The Price of Anarchy on Complex Networks
|
|
|
- Vernon Gordon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Price of Anarchy on Complex Networks NetSci. Conference May 22, 2006 HyeJin Youn, Hawoong Jeong Complex Systems & Statistical Physics Lab. (Dept. of Physics, KAIST, Korea)
2 Importance of networks & dynamics Protein Marriage map between 100 richest people in Korea Interaction Internet routing Traffic Networkon roads WWW H.Jeong et al (2001)
3 Network Dynamics States of both the nodes and the edges can change Dynamics of the networks : The topology of the network itself often evolves in time Dynamics on the networks : Agents are moving on the networks (E.g. Zero-range process, Contact process, Cascading failure, Shortest paths & OPTIMAL PATH) Latency function (like time or cost per person) length 1 Latency = travelers + width [# of ] length 1/width # of travelers
4 Network flow with congestion Cost function on path i Latency function length of path i # of agent on path i width of path i S T Given network with many agents going from S (source) to T (target), what will be the optimized distribution of agents for best performance?? Based on the model of Roughgarden & Tardos, 2000
5 Optimizations in physics Euler-Lagrange differential equation minimal free energy in thermodynamic physics Fitting experimental DATA with formula Low temperature behavior of disordered magnets There are two types of optimizations!!! Centralized control Minimizing Global Cost Global Optimization Decentralized control Each agent minimizes its its own personal cost User Optimization (Nash equilibrium)
6 The Price of Anarchy Decentralized control Each agent minimizes its own personal cost Centralized control Minimizing Global Cost total cost of User Optimum total cost ofglobal Optimum Price of Anarchy Koutsoupias & Papadimitriou, Price of Anarchy (Roughgarden & Tardos, 2000) Price we have to pay not being coordinated by central agency Price of being selfish
7 Price of Anarchy: Contrived Example Pigous s example: Congestion sensitive network 10 agents want to Go from S to T. S T What will be the min total cost, i.e. Global Optimum =? If x a =x, then x b =10-x, total cost=10ᆞx + (10-x) ᆞ(10-x) = x 2-10x+100=(x-5) x a =x b =5 with total cost 75
8 Price of Anarchy: Contrived Example Envy The upper agents get envious of people with lower costs! x a = x b =5 S T BUT Global Optimum = 5x10 + 5x5 = 75 75/10 = 7.5min driving in average
9 Price of Anarchy: Contrived Example x a = 5 S x b = 5 T What will be the User Optimum? (Nash Equilibrium: everyone happy)
10 Price of Anarchy: Contrived Example Move to Lower path x a = 5-1 x b = S T user cost = < 10
11 Price of Anarchy: Contrived Example again x a = x b = 6+1 S T user cost = < 10
12 Price of Anarchy: Contrived Example again x a = x b = 7+1 S T user cost = < 10
13 Price of Anarchy: Contrived Example again x a = x b = 8+1 S T user cost = < 10
14 Price of Anarchy: Contrived Example again x a = x b = 9+1 S T User Optimum = 10 x10 = 100 avg 10min travel time > avg 7.5-min travel time
15 Price of Anarchy: Contrived Example There is a gap between global optimum & user optimum! S x a = 5 vs 0 x b = 5 vs 10 T User Optimum = 10 x10 = 100 Global Optimum = 5x10 + 5x5 = 75 4/3 Price of Anarchy!
16 More realistic/complex example Assumption: traffic reaches at equilibrium Price of Anarchy on a real world the Boston Road Network (with real geometrical information like width, length, one-way etc) Traffic from central square (S) to copley square (T)
17 Boston Road Map
18 Boston Road Network Start (nodes 59, edges 108, regular-like) Latency function = ax + b End Width length
19 More realistic/complex example Assumption: traffic reaches at equilibrium Price of Anarchy on a real world the Boston Road Network (with real geometrical information) Global optimum : mapping to Min-cost Max-flow problem User optimum ~ approximate optimum: Metropolis Algorithm and Annealing method to find out the optimum configurations
20 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =1
21 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =2
22 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =3
23 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =4
24 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =5
25 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =6
26 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =7
27 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =8
28 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =9
29 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =10
30 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =11
31 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =12
32 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =13
33 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =14
34 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =15
35 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =16
36 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =17
37 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =18
38 User Optimum Global Optimum Number of traveler =19
39 Congestion distribution on the edges User Optimum Global Optimum Number of Agents: 20
40 Variation of POA with Agent # Reminder: POA = UE/GO Price of Anarchy number of agents
41 Why Price of Anarchy decreases? Fitness landscape for a simple case: Strategy a c b (x b )= xb 2 S l(x a )= 5 l(x b )= xb T 5 5 l(x b )= xb l(x a )= 5 c b (x b )= 5xb 2.5 Strategy b Fitness for User Optimum Fitness for Global Optimum l(x b )= 2xb 2.5 l(x a )= 5
42 Linear latency function: POA too small?? Nash Equilibrium 4/3 x (Global Optimum) - Roughgarden-Tardos More general edge latency function n > 1 S C= C(X) = X^3 T When n=3 UO = 1 GO = 0.37*1 + (0.63)^4 = POA = UA/GO = Bigger than 4/3 (n=1)
43 Upper bound of POA More general edge latency function POA GO n n Possibility of getting higher order of POA if using latency function with higher exponents
44 Making network more efficient without central government?? Lower PoA ~ better(?) system ( even w/o central control, user optimum is closer to global optimum, better!) Let s make better network with lower PoA Simple thought (by stupid government): construct more roads with tax money! Braess paradox (counter-intuitive consequences)
45 Braess s Paradox Again 10 travelers want to move from S to T. x 10 SS 0: cost-free express road T 10 x User Optimum without middle arc = 150 = Global Optimum increase User Optimum with middle arc = 200 Price of Anarchy = 200/150 = 4/3
46 Boston Road Network Start End
47 Affect of an Arc Removal on User Optimum Start End negative
48 Affect of Arc Removal on User Optimum Cost increment congestion negative NE positive NE PoA=UO/GO edge index 53 out of 108 edges are identified as deteriorating inefficiency! (ΔPoA<0) 19 out of 53 edges are found having made the decentralised system cost more! (ΔNE<0)
49 More systematic approaches Model network analysis Regular Lattice Erdos-Renyi Network Small-world Network Scale-free Network Multiple Sources & Targets Any correlation between PoA and other topological quantities?
