9.3 Transform Graphs of Linear Functions Use this blank page to compile the most important things you want to remember for cycle 9.
|
|
|
- Diana Evans
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
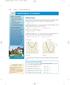
1 9. Transorm Graphs o Linear Functions Use this blank page to compile the most important things you want to remember or cycle 9.: Sec Math In-Sync by Jordan School District, Utah is licensed under a 6
2 Function Transormation Transormations o Functions It is diicult to see the eects o transormations on linear and eponential unctions, ecept or the vertical shit. Eamples: In the eamples below, k = or k = -. The original unctions are shown irst. In subsequent graphs, the original graphs are dashed. Original Function: Original Function: g The transormation k or g k is a vertical translation. Notice that i k is positive, the graph will shit up. I k is negative, then the graph will shit down. The output o the unction is being changed i.e. or g increased by, hence the downward and upward translation it s decreased by and or respectively. g Sec Math In-Sync by Jordan School District, Utah is licensed under a 64
3 The transormation k or kg is a vertical stretch or compression. I k is negative, the graph will be relected over the -ais. This transormation is very diicult to see with linear and eponential unctions unless looking at a relection with an eponential unction. Again, the output o the unction is being transormed i.e., the output is being multiplied by something, hence compressing, stretching, or relecting the output. 6 g The transormation k or g k is a horizontal stretch or compression. I k is negative, the graph will be relected over the y-ais. Again, the eects o this transormation are not easy to see with linear and eponential unctions. A relection over the y-ais with an eponential unction is more apparent. 6 g( ) The transormation k or g k, is a horizontal translation. Notice that i k is positive, the graph will shit to the let. I k is negative, then the graph will shit to the right. Again, the input o the unction is aected. ( ) 5 g ( ) Sec Math In-Sync by Jordan School District, Utah is licensed under a 65
4 9.a (build) Vertical Transormations Given the unction, perorm the ollowing transormations. Write the new equation and graph it on the graph provided. Be sure to label your new unction on the graph.. g g =. h h =. j h j = Indicate the transormation done to in order to obtain the ollowing equations. 7. g 5 8. h 9. j 5 Given the unction, perorm the ollowing transormations. Write the new equation. Graph it on the graph provided. Label your new unction on the graph.. g( ) ( ) 5. h( ) ( ) 5. j( ) h( ) 5 g = h = j = Indicate the transormation done to in order to obtain the ollowing equations. 6. g 7. h 8. j For each unction below write an equation rom the verbal description i and g 4 9. shit up 4. shit g down. shit g up. Shit down. Sec Math In-Sync by Jordan School District, Utah is licensed under a 66
5 . For large parties, a restaurant requires a reservation ee o $5, plus a $5 charge per person. The total charge or a party o people is 5 5. a) How will the graph o this unction change i the reservation ee is raised to $5? b) How will the graph change i the charge per person is lowered to $? 4. A lorist charges $5 or a vase, plus $4.5 or each lower. The total charge or the vase and lowers is given by the unction a) How will the graph change i the cost o the vase is raised to $5? b) How will the graph change i the charge per lower is lowered to $.? 5. A book club charges a membership ee o $ and then $ or each book purchased. a) Let y equal the total cost o membership in the club based on the number o books purchased. b) Write a second unction to represent the total cost o membership i the club raises its membership ee to $. c) Describe the relationship between the two unctions. 6. Kelly works as a salesperson. She earns a weekly base salary, plus a commission that is a percentage o her total sales. Her total weekly pay is described by., where is the total in sales dollars. a) What is Kelly s weekly base salary? b) What percentage o the total sales does Kelly receive as commission? c) What is the change in Kelly s salary plan i the weekly pay unction changes to g.5 d) What is the change i the unction is h. 4?? Sec Math In-Sync by Jordan School District, Utah is licensed under a 67
6 9.b (build) Horizontal and Vertical Linear EquationTransormations Part A: Vertical and Horizontal Shits. Begin with translations o linear equations. Think about slope intercept orm ( y m b), slope, and intercepts. Compare the unctions below to. a. b. 6 c. 5. Graph the unctions in # above. Use colored pencils. Label the lines. a. What part o the equation (y = m+b) did we change? b. What did this transormation do to the graph? c. Eplain why we call this a vertical translation transormation. Part B: Vertical shits and equations. Graph the equation 4. Label it. Write a contet or the unction. a. Move up. Sketch. Label this unction g =. Modiy the contet or the new unction. b. Move line down. Sketch. Label this unction r =. Modiy the contet or the new unction. c. Move line g up. Sketch. Label this unction v. Modiy the contet or the new unction. 4. What is the relationship o the unctions, g, r, and v? 5. To deine the vertical translation transormation o, we write k, where k is deining the vertical shit. Fill in the blanks or the ollowing: I k is the graph is translated up, and i k is the graph is translated down. Sec Math In-Sync by Jordan School District, Utah is licensed under a 68
7 Part C: Horizontal shits and equations 6. Graph and label. a. Graph and label. Describe the transormation. b. Graph and label. Describe the transormation. c. Graph and label. Describe the transormation. d. Graph and label. Describe the transormation. 7. How is changing in each equation? 8. How does it aect the graph o? What happened to the -intercept? 9. To deine the horizontal transormation o, we write k, where k is deining the horizontal shit. Fill in the blanks or the ollowing: I k is the graph is translated, and i k is the graph is translated.. I, what is the dierence in the transormations o and Part D: Practice Vertical and horizontal shits?. For each unction below, write an equation or the transormation described i. A vertical slide down 4.. A vertical slide down. 5. A vertical slide up A horizontal slide to the let. Indicate the transormation done to. A horizontal slide to the right. 4. A vertical slide up and a horizontal slide to the let A vertical slide down 5 and a horizontal slide to the right. given by the equation Sec Math In-Sync by Jordan School District, Utah is licensed under a 69
