6.4: SHELL METHOD 6.5: WORK AND ENERGY NAME: SOLUTIONS Math 1910 September 26, 2017
|
|
|
- Bennett Norris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 6.4: SHELL METHOD 6.5: WORK AND ENERGY NAME: SOLUTIONS Mt 9 September 26, 27 ONE-PAGE REVIEW Sell Metod: Wen you rotte te region between two grps round n xis, te segments prllel to te xis generte cylindricl sells. Te volume V of te solid of revolution is te integrl of te surfce res of te sells. V = rdiuseigt of sell dr. 2 Wt is te volume of te region between fx, fx, nd te x-xis for x [, b], rotted round te y-xis? V = xfx dx. 2 b te region between fx nd gx, fx gx, for x [, b] rotted round te y-xis? V = fx gx dx. 3 c te region between fx, fx nd te x-xis for x [, b], rotted round te line c? If c,v = x cfx dx. 4 If c,v = c xfx dx. 5 3 Te work W performed to move n object from to b long te x-xis by pplying force of mgnitude Fx is W = Fx dx. 4 To compute work ginst grvity, first decompose n object into N lyers of equl tickness y, nd ten express te work performed on tin lyer s Ly y, were Ly = g density re of y distnce lifted. Te totl work performed to lift te object from eigt to eigt b is W = Ly dy 6.
2 PROBLEMS Sketc te solid obtined by rotting te region undernet te grp of f over te intervl bout te given xis, nd clculte its volume using te sell metod. fx = x 3, x [, ], bout x = 2. SOLUTION: Ec sell s rdius 2 x nd eigt x 3, so te volume of tis solid is 2 xx 3 dx = x 2x 3 x 4 4 dx = 2 x5 = 3π 2 5. b fx = x 3, x [, ], bout x = 2. SOLUTION: Ec sell s rdius x 2 = x + 2 nd eigt x 3, so te volume of tis solid is 2 + xx 3 dx = x 2x 3 + x 4 4 dx = 2 + x5 = 7π
3 c fx =, x [, 2], bout x =. x 2 + SOLUTION: Ec sell s rdius x, nd eigt, so te volume of te solid is x x x 2 + dx = x = 5. 2 Use te most convenient metod disk/wser or sell to find te given volume of rottion. 3
4 Region between x = y5 y nd x =, rotted bout te y-xis. SOLUTION: Exmine te picture below, wic sows te region in question. If te indicted region is sliced verticlly, ten te top of te slice lies long one brnc of te prbol x = y5 y nd te bottom lies long te oter brnc. On te oter nd, if te region is sliced orizonlly, ten te rigt endpoint of slice is lwys long te prbol nd te left endpoint is on te y-xis. So it s esier to do orizontl slices. Now suppose te region is rotted bout te y-xis. Becuse orizontl slice is perpendiculr to te y-xis, we will clculte te volume of te resulting solid using te disk metod. Ec cross section is disk of rdius R = y5 y, so te volume is π y 2 5 y 2 dy = π 25y 2 y 3 + y 4 dy = π 25 3 y3 5 2 y y5 = 625π 6. 4
5 b Region between x = y5 y nd x =, rotted round te x-xis. SOLUTION: Exmine te?gure below, wic sows te region bounded by x = y5?y nd x =. If te indicted region is sliced verticlly, ten te top of te slice lies long one brnc of te prbol x = y5 y nd te bottom lies long te oter brnc. On te oter nd, if te region is sliced orizontlly, ten te rigt endpoint of te slice lwys lies long te prbol nd left endpoint lwys lies long te y-xis. Clerly, it will be esier to slice te region orizontlly. Now, suppose te region is rotted bout te x-xis. Becuse orizontl slice is prllel to te x-xis, we will clculte te volume of te resulting solid using te sell metod. Ec sell s rdius of y nd eigt of y5 y, so te volume is y 2 5 y dy = 5y 2 y 3 dy = 5 3 y3 5 4 y4 = 625π 6. 5
6 c Region between y = x 2 nd x = y 2, rotted bout x = 3. SOLUTION: Exmine te figure below, wic sows te region bounded by te y = x 2 nd x = y 2. If te indicted region is sliced verticlly, ten te top of te slice lies long x = y 2 nd te bottom lies long y = x 2. On te oter nd, if te region is sliced orizontlly, ten te rigt endpoint of te slice lwys lies long y = x 2 nd left endpoint lwys lies long x = y 2. Tus, for tis region, eiter coice of slice will be convenient. To proceed, let s coose verticl slice. Now rotte te region bout x = 3. Becuse verticl slice is prllel to x = 3, we will clculte te volume of te resulting solid using te sell metod. Ec sell s rdius of 3 x nd eigt of x x 2, so te volume is 3 x x x 2 dx = 3x /2 x 3/2 3x 2 + x 3 dx = 2x 3/2 25 x5/2 x x4 = 7π. 6
7 3 Clculte te work in Joules required to pump ll of te wter out of full tnk wit te spe described. Distnces re in meters, nd te density of wter is kg/m 3. A rectngulr tnk, wit wter exiting from smll ole in te top. SOLUTION: Plce te origin t te top of te box, nd let te positive y-xis point downwrd. Te volume of one lyer of wter is 32 y cubic meters, so te force needed to lift it is y = 336 y Newtons. Ec lyer must be lifted y meters, so te totl work needed to empty te tnk is 336y dy = 568y 3 5 = Joules. b A troug s in te picture, were te wter exits by pouring over te sides. SOLUTION: Plce te origin long te bottom edge of te troug, nd let te positive y-xis point upwrd. From similr tringles, te widt of lyer of wter t eigt y meters is so te volume of ec lyer is wc y = c Tus, te force needed to lift lyer is 98c w = yb meters, yb y meters 3. yb y Newtons. Ec lyer must be lifted y meters, so te totl work needed to empty te tnk is yb 3 98 yc + dy = 98c 3 + b2 Joules. 6 7
Area & Volume. Chapter 6.1 & 6.2 September 25, y = 1! x 2. Back to Area:
 Bck to Are: Are & Volume Chpter 6. & 6. Septemer 5, 6 We cn clculte the re etween the x-xis nd continuous function f on the intervl [,] using the definite integrl:! f x = lim$ f x * i )%x n i= Where fx
Bck to Are: Are & Volume Chpter 6. & 6. Septemer 5, 6 We cn clculte the re etween the x-xis nd continuous function f on the intervl [,] using the definite integrl:! f x = lim$ f x * i )%x n i= Where fx
a < a+ x < a+2 x < < a+n x = b, n A i n f(x i ) x. i=1 i=1
 Mth 33 Volume Stewrt 5.2 Geometry of integrls. In this section, we will lern how to compute volumes using integrls defined by slice nlysis. First, we recll from Clculus I how to compute res. Given the
Mth 33 Volume Stewrt 5.2 Geometry of integrls. In this section, we will lern how to compute volumes using integrls defined by slice nlysis. First, we recll from Clculus I how to compute res. Given the
SAMPLE PREREQUISITE PROBLEMS: CALCULUS
 SAMPLE PREREQUISITE PROBLEMS: CALCULUS Te following questions rise from ctul AP Clculus AB em questions; I went troug lots of questions, nd pulled out prts requiring lgebr nd trigonometr Tese problems
SAMPLE PREREQUISITE PROBLEMS: CALCULUS Te following questions rise from ctul AP Clculus AB em questions; I went troug lots of questions, nd pulled out prts requiring lgebr nd trigonometr Tese problems
