Implementation of Flight Simulator using 3-Dimensional Terrain Modeling
|
|
|
- Ambrose Johnston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Implementation of Flight Simulator using 3-Dimensional Terrain Modeling 1 1, First Author School of Computer Engineering, Hanshin University, Osan City, S. Korea, stryoo@hs.ac.kr Abstract During the last three decades, flight simulators have played an important role in the training of both military and commercial pilots because it enables us to cut down on the enormous cost that would be needed for a real flight. This paper presents the development of the flight simulator which consists of a terrain modeler, an object modeler, a terrain renderer and a flight path generator. A terrain modeler transforms the terrain information into a digital terrain model. The object modeler constructs and locates the virtual object, and the renderer represents the object using pseudo shading and image mapping. Finally, the flight path generator extracts the virtual path using the cubic spline curve Keywords: Digital Terrain Model(DTM), Triangulated Irregular Network(TIN), Flight Simulation 1. Introduction Digital elevation model (DEM) is often used as a generic term for Digital Surface Model (DSM) and Digital Terrain Models (DTM) [1, 2]. In most cases a Digital Terrain Model represents the bare ground without any objects like buildings and plants on it. Digital Surface Model on the other hand represents the earth's surface and includes all objects on it. Both of them have their uses in numerous applications: extracting the shape and elevation differences of the earth's surface, modeling the flow of water or movement of masses, engineering and infrastructure design, geomorphology and physical geography, gravimetric measurements, visualizing the earth's surface in traditional maps, 3D maps and models, 3D flight planning and flight simulation, line-of-sight-analysis and other areas. During the last three decades, flight simulators have played an important role in the training of both military and commercial pilots because it enables us to cut down on the enormous cost that would be needed for a real flight. To develop the flight simulation using digital terrain model, we suggest the flight simulator which consists of a terrain modeler, an object modeler, a terrain renderer and a flight path generator. Figure 1. The structure of the flight simulator International Journal of Digital Content Technology and its Applications(JDCTA) Volume 7, Number 12, August
2 2. Suggested Flight Simulator As shown in Figure 1, the flight simulator consists of a terrain modeler, an object modeler, a renderer and a flight-path generator. A terrain modeler makes a Digital Terrain Model using DEM. A DEM is a binary array that saves the height of each terrain and is the same as recording the height of each spot from the indicated terrain into a large binary array. An object modeler constructs virtual objects using a script file or an icon based primitives and locates them on the terrain. A renderer represents a three-dimensional object as a shaded two-dimensional projection on a view surface. A flight path generator extracts the virtual path for the flight simulation Terrain Modeler Figure 2 shows the flow of the terrain modeler that transforms DEM into a digital terrain model(dtm). Such a DTM has two primary forms of representation. The first is the rectangular grid model and the second is the triangulated irregular network(tin) model. To model the terrain, we use both of them Rectangular Grids Figure 2. The flow of the terrain model Rectangular grids are generated by rounding off known data points to the nearest grid point and then iteratively interpolating all the unassigned grid positions. The rectangular grid model is fast and simple and is suitable for flat area. However, it is hard to represent a curved region exactly[3][4] Triangulated irregular networks Triangulated network are created by linking triplets of nodes and maintaining pointers from each triangle to its three neighbors. Such network can be used to describe almost any surfaces. Compared to the rectangular grid model, the TIN produces more accurate surface representations with less data storage. To make such a TIN model, a preprocessing step that extracts surface-specific points and constructs a triangulated network with the extracted points is necessary[5, 6]. In this paper, the 8 neighborhood method for extracting surface-specific point and the delaunay triangulation method[3, 4, 7, 8, 9] for making a triangulated network are used. Figure 3 show the results of the rectangular grid model and TIN model. (a) DEM (b) Rectangular Grid Model (c) Triangulated Irregular Network Figure 3. Terrain modeling 211