8 9.c (reine) Linear Vertical and Horizontal Transormation Practice Given:. Sketch. a. Sketch the unction y given by the transormations to below in 4. b. Write the new equation or each transormation. y.. y. y y 4. 4 Graph and g. Describe the transormation rom the graph o, g 4 5., g , g 8. g, 4 to the graph o g. Describe the transormation(s) on the graph o 4 that result in the graph o g. g g 4. g 4 5. g 4 Given the ollowing transormations, rewrite the equation o. Translate up units and to the let. 4. Translate to the right 4 units. 5. Translate down units and to the let 6 units. 6. Translate to the let 8 units. 7. You have seen that the graph o g is the result o translating the graph o three units up. However, you can also think o this as a horizontal translation that is, a translation let or right. Graph g to get the graph o. g. Describe the horizontal translation o the graph o Sec Math In-Sync by Jordan School District, Utah is licensed under a 7
9 9.d HONORS (reine) Transormations Shits The unction () is graphed. It has a domain o [-, 5] or 5 and a range o [-, 4] or y y 4. Perorm the indicated transormations. Then ind the domain and range o the new unction and describe the transormation. Vertical Shits A. Graph B. Graph Horizontal Shits A. Graph B. Graph Vertical Stretch (or Shrink)(s) A. Graph B. Graph Sec Math In-Sync by Jordan School District, Utah is licensed under a 7
10 Horizontal Stretch (or Shrink) A. Graph B. Graph Relection over the -ais or y-ais A. Graph B. Graph Combining Transormations A. Graph B. Graph Doing Transormations rom a Verbal Description Write the transormation, graph and identiy the domain and range. A. Shited down two and to the right one. B. Graph moved to the let and has a vertical stretch o. C. Graph has a horizontal stretch o one hal and then moved up one. Sec Math In-Sync by Jordan School District, Utah is licensed under a 7
11 9.e HONORS (apply) Transormation Shit Practice Given the graph, table, and domain and range o () below: a. Complete the tables b. Sketch the resulting graph c. Record the new domain and range () - Domain:, - - Range:,. y ( ). y ( ). y ( ) 4. y ( ) 5. y ( ) - - y 7. y ( ) - - y 9. y y () Given the graph above or (), write the equation, graph the new unction, and indicate the domain and range or the ollowing:. Moved to the let and down.. Vertical stretch o and moved up.. Relection over the -ais and moved to the right. - - Sec Math In-Sync by Jordan School District, Utah is licensed under a 7
UNIT #2 TRANSFORMATIONS OF FUNCTIONS
 Name: Date: UNIT # TRANSFORMATIONS OF FUNCTIONS Part I Questions. The quadratic unction ollowing does,, () has a turning point at have a turning point? 7, 3, 5 5, 8. I g 7 3, then at which o the The structure
Name: Date: UNIT # TRANSFORMATIONS OF FUNCTIONS Part I Questions. The quadratic unction ollowing does,, () has a turning point at have a turning point? 7, 3, 5 5, 8. I g 7 3, then at which o the The structure
Transformations of Functions. Shifting Graphs. Similarly, you can obtain the graph of. g x x 2 2 f x 2. Vertical and Horizontal Shifts
 0_007.qd /7/05 : AM Page 7 7 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.7 Transormations o Functions What ou should learn Use vertical and horizontal shits to sketch graphs o unctions. Use relections to sketch
0_007.qd /7/05 : AM Page 7 7 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.7 Transormations o Functions What ou should learn Use vertical and horizontal shits to sketch graphs o unctions. Use relections to sketch
Name Class Date. To translate three units to the left, 3 from the -coordinate. To translate two units down, 2 from the -coordinate.
 Name Class Date 1-1 Eploring Transormations Going Deeper Essential question: What patterns govern transormations o unctions? 1 F-BF.2.3 EXPLORE Translating Points Translate the point (-2, 5) three units
Name Class Date 1-1 Eploring Transormations Going Deeper Essential question: What patterns govern transormations o unctions? 1 F-BF.2.3 EXPLORE Translating Points Translate the point (-2, 5) three units
Graphs of quadratics functions are parabolas opening up if a > 0, and down if a < 0. Examples:
 Quadratic Functions ( ) = a + b + c Graphs o quadratics unctions are parabolas opening up i a > 0, and down i a < 0. Eamples: = = + = = 0 MATH 80 Lecture B o 5 Ronald Brent 07 All rights reserved. Notes:
Quadratic Functions ( ) = a + b + c Graphs o quadratics unctions are parabolas opening up i a > 0, and down i a < 0. Eamples: = = + = = 0 MATH 80 Lecture B o 5 Ronald Brent 07 All rights reserved. Notes:
The Graph of an Equation Graph the following by using a table of values and plotting points.
 Calculus Preparation - Section 1 Graphs and Models Success in math as well as Calculus is to use a multiple perspective -- graphical, analytical, and numerical. Thanks to Rene Descartes we can represent
Calculus Preparation - Section 1 Graphs and Models Success in math as well as Calculus is to use a multiple perspective -- graphical, analytical, and numerical. Thanks to Rene Descartes we can represent
Math-3. Lesson 6-8. Graphs of the sine and cosine functions; and Periodic Behavior
 Math-3 Lesson 6-8 Graphs o the sine and cosine unctions; and Periodic Behavior What is a unction? () Function: a rule that matches each input to eactly one output. What is the domain o a unction? Domain:
Math-3 Lesson 6-8 Graphs o the sine and cosine unctions; and Periodic Behavior What is a unction? () Function: a rule that matches each input to eactly one output. What is the domain o a unction? Domain:
9.8 Graphing Rational Functions
 9. Graphing Rational Functions Lets begin with a deinition. Deinition: Rational Function A rational unction is a unction o the orm P where P and Q are polynomials. Q An eample o a simple rational unction
9. Graphing Rational Functions Lets begin with a deinition. Deinition: Rational Function A rational unction is a unction o the orm P where P and Q are polynomials. Q An eample o a simple rational unction
2. Graphical Transformations of Functions
 2. Graphical Transformations of Functions In this section we will discuss how the graph of a function may be transformed either by shifting, stretching or compressing, or reflection. In this section let
2. Graphical Transformations of Functions In this section we will discuss how the graph of a function may be transformed either by shifting, stretching or compressing, or reflection. In this section let
Section 4.2 Graphs of Exponential Functions
 238 Chapter 4 Section 4.2 Graphs of Eponential Functions Like with linear functions, the graph of an eponential function is determined by the values for the parameters in the function s formula. To get
238 Chapter 4 Section 4.2 Graphs of Eponential Functions Like with linear functions, the graph of an eponential function is determined by the values for the parameters in the function s formula. To get
Composite functions. [Type the document subtitle] Composite functions, working them out.