6.3 Volumes. Just as area is always positive, so is volume and our attitudes towards finding it.
 6.3 Volumes Just s re is lwys positive, so is volume nd our ttitudes towrds finding it. Let s review how to find the volume of regulr geometric prism, tht is, 3-dimensionl oject with two regulr fces seprted
6.3 Volumes Just s re is lwys positive, so is volume nd our ttitudes towrds finding it. Let s review how to find the volume of regulr geometric prism, tht is, 3-dimensionl oject with two regulr fces seprted
B. Definition: The volume of a solid of known integrable cross-section area A(x) from x = a
 Mth 176 Clculus Sec. 6.: Volume I. Volume By Slicing A. Introduction We will e trying to find the volume of solid shped using the sum of cross section res times width. We will e driving towrd developing
Mth 176 Clculus Sec. 6.: Volume I. Volume By Slicing A. Introduction We will e trying to find the volume of solid shped using the sum of cross section res times width. We will e driving towrd developing
MATH 2530: WORKSHEET 7. x 2 y dz dy dx =
 MATH 253: WORKSHT 7 () Wrm-up: () Review: polr coordintes, integrls involving polr coordintes, triple Riemnn sums, triple integrls, the pplictions of triple integrls (especilly to volume), nd cylindricl
MATH 253: WORKSHT 7 () Wrm-up: () Review: polr coordintes, integrls involving polr coordintes, triple Riemnn sums, triple integrls, the pplictions of triple integrls (especilly to volume), nd cylindricl
Yoplait with Areas and Volumes
 Yoplit with Ares nd Volumes Yoplit yogurt comes in two differently shped continers. One is truncted cone nd the other is n ellipticl cylinder (see photos below). In this exercise, you will determine the
Yoplit with Ares nd Volumes Yoplit yogurt comes in two differently shped continers. One is truncted cone nd the other is n ellipticl cylinder (see photos below). In this exercise, you will determine the
Class-XI Mathematics Conic Sections Chapter-11 Chapter Notes Key Concepts
 Clss-XI Mthemtics Conic Sections Chpter-11 Chpter Notes Key Concepts 1. Let be fixed verticl line nd m be nother line intersecting it t fixed point V nd inclined to it t nd ngle On rotting the line m round
Clss-XI Mthemtics Conic Sections Chpter-11 Chpter Notes Key Concepts 1. Let be fixed verticl line nd m be nother line intersecting it t fixed point V nd inclined to it t nd ngle On rotting the line m round
such that the S i cover S, or equivalently S
 MATH 55 Triple Integrls Fll 16 1. Definition Given solid in spce, prtition of consists of finite set of solis = { 1,, n } such tht the i cover, or equivlently n i. Furthermore, for ech i, intersects i
MATH 55 Triple Integrls Fll 16 1. Definition Given solid in spce, prtition of consists of finite set of solis = { 1,, n } such tht the i cover, or equivlently n i. Furthermore, for ech i, intersects i
4.1 Tangent Lines. y 2 y 1 = y 2 y 1
 41 Tangent Lines Introduction Recall tat te slope of a line tells us ow fast te line rises or falls Given distinct points (x 1, y 1 ) and (x 2, y 2 ), te slope of te line troug tese two points is cange
41 Tangent Lines Introduction Recall tat te slope of a line tells us ow fast te line rises or falls Given distinct points (x 1, y 1 ) and (x 2, y 2 ), te slope of te line troug tese two points is cange
6.2 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method
 mth ppliction: volumes by disks: volume prt ii 6 6 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method One of the simplest pplictions of integrtion (Theorem 6) nd the ccumultion process is to determine so-clled volumes
mth ppliction: volumes by disks: volume prt ii 6 6 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method One of the simplest pplictions of integrtion (Theorem 6) nd the ccumultion process is to determine so-clled volumes
6.2 Volumes by Disks, Washers, and Cross-Sections
 6.2 Volumes by Disks, Washers, and Cross-Sections General Principle: Disks Take slices PERPENDICULAR to axis of rotation and rotate around that axis. About x-axis: About y-axis: 1 Examples: Set up integrals
6.2 Volumes by Disks, Washers, and Cross-Sections General Principle: Disks Take slices PERPENDICULAR to axis of rotation and rotate around that axis. About x-axis: About y-axis: 1 Examples: Set up integrals
12.2 Investigate Surface Area
 Investigating g Geometry ACTIVITY Use before Lesson 12.2 12.2 Investigate Surface Area MATERIALS grap paper scissors tape Q U E S T I O N How can you find te surface area of a polyedron? A net is a pattern
Investigating g Geometry ACTIVITY Use before Lesson 12.2 12.2 Investigate Surface Area MATERIALS grap paper scissors tape Q U E S T I O N How can you find te surface area of a polyedron? A net is a pattern
9.1 apply the distance and midpoint formulas
 9.1 pply the distnce nd midpoint formuls DISTANCE FORMULA MIDPOINT FORMULA To find the midpoint between two points x, y nd x y 1 1,, we Exmple 1: Find the distnce between the two points. Then, find the
9.1 pply the distnce nd midpoint formuls DISTANCE FORMULA MIDPOINT FORMULA To find the midpoint between two points x, y nd x y 1 1,, we Exmple 1: Find the distnce between the two points. Then, find the
LECTURE 3-1 AREA OF A REGION BOUNDED BY CURVES
 7 CALCULUS II DR. YOU 98 LECTURE 3- AREA OF A REGION BOUNDED BY CURVES If y = f(x) and y = g(x) are continuous on an interval [a, b] and f(x) g(x) for all x in [a, b], then the area of the region between
7 CALCULUS II DR. YOU 98 LECTURE 3- AREA OF A REGION BOUNDED BY CURVES If y = f(x) and y = g(x) are continuous on an interval [a, b] and f(x) g(x) for all x in [a, b], then the area of the region between
Applications of the Definite Integral ( Areas and Volumes)
 Mth1242 Project II Nme: Applictions of the Definite Integrl ( Ares nd Volumes) In this project, we explore some pplictions of the definite integrl. We use integrls to find the re etween the grphs of two
Mth1242 Project II Nme: Applictions of the Definite Integrl ( Ares nd Volumes) In this project, we explore some pplictions of the definite integrl. We use integrls to find the re etween the grphs of two
MENSURATION-IV
 MENSURATION-IV Theory: A solid is figure bounded by one or more surfce. Hence solid hs length, bredth nd height. The plne surfces tht bind solid re clled its fces. The fundmentl difference between plne
MENSURATION-IV Theory: A solid is figure bounded by one or more surfce. Hence solid hs length, bredth nd height. The plne surfces tht bind solid re clled its fces. The fundmentl difference between plne
If f(x, y) is a surface that lies above r(t), we can think about the area between the surface and the curve.