50 PoAC network representation Number of Agents = 60 Regular Lattice (N=100) SW(N=100, r=3, p=0,0.1)
51 PoAC network representation Number of Agents = 60 ER(N=100, k=6) BA(N=100, m3) Thick and black edge: x+10 (wide and long) Thin and grey: 10x+1 size of node: PoAC method of spreading: using Kamada-Kawai(free) in Pajek except SW
52 PoA (s-t pair) Number of agents = 60 Number density <PoA> s-t pairs
53 PoAC distribution Number of agents = 60 Number density PoA centrality
54 <PoA> all S-T pairs, network <PoA> SW worst in POA! ER bad! SF good! RL best! Number of Agents
55 PoA (s-t pair) BC correlation Number of agents = 60 <PoA>bc(s)bc(t) BC(s)*BC(t)
56 PoA (S-T pair) degree correlation Number of agents = 60 <PoA>k(S)k(T) k(s)*k(t)
57 Summary & Conclusion Price of Anarchy on a network : price that a decentralized system should pay for not being coordinated, can be understood as a measure of inefficiency of the system. Price of Anarchy on a real world (Boston Road Network) - It is small, but it does exist! Reducing the Price of Anarchy Flow from to Central Square to Copley Square could be improved by removing some streets (NOT adding new streets!) - network modification (Braess s paradox) - Structural guidance of selfish users to the global optimized Efficiency in traffic dynamics: RL>BA>ER>SW?? Correlation with topological properties? Degree? More works are ongoing
58 Job opening at KAIST Funding: 2 nd phase Brain Korea 21 Project Several PostDoc & Research Professor positions are available in many fields. For more information, please contact H. Jeong (hjeong@kaist.ac.kr)
How Bad is Selfish Routing?
 How Bad is Selfish Routing? Tim Roughgarden and Éva Tardos Presented by Brighten Godfrey 1 Game Theory Two or more players For each player, a set of strategies For each combination of played strategies,
How Bad is Selfish Routing? Tim Roughgarden and Éva Tardos Presented by Brighten Godfrey 1 Game Theory Two or more players For each player, a set of strategies For each combination of played strategies,
Algorithmic Game Theory and Applications. Lecture 16: Selfish Network Routing, Congestion Games, and the Price of Anarchy.
 Algorithmic Game Theory and Applications Lecture 16: Selfish Network Routing, Congestion Games, and the Price of Anarchy Kousha Etessami games and the internet Basic idea: The internet is a huge experiment
Algorithmic Game Theory and Applications Lecture 16: Selfish Network Routing, Congestion Games, and the Price of Anarchy Kousha Etessami games and the internet Basic idea: The internet is a huge experiment
Algorithmic Game Theory and Applications. Lecture 16: Selfish Network Routing, Congestion Games, and the Price of Anarchy
 Algorithmic Game Theory and Applications Lecture 16: Selfish Network Routing, Congestion Games, and the Price of Anarchy Kousha Etessami warning, again 1 In the few remaining lectures, we will briefly
Algorithmic Game Theory and Applications Lecture 16: Selfish Network Routing, Congestion Games, and the Price of Anarchy Kousha Etessami warning, again 1 In the few remaining lectures, we will briefly
Games in Networks: the price of anarchy, stability and learning. Éva Tardos Cornell University
 Games in Networks: the price of anarchy, stability and learning Éva Tardos Cornell University Why care about Games? Users with a multitude of diverse economic interests sharing a Network (Internet) browsers
Games in Networks: the price of anarchy, stability and learning Éva Tardos Cornell University Why care about Games? Users with a multitude of diverse economic interests sharing a Network (Internet) browsers
Introduction to Algorithms / Algorithms I Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Algorithms and Game Theory Date: 12/3/15
 600.363 Introduction to Algorithms / 600.463 Algorithms I Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Algorithms and Game Theory Date: 12/3/15 25.1 Introduction Today we re going to spend some time discussing game
600.363 Introduction to Algorithms / 600.463 Algorithms I Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Algorithms and Game Theory Date: 12/3/15 25.1 Introduction Today we re going to spend some time discussing game
Topics in Artificial Intelligence: Multiagent Systems Selfish Routing in Computer Networks
 Topics in Artificial Intelligence: Multiagent Systems Selfish Routing in Computer Networks Sebastian Streg December 10, 2005 1 Introduction Efficiency in networks with lots of traffic is a serious problem
Topics in Artificial Intelligence: Multiagent Systems Selfish Routing in Computer Networks Sebastian Streg December 10, 2005 1 Introduction Efficiency in networks with lots of traffic is a serious problem
Example 1: An algorithmic view of the small world phenomenon
 Lecture Notes: Social Networks: Models, Algorithms, and Applications Lecture 1: Jan 17, 2012 Scribes: Preethi Ambati and Azar Aliyev Example 1: An algorithmic view of the small world phenomenon The story
Lecture Notes: Social Networks: Models, Algorithms, and Applications Lecture 1: Jan 17, 2012 Scribes: Preethi Ambati and Azar Aliyev Example 1: An algorithmic view of the small world phenomenon The story
Network games. Brighten Godfrey CS 538 September slides by Brighten Godfrey unless otherwise noted
 Network games Brighten Godfrey CS 538 September 27 2011 slides 2010-2011 by Brighten Godfrey unless otherwise noted Demo Game theory basics Games & networks: a natural fit Game theory Studies strategic
Network games Brighten Godfrey CS 538 September 27 2011 slides 2010-2011 by Brighten Godfrey unless otherwise noted Demo Game theory basics Games & networks: a natural fit Game theory Studies strategic
How Bad is Selfish Traffic Routing
 How Bad is Selfish Traffic Routing Malik Magdon-Ismail magdon@cs.rpi.edu (Joint Work with Costas Busch) July 6, 2006. Disclaimer: Theoretical talk; no theorems proved. Huge Numbers Many people believe,
How Bad is Selfish Traffic Routing Malik Magdon-Ismail magdon@cs.rpi.edu (Joint Work with Costas Busch) July 6, 2006. Disclaimer: Theoretical talk; no theorems proved. Huge Numbers Many people believe,
Selfish Caching in Distributed Systems: A Game-Theoretic Analysis
 Selfish Caching in Distributed Systems: A Game-Theoretic Analysis Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing July 5, 4 Byung-Gon Chun, Kamalika Chaudhuri, Hoeteck Wee, Marco Barreno, Christos Papadimitriou,
Selfish Caching in Distributed Systems: A Game-Theoretic Analysis Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing July 5, 4 Byung-Gon Chun, Kamalika Chaudhuri, Hoeteck Wee, Marco Barreno, Christos Papadimitriou,