![Composite functions. [Type the document subtitle] Composite functions, working them out. Composite functions. [Type the document subtitle] Composite functions, working them out.](/thumbs/76/73514886.jpg) Composite unctions [Type the document subtitle] Composite unctions, workin them out. luxvis 11/19/01 Composite Functions What are they? In the real world, it is not uncommon or the output o one thin to
Composite unctions [Type the document subtitle] Composite unctions, workin them out. luxvis 11/19/01 Composite Functions What are they? In the real world, it is not uncommon or the output o one thin to
Math-3 Lesson 1-7 Analyzing the Graphs of Functions
 Math- Lesson -7 Analyzing the Graphs o Functions Which unctions are symmetric about the y-axis? cosx sin x x We call unctions that are symmetric about the y -axis, even unctions. Which transormation is
Math- Lesson -7 Analyzing the Graphs o Functions Which unctions are symmetric about the y-axis? cosx sin x x We call unctions that are symmetric about the y -axis, even unctions. Which transormation is
6. 4 Transforming Linear Functions
 Name Class Date 6. Transforming Linear Functions Essential Question: What are the was in which ou can transform the graph of a linear function? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Building New Linear Functions b
Name Class Date 6. Transforming Linear Functions Essential Question: What are the was in which ou can transform the graph of a linear function? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Building New Linear Functions b
5.2 Properties of Rational functions
 5. Properties o Rational unctions A rational unction is a unction o the orm n n1 polynomial p an an 1 a1 a0 k k1 polynomial q bk bk 1 b1 b0 Eample 3 5 1 The domain o a rational unction is the set o all
5. Properties o Rational unctions A rational unction is a unction o the orm n n1 polynomial p an an 1 a1 a0 k k1 polynomial q bk bk 1 b1 b0 Eample 3 5 1 The domain o a rational unction is the set o all
Exponential Functions
 6. Eponential Functions Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of an eponential function? Eploring an Eponential Function Work with a partner. Cop and complete each table
6. Eponential Functions Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of an eponential function? Eploring an Eponential Function Work with a partner. Cop and complete each table
Transforming Linear Functions
 COMMON CORE Locker LESSON 6. Transforming Linear Functions Name Class Date 6. Transforming Linear Functions Essential Question: What are the was in which ou can transform the graph of a linear function?
COMMON CORE Locker LESSON 6. Transforming Linear Functions Name Class Date 6. Transforming Linear Functions Essential Question: What are the was in which ou can transform the graph of a linear function?
Rational Functions. Definition A rational function can be written in the form. where N(x) and D(x) are
 Rational Functions Deinition A rational unction can be written in the orm () N() where N() and D() are D() polynomials and D() is not the zero polynomial. *To ind the domain o a rational unction we must
Rational Functions Deinition A rational unction can be written in the orm () N() where N() and D() are D() polynomials and D() is not the zero polynomial. *To ind the domain o a rational unction we must
Problem 1: The relationship of height, in cm. and basketball players, names is a relation:
 Chapter - Functions and Graphs Chapter.1 - Functions, Relations and Ordered Pairs Relations A relation is a set of ordered pairs. Domain of a relation is the set consisting of all the first elements of
Chapter - Functions and Graphs Chapter.1 - Functions, Relations and Ordered Pairs Relations A relation is a set of ordered pairs. Domain of a relation is the set consisting of all the first elements of
Shifting, Reflecting, and Stretching Graphs
 Shifting, Reflecting, and Stretching s Shifting s 1 ( ) ( ) This is f ( ) This is f ( ) This is f ( ) What happens to the graph? f ( ) is f () shifted units to the right. f ( ) is f () shifted units to
Shifting, Reflecting, and Stretching s Shifting s 1 ( ) ( ) This is f ( ) This is f ( ) This is f ( ) What happens to the graph? f ( ) is f () shifted units to the right. f ( ) is f () shifted units to
1-2. Composition of Functions. OBJECTIVES Perform operations with functions. Find composite functions. Iterate functions using real numbers.
 - OBJECTIVES Perorm operations with unctions. Find composite unctions. Iterate unctions using real numbers. Composition o Functions BUSINESS Each year, thousands o people visit Yellowstone National Park
- OBJECTIVES Perorm operations with unctions. Find composite unctions. Iterate unctions using real numbers. Composition o Functions BUSINESS Each year, thousands o people visit Yellowstone National Park
This is a function because no vertical line can be drawn so that it intersects the graph more than once.
 Determine whether each relation is a function. Explain. 1. A function is a relation in which each element of the domain is paired with exactly one element of the range. So, this relation is a function.
Determine whether each relation is a function. Explain. 1. A function is a relation in which each element of the domain is paired with exactly one element of the range. So, this relation is a function.
3.6. Transformations of Graphs of Linear Functions
 . Transformations of Graphs of Linear Functions Essential Question How does the graph of the linear function f() = compare to the graphs of g() = f() + c and h() = f(c)? Comparing Graphs of Functions USING
. Transformations of Graphs of Linear Functions Essential Question How does the graph of the linear function f() = compare to the graphs of g() = f() + c and h() = f(c)? Comparing Graphs of Functions USING
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 7.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date What s the Inverse of an Eponent? Logarithmic Functions as Inverses Vocabulary Write the term that best completes each statement. 1. The of a number
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date What s the Inverse of an Eponent? Logarithmic Functions as Inverses Vocabulary Write the term that best completes each statement. 1. The of a number
Domain: The domain of f is all real numbers except those values for which Q(x) =0.
 Math 1330 Section.3.3: Rational Functions Definition: A rational function is a function that can be written in the form P() f(), where f and g are polynomials. Q() The domain of the rational function such
Math 1330 Section.3.3: Rational Functions Definition: A rational function is a function that can be written in the form P() f(), where f and g are polynomials. Q() The domain of the rational function such
c Sa diyya Hendrickson
 Transformations c Sa diyya Hendrickson Introduction Overview Vertical and Horizontal Transformations Important Facts to Remember Naming Transformations Reflections Stretches and Compressions The Rebel
Transformations c Sa diyya Hendrickson Introduction Overview Vertical and Horizontal Transformations Important Facts to Remember Naming Transformations Reflections Stretches and Compressions The Rebel
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS through 7.1.5
 SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 7.1. through 7.1.5 Students have used the equation = m + b throughout this course to graph lines and describe patterns. When the equation is written in -form, the m is the
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 7.1. through 7.1.5 Students have used the equation = m + b throughout this course to graph lines and describe patterns. When the equation is written in -form, the m is the
3. parallel: (b) and (c); perpendicular (a) and (b), (a) and (c)
 SECTION 1.1 1. Plot the points (0, 4), ( 2, 3), (1.5, 1), and ( 3, 0.5) in the Cartesian plane. 2. Simplify the expression 13 7 2. 3. Use the 3 lines whose equations are given. Which are parallel? Which
SECTION 1.1 1. Plot the points (0, 4), ( 2, 3), (1.5, 1), and ( 3, 0.5) in the Cartesian plane. 2. Simplify the expression 13 7 2. 3. Use the 3 lines whose equations are given. Which are parallel? Which
A Catalog of Essential Functions
 Section. A Catalog of Essential Functions Kiryl Tsishchanka A Catalog of Essential Functions In this course we consider 6 groups of important functions:. Linear Functions. Polynomials 3. Power functions.