 Line Integrls The ide of line integrl is very similr to tht of single integrls. If the function f(x) is bove the x-xis on the intervl [, b], then the integrl of f(x) over [, b] is the re under f over the
Line Integrls The ide of line integrl is very similr to tht of single integrls. If the function f(x) is bove the x-xis on the intervl [, b], then the integrl of f(x) over [, b] is the re under f over the
4.2 The Derivative. f(x + h) f(x) lim
 4.2 Te Derivative Introduction In te previous section, it was sown tat if a function f as a nonvertical tangent line at a point (x, f(x)), ten its slope is given by te it f(x + ) f(x). (*) Tis is potentially
4.2 Te Derivative Introduction In te previous section, it was sown tat if a function f as a nonvertical tangent line at a point (x, f(x)), ten its slope is given by te it f(x + ) f(x). (*) Tis is potentially
APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION
 Chpter 3 DACS 1 Lok 004/05 CHAPTER 5 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 5.1 Geometricl Interprettion-Definite Integrl (pge 36) 5. Are of Region (pge 369) 5..1 Are of Region Under Grph (pge 369) Figure 5.7 shows
Chpter 3 DACS 1 Lok 004/05 CHAPTER 5 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 5.1 Geometricl Interprettion-Definite Integrl (pge 36) 5. Are of Region (pge 369) 5..1 Are of Region Under Grph (pge 369) Figure 5.7 shows
Stained Glass Design. Teaching Goals:
 Stined Glss Design Time required 45-90 minutes Teching Gols: 1. Students pply grphic methods to design vrious shpes on the plne.. Students pply geometric trnsformtions of grphs of functions in order to
Stined Glss Design Time required 45-90 minutes Teching Gols: 1. Students pply grphic methods to design vrious shpes on the plne.. Students pply geometric trnsformtions of grphs of functions in order to
Iterated Integrals. f (x; y) dy dx. p(x) To evaluate a type I integral, we rst evaluate the inner integral Z q(x) f (x; y) dy.
 Iterted Integrls Type I Integrls In this section, we begin the study of integrls over regions in the plne. To do so, however, requires tht we exmine the importnt ide of iterted integrls, in which inde
Iterted Integrls Type I Integrls In this section, we begin the study of integrls over regions in the plne. To do so, however, requires tht we exmine the importnt ide of iterted integrls, in which inde
2.8 The derivative as a function
 CHAPTER 2. LIMITS 56 2.8 Te derivative as a function Definition. Te derivative of f(x) istefunction f (x) defined as follows f f(x + ) f(x) (x). 0 Note: tis differs from te definition in section 2.7 in
CHAPTER 2. LIMITS 56 2.8 Te derivative as a function Definition. Te derivative of f(x) istefunction f (x) defined as follows f f(x + ) f(x) (x). 0 Note: tis differs from te definition in section 2.7 in
, 1 1, A complex fraction is a quotient of rational expressions (including their sums) that result
 RT. Complex Fractions Wen working wit algebraic expressions, sometimes we come across needing to simplify expressions like tese: xx 9 xx +, xx + xx + xx, yy xx + xx + +, aa Simplifying Complex Fractions
RT. Complex Fractions Wen working wit algebraic expressions, sometimes we come across needing to simplify expressions like tese: xx 9 xx +, xx + xx + xx, yy xx + xx + +, aa Simplifying Complex Fractions
ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY. The curves obtained by slicing the cone with a plane not passing through the vertex are called conics.
 ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY Definition of Conic: The curves obtined by slicing the cone with plne not pssing through the vertex re clled conics. A Conic is the locus directrix of point which moves in plne, so
ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY Definition of Conic: The curves obtined by slicing the cone with plne not pssing through the vertex re clled conics. A Conic is the locus directrix of point which moves in plne, so
19.2 Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders
 Name Class Date 19 Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders Essential Question: How can you find te surface area of a prism or cylinder? Resource Locker Explore Developing a Surface Area Formula Surface area
Name Class Date 19 Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders Essential Question: How can you find te surface area of a prism or cylinder? Resource Locker Explore Developing a Surface Area Formula Surface area
VOLUMES. The volume of a cylinder is determined by multiplying the cross sectional area by the height. r h V. a) 10 mm 25 mm.
 OLUME OF A CYLINDER OLUMES Te volume of a cylinder is determined by multiplying te cross sectional area by te eigt. r Were: = volume r = radius = eigt Exercise 1 Complete te table ( =.14) r a) 10 mm 5
OLUME OF A CYLINDER OLUMES Te volume of a cylinder is determined by multiplying te cross sectional area by te eigt. r Were: = volume r = radius = eigt Exercise 1 Complete te table ( =.14) r a) 10 mm 5
Fig.1. Let a source of monochromatic light be incident on a slit of finite width a, as shown in Fig. 1.
 Answer on Question #5692, Physics, Optics Stte slient fetures of single slit Frunhofer diffrction pttern. The slit is verticl nd illuminted by point source. Also, obtin n expression for intensity distribution
Answer on Question #5692, Physics, Optics Stte slient fetures of single slit Frunhofer diffrction pttern. The slit is verticl nd illuminted by point source. Also, obtin n expression for intensity distribution
13.5 DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES and the GRADIENT VECTOR
 13.5 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector Contemporary Calculus 1 13.5 DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES and te GRADIENT VECTOR Directional Derivatives In Section 13.3 te partial derivatives f x and f
13.5 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector Contemporary Calculus 1 13.5 DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES and te GRADIENT VECTOR Directional Derivatives In Section 13.3 te partial derivatives f x and f
9.3 Warmup Find the value of x and y
 9.3 Wrmup Find te vlue of x nd y. 1. 2. 3. 4 x 10 4. 5. x 36 6. Are tese te sides of tringle? If yes, is te cute, otuse or rigt?. 4, 4, 10 Mrc 3, 2017 y Geometry 9.1 Similr Rigt Tringles. 9, 15,12 c. 2,
9.3 Wrmup Find te vlue of x nd y. 1. 2. 3. 4 x 10 4. 5. x 36 6. Are tese te sides of tringle? If yes, is te cute, otuse or rigt?. 4, 4, 10 Mrc 3, 2017 y Geometry 9.1 Similr Rigt Tringles. 9, 15,12 c. 2,
1 Drawing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrator
 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor 1 1 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor This Tutoril will show you how to drw simple objects with three-dimensionl ppernce. At first we will drw rrows indicting
Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor 1 1 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor This Tutoril will show you how to drw simple objects with three-dimensionl ppernce. At first we will drw rrows indicting
Classify solids. Find volumes of prisms and cylinders.