3 2.2. Object Modeler Figure 4. The process of an object modeler The object modeler is a module that constructs the object and positions the selected object. It can be divided into a modeler that constructs the virtual object based on the primitives and a mapper that positions the selected object onto the selected region (Figure 4). The object on the region can either consist of a single building or a number of buildings. The form of the building may also vary. Therefore, this object modeler should be able to contain all these different types of buildings.. Two different methods are used for generating objects. One is by using a script file and the other is by using the icon based primitives. A script file is necessary for the object modeling to produce according to the user s demand. This script file consists of the structured form, size and the direction value of each object. In the icon based approach, eight basic primitives, as shown in Figure 4, have been used for the object modeling. The mapper that positions the object onto the actual region is just as important as the object modeler. Objects that exist on the ground are not always located on flat ground. So, the mapper should calculate the shape and steepness of the object to place it in the correct position. Figure 5 shows the procedure of object generation. At first, selects the desired area on the terrain with the mouse. The selected area is flattened for object mapping, as shown in Figure 5.b. 'flattening' means changing the height of the selected region into the average height of the region. Secondly, chooses one from the icon based primitives. Finally, the user inputs the size, height and direction of the object using the dialog box. After these procedures, the object mapper locates the objects to the actual position on the ground as shown in Figure 5.c. (a) DTM (b) flattening (c) object mapping Figure 5. Flatting and object mapping of selected area 212
4 2.3. Terrain Renderer A digital terrain model is a two dimensional digital elevation map accompanied by a satellite image or an aerial photograph. Three dimensional visualization of the terrain represented by the DTM has been used in flight simulation, environmental planning, GIS applications and other areas[10, 11]. There are three approaches to rendering the terrain in this paper. One is a method giving the color according to its height, so-called pseudo shading(figure 6-a). This method is simple but not photorealistic. The other is the image mapping method[12]. This method maps a real image, taken from the satellite, onto the surface of the terrain(figure 6-b). Another method is rendering terrain using heightfield ray tracing(figure 6-c). Satellite image mapping method is a little bit slower than pseudo shading. However, most flight simulations use this mapping method, because it can generate a more realistic image. (a) pseudo shading (b) image mapping (c) height-field RT Figure 6. Terrain rendering 2.4. Flight Path Generator The flight path can be predetermined before the simulation if information such as the flight's route or its destination has been given. If the flight path has been predetermined by the above conditions, the simulation can be done without user control. The flight path can be determined by marking the flight's route with a few check points and connecting them with a smooth curve. In this study, the cubic spline curve algorithm[13] has been used to smoothly connect the random check points existing on the three-dimensional space. It has been made possible to select the flight path using mouse and dialog box. Figure 7 shows the flight path created by selecting 3 basic flight points. When the 3 basic flight points have been put in, a cubic spline curve using these three control points is created. This cubic spline curve is used in the virtual path. When the flight path makes a collision with the terrain, an error message is given and the flight path is adjusted in this study Figure 7. Extraction flight path by cubic spline 3. The Result of Flight Simulation Figure 8 shows the image of the flight simulation system. The main window displays 3 dimensional terrain model along the virtual path at each view point, the right-top window shows 2 dimensional virtual path on the terrain and the right-bottom window shows the location of current 3 dimensional 213
5 virtual path. Figure 8.a shows the image of the wireframe using the rectangular grid method, Figure 8.b the image of the pseudo shading, Figure 8.c the rendered image using triangulated irregular network and Figure 8.d the rendered image using the satellite image mapping method. Figure 9 is the final result of flight simulation using the digital terrain model. (a) wireframe (b) pseudo shading (rectangular grid) (c) pseudo shading (TIN) (d) satellite image mapping Figure 8. Suggested flight simulator system 4. Conclusions and Future Work In this study, a flight simulation has been implemented through terrain modeling, using the rectangular grid method and the TIN method, and rendering, using a wireframe, pseudo shading and the satellite image mapping method. Also, it can change the characteristic of an object using the object browser and can save or load the terrain information using a script file. Future work is necessary on the area of FOV(Field of View) for real time simulations and the research of collision detection & prevention. Also, we can improve on the satellite image mapping to get the high quality of the flight simulation and it is necessary to study the flight-path user input module using other media, not keyboard.. 