Section. A Catalog of Essential Functions Kiryl Tsishchanka A Catalog of Essential Functions In this course we consider 6 groups of important functions:. Linear Functions. Polynomials 3. Power functions.
Laurie s Notes. Overview of Section 6.3
 Overview of Section.3 Introduction In this lesson, eponential equations are defined. Students distinguish between linear and eponential equations, helping to focus on the definition of each. A linear function
Overview of Section.3 Introduction In this lesson, eponential equations are defined. Students distinguish between linear and eponential equations, helping to focus on the definition of each. A linear function
Unit 3: Absolute Value
 Name: Block: Unit 3: Absolute Value Day 1: Characteristics of Absolute Value Day 2: Transformations of Absolute Value Day 3: Absolute Value Equations Day 4: Absolute Value Inequalities 1 DAY1: The Absolute
Name: Block: Unit 3: Absolute Value Day 1: Characteristics of Absolute Value Day 2: Transformations of Absolute Value Day 3: Absolute Value Equations Day 4: Absolute Value Inequalities 1 DAY1: The Absolute
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS through 2.1.4
 SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 2.1.2 through 2.1.4 Students used the equation = m + b to graph lines and describe patterns in previous courses. Lesson 2.1.1 is a review. When the equation of a line is written
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 2.1.2 through 2.1.4 Students used the equation = m + b to graph lines and describe patterns in previous courses. Lesson 2.1.1 is a review. When the equation of a line is written
We want to determine what the graph of an exponential function y = a x looks like for all values of a such that 0 < a < 1
 Section 5 2B: Graphs of Decreasing Eponential Functions We want to determine what the graph of an eponential function y = a looks like for all values of a such that 0 < a < We will select a value of a
Section 5 2B: Graphs of Decreasing Eponential Functions We want to determine what the graph of an eponential function y = a looks like for all values of a such that 0 < a < We will select a value of a
Does the table or equation represent a linear or nonlinear function? Explain.
 Chapter Review Dnamic Solutions available at BigIdeasMath.com. Functions (pp. 0 0) Determine whether the relation is a function. Eplain. Ever input has eactl one output. Input, 5 7 9 Output, 5 9 So, the
Chapter Review Dnamic Solutions available at BigIdeasMath.com. Functions (pp. 0 0) Determine whether the relation is a function. Eplain. Ever input has eactl one output. Input, 5 7 9 Output, 5 9 So, the
The x-intercept can be found by setting y = 0 and solving for x: 16 3, 0
 y=-3/4x+4 and y=2 x I need to graph the functions so I can clearly describe the graphs Specifically mention any key points on the graphs, including intercepts, vertex, or start/end points. What is the
y=-3/4x+4 and y=2 x I need to graph the functions so I can clearly describe the graphs Specifically mention any key points on the graphs, including intercepts, vertex, or start/end points. What is the
.2 Transformations of Exponential Functions. Math
 .2 Transformations of Eponential Functions Math 30-1 1 Vertical Translation Given the graph of f() = 2 g() = 2 + 3 Shifts the graph up if k > 0. The graph of f() moves upward 3 units. (, y) (, y + k) (0,
.2 Transformations of Eponential Functions Math 30-1 1 Vertical Translation Given the graph of f() = 2 g() = 2 + 3 Shifts the graph up if k > 0. The graph of f() moves upward 3 units. (, y) (, y + k) (0,
Lesson #1: Exponential Functions and Their Inverses Day 2
 Unit 5: Logarithmic Functions Lesson #1: Exponential Functions and Their Inverses Day 2 Exponential Functions & Their Inverses Exponential Functions are in the form. The inverse of an exponential is a
Unit 5: Logarithmic Functions Lesson #1: Exponential Functions and Their Inverses Day 2 Exponential Functions & Their Inverses Exponential Functions are in the form. The inverse of an exponential is a
Graphing Review. Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic
 Graphing Review Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic Common Functions and Their Graphs Linear Functions A function f defined b a linear equation of the form = f() = m + b, where m and b are constants, is called
Graphing Review Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic Common Functions and Their Graphs Linear Functions A function f defined b a linear equation of the form = f() = m + b, where m and b are constants, is called
Lesson #6: Basic Transformations with the Absolute Value Function
 Lesson #6: Basic Transformations with the Absolute Value Function Recall: Piecewise Functions Graph:,, What parent function did this piecewise function create? The Absolute Value Function Algebra II with
Lesson #6: Basic Transformations with the Absolute Value Function Recall: Piecewise Functions Graph:,, What parent function did this piecewise function create? The Absolute Value Function Algebra II with
Announcements: Quiz next Week Worksheet for over the weekend. Turn UP! Maximize Academic Potential
 3/7/3 OBJ: SWBAT graph rational functions and recognize eponential functions. Bell Ringer: Start notes for Eponential functions Homework Requests: pg 46 #-9 odds 37, 39, 4, 43 Homework: p86 #-9 odds Read
3/7/3 OBJ: SWBAT graph rational functions and recognize eponential functions. Bell Ringer: Start notes for Eponential functions Homework Requests: pg 46 #-9 odds 37, 39, 4, 43 Homework: p86 #-9 odds Read
Section 4.4 Rational Functions and Their Graphs. 1, the line x = 0 (y-axis) is its vertical asymptote.
 Section 4.4 Rational Functions and Their Graphs p( ) A rational function can be epressed as where p() and q() are q( ) 3 polynomial functions and q() is not equal to 0. For eample, 16 is a rational function.
Section 4.4 Rational Functions and Their Graphs p( ) A rational function can be epressed as where p() and q() are q( ) 3 polynomial functions and q() is not equal to 0. For eample, 16 is a rational function.
Section 4.4 Rational Functions and Their Graphs
 Section 4.4 Rational Functions and Their Graphs p( ) A rational function can be epressed as where p() and q() are q( ) 3 polynomial functions and q() is not equal to 0. For eample, is a 16 rational function.
Section 4.4 Rational Functions and Their Graphs p( ) A rational function can be epressed as where p() and q() are q( ) 3 polynomial functions and q() is not equal to 0. For eample, is a 16 rational function.
