9.1 apply the distance and midpoint formulas
|
|
|
- Christina Pitts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 9.1 pply the distnce nd midpoint formuls DISTANCE FORMULA MIDPOINT FORMULA To find the midpoint between two points x, y nd x y 1 1,, we Exmple 1: Find the distnce between the two points. Then, find the midpoint of the line segment joining the two points. Round ll non-integer nswers to two deciml plces.. 1.5, 4 nd.3, 9 Distnce: Midpoint:, Wht re the differences between: Sclene Tringle Isosceles Tringle Equilterl Tringle Exmple : The vertices of tringle re given. Clssify the tringle s sclene, isosceles, or equilterl. 4, 1, 6 0, 1 It my be helpful to lbel the points! Distnce: Type of Tringle: Distnce: Distnce:
2 Exmple 3: Use the given distnce d between the two points to find the vlue of x., 7 x, 1 d 89 Exmple 4: Write n eqution for the perpendiculr bisector of the line segment joining the two points: 3, 4 D5, 6 C Remember to mke n eqution for line, we need point nd slope! Point: Find the midpoint of the segment. Slope: Find the slope of the segment, then pply the opposite reciprocl. Plce the Point nd Slope into y y mx 1 x 1
3 9. Grph nd Write Equtions for Prbols ( x ) 1. Eqution : S. F.: x x 8y 4 py Step 1: Get the squred vrible or lone. x 8y Step : Identify the vertex. If there re no numbers being dded to or subtrcted from the vribles, you cn ssume the vertex is t 0,0. Vertex, Step 3: Identify the p vlue. To do so, set whtever is in front of the non-squred vrible equl to 4p. Solve for p. 8 4p Step 4: Determine the direction of opening. If p is positive, the grph will open up. If p is negtive, it will open down. Step 5: Find the focus. The focus is point found by dding p to the y vlue of the vertex. It is lwys locted within the rc of the prbol. (lwys dd) Step 6: Find the directrix. The directrix is horizontl line y. To find the number, subtrct the p vlue from the y vlue of the vertex. (lwys subtrct) Step 7: Determine the xis of symmetry. The xis of symmetry will be verticl line x. It will be equl to the x-coordinte of the vertex. Opens Focus y x, Step 8: Grph this informtion long with two dditionl points to complete the grph. x y
4 . Eqution : x 36y 0 x y 3. Eqution : S. F.: x 8y 3 x h 4 py k x y
5 9. Dy : Grph nd Write Equtions for Prbols ( y ) 1. Eqution : S. F.: y y 3x 4 px Step 1: Get the squred vrible or lone. y 3x Step : Identify the vertex. If there re no numbers being dded to or subtrcted from the vribles, you cn ssume the vertex is t 0,0. Vertex, Step 3: Identify the p vlue. To do so, set whtever is in front of the nonsqured vrible equl to 4p. Solve for p. 3 4p Step 4: Determine the direction of opening. If p is positive, the grph will open right. If p is negtive, the grph will open left. Opens Step 5: Find the focus. The focus is point found by dding p to the x vlue of the vertex. Focus, Step 6: Find the directrix. The directrix is verticl line x. To find the number, subtrct the p vlue from the x vlue of the vertex. Step 7: Determine the xis of symmetry. The xis of symmetry will be horizontl line y. It will be equl to the y-coordinte of the vertex. x y Step 8: Grph this informtion long with two dditionl points to complete the grph. x y
6 . Eqution : 3y 4x x y 3. Eqution : S. F.: y 3 0x 4 y k 4 px h x y
7 9. Dy 3 (continued) Exmple 1: Write the stndrd form of the eqution of the prbol with the given focus 0, 4 nd vertex t, 0 0. Grph the given informtion to help you determine whether this would be n x 4py or y 4px eqution. Determine the p vlue. Plce the p vlue into the stndrd form nd simplify the eqution. 5 Exmple : Write the stndrd form of the eqution of the prbol with the given focus, 0 nd vertex t 0, 0. Grph the given informtion to help you determine whether this would be n x 4py or y 4px eqution. Determine the p vlue. Plce the p vlue into the stndrd form nd simplify the eqution. Exmple 3: Write the stndrd form of the eqution of the prbol with the given directrix 5 x nd vertex t, 0 0. Grph the given informtion to help you determine whether this would be n x 4py or y 4px eqution. Determine the p vlue. Plce the p vlue into the stndrd form nd simplify the eqution.
8 9.3 Grph nd Write equtions of circles Notice tht x nd Exmple 1: Eqution : 5y 5x 40 y re on the left side of the eqution, joined by plus sign, nd tht the x is listed first. Also notice tht the x nd y re lone (no numbers in front). 5y 5x 40 Step 1: Get the squred vribles or with the x listed first. on the left side of the equl sign Step : Identify the center. If there re no numbers being dded to or subtrcted from the vribles, you cn ssume the center is t 0,0. Center, Step 3: Identify the rdius. To do so, tke the squre root of the number on the right side of the equl sign. (no decimls) r = Step 4: Grph the center long with severl points, s determined by the rdius. x y Wht is the difference between the stndrd eqution of circle nd the stndrd eqution of the prbols?
9 S. F.: Exmple : Eqution : x h y k r y 1 x 5 64 x y Exmple 3: Write the stndrd form of the eqution of the circle with the given rdius r 5 nd whose center is t 7,1. x h y k S. F.: r Eqution: Exmple 4: Write the stndrd form of the eqution of the circle tht psses through the given point 8,14 nd whose center is the origin. x h y k S. F.: r Eqution:
10 9.4 Grph nd Write Equtions OF ELLIPSES An ellipse is the set of ll points P in plne such tht the sum of the distnces between P nd two fixed points, clled the foci, is constnt. Stndrd form of n ellipse with horizontl mjor xis. x h y k b 1 In ech problem, we will grph the center, the vertices, the co-vertices, nd the foci.
11 Eqution : 4x 5y 100 4x 5y x h y k S. F.: Step 1: Get the right side of the eqution equl to 1. b 1 Step : Identify the center. If there re no numbers being dded to or subtrcted from the vribles, you cn ssume the center is t0,0. If there re numbers being dded or subtrcted, tke the opposite of ech s the x nd y coordintes of the center. Center, Step 3: Determine which denomintor contins the. The is the lrger denomintor. The purpose of the vlue is to help us crete the mjor xis nd the vertices tht re on ech end of the mjor xis. Tody, the is under the x vrible, which mens tht the mjor xis will be horizontl like the x-xis. Find the nd determine how the mjor xis will look. Tke the squre root of to determine. Mjor xis: = = Step 4: The vertices re points t either end of the mjor xis. If the is under the x- vrible, the vertices cn be found by dding to the x vlue of the center. Vertices,, Step 5: Determine which denomintor contins the b. It will lwys be the smller of the two denomintors. It will help us determine the minor xis nd the co-vertices tht re on ech end. Tody, the b is under the y vrible, which mens tht the minor xis will be verticl like the y -xis. Find the b nd use it to determine b. Step 6: The co-vertices re points t either end of the minor xis. Since the b is under the y -vrible, the vertices cn be found by dding b to the y vlue of the center. Covertices Step 7: Determine the foci. Foci re two points locted on the mjor xis. c 5 4 Becuse, tody, the mjor xis is horizontl like the x-xis, we will find these c 1 two points by dding c to the x vlue of the center. C is determined by the formul: c b c 1 or Foci c 5,,,, Step 8: Grph the center, vertices, line long the mjor xis, co-vertices, line long the minor xis, nd foci. Use the mjor nd minor xis lines to help you sketch the ellipse.
