Lecture Notes of Möbuis Transformation in Hyperbolic Plane
|
|
|
- Solomon Walters
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Applied Mathematis, 04, 5, 6-5 Published Online August 04 in SiRes Leture Notes of Möbuis Transformation in Hyperboli Plane Rania B M Amer Department of Engineering Mathematis and Physis, Faulty of Engineering, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt drraniaamer@yahooom Reeived 6 May 04; revised July 04; aepted 4 July 04 Copyright 04 by author and Sientifi Researh Publishing In This work is liensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International Liense (CC BY Abstrat In this paper, I have provided a brief introdution on Möbius transformation and explored some basi properties of this kind of transformation For instane, Möbius transformation is lassified aording to the invariant points Moreover, we an see that Möbius transformation is hyperboli isometries that form a group ation PSL (,R on the upper half plane model Keywords The Upper Half-Plane Model, Möbius Transformation, Hyperboli Distane, Fixed Points, The Group PSL (,R Introdution Möbius transformations have appliations to problems in physis, engineering and mathematis Furthermore, the onformal mapping is represented as bilinear translation, linear frational transformation and Mobius transformation Möbius transformations are also alled homographi transformations, linear frational transformations, or frational linear transformations and it is a bijetive holomorphi funtion (onformal map [] [] The purpose of this paper is studied the properties of Möbius transformations in detail, and some definitions and theorems are given The basi properties of these transformations are introdued and lassified aording to the invariant points Möbius transformations are formed a group ation PSL (,R on the upper half plane model A Möbius transformation of the plane is a map f: C C f ( z, a, b,, d C and ad b 0 (- whih sending eah point to a orresponding point, where z is the omplex variable and the oeffiients a, b,, d How to ite this paper: Amer, RBM (04 Leture Notes of Möbuis Transformation in Hyperboli Plane Applied Mathematis, 5, 6-5
2 are omplex numbers [3] Definition (- The upper half plane model is defined by the set and the boundary of is defined by { z Im ( z 0} { x iy y 0} > + > (- { z Im ( z 0} { } { x iy y 0} { } + (-3 The lines (geodesis are vertial rays and semiirles orthogonal to H The angles are Eulidean angles Definition (- A Möbius transformations form a group whih is denoted by Mob ( Remark (-3 Sine Möbius transformation takes the form f ( z d d a+ bz If the point z, this means f so f ( and we get the following: + d z a 0, z z f If 0 f (, d a 3 If 0 f & f ( Lemma (-4 A Möbius transformation onsists of four omposition funtions Proof The four funtions are: d d translation by f ( z z + ; inversion and refletion with respet to real axis f ( z, f z then the plane inside turn out and the lines on the plane are lines or irles and right angles stay true and also the irles are irles; ( ad b 3 dilation and rotation f3( z f ( z ; a a 4 translation by f4( z f3 ( z +, ad b a ad b + a f4 f 3 f f + (-4 Remark (-5 We an write Möbius transformations as follows then f ( z a ad ( + b The inverse Möbius transformation is evaluated from the inverse of the metri A a b d b d a A (-5 7
3 f ( z Theorem (-6 Möbius transformations also preserve ross ratio Proof Given four distint points z, z, z 3, z 4, their ross ratio is defined by ( z z3 z z4 Z Z Z3 Z4 z z z3 z4 ( z z ( z z dz b (-6 z + a, ;,, ;, 3 4 The ross ratio is invariant of the group of all Möbius transformation so if we transform the four points z i into z i by an inversion, the ross ratio of these points are taken into its onjugate value, and the ross ratio is invariant under a produt of two or any even number of inversions and exhanging any two pairs of oordinates preserves the ross-ratio Then ( z z z z ( z z z z ( z z z z ( z z z z ( z z3( z z4 ( z z ( z z, ;,, ;,, ;,, ;, 3 4 Sine translation, rotation and dilation preserve ross ratio and Möbius transformation onsists of them so Möbius transformation preserves ross ratio Corollary (-7 If z 0, i,,3, 4, we get and therefore i ( ZZ, ; Z, Z ( zz, ; z, z 3 3 If any one of z i 0 for example z 3 0, then z z z z z ( z z( z z3 ( z z ( z z ( z z z 4 ;, ; 3, 4, z z z z z 3 ( z z z 4 ;, ; 3, 4, 3 4 3, ;, ( z, z; z3, z4 z z z3 z4 z z z z z z z z ( z z z ( z z z, ;, ;, 4;,, ;0, Sine the trae of matrix A is tr(a a + b and this trae is invariant under onjugation, this is mean, tr ( gag tr ( A (-7 (-8 (-9 (-0 (- (- (-3 Every Möbius transformation an be represented by normalized matrix A suh that its determinant equal one whih mean ad b Lemma (-8 Two Möbius transformations A, B with det A det B are onjugate if and only if Poof Let tr ( A tr ( B (-4 A a a, B b b a a b b
4 Sine matrix A and B are Möbius transformations, then Sine det A det B, then If and only if tr ( A tr ( B det A aa aa, 4 3 det B bb bb 4 3 aa a a bb bb, ( A a + a ( A ( a + a tr tr, 4 4 ( B b + b ( B ( b + b tr tr 4 4 then matrix A and matrix B must be onjugate The Fixed Points in Mobius Transformation Sine fixed points (ie invariant points is defined by f(z z, then z z a d z b 0, then the fixed points are given by A Möbius transformation is f ( z This mean z, a d ± a d + 4b ( a d ± ( a + d 4( ad b ( a d ( A ± tr 4 (-5 For non paraboli transformation, there are two fixed points 0, but for paraboli transformation, there is only fixed points beause the fixed points are oinide 3 The Types of Mobius Transformations There are Paraboli, ellipti, hyperboli and loxodromi whih are distinguished by looking at the trae tr(a a + b 3 For Paraboli Transformations tr (A 4, the paraboli Möbius transformations forms subgroup isomorphi to the group of matries PSL, [4], ( a a, (-6 0 whih desribes a translation z z+ a and this transformation is orientation preserving 3 For Hyperboli Transformations tr ( A 4 ( PSL(,, the hyperboli Möbius transformations forms subgroup isomorphi to the group of matries whih desribes a rotation θ e 0 0 e θ θ z e z and this transformation is orientation preserving, (-7 9
5 33 For Ellipti Transformations 4 tr ( A 0 ( PSL(, whih desribes a rotation, the ellipti Möbius transformations forms subgroup isomorphi to the group of matries 34 For Loxodromi Transformations tr ( A [ 0, 4] ( PSL(, z iθ e 0 0 e iθ e i θ z and this transformation is orientation preserving, (-8, the Loxodromi Möbius transformations forms subgroup isomorphi to the group of matries, k 0 0, (-9 k whih desribes a dilation (homothety z kz and this transformation is orientation preserving The differene between orientation preserving (invariant and orientation reversing: Rotation and translation are orientation-preserving Refletion and glide-refletion are orientation-reversing 3 A omposition of orientation-preserving funtions is orientation-preserving 4 A omposition of two orientation-reversing funtions is orientation-preserving 5 A omposition of one orientation-preserving funtion and one orientation-reversing funtion is orientationreversing 6 The determinant of the matrix A (whih mentioned above then the orientation-preserving but if the determinant of the matrix A then the orientation reversing f z suh that ad b f z with ad b 7 is orientation-preserving but is orientation-reversing, where z x + iy whih mean the point z in the imaginary axis 8 In Orientation preserving all non ollinear points A, B, C, the proper angle measures of the angles ABC and A'B'C' have the same sign but in orientation reversing all non ollinear points A, B, C, the proper angle measures of the angles ABC and A'B'C' have opposite signs 9 Orientation preserving isometries takes ounterlokwise angles to ounterlokwise angles, and it takes lokwise angles to lokwise angles An orientation reversing isometries takes ounterlokwise angles to lokwise angles, and it takes lokwise angles to ounterlokwise angles 4 Isometries in Mobius Transformation Definition (4- The group PSL(, [4] is the projetive speial linear group of dimension over the real numbers and the determinant of the elements of that group may be or so PSL(, SL(, ± and this group at on osα sinα by Möbius transformations and also the matries of this group onjugate to the matrix sinα osα suh that α [ 0, π] from the Jordan and normal form of a real by matrix and therefore the determinants of these matries must equal, we an see that the absolute value of the traes ( tr a+ b of the matries will be respetively less than, alled ellipti, greater than, alled hyperboli, and equal to, alled paraboli Definition (4- Let γ ( t x( t + iy ( t be path so the hyperboli distane between two points (a, b on the upper half plane dx + dy t x ( t + y ( t with metri ds is defined by infimum of dt t y whih an be written as y 0
