Circles - Probability
|
|
|
- Luke Walters
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section 10-1: Circles and Circumference SOL: G.10 The student will investigate and solve practical problems involving circles, using properties of angles, arcs, chords, tangents, and secants. Problems will include finding arc length and the area of a sector, and may be drawn from applications of architecture, art, and construction. Objective: Identify and use parts of circles Solve problems involving the circumference of a circle Vocabulary: Circle the locus (set) of all points in a plane equidistant for a given point Center the central point of a circle Chord any segment that endpoints are on the circle Diameter a chord that passes through the center of the circle Radius any segment that endpoints are the center and a point on the circle Key Concepts: Diameter (d) is twice the radius (r): d = 2r Circumference (C): C = 2πr = dπ Circles Diameter (d) y 90 Pie Charts Circles - Probability 135 y Center Chord 270 Radius (r) x Diameter (d) 135º = 3/8 360º or.375 or 37.5% Probability 0 = no chance 1 = for sure Radius (r) Center 45º = 1/8 180º 360º = 1/2 or º or 12.5% or.5 or 50% x 0 Circumference = 2πr = dπ Circumference = 2πr = dπ Concept Summary: Diameter of a circle is twice the radius Circumference, C, of a circle with diameter, d, or a radius, r, can be written in the form C = πd or C = 2πr Example 1: a) Name the circle b) Name the radius of the circle c) Name a chord of the circle d) Name a diameter of the circle
2 Example 2: Circle R has diameters ST and QM a) If ST = 18, find RS b) If RM = 24, find QM c) If RN = 2, find RP Example 3: The diameters of Circle X, Circle Y and Circle Z are 22 millimeters, 16 millimeters, and 10 millimeters, respectively. a) Find EZ b) Find XF Example 4: a) Find C if r = 22 centimeters b) Find C if d = 3 feet c) Find d and r to the nearest hundredth if C = 16.8 meters Homework: pg ; 1-6, 22, 28, 70, 71
3 Section 10-2: Measuring Angles and Arcs SOL: G.10 The student will investigate and solve practical problems involving circles.. Objective: Identify central angles, major arcs, minor arcs and semicircles, and find their measure Find arc length Vocabulary: Central Angle has the center of the circle as its vertex and two radii as sides Arc edge of the circle defined by a central angle Minor Arc an arc with the central angle less than 180 in measurement Major Arc an arc with the central angle greater than 180 in measurement Semicircle an arc with the central angle equal to 180 in measurement Arc Length part of the circumference of the circle corresponding to the arc Theorems: Theorem 10.1: In the same or in congruent circles, two arcs are congruent if and only if their corresponding central angles are congruent. Postulate 10.1, Arc Addition Postulate: The measure of an arc formed by two adjacent arcs is the sum of the measures of the two arcs. Key Concepts: The sum of central angles measures of a circle with no interior points in common is 360 Arc length Degree Measure of Arc l A = = Circumference Degree Measure of Circle 2πr 360 Semi-Circle EHF Circles - Arcs y Circles - Arcs y With no overlap, Central Angles sum to 360 E Diameter (d) BEG E Semi-Circle s Arc Length is ½ circumference Diameter (d) Measure is 180 G Center x Center x B Central Angle BHG H F G B BH s Arc Length is ( BCH/360 ) * Cir. Measure is m BCH Concept Summary: Sum of measures of central angles of a circle with no interior points in common is 360 Measure of each arc is related to the measure of its central angle Length of an arc is proportional to the length of the circumference H F
4 Example 1: Given Circle T with RV as a diameter, find a) m RTS b) m QTR Example 2: AD and BE are diameters a) m CZD b) m BZC Example 3: In circle P, m MNP = 46, PL bisects KPM and OP KN a) Find m arc OK b) Find m arc LM c) Find m arc KO Example 4: a) In circle B, AC = 9 and m ABD = 40, find the length of arc AD b) Find the length of arc DC Homework: pg ; 1, 7-9, 13-15, 39, 41, 73
5 Arc EWK Arc EV Arc GUF Arc HTF Chapter 10 Circles Section 10-3: Arcs and Chords SOL: G.10 The student will investigate and solve practical problems involving circles, using properties of angles, arcs, chords, tangents, and secants. Problems will include finding arc length and the area of a sector, and may be drawn from applications of architecture, art, and construction. Objective: Recognize and use relationships between arcs and chords Recognize and use relationships between arcs and diameters Vocabulary: Inscribed Polygon all vertices lie on the circle Circumscribed circle contains all vertices of a polygon Theorems: Theorem 10.2: In a circle or in congruent circles, two minor arcs are congruent if and only if their corresponding chords are congruent. Theorem 10.3: In a circle, if a diameter (or radius) is perpendicular to a chord, then it bisects the chord and its arc. Theorem 10.5: In a circle or in congruent circles, two chords are congruent if and only if they are equidistant from the center. Circles Arcs & Chords y G Chords K GH V U E R Diameter (d) Center S F x W X X Chords are equidistant from the center T K H Arc KE Arc HFG Concept Summary: The endpoints of a chord are also the endpoints of an arc Diameters perpendicular to chords bisect chords and intercepted arcs Example 1: The rotations of a tessellation can create twelve congruent central angles. Determine whether arc PQ is congruent to arc ST.