12 Eqution :. x h y k S. F.: 9x 16y 144 b 1 Center, Mjor xis: = Vertices,, Co-vertices,, c = Foci,,
13 3. x 5 4y x 1 y 3 8 Center, Mjor xis: Center, Mjor xis: = Vertices,, Vertices,, Co-vertices,, Co-vertices,, c = Foci,, Foci,,
14 9.4 Grph nd Write Equtions OF ELLIPSES (dy ) An ellipse is the set of ll points P in plne such tht the sum of the distnces between P nd two fixed points, clled the foci, is constnt. Stndrd form of n ellipse with verticl mjor xis. y k x h b 1 In ech problem, we will grph the center, the vertices, the co-vertices, nd the foci.
15 Eqution : 5x 4y 100 5x 4y y k x h S. F.: Step 1: Get the right side of the eqution equl to 1. b 1 Step : Identify the center. If there re no numbers being dded to or subtrcted from the vribles, you cn ssume the center is t 0,0. If there re numbers being dded or subtrcted, tke the opposite of ech s the x nd y coordintes of the center. Center, Step 3: Determine which denomintor contins the. The is the lrger denomintor. The purpose of the vlue is to help us crete the mjor xis nd the vertices tht re on ech end of the mjor xis. Tody, the is under the y vrible, which mens tht the mjor xis will be verticl like the y -xis. Find the nd determine the how the mjor xis will look. Tke the squre root of to determine. Mjor xis: = = Step 4: The vertices re points t either end of the mjor xis. If the is under the y - vrible, the vertices cn be found by dding to the y vlue of the center. Vertices,, Step 5: Determine which denomintor contins the b. It will lwys be the smller of the two denomintors. It will help us determine the minor xis nd the co-vertices tht re on ech end. Tody, the b is under the x vrible, which mens tht the minor xis will be horizontl like the x -xis. Find the b nd use it to determine b. Step 6: The co-vertices re points t either end of the minor xis. Since the b is under the x -vrible, the vertices cn be found by dding b to the x vlue of the center. Covertices Step 7: Determine the foci. Foci re two points locted on the mjor xis. c 5 4 Becuse, tody, the mjor xis is verticl like the y-xis, we will find these two c 1 points by dding c to the y vlue of the center. C is determined by the formul: c b c 1 or Foci c 5,,,, Step 8: Grph the center, vertices, line long the mjor xis, co-vertices, line long the minor xis, nd foci. Use the mjor nd minor xis lines to help you sketch the ellipse.
16 x y x 4 y Center, Mjor xis: Center, Mjor xis: = Vertices,, Vertices,, Co-vertices,, Co-vertices,, c = Foci,, Foci,,
17 9.5 Grph nd Write Equtions OF hyperbols A hyperbol is the set of ll point P such tht the difference of the distnces between P nd two fixed points, gin clled the foci, is constnt. Stndrd form of hyperbol with horizontl trnsverse xis. x h y k b 1 In ech problem, we will grph the center, the vertices, line through the trnsverse xis, the conjugte xis, the foci, nd the symptotes.
18 Eqution : 5x 4y 100 5x 4y x h y k S. F.: b 1 Step 1: Get the right side of the eqution equl to 1. Step : Identify the center nd grph it. Center, Step 3: Determine which denomintor contins the. The is lwys underneth the positively squred vrible. The purpose of the vlue is to help us crete the trnsverse xis nd the vertices tht re on ech end of the trnsverse xis. Tody, the is under the x vrible, which mens tht the trnsverse xis will be horizontl like the x-xis. Find the nd tke the squre root of to determine. = = Step 4: The vertices re points t either end of the trnsverse xis. If the is under the x-vrible, the vertices cn be found by dding to the x vlue of the center. Drw the vertices nd connect them to crete the trnsverse xis. Vertices,, Step 5: Determine which denomintor contins theb. It will lwys be below the negtively squre vrible. Tody, the b is under the y vrible. Find the b nd use it to determine b. Conjugte xis points: Step 6: The b vlue will help us crete the two points tht connect the conjugte xis. Since the b is under the y -vrible, the points cn be found by dding b to the y vlue of the center. Step 7: Determine the foci. Foci re two points locted beyond the trnsverse xis. Becuse, tody, the trnsverse xis is horizontl like the x-xis, we will find these two points by dding c to the x vlue of the center. C is determined by the formul: c b Step 8: Determine the symptotes. Wht s unique bout hyperbols is the presence of symptotes. For tody s hyperbols, in which the is under the x- b vrible, the eqution will be. We will strt from the center of the hyperbol nd b b pply this eqution s two different slopes: nd. We will drw the symptotes s dshed lines. They will help us crete the shpe of the brnches. Foci b 5 5,,,, nd 5 Step 9: Grph the center, the vertices, line through the trnsverse xis, the conjugte xis, the foci, nd the symptotes. Then sketch the shpe of the brnches.
19 . 4x 49y 196 = c = Asymptotes: Center Vertices Conjugte xis points Foci,,,,,,, 3. 4x y 36 Center, = Vertices,, b = Conjugte xis points,, c = Foci,, Asymptotes:
20 9.5 Grph nd Write Equtions OF hyperbols (Dy ) Stndrd form of hyperbol with verticl trnsverse xis. y k x h b 1 In ech problem, we will grph the center, the vertices, line through the trnsverse xis, the conjugte xis, the foci, nd the symptotes. 1. Eqution : 4y 16x 64 4y 16x 64 Step 1: Get the right side of the eqution equl to 1. Step : Identify the center nd grph it. Center, Step 3: Determine which denomintor contins the. Tody, the is under the y vrible, which mens tht the trnsverse xis will be verticl like the y-xis. = = Step 4: The vertices re points t either end of the trnsverse xis. If the is under the y-vrible, the vertices cn be found by dding to the y vlue of the center. Vertices Step 5: Determine which denomintor contins theb. It will lwys be below the negtively squre vrible. Tody, the b is under the x vrible. Step 6: The b vlue will help us crete the two points tht connect the conjugte xis. Since the b is under the x -vrible, the points cn be found by dding b to the x vlue of the center. Step 7: Determine the foci. Becuse, tody, the trnsverse xis is verticl like the y-xis, we will find these two points by dding c to the y vlue of the center. C is determined by the formul: c b Conjugte xis points: Foci Step 8: Determine the symptotes. For tody s hyperbols, in which the is under the y-vrible, the eqution will be. b b,,,,,, Step 9: Grph the center, the vertices, line through the trnsverse xis, the conjugte xis, the foci, nd the symptotes. Then sketch the shpe of the brnches.
21 . 9y 36x 36 Center, = Vertices,, Conjugte xis points,, c = Foci,, Asymptotes: 3. 10y 5x 100 Center, Vertices,, Conjugte xis points,, Foci,, Asymptotes:
22 9.6 clssify conic sections Any conic cn be described by generl second degree eqution, where A, B, C, D, E, nd F re just coefficients. Given ny conic eqution, we cn figure out whether it is Prbol, Circle, n Ellipse, or Hyperbol. Ax Bxy Cy Dx Ey F 0 1. x y x 4y 1 0 CTS: 1. Isolte the x s nd y s with prenthesis. If you hve both the squred nd liner version of the vrible, then you ll need to complete the squre.. Mke sure tht the coefficient on the squred vrible is 1. If not, pull out GCF. b 3. Find the c vlue with the eqution 4. Crefully blnce the eqution. 5. Fctor. 6. Bsed on wht you know bout the conic, rewrite it in its stndrd form..
