Transformations of Functions. Shifting Graphs. Similarly, you can obtain the graph of. g x x 2 2 f x 2. Vertical and Horizontal Shifts
|
|
|
- Garey Rich
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
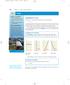
1 0_007.qd /7/05 : AM Page 7 7 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.7 Transormations o Functions What ou should learn Use vertical and horizontal shits to sketch graphs o unctions. Use relections to sketch graphs o unctions. Use nonrigid transormations to sketch graphs o unctions. Wh ou should learn it Knowing the graphs o common unctions and knowing how to shit, relect, and stretch graphs o unctions can help ou sketch a wide variet o simple unctions b hand. This skill is useul in sketching graphs o unctions that model real-lie data, such as in Eercise on page, where ou are asked to sketch the graph o a unction that models the amounts o mortgage debt outstanding rom 990 through 00. Shiting Graphs Man unctions have graphs that are simple transormations o the parent graphs summarized in Section.. For eample, ou can obtain the graph o h b shiting the graph o upward two units, as shown in Figure.7. In unction notation, h and are related as ollows. h Similarl, ou can obtain the graph o g Upward shit o two units b shiting the graph o to the right two units, as shown in Figure.77. In this case, the unctions g and have the ollowing relationship. g h() = + Right shit o two units () = g() = ( ) () = FIGURE.7 FIGURE.77 Ken Fisher/Gett Images In items and, be sure ou see that h c corresponds to a right shit and h c corresponds to a let shit or c > 0. The ollowing list summarizes this discussion about horizontal and vertical shits. Vertical and Horizontal Shits Let c be a positive real number. Vertical and horizontal shits in the graph o are represented as ollows.. Vertical shit c units upward: h c. Vertical shit c units downward: h c. Horizontal shit c units to the right: h c. Horizontal shit c units to the let: h c
2 0_007.qd /7/05 : AM Page 75 Section.7 Transormations o Functions 75 You might also wish to illustrate simple transormations o unctions numericall using tables to emphasize what happens to individual ordered pairs. For instance, i ou have, h,and g, ou can illustrate these transormations with the ollowing tables. h g Some graphs can be obtained rom combinations o vertical and horizontal shits, as demonstrated in Eample. Vertical and horizontal shits generate a amil o unctions, each with the same shape but at dierent locations in the plane. Eample Shits in the Graphs o a Function Use the graph o to sketch the graph o each unction. a. g b. h Solution a. Relative to the graph o, the graph o g is a downward shit o one unit, as shown in Figure.7. b. Relative to the graph o, the graph o h involves a let shit o two units and an upward shit o one unit, as shown in Figure.79. () = h() = ( + ) + () = g () = FIGURE.7 FIGURE.79 Now tr Eercise. In Figure.79, notice that the same result is obtained i the vertical shit precedes the horizontal shit or i the horizontal shit precedes the vertical shit. Graphing utilities are ideal tools or eploring translations o unctions. Graph, g, and h in same viewing window. Beore looking at the graphs, tr to predict how the graphs o g and h relate to the graph o. a. b. Eploration, g, h, g, h c., g, h
3 0_007.qd /7/05 : AM Page 7 7 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs () = h() = Relecting Graphs The second common tpe o transormation is a relection. For instance, i ou consider the -ais to be a mirror, the graph o h is the mirror image (or relection) o the graph o, as shown in Figure.0. FIGURE.0 Relections in the Coordinate Aes Relections in the coordinate aes o the graph o are represented as ollows.. Relection in the -ais: h () =. Relection in the -ais: h Eample Finding Equations rom Graphs FIGURE. The graph o the unction given b is shown in Figure.. Each o the graphs in Figure. is a transormation o the graph o. Find an equation or each o these unctions. 5 = g( ) = h( ) Eploration Reverse the order o transormations in Eample. Do ou obtain the same graph? Do the same or Eample. Do ou obtain the same graph? Eplain. FIGURE. Solution a. The graph o g is a relection in the -ais ollowed b an upward shit o two units o the graph o. So, the equation or g is g. b. The graph o h is a horizontal shit o three units to the right ollowed b a relection in the -ais o the graph o. So, the equation or h is h. Now tr Eercise 9.
4 0_007.qd /7/05 : AM Page 77 Section.7 Transormations o Functions 77 Eample Relections and Shits Compare the graph o each unction with the graph o. a. g b. h c. k Algebraic Solution a. The graph o g is a relection o the graph o in the -ais because g. b. The graph o h is a relection o the graph o in the -ais because h. c. The graph o k is a let shit o two units ollowed b a relection in the -ais because k. Graphical Solution a. Graph and g on the same set o coordinate aes. From the graph in Figure., ou can see that the graph o g is a relection o the graph o in the -ais. b. Graph and h on the same set o coordinate aes. From the graph in Figure., ou can see that the graph o h is a relection o the graph o in the -ais. c. Graph and k on the same set o coordinate aes. From the graph in Figure.5, ou can see that the graph o k is a let shit o two units o the graph o, ollowed b a relection in the -ais. () = g() = h() = () = FIGURE. FIGURE. () = k () = + Now tr Eercise 9. FIGURE.5 Activities. How are the graphs o and g related? Answer: The are relections o each other in the -ais.. Compare the graph o with the graph o g 9. Answer: g is shited to the right nine units. When sketching the graphs o unctions involving square roots, remember that the domain must be restricted to eclude negative numbers inside the radical. For instance, here are the domains o the unctions in Eample. Domain o g : 0 Domain o h : 0 Domain o k :
5 0_007.qd /7/05 : AM Page 7 7 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs FIGURE. g() = () = h() = () = FIGURE. () = FIGURE.7 5 g() = h() = Nonrigid Transormations Horizontal shits, vertical shits, and relections are rigid transormations because the basic shape o the graph is unchanged. These transormations change onl the position o the graph in the coordinate plane. Nonrigid transormations are those that cause a distortion a change in the shape o the original graph. For instance, a nonrigid transormation o the graph o is represented b g c, where the transormation is a vertical stretch i c > and a vertical shrink i 0 < c <. Another nonrigid transormation o the graph o is represented b h c, where the transormation is a horizontal shrink i c > and a horizontal stretch i 0 < c <. Eample Nonrigid Transormations Compare the graph o each unction with the graph o h a. b. Solution a. Relative to the graph o, the graph o h is a vertical stretch (each -value is multiplied b ) o the graph o. (See Figure..) b. Similarl, the graph o g g is a vertical shrink each -value is multiplied b o the graph o. (See Figure.7.) Now tr Eercise. Eample 5 Nonrigid Transormations Compare the graph o each unction with the graph o. a. g b. h Solution a. Relative to the graph o, the graph o g. is a horizontal shrink c > o the graph o. (See Figure..) b. Similarl, the graph o () = FIGURE.9 h is a horizontal stretch 0 < c < o the graph o. (See Figure.9.) Now tr Eercise 7.
