Taschenrechner. Ganzzahlarithmetik N Pi, 500. In[1]:= Out[1]= In[2]:=
|
|
|
- Georgiana Davidson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Taschenrechner In[]:=... Out[]=.99 In[]:= NPi, Out[]= Ganzzahlarithmetik In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= N Out[]=.99 9 In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= k k N Out[]=.
2 vortrag.nb In[9]:= FactorInteger Out[9]= In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= PrimeQ False FactorInteger 9 In[]:= Netprimen : n ; PrimeQn Netprimen : Netprimen In[]:= Netprime Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= PrimeQ True Algebraische Zahlen In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]=
3 vortrag.nb In[]:= Out[]= In[9]:= Out[9]= Simplify FullSimplify In[]:= y Out[]= In[]:= y Simplify Out[]= In[]:= Sin Π Out[]= In[]:= Sin Π Cos Π Simplify Out[]= In[]:= Sin Π Cos Π FullSimplify Out[]= In[]:= SinΠ Out[]= komplee Zahlen In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= ReEp y Out[]= cos In[]:= In[9]:= Out[9]= Clear, y ReEp y ReImy cos Im Rey
4 vortrag.nb In[]:= Out[]= CompleEpand cosy Rechnen mit Symbolen Polynome und rationale Funktionen In[]:= pol y y Out[]= y y In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= Epandpol y 9 y y y y 9 Factorpol y y y y y In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= rat Togetherrat Factorrat Factor Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= In[9]:= pol Factor, Modulus Epandpol Out[9]= In[]:= Factor Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= Factor, GaussianIntegers True In[]:= Factor, Etension Out[]=
5 vortrag.nb Lineare Algebra In[]:= In[]:= Hilbertmatrin : Table, j, n, k, n j k H Hilbertmatri 9 Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= In[]:= InverseH DetH Vandermonden : Table j k, j, n, k, n V Vandermonde Out[]=
6 vortrag.nb In[9]:= DetV Out[9]= In[]:= Out[]= FactorDetV Gleichungen In[]:= s Solve, Out[]=, In[]:=. s Out[]=, In[]:= s Solve, Out[]=,, In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= s N.99.,.9.,.9. NSolve,.9,.9,.99
7 vortrag.nb In[]:= Plot,,, Out[]=
8 vortrag.nb In[]:= s Solve, Out[]= , , , In[]:= Out[]= s N..,..,.99,.9
9 vortrag.nb 9 In[9]:= s Solve, Out[9]= In[]:= Out[]= Root &,, Root &,, Root &,, Root &,, Root &, s N.,.,.9,.9.,.9. In[]:= Out[]=. sk RootReduce k In[]:= Out[]= Solve y, y,, y, y,, y,, y,, y In[]:= ContourPlot y, y,,,, y,, Out[]= In[]:= Solve y, y,, y Out[]=, y,, y,, y,, y
10 vortrag.nb In[]:= ContourPlot y, y,,,, y,, Out[]= Graphische Darstellungen In[]:= PlotSin, Cos, Tan,,,, PlotStyle RGBColor,,, RGBColor,,, RGBColor,,, PlotRange, Out[]= In[]:= OptionsPlot Out[]= AlignmentPoint Center, AspectRatio, Aes True, AesLabel None, AesOrigin Automatic, Φ AesStyle, Background None, BaselinePosition Automatic, BaseStyle, ClippingStyle None, ColorFunction Automatic, ColorFunctionScaling True, ColorOutput Automatic, ContentSelectable Automatic, DisplayFunction $DisplayFunction, Epilog, Evaluated Automatic, EvaluationMonitor None, Eclusions Automatic, EclusionsStyle None, Filling None, FillingStyle Automatic, FormatType TraditionalForm, Frame False, FrameLabel None, FrameStyle, FrameTicks Automatic, FrameTicksStyle, GridLines None, GridLinesStyle, ImageMargins., ImagePadding All, ImageSize Automatic, LabelStyle, MaRecursion Automatic, Mesh None, MeshFunctions &, MeshShading None, MeshStyle Automatic, Method Automatic, PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal, PlotLabel None, PlotPoints Automatic, PlotRange Full, Automatic, PlotRangeClipping True, PlotRangePadding Automatic, PlotRegion Automatic, PlotStyle Automatic, PreserveImageOptions Automatic, Prolog, RegionFunction True &, RotateLabel True, Ticks Automatic, TicksStyle, WorkingPrecision MachinePrecision
11 vortrag.nb In[]:= PlotDA - y,, -, <, y, -, <E Out[]= In[9]:= - PlotD@Sin@Sqrt@ ^ y ^ DD Sqrt@ ^ y ^ D,, -, <, y, -, <, PlotPoints, PlotRange -., <D. Out[9]=.. - -
12 vortrag.nb In[]:= -, <, y, -, <, PlotPoints, PlotRange -, <D.. Out[]= In[]:= ContourPlot@Sin@D Sin@yD,, -, <, y, -, <, ColorFunction Hue, PlotPoints D Out[]= Analysis Ep@D - In[]:=, F LimitB Out[]= Ep@D - In[]:= SeriesB Out[]=,,, <F OI M
13 vortrag.nb Ep In[]:= ableitung Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= ableitung In[]:= eingabe Out[]= In[]:= Ploteingabe,,,. Out[]=.. In[]:= integral eingabe Out[]= tan tan tan log In[9]:= resultat integral Out[9]= Vereinfachung In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= resultat FullSimplify resultat eingabe FullSimplify Out[]=
1 Basic Plotting. Radii Speeds Offsets 1, 1, 1 2, 5, 19 0, 0, 0 1, 0.8, 0.4, 0.2, 0.4, 0.2 1, 10, 17, 26, 28, 37 0, Π, Π, 0, 0, Π
 1 Basic Plotting Placing wheels on wheels on wheels and giving them different rates of spin leads to some interesting parametric plots. The images show four examples. They arise from the values below,
1 Basic Plotting Placing wheels on wheels on wheels and giving them different rates of spin leads to some interesting parametric plots. The images show four examples. They arise from the values below,
Graphs of Functions, Limits, and
 Chapter Continuity Graphs of Functions, Limits, and ü. Plotting Graphs Students should read Chapter of Rogawski's Calculus [] for a detailed discussion of the material presented in this section. ü.. Basic
Chapter Continuity Graphs of Functions, Limits, and ü. Plotting Graphs Students should read Chapter of Rogawski's Calculus [] for a detailed discussion of the material presented in this section. ü.. Basic
6.2.1 Plotting Curves in Parametric Representation in 3-Dimensional Space
 6.2 Drawing Three-Dimensional Objects $Version 2015-04 - 21 10.0 for Mac OS X x86 (64- bit) (September 10, 2014) 1. Curves in space may be drawn in perspective. (ParametricPlot3D,ListPointPlot3D). 2. 2-dimensional
6.2 Drawing Three-Dimensional Objects $Version 2015-04 - 21 10.0 for Mac OS X x86 (64- bit) (September 10, 2014) 1. Curves in space may be drawn in perspective. (ParametricPlot3D,ListPointPlot3D). 2. 2-dimensional
\usepackage[final]{epsfig} <==== \usepackage{color} <====
![\usepackage[final]{epsfig} <==== \usepackage{color} <==== \usepackage[final]{epsfig} <==== \usepackage{color} <====](/thumbs/82/86424640.jpg) 6.4 Reworking Plots $Version 06-04-8 0.0 for Mac OS X x86 (64- bit) (September 0, 04) The size of a plot resulting from a command as described above may be changed in the process of editing. Also the position
6.4 Reworking Plots $Version 06-04-8 0.0 for Mac OS X x86 (64- bit) (September 0, 04) The size of a plot resulting from a command as described above may be changed in the process of editing. Also the position