23 . x y 4x x y 16x 4y y 4y x 6 0
Graphing Conic Sections
 Grphing Conic Sections Definition of Circle Set of ll points in plne tht re n equl distnce, clled the rdius, from fixed point in tht plne, clled the center. Grphing Circle (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 where
Grphing Conic Sections Definition of Circle Set of ll points in plne tht re n equl distnce, clled the rdius, from fixed point in tht plne, clled the center. Grphing Circle (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 where
Conic Sections Parabola Objective: Define conic section, parabola, draw a parabola, standard equations and their graphs
 Conic Sections Prol Ojective: Define conic section, prol, drw prol, stndrd equtions nd their grphs The curves creted y intersecting doule npped right circulr cone with plne re clled conic sections. If
Conic Sections Prol Ojective: Define conic section, prol, drw prol, stndrd equtions nd their grphs The curves creted y intersecting doule npped right circulr cone with plne re clled conic sections. If
Hyperbolas. Definition of Hyperbola
 CHAT Pre-Clculus Hyperols The third type of conic is clled hyperol. For n ellipse, the sum of the distnces from the foci nd point on the ellipse is fixed numer. For hyperol, the difference of the distnces
CHAT Pre-Clculus Hyperols The third type of conic is clled hyperol. For n ellipse, the sum of the distnces from the foci nd point on the ellipse is fixed numer. For hyperol, the difference of the distnces
Objective: Students will understand what it means to describe, graph and write the equation of a parabola. Parabolas
 Pge 1 of 8 Ojective: Students will understnd wht it mens to descrie, grph nd write the eqution of prol. Prols Prol: collection of ll points P in plne tht re the sme distnce from fixed point, the focus
Pge 1 of 8 Ojective: Students will understnd wht it mens to descrie, grph nd write the eqution of prol. Prols Prol: collection of ll points P in plne tht re the sme distnce from fixed point, the focus
Section 10.4 Hyperbolas
 66 Section 10.4 Hyperbols Objective : Definition of hyperbol & hyperbols centered t (0, 0). The third type of conic we will study is the hyperbol. It is defined in the sme mnner tht we defined the prbol
66 Section 10.4 Hyperbols Objective : Definition of hyperbol & hyperbols centered t (0, 0). The third type of conic we will study is the hyperbol. It is defined in the sme mnner tht we defined the prbol
Study Sheet ( )
 Key Terms prol circle Ellipse hyperol directrix focus focl length xis of symmetry vertex Study Sheet (11.1-11.4) Conic Section A conic section is section of cone. The ellipse, prol, nd hyperol, long with
Key Terms prol circle Ellipse hyperol directrix focus focl length xis of symmetry vertex Study Sheet (11.1-11.4) Conic Section A conic section is section of cone. The ellipse, prol, nd hyperol, long with
Class-XI Mathematics Conic Sections Chapter-11 Chapter Notes Key Concepts
 Clss-XI Mthemtics Conic Sections Chpter-11 Chpter Notes Key Concepts 1. Let be fixed verticl line nd m be nother line intersecting it t fixed point V nd inclined to it t nd ngle On rotting the line m round
Clss-XI Mthemtics Conic Sections Chpter-11 Chpter Notes Key Concepts 1. Let be fixed verticl line nd m be nother line intersecting it t fixed point V nd inclined to it t nd ngle On rotting the line m round
ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY. The curves obtained by slicing the cone with a plane not passing through the vertex are called conics.
 ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY Definition of Conic: The curves obtined by slicing the cone with plne not pssing through the vertex re clled conics. A Conic is the locus directrix of point which moves in plne, so
ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY Definition of Conic: The curves obtined by slicing the cone with plne not pssing through the vertex re clled conics. A Conic is the locus directrix of point which moves in plne, so
Algebra II Notes Unit Ten: Conic Sections
 Sllus Ojective: 0. The student will sketch the grph of conic section with centers either t or not t the origin. (PARABOLAS) Review: The Midpoint Formul The midpoint M of the line segment connecting the
Sllus Ojective: 0. The student will sketch the grph of conic section with centers either t or not t the origin. (PARABOLAS) Review: The Midpoint Formul The midpoint M of the line segment connecting the
MTH 146 Conics Supplement
 105- Review of Conics MTH 146 Conics Supplement In this section we review conics If ou ne more detils thn re present in the notes, r through section 105 of the ook Definition: A prol is the set of points
105- Review of Conics MTH 146 Conics Supplement In this section we review conics If ou ne more detils thn re present in the notes, r through section 105 of the ook Definition: A prol is the set of points
Date: 9.1. Conics: Parabolas
 Dte: 9. Conics: Prols Preclculus H. Notes: Unit 9 Conics Conic Sections: curves tht re formed y the intersection of plne nd doulenpped cone Syllus Ojectives:. The student will grph reltions or functions,
Dte: 9. Conics: Prols Preclculus H. Notes: Unit 9 Conics Conic Sections: curves tht re formed y the intersection of plne nd doulenpped cone Syllus Ojectives:. The student will grph reltions or functions,
10.5 Graphing Quadratic Functions
 0.5 Grphing Qudrtic Functions Now tht we cn solve qudrtic equtions, we wnt to lern how to grph the function ssocited with the qudrtic eqution. We cll this the qudrtic function. Grphs of Qudrtic Functions
0.5 Grphing Qudrtic Functions Now tht we cn solve qudrtic equtions, we wnt to lern how to grph the function ssocited with the qudrtic eqution. We cll this the qudrtic function. Grphs of Qudrtic Functions
50 AMC LECTURES Lecture 2 Analytic Geometry Distance and Lines. can be calculated by the following formula:
 5 AMC LECTURES Lecture Anlytic Geometry Distnce nd Lines BASIC KNOWLEDGE. Distnce formul The distnce (d) between two points P ( x, y) nd P ( x, y) cn be clculted by the following formul: d ( x y () x )
5 AMC LECTURES Lecture Anlytic Geometry Distnce nd Lines BASIC KNOWLEDGE. Distnce formul The distnce (d) between two points P ( x, y) nd P ( x, y) cn be clculted by the following formul: d ( x y () x )
Topics in Analytic Geometry
 Nme Chpter 10 Topics in Anltic Geometr Section 10.1 Lines Objective: In this lesson ou lerned how to find the inclintion of line, the ngle between two lines, nd the distnce between point nd line. Importnt
Nme Chpter 10 Topics in Anltic Geometr Section 10.1 Lines Objective: In this lesson ou lerned how to find the inclintion of line, the ngle between two lines, nd the distnce between point nd line. Importnt
Area & Volume. Chapter 6.1 & 6.2 September 25, y = 1! x 2. Back to Area:
 Bck to Are: Are & Volume Chpter 6. & 6. Septemer 5, 6 We cn clculte the re etween the x-xis nd continuous function f on the intervl [,] using the definite integrl:! f x = lim$ f x * i )%x n i= Where fx
Bck to Are: Are & Volume Chpter 6. & 6. Septemer 5, 6 We cn clculte the re etween the x-xis nd continuous function f on the intervl [,] using the definite integrl:! f x = lim$ f x * i )%x n i= Where fx
Pythagoras theorem and trigonometry (2)
 HPTR 10 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry (2) 31 HPTR Liner equtions In hpter 19, Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry were used to find the lengths of sides nd the sizes of ngles in right-ngled tringles. These
HPTR 10 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry (2) 31 HPTR Liner equtions In hpter 19, Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry were used to find the lengths of sides nd the sizes of ngles in right-ngled tringles. These
Name Date Class. cot. tan. cos. 1 cot 2 csc 2
 Fundmentl Trigonometric Identities To prove trigonometric identit, use the fundmentl identities to mke one side of the eqution resemle the other side. Reciprocl nd Rtio Identities csc sec sin cos Negtive-Angle
Fundmentl Trigonometric Identities To prove trigonometric identit, use the fundmentl identities to mke one side of the eqution resemle the other side. Reciprocl nd Rtio Identities csc sec sin cos Negtive-Angle
1. SEQUENCES INVOLVING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH (GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES)
 Numbers nd Opertions, Algebr, nd Functions 45. SEQUENCES INVOLVING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH (GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES) In sequence of terms involving eponentil growth, which the testing service lso clls geometric
Numbers nd Opertions, Algebr, nd Functions 45. SEQUENCES INVOLVING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH (GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES) In sequence of terms involving eponentil growth, which the testing service lso clls geometric
