Lecture 3.4 Differential Equation Based Schemes
|
|
|
- Philippa Perkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 3.4 Differential Equation Based Schemes 1
2 Differential Equation Based Schemes As stated in the previous lecture, another important and most widel used method of structured mesh generation is based on solving partial differential equations. These techniques ma be based on an one of the following schemes depending on the characteristics of the grid generation equations. The are: Hperbolic PDE based schemes Elliptic PDE based schemes Parabolic PDE based schemes 2
3 Elliptic PDE Based Methods In this lecture, Elliptic PDE based grid generation schemes will onl be discussed. These methods are particularl useful for confined phsical domains of turbomachiner flows. The elliptic PDEs for grid generation describe the variation of the bod fitting coordinates (ξ, η, ζ ) in the interior of the phsical domain, with prescribed values or slopes at the boundar. In the computational domain, however, the phsical coordinates (,, z) are treated as the unknown variables on the grid formed b the ξ=constant, η= constant and ζ=constant lines. The are determined b numericall solving the transformed grid generation equations. 3
4 Elliptic Solvers Consider the transformation functions, which are solutions of an elliptic Dirichlet boundar value problem. The mathematical problem is given b z z z P(,, z) Q(,, z) R(,, z) (3.4.1) with fied,, on the boundaries. P, Q and R are source functions, which can be used to grid point controlling. 4
5 Laplace Solvers The condition: P=Q=R=0, results in to uniform distribution of the points. The sstem then becomes the Laplacian. The Laplacian grid generation sstem satisfies the maimum and the minimum principles, i.e. both maimum and minimum for,, occur onl at the boundar. The solutions of the Laplacian operator,,, are either harmonic, sub-harmonic or super-harmonic. Therefore the are ver smooth functions. Further, the,, have continuous derivatives of all orders. This makes the solution of the transformed governing equation accurate 5
6 Two dimensional Transformation Functions Let us consider the bod fitting coordinate transformation, of the form = (,) and = (,). Therefore, one can write, (, ) d d d d (, ) d d d d (3.4.2) Considering the reverse transformation =(, ) and =(, ), (, ) d d (, ) d d (3.4.3) Combining the above two, we have 1 J 1 (3.4.4) 6
7 Two dimensional Transformation Functions One can therefore write the two dimensional transformation functions as f f ( f, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, f) (, ) (, ) (, ) ( f f ) ( f f ) (3.4.5) Note that the Jacobian, J, represents local area scaling factor and should not become zero. J J 7
8 Etension to Three Dimensions Etending the arguments to three dimensions, one can derive the relationships between the derivatives of the Cartesian coordinates (,,z) and the curvilinear coordinates (,, ) in the form: z z z z z z 1 (3.4.6) 8
9 Elliptic Solvers in 2D P 2 Q P 2 Q P (3.4.7) Q , 9
10 Demonstration Consider a planar region, as shown in Fig , in which a structured grid has to be generated Fig Phsical domain 10
11 Generate a rectangular (ξ, η) = (0,1)(0,1) uniforml discretized, as shown in Fig , (ξ i = i*δξ, η j =Δη, Δξ, Δη are the uniform step lengths in ξ, η directions, respectivel ) plane given b Fig Uniform grid in computation domain 11
12 Algorithm Map the boundaries (from phsical to computational) as shown in Fig Fig Mapping of phsical to computational domain Due to the mapping of the phsical boundaries over the boundaries of the computation domain,, are known along the boundaries of the computational domain. 12
13 Therefore, once, are computed in the interior of the computational domain, the required grid in the phsical domain is established. To obtain, in the interior of the computational domain, solve (using the boundar values of and as boundar conditions) P 2 Q P 2 Q (3.4.8) for, over the uniforml discretized computational domain 13
14 Multipl Connected Domain The algorithm described in the earlier slides works for simpl connected domains. For multipl connected domains, for eample like annular regions shown in Fig , artificial boundaries can be introduced to convert them in to simpl connected regions. Fig Introduction of artificial boundar 14
15 Boundar Conditions on the Artificial Boundaries Dirichlet boundar conditions over the artificial boundaries in the multipl-connected regions ma lead to non-smooth grid lines as shown in Fig Fig Non smooth grid lines over artificial boundar 15
16 Periodic Boundar Conditions on Artificial Cuts However Periodic boundar conditions over artificial cuts generate smooth grid lines as shown in Fig Fig Smooth grid over artificial boundaries 16
17 Grid Lines Attraction and Repulsion In general, grid points are attracted in the conve regions and repulsive in the concave regions as shown in the Fig Fig Grid point attraction and repulsion 17
18 Eercise Problems Repeat the eercise problems of Lecture 3.2 using PDE method. Generate uniform grid in square and cubical, rectangular and cubical region. Generate uniform grid in clindrical and spherical regions. Two-dimensional region bounded b circle of radius r = 1. Three-dimensional region bounded b sphere of radius r = 1. Annular region in 2D bounded b r = a and r = b with a < b. Annular region in 3D bounded b r = a and r = b with a < b. 18
19 Summar of Lecture 3.4 Mesh generation schemes b solving hperbolic, elliptic and parabolic partial differential equation methods are presented. The methods are eplained through eamples. END OF LECTURE
Grid and Mesh Generation. Introduction to its Concepts and Methods
 Grid and Mesh Generation Introduction to its Concepts and Methods Elements in a CFD software sstem Introduction What is a grid? The arrangement of the discrete points throughout the flow field is simpl
Grid and Mesh Generation Introduction to its Concepts and Methods Elements in a CFD software sstem Introduction What is a grid? The arrangement of the discrete points throughout the flow field is simpl
Lecture 3.2 Methods for Structured Mesh Generation
 Lecture 3.2 Methods for Structured Mesh Generation 1 There are several methods to develop the structured meshes: Algebraic methods, Interpolation methods, and methods based on solving partial differential
