PART A (5x5M =25M) dx +2xy 4x2 = 0 and passing through the origin. using the method of multipliers. PART B (5x10M = 50M)
|
|
|
- Oliver Wiggins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FIRST YEAR B.SC. MATHEMATICS PAPER I SEMESTER I DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS MODEL QUESTION PAPER (THEORY) Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 *This Paper Csists of Two parts. Follow the Instructis Carefully PART A (5x5M 25M) Answer any FIVE Questis, each questi carries FIVE marks 1. Obtain the equati of the curve whose differential equati is (1 + x 2 ) dy dx +2xy 4x2 0 and passing through the origin. 2. Solve the differential equati (1+e x/y ) dx + e x/y ( 1 x y )dy 0 3. Solve dx z(x+y) dy z(x y) 4. Solve y 2 logy xpy +p Solve (D 2-3D+2)y Coshx. 6. Solve y + 4y cosx.cos3x. dz x 2 +y 2 using the method of multipliers. 7. Solve x d 2 y dx 2 - dy dx +4x3 y x 5 (x>0) 8. Form the differential equati by eliminating a and b from z (x 2 +a)( y 2 +b). PART B (5x10M 50M) Answer All the FIVE questis, each questi carries TEN marks 9. a) Define orthogal trajectory and show that the system of cfocal cics self- orthogal where a,b are arbitrary cstants. (or) b) Define Integrating Factor. Solve (y 4 +2y)dx + (xy 3 + 2y 4-4x)dy a) Solve p 2 +2pycotx y 2 (or) b) Define clairaut s differential equati. Solve y 2px+p 4 x a) Define complementary functi of the differential equatis F(D)y b(x). Solve ( D 2 + 3D+2)y x e x Sinx (or) b) Define Auxilary equati of the differential equati F(D)y b(x). Solve [D 2 - (a+b)d+ab]y e ax + e bx 12. a) Apply the method of variati of parameters to solve d 2 y dx 2 + 4y 4tan2x (or) b) Solve x 2 d 2 y - x dy -3y dx 2 dx x2 logx 13. a) Solve p tanx + q tany tanz (or) b) Find a complete integral of z px +qy +p 2 +q 2 x 2 + y 2 a 2 +λ b 2 +λ 1 is
2 FIRST YEAR B.SC. MATHEMATICS PAPER I SEMESTER -I DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Practical -1 Differential Equatis of first order and first degree 1. Solve the differential equati (1+y 2 )+(x-e tan 1 y ) dy dx 0 2. Solve the differential equati (1+e x/y ) dx + e x/y ( 1 x y )dy 0 3. Solve the simultaneous equati method of multipliers. dx x(y 2 z 2 ) dy y(z 2 x 2 ) dz z(x 2 y 2 ) using the 4. Find the orthogal trajectories of cardioids r a ( 1- cosθ), where a is a parameter. 5. Solve the total differential equati 3x 2 dx+ 3y 2 dy ( x 3 +y 3 +e 2z )dz 0 6. Bacteria in a certain culture increase at a rate proportial to the number present. If the number doubles in e hour, how lg does it take for the number to triple? Practical -2 Differential Equatis of the first order, but not of the first degree 1. Solve the differential equati p 2 + 2py cot x y 2 2. Solve the differential equati y 2px + p 4 x 2 3. Solve the differential equati x 2 p 2 + yp (2x+y) + y 2 0 where p dy Clairaut s form by using the substituti y u and xy v dx by reducing it to 4. Solve the differential equati yp 2-2xp+y0 5. Solve the differential equati y 2 logy xpy+p 2 6. Solve the differential equati x 2 ( dy dx )2-2xy dy dx +2y2 x 2 0
3 Practical -3 Higher Order Linear Differential Equatis 1. Solve y - 4y x 2 + 3e x, given that y(0) 0 and y (0) 2 2. Solve y + 4y cosx.cos3x 3. Solve y +2y + 5y x sinx + x 2 e 2x 4. Solve (D 2 +4)y tan2x 5. Solve (D 2 +2)y x 2 e 3x + e x cos2x 6. Solve( D 2 4D+4)y x 2 +e x + cos2x Practical -4 Higher Order Linear Differential Equatis 1. Solve y + 3y + 2y 1 e x +1 by using the method of variati of parameters. 2. Solve (x 2 D 2 xd + 2)y x log x. 3. Solve x 2 y + xy y 0, given that x + 1 x is e integral. 4. Solve y 2 x y y xex 2 x 5. Solve x d 2 y dx 2 - dy dx +4x3 y x 5 (x>0) 6. Apply the Method of Variati of parameters to solve d2 y dx 2 + a2 y cosecx
4 Practical -5 Partial Differential Equatis 1. Find a partial differential equatis by eliminating a and b from z ax+by+a 2 +b Solve p tanx + q tany tanz. 3. Solve y 2 p xy x(z-2y). 4. Solve py + qx xyz 2 (x 2 -y 2 ). 5. Show that the equatis xp yq and Z(xp + yq) 2xy are compatible and solve them. 6. Find the complete integral of zpq p+q. Practical-6 5 Units 1. Solve the differential equati xy - dy dx y3 e x 2 2. Bacteria in a certain culture increase at a rate proportial to the number present. If the number N increases from 1000 to 2000 in 1 hour, how many are present at the end of 1.5 hours? 3. Solve ( px-y)(py+x) 2p 4. Solve (D 2-2D)y e x. sinx using the method of variati of parameters. 5. Solve [x 3 D 3 +3x 2 D 2 +xd+8]y 65cos(logx) 6. Solve (y z)p + (z x)q x - y
5 FIRST YEAR B.Sc. MATHEMATICS PAPER-I SOLID GEOMETRY-SEMESTER-II MODEL QUESTION PAPER (THEORY) Time: 3 Hrs. Max Marks: 75 This Paper Csists and Two parts. Follow the Instructis Carefully PART-A (5 x 5 25 M) Answer any FIVE questis, each questi carries FIVE marks. 1. Find the equati of the plane through the line of intersecti of the planes x+y+z1 and 2x+3y-z-4 and is parallel to x-axis. 2. Find the point of intersecti of the lines x 1 3 y 2 z 3 and x 1 y 5 z Find the equati of the line through the point (1,2,3) and parallel to the line x-y+2z5, 3x+y+z6. 4. Find the centre and the radius of the circle x 2 + y 2 + z 2 2y 4z 11, x + 2y + 2z Find the equati of the sphere which touches the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 x + 3y + 2z 3 0 at (1,1,-1) and passes through the origin. 6. Find the enveloping ce of a sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 2x + 4z 1 with its vertex at (1,1,1). 7. Find the equati to the ce which passes through the three coordinate axes and the lines x y z and x y z Find the equati of the cylinder whose generators are parallel to the line x y z and guiding curve is ellipse x 2 + 2y 2 1, z 3 PART-B (5 x 10 M 50 M) Answer ALL the questis, each questi carries TEN marks. 