Section 9.2 Hyperbolas
 Section 9. Hperols 597 Section 9. Hperols In the lst section, we lerned tht plnets hve pproimtel ellipticl orits round the sun. When n oject like comet is moving quickl, it is le to escpe the grvittionl
Section 9. Hperols 597 Section 9. Hperols In the lst section, we lerned tht plnets hve pproimtel ellipticl orits round the sun. When n oject like comet is moving quickl, it is le to escpe the grvittionl
Stained Glass Design. Teaching Goals:
 Stined Glss Design Time required 45-90 minutes Teching Gols: 1. Students pply grphic methods to design vrious shpes on the plne.. Students pply geometric trnsformtions of grphs of functions in order to
Stined Glss Design Time required 45-90 minutes Teching Gols: 1. Students pply grphic methods to design vrious shpes on the plne.. Students pply geometric trnsformtions of grphs of functions in order to
9.1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM (right triangles)
 Simplifying Rdicls: ) 1 b) 60 c) 11 d) 3 e) 7 Solve: ) x 4 9 b) 16 80 c) 9 16 9.1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM (right tringles) c If tringle is right tringle then b, b re the legs * c is clled the hypotenuse (side
Simplifying Rdicls: ) 1 b) 60 c) 11 d) 3 e) 7 Solve: ) x 4 9 b) 16 80 c) 9 16 9.1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM (right tringles) c If tringle is right tringle then b, b re the legs * c is clled the hypotenuse (side
Subtracting Fractions
 Lerning Enhncement Tem Model Answers: Adding nd Subtrcting Frctions Adding nd Subtrcting Frctions study guide. When the frctions both hve the sme denomintor (bottom) you cn do them using just simple dding
Lerning Enhncement Tem Model Answers: Adding nd Subtrcting Frctions Adding nd Subtrcting Frctions study guide. When the frctions both hve the sme denomintor (bottom) you cn do them using just simple dding
a < a+ x < a+2 x < < a+n x = b, n A i n f(x i ) x. i=1 i=1
 Mth 33 Volume Stewrt 5.2 Geometry of integrls. In this section, we will lern how to compute volumes using integrls defined by slice nlysis. First, we recll from Clculus I how to compute res. Given the
Mth 33 Volume Stewrt 5.2 Geometry of integrls. In this section, we will lern how to compute volumes using integrls defined by slice nlysis. First, we recll from Clculus I how to compute res. Given the
Summer Review Packet For Algebra 2 CP/Honors
 Summer Review Pcket For Alger CP/Honors Nme Current Course Mth Techer Introduction Alger uilds on topics studied from oth Alger nd Geometr. Certin topics re sufficientl involved tht the cll for some review
Summer Review Pcket For Alger CP/Honors Nme Current Course Mth Techer Introduction Alger uilds on topics studied from oth Alger nd Geometr. Certin topics re sufficientl involved tht the cll for some review
Angle properties of lines and polygons
 chievement Stndrd 91031 pply geometric resoning in solving problems Copy correctly Up to 3% of workbook Copying or scnning from ES workbooks is subject to the NZ Copyright ct which limits copying to 3%
chievement Stndrd 91031 pply geometric resoning in solving problems Copy correctly Up to 3% of workbook Copying or scnning from ES workbooks is subject to the NZ Copyright ct which limits copying to 3%
6.3 Volumes. Just as area is always positive, so is volume and our attitudes towards finding it.
 6.3 Volumes Just s re is lwys positive, so is volume nd our ttitudes towrds finding it. Let s review how to find the volume of regulr geometric prism, tht is, 3-dimensionl oject with two regulr fces seprted
6.3 Volumes Just s re is lwys positive, so is volume nd our ttitudes towrds finding it. Let s review how to find the volume of regulr geometric prism, tht is, 3-dimensionl oject with two regulr fces seprted
2 Computing all Intersections of a Set of Segments Line Segment Intersection
 15-451/651: Design & Anlysis of Algorithms Novemer 14, 2016 Lecture #21 Sweep-Line nd Segment Intersection lst chnged: Novemer 8, 2017 1 Preliminries The sweep-line prdigm is very powerful lgorithmic design
15-451/651: Design & Anlysis of Algorithms Novemer 14, 2016 Lecture #21 Sweep-Line nd Segment Intersection lst chnged: Novemer 8, 2017 1 Preliminries The sweep-line prdigm is very powerful lgorithmic design
Math 142, Exam 1 Information.
 Mth 14, Exm 1 Informtion. 9/14/10, LC 41, 9:30-10:45. Exm 1 will be bsed on: Sections 7.1-7.5. The corresponding ssigned homework problems (see http://www.mth.sc.edu/ boyln/sccourses/14f10/14.html) At
Mth 14, Exm 1 Informtion. 9/14/10, LC 41, 9:30-10:45. Exm 1 will be bsed on: Sections 7.1-7.5. The corresponding ssigned homework problems (see http://www.mth.sc.edu/ boyln/sccourses/14f10/14.html) At
Unit 5 Vocabulary. A function is a special relationship where each input has a single output.
 MODULE 3 Terms Definition Picture/Exmple/Nottion 1 Function Nottion Function nottion is n efficient nd effective wy to write functions of ll types. This nottion llows you to identify the input vlue with
MODULE 3 Terms Definition Picture/Exmple/Nottion 1 Function Nottion Function nottion is n efficient nd effective wy to write functions of ll types. This nottion llows you to identify the input vlue with
EXPONENTIAL & POWER GRAPHS
 Eponentil & Power Grphs EXPONENTIAL & POWER GRAPHS www.mthletics.com.u Eponentil EXPONENTIAL & Power & Grphs POWER GRAPHS These re grphs which result from equtions tht re not liner or qudrtic. The eponentil
Eponentil & Power Grphs EXPONENTIAL & POWER GRAPHS www.mthletics.com.u Eponentil EXPONENTIAL & Power & Grphs POWER GRAPHS These re grphs which result from equtions tht re not liner or qudrtic. The eponentil
MATH 2530: WORKSHEET 7. x 2 y dz dy dx =
 MATH 253: WORKSHT 7 () Wrm-up: () Review: polr coordintes, integrls involving polr coordintes, triple Riemnn sums, triple integrls, the pplictions of triple integrls (especilly to volume), nd cylindricl
MATH 253: WORKSHT 7 () Wrm-up: () Review: polr coordintes, integrls involving polr coordintes, triple Riemnn sums, triple integrls, the pplictions of triple integrls (especilly to volume), nd cylindricl
6.2 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method
 mth ppliction: volumes by disks: volume prt ii 6 6 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method One of the simplest pplictions of integrtion (Theorem 6) nd the ccumultion process is to determine so-clled volumes
mth ppliction: volumes by disks: volume prt ii 6 6 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method One of the simplest pplictions of integrtion (Theorem 6) nd the ccumultion process is to determine so-clled volumes
MSTH 236 ELAC SUMMER 2017 CP 1 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MSTH 236 ELAC SUMMER 2017 CP 1 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrse tht best completes ech sttement or nswers the question. Find the product. 1) (8y + 11)(4y 2-2y - 9) 1) Simplify the expression by combining
MSTH 236 ELAC SUMMER 2017 CP 1 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrse tht best completes ech sttement or nswers the question. Find the product. 1) (8y + 11)(4y 2-2y - 9) 1) Simplify the expression by combining
4-1 NAME DATE PERIOD. Study Guide. Parallel Lines and Planes P Q, O Q. Sample answers: A J, A F, and D E
 4-1 NAME DATE PERIOD Pges 142 147 Prllel Lines nd Plnes When plnes do not intersect, they re sid to e prllel. Also, when lines in the sme plne do not intersect, they re prllel. But when lines re not in
4-1 NAME DATE PERIOD Pges 142 147 Prllel Lines nd Plnes When plnes do not intersect, they re sid to e prllel. Also, when lines in the sme plne do not intersect, they re prllel. But when lines re not in
such that the S i cover S, or equivalently S
 MATH 55 Triple Integrls Fll 16 1. Definition Given solid in spce, prtition of consists of finite set of solis = { 1,, n } such tht the i cover, or equivlently n i. Furthermore, for ech i, intersects i
MATH 55 Triple Integrls Fll 16 1. Definition Given solid in spce, prtition of consists of finite set of solis = { 1,, n } such tht the i cover, or equivlently n i. Furthermore, for ech i, intersects i
ZZ - Advanced Math Review 2017
 ZZ - Advnced Mth Review Mtrix Multipliction Given! nd! find the sum of the elements of the product BA First, rewrite the mtrices in the correct order to multiply The product is BA hs order x since B is
ZZ - Advnced Mth Review Mtrix Multipliction Given! nd! find the sum of the elements of the product BA First, rewrite the mtrices in the correct order to multiply The product is BA hs order x since B is
called the vertex. The line through the focus perpendicular to the directrix is called the axis of the parabola.
