(ii) Explain how the trapezium rule could be used to obtain a more accurate estimate of the area. [1]
|
|
|
- Osborn Holland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C Integration. June 00 qu. Use the trapezium rule, with strips each of width, to estimate the area of the region bounded by the curve y = 7 +, the -ais, and the lines = and = 0. Give your answer correct to significant figures. [4] Eplain how the trapezium rule could be used to obtain a more accurate estimate of the area. []. June 00 qu.6 (a) Use integration to find the eact area of the region enclosed by the curve y = + 4, the -ais and the lines = and = 5. [4] (b) Find ( 6 y ) dy. [] (c) Evaluate 8 d. [4]. Jan 00 qu. The gradient of a curve is given by points (, 5) and (p, 5). dy d = 6 4. The curve passes through the distinct Find the equation of the curve. [4] Find the value of p. [] 4. Jan 00 qu.4 Use the trapezium rule, with 4 strips each of width 0.5, to find an approimate value for 5 log 0 ( + )d, giving your answer correct to significant figures. [4] 5 Use your answer to part to deduce an approimate value for log0 + d, showing your method clearly. [] 5. Jan 00 qu.5 The diagram shows parts of the curves y = + and 9 y =, which intersect at (, ) and (, 0). Use integration to find the eact area of the shaded region enclosed between the two curves. [7]
2 6. June 009 qu.4 Find the binomial epansion of ( 5), simplifying the terms. [4] Hence find ( 5) d. [4] 7. June 009 qu.6 dy The gradient of a curve is given by d = + a, where a is a constant. The curve passes through the points (, ) and (, 7). Find the equation of the curve. [8] 8. June 009 qu.9 Sketch the graph of y = 4k, where k is a constant such that k >. State the coordinates of any points of intersection with the aes. [] The point P on the curve y = 4k has its y-coordinate equal to 0k. Show that the -coordinate of P may be written as + log k 5. [4] (iii) (a) Use the trapezium rule, with two strips each of width, to find an epression for 9. Jan 009 qu. the approimate value of 4 d. [] (b) Given that this approimate value is equal to 6, find the value of k. [] Find ( + 8 5)d, [] d. [] 0. Jan 009 qu.4 0 k The diagram shows the curve y = 4 + and the line y = 9 which intersect at (, 9) and (, 9). Use integration to find the eact area of the shaded region enclosed by the curve and the line. [7]
3 . June 008 qu.5 The diagram shows the curve y = + +. The shaded region is bounded by the curve, the y-ais, and two lines parallel to the -ais which meet the curve where = and = 4. Show that the area of the shaded region is given by y 6y + 7 dy [] Hence find the eact area of the shaded region. [4]. June 008 qu.7 (a) Find + 5 d. [4] (b) Find 8 4 d. []. June 008 qu.9 ( ) ( ). 4 Hence evaluate 8 d. [] 7 5 (b) Use the trapezium rule, with four strips each of width 0.5, to find an approimate value for cos d, where is in radians. Give your answer correct to significant figures. [4] 0 4. Jan 008 qu. 7 Use the trapezium rule, with strips each of width, to estimate the value of + d. 4] 5. Jan 008 qu.5 dy The gradient of a curve is given by = d. The curve passes through the point (4, 50). Find the equation of the curve. [6]
4 6. Jan 008 qu.7 The diagram shows part of the curve y = and the line = 5. 5 ( ) Eplain why d does not give the total area of the regions shaded in the 0 diagram. [] Use integration to find the eact total area of the shaded regions. [7] 7. June 007 qu.4 The diagram shows the curve y = 4 +. Use the trapezium rule, with strips of width 0.5, to find an approimate value for the area of the region bounded by the curve y = 4 +, the -ais, and the lines = and =.Give your answer correct to significant figures. [4] State with a reason whether this approimation is an under-estimate or an over-estimate. [] 8. June 007 qu.6 (a) Find ( 4) d. [] 6 Hence evaluate ( 4) d. [] 6 (b) Find d. []
5 9. Jan 007 qu. ( ) Find 4 5 d [] dy The gradient of a curve is given by = 4 5. The curve passes through the point d (, 7). Find the equation of the curve. [] 0. Jan 007 qu.5 (b) Use the trapezium rule, with two strips of width, to find an approimate value for 9 log 0 d giving your answer correct to significant figures. [4]. Jan 007 qu.0 The diagram shows the graph of y =. Verify that the curve intersects the -ais at (9, 0). [] The shaded region is enclosed by the curve, the -ais and the line = a (where a > 9).Given that the area of the shaded region is 4 square units, find the value of a. [9]. June 006 qu. The gradient of a curve is given by d y =, and the curve passes through the point (4, 5). d Find the equation of the curve. [6]
6 . June 006 qu.4 The diagram shows the curve y = 4 and the line y = +. Find the -coordinates of the points of intersection of the curve and the line. [] Use integration to find the area of the shaded region bounded by the line and the curve. [6] 4. June 006 qu.9 Sketch the curve y =, and state the coordinates of any point where the curve crosses an ais. [] Use the trapezium rule, with 4 strips of width 0.5, to estimate the area of the region bounded by the curve y =, the aes, and the line =. [4] (iii) The point P on the curve y = has y-coordinate equal to. 6 log0 Prove that the -coordinate of P may be written as +. [4] log 5. Jan 006 qu.6 0 (a) Find ( + 4) d. [4] a (b) Find the value, in terms of a, of 4 d, where a is a constant greater than. [] d Deduce the value of 4. []
7 6. Jan 006 qu.8 The cubic polynomial + k + 6 is denoted by f(). It is given that ( + ) is a factor of f(). Show that k = 5, and factorise f() completely. [6] Find f ( ) d. [4] (iii) Eplain with the aid of a sketch why the answer to part does not give the area of the region between the curve y = f() and the -ais for. [] 7. June 005 qu. Find ( + )( + ) d [4] 9 Evaluate d 0 []
(ii) Use Simpson s rule with two strips to find an approximation to Use your answers to parts (i) and (ii) to show that ln 2.