OpenStax-CNX module: m Quadratic Functions. OpenStax OpenStax Precalculus. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49337 1 Quadratic Functions OpenStax OpenStax Precalculus This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m49337 1 Quadratic Functions OpenStax OpenStax Precalculus This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you
Identifying Slope and y-intercept slope y = mx + b
 Practice 1 Identifying m and b Identifying Slope and y-intercept slope y = mx + b y-intercept 1 1. For each of the following, identify the slope and y-intercept, OR use the slope and y-intercept to write
Practice 1 Identifying m and b Identifying Slope and y-intercept slope y = mx + b y-intercept 1 1. For each of the following, identify the slope and y-intercept, OR use the slope and y-intercept to write
2.1 Transformers: Shifty y s A Develop Understanding Task
 3 2.1 Transformers: Shifty y s A Develop Understanding Task Optima is designing a robot quilt for her new grandson. She plans for the robot to have a square face. The amount of fabric that she needs for
3 2.1 Transformers: Shifty y s A Develop Understanding Task Optima is designing a robot quilt for her new grandson. She plans for the robot to have a square face. The amount of fabric that she needs for
Chapter 11 GRAPHS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
 Chapter 11 GRAPHS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS 11.1 Graphs and Applications of Linear Equations Learning Objectives A Plot points associated with ordered pairs of numbers; determine the quadrant in which a point
Chapter 11 GRAPHS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS 11.1 Graphs and Applications of Linear Equations Learning Objectives A Plot points associated with ordered pairs of numbers; determine the quadrant in which a point
FOA/Algebra 1. Unit 2B Review - Linear Functions
 FOA/Algebra Unit B Review Name: Date: Block: Unit B Review - Linear Functions What you need to know & be able to do. Determine if a relation is a Things to remember Every input only has one output (each
FOA/Algebra Unit B Review Name: Date: Block: Unit B Review - Linear Functions What you need to know & be able to do. Determine if a relation is a Things to remember Every input only has one output (each
Math 1314 Lesson 24 Maxima and Minima of Functions of Several Variables
 Math 1314 Lesson 4 Maxima and Minima o Functions o Several Variables We learned to ind the maxima and minima o a unction o a single variable earlier in the course. We had a second derivative test to determine
Math 1314 Lesson 4 Maxima and Minima o Functions o Several Variables We learned to ind the maxima and minima o a unction o a single variable earlier in the course. We had a second derivative test to determine
Computer Data Analysis and Use of Excel
 Computer Data Analysis and Use o Excel I. Theory In this lab we will use Microsot EXCEL to do our calculations and error analysis. This program was written primarily or use by the business community, so
Computer Data Analysis and Use o Excel I. Theory In this lab we will use Microsot EXCEL to do our calculations and error analysis. This program was written primarily or use by the business community, so
= = The number system. Module. Glossary Math Tools... 33
 - > + > < - %. < + a = - = = b in. F - - Module The number sstem Lesson Rational and Irrational Numbers........ 8.NS. Lesson ompare and Order Numbers......... 8 8.NS., 8.NS. Lesson Estimate the Value of
- > + > < - %. < + a = - = = b in. F - - Module The number sstem Lesson Rational and Irrational Numbers........ 8.NS. Lesson ompare and Order Numbers......... 8 8.NS., 8.NS. Lesson Estimate the Value of
Unit 1 Notes / Secondary 2 Honors
 Unit 1 Notes / Secondary 2 Honors Day 1: Review Linear Equations Graphing and Solving LINEAR EQUATIONS: Slopes of Lines: 1. slope (m) = 2. Horizontal slope = Vertical slope= y y Slope Formula: Point-Slope
Unit 1 Notes / Secondary 2 Honors Day 1: Review Linear Equations Graphing and Solving LINEAR EQUATIONS: Slopes of Lines: 1. slope (m) = 2. Horizontal slope = Vertical slope= y y Slope Formula: Point-Slope
Lesson 21: Comparing Linear and Exponential Functions Again
 Lesson M Lesson : Comparing Linear and Eponential Functions Again Student Outcomes Students create models and understand the differences between linear and eponential models that are represented in different
Lesson M Lesson : Comparing Linear and Eponential Functions Again Student Outcomes Students create models and understand the differences between linear and eponential models that are represented in different
Cumulative Review Problems Packet # 1
 April 15, 009 Cumulative Review Problems Packet #1 page 1 Cumulative Review Problems Packet # 1 This set of review problems will help you prepare for the cumulative test on Friday, April 17. The test will
April 15, 009 Cumulative Review Problems Packet #1 page 1 Cumulative Review Problems Packet # 1 This set of review problems will help you prepare for the cumulative test on Friday, April 17. The test will
I Doubt It Lesson 6-1 Transforming Functions
 I Doubt It Lesson 6- Learning Targets: Graph transformations of functions and write the equations of the transformed functions. Describe the symmetry of the graphs of even and odd functions. SUGGESTED
I Doubt It Lesson 6- Learning Targets: Graph transformations of functions and write the equations of the transformed functions. Describe the symmetry of the graphs of even and odd functions. SUGGESTED
Graphs, Linear Equations, and Functions
 Graphs, Linear Equations, and Functions. The Rectangular R. Coordinate Fractions Sstem bjectives. Interpret a line graph.. Plot ordered pairs.. Find ordered pairs that satisf a given equation. 4. Graph
Graphs, Linear Equations, and Functions. The Rectangular R. Coordinate Fractions Sstem bjectives. Interpret a line graph.. Plot ordered pairs.. Find ordered pairs that satisf a given equation. 4. Graph
For full credit, show all work.
 ccelerated Review 7: Linear Equations Name: For full credit, show all work. 1. 2. For the situation described, first write an equation in the form y = mx + b. Then solve the problem. sales associate is
ccelerated Review 7: Linear Equations Name: For full credit, show all work. 1. 2. For the situation described, first write an equation in the form y = mx + b. Then solve the problem. sales associate is
9. f(x) = x f(x) = x g(x) = 2x g(x) = 5 2x. 13. h(x) = 1 3x. 14. h(x) = 2x f(x) = x x. 16.