6 Example 2: Circle W has a radius of 10 centimeters. Radius WL is perpendicular to chord HK which is 16 centimeters long. a) If m arc HL = 53, then find m arc MK b) Find L Example 3: Circle O has a radius of 25 units. Radius OC is perpendicular to chord AE which is 40 units long. a) If m arc MG = 35, then find m arc CG b) Find CH Example 4: Chords EF and GH are equidistant from the center. If the radius of circle P is 15 and EF = 24, find PR and RH. Example 5: Chords SZ and UV are equidistant from the center of circle X. If TX is 39 and XY is 15, find WZ and UV. Homework: pg 704-8; 1-3, 7-9, 23, 32, 40, 41
7 Section 10-4: Inscribed Angles SOL: G.10 The student will investigate and solve practical problems involving circles, using properties of angles, arcs, chords, tangents, and secants. Problems will include finding arc length and the area of a sector, and may be drawn from applications of architecture, art, and construction. Objective: Find measures of inscribed angles Find measures of angles of inscribed polygons Vocabulary: Inscribed Angle an angle with its vertex on the circle and chords as its sides Theorems: Theorem 10.6: If an angle is inscribed in a circle, then the measure of the angle equals one-half the measure of its intercepted arc (or the measure of the intercepted arc is twice the measure of the inscribed angle). Theorem 10.7: If two inscribed angles of a circle (or congruent circles) intercept congruent arcs or the same arc, then the angles are congruent. Theorem 10.8: An inscribed angle intercepts a diameter or semicircle, if and only if, the angle is a right angle. Theorem 10.9: If a quadrilateral is inscribed in a circle, then its opposite angles are supplementary. Circles Inscribed Angles Y y Center X Inscribe Angles -- Measure Y = ½ X (central angle) E K Measure Y = ½ measure Arc KEF F x Concept Summary: The measure of the inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc The angles of inscribed polygons can be found by using arc measures Example 1: In circle F, m arc WX = 20, m arc XY = 40, m arc UZ = 108 and m arc UW = m arc YZ. Find the measures of the numbered angles
8 Example 2: In circle A, m arc XY = 60, m arc YZ = 80, and m arc WX = m arc WZ. Find the measures of the numbered angles Example 3: Triangles TVU and TSU are inscribed in circle P with arc VU arc SU. Find the measure of each numbered angle if m 2 = x + 9 and 4 = 2x + 6. Example 4: Example 5: Quadrilateral QRST is inscribed in circle M. If m Q = 87, and m R = 102. Find m S and m T. Example 6: Quadrilateral BCDE is inscribed in circle X. If m B = 99, and m C = 76. Find m D and m E. Homework: pg ; 1-3, 11-13, 17-19, 36, 51
9 Section 10-5: Tangents SOL: G.10 The student will investigate and solve practical problems involving circles, using properties of angles, arcs, chords, tangents, and secants. Problems will include finding arc length and the area of a sector, and may be drawn from applications of architecture, art, and construction. Objective: Use properties of tangents Solve problems involving circumscribed polygons Vocabulary: Tangent a line that intersects a circle in exactly one point Point of tangency point where a tangent intersects a circle Theorems: Theorem 10.10: A line is tangent to a circle, if and only it, it is perpendicular to the radius drawn to the point of tangency. Theorem 10.11: If two segments from the same exterior point are tangent to a circle, then they are congruent. Circles Tangents y T K TK T Center TK and T are tangents Radii C and CK form 90 angles with the tangents x Tangents intersect a figure (circle) at only one point Concept Summary: A line that is tangent to a circle intersects the circle in exactly one point. A tangent is perpendicular to a radius of a circle Two segments tangent to a circle form the same exterior point are congruent Example 1: RS is tangent to circle Q at point R. Find y
10 Example 2: CD is tangent to circle B at point D. Find a Example 3: Determine whether BC is tangent to circle A Example 4: Determine whether EW is tangent to circle D Example 5: Determine whether WX is tangent to circle V Example 5: Triangle HK is circumscribed about circle G. Find the perimeter of HK if NK = L Homework: pg 721-5; 2-6, 8, 13-15, 40, 43
11 Section 10-6: Secants, Tangents, and Angle Measures SOL: G.10 The student will investigate and solve practical problems involving circles, using properties of angles, arcs, chords, tangents, and secants. Problems will include finding arc length and the area of a sector, and may be drawn from applications of architecture, art, and construction. Objective: Find measures of angles formed by lines intersecting on or inside a circle Find measures of angles formed by lines intersecting outside a circle Vocabulary: Secant a line that intersects a circle in exactly two points Theorems: Theorem 10.12: If two secants intersect in the interior of a circle, then the measure of an angle formed is onehalf the sum of the measure of the arcs intercepted by the angle and its vertical angle. Theorem 10.13: If a secant and a tangent intersect at the point of tangency, then the measure of each angle formed is one half the measure of its intercepted arc Theorem 10.14: If two secants, a secant and a tangent, or two tangents intersect in the exterior of a circle, then the measure of the angle formed is one-half the positive difference of the measures of the intercepted arcs. Circles Secants y Circles External Angles Two Secants Secant & Tangent Two Tangents Interior Angles formed by a Secant & a Tangent m 3 = ½ (m Arc MK) m 4 = ½ (m Arc LK) M K L K T K T S x Center P N M M M Interior Angles formed by 2 Secants m 1 = ½ (m Arc M + m Arc LK) m 2 = ½ (m Arc MK + m Arc L) L m = ½(m Arc MN m Arc LK) m = ½ m Arc MN m Arc LK m = ½(m Arc TM m Arc TK) m = ½ m Arc TM m Arc TK m = ½(m Arc TMS m Arc TS) m = ½ m Arc TMS m Arc TS Concept Summary: The interior angle is the average of the arcs formed by the chords The exterior angle is the ½ (Far arc Near Arc) The measure of an angle formed by two secant lines is half the positive difference of its intercepted arcs The measure of angle formed by a secant and tangent line is half its intercepted arc Example 1: Find the m 4, if m arc FG = 76 and m arc GH = 88 Example 2: Find the m 5, if m arc AC = 63 and m arc XY = 21
12 Example 3: Find RPS, if m arc PT = 114 and m arc TS = 136 Example 4: Find RPS, if m arc PT = 114 and m arc TS = 136 Example 5: Find x Example 6: Find x Example 7: Find x Homework: pg ; 1-6, 11-13, 21, 42