 C umerical Methods. June 00 qu. 6 (i) Show by calculation that the equation tan = 0, where is measured in radians, has a root between.0 and.. [] Use the iteration formula n+ = tan + n with a suitable starting
C umerical Methods. June 00 qu. 6 (i) Show by calculation that the equation tan = 0, where is measured in radians, has a root between.0 and.. [] Use the iteration formula n+ = tan + n with a suitable starting
C3 Integration 1. June 2010 qu. 4
 C Integration. June qu. 4 k The diagram shows part of the curve y =, where k is a positive constant. The points A and B on the curve have -coordinates and 6 respectively. Lines through A and B parallel
C Integration. June qu. 4 k The diagram shows part of the curve y =, where k is a positive constant. The points A and B on the curve have -coordinates and 6 respectively. Lines through A and B parallel
IB SL REVIEW and PRACTICE
 IB SL REVIEW and PRACTICE Topic: CALCULUS Here are sample problems that deal with calculus. You ma use the formula sheet for all problems. Chapters 16 in our Tet can help ou review. NO CALCULATOR Problems
IB SL REVIEW and PRACTICE Topic: CALCULUS Here are sample problems that deal with calculus. You ma use the formula sheet for all problems. Chapters 16 in our Tet can help ou review. NO CALCULATOR Problems
( ) 2. Integration. 1. Calculate (a) x2 (x 5) dx (b) y = x 2 6x. 2. Calculate the shaded area in the diagram opposite.
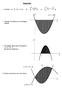 Integration 1. Calculate (a) ( 5) d (b) 4 + 3 1 d (c) ( ) + d 1 = 6. Calculate the shaded area in the diagram opposite. 3. The diagram shows part of the graph of = 7 10. 5 = + 0 4. Find the area between
Integration 1. Calculate (a) ( 5) d (b) 4 + 3 1 d (c) ( ) + d 1 = 6. Calculate the shaded area in the diagram opposite. 3. The diagram shows part of the graph of = 7 10. 5 = + 0 4. Find the area between
Worksheet A GRAPHS OF FUNCTIONS
 C GRAPHS F FUNCTINS Worksheet A Sketch and label each pair of graphs on the same set of aes showing the coordinates of any points where the graphs intersect. Write down the equations of any asymptotes.
C GRAPHS F FUNCTINS Worksheet A Sketch and label each pair of graphs on the same set of aes showing the coordinates of any points where the graphs intersect. Write down the equations of any asymptotes.
You will need to use a calculator for this worksheet A (1, 1)
 C Worksheet A y You will need to use a calculator for this worksheet y = B A (, ) O The diagram shows the curve y = which passes through the point A (, ) and the point B. a Copy and complete the table
C Worksheet A y You will need to use a calculator for this worksheet y = B A (, ) O The diagram shows the curve y = which passes through the point A (, ) and the point B. a Copy and complete the table
(i) Find the exact value of p. [4] Show that the area of the shaded region bounded by the curve, the x-axis and the line
![(i) Find the exact value of p. [4] Show that the area of the shaded region bounded by the curve, the x-axis and the line (i) Find the exact value of p. [4] Show that the area of the shaded region bounded by the curve, the x-axis and the line](/thumbs/90/103919535.jpg) H Math : Integration Apps 0. M p The diagram shows the curve e e and its maimum point M. The -coordinate of M is denoted b p. (i) Find the eact value of p. [] (ii) Show that the area of the shaded region
H Math : Integration Apps 0. M p The diagram shows the curve e e and its maimum point M. The -coordinate of M is denoted b p. (i) Find the eact value of p. [] (ii) Show that the area of the shaded region
Edexcel Core Mathematics 4 Integration
 Edecel Core Mathematics 4 Integration Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com Integration It might appear to be a bit obvious but you must remember all of your C work on differentiation if you are
Edecel Core Mathematics 4 Integration Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com Integration It might appear to be a bit obvious but you must remember all of your C work on differentiation if you are
Integration. Edexcel GCE. Core Mathematics C4
 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C Integration Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Advice to Candidates You must ensure that your answers
Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C Integration Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Advice to Candidates You must ensure that your answers
1. Use the Trapezium Rule with five ordinates to find an approximate value for the integral
 1. Use the Trapezium Rule with five ordinates to find an approximate value for the integral Show your working and give your answer correct to three decimal places. 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 When When When When When
1. Use the Trapezium Rule with five ordinates to find an approximate value for the integral Show your working and give your answer correct to three decimal places. 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 When When When When When
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 C Differentiation: Tangents & Normals. y A C R P O Q The diagram above shows part of the curve C with equation y = 6 + 8. The curve meets the y-ais at the point A and has a minimum at the point P. (a)
C Differentiation: Tangents & Normals. y A C R P O Q The diagram above shows part of the curve C with equation y = 6 + 8. The curve meets the y-ais at the point A and has a minimum at the point P. (a)
Core Mathematics 1 Graphs of Functions
 Regent College Maths Department Core Mathematics 1 Graphs of Functions Graphs of Functions September 2011 C1 Note Graphs of functions; sketching curves defined by simple equations. Here are some curves
Regent College Maths Department Core Mathematics 1 Graphs of Functions Graphs of Functions September 2011 C1 Note Graphs of functions; sketching curves defined by simple equations. Here are some curves
CURVE SKETCHING EXAM QUESTIONS
 CURVE SKETCHING EXAM QUESTIONS Question 1 (**) a) Express f ( x ) in the form ( ) 2 f x = x + 6x + 10, x R. f ( x) = ( x + a) 2 + b, where a and b are integers. b) Describe geometrically the transformations
CURVE SKETCHING EXAM QUESTIONS Question 1 (**) a) Express f ( x ) in the form ( ) 2 f x = x + 6x + 10, x R. f ( x) = ( x + a) 2 + b, where a and b are integers. b) Describe geometrically the transformations
The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations
 1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
Pegasys Publishing. CfE Higher Mathematics. Expressions and Functions Practice Assessment A
 Pegasys Publishing CfE Higher Mathematics Epressions and Functions Practice ssessment otes:. Read the question fully before answering it.. lways show your working.. Check your paper at the end if you have
Pegasys Publishing CfE Higher Mathematics Epressions and Functions Practice ssessment otes:. Read the question fully before answering it.. lways show your working.. Check your paper at the end if you have
UNIT 29 Using Graphs to Solve Equations: CSEC Revision Test
 UNIT 9 Using Graphs to Solve : UNIT 9 Using Graphs to Solve 1. Shell bus 3 litres of oil and 40 litres of gasoline for $30. The cost of one litre of oil is $ and the cost of one litre of gasoline is $.