Mechanism Design in Large Congestion Games
 Mechanism Design in Large Congestion Games Ryan Rogers, Aaron Roth, Jonathan Ullman, and Steven Wu July 22, 2015 Routing Game l e (y) Routing Game Routing Game A routing game G is defined by Routing Game
Mechanism Design in Large Congestion Games Ryan Rogers, Aaron Roth, Jonathan Ullman, and Steven Wu July 22, 2015 Routing Game l e (y) Routing Game Routing Game A routing game G is defined by Routing Game
Algorithms and Theory of Computation
 Algorithms and Theory of Computation Eric Friedman Juris Hartmanis John Hopcroft Bobby Kleinberg Jon Kleinberg Dexter Kozen David Shmoys Éva Tardos David Williamson What we do Core theoretical problems
Algorithms and Theory of Computation Eric Friedman Juris Hartmanis John Hopcroft Bobby Kleinberg Jon Kleinberg Dexter Kozen David Shmoys Éva Tardos David Williamson What we do Core theoretical problems
Understanding the Internet Graph. Christos H. Papadimitriou
 Understanding the Internet Graph Christos H. Papadimitriou www.cs.berkeley.edu/~christos Goals To understand the Internet topology using tools from graph and game theory To contribute to the rigorous foundations
Understanding the Internet Graph Christos H. Papadimitriou www.cs.berkeley.edu/~christos Goals To understand the Internet topology using tools from graph and game theory To contribute to the rigorous foundations
Tolls for heterogeneous selfish users in multicommodity networks and generalized congestion games
 Tolls for heterogeneous selfish users in multicommodity networks and generalized congestion games Lisa Fleischer Kamal Jain Mohammad Mahdian Abstract We prove the existence of tolls to induce multicommodity,
Tolls for heterogeneous selfish users in multicommodity networks and generalized congestion games Lisa Fleischer Kamal Jain Mohammad Mahdian Abstract We prove the existence of tolls to induce multicommodity,
Mechanisms for Internet Routing: A Study 1
 Mechanisms for Internet Routing: A Study 1 Aditya Akella Shuchi Chawla 3 Srini Seshan 4 July, 00 CMU-CS-0-163 School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 1513 Abstract In this
Mechanisms for Internet Routing: A Study 1 Aditya Akella Shuchi Chawla 3 Srini Seshan 4 July, 00 CMU-CS-0-163 School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 1513 Abstract In this
Pricing Networks with Selfish Routing
 Pricing Networks with Selfish Routing Richard Cole Yevgeniy Dodis Tim Roughgarden May 22, 2003 1 Introduction 1.1 Selfish Routing and Marginal Cost Pricing We study the negative consequences of selfish
Pricing Networks with Selfish Routing Richard Cole Yevgeniy Dodis Tim Roughgarden May 22, 2003 1 Introduction 1.1 Selfish Routing and Marginal Cost Pricing We study the negative consequences of selfish
Network Improvement for Equilibrium Routing
 Network Improvement for Equilibrium Routing UMANG BHASKAR University of Waterloo and KATRINA LIGETT California Institute of Technology Routing games are frequently used to model the behavior of traffic
Network Improvement for Equilibrium Routing UMANG BHASKAR University of Waterloo and KATRINA LIGETT California Institute of Technology Routing games are frequently used to model the behavior of traffic
Response Network Emerging from Simple Perturbation
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol 44, No 3, March 2004, pp 628 632 Response Network Emerging from Simple Perturbation S-W Son, D-H Kim, Y-Y Ahn and H Jeong Department of Physics, Korea Advanced
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol 44, No 3, March 2004, pp 628 632 Response Network Emerging from Simple Perturbation S-W Son, D-H Kim, Y-Y Ahn and H Jeong Department of Physics, Korea Advanced
Paradoxes of Traffic Engineering with Partially Optimal Routing
 Paradoxes of Traffic Engineering with Partially Optimal Routing Daron Acemoglu, Ramesh Johari, Asuman Ozdaglar Abstract Most large-scale communication networks, such as the Internet, consist of interconnected
Paradoxes of Traffic Engineering with Partially Optimal Routing Daron Acemoglu, Ramesh Johari, Asuman Ozdaglar Abstract Most large-scale communication networks, such as the Internet, consist of interconnected
Paradox Phenomena in Autonomously Self-Adapting Navigation
 BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 15, No 5 Special Issue on Control in Transportation Systems Sofia 2015 Print ISSN: 1311-9702; Online ISSN: 1314-4081 DOI: 10.1515/cait-2015-0018
BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 15, No 5 Special Issue on Control in Transportation Systems Sofia 2015 Print ISSN: 1311-9702; Online ISSN: 1314-4081 DOI: 10.1515/cait-2015-0018
Dynamics, Non-Cooperation, and Other Algorithmic Challenges in Peer-to-Peer Computing
 Dynamics, Non-Cooperation, and Other Algorithmic Challenges in Peer-to-Peer Computing Stefan Schmid Distributed Computing Group Oberseminar TU München, Germany December 2007 Networks Neuron Networks DISTRIBUTED
Dynamics, Non-Cooperation, and Other Algorithmic Challenges in Peer-to-Peer Computing Stefan Schmid Distributed Computing Group Oberseminar TU München, Germany December 2007 Networks Neuron Networks DISTRIBUTED
Strong Equilibrium in Cost Sharing Connection Games
 Strong Equilibrium in Cost Sharing Connection Games Amir Epstein School of Computer Science Tel-Aviv University Tel-Aviv, 69978, Israel amirep@tau.ac.il Michal Feldman School of Computer Science The Hebrew
Strong Equilibrium in Cost Sharing Connection Games Amir Epstein School of Computer Science Tel-Aviv University Tel-Aviv, 69978, Israel amirep@tau.ac.il Michal Feldman School of Computer Science The Hebrew
How Harmful The Paradox Can Be In The Cohen-Kelly Computer Network Model Using A Non-Cooperative Dynamic Load Balancing Policy
 How Harmful The Paradox Can Be In The Cohen-Kelly Computer Network Model Using A Non-Cooperative Dynamic Load Balancing Policy SAID FATHY EL-ZOGHDY 1 Menoufia University Faculty of Science Department of
How Harmful The Paradox Can Be In The Cohen-Kelly Computer Network Model Using A Non-Cooperative Dynamic Load Balancing Policy SAID FATHY EL-ZOGHDY 1 Menoufia University Faculty of Science Department of
Strategic Network Formation
 Strategic Network Formation Zhongjing Yu, Big Data Research Center, UESTC Email:junmshao@uestc.edu.cn http://staff.uestc.edu.cn/shaojunming What s meaning of Strategic Network Formation? Node : a individual.
Strategic Network Formation Zhongjing Yu, Big Data Research Center, UESTC Email:junmshao@uestc.edu.cn http://staff.uestc.edu.cn/shaojunming What s meaning of Strategic Network Formation? Node : a individual.