6 ( 0 ( + t x t y t hyp (, inf hyp ( γ inf d t d t t L t t y γ γ t t (-0 Remark (4-3 From this definition the geodesi between two points (x 0, y and (x 0, y on the vertial line with y > y has length ln(y /y but if two points do not lie on a vertial line so the geodesis is irular ar with enter on the x-axis as seen in Figure Remark (4-4 From the definition (- we an define the isometry of hyperboli plane as follows: Let a mapping f: and let A and B two points in, the mapping f is an isometry if the hyperboli distane d( AB, d( f( A, f( B Theorem (4-4 Möbius transformations at isometries in this mean PSL(, ats isometry on upper half plane by Möbius transformations Proof Möbius transformations preserve distane A bijetive map that preserves distane is alled an isometry beause an isometry is a transformation whih preserves distane Thus Möbius transformations are isometries of H A seond proof Sine the form of Möbius transformations are f ( z, differentiate this form yields to a ( dz f ( z dz df ( z dz ( ( Sine z z iy x + iy ( x iy z z iy z z Then ( z z ( z z dd z z dz dz dx + dy dx + dy y y (- From this equation we remark that Möbius transformations preserve the hyperboli metri so that Möbius transformations are hyperboli isometries A third proof From the definition of hyperboli distane, we want to show that Lhyp f ( γ ( t Lhyp ( γ ( t dz dzdz dx + d y, y Im z y Im z so the hyperboli metri is defined by Sine dx + dy dz dd z z ds, sine the right hand side y Im z z Im Figure The plane as boundary of half spae model of hyperboli spae
7 Let f ( z hyp γ, then ( γ ( x ( t + ( y ( t y( t ( γ L t dt Re( γ ( t Im ( γ ( t + Im dγdγ d t Im ( γ ( t azz + adz + bz + bd a z + adz + bz + bd γ dt (- (-3 and from ad b, then Sine the left hand side is Sine f ( γ Then hyp ( ( γ L f t aγ + b dγ d f( γ γ + d + d ( ( γ ( γ y Im( γ ( γ df ( γ ( γ (-4 d f (-5 0 Im and so df ( γ dγ ( γ + d d f ( γ df ( γ ( γ + d ( γ + d dγdγ γ + d dγdγ d d d 0 Im ( γ y (-6 γ + d y( t Im ( γ hyp dγ L f t t t t γ + d We get the left hand side equal the right hand side, and then the proof is omplete Lemma (4-5 Let Mobius transformations f ( z γ, then Proof The right hand side y Im γ Im z y ( γ dγ dz dγ dγ Im γ whih implies (-7 Im z Im dz Im z ( + + dγ a dz z d z d We get the left hand side equal the right hand side, and then the proof is omplete Remark (4-6 The group PSL(, ats on by Mobius transformation And therefore the left hand side
8 a b az b z + d This ation is faithful and and at disontinuously on so we an write Mob ( PSL(, Isom + Mob Isom + (-8 PSL, isomorphi to the group of all orientation preserving isometris of This mean whih preserve the hyperboli geometry of and therefore the elements in Möbius transformation at by isometries in [5] Theorem (4-7 All orientation-preserving isometries of are Mobius transformations, and all orientation-reversing isometries of are the omposition of a Mobius transformation and refletion through the imaginary axis Proof Isom whih identified with the group of Mobius transformations, and the group of orientation preserving isometries whih is the distane preserving maps are the Mobius transformations whih preserve and is denoted by Isom + ( whih identified with PSL(, PSL, ats on the boundary of the upper half plane by The isometry group of hyperboli plane is denoted by suh that and then, we get: a b az b z + d Mob ( : a, b,, d, ad b z + d a b : a, b,, d, ad b d : PSL, ( (-9 (-30 Let f(z is an isometry of, and by applying the transformations (rotation z kz and inversion z /z, we assume that :(, (, :(,0 (,0 g f z i i i i (-3 Let z, z be two points lie in positive imaginary axis Let the point z not lie in positive imaginary axis and draw two hyperboli irles with enter z and z and passing through z, we find these irles interset in z, z z and these irles are mapped into themselves under the isometry g f ( z so g f ( z z or z The first ase: If g f ( z z, we get f ( z suh that a, b,, d, ad b, whih is the orientation rez + d serving isometries is given by the map z z, that is the refletion in the imaginary axis and by omposition this with Möbius transformations This means all orientation-reversing isometries of are the omposition of a Mobius transformation and refletion through the imaginary axis suh that the refletions are isometries that have infinitely many fixed lie on the mirror line The seond ase: If g f ( z z, we get f ( z suh that a, b,, d, ad b, whih is the orientation prez + d serving isometries is given by the rotation z kz and inversion z /z This means all orientation-preserving isometry of are Mobius transformations and as we know Mobius transformations onsist of a rotation inversion and a translation Theorem (4-8 Möbius transformations preserve irles and lines (Figure Proof Let the transformation w /z is an inversion and every Möbius transformation (Figure 3 f(z of the form ( is a omposition of finitely many similarities and inversions [6]-[9] Sine w u + iv and z x + iy, then 3
9 Figure Cirle-preserving maps from the plane to itself Figure 3 Möbius transformation is omposition of multiple inversions From the equation of the irle x y u v u, v, x, y x + y x + y u + v u + v But if A 0, it is a line, if A 0, it is a irle (-3 A x + y + Bx + Cy + D 0 (-33 We an write again the Equation (-33 wrt u, v as follows A Bu Cv D( u v , whih is the equation of a irle If D 0, it is a line, if D 0, it is a irle So Möbius transformations preserve irles and lines Remark (4-9 From the last theorem (-5, we find that the irle goes through the origin may be mapped to the irle or the line Theorem (4-0 Möbius transformations preserve distane Proof From theorem (- Möbius transformations at isometries in and from definition of isometries we get that the distane between any two points in the hyperboli plane is invariant by Möbius transformations and Möbius transformations preserve irles (from translation and inversion and angles so Möbius transformations preserve distane 5 Conlusion The properties of Möbius transformations are introdued in detail, and some definitions and theorems are given to show that Möbius transformations are one-to-one, onto and onformal mapping Also, Möbius transformations map irles to irles and also, map the real line to the real line suh that the oeffiients a, b, and d are real Every orientation-preserving isometris of the hyperboli plane is Möbius transformations Every orientation-reversing isometris of the hyperboli plane is a omposition of Möbius transformations and refletion 4
10 Mob( is a group under omposition and Möbius transformations map the upper half-plane to itself bijetively So Möbius transformation maps vertial straight lines in and irles in with real enters to vertial straight lines and irles with real enters Furthermore, the onnetions between Möbius transformations, isometries of the hyperboli plane, and PSL(; R are presented Aknowledgements I wish to express my gratitude towards to Professor Dr William M Goldman, University of Maryland and Distinguished Sholar-Teaher Professor, Department of Mathematis, for his valuable, guidane, patiene and support I onsider myself very fortunate for being able to work with a very onsiderate and enouraging professor like him Referenes [] Yilmaz, N (009 On Some Mapping Properties of Möbius Transformations The Australian Journal of Mathematial Analysis and Appliations, 6, -8 [] Nehari, Z (95 Conformal Mapping MGraw-Hill Book, New York [3] John, O (00 The Geometry of Möbius Transformations University of Rohester, Rohester [4] Graeme, KO (0 Random Disrete Groups in the Spae of Möbuis Transformations Ms Thesis, Massey University, Albany [5] Aramayona, J (0 Hyperboli Strutures on Surfaes Leture Notes Series, IMS, NUS, 9 [6] Beardon, AF (995 The Geometry of Disrete Groups, Graduate Texts in Mathematis, 9 Springer-Verlag, New York [7] Jones, GA and Singerman, D (987 Complex Funtions, an Algebrai and Geometri Viewpoint Cambridge University Press, Cambridge [8] Lehner, J (964 Disontinuous Groups and Automorphi Funtions, Mathematial Surveys, 8 Amerian Mathematial Soiety, Providene [9] Seppälä, M and Sorvali, T (99 Geometry of Riemann Surfaes and Teihmüller Spaes, Chapter Elsevier Siene Publishing Company, INC, New York, -58 5
11 Sientifi Researh Publishing (SCIRP is one of the largest Open Aess journal publishers It is urrently publishing more than 00 open aess, online, peer-reviewed journals overing a wide range of aademi disiplines SCIRP serves the worldwide aademi ommunities and ontributes to the progress and appliation of siene with its publiation Other seleted journals from SCIRP are listed as below Submit your manusript to us via either submit@sirporg or Online Submission Portal
1. Inversions. A geometric construction relating points O, A and B looks as follows.
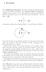 1. Inversions. 1.1. Definitions of inversion. Inversion is a kind of symmetry about a irle. It is defined as follows. he inversion of degree R 2 entered at a point maps a point to the point on the ray
1. Inversions. 1.1. Definitions of inversion. Inversion is a kind of symmetry about a irle. It is defined as follows. he inversion of degree R 2 entered at a point maps a point to the point on the ray
Gray Codes for Reflectable Languages
 Gray Codes for Refletable Languages Yue Li Joe Sawada Marh 8, 2008 Abstrat We lassify a type of language alled a refletable language. We then develop a generi algorithm that an be used to list all strings
Gray Codes for Refletable Languages Yue Li Joe Sawada Marh 8, 2008 Abstrat We lassify a type of language alled a refletable language. We then develop a generi algorithm that an be used to list all strings
Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ow.mit.edu 1.510 Introdution to Seismology Spring 008 For information about iting these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ow.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Leture Notes 3.3.007
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ow.mit.edu 1.510 Introdution to Seismology Spring 008 For information about iting these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ow.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Leture Notes 3.3.007
Colouring contact graphs of squares and rectilinear polygons de Berg, M.T.; Markovic, A.; Woeginger, G.