 Review of conic sections Conic sections re grphs of the form REVIEW OF CONIC SECTIONS prols ellipses hperols P(, ) F(, p) O p =_p REVIEW OF CONIC SECTIONS In this section we give geometric definitions
Review of conic sections Conic sections re grphs of the form REVIEW OF CONIC SECTIONS prols ellipses hperols P(, ) F(, p) O p =_p REVIEW OF CONIC SECTIONS In this section we give geometric definitions
MA1008. Calculus and Linear Algebra for Engineers. Course Notes for Section B. Stephen Wills. Department of Mathematics. University College Cork
 MA1008 Clculus nd Liner Algebr for Engineers Course Notes for Section B Stephen Wills Deprtment of Mthemtics University College Cork s.wills@ucc.ie http://euclid.ucc.ie/pges/stff/wills/teching/m1008/ma1008.html
MA1008 Clculus nd Liner Algebr for Engineers Course Notes for Section B Stephen Wills Deprtment of Mthemtics University College Cork s.wills@ucc.ie http://euclid.ucc.ie/pges/stff/wills/teching/m1008/ma1008.html
INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES
 INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES CASEY KELLEHER AND ALESSANDRA PANTANO 0.1. Introduction. In this ctivity set we re going to introduce notion from Algebric Topology clled simplicil homology. The min
INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES CASEY KELLEHER AND ALESSANDRA PANTANO 0.1. Introduction. In this ctivity set we re going to introduce notion from Algebric Topology clled simplicil homology. The min
Are You Ready for Algebra 3/Trigonometry? Summer Packet **Required for all Algebra 3/Trig CP and Honors students**
 Are You Red for Algebr /Trigonometr? Summer Pcket **Required for ll Algebr /Trig CP nd Honors students** Pge of The Algebr /Trigonometr course prepres students for Clculus nd college science courses. In
Are You Red for Algebr /Trigonometr? Summer Pcket **Required for ll Algebr /Trig CP nd Honors students** Pge of The Algebr /Trigonometr course prepres students for Clculus nd college science courses. In
Math 4 Review for Quarter 2 Cumulative Test
 Mth 4 Review for Qurter 2 Cumultive Test Nme: I. Right Tringle Trigonometry (3.1-3.3) Key Fcts Pythgoren Theorem - In right tringle, 2 + b 2 = c 2 where c is the hypotenuse s shown below. c b Trigonometric
Mth 4 Review for Qurter 2 Cumultive Test Nme: I. Right Tringle Trigonometry (3.1-3.3) Key Fcts Pythgoren Theorem - In right tringle, 2 + b 2 = c 2 where c is the hypotenuse s shown below. c b Trigonometric
1.1 Lines AP Calculus
 . Lines AP Clculus. LINES Notecrds from Section.: Rules for Rounding Round or Truncte ll finl nswers to 3 deciml plces. Do NOT round before ou rech our finl nswer. Much of Clculus focuses on the concept
. Lines AP Clculus. LINES Notecrds from Section.: Rules for Rounding Round or Truncte ll finl nswers to 3 deciml plces. Do NOT round before ou rech our finl nswer. Much of Clculus focuses on the concept
B. Definition: The volume of a solid of known integrable cross-section area A(x) from x = a
 Mth 176 Clculus Sec. 6.: Volume I. Volume By Slicing A. Introduction We will e trying to find the volume of solid shped using the sum of cross section res times width. We will e driving towrd developing
Mth 176 Clculus Sec. 6.: Volume I. Volume By Slicing A. Introduction We will e trying to find the volume of solid shped using the sum of cross section res times width. We will e driving towrd developing
12-B FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS
 -B Frctions nd Decimls. () If ll four integers were negtive, their product would be positive, nd so could not equl one of them. If ll four integers were positive, their product would be much greter thn
-B Frctions nd Decimls. () If ll four integers were negtive, their product would be positive, nd so could not equl one of them. If ll four integers were positive, their product would be much greter thn
Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of a rational function?
 8. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS A..A A..G A..H A..K Grphing Rtionl Functions Essentil Question Wht re some of the chrcteristics of the grph of rtionl function? The prent function for rtionl functions
8. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS A..A A..G A..H A..K Grphing Rtionl Functions Essentil Question Wht re some of the chrcteristics of the grph of rtionl function? The prent function for rtionl functions
Introduction Transformation formulae Polar graphs Standard curves Polar equations Test GRAPHS INU0114/514 (MATHS 1)
 POLAR EQUATIONS AND GRAPHS GEOMETRY INU4/54 (MATHS ) Dr Adrin Jnnett MIMA CMth FRAS Polr equtions nd grphs / 6 Adrin Jnnett Objectives The purpose of this presenttion is to cover the following topics:
POLAR EQUATIONS AND GRAPHS GEOMETRY INU4/54 (MATHS ) Dr Adrin Jnnett MIMA CMth FRAS Polr equtions nd grphs / 6 Adrin Jnnett Objectives The purpose of this presenttion is to cover the following topics:
Yoplait with Areas and Volumes
 Yoplit with Ares nd Volumes Yoplit yogurt comes in two differently shped continers. One is truncted cone nd the other is n ellipticl cylinder (see photos below). In this exercise, you will determine the
Yoplit with Ares nd Volumes Yoplit yogurt comes in two differently shped continers. One is truncted cone nd the other is n ellipticl cylinder (see photos below). In this exercise, you will determine the
If f(x, y) is a surface that lies above r(t), we can think about the area between the surface and the curve.
 Line Integrls The ide of line integrl is very similr to tht of single integrls. If the function f(x) is bove the x-xis on the intervl [, b], then the integrl of f(x) over [, b] is the re under f over the
Line Integrls The ide of line integrl is very similr to tht of single integrls. If the function f(x) is bove the x-xis on the intervl [, b], then the integrl of f(x) over [, b] is the re under f over the
Study Guide for Exam 3
 Mth 05 Elementry Algebr Fll 00 Study Guide for Em Em is scheduled for Thursdy, November 8 th nd ill cover chpters 5 nd. You my use "5" note crd (both sides) nd scientific clcultor. You re epected to no
Mth 05 Elementry Algebr Fll 00 Study Guide for Em Em is scheduled for Thursdy, November 8 th nd ill cover chpters 5 nd. You my use "5" note crd (both sides) nd scientific clcultor. You re epected to no
What do all those bits mean now? Number Systems and Arithmetic. Introduction to Binary Numbers. Questions About Numbers
 Wht do ll those bits men now? bits (...) Number Systems nd Arithmetic or Computers go to elementry school instruction R-formt I-formt... integer dt number text chrs... floting point signed unsigned single
Wht do ll those bits men now? bits (...) Number Systems nd Arithmetic or Computers go to elementry school instruction R-formt I-formt... integer dt number text chrs... floting point signed unsigned single
Iterated Integrals. f (x; y) dy dx. p(x) To evaluate a type I integral, we rst evaluate the inner integral Z q(x) f (x; y) dy.
