Understanding FFT- based algorithm to calculate image displacements with IDL programming language Cynthia Rodriguez University of Texas at San Antonio
|
|
|
- Georgia Osborne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Understanding FFT- based algorithm to calculate image displacements with IDL programming language Cynthia Rodriguez University of Texas at San Antonio ABSTRACT There are many ways automatic image registration can be solved. However, not many have been implemented into a software package like ENVI. The following descriptions of the shift_idl.pro and srs_idl.pro programs will prove to be a difference. These two programs aim to be a solution to automatic image registration for the state-of-the-art software ENVI (Environment for Visualizing Images) through an FFT based algorithm. FFT an acronym for Fast Fourier Transform is an algorithm known for successfully performing automatic image registration. Using IDL (Interactive Data Language) we are able to implement this algorithm with IDL s built-in FFT function. With the aid of the programming code from shift_idl.pro and srs_idl.pro, I hope to get a better understanding of how FFT based algorithm is used to calculate image displacements. INTRODUCTION There is a saying that states Don t reinvent the wheel which basically means, if it s already been programmed, don t program it again. Instead it is strongly suggested to reuse the existing code. Doing this provides time saved. This is a highly accepted and encouraged practice. However to reuse someone
2 else s code demands patience, coding expertise, and notes, lots of notes in some cases. In general, programming languages are like human languages in that the person/programmer using the language can contribute their own style to the language even though the language has defined syntactic and semantic rules. For example, there is more than one way to execute a loop. There are for loops, while loops, and do loops. In addition, to considering a programmer s style, there is also the fact of understanding the goal of the program. This is something that must be taken into context. What is the programmer trying to accomplish? Furthermore, if the program is a highly advanced mathematical program, than without a doubt comments and notes will be needed. Therefore, in order to accurately understand the two programs shift_idl.pro and srs_idl.pro, I felt that a thorough walk through of the code and notes/comments was the most effective way to learn how automatic image registration could be accomplished. STUDY AREA and DATA To understand how IDL programming can be used to solve automatic image displacement, I used shift_idl.pro and srs_idl.pro IDL programs. These two programs were created by Hongjie Xie, Nigel Hicks, G. Randy Keller, Haitao Huang, and Vladik Kreinovich. The images used to test the programs were an original image, and the other a simulated image taken from using the original image and transforming it by a scaling of 1.3, rotation of 19 degrees to the east, and a shifting to the east (right) by 19 rows (pixels). These two images were used to test the procedures shift, rotation and scaling. The algorithm coded requires
3 that both images have the same size of resolution. However, the images can be in different coordinate systems. In addition, to the provided code, I also used an article called An IDL/ENVI implementation of the FFT-based algorithm for automatic image registration that helped guide me through the steps of the code. METHODS In order to understand how the two programs solve automatic image registration, I first decided to read the article and get a little foundation on what image registration was. The definition of automatic image registration is that it is the process that aligns one image to a second image of the same scene through a program. This is done so that the properties of an object being imaged can be addressable by the same coordinate pair from either one of the images. I then
4 needed to find out what the FFT based algorithm was. From the article, I learned that FFT stands for Fast Fourier Transform, and that it is a proven successful factor in solving image registration. The main formula behind FFT is getting the Ratio of FFT on image1 times conjugate of FFT on image2 and then with all of this, divide it by the absolute of FFT on image 1 and FFT on image 2. Ratio = F1 conj(f2 ) / F1F2 Once the ratio is calculated, then apply an inverse fourier transform. Based on these calculations you will find the displacement between two images. Ex: Ratio = (x0,y0), [I2(x,y) = I1(x-x0, y-y0)] When this algorithm is implemented in coding, you get a result of a single array with values close to zero everywhere except for a small area around a single point. To locate this point call the function Max (build-in IDL function) to find the position of Max value. This position is the exact shift displacement between the images (x0, y0). Using this displacement you can optimally register the images. With this gained knowledge, I now felt confident to understand the coding for shift_idl. Doing a step by step walkthrough of the program, I noticed the beginning of the program was pretty standard IDL code of initiating variables and opening the two image files and reading the data into a declared doubledimension arrays. Once the data was received, the code then calls FFT on both images. With the forward fast fourier transform calculations, the code then computes the Ratio and inverse fourier transform on the ratio. Next the code calls MAX function to locate the max value position. Using Max position, the programmer then gets the coordinates of the displacement by performing MOD
5 and DIVIDE operators to get X shift in columns and Y- shift in rows. Last the code runs a conditional statement to check for shifts to the west and north and makes them negative numbers while the shifts to the east and south stay positive numbers. After understanding shift_idl.pro, I proceeded to analyze the code for srs_idl.pro which includes a rotation and scaling as well as shifts. The main idea behind representing rotation and scaling as shifts was to convert rectangular coordinates (x, y) to log-polar coordinates (log (p), θ). However by doing this, it was discovered that certain points newly created didn t match with the points on the original rectangular grid. Due to the unmatched coordinates, the referenced article concluded to use bilinear interpolation to solve the problem. Bilinear interpolation basically gets the surrounding intensities around the current point and interpolates it. Accordingly, it can then get the correct value on the new grid. With this knowledge, I next started a step-by step walkthrough of the srs_idl.pro code. I noticed it begins like shift_idl.pro, but the difference is that since srs_idl.pro contains more programming code than shift_idl.pro, the srs_idl.pro program makes a point to provide easily modulated code of functions. This provides easier reading and change and reuse if necessary. The first functions in this program LoadImage, Normalize, ShiftArr, main task is to get the data ready in a predefined format so that calculations can be made more easily. LoadImage opens and reads image files into Im1 and Im2 variable. Normalize gets the grid values in an array and makes the array a floating array and divides values by to make values between 0 and 1. ShiftArr makes values in the array