 Colouring ontat graphs of squares and retilinear polygons de Berg, M.T.; Markovi, A.; Woeginger, G. Published in: nd European Workshop on Computational Geometry (EuroCG 06), 0 Marh - April, Lugano, Switzerland
Colouring ontat graphs of squares and retilinear polygons de Berg, M.T.; Markovi, A.; Woeginger, G. Published in: nd European Workshop on Computational Geometry (EuroCG 06), 0 Marh - April, Lugano, Switzerland
Directed Rectangle-Visibility Graphs have. Abstract. Visibility representations of graphs map vertices to sets in Euclidean space and
 Direted Retangle-Visibility Graphs have Unbounded Dimension Kathleen Romanik DIMACS Center for Disrete Mathematis and Theoretial Computer Siene Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey P.O. Box 1179,
Direted Retangle-Visibility Graphs have Unbounded Dimension Kathleen Romanik DIMACS Center for Disrete Mathematis and Theoretial Computer Siene Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey P.O. Box 1179,
Vertex Unfoldings of Orthogonal Polyhedra: Positive, Negative, and Inconclusive Results
 CCCG 2018, Winnipeg, Canada, August 8 10, 2018 Vertex Unfoldings of Orthogonal Polyhedra: Positive, Negative, and Inonlusive Results Luis A. Garia Andres Gutierrrez Isaa Ruiz Andrew Winslow Abstrat We
CCCG 2018, Winnipeg, Canada, August 8 10, 2018 Vertex Unfoldings of Orthogonal Polyhedra: Positive, Negative, and Inonlusive Results Luis A. Garia Andres Gutierrrez Isaa Ruiz Andrew Winslow Abstrat We
p[4] p[3] p[2] p[1] p[0]
![p[4] p[3] p[2] p[1] p[0] p[4] p[3] p[2] p[1] p[0]](/thumbs/89/99614723.jpg) CMSC 425 : Sring 208 Dave Mount and Roger Eastman Homework Due: Wed, Marh 28, :00m. Submit through ELMS as a df file. It an either be distilled from a tyeset doument or handwritten, sanned, and enhaned
CMSC 425 : Sring 208 Dave Mount and Roger Eastman Homework Due: Wed, Marh 28, :00m. Submit through ELMS as a df file. It an either be distilled from a tyeset doument or handwritten, sanned, and enhaned
We P9 16 Eigenray Tracing in 3D Heterogeneous Media
 We P9 Eigenray Traing in 3D Heterogeneous Media Z. Koren* (Emerson), I. Ravve (Emerson) Summary Conventional two-point ray traing in a general 3D heterogeneous medium is normally performed by a shooting
We P9 Eigenray Traing in 3D Heterogeneous Media Z. Koren* (Emerson), I. Ravve (Emerson) Summary Conventional two-point ray traing in a general 3D heterogeneous medium is normally performed by a shooting
arxiv: v1 [cs.gr] 10 Apr 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cs.gr] 10 Apr 2015 arxiv: v1 [cs.gr] 10 Apr 2015](/thumbs/92/109500704.jpg) REAL-TIME TOOL FOR AFFINE TRANSFORMATIONS OF TWO DIMENSIONAL IFS FRACTALS ELENA HADZIEVA AND MARIJA SHUMINOSKA arxiv:1504.02744v1 s.gr 10 Apr 2015 Abstrat. This work introdues a novel tool for interative,
REAL-TIME TOOL FOR AFFINE TRANSFORMATIONS OF TWO DIMENSIONAL IFS FRACTALS ELENA HADZIEVA AND MARIJA SHUMINOSKA arxiv:1504.02744v1 s.gr 10 Apr 2015 Abstrat. This work introdues a novel tool for interative,
LAMC Junior Circle April 15, Constructing Triangles.
 LAMC Junior Cirle April 15, 2012 Olga Radko radko@math.ula.edu Oleg Gleizer oleg1140@gmail.om Construting Triangles. Copyright: for home use only. This handout is a part of the book in preparation. Using
LAMC Junior Cirle April 15, 2012 Olga Radko radko@math.ula.edu Oleg Gleizer oleg1140@gmail.om Construting Triangles. Copyright: for home use only. This handout is a part of the book in preparation. Using
Year 11 GCSE Revision - Re-visit work
 Week beginning 6 th 13 th 20 th HALF TERM 27th Topis for revision Fators, multiples and primes Indies Frations, Perentages, Deimals Rounding 6 th Marh Ratio Year 11 GCSE Revision - Re-visit work Understand
Week beginning 6 th 13 th 20 th HALF TERM 27th Topis for revision Fators, multiples and primes Indies Frations, Perentages, Deimals Rounding 6 th Marh Ratio Year 11 GCSE Revision - Re-visit work Understand
Smooth Trajectory Planning Along Bezier Curve for Mobile Robots with Velocity Constraints
 Smooth Trajetory Planning Along Bezier Curve for Mobile Robots with Veloity Constraints Gil Jin Yang and Byoung Wook Choi Department of Eletrial and Information Engineering Seoul National University of
Smooth Trajetory Planning Along Bezier Curve for Mobile Robots with Veloity Constraints Gil Jin Yang and Byoung Wook Choi Department of Eletrial and Information Engineering Seoul National University of
A DYNAMIC ACCESS CONTROL WITH BINARY KEY-PAIR
 Malaysian Journal of Computer Siene, Vol 10 No 1, June 1997, pp 36-41 A DYNAMIC ACCESS CONTROL WITH BINARY KEY-PAIR Md Rafiqul Islam, Harihodin Selamat and Mohd Noor Md Sap Faulty of Computer Siene and
Malaysian Journal of Computer Siene, Vol 10 No 1, June 1997, pp 36-41 A DYNAMIC ACCESS CONTROL WITH BINARY KEY-PAIR Md Rafiqul Islam, Harihodin Selamat and Mohd Noor Md Sap Faulty of Computer Siene and
Detection and Recognition of Non-Occluded Objects using Signature Map
 6th WSEAS International Conferene on CIRCUITS, SYSTEMS, ELECTRONICS,CONTROL & SIGNAL PROCESSING, Cairo, Egypt, De 9-31, 007 65 Detetion and Reognition of Non-Oluded Objets using Signature Map Sangbum Park,
6th WSEAS International Conferene on CIRCUITS, SYSTEMS, ELECTRONICS,CONTROL & SIGNAL PROCESSING, Cairo, Egypt, De 9-31, 007 65 Detetion and Reognition of Non-Oluded Objets using Signature Map Sangbum Park,
Introduction to Complex Analysis
 Introduction to Complex Analysis George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 413 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Complex Analysis October 2014 1 / 50 Outline
Introduction to Complex Analysis George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 413 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Complex Analysis October 2014 1 / 50 Outline
Development Length: Compression Bars
 CHAPTER Reinfored Conrete Design Fifth Edition DEVELOPMENT, SPLICES, AND SIMPLE SPAN BAR CUTOFFS A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Part I Conrete Design
CHAPTER Reinfored Conrete Design Fifth Edition DEVELOPMENT, SPLICES, AND SIMPLE SPAN BAR CUTOFFS A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Part I Conrete Design
Algorithms for External Memory Lecture 6 Graph Algorithms - Weighted List Ranking
 Algorithms for External Memory Leture 6 Graph Algorithms - Weighted List Ranking Leturer: Nodari Sithinava Sribe: Andi Hellmund, Simon Ohsenreither 1 Introdution & Motivation After talking about I/O-effiient
Algorithms for External Memory Leture 6 Graph Algorithms - Weighted List Ranking Leturer: Nodari Sithinava Sribe: Andi Hellmund, Simon Ohsenreither 1 Introdution & Motivation After talking about I/O-effiient
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 6
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 6 Unit 6 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS MATH 1206 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS INTRODUCTION 3 1. TRIGONOMETRY OF OBLIQUE TRIANGLES 5 LAW OF SINES 5 AMBIGUITY AND AREA OF A TRIANGLE
MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 6 Unit 6 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS MATH 1206 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS INTRODUCTION 3 1. TRIGONOMETRY OF OBLIQUE TRIANGLES 5 LAW OF SINES 5 AMBIGUITY AND AREA OF A TRIANGLE
HIGHER ORDER full-wave three-dimensional (3-D) large-domain techniques in
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NIŠ) SER.: ELEC. ENERG. vol. 21, no. 2, August 2008, 209-220 Comparison of Higher Order FEM and MoM/SIE Approahes in Analyses of Closed- and Open-Region Eletromagneti Problems Milan
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NIŠ) SER.: ELEC. ENERG. vol. 21, no. 2, August 2008, 209-220 Comparison of Higher Order FEM and MoM/SIE Approahes in Analyses of Closed- and Open-Region Eletromagneti Problems Milan
Drawing lines. Naïve line drawing algorithm. drawpixel(x, round(y)); double dy = y1 - y0; double dx = x1 - x0; double m = dy / dx; double y = y0;
 Naïve line drawing algorithm // Connet to grid points(x0,y0) and // (x1,y1) by a line. void drawline(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1) { int x; double dy = y1 - y0; double dx = x1 - x0; double m = dy / dx;