HydroperoxyCyclophosphamideDoses 0, 0.32`, 0.5`, 0.79`, 1.2`, 2, 3.2`, 5.07`, 8, 12.67`, 20;
 In[1]:= HydroperoxyCyclophosphamideDoses 0, 0.32`, 0.5`, 0.79`, 1.2`, 2, 3.2`, 5.07`, 8, 12.67`, 20; In[2]:= In[3]:= VincristineDoses 0, 0.00032`, 0.000507`, 0.0008`, 0.00127`, 0.002`, 0.0032`, 0.00507`,
In[1]:= HydroperoxyCyclophosphamideDoses 0, 0.32`, 0.5`, 0.79`, 1.2`, 2, 3.2`, 5.07`, 8, 12.67`, 20; In[2]:= In[3]:= VincristineDoses 0, 0.00032`, 0.000507`, 0.0008`, 0.00127`, 0.002`, 0.0032`, 0.00507`,
1. Introduction and Survey
 . Introduction and Survey In the st century computers are in the process of changing all aspects of our lives. That includes also mathematics - both the way we do it and even the kind of problems that
. Introduction and Survey In the st century computers are in the process of changing all aspects of our lives. That includes also mathematics - both the way we do it and even the kind of problems that
Teaching Complex Analysis as a Lab- Type ( flipped ) Course with a Focus on Geometric Interpretations using Mathematica
 Teaching Complex Analysis as a Lab- Type ( flipped ) Course with a Focus on Geometric Interpretations using Mathematica Bill Kinney, Bethel University, St. Paul, MN 2 KinneyComplexAnalysisLabCourse.nb
Teaching Complex Analysis as a Lab- Type ( flipped ) Course with a Focus on Geometric Interpretations using Mathematica Bill Kinney, Bethel University, St. Paul, MN 2 KinneyComplexAnalysisLabCourse.nb
{σ 1}; Hessian2D[f_] := yleft = -12; xright = 5; yright = 5; max4 = FindMaximum[Det[Hessian2D[f]] // Evaluate, {{x, -10}, {y, -10}}][[2, ;;, 2]]
![{σ 1}; Hessian2D[f_] := yleft = -12; xright = 5; yright = 5; max4 = FindMaximum[Det[Hessian2D[f]] // Evaluate, {{x, -10}, {y, -10}}][[2, ;;, 2]] {σ 1}; Hessian2D[f_] := yleft = -12; xright = 5; yright = 5; max4 = FindMaximum[Det[Hessian2D[f]] // Evaluate, {{x, -10}, {y, -10}}][[2, ;;, 2]]](/thumbs/87/97226018.jpg) g[x_, y_] := f[x_, y_] := x 1 2 +y 2 2 * π * σ * 2 e- 2*σ 2 ; 10 g[x, y] + g[x + i, y] + g[x, y + i] + g[x + 10, y + 10] /. {σ 1}; i=1 10 i=1 Hessian2D[f_] := D[D[f[x, y], {x}], {x}] D[D[f[x, y], {x}],
g[x_, y_] := f[x_, y_] := x 1 2 +y 2 2 * π * σ * 2 e- 2*σ 2 ; 10 g[x, y] + g[x + i, y] + g[x, y + i] + g[x + 10, y + 10] /. {σ 1}; i=1 10 i=1 Hessian2D[f_] := D[D[f[x, y], {x}], {x}] D[D[f[x, y], {x}],
GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF SURFACES
 9- Graphical representation of surfaces 1 9 GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF SURFACES 9.1. Figures defined in Mathematica ô Graphics3D[ ] ø Spheres Sphere of centre 1, 1, 1 and radius 2 Clear "Global` " Graphics3D
9- Graphical representation of surfaces 1 9 GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF SURFACES 9.1. Figures defined in Mathematica ô Graphics3D[ ] ø Spheres Sphere of centre 1, 1, 1 and radius 2 Clear "Global` " Graphics3D
REPRESENTATION OF CURVES IN PARAMETRIC FORM
 - Representation of curves in parametric form 1 REPRESENTATION OF CURVES IN PARAMETRIC FORM.1. Parametrization of curves in the plane Given a curve in parametric form, its graphical representation in a
- Representation of curves in parametric form 1 REPRESENTATION OF CURVES IN PARAMETRIC FORM.1. Parametrization of curves in the plane Given a curve in parametric form, its graphical representation in a
4. Mathematica. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 Starting Mathematica Starting Mathematica from an X-terminal (Maths)
 4. Mathematica 4.1 Introduction Mathematica is a general purpose computer algebra system. That means it can do algebraic manipulations (including calculus and matrix manipulation) and it can also be used
4. Mathematica 4.1 Introduction Mathematica is a general purpose computer algebra system. That means it can do algebraic manipulations (including calculus and matrix manipulation) and it can also be used
Assignment 1. Prolog to Problem 1. Two cylinders. ü Visualization. Problems by Branko Curgus
 Assignment In[]:= Problems by Branko Curgus SetOptions $FrontEndSession, Magnification Prolog to Problem. Two cylinders In[]:= This is a tribute to a problem that I was assigned as an undergraduate student
Assignment In[]:= Problems by Branko Curgus SetOptions $FrontEndSession, Magnification Prolog to Problem. Two cylinders In[]:= This is a tribute to a problem that I was assigned as an undergraduate student
Examples of Fourier series
 Examples of Fourier series Preliminaries In[]:= Below is the definition of a periodic extension of a function defined on L, L. This definition takes a function as a variable. The function has to be inputted
Examples of Fourier series Preliminaries In[]:= Below is the definition of a periodic extension of a function defined on L, L. This definition takes a function as a variable. The function has to be inputted
Wolfram Mathematica Tutorial Collection. Visualization and Graphics
 Wolfram Mathematica Tutorial Collection Visualization and Graphics For use with Wolfram Mathematica 7.0 and later. For the latest updates and corrections to this manual: visit reference.wolfram.com For
Wolfram Mathematica Tutorial Collection Visualization and Graphics For use with Wolfram Mathematica 7.0 and later. For the latest updates and corrections to this manual: visit reference.wolfram.com For
The notebook interface is the usual one and is quite sophisticated. (It was used to create these notes, for instance.)
 4. Mathematica 4. Introduction Mathematica is a general purpose computer algebra system. That means it can do algebraic manipulations (including calculus and matrix manipulation) and it can also be used
4. Mathematica 4. Introduction Mathematica is a general purpose computer algebra system. That means it can do algebraic manipulations (including calculus and matrix manipulation) and it can also be used
OffPlot::"plnr"; OffGraphics::"gptn"; OffParametricPlot3D::"plld" Needs"Graphics`Arrow`" Needs"VisualLA`"
 Printed from the Mathematica Help Browser of.: Transformation of Functions In this section, we will explore three types of transformations:.) Shifting.) Reflections (or flips).) Stretches and compressions
Printed from the Mathematica Help Browser of.: Transformation of Functions In this section, we will explore three types of transformations:.) Shifting.) Reflections (or flips).) Stretches and compressions
Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f 1, f 2,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i.