6 negative values, if MOD 2 equals 1. From then it next calls FFT on both images and then abs function to get absolute values of image1 and image2. Afterwards, it calls HighPass function which removes low frequency noise to the absolute values. The code next calls LogPolar function on both images to transform the rectangular coordinates to log polar coordinates in the process also calculating bilinear interpolation to get accurate coordinates on the new grid. In order for this function to run properly, the polar plane must have the exact same number of rows as the rectangular plane. To achieve this a nested for loop was created to go through each index in the array and individually get the original coordinate and transfer it to the log polar coordinate. The code now is able to use the polar coordinates and find out the scale and rotation shifts by calling FFT function to both image1 and image2. Then it finds the ratio by calling function Ritio, and next calling FFT inverse function on the ratio. Afterwards, the code calls the absolute function to the values. Now, the code can call Max function to find the max position in the array of absolute values. With the max position it can then calculate and find the values for scale and angle using the Max location. scale=b^(position MOD rows) angle=180.0 * (position/rows) /cols Once the angle is found the programmer makes a conditional statement to check to see if the angle is greater than or less than 90 degrees. If an angle is greater than 90 or equal to 90, the angle is positive and the image is rotated to the east relative to the base image. The actual angle rotation is 180 minus the computed angle. If the angle is less than 90 degrees, than the angle is negative and the
7 image is rotated to the west. The article referenced says that the angle is always between 0 and 180, because it assumes that the image received will never be completely upside down. The image, if upside down, will be manually corrected to right side up. After the angle and scale have been computed, the code creates a new image3 with the function ROT which constructs a new image by doing reverse rotation and reverse scaling. Now that we have the data for the new image3, the programmer calls FFT function for both image1 and image3. The rest of the code is exactly like shift_idl.pro. Basically once again the programmer uses the FFT values to compute the Ratio and call inverse FFT on the Ratio. Then the code uses Max function to locate the max value in the array, and with the max position found, it gets the X and Y coordinates. Last the program checks to see if coordinates are out of bounds and adjust accordingly for north and west shifts which are computed as negative. RESULTS and DISCUSSION The results of both programs are identical in that each program s goal is to get the calculation of the shift displacement between two images. The difference is that srs_idl.pro has to go through more steps of calculating since not only does the code compute shift, but also rotation and scaling displacements. In summary, the shift only program contains only two forward FFTs and one inverse FFT. While on the other hand, the scale, rotation, and shift program contains six forward FFTs and two inverse FFTs. This involves a lot more computation, therefore this program requires more time and memory. Once more over, FFT-
8 based algorithm is a proven success in solving image registration. Understanding its implementation in two programs shift_idl.pro and srs_idl.pro was accomplished through the aid of the referenced article. Conclusion, I was able to understand how FFT-base algorithm is used with IDL programming language to solve automatic image registration.
9 REFERNCES Cynthia Rodriguez Hongjie Xie, Nigel Hicks, G. Randy Keller, Haitao Huang, Vladik Kreinovich. An DL/ENVI implementation of the FFT-based algorithm for autonmatic image registration. Department of Geological Sciences, Pan American Center for Earth and Environmental Studies (PACES), University of Texas at El Paso, Texas 79968, USA. March 26, 2003.
Answers. Chapter 2. 1) Give the coordinates of the following points:
 Answers Chapter 2 1) Give the coordinates of the following points: a (-2.5, 3) b (1, 2) c (2.5, 2) d (-1, 1) e (0, 0) f (2, -0.5) g (-0.5, -1.5) h (0, -2) j (-3, -2) 1 2) List the 48 different possible
Answers Chapter 2 1) Give the coordinates of the following points: a (-2.5, 3) b (1, 2) c (2.5, 2) d (-1, 1) e (0, 0) f (2, -0.5) g (-0.5, -1.5) h (0, -2) j (-3, -2) 1 2) List the 48 different possible
IMAGE PROCESSING AND IMAGE REGISTRATION ON SPIRAL ARCHITECTURE WITH salib
 IMAGE PROCESSING AND IMAGE REGISTRATION ON SPIRAL ARCHITECTURE WITH salib Stefan Bobe 1 and Gerald Schaefer 2,* 1 University of Applied Sciences, Bielefeld, Germany. 2 School of Computing and Informatics,
IMAGE PROCESSING AND IMAGE REGISTRATION ON SPIRAL ARCHITECTURE WITH salib Stefan Bobe 1 and Gerald Schaefer 2,* 1 University of Applied Sciences, Bielefeld, Germany. 2 School of Computing and Informatics,
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images
 Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Convert Local Coordinate Systems to Standard Coordinate Systems
 BENTLEY SYSTEMS, INC. Convert Local Coordinate Systems to Standard Coordinate Systems Using 2D Conformal Transformation in MicroStation V8i and Bentley Map V8i Jim McCoy P.E. and Alain Robert 4/18/2012
BENTLEY SYSTEMS, INC. Convert Local Coordinate Systems to Standard Coordinate Systems Using 2D Conformal Transformation in MicroStation V8i and Bentley Map V8i Jim McCoy P.E. and Alain Robert 4/18/2012
Automatic alignment of infrared video frames for equipment leak detection
 Analytica Chimica Acta 584 (2007) 223 227 Automatic alignment of infrared video frames for equipment leak detection Liming Zhou, Yousheng Zeng Providence Engineering and Environmental Group LLC, Baton
Analytica Chimica Acta 584 (2007) 223 227 Automatic alignment of infrared video frames for equipment leak detection Liming Zhou, Yousheng Zeng Providence Engineering and Environmental Group LLC, Baton
MathZoom, Summer, 2014
 A one-dimensional bug starts at the origin and each minute moves either left or right exactly one unit. Suppose it makes there moves with equal likelihood. That is the probability of a move to the left
A one-dimensional bug starts at the origin and each minute moves either left or right exactly one unit. Suppose it makes there moves with equal likelihood. That is the probability of a move to the left
The mathematics behind projections
 The mathematics behind projections This is an article from my home page: www.olewitthansen.dk Ole Witt-Hansen 2005 (2015) Contents 1. The mathematics behind projections and 3-dim graphics...1 1.1 Central
The mathematics behind projections This is an article from my home page: www.olewitthansen.dk Ole Witt-Hansen 2005 (2015) Contents 1. The mathematics behind projections and 3-dim graphics...1 1.1 Central
N-Views (1) Homographies and Projection