5. Acknowledgements This research was supported by Hanshin University Research Grant 6. References [1] John P. Wilson, Digital terrain modeling, Geomorphology, Volume 137, Issue 1, pp , [2] F. Schroder and P. Robbach, Managing The Complexity of Digital Terrain Models, Computer & Graphics, Vol. 18, No. 6, pp ,
6 [3] B. K. Choi and H. Y. Shin, Triangulation of scattered data in 3D space, Computer-aided design, Vol. 20, No. 5, pp , [4] Lee J., Comparison of existing methods for building triangulated irregular network models of terrain from grid digital elevation models, Int. J. of GIS 5(3), pp , [5] T. K. Peuker and D. H. Douglas, Detection of surface-specific points by local parallel processing of discrete terrain elevation data, Computer Vision Graphics and Image Processing, Vol. 4, pp , [6] S. Takahashi, Algorithms for Extracting Correct Critical Points and Constructing Topological Graphs from Discrete Geographical Elevation Data, Eurographics '95, Vol. 14, pp , [7] Franz Aurenhammer, Voronoi Diagrams A Survey of a Fundamental Geometric Data Structure, ACM Computing Surveys, Vol. 23, No. 3, [8] B. Joe, Construction of three-dimensional Delaunay triangulations using local transformations, Computer Aided Geometric Design, Vol. 8, pp , [9] A. Mirante and N. Weingarten, The radial sweep algorithm for constructing triangulated irregular networks, IEEE Computer Graphics & Application, Vol. 2, pp , [10] Hou Han-dana and Zhang Jian-feib, Research on Real-Time Visualization of Large-scale 3D Terrain, Procedia Engineering, Volume 29, issue (2012), pp , [11] Che Mat RUZINOOR, Abdul Rashid Mohamed SHARIFF, Biswajeet PRADHAN, Mahmud RODZI AHMAD and Mohd Shafry Mohd RAHIM, A review on 3D terrain visualization of GIS data: techniques and software, Geo-spatial Information Science, Vol.15, Issue 2, pp , [12] B. Geymayer, M. Prantl, H. Muller-Seelich and B. Tabatabai, Animation of Landscapes Using Satellite Imagery, Eurographics '91, Vol. 10, pp , [13] David F. Rogers and J. Alan Adams, Mathematical Elements for Computer Graphics, McGraw- Hill International Editions, USA, Figure 9. The result of flight simulation using DTM 215
DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELLING. Endre Katona University of Szeged Department of Informatics
 DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELLING Endre Katona University of Szeged Department of Informatics katona@inf.u-szeged.hu The problem: data sources data structures algorithms DTM = Digital Terrain Model Terrain function:
DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELLING Endre Katona University of Szeged Department of Informatics katona@inf.u-szeged.hu The problem: data sources data structures algorithms DTM = Digital Terrain Model Terrain function:
Statistical surfaces and interpolation. This is lecture ten
 Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
Online 3D terrain visualisation using Unity 3D game engine: A comparison of different contour intervals terrain data draped with UAV images
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Online 3D terrain visualisation using Unity 3D game engine: A comparison of different contour intervals terrain data draped with
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Online 3D terrain visualisation using Unity 3D game engine: A comparison of different contour intervals terrain data draped with
Investigation of Sampling and Interpolation Techniques for DEMs Derived from Different Data Sources
 Investigation of Sampling and Interpolation Techniques for DEMs Derived from Different Data Sources FARRAG ALI FARRAG 1 and RAGAB KHALIL 2 1: Assistant professor at Civil Engineering Department, Faculty
Investigation of Sampling and Interpolation Techniques for DEMs Derived from Different Data Sources FARRAG ALI FARRAG 1 and RAGAB KHALIL 2 1: Assistant professor at Civil Engineering Department, Faculty
DATA MODELS IN GIS. Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi
 DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
MATLAB Tools for LIDAR Data Conversion, Visualization, and Processing
 MATLAB Tools for LIDAR Data Conversion, Visualization, and Processing Xiao Wang a, Kaijing Zhou a, Jie Yang a, Yilong Lu *a a Nanyang Technological University, 50 Nanyang Avenue, Singapore 639798 ABSTRACT
MATLAB Tools for LIDAR Data Conversion, Visualization, and Processing Xiao Wang a, Kaijing Zhou a, Jie Yang a, Yilong Lu *a a Nanyang Technological University, 50 Nanyang Avenue, Singapore 639798 ABSTRACT