Nash Equilibrium Load Balancing
 Nash Equilibrium Load Balancing Computer Science Department Collaborators: A. Kothari, C. Toth, Y. Zhou Load Balancing A set of m servers or machines. A set of n clients or jobs. Each job can be run only
Nash Equilibrium Load Balancing Computer Science Department Collaborators: A. Kothari, C. Toth, Y. Zhou Load Balancing A set of m servers or machines. A set of n clients or jobs. Each job can be run only
Convergence Issues in Competitive Games
 Convergence Issues in Competitive Games Vahab S Mirrokni 1, Adrian Vetta 2 and A Sidoropoulous 3 1 Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL), MIT mail: mirrokni@theorylcsmitedu 2
Convergence Issues in Competitive Games Vahab S Mirrokni 1, Adrian Vetta 2 and A Sidoropoulous 3 1 Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL), MIT mail: mirrokni@theorylcsmitedu 2
Graph theory and GIS
 Geoinformatics FCE CTU 2009 Workshop 18th september 2009 Contents Graph as such Definition Alternative definition Undirected graphs Graphs as a model of reality Contents Graph as such Definition Alternative
Geoinformatics FCE CTU 2009 Workshop 18th september 2009 Contents Graph as such Definition Alternative definition Undirected graphs Graphs as a model of reality Contents Graph as such Definition Alternative
Nash equilibria in Voronoi Games on Graphs
 Nash equilibria in Voronoi Games on Graphs Christoph Dürr, Nguyễn Kim Thắng (Ecole Polytechnique) ESA, Eilat October 07 Plan Motivation : Study the interaction between selfish agents on Internet k players,
Nash equilibria in Voronoi Games on Graphs Christoph Dürr, Nguyễn Kim Thắng (Ecole Polytechnique) ESA, Eilat October 07 Plan Motivation : Study the interaction between selfish agents on Internet k players,
Traffic Flow Control in Vehicular Communication Networks
 Published in: American Control Conference (ACC), 2017. Traffic Flow Control in Vehicular Communication Networks Teng Liu, Alhussein A. Abouzeid, and A. Agung Julius Department of Electrical, Computer,
Published in: American Control Conference (ACC), 2017. Traffic Flow Control in Vehicular Communication Networks Teng Liu, Alhussein A. Abouzeid, and A. Agung Julius Department of Electrical, Computer,
Improved Equilibria via Public Service Advertising
 Improved Equilibria via Public Service Advertising Maria-Florina Balcan Avrim Blum Yishay Mansour August 12, 2008 Abstract Many natural games have both high and low cost Nash equilibria: their Price of
Improved Equilibria via Public Service Advertising Maria-Florina Balcan Avrim Blum Yishay Mansour August 12, 2008 Abstract Many natural games have both high and low cost Nash equilibria: their Price of
Analysing Latency and Link Utilization of Selfish Overlay Routing
 International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Vol. 1, No. 1, January-June 2010, pp. 143-147 S. Prayla Shyry1 & V. Ramachandran2 Research Scholar, Sathyabama University, Chennai, India Professor,
International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Vol. 1, No. 1, January-June 2010, pp. 143-147 S. Prayla Shyry1 & V. Ramachandran2 Research Scholar, Sathyabama University, Chennai, India Professor,
A PARADOX OF CONGESTION IN A QUEUING NETWORK
 J. Appl. Prob. 27, 730-734 (1990) Printed in Israel
J. Appl. Prob. 27, 730-734 (1990) Printed in Israel
CHAPTER 4 WEIGHT-BASED DESIRABILITY METHOD TO SOLVE MULTI-RESPONSE PROBLEMS
 72 CHAPTER 4 WEIGHT-BASED DESIRABILITY METHOD TO SOLVE MULTI-RESPONSE PROBLEMS 4.1 INTRODUCTION Optimizing the quality of a product is widespread in the industry. Products have to be manufactured such
72 CHAPTER 4 WEIGHT-BASED DESIRABILITY METHOD TO SOLVE MULTI-RESPONSE PROBLEMS 4.1 INTRODUCTION Optimizing the quality of a product is widespread in the industry. Products have to be manufactured such
Improved Equilibria via Public Service Advertising
 Carnegie Mellon University Research Showcase @ CMU Computer Science Department School of Computer Science 1-2009 Improved Equilibria via Public Service Advertising Maria-Florina Balcan Carnegie Mellon
Carnegie Mellon University Research Showcase @ CMU Computer Science Department School of Computer Science 1-2009 Improved Equilibria via Public Service Advertising Maria-Florina Balcan Carnegie Mellon
Optimal tour along pubs in the UK
 1 From Facebook Optimal tour along 24727 pubs in the UK Road distance (by google maps) see also http://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/pubs/index.html (part of TSP homepage http://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/
1 From Facebook Optimal tour along 24727 pubs in the UK Road distance (by google maps) see also http://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/pubs/index.html (part of TSP homepage http://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/
THE PRICE OF STABILITY FOR NETWORK DESIGN WITH FAIR COST ALLOCATION
 THE PRICE OF STABILITY FOR NETWORK DESIGN WITH FAIR COST ALLOCATION ELLIOT ANSHELEVICH, ANIRBAN DASGUPTA, JON KLEINBERG, ÉVA TARDOS, TOM WEXLER, AND TIM ROUGHGARDEN Abstract. Network design is a fundamental
THE PRICE OF STABILITY FOR NETWORK DESIGN WITH FAIR COST ALLOCATION ELLIOT ANSHELEVICH, ANIRBAN DASGUPTA, JON KLEINBERG, ÉVA TARDOS, TOM WEXLER, AND TIM ROUGHGARDEN Abstract. Network design is a fundamental
Bottleneck Routing Games on Grids. Costas Busch Rajgopal Kannan Alfred Samman Department of Computer Science Louisiana State University
 Bottleneck Routing Games on Grids ostas Busch Rajgopal Kannan Alfred Samman Department of omputer Science Louisiana State University 1 Talk Outline Introduction Basic Game hannel Game xtensions 2 2-d Grid:
Bottleneck Routing Games on Grids ostas Busch Rajgopal Kannan Alfred Samman Department of omputer Science Louisiana State University 1 Talk Outline Introduction Basic Game hannel Game xtensions 2 2-d Grid:
A Time-To-Live Based Reservation Algorithm on Fully Decentralized Resource Discovery in Grid Computing
 A Time-To-Live Based Reservation Algorithm on Fully Decentralized Resource Discovery in Grid Computing Sanya Tangpongprasit, Takahiro Katagiri, Hiroki Honda, Toshitsugu Yuba Graduate School of Information
A Time-To-Live Based Reservation Algorithm on Fully Decentralized Resource Discovery in Grid Computing Sanya Tangpongprasit, Takahiro Katagiri, Hiroki Honda, Toshitsugu Yuba Graduate School of Information
Anarchy is free in network creation
 Anarchy is free in network creation Ronald Graham Linus Hamilton Ariel Levavi Po-Shen Loh Abstract The Internet has emerged as perhaps the most important network in modern computing, but rather miraculously,
Anarchy is free in network creation Ronald Graham Linus Hamilton Ariel Levavi Po-Shen Loh Abstract The Internet has emerged as perhaps the most important network in modern computing, but rather miraculously,
Classification of Optimization Problems and the Place of Calculus of Variations in it
 Lecture 1 Classification of Optimization Problems and the Place of Calculus of Variations in it ME256 Indian Institute of Science G. K. Ananthasuresh Professor, Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute
Lecture 1 Classification of Optimization Problems and the Place of Calculus of Variations in it ME256 Indian Institute of Science G. K. Ananthasuresh Professor, Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute
Anarchy is Free in Network Creation
 Anarchy is Free in Network Creation Ronald Graham 1, Linus Hamilton 2, Ariel Levavi 1, and Po-Shen Loh 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla,
Anarchy is Free in Network Creation Ronald Graham 1, Linus Hamilton 2, Ariel Levavi 1, and Po-Shen Loh 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla,
Recall: The Routing problem: Local decisions. Recall: Multidimensional Meshes and Tori. Properties of Routing Algorithms
 CS252 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 16 Multiprocessor Networks (con t) March 14 th, 212 John Kubiatowicz Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~kubitron/cs252
CS252 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 16 Multiprocessor Networks (con t) March 14 th, 212 John Kubiatowicz Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~kubitron/cs252
Integrating System Optimum and User Equilibrium in Traffic Assignment via Evolutionary Search and Multiagent Reinforcement Learning
 Integrating System Optimum and User Equilibrium in Traffic ssignment via Evolutionary Search and Multiagent Reinforcement Learning na L. C. Bazzan 1 and Camelia Chira 2 1 Programa de Pós-Graduação em Computação
Integrating System Optimum and User Equilibrium in Traffic ssignment via Evolutionary Search and Multiagent Reinforcement Learning na L. C. Bazzan 1 and Camelia Chira 2 1 Programa de Pós-Graduação em Computação
A Game Theoretic Analysis of Network Design with Socially-Aware Users
 A Game Theoretic Analysis of Network Design with Socially-Aware Users Jocelyne Elias, Fabio Martignon, Konstantin Avrachenkov, Giovanni Neglia Abstract In many scenarios network design is not enforced
A Game Theoretic Analysis of Network Design with Socially-Aware Users Jocelyne Elias, Fabio Martignon, Konstantin Avrachenkov, Giovanni Neglia Abstract In many scenarios network design is not enforced
MIDTERM EXAMINATION Networked Life (NETS 112) November 21, 2013 Prof. Michael Kearns
 MIDTERM EXAMINATION Networked Life (NETS 112) November 21, 2013 Prof. Michael Kearns This is a closed-book exam. You should have no material on your desk other than the exam itself and a pencil or pen.
