Integrating ICT into mathematics at KS4&5
|
|
|
- Alexandra Nash
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Integrating ICT into mathematics at KS4&5 Tom Button This session will detail the was in which ICT can currentl be used in the teaching and learning of Mathematics and how best to eploit these at GCSE and A level. Topics covered will include software, hardware, teaching ideas and suggestions for was to encourage the use of ICT within a department. Wh integrate ICT into mathematics teaching? Appropriate use of ICT can: Demonstrate ideas/links between topics more effectivel Allow students to generalise more easil Calculate/plot quickl without numerical errors Engage students in mathematics
2 Essentials Software Graph plotter Spreadsheet Hardware Data projector Occasional access to a computer suite Autograph Constant controller Dnamic tet-boes (v.) Scribble tool Other useful tools D Vectors Differential equations (C4 and DE) For more eamples see: Geogebra Slider Dnamic tet Other useful tools Slope
3 Ecel Spreadsheet algebra Labelling cells Sliders/scroll bars NB 00% view is better for class presentations Other software Interactive activities for GCSE Mathematics Interactive AS Core Mathematics Omnigraph TI-nspire IP Mechanics GSP/Cabri Fathom Lindo Maima Tarsia Hardware Data projector Interactive Whiteboard Wireless graphics tablet Graphical calculators Handhelds/palmtops/laptops Data-logger
4 Teaching ideas Pure Ideas for AS Core and A Core Differential Equations Autograph: st and nd order DEs Numerical Methods (inc. C) Ecel Mechanics IP Interactive Maths Flash interactive animations Geogebra Statistics Use D graphs on Autograph Encourage students to use Ecel to find statistics long-hand Decision PowerPoint is useful Teaching ideas GCSE Percentages Calculating percentages and reverse percentages with a spreadsheet. Straight line graphs Investigate straight line graphs with Autograph/Geogebra Inequalities Investigate inequalities with Autograph Transformations Transformations with Autograph/Geogebra Trigonometr Using a spreadsheet to investigate Pthagorean triples Geogebra/GSP for basic trigonometr and sine/cosine rule Circle theorems Geogebra/GSP for circle theorems Averages Spreadsheet for averages/moving averages Encouraging the use of ICT Have a member of staff whose specific role it is to promote the use of ICT research indicates this is essential If ou have an IWB ensure all members of staff regularl teach with it Have some PCs in communal/drop-in areas Demand the use of IT rooms 4
5 Suggested ideas for using ICT in AS Core Algebra Quadratics Graphic calculators or Autograph/Geogebra can be used to think about the link between: the factorised form of a quadratic and the aes intercepts of the graph: the completed square form of the quadratic and the turning point: ( )( 4) = 4 5 = + = ( ) Similarl, a graphical approach to simultaneous equations will prepare the students for Chapter and give students a visual insight into wh, with linear and quadratic simultaneous equations, it is necessar to substitute back into the linear equation. Graphs There are also opportunities to investigate a range of other questions supported b a graph-plotting device: o Can a quartic equation have three roots? o Given a straight line = p+ q and a quadratic = a + b + c what can = p + q a + b + c? o ou tell about the aes intercepts of ( )( ) Plot the graph of =. Investigate the each of the following in turn, using several values of a and eplain the effect it has : ( ) ( ) = + a, = + a, = a, = a In Autograph, the button allows ou to define a function, sa ( ) then enter equations = f ( ) + k, f ( k) compare these graphs. (, ) f =. You can = etc. The slow plot mode allows ou to In Geogebra functions can be entered directl into the Input bar, e.g. f()=^. Then a slider (Named a ) can be added and equations such as =f(+a) and =a*f() can be inputted. o If the curve f ( ) what do ou know about the factors of f ( )? o Draw the graphs of = ( + + 5)( ) and ( ) the link between these graphs and the value f ( ) = touches but does not cross the ais at the point = a = f = 4 6. Eplain
6 o Choose another non-linear function f ( ) and plot the graph of f ( ) above investigate each of the following in turn: = f + a, = f + a, = af. = f a ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) =. As Inequalities Graphic calculators can be used which can be compared to illustrate inequalities such as with the simplified version < < 0) + < (or( )( ) whereas Autograph shades the unwanted values of : Coordinate Geometr Equation of a line Use a graph-plotter or graphical calculator to plot a line through two points, then work out the equation of the line and check if it is correct. On the TI-8Plus, LINE (,4,5,) will draw a line through the points (,4) and (5,). Circles You can use a graph-plotter or graphical calculator to illustrate the affect ab, and r a + b = r, or analse the points of intersection of a line and a circle. provides a dnamic approach to teaching circles. Also on the TI-8Plus eperiment with circle from the draw menu: have in the equation of the circle ( ) ( )
7 What features of Circle(,4,5) meant that the circle passed through the origin? Describe what Circle(-,-4,5) would look like then check using our calculator. Find another circle which passes through (a) the origin, (b) the point (,). Draw two circles which touch but not at the origin: Draw other touching circle patterns: The constant controller in Autograph also gives the student a dnamic understanding of the role plaed b coefficients and constants in the equations of curves. See Sliders in Geogebra can also be used in a similar manner. Sequences and Series Introduction to sequences and series Sequences and series can be entered into Ecel to reinforce concepts such as Σ-notation. Binomial Students could be encouraged to write an ecel spreadsheet to generate Pascal s triangle (cell B = Cell A + Cell B):
8 Link with Statistics: could be used to discuss the general shape of the binomial distribution. This also gives a ver visual wa of displaing the answers to Statistics tetbook questions. APs and GPs illustrates the wa the first term and common difference affect the graphs of the terms of the A.P. and the sum to n terms against n. repeats this for G.P.s. clearl illustrating the importance of r < Trigonometr Graphs of trigonometric functions In Autograph under File>New etras page>trigonometr the trigonometric functions are plotted from the unit circle. You could also plot = sin, = cos, highlighting and eplaining their similarities, and then = sin + cos. Graphic calculators can be used to draw the trigonometric graphs from the unit circle. For eample on the TI-8Plus ou could briefl discuss parametric equations and then: Graphs of trigonometric functions and solving equations The spreadsheet generates the trigonometric graphs and shows how to solve basic trigonometric equations. This is highl recommended! Transformations of graphs Graphics calculators and Autograph/Geogebra are useful when investigating transformations of graphs: = sin = sin + = sin = sin -
9 .5 ( ) = cos 60.5 = cos Using the button define f ( ) = sin and then enter the equations f ( ) f ( k) - = + k, =, etc. Using the slow plot mode allows ou to compare these graphs. NB In Geogebra the degrees sign is used to indicate angles are measured in degrees. If it is omitted the graphs will be drawn in radians. e.g. =sin( ) will plot the graph in degrees and =sin() will plot it in radians. Logarithms and Eponentials Logarithms In Autograph the reflection in = button: allows ou to compare the reflection of = log with = 0 : 4 Use the button define f ( ) = log and then enter the equations f( ) f( ) = + log and =.Using the slow plot mode allows ou to compare these two graphs. This can be used to demonstrate the laws of logs. Reduction to linear form Ecel can be used to generate a table of data and the scatter graph and line of best fit can be added to the spreadsheet. Differentiation Finding the gradient of the tangent to a curve at a point On Autograph plot a curve then add a point to the curve. Select the point, right-click (or Object menu) and select Tangent. The point can then be moved along the curve and the values of the gradient of the tangent to the curve at the point can be seen in the equation of the tangent.