Lecture 3.2 Methods for Structured Mesh Generation 1 There are several methods to develop the structured meshes: Algebraic methods, Interpolation methods, and methods based on solving partial differential
Module 3 Mesh Generation
 Module 3 Mesh Generation 1 Lecture 3.1 Introduction 2 Mesh Generation Strategy Mesh generation is an important pre-processing step in CFD of turbomachinery, quite analogous to the development of solid
Module 3 Mesh Generation 1 Lecture 3.1 Introduction 2 Mesh Generation Strategy Mesh generation is an important pre-processing step in CFD of turbomachinery, quite analogous to the development of solid
8.6 Three-Dimensional Cartesian Coordinate System
 SECTION 8.6 Three-Dimensional Cartesian Coordinate Sstem 69 What ou ll learn about Three-Dimensional Cartesian Coordinates Distance and Midpoint Formulas Equation of a Sphere Planes and Other Surfaces
SECTION 8.6 Three-Dimensional Cartesian Coordinate Sstem 69 What ou ll learn about Three-Dimensional Cartesian Coordinates Distance and Midpoint Formulas Equation of a Sphere Planes and Other Surfaces
Digital Geometry Processing Parameterization I
 Problem Definition Given a surface (mesh) S in R 3 and a domain find a bective F: S Typical Domains Cutting to a Disk disk = genus zero + boundary sphere = closed genus zero Creates artificial boundary
Problem Definition Given a surface (mesh) S in R 3 and a domain find a bective F: S Typical Domains Cutting to a Disk disk = genus zero + boundary sphere = closed genus zero Creates artificial boundary
Two Dimensional Viewing
 Two Dimensional Viewing Dr. S.M. Malaek Assistant: M. Younesi Two Dimensional Viewing Basic Interactive Programming Basic Interactive Programming User controls contents, structure, and appearance of objects
Two Dimensional Viewing Dr. S.M. Malaek Assistant: M. Younesi Two Dimensional Viewing Basic Interactive Programming Basic Interactive Programming User controls contents, structure, and appearance of objects
An introduction to mesh generation Part IV : elliptic meshing
 Elliptic An introduction to mesh generation Part IV : elliptic meshing Department of Civil Engineering, Université catholique de Louvain, Belgium Elliptic Curvilinear Meshes Basic concept A curvilinear
Elliptic An introduction to mesh generation Part IV : elliptic meshing Department of Civil Engineering, Université catholique de Louvain, Belgium Elliptic Curvilinear Meshes Basic concept A curvilinear
computational field which is always rectangular by construction.
 I. INTRODUCTION The numerical solution of partial differential equations requires some discretization of the field into a collection of points or elemental volumes (cells). The differential equations are
I. INTRODUCTION The numerical solution of partial differential equations requires some discretization of the field into a collection of points or elemental volumes (cells). The differential equations are
13.4 TANGENT PLANES and DIFFERENTIALS
 3.4 Tangent Planes and Differentials Contemporar Calculus 3.4 TANGENT PLANES and DIFFERENTIALS In Section.8 we were able to use the derivative f ' of a function = f() of one variable to find the equation
3.4 Tangent Planes and Differentials Contemporar Calculus 3.4 TANGENT PLANES and DIFFERENTIALS In Section.8 we were able to use the derivative f ' of a function = f() of one variable to find the equation
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems
 1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
Application of a Coordinate Transformation and Discretization Method for Computational Fluid Dynamics
 Application of a Coordinate Transformation and Discretization Method for Computational Fluid Dnamics 1 Douglas F. Hunsaker Utah State Universit An overview of the computational methods implemented in a
Application of a Coordinate Transformation and Discretization Method for Computational Fluid Dnamics 1 Douglas F. Hunsaker Utah State Universit An overview of the computational methods implemented in a
NUMERICAL PERFORMANCE OF COMPACT FOURTH ORDER FORMULATION OF THE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS
 Published in : Communications in Numerical Methods in Engineering (008 Commun.Numer.Meth.Engng. 008; Vol : pp 003-019 NUMERICAL PERFORMANCE OF COMPACT FOURTH ORDER FORMULATION OF THE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS
Published in : Communications in Numerical Methods in Engineering (008 Commun.Numer.Meth.Engng. 008; Vol : pp 003-019 NUMERICAL PERFORMANCE OF COMPACT FOURTH ORDER FORMULATION OF THE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS
GRAPHICS OUTPUT PRIMITIVES
 CHAPTER 3 GRAPHICS OUTPUT PRIMITIVES LINE DRAWING ALGORITHMS DDA Line Algorithm Bresenham Line Algorithm Midpoint Circle Algorithm Midpoint Ellipse Algorithm CG - Chapter-3 LINE DRAWING Line drawing is
CHAPTER 3 GRAPHICS OUTPUT PRIMITIVES LINE DRAWING ALGORITHMS DDA Line Algorithm Bresenham Line Algorithm Midpoint Circle Algorithm Midpoint Ellipse Algorithm CG - Chapter-3 LINE DRAWING Line drawing is
3.5 Rational Functions
 0 Chapter Polnomial and Rational Functions Rational Functions For a rational function, find the domain and graph the function, identifing all of the asmptotes Solve applied problems involving rational
0 Chapter Polnomial and Rational Functions Rational Functions For a rational function, find the domain and graph the function, identifing all of the asmptotes Solve applied problems involving rational
ACTIVITY 9 Continued Lesson 9-2
 Continued Lesson 9- Lesson 9- PLAN Pacing: 1 class period Chunking the Lesson Eample A Eample B #1 #3 Lesson Practice M Notes Learning Targets: Graph on a coordinate plane the solutions of a linear inequalit
Continued Lesson 9- Lesson 9- PLAN Pacing: 1 class period Chunking the Lesson Eample A Eample B #1 #3 Lesson Practice M Notes Learning Targets: Graph on a coordinate plane the solutions of a linear inequalit
11.6 Start Thinking Warm Up Cumulative Review Warm Up
 11.6 Start Thinking The diagrams show a cube and a pyramid. Each has a square base with an area of 25 square inches and a height of 5 inches. How do the volumes of the two figures compare? Eplain your
11.6 Start Thinking The diagrams show a cube and a pyramid. Each has a square base with an area of 25 square inches and a height of 5 inches. How do the volumes of the two figures compare? Eplain your
Quad-Tree Based Geometric-Adapted Cartesian Grid Generation