MIDTERM EXAMINATION Networked Life (NETS 112) November 21, 2013 Prof. Michael Kearns This is a closed-book exam. You should have no material on your desk other than the exam itself and a pencil or pen.
AVB Latency Math. v5 Nov, AVB Face to Face Dallas, TX Don Pannell -
 AVB Latency Math v5 Nov, 2010 802.1 AVB Face to Face Dallas, TX Don Pannell - dpannell@marvell.com 1 History V5 This version Changes marked in Red Add Class A Bridge Math - Nov 2010 Dallas, TX V4 1 st
AVB Latency Math v5 Nov, 2010 802.1 AVB Face to Face Dallas, TX Don Pannell - dpannell@marvell.com 1 History V5 This version Changes marked in Red Add Class A Bridge Math - Nov 2010 Dallas, TX V4 1 st
ROUTING PROTOCOLS WITH SMALLEST MAXIMAL LATENCY
 PERIODICA POLYTECHNICA SER. EL. ENG. VOL. 49, NO. 3 4, PP. 209 221 (2005) ROUTING PROTOCOLS WITH SMALLEST MAXIMAL LATENCY Gábor KURUC and Krisztina LÓJA Vodafone Hungary Co. e-mail: gabor.kuruc@vodafone.com
PERIODICA POLYTECHNICA SER. EL. ENG. VOL. 49, NO. 3 4, PP. 209 221 (2005) ROUTING PROTOCOLS WITH SMALLEST MAXIMAL LATENCY Gábor KURUC and Krisztina LÓJA Vodafone Hungary Co. e-mail: gabor.kuruc@vodafone.com
Gibbs Sampling. Stephen F. Altschul. National Center for Biotechnology Information National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health
 Gibbs Sampling Stephen F. Altschul National Center for Biotechnology Information National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health Optimization in High-Dimensional Space Smooth and simple landscapes
Gibbs Sampling Stephen F. Altschul National Center for Biotechnology Information National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health Optimization in High-Dimensional Space Smooth and simple landscapes
Lecture Notes on Congestion Games
 Lecture Notes on Department of Computer Science RWTH Aachen SS 2005 Definition and Classification Description of n agents share a set of resources E strategy space of player i is S i 2 E latency for resource
Lecture Notes on Department of Computer Science RWTH Aachen SS 2005 Definition and Classification Description of n agents share a set of resources E strategy space of player i is S i 2 E latency for resource
Cooperation in Multi-Organization Scheduling
 Cooperation in Multi-Organization Scheduling Fanny Pascual ½, Krzysztof Rzadca, Denis Trystram ½ INRIA Rhône-Alpes, France LIG Grenoble University, France Polish-Japanese Institute of Information Technology,
Cooperation in Multi-Organization Scheduling Fanny Pascual ½, Krzysztof Rzadca, Denis Trystram ½ INRIA Rhône-Alpes, France LIG Grenoble University, France Polish-Japanese Institute of Information Technology,
Lab Activity #2- Statistics and Graphing
 Lab Activity #2- Statistics and Graphing Graphical Representation of Data and the Use of Google Sheets : Scientists answer posed questions by performing experiments which provide information about a given
Lab Activity #2- Statistics and Graphing Graphical Representation of Data and the Use of Google Sheets : Scientists answer posed questions by performing experiments which provide information about a given
CS 268: Computer Networking. Adding New Functionality to the Internet
 CS 268: Computer Networking L-16 Changing the Network Adding New Functionality to the Internet Overlay networks Active networks Assigned reading Resilient Overlay Networks Active network vision and reality:
CS 268: Computer Networking L-16 Changing the Network Adding New Functionality to the Internet Overlay networks Active networks Assigned reading Resilient Overlay Networks Active network vision and reality:
Urban dashboardistics Damon Wischik Dept. of Computer Science and Technology
 Urban dashboardistics Damon Wischik Dept. of Computer Science and Technology UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE Wardrop modelled route choice by drivers in a traffic network. Braess discovered paradoxical outcomes
Urban dashboardistics Damon Wischik Dept. of Computer Science and Technology UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE Wardrop modelled route choice by drivers in a traffic network. Braess discovered paradoxical outcomes
Horizontal and Vertical Curve Design
 Horizontal and Vertical Curve Design CE 576 Highway Design and Traffic Safety Dr. Ahmed Abdel-Rahim Horizontal Alignment Horizontal curve is critical. Vehicle cornering capability is thus a key concern
Horizontal and Vertical Curve Design CE 576 Highway Design and Traffic Safety Dr. Ahmed Abdel-Rahim Horizontal Alignment Horizontal curve is critical. Vehicle cornering capability is thus a key concern
Error Analysis, Statistics and Graphing
 Error Analysis, Statistics and Graphing This semester, most of labs we require us to calculate a numerical answer based on the data we obtain. A hard question to answer in most cases is how good is your
Error Analysis, Statistics and Graphing This semester, most of labs we require us to calculate a numerical answer based on the data we obtain. A hard question to answer in most cases is how good is your
Competitive Routing over Time
 Competitive Routing over Time Martin Hoefer Vahab S. Mirrokni Heiko Röglin Shang-Hua Teng June 7, 2011 Abstract Congestion games are a fundamental and widely studied model for selfish allocation problems
Competitive Routing over Time Martin Hoefer Vahab S. Mirrokni Heiko Röglin Shang-Hua Teng June 7, 2011 Abstract Congestion games are a fundamental and widely studied model for selfish allocation problems
Complex Networks. Structure and Dynamics
 Complex Networks Structure and Dynamics Ying-Cheng Lai Department of Mathematics and Statistics Department of Electrical Engineering Arizona State University Collaborators! Adilson E. Motter, now at Max-Planck
Complex Networks Structure and Dynamics Ying-Cheng Lai Department of Mathematics and Statistics Department of Electrical Engineering Arizona State University Collaborators! Adilson E. Motter, now at Max-Planck
Chemistry 1A Graphing Tutorial CSUS Department of Chemistry
 Chemistry 1A Graphing Tutorial CSUS Department of Chemistry Please go to the Lab webpage to download your own copy for reference. 1 When you open Microsoft Excel 2003, you will see a blank worksheet: Enter
Chemistry 1A Graphing Tutorial CSUS Department of Chemistry Please go to the Lab webpage to download your own copy for reference. 1 When you open Microsoft Excel 2003, you will see a blank worksheet: Enter
Lecture 12 November 28, Wireless Access. Graduate course in Communications Engineering. University of Rome La Sapienza. Rome, Italy
