Parabolic Microphone
123 Helpful Illustration:
124 Final Answer: Thus, the feedhorn should be 29 inches.
125 Performance Task 11: Please download, print and answer the Let s Practice 11. Kindly work independently.
Chapter 5: The Hyperbola
 Chapter 5: The Hyperbola SSMth1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 5: The Hyperbola Lecture 17: Introduction to Hyperbola Lecture 18: The
Chapter 5: The Hyperbola SSMth1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 5: The Hyperbola Lecture 17: Introduction to Hyperbola Lecture 18: The
MATH 110 analytic geometry Conics. The Parabola
 1 MATH 11 analytic geometry Conics The graph of a second-degree equation in the coordinates x and y is called a conic section or, more simply, a conic. This designation derives from the fact that the curve
1 MATH 11 analytic geometry Conics The graph of a second-degree equation in the coordinates x and y is called a conic section or, more simply, a conic. This designation derives from the fact that the curve
Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry
 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.1 The Ellipse 9.2 The Hyperbola 9.3 The Parabola 9.4 Rotation of Axes 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Conic
Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.1 The Ellipse 9.2 The Hyperbola 9.3 The Parabola 9.4 Rotation of Axes 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Conic
Unit 5: Quadratic Functions
 Unit 5: Quadratic Functions LESSON #5: THE PARABOLA GEOMETRIC DEFINITION DIRECTRIX FOCUS LATUS RECTUM Geometric Definition of a Parabola Quadratic Functions Geometrically, a parabola is the set of all
Unit 5: Quadratic Functions LESSON #5: THE PARABOLA GEOMETRIC DEFINITION DIRECTRIX FOCUS LATUS RECTUM Geometric Definition of a Parabola Quadratic Functions Geometrically, a parabola is the set of all
Assignment 3/17/15. Section 10.2(p 568) 2 12 (E) (E)
 Section 10.2 Warm Up Assignment 3/17/15 Section 10.2(p 568) 2 12 (E) 24 40 (E) Objective We are going to find equations for parabolas identify the vertex, focus, and directrix of a parabola The parabola
Section 10.2 Warm Up Assignment 3/17/15 Section 10.2(p 568) 2 12 (E) 24 40 (E) Objective We are going to find equations for parabolas identify the vertex, focus, and directrix of a parabola The parabola
Chapter 8.1 Conic Sections/Parabolas. Honors Pre-Calculus Rogers High School
 Chapter 8.1 Conic Sections/Parabolas Honors Pre-Calculus Rogers High School Introduction to Conic Sections Conic sections are defined geometrically as the result of the intersection of a plane with a right
Chapter 8.1 Conic Sections/Parabolas Honors Pre-Calculus Rogers High School Introduction to Conic Sections Conic sections are defined geometrically as the result of the intersection of a plane with a right
Math 155, Lecture Notes- Bonds
 Math 155, Lecture Notes- Bonds Name Section 10.1 Conics and Calculus In this section, we will study conic sections from a few different perspectives. We will consider the geometry-based idea that conics
Math 155, Lecture Notes- Bonds Name Section 10.1 Conics and Calculus In this section, we will study conic sections from a few different perspectives. We will consider the geometry-based idea that conics
Conic Sections. College Algebra
 Conic Sections College Algebra Conic Sections A conic section, or conic, is a shape resulting from intersecting a right circular cone with a plane. The angle at which the plane intersects the cone determines
Conic Sections College Algebra Conic Sections A conic section, or conic, is a shape resulting from intersecting a right circular cone with a plane. The angle at which the plane intersects the cone determines
UNIT 5 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Lesson 7: Building Functions Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: multiplying linear expressions factoring quadratic equations finding the value of a in the vertex form of a quadratic equation
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: multiplying linear expressions factoring quadratic equations finding the value of a in the vertex form of a quadratic equation
Ex. 1-3: Put each circle below in the correct equation form as listed!! above, then determine the center and radius of each circle.