 Section 4.2 Absolute Value 367 4.2 Eercises For each of the functions in Eercises 1-8, as in Eamples 7 and 8 in the narrative, mark the critical value on a number line, then mark the sign of the epression
Section 4.2 Absolute Value 367 4.2 Eercises For each of the functions in Eercises 1-8, as in Eamples 7 and 8 in the narrative, mark the critical value on a number line, then mark the sign of the epression
2-2 Adding Integers. Warm Up Problem of the Day Lesson Presentation Lesson Quizzes
 Warm Up Problem of the Day Lesson Presentation Lesson Quizzes Warm Up Find each absolute value. 1. 8 2. 6 3. 9 4. 7 5. 12 6. 53 Problem of the Day Jan s yearly salary is $30,000, and it will be increased
Warm Up Problem of the Day Lesson Presentation Lesson Quizzes Warm Up Find each absolute value. 1. 8 2. 6 3. 9 4. 7 5. 12 6. 53 Problem of the Day Jan s yearly salary is $30,000, and it will be increased
Example 1: Use the graph of the function f given below to find the following. a. Find the domain of f and list your answer in interval notation
 When working with the graph of a function, the inputs (the elements of the domain) are always the values on the horizontal ais (-ais) and the outputs (the elements of the range) are always the values on
When working with the graph of a function, the inputs (the elements of the domain) are always the values on the horizontal ais (-ais) and the outputs (the elements of the range) are always the values on
Begin Notes Immediately. Look at Example Below!!! Glue in Notebook
 Begin Notes Immediately Look at Eample Below!!! Glue in Notebook Graphing Rational Functions The Parent Function can be transformed by using f( ) 1 f ( ) a k h What do a, h and k represent? a the vertical
Begin Notes Immediately Look at Eample Below!!! Glue in Notebook Graphing Rational Functions The Parent Function can be transformed by using f( ) 1 f ( ) a k h What do a, h and k represent? a the vertical
In math, the rate of change is called the slope and is often described by the ratio rise
 Chapter 3 Equations of Lines Sec. Slope The idea of slope is used quite often in our lives, however outside of school, it goes by different names. People involved in home construction might talk about
Chapter 3 Equations of Lines Sec. Slope The idea of slope is used quite often in our lives, however outside of school, it goes by different names. People involved in home construction might talk about
4.2 Linear Equations in Point-Slope Form
 4.2 Linear Equations in Point-Slope Form Learning Objectives Write an equation in point-slope form. Graph an equation in point-slope form. Write a linear function in point-slope form. Solve real-world
4.2 Linear Equations in Point-Slope Form Learning Objectives Write an equation in point-slope form. Graph an equation in point-slope form. Write a linear function in point-slope form. Solve real-world
TIPS4RM: MHF4U: Unit 1 Polynomial Functions
 TIPSRM: MHFU: Unit Polnomial Functions 008 .5.: Polnomial Concept Attainment Activit Compare and contrast the eamples and non-eamples of polnomial functions below. Through reasoning, identif attributes
TIPSRM: MHFU: Unit Polnomial Functions 008 .5.: Polnomial Concept Attainment Activit Compare and contrast the eamples and non-eamples of polnomial functions below. Through reasoning, identif attributes
Graphing square root functions. What would be the base graph for the square root function? What is the table of values?
 Unit 3 (Chapter 2) Radical Functions (Square Root Functions Sketch graphs of radical functions b appling translations, stretches and reflections to the graph of Analze transformations to identif the of
Unit 3 (Chapter 2) Radical Functions (Square Root Functions Sketch graphs of radical functions b appling translations, stretches and reflections to the graph of Analze transformations to identif the of
Tangent line problems
 You will find lots of practice problems and homework problems that simply ask you to differentiate. The following examples are to illustrate some of the types of tangent line problems that you may come
You will find lots of practice problems and homework problems that simply ask you to differentiate. The following examples are to illustrate some of the types of tangent line problems that you may come
Session 3. Rational and Radical Equations. Math 30-1 R 3. (Revisit, Review and Revive)
 Session 3 Rational and Radical Equations Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) Rational Functions Review Specific Outcome 14 Graph and analyze rational functions (limited to numerators and denominators
Session 3 Rational and Radical Equations Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) Rational Functions Review Specific Outcome 14 Graph and analyze rational functions (limited to numerators and denominators
What is the relationship between the real roots of a polynomial equation and the x-intercepts of the corresponding polynomial function?
 3.3 Characteristics of Polnomial Functions in Factored Form INVESTIGATE the Math The graphs of the functions f () 5 1 and g() 5 1 are shown.? GOAL Determine the equation of a polnomial function that describes
3.3 Characteristics of Polnomial Functions in Factored Form INVESTIGATE the Math The graphs of the functions f () 5 1 and g() 5 1 are shown.? GOAL Determine the equation of a polnomial function that describes
Chapter 3 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain
 Chapter 3 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain Yinghua He School o Computer Science and Technology Tianjin University Image enhancement approaches Spatial domain image plane itsel Spatial domain methods
Chapter 3 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain Yinghua He School o Computer Science and Technology Tianjin University Image enhancement approaches Spatial domain image plane itsel Spatial domain methods
Lesson 8.1 Exercises, pages
 Lesson 8.1 Eercises, pages 1 9 A. Complete each table of values. a) -3 - -1 1 3 3 11 8 5-1 - -7 3 11 8 5 1 7 To complete the table for 3, take the absolute value of each value of 3. b) - -3 - -1 1 3 3
Lesson 8.1 Eercises, pages 1 9 A. Complete each table of values. a) -3 - -1 1 3 3 11 8 5-1 - -7 3 11 8 5 1 7 To complete the table for 3, take the absolute value of each value of 3. b) - -3 - -1 1 3 3
Exploring Quadratic Graphs
 Exploring Quadratic Graphs The general quadratic function is y=ax 2 +bx+c It has one of two basic graphs shapes, as shown below: It is a symmetrical "U"-shape or "hump"-shape, depending on the sign of
Exploring Quadratic Graphs The general quadratic function is y=ax 2 +bx+c It has one of two basic graphs shapes, as shown below: It is a symmetrical "U"-shape or "hump"-shape, depending on the sign of
Graphing Techniques and Transformations. Learning Objectives. Remarks
 Graphing Techniques and Transformations Learning Objectives 1. Graph functions using vertical and horizontal shifts 2. Graph functions using compressions and stretches. Graph functions using reflections
Graphing Techniques and Transformations Learning Objectives 1. Graph functions using vertical and horizontal shifts 2. Graph functions using compressions and stretches. Graph functions using reflections
3-2. Families of Graphs. Look Back. OBJECTIVES Identify transformations of simple graphs. Sketch graphs of related functions.
 3-2 BJECTIVES Identif transformations of simple graphs. Sketch graphs of related functions. Families of Graphs ENTERTAINMENT At some circuses, a human cannonball is shot out of a special cannon. In order
3-2 BJECTIVES Identif transformations of simple graphs. Sketch graphs of related functions. Families of Graphs ENTERTAINMENT At some circuses, a human cannonball is shot out of a special cannon. In order
Absolute Value Function. Some properties of Absolute value: 1. ex. because
 Absolute Value Function The absolute value of a number considers only the magnitude of the number and not the sign. Examples: and Some properties of Absolute value: 1. ex. because 2. ex. 3. ex. and 4.
Absolute Value Function The absolute value of a number considers only the magnitude of the number and not the sign. Examples: and Some properties of Absolute value: 1. ex. because 2. ex. 3. ex. and 4.
Name: Class: Date: a. Use inequality statements to write the domain and range of f(x).
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 9 Review 1. The graph of the square root function, f(), is shown. a. Use inequality statements to write the domain and range of f(). b. Sketch the graph obtained by shifting
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 9 Review 1. The graph of the square root function, f(), is shown. a. Use inequality statements to write the domain and range of f(). b. Sketch the graph obtained by shifting
6, 1 0, f x x 1 2 x h x x x 3, f x sin x cos x, f x x 2 6x 5 f x 4x 3 5x 30. g x x3 8x 31. f x x f x x2 3x 4 33.