 Lecture 12 November 28, 2018 Wireless Access Graduate course in Communications Engineering University of Rome La Sapienza Rome, Italy 2018-2019 Application of Game Theory to Network Selection Outline Network
Lecture 12 November 28, 2018 Wireless Access Graduate course in Communications Engineering University of Rome La Sapienza Rome, Italy 2018-2019 Application of Game Theory to Network Selection Outline Network
Fast Convergence of Regularized Learning in Games
 Fast Convergence of Regularized Learning in Games Vasilis Syrgkanis Alekh Agarwal Haipeng Luo Robert Schapire Microsoft Research NYC Microsoft Research NYC Princeton University Microsoft Research NYC Strategic
Fast Convergence of Regularized Learning in Games Vasilis Syrgkanis Alekh Agarwal Haipeng Luo Robert Schapire Microsoft Research NYC Microsoft Research NYC Princeton University Microsoft Research NYC Strategic
On Selfish Routing in Internet-Like Environments
 On Selfish Routing in Internet-Like Environments Lili Qiu Yang Richard Yang Yin Zhang Scott Shenker Microsoft Research Yale University AT&T Labs Research ICSI liliq@microsoft.com yry@cs.yale.edu yzhang@research.att.com
On Selfish Routing in Internet-Like Environments Lili Qiu Yang Richard Yang Yin Zhang Scott Shenker Microsoft Research Yale University AT&T Labs Research ICSI liliq@microsoft.com yry@cs.yale.edu yzhang@research.att.com
Examples of P vs NP: More Problems
 Examples of P vs NP: More Problems COMP1600 / COMP6260 Dirk Pattinson Australian National University Semester 2, 2017 Catch Up / Drop in Lab When Fridays, 15.00-17.00 Where N335, CSIT Building (bldg 108)
Examples of P vs NP: More Problems COMP1600 / COMP6260 Dirk Pattinson Australian National University Semester 2, 2017 Catch Up / Drop in Lab When Fridays, 15.00-17.00 Where N335, CSIT Building (bldg 108)
Routing Metric. ARPANET Routing Algorithms. Problem with D-SPF. Advanced Computer Networks
 Advanced Computer Networks Khanna and Zinky, The Revised ARPANET Routing Metric, Proc. of ACM SIGCOMM '89, 19(4):45 46, Sep. 1989 Routing Metric Distributed route computation is a function of link cost
Advanced Computer Networks Khanna and Zinky, The Revised ARPANET Routing Metric, Proc. of ACM SIGCOMM '89, 19(4):45 46, Sep. 1989 Routing Metric Distributed route computation is a function of link cost
One type of these solutions is automatic license plate character recognition (ALPR).
 1.0 Introduction Modelling, Simulation & Computing Laboratory (msclab) A rapid technical growth in the area of computer image processing has increased the need for an efficient and affordable security,
1.0 Introduction Modelling, Simulation & Computing Laboratory (msclab) A rapid technical growth in the area of computer image processing has increased the need for an efficient and affordable security,
Bottleneck Links, Variable Demand, and the Tragedy of the Commons
 Bottleneck Links, Variable Demand, and the Tragedy of the Commons Richard Cole Yevgeniy Dodis Ý Tim Roughgarden Þ April 8, 25 Abstract The price of anarchy, a measure of the inefficiency of selfish behavior,
Bottleneck Links, Variable Demand, and the Tragedy of the Commons Richard Cole Yevgeniy Dodis Ý Tim Roughgarden Þ April 8, 25 Abstract The price of anarchy, a measure of the inefficiency of selfish behavior,
Interconnection Networks: Topology. Prof. Natalie Enright Jerger
 Interconnection Networks: Topology Prof. Natalie Enright Jerger Topology Overview Definition: determines arrangement of channels and nodes in network Analogous to road map Often first step in network design
Interconnection Networks: Topology Prof. Natalie Enright Jerger Topology Overview Definition: determines arrangement of channels and nodes in network Analogous to road map Often first step in network design
Coordination Mechanisms
 Coordination Mechanisms George Christodoulou Elias Koutsoupias Akash Nanavati Abstract We introduce the notion of coordination mechanisms to improve the performance in systems with independent selfish
Coordination Mechanisms George Christodoulou Elias Koutsoupias Akash Nanavati Abstract We introduce the notion of coordination mechanisms to improve the performance in systems with independent selfish
CS-E5740. Complex Networks. Scale-free networks
 CS-E5740 Complex Networks Scale-free networks Course outline 1. Introduction (motivation, definitions, etc. ) 2. Static network models: random and small-world networks 3. Growing network models: scale-free
CS-E5740 Complex Networks Scale-free networks Course outline 1. Introduction (motivation, definitions, etc. ) 2. Static network models: random and small-world networks 3. Growing network models: scale-free
Constant Price of Anarchy in Network Creation Games via Public Service Advertising
 Constant Price of Anarchy in Network Creation Games via Public Service Advertising Erik D. Demaine and Morteza Zadimoghaddam MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, Cambridge, MA 02139,
Constant Price of Anarchy in Network Creation Games via Public Service Advertising Erik D. Demaine and Morteza Zadimoghaddam MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, Cambridge, MA 02139,
Pheromone Static Routing Strategy for Complex Networks. Abstract
 Pheromone Static Routing Strategy for Complex Networks Xiang Ling 1, Henry Y.K. Lau 2, Rui Jiang 1, and Mao-Bin Hu 1 1.School of Engineering Science, University of Science and Technology of China, arxiv:1108.6119v1
Pheromone Static Routing Strategy for Complex Networks Xiang Ling 1, Henry Y.K. Lau 2, Rui Jiang 1, and Mao-Bin Hu 1 1.School of Engineering Science, University of Science and Technology of China, arxiv:1108.6119v1
Lecture 2 Optimization with equality constraints
 Lecture 2 Optimization with equality constraints Constrained optimization The idea of constrained optimisation is that the choice of one variable often affects the amount of another variable that can be
Lecture 2 Optimization with equality constraints Constrained optimization The idea of constrained optimisation is that the choice of one variable often affects the amount of another variable that can be
Different Optimal Solutions in Shared Path Graphs
 Different Optimal Solutions in Shared Path Graphs Kira Goldner Oberlin College Oberlin, OH 44074 (610) 324-3931 ksgoldner@gmail.com ABSTRACT We examine an expansion upon the basic shortest path in graphs
Different Optimal Solutions in Shared Path Graphs Kira Goldner Oberlin College Oberlin, OH 44074 (610) 324-3931 ksgoldner@gmail.com ABSTRACT We examine an expansion upon the basic shortest path in graphs
Properties of Biological Networks
 Properties of Biological Networks presented by: Ola Hamud June 12, 2013 Supervisor: Prof. Ron Pinter Based on: NETWORK BIOLOGY: UNDERSTANDING THE CELL S FUNCTIONAL ORGANIZATION By Albert-László Barabási