Naïve line drawing algorithm // Connet to grid points(x0,y0) and // (x1,y1) by a line. void drawline(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1) { int x; double dy = y1 - y0; double dx = x1 - x0; double m = dy / dx;
Rotation Invariant Spherical Harmonic Representation of 3D Shape Descriptors
 Eurographis Symposium on Geometry Proessing (003) L. Kobbelt, P. Shröder, H. Hoppe (Editors) Rotation Invariant Spherial Harmoni Representation of 3D Shape Desriptors Mihael Kazhdan, Thomas Funkhouser,
Eurographis Symposium on Geometry Proessing (003) L. Kobbelt, P. Shröder, H. Hoppe (Editors) Rotation Invariant Spherial Harmoni Representation of 3D Shape Desriptors Mihael Kazhdan, Thomas Funkhouser,
Cambridge University Press Hyperbolic Geometry from a Local Viewpoint Linda Keen and Nikola Lakic Excerpt More information
 Introduction Geometry is the study of spatial relationships, such as the familiar assertion from elementary plane Euclidean geometry that, if two triangles have sides of the same lengths, then they are
Introduction Geometry is the study of spatial relationships, such as the familiar assertion from elementary plane Euclidean geometry that, if two triangles have sides of the same lengths, then they are
A Unique Common Fixed Point Theorem in Cone Metric Type Spaces
 Universal Journal of Applied Mathematis (): 33-38, 03 DOI: 0.389/ujam.03.000 http://www.hrpub.org A Unique Common Fixed Point Theorem in Cone Metri Type Spaes K. P. R. Rao, G.N.V.Kishore,, P.R.Sobhana
Universal Journal of Applied Mathematis (): 33-38, 03 DOI: 0.389/ujam.03.000 http://www.hrpub.org A Unique Common Fixed Point Theorem in Cone Metri Type Spaes K. P. R. Rao, G.N.V.Kishore,, P.R.Sobhana
2. Triangle ABC and triangle DEF are graphed on the set of axes below. 3. Quadrilateral ABCD is graphed on the set of axes below.
 Review Session 1 Pratie Problems l. The verties of AJKL have oordinates J(5,1), K( 2, 3), and Under whih transformation is the image AJ'K t L t not ongruent to AJKL? l) a translation of two units to the
Review Session 1 Pratie Problems l. The verties of AJKL have oordinates J(5,1), K( 2, 3), and Under whih transformation is the image AJ'K t L t not ongruent to AJKL? l) a translation of two units to the
CleanUp: Improving Quadrilateral Finite Element Meshes
 CleanUp: Improving Quadrilateral Finite Element Meshes Paul Kinney MD-10 ECC P.O. Box 203 Ford Motor Company Dearborn, MI. 8121 (313) 28-1228 pkinney@ford.om Abstrat: Unless an all quadrilateral (quad)
CleanUp: Improving Quadrilateral Finite Element Meshes Paul Kinney MD-10 ECC P.O. Box 203 Ford Motor Company Dearborn, MI. 8121 (313) 28-1228 pkinney@ford.om Abstrat: Unless an all quadrilateral (quad)
Extracting Partition Statistics from Semistructured Data
 Extrating Partition Statistis from Semistrutured Data John N. Wilson Rihard Gourlay Robert Japp Mathias Neumüller Department of Computer and Information Sienes University of Strathlyde, Glasgow, UK {jnw,rsg,rpj,mathias}@is.strath.a.uk
Extrating Partition Statistis from Semistrutured Data John N. Wilson Rihard Gourlay Robert Japp Mathias Neumüller Department of Computer and Information Sienes University of Strathlyde, Glasgow, UK {jnw,rsg,rpj,mathias}@is.strath.a.uk
What is a vector in hyperbolic geometry? And, what is a hyperbolic linear transformation?
 What is a vector in hyperbolic geometry? And, what is a hyperbolic linear transformation? Ken Li, Dennis Merino, and Edgar N. Reyes Southeastern Louisiana University Hammond, LA USA 70402 1 Introduction
What is a vector in hyperbolic geometry? And, what is a hyperbolic linear transformation? Ken Li, Dennis Merino, and Edgar N. Reyes Southeastern Louisiana University Hammond, LA USA 70402 1 Introduction
Chromaticity-matched Superimposition of Foreground Objects in Different Environments
 FCV216, the 22nd Korea-Japan Joint Workshop on Frontiers of Computer Vision Chromatiity-mathed Superimposition of Foreground Objets in Different Environments Yohei Ogura Graduate Shool of Siene and Tehnology
FCV216, the 22nd Korea-Japan Joint Workshop on Frontiers of Computer Vision Chromatiity-mathed Superimposition of Foreground Objets in Different Environments Yohei Ogura Graduate Shool of Siene and Tehnology
Supplementary Material: Geometric Calibration of Micro-Lens-Based Light-Field Cameras using Line Features
 Supplementary Material: Geometri Calibration of Miro-Lens-Based Light-Field Cameras using Line Features Yunsu Bok, Hae-Gon Jeon and In So Kweon KAIST, Korea As the supplementary material, we provide detailed
Supplementary Material: Geometri Calibration of Miro-Lens-Based Light-Field Cameras using Line Features Yunsu Bok, Hae-Gon Jeon and In So Kweon KAIST, Korea As the supplementary material, we provide detailed
Naïve Bayesian Rough Sets Under Fuzziness
 IJMSA: Vol. 6, No. 1-2, January-June 2012, pp. 19 25 Serials Publiations ISSN: 0973-6786 Naïve ayesian Rough Sets Under Fuzziness G. GANSAN 1,. KRISHNAVNI 2 T. HYMAVATHI 3 1,2,3 Department of Mathematis,
IJMSA: Vol. 6, No. 1-2, January-June 2012, pp. 19 25 Serials Publiations ISSN: 0973-6786 Naïve ayesian Rough Sets Under Fuzziness G. GANSAN 1,. KRISHNAVNI 2 T. HYMAVATHI 3 1,2,3 Department of Mathematis,
274 Curves on Surfaces, Lecture 5
 274 Curves on Surfaces, Lecture 5 Dylan Thurston Notes by Qiaochu Yuan Fall 2012 5 Ideal polygons Previously we discussed three models of the hyperbolic plane: the Poincaré disk, the upper half-plane,
274 Curves on Surfaces, Lecture 5 Dylan Thurston Notes by Qiaochu Yuan Fall 2012 5 Ideal polygons Previously we discussed three models of the hyperbolic plane: the Poincaré disk, the upper half-plane,
Plot-to-track correlation in A-SMGCS using the target images from a Surface Movement Radar
 Plot-to-trak orrelation in A-SMGCS using the target images from a Surfae Movement Radar G. Golino Radar & ehnology Division AMS, Italy ggolino@amsjv.it Abstrat he main topi of this paper is the formulation
Plot-to-trak orrelation in A-SMGCS using the target images from a Surfae Movement Radar G. Golino Radar & ehnology Division AMS, Italy ggolino@amsjv.it Abstrat he main topi of this paper is the formulation
Total 100
 CS331 SOLUTION Problem # Points 1 10 2 15 3 25 4 20 5 15 6 15 Total 100 1. ssume you are dealing with a ompiler for a Java-like language. For eah of the following errors, irle whih phase would normally
CS331 SOLUTION Problem # Points 1 10 2 15 3 25 4 20 5 15 6 15 Total 100 1. ssume you are dealing with a ompiler for a Java-like language. For eah of the following errors, irle whih phase would normally
Chemical, Biological and Radiological Hazard Assessment: A New Model of a Plume in a Complex Urban Environment
 hemial, Biologial and Radiologial Haard Assessment: A New Model of a Plume in a omplex Urban Environment Skvortsov, A.T., P.D. Dawson, M.D. Roberts and R.M. Gailis HPP Division, Defene Siene and Tehnology
hemial, Biologial and Radiologial Haard Assessment: A New Model of a Plume in a omplex Urban Environment Skvortsov, A.T., P.D. Dawson, M.D. Roberts and R.M. Gailis HPP Division, Defene Siene and Tehnology
Some irrational polygons have many periodic billiard paths
 Some irrational polygons have many periodic billiard paths W. Patrick Hooper Northwestern University Spring Topology and Dynamics Conference Milwaukee, Wisconsin March 5, 8 Lower bounds on growth rates
Some irrational polygons have many periodic billiard paths W. Patrick Hooper Northwestern University Spring Topology and Dynamics Conference Milwaukee, Wisconsin March 5, 8 Lower bounds on growth rates
Notes on Spherical Geometry
 Notes on Spherical Geometry Abhijit Champanerkar College of Staten Island & The Graduate Center, CUNY Spring 2018 1. Vectors and planes in R 3 To review vector, dot and cross products, lines and planes
Notes on Spherical Geometry Abhijit Champanerkar College of Staten Island & The Graduate Center, CUNY Spring 2018 1. Vectors and planes in R 3 To review vector, dot and cross products, lines and planes
Math 407 Solutions to Exam 3 April 24, Let f = u + iv, and let Γ be parmetrized by Γ = (x (t),y(t)) = x (t) +iy (t) for a t b.