 Chapter Applications o Dierentiation Review Eercises See CalcChat.com or tutorial help and worked-out solutions to odd-numbered eercises. Finding Etrema on a Closed Interval In Eercises, ind the absolute
Chapter Applications o Dierentiation Review Eercises See CalcChat.com or tutorial help and worked-out solutions to odd-numbered eercises. Finding Etrema on a Closed Interval In Eercises, ind the absolute
DLA Review Printable Version
 1. In the equation y = 7x + 3, as the value of x decreases by 1, what happens to the value of y?. A cell phone company charges $.00 a month plus an additional $0.10 per call. A competitor charges $10.00
1. In the equation y = 7x + 3, as the value of x decreases by 1, what happens to the value of y?. A cell phone company charges $.00 a month plus an additional $0.10 per call. A competitor charges $10.00
3.1 Functions. The relation {(2, 7), (3, 8), (3, 9), (4, 10)} is not a function because, when x is 3, y can equal 8 or 9.
 3. Functions Cubic packages with edge lengths of cm, 7 cm, and 8 cm have volumes of 3 or cm 3, 7 3 or 33 cm 3, and 8 3 or 5 cm 3. These values can be written as a relation, which is a set of ordered pairs,
3. Functions Cubic packages with edge lengths of cm, 7 cm, and 8 cm have volumes of 3 or cm 3, 7 3 or 33 cm 3, and 8 3 or 5 cm 3. These values can be written as a relation, which is a set of ordered pairs,
Transformation of curve. a. reflect the portion of the curve that is below the x-axis about the x-axis
 Given graph of y f = and sketch:. Linear Transformation cf ( b + a) + d a. translate a along the -ais. f b. scale b along the -ais c. scale c along the y-ais d. translate d along the y-ais Transformation
Given graph of y f = and sketch:. Linear Transformation cf ( b + a) + d a. translate a along the -ais. f b. scale b along the -ais c. scale c along the y-ais d. translate d along the y-ais Transformation
Algebra Review (Summer Version) Homework Problems
 MATH 119 Algebra Review (Summer Version) Homework Problems The following set is only to review the Algebra needed for this class. It should be familiar to you from previous class such as M110, M111 or
MATH 119 Algebra Review (Summer Version) Homework Problems The following set is only to review the Algebra needed for this class. It should be familiar to you from previous class such as M110, M111 or
Essential Question: How do you graph an exponential function of the form f (x) = ab x? Explore Exploring Graphs of Exponential Functions. 1.
 Locker LESSON 4.4 Graphing Eponential Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.7e Graph eponential and logarithmic functions, showing intercepts and end behavior, and trigonometric
Locker LESSON 4.4 Graphing Eponential Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.7e Graph eponential and logarithmic functions, showing intercepts and end behavior, and trigonometric
Solving Quadratics Algebraically Investigation
 Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math 1 Day 1: Factoring Review and Solving For Zeroes Algebraically Warm-Up: 1. Write an equivalent epression for each of the problems below: a. ( + )( + 4) b. ( 5)( + 8)
Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math 1 Day 1: Factoring Review and Solving For Zeroes Algebraically Warm-Up: 1. Write an equivalent epression for each of the problems below: a. ( + )( + 4) b. ( 5)( + 8)
2.1 Linear Equations in Two Variables
 2.1 Linear Equations in Two Variables Concept 1: The Rectangular Coordinate System 2. Let a and b represent nonzero real numbers. Then 1. An ordered pair of the form (0, b) represents a point on which
2.1 Linear Equations in Two Variables Concept 1: The Rectangular Coordinate System 2. Let a and b represent nonzero real numbers. Then 1. An ordered pair of the form (0, b) represents a point on which
Computer Data Analysis and Plotting
 Phys 122 February 6, 2006 quark%//~bland/docs/manuals/ph122/pcintro/pcintro.doc Computer Data Analysis and Plotting In this lab we will use Microsot EXCEL to do our calculations. This program has been
Phys 122 February 6, 2006 quark%//~bland/docs/manuals/ph122/pcintro/pcintro.doc Computer Data Analysis and Plotting In this lab we will use Microsot EXCEL to do our calculations. This program has been
Essential Question What are the characteristics of the graph of the tangent function?
 8.5 Graphing Other Trigonometric Functions Essential Question What are the characteristics of the graph of the tangent function? Graphing the Tangent Function Work with a partner. a. Complete the table
8.5 Graphing Other Trigonometric Functions Essential Question What are the characteristics of the graph of the tangent function? Graphing the Tangent Function Work with a partner. a. Complete the table
Obtaining Information from a Function s Graph.
 Obtaining Information from a Function s Graph Summary about using closed dots, open dots, and arrows on the graphs 1 A closed dot indicate that the graph does not extend beyond this point and the point
Obtaining Information from a Function s Graph Summary about using closed dots, open dots, and arrows on the graphs 1 A closed dot indicate that the graph does not extend beyond this point and the point
1.1. Parent Functions and Transformations Essential Question What are the characteristics of some of the basic parent functions?