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
Lecture 4: Digital Elevation Models
 Lecture 4: Digital Elevation Models GEOG413/613 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 Digital Terrain Modeling Terms: DEM, DTM, DTEM, DSM, DHM not synonyms. The concepts they illustrate are different Digital Terrain Modeling
Lecture 4: Digital Elevation Models GEOG413/613 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 Digital Terrain Modeling Terms: DEM, DTM, DTEM, DSM, DHM not synonyms. The concepts they illustrate are different Digital Terrain Modeling
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Environmental Sciences 36 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Environmental Sciences 36 (2016 ) 184 190 International Conference on Geographies of Health and Living in Cities: Making Cities Healthy
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Environmental Sciences 36 (2016 ) 184 190 International Conference on Geographies of Health and Living in Cities: Making Cities Healthy
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Geostatistics Predictions with Deterministic Procedures
 Instituto Superior de Estatística e Gestão de Informação Universidade Nova de Lisboa Master of Science in Geospatial Technologies Geostatistics Predictions with Deterministic Procedures Carlos Alberto
Instituto Superior de Estatística e Gestão de Informação Universidade Nova de Lisboa Master of Science in Geospatial Technologies Geostatistics Predictions with Deterministic Procedures Carlos Alberto
Algorithms for GIS csci3225
 Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Class #2. Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures
 Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS
 STUDIA UNIV. BABEŞ BOLYAI, INFORMATICA, Volume XLV, Number 1, 2000 IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS GABRIELA DROJ Abstract. The change from paper maps to GIS, in various kinds of geographical
STUDIA UNIV. BABEŞ BOLYAI, INFORMATICA, Volume XLV, Number 1, 2000 IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS GABRIELA DROJ Abstract. The change from paper maps to GIS, in various kinds of geographical
ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 Published in SPIE Proceedings, Vol.3084, 1997, p 336-343 Computer 3-d site model generation based on aerial images Sergei Y. Zheltov, Yuri B. Blokhinov, Alexander A. Stepanov, Sergei V. Skryabin, Alexander
Published in SPIE Proceedings, Vol.3084, 1997, p 336-343 Computer 3-d site model generation based on aerial images Sergei Y. Zheltov, Yuri B. Blokhinov, Alexander A. Stepanov, Sergei V. Skryabin, Alexander
Experiments on Generation of 3D Virtual Geographic Environment Based on Laser Scanning Technique
 Experiments on Generation of 3D Virtual Geographic Environment Based on Laser Scanning Technique Jie Du 1, Fumio Yamazaki 2 Xiaoyong Chen 3 Apisit Eiumnoh 4, Michiro Kusanagi 3, R.P. Shrestha 4 1 School
Experiments on Generation of 3D Virtual Geographic Environment Based on Laser Scanning Technique Jie Du 1, Fumio Yamazaki 2 Xiaoyong Chen 3 Apisit Eiumnoh 4, Michiro Kusanagi 3, R.P. Shrestha 4 1 School
[Youn *, 5(11): November 2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor
![[Youn *, 5(11): November 2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor [Youn *, 5(11): November 2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor](/thumbs/91/105079225.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES AUTOMATIC EXTRACTING DEM FROM DSM WITH CONSECUTIVE MORPHOLOGICAL FILTERING Junhee Youn *1 & Tae-Hoon Kim 2 *1,2 Korea Institute of Civil Engineering
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES AUTOMATIC EXTRACTING DEM FROM DSM WITH CONSECUTIVE MORPHOLOGICAL FILTERING Junhee Youn *1 & Tae-Hoon Kim 2 *1,2 Korea Institute of Civil Engineering
AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF TERRAIN SKELETON LINES FROM DIGITAL ELEVATION MODELS
 AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF TERRAIN SKELETON LINES FROM DIGITAL ELEVATION MODELS F. Gülgen, T. Gökgöz Yildiz Technical University, Department of Geodetic and Photogrammetric Engineering, 34349 Besiktas Istanbul,
AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF TERRAIN SKELETON LINES FROM DIGITAL ELEVATION MODELS F. Gülgen, T. Gökgöz Yildiz Technical University, Department of Geodetic and Photogrammetric Engineering, 34349 Besiktas Istanbul,
Training i Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods September 2011
 Training i Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Geometric Operations Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl ITC FACULTY OF GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND
Training i Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Geometric Operations Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl ITC FACULTY OF GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND
Literature review for 3D Design Terrain Models for Construction Plans and GPS Control of Highway Construction Equipment