 HdPlot.nb? Plot Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f, f,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i. Plot Sin 7 x Exp x ^, x,, 4.5 3 4.5 Plot Sin
HdPlot.nb? Plot Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f, f,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i. Plot Sin 7 x Exp x ^, x,, 4.5 3 4.5 Plot Sin
surface length L = 1 4 Mathematica Code for streamfunction vorticity CFD
 inflow y H i,n y outflow i,1 i,0 starting length Xs surface length L = 1 Figure 1: Eternal boundary layer control volume. 4 Mathematica Code for streamfunction vorticity CFD Listed below is a Mathematica
inflow y H i,n y outflow i,1 i,0 starting length Xs surface length L = 1 Figure 1: Eternal boundary layer control volume. 4 Mathematica Code for streamfunction vorticity CFD Listed below is a Mathematica
Graphical Extensions of the Package TuGames
 Graphical Extensions of the Package TuGames Holger I. MEINHARDT Institute for Statistics and Economic Theory University of Karlsruhe Englerstr. 11,Bd. 11.40 D-76128 Karlsruhe E-mails: hme@vwl3.wiwi.uni-karlsruhe.de,
Graphical Extensions of the Package TuGames Holger I. MEINHARDT Institute for Statistics and Economic Theory University of Karlsruhe Englerstr. 11,Bd. 11.40 D-76128 Karlsruhe E-mails: hme@vwl3.wiwi.uni-karlsruhe.de,
Mathematica examples relevant to Bessel functions
 Mathematica eamples relevant to Bessel functions The original Bessel function---that discussed etensively in Boas Also called Bessel functions of the first kind, or cylindrical Bessel functions It is a
Mathematica eamples relevant to Bessel functions The original Bessel function---that discussed etensively in Boas Also called Bessel functions of the first kind, or cylindrical Bessel functions It is a
Problem #130 Ant On Cylinders
 Problem #130 Ant On Cyliners The Distance The Ant Travels Along The Surface John Snyer November, 009 Problem Consier the soli boune by the three right circular cyliners x y (greenish-yellow), x z (re),
Problem #130 Ant On Cyliners The Distance The Ant Travels Along The Surface John Snyer November, 009 Problem Consier the soli boune by the three right circular cyliners x y (greenish-yellow), x z (re),
Finite Difference Solution of the 1D Helmholtz Differential Equation
 1 Printed from the Mathematica elp System Finite ifference Solution of the 1 elmholtz ifferential Equation Initialization Code (optional) checktermat_? NumberQ@ð &LE := If@Abs@t - 1 $MachineEpsilon 1 If@Abs@t
1 Printed from the Mathematica elp System Finite ifference Solution of the 1 elmholtz ifferential Equation Initialization Code (optional) checktermat_? NumberQ@ð &LE := If@Abs@t - 1 $MachineEpsilon 1 If@Abs@t
Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f 1, f 2,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i.
 HdPlot.nb In[]:=? Plot Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f, f,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i. In[]:= Plot Sin 7 x Exp x ^, x,, 4.5
HdPlot.nb In[]:=? Plot Plot f, x, x min, x max generates a plot of f as a function of x from x min to x max. Plot f, f,, x, x min, x max plots several functions f i. In[]:= Plot Sin 7 x Exp x ^, x,, 4.5
sinc interpolation to reconstruct a signal from its samples
 sinc interpolation to reconstruct a signal from its samples Initialization Code Manipulate ManipulateAprocess@ Fs, fund, ItemA GridA9 9Control@Fs,, Row@Style@"sampling frequency", D, Style@ " HHzL", ItalicD
sinc interpolation to reconstruct a signal from its samples Initialization Code Manipulate ManipulateAprocess@ Fs, fund, ItemA GridA9 9Control@Fs,, Row@Style@"sampling frequency", D, Style@ " HHzL", ItalicD
4. Graphiken Graphiques
 KURS_04_New.NB Kurs Cours 4. Graphiken Graphiques Die Gliederung dieses Kurses folgt in groben Zügen dem Buch von Nancy Blachman: A Practical Approach... Hinweis: Kapitel 4 lesen! Run mit WIN+Mathematica
KURS_04_New.NB Kurs Cours 4. Graphiken Graphiques Die Gliederung dieses Kurses folgt in groben Zügen dem Buch von Nancy Blachman: A Practical Approach... Hinweis: Kapitel 4 lesen! Run mit WIN+Mathematica
23.1 Setting up Mathematica Packages
 23. Procedures and Packages 2015-06-15 $Version 10.0 for Mac OS X x86 (64- bit) (September 10, 2014) 23.1 Setting up Mathematica Packages In a typical Mathematica package there are generally two kinds
23. Procedures and Packages 2015-06-15 $Version 10.0 for Mac OS X x86 (64- bit) (September 10, 2014) 23.1 Setting up Mathematica Packages In a typical Mathematica package there are generally two kinds
Computational methods in Mathematics
 Computational methods in Mathematics José Carlos Díaz Ramos Cristina Vidal Castiñeira June 13, 2014 1 Graphics Mathematica represents all graphics in terms of a collection of graphics primitives. The primitives
Computational methods in Mathematics José Carlos Díaz Ramos Cristina Vidal Castiñeira June 13, 2014 1 Graphics Mathematica represents all graphics in terms of a collection of graphics primitives. The primitives
Making Holes and Windows in Surfaces
 The Mathematica Journal Making Holes and Windows in Surfaces Alan Horwitz In this article, we demonstrate makehole, a program which removes points from any Graphics or Graphics3D picture whose coordinates
The Mathematica Journal Making Holes and Windows in Surfaces Alan Horwitz In this article, we demonstrate makehole, a program which removes points from any Graphics or Graphics3D picture whose coordinates
CurvesGraphics. A free package for Advanced Calculus illustrations. Gianluca Gorni. Arrows on 2D curves. Motivation
 CurvesGraphics A free package for Advanced Calculus illustrations. Gianluca Gorni Motivation As a teacher of Calculus and Mathematical Analysis at college and university level, I feel that Mathematica
CurvesGraphics A free package for Advanced Calculus illustrations. Gianluca Gorni Motivation As a teacher of Calculus and Mathematical Analysis at college and university level, I feel that Mathematica
Newton s Method. Example : Find the root of f (x) =
 Newton s Method Example : Find the root of f (x) = If we draw the graph of f (x), we can see that the root of f (x) = 0 is the x - coordinate of the point where the curve intersects with the x - axis.
Newton s Method Example : Find the root of f (x) = If we draw the graph of f (x), we can see that the root of f (x) = 0 is the x - coordinate of the point where the curve intersects with the x - axis.