 Quad-Tree Based Geometric-Adapted Cartesian Grid Generation EMRE KARA1, AHMET ĐHSAN KUTLAR1, MEHMET HALUK AKSEL 1Department of Mechanical Engineering Universit of Gaziantep 7310 Gaziantep TURKEY Mechanical
Quad-Tree Based Geometric-Adapted Cartesian Grid Generation EMRE KARA1, AHMET ĐHSAN KUTLAR1, MEHMET HALUK AKSEL 1Department of Mechanical Engineering Universit of Gaziantep 7310 Gaziantep TURKEY Mechanical
A numerical grid and grid less (Mesh less) techniques for the solution of 2D Laplace equation
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2014, 5(1):150-155 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC A numerical grid and grid less (Mesh less) techniques for
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2014, 5(1):150-155 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC A numerical grid and grid less (Mesh less) techniques for
Computer Graphics. Modelling in 2D. 2D primitives. Lines and Polylines. OpenGL polygon primitives. Special polygons
 Computer Graphics Modelling in D Lecture School of EECS Queen Mar, Universit of London D primitives Digital line algorithms Digital circle algorithms Polgon filling CG - p.hao@qmul.ac.uk D primitives Line
Computer Graphics Modelling in D Lecture School of EECS Queen Mar, Universit of London D primitives Digital line algorithms Digital circle algorithms Polgon filling CG - p.hao@qmul.ac.uk D primitives Line
A SCATTERED DATA INTERPOLANT FOR THE SOLUTION OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL PDES
 European Conference on Computational Fluid Dnamics ECCOMAS CFD 26 P. Wesseling, E. Oñate and J. Périau (Eds) c TU Delft, The Netherlands, 26 A SCATTERED DATA INTERPOLANT FOR THE SOLUTION OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL
European Conference on Computational Fluid Dnamics ECCOMAS CFD 26 P. Wesseling, E. Oñate and J. Périau (Eds) c TU Delft, The Netherlands, 26 A SCATTERED DATA INTERPOLANT FOR THE SOLUTION OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL
Chapter 4 Section 1 Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables
 Chapter 4 Section 1 Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Epressions of the tpe + 2 8 and 3 > 6 are called linear inequalities in two variables. A solution of a linear inequalit in two variables
Chapter 4 Section 1 Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Epressions of the tpe + 2 8 and 3 > 6 are called linear inequalities in two variables. A solution of a linear inequalit in two variables
Functions: The domain and range
 Mathematics Learning Centre Functions: The domain and range Jackie Nicholas Jacquie Hargreaves Janet Hunter c 6 Universit of Sdne Mathematics Learning Centre, Universit of Sdne Functions In these notes
Mathematics Learning Centre Functions: The domain and range Jackie Nicholas Jacquie Hargreaves Janet Hunter c 6 Universit of Sdne Mathematics Learning Centre, Universit of Sdne Functions In these notes
7.5. Systems of Inequalities. The Graph of an Inequality. What you should learn. Why you should learn it
 0_0705.qd /5/05 9:5 AM Page 5 Section 7.5 7.5 Sstems of Inequalities 5 Sstems of Inequalities What ou should learn Sketch the graphs of inequalities in two variables. Solve sstems of inequalities. Use
0_0705.qd /5/05 9:5 AM Page 5 Section 7.5 7.5 Sstems of Inequalities 5 Sstems of Inequalities What ou should learn Sketch the graphs of inequalities in two variables. Solve sstems of inequalities. Use
Parameterization of Meshes
 2-Manifold Parameterization of Meshes What makes for a smooth manifold? locally looks like Euclidian space collection of charts mutually compatible on their overlaps form an atlas Parameterizations are
2-Manifold Parameterization of Meshes What makes for a smooth manifold? locally looks like Euclidian space collection of charts mutually compatible on their overlaps form an atlas Parameterizations are
Essential Question How many turning points can the graph of a polynomial function have?
 .8 Analzing Graphs of Polnomial Functions Essential Question How man turning points can the graph of a polnomial function have? A turning point of the graph of a polnomial function is a point on the graph
.8 Analzing Graphs of Polnomial Functions Essential Question How man turning points can the graph of a polnomial function have? A turning point of the graph of a polnomial function is a point on the graph
Modeling with CMU Mini-FEA Program
 Modeling with CMU Mini-FEA Program Introduction Finite element analsis (FEA) allows ou analze the stresses and displacements in a bod when forces are applied. FEA determines the stresses and displacements
Modeling with CMU Mini-FEA Program Introduction Finite element analsis (FEA) allows ou analze the stresses and displacements in a bod when forces are applied. FEA determines the stresses and displacements
Boundary/Contour Fitted Grid Generation for Effective Visualizations in a Digital Library of Mathematical Functions
 Boundary/Contour Fitted Grid Generation for Effective Visualizations in a Digital Library of Mathematical Functions Bonita Saunders Qiming Wang National Institute of Standards and Technology Bureau Drive
Boundary/Contour Fitted Grid Generation for Effective Visualizations in a Digital Library of Mathematical Functions Bonita Saunders Qiming Wang National Institute of Standards and Technology Bureau Drive
Multibody Motion Estimation and Segmentation from Multiple Central Panoramic Views
 Multibod Motion Estimation and Segmentation from Multiple Central Panoramic Views Omid Shakernia René Vidal Shankar Sastr Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences Universit of California
Multibod Motion Estimation and Segmentation from Multiple Central Panoramic Views Omid Shakernia René Vidal Shankar Sastr Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences Universit of California
Assignment 4: Mesh Parametrization
 CSCI-GA.3033-018 - Geometric Modeling Assignment 4: Mesh Parametrization In this exercise you will Familiarize yourself with vector field design on surfaces. Create scalar fields whose gradients align
CSCI-GA.3033-018 - Geometric Modeling Assignment 4: Mesh Parametrization In this exercise you will Familiarize yourself with vector field design on surfaces. Create scalar fields whose gradients align
2.8 Distance and Midpoint Formulas; Circles
 Section.8 Distance and Midpoint Formulas; Circles 9 Eercises 89 90 are based on the following cartoon. B.C. b permission of Johnn Hart and Creators Sndicate, Inc. 89. Assuming that there is no such thing