 Iterted Integrls Type I Integrls In this section, we begin the study of integrls over regions in the plne. To do so, however, requires tht we exmine the importnt ide of iterted integrls, in which inde
Iterted Integrls Type I Integrls In this section, we begin the study of integrls over regions in the plne. To do so, however, requires tht we exmine the importnt ide of iterted integrls, in which inde
RATIONAL EQUATION: APPLICATIONS & PROBLEM SOLVING
 RATIONAL EQUATION: APPLICATIONS & PROBLEM SOLVING When finding the LCD of problem involving the ddition or subtrction of frctions, it my be necessry to fctor some denomintors to discover some restricted
RATIONAL EQUATION: APPLICATIONS & PROBLEM SOLVING When finding the LCD of problem involving the ddition or subtrction of frctions, it my be necessry to fctor some denomintors to discover some restricted
Math 464 Fall 2012 Notes on Marginal and Conditional Densities October 18, 2012
 Mth 464 Fll 2012 Notes on Mrginl nd Conditionl Densities klin@mth.rizon.edu October 18, 2012 Mrginl densities. Suppose you hve 3 continuous rndom vribles X, Y, nd Z, with joint density f(x,y,z. The mrginl
Mth 464 Fll 2012 Notes on Mrginl nd Conditionl Densities klin@mth.rizon.edu October 18, 2012 Mrginl densities. Suppose you hve 3 continuous rndom vribles X, Y, nd Z, with joint density f(x,y,z. The mrginl
Fig.1. Let a source of monochromatic light be incident on a slit of finite width a, as shown in Fig. 1.
 Answer on Question #5692, Physics, Optics Stte slient fetures of single slit Frunhofer diffrction pttern. The slit is verticl nd illuminted by point source. Also, obtin n expression for intensity distribution
Answer on Question #5692, Physics, Optics Stte slient fetures of single slit Frunhofer diffrction pttern. The slit is verticl nd illuminted by point source. Also, obtin n expression for intensity distribution
SIMPLIFYING ALGEBRA PASSPORT.
 SIMPLIFYING ALGEBRA PASSPORT www.mthletics.com.u This booklet is ll bout turning complex problems into something simple. You will be ble to do something like this! ( 9- # + 4 ' ) ' ( 9- + 7-) ' ' Give
SIMPLIFYING ALGEBRA PASSPORT www.mthletics.com.u This booklet is ll bout turning complex problems into something simple. You will be ble to do something like this! ( 9- # + 4 ' ) ' ( 9- + 7-) ' ' Give
Conic Sections. College Algebra
 Conic Sections College Algebra Conic Sections A conic section, or conic, is a shape resulting from intersecting a right circular cone with a plane. The angle at which the plane intersects the cone determines
Conic Sections College Algebra Conic Sections A conic section, or conic, is a shape resulting from intersecting a right circular cone with a plane. The angle at which the plane intersects the cone determines
Grade 7/8 Math Circles Geometric Arithmetic October 31, 2012
 Fculty of Mthemtics Wterloo, Ontrio N2L 3G1 Grde 7/8 Mth Circles Geometric Arithmetic Octoer 31, 2012 Centre for Eduction in Mthemtics nd Computing Ancient Greece hs given irth to some of the most importnt
Fculty of Mthemtics Wterloo, Ontrio N2L 3G1 Grde 7/8 Mth Circles Geometric Arithmetic Octoer 31, 2012 Centre for Eduction in Mthemtics nd Computing Ancient Greece hs given irth to some of the most importnt
Mid-Chapter Quiz: Lessons 7-1 through 7-3
 Write an equation for and graph a parabola with the given focus F and vertex V 1. F(1, 5), V(1, 3) Because the focus and vertex share the same x coordinate, the graph is vertical. The focus is (h, k +
Write an equation for and graph a parabola with the given focus F and vertex V 1. F(1, 5), V(1, 3) Because the focus and vertex share the same x coordinate, the graph is vertical. The focus is (h, k +
x )Scales are the reciprocal of each other. e
 9. Reciprocls A Complete Slide Rule Mnul - eville W Young Chpter 9 Further Applictions of the LL scles The LL (e x ) scles nd the corresponding LL 0 (e -x or Exmple : 0.244 4.. Set the hir line over 4.
9. Reciprocls A Complete Slide Rule Mnul - eville W Young Chpter 9 Further Applictions of the LL scles The LL (e x ) scles nd the corresponding LL 0 (e -x or Exmple : 0.244 4.. Set the hir line over 4.
Solutions to Math 41 Final Exam December 12, 2011
 Solutions to Mth Finl Em December,. ( points) Find ech of the following its, with justifiction. If there is n infinite it, then eplin whether it is or. ( ) / ln() () (5 points) First we compute the it:
Solutions to Mth Finl Em December,. ( points) Find ech of the following its, with justifiction. If there is n infinite it, then eplin whether it is or. ( ) / ln() () (5 points) First we compute the it:
Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics. A circle is
 Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
8.2 Areas in the Plane
 39 Chpter 8 Applictions of Definite Integrls 8. Ares in the Plne Wht ou will lern out... Are Between Curves Are Enclosed Intersecting Curves Boundries with Chnging Functions Integrting with Respect to
39 Chpter 8 Applictions of Definite Integrls 8. Ares in the Plne Wht ou will lern out... Are Between Curves Are Enclosed Intersecting Curves Boundries with Chnging Functions Integrting with Respect to
9 4. CISC - Curriculum & Instruction Steering Committee. California County Superintendents Educational Services Association
 9. CISC - Curriculum & Instruction Steering Committee The Winning EQUATION A HIGH QUALITY MATHEMATICS PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM FOR TEACHERS IN GRADES THROUGH ALGEBRA II STRAND: NUMBER SENSE: Rtionl
9. CISC - Curriculum & Instruction Steering Committee The Winning EQUATION A HIGH QUALITY MATHEMATICS PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM FOR TEACHERS IN GRADES THROUGH ALGEBRA II STRAND: NUMBER SENSE: Rtionl
Answer Key Lesson 6: Workshop: Angles and Lines
 nswer Key esson 6: tudent Guide ngles nd ines Questions 1 3 (G p. 406) 1. 120 ; 360 2. hey re the sme. 3. 360 Here re four different ptterns tht re used to mke quilts. Work with your group. se your Power
nswer Key esson 6: tudent Guide ngles nd ines Questions 1 3 (G p. 406) 1. 120 ; 360 2. hey re the sme. 3. 360 Here re four different ptterns tht re used to mke quilts. Work with your group. se your Power
The Reciprocal Function Family. Objectives To graph reciprocal functions To graph translations of reciprocal functions
 - The Reciprocl Function Fmil Objectives To grph reciprocl functions To grph trnsltions of reciprocl functions Content Stndrds F.BF.3 Identif the effect on the grph of replcing f () b f() k, kf(), f(k),
- The Reciprocl Function Fmil Objectives To grph reciprocl functions To grph trnsltions of reciprocl functions Content Stndrds F.BF.3 Identif the effect on the grph of replcing f () b f() k, kf(), f(k),
Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 2 4 x 0
 Pre-Calculus Section 1.1 Completing the Square Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 4 x 0. 3x 3y
Pre-Calculus Section 1.1 Completing the Square Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 4 x 0. 3x 3y
Improper Integrals. October 4, 2017
 Improper Integrls October 4, 7 Introduction We hve seen how to clculte definite integrl when the it is rel number. However, there re times when we re interested to compute the integrl sy for emple 3. Here
Improper Integrls October 4, 7 Introduction We hve seen how to clculte definite integrl when the it is rel number. However, there re times when we re interested to compute the integrl sy for emple 3. Here
1 Drawing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrator
 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor 1 1 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor This Tutoril will show you how to drw simple objects with three-dimensionl ppernce. At first we will drw rrows indicting
Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor 1 1 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor This Tutoril will show you how to drw simple objects with three-dimensionl ppernce. At first we will drw rrows indicting