 Literature review for 3D Design Terrain Models for Construction Plans and GPS Control of Highway Construction Equipment Cassie Hintz Construction and Materials Support Center Department of Civil and Environmental
Literature review for 3D Design Terrain Models for Construction Plans and GPS Control of Highway Construction Equipment Cassie Hintz Construction and Materials Support Center Department of Civil and Environmental
MONO-IMAGE INTERSECTION FOR ORTHOIMAGE REVISION
 MONO-IMAGE INTERSECTION FOR ORTHOIMAGE REVISION Mohamed Ibrahim Zahran Associate Professor of Surveying and Photogrammetry Faculty of Engineering at Shoubra, Benha University ABSTRACT This research addresses
MONO-IMAGE INTERSECTION FOR ORTHOIMAGE REVISION Mohamed Ibrahim Zahran Associate Professor of Surveying and Photogrammetry Faculty of Engineering at Shoubra, Benha University ABSTRACT This research addresses
Understanding Geospatial Data Models
 Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction to 3D Data: Modeling with ArcGIS 3D Analyst and Google Earth CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 3D Data: Modeling with ArcGIS 3D Analyst and Google Earth Introduction to 3D Data is a self - study tutorial workbook that teaches you how to create data and maps with ESRI s
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 3D Data: Modeling with ArcGIS 3D Analyst and Google Earth Introduction to 3D Data is a self - study tutorial workbook that teaches you how to create data and maps with ESRI s
Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing. David Eppstein
 Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science (including joint work with Marshall Bern from WADS 01 and SODA 03) Outline
Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science (including joint work with Marshall Bern from WADS 01 and SODA 03) Outline
Contents of Lecture. Surface (Terrain) Data Models. Terrain Surface Representation. Sampling in Surface Model DEM
 Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
FOUR ADVANCES IN HANDLING UNCERTAINTIES IN SPATIAL DATA AND ANALYSIS
 FOUR ADVANCES IN HANDLING UNCERTAINTIES IN SPATIAL DATA AND ANALYSIS Wenzhong Shi Advanced Research Centre for Spatial Information Technology Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong
FOUR ADVANCES IN HANDLING UNCERTAINTIES IN SPATIAL DATA AND ANALYSIS Wenzhong Shi Advanced Research Centre for Spatial Information Technology Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong
CPSC 695. Methods for interpolation and analysis of continuing surfaces in GIS Dr. M. Gavrilova
 CPSC 695 Methods for interpolation and analysis of continuing surfaces in GIS Dr. M. Gavrilova Overview Data sampling for continuous surfaces Interpolation methods Global interpolation Local interpolation
CPSC 695 Methods for interpolation and analysis of continuing surfaces in GIS Dr. M. Gavrilova Overview Data sampling for continuous surfaces Interpolation methods Global interpolation Local interpolation
THE CONTOUR TREE - A POWERFUL CONCEPTUAL STRUCTURE FOR REPRESENTING THE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG CONTOUR LINES ON A TOPOGRAPHIC MAP
 THE CONTOUR TREE - A POWERFUL CONCEPTUAL STRUCTURE FOR REPRESENTING THE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG CONTOUR LINES ON A TOPOGRAPHIC MAP Adrian ALEXEI*, Mariana BARBARESSO* *Military Equipment and Technologies Research
THE CONTOUR TREE - A POWERFUL CONCEPTUAL STRUCTURE FOR REPRESENTING THE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG CONTOUR LINES ON A TOPOGRAPHIC MAP Adrian ALEXEI*, Mariana BARBARESSO* *Military Equipment and Technologies Research
Estimating the Accuracy of Digital Elevation Model Produced by Surfer Package
 International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 4, Issue 11, November 213] 2 ISSN 247-3338 Estimating the Accuracy of Digital Elevation Model Produced by Surfer Package Dr. Nagi
International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 4, Issue 11, November 213] 2 ISSN 247-3338 Estimating the Accuracy of Digital Elevation Model Produced by Surfer Package Dr. Nagi
Point Cloud Classification
 Point Cloud Classification Introduction VRMesh provides a powerful point cloud classification and feature extraction solution. It automatically classifies vegetation, building roofs, and ground points.
Point Cloud Classification Introduction VRMesh provides a powerful point cloud classification and feature extraction solution. It automatically classifies vegetation, building roofs, and ground points.
Surfaces, meshes, and topology
 Surfaces from Point Samples Surfaces, meshes, and topology A surface is a 2-manifold embedded in 3- dimensional Euclidean space Such surfaces are often approximated by triangle meshes 2 1 Triangle mesh
Surfaces from Point Samples Surfaces, meshes, and topology A surface is a 2-manifold embedded in 3- dimensional Euclidean space Such surfaces are often approximated by triangle meshes 2 1 Triangle mesh