10 On Geogebra plot a curve then add a point to the curve. Add a tangent to the curve at the point (4 th menu) and then add a Slope (7 th menu) at the point. The point can then be moved along the curve and the values of the gradient of the tangent to the curve at the point can be seen from the gradient triangle. On the TI-8Plus Using 6 on the CALC menu will draw the tangent to the curve at the chosen 5 on the DRAW menu point giving its equation: will give the gradient of a curve at a chosen point: Gradient functions Autograph allows ou to enter a function ( = 4 in red) and using the button it will plot the gradient for each value of (in blue) thereb generating the gradient function curve ( = 4) To plot a derivative on Geogebra input =f (). Stationar points On Autograph draw a curve, select it and then right-click. Solve f ()=0 will give ou the stationar point. On the TI-8Plus: Draw the graph From the CALC to find the minimum = + 5 menu choose value of :
11 Integration Finding areas In Autograph ou can enter a curve ( = in red) then using the integral function button click on a point on the curve and it will draw the integral curve passing through d this point. In this wa it solves the differential equation = passing through a d specific point Also in Autograph ou can left click on a curve, then right click and choose the option find area. After selecting the area required it will be displaed in the status bar Numerical integration On a TI-8Plus Showing 4 56 d=. Showing ( ) + 5 d=. Autograph Further eamples of the use of Autograph can be seen at:
12 Suggested ideas for using ICT in A Core Core Chapter : Natural logarithms and eponentials The eponential function Differentiating = a with autograph The value of e can be approimated b plotting = a then adding the gradient function. As the value of a is changed with the constant controller students should observe that d k a the gradient function is of the form d = where the value of k depends on the value of a. (For a =, k 0.7; a =, k.; a = 4, k.4: these can be returned to later as k = lna). The students should then be able to observe that there eists a value of a between and such that k =, i.e. a function whose derivative is itself. Scaling in on the aes and the constant controller leads to a value of approimatel.7. Differentiating = a with Geogebra. Add a slider (which should be "a"). Input =a^ (ou ma want to var a at this point). Add a New Point on the curve (this should be "A") 4. Add the tangent at A 5. Add the slope at A As an alternative to points -5 ou can Input: Derivative[f()] or f ()
13 Epressing e as the sum of terms with Ecel. Ask students to suggest an infinite polnomial which when differentiated term-b term would remain unchanged. The will hopefull(!) come up with e = !!! Enter a value for in Cell:A, start with. Start columns labelled n and term. Enter the numbers 0,,,, in the n column. In the first row of the term column enter =$A$^B/FACT(B) Fill-down the term column with this formula. Sum the term column. The value of can then be changed and their formula verified. Chapter : Functions Investigating transformations of functions with Geogebra Functions can be inputted directl into the Input bar. e.g. f()=^+ Parameters can be defined b adding sliders. Graphs can then be plotted to investigate = f(), = af(), = f(b), = f() + c, = f( + d), = f(), = f( ) and the values of the parameters can be altered with the sliders. Investigating transformations of functions with Autograph The function button allows functions to be entered for f() and g(). Graphs can then be plotted to investigate = f(), = af(), = f(b), = f() + c, = f( + d), = f(), = f( ) and the values of the parameters can be altered with the constant controller. Investigating inverse functions with Autograph Functions can be entered as above and the graphs of = f() and = f() can be compared. Alternativel for a graph entered directl (i.e. not as a function), the reflection button, will displa the line = and the graph reflected in =. Students can use this to investigate inverse functions.
14 Chapter 4: Techniques for differentiation Derivative of sin and cos b observing the tangent on Autograph The tangent to = sin can be displaed b adding a point to the graph and then right clicking on the point and selecting Tangent. Students should then observe that gradient varies from (at 0) to 0 (at π/) etc. which suggests cos. Students can then investigate cos, asin and sin(b). Derivative of sin and cos b observing the tangent on Geogebra The gradient of the tangent to =cos() can be displaed b adding a curve to the line, drawing the tangent to the curve at the point and then adding the slope at that point. NB =cos() will plot the graph with the angle measured in radians and =cos( ) will plot the graph with the angle measured in degrees. Chapter 6: Numerical solution of equations Ecel and Autograph can be used etensivel for this see the online resources.
15 Core 4 (MEI): Chapter 7: Algebra Use of Ecel for evaluating ( + ) n for small. Set students the task of produce a spreadsheet that will calculate the first few terms in the epansion of ( + ) n for small and identifing how man terms are needed for the sum to be accurate to a certain number of d.p. To do this: Label 6 columns:, n, r, coeff, term and sum Enter 0. in Cell A. Enter 0.5 in Cell B. Enter the values 0,,, in Cells C, C, C4 Enter in Cell D. Enter =B in Cell D. Enter =D*($B$-(C4-))/C4 in Cell D4 and Fill-down the rest of this column with this formula. Enter =D*$A$^C in Cell E and Fill-down the rest of this column with this formula. Enter =E in Cell F. Enter =F+E in Cell F and Fill-down the rest of this column with this formula. The values in the cumulative sum column can be compared with the true value of ( + ) n and both and n can be varied. Chapter 8: Trigonometr Identities Double angle formulae in Geogebra Define points A:(0,0), B(,0) and C: (-,0). Use these to draw the unit circle. Add a point on the circle D. Add a point E:((D),0) Draw segments AD, BD, CD and ED. Add angles ACD and BAD The resulting diagram can be used to prove the double angle formulae.