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 MATH 6 The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus (FTC) gives method of finding the signed re etween the grph of f nd the x-xis on the intervl [, ]. The theorem is: FTC: If f is
MATH 6 The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus (FTC) gives method of finding the signed re etween the grph of f nd the x-xis on the intervl [, ]. The theorem is: FTC: If f is
4452 Mathematical Modeling Lecture 4: Lagrange Multipliers
 Mth Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Pge 4452 Mthemticl Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Lgrnge multipliers re high powered mthemticl technique to find the mximum nd minimum of multidimensionl
Mth Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Pge 4452 Mthemticl Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Lgrnge multipliers re high powered mthemticl technique to find the mximum nd minimum of multidimensionl
CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS
 CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Writing equations of conic sections ) Graphing equations of conic sections 3) Solving quadratic systems Section: Essential Question 8-1 Apply
CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Writing equations of conic sections ) Graphing equations of conic sections 3) Solving quadratic systems Section: Essential Question 8-1 Apply
1.5 Extrema and the Mean Value Theorem
 .5 Extrem nd the Men Vlue Theorem.5. Mximum nd Minimum Vlues Definition.5. (Glol Mximum). Let f : D! R e function with domin D. Then f hs n glol mximum vlue t point c, iff(c) f(x) for ll x D. The vlue
.5 Extrem nd the Men Vlue Theorem.5. Mximum nd Minimum Vlues Definition.5. (Glol Mximum). Let f : D! R e function with domin D. Then f hs n glol mximum vlue t point c, iff(c) f(x) for ll x D. The vlue
APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION
 Chpter 3 DACS 1 Lok 004/05 CHAPTER 5 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 5.1 Geometricl Interprettion-Definite Integrl (pge 36) 5. Are of Region (pge 369) 5..1 Are of Region Under Grph (pge 369) Figure 5.7 shows
Chpter 3 DACS 1 Lok 004/05 CHAPTER 5 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 5.1 Geometricl Interprettion-Definite Integrl (pge 36) 5. Are of Region (pge 369) 5..1 Are of Region Under Grph (pge 369) Figure 5.7 shows
Applications of the Definite Integral ( Areas and Volumes)
 Mth1242 Project II Nme: Applictions of the Definite Integrl ( Ares nd Volumes) In this project, we explore some pplictions of the definite integrl. We use integrls to find the re etween the grphs of two
Mth1242 Project II Nme: Applictions of the Definite Integrl ( Ares nd Volumes) In this project, we explore some pplictions of the definite integrl. We use integrls to find the re etween the grphs of two
Introduction to Integration
 Introduction to Integrtion Definite integrls of piecewise constnt functions A constnt function is function of the form Integrtion is two things t the sme time: A form of summtion. The opposite of differentition.
Introduction to Integrtion Definite integrls of piecewise constnt functions A constnt function is function of the form Integrtion is two things t the sme time: A form of summtion. The opposite of differentition.
Integration. September 28, 2017
 Integrtion September 8, 7 Introduction We hve lerned in previous chpter on how to do the differentition. It is conventionl in mthemtics tht we re supposed to lern bout the integrtion s well. As you my
Integrtion September 8, 7 Introduction We hve lerned in previous chpter on how to do the differentition. It is conventionl in mthemtics tht we re supposed to lern bout the integrtion s well. As you my
What do all those bits mean now? Number Systems and Arithmetic. Introduction to Binary Numbers. Questions About Numbers
 Wht do ll those bits men now? bits (...) Number Systems nd Arithmetic or Computers go to elementry school instruction R-formt I-formt... integer dt number text chrs... floting point signed unsigned single
Wht do ll those bits men now? bits (...) Number Systems nd Arithmetic or Computers go to elementry school instruction R-formt I-formt... integer dt number text chrs... floting point signed unsigned single
Unit #9 : Definite Integral Properties, Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties, Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties, Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet
 Name: Period: ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet Algebra II Unit 10 Plan: This plan is subject to change at the teacher s discretion. Section Topic Formative Work Due Date 10.3 Circles
Name: Period: ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet Algebra II Unit 10 Plan: This plan is subject to change at the teacher s discretion. Section Topic Formative Work Due Date 10.3 Circles
Moments and products of inertia and radii of gyration about central axes. I x ¼ I y ¼ Ix 0 ¼ a4. r x ¼ r y ¼ r 0 x ¼ 0:2887a.
 TBLE.1 Properties of sections NOTTION: ¼ re ðlengthþ 2 ; y ¼ distnce to extreme fiber (length); I ¼ moment of inerti ðlength Þ; r ¼ rdius of gyrtion (length); Z ¼ plstic section modulus ðlength 3 Þ;SF¼
TBLE.1 Properties of sections NOTTION: ¼ re ðlengthþ 2 ; y ¼ distnce to extreme fiber (length); I ¼ moment of inerti ðlength Þ; r ¼ rdius of gyrtion (length); Z ¼ plstic section modulus ðlength 3 Þ;SF¼
Unit 12 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork
 Unit 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork Back in Unit 7, we delved into the algebra and geometry of lines. We showed that lines can be written in several forms: a) the general form: Ax + By + C =
Unit 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork Back in Unit 7, we delved into the algebra and geometry of lines. We showed that lines can be written in several forms: a) the general form: Ax + By + C =
Ray surface intersections
 Ry surfce intersections Some primitives Finite primitives: polygons spheres, cylinders, cones prts of generl qudrics Infinite primitives: plnes infinite cylinders nd cones generl qudrics A finite primitive
Ry surfce intersections Some primitives Finite primitives: polygons spheres, cylinders, cones prts of generl qudrics Infinite primitives: plnes infinite cylinders nd cones generl qudrics A finite primitive
Chapter 10. Exploring Conic Sections
 Chapter 10 Exploring Conic Sections Conics A conic section is a curve formed by the intersection of a plane and a hollow cone. Each of these shapes are made by slicing the cone and observing the shape
Chapter 10 Exploring Conic Sections Conics A conic section is a curve formed by the intersection of a plane and a hollow cone. Each of these shapes are made by slicing the cone and observing the shape
3 FRACTIONS. Before you start. Objectives
 FRATIONS Only one eighth of n iceberg shows bove the surfce of the wter, which leves most of it hidden. The lrgest northern hemisphere iceberg ws encountered ner Bffin Islnd in nd in 1. It ws 1 km long,
FRATIONS Only one eighth of n iceberg shows bove the surfce of the wter, which leves most of it hidden. The lrgest northern hemisphere iceberg ws encountered ner Bffin Islnd in nd in 1. It ws 1 km long,
EECS 281: Homework #4 Due: Thursday, October 7, 2004
 EECS 28: Homework #4 Due: Thursdy, October 7, 24 Nme: Emil:. Convert the 24-bit number x44243 to mime bse64: QUJD First, set is to brek 8-bit blocks into 6-bit blocks, nd then convert: x44243 b b 6 2 9
EECS 28: Homework #4 Due: Thursdy, October 7, 24 Nme: Emil:. Convert the 24-bit number x44243 to mime bse64: QUJD First, set is to brek 8-bit blocks into 6-bit blocks, nd then convert: x44243 b b 6 2 9
Questions About Numbers. Number Systems and Arithmetic. Introduction to Binary Numbers. Negative Numbers?