 CS 4495 Computer Vision N-Views (1) Homographies and Projection Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia PS 2: Get SDD and Normalized Correlation working for a given windows size say
CS 4495 Computer Vision N-Views (1) Homographies and Projection Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia PS 2: Get SDD and Normalized Correlation working for a given windows size say
Using Coordinate Systems
 Using Coordinate Systems In This Chapter 5 As you draw you use the coordinate system to specify points in the drawing. You can locate and use your own movable user coordinate system (UCS) for working on
Using Coordinate Systems In This Chapter 5 As you draw you use the coordinate system to specify points in the drawing. You can locate and use your own movable user coordinate system (UCS) for working on
Geometric Correction
 CEE 6150: Digital Image Processing Geometric Correction 1 Sources of Distortion Sensor Characteristics optical distortion aspect ratio non-linear mirror velocity detector geometry & scanning sequence Viewing
CEE 6150: Digital Image Processing Geometric Correction 1 Sources of Distortion Sensor Characteristics optical distortion aspect ratio non-linear mirror velocity detector geometry & scanning sequence Viewing
Class IX Mathematics (Ex. 3.1) Questions
 Class IX Mathematics (Ex. 3.1) Questions 1. How will you describe the position of a table lamp on your study table to another person? 2. (Street Plan): A city has two main roads which cross each other
Class IX Mathematics (Ex. 3.1) Questions 1. How will you describe the position of a table lamp on your study table to another person? 2. (Street Plan): A city has two main roads which cross each other
Installing and Using Trackside Cameras Revised November 2008
 Installing and Using Trackside Cameras Revised November 2008 Trackside cameras are a useful and creative way to add visual interest to your route. Rather than just look out the windshield of the locomotive
Installing and Using Trackside Cameras Revised November 2008 Trackside cameras are a useful and creative way to add visual interest to your route. Rather than just look out the windshield of the locomotive
Decision Making under Interval Uncertainty: What Can and What Cannot Be Computed in Linear Time and in Real Time
 Decision Making under Interval Uncertainty: What Can and What Cannot Be Computed in Linear Time and in Real Time Olga Kosheleva and Vladik Kreinovich University of Texas at El Paso 500 W. University El
Decision Making under Interval Uncertainty: What Can and What Cannot Be Computed in Linear Time and in Real Time Olga Kosheleva and Vladik Kreinovich University of Texas at El Paso 500 W. University El
New Shapes from Input Table: You can also create a new shapefile using data from an input table. You have three options in this case:
 NAME: Distance/Azimuth Tools v. 1.6 Last modified: February 21, 2005 TOPICS: ArcView 3.x, Distance, Bearing, Azimuth, Angle, Point, Line, Polyline, Polygon, Shape, View, Analysis, Tools, Vertices, Shift
NAME: Distance/Azimuth Tools v. 1.6 Last modified: February 21, 2005 TOPICS: ArcView 3.x, Distance, Bearing, Azimuth, Angle, Point, Line, Polyline, Polygon, Shape, View, Analysis, Tools, Vertices, Shift
Computer Vision I. Announcements. Fourier Tansform. Efficient Implementation. Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 13.
 Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SANTA CRUZ BOARD OF STUDIES IN COMPUTER ENGINEERING
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SANTA CRUZ BOARD OF STUDIES IN COMPUTER ENGINEERING CMPE13/L: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING IN C SPRING 2012 Lab 3 Matrix Math Introduction Reading In this lab you will write a
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SANTA CRUZ BOARD OF STUDIES IN COMPUTER ENGINEERING CMPE13/L: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING IN C SPRING 2012 Lab 3 Matrix Math Introduction Reading In this lab you will write a
Announcements. Image Matching! Source & Destination Images. Image Transformation 2/ 3/ 16. Compare a big image to a small image
 2/3/ Announcements PA is due in week Image atching! Leave time to learn OpenCV Think of & implement something creative CS 50 Lecture #5 February 3 rd, 20 2/ 3/ 2 Compare a big image to a small image So
2/3/ Announcements PA is due in week Image atching! Leave time to learn OpenCV Think of & implement something creative CS 50 Lecture #5 February 3 rd, 20 2/ 3/ 2 Compare a big image to a small image So
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATION. Lecture 6
 COORDINATE TRANSFORMATION Lecture 6 SGU 1053 SURVEY COMPUTATION 1 Introduction Geomatic professional are mostly confronted in their work with transformations from one two/three-dimensional coordinate system
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATION Lecture 6 SGU 1053 SURVEY COMPUTATION 1 Introduction Geomatic professional are mostly confronted in their work with transformations from one two/three-dimensional coordinate system
Using Word & Excel to Label and Calculate Catchment Areas and Rainfall Income
 Using Word & Excel to Label and Calculate Catchment Areas and Rainfall Income There are lots of little details you ll need to understand to use Word as a drawing tool, but each individual detail is pretty
Using Word & Excel to Label and Calculate Catchment Areas and Rainfall Income There are lots of little details you ll need to understand to use Word as a drawing tool, but each individual detail is pretty
Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions
 Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Variable is a letter or symbol that represents a number. Variable (algebraic)
Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Variable is a letter or symbol that represents a number. Variable (algebraic)
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CONTOURS! Self-Paced Lab Due Friday! WEEK SIX Lecture RASTER ANALYSES Joe Wheaton YOUR EXCERCISE Integer Elevations Rounded up
HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CONTOURS! Self-Paced Lab Due Friday! WEEK SIX Lecture RASTER ANALYSES Joe Wheaton YOUR EXCERCISE Integer Elevations Rounded up
Binary, Hexadecimal and Octal number system
 Binary, Hexadecimal and Octal number system Binary, hexadecimal, and octal refer to different number systems. The one that we typically use is called decimal. These number systems refer to the number of
Binary, Hexadecimal and Octal number system Binary, hexadecimal, and octal refer to different number systems. The one that we typically use is called decimal. These number systems refer to the number of
Image Processing, Warping, and Sampling
 Image Processing, Warping, and Sampling Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 4.8 FvDFH Ch. 14.10 Outline Image Processing Image Warping Image Sampling Image Processing What about the case when the modification
Image Processing, Warping, and Sampling Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 4.8 FvDFH Ch. 14.10 Outline Image Processing Image Warping Image Sampling Image Processing What about the case when the modification
Basics of Computational Geometry