Scaffold protein titration motif
 Scaffold protein titration motif The model description This particular motif describe one phosphorylation-desphosphorylation cycle (can be generalized to any futile cycles) with both kinase (K) and phosphatase
Scaffold protein titration motif The model description This particular motif describe one phosphorylation-desphosphorylation cycle (can be generalized to any futile cycles) with both kinase (K) and phosphatase
H* Define 2 Points in R 3 *L P = 81, 2, 3< Q = 84, 6, 6< PQvec = Q - P. H* Plot a Single Red Point of "Size" 0.05 *L
 Define and plotting a point and vector H* Define 2 Points in R 3 *L P = 81, 2, 3< Q = 84, 6, 6< PQvec = Q - P H* Plot a Single Red Point of "Size" 0.05 *L Graphics3D@8PointSize@0.05D, Red, Point@PD
Define and plotting a point and vector H* Define 2 Points in R 3 *L P = 81, 2, 3< Q = 84, 6, 6< PQvec = Q - P H* Plot a Single Red Point of "Size" 0.05 *L Graphics3D@8PointSize@0.05D, Red, Point@PD
A plane. Or, with more details, NotebookDirectory. C:\Dropbox\Work\myweb\Courses\Math_pages\Math_225\
 In[1]:= NotebookDirectory Out[1]= C:\Dropbox\Work\myweb\Courses\Math_pages\Math_5\ A plane Given a point in R 3 (below it is vr) and two non-collinear vectors (below uu and vv) the parametric equation
In[1]:= NotebookDirectory Out[1]= C:\Dropbox\Work\myweb\Courses\Math_pages\Math_5\ A plane Given a point in R 3 (below it is vr) and two non-collinear vectors (below uu and vv) the parametric equation
The differential structure of images Prof. Bart M. ter Haar Romeny, PhD
 The differential structure of images Prof. Bart M. ter Haar Romeny, PhD Brainnetome Workshop 9-10 October 015, Beijing, China Init The 1-D Gaussian kernel: gauss[x_, Σ_ /; Σ > 0] := Σ 1 Π e - x Σ ; The
The differential structure of images Prof. Bart M. ter Haar Romeny, PhD Brainnetome Workshop 9-10 October 015, Beijing, China Init The 1-D Gaussian kernel: gauss[x_, Σ_ /; Σ > 0] := Σ 1 Π e - x Σ ; The
General::spell1 : Possible spelling error: new symbol name "rchnl1" is similar to existing symbol "rchnh1". More
 RangeDutyCycle.nb 1 Range and Displays inspiral range and duty cycle of S5. Setup Parameters In[9]:= rchnh1 "H1:DMT SNSM_EFFECTIVE_RANGE_MPC"; rchnh "H:DMT SNSM_EFFECTIVE_RANGE_MPC"; rchnl1 "L1:DMT SNSM_EFFECTIVE_RANGE_MPC";
RangeDutyCycle.nb 1 Range and Displays inspiral range and duty cycle of S5. Setup Parameters In[9]:= rchnh1 "H1:DMT SNSM_EFFECTIVE_RANGE_MPC"; rchnh "H:DMT SNSM_EFFECTIVE_RANGE_MPC"; rchnl1 "L1:DMT SNSM_EFFECTIVE_RANGE_MPC";
1. How Mathematica works
 Departments of Civil Engineering and Mathematics CE 109: Computing for Engineering Mathematica Session 1: Introduction to the system Mathematica is a piece of software described by its manufacturers as
Departments of Civil Engineering and Mathematics CE 109: Computing for Engineering Mathematica Session 1: Introduction to the system Mathematica is a piece of software described by its manufacturers as
Finite Difference Solution of the Convection-Diffusion Equation in 1D
 1 Printed from the Mathematica elp System Finite ifference Solution of the Convection-iffusion Equation in 1 Initialization Code (optional) Manipulate ManipulateB gtick; finalisplayimage, u, u, grid, systemmatrix,
1 Printed from the Mathematica elp System Finite ifference Solution of the Convection-iffusion Equation in 1 Initialization Code (optional) Manipulate ManipulateB gtick; finalisplayimage, u, u, grid, systemmatrix,
Inverse Iteration Algorithms for Julia Sets
 Inverse Iteration Algorithms for Julia Sets by Mark McClure Inverse iteration algorithms are extremely fast methods to generate images of Julia sets. While they are fairly simple to understand and implement,
Inverse Iteration Algorithms for Julia Sets by Mark McClure Inverse iteration algorithms are extremely fast methods to generate images of Julia sets. While they are fairly simple to understand and implement,
Functions f and g are called a funny cosine and a funny sine if they satisfy the following properties:
 Assignment problems by Branko Ćurgus posted on 2070720 Problem. Funny trigonometry and its beauty ü Few Mathematica comments There are several standard Mathematica functions that can be useful here. For
Assignment problems by Branko Ćurgus posted on 2070720 Problem. Funny trigonometry and its beauty ü Few Mathematica comments There are several standard Mathematica functions that can be useful here. For
Econ 353 Final Project Mark Gillis University of Victoria. Mathematica Model Portfolio
 Econ 353 Final Project Mark Gillis University of Victoria Mathematica Model Portfolio Introduction The following is a portfolio of Mathematica models that I created predominately for the purpose of teaching.
Econ 353 Final Project Mark Gillis University of Victoria Mathematica Model Portfolio Introduction The following is a portfolio of Mathematica models that I created predominately for the purpose of teaching.
Simulations of the Angular Dependence of the Dipole-Dipole Interaction
 Ursinus College Digital Commons @ Ursinus College Physics and Astronomy Summer Fellows Student Research 7-24-2015 Simulations of the Angular Dependence of the Dipole-Dipole Interaction Matan Peleg Ursinus
Ursinus College Digital Commons @ Ursinus College Physics and Astronomy Summer Fellows Student Research 7-24-2015 Simulations of the Angular Dependence of the Dipole-Dipole Interaction Matan Peleg Ursinus
Math 126: Calculus III Section 12.5: Equation of Lines and Planes
 1 Math 16: Calculus III Section 1.5: Equation of Lines and Planes Vector equations of lines Consider the position vector r 0 (which gives points to a point on the line) and the direction v line). Additional
1 Math 16: Calculus III Section 1.5: Equation of Lines and Planes Vector equations of lines Consider the position vector r 0 (which gives points to a point on the line) and the direction v line). Additional
open a text line to annotate your work is Alt-7. From Eq. 2.5 we use the "sum" function in Mathematica to consider the (finite) sum
 Lecture Our goal here is to begin to learn to use Mathematica while at the same time use it to eplore the concepts in the tet. You are encouraged to confirm the Mathematica results and the mechanical issue
Lecture Our goal here is to begin to learn to use Mathematica while at the same time use it to eplore the concepts in the tet. You are encouraged to confirm the Mathematica results and the mechanical issue
Algebra. Mathematica QuickStart for Calculus 101C. Solving Equations. Factoring. Exact Solutions to single equation:
 Mathematica QuickStart for Calculus 101C Algebra Solving Equations Exact Solutions to single equation: In[88]:= Solve@x^3 + 5 x - 6 ã 0, xd Out[88]= :8x Ø 1, :x Ø 1 2 I-1 + Â 23
Mathematica QuickStart for Calculus 101C Algebra Solving Equations Exact Solutions to single equation: In[88]:= Solve@x^3 + 5 x - 6 ã 0, xd Out[88]= :8x Ø 1, :x Ø 1 2 I-1 + Â 23
If you ask most people what A s strategy should be when all 3 duelists are alive, there are two common answers:
 The Truel Problem Imagine that you have a three-way duel (or truel ). The three duelists are named A, B, and C and have accuracy probabilities of a, b, and c with 0 < a < b < c < 1. The rules of the duel
The Truel Problem Imagine that you have a three-way duel (or truel ). The three duelists are named A, B, and C and have accuracy probabilities of a, b, and c with 0 < a < b < c < 1. The rules of the duel
Mathematica Basics. Exponential Functions Exp[expression] Natural Logarithms (ln) Log[expression]
![Mathematica Basics. Exponential Functions Exp[expression] Natural Logarithms (ln) Log[expression] Mathematica Basics. Exponential Functions Exp[expression] Natural Logarithms (ln) Log[expression]](/thumbs/82/86424514.jpg) Mathematica Basics To evaluate a Mathematica command, press [Shift]+[Enter]. Pay attention to spaces! Mathematica interprets some of them as multiplication. Syntax, capitalization and punctuation are meaningful.