 Day 1 Conics - Circles Equation of a Circle The circle with center (h, k) and radius r is the set of all points (x, y) that satisfies!! (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 Ex. 1-3: Put each circle below in the correct
Day 1 Conics - Circles Equation of a Circle The circle with center (h, k) and radius r is the set of all points (x, y) that satisfies!! (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 Ex. 1-3: Put each circle below in the correct
3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS
 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Finding the Zeros of a Quadratic Function Examples 1 and and more Find the zeros of f(x) = x x 6. Solution by Factoring f(x) = x x 6 = (x 3)(x + )
3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Finding the Zeros of a Quadratic Function Examples 1 and and more Find the zeros of f(x) = x x 6. Solution by Factoring f(x) = x x 6 = (x 3)(x + )
Geometry: Conic Sections
 Conic Sections Introduction When a right circular cone is intersected by a plane, as in figure 1 below, a family of four types of curves results. Because of their relationship to the cone, they are called
Conic Sections Introduction When a right circular cone is intersected by a plane, as in figure 1 below, a family of four types of curves results. Because of their relationship to the cone, they are called
Algebra II. Slide 1 / 181. Slide 2 / 181. Slide 3 / 181. Conic Sections Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 181 Algebra II Slide 2 / 181 Conic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 181 Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Introduction
Slide 1 / 181 Algebra II Slide 2 / 181 Conic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 181 Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Introduction
CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS
 CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Writing equations of conic sections ) Graphing equations of conic sections 3) Solving quadratic systems Section: Essential Question 8-1 Apply
CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Writing equations of conic sections ) Graphing equations of conic sections 3) Solving quadratic systems Section: Essential Question 8-1 Apply
Lecture 5. If, as shown in figure, we form a right triangle With P1 and P2 as vertices, then length of the horizontal
 Distance; Circles; Equations of the form Lecture 5 y = ax + bx + c In this lecture we shall derive a formula for the distance between two points in a coordinate plane, and we shall use that formula to
Distance; Circles; Equations of the form Lecture 5 y = ax + bx + c In this lecture we shall derive a formula for the distance between two points in a coordinate plane, and we shall use that formula to
Algebra II Quadratic Functions
 1 Algebra II Quadratic Functions 2014-10-14 www.njctl.org 2 Ta b le o f C o n te n t Key Terms click on the topic to go to that section Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Combining Transformations
1 Algebra II Quadratic Functions 2014-10-14 www.njctl.org 2 Ta b le o f C o n te n t Key Terms click on the topic to go to that section Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Combining Transformations
Module 3: Stand Up Conics
 MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
Accelerated Pre-Calculus Unit 1 Task 1: Our Only Focus: Circles & Parabolas Review
 Accelerated Pre-Calculus Unit 1 Task 1: Our Only Focus: Circles & Parabolas Review Name: Date: Period: For most students, you last learned about conic sections in Analytic Geometry, which was a while ago.
Accelerated Pre-Calculus Unit 1 Task 1: Our Only Focus: Circles & Parabolas Review Name: Date: Period: For most students, you last learned about conic sections in Analytic Geometry, which was a while ago.
We start by looking at a double cone. Think of this as two pointy ice cream cones that are connected at the small tips:
 Math 1330 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text. We start
Math 1330 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text. We start
Figures adapted from Mathworld.wolfram.com and vectosite.net.
 MTH 11 CONIC SECTIONS 1 The four basic types of conic sections we will discuss are: circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas. They were named conic by the Greeks who used them to describe the intersection
MTH 11 CONIC SECTIONS 1 The four basic types of conic sections we will discuss are: circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas. They were named conic by the Greeks who used them to describe the intersection
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students. Francis Joseph H. Campeña, De La Salle University Manila
 KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila January 26, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila January 26, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
Chapter 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry
 Chapter 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry What You ll Learn: 9.1 Introduction to Conics: Parabolas 9.2 Ellipses 9.3 Hyperbolas 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Polar Coordinates 9.7 Graphs of Polar Equations 9.1
Chapter 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry What You ll Learn: 9.1 Introduction to Conics: Parabolas 9.2 Ellipses 9.3 Hyperbolas 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Polar Coordinates 9.7 Graphs of Polar Equations 9.1
1.) Write the equation of a circle in standard form with radius 3 and center (-3,4). Then graph the circle.
 Welcome to the world of conic sections! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bfonicn4bbg Some examples of conics in the real world: Parabolas Ellipse Hyperbola Your Assignment: Circle -Find at least four pictures
Welcome to the world of conic sections! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bfonicn4bbg Some examples of conics in the real world: Parabolas Ellipse Hyperbola Your Assignment: Circle -Find at least four pictures
Mid-Chapter Quiz: Lessons 7-1 through 7-3
 Write an equation for and graph a parabola with the given focus F and vertex V 1. F(1, 5), V(1, 3) Because the focus and vertex share the same x coordinate, the graph is vertical. The focus is (h, k +
Write an equation for and graph a parabola with the given focus F and vertex V 1. F(1, 5), V(1, 3) Because the focus and vertex share the same x coordinate, the graph is vertical. The focus is (h, k +
Chapter 10. Exploring Conic Sections
 Chapter 10 Exploring Conic Sections Conics A conic section is a curve formed by the intersection of a plane and a hollow cone. Each of these shapes are made by slicing the cone and observing the shape