Section.8 Distance and Midpoint Formulas; Circles 9 Eercises 89 90 are based on the following cartoon. B.C. b permission of Johnn Hart and Creators Sndicate, Inc. 89. Assuming that there is no such thing
SOLVING PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS ON POINT CLOUDS
 SOLVING PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS ON POINT CLOUDS JIAN LIANG AND HONGKAI ZHAO Abstract. In this paper we present a general framework for solving partial differential equations on manifolds represented
SOLVING PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS ON POINT CLOUDS JIAN LIANG AND HONGKAI ZHAO Abstract. In this paper we present a general framework for solving partial differential equations on manifolds represented
Section 9.3: Functions and their Graphs
 Section 9.: Functions and their Graphs Graphs provide a wa of displaing, interpreting, and analzing data in a visual format. In man problems, we will consider two variables. Therefore, we will need to
Section 9.: Functions and their Graphs Graphs provide a wa of displaing, interpreting, and analzing data in a visual format. In man problems, we will consider two variables. Therefore, we will need to
Journal of Engineering Research and Studies E-ISSN
 Journal of Engineering Research and Studies E-ISS 0976-79 Research Article SPECTRAL SOLUTIO OF STEADY STATE CODUCTIO I ARBITRARY QUADRILATERAL DOMAIS Alavani Chitra R 1*, Joshi Pallavi A 1, S Pavitran
Journal of Engineering Research and Studies E-ISS 0976-79 Research Article SPECTRAL SOLUTIO OF STEADY STATE CODUCTIO I ARBITRARY QUADRILATERAL DOMAIS Alavani Chitra R 1*, Joshi Pallavi A 1, S Pavitran
QUIZ 4 (CHAPTER 17) SOLUTIONS MATH 252 FALL 2008 KUNIYUKI SCORED OUT OF 125 POINTS MULTIPLIED BY % POSSIBLE
 QUIZ 4 (CHAPTER 17) SOLUTIONS MATH 5 FALL 8 KUNIYUKI SCORED OUT OF 15 POINTS MULTIPLIED BY.84 15% POSSIBLE 1) Reverse the order of integration, and evaluate the resulting double integral: 16 y dx dy. Give
QUIZ 4 (CHAPTER 17) SOLUTIONS MATH 5 FALL 8 KUNIYUKI SCORED OUT OF 15 POINTS MULTIPLIED BY.84 15% POSSIBLE 1) Reverse the order of integration, and evaluate the resulting double integral: 16 y dx dy. Give
Understanding Quadrilaterals
 12 Understanding Quadrilaterals introduction In previous classes, you have learnt about curves, open and closed curves, polygons, quadrilaterals etc. In this chapter, we shall review, revise and strengthen
12 Understanding Quadrilaterals introduction In previous classes, you have learnt about curves, open and closed curves, polygons, quadrilaterals etc. In this chapter, we shall review, revise and strengthen
Graphing Systems of Linear Inequalities in Two Variables
 5.5 Graphing Sstems of Linear Inequalities in Two Variables 5.5 OBJECTIVES 1. Graph a sstem of linear inequalities in two variables 2. Solve an application of a sstem of linear inequalities In Section
5.5 Graphing Sstems of Linear Inequalities in Two Variables 5.5 OBJECTIVES 1. Graph a sstem of linear inequalities in two variables 2. Solve an application of a sstem of linear inequalities In Section
Further Differentiation
 Worksheet 39 Further Differentiation Section Discriminant Recall that the epression a + b + c is called a quadratic, or a polnomial of degree The graph of a quadratic is called a parabola, and looks like
Worksheet 39 Further Differentiation Section Discriminant Recall that the epression a + b + c is called a quadratic, or a polnomial of degree The graph of a quadratic is called a parabola, and looks like
AP CALCULUS BC PACKET 2 FOR UNIT 4 SECTIONS 6.1 TO 6.3 PREWORK FOR UNIT 4 PT 2 HEIGHT UNDER A CURVE
 AP CALCULUS BC PACKET FOR UNIT 4 SECTIONS 6. TO 6.3 PREWORK FOR UNIT 4 PT HEIGHT UNDER A CURVE Find an expression for the height of an vertical segment that can be drawn into the shaded region... = x =
AP CALCULUS BC PACKET FOR UNIT 4 SECTIONS 6. TO 6.3 PREWORK FOR UNIT 4 PT HEIGHT UNDER A CURVE Find an expression for the height of an vertical segment that can be drawn into the shaded region... = x =
COMPARISON BETWEEN ALGEBRAIC GRID AND ELLIPTIC GRID OVER AN AIRFOIL
 COMPARISON BETWEEN ALGEBRAIC GRID AND ELLIPTIC GRID OVER AN AIRFOIL Latha S 1, Gayathri R 2 ABSTRACT 1 Student, 2 Faculty, Aerospace Engineering Karunya University,(India) This project work gives a platform
COMPARISON BETWEEN ALGEBRAIC GRID AND ELLIPTIC GRID OVER AN AIRFOIL Latha S 1, Gayathri R 2 ABSTRACT 1 Student, 2 Faculty, Aerospace Engineering Karunya University,(India) This project work gives a platform
2.3 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree with Modeling
 SECTION 2.3 Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree with Modeling 185 2.3 Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree with Modeling What ou ll learn about Graphs of Polnomial Functions End Behavior of Polnomial
SECTION 2.3 Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree with Modeling 185 2.3 Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree with Modeling What ou ll learn about Graphs of Polnomial Functions End Behavior of Polnomial
5-8. Systems of Linear Inequalities. Vocabulary. Lesson. Mental Math
 Lesson 5-8 Systems of Linear Inequalities Vocabulary feasible set, feasible region BIG IDEA The solution to a system of linear inequalities in two variables is either the empty set, the interior of a polygon,
Lesson 5-8 Systems of Linear Inequalities Vocabulary feasible set, feasible region BIG IDEA The solution to a system of linear inequalities in two variables is either the empty set, the interior of a polygon,
Graphics Output Primitives
 Important Graphics Output Primitives Graphics Output Primitives in 2D polgons, circles, ellipses & other curves piel arra operations in 3D triangles & other polgons Werner Purgathofer / Computergraphik
Important Graphics Output Primitives Graphics Output Primitives in 2D polgons, circles, ellipses & other curves piel arra operations in 3D triangles & other polgons Werner Purgathofer / Computergraphik
Optimization Methods: Optimization using Calculus-Stationary Points 1. Module - 2 Lecture Notes 1
 Optimization Methods: Optimization using Calculus-Stationary Points 1 Module - Lecture Notes 1 Stationary points: Functions of Single and Two Variables Introduction In this session, stationary points of
Optimization Methods: Optimization using Calculus-Stationary Points 1 Module - Lecture Notes 1 Stationary points: Functions of Single and Two Variables Introduction In this session, stationary points of