6 0_007.qd /7/05 : AM Page 79 Section.7 Transormations o Functions 79.7 Eercises VOCABULARY CHECK: In Eercises 5, ill in the blanks.. Horizontal shits, vertical shits, and relections are called transormations.. A relection in the -ais o is represented b h, while a relection in the -ais o is represented b h.. Transormations that cause a distortion in the shape o the graph o are called transormations.. A nonrigid transormation o represented b h c is a i c > and a i 0 < c <. 5. A nonrigid transormation o represented b g c is a i c > and a i 0 < c <.. Match the rigid transormation o with the correct representation o the graph o h, where c > 0. h c (i) A horizontal shit o, c units to the right h c (ii) A vertical shit o, c units downward (c) h c (iii) A horizontal shit o, c units to the let (d) h c (iv) A vertical shit o, c units upward PREREQUISITE SKILLS REVIEW: Practice and review algebra skills needed or this section at For each unction, sketch (on the same set o coordinate aes) a graph o each unction or c,, and. c c (c) c. For each unction, sketch (on the same set o coordinate aes) a graph o each unction or c,,, and. c c (c) c. For each unction, sketch (on the same set o coordinate aes) a graph o each unction or c, 0, and. c c (c) c. For each unction, sketch (on the same set o coordinate aes) a graph o each unction or c,,, and. c, c, c, c, < 0 0 < 0 0 In Eercises 5, use the graph o to sketch each graph.to print an enlarged cop o the graph go to the website (c) (c) (d) (d) (e) (e) () () (g) (g) (, 0) (, ) (, ) (0, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (0, ) FIGURE FOR 5 FIGURE FOR (c) (c) (d) (d) (e) (e) () () (g) 0 (g)
7 0_007.qd /7/05 : AM Page 0 0 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs (, ) (0, ) (, 0) (, ) (0, 5) (, 0) (, 0) 0 (, ) (, ) 0. Use the graph o to write an equation or each FIGURE FOR 7 FIGURE FOR 9. Use the graph o to write an equation or each (c) 0. Use the graph o to write an equation or each (c) (d) (d) (c). Use the graph o to write an equation or each (c) In Eercises, identi the parent unction and the transormation shown in the graph. Write an equation or the unction shown in the graph. (d) (d)
8 0_007.qd /7/05 : AM Page Section.7 Transormations o Functions In Eercises 9, g is related to one o the parent unctions described in this chapter. Identi the parent unction. Describe the sequence o tranormations rom to g. (c) Sketch the graph o g. (d) Use unction notation to write g in terms o. 9. g 0. g. g 7. g. g. g 7 5. g 5. g g. g 9. g 0. g 0. g. g 5. g. g 9 5. g. g 5 7. g 9. g 9. g 7 0. g. g. g In Eercises 50, write an equation or the unction that is described b the given characteristics.. The shape o, but moved two units to the right and eight units downward. The shape o, but moved three units to the let, seven units upward, and relected in the -ais 5. The shape o, but moved units to the right. The shape o, but moved si units to the let, si units downward, and relected in the -ais 7. The shape o, but moved 0 units upward and relected in the -ais. The shape o, but moved one unit to the let and seven units downward 9. The shape o, but moved si units to the let and relected in both the -ais and the -ais 50. The shape o, but moved nine units downward and relected in both the -ais and the -ais 5. Use the graph o to write an equation or each 5. Use the graph o to write an equation or each 5. Use the graph o to write an equation or each 5. Use the graph o to write an equation or each 0 5 (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) 0 (, ) (, 7) (, ) (, )
9 0_007.qd /7/05 : AM Page Chapter Functions and Their Graphs In Eercises 55 0, identi the parent unction and the transormation shown in the graph. Write an equation or the unction shown in the graph. Then use a graphing utilit to veri our answer Graphical Analsis In Eercises, use the viewing window shown to write a possible equation or the transormation o the parent unction Graphical Reasoning In Eercises 5 and, use the graph o to sketch the graph o g. To print an enlarged cop o the graph, go to the website g (c) g g (e) g g 5 g (c) g (d) g (e) g () g 0 5 g (d) () g 7. Fuel Use The amounts o uel F (in billions o gallons) used b trucks rom 90 through 00 can be approimated b the unction F t t, 0 t where t represents the ear, with t 0 corresponding to 90. (Source: U.S. Federal Highwa Administration) Describe the transormation o the parent unction. Then sketch the graph over the speciied domain. Find the average rate o change o the unction rom 90 to 00. Interpret our answer in the contet o the problem. (c) Rewrite the unction so that t 0 represents 990. Eplain how ou got our answer. (d) Use the model rom part (c) to predict the amount o uel used b trucks in 00. Does our answer seem reasonable? Eplain. Model It
10 0_007.qd /7/05 : PM Page Section.7 Transormations o Functions. Finance The amounts M (in trillions o dollars) o mortgage debt outstanding in the United States rom 990 through 00 can be approimated b the unction M t t 0.9, where t represents the ear, with t 0 corresponding to 990. (Source: Board o Governors o the Federal Reserve Sstem) Describe the transormation o the parent unction. Then sketch the graph over the speciied domain. Rewrite the unction so that t 0 represents 000. Eplain how ou got our answer. Snthesis True or False? In Eercises 9 and 70, determine whether the statement is true or alse. Justi our answer. 9. The graphs o and are identical. 70. I the graph o the parent unction is moved si units to the right, three units upward, and relected in the -ais, then the point, 9 will lie on the graph o the transormation. 7. Describing Proits Management originall predicted that the proits rom the sales o a new product would be approimated b the graph o the unction shown. The actual proits are shown b the unction g along with a verbal description. Use the concepts o transormations o graphs to write g in terms o. 0,000 0,000 The proits were onl three-ourths as large as epected. The proits were consistentl $0,000 greater than predicted. 0 t t 0,000 0,000 0,000 0,000 g g t t (c) There was a two-ear dela in the introduction o the product. Ater sales began, proits grew as epected. 7. Eplain wh the graph o is a relection o the graph o about the -ais. 7. The graph o passes through the points 0,,,, and,. Find the corresponding points on the graph o. 7. Think About It You can use either o two methods to graph a unction: plotting points or translating a parent unction as shown in this section. Which method o graphing do ou preer to use or each unction? Eplain. Skills Review In Eercises 75, perorm the operation and simpli ,000 0,000 In Eercises and, evaluate the unction at the speciied values o the independent variable and simpli.. (c). 0 0 (c) 0 In Eercises 5, ind the domain o the unction g t
9.3 Transform Graphs of Linear Functions Use this blank page to compile the most important things you want to remember for cycle 9.