9. a) A variable plane is at a cstant distance P from the origin and meets the axes in A,B,C. Show that the locus of the centroid of the tetrahedr OABC is x -2 + y -2 +z P -2. b) Find the bisecting plane of the acute angle between the planes 3x-2y-6z+20, -2x+y-2z a) Prove that the lines x 1 y 2 z 3 ; x 2 y 3 z 4 are coplanar. Also find their point of intersecti and the plane ctaining the lines. b) Find the Shortest distance and equatis of the line of Shortest distance between the lines 3x- 9y+5z0 x+y-z and 6x+8y+3z-100 x+2y+z a) Show that the two circles x 2 +y 2 +z 2 -y+2z0; x-y+z-20 and x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +x-3y+z-50, 2x-y+4z-10 lie the same sphere and find its equati b) Find the limiting points of the coaxial system defined by the spheres x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +2x-4y-2z+60 and x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +2x-4y-2z a) Find the equati to the right circular ce whose vertex (2,-3,5), axes PQ which makes equal angles with the axes and semi-vertical angle if b) If x y z represents e of a set of three mutually perpendicular generators of a ce yz+6zx-14xy0, find the equatis of the other two. 13. a) Find the equati of the right circular cylinder of radius 2 and whose axis passes through the point (1,2,3) and has directis cosines proportial to (2,-3,6). b) Find the equati of the enveloping cylinder of the sphere x 2 +y 2 +z 2-2x+4y-10, having its generators parallel to the line xyz.
6 FIRST B.Sc MATHEMATICS PAPER I SEMESTER II SOLID GEOMETRY PRACTICAL-1 The Plane 1. Find the bisecting plane of the acute angle between the planes 3x-2y+6z+2 0, -2x+y-2z Find the equati of planes bisecting the angles between the planes 3x-6y+2z+5 0, 4x-12y+3z-3 0 and specify the e, which bisects the obtuse angle. 3. Find the equati of the plane through the line of intersecti of the planes x-3y+2z 0 and 3x-y-2z-5 0 and passing through (1,1,1). 4. Find the equati of the plan through the line of intersecti of the planes x+y+z 1 and 2x+3y-z -4 and is parallel to x axis. 5. Show that the equati x 2 +4y 2 +9z 2-12yz-6zx+4xy+5x+10y-15z+6 0 represents a pair of parallel planes and find the distance between them. 6. Show that the equati 2x 2-3y 2 +4z 2 +xy+6zx-yz 0 represents a pair of parallel planes and find the angle between them PRACTICAL 2 The Line 1. Find the length and equatis of Shortest distance. between the lines x 3 x+3 3 lines. y z 3 1 ; y+7 z 6 and also find the points in which the Shortest distance. meets the given Find the length and eqn. of Shortest distance between the lines x 1 y 2 z 1 ; x+y+2z-3 0 2x+3y+3z-4 3. Find the length and equati of Shortest distance between the lines 5x-y-z 0 x-2y+z+3 and 7x-4y-2z 0 x-y+z-3 4. Find the image of the point (2,-1,3) in the plane 3x-2y+z 9 5. Prove that the lines x 1 y 2 z 3 ; x 2 y 3 z 4 are coplanar. Also find their point of intersecti and the plane ctaining the lines. 6. Examine the nature of intersecti of the planes x+2y+3z+1 0, x-y-z-20, x+2y+3z+40
7 PRACTICAL 3 SPHERE 1. Find the equati of the sphere which passes through the circle x 2 +y 2 +z 2 5, x+2y+3z 3 and touching the plane 4x+3y Find the equati of the sphere which has the circle x 2 +y 2 +z 2 -x+z-2 0, x+2y-z-4 0 as the great circle. 3. Show that the two circles x 2 +y 2 +z 2 -y+2z 0, x-y+z-20 and x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +x-3y+z-5 0, 2xy+4z-1 0 lines the same sphere and find its equati. 4. Find the equati of the sphere intersecting the spheres x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +x-3z-2 0, x 2 +y 2 +z x + 3 y+2 0 orthogally and passing through the points (0,3,0), (-2,-1,-4) Find the limiting points of the coaxal defined by spheres x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +4x-2y+2z+6 0 and x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +2x-4y-2z Find the limiting points of the coaxal system of spheres given by x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +3x-3y+6 0, x 2 +y 2 +z 2-6y-6z+6 0 PRACTICAL 4 CONES 1. Find the equati of the right circular ce whose vertex at p(2,-3,5), axis PQ that makes equal angle with axes and Semi-vertical angle is Prove that the ces ax 2 +by 2 +cz 2 0, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a b c 0 are reciprocal. 3. Find the vertex of the ce 7x 2 +2y 2 +2z 2-10xz+10xy +26x-2y+2z Find the equati of the ce with vertex (1,1,2) and guiding curve x 2 +y 2 4, z 0 5. If x y z ; represents e of a set of three mutually perpendicular generators of the ce 5yz-8zx-3xy 0 then find the other two generators 6. Find the equati of the right circular ce whose vertex at p (2,-3,5), axis PQ which makes equal angles with axes and passes through A(1,-2,3)
8 PRACTICAL -5 CYLINDERS AND CONICOIDS 1. Find the equati of the enveloping cylinder of the sphere x 2 +y 2 +z 2-2x+4y-1 0, having its generators parallel to the line xyz 2. Find the equati of the right circular cylinder of radius 2 whose axis passes through (1,2,3) and has directi cosines. proportial to (2,-3,6) 3. Find the equati to the cylinder whose generators are parallel to the cylinder whose generators are parallel to the line x 2 +2y 2 1,z3 x y z ; and the guiding curve is the ellipse Find the equati to the right circular cylinder whose guiding curve is a circle x 2 +y 2 +z 2 9, x-y+z 3 5. Show that the plane 3x+12y-6z-17 0 touches the cicoid 3x 2-6y 2 +9z and final the point of ctact. 6. Prove that locus of poles of the tangent planes to a 2 x 2 +b 2 y 2 -c 2 z 2 1 w.r.t α 2 x 2 +β 2 y 2 +γ 2 z 2 1 is the hyperboloid of e sheet. PRACTICAL -6 ALL UNITS 1. Prove that the equati 2x 2-6y 2-12z 2 +18yz+2zx+xy 0 represents a pair of planes. Also find the angle between them. 2. Show that the lines 2x+3y-4z03x-4y+z-7; and 5x-y-3z+120x-7y+5z-6 are parallel 3. Show that the four points (-8,5,2),(-5,2,2),(-7,6,6), (-4,3,6) are ccyclic 4. Find the enveloping ce of the sphere x 2 +y 2 +z 2-2x+4z 1 with its vertex at (1,1,1) 5. Find the equati of the cylinder whose generators are parallel to x y z passes through the curve x 2 +y 2 16, z0 and which 6. Show that the plane 2x-2y+z+120 touches the sphere x 2 +y 2 +z 2-2x-4y+2z-3 0 and find the point of ctact.