3D GIS MODELING APPLICATION FOR DEVELOPING THE BUTUAN CITY 3D MODEL
 3D GIS MODELING APPLICATION FOR DEVELOPING THE BUTUAN CITY 3D MODEL Alexander T. Demetillo, Michelle V. Japitana and Peter John A. Galamiton CLAIMS-GIS Project, College of Engineering and Information Technology,
3D GIS MODELING APPLICATION FOR DEVELOPING THE BUTUAN CITY 3D MODEL Alexander T. Demetillo, Michelle V. Japitana and Peter John A. Galamiton CLAIMS-GIS Project, College of Engineering and Information Technology,
Digital photogrammetry project with very high-resolution stereo pairs acquired by DigitalGlobe, Inc. satellite Worldview-2
 White PAPER Greater area of the City of La Paz, Bolivia Digital photogrammetry project with very high-resolution stereo pairs acquired by DigitalGlobe, Inc. satellite Worldview-2 By: Engineers Nelson Mattie,
White PAPER Greater area of the City of La Paz, Bolivia Digital photogrammetry project with very high-resolution stereo pairs acquired by DigitalGlobe, Inc. satellite Worldview-2 By: Engineers Nelson Mattie,
Geographic Surfaces. David Tenenbaum EEOS 383 UMass Boston
 Geographic Surfaces Up to this point, we have talked about spatial data models that operate in two dimensions How about the rd dimension? Surface the continuous variation in space of a third dimension
Geographic Surfaces Up to this point, we have talked about spatial data models that operate in two dimensions How about the rd dimension? Surface the continuous variation in space of a third dimension
LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY
 LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce and explore surface data analysis using a vector data model: TIN. We
LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce and explore surface data analysis using a vector data model: TIN. We
Automatic generation of 3-d building models from multiple bounded polygons
 icccbe 2010 Nottingham University Press Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering W Tizani (Editor) Automatic generation of 3-d building models from multiple
icccbe 2010 Nottingham University Press Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering W Tizani (Editor) Automatic generation of 3-d building models from multiple
Automatic DTM Extraction from Dense Raw LIDAR Data in Urban Areas
 Automatic DTM Extraction from Dense Raw LIDAR Data in Urban Areas Nizar ABO AKEL, Ofer ZILBERSTEIN and Yerach DOYTSHER, Israel Key words: LIDAR, DSM, urban areas, DTM extraction. SUMMARY Although LIDAR
Automatic DTM Extraction from Dense Raw LIDAR Data in Urban Areas Nizar ABO AKEL, Ofer ZILBERSTEIN and Yerach DOYTSHER, Israel Key words: LIDAR, DSM, urban areas, DTM extraction. SUMMARY Although LIDAR
Using Hierarchical Warp Stereo for Topography. Introduction
 Using Hierarchical Warp Stereo for Topography Dr. Daniel Filiberti ECE/OPTI 531 Image Processing Lab for Remote Sensing Introduction Topography from Stereo Given a set of stereoscopic imagery, two perspective
Using Hierarchical Warp Stereo for Topography Dr. Daniel Filiberti ECE/OPTI 531 Image Processing Lab for Remote Sensing Introduction Topography from Stereo Given a set of stereoscopic imagery, two perspective
BUILDING DETECTION AND STRUCTURE LINE EXTRACTION FROM AIRBORNE LIDAR DATA
 BUILDING DETECTION AND STRUCTURE LINE EXTRACTION FROM AIRBORNE LIDAR DATA C. K. Wang a,, P.H. Hsu a, * a Dept. of Geomatics, National Cheng Kung University, No.1, University Road, Tainan 701, Taiwan. China-
BUILDING DETECTION AND STRUCTURE LINE EXTRACTION FROM AIRBORNE LIDAR DATA C. K. Wang a,, P.H. Hsu a, * a Dept. of Geomatics, National Cheng Kung University, No.1, University Road, Tainan 701, Taiwan. China-
Terrain correction. Backward geocoding. Terrain correction and ortho-rectification. Why geometric terrain correction? Rüdiger Gens
 Terrain correction and ortho-rectification Terrain correction Rüdiger Gens Why geometric terrain correction? Backward geocoding remove effects of side looking geometry of SAR images necessary step to allow
Terrain correction and ortho-rectification Terrain correction Rüdiger Gens Why geometric terrain correction? Backward geocoding remove effects of side looking geometry of SAR images necessary step to allow
Digital Elevation Models (DEM)
 Digital Elevation Models (DEM) Digital representation of the terrain surface also referred to as Digital Terrain Models (DTM) Digital Elevation Models (DEM) How has relief depiction changed with digital
Digital Elevation Models (DEM) Digital representation of the terrain surface also referred to as Digital Terrain Models (DTM) Digital Elevation Models (DEM) How has relief depiction changed with digital
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Geo-Environment. Close-Range Photogrammetry For Landslide Monitoring
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Geo-Environment Journal homepage:http://ijceg.ump.edu.my ISSN:21802742 Close-Range Photogrammetry For Landslide Monitoring Munirah Bt Radin Mohd Mokhtar,