Answers Investigation 2
 Answers Investigation Applications 1. a. I = 1n + 150 b. E = 50 + 4.5n c. +675; if you substitute 100 T-shirts into the income equation, you will get 1(100) + 150 = 1,50 in income, and if you substitute
Answers Investigation Applications 1. a. I = 1n + 150 b. E = 50 + 4.5n c. +675; if you substitute 100 T-shirts into the income equation, you will get 1(100) + 150 = 1,50 in income, and if you substitute
Lesson 5.3 Exercises, pages
 Lesson 5.3 Eercises, pages 37 3 A. Determine whether each ordered pair is a solution of the quadratic inequalit: 3 - a) (-3, ) b) (, 5) Substitute each ordered pair in» 3. L.S. ; R.S.: 3( 3) 3 L.S. 5;
Lesson 5.3 Eercises, pages 37 3 A. Determine whether each ordered pair is a solution of the quadratic inequalit: 3 - a) (-3, ) b) (, 5) Substitute each ordered pair in» 3. L.S. ; R.S.: 3( 3) 3 L.S. 5;
Parameterization of triangular meshes
 Parameterization of triangular meshes Michael S. Floater November 10, 2009 Triangular meshes are often used to represent surfaces, at least initially, one reason being that meshes are relatively easy to
Parameterization of triangular meshes Michael S. Floater November 10, 2009 Triangular meshes are often used to represent surfaces, at least initially, one reason being that meshes are relatively easy to
2.3. Horizontal and Vertical Translations of Functions. Investigate
 .3 Horizontal and Vertical Translations of Functions When a video game developer is designing a game, she might have several objects displaed on the computer screen that move from one place to another
.3 Horizontal and Vertical Translations of Functions When a video game developer is designing a game, she might have several objects displaed on the computer screen that move from one place to another
GENERATION OF STRUCTURED BLOCK BOUNDARY GRIDS
 Congreso de Métodos Numéricos en Ingeniería 2005 Granada, 4 a 7 de julio, 2005 c SEMNI, España, 2005 GENERATION OF STRUCTURED BLOCK BOUNDARY GRIDS Eça L. 1, Hoekstra M. 2 and Windt J. 2 1: Mechanical Engineering
Congreso de Métodos Numéricos en Ingeniería 2005 Granada, 4 a 7 de julio, 2005 c SEMNI, España, 2005 GENERATION OF STRUCTURED BLOCK BOUNDARY GRIDS Eça L. 1, Hoekstra M. 2 and Windt J. 2 1: Mechanical Engineering
Graphs, Linear Equations, and Functions
 Graphs, Linear Equations, and Functions. The Rectangular R. Coordinate Fractions Sstem bjectives. Interpret a line graph.. Plot ordered pairs.. Find ordered pairs that satisf a given equation. 4. Graph
Graphs, Linear Equations, and Functions. The Rectangular R. Coordinate Fractions Sstem bjectives. Interpret a line graph.. Plot ordered pairs.. Find ordered pairs that satisf a given equation. 4. Graph
AN ADAPTIVE MESH REDISTRIBUTION ALGORITHM FOR CONVECTION-DOMINATED PROBLEMS. Zheng-Ru Zhang and Tao Tang
 COMMUNICATIONS ON Website: http://aimsciences.org PURE AND APPLIED ANALYSIS Volume, Number 3, september pp. 34 357 AN ADAPTIVE MESH REDISTRIBUTION ALGORITHM FOR CONVECTION-DOMINATED PROBLEMS Zheng-Ru Zhang
COMMUNICATIONS ON Website: http://aimsciences.org PURE AND APPLIED ANALYSIS Volume, Number 3, september pp. 34 357 AN ADAPTIVE MESH REDISTRIBUTION ALGORITHM FOR CONVECTION-DOMINATED PROBLEMS Zheng-Ru Zhang
Appendix F: Systems of Inequalities
 A0 Appendi F Sstems of Inequalities Appendi F: Sstems of Inequalities F. Solving Sstems of Inequalities The Graph of an Inequalit The statements < and are inequalities in two variables. An ordered pair
A0 Appendi F Sstems of Inequalities Appendi F: Sstems of Inequalities F. Solving Sstems of Inequalities The Graph of an Inequalit The statements < and are inequalities in two variables. An ordered pair
Derivatives 3: The Derivative as a Function
 Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function 77 Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function Model : Graph of a Function 9 8 7 6 5 g() - - - 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 - - -5-6 -7 Construct Your Understanding
Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function 77 Derivatives : The Derivative as a Function Model : Graph of a Function 9 8 7 6 5 g() - - - 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 - - -5-6 -7 Construct Your Understanding
Reteaching Golden Ratio
 Name Date Class Golden Ratio INV 11 You have investigated fractals. Now ou will investigate the golden ratio. The Golden Ratio in Line Segments The golden ratio is the irrational number 1 5. c On the line
Name Date Class Golden Ratio INV 11 You have investigated fractals. Now ou will investigate the golden ratio. The Golden Ratio in Line Segments The golden ratio is the irrational number 1 5. c On the line
Here are some guidelines for solving a linear programming problem in two variables in which an objective function is to be maximized or minimized.
 Appendi F. Linear Programming F F. Linear Programming Linear Programming: A Graphical Approach Man applications in business and economics involve a process called optimization, in which ou are asked to
Appendi F. Linear Programming F F. Linear Programming Linear Programming: A Graphical Approach Man applications in business and economics involve a process called optimization, in which ou are asked to
Math 2130 Practice Problems Sec Name. Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate.
 Math 10 Practice Problems Sec 1.-1. Name Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate. 1) 5 5 - x dy dx -5 0 A) 5 B) C) 15 D) 5 ) 0 0-8 - 6 - x (8 + ln 9) A) 1 1 + x
Math 10 Practice Problems Sec 1.-1. Name Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate. 1) 5 5 - x dy dx -5 0 A) 5 B) C) 15 D) 5 ) 0 0-8 - 6 - x (8 + ln 9) A) 1 1 + x
Chapter 3. Selected advancements in finite element method
 Chapter 3. elected advancements in finite element method Learning outcomes After working through the material in this chapter ou should be able to: 1. Understand the idea behind isoparametric elements
Chapter 3. elected advancements in finite element method Learning outcomes After working through the material in this chapter ou should be able to: 1. Understand the idea behind isoparametric elements
Lesson 2.1 Exercises, pages 90 96
 Lesson.1 Eercises, pages 9 96 A. a) Complete the table of values. 1 1 1 1 1. 1 b) For each function in part a, sketch its graph then state its domain and range. For : the domain is ; and the range is.