UNIT 9 Using Graphs to Solve : UNIT 9 Using Graphs to Solve 1. Shell bus 3 litres of oil and 40 litres of gasoline for $30. The cost of one litre of oil is $ and the cost of one litre of gasoline is $.
Core Mathematics 3 Functions
 http://kumarmaths.weebly.com/ Core Mathematics 3 Functions Core Maths 3 Functions Page 1 Functions C3 The specifications suggest that you should be able to do the following: Understand the definition of
http://kumarmaths.weebly.com/ Core Mathematics 3 Functions Core Maths 3 Functions Page 1 Functions C3 The specifications suggest that you should be able to do the following: Understand the definition of
Section 9.3: Functions and their Graphs
 Section 9.: Functions and their Graphs Graphs provide a wa of displaing, interpreting, and analzing data in a visual format. In man problems, we will consider two variables. Therefore, we will need to
Section 9.: Functions and their Graphs Graphs provide a wa of displaing, interpreting, and analzing data in a visual format. In man problems, we will consider two variables. Therefore, we will need to
TANGENTS AND NORMALS
 Mathematics Revision Guides Tangents and Normals Page 1 of 8 MK HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C1 Edecel: C OCR: C1 OCR MEI: C TANGENTS AND NORMALS Version : 1 Date:
Mathematics Revision Guides Tangents and Normals Page 1 of 8 MK HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C1 Edecel: C OCR: C1 OCR MEI: C TANGENTS AND NORMALS Version : 1 Date:
2. Find the equation of the normal to the curve with equation y = x at the point (1, 2). (Total 4 marks)
 CHAPTER 3 REVIEW FOR SLs ONLY 1. Find the coordinates of the point on the graph of = 2 at which the tangent is parallel to the line = 5. (Total 4 marks) 2. Find the equation of the normal to the curve
CHAPTER 3 REVIEW FOR SLs ONLY 1. Find the coordinates of the point on the graph of = 2 at which the tangent is parallel to the line = 5. (Total 4 marks) 2. Find the equation of the normal to the curve
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1
 P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
Radical Functions Review
 Radical Functions Review Specific Outcome 3 Graph and analyze radical functions (limited to functions involving one radical) Acceptable Standard sketch and analyze (domain, range, invariant points, - and
Radical Functions Review Specific Outcome 3 Graph and analyze radical functions (limited to functions involving one radical) Acceptable Standard sketch and analyze (domain, range, invariant points, - and
Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Paper Reference(s) 666/0 Edecel GCE Core Mathematics C Bronze Level B Time: hour 0 minutes Materials required for eamination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Candidates
Paper Reference(s) 666/0 Edecel GCE Core Mathematics C Bronze Level B Time: hour 0 minutes Materials required for eamination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Candidates
Session 3. Rational and Radical Equations. Math 30-1 R 3. (Revisit, Review and Revive)
 Session 3 Rational and Radical Equations Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) Rational Functions Review Specific Outcome 14 Graph and analyze rational functions (limited to numerators and denominators
Session 3 Rational and Radical Equations Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) Rational Functions Review Specific Outcome 14 Graph and analyze rational functions (limited to numerators and denominators
x 16 d( x) 16 n( x) 36 d( x) zeros: x 2 36 = 0 x 2 = 36 x = ±6 Section Yes. Since 1 is a polynomial (of degree 0), P(x) =
 9 CHAPTER POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS Section -. Yes. Since is a polynomial (of degree 0), P() P( ) is a rational function if P() is a polynomial.. A vertical asymptote is a vertical line a that
9 CHAPTER POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS Section -. Yes. Since is a polynomial (of degree 0), P() P( ) is a rational function if P() is a polynomial.. A vertical asymptote is a vertical line a that
Area and Volume. where x right and x left are written in terms of y.
 Area and Volume Area between two curves Sketch the region and determine the points of intersection. Draw a small strip either as dx or dy slicing. Use the following templates to set up a definite integral:
Area and Volume Area between two curves Sketch the region and determine the points of intersection. Draw a small strip either as dx or dy slicing. Use the following templates to set up a definite integral:
Topic 6: Calculus Integration Volume of Revolution Paper 2
 Topic 6: Calculus Integration Standard Level 6.1 Volume of Revolution Paper 1. Let f(x) = x ln(4 x ), for < x
Topic 6: Calculus Integration Standard Level 6.1 Volume of Revolution Paper 1. Let f(x) = x ln(4 x ), for < x
Mathematics (JUN11MPC201) General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June Unit Pure Core TOTAL
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Pure Core 2 Wednesday 18 May 2011 General Certificate of Education Advanced
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Pure Core 2 Wednesday 18 May 2011 General Certificate of Education Advanced
Chapter 7 curve. 3. x=y-y 2, x=0, about the y axis. 6. y=x, y= x,about y=1
 Chapter 7 curve Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the region bounded by the given cures about the specified line. Sketch the region, the solid, and a typical disk or washer.. y-/, =, =;
Chapter 7 curve Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the region bounded by the given cures about the specified line. Sketch the region, the solid, and a typical disk or washer.. y-/, =, =;
SPM Add Math Form 5 Chapter 3 Integration
 SPM Add Math Form Chapter Integration INDEFINITE INTEGRAL CHAPTER : INTEGRATION Integration as the reverse process of differentiation ) y if dy = x. Given that d Integral of ax n x + c = x, where c is
SPM Add Math Form Chapter Integration INDEFINITE INTEGRAL CHAPTER : INTEGRATION Integration as the reverse process of differentiation ) y if dy = x. Given that d Integral of ax n x + c = x, where c is