16 Graphs Use of Autograph/Geogebra to discover/displa identities (e.g. can the graph of = cos be transformed into the graph of = cos b means of a stretch and a translation? Use the constant controller/slider to find values of a and b so that the graph of = asin + bcos is the same as = Rcos( + 0 ) Small angle approimations Use of Autograph/Geogebra to find small angle approimations for sin, cos and tan:, and respectivel can be demonstrated/discovered b drawing the tangents to the curves at = 0 and the range for which the are valid can be demonstrated. Chapter 9: Parametric Equations Parametric equations can be entered into Autograph using the parameter t and a comma to separate the and equations. Parametric curves can be entered into Geogebra using the snta: Curve[epression for, epression for, parameter, lower limit, upper limit] e.g. Curve[t, t^, t, -5, 5] Parametric equations can also be entered into most graphical calculators Chapter 0: Further techniques for integration Autograph Volumes of revolution See: Chapter : Vectors Vectors on Autograph See C4 Vectors with Autograph :
17 Chapter : Differential equations Differential equations on Autograph st order DEs can be displaed on Autograph b entering d... d = this then gives a tangent field. Clicking on the screen at a point gives a particular solution through that point. The tangent fields can be used to eplain wh d k d = generates an eponential curve and d k d = generates a parabola. Autograph Further eamples of the use of Autograph can be seen at: Further Information For further information, including advice about the use of ICT in AS Core see:
IB SL REVIEW and PRACTICE
 IB SL REVIEW and PRACTICE Topic: CALCULUS Here are sample problems that deal with calculus. You ma use the formula sheet for all problems. Chapters 16 in our Tet can help ou review. NO CALCULATOR Problems
IB SL REVIEW and PRACTICE Topic: CALCULUS Here are sample problems that deal with calculus. You ma use the formula sheet for all problems. Chapters 16 in our Tet can help ou review. NO CALCULATOR Problems
MEI GeoGebra Tasks for AS Pure
 Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x 2 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Use the Intersect tool to find the points of intersection of
Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x 2 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Use the Intersect tool to find the points of intersection of
MEI GeoGebra Tasks for A2 Core
 Task 1: Functions The Modulus Function 1. Plot the graph of y = x : use y = x or y = abs(x) 2. Plot the graph of y = ax+b : use y = ax + b or y = abs(ax+b) If prompted click Create Sliders. What combination
Task 1: Functions The Modulus Function 1. Plot the graph of y = x : use y = x or y = abs(x) 2. Plot the graph of y = ax+b : use y = ax + b or y = abs(ax+b) If prompted click Create Sliders. What combination
MEI Desmos Tasks for AS Pure
 Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x² 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Select the points of intersection of the line and the curve. What
Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x² 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Select the points of intersection of the line and the curve. What
Applications of Differentiation
 Contents 1 Applications of Differentiation 1.1 Tangents and Normals 1. Maima and Minima 14 1. The Newton-Raphson Method 8 1.4 Curvature 47 1.5 Differentiation of Vectors 54 1.6 Case Stud: Comple Impedance
Contents 1 Applications of Differentiation 1.1 Tangents and Normals 1. Maima and Minima 14 1. The Newton-Raphson Method 8 1.4 Curvature 47 1.5 Differentiation of Vectors 54 1.6 Case Stud: Comple Impedance
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS through 2.1.4
 SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 2.1.2 through 2.1.4 Students used the equation = m + b to graph lines and describe patterns in previous courses. Lesson 2.1.1 is a review. When the equation of a line is written
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 2.1.2 through 2.1.4 Students used the equation = m + b to graph lines and describe patterns in previous courses. Lesson 2.1.1 is a review. When the equation of a line is written
MATHEMATICAL METHODS UNITS 3 AND Sketching Polynomial Graphs
 Maths Methods 1 MATHEMATICAL METHODS UNITS 3 AND 4.3 Sketching Polnomial Graphs ou are required to e ale to sketch the following graphs. 1. Linear functions. Eg. = ax + These graphs when drawn will form
Maths Methods 1 MATHEMATICAL METHODS UNITS 3 AND 4.3 Sketching Polnomial Graphs ou are required to e ale to sketch the following graphs. 1. Linear functions. Eg. = ax + These graphs when drawn will form
Worksheet A GRAPHS OF FUNCTIONS
 C GRAPHS F FUNCTINS Worksheet A Sketch and label each pair of graphs on the same set of aes showing the coordinates of any points where the graphs intersect. Write down the equations of any asymptotes.
C GRAPHS F FUNCTINS Worksheet A Sketch and label each pair of graphs on the same set of aes showing the coordinates of any points where the graphs intersect. Write down the equations of any asymptotes.
MEI Casio Tasks for A2 Core
 Task 1: Functions The Modulus Function The modulus function, abs(x), is found using OPTN > NUMERIC > Abs 2. Add the graph y = x, Y1=Abs(x): iyqfl 3. Add the graph y = ax+b, Y2=Abs(Ax+B): iyqaff+agl 4.
Task 1: Functions The Modulus Function The modulus function, abs(x), is found using OPTN > NUMERIC > Abs 2. Add the graph y = x, Y1=Abs(x): iyqfl 3. Add the graph y = ax+b, Y2=Abs(Ax+B): iyqaff+agl 4.
Topic 2 Transformations of Functions
 Week Topic Transformations of Functions Week Topic Transformations of Functions This topic can be a little trick, especiall when one problem has several transformations. We re going to work through each
Week Topic Transformations of Functions Week Topic Transformations of Functions This topic can be a little trick, especiall when one problem has several transformations. We re going to work through each
Introduction to Geogebra
 Aims Introduction to Geogebra Using Geogebra in the A-Level/Higher GCSE Classroom To provide examples of the effective use of Geogebra in the teaching and learning of mathematics at A-Level/Higher GCSE.
Aims Introduction to Geogebra Using Geogebra in the A-Level/Higher GCSE Classroom To provide examples of the effective use of Geogebra in the teaching and learning of mathematics at A-Level/Higher GCSE.
Developed in Consultation with Tennessee Educators
 Developed in Consultation with Tennessee Educators Table of Contents Letter to the Student........................................ Test-Taking Checklist........................................ Tennessee
Developed in Consultation with Tennessee Educators Table of Contents Letter to the Student........................................ Test-Taking Checklist........................................ Tennessee
0 COORDINATE GEOMETRY
 0 COORDINATE GEOMETRY Coordinate Geometr 0-1 Equations of Lines 0- Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 0- Intersecting Lines 0- Midpoints, Distance Formula, Segment Lengths 0- Equations of Circles 0-6 Problem
0 COORDINATE GEOMETRY Coordinate Geometr 0-1 Equations of Lines 0- Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 0- Intersecting Lines 0- Midpoints, Distance Formula, Segment Lengths 0- Equations of Circles 0-6 Problem
Using Characteristics of a Quadratic Function to Describe Its Graph. The graphs of quadratic functions can be described using key characteristics:
 Chapter Summar Ke Terms standard form of a quadratic function (.1) factored form of a quadratic function (.1) verte form of a quadratic function (.1) concavit of a parabola (.1) reference points (.) transformation
Chapter Summar Ke Terms standard form of a quadratic function (.1) factored form of a quadratic function (.1) verte form of a quadratic function (.1) concavit of a parabola (.1) reference points (.) transformation
y = f(x) x (x, f(x)) f(x) g(x) = f(x) + 2 (x, g(x)) 0 (0, 1) 1 3 (0, 3) 2 (2, 3) 3 5 (2, 5) 4 (4, 3) 3 5 (4, 5) 5 (5, 5) 5 7 (5, 7)
 0 Relations and Functions.7 Transformations In this section, we stud how the graphs of functions change, or transform, when certain specialized modifications are made to their formulas. The transformations
0 Relations and Functions.7 Transformations In this section, we stud how the graphs of functions change, or transform, when certain specialized modifications are made to their formulas. The transformations
TANGENTS AND NORMALS
 Mathematics Revision Guides Tangents and Normals Page 1 of 8 MK HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C1 Edecel: C OCR: C1 OCR MEI: C TANGENTS AND NORMALS Version : 1 Date:
Mathematics Revision Guides Tangents and Normals Page 1 of 8 MK HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C1 Edecel: C OCR: C1 OCR MEI: C TANGENTS AND NORMALS Version : 1 Date:
science. In this course we investigate problems both algebraically and graphically.
 Section. Graphs. Graphs Much of algebra is concerned with solving equations. Man algebraic techniques have been developed to provide insights into various sorts of equations and those techniques are essential
Section. Graphs. Graphs Much of algebra is concerned with solving equations. Man algebraic techniques have been developed to provide insights into various sorts of equations and those techniques are essential
Module 2, Section 2 Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
 Principles of Mathematics Section, Introduction 5 Module, Section Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Introduction You have studied trigonometric ratios since Grade 9 Mathematics. In this module ou will
Principles of Mathematics Section, Introduction 5 Module, Section Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Introduction You have studied trigonometric ratios since Grade 9 Mathematics. In this module ou will
Graphing square root functions. What would be the base graph for the square root function? What is the table of values?