Chapter 10 Exploring Conic Sections Conics A conic section is a curve formed by the intersection of a plane and a hollow cone. Each of these shapes are made by slicing the cone and observing the shape
Quadratic Functions CHAPTER. 1.1 Lots and Projectiles Introduction to Quadratic Functions p. 31
 CHAPTER Quadratic Functions Arches are used to support the weight of walls and ceilings in buildings. Arches were first used in architecture by the Mesopotamians over 4000 years ago. Later, the Romans
CHAPTER Quadratic Functions Arches are used to support the weight of walls and ceilings in buildings. Arches were first used in architecture by the Mesopotamians over 4000 years ago. Later, the Romans
Unit 12 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork
 Unit 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork Back in Unit 7, we delved into the algebra and geometry of lines. We showed that lines can be written in several forms: a) the general form: Ax + By + C =
Unit 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork Back in Unit 7, we delved into the algebra and geometry of lines. We showed that lines can be written in several forms: a) the general form: Ax + By + C =
, minor axis of length 12. , asymptotes y 2x. 16y
 Math 4 Midterm 1 Review CONICS [1] Find the equations of the following conics. If the equation corresponds to a circle find its center & radius. If the equation corresponds to a parabola find its focus
Math 4 Midterm 1 Review CONICS [1] Find the equations of the following conics. If the equation corresponds to a circle find its center & radius. If the equation corresponds to a parabola find its focus
Multivariable Calculus
 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
Conic Sections: Parabolas
 Conic Sections: Parabolas Why are the graphs of parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas called 'conic sections'? Because if you pass a plane through a double cone, the intersection of the plane and the cone
Conic Sections: Parabolas Why are the graphs of parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas called 'conic sections'? Because if you pass a plane through a double cone, the intersection of the plane and the cone
Properties of Quadratic functions
 Name Today s Learning Goals: #1 How do we determine the axis of symmetry and vertex of a quadratic function? Properties of Quadratic functions Date 5-1 Properties of a Quadratic Function A quadratic equation
Name Today s Learning Goals: #1 How do we determine the axis of symmetry and vertex of a quadratic function? Properties of Quadratic functions Date 5-1 Properties of a Quadratic Function A quadratic equation
1.8 Coordinate Geometry. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 1.8 Coordinate Geometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives The Coordinate Plane The Distance and Midpoint Formulas Graphs of Equations in Two Variables Intercepts Circles Symmetry
1.8 Coordinate Geometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives The Coordinate Plane The Distance and Midpoint Formulas Graphs of Equations in Two Variables Intercepts Circles Symmetry
CHAPTER 6 Quadratic Functions
 CHAPTER 6 Quadratic Functions Math 1201: Linear Functions is the linear term 3 is the leading coefficient 4 is the constant term Math 2201: Quadratic Functions Math 3201: Cubic, Quartic, Quintic Functions
CHAPTER 6 Quadratic Functions Math 1201: Linear Functions is the linear term 3 is the leading coefficient 4 is the constant term Math 2201: Quadratic Functions Math 3201: Cubic, Quartic, Quintic Functions
Algebra II. Midpoint and Distance Formula. Slide 1 / 181 Slide 2 / 181. Slide 3 / 181. Slide 4 / 181. Slide 6 / 181. Slide 5 / 181.
 Slide 1 / 181 Slide 2 / 181 lgebra II onic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 181 Slide 4 / 181 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and istance Formulas
Slide 1 / 181 Slide 2 / 181 lgebra II onic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 181 Slide 4 / 181 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and istance Formulas
9.3 Hyperbolas and Rotation of Conics
 9.3 Hyperbolas and Rotation of Conics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Write equations of hyperbolas in standard form. Find asymptotes of and graph hyperbolas. Use
9.3 Hyperbolas and Rotation of Conics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Write equations of hyperbolas in standard form. Find asymptotes of and graph hyperbolas. Use
Assignment Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Assignment.1-.3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) The arch beneath a bridge is semi-elliptical, a one-way
Assignment.1-.3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) The arch beneath a bridge is semi-elliptical, a one-way
MAC Learning Objectives. Module 4. Quadratic Functions and Equations. - Quadratic Functions - Solving Quadratic Equations
 MAC 1105 Module 4 Quadratic Functions and Equations Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Understand basic concepts about quadratic functions and their graphs. 2. Complete
MAC 1105 Module 4 Quadratic Functions and Equations Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Understand basic concepts about quadratic functions and their graphs. 2. Complete
Name: Date: 1. Match the equation with its graph. Page 1
 Name: Date: 1. Match the equation with its graph. y 6x A) C) Page 1 D) E) Page . Match the equation with its graph. ( x3) ( y3) A) C) Page 3 D) E) Page 4 3. Match the equation with its graph. ( x ) y 1
Name: Date: 1. Match the equation with its graph. y 6x A) C) Page 1 D) E) Page . Match the equation with its graph. ( x3) ( y3) A) C) Page 3 D) E) Page 4 3. Match the equation with its graph. ( x ) y 1
Polynomial and Rational Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.1 Quadratic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Analyze graphs of quadratic
2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.1 Quadratic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Analyze graphs of quadratic
ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet
 Name: Period: ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet Algebra II Unit 10 Plan: This plan is subject to change at the teacher s discretion. Section Topic Formative Work Due Date 10.3 Circles
Name: Period: ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet Algebra II Unit 10 Plan: This plan is subject to change at the teacher s discretion. Section Topic Formative Work Due Date 10.3 Circles
Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics. A circle is
 Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
Quadratic Functions. *These are all examples of polynomial functions.