If the center of the sphere is the origin the the equation is. x y z 2ux 2vy 2wz d 0 -(2)
 Sphere Definition: A sphere is the locus of a point which remains at a constant distance from a fixed point. The fixed point is called the centre and the constant distance is the radius of the sphere.
Sphere Definition: A sphere is the locus of a point which remains at a constant distance from a fixed point. The fixed point is called the centre and the constant distance is the radius of the sphere.
12 - THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY Page 1 ( Answers at the end of all questions ) = 2. ( d ) - 3. ^i - 2. ^j c 3. ( d )
 - THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY Page ( ) If the angle θ between the line x - y + x + y - z - and the plane λ x + 4 0 is such that sin θ, then the value of λ is - 4-4 [ AIEEE 00 ] ( ) If the plane ax - ay
- THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY Page ( ) If the angle θ between the line x - y + x + y - z - and the plane λ x + 4 0 is such that sin θ, then the value of λ is - 4-4 [ AIEEE 00 ] ( ) If the plane ax - ay
Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Vectors and the Geometry of Space In Figure 11.43, consider the line L through the point P(x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and parallel to the vector. The vector v is a direction vector for the line L, and a, b, and c
Vectors and the Geometry of Space In Figure 11.43, consider the line L through the point P(x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and parallel to the vector. The vector v is a direction vector for the line L, and a, b, and c
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA SSCE 1993 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS II TUTORIAL 2. 1 x cos dy dx x y dy dx. y cosxdy dx
 UNIVESITI TEKNOLOI MALAYSIA SSCE 99 ENINEEIN MATHEMATICS II TUTOIAL. Evaluate the following iterated integrals. (e) (g) (i) x x x sinx x e x y dy dx x dy dx y y cosxdy dx xy x + dxdy (f) (h) (y + x)dy
UNIVESITI TEKNOLOI MALAYSIA SSCE 99 ENINEEIN MATHEMATICS II TUTOIAL. Evaluate the following iterated integrals. (e) (g) (i) x x x sinx x e x y dy dx x dy dx y y cosxdy dx xy x + dxdy (f) (h) (y + x)dy
CHAPTER 3. Cylinder. ) be any point on the cylinder. The equation of the generator through the point P and parallel to equation (2) are
 CAPTER 3 Cylinder 3.. DENTON A cylinder is a surface generated by a straight line which is parallel to a fixed line and intersects a given curve or touches a given surface. The fixed line is called the
CAPTER 3 Cylinder 3.. DENTON A cylinder is a surface generated by a straight line which is parallel to a fixed line and intersects a given curve or touches a given surface. The fixed line is called the
THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
 For more important questions visit : www4onocom CHAPTER 11 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY POINTS TO REMEMBER Distance between points P(x 1 ) and Q(x, y, z ) is PQ x x y y z z 1 1 1 (i) The coordinates of point
For more important questions visit : www4onocom CHAPTER 11 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY POINTS TO REMEMBER Distance between points P(x 1 ) and Q(x, y, z ) is PQ x x y y z z 1 1 1 (i) The coordinates of point
Name: Class: Date: 1. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint.
 . Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint. f (x, y) = x y, x + y = 8. Set up the triple integral of an arbitrary continuous function
. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint. f (x, y) = x y, x + y = 8. Set up the triple integral of an arbitrary continuous function
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today Tangent Planes and Linear Approximation and the Gradient Vector Vector Functions 1/21 Recall in one-variable calculus, as we zoom in toward a point on a curve, the graph becomes
What you will learn today Tangent Planes and Linear Approximation and the Gradient Vector Vector Functions 1/21 Recall in one-variable calculus, as we zoom in toward a point on a curve, the graph becomes
Functions of Several Variables
 . Functions of Two Variables Functions of Several Variables Rectangular Coordinate System in -Space The rectangular coordinate system in R is formed by mutually perpendicular axes. It is a right handed
. Functions of Two Variables Functions of Several Variables Rectangular Coordinate System in -Space The rectangular coordinate system in R is formed by mutually perpendicular axes. It is a right handed
Analytical Solid Geometry
 Analytical Solid Geometry Distance formula(without proof) Division Formula Direction cosines Direction ratios Planes Straight lines Books Higher Engineering Mathematics by B S Grewal Higher Engineering
Analytical Solid Geometry Distance formula(without proof) Division Formula Direction cosines Direction ratios Planes Straight lines Books Higher Engineering Mathematics by B S Grewal Higher Engineering
Three Dimensional Geometry
 Three Dimensional Geometry Teaching learning points Distance between two given points P(x, y, z ) and Q(x, y, z ) is PQ = ( x x ) + ( y y ) + ( z z ) Direction ratio of line joining the points (x, y, z
Three Dimensional Geometry Teaching learning points Distance between two given points P(x, y, z ) and Q(x, y, z ) is PQ = ( x x ) + ( y y ) + ( z z ) Direction ratio of line joining the points (x, y, z
Math 2130 Practice Problems Sec Name. Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate.