 9. Transorm Graphs o Linear Functions Use this blank page to compile the most important things you want to remember or cycle 9.: Sec Math In-Sync by Jordan School District, Utah is licensed under a 6 Function
9. Transorm Graphs o Linear Functions Use this blank page to compile the most important things you want to remember or cycle 9.: Sec Math In-Sync by Jordan School District, Utah is licensed under a 6 Function
UNIT #2 TRANSFORMATIONS OF FUNCTIONS
 Name: Date: UNIT # TRANSFORMATIONS OF FUNCTIONS Part I Questions. The quadratic unction ollowing does,, () has a turning point at have a turning point? 7, 3, 5 5, 8. I g 7 3, then at which o the The structure
Name: Date: UNIT # TRANSFORMATIONS OF FUNCTIONS Part I Questions. The quadratic unction ollowing does,, () has a turning point at have a turning point? 7, 3, 5 5, 8. I g 7 3, then at which o the The structure
Shifting, Reflecting, and Stretching Graphs
 Shifting, Reflecting, and Stretching s Shifting s 1 ( ) ( ) This is f ( ) This is f ( ) This is f ( ) What happens to the graph? f ( ) is f () shifted units to the right. f ( ) is f () shifted units to
Shifting, Reflecting, and Stretching s Shifting s 1 ( ) ( ) This is f ( ) This is f ( ) This is f ( ) What happens to the graph? f ( ) is f () shifted units to the right. f ( ) is f () shifted units to
Name Class Date. To translate three units to the left, 3 from the -coordinate. To translate two units down, 2 from the -coordinate.
 Name Class Date 1-1 Eploring Transormations Going Deeper Essential question: What patterns govern transormations o unctions? 1 F-BF.2.3 EXPLORE Translating Points Translate the point (-2, 5) three units
Name Class Date 1-1 Eploring Transormations Going Deeper Essential question: What patterns govern transormations o unctions? 1 F-BF.2.3 EXPLORE Translating Points Translate the point (-2, 5) three units
7.5. Systems of Inequalities. The Graph of an Inequality. What you should learn. Why you should learn it
 0_0705.qd /5/05 9:5 AM Page 5 Section 7.5 7.5 Sstems of Inequalities 5 Sstems of Inequalities What ou should learn Sketch the graphs of inequalities in two variables. Solve sstems of inequalities. Use
0_0705.qd /5/05 9:5 AM Page 5 Section 7.5 7.5 Sstems of Inequalities 5 Sstems of Inequalities What ou should learn Sketch the graphs of inequalities in two variables. Solve sstems of inequalities. Use
3.6. Transformations of Graphs of Linear Functions
 . Transformations of Graphs of Linear Functions Essential Question How does the graph of the linear function f() = compare to the graphs of g() = f() + c and h() = f(c)? Comparing Graphs of Functions USING
. Transformations of Graphs of Linear Functions Essential Question How does the graph of the linear function f() = compare to the graphs of g() = f() + c and h() = f(c)? Comparing Graphs of Functions USING
1.5 LIMITS. The Limit of a Function
 60040_005.qd /5/05 :0 PM Page 49 SECTION.5 Limits 49.5 LIMITS Find its of functions graphicall and numericall. Use the properties of its to evaluate its of functions. Use different analtic techniques to
60040_005.qd /5/05 :0 PM Page 49 SECTION.5 Limits 49.5 LIMITS Find its of functions graphicall and numericall. Use the properties of its to evaluate its of functions. Use different analtic techniques to
Graphs of quadratics functions are parabolas opening up if a > 0, and down if a < 0. Examples:
 Quadratic Functions ( ) = a + b + c Graphs o quadratics unctions are parabolas opening up i a > 0, and down i a < 0. Eamples: = = + = = 0 MATH 80 Lecture B o 5 Ronald Brent 07 All rights reserved. Notes:
Quadratic Functions ( ) = a + b + c Graphs o quadratics unctions are parabolas opening up i a > 0, and down i a < 0. Eamples: = = + = = 0 MATH 80 Lecture B o 5 Ronald Brent 07 All rights reserved. Notes:
Exponential Functions
 6. Eponential Functions Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of an eponential function? Eploring an Eponential Function Work with a partner. Cop and complete each table
6. Eponential Functions Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of an eponential function? Eploring an Eponential Function Work with a partner. Cop and complete each table
Inclination of a Line
 0_00.qd 78 /8/05 Chapter 0 8:5 AM Page 78 Topics in Analtic Geometr 0. Lines What ou should learn Find the inclination of a line. Find the angle between two lines. Find the distance between a point and
0_00.qd 78 /8/05 Chapter 0 8:5 AM Page 78 Topics in Analtic Geometr 0. Lines What ou should learn Find the inclination of a line. Find the angle between two lines. Find the distance between a point and
3.6 Graphing Piecewise-Defined Functions and Shifting and Reflecting Graphs of Functions
 76 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Find the equation of each line. Write the equation in the form = a, = b, or = m + b. For Eercises through 7, write the equation in the form f = m + b.. Through (, 6) and
76 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Find the equation of each line. Write the equation in the form = a, = b, or = m + b. For Eercises through 7, write the equation in the form f = m + b.. Through (, 6) and
Math 1050 Lab Activity: Graphing Transformations
 Math 00 Lab Activit: Graphing Transformations Name: We'll focus on quadratic functions to eplore graphing transformations. A quadratic function is a second degree polnomial function. There are two common
Math 00 Lab Activit: Graphing Transformations Name: We'll focus on quadratic functions to eplore graphing transformations. A quadratic function is a second degree polnomial function. There are two common
Transformations of Functions. 1. Shifting, reflecting, and stretching graphs Symmetry of functions and equations
 Chapter Transformations of Functions TOPICS.5.. Shifting, reflecting, and stretching graphs Smmetr of functions and equations TOPIC Horizontal Shifting/ Translation Horizontal Shifting/ Translation Shifting,
Chapter Transformations of Functions TOPICS.5.. Shifting, reflecting, and stretching graphs Smmetr of functions and equations TOPIC Horizontal Shifting/ Translation Horizontal Shifting/ Translation Shifting,
The Graph of an Equation
 60_0P0.qd //0 :6 PM Page CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Archive Photos Section P. RENÉ DESCARTES (96 60) Descartes made man contributions to philosoph, science, and mathematics. The idea of representing
60_0P0.qd //0 :6 PM Page CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Archive Photos Section P. RENÉ DESCARTES (96 60) Descartes made man contributions to philosoph, science, and mathematics. The idea of representing
3.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree
 71_00.qp 1/7/06 1: PM Page 6 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree 6. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree What ou should learn Graphs of Polnomial Functions You should be able to sketch accurate
71_00.qp 1/7/06 1: PM Page 6 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree 6. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree What ou should learn Graphs of Polnomial Functions You should be able to sketch accurate
1.1. Parent Functions and Transformations Essential Question What are the characteristics of some of the basic parent functions?