Lesson.1 Eercises, pages 9 96 A. a) Complete the table of values. 1 1 1 1 1. 1 b) For each function in part a, sketch its graph then state its domain and range. For : the domain is ; and the range is.
9. f(x) = x f(x) = x g(x) = 2x g(x) = 5 2x. 13. h(x) = 1 3x. 14. h(x) = 2x f(x) = x x. 16.
 Section 4.2 Absolute Value 367 4.2 Eercises For each of the functions in Eercises 1-8, as in Eamples 7 and 8 in the narrative, mark the critical value on a number line, then mark the sign of the epression
Section 4.2 Absolute Value 367 4.2 Eercises For each of the functions in Eercises 1-8, as in Eamples 7 and 8 in the narrative, mark the critical value on a number line, then mark the sign of the epression
4.3 Maximum and Minimum Values of a Function
 MA: Prepared b Asst.Prof.Dr. Archara Pacheenburawana 83 4.3 Maimum and Minimum Values of a Function Some of the most important applications of differential calculus are optimization problems, in which
MA: Prepared b Asst.Prof.Dr. Archara Pacheenburawana 83 4.3 Maimum and Minimum Values of a Function Some of the most important applications of differential calculus are optimization problems, in which
Matrix Representations
 CONDENSED LESSON 6. Matri Representations In this lesson, ou Represent closed sstems with transition diagrams and transition matrices Use matrices to organize information Sandra works at a da-care center.
CONDENSED LESSON 6. Matri Representations In this lesson, ou Represent closed sstems with transition diagrams and transition matrices Use matrices to organize information Sandra works at a da-care center.
Section 4.4 Concavity and Points of Inflection
 Section 4.4 Concavit and Points of Inflection In Chapter 3, ou saw that the second derivative of a function has applications in problems involving velocit and acceleration or in general rates-of-change
Section 4.4 Concavit and Points of Inflection In Chapter 3, ou saw that the second derivative of a function has applications in problems involving velocit and acceleration or in general rates-of-change
Polar Functions Polar coordinates
 548 Chapter 1 Parametric, Vector, and Polar Functions 1. What ou ll learn about Polar Coordinates Polar Curves Slopes of Polar Curves Areas Enclosed b Polar Curves A Small Polar Galler... and wh Polar
548 Chapter 1 Parametric, Vector, and Polar Functions 1. What ou ll learn about Polar Coordinates Polar Curves Slopes of Polar Curves Areas Enclosed b Polar Curves A Small Polar Galler... and wh Polar
Fast marching methods
 1 Fast marching methods Lecture 3 Alexander & Michael Bronstein tosca.cs.technion.ac.il/book Numerical geometry of non-rigid shapes Stanford University, Winter 2009 Metric discretization 2 Approach I:
1 Fast marching methods Lecture 3 Alexander & Michael Bronstein tosca.cs.technion.ac.il/book Numerical geometry of non-rigid shapes Stanford University, Winter 2009 Metric discretization 2 Approach I:
MODELING MIXED BOUNDARY PROBLEMS WITH THE COMPLEX VARIABLE BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHOD (CVBEM) USING MATLAB AND MATHEMATICA
 A. N. Johnson et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 3, No. 3 (2015) 269 278 MODELING MIXED BOUNDARY PROBLEMS WITH THE COMPLEX VARIABLE BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHOD (CVBEM) USING MATLAB AND MATHEMATICA
A. N. Johnson et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 3, No. 3 (2015) 269 278 MODELING MIXED BOUNDARY PROBLEMS WITH THE COMPLEX VARIABLE BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHOD (CVBEM) USING MATLAB AND MATHEMATICA
1.2 Visualizing and Graphing Data
 6360_ch01pp001-075.qd 10/16/08 4:8 PM Page 1 1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Functions and Graphs 9. Volume of a Cone The volume V of a cone is given b V = 1 3 pr h, where r is its radius and h is its height.
6360_ch01pp001-075.qd 10/16/08 4:8 PM Page 1 1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Functions and Graphs 9. Volume of a Cone The volume V of a cone is given b V = 1 3 pr h, where r is its radius and h is its height.
Glossary alternate interior angles absolute value function Example alternate exterior angles Example angle of rotation Example
 Glossar A absolute value function An absolute value function is a function that can be written in the form, where is an number or epression. alternate eterior angles alternate interior angles Alternate
Glossar A absolute value function An absolute value function is a function that can be written in the form, where is an number or epression. alternate eterior angles alternate interior angles Alternate
C URVES AND V ECTORS
 96-ch- SB5-Ostebee June 6, 9:57 C H A P T E R O U T L I N E. Three-Dimensional Space. Curves and Parametric Equations. Polar Coordinates and Polar Curves.4 Vectors.5 Vector-Valued Functions, Derivatives,
96-ch- SB5-Ostebee June 6, 9:57 C H A P T E R O U T L I N E. Three-Dimensional Space. Curves and Parametric Equations. Polar Coordinates and Polar Curves.4 Vectors.5 Vector-Valued Functions, Derivatives,
Chapter 13. Boundary Value Problems for Partial Differential Equations* Linz 2002/ page
 Chapter 13 Boundary Value Problems for Partial Differential Equations* E lliptic equations constitute the third category of partial differential equations. As a prototype, we take the Poisson equation
Chapter 13 Boundary Value Problems for Partial Differential Equations* E lliptic equations constitute the third category of partial differential equations. As a prototype, we take the Poisson equation
Section 4.2 Graphing Lines
 Section. Graphing Lines Objectives In this section, ou will learn to: To successfull complete this section, ou need to understand: Identif collinear points. The order of operations (1.) Graph the line
Section. Graphing Lines Objectives In this section, ou will learn to: To successfull complete this section, ou need to understand: Identif collinear points. The order of operations (1.) Graph the line
Database Design 1DL400. Assignment 2:2
 Uppsala Universit Department of Information Technolog Kjell Orsborn Assignment : - Database Design II Database Design DL00 Assignment : A Scientific Database for Mesh-Based Data. Goals This eercise consists
Uppsala Universit Department of Information Technolog Kjell Orsborn Assignment : - Database Design II Database Design DL00 Assignment : A Scientific Database for Mesh-Based Data. Goals This eercise consists
Excel based finite difference modeling of ground water flow
 Journal of Himalaan Eart Sciences 39(006) 49-53 Ecel based finite difference modeling of ground water flow M. Gulraiz Akter 1, Zulfiqar Amad 1 and Kalid Amin Kan 1 Department of Eart Sciences, Quaid-i-Azam
Journal of Himalaan Eart Sciences 39(006) 49-53 Ecel based finite difference modeling of ground water flow M. Gulraiz Akter 1, Zulfiqar Amad 1 and Kalid Amin Kan 1 Department of Eart Sciences, Quaid-i-Azam