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Geo-Environment Journal homepage:http://ijceg.ump.edu.my ISSN:21802742 Close-Range Photogrammetry For Landslide Monitoring Munirah Bt Radin Mohd Mokhtar,
CO-REGISTERING AND NORMALIZING STEREO-BASED ELEVATION DATA TO SUPPORT BUILDING DETECTION IN VHR IMAGES
 CO-REGISTERING AND NORMALIZING STEREO-BASED ELEVATION DATA TO SUPPORT BUILDING DETECTION IN VHR IMAGES Alaeldin Suliman, Yun Zhang, Raid Al-Tahir Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, University
CO-REGISTERING AND NORMALIZING STEREO-BASED ELEVATION DATA TO SUPPORT BUILDING DETECTION IN VHR IMAGES Alaeldin Suliman, Yun Zhang, Raid Al-Tahir Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, University
Computer Database Structure for Managing Data :-
 The Map as an Abstraction of Space :- We begin the process of abstraction by conceptualizing what we encounter as a group of points, lines, areas and surfaces. We make decision about which object to take
The Map as an Abstraction of Space :- We begin the process of abstraction by conceptualizing what we encounter as a group of points, lines, areas and surfaces. We make decision about which object to take
geobrowser3d.com The Power of 3D GIS Tools in your Browser
 geobrowser3d.com 1 The Power of 3D GIS Tools in your Browser Overview Introduction Modules Success Stories Build your own What is GeoBrowser3D Interactive 3D visualization system Modular platform OGC compliant
geobrowser3d.com 1 The Power of 3D GIS Tools in your Browser Overview Introduction Modules Success Stories Build your own What is GeoBrowser3D Interactive 3D visualization system Modular platform OGC compliant
Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (hytoiy wpark tjkim Working Group
 THE DEVELOPMENT OF AN ACCURATE DEM EXTRACTION STRATEGY FOR SATELLITE IMAGE PAIRS USING EPIPOLARITY OF LINEAR PUSHBROOM SENSORS AND INTELLIGENT INTERPOLATION SCHEME Hae-Yeoun Lee *, Wonkyu Park **, Taejung
THE DEVELOPMENT OF AN ACCURATE DEM EXTRACTION STRATEGY FOR SATELLITE IMAGE PAIRS USING EPIPOLARITY OF LINEAR PUSHBROOM SENSORS AND INTELLIGENT INTERPOLATION SCHEME Hae-Yeoun Lee *, Wonkyu Park **, Taejung
3D Terrain Modelling of the Amyntaio Ptolemais Basin
 2nd International Workshop in Geoenvironment and 1 3D Terrain Modelling of the Amyntaio Ptolemais Basin G. Argyris, I. Kapageridis and A. Triantafyllou Department of Geotechnology and Environmental Engineering,
2nd International Workshop in Geoenvironment and 1 3D Terrain Modelling of the Amyntaio Ptolemais Basin G. Argyris, I. Kapageridis and A. Triantafyllou Department of Geotechnology and Environmental Engineering,
Multipatched B-Spline Surfaces and Automatic Rough Cut Path Generation
 Int J Adv Manuf Technol (2000) 16:100 106 2000 Springer-Verlag London Limited Multipatched B-Spline Surfaces and Automatic Rough Cut Path Generation S. H. F. Chuang and I. Z. Wang Department of Mechanical
Int J Adv Manuf Technol (2000) 16:100 106 2000 Springer-Verlag London Limited Multipatched B-Spline Surfaces and Automatic Rough Cut Path Generation S. H. F. Chuang and I. Z. Wang Department of Mechanical
Research on Impact of Ground Control Point Distribution on Image Geometric Rectification Based on Voronoi Diagram
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 11 (2011) 365 371 Research on Impact of Ground Control Point Distribution on Image Geometric Rectification Based on Voronoi Diagram
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 11 (2011) 365 371 Research on Impact of Ground Control Point Distribution on Image Geometric Rectification Based on Voronoi Diagram
AUTOMATIC GENERATION OF DIGITAL BUILDING MODELS FOR COMPLEX STRUCTURES FROM LIDAR DATA
 AUTOMATIC GENERATION OF DIGITAL BUILDING MODELS FOR COMPLEX STRUCTURES FROM LIDAR DATA Changjae Kim a, Ayman Habib a, *, Yu-Chuan Chang a a Geomatics Engineering, University of Calgary, Canada - habib@geomatics.ucalgary.ca,
AUTOMATIC GENERATION OF DIGITAL BUILDING MODELS FOR COMPLEX STRUCTURES FROM LIDAR DATA Changjae Kim a, Ayman Habib a, *, Yu-Chuan Chang a a Geomatics Engineering, University of Calgary, Canada - habib@geomatics.ucalgary.ca,
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL. Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14
 Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis DEM (digital elevation model) and TIN (triangulated irregular network) are two
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis DEM (digital elevation model) and TIN (triangulated irregular network) are two
A METHOD TO PREDICT ACCURACY OF LEAST SQUARES SURFACE MATCHING FOR AIRBORNE LASER SCANNING DATA SETS
 A METHOD TO PREDICT ACCURACY OF LEAST SQUARES SURFACE MATCHING FOR AIRBORNE LASER SCANNING DATA SETS Robert Pâquet School of Engineering, University of Newcastle Callaghan, NSW 238, Australia (rpaquet@mail.newcastle.edu.au)