Mathematica Basics To evaluate a Mathematica command, press [Shift]+[Enter]. Pay attention to spaces! Mathematica interprets some of them as multiplication. Syntax, capitalization and punctuation are meaningful.
AMS Portfolio Theory and Capital Markets I
 ams-511-ws01-sol.nb 1 AMS 691.02 - Portfolio Theory and Capital Markets I Workshop 01 Solution Robert J Frey, Research Professor Stony Brook University, Applied Mathematics and Statistics frey@ams.sunysb.edu
ams-511-ws01-sol.nb 1 AMS 691.02 - Portfolio Theory and Capital Markets I Workshop 01 Solution Robert J Frey, Research Professor Stony Brook University, Applied Mathematics and Statistics frey@ams.sunysb.edu
Clear["Global`* "] (* Marko Horbatsch, York University, Toronto, Canada * )
![Clear[Global`* ] (* Marko Horbatsch, York University, Toronto, Canada * ) Clear[Global`* ] (* Marko Horbatsch, York University, Toronto, Canada * )](/thumbs/82/86248963.jpg) Clear["Global`* "] (* Marko Horbatsch, York University, Toronto, Canada * ) (* We solve for the vector potential of a spinning spherical shell with surface charge σ. The colume current density is j_phi
Clear["Global`* "] (* Marko Horbatsch, York University, Toronto, Canada * ) (* We solve for the vector potential of a spinning spherical shell with surface charge σ. The colume current density is j_phi
Explore 3D Figures. Dr. Jing Wang (517) , Lansing Community College, Michigan, USA
 Explore 3D Figures Dr. Jing Wang (517)2675965, wangj@lcc.edu Lansing Community College, Michigan, USA Part I. 3D Modeling In this part, we create 3D models using Mathematica for various solids in 3D space,
Explore 3D Figures Dr. Jing Wang (517)2675965, wangj@lcc.edu Lansing Community College, Michigan, USA Part I. 3D Modeling In this part, we create 3D models using Mathematica for various solids in 3D space,
MATH 162 Calculus II Computer Laboratory Topic: Introduction to Mathematica & Parametrizations
 MATH 162 Calculus II Computer Laboratory Topic: Introduction to Mathematica & Goals of the lab: To learn some basic operations in Mathematica, such as how to define a function, and how to produce various
MATH 162 Calculus II Computer Laboratory Topic: Introduction to Mathematica & Goals of the lab: To learn some basic operations in Mathematica, such as how to define a function, and how to produce various
Defining and Plotting a Parametric Curve in 3D a(t)=(x(t),y(t),z(t)) H* clears all previous assingments so we can reuse them *L
 Defining and Plotting a Parametric Curve in 3D a(t)=(x(t),y(t),z(t)) Clear@"Global`*"D H* clears all previous assingments so we can reuse them *L H* Define vector functions in 3D of one variable t, i.e.
Defining and Plotting a Parametric Curve in 3D a(t)=(x(t),y(t),z(t)) Clear@"Global`*"D H* clears all previous assingments so we can reuse them *L H* Define vector functions in 3D of one variable t, i.e.
Plots & Animations. Simple 2d plots x
 Plots & Animations Simple 2d plots Physical processes and corresponding mathematical formulas can be visualized by plots. The simplest plot of a single function f[x] can be created as follows f@x_d :=
Plots & Animations Simple 2d plots Physical processes and corresponding mathematical formulas can be visualized by plots. The simplest plot of a single function f[x] can be created as follows f@x_d :=
Visualization of Complex Functions
 complexvis.nb Visualization of Complex Functions Bernd Thaller, University of Graz, Austria Source: This article appeared first in The Mathematica Journal 7(), 63-8 (998), The package ComplexPlot.m described
complexvis.nb Visualization of Complex Functions Bernd Thaller, University of Graz, Austria Source: This article appeared first in The Mathematica Journal 7(), 63-8 (998), The package ComplexPlot.m described
Mathematica Notebook for Background: Physics and Math of Shading
 Mathematica Notebook for Background: Physics and Math of Shading In[1]:= This notebook contains some computations referenced in the course notes. Off NIntegrate::inumr SetOptions Plot, PlotRange All ;
Mathematica Notebook for Background: Physics and Math of Shading In[1]:= This notebook contains some computations referenced in the course notes. Off NIntegrate::inumr SetOptions Plot, PlotRange All ;
Parametric Curves, Polar Plots and 2D Graphics
 Parametric Curves, Polar Plots and 2D Graphics Fall 2016 In[213]:= Clear "Global`*" 2 2450notes2_fall2016.nb Parametric Equations In chapter 9, we introduced parametric equations so that we could easily
Parametric Curves, Polar Plots and 2D Graphics Fall 2016 In[213]:= Clear "Global`*" 2 2450notes2_fall2016.nb Parametric Equations In chapter 9, we introduced parametric equations so that we could easily
Fine Arts and Solow Model: A Clarification
 San Jose State University From the SelectedWorks of Yeung-Nan Shieh 2008 Fine Arts and Solow Model: A Clarification Yeung-Nan Shieh, San Jose State University Jason Kao Available at: https://works.bepress.com/yeung-nan_shieh/9/
San Jose State University From the SelectedWorks of Yeung-Nan Shieh 2008 Fine Arts and Solow Model: A Clarification Yeung-Nan Shieh, San Jose State University Jason Kao Available at: https://works.bepress.com/yeung-nan_shieh/9/
Mathematica - a First Glance
 Mathematica - a First Glance Peter Fischer, ZITI Tools - Introduction to Mathematica P. Fischer, ZITI, Uni Heidelberg 1 What is Mathematica? Initially: algebraic manipulation of formulae Integration Differentiation
Mathematica - a First Glance Peter Fischer, ZITI Tools - Introduction to Mathematica P. Fischer, ZITI, Uni Heidelberg 1 What is Mathematica? Initially: algebraic manipulation of formulae Integration Differentiation
4. Dynamic Interactivity
 4. Dynamic Interactivity Mathematica has several dynamic elements. It is very useful for visualization of the results if the problem contains some parameters and one wants to study it under the change
4. Dynamic Interactivity Mathematica has several dynamic elements. It is very useful for visualization of the results if the problem contains some parameters and one wants to study it under the change
Complex functions, Laurent Series & residues using Mathematica
 Complex functions, Laurent Series & residues using Mathematica Complex functions Real and Imaginary parts of functions can be obtained using ComplexExpand, which treats all variables (here x and y) as
Complex functions, Laurent Series & residues using Mathematica Complex functions Real and Imaginary parts of functions can be obtained using ComplexExpand, which treats all variables (here x and y) as
Computed Tomography simulation using Radon Transform (incremental angles version)
 1 Computed Tomography simulation using Radon Transform (incremental angles version) Initialization Code (optional) Manipulate ManipulateB Row@ H* reset event ynamic@refresh@ If@Not@event "reset", If@originalImage