Questions Q1. (a) Find the values of the constants A, B and C. (4) b) Hence find
 Questions Q1. (a) Find the values of the constants A, B and C. (4) b) Hence find (ii) Find, leaving your answer in the form a + ln b, where a and b are constants. (6) (Total 10 marks) Q2. (a) Find the
Questions Q1. (a) Find the values of the constants A, B and C. (4) b) Hence find (ii) Find, leaving your answer in the form a + ln b, where a and b are constants. (6) (Total 10 marks) Q2. (a) Find the
MEI Desmos Tasks for AS Pure
 Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x² 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Select the points of intersection of the line and the curve. What
Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x² 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Select the points of intersection of the line and the curve. What
C3 Numerical methods
 Verulam School C3 Numerical methods 138 min 108 marks 1. (a) The diagram shows the curve y =. The region R, shaded in the diagram, is bounded by the curve and by the lines x = 1, x = 5 and y = 0. The region
Verulam School C3 Numerical methods 138 min 108 marks 1. (a) The diagram shows the curve y =. The region R, shaded in the diagram, is bounded by the curve and by the lines x = 1, x = 5 and y = 0. The region
APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION
 6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION The volume of a sphere is the limit of sums of volumes of approimating clinders. In this chapter we eplore some of the applications of the definite integral b using it to
6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION The volume of a sphere is the limit of sums of volumes of approimating clinders. In this chapter we eplore some of the applications of the definite integral b using it to
Core Mathematics 1 Transformations of Graphs
 Regent College Maths Department Core Mathematics 1 Transformations of Graphs Transformations of Graphs September 2011 C1 Note Knowledge of the effect of simple transformations on the graph of y f( x)
Regent College Maths Department Core Mathematics 1 Transformations of Graphs Transformations of Graphs September 2011 C1 Note Knowledge of the effect of simple transformations on the graph of y f( x)
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 7.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date What s the Inverse of an Eponent? Logarithmic Functions as Inverses Vocabulary Write the term that best completes each statement. 1. The of a number
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date What s the Inverse of an Eponent? Logarithmic Functions as Inverses Vocabulary Write the term that best completes each statement. 1. The of a number
PAST QUESTIONS ON INTEGRATION PAPER 1
 PAST QUESTIONS ON INTEGRATION PAPER 1 1. Q9 Nov 2001 2. Q11 Nov 2001 3. The diagram shows the curve y = and the line y = x intersecting at O and P. Find the coordinates of P, [1] the area of the shaded
PAST QUESTIONS ON INTEGRATION PAPER 1 1. Q9 Nov 2001 2. Q11 Nov 2001 3. The diagram shows the curve y = and the line y = x intersecting at O and P. Find the coordinates of P, [1] the area of the shaded
Systems of Equations and Inequalities. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 5 Systems of Equations and Inequalities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 5.5 Systems of Inequalities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphing an Inequality Systems
5 Systems of Equations and Inequalities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 5.5 Systems of Inequalities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphing an Inequality Systems
GRAPHS AND GRAPHICAL SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS
 GRAPHS AND GRAPHICAL SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS 1.1 DIFFERENT TYPES AND SHAPES OF GRAPHS: A graph can be drawn to represent are equation connecting two variables. There are different tpes of equations which
GRAPHS AND GRAPHICAL SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS 1.1 DIFFERENT TYPES AND SHAPES OF GRAPHS: A graph can be drawn to represent are equation connecting two variables. There are different tpes of equations which
Lecture 11 (Application of Integration) Areas between Curves Let and be continuous and on. Let s look at the region between and on.
 Lecture 11 (Application of Integration) Areas between Curves Let and be continuous and on. Let s look at the region between and on. Definition: The area of the region bounded by the curves and, and the
Lecture 11 (Application of Integration) Areas between Curves Let and be continuous and on. Let s look at the region between and on. Definition: The area of the region bounded by the curves and, and the
UNIT #2 TRANSFORMATIONS OF FUNCTIONS
 Name: Date: UNIT # TRANSFORMATIONS OF FUNCTIONS Part I Questions. The quadratic unction ollowing does,, () has a turning point at have a turning point? 7, 3, 5 5, 8. I g 7 3, then at which o the The structure
Name: Date: UNIT # TRANSFORMATIONS OF FUNCTIONS Part I Questions. The quadratic unction ollowing does,, () has a turning point at have a turning point? 7, 3, 5 5, 8. I g 7 3, then at which o the The structure
Year 12. Core 1 and 2. Easter Revision Exam Questions
 Year 12 Core 1 and 2 Easter Revision 2014 Exam Questions The Redhill Academy 1 Session 1: Transforming Graphs 1. y (0, 7) y = f( x) O (7, 0) x The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve with equation
Year 12 Core 1 and 2 Easter Revision 2014 Exam Questions The Redhill Academy 1 Session 1: Transforming Graphs 1. y (0, 7) y = f( x) O (7, 0) x The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve with equation
Lesson 2.1 Exercises, pages 90 96
 Lesson.1 Eercises, pages 9 96 A. a) Complete the table of values. 1 1 1 1 1. 1 b) For each function in part a, sketch its graph then state its domain and range. For : the domain is ; and the range is.
Lesson.1 Eercises, pages 9 96 A. a) Complete the table of values. 1 1 1 1 1. 1 b) For each function in part a, sketch its graph then state its domain and range. For : the domain is ; and the range is.