13 Section 10-7: Special Segments in a Circle SOL: G.10 The student will investigate and solve practical problems involving circles, using properties of angles, arcs, chords, tangents, and secants. Problems will include finding arc length and the area of a sector, and may be drawn from applications of architecture, art, and construction. Objective: Find measures of segments that intersect in the interior of a circle Find measures of segments that intersect in the exterior of a circle Vocabulary: None New Theorems: Theorem 10.15: If two chords intersect in a circle, then the products of the measures of the segments of the chords are equal. Theorem 10.16: If two secant lines are drawn to a circle from an exterior point, then the product of the measures of one secant segment and its external secant segment is equal to the product of the measures of the other secant segment and its external secant segment Theorem 10.17: If a tangent segment and a secant segment are drawn to a circle from an exterior point, then the square of the measure of the tangent segment is equal to the product of the measures of the secant segment and its external secant segment. Circles Special Segments Two Chords Inside a Circle Two Secants From Outside Point Secant & Tangent From Outside Point L K L K T K N M N M M L M = N K K M = L N T T = K M Inside the circle, it s the pieces of the chords multiplied together Outside the circle, it s the pieces outside multiplied by the whole length Concept Summary: The lengths of intersecting chords in a circle can be found by using the products of the measures of the segments The secant segment product also applies to segments that intersect outside the circle, and to a secant segment and a tangent Example 1: Find x
14 Example 2: Find x Example 3: Find x, if EF = 10, EH = 8, and FG = 24. Example 4: Find x if GO = 27, OM = 25 and IK = 24. Homework: pg ; 1, 3, 6, 7, 10-12, 32
15 Section 10-8: Equations of Circles SOL: G.10 The student will investigate and solve practical problems involving circles, using properties of angles, arcs, chords, tangents, and secants. Problems will include finding arc length and the area of a sector, and may be drawn from applications of architecture, art, and construction. Objective: Write the equation of a circle Graph a circle on the coordinate plane Vocabulary: None New Key Concepts: Equations of Circles Center at (-6,7) y Center at (6,6) r=3 (x+7) 2 + (y-7) 2 = 9 Center at (0,0) r=4 (x-6) 2 + (y-6) 2 = 16 r=2 x Center at (-7,-7) r=2 (x+7) 2 + (y+7) 2 = 4 x 2 + y 2 = 4 Center at (8,6) r=1 (x-8) 2 + (y+6) 2 = 1 Concept Summary: The coordinates of the center of a circle (h, k) and its radius r can be used to write an equation for the circle in the form (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 A circle can be graphed on a coordinate plane by using the equation written in standard form A circle can be graphed through any three noncollinear points on the coordinate plane Example 1: Write an equation for a circle with the center at (3, 3), d = 12. Example 2a: Write an equation for each circle with center at (0, 5), d = 18. Example 2b: Write an equation for a circle with the center at (7, 0), r = 20. Homework: pg ; 1-4, 13-15, 27, 28, 41, 44
16 Lesson Minute Check: Refer to F. 1. Name a radius 2. Name a chord 3. Name a diameter Refer to the figure and find each measure 4. BC 5. DE 6. Which segment in C is a diameter? A. AC B. CD C. CB D. AB Refer to P. Find each measure. 4. m arc LM Lesson Minute Check: In O, BD is a diameter and m AOD =55. Find each measure. 1. m COB 2. m DOC 3. m AOB 5. m arc MOL 6. If the measure of an arc is 68, what is the measure of its central angle? A. 34 B. 68 C. 102 D. 136 Lesson Minute Check: The radius of R is 35, LM NO, LM = 45 and m arc LM = 80. Find each measure. 1. m arc NO 2. m arc NQ 3. NO 4. NT 5. RT 6. Which congruence statement is true if RS and TU are congruent chords of V? A. RS SU B. RS TU C. ST RU D. RS ST
17 Lesson Minute Check: Refer to the figure and find each measure. 1. m 1 2. m 2 3. m 3 4. m 4 5. In B, find x if m A = 3x + 9 and m B = 8x If an inscribed angle has a measure of 110, what is the measure of its intercepted arc? A. 55 B. 70 C. 110 D. 220 Lesson Minute Check: Determine whether each segment is tangent to the given circle. 1. BC 2. QR Find x. Assume that the segments that appear to be tangents are tangents What is the measure of PS? A. 10 B. 12 C. 14 D. 18 Lesson Minute Check: Find x. Assume that any segment that appears to be tangent is tangent What is the measure of XYZ if YZ is tangent to the circle? A. 55 B. 70 C. 125 D. 250
18 Lesson 10-7 Find x. 5-Minute Check: Find x in the figure A. 6 B. 8 C. 12 D. 16
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with
 Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
Geometry Definitions and Theorems. Chapter 9. Definitions and Important Terms & Facts
 Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
10-1 Circles & Circumference
 10-1 Circles & Circumference Radius- Circle- Formula- Chord- Diameter- Circumference- Formula- Formula- Two circles are congruent if and only if they have congruent radii All circles are similar Concentric
10-1 Circles & Circumference Radius- Circle- Formula- Chord- Diameter- Circumference- Formula- Formula- Two circles are congruent if and only if they have congruent radii All circles are similar Concentric
Examples: The name of the circle is: The radii of the circle are: The chords of the circle are: The diameter of the circle is:
 Geometry P Lesson 10-1: ircles and ircumference Page 1 of 1 Objectives: To identify and use parts of circles To solve problems involving the circumference of a circle Geometry Standard: 8 Examples: The
Geometry P Lesson 10-1: ircles and ircumference Page 1 of 1 Objectives: To identify and use parts of circles To solve problems involving the circumference of a circle Geometry Standard: 8 Examples: The
Topic 7: Properties of Circles
 This Packet Belongs to (Student Name) Topic 7: Properties of Circles Unit 6 Properties of Circles Module 15: Angles and Segments in Circles 15.1 Central Angles and Inscribed Angles 15.2 Angles in Inscribed
This Packet Belongs to (Student Name) Topic 7: Properties of Circles Unit 6 Properties of Circles Module 15: Angles and Segments in Circles 15.1 Central Angles and Inscribed Angles 15.2 Angles in Inscribed
6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles
 Chapter 6 Circles 6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles Definitions 32. A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle.