1 Computed Tomography simulation using Radon Transform (incremental angles version) Initialization Code (optional) Manipulate ManipulateB Row@ H* reset event ynamic@refresh@ If@Not@event "reset", If@originalImage
1 The Inverse Problem
 The Inverse Problem We have learned that a general solution of a first-order differential equation y = f H, yl (..) is a one-parameter family of (either eplicit or implicit) solutions. Finding a general
The Inverse Problem We have learned that a general solution of a first-order differential equation y = f H, yl (..) is a one-parameter family of (either eplicit or implicit) solutions. Finding a general
Lecture 07. (with solutions) Summer 2001 Victor Adamchik. 2 as an infinite product of nested square roots. M #'((((((((((((((((((((((((((((( 2 ] # N
![Lecture 07. (with solutions) Summer 2001 Victor Adamchik. 2 as an infinite product of nested square roots. M #'((((((((((((((((((((((((((((( 2 ] # N Lecture 07. (with solutions) Summer 2001 Victor Adamchik. 2 as an infinite product of nested square roots. M #'((((((((((((((((((((((((((((( 2 ] # N](/thumbs/87/95112751.jpg) Lecture 07 (with solutions) Summer 00 Victor Adamchik Off#General::spell'; Off#General::spell'; $Line 0; Exercise Vieta's formula, developed in 593, expresses cccc as an infinite product of nested square
Lecture 07 (with solutions) Summer 00 Victor Adamchik Off#General::spell'; Off#General::spell'; $Line 0; Exercise Vieta's formula, developed in 593, expresses cccc as an infinite product of nested square
Examples of Conformal Maps and of Critical Points
 Examples of Conformal Maps and of Critical Points We know that an analytic function f(z) is conformal (preserves angles and orientation) at all points where the derivative f (z) is not zero. Here we look
Examples of Conformal Maps and of Critical Points We know that an analytic function f(z) is conformal (preserves angles and orientation) at all points where the derivative f (z) is not zero. Here we look
Triple Integrals: Setting up the Integral
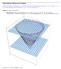 Triple Integrals: Setting up the Integral. Set up the integral of a function f x, y, z over the region above the upper nappe of the cone z x y from z to z. Use the following orders of integration: d x
Triple Integrals: Setting up the Integral. Set up the integral of a function f x, y, z over the region above the upper nappe of the cone z x y from z to z. Use the following orders of integration: d x
Mathematical Experiments with Mathematica
 Mathematical Experiments with Mathematica Instructor: Valentina Kiritchenko Classes: F 12:00-1:20 pm E-mail : vkiritchenko@yahoo.ca, vkiritch@hse.ru Office hours : Th 5:00-6:20 pm, F 3:30-5:00 pm 1. Syllabus
Mathematical Experiments with Mathematica Instructor: Valentina Kiritchenko Classes: F 12:00-1:20 pm E-mail : vkiritchenko@yahoo.ca, vkiritch@hse.ru Office hours : Th 5:00-6:20 pm, F 3:30-5:00 pm 1. Syllabus
Quickstart: Mathematica for Calculus I (Version 9.0) C. G. Melles Mathematics Department United States Naval Academy September 2, 2013
 Quickstart: Mathematica for Calculus I (Version 9.0) C. G. Melles Mathematics Department United States Naval Academy September, 0 Contents. Getting Started. Basic plotting. Solving equations, approximating
Quickstart: Mathematica for Calculus I (Version 9.0) C. G. Melles Mathematics Department United States Naval Academy September, 0 Contents. Getting Started. Basic plotting. Solving equations, approximating
print the expri with no spaces inbetween, but with a newline at the end. The output of Print[] is not a string
![print the expri with no spaces inbetween, but with a newline at the end. The output of Print[] is not a string print the expri with no spaces inbetween, but with a newline at the end. The output of Print[] is not a string](/thumbs/95/123651960.jpg) 15. Output and Input 2016-06-13 $Version 10.0 for Mac OS X x86 (64- bit) (December 4, 2014) Clear[a, b, c, x] 15.1 Printing Data and Expressions Print[expr1,expr2,...] print the expri with no spaces inbetween,
15. Output and Input 2016-06-13 $Version 10.0 for Mac OS X x86 (64- bit) (December 4, 2014) Clear[a, b, c, x] 15.1 Printing Data and Expressions Print[expr1,expr2,...] print the expri with no spaces inbetween,
Computation of slant specified by cues
 Computation of slant specified by cues Slant from perspective convergence, part 1: Construction of the projection (x1, y1) on the screen (blue) of point (x0, y0) of the rectangle (red) that is slanted
Computation of slant specified by cues Slant from perspective convergence, part 1: Construction of the projection (x1, y1) on the screen (blue) of point (x0, y0) of the rectangle (red) that is slanted
Some Examples to Show That Objects Be Presented by Mathematical Equations
 American Journal of Computational Mathematics, 01,, 199-06 http://dx.doi.org/10.436/ajcm.01.305 Published Online September 01 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajcm) Some Examples to Show That Objects Be Presented
American Journal of Computational Mathematics, 01,, 199-06 http://dx.doi.org/10.436/ajcm.01.305 Published Online September 01 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajcm) Some Examples to Show That Objects Be Presented
Procedural vs functional programming
 2 procvsfuncprog2.nb Procedural vs functional programming Basic examples with Mathematica Hugo Touchette School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary, University of London Programming Seminar ate: 27 October
2 procvsfuncprog2.nb Procedural vs functional programming Basic examples with Mathematica Hugo Touchette School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary, University of London Programming Seminar ate: 27 October
Billiard Paths on Arbitrary Tables
 Billiard Paths on Arbitrary Tables Note: The first time you evaluate a cell in this notebook you will get a popup asking you if you want to evaluate all initialization cells in the notebook - say Yes to
Billiard Paths on Arbitrary Tables Note: The first time you evaluate a cell in this notebook you will get a popup asking you if you want to evaluate all initialization cells in the notebook - say Yes to
Shelf Life Determination by Two Criteria from Digitized Temperature Data.nb
 Shelf Life Determination by Two Criteria from Digitized Temperature Data.nb Programmed by: Mark D. Normand Last modified: June 29, 2015 Developed as part of a project on vitamin loss kinetics in space
Shelf Life Determination by Two Criteria from Digitized Temperature Data.nb Programmed by: Mark D. Normand Last modified: June 29, 2015 Developed as part of a project on vitamin loss kinetics in space