Properties of Biological Networks presented by: Ola Hamud June 12, 2013 Supervisor: Prof. Ron Pinter Based on: NETWORK BIOLOGY: UNDERSTANDING THE CELL S FUNCTIONAL ORGANIZATION By Albert-László Barabási
Chapter 2: Linear Equations and Functions
 Chapter 2: Linear Equations and Functions Chapter 2: Linear Equations and Functions Assignment Sheet Date Topic Assignment Completed 2.1 Functions and their Graphs and 2.2 Slope and Rate of Change 2.1
Chapter 2: Linear Equations and Functions Chapter 2: Linear Equations and Functions Assignment Sheet Date Topic Assignment Completed 2.1 Functions and their Graphs and 2.2 Slope and Rate of Change 2.1
Kapitel 5: Local Search
 Inhalt: Kapitel 5: Local Search Gradient Descent (Hill Climbing) Metropolis Algorithm and Simulated Annealing Local Search in Hopfield Neural Networks Local Search for Max-Cut Single-flip neighborhood
Inhalt: Kapitel 5: Local Search Gradient Descent (Hill Climbing) Metropolis Algorithm and Simulated Annealing Local Search in Hopfield Neural Networks Local Search for Max-Cut Single-flip neighborhood
On Selfish Routing in Internet-Like Environments
 IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING, VOL. X, NO. X, APRIL 24 1 On Selfish Routing in Internet-Like Environments Lili Qiu, Member, IEEE, Yang Richard Yang, Member, IEEE, Yin Zhang, Member, IEEE, and Scott
IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING, VOL. X, NO. X, APRIL 24 1 On Selfish Routing in Internet-Like Environments Lili Qiu, Member, IEEE, Yang Richard Yang, Member, IEEE, Yin Zhang, Member, IEEE, and Scott
Introduction to Linear Programming. Algorithmic and Geometric Foundations of Optimization
 Introduction to Linear Programming Algorithmic and Geometric Foundations of Optimization Optimization and Linear Programming Mathematical programming is a class of methods for solving problems which ask
Introduction to Linear Programming Algorithmic and Geometric Foundations of Optimization Optimization and Linear Programming Mathematical programming is a class of methods for solving problems which ask
A Survey of Uniqueness Results for Selfish Routing
 A Survey of Uniqueness Results for Selfish Routing Nahum Shimkin epartment of Electrical Engineering Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Haifa 32000, Israel shimkin@ee.technion.ac.il Abstract. We
A Survey of Uniqueness Results for Selfish Routing Nahum Shimkin epartment of Electrical Engineering Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Haifa 32000, Israel shimkin@ee.technion.ac.il Abstract. We
Math 1525 Excel Lab 1 Introduction to Excel Spring, 2001
 Math 1525 Excel Lab 1 Introduction to Excel Spring, 2001 Goal: The goal of Lab 1 is to introduce you to Microsoft Excel, to show you how to graph data and functions, and to practice solving problems with
Math 1525 Excel Lab 1 Introduction to Excel Spring, 2001 Goal: The goal of Lab 1 is to introduce you to Microsoft Excel, to show you how to graph data and functions, and to practice solving problems with
Project: A survey and Critique on Algorithmic Mechanism Design
 Project: A survey and Critique on Algorithmic Mechanism Design 1 Motivation One can think of many systems where agents act according to their self interest. Therefore, when we are in the process of designing
Project: A survey and Critique on Algorithmic Mechanism Design 1 Motivation One can think of many systems where agents act according to their self interest. Therefore, when we are in the process of designing
THE COMPETITIVE FACILITY LOCATION PROBLEM IN A DUOPOLY
 THE COMPETITIVE FACILITY LOCATION PROBLEM IN A DUOPOLY Y. GUR, D. SABAN, AND N.E. STIER-MOSES, Graduate School of Business, Columbia University, New York, USA Universidad Torcuato Di Tella, School of Business,
THE COMPETITIVE FACILITY LOCATION PROBLEM IN A DUOPOLY Y. GUR, D. SABAN, AND N.E. STIER-MOSES, Graduate School of Business, Columbia University, New York, USA Universidad Torcuato Di Tella, School of Business,
Network Formation Games and the Potential Function Method
 CHAPTER 19 Network Formation Games and the Potential Function Method Éva Tardos and Tom Wexler Abstract Large computer networks such as the Internet are built, operated, and used by a large number of diverse
CHAPTER 19 Network Formation Games and the Potential Function Method Éva Tardos and Tom Wexler Abstract Large computer networks such as the Internet are built, operated, and used by a large number of diverse
CS364A: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture #19: Pure Nash Equilibria and PLS-Completeness
 CS364A: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture #19: Pure Nash Equilibria and PLS-Completeness Tim Roughgarden December 2, 2013 1 The Big Picture We now have an impressive list of tractability results polynomial-time
CS364A: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture #19: Pure Nash Equilibria and PLS-Completeness Tim Roughgarden December 2, 2013 1 The Big Picture We now have an impressive list of tractability results polynomial-time
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu 10/4/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis, http://cs224w.stanford.edu
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu 10/4/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis, http://cs224w.stanford.edu
15.082J and 6.855J. Lagrangian Relaxation 2 Algorithms Application to LPs
 15.082J and 6.855J Lagrangian Relaxation 2 Algorithms Application to LPs 1 The Constrained Shortest Path Problem (1,10) 2 (1,1) 4 (2,3) (1,7) 1 (10,3) (1,2) (10,1) (5,7) 3 (12,3) 5 (2,2) 6 Find the shortest
15.082J and 6.855J Lagrangian Relaxation 2 Algorithms Application to LPs 1 The Constrained Shortest Path Problem (1,10) 2 (1,1) 4 (2,3) (1,7) 1 (10,3) (1,2) (10,1) (5,7) 3 (12,3) 5 (2,2) 6 Find the shortest
08. First and second degree equations
 08. First and second degree equations GRAPH THEORY Based on Chris K. Caldwell work: http://primes.utm.edu/cgi-bin/caldwell/tutor/graph/index.html INTRODUCTION Consider the next problem: Old Königsberg
08. First and second degree equations GRAPH THEORY Based on Chris K. Caldwell work: http://primes.utm.edu/cgi-bin/caldwell/tutor/graph/index.html INTRODUCTION Consider the next problem: Old Königsberg
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS QUEEN S UNIVERSITY AT KINGSTON MATH 121/124 - APR 2014 A. Ableson, T. Day, A. Hoefel
 Page 1 of 18 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS QUEEN S UNIVERSITY AT KINGSTON MATH 121/124 - APR 2014 A. Ableson, T. Day, A. Hoefel INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions, writing clearly in the space