Chapter 6 Circles 6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles Definitions 32. A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle.
Chapter 6. Sir Migo Mendoza
 Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
Modeling with Geometry
 Modeling with Geometry 6.3 Parallelograms https://mathbitsnotebook.com/geometry/quadrilaterals/qdparallelograms.html Properties of Parallelograms Sides A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs
Modeling with Geometry 6.3 Parallelograms https://mathbitsnotebook.com/geometry/quadrilaterals/qdparallelograms.html Properties of Parallelograms Sides A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs
Notes Circle Basics Standard:
 Notes Circle Basics M RECALL EXAMPLES Give an example of each of the following: 1. Name the circle 2. Radius 3. Chord 4. Diameter 5. Secant 6. Tangent (line) 7. Point of tangency 8. Tangent (segment) DEFINTION
Notes Circle Basics M RECALL EXAMPLES Give an example of each of the following: 1. Name the circle 2. Radius 3. Chord 4. Diameter 5. Secant 6. Tangent (line) 7. Point of tangency 8. Tangent (segment) DEFINTION
Perimeter. Area. Surface Area. Volume. Circle (circumference) C = 2πr. Square. Rectangle. Triangle. Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh
 Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Postulates, Theorems, and Corollaries. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Geometry - Chapter 12 Test SAMPLE
 Class: Date: Geometry - Chapter 12 Test SAMPLE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the value of x. If necessary, round your answer to
Class: Date: Geometry - Chapter 12 Test SAMPLE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the value of x. If necessary, round your answer to
Lines That Intersect Circles
 LESSON 11-1 Lines That Intersect Circles Lesson Objectives (p. 746): Vocabulary 1. Interior of a circle (p. 746): 2. Exterior of a circle (p. 746): 3. Chord (p. 746): 4. Secant (p. 746): 5. Tangent of
LESSON 11-1 Lines That Intersect Circles Lesson Objectives (p. 746): Vocabulary 1. Interior of a circle (p. 746): 2. Exterior of a circle (p. 746): 3. Chord (p. 746): 4. Secant (p. 746): 5. Tangent of
Theorems & Postulates Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 30-60 -90 Triangle In a 30-60 -90 triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is two times the length of the shorter leg, and the length of the longer leg is the length
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 30-60 -90 Triangle In a 30-60 -90 triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is two times the length of the shorter leg, and the length of the longer leg is the length
Geometry. Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section.
 Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties
 Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY. 3 rd Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource for
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource for
Unit 9 Syllabus: Circles
 ate Period Unit 9 Syllabus: ircles ay Topic 1 Tangent Lines 2 hords and rcs and Inscribed ngles 3 Review/Graded lasswork 4 Review from before reak 5 Finding ngle Measures 6 Finding Segment Lengths 7 Review
ate Period Unit 9 Syllabus: ircles ay Topic 1 Tangent Lines 2 hords and rcs and Inscribed ngles 3 Review/Graded lasswork 4 Review from before reak 5 Finding ngle Measures 6 Finding Segment Lengths 7 Review
1. AREAS. Geometry 199. A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh. B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh. C. Rhombus = 1 product of the diagonals = 1 dd
 Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
High School Mathematics Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards
 High School Mathematics Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Table of Contents Reasoning, Lines, and Transformations Basics of Geometry 1 Basics of Geometry 2 Geometry Notation Logic Notation Set Notation
High School Mathematics Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Table of Contents Reasoning, Lines, and Transformations Basics of Geometry 1 Basics of Geometry 2 Geometry Notation Logic Notation Set Notation
Geometry Practice. 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles.
 Geometry Practice Name 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles. 2. Planes that meet to form right angles are called planes. 3. Lines that cross are called lines. 4.
Geometry Practice Name 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles. 2. Planes that meet to form right angles are called planes. 3. Lines that cross are called lines. 4.
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS GEOMETRY. 3 rd Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
FRANKLIN-SIMPSON HIGH SCHOOL
 FRANKLIN-SIMPSON HIGH SCHOOL Course Name: Geometry Unit Name: Going in Circles Quality Core Objectives: B.1. C.1. D.1. Mathematical Processes Logic and Proof Points, Lines, Planes, and Space Unit 13 Going
FRANKLIN-SIMPSON HIGH SCHOOL Course Name: Geometry Unit Name: Going in Circles Quality Core Objectives: B.1. C.1. D.1. Mathematical Processes Logic and Proof Points, Lines, Planes, and Space Unit 13 Going
1 Triangle ABC is graphed on the set of axes below. 3 As shown in the diagram below, EF intersects planes P, Q, and R.
 1 Triangle ABC is graphed on the set of axes below. 3 As shown in the diagram below, EF intersects planes P, Q, and R. Which transformation produces an image that is similar to, but not congruent to, ABC?
1 Triangle ABC is graphed on the set of axes below. 3 As shown in the diagram below, EF intersects planes P, Q, and R. Which transformation produces an image that is similar to, but not congruent to, ABC?
SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal)
 1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide
 Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Chapter 10 Similarity
 Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
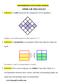 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
Chapter 11 Areas of Polygons and Circles
 Section 11-1: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles SOL: G.14 The student will use similar geometric objects in two- or three-dimensions to a) compare ratios between side lengths, perimeters, areas, and
Section 11-1: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles SOL: G.14 The student will use similar geometric objects in two- or three-dimensions to a) compare ratios between side lengths, perimeters, areas, and
GEOMETRY is the study of points in space
 CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
EUCLID S GEOMETRY. Raymond Hoobler. January 27, 2008
 EUCLID S GEOMETRY Raymond Hoobler January 27, 2008 Euclid rst codi ed the procedures and results of geometry, and he did such a good job that even today it is hard to improve on his presentation. He lived
EUCLID S GEOMETRY Raymond Hoobler January 27, 2008 Euclid rst codi ed the procedures and results of geometry, and he did such a good job that even today it is hard to improve on his presentation. He lived
fall08ge Geometry Regents Exam Test Sampler fall08 4 The diagram below shows the construction of the perpendicular bisector of AB.
 fall08ge 1 Isosceles trapezoid ABCD has diagonals AC and BD. If AC = 5x + 13 and BD = 11x 5, what is the value of x? 1) 8 4 The diagram below shows the construction of the perpendicular bisector of AB.
fall08ge 1 Isosceles trapezoid ABCD has diagonals AC and BD. If AC = 5x + 13 and BD = 11x 5, what is the value of x? 1) 8 4 The diagram below shows the construction of the perpendicular bisector of AB.