2. Give an example of a non-constant function f(x, y) such that the average value of f over is 0.
 Midterm 3 Review Short Answer 2. Give an example of a non-constant function f(x, y) such that the average value of f over is 0. 3. Compute the Riemann sum for the double integral where for the given grid
Midterm 3 Review Short Answer 2. Give an example of a non-constant function f(x, y) such that the average value of f over is 0. 3. Compute the Riemann sum for the double integral where for the given grid
LESSON 5.3 SYSTEMS OF INEQUALITIES
 LESSON 5. SYSTEMS OF INEQUALITIES LESSON 5. SYSTEMS OF INEQUALITIES OVERVIEW Here s what ou ll learn in this lesson: Solving Linear Sstems a. Solving sstems of linear inequalities b graphing As a conscientious
LESSON 5. SYSTEMS OF INEQUALITIES LESSON 5. SYSTEMS OF INEQUALITIES OVERVIEW Here s what ou ll learn in this lesson: Solving Linear Sstems a. Solving sstems of linear inequalities b graphing As a conscientious
Chap 7, 2009 Spring Yeong Gil Shin
 Three-Dimensional i Viewingi Chap 7, 29 Spring Yeong Gil Shin Viewing i Pipeline H d fi i d? How to define a window? How to project onto the window? Rendering "Create a picture (in a snthetic camera) Specification
Three-Dimensional i Viewingi Chap 7, 29 Spring Yeong Gil Shin Viewing i Pipeline H d fi i d? How to define a window? How to project onto the window? Rendering "Create a picture (in a snthetic camera) Specification
5.2 Graphing Polynomial Functions
 Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Polnomial Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F.IF.7c Graph polnomial functions, identifing zeros when suitable factorizations are available, and showing
Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Polnomial Functions Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F.IF.7c Graph polnomial functions, identifing zeros when suitable factorizations are available, and showing
3.6 Graphing Piecewise-Defined Functions and Shifting and Reflecting Graphs of Functions
 76 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Find the equation of each line. Write the equation in the form = a, = b, or = m + b. For Eercises through 7, write the equation in the form f = m + b.. Through (, 6) and
76 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Find the equation of each line. Write the equation in the form = a, = b, or = m + b. For Eercises through 7, write the equation in the form f = m + b.. Through (, 6) and
Digital Image Processing. Prof. P. K. Biswas. Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering
 Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Image Enhancement Frequency Domain Processing
Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Image Enhancement Frequency Domain Processing
= f (a, b) + (hf x + kf y ) (a,b) +
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
FAST NUMERICAL CALCULATIONS OF 3-D PHASED ARRAY WAVE FIELDS BASED ON TRANSIENT POINT SOURCE SYNTHESIS
 FAST NUMERICAL CALCULATIONS OF 3-D PHASED ARRAY WAVE FIELDS BASED ON TRANSIENT POINT SOURCE SYNTHESIS Frank SCHUBERT, Bożena LAMEK FRAUNHOFER IZFP, Dresden, German. 1. INTRODUCTION The increasing interest
FAST NUMERICAL CALCULATIONS OF 3-D PHASED ARRAY WAVE FIELDS BASED ON TRANSIENT POINT SOURCE SYNTHESIS Frank SCHUBERT, Bożena LAMEK FRAUNHOFER IZFP, Dresden, German. 1. INTRODUCTION The increasing interest
D DAVID PUBLISHING. Finite Element Analysis of Polygon Shaped Shell Roof. 1. Introduction. Attia Mousa 1 and Hesham El Naggar 2
 Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture 11 (17) 4-4 doi: 1.1765/194-759/17.5. D DAVID PUBLISHING Finite Element Analsis of Polgon Shaped Shell Roof Attia Mousa 1 and Hesham El Naggar 1. Professor
Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture 11 (17) 4-4 doi: 1.1765/194-759/17.5. D DAVID PUBLISHING Finite Element Analsis of Polgon Shaped Shell Roof Attia Mousa 1 and Hesham El Naggar 1. Professor
Content Standards Two-Variable Inequalities
 -8 Content Standards Two-Variable Inequalities A.CED. Create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities; graph equations on coordinate aes with labels and scales.
-8 Content Standards Two-Variable Inequalities A.CED. Create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities; graph equations on coordinate aes with labels and scales.