Page 1 of 18 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS QUEEN S UNIVERSITY AT KINGSTON MATH 121/124 - APR 2014 A. Ableson, T. Day, A. Hoefel INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions, writing clearly in the space
GCSE 4353/02 MATHEMATICS (UNITISED SCHEME) UNIT 3: Calculator-Allowed Mathematics HIGHER TIER
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names GCSE 4353/2 MATHEMATICS (UNITISED SCHEME) UNIT 3: Calculator-Allowed Mathematics HIGHER TIER A.M. MONDAY, 17 June 213 1 3 hours 4 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names GCSE 4353/2 MATHEMATICS (UNITISED SCHEME) UNIT 3: Calculator-Allowed Mathematics HIGHER TIER A.M. MONDAY, 17 June 213 1 3 hours 4 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
Introduction to algorithmic mechanism design
 Introduction to algorithmic mechanism design Elias Koutsoupias Department of Computer Science University of Oxford EWSCS 2014 March 5-7, 2014 Part I Game Theory and Computer Science Why Game Theory and
Introduction to algorithmic mechanism design Elias Koutsoupias Department of Computer Science University of Oxford EWSCS 2014 March 5-7, 2014 Part I Game Theory and Computer Science Why Game Theory and
hp calculators HP 35s Using Calculator Memories to Help Solve Problems Variables and Memory Registers Practice Examples: Storing and Using a Constant
 HP 35s Using Calculator Memories to Help Solve Problems Variables and Memory Registers Practice Examples: Storing and Using a Constant Storing a Temporary Result Exchanging and Viewing Registers Other
HP 35s Using Calculator Memories to Help Solve Problems Variables and Memory Registers Practice Examples: Storing and Using a Constant Storing a Temporary Result Exchanging and Viewing Registers Other
minimize ½(x 1 + 2x 2 + x 32 ) subject to x 1 + x 2 + x 3 = 5
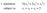 minimize ½(x 1 2 + 2x 2 2 + x 32 ) subject to x 1 + x 2 + x 3 = 5 In this Chapter We will study a new theory for constrained optimization Local optimality condition Easier to implement Deeper insights
minimize ½(x 1 2 + 2x 2 2 + x 32 ) subject to x 1 + x 2 + x 3 = 5 In this Chapter We will study a new theory for constrained optimization Local optimality condition Easier to implement Deeper insights
On Selfish Routing in Internet-Like Environments
 1 On Selfish Routing in Internet-Like Environments Lili Qiu Yang Richard Yang Yin Zhang Scott Shenker UT Austin Yale University UT Austin UC Berkeley lili@cs.utexas.edu yry@cs.yale.edu yzhang@cs.utexas.edu
1 On Selfish Routing in Internet-Like Environments Lili Qiu Yang Richard Yang Yin Zhang Scott Shenker UT Austin Yale University UT Austin UC Berkeley lili@cs.utexas.edu yry@cs.yale.edu yzhang@cs.utexas.edu
SHAPE, SPACE & MEASURE
 STAGE 1 Know the place value headings up to millions Recall primes to 19 Know the first 12 square numbers Know the Roman numerals I, V, X, L, C, D, M Know the % symbol Know percentage and decimal equivalents
STAGE 1 Know the place value headings up to millions Recall primes to 19 Know the first 12 square numbers Know the Roman numerals I, V, X, L, C, D, M Know the % symbol Know percentage and decimal equivalents
New Trials on Test Data Generation: Analysis of Test Data Space and Design of Improved Algorithm
 New Trials on Test Data Generation: Analysis of Test Data Space and Design of Improved Algorithm So-Yeong Jeon 1 and Yong-Hyuk Kim 2,* 1 Department of Computer Science, Korea Advanced Institute of Science
New Trials on Test Data Generation: Analysis of Test Data Space and Design of Improved Algorithm So-Yeong Jeon 1 and Yong-Hyuk Kim 2,* 1 Department of Computer Science, Korea Advanced Institute of Science
2 + (-2) = 0. Hinojosa 7 th. Math Vocabulary Words. Unit 1. Word Definition Picture. The opposite of a number. Additive Inverse
 Unit 1 Word Definition Picture Additive Inverse The opposite of a number 2 + (-2) = 0 Equal Amount The same in quantity = Fraction A number in the form a/b, where b 0. Half One of two equal parts of a
Unit 1 Word Definition Picture Additive Inverse The opposite of a number 2 + (-2) = 0 Equal Amount The same in quantity = Fraction A number in the form a/b, where b 0. Half One of two equal parts of a
Department of Mathematics Oleg Burdakov of 30 October Consider the following linear programming problem (LP):
 Linköping University Optimization TAOP3(0) Department of Mathematics Examination Oleg Burdakov of 30 October 03 Assignment Consider the following linear programming problem (LP): max z = x + x s.t. x x
Linköping University Optimization TAOP3(0) Department of Mathematics Examination Oleg Burdakov of 30 October 03 Assignment Consider the following linear programming problem (LP): max z = x + x s.t. x x
8/28/2003 SIGCOMM '2003 2
 On Selfish Routing In Internet-like Environments Lili Qiu (Microsoft Research) Yang Richard Yang (Yale University) Yin Zhang (AT&T Labs Research) Scott Shenker (ICSI) ACM SIGCOMM 2003 Presented by Giang
On Selfish Routing In Internet-like Environments Lili Qiu (Microsoft Research) Yang Richard Yang (Yale University) Yin Zhang (AT&T Labs Research) Scott Shenker (ICSI) ACM SIGCOMM 2003 Presented by Giang
Convex Optimization and Machine Learning
 Convex Optimization and Machine Learning Mengliu Zhao Machine Learning Reading Group School of Computing Science Simon Fraser University March 12, 2014 Mengliu Zhao SFU-MLRG March 12, 2014 1 / 25 Introduction
Convex Optimization and Machine Learning Mengliu Zhao Machine Learning Reading Group School of Computing Science Simon Fraser University March 12, 2014 Mengliu Zhao SFU-MLRG March 12, 2014 1 / 25 Introduction
Cross-Monotonic Multicast
 Cross-Monotonic Multicast Zongpeng Li Department of Computer Science University of Calgary April 17, 2008 1 Multicast Multicast models one-to-many data dissemination in a computer network Example: live
Cross-Monotonic Multicast Zongpeng Li Department of Computer Science University of Calgary April 17, 2008 1 Multicast Multicast models one-to-many data dissemination in a computer network Example: live
Activity Graphical Analysis with Excel and Logger Pro
 Activity Graphical Analysis with Excel and Logger Pro Purpose Vernier s Logger Pro is a graphical analysis software that will allow you to collect, graph and manipulate data. Microsoft s Excel is a spreadsheet
Activity Graphical Analysis with Excel and Logger Pro Purpose Vernier s Logger Pro is a graphical analysis software that will allow you to collect, graph and manipulate data. Microsoft s Excel is a spreadsheet