Name Class Date. Lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x?
 12-1 Practice Tangent Lines Lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x? 1. To start, identify the type of geometric figure formed by the tangent
12-1 Practice Tangent Lines Lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x? 1. To start, identify the type of geometric figure formed by the tangent
Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards
 Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Mathematics vocabulary word wall cards provide a display of mathematics content words and associated visual cues to assist in vocabulary development. The cards should
Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Mathematics vocabulary word wall cards provide a display of mathematics content words and associated visual cues to assist in vocabulary development. The cards should
MANHATTAN HUNTER SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY CURRICULUM
 COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
 Tools of Geometry 1. X + 9 = 24 2. 25 X = 15 3. X + 3 = -2X -10 4. 3X + 4Y = 2 Place in slope intercept form. 5. Y = ½ X 2 What is the slope? What is the Y- Intercept? Inductive Reasoning is reasoning
Tools of Geometry 1. X + 9 = 24 2. 25 X = 15 3. X + 3 = -2X -10 4. 3X + 4Y = 2 Place in slope intercept form. 5. Y = ½ X 2 What is the slope? What is the Y- Intercept? Inductive Reasoning is reasoning
Chapter 2 Diagnostic Test
 Chapter Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 68 7. Calculate each unknown side length. Round to two decimal places, if necessary. a) b). Solve each equation. Round to one decimal place, if necessary. a)
Chapter Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 68 7. Calculate each unknown side length. Round to two decimal places, if necessary. a) b). Solve each equation. Round to one decimal place, if necessary. a)
Angles. Classification Acute Right Obtuse. Complementary s 2 s whose sum is 90 Supplementary s 2 s whose sum is 180. Angle Addition Postulate
 ngles Classification cute Right Obtuse Complementary s 2 s whose sum is 90 Supplementary s 2 s whose sum is 180 ngle ddition Postulate If the exterior sides of two adj s lie in a line, they are supplementary
ngles Classification cute Right Obtuse Complementary s 2 s whose sum is 90 Supplementary s 2 s whose sum is 180 ngle ddition Postulate If the exterior sides of two adj s lie in a line, they are supplementary
Term Definition Figure
 Notes LT 1.1 - Distinguish and apply basic terms of geometry (coplanar, collinear, bisectors, congruency, parallel, perpendicular, etc.) Term Definition Figure collinear on the same line (note: you do
Notes LT 1.1 - Distinguish and apply basic terms of geometry (coplanar, collinear, bisectors, congruency, parallel, perpendicular, etc.) Term Definition Figure collinear on the same line (note: you do
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Geometry A Year-at-a-Glance Year-at-a-Glance
 Year-at-a-Glance 2018-2019 Year-at-a-Glance FIRST SEMESTER SECOND SEMESTER Unit 1 Foundations of Geometry Unit 2 Circles Unit 3 Equations of Lines and Angle-Pairs Unit 4 Congruence Unit 5 Triangles 1st
Year-at-a-Glance 2018-2019 Year-at-a-Glance FIRST SEMESTER SECOND SEMESTER Unit 1 Foundations of Geometry Unit 2 Circles Unit 3 Equations of Lines and Angle-Pairs Unit 4 Congruence Unit 5 Triangles 1st
Geometry SIA #3 Practice Exam
 Class: Date: Geometry SIA #3 Practice Exam Short Answer 1. Which point is the midpoint of AE? 2. Find the midpoint of PQ. 3. Find the coordinates of the midpoint of the segment whose endpoints are H(2,
Class: Date: Geometry SIA #3 Practice Exam Short Answer 1. Which point is the midpoint of AE? 2. Find the midpoint of PQ. 3. Find the coordinates of the midpoint of the segment whose endpoints are H(2,
Term Definition Figure
 Geometry Unit 1 Packet - Language of Geometry Name: #: Video Notes LT 1.1 - Distinguish and apply basic terms of geometry (coplanar, collinear, bisectors, congruent, parallel, perpendicular, etc.) Term
Geometry Unit 1 Packet - Language of Geometry Name: #: Video Notes LT 1.1 - Distinguish and apply basic terms of geometry (coplanar, collinear, bisectors, congruent, parallel, perpendicular, etc.) Term
Geometry: A Complete Course
 Geometry: Complete Course with Trigonometry) Module E - Course Notes Written by: Thomas E. Clark Geometry: Complete Course with Trigonometry) Module E - Course Notes Copyright 2014 by VideotextInteractive
Geometry: Complete Course with Trigonometry) Module E - Course Notes Written by: Thomas E. Clark Geometry: Complete Course with Trigonometry) Module E - Course Notes Copyright 2014 by VideotextInteractive
FGCU Invitational Geometry Individual 2014
 All numbers are assumed to be real. Diagrams are not drawn to scale. For all questions, NOTA represents none of the above answers is correct. For problems 1 and 2, refer to the figure in which AC BC and
All numbers are assumed to be real. Diagrams are not drawn to scale. For all questions, NOTA represents none of the above answers is correct. For problems 1 and 2, refer to the figure in which AC BC and
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Pearson Mathematics Geometry
 A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
Unit Number of Days Dates. 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/ Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9
 8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
Geometry: A Complete Course
 Geometry: omplete ourse with Trigonometry) Module Progress Tests Written by: Larry. ollins Geometry: omplete ourse with Trigonometry) Module - Progress Tests opyright 2014 by VideotextInteractive Send
Geometry: omplete ourse with Trigonometry) Module Progress Tests Written by: Larry. ollins Geometry: omplete ourse with Trigonometry) Module - Progress Tests opyright 2014 by VideotextInteractive Send
Circles and Polygons Long-Term Memory Review Review 1 (Note: Figures are not drawn to scale.)