 1.1 Parent Functions and Transformations Essential Question What are the characteristics of some of the basic parent functions? Identifing Basic Parent Functions JUSTIFYING CONCLUSIONS To be proficient
1.1 Parent Functions and Transformations Essential Question What are the characteristics of some of the basic parent functions? Identifing Basic Parent Functions JUSTIFYING CONCLUSIONS To be proficient
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Figure Electron micrograph of E. Coli bacteria (credit: Mattosaurus, Wikimedia Commons) CHAPTER OUTLINE. Eponential Functions. Logarithmic Properties. Graphs of Eponential
Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Figure Electron micrograph of E. Coli bacteria (credit: Mattosaurus, Wikimedia Commons) CHAPTER OUTLINE. Eponential Functions. Logarithmic Properties. Graphs of Eponential
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Figure Electron micrograph of E. Coli bacteria (credit: Mattosaurus, Wikimedia Commons) Chapter Outline. Eponential Functions. Logarithmic Properties. Graphs of Eponential
Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Figure Electron micrograph of E. Coli bacteria (credit: Mattosaurus, Wikimedia Commons) Chapter Outline. Eponential Functions. Logarithmic Properties. Graphs of Eponential
Partial Fraction Decomposition
 Section 7. Partial Fractions 53 Partial Fraction Decomposition Algebraic techniques for determining the constants in the numerators of partial fractions are demonstrated in the eamples that follow. Note
Section 7. Partial Fractions 53 Partial Fraction Decomposition Algebraic techniques for determining the constants in the numerators of partial fractions are demonstrated in the eamples that follow. Note
Appendix C: Review of Graphs, Equations, and Inequalities
 Appendi C: Review of Graphs, Equations, and Inequalities C. What ou should learn Just as ou can represent real numbers b points on a real number line, ou can represent ordered pairs of real numbers b points
Appendi C: Review of Graphs, Equations, and Inequalities C. What ou should learn Just as ou can represent real numbers b points on a real number line, ou can represent ordered pairs of real numbers b points
6. f(x) = x f(x) = x f(x) = x f(x) = 3 x. 10. f(x) = x + 3
 Section 9.1 The Square Root Function 879 9.1 Eercises In Eercises 1-, complete each of the following tasks. i. Set up a coordinate sstem on a sheet of graph paper. Label and scale each ais. ii. Complete
Section 9.1 The Square Root Function 879 9.1 Eercises In Eercises 1-, complete each of the following tasks. i. Set up a coordinate sstem on a sheet of graph paper. Label and scale each ais. ii. Complete
Laurie s Notes. Overview of Section 6.3
 Overview of Section.3 Introduction In this lesson, eponential equations are defined. Students distinguish between linear and eponential equations, helping to focus on the definition of each. A linear function
Overview of Section.3 Introduction In this lesson, eponential equations are defined. Students distinguish between linear and eponential equations, helping to focus on the definition of each. A linear function
Math-3 Lesson 1-7 Analyzing the Graphs of Functions
 Math- Lesson -7 Analyzing the Graphs o Functions Which unctions are symmetric about the y-axis? cosx sin x x We call unctions that are symmetric about the y -axis, even unctions. Which transormation is
Math- Lesson -7 Analyzing the Graphs o Functions Which unctions are symmetric about the y-axis? cosx sin x x We call unctions that are symmetric about the y -axis, even unctions. Which transormation is
Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention 1-1. Exploring Transformations. 2 Holt McDougal Algebra 2. Name Date Class
 Lesson - Read to Go n? Skills Intervention Eploring Transformations Find these vocabular words in the lesson and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular transformation translation reflection stretch Translating
Lesson - Read to Go n? Skills Intervention Eploring Transformations Find these vocabular words in the lesson and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular transformation translation reflection stretch Translating
9. f(x) = x f(x) = x g(x) = 2x g(x) = 5 2x. 13. h(x) = 1 3x. 14. h(x) = 2x f(x) = x x. 16.
 Section 4.2 Absolute Value 367 4.2 Eercises For each of the functions in Eercises 1-8, as in Eamples 7 and 8 in the narrative, mark the critical value on a number line, then mark the sign of the epression
Section 4.2 Absolute Value 367 4.2 Eercises For each of the functions in Eercises 1-8, as in Eamples 7 and 8 in the narrative, mark the critical value on a number line, then mark the sign of the epression
ACTIVITY: Graphing a Linear Equation. 2 x x + 1?
 . Graphing Linear Equations How can ou draw its graph? How can ou recognize a linear equation? ACTIVITY: Graphing a Linear Equation Work with a partner. a. Use the equation = + to complete the table. (Choose
. Graphing Linear Equations How can ou draw its graph? How can ou recognize a linear equation? ACTIVITY: Graphing a Linear Equation Work with a partner. a. Use the equation = + to complete the table. (Choose
Math-3. Lesson 6-8. Graphs of the sine and cosine functions; and Periodic Behavior
 Math-3 Lesson 6-8 Graphs o the sine and cosine unctions; and Periodic Behavior What is a unction? () Function: a rule that matches each input to eactly one output. What is the domain o a unction? Domain:
Math-3 Lesson 6-8 Graphs o the sine and cosine unctions; and Periodic Behavior What is a unction? () Function: a rule that matches each input to eactly one output. What is the domain o a unction? Domain:
P.5 The Cartesian Plane
 7_0P0.qp //07 8: AM Page 8 8 Chapter P Prerequisites P. The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane Just as ou can represent real numbers b points on a real number line, ou can represent ordered pairs of real
7_0P0.qp //07 8: AM Page 8 8 Chapter P Prerequisites P. The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane Just as ou can represent real numbers b points on a real number line, ou can represent ordered pairs of real
Appendix F: Systems of Inequalities
 A0 Appendi F Sstems of Inequalities Appendi F: Sstems of Inequalities F. Solving Sstems of Inequalities The Graph of an Inequalit The statements < and are inequalities in two variables. An ordered pair
A0 Appendi F Sstems of Inequalities Appendi F: Sstems of Inequalities F. Solving Sstems of Inequalities The Graph of an Inequalit The statements < and are inequalities in two variables. An ordered pair
Unit 5 Lesson 2 Investigation 1
 Name: Investigation 1 Modeling Rigid Transformations CPMP-Tools Computer graphics enable designers to model two- and three-dimensional figures and to also easil manipulate those figures. For eample, interior
Name: Investigation 1 Modeling Rigid Transformations CPMP-Tools Computer graphics enable designers to model two- and three-dimensional figures and to also easil manipulate those figures. For eample, interior
Chapter 3. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Selected Applications
 Chapter Eponential and Logarithmic Functions. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs. Properties of Logarithms. Solving Eponential and Logarithmic Equations.5 Eponential
Chapter Eponential and Logarithmic Functions. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs. Properties of Logarithms. Solving Eponential and Logarithmic Equations.5 Eponential
The Graph Scale-Change Theorem
 Lesson 3-5 Lesson 3-5 The Graph Scale-Change Theorem Vocabular horizontal and vertical scale change, scale factor size change BIG IDEA The graph of a function can be scaled horizontall, verticall, or in
Lesson 3-5 Lesson 3-5 The Graph Scale-Change Theorem Vocabular horizontal and vertical scale change, scale factor size change BIG IDEA The graph of a function can be scaled horizontall, verticall, or in
p Graph square root functions. VOCABULARY Radical expression Radical function Square root function Parent square root function
 . Graph Square Root Functions Goal p Graph square root functions. Your Notes VOCABULARY Radical epression Radical function Square root function Parent square root function PARENT FUNCTION FOR SQUARE ROOT
. Graph Square Root Functions Goal p Graph square root functions. Your Notes VOCABULARY Radical epression Radical function Square root function Parent square root function PARENT FUNCTION FOR SQUARE ROOT
The Graph of an Equation Graph the following by using a table of values and plotting points.