WJEC LEVEL 2 CERTIFICATE 9550/01 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number WJEC LEVEL 2 CERTIFICATE 9550/01 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS A.M. MONDAY, 24 June 2013 2 1 hours 2 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A calculator will be required for
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number WJEC LEVEL 2 CERTIFICATE 9550/01 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS A.M. MONDAY, 24 June 2013 2 1 hours 2 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A calculator will be required for
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
 00-CE A MATH HONG KONG EXAMINATIONS AUTHORITY HONG KONG CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION EXAMINATION 00 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 8.0 am.00 am ½ hours This paper must be answered in English. Answer ALL questions
00-CE A MATH HONG KONG EXAMINATIONS AUTHORITY HONG KONG CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION EXAMINATION 00 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 8.0 am.00 am ½ hours This paper must be answered in English. Answer ALL questions
x=2 26. y 3x Use calculus to find the area of the triangle with the given vertices. y sin x cos 2x dx 31. y sx 2 x dx
 4 CHAPTER 6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 6. EXERCISES 4 Find the area of the shaded region.. =5-. (4, 4) =. 4. = - = (_, ) = -4 =œ + = + =.,. sin,. cos, sin,, 4. cos, cos, 5., 6., 7.,, 4, 8., 8, 4 4, =_
4 CHAPTER 6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 6. EXERCISES 4 Find the area of the shaded region.. =5-. (4, 4) =. 4. = - = (_, ) = -4 =œ + = + =.,. sin,. cos, sin,, 4. cos, cos, 5., 6., 7.,, 4, 8., 8, 4 4, =_
If ( ) is approximated by a left sum using three inscribed rectangles of equal width on the x-axis, then the approximation is
 More Integration Page 1 Directions: Solve the following problems using the available space for scratchwork. Indicate your answers on the front page. Do not spend too much time on any one problem. Note:
More Integration Page 1 Directions: Solve the following problems using the available space for scratchwork. Indicate your answers on the front page. Do not spend too much time on any one problem. Note:
Checkpoint: Assess Your Understanding, pages
 Checkpoint: Assess Your Understanding, pages 1 18.1 1. Multiple Choice Given the graph of the function f(), which graph below right represents = f()? f() D C A B Chapter : Radical and Rational Functions
Checkpoint: Assess Your Understanding, pages 1 18.1 1. Multiple Choice Given the graph of the function f(), which graph below right represents = f()? f() D C A B Chapter : Radical and Rational Functions
Graphing square root functions. What would be the base graph for the square root function? What is the table of values?
 Unit 3 (Chapter 2) Radical Functions (Square Root Functions Sketch graphs of radical functions b appling translations, stretches and reflections to the graph of Analze transformations to identif the of
Unit 3 (Chapter 2) Radical Functions (Square Root Functions Sketch graphs of radical functions b appling translations, stretches and reflections to the graph of Analze transformations to identif the of
STEP Support Programme. Assignment 13
 STEP Support Programme Assignment 13 Warm-up You probably already know that for a graph with gradient dy : if dy > 0 then the graph is increasing ; if dy < 0 then the graph is decreasing. The sign of the
STEP Support Programme Assignment 13 Warm-up You probably already know that for a graph with gradient dy : if dy > 0 then the graph is increasing ; if dy < 0 then the graph is decreasing. The sign of the
The base of a solid is the region in the first quadrant bounded above by the line y = 2, below by
 Chapter 7 1) (AB/BC, calculator) The base of a solid is the region in the first quadrant bounded above by the line y =, below by y sin 1 x, and to the right by the line x = 1. For this solid, each cross-section
Chapter 7 1) (AB/BC, calculator) The base of a solid is the region in the first quadrant bounded above by the line y =, below by y sin 1 x, and to the right by the line x = 1. For this solid, each cross-section
Functions Review Packet from November Questions. 1. The diagrams below show the graphs of two functions, y = f(x), and y = g(x). y y
 Functions Review Packet from November Questions. The diagrams below show the graphs of two functions, = f(), and = g()..5 = f( ) = g( ).5 6º 8º.5 8º 6º.5 State the domain and range of the function f; the
Functions Review Packet from November Questions. The diagrams below show the graphs of two functions, = f(), and = g()..5 = f( ) = g( ).5 6º 8º.5 8º 6º.5 State the domain and range of the function f; the
9.1 Exercises. Section 9.1 The Square Root Function 879. In Exercises 1-10, complete each of the following tasks.
 Section 9. The Square Root Function 879 9. Eercises In Eercises -, complete each of the following tasks. i. Set up a coordinate sstem on a sheet of graph paper. Label and scale each ais. ii. Complete the
Section 9. The Square Root Function 879 9. Eercises In Eercises -, complete each of the following tasks. i. Set up a coordinate sstem on a sheet of graph paper. Label and scale each ais. ii. Complete the
Rational functions and graphs. Section 2: Graphs of rational functions
 Rational functions and graphs Section : Graphs of rational functions Notes and Eamples These notes contain subsections on Graph sketching Turning points and restrictions on values Graph sketching You can
Rational functions and graphs Section : Graphs of rational functions Notes and Eamples These notes contain subsections on Graph sketching Turning points and restrictions on values Graph sketching You can
MEI GeoGebra Tasks for AS Pure
 Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x 2 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Use the Intersect tool to find the points of intersection of
Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x 2 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Use the Intersect tool to find the points of intersection of
with x 1 ¼ 1 to find the values of x 2 and x 3, giving your answers to three decimal places
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Pure Core 3 Friday 11 June 2010 General Certificate of Education Advanced
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Pure Core 3 Friday 11 June 2010 General Certificate of Education Advanced
y 4 y 1 y Click here for answers. Click here for solutions. VOLUMES
 SECTION 7. VOLUMES 7. VOLUMES A Click here for answers. S Click here for solutions. 5 Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the region bounded by the given curves about the specified line.
SECTION 7. VOLUMES 7. VOLUMES A Click here for answers. S Click here for solutions. 5 Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the region bounded by the given curves about the specified line.