 Unit 3 (Chapter 2) Radical Functions (Square Root Functions Sketch graphs of radical functions b appling translations, stretches and reflections to the graph of Analze transformations to identif the of
Unit 3 (Chapter 2) Radical Functions (Square Root Functions Sketch graphs of radical functions b appling translations, stretches and reflections to the graph of Analze transformations to identif the of
1.2. Characteristics of Polynomial Functions. What are the key features of the graphs of polynomial functions?
 1.2 Characteristics of Polnomial Functions In Section 1.1, ou eplored the features of power functions, which are single-term polnomial functions. Man polnomial functions that arise from real-world applications
1.2 Characteristics of Polnomial Functions In Section 1.1, ou eplored the features of power functions, which are single-term polnomial functions. Man polnomial functions that arise from real-world applications
2.4. Families of Polynomial Functions
 2. Families of Polnomial Functions Crstal pieces for a large chandelier are to be cut according to the design shown. The graph shows how the design is created using polnomial functions. What do all the
2. Families of Polnomial Functions Crstal pieces for a large chandelier are to be cut according to the design shown. The graph shows how the design is created using polnomial functions. What do all the
Honors Precalculus: Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically. Page 1
 Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically 1. Plot points on the Cartesian coordinate plane. P.1 2. Represent data graphically using scatter plots, bar graphs, & line graphs. P.1
Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically 1. Plot points on the Cartesian coordinate plane. P.1 2. Represent data graphically using scatter plots, bar graphs, & line graphs. P.1
YEAR 12 Core 1 & 2 Maths Curriculum (A Level Year 1)
 YEAR 12 Core 1 & 2 Maths Curriculum (A Level Year 1) Algebra and Functions Quadratic Functions Equations & Inequalities Binomial Expansion Sketching Curves Coordinate Geometry Radian Measures Sine and
YEAR 12 Core 1 & 2 Maths Curriculum (A Level Year 1) Algebra and Functions Quadratic Functions Equations & Inequalities Binomial Expansion Sketching Curves Coordinate Geometry Radian Measures Sine and
MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR
 European Schools Office of the Secretary-General Pedagogical Development Unit Ref.: 011-01-D-7-en- Orig.: EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR 4 period/week course APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING
European Schools Office of the Secretary-General Pedagogical Development Unit Ref.: 011-01-D-7-en- Orig.: EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR 4 period/week course APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS through 7.1.5
 SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 7.1. through 7.1.5 Students have used the equation = m + b throughout this course to graph lines and describe patterns. When the equation is written in -form, the m is the
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 7.1. through 7.1.5 Students have used the equation = m + b throughout this course to graph lines and describe patterns. When the equation is written in -form, the m is the
Graphing Polynomial Functions
 LESSON 7 Graphing Polnomial Functions Graphs of Cubic and Quartic Functions UNDERSTAND A parent function is the most basic function of a famil of functions. It preserves the shape of the entire famil.
LESSON 7 Graphing Polnomial Functions Graphs of Cubic and Quartic Functions UNDERSTAND A parent function is the most basic function of a famil of functions. It preserves the shape of the entire famil.
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Figure Electron micrograph of E. Coli bacteria (credit: Mattosaurus, Wikimedia Commons) CHAPTER OUTLINE. Eponential Functions. Logarithmic Properties. Graphs of Eponential
Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Figure Electron micrograph of E. Coli bacteria (credit: Mattosaurus, Wikimedia Commons) CHAPTER OUTLINE. Eponential Functions. Logarithmic Properties. Graphs of Eponential
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Figure Electron micrograph of E. Coli bacteria (credit: Mattosaurus, Wikimedia Commons) Chapter Outline. Eponential Functions. Logarithmic Properties. Graphs of Eponential
Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Figure Electron micrograph of E. Coli bacteria (credit: Mattosaurus, Wikimedia Commons) Chapter Outline. Eponential Functions. Logarithmic Properties. Graphs of Eponential
Section 4.2 Graphing Lines
 Section. Graphing Lines Objectives In this section, ou will learn to: To successfull complete this section, ou need to understand: Identif collinear points. The order of operations (1.) Graph the line
Section. Graphing Lines Objectives In this section, ou will learn to: To successfull complete this section, ou need to understand: Identif collinear points. The order of operations (1.) Graph the line
Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Chapter 8: Graphical analysis Section 5. Graph sketching
 Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Chapter 8: Graphical analsis Section 5 Graph sketching What ou need to know alread: How to compute and interpret limits How to perform first and second derivative
Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Chapter 8: Graphical analsis Section 5 Graph sketching What ou need to know alread: How to compute and interpret limits How to perform first and second derivative
GRAPHS AND GRAPHICAL SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS
 GRAPHS AND GRAPHICAL SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS 1.1 DIFFERENT TYPES AND SHAPES OF GRAPHS: A graph can be drawn to represent are equation connecting two variables. There are different tpes of equations which
GRAPHS AND GRAPHICAL SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS 1.1 DIFFERENT TYPES AND SHAPES OF GRAPHS: A graph can be drawn to represent are equation connecting two variables. There are different tpes of equations which
Unit 2: Function Transformation Chapter 1
 Basic Transformations Reflections Inverses Unit 2: Function Transformation Chapter 1 Section 1.1: Horizontal and Vertical Transformations A of a function alters the and an combination of the of the graph.
Basic Transformations Reflections Inverses Unit 2: Function Transformation Chapter 1 Section 1.1: Horizontal and Vertical Transformations A of a function alters the and an combination of the of the graph.
9-1 GCSE Maths. GCSE Mathematics has a Foundation tier (Grades 1 5) and a Higher tier (Grades 4 9).
 9-1 GCSE Maths GCSE Mathematics has a Foundation tier (Grades 1 5) and a Higher tier (Grades 4 9). In each tier, there are three exams taken at the end of Year 11. Any topic may be assessed on each of
9-1 GCSE Maths GCSE Mathematics has a Foundation tier (Grades 1 5) and a Higher tier (Grades 4 9). In each tier, there are three exams taken at the end of Year 11. Any topic may be assessed on each of
dt Acceleration is the derivative of velocity with respect to time. If a body's position at time t is S = f(t), the body's acceleration at time t is
 APPLICATIN F DERIVATIVE INTRDUCTIN In this section we eamine some applications in which derivatives are used to represent and interpret the rates at which things change in the world around us. Let S be
APPLICATIN F DERIVATIVE INTRDUCTIN In this section we eamine some applications in which derivatives are used to represent and interpret the rates at which things change in the world around us. Let S be
2.8 Distance and Midpoint Formulas; Circles
 Section.8 Distance and Midpoint Formulas; Circles 9 Eercises 89 90 are based on the following cartoon. B.C. b permission of Johnn Hart and Creators Sndicate, Inc. 89. Assuming that there is no such thing
Section.8 Distance and Midpoint Formulas; Circles 9 Eercises 89 90 are based on the following cartoon. B.C. b permission of Johnn Hart and Creators Sndicate, Inc. 89. Assuming that there is no such thing
Year 8 Mathematics Curriculum Map
 Year 8 Mathematics Curriculum Map Topic Algebra 1 & 2 Number 1 Title (Levels of Exercise) Objectives Sequences *To generate sequences using term-to-term and position-to-term rule. (5-6) Quadratic Sequences
Year 8 Mathematics Curriculum Map Topic Algebra 1 & 2 Number 1 Title (Levels of Exercise) Objectives Sequences *To generate sequences using term-to-term and position-to-term rule. (5-6) Quadratic Sequences
AQA GCSE Maths - Higher Self-Assessment Checklist
 AQA GCSE Maths - Higher Self-Assessment Checklist Number 1 Use place value when calculating with decimals. 1 Order positive and negative integers and decimals using the symbols =,, , and. 1 Round to
AQA GCSE Maths - Higher Self-Assessment Checklist Number 1 Use place value when calculating with decimals. 1 Order positive and negative integers and decimals using the symbols =,, , and. 1 Round to
Essential Question: How do you graph an exponential function of the form f (x) = ab x? Explore Exploring Graphs of Exponential Functions. 1.