 Math 7 Solutions to Exam 3 April, 3 1. (1 Define the following: (a f (z dz, where Γ is a smooth curve with finite length. Γ Let f u + iv, and let Γ be parmetrized by Γ (x (t,y(t x (t +iy (t for a t b.
Math 7 Solutions to Exam 3 April, 3 1. (1 Define the following: (a f (z dz, where Γ is a smooth curve with finite length. Γ Let f u + iv, and let Γ be parmetrized by Γ (x (t,y(t x (t +iy (t for a t b.
Exploring the Commonality in Feature Modeling Notations
 Exploring the Commonality in Feature Modeling Notations Miloslav ŠÍPKA Slovak University of Tehnology Faulty of Informatis and Information Tehnologies Ilkovičova 3, 842 16 Bratislava, Slovakia miloslav.sipka@gmail.om
Exploring the Commonality in Feature Modeling Notations Miloslav ŠÍPKA Slovak University of Tehnology Faulty of Informatis and Information Tehnologies Ilkovičova 3, 842 16 Bratislava, Slovakia miloslav.sipka@gmail.om
An Efficient and Scalable Approach to CNN Queries in a Road Network
 An Effiient and Salable Approah to CNN Queries in a Road Network Hyung-Ju Cho Chin-Wan Chung Dept. of Eletrial Engineering & Computer Siene Korea Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology 373- Kusong-dong,
An Effiient and Salable Approah to CNN Queries in a Road Network Hyung-Ju Cho Chin-Wan Chung Dept. of Eletrial Engineering & Computer Siene Korea Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology 373- Kusong-dong,
7. The Gauss-Bonnet theorem
 7. The Gauss-Bonnet theorem 7.1 Hyperbolic polygons In Euclidean geometry, an n-sided polygon is a subset of the Euclidean plane bounded by n straight lines. Thus the edges of a Euclidean polygon are formed
7. The Gauss-Bonnet theorem 7.1 Hyperbolic polygons In Euclidean geometry, an n-sided polygon is a subset of the Euclidean plane bounded by n straight lines. Thus the edges of a Euclidean polygon are formed
A Novel Validity Index for Determination of the Optimal Number of Clusters
 IEICE TRANS. INF. & SYST., VOL.E84 D, NO.2 FEBRUARY 2001 281 LETTER A Novel Validity Index for Determination of the Optimal Number of Clusters Do-Jong KIM, Yong-Woon PARK, and Dong-Jo PARK, Nonmembers
IEICE TRANS. INF. & SYST., VOL.E84 D, NO.2 FEBRUARY 2001 281 LETTER A Novel Validity Index for Determination of the Optimal Number of Clusters Do-Jong KIM, Yong-Woon PARK, and Dong-Jo PARK, Nonmembers
Mirrors of reflections of regular maps
 ISSN 1855-3966 (printed edn), ISSN 1855-3974 (electronic edn) ARS MATHEMATICA CONTEMPORANEA 15 (018) 347 354 https://doiorg/106493/1855-3974145911d (Also available at http://amc-journaleu) Mirrors of reflections
ISSN 1855-3966 (printed edn), ISSN 1855-3974 (electronic edn) ARS MATHEMATICA CONTEMPORANEA 15 (018) 347 354 https://doiorg/106493/1855-3974145911d (Also available at http://amc-journaleu) Mirrors of reflections
Measurement of the stereoscopic rangefinder beam angular velocity using the digital image processing method
 Measurement of the stereosopi rangefinder beam angular veloity using the digital image proessing method ROMAN VÍTEK Department of weapons and ammunition University of defense Kouniova 65, 62 Brno CZECH
Measurement of the stereosopi rangefinder beam angular veloity using the digital image proessing method ROMAN VÍTEK Department of weapons and ammunition University of defense Kouniova 65, 62 Brno CZECH
1. Introduction. 2. The Probable Stope Algorithm
 1. Introdution Optimization in underground mine design has reeived less attention than that in open pit mines. This is mostly due to the diversity o underground mining methods and omplexity o underground
1. Introdution Optimization in underground mine design has reeived less attention than that in open pit mines. This is mostly due to the diversity o underground mining methods and omplexity o underground
Triangle LMN and triangle OPN are similar triangles. Find the angle measurements for x, y, and z.
 1 Use measurements of the two triangles elow to find x and y. Are the triangles similar or ongruent? Explain. 1a Triangle LMN and triangle OPN are similar triangles. Find the angle measurements for x,
1 Use measurements of the two triangles elow to find x and y. Are the triangles similar or ongruent? Explain. 1a Triangle LMN and triangle OPN are similar triangles. Find the angle measurements for x,
with respect to the normal in each medium, respectively. The question is: How are θ
 Prof. Raghuveer Parthasarathy University of Oregon Physis 35 Winter 8 3 R EFRACTION When light travels from one medium to another, it may hange diretion. This phenomenon familiar whenever we see the bent
Prof. Raghuveer Parthasarathy University of Oregon Physis 35 Winter 8 3 R EFRACTION When light travels from one medium to another, it may hange diretion. This phenomenon familiar whenever we see the bent
On - Line Path Delay Fault Testing of Omega MINs M. Bellos 1, E. Kalligeros 1, D. Nikolos 1,2 & H. T. Vergos 1,2
 On - Line Path Delay Fault Testing of Omega MINs M. Bellos, E. Kalligeros, D. Nikolos,2 & H. T. Vergos,2 Dept. of Computer Engineering and Informatis 2 Computer Tehnology Institute University of Patras,
On - Line Path Delay Fault Testing of Omega MINs M. Bellos, E. Kalligeros, D. Nikolos,2 & H. T. Vergos,2 Dept. of Computer Engineering and Informatis 2 Computer Tehnology Institute University of Patras,
Torpedo Trajectory Visual Simulation Based on Nonlinear Backstepping Control
 orpedo rajetory Visual Simulation Based on Nonlinear Bakstepping Control Peng Hai-jun 1, Li Hui-zhou Chen Ye 1, 1. Depart. of Weaponry Eng, Naval Univ. of Engineering, Wuhan 400, China. Depart. of Aeronautial
orpedo rajetory Visual Simulation Based on Nonlinear Bakstepping Control Peng Hai-jun 1, Li Hui-zhou Chen Ye 1, 1. Depart. of Weaponry Eng, Naval Univ. of Engineering, Wuhan 400, China. Depart. of Aeronautial
Sequential Incremental-Value Auctions
 Sequential Inremental-Value Autions Xiaoming Zheng and Sven Koenig Department of Computer Siene University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-0781 {xiaominz,skoenig}@us.edu Abstrat We study the
Sequential Inremental-Value Autions Xiaoming Zheng and Sven Koenig Department of Computer Siene University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-0781 {xiaominz,skoenig}@us.edu Abstrat We study the
Projections. Let us start with projections in 2D, because there are easier to visualize.