 Calculus Preparation - Section 1 Graphs and Models Success in math as well as Calculus is to use a multiple perspective -- graphical, analytical, and numerical. Thanks to Rene Descartes we can represent
Calculus Preparation - Section 1 Graphs and Models Success in math as well as Calculus is to use a multiple perspective -- graphical, analytical, and numerical. Thanks to Rene Descartes we can represent
Lesson 11-2 Shrinking, Stretching, and Reflecting Parabolas ACTIVITY 11
 ACTIVITY 11 Lesson 11- M Notes Unlike a rigid transformation, a vertical stretch or vertical shrink will change the shape of the graph. A vertical stretch stretches a graph awa from the -ais b a factor
ACTIVITY 11 Lesson 11- M Notes Unlike a rigid transformation, a vertical stretch or vertical shrink will change the shape of the graph. A vertical stretch stretches a graph awa from the -ais b a factor
8.5 Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs
 CHAPTER 8 Quadratic Equations and Functions 8. Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs S Graph Quadratic Functions of the Form f = + k. Graph Quadratic Functions of the Form f = - h. Graph Quadratic Functions
CHAPTER 8 Quadratic Equations and Functions 8. Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs S Graph Quadratic Functions of the Form f = + k. Graph Quadratic Functions of the Form f = - h. Graph Quadratic Functions
LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING
 LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING 137 OVERVIEW Here s what ou ll learn in this lesson: Plotting Points a. The -plane b. The -ais and -ais c. The origin d. Ordered
LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING LESSON 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHING 137 OVERVIEW Here s what ou ll learn in this lesson: Plotting Points a. The -plane b. The -ais and -ais c. The origin d. Ordered
Graphing f ( x) = ax 2 + c
 . Graphing f ( ) = a + c Essential Question How does the value of c affect the graph of f () = a + c? Graphing = a + c Work with a partner. Sketch the graphs of the functions in the same coordinate plane.
. Graphing f ( ) = a + c Essential Question How does the value of c affect the graph of f () = a + c? Graphing = a + c Work with a partner. Sketch the graphs of the functions in the same coordinate plane.
2.3. Horizontal and Vertical Translations of Functions. Investigate
 .3 Horizontal and Vertical Translations of Functions When a video game developer is designing a game, she might have several objects displaed on the computer screen that move from one place to another
.3 Horizontal and Vertical Translations of Functions When a video game developer is designing a game, she might have several objects displaed on the computer screen that move from one place to another
2.3. One-to-One and Inverse Functions. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 One-to-One and Inverse Functions 2. Introduction In this Section we eamine more terminolog associated with functions. We eplain one-to-one and man-to-one functions and show how the rule associated with
One-to-One and Inverse Functions 2. Introduction In this Section we eamine more terminolog associated with functions. We eplain one-to-one and man-to-one functions and show how the rule associated with
Graphs and Functions
 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions. Graphing Equations. Introduction to Functions. Graphing Linear Functions. The Slope of a Line. Equations of Lines Integrated Review Linear Equations in Two Variables.6 Graphing
CHAPTER Graphs and Functions. Graphing Equations. Introduction to Functions. Graphing Linear Functions. The Slope of a Line. Equations of Lines Integrated Review Linear Equations in Two Variables.6 Graphing
Graph each pair of functions on the same coordinate plane See margin. Technology Activity: A Family of Functions
 - What You ll Learn To analze translations To analze stretches, shrinks, and reflections...and Wh To analze a fabric design, as in Eample Families of Functions Check Skills You ll Need G for Help Lessons
- What You ll Learn To analze translations To analze stretches, shrinks, and reflections...and Wh To analze a fabric design, as in Eample Families of Functions Check Skills You ll Need G for Help Lessons
Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of work b Horia Varlan;
Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of work b Horia Varlan;
3.5 Rational Functions
 0 Chapter Polnomial and Rational Functions Rational Functions For a rational function, find the domain and graph the function, identifing all of the asmptotes Solve applied problems involving rational
0 Chapter Polnomial and Rational Functions Rational Functions For a rational function, find the domain and graph the function, identifing all of the asmptotes Solve applied problems involving rational
Derivatives 3: The Derivative as a Function
 Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function 77 Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function Model : Graph of a Function 9 8 7 6 5 g() - - - 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 - - -5-6 -7 Construct Your Understanding
Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function 77 Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function Model : Graph of a Function 9 8 7 6 5 g() - - - 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 - - -5-6 -7 Construct Your Understanding
Lesson 2.1 Exercises, pages 90 96
 Lesson.1 Eercises, pages 9 96 A. a) Complete the table of values. 1 1 1 1 1. 1 b) For each function in part a, sketch its graph then state its domain and range. For : the domain is ; and the range is.
Lesson.1 Eercises, pages 9 96 A. a) Complete the table of values. 1 1 1 1 1. 1 b) For each function in part a, sketch its graph then state its domain and range. For : the domain is ; and the range is.
Graphing square root functions. What would be the base graph for the square root function? What is the table of values?
 Unit 3 (Chapter 2) Radical Functions (Square Root Functions Sketch graphs of radical functions b appling translations, stretches and reflections to the graph of Analze transformations to identif the of
Unit 3 (Chapter 2) Radical Functions (Square Root Functions Sketch graphs of radical functions b appling translations, stretches and reflections to the graph of Analze transformations to identif the of
Chapter 1. Functions and Their Graphs. Selected Applications
 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs. Lines in the Plane. Functions. Graphs of Functions. Shifting, Reflecting, and Stretching Graphs.5 Combinations of Functions. Inverse Functions.7 Linear Models and Scatter
Chapter Functions and Their Graphs. Lines in the Plane. Functions. Graphs of Functions. Shifting, Reflecting, and Stretching Graphs.5 Combinations of Functions. Inverse Functions.7 Linear Models and Scatter
Check Skills You ll Need (For help, go to Lesson 1-2.) Evaluate each expression for the given value of x.
 A_3eSE_00X 0/6/005 :3 AM Page - Eploring Eponential Models Lesson Preview What You ll Learn To model eponential growth To model eponential deca... And Wh To model a car s depreciation, as in Eample 6 Check
A_3eSE_00X 0/6/005 :3 AM Page - Eploring Eponential Models Lesson Preview What You ll Learn To model eponential growth To model eponential deca... And Wh To model a car s depreciation, as in Eample 6 Check
TIPS4RM: MHF4U: Unit 1 Polynomial Functions
 TIPSRM: MHFU: Unit Polnomial Functions 008 .5.: Polnomial Concept Attainment Activit Compare and contrast the eamples and non-eamples of polnomial functions below. Through reasoning, identif attributes
TIPSRM: MHFU: Unit Polnomial Functions 008 .5.: Polnomial Concept Attainment Activit Compare and contrast the eamples and non-eamples of polnomial functions below. Through reasoning, identif attributes
2-1. The Language of Functions. Vocabulary
 Chapter Lesson -1 BIG IDEA A function is a special tpe of relation that can be described b ordered pairs, graphs, written rules or algebraic rules such as equations. On pages 78 and 79, nine ordered pairs
Chapter Lesson -1 BIG IDEA A function is a special tpe of relation that can be described b ordered pairs, graphs, written rules or algebraic rules such as equations. On pages 78 and 79, nine ordered pairs
Functions and Their Graphs
 Functions and Their Graphs. Rectangular Coordinates. Graphs of Equations. Linear Equations in Two Variables. Functions.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions. A Librar of Parent Functions.7 Transformations of
Functions and Their Graphs. Rectangular Coordinates. Graphs of Equations. Linear Equations in Two Variables. Functions.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions. A Librar of Parent Functions.7 Transformations of
Unit 2: Function Transformation Chapter 1
 Basic Transformations Reflections Inverses Unit 2: Function Transformation Chapter 1 Section 1.1: Horizontal and Vertical Transformations A of a function alters the and an combination of the of the graph.