 Review 1 (Note: Figures are not drawn to scale.) 1. Fill in the lank: In circle below, the angle shown is a/an angle. 2. The measure of a central angle and the measure of the arc that it intersects are
Review 1 (Note: Figures are not drawn to scale.) 1. Fill in the lank: In circle below, the angle shown is a/an angle. 2. The measure of a central angle and the measure of the arc that it intersects are
Geometry Rules. Triangles:
 Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Angles. An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex.
 Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips
 & present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
& present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
Geometric Constructions
 Materials: Compass, Straight Edge, Protractor Construction 1 Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; Or construct the midpoint of a line segment. Construction 2 Given a point on a line,
Materials: Compass, Straight Edge, Protractor Construction 1 Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; Or construct the midpoint of a line segment. Construction 2 Given a point on a line,
UNIT 5 GEOMETRY TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 5
 UNIT 5 GEOMETRY TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 5 Geometry Unit 5 Overview: Circles With and Without Coordinates In this unit, students prove basic theorems about circles, with particular attention
UNIT 5 GEOMETRY TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 5 Geometry Unit 5 Overview: Circles With and Without Coordinates In this unit, students prove basic theorems about circles, with particular attention
Reteaching Exploring Angles of Polygons
 Name Date lass Eploring Angles of Polygons INV X 3 You have learned to identify interior and eterior angles in polygons. Now you will determine angle measures in regular polygons. Interior Angles Sum of
Name Date lass Eploring Angles of Polygons INV X 3 You have learned to identify interior and eterior angles in polygons. Now you will determine angle measures in regular polygons. Interior Angles Sum of
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Construction Instructions. Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment.
 Construction Instructions Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1.) Begin with line segment XY. 2.) Place the compass at point X. Adjust
Construction Instructions Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1.) Begin with line segment XY. 2.) Place the compass at point X. Adjust
Montclair Public Schools Math Curriculum Unit Planning Template Unit # SLO # MC 2 MC 3
 Subject Geometry High Honors Grade Montclair Public Schools Math Curriculum Unit Planning Template Unit # Pacing 8-10 9 10 weeks Unit Circles, Conic Sections, Area & 3-D Measurements Name Overview Unit
Subject Geometry High Honors Grade Montclair Public Schools Math Curriculum Unit Planning Template Unit # Pacing 8-10 9 10 weeks Unit Circles, Conic Sections, Area & 3-D Measurements Name Overview Unit
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
m 6 + m 3 = 180⁰ m 1 m 4 m 2 m 5 = 180⁰ m 6 m 2 1. In the figure below, p q. Which of the statements is NOT true?
 1. In the figure below, p q. Which of the statements is NOT true? m 1 m 4 m 6 m 2 m 6 + m 3 = 180⁰ m 2 m 5 = 180⁰ 2. Look at parallelogram ABCD below. How could you prove that ABCD is a rhombus? Show that
1. In the figure below, p q. Which of the statements is NOT true? m 1 m 4 m 6 m 2 m 6 + m 3 = 180⁰ m 2 m 5 = 180⁰ 2. Look at parallelogram ABCD below. How could you prove that ABCD is a rhombus? Show that
Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1
 Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1 Lesson 1.1 Defined Terms: Undefined Terms: Point: Line: Plane: Space: Postulate 1: Postulate : terms that are explained using undefined and/or other defined terms
Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1 Lesson 1.1 Defined Terms: Undefined Terms: Point: Line: Plane: Space: Postulate 1: Postulate : terms that are explained using undefined and/or other defined terms
TENTH YEAR MATHEMATICS
 10 The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION TENTH YEAR MATHEMATICS Wednesday, August 16, 1967-8 :30 to 11 :30 a.m., only The last page of the booklet is the answer sheet,
10 The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION TENTH YEAR MATHEMATICS Wednesday, August 16, 1967-8 :30 to 11 :30 a.m., only The last page of the booklet is the answer sheet,
Section Congruence Through Constructions
 Section 10.1 - Congruence Through Constructions Definitions: Similar ( ) objects have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Congruent ( =) objects have the same size as well as the same shape.
Section 10.1 - Congruence Through Constructions Definitions: Similar ( ) objects have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Congruent ( =) objects have the same size as well as the same shape.
added to equal quantities, their sum is equal. Same holds for congruence.
 Mr. Cheung s Geometry Cheat Sheet Theorem List Version 6.0 Updated 3/14/14 (The following is to be used as a guideline. The rest you need to look up on your own, but hopefully this will help. The original
Mr. Cheung s Geometry Cheat Sheet Theorem List Version 6.0 Updated 3/14/14 (The following is to be used as a guideline. The rest you need to look up on your own, but hopefully this will help. The original
The radius for a regular polygon is the same as the radius of the circumscribed circle.
 Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Geometry Curriculum Guide Lunenburg County Public Schools June 2014
 Marking Period: 1 Days: 4 Reporting Category/Strand: Reasoning, Lines, and Transformations SOL G.1 The student will construct and judge the validity of a logical argument consisting of a set of premises
Marking Period: 1 Days: 4 Reporting Category/Strand: Reasoning, Lines, and Transformations SOL G.1 The student will construct and judge the validity of a logical argument consisting of a set of premises
Honors Midterm Review
 Name: Date: 1. Draw all lines of symmetry for these shapes. 4. A windmill has eight equally-spaced blades that rotate in the clockwise direction. 2. Use the figure below to answer the question that follows.
Name: Date: 1. Draw all lines of symmetry for these shapes. 4. A windmill has eight equally-spaced blades that rotate in the clockwise direction. 2. Use the figure below to answer the question that follows.
Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide
 Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never
 1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
a) 1/3 area of triangle ABC b) 3.6 c) 3 d) e) Euclid s fifth postulate is equivalent to: Given a line and a point not on that line
 1. Given is a right triangle with AD a perpendicular from the right angle to the hypotenuse, find the length of AD given AB = 6, BC = 10 and AC = 8. B D A C a) 7.5 b) 6.5 c) 4.8 d) e) 2. Using the figure
1. Given is a right triangle with AD a perpendicular from the right angle to the hypotenuse, find the length of AD given AB = 6, BC = 10 and AC = 8. B D A C a) 7.5 b) 6.5 c) 4.8 d) e) 2. Using the figure
Geometry First Semester Practice Final (cont)
 49. Determine the width of the river, AE, if A. 6.6 yards. 10 yards C. 12.8 yards D. 15 yards Geometry First Semester Practice Final (cont) 50. In the similar triangles shown below, what is the value of
49. Determine the width of the river, AE, if A. 6.6 yards. 10 yards C. 12.8 yards D. 15 yards Geometry First Semester Practice Final (cont) 50. In the similar triangles shown below, what is the value of
Section 1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes
 Section 1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes I CAN. Identify and model points, lines, and planes. Identify collinear and coplanar points and intersecting lines and planes in space. Undefined Term- Words, usually
Section 1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes I CAN. Identify and model points, lines, and planes. Identify collinear and coplanar points and intersecting lines and planes in space. Undefined Term- Words, usually
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12
 West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12 Unit 1: Basics of Geometry Content Area: Mathematics Course & Grade Level: Basic Geometry, 9 12 Summary and Rationale This unit
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12 Unit 1: Basics of Geometry Content Area: Mathematics Course & Grade Level: Basic Geometry, 9 12 Summary and Rationale This unit
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 Math 121 Fall 2017 - Practice Exam - Chapters 5 & 6 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The simplified form of the ratio 6 inches to 1 foot is 6:1. 2. The triple (20,21,29) is a Pythagorean
Math 121 Fall 2017 - Practice Exam - Chapters 5 & 6 Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The simplified form of the ratio 6 inches to 1 foot is 6:1. 2. The triple (20,21,29) is a Pythagorean
sample 9 final 512 Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: sample 9 final 512 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In each pair of triangles, parts are congruent as marked. Which pair
Name: Class: Date: sample 9 final 512 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In each pair of triangles, parts are congruent as marked. Which pair
GEOMETRY SPRING SEMESTER FINALS REVIEW PACKET
 Name Date Class GEOMETRY SPRING SEMESTER FINALS REVIEW PACKET For 1 2, use the graph. 6. State the converse of the statement. Then determine whether the converse is true. Explain. If two angles are vertical
Name Date Class GEOMETRY SPRING SEMESTER FINALS REVIEW PACKET For 1 2, use the graph. 6. State the converse of the statement. Then determine whether the converse is true. Explain. If two angles are vertical
Geometry Vocabulary Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Pre-AP Geometry Spring Semester Exam Review 2015
 hapter 8 1. Find.. 25.4. 11.57. 3 D. 28 3. Find.. 3.73. 4. 2 D. 8.77 5. Find, y, k, and m. = k= Pre-P Geometry Spring Semester Eam Review 2015 40 18 25 y= m= 2. Find.. 5 2.. 5 D. 2 4. Find.. 3 2. 2. D.
hapter 8 1. Find.. 25.4. 11.57. 3 D. 28 3. Find.. 3.73. 4. 2 D. 8.77 5. Find, y, k, and m. = k= Pre-P Geometry Spring Semester Eam Review 2015 40 18 25 y= m= 2. Find.. 5 2.. 5 D. 2 4. Find.. 3 2. 2. D.
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Geometry 2015 correlated to the New York Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Geometry
 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Geometry 2015 correlated to the New York Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Geometry Standards for Mathematical Practice SMP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Geometry 2015 correlated to the New York Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Geometry Standards for Mathematical Practice SMP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere
Course: Geometry PAP Prosper ISD Course Map Grade Level: Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block Days. Unit Title
 Unit Title Unit 1: Geometric Structure Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block 1 st 9 weeks Description of What Students will Focus on on the terms and statements that are the basis for geometry. able to use terms
Unit Title Unit 1: Geometric Structure Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block 1 st 9 weeks Description of What Students will Focus on on the terms and statements that are the basis for geometry. able to use terms
M2 GEOMETRY REVIEW FOR MIDTERM EXAM
 M2 GEOMETRY REVIEW FOR MIDTERM EXAM #1-11: True or false? If false, replace the underlined word or phrase to make a true sentence. 1. Two lines are perpendicular if they intersect to form a right angle.
M2 GEOMETRY REVIEW FOR MIDTERM EXAM #1-11: True or false? If false, replace the underlined word or phrase to make a true sentence. 1. Two lines are perpendicular if they intersect to form a right angle.