 Math 10 Practice Problems Sec 1.-1. Name Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate. 1) 5 5 - x dy dx -5 0 A) 5 B) C) 15 D) 5 ) 0 0-8 - 6 - x (8 + ln 9) A) 1 1 + x
Math 10 Practice Problems Sec 1.-1. Name Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate. 1) 5 5 - x dy dx -5 0 A) 5 B) C) 15 D) 5 ) 0 0-8 - 6 - x (8 + ln 9) A) 1 1 + x
Class IX Chapter 11 Constructions Maths
 1 Class IX Chapter 11 Constructions Maths 1: Exercise 11.1 Question Construct an angle of 90 at the initial point of a given ray and justify the construction. Answer: The below given steps will be followed
1 Class IX Chapter 11 Constructions Maths 1: Exercise 11.1 Question Construct an angle of 90 at the initial point of a given ray and justify the construction. Answer: The below given steps will be followed
Grad operator, triple and line integrals. Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures
 Grad operator, triple and line integrals Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures 1 .1 The grad operator Let f(x 1, x,..., x n ) be a function of the n variables
Grad operator, triple and line integrals Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures 1 .1 The grad operator Let f(x 1, x,..., x n ) be a function of the n variables
Rectangular Coordinates in Space
 Rectangular Coordinates in Space Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Rectangular Coordinates in Space Today 1 / 11 Introduction We quickly review one and two-dimensional spaces and then
Rectangular Coordinates in Space Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Rectangular Coordinates in Space Today 1 / 11 Introduction We quickly review one and two-dimensional spaces and then
4 = 1 which is an ellipse of major axis 2 and minor axis 2. Try the plane z = y2
 12.6 Quadrics and Cylinder Surfaces: Example: What is y = x? More correctly what is {(x,y,z) R 3 : y = x}? It s a plane. What about y =? Its a cylinder surface. What about y z = Again a cylinder surface
12.6 Quadrics and Cylinder Surfaces: Example: What is y = x? More correctly what is {(x,y,z) R 3 : y = x}? It s a plane. What about y =? Its a cylinder surface. What about y z = Again a cylinder surface
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV. Exam I (Friday, April 29) will cover sections
 REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
PARABOLA SYNOPSIS 1.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP
 PARABOLA SYNOPSIS.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP PM = where PM is perpendicular to the directrix, then the locus of P is a parabola... S ax + hxy
PARABOLA SYNOPSIS.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP PM = where PM is perpendicular to the directrix, then the locus of P is a parabola... S ax + hxy
volume & surface area of a right circular cone cut by a plane parallel to symmetrical axis (Hyperbolic section)
 From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter December 25, 2016 volume & surface area of a right circular cone cut by a plane parallel to symmetrical axis (Hyperbolic section) Harish
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter December 25, 2016 volume & surface area of a right circular cone cut by a plane parallel to symmetrical axis (Hyperbolic section) Harish
Preliminary Mathematics Extension 1
 Phone: (0) 8007 684 Email: info@dc.edu.au Web: dc.edu.au 018 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE COURSE MATERIALS Preliminary Mathematics Extension 1 Parametric Equations Term 1 Week 1 Name. Class day and time Teacher
Phone: (0) 8007 684 Email: info@dc.edu.au Web: dc.edu.au 018 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE COURSE MATERIALS Preliminary Mathematics Extension 1 Parametric Equations Term 1 Week 1 Name. Class day and time Teacher
Mathematical Analysis of Tetrahedron (solid angle subtended by any tetrahedron at its vertex)
 From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter March 29, 2015 Mathematical Analysis of Tetrahedron solid angle subtended by any tetrahedron at its vertex) Harish Chandra Rajpoot Rajpoot,
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter March 29, 2015 Mathematical Analysis of Tetrahedron solid angle subtended by any tetrahedron at its vertex) Harish Chandra Rajpoot Rajpoot,
Elements of three dimensional geometry
 Lecture No-3 Elements of three dimensional geometr Distance formula in three dimension Let P( x1, 1, z1) and Q( x2, 2, z 2) be two points such that PQ is not parallel to one of the 2 2 2 coordinate axis
Lecture No-3 Elements of three dimensional geometr Distance formula in three dimension Let P( x1, 1, z1) and Q( x2, 2, z 2) be two points such that PQ is not parallel to one of the 2 2 2 coordinate axis
Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( ) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent
 Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas
 AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas This document covers all the specific areas of the AQA GCSE Further Maths course, your job is to review all the topic areas, answering the questions if you feel you need
AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas This document covers all the specific areas of the AQA GCSE Further Maths course, your job is to review all the topic areas, answering the questions if you feel you need
Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations
 February 21, 2007 Tangent Planes Tangent Planes Let S be a surface with equation z = f (x, y). Tangent Planes Let S be a surface with equation z = f (x, y). Let P(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) be a point on S. Tangent
February 21, 2007 Tangent Planes Tangent Planes Let S be a surface with equation z = f (x, y). Tangent Planes Let S be a surface with equation z = f (x, y). Let P(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) be a point on S. Tangent
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 2003
 Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Contents. MATH 32B-2 (18W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables. 1 Homework 1 - Solutions 3. 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 13
 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Homework - Solutions 3 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 3 3 Homework 3 - Solutions 9 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus
MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Homework - Solutions 3 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 3 3 Homework 3 - Solutions 9 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus
You may know these...