 Locker LESSON 4.4 Graphing Eponential Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.7e Graph eponential and logarithmic functions, showing intercepts and end behavior, and trigonometric
Locker LESSON 4.4 Graphing Eponential Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.7e Graph eponential and logarithmic functions, showing intercepts and end behavior, and trigonometric
Find the Relationship: An Exercise in Graphical Analysis
 Find the Relationship: An Eercise in Graphical Analsis In several laborator investigations ou do this ear, a primar purpose will be to find the mathematical relationship between two variables. For eample,
Find the Relationship: An Eercise in Graphical Analsis In several laborator investigations ou do this ear, a primar purpose will be to find the mathematical relationship between two variables. For eample,
PATTERNS AND ALGEBRA. He opened mathematics to many discoveries and exciting applications.
 PATTERNS AND ALGEBRA The famous French philosopher and mathematician René Descartes (596 65) made a great contribution to mathematics in 67 when he published a book linking algebra and geometr for the
PATTERNS AND ALGEBRA The famous French philosopher and mathematician René Descartes (596 65) made a great contribution to mathematics in 67 when he published a book linking algebra and geometr for the
Laurie s Notes. Overview of Section 6.3
 Overview of Section.3 Introduction In this lesson, eponential equations are defined. Students distinguish between linear and eponential equations, helping to focus on the definition of each. A linear function
Overview of Section.3 Introduction In this lesson, eponential equations are defined. Students distinguish between linear and eponential equations, helping to focus on the definition of each. A linear function
Name Class Date. subtract 3 from each side. w 5z z 5 2 w p - 9 = = 15 + k = 10m. 10. n =
 Reteaching Solving Equations To solve an equation that contains a variable, find all of the values of the variable that make the equation true. Use the equalit properties of real numbers and inverse operations
Reteaching Solving Equations To solve an equation that contains a variable, find all of the values of the variable that make the equation true. Use the equalit properties of real numbers and inverse operations
Concept: Slope of a Line
 Concept: Slope of a Line Warm Up Name: The following suggested activities would serve as a review to consolidate previous learning. While promoting rich mathematical dialog, the will also provide students
Concept: Slope of a Line Warm Up Name: The following suggested activities would serve as a review to consolidate previous learning. While promoting rich mathematical dialog, the will also provide students
Unit 3 Higher topic list
 This is a comprehensive list of the topics to be studied for the Edexcel unit 3 modular exam. Beside the topics listed are the relevant tasks on www.mymaths.co.uk that students can use to practice. Logon
This is a comprehensive list of the topics to be studied for the Edexcel unit 3 modular exam. Beside the topics listed are the relevant tasks on www.mymaths.co.uk that students can use to practice. Logon
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
 00-CE A MATH HONG KONG EXAMINATIONS AUTHORITY HONG KONG CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION EXAMINATION 00 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 8.0 am.00 am ½ hours This paper must be answered in English. Answer ALL questions
00-CE A MATH HONG KONG EXAMINATIONS AUTHORITY HONG KONG CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION EXAMINATION 00 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 8.0 am.00 am ½ hours This paper must be answered in English. Answer ALL questions
TIPS4RM: MHF4U: Unit 1 Polynomial Functions
 TIPSRM: MHFU: Unit Polnomial Functions 008 .5.: Polnomial Concept Attainment Activit Compare and contrast the eamples and non-eamples of polnomial functions below. Through reasoning, identif attributes
TIPSRM: MHFU: Unit Polnomial Functions 008 .5.: Polnomial Concept Attainment Activit Compare and contrast the eamples and non-eamples of polnomial functions below. Through reasoning, identif attributes
(ii) Use Simpson s rule with two strips to find an approximation to Use your answers to parts (i) and (ii) to show that ln 2.
 C umerical Methods. June 00 qu. 6 (i) Show by calculation that the equation tan = 0, where is measured in radians, has a root between.0 and.. [] Use the iteration formula n+ = tan + n with a suitable starting
C umerical Methods. June 00 qu. 6 (i) Show by calculation that the equation tan = 0, where is measured in radians, has a root between.0 and.. [] Use the iteration formula n+ = tan + n with a suitable starting
Exploration 6-1a: Sine and Cosine Graphs, Manually
 Group Members: Exploration 6-1a: Sine and Cosine Graphs, Manuall Objective: Find the shape of sine and cosine graphs b plotting them on graph paper. 1 90 180 270 450 540 630 720 1 1 90 180 270 450 540
Group Members: Exploration 6-1a: Sine and Cosine Graphs, Manuall Objective: Find the shape of sine and cosine graphs b plotting them on graph paper. 1 90 180 270 450 540 630 720 1 1 90 180 270 450 540
5.2 Graphing Polynomial Functions
 Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Polnomial Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F.IF.7c Graph polnomial functions, identifing zeros when suitable factorizations are available, and showing
Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Polnomial Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F.IF.7c Graph polnomial functions, identifing zeros when suitable factorizations are available, and showing
2.3 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree with Modeling
 SECTION 2.3 Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree with Modeling 185 2.3 Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree with Modeling What ou ll learn about Graphs of Polnomial Functions End Behavior of Polnomial
SECTION 2.3 Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree with Modeling 185 2.3 Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree with Modeling What ou ll learn about Graphs of Polnomial Functions End Behavior of Polnomial
Department Curriculum Map (new GCSE)
 Department Curriculum Map 2014-15 (new GCSE) Department Mathematics required in Year 11 Foundation 1. Structure and calculation: N1 to N9 Fractions, decimals and percentages: N10 to N12 Measure and accuracy:
Department Curriculum Map 2014-15 (new GCSE) Department Mathematics required in Year 11 Foundation 1. Structure and calculation: N1 to N9 Fractions, decimals and percentages: N10 to N12 Measure and accuracy:
Derivatives 3: The Derivative as a Function
 Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function 77 Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function Model : Graph of a Function 9 8 7 6 5 g() - - - 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 - - -5-6 -7 Construct Your Understanding
Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function 77 Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function Model : Graph of a Function 9 8 7 6 5 g() - - - 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 - - -5-6 -7 Construct Your Understanding
Making Graphs from a Table of Values and Understanding the Graphs of Horizontal and Vertical Lines Blue Level Problems
 Making Graphs from a Table of Values and Understanding the Graphs of Horizontal and Vertical Lines Blue Level Problems. Coordinate Triangle? We have a triangle ABC, and it has an area of units^. Point
Making Graphs from a Table of Values and Understanding the Graphs of Horizontal and Vertical Lines Blue Level Problems. Coordinate Triangle? We have a triangle ABC, and it has an area of units^. Point
ANGLES See the Math Notes boxes in Lessons and for more information about angle relationships.