The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses. Geometry. Course Outline
 The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses Course Outline Course Outline Page 2 of 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 ACT Course Standards A. Prerequisites 1. Skills Acquired by Students
The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses Course Outline Course Outline Page 2 of 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 ACT Course Standards A. Prerequisites 1. Skills Acquired by Students
Geometry. Chapter 1 Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles
 Geometry Chapter 1 Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW ALL WORK. *** Algebraic Equations Review Keystone Vocabulary
Geometry Chapter 1 Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW ALL WORK. *** Algebraic Equations Review Keystone Vocabulary
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Geometry Indiana Standards Worktext Correlations
 Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
SOL Chapter Due Date
 Name: Block: Date: Geometry SOL Review SOL Chapter Due Date G.1 2.2-2.4 G.2 3.1-3.5 G.3 1.3, 4.8, 6.7, 9 G.4 N/A G.5 5.5 G.6 4.1-4.7 G.7 6.1-6.6 G.8 7.1-7.7 G.9 8.2-8.6 G.10 1.6, 8.1 G.11 10.1-10.6, 11.5,
Name: Block: Date: Geometry SOL Review SOL Chapter Due Date G.1 2.2-2.4 G.2 3.1-3.5 G.3 1.3, 4.8, 6.7, 9 G.4 N/A G.5 5.5 G.6 4.1-4.7 G.7 6.1-6.6 G.8 7.1-7.7 G.9 8.2-8.6 G.10 1.6, 8.1 G.11 10.1-10.6, 11.5,
CURRICULUM GUIDE. Honors Geometry
 CURRICULUM GUIDE Honors Geometry This level of Geometry is approached at an accelerated pace. Topics of postulates, theorems and proofs are discussed both traditionally and with a discovery approach. The
CURRICULUM GUIDE Honors Geometry This level of Geometry is approached at an accelerated pace. Topics of postulates, theorems and proofs are discussed both traditionally and with a discovery approach. The
Geometry 2 Final Review
 Name: Period: Date: Geometry 2 Final Review 1 Find x in ABC. 5 Find x in ABC. 2 Find x in STU. 6 Find cos A in ABC. 3 Find y in XYZ. 7 Find x to the nearest tenth. 4 Find x in HJK. 8 Find the angle of
Name: Period: Date: Geometry 2 Final Review 1 Find x in ABC. 5 Find x in ABC. 2 Find x in STU. 6 Find cos A in ABC. 3 Find y in XYZ. 7 Find x to the nearest tenth. 4 Find x in HJK. 8 Find the angle of
Grade IX. Mathematics Geometry Notes. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade IX Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen The distance of a point from the y - axis is called its x -coordinate, or abscissa, and the distance of the point from the x -axis is called its y-coordinate,
Grade IX Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen The distance of a point from the y - axis is called its x -coordinate, or abscissa, and the distance of the point from the x -axis is called its y-coordinate,
NOTES: Tangents to Circles
 Unit# ssign # TS: Tangents to ircles GL Identify segments and lines related to circles and use properties of a tangent to a circle VULRY circle is the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant
Unit# ssign # TS: Tangents to ircles GL Identify segments and lines related to circles and use properties of a tangent to a circle VULRY circle is the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK
 Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
Aldine ISD Benchmark Targets /Geometry SUMMER 2004
 ASSURANCES: By the end of Geometry, the student will be able to: 1. Use properties of triangles and quadrilaterals to solve problems. 2. Identify, classify, and draw two and three-dimensional objects (prisms,
ASSURANCES: By the end of Geometry, the student will be able to: 1. Use properties of triangles and quadrilaterals to solve problems. 2. Identify, classify, and draw two and three-dimensional objects (prisms,
b. find the lateral area of the cylinder c. If the radius is doubled, what happens to the volume?
 im: How do we find the volume and surface area of pyramids? o Now: If the radius and the height of a cylinder is 4 a. find the volume of the cylinder b. find the lateral area of the cylinder c. If the
im: How do we find the volume and surface area of pyramids? o Now: If the radius and the height of a cylinder is 4 a. find the volume of the cylinder b. find the lateral area of the cylinder c. If the
0817geo. Geometry CCSS Regents Exam AB DE.
 0817geo 1 A two-dimensional cross section is taken of a three-dimensional object. If this cross section is a triangle, what can not be the three-dimensional object? 1) cone 2) cylinder ) pyramid 4) rectangular
0817geo 1 A two-dimensional cross section is taken of a three-dimensional object. If this cross section is a triangle, what can not be the three-dimensional object? 1) cone 2) cylinder ) pyramid 4) rectangular
Geometry Spring Semester Review
 hapter 5 Geometry Spring Semester Review 1. In PM,. m P > m. m P > m M. m > m P. m M > m P 7 M 2. Find the shortest side of the figure QU. Q Q 80 4. QU. U. 50 82 U 3. In EFG, m E = 5 + 2, m F = -, and
hapter 5 Geometry Spring Semester Review 1. In PM,. m P > m. m P > m M. m > m P. m M > m P 7 M 2. Find the shortest side of the figure QU. Q Q 80 4. QU. U. 50 82 U 3. In EFG, m E = 5 + 2, m F = -, and
MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS
 MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS KEY IDEAS 1. To copy a segment, follow the steps given: Given: AB Construct: PQ congruent to AB 1. Use a straightedge to draw a line, l. 2. Choose a point on line l and label
MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS KEY IDEAS 1. To copy a segment, follow the steps given: Given: AB Construct: PQ congruent to AB 1. Use a straightedge to draw a line, l. 2. Choose a point on line l and label
Geometry Core Content EOC Exam Review
 Geometry Core Content EOC Exam Review 1. What is the midpoint of a line segment with endpoints ( 3, 7) and (6, 5)? 2. What is the midpoint of a line segment with endpoints ( 1, -5) and (-10, 3)? 3. In
Geometry Core Content EOC Exam Review 1. What is the midpoint of a line segment with endpoints ( 3, 7) and (6, 5)? 2. What is the midpoint of a line segment with endpoints ( 1, -5) and (-10, 3)? 3. In
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes
 Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
, y 2. ), then PQ = - y 1 ) 2. x 1 + x 2
 Tools of Geometry Chapter 1 Undefined Terms (p. 5) A point is a location. It has neither shape nor size. A line is made up of points and has no thickness or width. A plane is a flat surface made up of
Tools of Geometry Chapter 1 Undefined Terms (p. 5) A point is a location. It has neither shape nor size. A line is made up of points and has no thickness or width. A plane is a flat surface made up of
Geometry Lesson 1-1: Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Name Hr Pg. 5 (1, 3-22, 25, 26)
 Geometry Lesson 1-1: Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Name Hr Pg. 5 (1, 3-22, 25, 26) Learning Target: At the end of today s lesson we will be able to successfully name and sketch geometric figures.
Geometry Lesson 1-1: Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Name Hr Pg. 5 (1, 3-22, 25, 26) Learning Target: At the end of today s lesson we will be able to successfully name and sketch geometric figures.