 11.4 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders Essential Question How can you find te volume of a prism or cylinder tat is not a rigt prism or rigt cylinder? Recall tat te volume V of a rigt prism or a rigt cylinder
11.4 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders Essential Question How can you find te volume of a prism or cylinder tat is not a rigt prism or rigt cylinder? Recall tat te volume V of a rigt prism or a rigt cylinder
3.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 288 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES 3.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector 3.6.1 Functions of two Variables Directional Derivatives Let us first quickly review, one more time, te
288 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES 3.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector 3.6.1 Functions of two Variables Directional Derivatives Let us first quickly review, one more time, te
Math 35 Review Sheet, Spring 2014
 Mth 35 Review heet, pring 2014 For the finl exm, do ny 12 of the 15 questions in 3 hours. They re worth 8 points ech, mking 96, with 4 more points for netness! Put ll your work nd nswers in the provided
Mth 35 Review heet, pring 2014 For the finl exm, do ny 12 of the 15 questions in 3 hours. They re worth 8 points ech, mking 96, with 4 more points for netness! Put ll your work nd nswers in the provided
Numerical Derivatives
 Lab 15 Numerical Derivatives Lab Objective: Understand and implement finite difference approximations of te derivative in single and multiple dimensions. Evaluate te accuracy of tese approximations. Ten
Lab 15 Numerical Derivatives Lab Objective: Understand and implement finite difference approximations of te derivative in single and multiple dimensions. Evaluate te accuracy of tese approximations. Ten
Unit #9 : Definite Integral Properties, Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties, Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties, Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
Section 1.2 The Slope of a Tangent
 Section 1.2 Te Slope of a Tangent You are familiar wit te concept of a tangent to a curve. Wat geometric interpretation can be given to a tangent to te grap of a function at a point? A tangent is te straigt
Section 1.2 Te Slope of a Tangent You are familiar wit te concept of a tangent to a curve. Wat geometric interpretation can be given to a tangent to te grap of a function at a point? A tangent is te straigt
2 The Derivative. 2.0 Introduction to Derivatives. Slopes of Tangent Lines: Graphically
 2 Te Derivative Te two previous capters ave laid te foundation for te study of calculus. Tey provided a review of some material you will need and started to empasize te various ways we will view and use
2 Te Derivative Te two previous capters ave laid te foundation for te study of calculus. Tey provided a review of some material you will need and started to empasize te various ways we will view and use
All truths are easy to understand once they are discovered; the point is to discover them. Galileo
 Section 7. olume All truts are easy to understand once tey are discovered; te point is to discover tem. Galileo Te main topic of tis section is volume. You will specifically look at ow to find te volume
Section 7. olume All truts are easy to understand once tey are discovered; te point is to discover tem. Galileo Te main topic of tis section is volume. You will specifically look at ow to find te volume
50 AMC LECTURES Lecture 2 Analytic Geometry Distance and Lines. can be calculated by the following formula:
 5 AMC LECTURES Lecture Anlytic Geometry Distnce nd Lines BASIC KNOWLEDGE. Distnce formul The distnce (d) between two points P ( x, y) nd P ( x, y) cn be clculted by the following formul: d ( x y () x )
5 AMC LECTURES Lecture Anlytic Geometry Distnce nd Lines BASIC KNOWLEDGE. Distnce formul The distnce (d) between two points P ( x, y) nd P ( x, y) cn be clculted by the following formul: d ( x y () x )
Read pages in the book, up to the investigation. Pay close attention to Example A and how to identify the height.
 C 8 Noteseet L Key In General ON LL PROBLEMS!!. State te relationsip (or te formula).. Sustitute in known values. 3. Simplify or Solve te equation. Use te order of operations in te correct order. Order
C 8 Noteseet L Key In General ON LL PROBLEMS!!. State te relationsip (or te formula).. Sustitute in known values. 3. Simplify or Solve te equation. Use te order of operations in te correct order. Order
arxiv: v2 [math.ho] 4 Jun 2012
![arxiv: v2 [math.ho] 4 Jun 2012 arxiv: v2 [math.ho] 4 Jun 2012](/thumbs/76/73512534.jpg) Volumes of olids of Revolution. Unified pproch Jorge Mrtín-Morles nd ntonio M. Oller-Mrcén jorge@unizr.es, oller@unizr.es rxiv:5.v [mth.ho] Jun Centro Universitrio de l Defens - IUM. cdemi Generl Militr,
Volumes of olids of Revolution. Unified pproch Jorge Mrtín-Morles nd ntonio M. Oller-Mrcén jorge@unizr.es, oller@unizr.es rxiv:5.v [mth.ho] Jun Centro Universitrio de l Defens - IUM. cdemi Generl Militr,
MA 124 (Calculus II) Lecture 2: January 24, 2019 Section A3. Professor Jennifer Balakrishnan,
 Wht is on tody Professor Jennifer Blkrishnn, jbl@bu.edu 1 Velocity nd net chnge 1 2 Regions between curves 3 1 Velocity nd net chnge Briggs-Cochrn-Gillett 6.1 pp. 398-46 Suppose you re driving long stright
Wht is on tody Professor Jennifer Blkrishnn, jbl@bu.edu 1 Velocity nd net chnge 1 2 Regions between curves 3 1 Velocity nd net chnge Briggs-Cochrn-Gillett 6.1 pp. 398-46 Suppose you re driving long stright
Right Triangle Trigonometry
 Rigt Tringle Trigonometry Trigonometry comes from te Greek trigon (tringle) nd metron (mesure) nd is te study of te reltion between side lengts nd ngles of tringles. Angles A ry is strigt lf line tt stretces
Rigt Tringle Trigonometry Trigonometry comes from te Greek trigon (tringle) nd metron (mesure) nd is te study of te reltion between side lengts nd ngles of tringles. Angles A ry is strigt lf line tt stretces
Math 17 - Review. Review for Chapter 12
 Mth 17 - eview Ying Wu eview for hpter 12 1. Given prmetric plnr curve x = f(t), y = g(t), where t b, how to eliminte the prmeter? (Use substitutions, or use trigonometry identities, etc). How to prmeterize
Mth 17 - eview Ying Wu eview for hpter 12 1. Given prmetric plnr curve x = f(t), y = g(t), where t b, how to eliminte the prmeter? (Use substitutions, or use trigonometry identities, etc). How to prmeterize