 You may know these... Chapter 1: Multivariables Functions 1.1 Functions of Two Variables 1.1.1 Function representations 1.1. 3-D Coordinate System 1.1.3 Graph of two variable functions 1.1.4 Sketching
You may know these... Chapter 1: Multivariables Functions 1.1 Functions of Two Variables 1.1.1 Function representations 1.1. 3-D Coordinate System 1.1.3 Graph of two variable functions 1.1.4 Sketching
EM225 Projective Geometry Part 2
 EM225 Projective Geometry Part 2 eview In projective geometry, we regard figures as being the same if they can be made to appear the same as in the diagram below. In projective geometry: a projective point
EM225 Projective Geometry Part 2 eview In projective geometry, we regard figures as being the same if they can be made to appear the same as in the diagram below. In projective geometry: a projective point
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Workbook. MAT 397: Calculus III
 Workbook MAT 397: Calculus III Instructor: Caleb McWhorter Name: Summer 2017 Contents Preface..................................................... 2 1 Spatial Geometry & Vectors 3 1.1 Basic n Euclidean
Workbook MAT 397: Calculus III Instructor: Caleb McWhorter Name: Summer 2017 Contents Preface..................................................... 2 1 Spatial Geometry & Vectors 3 1.1 Basic n Euclidean
Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips
 & present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
& present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
MATH 116 REVIEW PROBLEMS for the FINAL EXAM
 MATH 116 REVIEW PROBLEMS for the FINAL EXAM The following questions are taken from old final exams of various calculus courses taught in Bilkent University 1. onsider the line integral (2xy 2 z + y)dx
MATH 116 REVIEW PROBLEMS for the FINAL EXAM The following questions are taken from old final exams of various calculus courses taught in Bilkent University 1. onsider the line integral (2xy 2 z + y)dx
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Chapter 15: Functions of Several Variables
 Chapter 15: Functions of Several Variables Section 15.1 Elementary Examples a. Notation: Two Variables b. Example c. Notation: Three Variables d. Functions of Several Variables e. Examples from the Sciences
Chapter 15: Functions of Several Variables Section 15.1 Elementary Examples a. Notation: Two Variables b. Example c. Notation: Three Variables d. Functions of Several Variables e. Examples from the Sciences
5200/7200 Fall 2007 Concurrence theorems for triangles
 5200/7200 Fall 2007 Concurrence theorems for triangles There are two basic concurrence theorems for triangles that hold in neutral geometry, that of medians and of angle bisectors, but it seems hard to
5200/7200 Fall 2007 Concurrence theorems for triangles There are two basic concurrence theorems for triangles that hold in neutral geometry, that of medians and of angle bisectors, but it seems hard to
Analytical Solid Geometry
 Analytical Solid Geometry Distance formula(without proof) Division Formula Direction cosines Direction ratios Planes Straight lines Books Higher Engineering Mathematics By B S Grewal Higher Engineering
Analytical Solid Geometry Distance formula(without proof) Division Formula Direction cosines Direction ratios Planes Straight lines Books Higher Engineering Mathematics By B S Grewal Higher Engineering
MAT203 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS
 MAT203 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT203 covers essentially the same material as MAT201, but is more in depth and theoretical. Exam problems are often more sophisticated in scope and difficulty
MAT203 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT203 covers essentially the same material as MAT201, but is more in depth and theoretical. Exam problems are often more sophisticated in scope and difficulty
4. The following diagram shows the triangle AOP, where OP = 2 cm, AP = 4 cm and AO = 3 cm.
 Circular Functions and Trig - Practice Problems (to 07) 1. In the triangle PQR, PR = 5 cm, QR = 4 cm and PQ = 6 cm. Calculate (a) the size of ; (b) the area of triangle PQR. 2. The following diagram shows
Circular Functions and Trig - Practice Problems (to 07) 1. In the triangle PQR, PR = 5 cm, QR = 4 cm and PQ = 6 cm. Calculate (a) the size of ; (b) the area of triangle PQR. 2. The following diagram shows
Three Dimensional Geometry. Linear Programming
 Three Dimensional Geometry Linear Programming A plane is determined uniquely if any one of the following is known: The normal to the plane and its distance from the origin is given, i.e. equation of a
Three Dimensional Geometry Linear Programming A plane is determined uniquely if any one of the following is known: The normal to the plane and its distance from the origin is given, i.e. equation of a
Geometry Vocabulary Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
MAT175 Overview and Sample Problems
 MAT175 Overview and Sample Problems The course begins with a quick review/overview of one-variable integration including the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, u-substitutions, integration by parts, and
MAT175 Overview and Sample Problems The course begins with a quick review/overview of one-variable integration including the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, u-substitutions, integration by parts, and
Multiple Integrals. max x i 0
 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals Definite integrals appear when one solves Area problem. Find the area A of the region bounded above by the curve y = f(x), below by the x-axis, and on the sides by
Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals Definite integrals appear when one solves Area problem. Find the area A of the region bounded above by the curve y = f(x), below by the x-axis, and on the sides by
MATH 2023 Multivariable Calculus
 MATH 2023 Multivariable Calculus Problem Sets Note: Problems with asterisks represent supplementary informations. You may want to read their solutions if you like, but you don t need to work on them. Set
MATH 2023 Multivariable Calculus Problem Sets Note: Problems with asterisks represent supplementary informations. You may want to read their solutions if you like, but you don t need to work on them. Set
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4, MATH 253
 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4, MATH 253. Prove that the following differential equations are satisfied by the given functions: (a) 2 u 2 + 2 u y 2 + 2 u z 2 =0,whereu =(x2 + y 2 + z 2 ) /2. (b) x w + y w y +
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4, MATH 253. Prove that the following differential equations are satisfied by the given functions: (a) 2 u 2 + 2 u y 2 + 2 u z 2 =0,whereu =(x2 + y 2 + z 2 ) /2. (b) x w + y w y +
Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 ouble Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 ouble Integrals over more general regions, efinition, Evaluation of ouble Integrals, Properties of ouble Integrals
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 ouble Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 ouble Integrals over more general regions, efinition, Evaluation of ouble Integrals, Properties of ouble Integrals
8(x 2) + 21(y 1) + 6(z 3) = 0 8x + 21y + 6z = 55.
 MATH 24 -Review for Final Exam. Let f(x, y, z) x 2 yz + y 3 z x 2 + z, and a (2,, 3). Note: f (2xyz 2x, x 2 z + 3y 2 z, x 2 y + y 3 + ) f(a) (8, 2, 6) (a) Find all stationary points (if any) of f. et f.
MATH 24 -Review for Final Exam. Let f(x, y, z) x 2 yz + y 3 z x 2 + z, and a (2,, 3). Note: f (2xyz 2x, x 2 z + 3y 2 z, x 2 y + y 3 + ) f(a) (8, 2, 6) (a) Find all stationary points (if any) of f. et f.
Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems
 Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 17 Notes These notes correspond to Section 10.1 in the text. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems Over the course of the next several lectures, we will
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 17 Notes These notes correspond to Section 10.1 in the text. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems Over the course of the next several lectures, we will
Volume by Slicing (Disks & Washers)
 Volume by Slicing Disks & Washers) SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: As you work through the problems listed below, you should reference Chapter 6. of the recommended textbook or the equivalent chapter in
Volume by Slicing Disks & Washers) SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: As you work through the problems listed below, you should reference Chapter 6. of the recommended textbook or the equivalent chapter in
Multivariable Calculus
 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
with slopes m 1 and m 2 ), if and only if its coordinates satisfy the equation y y 0 = 0 and Ax + By + C 2
 CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
Applications of Triple Integrals
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
S56 (5.3) Higher Straight Line.notebook June 22, 2015
 Daily Practice 5.6.2015 Q1. Simplify Q2. Evaluate L.I: Today we will be revising over our knowledge of the straight line. Q3. Write in completed square form x 2 + 4x + 7 Q4. State the equation of the line
Daily Practice 5.6.2015 Q1. Simplify Q2. Evaluate L.I: Today we will be revising over our knowledge of the straight line. Q3. Write in completed square form x 2 + 4x + 7 Q4. State the equation of the line
Equation of tangent plane: for implicitly defined surfaces section 12.9
 Equation of tangent plane: for implicitly defined surfaces section 12.9 Some surfaces are defined implicitly, such as the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1. In general an implicitly defined surface has the equation
Equation of tangent plane: for implicitly defined surfaces section 12.9 Some surfaces are defined implicitly, such as the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1. In general an implicitly defined surface has the equation
Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-2
 1 Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-2 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 80 General Instructions: a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four
1 Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-2 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 80 General Instructions: a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four
6. Find the equation of the plane that passes through the point (-1,2,1) and contains the line x = y = z.
 Week 1 Worksheet Sections from Thomas 13 th edition: 12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 13.1 1. A plane is a set of points that satisfies an equation of the form c 1 x + c 2 y + c 3 z = c 4. (a) Find any three distinct
Week 1 Worksheet Sections from Thomas 13 th edition: 12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 13.1 1. A plane is a set of points that satisfies an equation of the form c 1 x + c 2 y + c 3 z = c 4. (a) Find any three distinct
14.4: Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations
 14.4: Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations Marius Ionescu October 15, 2012 Marius Ionescu () 14.4: Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations October 15, 2012 1 / 13 Tangent Planes Marius Ionescu ()
14.4: Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations Marius Ionescu October 15, 2012 Marius Ionescu () 14.4: Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations October 15, 2012 1 / 13 Tangent Planes Marius Ionescu ()
Example is the school of mankind, and they will learn at no other. Edmund Burke ( )
 Examples Example is the school of mankind, they will learn at no other. Edmund Burke (79 797) This section, like the previous section, is organised into 9 groups:. Trigonometry. Circles. Triangles.4 Quadrilaterals.5
Examples Example is the school of mankind, they will learn at no other. Edmund Burke (79 797) This section, like the previous section, is organised into 9 groups:. Trigonometry. Circles. Triangles.4 Quadrilaterals.5
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Calculus III-Final review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the corresponding position vector. 1) Define the points P = (-,
Calculus III-Final review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the corresponding position vector. 1) Define the points P = (-,
MA 243 Calculus III Fall Assignment 1. Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals)
 MA 43 Calculus III Fall 8 Dr. E. Jacobs Assignments Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals) Assignment. Spheres and Other Surfaces Read. -. and.6 Section./Problems
MA 43 Calculus III Fall 8 Dr. E. Jacobs Assignments Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals) Assignment. Spheres and Other Surfaces Read. -. and.6 Section./Problems
14.5 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 14.5 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector 1. Directional Derivatives. Recall z = f (x, y) and the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as f (x 0 + h, y 0 ) f (x 0, y 0 ) f x (x 0, y 0
14.5 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector 1. Directional Derivatives. Recall z = f (x, y) and the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as f (x 0 + h, y 0 ) f (x 0, y 0 ) f x (x 0, y 0
Unit 12 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork
 Unit 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork Back in Unit 7, we delved into the algebra and geometry of lines. We showed that lines can be written in several forms: a) the general form: Ax + By + C =
Unit 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork Back in Unit 7, we delved into the algebra and geometry of lines. We showed that lines can be written in several forms: a) the general form: Ax + By + C =
Geometry Definitions and Theorems. Chapter 9. Definitions and Important Terms & Facts
 Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS. Page. 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary Assignments...2
 PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary...1 3. Assignments...2 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2010 Assignment Date to be Posted
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary...1 3. Assignments...2 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2010 Assignment Date to be Posted
Section 13.5: Equations of Lines and Planes. 1 Objectives. 2 Assignments. 3 Lecture Notes
 Section 13.5: Equations of Lines and Planes 1 Objectives 1. Find vector, symmetric, or parametric equations for a line in space given two points on the line, given a point on the line and a vector parallel
Section 13.5: Equations of Lines and Planes 1 Objectives 1. Find vector, symmetric, or parametric equations for a line in space given two points on the line, given a point on the line and a vector parallel
Section 2.5. Functions and Surfaces
 Section 2.5. Functions and Surfaces ² Brief review for one variable functions and curves: A (one variable) function is rule that assigns to each member x in a subset D in R 1 a unique real number denoted
Section 2.5. Functions and Surfaces ² Brief review for one variable functions and curves: A (one variable) function is rule that assigns to each member x in a subset D in R 1 a unique real number denoted
Trig Practice 09 & Nov The diagram below shows a curve with equation y = 1 + k sin x, defined for 0 x 3π.