 Look at: f(x) = 4x-7 f(x) = 3 f(x) = x 2 + 4 Quadratic Functions *These are all examples of polynomial functions. Definition: Let n be a nonnegative integer and let a n, a n 1,..., a 2, a 1, a 0 be real
Look at: f(x) = 4x-7 f(x) = 3 f(x) = x 2 + 4 Quadratic Functions *These are all examples of polynomial functions. Definition: Let n be a nonnegative integer and let a n, a n 1,..., a 2, a 1, a 0 be real
Pre-Calculus. 2) Find the equation of the circle having (2, 5) and (-2, -1) as endpoints of the diameter.
 Pre-Calculus Conic Review Name Block Date Circles: 1) Determine the center and radius of each circle. a) ( x 5) + ( y + 6) = 11 b) x y x y + 6 + 16 + 56 = 0 ) Find the equation of the circle having (,
Pre-Calculus Conic Review Name Block Date Circles: 1) Determine the center and radius of each circle. a) ( x 5) + ( y + 6) = 11 b) x y x y + 6 + 16 + 56 = 0 ) Find the equation of the circle having (,
Section 9.3 Graphing Quadratic Functions
 Section 9.3 Graphing Quadratic Functions A Quadratic Function is an equation that can be written in the following Standard Form., where a 0. Every quadratic function has a U-shaped graph called a. If the
Section 9.3 Graphing Quadratic Functions A Quadratic Function is an equation that can be written in the following Standard Form., where a 0. Every quadratic function has a U-shaped graph called a. If the
MATHS METHODS QUADRATICS REVIEW. A reminder of some of the laws of expansion, which in reverse are a quick reference for rules of factorisation
 MATHS METHODS QUADRATICS REVIEW LAWS OF EXPANSION A reminder of some of the laws of expansion, which in reverse are a quick reference for rules of factorisation a) b) c) d) e) FACTORISING Exercise 4A Q6ace,7acegi
MATHS METHODS QUADRATICS REVIEW LAWS OF EXPANSION A reminder of some of the laws of expansion, which in reverse are a quick reference for rules of factorisation a) b) c) d) e) FACTORISING Exercise 4A Q6ace,7acegi
ATHS FC Math Department Al Ain Remedial Plan
 ATHS FC Math Department Al Ain Remedial Plan Section Name ID Date Lesson Marks 10.1, 10.2 and 10.3 Lesson 10.1 (Midpoint and Distance formula) Question: 1 Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints
ATHS FC Math Department Al Ain Remedial Plan Section Name ID Date Lesson Marks 10.1, 10.2 and 10.3 Lesson 10.1 (Midpoint and Distance formula) Question: 1 Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints
) 2 + (y 2. x 1. y c x2 = y
 Graphing Parabola Parabolas A parabola is a set of points P whose distance from a fixed point, called the focus, is equal to the perpendicular distance from P to a line, called the directrix. Since this
Graphing Parabola Parabolas A parabola is a set of points P whose distance from a fixed point, called the focus, is equal to the perpendicular distance from P to a line, called the directrix. Since this
Standard Equation of a Circle
 Math 335 Trigonometry Conics We will study all 4 types of conic sections, which are curves that result from the intersection of a right circular cone and a plane that does not contain the vertex. (If the
Math 335 Trigonometry Conics We will study all 4 types of conic sections, which are curves that result from the intersection of a right circular cone and a plane that does not contain the vertex. (If the
Slide 2 / 222. Algebra II. Quadratic Functions
 Slide 1 / 222 Slide 2 / 222 Algebra II Quadratic Functions 2014-10-14 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 222 Table of Contents Key Terms Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Combining Transformations (review)
Slide 1 / 222 Slide 2 / 222 Algebra II Quadratic Functions 2014-10-14 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 222 Table of Contents Key Terms Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Combining Transformations (review)
Summary of Formulas: see
 To review the Conic Sections, Identify them and sketch them from the given equations, watch the following set of YouTube videos. They are followed by several practice problems for you to try, covering
To review the Conic Sections, Identify them and sketch them from the given equations, watch the following set of YouTube videos. They are followed by several practice problems for you to try, covering
UNIT 3 EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS Lesson 3: Creating Quadratic Equations in Two or More Variables
 Guided Practice Example 1 Find the y-intercept and vertex of the function f(x) = 2x 2 + x + 3. Determine whether the vertex is a minimum or maximum point on the graph. 1. Determine the y-intercept. The
Guided Practice Example 1 Find the y-intercept and vertex of the function f(x) = 2x 2 + x + 3. Determine whether the vertex is a minimum or maximum point on the graph. 1. Determine the y-intercept. The
We start by looking at a double cone. Think of this as two pointy ice cream cones that are connected at the small tips:
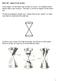 Math 1330 Chapter 8 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text.
Math 1330 Chapter 8 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text.
Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 2 4 x 0
 Pre-Calculus Section 1.1 Completing the Square Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 4 x 0. 3x 3y
Pre-Calculus Section 1.1 Completing the Square Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 4 x 0. 3x 3y
13.1 2/20/2018. Conic Sections. Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles
 13 Conic Sections 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles 13.2 Conic Sections: Ellipses 13.3 Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 13.4 Nonlinear Systems of Equations 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles
13 Conic Sections 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles 13.2 Conic Sections: Ellipses 13.3 Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 13.4 Nonlinear Systems of Equations 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles
Analytic Geometry. Affine space. 3D y. Dimensions
 y x Analytic Geometry Analytic geometry, usually called coordinate geometry or analytical geometry, is the study of geometry using the principles of algebra The link between algebra and geometry was made
y x Analytic Geometry Analytic geometry, usually called coordinate geometry or analytical geometry, is the study of geometry using the principles of algebra The link between algebra and geometry was made
Unit 3, Lesson 3.1 Creating and Graphing Equations Using Standard Form
 Unit 3, Lesson 3.1 Creating and Graphing Equations Using Standard Form Imagine the path of a basketball as it leaves a player s hand and swooshes through the net. Or, imagine the path of an Olympic diver
Unit 3, Lesson 3.1 Creating and Graphing Equations Using Standard Form Imagine the path of a basketball as it leaves a player s hand and swooshes through the net. Or, imagine the path of an Olympic diver
Name. Center axis. Introduction to Conic Sections
 Name Introduction to Conic Sections Center axis This introduction to conic sections is going to focus on what they some of the skills needed to work with their equations and graphs. year, we will only
Name Introduction to Conic Sections Center axis This introduction to conic sections is going to focus on what they some of the skills needed to work with their equations and graphs. year, we will only
II. Functions. 61. Find a way to graph the line from the problem 59 on your calculator. Sketch the calculator graph here, including the window values:
 II Functions Week 4 Functions: graphs, tables and formulas Problem of the Week: The Farmer s Fence A field bounded on one side by a river is to be fenced on three sides so as to form a rectangular enclosure
II Functions Week 4 Functions: graphs, tables and formulas Problem of the Week: The Farmer s Fence A field bounded on one side by a river is to be fenced on three sides so as to form a rectangular enclosure
Chapter 8.1: Circular Functions (Trigonometry)
 Chapter 8.1: Circular Functions (Trigonometry) SSMTH1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Strands Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 8.1: Circular Functions Lecture 8.1: Basic
Chapter 8.1: Circular Functions (Trigonometry) SSMTH1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Strands Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 8.1: Circular Functions Lecture 8.1: Basic
UNIT 5 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Lesson 6: Analyzing Quadratic Functions Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: factoring quadratic expressions finding the vertex of a quadratic function Introduction We have studied the key features of the
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: factoring quadratic expressions finding the vertex of a quadratic function Introduction We have studied the key features of the
8.2 Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas
 8.2 Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas Where is the focus and directrix compared to the vertex? How do you know what direction a parabola opens? How do you write the equation of a parabola given the
8.2 Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas Where is the focus and directrix compared to the vertex? How do you know what direction a parabola opens? How do you write the equation of a parabola given the
This is called the vertex form of the quadratic equation. To graph the equation
 Name Period Date: Topic: 7-5 Graphing ( ) Essential Question: What is the vertex of a parabola, and what is its axis of symmetry? Standard: F-IF.7a Objective: Graph linear and quadratic functions and show
Name Period Date: Topic: 7-5 Graphing ( ) Essential Question: What is the vertex of a parabola, and what is its axis of symmetry? Standard: F-IF.7a Objective: Graph linear and quadratic functions and show
You ll use the six trigonometric functions of an angle to do this. In some cases, you will be able to use properties of the = 46
 Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
Circles & Other Conics
 SECONDARY MATH TWO An Integrated Approach MODULE 8 Circles & Other Conics The Scott Hendrickson, Joleigh Honey, Barbara Kuehl, Travis Lemon, Janet Sutorius 2017 Original work 2013 in partnership with the
SECONDARY MATH TWO An Integrated Approach MODULE 8 Circles & Other Conics The Scott Hendrickson, Joleigh Honey, Barbara Kuehl, Travis Lemon, Janet Sutorius 2017 Original work 2013 in partnership with the
Chapter 1. Linear Equations and Straight Lines. 2 of 71. Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Straight Lines 2 of 71 Outline 1.1 Coordinate Systems and Graphs 1.4 The Slope of a Straight Line 1.3 The Intersection Point of a Pair of Lines 1.2 Linear Inequalities 1.5
Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Straight Lines 2 of 71 Outline 1.1 Coordinate Systems and Graphs 1.4 The Slope of a Straight Line 1.3 The Intersection Point of a Pair of Lines 1.2 Linear Inequalities 1.5
3.1 Investigating Quadratic Functions in Vertex Form
 Math 2200 Date: 3.1 Investigating Quadratic Functions in Vertex Form Degree of a Function - refers to the highest exponent on the variable in an expression or equation. In Math 1201, you learned about
Math 2200 Date: 3.1 Investigating Quadratic Functions in Vertex Form Degree of a Function - refers to the highest exponent on the variable in an expression or equation. In Math 1201, you learned about
Acc. Pre Calculus Day 5 - Parabolas Notesheet PARABOLAS
 Acc. Pre Calculus Day 5 - Parabolas Notesheet Name Date Block 1) Complete these truths about parabolas: * Parabolas are - shaped. PARABOLAS * Parabolas have a line of. * Parabolas are the graphs of functions.