 Basics of Computational Geometry Nadeem Mohsin October 12, 2013 1 Contents This handout covers the basic concepts of computational geometry. Rather than exhaustively covering all the algorithms, it deals
Basics of Computational Geometry Nadeem Mohsin October 12, 2013 1 Contents This handout covers the basic concepts of computational geometry. Rather than exhaustively covering all the algorithms, it deals
BoA Tools Page 1 / 31
 BoA Tools Page 1 / 31 Standard tools Overview 2 Work pane 3 3D-2D file Main palette 6 Layout Main Palette 9 Navigation tools 11 Workplane Palette 14 Cursor Palette 21 Numeric control 24 Selection by Criteria
BoA Tools Page 1 / 31 Standard tools Overview 2 Work pane 3 3D-2D file Main palette 6 Layout Main Palette 9 Navigation tools 11 Workplane Palette 14 Cursor Palette 21 Numeric control 24 Selection by Criteria
Polar Coordinates. 2, π and ( )
 Polar Coordinates Up to this point we ve dealt exclusively with the Cartesian (or Rectangular, or x-y) coordinate system. However, as we will see, this is not always the easiest coordinate system to work
Polar Coordinates Up to this point we ve dealt exclusively with the Cartesian (or Rectangular, or x-y) coordinate system. However, as we will see, this is not always the easiest coordinate system to work
IMPROVED MOTION-BASED LOCALIZED SUPER RESOLUTION TECHNIQUE USING DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM FOR LOW RESOLUTION VIDEO ENHANCEMENT
 17th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 009) Glasgow, Scotland, August 4-8, 009 IMPROVED MOTION-BASED LOCALIZED SUPER RESOLUTION TECHNIQUE USING DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM FOR LOW RESOLUTION
17th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 009) Glasgow, Scotland, August 4-8, 009 IMPROVED MOTION-BASED LOCALIZED SUPER RESOLUTION TECHNIQUE USING DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM FOR LOW RESOLUTION
Research Institute of Uranium Geology,Beijing , China a
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 2014-06-25 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 971-973, pp 1607-1610 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.971-973.1607 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Discussion on Development
Advanced Materials Research Online: 2014-06-25 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 971-973, pp 1607-1610 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.971-973.1607 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Discussion on Development
2D Tutorial. Project Description: Running VisualAnalysis: Setting Up the Project:
 2D Tutorial Project Description: This project has been set-up to demonstrate the basic features of VisualAnalysis. You will model and analyze the following two-dimensional frame with a curved glue-laminated
2D Tutorial Project Description: This project has been set-up to demonstrate the basic features of VisualAnalysis. You will model and analyze the following two-dimensional frame with a curved glue-laminated
MIT Programming Contest Team Contest 1 Problems 2008
 MIT Programming Contest Team Contest 1 Problems 2008 October 5, 2008 1 Edit distance Given a string, an edit script is a set of instructions to turn it into another string. There are four kinds of instructions
MIT Programming Contest Team Contest 1 Problems 2008 October 5, 2008 1 Edit distance Given a string, an edit script is a set of instructions to turn it into another string. There are four kinds of instructions
Linear Algebra Part I - Linear Spaces
 Linear Algebra Part I - Linear Spaces Simon Julier Department of Computer Science, UCL S.Julier@cs.ucl.ac.uk http://moodle.ucl.ac.uk/course/view.php?id=11547 GV01 - Mathematical Methods, Algorithms and
Linear Algebra Part I - Linear Spaces Simon Julier Department of Computer Science, UCL S.Julier@cs.ucl.ac.uk http://moodle.ucl.ac.uk/course/view.php?id=11547 GV01 - Mathematical Methods, Algorithms and
GEOG 4110/5100 Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture 4
 GEOG 4110/5100 Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture 4 Geometric Distortion Relevant Reading: Richards, Sections 2.11-2.17 Geometric Distortion Geometric Distortion: Errors in image geometry, (location, dimensions,
GEOG 4110/5100 Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture 4 Geometric Distortion Relevant Reading: Richards, Sections 2.11-2.17 Geometric Distortion Geometric Distortion: Errors in image geometry, (location, dimensions,
Simple Linear Interpolation Explains All Usual Choices in Fuzzy Techniques: Membership Functions, t-norms, t-conorms, and Defuzzification
 Simple Linear Interpolation Explains All Usual Choices in Fuzzy Techniques: Membership Functions, t-norms, t-conorms, and Defuzzification Vladik Kreinovich, Jonathan Quijas, Esthela Gallardo, Caio De Sa
Simple Linear Interpolation Explains All Usual Choices in Fuzzy Techniques: Membership Functions, t-norms, t-conorms, and Defuzzification Vladik Kreinovich, Jonathan Quijas, Esthela Gallardo, Caio De Sa
Lab 21.1 The Tangent Galvanometer
 Name School Date Lab 21.1 The Tangent Galvanometer Purpose To investigate the magnetic field at the center of a current-carrying loop of wire. To verify the right-hand rule for the field inside a current
Name School Date Lab 21.1 The Tangent Galvanometer Purpose To investigate the magnetic field at the center of a current-carrying loop of wire. To verify the right-hand rule for the field inside a current
Displaying Strike and Dip Measurements on Your Map in Surfer
 Displaying Strike and Dip Measurements on Your Map in Surfer Measuring strike and dip is a fundamental part of geological mapping, and displaying strike and dip information on a map is an effective way
Displaying Strike and Dip Measurements on Your Map in Surfer Measuring strike and dip is a fundamental part of geological mapping, and displaying strike and dip information on a map is an effective way
Fuel Cell Preparation. The anode supported SOFC studied was Ni-YSZ/YSZ/LSM-
 Supplemental Information Fuel Cell Preparation. The anode supported SOFC studied was Ni-YSZ/YSZ/LSM- YSZ,LSM (YSZ = 8 mol% Y 2 O 3 -stabilized ZrO 2 and LSM = La 0.8 Sr 0.2 MnO 3 ). The anode substrates,
Supplemental Information Fuel Cell Preparation. The anode supported SOFC studied was Ni-YSZ/YSZ/LSM- YSZ,LSM (YSZ = 8 mol% Y 2 O 3 -stabilized ZrO 2 and LSM = La 0.8 Sr 0.2 MnO 3 ). The anode substrates,
Introduction to Digital Image Processing
 Fall 2005 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain: Histograms, Arithmetic/Logic Operators, Basics of Spatial Filtering, Smoothing Spatial Filters Tuesday, February 7 2006, Overview (1): Before We Begin
Fall 2005 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain: Histograms, Arithmetic/Logic Operators, Basics of Spatial Filtering, Smoothing Spatial Filters Tuesday, February 7 2006, Overview (1): Before We Begin
Chapter 3 Image Registration. Chapter 3 Image Registration
 Chapter 3 Image Registration Distributed Algorithms for Introduction (1) Definition: Image Registration Input: 2 images of the same scene but taken from different perspectives Goal: Identify transformation