 CC1 Basic Definitions Defense Practice ANGLES 2.1.1 2.1.5 Applications of geometr in everda settings often involve the measures of angles. In this chapter we begin our stud of angle measurement. After
CC1 Basic Definitions Defense Practice ANGLES 2.1.1 2.1.5 Applications of geometr in everda settings often involve the measures of angles. In this chapter we begin our stud of angle measurement. After
Intermediate Algebra. Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technology
 Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technolog c 2017 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. The essence of the license
Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technolog c 2017 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. The essence of the license
String Graphs Part 1 + 2
 String Graphs Part + Answers 7 8 9 TI-Nspire Investigation Student 45 min Aim Connect the outcomes of Advanced Strings Graphs Part and Advanced Strings Part using transformation matrices Visualising the
String Graphs Part + Answers 7 8 9 TI-Nspire Investigation Student 45 min Aim Connect the outcomes of Advanced Strings Graphs Part and Advanced Strings Part using transformation matrices Visualising the
1) y = 2x 7 2) (-2, 3) ( 3, -1) 3) table. 4) y 5 = ½ ( x 4) 5) 2x + 4y = 7 6) y = 5 7) 8) 9) (-1, 5) (0, 4) 10) y = -3x 7. 11) 2y = -3x 5 12) x = 5
 I SPY Slope! Geometr tetbook 3-6, pg 165 (), pg 172 (calculator) Name: Date: _ Period: Strategies: On a graph or a table rise ( Δ) Slope = run Δ ( ) Given 2 points Slope = 2 2 In an equation 1 1 1) = 2
I SPY Slope! Geometr tetbook 3-6, pg 165 (), pg 172 (calculator) Name: Date: _ Period: Strategies: On a graph or a table rise ( Δ) Slope = run Δ ( ) Given 2 points Slope = 2 2 In an equation 1 1 1) = 2
3.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree
 71_00.qp 1/7/06 1: PM Page 6 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree 6. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree What ou should learn Graphs of Polnomial Functions You should be able to sketch accurate
71_00.qp 1/7/06 1: PM Page 6 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree 6. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree What ou should learn Graphs of Polnomial Functions You should be able to sketch accurate
Transformations of Functions. 1. Shifting, reflecting, and stretching graphs Symmetry of functions and equations
 Chapter Transformations of Functions TOPICS.5.. Shifting, reflecting, and stretching graphs Smmetr of functions and equations TOPIC Horizontal Shifting/ Translation Horizontal Shifting/ Translation Shifting,
Chapter Transformations of Functions TOPICS.5.. Shifting, reflecting, and stretching graphs Smmetr of functions and equations TOPIC Horizontal Shifting/ Translation Horizontal Shifting/ Translation Shifting,
Answers. Chapter 4. Cumulative Review Chapters 1 3, pp Chapter Self-Test, p Getting Started, p a) 49 c) e)
 . 7" " " 7 "7.. "66 ( ") cm. a, (, ), b... m b.7 m., because t t has b ac 6., so there are two roots. Because parabola opens down and is above t-ais for small positive t, at least one of these roots is
. 7" " " 7 "7.. "66 ( ") cm. a, (, ), b... m b.7 m., because t t has b ac 6., so there are two roots. Because parabola opens down and is above t-ais for small positive t, at least one of these roots is
Graphing Calculator Graphing with the TI-86
 Graphing Calculator Graphing with the TI-86 I. Introduction The TI-86 has fift kes, man of which perform multiple functions when used in combination. Each ke has a smbol printed on its face. When a ke
Graphing Calculator Graphing with the TI-86 I. Introduction The TI-86 has fift kes, man of which perform multiple functions when used in combination. Each ke has a smbol printed on its face. When a ke
This lesson gives students practice in graphing
 NATIONAL MATH + SCIENCE INITIATIVE Mathematics 9 7 5 1 1 5 7 LEVEL Grade, Algebra 1, or Math 1 in a unit on solving sstems of equations MODULE/CONNECTION TO AP* Areas and Volumes *Advanced Placement and
NATIONAL MATH + SCIENCE INITIATIVE Mathematics 9 7 5 1 1 5 7 LEVEL Grade, Algebra 1, or Math 1 in a unit on solving sstems of equations MODULE/CONNECTION TO AP* Areas and Volumes *Advanced Placement and
20 Calculus and Structures
 0 Calculus and Structures CHAPTER FUNCTIONS Calculus and Structures Copright LESSON FUNCTIONS. FUNCTIONS A function f is a relationship between an input and an output and a set of instructions as to how
0 Calculus and Structures CHAPTER FUNCTIONS Calculus and Structures Copright LESSON FUNCTIONS. FUNCTIONS A function f is a relationship between an input and an output and a set of instructions as to how
Investigation Free Fall
 Investigation Free Fall Name Period Date You will need: a motion sensor, a small pillow or other soft object What function models the height of an object falling due to the force of gravit? Use a motion
Investigation Free Fall Name Period Date You will need: a motion sensor, a small pillow or other soft object What function models the height of an object falling due to the force of gravit? Use a motion
GCSE Higher Revision List
 GCSE Higher Revision List Level 8/9 Topics I can work with exponential growth and decay on the calculator. I can convert a recurring decimal to a fraction. I can simplify expressions involving powers or
GCSE Higher Revision List Level 8/9 Topics I can work with exponential growth and decay on the calculator. I can convert a recurring decimal to a fraction. I can simplify expressions involving powers or
Mathematics. Year 7. Autumn Term
 Mathematics Year 7 Autumn Term Decimals o Use place value with decimals o Add and subtract, multiply and divide decimal numbers Basic Arithmetic o Multiply by a two or three digit number o Divide by a
Mathematics Year 7 Autumn Term Decimals o Use place value with decimals o Add and subtract, multiply and divide decimal numbers Basic Arithmetic o Multiply by a two or three digit number o Divide by a
FOUNDATION HIGHER. F Autumn 1, Yr 9 Autumn 2, Yr 9 Spring 1, Yr 9 Spring 2, Yr 9 Summer 1, Yr 9 Summer 2, Yr 9
 Year: 9 GCSE Mathematics FOUNDATION F Autumn 1, Yr 9 Autumn 2, Yr 9 Spring 1, Yr 9 Spring 2, Yr 9 Summer 1, Yr 9 Summer 2, Yr 9 HIGHER Integers and place value Decimals Indices, powers and roots Factors,multiples
Year: 9 GCSE Mathematics FOUNDATION F Autumn 1, Yr 9 Autumn 2, Yr 9 Spring 1, Yr 9 Spring 2, Yr 9 Summer 1, Yr 9 Summer 2, Yr 9 HIGHER Integers and place value Decimals Indices, powers and roots Factors,multiples
Mastery. PRECALCULUS Student Learning Targets
 PRECALCULUS Student Learning Targets Big Idea: Sequences and Series 1. I can describe a sequence as a function where the domain is the set of natural numbers. Connections (Pictures, Vocabulary, Definitions,
PRECALCULUS Student Learning Targets Big Idea: Sequences and Series 1. I can describe a sequence as a function where the domain is the set of natural numbers. Connections (Pictures, Vocabulary, Definitions,
Term Key topics What most pupils will learn (prior assessment may alter starting point & content) How might this learning be extended?