Acc. Pre Calculus Day 5 - Parabolas Notesheet Name Date Block 1) Complete these truths about parabolas: * Parabolas are - shaped. PARABOLAS * Parabolas have a line of. * Parabolas are the graphs of functions.
3.1 Quadratic Functions in Vertex Form
 3.1 Quadratic Functions in Vertex Form 1) Identify quadratic functions in vertex form. 2) Determine the effect of a, p, and q on the graph of a quadratic function in vertex form where y = a(x p)² + q 3)
3.1 Quadratic Functions in Vertex Form 1) Identify quadratic functions in vertex form. 2) Determine the effect of a, p, and q on the graph of a quadratic function in vertex form where y = a(x p)² + q 3)
Final Exam Review Algebra Semester 1
 Final Exam Review Algebra 015-016 Semester 1 Name: Module 1 Find the inverse of each function. 1. f x 10 4x. g x 15x 10 Use compositions to check if the two functions are inverses. 3. s x 7 x and t(x)
Final Exam Review Algebra 015-016 Semester 1 Name: Module 1 Find the inverse of each function. 1. f x 10 4x. g x 15x 10 Use compositions to check if the two functions are inverses. 3. s x 7 x and t(x)
Chapter. Implicit Function Graphs
 Chapter 14 Implicit Function Graphs You can graph any one of the following types of implicit functions using the calculator s built-in functions. Parabolic graph Circle graph Elliptical graph Hyperbolic
Chapter 14 Implicit Function Graphs You can graph any one of the following types of implicit functions using the calculator s built-in functions. Parabolic graph Circle graph Elliptical graph Hyperbolic
1. Answer: x or x. Explanation Set up the two equations, then solve each equation. x. Check
 Thinkwell s Placement Test 5 Answer Key If you answered 7 or more Test 5 questions correctly, we recommend Thinkwell's Algebra. If you answered fewer than 7 Test 5 questions correctly, we recommend Thinkwell's
Thinkwell s Placement Test 5 Answer Key If you answered 7 or more Test 5 questions correctly, we recommend Thinkwell's Algebra. If you answered fewer than 7 Test 5 questions correctly, we recommend Thinkwell's
Section 6.2: Properties of Graphs of Quadratic Functions. Vertex:
 Section 6.2: Properties of Graphs of Quadratic Functions determine the vertex of a quadratic in standard form sketch the graph determine the y intercept, x intercept(s), the equation of the axis of symmetry,
Section 6.2: Properties of Graphs of Quadratic Functions determine the vertex of a quadratic in standard form sketch the graph determine the y intercept, x intercept(s), the equation of the axis of symmetry,
Math Analysis Chapter 1 Notes: Functions and Graphs
 Math Analysis Chapter 1 Notes: Functions and Graphs Day 6: Section 1-1 Graphs Points and Ordered Pairs The Rectangular Coordinate System (aka: The Cartesian coordinate system) Practice: Label each on the
Math Analysis Chapter 1 Notes: Functions and Graphs Day 6: Section 1-1 Graphs Points and Ordered Pairs The Rectangular Coordinate System (aka: The Cartesian coordinate system) Practice: Label each on the
Substituting a 2 b 2 for c 2 and using a little algebra, we can then derive the standard equation for an ellipse centred at the origin,
 Conics onic sections are the curves which result from the intersection of a plane with a cone. These curves were studied and revered by the ancient Greeks, and were written about extensively by both Euclid
Conics onic sections are the curves which result from the intersection of a plane with a cone. These curves were studied and revered by the ancient Greeks, and were written about extensively by both Euclid
EXERCISE SET 10.2 MATD 0390 DUE DATE: INSTRUCTOR
 EXERCISE SET 10. STUDENT MATD 090 DUE DATE: INSTRUCTOR You have studied the method known as "completing the square" to solve quadratic equations. Another use for this method is in transforming the equation
EXERCISE SET 10. STUDENT MATD 090 DUE DATE: INSTRUCTOR You have studied the method known as "completing the square" to solve quadratic equations. Another use for this method is in transforming the equation
Math 2 Coordinate Geometry Part 3 Inequalities & Quadratics
 Math 2 Coordinate Geometry Part 3 Inequalities & Quadratics 1 DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO POINTS - REVIEW To find the distance between two points, use the Pythagorean theorem. The difference between x 1 and x
Math 2 Coordinate Geometry Part 3 Inequalities & Quadratics 1 DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO POINTS - REVIEW To find the distance between two points, use the Pythagorean theorem. The difference between x 1 and x
Math Analysis Chapter 1 Notes: Functions and Graphs
 Math Analysis Chapter 1 Notes: Functions and Graphs Day 6: Section 1-1 Graphs; Section 1- Basics of Functions and Their Graphs Points and Ordered Pairs The Rectangular Coordinate System (aka: The Cartesian
Math Analysis Chapter 1 Notes: Functions and Graphs Day 6: Section 1-1 Graphs; Section 1- Basics of Functions and Their Graphs Points and Ordered Pairs The Rectangular Coordinate System (aka: The Cartesian
Quadratic Functions (Section 2-1)
 Quadratic Functions (Section 2-1) Section 2.1, Definition of Polynomial Function f(x) = a is the constant function f(x) = mx + b where m 0 is a linear function f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c with a 0 is a quadratic