Chapter 3 Image Registration Distributed Algorithms for Introduction (1) Definition: Image Registration Input: 2 images of the same scene but taken from different perspectives Goal: Identify transformation
CSC 305 The Graphics Pipeline-1
 C. O. P. d y! "#"" (-1, -1) (1, 1) x z CSC 305 The Graphics Pipeline-1 by Brian Wyvill The University of Victoria Graphics Group Perspective Viewing Transformation l l l Tools for creating and manipulating
C. O. P. d y! "#"" (-1, -1) (1, 1) x z CSC 305 The Graphics Pipeline-1 by Brian Wyvill The University of Victoria Graphics Group Perspective Viewing Transformation l l l Tools for creating and manipulating
Search in discrete and continuous spaces
 UNSW COMP3431: Robot Architectures S2 2006 1 Overview Assignment #1 Answer Sheet Search in discrete and continuous spaces Due: Start of Lab, Week 6 (1pm, 30 August 2006) The goal of this assignment is
UNSW COMP3431: Robot Architectures S2 2006 1 Overview Assignment #1 Answer Sheet Search in discrete and continuous spaces Due: Start of Lab, Week 6 (1pm, 30 August 2006) The goal of this assignment is
Lecture 25: Affine Transformations and Barycentric Coordinates
 Lecture 25: Affine Transformations and Barycentric Coordinates ECE 417: Multimedia Signal Processing Mark Hasegawa-Johnson University of Illinois 11/28/2017 1 Moving Points Around 2 Affine Transformations
Lecture 25: Affine Transformations and Barycentric Coordinates ECE 417: Multimedia Signal Processing Mark Hasegawa-Johnson University of Illinois 11/28/2017 1 Moving Points Around 2 Affine Transformations
Co-registration and complex interpolation
 Co-registration and complex interpolation Dominique Derauw and Stéphane Roose Centre Spatial de Liège, University of Liège Avenue du Pré Aily, B4031 Angleur, Belgium. Phone.:.. 32 41 67 66 68 Fax.:.. 32
Co-registration and complex interpolation Dominique Derauw and Stéphane Roose Centre Spatial de Liège, University of Liège Avenue du Pré Aily, B4031 Angleur, Belgium. Phone.:.. 32 41 67 66 68 Fax.:.. 32
CS195H Homework 1 Grid homotopies and free groups. Due: February 5, 2015, before class
 CS195H Homework 1 Grid homotopies and free groups This second homework is almost all about grid homotopies and grid curves, but with a little math in the middle. This homework, last year, took people about
CS195H Homework 1 Grid homotopies and free groups This second homework is almost all about grid homotopies and grid curves, but with a little math in the middle. This homework, last year, took people about
Image processing in frequency Domain
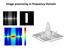 Image processing in frequency Domain Introduction to Frequency Domain Deal with images in: -Spatial domain -Frequency domain Frequency Domain In the frequency or Fourier domain, the value and location
Image processing in frequency Domain Introduction to Frequency Domain Deal with images in: -Spatial domain -Frequency domain Frequency Domain In the frequency or Fourier domain, the value and location
Transformations. Lesson Summary: Students will explore rotations, translations, and reflections in a plane.
 Transformations Lesson Summary: Students will explore rotations, translations, and reflections in a plane. Key Words: Transformation, translation, reflection, rotation Background knowledge: Students should
Transformations Lesson Summary: Students will explore rotations, translations, and reflections in a plane. Key Words: Transformation, translation, reflection, rotation Background knowledge: Students should
Laser sensors. Transmitter. Receiver. Basilio Bona ROBOTICA 03CFIOR
 Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 3 Laser sensors Rays are transmitted and received coaxially The target is illuminated by collimated rays The receiver measures the time of flight (back and
Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 3 Laser sensors Rays are transmitted and received coaxially The target is illuminated by collimated rays The receiver measures the time of flight (back and
Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods
 Connexions module: m42128 1 Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Connexions module: m42128 1 Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Mathematics (www.tiwariacademy.com)
 () Miscellaneous Exercise on Chapter 10 Question 1: Find the values of k for which the line is (a) Parallel to the x-axis, (b) Parallel to the y-axis, (c) Passing through the origin. Answer 1: The given
() Miscellaneous Exercise on Chapter 10 Question 1: Find the values of k for which the line is (a) Parallel to the x-axis, (b) Parallel to the y-axis, (c) Passing through the origin. Answer 1: The given
Tentti/Exam Midterm 2/Välikoe 2, December
 1: 2: 3: Extra: Total 1-3: / 23 4: 5: 6: Total 4-6: / 20 Aalto ME-C3100 Computer Graphics, Fall 2015 Lehtinen / Kemppinen, Ollikainen, Puomio Tentti/Exam Midterm 2/Välikoe 2, December 16 2015 Name, student
1: 2: 3: Extra: Total 1-3: / 23 4: 5: 6: Total 4-6: / 20 Aalto ME-C3100 Computer Graphics, Fall 2015 Lehtinen / Kemppinen, Ollikainen, Puomio Tentti/Exam Midterm 2/Välikoe 2, December 16 2015 Name, student
CS354 Computer Graphics Rotations and Quaternions
 Slide Credit: Don Fussell CS354 Computer Graphics Rotations and Quaternions Qixing Huang April 4th 2018 Orientation Position and Orientation The position of an object can be represented as a translation
Slide Credit: Don Fussell CS354 Computer Graphics Rotations and Quaternions Qixing Huang April 4th 2018 Orientation Position and Orientation The position of an object can be represented as a translation
Anno accademico 2006/2007. Davide Migliore
 Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
How To Get Your Word Document. Ready For Your Editor
 How To Get Your Word Document Ready For Your Editor When your document is ready to send to your editor you ll want to have it set out to look as professional as possible. This isn t just to make it look
How To Get Your Word Document Ready For Your Editor When your document is ready to send to your editor you ll want to have it set out to look as professional as possible. This isn t just to make it look
February 13, notebook
 Module 12 Lesson 1: Graphing on the coordinate plane Lesson 2: Independent and dependent variables in tables and graphs Lesson 3: Writing equations from tables Lesson 4: Representing Algebraic relationships
Module 12 Lesson 1: Graphing on the coordinate plane Lesson 2: Independent and dependent variables in tables and graphs Lesson 3: Writing equations from tables Lesson 4: Representing Algebraic relationships
Alaska Mathematics Standards Vocabulary Word List Grade 7
 1 estimate proportion proportional relationship rate ratio rational coefficient rational number scale Ratios and Proportional Relationships To find a number close to an exact amount; an estimate tells
1 estimate proportion proportional relationship rate ratio rational coefficient rational number scale Ratios and Proportional Relationships To find a number close to an exact amount; an estimate tells
Microsoft Office Excel 2007
 Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Using Excel To Manage Data 1/21/2009 Microsoft Excel 1 Welcome to Excel Excel is a computerized spreadsheet, which is an important tool that helps you report and analyze data.
Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Using Excel To Manage Data 1/21/2009 Microsoft Excel 1 Welcome to Excel Excel is a computerized spreadsheet, which is an important tool that helps you report and analyze data.
Did you ever think that a four hundred year-old spider may be why we study linear relationships today?
 Show Me: Determine if a Function is Linear M8221 Did you ever think that a four hundred year-old spider may be why we study linear relationships today? Supposedly, while lying in bed Rene Descartes noticed
Show Me: Determine if a Function is Linear M8221 Did you ever think that a four hundred year-old spider may be why we study linear relationships today? Supposedly, while lying in bed Rene Descartes noticed
Excel Part 2 Textbook Addendum
 Excel Part 2 Textbook Addendum 1. Page 9 Range Names Sort Alert After completing Activity 1-1, observe what happens if you sort the data in ascending order by Quarter 3. After sorting the data, chances
Excel Part 2 Textbook Addendum 1. Page 9 Range Names Sort Alert After completing Activity 1-1, observe what happens if you sort the data in ascending order by Quarter 3. After sorting the data, chances
Anamorphic Art with a Tilted Cylinder
 Anamorphic Art with a Tilted Cylinder Erika Gerhold and Angela Rose Math and Computer Science Salisbury University 1101 Camden Avenue Salisbury Maryland 21801 USA Faculty Advisor: Dr. Don Spickler Abstract
Anamorphic Art with a Tilted Cylinder Erika Gerhold and Angela Rose Math and Computer Science Salisbury University 1101 Camden Avenue Salisbury Maryland 21801 USA Faculty Advisor: Dr. Don Spickler Abstract
Tools, Tips and Workflows Thinning Feature Vertices in LP360 LP360,
 LP360, 2017.1 l L. Graham 7 January 2017 We have lot of LP360 customers with a variety of disparate feature collection and editing needs. To begin to address these needs, we introduced a completely new
LP360, 2017.1 l L. Graham 7 January 2017 We have lot of LP360 customers with a variety of disparate feature collection and editing needs. To begin to address these needs, we introduced a completely new
CW High School. Advanced Math A. 1.1 I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description for a function, its name, and its graph.
 1. Functions and Math Models (10.00%) 1.1 I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description for a function, its name, and its graph. 4 Pro cient I can make connections between the algebraic
1. Functions and Math Models (10.00%) 1.1 I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description for a function, its name, and its graph. 4 Pro cient I can make connections between the algebraic
Introduction to Octave/Matlab. Deployment of Telecommunication Infrastructures
 Introduction to Octave/Matlab Deployment of Telecommunication Infrastructures 1 What is Octave? Software for numerical computations and graphics Particularly designed for matrix computations Solving equations,
Introduction to Octave/Matlab Deployment of Telecommunication Infrastructures 1 What is Octave? Software for numerical computations and graphics Particularly designed for matrix computations Solving equations,
of Nebraska - Lincoln
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MA xam xpository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2006 axicab Geometry Kyle Lannin Poore University of
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MA xam xpository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2006 axicab Geometry Kyle Lannin Poore University of
6.1 Polar Coordinates
 6.1 Polar Coordinates Introduction This chapter introduces and explores the polar coordinate system, which is based on a radius and theta. Students will learn how to plot points and basic graphs in this
6.1 Polar Coordinates Introduction This chapter introduces and explores the polar coordinate system, which is based on a radius and theta. Students will learn how to plot points and basic graphs in this
Chapter 5. Transforming Shapes
 Chapter 5 Transforming Shapes It is difficult to walk through daily life without being able to see geometric transformations in your surroundings. Notice how the leaves of plants, for example, are almost
Chapter 5 Transforming Shapes It is difficult to walk through daily life without being able to see geometric transformations in your surroundings. Notice how the leaves of plants, for example, are almost
6.001 Notes: Section 6.1
 6.001 Notes: Section 6.1 Slide 6.1.1 When we first starting talking about Scheme expressions, you may recall we said that (almost) every Scheme expression had three components, a syntax (legal ways of
6.001 Notes: Section 6.1 Slide 6.1.1 When we first starting talking about Scheme expressions, you may recall we said that (almost) every Scheme expression had three components, a syntax (legal ways of
0. Introduction: What is Computer Graphics? 1. Basics of scan conversion (line drawing) 2. Representing 2D curves
 CSC 418/2504: Computer Graphics Course web site (includes course information sheet): http://www.dgp.toronto.edu/~elf Instructor: Eugene Fiume Office: BA 5266 Phone: 416 978 5472 (not a reliable way) Email:
CSC 418/2504: Computer Graphics Course web site (includes course information sheet): http://www.dgp.toronto.edu/~elf Instructor: Eugene Fiume Office: BA 5266 Phone: 416 978 5472 (not a reliable way) Email:
Learning Task: New York City
 Learning Task: New York City Georgia Department of Education Name Date Mathematical Goals Find the point on a line segment that separates the segments into a given ratio. Essential Questions How can a
Learning Task: New York City Georgia Department of Education Name Date Mathematical Goals Find the point on a line segment that separates the segments into a given ratio. Essential Questions How can a
Flattening without picking
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 112, November 11, 2002, pages 141 151 Flattening without picking Jesse Lomask and Jon Claerbout 1 ABSTRACT We introduce an analytical method for integrating dip information
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 112, November 11, 2002, pages 141 151 Flattening without picking Jesse Lomask and Jon Claerbout 1 ABSTRACT We introduce an analytical method for integrating dip information
Trigonometry
 Trigonometry - 020171 Department: Math Level: Standard Length of Class: Semester Number of Credits: 1 Grades: 11-12 Prerequisites: Algebra 2 Application Needed: No College credit available: No Credit completion
Trigonometry - 020171 Department: Math Level: Standard Length of Class: Semester Number of Credits: 1 Grades: 11-12 Prerequisites: Algebra 2 Application Needed: No College credit available: No Credit completion
(Refer Slide Time: 00:02:00)
 Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 18 Polyfill - Scan Conversion of a Polygon Today we will discuss the concepts
Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 18 Polyfill - Scan Conversion of a Polygon Today we will discuss the concepts
360 Full View Spherical Mosaic
 360 Full View Spherical Mosaic Huang Wenfan Huang Yehui Rong Nan U017865B U017844X U018274R Objective Full spherical mosaic 360 x 180. All images are taken with camera mounted on a tripod. Registration
360 Full View Spherical Mosaic Huang Wenfan Huang Yehui Rong Nan U017865B U017844X U018274R Objective Full spherical mosaic 360 x 180. All images are taken with camera mounted on a tripod. Registration
Image Compression With Haar Discrete Wavelet Transform
 Image Compression With Haar Discrete Wavelet Transform Cory Cox ME 535: Computational Techniques in Mech. Eng. Figure 1 : An example of the 2D discrete wavelet transform that is used in JPEG2000. Source:
Image Compression With Haar Discrete Wavelet Transform Cory Cox ME 535: Computational Techniques in Mech. Eng. Figure 1 : An example of the 2D discrete wavelet transform that is used in JPEG2000. Source:
CONTENTS: Array Usage Multi-Dimensional Arrays Reference Types. COMP-202 Unit 6: Arrays
 CONTENTS: Array Usage Multi-Dimensional Arrays Reference Types COMP-202 Unit 6: Arrays Introduction (1) Suppose you want to write a program that asks the user to enter the numeric final grades of 350 COMP-202
CONTENTS: Array Usage Multi-Dimensional Arrays Reference Types COMP-202 Unit 6: Arrays Introduction (1) Suppose you want to write a program that asks the user to enter the numeric final grades of 350 COMP-202
Introduction to Medical Imaging. Cone-Beam CT. Klaus Mueller. Computer Science Department Stony Brook University
 Introduction to Medical Imaging Cone-Beam CT Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University Introduction Available cone-beam reconstruction methods: exact approximate algebraic Our discussion:
Introduction to Medical Imaging Cone-Beam CT Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University Introduction Available cone-beam reconstruction methods: exact approximate algebraic Our discussion:
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 100, April 20, 1999, pages
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 100, April 20, 1999, pages 251 256 250 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 100, April 20, 1999, pages 251 256 Helical meshes on spheres and cones Jon Claerbout 1 keywords:
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 100, April 20, 1999, pages 251 256 250 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 100, April 20, 1999, pages 251 256 Helical meshes on spheres and cones Jon Claerbout 1 keywords:
Importing Your Own Data
 Importing Your Own Data OpenDX Data Grid Types Surfaces Volumes Regular: R positions, R connections Deformed Regular: IR positions, R connections Irregular: IR positions, IR connections R = regular IR
Importing Your Own Data OpenDX Data Grid Types Surfaces Volumes Regular: R positions, R connections Deformed Regular: IR positions, R connections Irregular: IR positions, IR connections R = regular IR
Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross Product
 University of Babylon College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. Subject : Mathematics III Class : 2 nd year - first semester Date: / 10 / 2016 2016 \ 2017 Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross
University of Babylon College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. Subject : Mathematics III Class : 2 nd year - first semester Date: / 10 / 2016 2016 \ 2017 Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross
Image Mosaicing with Motion Segmentation from Video
 Image Mosaicing with Motion Segmentation from Video Augusto Román and Taly Gilat EE392J Digital Video Processing Winter 2002 Introduction: Many digital cameras these days include the capability to record
Image Mosaicing with Motion Segmentation from Video Augusto Román and Taly Gilat EE392J Digital Video Processing Winter 2002 Introduction: Many digital cameras these days include the capability to record
Computation of Slope
 Computation of Slope Prepared by David R. Maidment and David Tarboton GIS in Water Resources Class University of Texas at Austin September 2011, Revised December 2011 There are various ways in which slope
Computation of Slope Prepared by David R. Maidment and David Tarboton GIS in Water Resources Class University of Texas at Austin September 2011, Revised December 2011 There are various ways in which slope
Image Analysis. Rasmus R. Paulsen DTU Compute. DTU Compute
 Rasmus R. Paulsen rapa@dtu.dk http://www.compute.dtu.dk/courses/02502 Plenty of slides adapted from Thomas Moeslunds lectures Lecture 8 Geometric Transformation 2, Technical University of Denmark What
Rasmus R. Paulsen rapa@dtu.dk http://www.compute.dtu.dk/courses/02502 Plenty of slides adapted from Thomas Moeslunds lectures Lecture 8 Geometric Transformation 2, Technical University of Denmark What
Tips and Techniques for Designing the Perfect Layout with SAS Visual Analytics
 SAS2166-2018 Tips and Techniques for Designing the Perfect Layout with SAS Visual Analytics Ryan Norris and Brian Young, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC ABSTRACT Do you want to create better reports but find
SAS2166-2018 Tips and Techniques for Designing the Perfect Layout with SAS Visual Analytics Ryan Norris and Brian Young, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC ABSTRACT Do you want to create better reports but find
Advanced Computer Graphics
 G22.2274 001, Fall 2009 Advanced Computer Graphics Project details and tools 1 Project Topics Computer Animation Geometric Modeling Computational Photography Image processing 2 Optimization All projects
G22.2274 001, Fall 2009 Advanced Computer Graphics Project details and tools 1 Project Topics Computer Animation Geometric Modeling Computational Photography Image processing 2 Optimization All projects
Simulation of rotation and scaling algorithm for numerically modelled structures
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of rotation and scaling algorithm for numerically modelled structures To cite this article: S K Ruhit et al 2018 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of rotation and scaling algorithm for numerically modelled structures To cite this article: S K Ruhit et al 2018 IOP
LED Tetris. Final Project Report December 9, 2016 Robert Linden and Paul Slaats GitHub Url: https://github.com/robertmlinden/e155-tetris
 LED Tetris Final Project Report December 9, 2016 Robert Linden and Paul Slaats GitHub Url: https://github.com/robertmlinden/e155-tetris Abstract: There is no easy method to create a game of Tetris with
LED Tetris Final Project Report December 9, 2016 Robert Linden and Paul Slaats GitHub Url: https://github.com/robertmlinden/e155-tetris Abstract: There is no easy method to create a game of Tetris with