Basic Transformations Reflections Inverses Unit 2: Function Transformation Chapter 1 Section 1.1: Horizontal and Vertical Transformations A of a function alters the and an combination of the of the graph.
Radical Functions Review
 Radical Functions Review Specific Outcome 3 Graph and analyze radical functions (limited to functions involving one radical) Acceptable Standard sketch and analyze (domain, range, invariant points, - and
Radical Functions Review Specific Outcome 3 Graph and analyze radical functions (limited to functions involving one radical) Acceptable Standard sketch and analyze (domain, range, invariant points, - and
y = f(x) x (x, f(x)) f(x) g(x) = f(x) + 2 (x, g(x)) 0 (0, 1) 1 3 (0, 3) 2 (2, 3) 3 5 (2, 5) 4 (4, 3) 3 5 (4, 5) 5 (5, 5) 5 7 (5, 7)
 0 Relations and Functions.7 Transformations In this section, we stud how the graphs of functions change, or transform, when certain specialized modifications are made to their formulas. The transformations
0 Relations and Functions.7 Transformations In this section, we stud how the graphs of functions change, or transform, when certain specialized modifications are made to their formulas. The transformations
Essential Question: How do you graph an exponential function of the form f (x) = ab x? Explore Exploring Graphs of Exponential Functions. 1.
 Locker LESSON 4.4 Graphing Eponential Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.7e Graph eponential and logarithmic functions, showing intercepts and end behavior, and trigonometric
Locker LESSON 4.4 Graphing Eponential Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.7e Graph eponential and logarithmic functions, showing intercepts and end behavior, and trigonometric
Chapter 5: Polynomial Functions
 Chapter : Polnomial Functions Section.1 Chapter : Polnomial Functions Section.1: Eploring the Graphs of Polnomial Functions Terminolog: Polnomial Function: A function that contains onl the operations of
Chapter : Polnomial Functions Section.1 Chapter : Polnomial Functions Section.1: Eploring the Graphs of Polnomial Functions Terminolog: Polnomial Function: A function that contains onl the operations of
Session 3. Rational and Radical Equations. Math 30-1 R 3. (Revisit, Review and Revive)
 Session 3 Rational and Radical Equations Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) Rational Functions Review Specific Outcome 14 Graph and analyze rational functions (limited to numerators and denominators
Session 3 Rational and Radical Equations Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) Rational Functions Review Specific Outcome 14 Graph and analyze rational functions (limited to numerators and denominators
ACTIVITY: Representing Data by a Linear Equation
 9.2 Lines of Fit How can ou use data to predict an event? ACTIVITY: Representing Data b a Linear Equation Work with a partner. You have been working on a science project for 8 months. Each month, ou measured
9.2 Lines of Fit How can ou use data to predict an event? ACTIVITY: Representing Data b a Linear Equation Work with a partner. You have been working on a science project for 8 months. Each month, ou measured
Vocabulary. Term Page Definition Clarifying Example. dependent variable. domain. function. independent variable. parent function.
 CHAPTER 1 Vocabular The table contains important vocabular terms from Chapter 1. As ou work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifing eample. dependent variable Term Page
CHAPTER 1 Vocabular The table contains important vocabular terms from Chapter 1. As ou work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifing eample. dependent variable Term Page
12.2 Techniques for Evaluating Limits
 335_qd /4/5 :5 PM Page 863 Section Tecniques for Evaluating Limits 863 Tecniques for Evaluating Limits Wat ou sould learn Use te dividing out tecnique to evaluate its of functions Use te rationalizing
335_qd /4/5 :5 PM Page 863 Section Tecniques for Evaluating Limits 863 Tecniques for Evaluating Limits Wat ou sould learn Use te dividing out tecnique to evaluate its of functions Use te rationalizing
2/22/ Transformations but first 1.3 Recap. Section Objectives: Students will know how to analyze graphs of functions.
 1 2 3 4 1.4 Transformations but first 1.3 Recap Section Objectives: Students will know how to analyze graphs of functions. 5 Recap of Important information 1.2 Functions and their Graphs Vertical line
1 2 3 4 1.4 Transformations but first 1.3 Recap Section Objectives: Students will know how to analyze graphs of functions. 5 Recap of Important information 1.2 Functions and their Graphs Vertical line
Section 4.3 Features of a Line
 Section.3 Features of a Line Objectives In this section, ou will learn to: To successfull complete this section, ou need to understand: Identif the - and -intercepts of a line. Plotting points in the --plane
Section.3 Features of a Line Objectives In this section, ou will learn to: To successfull complete this section, ou need to understand: Identif the - and -intercepts of a line. Plotting points in the --plane
c Sa diyya Hendrickson
 Transformations c Sa diyya Hendrickson Introduction Overview Vertical and Horizontal Transformations Important Facts to Remember Naming Transformations Reflections Stretches and Compressions The Rebel
Transformations c Sa diyya Hendrickson Introduction Overview Vertical and Horizontal Transformations Important Facts to Remember Naming Transformations Reflections Stretches and Compressions The Rebel
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 9-1 Multiple Representations of Functions
 9A Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 9-1 Multiple Representations of Functions Using Multiple Representations to Solve Problems The table shows the sum of the interior angles of polgons and the number
9A Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 9-1 Multiple Representations of Functions Using Multiple Representations to Solve Problems The table shows the sum of the interior angles of polgons and the number
= = The number system. Module. Glossary Math Tools... 33
 - > + > < - %. < + a = - = = b in. F - - Module The number sstem Lesson Rational and Irrational Numbers........ 8.NS. Lesson ompare and Order Numbers......... 8 8.NS., 8.NS. Lesson Estimate the Value of
- > + > < - %. < + a = - = = b in. F - - Module The number sstem Lesson Rational and Irrational Numbers........ 8.NS. Lesson ompare and Order Numbers......... 8 8.NS., 8.NS. Lesson Estimate the Value of
Graphing Radical Functions
 17 LESSON Graphing Radical Functions Basic Graphs of Radical Functions UNDERSTAND The parent radical function, 5, is shown. 5 0 0 1 1 9 0 10 The function takes the principal, or positive, square root of.
17 LESSON Graphing Radical Functions Basic Graphs of Radical Functions UNDERSTAND The parent radical function, 5, is shown. 5 0 0 1 1 9 0 10 The function takes the principal, or positive, square root of.