Quadratic Functions (Section 2-1) Section 2.1, Definition of Polynomial Function f(x) = a is the constant function f(x) = mx + b where m 0 is a linear function f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c with a 0 is a quadratic
Conics. By: Maya, Dietrich, and Jesse
 Conics By: Maya, Dietrich, and Jesse Exploring Conics (This is basically the summary too) A conic section curve formed by intersection of a plane and double cone: by changing plane, one can create parabola,
Conics By: Maya, Dietrich, and Jesse Exploring Conics (This is basically the summary too) A conic section curve formed by intersection of a plane and double cone: by changing plane, one can create parabola,
MAC Rev.S Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives (Cont.) Module 4 Quadratic Functions and Equations
 MAC 1140 Module 4 Quadratic Functions and Equations Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. understand basic concepts about quadratic functions and their graphs.. complete
MAC 1140 Module 4 Quadratic Functions and Equations Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. understand basic concepts about quadratic functions and their graphs.. complete
arxiv: v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013
![arxiv: v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013 arxiv: v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013](/thumbs/74/70304288.jpg) Solution of Sondow s problem: a synthetic proof of the tangency property of the parbelos Emmanuel Tsukerman arxiv:1210.5580v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013 Abstract In a recent paper titled The parbelos, a parabolic
Solution of Sondow s problem: a synthetic proof of the tangency property of the parbelos Emmanuel Tsukerman arxiv:1210.5580v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013 Abstract In a recent paper titled The parbelos, a parabolic
Assignment Assignment for Lesson 14.1
 Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date The Origin of Parabolas Parabolas Centered at the Origin 1. Consider the parabola represented by the equation y 2 12x 0. a. Write the equation of the parabola
Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date The Origin of Parabolas Parabolas Centered at the Origin 1. Consider the parabola represented by the equation y 2 12x 0. a. Write the equation of the parabola
Study Guide and Review
 Graph the hyperbola given by each equation. 30. = 1 The equation is in standard form, and h = 6 and k = 3. Because a 2 = 30 and b 2 = 8, a = 5.5 and b =. The values of a and b can be used to find c. c
Graph the hyperbola given by each equation. 30. = 1 The equation is in standard form, and h = 6 and k = 3. Because a 2 = 30 and b 2 = 8, a = 5.5 and b =. The values of a and b can be used to find c. c
UNIT 8: SOLVING AND GRAPHING QUADRATICS. 8-1 Factoring to Solve Quadratic Equations. Solve each equation:
 UNIT 8: SOLVING AND GRAPHING QUADRATICS 8-1 Factoring to Solve Quadratic Equations Zero Product Property For all numbers a & b Solve each equation: If: ab 0, 1. (x + 3)(x 5) = 0 Then one of these is true:
UNIT 8: SOLVING AND GRAPHING QUADRATICS 8-1 Factoring to Solve Quadratic Equations Zero Product Property For all numbers a & b Solve each equation: If: ab 0, 1. (x + 3)(x 5) = 0 Then one of these is true:
Look up partial Decomposition to use for problems #65-67 Do Not solve problems #78,79
 Franklin Township Summer Assignment 2017 AP calculus AB Summer assignment Students should use the Mathematics summer assignment to identify subject areas that need attention in preparation for the study
Franklin Township Summer Assignment 2017 AP calculus AB Summer assignment Students should use the Mathematics summer assignment to identify subject areas that need attention in preparation for the study
Unit 2: Functions and Graphs
 AMHS Precalculus - Unit 16 Unit : Functions and Graphs Functions A function is a rule that assigns each element in the domain to exactly one element in the range. The domain is the set of all possible
AMHS Precalculus - Unit 16 Unit : Functions and Graphs Functions A function is a rule that assigns each element in the domain to exactly one element in the range. The domain is the set of all possible
Math 370 Exam 5 Review Name
 Math 370 Exam 5 Review Name Graph the ellipse and locate the foci. 1) x2 6 + y2 = 1 1) Objective: (9.1) Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin Graph the ellipse. 2) (x + 2)2 + (y + 1)2 9 = 1 2) Objective:
Math 370 Exam 5 Review Name Graph the ellipse and locate the foci. 1) x2 6 + y2 = 1 1) Objective: (9.1) Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin Graph the ellipse. 2) (x + 2)2 + (y + 1)2 9 = 1 2) Objective:
Practice Test - Chapter 7
 Write an equation for an ellipse with each set of characteristics. 1. vertices (7, 4), ( 3, 4); foci (6, 4), ( 2, 4) The distance between the vertices is 2a. 2a = 7 ( 3) a = 5; a 2 = 25 The distance between
Write an equation for an ellipse with each set of characteristics. 1. vertices (7, 4), ( 3, 4); foci (6, 4), ( 2, 4) The distance between the vertices is 2a. 2a = 7 ( 3) a = 5; a 2 = 25 The distance between
Each point P in the xy-plane corresponds to an ordered pair (x, y) of real numbers called the coordinates of P.