 Learning overview for: Mathematics Term Key topics What most pupils will learn (prior assessment may alter starting point & content) Number Factors, multiples and primes HCF and LCM Calculate with negative
Learning overview for: Mathematics Term Key topics What most pupils will learn (prior assessment may alter starting point & content) Number Factors, multiples and primes HCF and LCM Calculate with negative
Section 1.4 Limits involving infinity
 Section. Limits involving infinit (/3/08) Overview: In later chapters we will need notation and terminolog to describe the behavior of functions in cases where the variable or the value of the function
Section. Limits involving infinit (/3/08) Overview: In later chapters we will need notation and terminolog to describe the behavior of functions in cases where the variable or the value of the function
5.6 Translations and Combinations of Transformations
 5.6 Translations and Combinations of Transformations The highest tides in the world are found in the Ba of Fund. Tides in one area of the ba cause the water level to rise to 6 m above average sea level
5.6 Translations and Combinations of Transformations The highest tides in the world are found in the Ba of Fund. Tides in one area of the ba cause the water level to rise to 6 m above average sea level
SECTION 3-4 Rational Functions
 20 3 Polnomial and Rational Functions 0. Shipping. A shipping bo is reinforced with steel bands in all three directions (see the figure). A total of 20. feet of steel tape is to be used, with 6 inches
20 3 Polnomial and Rational Functions 0. Shipping. A shipping bo is reinforced with steel bands in all three directions (see the figure). A total of 20. feet of steel tape is to be used, with 6 inches
4.6 Graphs of Other Trigonometric Functions
 .6 Graphs of Other Trigonometric Functions Section.6 Graphs of Other Trigonometric Functions 09 Graph of the Tangent Function Recall that the tangent function is odd. That is, tan tan. Consequentl, the
.6 Graphs of Other Trigonometric Functions Section.6 Graphs of Other Trigonometric Functions 09 Graph of the Tangent Function Recall that the tangent function is odd. That is, tan tan. Consequentl, the
STRAND G: Relations, Functions and Graphs
 UNIT G Using Graphs to Solve Equations: Tet STRAND G: Relations, Functions and Graphs G Using Graphs to Solve Equations Tet Contents * * Section G. Solution of Simultaneous Equations b Graphs G. Graphs
UNIT G Using Graphs to Solve Equations: Tet STRAND G: Relations, Functions and Graphs G Using Graphs to Solve Equations Tet Contents * * Section G. Solution of Simultaneous Equations b Graphs G. Graphs
Unit I - Chapter 3 Polynomial Functions 3.1 Characteristics of Polynomial Functions
 Math 3200 Unit I Ch 3 - Polnomial Functions 1 Unit I - Chapter 3 Polnomial Functions 3.1 Characteristics of Polnomial Functions Goal: To Understand some Basic Features of Polnomial functions: Continuous
Math 3200 Unit I Ch 3 - Polnomial Functions 1 Unit I - Chapter 3 Polnomial Functions 3.1 Characteristics of Polnomial Functions Goal: To Understand some Basic Features of Polnomial functions: Continuous
2.3. Horizontal and Vertical Translations of Functions. Investigate
 .3 Horizontal and Vertical Translations of Functions When a video game developer is designing a game, she might have several objects displaed on the computer screen that move from one place to another
.3 Horizontal and Vertical Translations of Functions When a video game developer is designing a game, she might have several objects displaed on the computer screen that move from one place to another
3.5 Rational Functions
 0 Chapter Polnomial and Rational Functions Rational Functions For a rational function, find the domain and graph the function, identifing all of the asmptotes Solve applied problems involving rational
0 Chapter Polnomial and Rational Functions Rational Functions For a rational function, find the domain and graph the function, identifing all of the asmptotes Solve applied problems involving rational
Matrix Representations
 CONDENSED LESSON 6. Matri Representations In this lesson, ou Represent closed sstems with transition diagrams and transition matrices Use matrices to organize information Sandra works at a da-care center.
CONDENSED LESSON 6. Matri Representations In this lesson, ou Represent closed sstems with transition diagrams and transition matrices Use matrices to organize information Sandra works at a da-care center.
3x 4y 2. 3y 4. Math 65 Weekly Activity 1 (50 points) Name: Simplify the following expressions. Make sure to use the = symbol appropriately.
 Math 65 Weekl Activit 1 (50 points) Name: Simplif the following epressions. Make sure to use the = smbol appropriatel. Due (1) (a) - 4 (b) ( - ) 4 () 8 + 5 6 () 1 5 5 Evaluate the epressions when = - and
Math 65 Weekl Activit 1 (50 points) Name: Simplif the following epressions. Make sure to use the = smbol appropriatel. Due (1) (a) - 4 (b) ( - ) 4 () 8 + 5 6 () 1 5 5 Evaluate the epressions when = - and
Session 3. Rational and Radical Equations. Math 30-1 R 3. (Revisit, Review and Revive)
 Session 3 Rational and Radical Equations Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) Rational Functions Review Specific Outcome 14 Graph and analyze rational functions (limited to numerators and denominators
Session 3 Rational and Radical Equations Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) Rational Functions Review Specific Outcome 14 Graph and analyze rational functions (limited to numerators and denominators
The Straight Line. m is undefined. Use. Show that mab
 The Straight Line What is the gradient of a horizontal line? What is the equation of a horizontal line? So the equation of the x-axis is? What is the gradient of a vertical line? What is the equation of
The Straight Line What is the gradient of a horizontal line? What is the equation of a horizontal line? So the equation of the x-axis is? What is the gradient of a vertical line? What is the equation of
M110 PreCalculus Diagnostic Test
 M0 PreCalculus Diagnostic Test Success in a first year Calculus class is highly dependent on your algebra skills. The following is a selfdiagnostic test to be taken by students prior to entering a Math
M0 PreCalculus Diagnostic Test Success in a first year Calculus class is highly dependent on your algebra skills. The following is a selfdiagnostic test to be taken by students prior to entering a Math
Higher Course Year /16
 Higher Course Year 11 2015/16 Main heading Outcomes MathsWatch clip number Number Surds Use surds in calculations Simplify surds Rationalise surds 157 158 Expand brackets with surds Use surds in problems
Higher Course Year 11 2015/16 Main heading Outcomes MathsWatch clip number Number Surds Use surds in calculations Simplify surds Rationalise surds 157 158 Expand brackets with surds Use surds in problems
Lines and Their Slopes
 8.2 Lines and Their Slopes Linear Equations in Two Variables In the previous chapter we studied linear equations in a single variable. The solution of such an equation is a real number. A linear equation
8.2 Lines and Their Slopes Linear Equations in Two Variables In the previous chapter we studied linear equations in a single variable. The solution of such an equation is a real number. A linear equation
Transformations of Absolute Value Functions. Compression A compression is a. function a function of the form f(x) = a 0 x - h 0 + k
 - Transformations of Absolute Value Functions TEKS FOCUS VOCABULARY Compression A compression is a TEKS (6)(C) Analze the effect on the graphs of f() = when f() is replaced b af(), f(b), f( - c), and f()
- Transformations of Absolute Value Functions TEKS FOCUS VOCABULARY Compression A compression is a TEKS (6)(C) Analze the effect on the graphs of f() = when f() is replaced b af(), f(b), f( - c), and f()