 IB Math High Level Year : Trig: Practice 09 & 0N Trig Practice 09 & Nov 0. The diagram below shows a curve with equation y = + k sin x, defined for 0 x. The point A, lies on the curve and B(a, b) is the
IB Math High Level Year : Trig: Practice 09 & 0N Trig Practice 09 & Nov 0. The diagram below shows a curve with equation y = + k sin x, defined for 0 x. The point A, lies on the curve and B(a, b) is the
Revision Problems for Examination 2 in Algebra 1
 Centre for Mathematical Sciences Mathematics, Faculty of Science Revision Problems for Examination in Algebra. Let l be the line that passes through the point (5, 4, 4) and is at right angles to the plane
Centre for Mathematical Sciences Mathematics, Faculty of Science Revision Problems for Examination in Algebra. Let l be the line that passes through the point (5, 4, 4) and is at right angles to the plane
12.6 Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces
 12 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 12.6 and Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and We have already looked at two special types of surfaces:
12 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 12.6 and Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and We have already looked at two special types of surfaces:
 CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
f (Pijk ) V. may form the Riemann sum: . Definition. The triple integral of f over the rectangular box B is defined to f (x, y, z) dv = lim
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals..1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections.2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals.3
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals..1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections.2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals.3
B.Stat / B.Math. Entrance Examination 2017
 B.Stat / B.Math. Entrance Examination 017 BOOKLET NO. TEST CODE : UGA Forenoon Questions : 0 Time : hours Write your Name, Registration Number, Test Centre, Test Code and the Number of this Booklet in
B.Stat / B.Math. Entrance Examination 017 BOOKLET NO. TEST CODE : UGA Forenoon Questions : 0 Time : hours Write your Name, Registration Number, Test Centre, Test Code and the Number of this Booklet in
True/False. MATH 1C: SAMPLE EXAM 1 c Jeffrey A. Anderson ANSWER KEY
 MATH 1C: SAMPLE EXAM 1 c Jeffrey A. Anderson ANSWER KEY True/False 10 points: points each) For the problems below, circle T if the answer is true and circle F is the answer is false. After you ve chosen
MATH 1C: SAMPLE EXAM 1 c Jeffrey A. Anderson ANSWER KEY True/False 10 points: points each) For the problems below, circle T if the answer is true and circle F is the answer is false. After you ve chosen
Analytic Spherical Geometry:
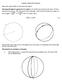 Analytic Spherical Geometry: Begin with a sphere of radius R, with center at the origin O. Measuring the length of a segment (arc) on a sphere. Let A and B be any two points on the sphere. We know that
Analytic Spherical Geometry: Begin with a sphere of radius R, with center at the origin O. Measuring the length of a segment (arc) on a sphere. Let A and B be any two points on the sphere. We know that
Unit Number of Days Dates. 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/ Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9
 8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III December 21, 2009
 Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III December 21, 2009 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III December 21, 2009 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Math 253, Section 102, Fall 2006 Practice Final Solutions
 Math 253, Section 102, Fall 2006 Practice Final Solutions 1 2 1. Determine whether the two lines L 1 and L 2 described below intersect. If yes, find the point of intersection. If not, say whether they
Math 253, Section 102, Fall 2006 Practice Final Solutions 1 2 1. Determine whether the two lines L 1 and L 2 described below intersect. If yes, find the point of intersection. If not, say whether they
Quadric Surfaces. Philippe B. Laval. Today KSU. Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Today 1 / 24
 Quadric Surfaces Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Today 1 / 24 Introduction A quadric surface is the graph of a second degree equation in three variables. The general
Quadric Surfaces Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Today 1 / 24 Introduction A quadric surface is the graph of a second degree equation in three variables. The general
Geometry 2 Final Review
 Name: Period: Date: Geometry 2 Final Review 1 Find x in ABC. 5 Find x in ABC. 2 Find x in STU. 6 Find cos A in ABC. 3 Find y in XYZ. 7 Find x to the nearest tenth. 4 Find x in HJK. 8 Find the angle of
Name: Period: Date: Geometry 2 Final Review 1 Find x in ABC. 5 Find x in ABC. 2 Find x in STU. 6 Find cos A in ABC. 3 Find y in XYZ. 7 Find x to the nearest tenth. 4 Find x in HJK. 8 Find the angle of
Quadric Surfaces. Philippe B. Laval. Spring 2012 KSU. Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Spring /
 .... Quadric Surfaces Philippe B. Laval KSU Spring 2012 Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Spring 2012 1 / 15 Introduction A quadric surface is the graph of a second degree equation in three variables.
.... Quadric Surfaces Philippe B. Laval KSU Spring 2012 Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Spring 2012 1 / 15 Introduction A quadric surface is the graph of a second degree equation in three variables.
Geometry 1-1. Non-collinear Points not on the same line. Need at least 3 points to be non-collinear since two points are always collinear
 Name Geometry 1-1 Undefined terms terms which cannot be defined only described. Point, line, plane Point a location in space Line a series of points that extends indefinitely in opposite directions. It
Name Geometry 1-1 Undefined terms terms which cannot be defined only described. Point, line, plane Point a location in space Line a series of points that extends indefinitely in opposite directions. It
Curvilinear Coordinates
 Curvilinear Coordinates Cylindrical Coordinates A 3-dimensional coordinate transformation is a mapping of the form T (u; v; w) = hx (u; v; w) ; y (u; v; w) ; z (u; v; w)i Correspondingly, a 3-dimensional
Curvilinear Coordinates Cylindrical Coordinates A 3-dimensional coordinate transformation is a mapping of the form T (u; v; w) = hx (u; v; w) ; y (u; v; w) ; z (u; v; w)i Correspondingly, a 3-dimensional
Review Exercise. 1. Determine vector and parametric equations of the plane that contains the
 Review Exercise 1. Determine vector and parametric equations of the plane that contains the points A11, 2, 12, B12, 1, 12, and C13, 1, 42. 2. In question 1, there are a variety of different answers possible,
Review Exercise 1. Determine vector and parametric equations of the plane that contains the points A11, 2, 12, B12, 1, 12, and C13, 1, 42. 2. In question 1, there are a variety of different answers possible,
1 Vector Functions and Space Curves
 ontents 1 Vector Functions and pace urves 2 1.1 Limits, Derivatives, and Integrals of Vector Functions...................... 2 1.2 Arc Length and urvature..................................... 2 1.3 Motion
ontents 1 Vector Functions and pace urves 2 1.1 Limits, Derivatives, and Integrals of Vector Functions...................... 2 1.2 Arc Length and urvature..................................... 2 1.3 Motion
Notes on Spherical Geometry
 Notes on Spherical Geometry Abhijit Champanerkar College of Staten Island & The Graduate Center, CUNY Spring 2018 1. Vectors and planes in R 3 To review vector, dot and cross products, lines and planes
Notes on Spherical Geometry Abhijit Champanerkar College of Staten Island & The Graduate Center, CUNY Spring 2018 1. Vectors and planes in R 3 To review vector, dot and cross products, lines and planes
Quiz 6 Practice Problems
 Quiz 6 Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not
Quiz 6 Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not
Grade IX. Mathematics Geometry Notes. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade IX Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen The distance of a point from the y - axis is called its x -coordinate, or abscissa, and the distance of the point from the x -axis is called its y-coordinate,
Grade IX Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen The distance of a point from the y - axis is called its x -coordinate, or abscissa, and the distance of the point from the x -axis is called its y-coordinate,
Triangles. Leg = s. Hypotenuse = s 2
 Honors Geometry Second Semester Final Review This review is designed to give the student a BASIC outline of what needs to be reviewed for the second semester final exam in Honors Geometry. It is up to
Honors Geometry Second Semester Final Review This review is designed to give the student a BASIC outline of what needs to be reviewed for the second semester final exam in Honors Geometry. It is up to
Geometry. Oklahoma Math Day INSTRUCTIONS:
 Oklahoma Math Day November 16, 016 Geometry INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Do not begin the test until told to do so.. Calculators are not permitted. 3. Be sure to enter your name and high school code on the answer
Oklahoma Math Day November 16, 016 Geometry INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Do not begin the test until told to do so.. Calculators are not permitted. 3. Be sure to enter your name and high school code on the answer
Math 1330 Final Exam Review Covers all material covered in class this semester.