 Lecture 7, Part I: Section 1.1 Rectangular Coordinates Rectangular or Cartesian coordinate system Pythagorean theorem Distance formula Midpoint formula Lecture 7, Part II: Section 1.2 Graph of Equations
Lecture 7, Part I: Section 1.1 Rectangular Coordinates Rectangular or Cartesian coordinate system Pythagorean theorem Distance formula Midpoint formula Lecture 7, Part II: Section 1.2 Graph of Equations
6.4 Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function
 6.4 Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function Recall from 6.1 and 6.2: Standard Form The standard form of a quadratic is: f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c or y = ax 2 + bx + c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0.
6.4 Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function Recall from 6.1 and 6.2: Standard Form The standard form of a quadratic is: f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c or y = ax 2 + bx + c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0.
Objective Mathematics
 6. In angle etween the pair of tangents drawn from a 1. If straight line y = mx + c is tangential to paraola y 16( x 4), then exhaustive set of values of 'c' is given y (a) R /( 4, 4) () R /(, ) (c) R
6. In angle etween the pair of tangents drawn from a 1. If straight line y = mx + c is tangential to paraola y 16( x 4), then exhaustive set of values of 'c' is given y (a) R /( 4, 4) () R /(, ) (c) R
Lesson 1: Analyzing Quadratic Functions
 UNIT QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND MODELING Lesson 1: Analyzing Quadratic Functions Common Core State Standards F IF.7 F IF.8 Essential Questions Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features
UNIT QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND MODELING Lesson 1: Analyzing Quadratic Functions Common Core State Standards F IF.7 F IF.8 Essential Questions Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Math 8 Honors Coordinate Geometry part 3 Unit Updated July 29, 2016
 Review how to find the distance between two points To find the distance between two points, use the Pythagorean theorem. The difference between is one leg and the difference between and is the other leg.
Review how to find the distance between two points To find the distance between two points, use the Pythagorean theorem. The difference between is one leg and the difference between and is the other leg.
Chapter 11. Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates
 Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ayman H. Sakka Chapter 11 Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates In this chapter we study new ways to define curves in the plane, give geometric definitions of parabolas, ellipses,
Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ayman H. Sakka Chapter 11 Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates In this chapter we study new ways to define curves in the plane, give geometric definitions of parabolas, ellipses,
Section 7.2 Characteristics of Quadratic Functions
 Section 7. Characteristics of Quadratic Functions A QUADRATIC FUNCTION is a function of the form " # $ N# 1 & ;# & 0 Characteristics Include:! Three distinct terms each with its own coefficient:! An x
Section 7. Characteristics of Quadratic Functions A QUADRATIC FUNCTION is a function of the form " # $ N# 1 & ;# & 0 Characteristics Include:! Three distinct terms each with its own coefficient:! An x
The point (x, y) lies on the circle of radius r and center (h, k) iff. x h y k r
 NOTES +: ANALYTIC GEOMETRY NAME LESSON. GRAPHS OF EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES (CIRCLES). Standard form of a Circle The point (x, y) lies on the circle of radius r and center (h, k) iff x h y k r Center:
NOTES +: ANALYTIC GEOMETRY NAME LESSON. GRAPHS OF EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES (CIRCLES). Standard form of a Circle The point (x, y) lies on the circle of radius r and center (h, k) iff x h y k r Center:
Unit #3: Quadratic Functions Lesson #13: The Almighty Parabola. Day #1
 Algebra I Unit #3: Quadratic Functions Lesson #13: The Almighty Parabola Name Period Date Day #1 There are some important features about the graphs of quadratic functions we are going to explore over the
Algebra I Unit #3: Quadratic Functions Lesson #13: The Almighty Parabola Name Period Date Day #1 There are some important features about the graphs of quadratic functions we are going to explore over the
UNIT 3B CREATING AND GRAPHING EQUATIONS Lesson 4: Solving Systems of Equations Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: graphing multiple equations on a graphing calculator graphing quadratic equations graphing linear equations Introduction A system
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: graphing multiple equations on a graphing calculator graphing quadratic equations graphing linear equations Introduction A system
EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS
 EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS Steps to Find the Median of a Triangle: -Find the midpoint of a segment using the midpoint formula. -Use the vertex and midpoint to find the
EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS Steps to Find the Median of a Triangle: -Find the midpoint of a segment using the midpoint formula. -Use the vertex and midpoint to find the