Graphing Review. Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic
 Graphing Review Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic Common Functions and Their Graphs Linear Functions A function f defined b a linear equation of the form = f() = m + b, where m and b are constants, is called
Graphing Review Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic Common Functions and Their Graphs Linear Functions A function f defined b a linear equation of the form = f() = m + b, where m and b are constants, is called
1. y = f(x) y = f(x + 3) 3. y = f(x) y = f(x 1) 5. y = 3f(x) 6. y = f(3x) 7. y = f(x) 8. y = f( x) 9. y = f(x 3) + 1
 .7 Transformations.7. Eercises To see all of the help resources associated with this section, click OSttS Chapter b. Suppose (, ) is on the graph of = f(). In Eercises - 8, use Theorem.7 to find a point
.7 Transformations.7. Eercises To see all of the help resources associated with this section, click OSttS Chapter b. Suppose (, ) is on the graph of = f(). In Eercises - 8, use Theorem.7 to find a point
A Formal Definition of Limit
 5 CHAPTER Limits and Their Properties L + ε L L ε (c, L) c + δ c c δ The - definition of the it of f as approaches c Figure. A Formal Definition of Limit Let s take another look at the informal description
5 CHAPTER Limits and Their Properties L + ε L L ε (c, L) c + δ c c δ The - definition of the it of f as approaches c Figure. A Formal Definition of Limit Let s take another look at the informal description
Warm - Up. Sunday, February 1, HINT: plot points first then connect the dots. Draw a graph with the following characteristics:
 Warm - Up Sunday, February 1, 2015 Draw a graph with the following characteristics: Maximums at (-3,4) and (2,2) Minimum at (-1,-3) X intercepts at (-4,0), (-2,0), (1,0), and (3,0) Y intercept at (0,-2)
Warm - Up Sunday, February 1, 2015 Draw a graph with the following characteristics: Maximums at (-3,4) and (2,2) Minimum at (-1,-3) X intercepts at (-4,0), (-2,0), (1,0), and (3,0) Y intercept at (0,-2)
Appendix F: Systems of Inequalities
 Appendi F: Sstems of Inequalities F. Solving Sstems of Inequalities The Graph of an Inequalit What ou should learn The statements < and ⱖ are inequalities in two variables. An ordered pair 共a, b兲 is a
Appendi F: Sstems of Inequalities F. Solving Sstems of Inequalities The Graph of an Inequalit What ou should learn The statements < and ⱖ are inequalities in two variables. An ordered pair 共a, b兲 is a
Intermediate Algebra. Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technology
 Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technolog c 2017 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. The essence of the license
Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technolog c 2017 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. The essence of the license
4.6 Graphs of Other Trigonometric Functions
 .6 Graphs of Other Trigonometric Functions Section.6 Graphs of Other Trigonometric Functions 09 Graph of the Tangent Function Recall that the tangent function is odd. That is, tan tan. Consequentl, the
.6 Graphs of Other Trigonometric Functions Section.6 Graphs of Other Trigonometric Functions 09 Graph of the Tangent Function Recall that the tangent function is odd. That is, tan tan. Consequentl, the
Online Homework Hints and Help Extra Practice
 Evaluate: Homework and Practice Use a graphing calculator to graph the polnomial function. Then use the graph to determine the function s domain, range, and end behavior. (Use interval notation for the
Evaluate: Homework and Practice Use a graphing calculator to graph the polnomial function. Then use the graph to determine the function s domain, range, and end behavior. (Use interval notation for the
Section 5.7 Negative Exponents and Scientific Notation. What is YOUR Share?
 Section. Negative Eponents and Scientific Notation What is YOUR Share? In a recent ear there was a budget deficit of about $,0,000,000,000 and there were approimatel 0,000,000 Americans. In this section
Section. Negative Eponents and Scientific Notation What is YOUR Share? In a recent ear there was a budget deficit of about $,0,000,000,000 and there were approimatel 0,000,000 Americans. In this section
CHECK Your Understanding
 CHECK Your Understanding. State the domain and range of each relation. Then determine whether the relation is a function, and justif our answer.. a) e) 5(, ), (, 9), (, 7), (, 5), (, ) 5 5 f) 55. State
CHECK Your Understanding. State the domain and range of each relation. Then determine whether the relation is a function, and justif our answer.. a) e) 5(, ), (, 9), (, 7), (, 5), (, ) 5 5 f) 55. State
Vertical and Horizontal Translations. Graph each pair of functions on the same coordinate plane See margin
 - Lesson Preview What You ll Learn BJECTIVE BJECTIVE To analze vertical translations To analze horizontal translations... And Wh To analze a fabric design, as in Eample BJECTIVE Vertical and Horizontal
- Lesson Preview What You ll Learn BJECTIVE BJECTIVE To analze vertical translations To analze horizontal translations... And Wh To analze a fabric design, as in Eample BJECTIVE Vertical and Horizontal
2.2 Absolute Value Functions
 . Absolute Value Functions 7. Absolute Value Functions There are a few was to describe what is meant b the absolute value of a real number. You ma have been taught that is the distance from the real number
. Absolute Value Functions 7. Absolute Value Functions There are a few was to describe what is meant b the absolute value of a real number. You ma have been taught that is the distance from the real number
Section 9.3: Functions and their Graphs
 Section 9.: Functions and their Graphs Graphs provide a wa of displaing, interpreting, and analzing data in a visual format. In man problems, we will consider two variables. Therefore, we will need to
Section 9.: Functions and their Graphs Graphs provide a wa of displaing, interpreting, and analzing data in a visual format. In man problems, we will consider two variables. Therefore, we will need to
1.1 Horizontal & Vertical Translations
 Unit II Transformations of Functions. Horizontal & Vertical Translations Goal: Demonstrate an understanding of the effects of horizontal and vertical translations on the graphs of functions and their related
Unit II Transformations of Functions. Horizontal & Vertical Translations Goal: Demonstrate an understanding of the effects of horizontal and vertical translations on the graphs of functions and their related
9.8 Graphing Rational Functions
 9. Graphing Rational Functions Lets begin with a deinition. Deinition: Rational Function A rational unction is a unction o the orm P where P and Q are polynomials. Q An eample o a simple rational unction
9. Graphing Rational Functions Lets begin with a deinition. Deinition: Rational Function A rational unction is a unction o the orm P where P and Q are polynomials. Q An eample o a simple rational unction
7h2 Graphing Basic Rational Functions (Gebrochenrationaler Funktionen)
 7h Graphing Basic Rational Functions (Gebrochenrationaler Funktionen) Goals: Graph rational functions Find the zeros and y-intercepts Identify and understand the asymptotes Match graphs to their equations
7h Graphing Basic Rational Functions (Gebrochenrationaler Funktionen) Goals: Graph rational functions Find the zeros and y-intercepts Identify and understand the asymptotes Match graphs to their equations
10.7. Polar Coordinates. Introduction. What you should learn. Why you should learn it. Example 1. Plotting Points on the Polar Coordinate System
 _7.qxd /8/5 9: AM Page 779 Section.7 Polar Coordinates 779.7 Polar Coordinates What ou should learn Plot points on the polar coordinate sstem. Convert points from rectangular to polar form and vice versa.
_7.qxd /8/5 9: AM Page 779 Section.7 Polar Coordinates 779.7 Polar Coordinates What ou should learn Plot points on the polar coordinate sstem. Convert points from rectangular to polar form and vice versa.