 1.1 Parent Functions and Transformations Essential Question What are the characteristics of some of the basic parent functions? Identifing Basic Parent Functions JUSTIFYING CONCLUSIONS To be proficient
1.1 Parent Functions and Transformations Essential Question What are the characteristics of some of the basic parent functions? Identifing Basic Parent Functions JUSTIFYING CONCLUSIONS To be proficient
SECONDARY MATH TRANSFORMATIONS
 SECONDARY MATH 3 3-3 TRANSFORMATIONS WARM UP WHAT YOU WILL LEARN How to transform functions from the parent function How to describe a transformation How to write an equation of a transformed function
SECONDARY MATH 3 3-3 TRANSFORMATIONS WARM UP WHAT YOU WILL LEARN How to transform functions from the parent function How to describe a transformation How to write an equation of a transformed function
Transformations of Absolute Value Functions. Compression A compression is a. function a function of the form f(x) = a 0 x - h 0 + k
 - Transformations of Absolute Value Functions TEKS FOCUS VOCABULARY Compression A compression is a TEKS (6)(C) Analze the effect on the graphs of f() = when f() is replaced b af(), f(b), f( - c), and f()
- Transformations of Absolute Value Functions TEKS FOCUS VOCABULARY Compression A compression is a TEKS (6)(C) Analze the effect on the graphs of f() = when f() is replaced b af(), f(b), f( - c), and f()
x 16 d( x) 16 n( x) 36 d( x) zeros: x 2 36 = 0 x 2 = 36 x = ±6 Section Yes. Since 1 is a polynomial (of degree 0), P(x) =
 9 CHAPTER POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS Section -. Yes. Since is a polynomial (of degree 0), P() P( ) is a rational function if P() is a polynomial.. A vertical asymptote is a vertical line a that
9 CHAPTER POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS Section -. Yes. Since is a polynomial (of degree 0), P() P( ) is a rational function if P() is a polynomial.. A vertical asymptote is a vertical line a that
2-5 Graphing Special Functions. Graph each function. Identify the domain and range. SOLUTION:
 Graph each function Identify the domain and range Write the piecewise-defined function shown in each graph 1 3 The left portion of the graph is the line g(x) = x + 4 There is an open circle at ( 2, 2),
Graph each function Identify the domain and range Write the piecewise-defined function shown in each graph 1 3 The left portion of the graph is the line g(x) = x + 4 There is an open circle at ( 2, 2),
Quadratic Functions (Section 2-1)
 Quadratic Functions (Section 2-1) Section 2.1, Definition of Polynomial Function f(x) = a is the constant function f(x) = mx + b where m 0 is a linear function f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c with a 0 is a quadratic
Quadratic Functions (Section 2-1) Section 2.1, Definition of Polynomial Function f(x) = a is the constant function f(x) = mx + b where m 0 is a linear function f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c with a 0 is a quadratic
Linear Modeling Elementary Education 4
 Linear Modeling Elementary Education 4 Mathematical modeling is simply the act of building a model (usually in the form of graphs) which provides a picture of a numerical situation. Linear Modeling is
Linear Modeling Elementary Education 4 Mathematical modeling is simply the act of building a model (usually in the form of graphs) which provides a picture of a numerical situation. Linear Modeling is
Skill Sets Chapter 5 Functions
 Skill Sets Chapter 5 Functions No. Skills Examples o questions involving the skills. Sketch the graph o the (Lecture Notes Example (b)) unction according to the g : x x x, domain. x, x - Students tend
Skill Sets Chapter 5 Functions No. Skills Examples o questions involving the skills. Sketch the graph o the (Lecture Notes Example (b)) unction according to the g : x x x, domain. x, x - Students tend
Math Analysis Chapter 1 Notes: Functions and Graphs
 Math Analysis Chapter 1 Notes: Functions and Graphs Day 6: Section 1-1 Graphs Points and Ordered Pairs The Rectangular Coordinate System (aka: The Cartesian coordinate system) Practice: Label each on the
Math Analysis Chapter 1 Notes: Functions and Graphs Day 6: Section 1-1 Graphs Points and Ordered Pairs The Rectangular Coordinate System (aka: The Cartesian coordinate system) Practice: Label each on the
UNIT 4 NOTES. 4-1 and 4-2 Coordinate Plane
 UNIT 4 NOTES 4-1 and 4-2 Coordinate Plane y Ordered pairs on a graph have several names. (X coordinate, Y coordinate) (Domain, Range) (Input,Output) Plot these points and label them: a. (3,-4) b. (-5,2)
UNIT 4 NOTES 4-1 and 4-2 Coordinate Plane y Ordered pairs on a graph have several names. (X coordinate, Y coordinate) (Domain, Range) (Input,Output) Plot these points and label them: a. (3,-4) b. (-5,2)
Notes Rules for Transformations of Functions If f x is the original functions, a > 0 and c > 0.
 9.1.2 Parabola Investigation Do Now 1. Vertical means and horizontal is. 2. Another word for compress is. 3. Given the statement 0 < a < 1, a represents numbers like 4. Given the statement a > 1, a represents
9.1.2 Parabola Investigation Do Now 1. Vertical means and horizontal is. 2. Another word for compress is. 3. Given the statement 0 < a < 1, a represents numbers like 4. Given the statement a > 1, a represents
Graphing Radical Functions
 17 LESSON Graphing Radical Functions Basic Graphs of Radical Functions UNDERSTAND The parent radical function, 5, is shown. 5 0 0 1 1 9 0 10 The function takes the principal, or positive, square root of.
17 LESSON Graphing Radical Functions Basic Graphs of Radical Functions UNDERSTAND The parent radical function, 5, is shown. 5 0 0 1 1 9 0 10 The function takes the principal, or positive, square root of.
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Investigating Quadratic Functions in Vertex Form
 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Investigating Quadratic Functions in Verte Form The two forms of a quadratic function that have been eplored previousl are: Factored form: f ( ) a( r)( s) Standard form: f ( ) a b c
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Investigating Quadratic Functions in Verte Form The two forms of a quadratic function that have been eplored previousl are: Factored form: f ( ) a( r)( s) Standard form: f ( ) a b c
11.4. You may have heard about the Richter scale rating. The Richter scale was. I Feel the Earth Move Logarithmic Functions KEY TERMS LEARNING GOALS
 I Feel the Earth Move Logarithmic Functions. LEARNING GOALS KEY TERMS In this lesson, ou will: Graph the inverses of eponential functions with bases of, 1, and e. Recognize the inverse of an eponential
I Feel the Earth Move Logarithmic Functions. LEARNING GOALS KEY TERMS In this lesson, ou will: Graph the inverses of eponential functions with bases of, 1, and e. Recognize the inverse of an eponential
Note that ALL of these points are Intercepts(along an axis), something you should see often in later work.
 SECTION 1.1: Plotting Coordinate Points on the X-Y Graph This should be a review subject, as it was covered in the prerequisite coursework. But as a reminder, and for practice, plot each of the following
SECTION 1.1: Plotting Coordinate Points on the X-Y Graph This should be a review subject, as it was covered in the prerequisite coursework. But as a reminder, and for practice, plot each of the following
Algebra I EOC Packet #
 1. Which inequality best describes the graph shown below? A y > x + 5 B y < x + 5 C y < x + 5 D y > x + 5 2. The table shows a set of values for x and y. x -3-2 1 3 6 y 7 5-1 -5-11 Which equation best
1. Which inequality best describes the graph shown below? A y > x + 5 B y < x + 5 C y < x + 5 D y > x + 5 2. The table shows a set of values for x and y. x -3-2 1 3 6 y 7 5-1 -5-11 Which equation best
This lesson combines vertical translations and dilations in several quadratic and inverse variation modeling applications.
 Learning Objectives Combined Vertical Transformations Algebra ; Pre-Calculus Time required: 90 min. This lesson combines vertical translations and dilations in several quadratic and inverse variation modeling
Learning Objectives Combined Vertical Transformations Algebra ; Pre-Calculus Time required: 90 min. This lesson combines vertical translations and dilations in several quadratic and inverse variation modeling