and stay in view until you release the mouse button, at which point the image grid will reappear. You can keep switching back and forth between the
 Conformal Maps The purpose of this category is to help visualize the mapping properties of a complex analytic function. The basic method for using this category is to first, as usual, choose a canned object
Conformal Maps The purpose of this category is to help visualize the mapping properties of a complex analytic function. The basic method for using this category is to first, as usual, choose a canned object
Higher Surveying Dr. Ajay Dashora Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Higher Surveying Dr. Ajay Dashora Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 2 Lecture - 03 Coordinate System and Reference Frame Hello everyone. Welcome back on
Higher Surveying Dr. Ajay Dashora Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 2 Lecture - 03 Coordinate System and Reference Frame Hello everyone. Welcome back on
UNIT 2 2D TRANSFORMATIONS
 UNIT 2 2D TRANSFORMATIONS Introduction With the procedures for displaying output primitives and their attributes, we can create variety of pictures and graphs. In many applications, there is also a need
UNIT 2 2D TRANSFORMATIONS Introduction With the procedures for displaying output primitives and their attributes, we can create variety of pictures and graphs. In many applications, there is also a need
CS4670: Computer Vision
 CS4670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 9: Image alignment http://www.wired.com/gadgetlab/2010/07/camera-software-lets-you-see-into-the-past/ Szeliski: Chapter 6.1 Reading All 2D Linear Transformations
CS4670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 9: Image alignment http://www.wired.com/gadgetlab/2010/07/camera-software-lets-you-see-into-the-past/ Szeliski: Chapter 6.1 Reading All 2D Linear Transformations
Evolving Region Moving Object Random Dataset Generator
 Evolving Region Moving Object Random Dataset Generator Berkay Aydin 1 * Abstract Large-scale spatio-temporal data is crucial for testing the spatio-temporal pattern mining algorithms. In this paper we
Evolving Region Moving Object Random Dataset Generator Berkay Aydin 1 * Abstract Large-scale spatio-temporal data is crucial for testing the spatio-temporal pattern mining algorithms. In this paper we
VANSTEENKISTE LEO DAE GD ENG UNFOLD SHADER. Introduction
 VANSTEENKISTE LEO 2015 G E O M E T RY S H A D E R 2 DAE GD ENG UNFOLD SHADER Introduction Geometry shaders are a powerful tool for technical artists, but they always seem to be used for the same kind of
VANSTEENKISTE LEO 2015 G E O M E T RY S H A D E R 2 DAE GD ENG UNFOLD SHADER Introduction Geometry shaders are a powerful tool for technical artists, but they always seem to be used for the same kind of
CV: 3D sensing and calibration
 CV: 3D sensing and calibration Coordinate system changes; perspective transformation; Stereo and structured light MSU CSE 803 1 roadmap using multiple cameras using structured light projector 3D transformations
CV: 3D sensing and calibration Coordinate system changes; perspective transformation; Stereo and structured light MSU CSE 803 1 roadmap using multiple cameras using structured light projector 3D transformations
Agisoft PhotoScan Tutorial
 Agisoft PhotoScan Tutorial Agisoft PhotoScan is a photogrammetry software that allows you to build 3D models from digital photographs. Photogrammetry requires a series of photographs of an object from
Agisoft PhotoScan Tutorial Agisoft PhotoScan is a photogrammetry software that allows you to build 3D models from digital photographs. Photogrammetry requires a series of photographs of an object from
OpenGL Transformations
 OpenGL Transformations R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 02/18/2014 Introduction The most essential aspect of OpenGL is the vertex pipeline described in
OpenGL Transformations R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 02/18/2014 Introduction The most essential aspect of OpenGL is the vertex pipeline described in
Module 7 Defining Coordinate Systems
 Module 7 Defining Coordinate Systems Introduction Objectives Outline of Topics Covered The use of coordinate systems is very important in managing 3D spatial data including point clouds. In this module
Module 7 Defining Coordinate Systems Introduction Objectives Outline of Topics Covered The use of coordinate systems is very important in managing 3D spatial data including point clouds. In this module
What You ll See in This Chapter. Word Cloud. René Descartes. Introduction. Ian Parberry University of North Texas. Fletcher Dunn
 What You ll See in This Chapter Chapter 1: Cartesian Coordinate Systems Fletcher Dunn Valve Software Ian Parberry University of North Texas This chapter describes the basic concepts of 3D math. It is divided
What You ll See in This Chapter Chapter 1: Cartesian Coordinate Systems Fletcher Dunn Valve Software Ian Parberry University of North Texas This chapter describes the basic concepts of 3D math. It is divided
Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates
 433-324 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
433-324 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
Introduction to IDL. Lecture 2
 Introduction to IDL Lecture 2 ITT: solutions for data visualization and image analysis http://www.ittvis.com/ IDL, programming language ENVI, image processing based on IDL IDL Data visualization and image
Introduction to IDL Lecture 2 ITT: solutions for data visualization and image analysis http://www.ittvis.com/ IDL, programming language ENVI, image processing based on IDL IDL Data visualization and image
CSE151 Assignment 2 Markov Decision Processes in the Grid World
 CSE5 Assignment Markov Decision Processes in the Grid World Grace Lin A484 gclin@ucsd.edu Tom Maddock A55645 tmaddock@ucsd.edu Abstract Markov decision processes exemplify sequential problems, which are
CSE5 Assignment Markov Decision Processes in the Grid World Grace Lin A484 gclin@ucsd.edu Tom Maddock A55645 tmaddock@ucsd.edu Abstract Markov decision processes exemplify sequential problems, which are
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates
 COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
Image georeferencing is the process of developing a model to transform from pixel coordinates into GIS coordinates such as meters on the ground.
 Image georeferencing is the process of developing a model to transform from pixel coordinates into GIS coordinates such as meters on the ground. Image rectification is the process of using your georeferencing
Image georeferencing is the process of developing a model to transform from pixel coordinates into GIS coordinates such as meters on the ground. Image rectification is the process of using your georeferencing