 Projetions Let us start ith projetions in D, beause there are easier to visualie. Projetion parallel to the -ais: Ever point in the -plane ith oordinates (, ) ill be transformed into the point ith oordinates
Projetions Let us start ith projetions in D, beause there are easier to visualie. Projetion parallel to the -ais: Ever point in the -plane ith oordinates (, ) ill be transformed into the point ith oordinates
Grade 6. Mathematics. Student Booklet SPRING 2009 RELEASED ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS. Assessment of Reading, Writing and Mathematics, Junior Division
 Grade 6 Assessment of Reading, Writing and Mathematis, Junior Division Student Booklet Mathematis SPRING 2009 RELEASED ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS Please note: The format of these booklets is slightly different
Grade 6 Assessment of Reading, Writing and Mathematis, Junior Division Student Booklet Mathematis SPRING 2009 RELEASED ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS Please note: The format of these booklets is slightly different
Multiple-Criteria Decision Analysis: A Novel Rank Aggregation Method
 3537 Multiple-Criteria Deision Analysis: A Novel Rank Aggregation Method Derya Yiltas-Kaplan Department of Computer Engineering, Istanbul University, 34320, Avilar, Istanbul, Turkey Email: dyiltas@ istanbul.edu.tr
3537 Multiple-Criteria Deision Analysis: A Novel Rank Aggregation Method Derya Yiltas-Kaplan Department of Computer Engineering, Istanbul University, 34320, Avilar, Istanbul, Turkey Email: dyiltas@ istanbul.edu.tr
Dr.Hazeem Al-Khafaji Dept. of Computer Science, Thi-Qar University, College of Science, Iraq
 Volume 4 Issue 6 June 014 ISSN: 77 18X International Journal of Advaned Researh in Computer Siene and Software Engineering Researh Paper Available online at: www.ijarsse.om Medial Image Compression using
Volume 4 Issue 6 June 014 ISSN: 77 18X International Journal of Advaned Researh in Computer Siene and Software Engineering Researh Paper Available online at: www.ijarsse.om Medial Image Compression using
Optimization of Two-Stage Cylindrical Gear Reducer with Adaptive Boundary Constraints
 5 JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE VOL. 8 NO. 8 AUGUST Optimization of Two-Stage Cylindrial Gear Reduer with Adaptive Boundary Constraints Xueyi Li College of Mehanial and Eletroni Engineering Shandong University of
5 JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE VOL. 8 NO. 8 AUGUST Optimization of Two-Stage Cylindrial Gear Reduer with Adaptive Boundary Constraints Xueyi Li College of Mehanial and Eletroni Engineering Shandong University of
Aspects of Geometry. Finite models of the projective plane and coordinates
 Review Sheet There will be an exam on Thursday, February 14. The exam will cover topics up through material from projective geometry through Day 3 of the DIY Hyperbolic geometry packet. Below are some
Review Sheet There will be an exam on Thursday, February 14. The exam will cover topics up through material from projective geometry through Day 3 of the DIY Hyperbolic geometry packet. Below are some
Dynamic Algorithms Multiple Choice Test
 3226 Dynami Algorithms Multiple Choie Test Sample test: only 8 questions 32 minutes (Real test has 30 questions 120 minutes) Årskort Name Eah of the following 8 questions has 4 possible answers of whih
3226 Dynami Algorithms Multiple Choie Test Sample test: only 8 questions 32 minutes (Real test has 30 questions 120 minutes) Årskort Name Eah of the following 8 questions has 4 possible answers of whih
Calculation of typical running time of a branch-and-bound algorithm for the vertex-cover problem
 Calulation of typial running time of a branh-and-bound algorithm for the vertex-over problem Joni Pajarinen, Joni.Pajarinen@iki.fi Otober 21, 2007 1 Introdution The vertex-over problem is one of a olletion
Calulation of typial running time of a branh-and-bound algorithm for the vertex-over problem Joni Pajarinen, Joni.Pajarinen@iki.fi Otober 21, 2007 1 Introdution The vertex-over problem is one of a olletion
Fuzzy Meta Node Fuzzy Metagraph and its Cluster Analysis
 Journal of Computer Siene 4 (): 9-97, 008 ISSN 549-3636 008 Siene Publiations Fuzzy Meta Node Fuzzy Metagraph and its Cluster Analysis Deepti Gaur, Aditya Shastri and Ranjit Biswas Department of Computer
Journal of Computer Siene 4 (): 9-97, 008 ISSN 549-3636 008 Siene Publiations Fuzzy Meta Node Fuzzy Metagraph and its Cluster Analysis Deepti Gaur, Aditya Shastri and Ranjit Biswas Department of Computer
Plane-based Calibration of a Camera with Varying Focal Length: the Centre Line Constraint
 Planebased Calibration of a Camera with Varying Foal Length: the Centre Line Constraint Pierre GURDOS and René PAYRISSAT IRITUPS TCI 118 route de Narbonne 31062 Toulouse Cedex 4 FRANCE PierreGurdjos@iritfr
Planebased Calibration of a Camera with Varying Foal Length: the Centre Line Constraint Pierre GURDOS and René PAYRISSAT IRITUPS TCI 118 route de Narbonne 31062 Toulouse Cedex 4 FRANCE PierreGurdjos@iritfr
Video Data and Sonar Data: Real World Data Fusion Example
 14th International Conferene on Information Fusion Chiago, Illinois, USA, July 5-8, 2011 Video Data and Sonar Data: Real World Data Fusion Example David W. Krout Applied Physis Lab dkrout@apl.washington.edu
14th International Conferene on Information Fusion Chiago, Illinois, USA, July 5-8, 2011 Video Data and Sonar Data: Real World Data Fusion Example David W. Krout Applied Physis Lab dkrout@apl.washington.edu
Discrete Contours in Multiple Views: Approximation and Recognition
 Disrete Contours in Multiple Views: Approximation and Reognition M. Pawan Kumar, Saurabh Goyal, Sujit Kuthirummal, C. V. Jawahar, and P. J. Narayanan Centre for Visual Information ehnology International
Disrete Contours in Multiple Views: Approximation and Reognition M. Pawan Kumar, Saurabh Goyal, Sujit Kuthirummal, C. V. Jawahar, and P. J. Narayanan Centre for Visual Information ehnology International
The Alpha Torque and Quantum Physics
 The Alpha Torque and Quantum Physis Zhiliang Cao, Henry Cao williamao15000@yahoo.om, henry.gu.ao@gmail.om July 18, 010 Abstrat In the enter of the unierse, there isn t a super massie blak hole or any speifi
The Alpha Torque and Quantum Physis Zhiliang Cao, Henry Cao williamao15000@yahoo.om, henry.gu.ao@gmail.om July 18, 010 Abstrat In the enter of the unierse, there isn t a super massie blak hole or any speifi
3D Model Based Pose Estimation For Omnidirectional Stereovision
 3D Model Based Pose Estimation For Omnidiretional Stereovision Guillaume Caron, Eri Marhand and El Mustapha Mouaddib Abstrat Robot vision has a lot to win as well with wide field of view indued by atadioptri
3D Model Based Pose Estimation For Omnidiretional Stereovision Guillaume Caron, Eri Marhand and El Mustapha Mouaddib Abstrat Robot vision has a lot to win as well with wide field of view indued by atadioptri
Particle Swarm Optimization for the Design of High Diffraction Efficient Holographic Grating
 Original Artile Partile Swarm Optimization for the Design of High Diffration Effiient Holographi Grating A.K. Tripathy 1, S.K. Das, M. Sundaray 3 and S.K. Tripathy* 4 1, Department of Computer Siene, Berhampur
Original Artile Partile Swarm Optimization for the Design of High Diffration Effiient Holographi Grating A.K. Tripathy 1, S.K. Das, M. Sundaray 3 and S.K. Tripathy* 4 1, Department of Computer Siene, Berhampur