 Questions About Numbers Number Systems nd Arithmetic or Computers go to elementry school How do you represent negtive numbers? frctions? relly lrge numbers? relly smll numbers? How do you do rithmetic?
Questions About Numbers Number Systems nd Arithmetic or Computers go to elementry school How do you represent negtive numbers? frctions? relly lrge numbers? relly smll numbers? How do you do rithmetic?
Multivariable Calculus
 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
Rational Numbers---Adding Fractions With Like Denominators.
 Rtionl Numbers---Adding Frctions With Like Denomintors. A. In Words: To dd frctions with like denomintors, dd the numertors nd write the sum over the sme denomintor. B. In Symbols: For frctions c nd b
Rtionl Numbers---Adding Frctions With Like Denomintors. A. In Words: To dd frctions with like denomintors, dd the numertors nd write the sum over the sme denomintor. B. In Symbols: For frctions c nd b
Geometric transformations
 Geometric trnsformtions Computer Grphics Some slides re bsed on Shy Shlom slides from TAU mn n n m m T A,,,,,, 2 1 2 22 12 1 21 11 Rows become columns nd columns become rows nm n n m m A,,,,,, 1 1 2 22
Geometric trnsformtions Computer Grphics Some slides re bsed on Shy Shlom slides from TAU mn n n m m T A,,,,,, 2 1 2 22 12 1 21 11 Rows become columns nd columns become rows nm n n m m A,,,,,, 1 1 2 22
Section 3.1: Sequences and Series
 Section.: Sequences d Series Sequences Let s strt out with the definition of sequence: sequence: ordered list of numbers, often with definite pttern Recll tht in set, order doesn t mtter so this is one
Section.: Sequences d Series Sequences Let s strt out with the definition of sequence: sequence: ordered list of numbers, often with definite pttern Recll tht in set, order doesn t mtter so this is one
HW Stereotactic Targeting
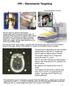 HW Stereotctic Trgeting We re bout to perform stereotctic rdiosurgery with the Gmm Knife under CT guidnce. We instrument the ptient with bse ring nd for CT scnning we ttch fiducil cge (FC). Above: bse
HW Stereotctic Trgeting We re bout to perform stereotctic rdiosurgery with the Gmm Knife under CT guidnce. We instrument the ptient with bse ring nd for CT scnning we ttch fiducil cge (FC). Above: bse
Fall 2018 Midterm 1 October 11, ˆ You may not ask questions about the exam except for language clarifications.
 15-112 Fll 2018 Midterm 1 October 11, 2018 Nme: Andrew ID: Recittion Section: ˆ You my not use ny books, notes, extr pper, or electronic devices during this exm. There should be nothing on your desk or
15-112 Fll 2018 Midterm 1 October 11, 2018 Nme: Andrew ID: Recittion Section: ˆ You my not use ny books, notes, extr pper, or electronic devices during this exm. There should be nothing on your desk or
MA 124 (Calculus II) Lecture 2: January 24, 2019 Section A3. Professor Jennifer Balakrishnan,
 Wht is on tody Professor Jennifer Blkrishnn, jbl@bu.edu 1 Velocity nd net chnge 1 2 Regions between curves 3 1 Velocity nd net chnge Briggs-Cochrn-Gillett 6.1 pp. 398-46 Suppose you re driving long stright
Wht is on tody Professor Jennifer Blkrishnn, jbl@bu.edu 1 Velocity nd net chnge 1 2 Regions between curves 3 1 Velocity nd net chnge Briggs-Cochrn-Gillett 6.1 pp. 398-46 Suppose you re driving long stright
1.1. Interval Notation and Set Notation Essential Question When is it convenient to use set-builder notation to represent a set of numbers?
 1.1 TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS Prepring for 2A.6.K, 2A.7.I Intervl Nottion nd Set Nottion Essentil Question When is it convenient to use set-uilder nottion to represent set of numers? A collection
1.1 TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS Prepring for 2A.6.K, 2A.7.I Intervl Nottion nd Set Nottion Essentil Question When is it convenient to use set-uilder nottion to represent set of numers? A collection
1.) Write the equation of a circle in standard form with radius 3 and center (-3,4). Then graph the circle.
 Welcome to the world of conic sections! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bfonicn4bbg Some examples of conics in the real world: Parabolas Ellipse Hyperbola Your Assignment: Circle -Find at least four pictures
Welcome to the world of conic sections! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bfonicn4bbg Some examples of conics in the real world: Parabolas Ellipse Hyperbola Your Assignment: Circle -Find at least four pictures
TASK SPECIFIC DESCRIPTION
 MYP Algebr II/Trig Unit 2 Ch. 4 Trnsformtions Project Nme: Block: - Due Dte: Tuesdy, 11/7 (B-dy) & Wednesdy, 11/8 (A-dy) Mterils: Grph pper, ruler, protrctor, compss, highlight mrkers/colored pencils SCORE:
MYP Algebr II/Trig Unit 2 Ch. 4 Trnsformtions Project Nme: Block: - Due Dte: Tuesdy, 11/7 (B-dy) & Wednesdy, 11/8 (A-dy) Mterils: Grph pper, ruler, protrctor, compss, highlight mrkers/colored pencils SCORE:
Integration. October 25, 2016
 Integrtion October 5, 6 Introduction We hve lerned in previous chpter on how to do the differentition. It is conventionl in mthemtics tht we re supposed to lern bout the integrtion s well. As you my hve
Integrtion October 5, 6 Introduction We hve lerned in previous chpter on how to do the differentition. It is conventionl in mthemtics tht we re supposed to lern bout the integrtion s well. As you my hve
Naming 3D objects. 1 Name the 3D objects labelled in these models. Use the word bank to help you.
 Nming 3D ojects 1 Nme the 3D ojects lelled in these models. Use the word nk to help you. Word nk cue prism sphere cone cylinder pyrmid D A C F A B C D cone cylinder cue cylinder E B E prism F cue G G pyrmid
Nming 3D ojects 1 Nme the 3D ojects lelled in these models. Use the word nk to help you. Word nk cue prism sphere cone cylinder pyrmid D A C F A B C D cone cylinder cue cylinder E B E prism F cue G G pyrmid
1 Quad-Edge Construction Operators
 CS48: Computer Grphics Hndout # Geometric Modeling Originl Hndout #5 Stnford University Tuesdy, 8 December 99 Originl Lecture #5: 9 November 99 Topics: Mnipultions with Qud-Edge Dt Structures Scribe: Mike
CS48: Computer Grphics Hndout # Geometric Modeling Originl Hndout #5 Stnford University Tuesdy, 8 December 99 Originl Lecture #5: 9 November 99 Topics: Mnipultions with Qud-Edge Dt Structures Scribe: Mike
Thirty-fourth Annual Columbus State Invitational Mathematics Tournament. Instructions
 Thirty-fourth Annul Columbus Stte Invittionl Mthemtics Tournment Sponsored by Columbus Stte University Deprtment of Mthemtics Februry, 008 ************************* The Mthemtics Deprtment t Columbus Stte
Thirty-fourth Annul Columbus Stte Invittionl Mthemtics Tournment Sponsored by Columbus Stte University Deprtment of Mthemtics Februry, 008 ************************* The Mthemtics Deprtment t Columbus Stte