Instructor: Virginia Davis Course: Foundations for College Math (1)
 5/19/01 Final Eam Review Ch 10,11-Virginia Davis Student: Date: Instructor: Virginia Davis Course: Foundations for College Math (1) Assignment: Final Eam Review Ch 10,11 1. Simplif b factoring. Assume
5/19/01 Final Eam Review Ch 10,11-Virginia Davis Student: Date: Instructor: Virginia Davis Course: Foundations for College Math (1) Assignment: Final Eam Review Ch 10,11 1. Simplif b factoring. Assume
Integrating ICT into mathematics at KS4&5
 Integrating ICT into mathematics at KS4&5 Tom Button tom.button@mei.org.uk www.mei.org.uk/ict/ This session will detail the was in which ICT can currentl be used in the teaching and learning of Mathematics
Integrating ICT into mathematics at KS4&5 Tom Button tom.button@mei.org.uk www.mei.org.uk/ict/ This session will detail the was in which ICT can currentl be used in the teaching and learning of Mathematics
MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS METHODS FOR ADVANCED MATHEMATICS, C3. Practice Paper C3-B
 MEI Mathematics in Education and Industry MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS METHODS FOR ADVANCED MATHEMATICS, C3 Practice Paper C3-B Additional materials: Answer booklet/paper Graph paper List of formulae (MF)
MEI Mathematics in Education and Industry MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS METHODS FOR ADVANCED MATHEMATICS, C3 Practice Paper C3-B Additional materials: Answer booklet/paper Graph paper List of formulae (MF)
Tuesday 22 January 2008 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Paper Reference(s) 6666/0 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C4 Advanced Level Tuesday 22 January 2008 Afternoon Time: hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included
Paper Reference(s) 6666/0 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C4 Advanced Level Tuesday 22 January 2008 Afternoon Time: hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included
In this chapter, we will investigate what have become the standard applications of the integral:
 Chapter 8 Overview: Applications of Integrals Calculus, like most mathematical fields, began with trying to solve everyday problems. The theory and operations were formalized later. As early as 70 BC,
Chapter 8 Overview: Applications of Integrals Calculus, like most mathematical fields, began with trying to solve everyday problems. The theory and operations were formalized later. As early as 70 BC,
Trig Functions, Equations & Identities May a. [2 marks] Let. For what values of x does Markscheme (M1)
![Trig Functions, Equations & Identities May a. [2 marks] Let. For what values of x does Markscheme (M1) Trig Functions, Equations & Identities May a. [2 marks] Let. For what values of x does Markscheme (M1)](/thumbs/82/86594449.jpg) Trig Functions, Equations & Identities May 2008-2014 1a. Let. For what values of x does () 1b. [5 marks] not exist? Simplify the expression. EITHER OR [5 marks] 2a. 1 In the triangle ABC,, AB = BC + 1.
Trig Functions, Equations & Identities May 2008-2014 1a. Let. For what values of x does () 1b. [5 marks] not exist? Simplify the expression. EITHER OR [5 marks] 2a. 1 In the triangle ABC,, AB = BC + 1.
WHAT YOU SHOULD LEARN
 GRAPHS OF EQUATIONS WHAT YOU SHOULD LEARN Sketch graphs of equations. Find x- and y-intercepts of graphs of equations. Use symmetry to sketch graphs of equations. Find equations of and sketch graphs of
GRAPHS OF EQUATIONS WHAT YOU SHOULD LEARN Sketch graphs of equations. Find x- and y-intercepts of graphs of equations. Use symmetry to sketch graphs of equations. Find equations of and sketch graphs of
practice: quadratic functions [102 marks]
![practice: quadratic functions [102 marks] practice: quadratic functions [102 marks]](/thumbs/79/78903895.jpg) practice: quadratic functions [102 marks] A quadratic function, f(x) = a x 2 + bx, is represented by the mapping diagram below. 1a. Use the mapping diagram to write down two equations in terms of a and
practice: quadratic functions [102 marks] A quadratic function, f(x) = a x 2 + bx, is represented by the mapping diagram below. 1a. Use the mapping diagram to write down two equations in terms of a and
SPM Past Year Questions : AM Form 5 Chapter 3 - Integration
 SPM Past Year Questions : AM Form Chapter - Integration SPM PAST YEAR QUESTIONS ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS FORM CHAPTER : INTEGRATION SPM 99 a) Find i) (4 - )(4 ) d, ii) 8 ( - ) d b) Given f ( ) d 8, find
SPM Past Year Questions : AM Form Chapter - Integration SPM PAST YEAR QUESTIONS ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS FORM CHAPTER : INTEGRATION SPM 99 a) Find i) (4 - )(4 ) d, ii) 8 ( - ) d b) Given f ( ) d 8, find
Differentiation and Integration
 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C Advanced Subsidiary Differentiation and Integration Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Pink or Green) Items included with question papers Nil Advice
Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C Advanced Subsidiary Differentiation and Integration Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Pink or Green) Items included with question papers Nil Advice
ACTIVITY #6 SLOPE IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS AND VERTICAL CHANGE ON A PLANE
 ACTIVITY # SLOPE IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS AND VERTICAL CHANGE ON A PLANE Name: VERTICAL CHANGE AND SLOPE IN TWO DIMENSIONS The first three problems eplain how to compute slope looking at a figure, WITHOUT
ACTIVITY # SLOPE IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS AND VERTICAL CHANGE ON A PLANE Name: VERTICAL CHANGE AND SLOPE IN TWO DIMENSIONS The first three problems eplain how to compute slope looking at a figure, WITHOUT
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0569484449* ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 4037/ Paper May/June 017 hours Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional Materials are required.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0569484449* ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 4037/ Paper May/June 017 hours Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional Materials are required.
Focusing properties of spherical and parabolic mirrors
 Physics 5B Winter 008 Focusing properties of spherical and parabolic mirrors 1 General considerations Consider a curved mirror surface that is constructed as follows Start with a curve, denoted by y()
Physics 5B Winter 008 Focusing properties of spherical and parabolic mirrors 1 General considerations Consider a curved mirror surface that is constructed as follows Start with a curve, denoted by y()
Education Resources. This section is designed to provide examples which develop routine skills necessary for completion of this section.
 Education Resources Trigonometry Higher Mathematics Supplementary Resources Section A This section is designed to provide examples which develop routine skills necessary for completion of this section.
Education Resources Trigonometry Higher Mathematics Supplementary Resources Section A This section is designed to provide examples which develop routine skills necessary for completion of this section.