Copyright. Anna Marie Bouboulis
 Copyright by Anna Marie Bouboulis 2013 The Report committee for Anna Marie Bouboulis Certifies that this is the approved version of the following report: Poincaré Disc Models in Hyperbolic Geometry APPROVED
Copyright by Anna Marie Bouboulis 2013 The Report committee for Anna Marie Bouboulis Certifies that this is the approved version of the following report: Poincaré Disc Models in Hyperbolic Geometry APPROVED
Algorithms, Mechanisms and Procedures for the Computer-aided Project Generation System
 Algorithms, Mehanisms and Proedures for the Computer-aided Projet Generation System Anton O. Butko 1*, Aleksandr P. Briukhovetskii 2, Dmitry E. Grigoriev 2# and Konstantin S. Kalashnikov 3 1 Department
Algorithms, Mehanisms and Proedures for the Computer-aided Projet Generation System Anton O. Butko 1*, Aleksandr P. Briukhovetskii 2, Dmitry E. Grigoriev 2# and Konstantin S. Kalashnikov 3 1 Department
Parallelizing Frequent Web Access Pattern Mining with Partial Enumeration for High Speedup
 Parallelizing Frequent Web Aess Pattern Mining with Partial Enumeration for High Peiyi Tang Markus P. Turkia Department of Computer Siene Department of Computer Siene University of Arkansas at Little Rok
Parallelizing Frequent Web Aess Pattern Mining with Partial Enumeration for High Peiyi Tang Markus P. Turkia Department of Computer Siene Department of Computer Siene University of Arkansas at Little Rok
The Happy Ending Problem
 The Happy Ending Problem Neeldhara Misra STATUTORY WARNING This doument is a draft version 1 Introdution The Happy Ending problem first manifested itself on a typial wintery evening in 1933 These evenings
The Happy Ending Problem Neeldhara Misra STATUTORY WARNING This doument is a draft version 1 Introdution The Happy Ending problem first manifested itself on a typial wintery evening in 1933 These evenings
Z Combinatorial Filters: Sensor Beams, Obstacles, and Possible Paths
 Z Combinatorial Filters: Sensor Beams, Obstales, and Possible Paths BENJAMIN TOVAR, Northwestern University FRED COHEN, University of Rohester LEONARDO BOBADILLA, University of Illinois JUSTIN CZARNOWSKI,
Z Combinatorial Filters: Sensor Beams, Obstales, and Possible Paths BENJAMIN TOVAR, Northwestern University FRED COHEN, University of Rohester LEONARDO BOBADILLA, University of Illinois JUSTIN CZARNOWSKI,
A Novel Bit Level Time Series Representation with Implication of Similarity Search and Clustering
 A Novel Bit Level Time Series Representation with Impliation of Similarity Searh and lustering hotirat Ratanamahatana, Eamonn Keogh, Anthony J. Bagnall 2, and Stefano Lonardi Dept. of omputer Siene & Engineering,
A Novel Bit Level Time Series Representation with Impliation of Similarity Searh and lustering hotirat Ratanamahatana, Eamonn Keogh, Anthony J. Bagnall 2, and Stefano Lonardi Dept. of omputer Siene & Engineering,
Modeling of Wire Electrochemical Machining
 A publiation of 91 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 41, 214 Guest Editors: Simonetta Palmas, Mihele Masia, Annalisa Vaa Copyright 214, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-32-7; ISSN 2283-9216
A publiation of 91 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 41, 214 Guest Editors: Simonetta Palmas, Mihele Masia, Annalisa Vaa Copyright 214, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-32-7; ISSN 2283-9216
Contributions to the cinematic and dynamic study of parallel mechanism robots with four degrees of freedom
 Equation Chapter Setion Forgó Zoltán, eng. hd. andidate Contributions to the inemati and dynami study of parallel mehanism robots with four degrees of freedom Abstrat of hd hesis Sientifi oordinator: Niolae
Equation Chapter Setion Forgó Zoltán, eng. hd. andidate Contributions to the inemati and dynami study of parallel mehanism robots with four degrees of freedom Abstrat of hd hesis Sientifi oordinator: Niolae
Dubna 2018: lines on cubic surfaces
 Dubna 2018: lines on cubic surfaces Ivan Cheltsov 20th July 2018 Lecture 1: projective plane Complex plane Definition A line in C 2 is a subset that is given by ax + by + c = 0 for some complex numbers
Dubna 2018: lines on cubic surfaces Ivan Cheltsov 20th July 2018 Lecture 1: projective plane Complex plane Definition A line in C 2 is a subset that is given by ax + by + c = 0 for some complex numbers
A {k, n}-secret Sharing Scheme for Color Images
 A {k, n}-seret Sharing Sheme for Color Images Rastislav Luka, Konstantinos N. Plataniotis, and Anastasios N. Venetsanopoulos The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Dept. of Eletrial and Computer Engineering, University
A {k, n}-seret Sharing Sheme for Color Images Rastislav Luka, Konstantinos N. Plataniotis, and Anastasios N. Venetsanopoulos The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Dept. of Eletrial and Computer Engineering, University
Teichmüller Space and Fenchel-Nielsen Coordinates
 Teichmüller Space and Fenchel-Nielsen Coordinates Nathan Lopez November 30, 2015 Abstract Here we give an overview of Teichmüller space and its realization as a smooth manifold through Fenchel- Nielsen
Teichmüller Space and Fenchel-Nielsen Coordinates Nathan Lopez November 30, 2015 Abstract Here we give an overview of Teichmüller space and its realization as a smooth manifold through Fenchel- Nielsen
Facility Location: Distributed Approximation
 Faility Loation: Distributed Approximation Thomas Mosibroda Roger Wattenhofer Distributed Computing Group PODC 2005 Where to plae ahes in the Internet? A distributed appliation that has to dynamially plae
Faility Loation: Distributed Approximation Thomas Mosibroda Roger Wattenhofer Distributed Computing Group PODC 2005 Where to plae ahes in the Internet? A distributed appliation that has to dynamially plae
Simulation of Crystallographic Texture and Anisotropie of Polycrystals during Metal Forming with Respect to Scaling Aspects
 Raabe, Roters, Wang Simulation of Crystallographi Texture and Anisotropie of Polyrystals during Metal Forming with Respet to Saling Aspets D. Raabe, F. Roters, Y. Wang Max-Plank-Institut für Eisenforshung,
Raabe, Roters, Wang Simulation of Crystallographi Texture and Anisotropie of Polyrystals during Metal Forming with Respet to Saling Aspets D. Raabe, F. Roters, Y. Wang Max-Plank-Institut für Eisenforshung,
The SODA AOSE Methodology
 The SODA AOSE Methodology Multiagent Systems LM Sistemi Multiagente LM Ambra Molesini & Andrea Omiini {ambra.molesini, andrea.omiini}@unibo.it Dipartimento di Informatia Sienza e Ingegneria (DISI) Alma
The SODA AOSE Methodology Multiagent Systems LM Sistemi Multiagente LM Ambra Molesini & Andrea Omiini {ambra.molesini, andrea.omiini}@unibo.it Dipartimento di Informatia Sienza e Ingegneria (DISI) Alma
Contour Box: Rejecting Object Proposals Without Explicit Closed Contours
 Contour Box: Rejeting Objet Proposals Without Expliit Closed Contours Cewu Lu, Shu Liu Jiaya Jia Chi-Keung Tang The Hong Kong University of Siene and Tehnology Stanford University The Chinese University
Contour Box: Rejeting Objet Proposals Without Expliit Closed Contours Cewu Lu, Shu Liu Jiaya Jia Chi-Keung Tang The Hong Kong University of Siene and Tehnology Stanford University The Chinese University
1. The collection of the vowels in the word probability. 2. The collection of real numbers that satisfy the equation x 9 = 0.