NUMBERS VECTORS. (essentially) infinite precision is available
 NUMBERS In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= In[3]:= Out[3]= N@Exp@D, D.790330773977770937000 N@Log@D, D 0.937099309737070330 N@Pi, D 3.93979333337997939937 (essentially) infinite precision is available In[]:=
NUMBERS In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= In[3]:= Out[3]= N@Exp@D, D.790330773977770937000 N@Log@D, D 0.937099309737070330 N@Pi, D 3.93979333337997939937 (essentially) infinite precision is available In[]:=
Copyright 1996,1997, All rights reserved, Izumi Ohzawa,
 CXmodelWhyBB-BD.ma 1 This Mathematica Notebook contains computations and derivations used to create plots in Figs. 8, 9 and 10 of our paper Ohzawa, DeAngelis, Freeman, Encoding of Binocular Disparity by
CXmodelWhyBB-BD.ma 1 This Mathematica Notebook contains computations and derivations used to create plots in Figs. 8, 9 and 10 of our paper Ohzawa, DeAngelis, Freeman, Encoding of Binocular Disparity by
A practical guide for using Mathematica in problem sets. 2. Prerequisites: variables, functions, rule replacements, prefixes/suffixes, and lists
 How to Mathematica A practical guide for using Mathematica in problem sets Ben Bartlett - Ruddock 17 2017 Ruddock Upperclassman Workshop: 24 April, 9pm Contents: 0. Wolfram documentation 1. Formatting
How to Mathematica A practical guide for using Mathematica in problem sets Ben Bartlett - Ruddock 17 2017 Ruddock Upperclassman Workshop: 24 April, 9pm Contents: 0. Wolfram documentation 1. Formatting
Linear Cournot Duopoly
 Linear Cournot Duopoly Definition p = a - b q + q2 ; Q = q + q2; π = p - c q; π2 = p - c2 q2; CS = 2 b q + q2 ^2; PS = π + π2; SW = CS + PS; Calculating Equilibrium FOCs are D[π, q]; FOCDuoq = % D[π2,
Linear Cournot Duopoly Definition p = a - b q + q2 ; Q = q + q2; π = p - c q; π2 = p - c2 q2; CS = 2 b q + q2 ^2; PS = π + π2; SW = CS + PS; Calculating Equilibrium FOCs are D[π, q]; FOCDuoq = % D[π2,
ncells 6-param double logistic.nb
 ncells 6-param double logistic.nb This Mathematica 7 notebook presents, generates data from and retrieves the parameters of a 6- parameter continuous deterministic model of microbial growth and mortality,
ncells 6-param double logistic.nb This Mathematica 7 notebook presents, generates data from and retrieves the parameters of a 6- parameter continuous deterministic model of microbial growth and mortality,
Mathematica for Dirac delta functions and Green functions
 Mathematica for Dirac delta functions and Green functions DiracDelta function Mathematic has Dirac s delta function built in for use in integrals and solving differential equations. If you evaluate it
Mathematica for Dirac delta functions and Green functions DiracDelta function Mathematic has Dirac s delta function built in for use in integrals and solving differential equations. If you evaluate it
Fine Arts in Solow Model. Abstract
 Fine Arts in Solow Model Tetsuya Saito Department of Economics, SUNY at Buffalo Abstract Applying some built-in functions of Mathematica, this note provides some graphics derived from convergent paths
Fine Arts in Solow Model Tetsuya Saito Department of Economics, SUNY at Buffalo Abstract Applying some built-in functions of Mathematica, this note provides some graphics derived from convergent paths
Constructing Curves and Surfaces through Specified Points
 Constructing Curves and Surfaces through Specified Points Project Template Chapter 10 of Anton/Rorres, Elementary Linear Algebra, 10th edition, consists of 20 sections of Applications, the first of which
Constructing Curves and Surfaces through Specified Points Project Template Chapter 10 of Anton/Rorres, Elementary Linear Algebra, 10th edition, consists of 20 sections of Applications, the first of which
Assignment #4 Curvature-based interest operators, more spatial frequency filtering, and illusions
 Computational Vision U. Minn. Psy 5036 Assignment #4 Curvature-based interest operators, more spatial frequency filtering, and illusions Goals: 1) use symbolic processing to calculate a Hessian interest
Computational Vision U. Minn. Psy 5036 Assignment #4 Curvature-based interest operators, more spatial frequency filtering, and illusions Goals: 1) use symbolic processing to calculate a Hessian interest
Mathematica Notebook for the SIGGRAPH 2013 talk Background: Physics and Math of Shading
 Mathematica Notebook for the SIGGRAPH 03 talk Background: Physics and Math of Shading This notebook contains some computations referenced in the course notes. Off@NIntegrate::inumrD SetOptions@Plot, PlotRange
Mathematica Notebook for the SIGGRAPH 03 talk Background: Physics and Math of Shading This notebook contains some computations referenced in the course notes. Off@NIntegrate::inumrD SetOptions@Plot, PlotRange
Shape - preserving functions
 Shape - preserving functions Introduction This Mathematica notebook is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution - ShareAlike 3.0 License It creates the demonstrations used in my post Maps. Graphs
Shape - preserving functions Introduction This Mathematica notebook is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution - ShareAlike 3.0 License It creates the demonstrations used in my post Maps. Graphs
Introduction to Neural Networks U. Minn. Psy Kalman filter. Review Discriminant functions (Lecture 11) Initialize
 Introduction to Neural Networks U. Minn. Psy 5038 Kalman filter Initialize Read in Statistical Add-in packages: In[1]:= Off@General::spell1D; Needs@"ErrorBarPlots`"D; Needs@"MultivariateStatistics`"D;
Introduction to Neural Networks U. Minn. Psy 5038 Kalman filter Initialize Read in Statistical Add-in packages: In[1]:= Off@General::spell1D; Needs@"ErrorBarPlots`"D; Needs@"MultivariateStatistics`"D;
HW 2, CEE 744, Structural dynamics, Spring 2013
 HW 2 C 744 Structural dynamics Spring 2013 Nasser M. Abbasi February 17 2013 ifferent shape functions were used for estimating the wind tower natural frequency using the method of generalized single degree
HW 2 C 744 Structural dynamics Spring 2013 Nasser M. Abbasi February 17 2013 ifferent shape functions were used for estimating the wind tower natural frequency using the method of generalized single degree
Mathematics Computer Laboratory - Math Version 11 Lab 6 - Trigonometric Functions c
 Mathematics Computer Laboratory - Math 100 - Version 11 Lab 6 - Trigonometric Functions c Due You should only turn in exercises in this lab with its title and your name in Title and Subtitle font, respectively.
Mathematics Computer Laboratory - Math 100 - Version 11 Lab 6 - Trigonometric Functions c Due You should only turn in exercises in this lab with its title and your name in Title and Subtitle font, respectively.