3.6 Graphing Piecewise-Defined Functions and Shifting and Reflecting Graphs of Functions
 76 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Find the equation of each line. Write the equation in the form = a, = b, or = m + b. For Eercises through 7, write the equation in the form f = m + b.. Through (, 6) and
76 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Find the equation of each line. Write the equation in the form = a, = b, or = m + b. For Eercises through 7, write the equation in the form f = m + b.. Through (, 6) and
Lesson 5.3 Exercises, pages
 Lesson 5.3 Eercises, pages 37 3 A. Determine whether each ordered pair is a solution of the quadratic inequalit: 3 - a) (-3, ) b) (, 5) Substitute each ordered pair in» 3. L.S. ; R.S.: 3( 3) 3 L.S. 5;
Lesson 5.3 Eercises, pages 37 3 A. Determine whether each ordered pair is a solution of the quadratic inequalit: 3 - a) (-3, ) b) (, 5) Substitute each ordered pair in» 3. L.S. ; R.S.: 3( 3) 3 L.S. 5;
STRAND G: Relations, Functions and Graphs
 UNIT G Using Graphs to Solve Equations: Tet STRAND G: Relations, Functions and Graphs G Using Graphs to Solve Equations Tet Contents * * Section G. Solution of Simultaneous Equations b Graphs G. Graphs
UNIT G Using Graphs to Solve Equations: Tet STRAND G: Relations, Functions and Graphs G Using Graphs to Solve Equations Tet Contents * * Section G. Solution of Simultaneous Equations b Graphs G. Graphs
Graphing Rational Functions
 5 LESSON Graphing Rational Functions Points of Discontinuit and Vertical Asmptotes UNDERSTAND The standard form of a rational function is f () 5 P(), where P () and Q () Q() are polnomial epressions. Remember
5 LESSON Graphing Rational Functions Points of Discontinuit and Vertical Asmptotes UNDERSTAND The standard form of a rational function is f () 5 P(), where P () and Q () Q() are polnomial epressions. Remember
(i) h(7,8,24) (ii) h(6,5,6) (iii) h( 7,8,9) (iv) h(10,9, 16) (iv) g 3,32 8
 M252 Practice Eam for 12.1-12.9 1. Find and simplify the function values. f ( y, ) = 5 10y (i) f(0,0) (ii) f(0,1) (iii) f(3,9) (iv) f(1,y) (v) f(,0) (vi) f(t,1) 2. Find and simplify the function values.
M252 Practice Eam for 12.1-12.9 1. Find and simplify the function values. f ( y, ) = 5 10y (i) f(0,0) (ii) f(0,1) (iii) f(3,9) (iv) f(1,y) (v) f(,0) (vi) f(t,1) 2. Find and simplify the function values.
More About Factoring Trinomials
 Section 6.3 More About Factoring Trinomials 239 83. x 2 17x 70 x 7 x 10 Width of rectangle: Length of rectangle: x 7 x 10 Width of shaded region: 7 Length of shaded region: x 10 x 10 Area of shaded region:
Section 6.3 More About Factoring Trinomials 239 83. x 2 17x 70 x 7 x 10 Width of rectangle: Length of rectangle: x 7 x 10 Width of shaded region: 7 Length of shaded region: x 10 x 10 Area of shaded region:
Lesson 10.4 Multiplying Binomials
 Lesson 0.4 Multiplying Binomials Objectives Use algebra tiles and geometric representations to multiply two binomials. Use the FOIL method to multiply two binomials. A small patio is 4 feet by 6 feet.
Lesson 0.4 Multiplying Binomials Objectives Use algebra tiles and geometric representations to multiply two binomials. Use the FOIL method to multiply two binomials. A small patio is 4 feet by 6 feet.
AP Calculus. Areas and Volumes. Student Handout
 AP Calculus Areas and Volumes Student Handout 016-017 EDITION Use the following link or scan the QR code to complete the evaluation for the Study Session https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/s_sss Copyright
AP Calculus Areas and Volumes Student Handout 016-017 EDITION Use the following link or scan the QR code to complete the evaluation for the Study Session https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/s_sss Copyright
Transformation of curve. a. reflect the portion of the curve that is below the x-axis about the x-axis
 Given graph of y f = and sketch:. Linear Transformation cf ( b + a) + d a. translate a along the -ais. f b. scale b along the -ais c. scale c along the y-ais d. translate d along the y-ais Transformation
Given graph of y f = and sketch:. Linear Transformation cf ( b + a) + d a. translate a along the -ais. f b. scale b along the -ais c. scale c along the y-ais d. translate d along the y-ais Transformation
MATHSCAPE 10 EXTENSION
 Mathscape 10 Etension Teaching Program Page 1 Stage 5 MATHSCAPE 10 EXTENSION Term Chapter Time 1 1. Consumer arithmetic weeks / 8 hrs. Trigonometry weeks / 8 hrs 3. Volume and surface area weeks / 8 hrs
Mathscape 10 Etension Teaching Program Page 1 Stage 5 MATHSCAPE 10 EXTENSION Term Chapter Time 1 1. Consumer arithmetic weeks / 8 hrs. Trigonometry weeks / 8 hrs 3. Volume and surface area weeks / 8 hrs
Section A Transformations of Graphs Grade A*
 Name: Teacher Assessment Section A Grade A*. The diagram shows the graph of = for. 5 5 5 Each of the graphs below is a transformation of this graph. Write down the equation of each graph. 5 (a) 5 (b) 5
Name: Teacher Assessment Section A Grade A*. The diagram shows the graph of = for. 5 5 5 Each of the graphs below is a transformation of this graph. Write down the equation of each graph. 5 (a) 5 (b) 5
Lesson 8.1 Exercises, pages
 Lesson 8.1 Eercises, pages 1 9 A. Complete each table of values. a) -3 - -1 1 3 3 11 8 5-1 - -7 3 11 8 5 1 7 To complete the table for 3, take the absolute value of each value of 3. b) - -3 - -1 1 3 3
Lesson 8.1 Eercises, pages 1 9 A. Complete each table of values. a) -3 - -1 1 3 3 11 8 5-1 - -7 3 11 8 5 1 7 To complete the table for 3, take the absolute value of each value of 3. b) - -3 - -1 1 3 3
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral
 Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral More on Area More on Area Integrating the vertical separation gives Riemann Sums of the form More on Area Example Find the area A of the set shaded in Figure
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral More on Area More on Area Integrating the vertical separation gives Riemann Sums of the form More on Area Example Find the area A of the set shaded in Figure
Technology Assignment: Limits at Infinity
 The goal of this technology assignment is to find the location of the horizontal asymptote for your model from Technology Assignment: Rational Model. You will produce a graph similar to the one below.
The goal of this technology assignment is to find the location of the horizontal asymptote for your model from Technology Assignment: Rational Model. You will produce a graph similar to the one below.