Deletion The Two Child Case 10 Delete(5) Deletion The Two Child Case. Balanced BST. Finally
 Deletion Te Two Cild Cse Delete() Deletion Te Two Cild Cse Ide: Replce te deleted node wit vlue gurnteed to e etween te two cild sutrees! Options: succ from rigt sutree: findmin(t.rigt) pred from left
Deletion Te Two Cild Cse Delete() Deletion Te Two Cild Cse Ide: Replce te deleted node wit vlue gurnteed to e etween te two cild sutrees! Options: succ from rigt sutree: findmin(t.rigt) pred from left
Pythagoras theorem and trigonometry (2)
 HPTR 10 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry (2) 31 HPTR Liner equtions In hpter 19, Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry were used to find the lengths of sides nd the sizes of ngles in right-ngled tringles. These
HPTR 10 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry (2) 31 HPTR Liner equtions In hpter 19, Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry were used to find the lengths of sides nd the sizes of ngles in right-ngled tringles. These
Math 1206 Calculus Sec. 5.6: Substitution and Area Between Curves (Part 2) Overview of Area Between Two Curves
 Math 1206 Calculus Sec. 5.6: Substitution and Area Between Curves (Part 2) III. Overview of Area Between Two Curves With a few modifications the area under a curve represented by a definite integral can
Math 1206 Calculus Sec. 5.6: Substitution and Area Between Curves (Part 2) III. Overview of Area Between Two Curves With a few modifications the area under a curve represented by a definite integral can
Chapter K. Geometric Optics. Blinn College - Physics Terry Honan
 Capter K Geometric Optics Blinn College - Pysics 2426 - Terry Honan K. - Properties of Ligt Te Speed of Ligt Te speed of ligt in a vacuum is approximately c > 3.0µ0 8 mês. Because of its most fundamental
Capter K Geometric Optics Blinn College - Pysics 2426 - Terry Honan K. - Properties of Ligt Te Speed of Ligt Te speed of ligt in a vacuum is approximately c > 3.0µ0 8 mês. Because of its most fundamental
8/6/2010 Assignment Previewer
 Week 4 Friday Homework (1321979) Question 1234567891011121314151617181920 1. Question DetailsSCalcET6 2.7.003. [1287988] Consider te parabola y 7x - x 2. (a) Find te slope of te tangent line to te parabola
Week 4 Friday Homework (1321979) Question 1234567891011121314151617181920 1. Question DetailsSCalcET6 2.7.003. [1287988] Consider te parabola y 7x - x 2. (a) Find te slope of te tangent line to te parabola
Lecture 4: Geometry II
 Lecture 4: Geometry II LPSS MATHCOUNTS 19 May 2004 Some Well-Known Pytagorean Triples A Pytagorean triple is a set of tree relatively prime 1 natural numers a,, and c satisfying a 2 + 2 = c 2 : 3 2 + 4
Lecture 4: Geometry II LPSS MATHCOUNTS 19 May 2004 Some Well-Known Pytagorean Triples A Pytagorean triple is a set of tree relatively prime 1 natural numers a,, and c satisfying a 2 + 2 = c 2 : 3 2 + 4
When the dimensions of a solid increase by a factor of k, how does the surface area change? How does the volume change?
 8.4 Surface Areas and Volumes of Similar Solids Wen te dimensions of a solid increase by a factor of k, ow does te surface area cange? How does te volume cange? 1 ACTIVITY: Comparing Surface Areas and
8.4 Surface Areas and Volumes of Similar Solids Wen te dimensions of a solid increase by a factor of k, ow does te surface area cange? How does te volume cange? 1 ACTIVITY: Comparing Surface Areas and
Section 10.4 Hyperbolas
 66 Section 10.4 Hyperbols Objective : Definition of hyperbol & hyperbols centered t (0, 0). The third type of conic we will study is the hyperbol. It is defined in the sme mnner tht we defined the prbol
66 Section 10.4 Hyperbols Objective : Definition of hyperbol & hyperbols centered t (0, 0). The third type of conic we will study is the hyperbol. It is defined in the sme mnner tht we defined the prbol
Areas of Triangles and Parallelograms. Bases of a parallelogram. Height of a parallelogram THEOREM 11.3: AREA OF A TRIANGLE. a and its corresponding.
 11.1 Areas of Triangles and Parallelograms Goal p Find areas of triangles and parallelograms. Your Notes VOCABULARY Bases of a parallelogram Heigt of a parallelogram POSTULATE 4: AREA OF A SQUARE POSTULATE
11.1 Areas of Triangles and Parallelograms Goal p Find areas of triangles and parallelograms. Your Notes VOCABULARY Bases of a parallelogram Heigt of a parallelogram POSTULATE 4: AREA OF A SQUARE POSTULATE
Section 2.3: Calculating Limits using the Limit Laws
 Section 2.3: Calculating Limits using te Limit Laws In previous sections, we used graps and numerics to approimate te value of a it if it eists. Te problem wit tis owever is tat it does not always give
Section 2.3: Calculating Limits using te Limit Laws In previous sections, we used graps and numerics to approimate te value of a it if it eists. Te problem wit tis owever is tat it does not always give
5/27/12. Objectives 7.1. Area of a Region Between Two Curves. Find the area of a region between two curves using integration.
 Objectives 7.1 Find the area of a region between two curves using integration. Find the area of a region between intersecting curves using integration. Describe integration as an accumulation process.
Objectives 7.1 Find the area of a region between two curves using integration. Find the area of a region between intersecting curves using integration. Describe integration as an accumulation process.
V = 2πx(1 x) dx. x 2 dx. 3 x3 0
 Wednesday, September 3, 215 Page 462 Problem 1 Problem. Use the shell method to set up and evaluate the integral that gives the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region (y = x, y =, x = 2)
Wednesday, September 3, 215 Page 462 Problem 1 Problem. Use the shell method to set up and evaluate the integral that gives the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region (y = x, y =, x = 2)
( ) ( ) Mat 241 Homework Set 5 Due Professor David Schultz. x y. 9 4 The domain is the interior of the hyperbola.
 Mat 4 Homework Set 5 Due Professor David Scultz Directions: Sow all algebraic steps neatly and concisely using proper matematical symbolism. Wen graps and tecnology are to be implemented, do so appropriately.
Mat 4 Homework Set 5 Due Professor David Scultz Directions: Sow all algebraic steps neatly and concisely using proper matematical symbolism. Wen graps and tecnology are to be implemented, do so appropriately.