Travelling fronts in stochastic Stokes' drifts H1 ê 3L Adrien Blanchet, Jean Dolbeault, and Michal Kowalczyk
 85-.nb Travelling fronts in stochastic Stokes' drifts H ê 3L Adrien Blanchet, Jean Dolbeault, and Michal Kowalczyk Off@NIntegrate::"slwcon"D Off@General::"spell"D Off@NIntegrate::"ncvb"D Off@NIntegrate::"ploss"D
85-.nb Travelling fronts in stochastic Stokes' drifts H ê 3L Adrien Blanchet, Jean Dolbeault, and Michal Kowalczyk Off@NIntegrate::"slwcon"D Off@General::"spell"D Off@NIntegrate::"ncvb"D Off@NIntegrate::"ploss"D
Curves Dr Richard Kenderdine
 Curves Dr Richard Kenderdine Kenderdine Maths Tutoring 1 December 01 This note shows some interesting curves not usually encountered. Most of the examples exist as families that can be altered by changing
Curves Dr Richard Kenderdine Kenderdine Maths Tutoring 1 December 01 This note shows some interesting curves not usually encountered. Most of the examples exist as families that can be altered by changing
MATHEMATICA LAB SKILLS ACTIVITY 2: ANALYZING DATA IN MATHEMATICA
 MATHEMATICA LAB SKILLS ACTIVITY 2: ANALYZING DATA IN MATHEMATICA LEARNING GOALS You will be 1. able to define and use functions in Mathematica. 2. able to scale and shift lists (arrays) of data. 3. able
MATHEMATICA LAB SKILLS ACTIVITY 2: ANALYZING DATA IN MATHEMATICA LEARNING GOALS You will be 1. able to define and use functions in Mathematica. 2. able to scale and shift lists (arrays) of data. 3. able
Computational Vision U. Minn. Psy 5036 Daniel Kersten Lecture 17: Shape from shading, the Bas-relief ambiguity
 Computational Vision U. Minn. Psy 5036 Daniel Kersten Lecture 17: Shape from shading, the Bas-relief ambiguity Initialize In[68]:= Off@General::spell1D; SetOptions@ArrayPlot, ColorFunction Ø "GrayTones",
Computational Vision U. Minn. Psy 5036 Daniel Kersten Lecture 17: Shape from shading, the Bas-relief ambiguity Initialize In[68]:= Off@General::spell1D; SetOptions@ArrayPlot, ColorFunction Ø "GrayTones",
Formal ambiguities seen by analyzing the generative model, the bas-relief transform. Learning scene parameters from images
 Computational Vision U. Minn. Psy 536 Daniel Kersten Lecture 7: Shape from shading cont'd http://vision.psych.umn.edu/www/kersten-lab/courses/psy536/syllabusf2.html) Initialize Outline Last time Inference
Computational Vision U. Minn. Psy 536 Daniel Kersten Lecture 7: Shape from shading cont'd http://vision.psych.umn.edu/www/kersten-lab/courses/psy536/syllabusf2.html) Initialize Outline Last time Inference
HANDS-ON START TO WOLFRAM MATHEMATICA. and Programming with the Wolfram Language. Cliff Hastings Kelvin Mischo Michael Morrison.
 HANDS-ON START TO WOLFRAM MATHEMATICA and Programming with the Wolfram Language Cliff Hastings Kelvin Mischo Michael Morrison Champaign 11 11 1 111THE COMPLETE OVERVIEW 1 Chapter 1 The Very Basics 3 Chapter
HANDS-ON START TO WOLFRAM MATHEMATICA and Programming with the Wolfram Language Cliff Hastings Kelvin Mischo Michael Morrison Champaign 11 11 1 111THE COMPLETE OVERVIEW 1 Chapter 1 The Very Basics 3 Chapter
H*by Nasser M. Abbasi, *L
 In[27]:= Manipulate@ H*by Nasser M. Abbasi 6 2 14*L tick; Module@mass = dx * dz * dy eq1 eq2 eq3 r angle t to Ix Iy Iz thetax thetay thetaz sol g debug = False lengthofw Ix = getix@mass dx dz dy; Iy =
In[27]:= Manipulate@ H*by Nasser M. Abbasi 6 2 14*L tick; Module@mass = dx * dz * dy eq1 eq2 eq3 r angle t to Ix Iy Iz thetax thetay thetaz sol g debug = False lengthofw Ix = getix@mass dx dz dy; Iy =
Dither Removal. Bart M. ter Haar Romeny. Image Dithering. This article has not been updated for Mathematica 8.
 This article has not been updated for Mathematica 8. The Mathematica Journal Dither Removal Bart M. ter Haar Romeny Mathematica is ideal for explaining the design of seemingly complex mathematical methods.
This article has not been updated for Mathematica 8. The Mathematica Journal Dither Removal Bart M. ter Haar Romeny Mathematica is ideal for explaining the design of seemingly complex mathematical methods.
Interfacing to Zemax OpticStudio from Mathematica
 Interfacing to Zemax OpticStudio from Mathematica Beginning with the release of OpticStudio 15, OpticStudio supports an new extension programming capability, ZOS-API, that allows external applications
Interfacing to Zemax OpticStudio from Mathematica Beginning with the release of OpticStudio 15, OpticStudio supports an new extension programming capability, ZOS-API, that allows external applications
Zajecia 1. Krotkie wprowadzenie do srodowiska Mathematica 4^ D D 1. ?
 Zajecia Krotkie wprowadzenie do srodowiska Mathematica In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= In[7]:= Out[7]= In[8]:= Out[8]= In[9]:= Out[9]= + ^ Sqrt@D Log@0, 00D Sin@Pi D In[0]:=! Out[0]= In[]:= Out[]=
Zajecia Krotkie wprowadzenie do srodowiska Mathematica In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= In[]:= Out[]= In[7]:= Out[7]= In[8]:= Out[8]= In[9]:= Out[9]= + ^ Sqrt@D Log@0, 00D Sin@Pi D In[0]:=! Out[0]= In[]:= Out[]=
Analytical-Equations to Generate the Free Electron Current Vector Field and the Angular-Momentum-Density Function
 Append IV 799.nb Analtcal-quatons to Generate the Free lectron Current Vector Feld and the Angular-omentum-enst Functon Y Hf, ql 9 Blaclght Power Inc Updated 7-9-9 Please consult the Grand Unfed Theor
Append IV 799.nb Analtcal-quatons to Generate the Free lectron Current Vector Feld and the Angular-omentum-enst Functon Y Hf, ql 9 Blaclght Power Inc Updated 7-9-9 Please consult the Grand Unfed Theor
ü 1.1 Getting Started
 Chapter 1 Introduction Welcome to Mathematica! This tutorial manual is intended as a supplement to Rogawski's Calculus textbook and aimed at students looking to quickly learn Mathematica through examples.
Chapter 1 Introduction Welcome to Mathematica! This tutorial manual is intended as a supplement to Rogawski's Calculus textbook and aimed at students looking to quickly learn Mathematica through examples.
UNIVERSITY of CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
 UNIVERSITY of CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ INVESTIGATIONS OF THE CHAOTIC WATER WHEEL A thesis submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of BACHELOR OF SCIENCE in PHYSICS by Davidson
UNIVERSITY of CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ INVESTIGATIONS OF THE CHAOTIC WATER WHEEL A thesis submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of BACHELOR OF SCIENCE in PHYSICS by Davidson

 Overview of Basic Graphics Commands In[]:=
Overview of Basic Graphics Commands In[]:=