 C HPTER 1 SETS I. DEFINITION OF SET We begin our study of probability with the disussion of the basi onept of set. We assume that there is a ommon understanding of what is meant by the notion of a olletion
C HPTER 1 SETS I. DEFINITION OF SET We begin our study of probability with the disussion of the basi onept of set. We assume that there is a ommon understanding of what is meant by the notion of a olletion
Fuzzy Pre-semi-closed Sets
 BULLETIN of the Malaysian Mathematial Sienes Soiety http://mathusmmy/bulletin Bull Malays Math Si So () 1() (008), Fuzzy Pre-semi-losed Sets 1 S Murugesan and P Thangavelu 1 Department of Mathematis, Sri
BULLETIN of the Malaysian Mathematial Sienes Soiety http://mathusmmy/bulletin Bull Malays Math Si So () 1() (008), Fuzzy Pre-semi-losed Sets 1 S Murugesan and P Thangavelu 1 Department of Mathematis, Sri
Orientation of the coordinate system
 Orientation of the oordinate system Right-handed oordinate system: -axis by a positive, around the -axis. The -axis is mapped to the i.e., antilokwise, rotation of The -axis is mapped to the -axis by a
Orientation of the oordinate system Right-handed oordinate system: -axis by a positive, around the -axis. The -axis is mapped to the i.e., antilokwise, rotation of The -axis is mapped to the -axis by a
Face and Facial Feature Tracking for Natural Human-Computer Interface
 Fae and Faial Feature Traking for Natural Human-Computer Interfae Vladimir Vezhnevets Graphis & Media Laboratory, Dept. of Applied Mathematis and Computer Siene of Mosow State University Mosow, Russia
Fae and Faial Feature Traking for Natural Human-Computer Interfae Vladimir Vezhnevets Graphis & Media Laboratory, Dept. of Applied Mathematis and Computer Siene of Mosow State University Mosow, Russia
Implementing Load-Balanced Switches With Fat-Tree Networks
 Implementing Load-Balaned Swithes With Fat-Tree Networks Hung-Shih Chueh, Ching-Min Lien, Cheng-Shang Chang, Jay Cheng, and Duan-Shin Lee Department of Eletrial Engineering & Institute of Communiations
Implementing Load-Balaned Swithes With Fat-Tree Networks Hung-Shih Chueh, Ching-Min Lien, Cheng-Shang Chang, Jay Cheng, and Duan-Shin Lee Department of Eletrial Engineering & Institute of Communiations
Cluster-Based Cumulative Ensembles
 Cluster-Based Cumulative Ensembles Hanan G. Ayad and Mohamed S. Kamel Pattern Analysis and Mahine Intelligene Lab, Eletrial and Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1,
Cluster-Based Cumulative Ensembles Hanan G. Ayad and Mohamed S. Kamel Pattern Analysis and Mahine Intelligene Lab, Eletrial and Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1,
Simultaneous image orientation in GRASS
 Simultaneous image orientation in GRASS Alessandro BERGAMINI, Alfonso VITTI, Paolo ATELLI Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Università degli Studi di Trento, via Mesiano 77, 38 Trento, tel.
Simultaneous image orientation in GRASS Alessandro BERGAMINI, Alfonso VITTI, Paolo ATELLI Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Università degli Studi di Trento, via Mesiano 77, 38 Trento, tel.
Perspective Mappings. Contents
 Perspective Mappings David Eberly, Geometric Tools, Redmond WA 98052 https://www.geometrictools.com/ This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. To view a copy
Perspective Mappings David Eberly, Geometric Tools, Redmond WA 98052 https://www.geometrictools.com/ This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. To view a copy
Boundary Correct Real-Time Soft Shadows
 Boundary Corret Real-Time Soft Shadows Bjarke Jakobsen Niels J. Christensen Bent D. Larsen Kim S. Petersen Informatis and Mathematial Modelling Tehnial University of Denmark {bj, nj, bdl}@imm.dtu.dk, kim@deadline.dk
Boundary Corret Real-Time Soft Shadows Bjarke Jakobsen Niels J. Christensen Bent D. Larsen Kim S. Petersen Informatis and Mathematial Modelling Tehnial University of Denmark {bj, nj, bdl}@imm.dtu.dk, kim@deadline.dk
Triangles. Learning Objectives. Pre-Activity
 Setion 3.2 Pre-tivity Preparation Triangles Geena needs to make sure that the dek she is building is perfetly square to the brae holding the dek in plae. How an she use geometry to ensure that the boards
Setion 3.2 Pre-tivity Preparation Triangles Geena needs to make sure that the dek she is building is perfetly square to the brae holding the dek in plae. How an she use geometry to ensure that the boards
Time delay estimation of reverberant meeting speech: on the use of multichannel linear prediction
 University of Wollongong Researh Online Faulty of Informatis - apers (Arhive) Faulty of Engineering and Information Sienes 7 Time delay estimation of reverberant meeting speeh: on the use of multihannel
University of Wollongong Researh Online Faulty of Informatis - apers (Arhive) Faulty of Engineering and Information Sienes 7 Time delay estimation of reverberant meeting speeh: on the use of multihannel
Finding the Equation of a Straight Line
 Finding the Equation of a Straight Line You should have, before now, ome aross the equation of a straight line, perhaps at shool. Engineers use this equation to help determine how one quantity is related
Finding the Equation of a Straight Line You should have, before now, ome aross the equation of a straight line, perhaps at shool. Engineers use this equation to help determine how one quantity is related
And, the (low-pass) Butterworth filter of order m is given in the frequency domain by
 Problem Set no.3.a) The ideal low-pass filter is given in the frequeny domain by B ideal ( f ), f f; =, f > f. () And, the (low-pass) Butterworth filter of order m is given in the frequeny domain by B
Problem Set no.3.a) The ideal low-pass filter is given in the frequeny domain by B ideal ( f ), f f; =, f > f. () And, the (low-pass) Butterworth filter of order m is given in the frequeny domain by B
Unsupervised Stereoscopic Video Object Segmentation Based on Active Contours and Retrainable Neural Networks
 Unsupervised Stereosopi Video Objet Segmentation Based on Ative Contours and Retrainable Neural Networks KLIMIS NTALIANIS, ANASTASIOS DOULAMIS, and NIKOLAOS DOULAMIS National Tehnial University of Athens
Unsupervised Stereosopi Video Objet Segmentation Based on Ative Contours and Retrainable Neural Networks KLIMIS NTALIANIS, ANASTASIOS DOULAMIS, and NIKOLAOS DOULAMIS National Tehnial University of Athens
The Minimum Redundancy Maximum Relevance Approach to Building Sparse Support Vector Machines
 The Minimum Redundany Maximum Relevane Approah to Building Sparse Support Vetor Mahines Xiaoxing Yang, Ke Tang, and Xin Yao, Nature Inspired Computation and Appliations Laboratory (NICAL), Shool of Computer
The Minimum Redundany Maximum Relevane Approah to Building Sparse Support Vetor Mahines Xiaoxing Yang, Ke Tang, and Xin Yao, Nature Inspired Computation and Appliations Laboratory (NICAL), Shool of Computer
FUZZY WATERSHED FOR IMAGE SEGMENTATION
 FUZZY WATERSHED FOR IMAGE SEGMENTATION Ramón Moreno, Manuel Graña Computational Intelligene Group, Universidad del País Vaso, Spain http://www.ehu.es/winto; {ramon.moreno,manuel.grana}@ehu.es Abstrat The
FUZZY WATERSHED FOR IMAGE SEGMENTATION Ramón Moreno, Manuel Graña Computational Intelligene Group, Universidad del País Vaso, Spain http://www.ehu.es/winto; {ramon.moreno,manuel.grana}@ehu.es Abstrat The
Background for Surface Integration
 Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
An Alternative Approach to the Fuzzifier in Fuzzy Clustering to Obtain Better Clustering Results
 An Alternative Approah to the Fuzziier in Fuzzy Clustering to Obtain Better Clustering Results Frank Klawonn Department o Computer Siene University o Applied Sienes BS/WF Salzdahlumer Str. 46/48 D-38302
An Alternative Approah to the Fuzziier in Fuzzy Clustering to Obtain Better Clustering Results Frank Klawonn Department o Computer Siene University o Applied Sienes BS/WF Salzdahlumer Str. 46/48 D-38302
Geometrically maximal knots
 Geometrically maximal knots Abhijit Champanerkar Department of Mathematics, College of Staten Island & The Graduate Center, CUNY Discussion Meeting on Knot theory and its Applications IISER Mohali, India
Geometrically maximal knots Abhijit Champanerkar Department of Mathematics, College of Staten Island & The Graduate Center, CUNY Discussion Meeting on Knot theory and its Applications IISER Mohali, India
A Dual-Hamiltonian-Path-Based Multicasting Strategy for Wormhole-Routed Star Graph Interconnection Networks
 A Dual-Hamiltonian-Path-Based Multiasting Strategy for Wormhole-Routed Star Graph Interonnetion Networks Nen-Chung Wang Department of Information and Communiation Engineering Chaoyang University of Tehnology,
A Dual-Hamiltonian-Path-Based Multiasting Strategy for Wormhole-Routed Star Graph Interonnetion Networks Nen-Chung Wang Department of Information and Communiation Engineering Chaoyang University of Tehnology,
Adobe Certified Associate
 Adobe Certified Assoiate About the Adobe Certified Assoiate (ACA) Program The Adobe Certified Assoiate (ACA) program is for graphi designers, Web designers, video prodution designers, and digital professionals
Adobe Certified Assoiate About the Adobe Certified Assoiate (ACA) Program The Adobe Certified Assoiate (ACA) program is for graphi designers, Web designers, video prodution designers, and digital professionals