EXERCISES 6.1. Cross-Sectional Areas. 6.1 Volumes by Slicing and Rotation About an Axis 405
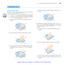 6. Volumes b Slicing and Rotation About an Ais 5 EXERCISES 6. Cross-Sectional Areas In Eercises and, find a formula for te area A() of te crosssections of te solid perpendicular to te -ais.. Te solid lies
6. Volumes b Slicing and Rotation About an Ais 5 EXERCISES 6. Cross-Sectional Areas In Eercises and, find a formula for te area A() of te crosssections of te solid perpendicular to te -ais.. Te solid lies
Hash-Based Indexes. Chapter 11. Comp 521 Files and Databases Spring
 Has-Based Indexes Capter 11 Comp 521 Files and Databases Spring 2010 1 Introduction As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: Data record wit key value k
Has-Based Indexes Capter 11 Comp 521 Files and Databases Spring 2010 1 Introduction As for any index, 3 alternatives for data entries k*: Data record wit key value k
Physics 208: Electricity and Magnetism Exam 1, Secs Feb IMPORTANT. Read these directions carefully:
 Physics 208: Electricity nd Mgnetism Exm 1, Secs. 506 510 11 Feb. 2004 Instructor: Dr. George R. Welch, 415 Engineering-Physics, 845-7737 Print your nme netly: Lst nme: First nme: Sign your nme: Plese
Physics 208: Electricity nd Mgnetism Exm 1, Secs. 506 510 11 Feb. 2004 Instructor: Dr. George R. Welch, 415 Engineering-Physics, 845-7737 Print your nme netly: Lst nme: First nme: Sign your nme: Plese
Matlab s Numerical Integration Commands
 Mtlb s Numericl Integrtion Commnds The relevnt commnds we consider re qud nd dblqud, triplequd. See the Mtlb help files for other integrtion commnds. By the wy, qud refers to dptive qudrture. To integrte:
Mtlb s Numericl Integrtion Commnds The relevnt commnds we consider re qud nd dblqud, triplequd. See the Mtlb help files for other integrtion commnds. By the wy, qud refers to dptive qudrture. To integrte:
12.2 TECHNIQUES FOR EVALUATING LIMITS
 Section Tecniques for Evaluating Limits 86 TECHNIQUES FOR EVALUATING LIMITS Wat ou sould learn Use te dividing out tecnique to evaluate its of functions Use te rationalizing tecnique to evaluate its of
Section Tecniques for Evaluating Limits 86 TECHNIQUES FOR EVALUATING LIMITS Wat ou sould learn Use te dividing out tecnique to evaluate its of functions Use te rationalizing tecnique to evaluate its of
CS 234. Module 6. October 16, CS 234 Module 6 ADT Dictionary 1 / 33
 CS 234 Module 6 October 16, 2018 CS 234 Module 6 ADT Dictionary 1 / 33 Idea for an ADT Te ADT Dictionary stores pairs (key, element), were keys are distinct and elements can be any data. Notes: Tis is
CS 234 Module 6 October 16, 2018 CS 234 Module 6 ADT Dictionary 1 / 33 Idea for an ADT Te ADT Dictionary stores pairs (key, element), were keys are distinct and elements can be any data. Notes: Tis is
MAPI Computer Vision
 MAPI Computer Vision Multiple View Geometry In tis module we intend to present several tecniques in te domain of te 3D vision Manuel Joao University of Mino Dep Industrial Electronics - Applications -
MAPI Computer Vision Multiple View Geometry In tis module we intend to present several tecniques in te domain of te 3D vision Manuel Joao University of Mino Dep Industrial Electronics - Applications -
each node in the tree, the difference in height of its two subtrees is at the most p. AVL tree is a BST that is height-balanced-1-tree.
 Data Structures CSC212 1 AVL Trees A binary tree is a eigt-balanced-p-tree if for eac node in te tree, te difference in eigt of its two subtrees is at te most p. AVL tree is a BST tat is eigt-balanced-tree.
Data Structures CSC212 1 AVL Trees A binary tree is a eigt-balanced-p-tree if for eac node in te tree, te difference in eigt of its two subtrees is at te most p. AVL tree is a BST tat is eigt-balanced-tree.
You should be able to visually approximate the slope of a graph. The slope m of the graph of f at the point x, f x is given by
 Section. Te Tangent Line Problem 89 87. r 5 sin, e, 88. r sin sin Parabola 9 9 Hperbola e 9 9 9 89. 7,,,, 5 7 8 5 ortogonal 9. 5, 5,, 5, 5. Not multiples of eac oter; neiter parallel nor ortogonal 9.,,,
Section. Te Tangent Line Problem 89 87. r 5 sin, e, 88. r sin sin Parabola 9 9 Hperbola e 9 9 9 89. 7,,,, 5 7 8 5 ortogonal 9. 5, 5,, 5, 5. Not multiples of eac oter; neiter parallel nor ortogonal 9.,,,
Linear Interpolating Splines
 Jim Lambers MAT 772 Fall Semester 2010-11 Lecture 17 Notes Tese notes correspond to Sections 112, 11, and 114 in te text Linear Interpolating Splines We ave seen tat ig-degree polynomial interpolation
Jim Lambers MAT 772 Fall Semester 2010-11 Lecture 17 Notes Tese notes correspond to Sections 112, 11, and 114 in te text Linear Interpolating Splines We ave seen tat ig-degree polynomial interpolation
Topic 6: Calculus Integration Volume of Revolution Paper 2
 Topic 6: Calculus Integration Standard Level 6.1 Volume of Revolution Paper 1. Let f(x) = x ln(4 x ), for < x
Topic 6: Calculus Integration Standard Level 6.1 Volume of Revolution Paper 1. Let f(x) = x ln(4 x ), for < x
Name Class. (a) (b) (c) 2. Find the volume of the solid formed by revolving the region bounded by the graphs of
 Applications of Integration Test Form A. Determine the area of the region bounded by the graphs of y x 4x and y x 4. (a) 9 9 (b) 6 (c). Find the volume of the solid formed by revolving the region bounded
Applications of Integration Test Form A. Determine the area of the region bounded by the graphs of y x 4x and y x 4. (a) 9 9 (b) 6 (c). Find the volume of the solid formed by revolving the region bounded
Conic Sections Parabola Objective: Define conic section, parabola, draw a parabola, standard equations and their graphs
 Conic Sections Prol Ojective: Define conic section, prol, drw prol, stndrd equtions nd their grphs The curves creted y intersecting doule npped right circulr cone with plne re clled conic sections. If
Conic Sections Prol Ojective: Define conic section, prol, drw prol, stndrd equtions nd their grphs The curves creted y intersecting doule npped right circulr cone with plne re clled conic sections. If
12.2 Techniques for Evaluating Limits
 335_qd /4/5 :5 PM Page 863 Section Tecniques for Evaluating Limits 863 Tecniques for Evaluating Limits Wat ou sould learn Use te dividing out tecnique to evaluate its of functions Use te rationalizing