Mathematics MPC2. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination. Unit Pure Core 2
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Pure Core 2 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Pure Core 2 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination
QUADRATIC AND CUBIC GRAPHS
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE QUADRATIC AND CUBIC GRAPHS KCSE 1989 2012 Form 3 Mathematics Working Space 1. 1989 Q22 P1 (a) Using the grid provided below draw the graph of y = -2x 2 + x + 8 for values
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE QUADRATIC AND CUBIC GRAPHS KCSE 1989 2012 Form 3 Mathematics Working Space 1. 1989 Q22 P1 (a) Using the grid provided below draw the graph of y = -2x 2 + x + 8 for values
Algebra 1 End-of-Course Review
 Name Date 1-11 End-of-Course Review Solve the equation, if possible. 4 8 4 1.. y Solve the inequality, if possible. h 4.. 8 16 4 10 4 5 5. 8 16 4 6. You sell magazine subscriptions and earn $ for every
Name Date 1-11 End-of-Course Review Solve the equation, if possible. 4 8 4 1.. y Solve the inequality, if possible. h 4.. 8 16 4 10 4 5 5. 8 16 4 6. You sell magazine subscriptions and earn $ for every
YEAR 12 Core 1 & 2 Maths Curriculum (A Level Year 1)
 YEAR 12 Core 1 & 2 Maths Curriculum (A Level Year 1) Algebra and Functions Quadratic Functions Equations & Inequalities Binomial Expansion Sketching Curves Coordinate Geometry Radian Measures Sine and
YEAR 12 Core 1 & 2 Maths Curriculum (A Level Year 1) Algebra and Functions Quadratic Functions Equations & Inequalities Binomial Expansion Sketching Curves Coordinate Geometry Radian Measures Sine and
HSC Mathematics - Extension 1. Workshop E2
 HSC Mathematics - Extension Workshop E Presented by Richard D. Kenderdine BSc, GradDipAppSc(IndMaths), SurvCert, MAppStat, GStat School of Mathematics and Applied Statistics University of Wollongong Moss
HSC Mathematics - Extension Workshop E Presented by Richard D. Kenderdine BSc, GradDipAppSc(IndMaths), SurvCert, MAppStat, GStat School of Mathematics and Applied Statistics University of Wollongong Moss
Least Squares Regression
 restart; We load the packages we need. with(plots):with(student[linearalgebra]):with(student [NumericalAnalysis]): We look at two different sets of data and their scatterplots. The first set of data: X:=[[,.3],[,3.5],[3,4.],[4,5.0],[5,7.0],[6,8.8],[7,0.],[8,.5],[9,3.0],[0,5.6]];
restart; We load the packages we need. with(plots):with(student[linearalgebra]):with(student [NumericalAnalysis]): We look at two different sets of data and their scatterplots. The first set of data: X:=[[,.3],[,3.5],[3,4.],[4,5.0],[5,7.0],[6,8.8],[7,0.],[8,.5],[9,3.0],[0,5.6]];
MATH College Algebra Review for Test 1
 MATH 34 - College Algebra Review for Test Section.2. For the relation {(,4), (,2), (5, )}, (a) what is the domain and (b) what is the range? 2. (a) For the table of data shown in the table at the right,
MATH 34 - College Algebra Review for Test Section.2. For the relation {(,4), (,2), (5, )}, (a) what is the domain and (b) what is the range? 2. (a) For the table of data shown in the table at the right,
SECTION 3-4 Rational Functions
 20 3 Polnomial and Rational Functions 0. Shipping. A shipping bo is reinforced with steel bands in all three directions (see the figure). A total of 20. feet of steel tape is to be used, with 6 inches
20 3 Polnomial and Rational Functions 0. Shipping. A shipping bo is reinforced with steel bands in all three directions (see the figure). A total of 20. feet of steel tape is to be used, with 6 inches
2.4. Families of Polynomial Functions
 2. Families of Polnomial Functions Crstal pieces for a large chandelier are to be cut according to the design shown. The graph shows how the design is created using polnomial functions. What do all the
2. Families of Polnomial Functions Crstal pieces for a large chandelier are to be cut according to the design shown. The graph shows how the design is created using polnomial functions. What do all the
Section 18-1: Graphical Representation of Linear Equations and Functions
 Section 18-1: Graphical Representation of Linear Equations and Functions Prepare a table of solutions and locate the solutions on a coordinate system: f(x) = 2x 5 Learning Outcome 2 Write x + 3 = 5 as
Section 18-1: Graphical Representation of Linear Equations and Functions Prepare a table of solutions and locate the solutions on a coordinate system: f(x) = 2x 5 Learning Outcome 2 Write x + 3 = 5 as
Name: Class: Date: a. Use inequality statements to write the domain and range of f(x).
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 9 Review 1. The graph of the square root function, f(), is shown. a. Use inequality statements to write the domain and range of f(). b. Sketch the graph obtained by shifting
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 9 Review 1. The graph of the square root function, f(), is shown. a. Use inequality statements to write the domain and range of f(). b. Sketch the graph obtained by shifting
PRACTICE FINAL - MATH 1210, Spring 2012 CHAPTER 1
 PRACTICE FINAL - MATH 2, Spring 22 The Final will have more material from Chapter 4 than other chapters. To study for chapters -3 you should review the old practice eams IN ADDITION TO what appears here.
PRACTICE FINAL - MATH 2, Spring 22 The Final will have more material from Chapter 4 than other chapters. To study for chapters -3 you should review the old practice eams IN ADDITION TO what appears here.
Unit 4 Trigonometry. Study Notes 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry (Section 8.1)
 Unit 4 Trigonometr Stud Notes 1 Right Triangle Trigonometr (Section 8.1) Objective: Evaluate trigonometric functions of acute angles. Use a calculator to evaluate trigonometric functions. Use trigonometric
Unit 4 Trigonometr Stud Notes 1 Right Triangle Trigonometr (Section 8.1) Objective: Evaluate trigonometric functions of acute angles. Use a calculator to evaluate trigonometric functions. Use trigonometric
Paper Reference(s) 6672 Edexcel GCE Pure Mathematics P2 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 20 January 2003 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Paper Reference(s) 6672 Edexcel GCE Pure Mathematics P2 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 20 January 2003 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Answer Book (AB16) Graph Paper
Paper Reference(s) 6672 Edexcel GCE Pure Mathematics P2 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 20 January 2003 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Answer Book (AB16) Graph Paper
Exam 3 SCORE. MA 114 Exam 3 Spring Section and/or TA:
 MA 114 Exam 3 Spring 217 Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test.
MA 114 Exam 3 Spring 217 Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test.