Transformations using matrices
 Transformations using matrices 6 sllabusref eferenceence Core topic: Matrices and applications In this cha 6A 6B 6C 6D 6E 6F 6G chapter Geometric transformations and matri algebra Linear transformations
Transformations using matrices 6 sllabusref eferenceence Core topic: Matrices and applications In this cha 6A 6B 6C 6D 6E 6F 6G chapter Geometric transformations and matri algebra Linear transformations
Maths Curriculum Map
 Year 7 Maths Curriculum Map Autumn Spring Summer Analysing Data: Calculating Averages Construct and Interpret Charts Number Skills: Order of operations Rounding and estimating Negative numbers Prime numbers,
Year 7 Maths Curriculum Map Autumn Spring Summer Analysing Data: Calculating Averages Construct and Interpret Charts Number Skills: Order of operations Rounding and estimating Negative numbers Prime numbers,
Course Number 432/433 Title Algebra II (A & B) H Grade # of Days 120
 Whitman-Hanson Regional High School provides all students with a high- quality education in order to develop reflective, concerned citizens and contributing members of the global community. Course Number
Whitman-Hanson Regional High School provides all students with a high- quality education in order to develop reflective, concerned citizens and contributing members of the global community. Course Number
The Sine and Cosine Functions
 Lesson -5 Lesson -5 The Sine and Cosine Functions Vocabular BIG IDEA The values of cos and sin determine functions with equations = sin and = cos whose domain is the set of all real numbers. From the eact
Lesson -5 Lesson -5 The Sine and Cosine Functions Vocabular BIG IDEA The values of cos and sin determine functions with equations = sin and = cos whose domain is the set of all real numbers. From the eact
THE INVERSE GRAPH. Finding the equation of the inverse. What is a function? LESSON
 LESSON THE INVERSE GRAPH The reflection of a graph in the line = will be the graph of its inverse. f() f () The line = is drawn as the dotted line. Imagine folding the page along the dotted line, the two
LESSON THE INVERSE GRAPH The reflection of a graph in the line = will be the graph of its inverse. f() f () The line = is drawn as the dotted line. Imagine folding the page along the dotted line, the two
(ii) Explain how the trapezium rule could be used to obtain a more accurate estimate of the area. [1]
![(ii) Explain how the trapezium rule could be used to obtain a more accurate estimate of the area. [1] (ii) Explain how the trapezium rule could be used to obtain a more accurate estimate of the area. [1]](/thumbs/82/84800654.jpg) C Integration. June 00 qu. Use the trapezium rule, with strips each of width, to estimate the area of the region bounded by the curve y = 7 +, the -ais, and the lines = and = 0. Give your answer correct
C Integration. June 00 qu. Use the trapezium rule, with strips each of width, to estimate the area of the region bounded by the curve y = 7 +, the -ais, and the lines = and = 0. Give your answer correct
Algebra 2 Semester 2 Final Exam Study Outline Semester 2 Final Exam Study Tips and Information
 Algebra 2 Semester 2 Final Exam Study Outline 2013 Semester 2 Final Exam Study Tips and Information The final exam is CUMULATIVE and will include all concepts taught from Chapter 1 through Chapter 13.
Algebra 2 Semester 2 Final Exam Study Outline 2013 Semester 2 Final Exam Study Tips and Information The final exam is CUMULATIVE and will include all concepts taught from Chapter 1 through Chapter 13.
What is the relationship between the real roots of a polynomial equation and the x-intercepts of the corresponding polynomial function?
 3.3 Characteristics of Polnomial Functions in Factored Form INVESTIGATE the Math The graphs of the functions f () 5 1 and g() 5 1 are shown.? GOAL Determine the equation of a polnomial function that describes
3.3 Characteristics of Polnomial Functions in Factored Form INVESTIGATE the Math The graphs of the functions f () 5 1 and g() 5 1 are shown.? GOAL Determine the equation of a polnomial function that describes
FURTHER MATHS. WELCOME TO A Level FURTHER MATHEMATICS AT CARDINAL NEWMAN CATHOLIC SCHOOL
 FURTHER MATHS WELCOME TO A Level FURTHER MATHEMATICS AT CARDINAL NEWMAN CATHOLIC SCHOOL This two-year Edexcel Pearson syllabus is intended for high ability candidates who have achieved, or are likely to
FURTHER MATHS WELCOME TO A Level FURTHER MATHEMATICS AT CARDINAL NEWMAN CATHOLIC SCHOOL This two-year Edexcel Pearson syllabus is intended for high ability candidates who have achieved, or are likely to
Four Ways to Represent a Function: We can describe a specific function in the following four ways: * verbally (by a description in words);
 MA19, Activit 23: What is a Function? (Section 3.1, pp. 214-22) Date: Toda s Goal: Assignments: Perhaps the most useful mathematical idea for modeling the real world is the concept of a function. We eplore
MA19, Activit 23: What is a Function? (Section 3.1, pp. 214-22) Date: Toda s Goal: Assignments: Perhaps the most useful mathematical idea for modeling the real world is the concept of a function. We eplore
Mathematics GCSE 9-1 Curriculum Planner (3 Year Course)
 Mathematics GCSE 9-1 Curriculum Planner (3 Year Course) Year 9 Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 HT 9 1 0 Chapter 1 Calculations Chapter 2 Expressions Ch 1, 2 Test Chapter 3 Angles, polygons Chapter 3 11 12 13 14 15
Mathematics GCSE 9-1 Curriculum Planner (3 Year Course) Year 9 Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 HT 9 1 0 Chapter 1 Calculations Chapter 2 Expressions Ch 1, 2 Test Chapter 3 Angles, polygons Chapter 3 11 12 13 14 15
Cecil Jones Academy Mathematics Fundamentals
 Year 10 Fundamentals Core Knowledge Unit 1 Unit 2 Estimate with powers and roots Calculate with powers and roots Explore the impact of rounding Investigate similar triangles Explore trigonometry in right-angled
Year 10 Fundamentals Core Knowledge Unit 1 Unit 2 Estimate with powers and roots Calculate with powers and roots Explore the impact of rounding Investigate similar triangles Explore trigonometry in right-angled
Chislehurst and Sidcup Grammar School Mathematics Department Year 9 Programme of Study
 Chislehurst and Sidcup Grammar School Mathematics Department Year 9 Programme of Study Timings Topics Autumn Term - 1 st half (7 weeks - 21 lessons) 1. Algebra 1: Expressions, Formulae, Equations and Inequalities
Chislehurst and Sidcup Grammar School Mathematics Department Year 9 Programme of Study Timings Topics Autumn Term - 1 st half (7 weeks - 21 lessons) 1. Algebra 1: Expressions, Formulae, Equations and Inequalities
Now each of you should be familiar with inverses from your previous mathematical
 5. Inverse Functions TOOTLIFTST: Knowledge of derivatives of basic functions, including power, eponential, logarithmic, trigonometric, and inverse trigonometric functions. Now each of you should be familiar
5. Inverse Functions TOOTLIFTST: Knowledge of derivatives of basic functions, including power, eponential, logarithmic, trigonometric, and inverse trigonometric functions. Now each of you should be familiar
( ) 2. Integration. 1. Calculate (a) x2 (x 5) dx (b) y = x 2 6x. 2. Calculate the shaded area in the diagram opposite.
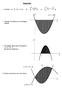 Integration 1. Calculate (a) ( 5) d (b) 4 + 3 1 d (c) ( ) + d 1 = 6. Calculate the shaded area in the diagram opposite. 3. The diagram shows part of the graph of = 7 10. 5 = + 0 4. Find the area between
Integration 1. Calculate (a) ( 5) d (b) 4 + 3 1 d (c) ( ) + d 1 = 6. Calculate the shaded area in the diagram opposite. 3. The diagram shows part of the graph of = 7 10. 5 = + 0 4. Find the area between