335_qd /4/5 :5 PM Page 863 Section Tecniques for Evaluating Limits 863 Tecniques for Evaluating Limits Wat ou sould learn Use te dividing out tecnique to evaluate its of functions Use te rationalizing
MATH 5a Spring 2018 READING ASSIGNMENTS FOR CHAPTER 2
 MATH 5a Spring 2018 READING ASSIGNMENTS FOR CHAPTER 2 Note: Tere will be a very sort online reading quiz (WebWork) on eac reading assignment due one our before class on its due date. Due dates can be found
MATH 5a Spring 2018 READING ASSIGNMENTS FOR CHAPTER 2 Note: Tere will be a very sort online reading quiz (WebWork) on eac reading assignment due one our before class on its due date. Due dates can be found
1. SEQUENCES INVOLVING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH (GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES)
 Numbers nd Opertions, Algebr, nd Functions 45. SEQUENCES INVOLVING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH (GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES) In sequence of terms involving eponentil growth, which the testing service lso clls geometric
Numbers nd Opertions, Algebr, nd Functions 45. SEQUENCES INVOLVING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH (GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES) In sequence of terms involving eponentil growth, which the testing service lso clls geometric
Vector Processing Contours
 Vector Processing Contours Andrey Kirsanov Department of Automation and Control Processes MAMI Moscow State Tecnical University Moscow, Russia AndKirsanov@yandex.ru A.Vavilin and K-H. Jo Department of
Vector Processing Contours Andrey Kirsanov Department of Automation and Control Processes MAMI Moscow State Tecnical University Moscow, Russia AndKirsanov@yandex.ru A.Vavilin and K-H. Jo Department of
MAC-CPTM Situations Project
 raft o not use witout permission -P ituations Project ituation 20: rea of Plane Figures Prompt teacer in a geometry class introduces formulas for te areas of parallelograms, trapezoids, and romi. e removes
raft o not use witout permission -P ituations Project ituation 20: rea of Plane Figures Prompt teacer in a geometry class introduces formulas for te areas of parallelograms, trapezoids, and romi. e removes
2.5 Evaluating Limits Algebraically
 SECTION.5 Evaluating Limits Algebraically 3.5 Evaluating Limits Algebraically Preinary Questions. Wic of te following is indeterminate at x? x C x ; x x C ; x x C 3 ; x C x C 3 At x, x isofteform 0 xc3
SECTION.5 Evaluating Limits Algebraically 3.5 Evaluating Limits Algebraically Preinary Questions. Wic of te following is indeterminate at x? x C x ; x x C ; x x C 3 ; x C x C 3 At x, x isofteform 0 xc3
It is recommended to change the limits of integration while doing a substitution.
 MAT 21 eptember 7, 216 Review Indrjit Jn. Generl Tips It is recommended to chnge the limits of integrtion while doing substitution. First write the min formul (eg. centroid, moment of inerti, mss, work
MAT 21 eptember 7, 216 Review Indrjit Jn. Generl Tips It is recommended to chnge the limits of integrtion while doing substitution. First write the min formul (eg. centroid, moment of inerti, mss, work
2 Computing all Intersections of a Set of Segments Line Segment Intersection
 15-451/651: Design & Anlysis of Algorithms Novemer 14, 2016 Lecture #21 Sweep-Line nd Segment Intersection lst chnged: Novemer 8, 2017 1 Preliminries The sweep-line prdigm is very powerful lgorithmic design
15-451/651: Design & Anlysis of Algorithms Novemer 14, 2016 Lecture #21 Sweep-Line nd Segment Intersection lst chnged: Novemer 8, 2017 1 Preliminries The sweep-line prdigm is very powerful lgorithmic design
Applications of Integration
 Week 12. Applications of Integration 12.1.Areas Between Curves Example 12.1. Determine the area of the region enclosed by y = x 2 and y = x. Solution. First you need to find the points where the two functions
Week 12. Applications of Integration 12.1.Areas Between Curves Example 12.1. Determine the area of the region enclosed by y = x 2 and y = x. Solution. First you need to find the points where the two functions
Materials: Whiteboard, TI-Nspire classroom set, quadratic tangents program, and a computer projector.
 Adam Clinc Lesson: Deriving te Derivative Grade Level: 12 t grade, Calculus I class Materials: Witeboard, TI-Nspire classroom set, quadratic tangents program, and a computer projector. Goals/Objectives:
Adam Clinc Lesson: Deriving te Derivative Grade Level: 12 t grade, Calculus I class Materials: Witeboard, TI-Nspire classroom set, quadratic tangents program, and a computer projector. Goals/Objectives:
Haar Transform CS 430 Denbigh Starkey
 Haar Transform CS Denbig Starkey. Background. Computing te transform. Restoring te original image from te transform 7. Producing te transform matrix 8 5. Using Haar for lossless compression 6. Using Haar
Haar Transform CS Denbig Starkey. Background. Computing te transform. Restoring te original image from te transform 7. Producing te transform matrix 8 5. Using Haar for lossless compression 6. Using Haar
2.3 Additional Relations
 3 2.3 Additional Relations Figure 2.3 identiies additional relations, indicating te locations o te object and image, and te ratio o teir eigts (magniication) and orientations. Ray enters te lens parallel
3 2.3 Additional Relations Figure 2.3 identiies additional relations, indicating te locations o te object and image, and te ratio o teir eigts (magniication) and orientations. Ray enters te lens parallel
PLK-B SERIES Technical Manual (USA Version) CLICK HERE FOR CONTENTS
 PLK-B SERIES Technical Manual (USA Version) CLICK ERE FOR CONTENTS CONTROL BOX PANEL MOST COMMONLY USED FUNCTIONS INITIAL READING OF SYSTEM SOFTWARE/PAGES 1-2 RE-INSTALLATION OF TE SYSTEM SOFTWARE/PAGES
PLK-B SERIES Technical Manual (USA Version) CLICK ERE FOR CONTENTS CONTROL BOX PANEL MOST COMMONLY USED FUNCTIONS INITIAL READING OF SYSTEM SOFTWARE/PAGES 1-2 RE-INSTALLATION OF TE SYSTEM SOFTWARE/PAGES
NOTES: A quick overview of 2-D geometry
 NOTES: A quick overview of 2-D geometry Wat is 2-D geometry? Also called plane geometry, it s te geometry tat deals wit two dimensional sapes flat tings tat ave lengt and widt, suc as a piece of paper.
NOTES: A quick overview of 2-D geometry Wat is 2-D geometry? Also called plane geometry, it s te geometry tat deals wit two dimensional sapes flat tings tat ave lengt and widt, suc as a piece of paper.