 Math 1330 Final Exam Review Covers all material covered in class this semester. 1. Give an equation that could represent each graph. A. Recall: For other types of polynomials: End Behavior An even-degree
Math 1330 Final Exam Review Covers all material covered in class this semester. 1. Give an equation that could represent each graph. A. Recall: For other types of polynomials: End Behavior An even-degree
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA SSE 1893 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS TUTORIAL 5
 UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA SSE 189 ENGINEERING MATHEMATIS TUTORIAL 5 1. Evaluate the following surface integrals (i) (x + y) ds, : part of the surface 2x+y+z = 6 in the first octant. (ii) (iii) (iv)
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA SSE 189 ENGINEERING MATHEMATIS TUTORIAL 5 1. Evaluate the following surface integrals (i) (x + y) ds, : part of the surface 2x+y+z = 6 in the first octant. (ii) (iii) (iv)
Quadric surface. Ellipsoid
 Quadric surface Quadric surfaces are the graphs of any equation that can be put into the general form 11 = a x + a y + a 33z + a1xy + a13xz + a 3yz + a10x + a 0y + a 30z + a 00 where a ij R,i, j = 0,1,,
Quadric surface Quadric surfaces are the graphs of any equation that can be put into the general form 11 = a x + a y + a 33z + a1xy + a13xz + a 3yz + a10x + a 0y + a 30z + a 00 where a ij R,i, j = 0,1,,
The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations
 1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
Downloaded from
 Top Concepts Class XI: Maths Ch : Trigonometric Function Chapter Notes. An angle is a measure of rotation of a given ray about its initial point. The original ray is called the initial side and the final
Top Concepts Class XI: Maths Ch : Trigonometric Function Chapter Notes. An angle is a measure of rotation of a given ray about its initial point. The original ray is called the initial side and the final
Answer sheet: Second Midterm for Math 2339
 Answer sheet: Second Midterm for Math 2339 October 26, 2010 Problem 1. True or false: (check one of the box, and briefly explain why) (1) If a twice differentiable f(x,y) satisfies f x (a,b) = f y (a,b)
Answer sheet: Second Midterm for Math 2339 October 26, 2010 Problem 1. True or false: (check one of the box, and briefly explain why) (1) If a twice differentiable f(x,y) satisfies f x (a,b) = f y (a,b)
12 m. 30 m. The Volume of a sphere is 36 cubic units. Find the length of the radius.
 NAME DATE PER. REVIEW #18: SPHERES, COMPOSITE FIGURES, & CHANGING DIMENSIONS PART 1: SURFACE AREA & VOLUME OF SPHERES Find the measure(s) indicated. Answers to even numbered problems should be rounded
NAME DATE PER. REVIEW #18: SPHERES, COMPOSITE FIGURES, & CHANGING DIMENSIONS PART 1: SURFACE AREA & VOLUME OF SPHERES Find the measure(s) indicated. Answers to even numbered problems should be rounded
ASSIGNMENT BOOKLET. Bachelor s Degree Programme. Analytical Geometry
 ASSIGNMENT BOOKLET MTE-05 Bachelor s Degree Programme Analytical Geometry (Valid from st January, 0 to st December, 0) School of Sciences Indira Gandhi National Open University Maidan Garhi New Delhi-0068
ASSIGNMENT BOOKLET MTE-05 Bachelor s Degree Programme Analytical Geometry (Valid from st January, 0 to st December, 0) School of Sciences Indira Gandhi National Open University Maidan Garhi New Delhi-0068
Mrs. Daniel s Geometry Vocab List
 Mrs. Daniel s Geometry Vocab List Geometry Definition: a branch of mathematics concerned with questions of shape, size, relative position of figures, and the properties of space. Refectional Symmetry Definition:
Mrs. Daniel s Geometry Vocab List Geometry Definition: a branch of mathematics concerned with questions of shape, size, relative position of figures, and the properties of space. Refectional Symmetry Definition:
4. LINE AND PATH INTEGRALS
 Universidad arlos III de Madrid alculus II 4. LINE AN PATH INTEGRALS Marina elgado Téllez de epeda Parametrizations of important curves: ircumference: (x a) 2 + (y b) 2 = r 2 1 (t) = (a + cos t,b + sin
Universidad arlos III de Madrid alculus II 4. LINE AN PATH INTEGRALS Marina elgado Téllez de epeda Parametrizations of important curves: ircumference: (x a) 2 + (y b) 2 = r 2 1 (t) = (a + cos t,b + sin