OUTPUT PRIMITIVES. CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics METU, 2007
 OUTPUT PRIMITIVES CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics METU, 007 Recap: The basic forward projection pipeline: MCS Model Model Modeling Transformations M M 3D World Scene Viewing Transformations
OUTPUT PRIMITIVES CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics METU, 007 Recap: The basic forward projection pipeline: MCS Model Model Modeling Transformations M M 3D World Scene Viewing Transformations
Computer Graphics. Lecture 3 Graphics Output Primitives. Somsak Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL
 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Graphics Output Primitives Somsa Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL Outline Line Drawing Algorithms Circle-, Ellipse-Generating Algorithms Fill-Area Primitives Polgon Fill
Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Graphics Output Primitives Somsa Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL Outline Line Drawing Algorithms Circle-, Ellipse-Generating Algorithms Fill-Area Primitives Polgon Fill
A new Eulerian computational method for the propagation of short acoustic and electromagnetic pulses
 A new Eulerian computational method for the propagation of short acoustic and electromagnetic pulses J. Steinhoff, M. Fan & L. Wang. Abstract A new method is described to compute short acoustic or electromagnetic
A new Eulerian computational method for the propagation of short acoustic and electromagnetic pulses J. Steinhoff, M. Fan & L. Wang. Abstract A new method is described to compute short acoustic or electromagnetic
Parameterization. Michael S. Floater. November 10, 2011
 Parameterization Michael S. Floater November 10, 2011 Triangular meshes are often used to represent surfaces, at least initially, one reason being that meshes are relatively easy to generate from point
Parameterization Michael S. Floater November 10, 2011 Triangular meshes are often used to represent surfaces, at least initially, one reason being that meshes are relatively easy to generate from point
Partial Differential Equations
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Partial Differential Equations Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Motivation various dynamic effects and physical processes are described
Simulation in Computer Graphics Partial Differential Equations Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Motivation various dynamic effects and physical processes are described
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 00 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Third E CHAPTER 7 Transformations MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas
00 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Third E CHAPTER 7 Transformations MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas
Graphing f ( x) = ax 2 + c
 . Graphing f ( ) = a + c Essential Question How does the value of c affect the graph of f () = a + c? Graphing = a + c Work with a partner. Sketch the graphs of the functions in the same coordinate plane.
. Graphing f ( ) = a + c Essential Question How does the value of c affect the graph of f () = a + c? Graphing = a + c Work with a partner. Sketch the graphs of the functions in the same coordinate plane.
REMARKS. 8.2 Graphs of Quadratic Functions. A Graph of y = ax 2 + bx + c, where a > 0
 8. Graphs of Quadratic Functions In an earlier section, we have learned that the graph of the linear function = m + b, where the highest power of is 1, is a straight line. What would the shape of the graph
8. Graphs of Quadratic Functions In an earlier section, we have learned that the graph of the linear function = m + b, where the highest power of is 1, is a straight line. What would the shape of the graph
1) Find. a) b) c) d) e) 2) The function g is defined by the formula. Find the slope of the tangent line at x = 1. a) b) c) e) 3) Find.
 1 of 7 1) Find 2) The function g is defined by the formula Find the slope of the tangent line at x = 1. 3) Find 5 1 The limit does not exist. 4) The given function f has a removable discontinuity at x
1 of 7 1) Find 2) The function g is defined by the formula Find the slope of the tangent line at x = 1. 3) Find 5 1 The limit does not exist. 4) The given function f has a removable discontinuity at x
Math 20C. Lecture Examples.
 Math 0C. Lecture Eamples. (8/30/08) Section 14.1, Part 1. Functions of two variables Definition 1 A function f of the two variables and is a rule = f(,) that assigns a number denoted f(,), to each point
Math 0C. Lecture Eamples. (8/30/08) Section 14.1, Part 1. Functions of two variables Definition 1 A function f of the two variables and is a rule = f(,) that assigns a number denoted f(,), to each point
Implicit differentiation
 Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Chapter 4: Basic differentiation rules Section 5 Implicit differentiation What ou need to know alread: Basic rules of differentiation, including the chain rule.
Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Chapter 4: Basic differentiation rules Section 5 Implicit differentiation What ou need to know alread: Basic rules of differentiation, including the chain rule.
A9.1 Linear programming
 pplications 9. Linear programming 9. Linear programming efore ou start You should be able to: show b shading a region defined b one or more linear inequalities. Wh do this? Linear programming is an eample
pplications 9. Linear programming 9. Linear programming efore ou start You should be able to: show b shading a region defined b one or more linear inequalities. Wh do this? Linear programming is an eample
Finite Element Convergence for Time-Dependent PDEs with a Point Source in COMSOL 4.2
 Finite Element Convergence for Time-Dependent PDEs with a Point Source in COMSOL 4.2 David W. Trott and Matthias K. Gobbert Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore County,
Finite Element Convergence for Time-Dependent PDEs with a Point Source in COMSOL 4.2 David W. Trott and Matthias K. Gobbert Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore County,
Online Homework Hints and Help Extra Practice
 Evaluate: Homework and Practice Use a graphing calculator to graph the polnomial function. Then use the graph to determine the function s domain, range, and end behavior. (Use interval notation for the
Evaluate: Homework and Practice Use a graphing calculator to graph the polnomial function. Then use the graph to determine the function s domain, range, and end behavior. (Use interval notation for the
PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES
 9 ARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND OLAR COORDINATES So far we have described plane curves b giving as a function of f or as a function of t or b giving a relation between and that defines implicitl as a function
9 ARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND OLAR COORDINATES So far we have described plane curves b giving as a function of f or as a function of t or b giving a relation between and that defines implicitl as a function
Appendix C: Review of Graphs, Equations, and Inequalities
 Appendi C: Review of Graphs, Equations, and Inequalities C. What ou should learn Just as ou can represent real numbers b points on a real number line, ou can represent ordered pairs of real numbers b points
Appendi C: Review of Graphs, Equations, and Inequalities C. What ou should learn Just as ou can represent real numbers b points on a real number line, ou can represent ordered pairs of real numbers b points
6.1. Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables. INVESTIGATE the Math. Reflecting
 6.1 Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables YOU WILL NEED graphing technolog OR graph paper, ruler, and coloured pencils EXPLORE For which inequalities is (3, 1) a possible solution? How do ou know?
6.1 Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables YOU WILL NEED graphing technolog OR graph paper, ruler, and coloured pencils EXPLORE For which inequalities is (3, 1) a possible solution? How do ou know?
The Graph of an Equation
 60_0P0.qd //0 :6 PM Page CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Archive Photos Section P. RENÉ DESCARTES (96 60) Descartes made man contributions to philosoph, science, and mathematics. The idea of representing
60_0P0.qd //0 :6 PM Page CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Archive Photos Section P. RENÉ DESCARTES (96 60) Descartes made man contributions to philosoph, science, and mathematics. The idea of representing
Discrete Geometry Processing
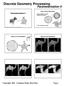 Non Convex Boundary Convex boundary creates significant distortion Free boundary is better Some slides from the Mesh Parameterization Course (Siggraph Asia 008) 1 Fixed vs Free Boundary Fixed vs Free Boundary
Non Convex Boundary Convex boundary creates significant distortion Free boundary is better Some slides from the Mesh Parameterization Course (Siggraph Asia 008) 1 Fixed vs Free Boundary Fixed vs Free Boundary