The (, D) and (, N) problems in double-step digraphs with unilateral distance
 Electronic Journal of Grap Teory and Applications () (), Te (, D) and (, N) problems in double-step digraps wit unilateral distance C Dalfó, MA Fiol Departament de Matemàtica Aplicada IV Universitat Politècnica
Electronic Journal of Grap Teory and Applications () (), Te (, D) and (, N) problems in double-step digraps wit unilateral distance C Dalfó, MA Fiol Departament de Matemàtica Aplicada IV Universitat Politècnica
P(r)dr = probability of generating a random number in the interval dr near r. For this probability idea to make sense we must have
 Rndom Numers nd Monte Crlo Methods Rndom Numer Methods The integrtion methods discussed so fr ll re sed upon mking polynomil pproximtions to the integrnd. Another clss of numericl methods relies upon using
Rndom Numers nd Monte Crlo Methods Rndom Numer Methods The integrtion methods discussed so fr ll re sed upon mking polynomil pproximtions to the integrnd. Another clss of numericl methods relies upon using
8.2 Areas in the Plane
 39 Chpter 8 Applictions of Definite Integrls 8. Ares in the Plne Wht ou will lern out... Are Between Curves Are Enclosed Intersecting Curves Boundries with Chnging Functions Integrting with Respect to
39 Chpter 8 Applictions of Definite Integrls 8. Ares in the Plne Wht ou will lern out... Are Between Curves Are Enclosed Intersecting Curves Boundries with Chnging Functions Integrting with Respect to
MTH 146 Conics Supplement
 105- Review of Conics MTH 146 Conics Supplement In this section we review conics If ou ne more detils thn re present in the notes, r through section 105 of the ook Definition: A prol is the set of points
105- Review of Conics MTH 146 Conics Supplement In this section we review conics If ou ne more detils thn re present in the notes, r through section 105 of the ook Definition: A prol is the set of points
Data Structures and Programming Spring 2014, Midterm Exam.
 Data Structures and Programming Spring 2014, Midterm Exam. 1. (10 pts) Order te following functions 2.2 n, log(n 10 ), 2 2012, 25n log(n), 1.1 n, 2n 5.5, 4 log(n), 2 10, n 1.02, 5n 5, 76n, 8n 5 + 5n 2
Data Structures and Programming Spring 2014, Midterm Exam. 1. (10 pts) Order te following functions 2.2 n, log(n 10 ), 2 2012, 25n log(n), 1.1 n, 2n 5.5, 4 log(n), 2 10, n 1.02, 5n 5, 76n, 8n 5 + 5n 2
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 MATH 6 The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus (FTC) gives method of finding the signed re etween the grph of f nd the x-xis on the intervl [, ]. The theorem is: FTC: If f is
MATH 6 The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus (FTC) gives method of finding the signed re etween the grph of f nd the x-xis on the intervl [, ]. The theorem is: FTC: If f is
Surfaces. Differential Geometry Lia Vas
 Differentil Geometry Li Vs Surfces When studying curves, we studied how the curve twisted nd turned in spce. We now turn to surfces, two-dimensionl objects in three-dimensionl spce nd exmine how the concept
Differentil Geometry Li Vs Surfces When studying curves, we studied how the curve twisted nd turned in spce. We now turn to surfces, two-dimensionl objects in three-dimensionl spce nd exmine how the concept
MTH-112 Quiz 1 - Solutions
 MTH- Quiz - Solutions Words in italics are for eplanation purposes onl (not necessar to write in te tests or. Determine weter te given relation is a function. Give te domain and range of te relation. {(,
MTH- Quiz - Solutions Words in italics are for eplanation purposes onl (not necessar to write in te tests or. Determine weter te given relation is a function. Give te domain and range of te relation. {(,
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 2003
 Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Homework 8. Due: Tuesday, March 31st, 2009
 MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 9 Homework 8 Due: Tuesday, March 3st, 9 Section 6.5, pg. 54: 7, 3. Section 6.6, pg. 58:, 3. Section 6.7, pg. 66: 3, 5, 47. Section 6.8, pg. 73: 33, 38. Section
MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 9 Homework 8 Due: Tuesday, March 3st, 9 Section 6.5, pg. 54: 7, 3. Section 6.6, pg. 58:, 3. Section 6.7, pg. 66: 3, 5, 47. Section 6.8, pg. 73: 33, 38. Section
Hash-Based Indexes. Chapter 11. Comp 521 Files and Databases Fall
 Has-Based Indexes Capter 11 Comp 521 Files and Databases Fall 2012 1 Introduction Hasing maps a searc key directly to te pid of te containing page/page-overflow cain Doesn t require intermediate page fetces
Has-Based Indexes Capter 11 Comp 521 Files and Databases Fall 2012 1 Introduction Hasing maps a searc key directly to te pid of te containing page/page-overflow cain Doesn t require intermediate page fetces
Supplemental Notes: Line Integrals
 Nottion: Supplementl Notes: Line Integrls Let be n oriented curve prmeterized by r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t) where t b. denotes the curve with its orienttion reversed. 1 + 2 mens tke curve 1 nd curve 2 nd
Nottion: Supplementl Notes: Line Integrls Let be n oriented curve prmeterized by r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t) where t b. denotes the curve with its orienttion reversed. 1 + 2 mens tke curve 1 nd curve 2 nd
THANK YOU FOR YOUR PURCHASE!
 THANK YOU FOR YOUR PURCHASE! Te resources included in tis purcase were designed and created by me. I ope tat you find tis resource elpful in your classroom. Please feel free to contact me wit any questions
THANK YOU FOR YOUR PURCHASE! Te resources included in tis purcase were designed and created by me. I ope tat you find tis resource elpful in your classroom. Please feel free to contact me wit any questions
Greedy Algorithms Spanning Trees
 Greedy Algoritms Spnning Trees Cpter 1, Wt mkes greedy lgoritm? Fesible Hs to stisfy te problem s constrints Loclly Optiml Te greedy prt Hs to mke te best locl coice mong ll fesible coices vilble on tt
Greedy Algoritms Spnning Trees Cpter 1, Wt mkes greedy lgoritm? Fesible Hs to stisfy te problem s constrints Loclly Optiml Te greedy prt Hs to mke te best locl coice mong ll fesible coices vilble on tt
CS 234. Module 6. October 25, CS 234 Module 6 ADT Dictionary 1 / 22
 CS 234 Module 6 October 25, 2016 CS 234 Module 6 ADT Dictionary 1 / 22 Case study Problem: Find a way to store student records for a course, wit unique IDs for eac student, were records can be accessed,
CS 234 Module 6 October 25, 2016 CS 234 Module 6 ADT Dictionary 1 / 22 Case study Problem: Find a way to store student records for a course, wit unique IDs for eac student, were records can be accessed,