ACTIVITY: Graphing a Linear Equation. 2 x x + 1?
 . Graphing Linear Equations How can ou draw its graph? How can ou recognize a linear equation? ACTIVITY: Graphing a Linear Equation Work with a partner. a. Use the equation = + to complete the table. (Choose
. Graphing Linear Equations How can ou draw its graph? How can ou recognize a linear equation? ACTIVITY: Graphing a Linear Equation Work with a partner. a. Use the equation = + to complete the table. (Choose
Here are some guidelines for solving a linear programming problem in two variables in which an objective function is to be maximized or minimized.
 Appendi F. Linear Programming F F. Linear Programming Linear Programming: A Graphical Approach Man applications in business and economics involve a process called optimization, in which ou are asked to
Appendi F. Linear Programming F F. Linear Programming Linear Programming: A Graphical Approach Man applications in business and economics involve a process called optimization, in which ou are asked to
Section 2.2: Absolute Value Functions, from College Algebra: Corrected Edition by Carl Stitz, Ph.D. and Jeff Zeager, Ph.D. is available under a
 Section.: Absolute Value Functions, from College Algebra: Corrected Edition b Carl Stitz, Ph.D. and Jeff Zeager, Ph.D. is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike.0 license.
Section.: Absolute Value Functions, from College Algebra: Corrected Edition b Carl Stitz, Ph.D. and Jeff Zeager, Ph.D. is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike.0 license.
Exponential Functions. Christopher Thomas
 Mathematics Learning Centre Eponential Functions Christopher Thomas c 1998 Universit of Sdne Mathematics Learning Centre, Universit of Sdne 1 1 Eponential Functions 1.1 The functions =2 and =2 From our
Mathematics Learning Centre Eponential Functions Christopher Thomas c 1998 Universit of Sdne Mathematics Learning Centre, Universit of Sdne 1 1 Eponential Functions 1.1 The functions =2 and =2 From our
Section 4.2 Graphs of Exponential Functions
 238 Chapter 4 Section 4.2 Graphs of Eponential Functions Like with linear functions, the graph of an eponential function is determined by the values for the parameters in the function s formula. To get
238 Chapter 4 Section 4.2 Graphs of Eponential Functions Like with linear functions, the graph of an eponential function is determined by the values for the parameters in the function s formula. To get
PATTERNS AND ALGEBRA. He opened mathematics to many discoveries and exciting applications.
 PATTERNS AND ALGEBRA The famous French philosopher and mathematician René Descartes (596 65) made a great contribution to mathematics in 67 when he published a book linking algebra and geometr for the
PATTERNS AND ALGEBRA The famous French philosopher and mathematician René Descartes (596 65) made a great contribution to mathematics in 67 when he published a book linking algebra and geometr for the
4 B. 4 D. 4 F. 3. What are some common characteristics of the graphs of cubic and quartic polynomial functions?
 .1 Graphing Polnomial Functions COMMON CORE Learning Standards HSF-IF.B. HSF-IF.C.7c Essential Question What are some common characteristics of the graphs of cubic and quartic polnomial functions? A polnomial
.1 Graphing Polnomial Functions COMMON CORE Learning Standards HSF-IF.B. HSF-IF.C.7c Essential Question What are some common characteristics of the graphs of cubic and quartic polnomial functions? A polnomial
Lines and Their Slopes
 8.2 Lines and Their Slopes Linear Equations in Two Variables In the previous chapter we studied linear equations in a single variable. The solution of such an equation is a real number. A linear equation
8.2 Lines and Their Slopes Linear Equations in Two Variables In the previous chapter we studied linear equations in a single variable. The solution of such an equation is a real number. A linear equation
3.1 Sequences of Transformations
 Name lass Date 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Essential Question: What happens when ou appl more than one transformation to a figure? Eplore ombining Rotations or Reflections transformation is a function
Name lass Date 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Essential Question: What happens when ou appl more than one transformation to a figure? Eplore ombining Rotations or Reflections transformation is a function
Graphing Cubic Functions
 Locker 8 - - - - - -8 LESSON. Graphing Cubic Functions Name Class Date. Graphing Cubic Functions Essential Question: How are the graphs of f () = a ( - h) + k and f () = ( related to the graph of f ()
Locker 8 - - - - - -8 LESSON. Graphing Cubic Functions Name Class Date. Graphing Cubic Functions Essential Question: How are the graphs of f () = a ( - h) + k and f () = ( related to the graph of f ()
Transforming Polynomial Functions
 5-9 Transforming Polnomial Functions Content Standards F.BF.3 Identif the effect on the graph of replacing f() b f() k, k f(), f(k), and f( k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative) find
5-9 Transforming Polnomial Functions Content Standards F.BF.3 Identif the effect on the graph of replacing f() b f() k, k f(), f(k), and f( k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative) find
ACTIVITY: Describing an Exponential Function
 6. Eponential Functions eponential function? What are the characteristics of an ACTIVITY: Describing an Eponential Function Work with a partner. The graph below shows estimates of the population of Earth
6. Eponential Functions eponential function? What are the characteristics of an ACTIVITY: Describing an Eponential Function Work with a partner. The graph below shows estimates of the population of Earth
Concept Explanation Examples Distance formula The distance between (x 1, y 1 ) and (x 2, y 2 ) is d = 2(x 2 - x 1 ) 2 + ( y 2 - y 1 ) 2.
 660_ch0pp00-075.qd 0/6/08 4:8 PM Page 4 4 CHAPTER Introduction to Functions and Graphs continued from previous page Concept Eplanation Eamples Distance formula The distance between (, y ) and (, y ) is
660_ch0pp00-075.qd 0/6/08 4:8 PM Page 4 4 CHAPTER Introduction to Functions and Graphs continued from previous page Concept Eplanation Eamples Distance formula The distance between (, y ) and (, y ) is
5.2. Exploring Quotients of Polynomial Functions. EXPLORE the Math. Each row shows the graphs of two polynomial functions.
 YOU WILL NEED graph paper coloured pencils or pens graphing calculator or graphing software Eploring Quotients of Polnomial Functions EXPLORE the Math Each row shows the graphs of two polnomial functions.
YOU WILL NEED graph paper coloured pencils or pens graphing calculator or graphing software Eploring Quotients of Polnomial Functions EXPLORE the Math Each row shows the graphs of two polnomial functions.
Investigation Recursive Toothpick Patterns
 Investigation Recursive Toothpick Patterns Name Period Date You will need: a bo of toothpicks In this investigation ou will learn to create and appl recursive sequences b modeling them with puzzle pieces
Investigation Recursive Toothpick Patterns Name Period Date You will need: a bo of toothpicks In this investigation ou will learn to create and appl recursive sequences b modeling them with puzzle pieces
PROBLEM SOLVING WITH EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS
 Topic 21: Problem solving with eponential functions 323 PROBLEM SOLVING WITH EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS Lesson 21.1 Finding function rules from graphs 21.1 OPENER 1. Plot the points from the table onto the
Topic 21: Problem solving with eponential functions 323 PROBLEM SOLVING WITH EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS Lesson 21.1 Finding function rules from graphs 21.1 OPENER 1. Plot the points from the table onto the