A METHOD TO PREDICT ACCURACY OF LEAST SQUARES SURFACE MATCHING FOR AIRBORNE LASER SCANNING DATA SETS Robert Pâquet School of Engineering, University of Newcastle Callaghan, NSW 238, Australia (rpaquet@mail.newcastle.edu.au)
Repeat-pass SAR Interferometry Experiments with Gaofen-3: A Case Study of Ningbo Area
 Repeat-pass SAR Interferometry Experiments with Gaofen-3: A Case Study of Ningbo Area Tao Zhang, Xiaolei Lv, Bing Han, Bin Lei and Jun Hong Key Laboratory of Technology in Geo-spatial Information Processing
Repeat-pass SAR Interferometry Experiments with Gaofen-3: A Case Study of Ningbo Area Tao Zhang, Xiaolei Lv, Bing Han, Bin Lei and Jun Hong Key Laboratory of Technology in Geo-spatial Information Processing
Data Representation in Visualisation
 Data Representation in Visualisation Visualisation Lecture 4 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Taku Komura Data Representation 1 Data Representation We have
Data Representation in Visualisation Visualisation Lecture 4 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Taku Komura Data Representation 1 Data Representation We have
Lesson 5 overview. Concepts. Interpolators. Assessing accuracy Exercise 5
 Interpolation Tools Lesson 5 overview Concepts Sampling methods Creating continuous surfaces Interpolation Density surfaces in GIS Interpolators IDW, Spline,Trend, Kriging,Natural neighbors TopoToRaster
Interpolation Tools Lesson 5 overview Concepts Sampling methods Creating continuous surfaces Interpolation Density surfaces in GIS Interpolators IDW, Spline,Trend, Kriging,Natural neighbors TopoToRaster
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR)
 Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) http://code.google.com/creative/radiohead/ Types of aerial sensors passive active 1 Active sensors for mapping terrain Radar transmits microwaves in pulses determines
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) http://code.google.com/creative/radiohead/ Types of aerial sensors passive active 1 Active sensors for mapping terrain Radar transmits microwaves in pulses determines
What can we represent as a Surface?
 Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
GY461 GIS 1: Environmental Campus Topography Project with ArcGIS 9.x
 I. Introduction GY461 GIS 1: Environmental In this project you will use data from a topographic survey of the USA campus to generate 2 separate maps: 1. A color-coded 2-dimensional topographic contour
I. Introduction GY461 GIS 1: Environmental In this project you will use data from a topographic survey of the USA campus to generate 2 separate maps: 1. A color-coded 2-dimensional topographic contour
Outline of Presentation. Introduction to Overwatch Geospatial Software Feature Analyst and LIDAR Analyst Software
 Outline of Presentation Automated Feature Extraction from Terrestrial and Airborne LIDAR Presented By: Stuart Blundell Overwatch Geospatial - VLS Ops Co-Author: David W. Opitz Overwatch Geospatial - VLS
Outline of Presentation Automated Feature Extraction from Terrestrial and Airborne LIDAR Presented By: Stuart Blundell Overwatch Geospatial - VLS Ops Co-Author: David W. Opitz Overwatch Geospatial - VLS
Assimilation of Break line and LiDAR Data within ESRI s Terrain Data Structure (TDS) for creating a Multi-Resolution Terrain Model
 Assimilation of Break line and LiDAR Data within ESRI s Terrain Data Structure (TDS) for creating a Multi-Resolution Terrain Model Tarig A. Ali Department of Civil Engineering American University of Sharjah,
Assimilation of Break line and LiDAR Data within ESRI s Terrain Data Structure (TDS) for creating a Multi-Resolution Terrain Model Tarig A. Ali Department of Civil Engineering American University of Sharjah,
Exercise 1: Introduction to ILWIS with the Riskcity dataset
 Exercise 1: Introduction to ILWIS with the Riskcity dataset Expected time: 2.5 hour Data: data from subdirectory: CENN_DVD\ILWIS_ExerciseData\IntroRiskCity Objectives: After this exercise you will be able
Exercise 1: Introduction to ILWIS with the Riskcity dataset Expected time: 2.5 hour Data: data from subdirectory: CENN_DVD\ILWIS_ExerciseData\IntroRiskCity Objectives: After this exercise you will be able
3D highway route-planning system on the virtual terrain by aerial photographs
 3D highway route-planning system on the virtual terrain by aerial photographs Koji MAKANAE * Abstract: In this study, a virtual reality highway route-planning system (VR-HRPS) was developed. VR-HRPS enables
3D highway route-planning system on the virtual terrain by aerial photographs Koji MAKANAE * Abstract: In this study, a virtual reality highway route-planning system (VR-HRPS) was developed. VR-HRPS enables
Automatic Building Extrusion from a TIN model Using LiDAR and Ordnance Survey Landline Data
 Automatic Building Extrusion from a TIN model Using LiDAR and Ordnance Survey Landline Data Rebecca O.C. Tse, Maciej Dakowicz, Christopher Gold and Dave Kidner University of Glamorgan, Treforest, Mid Glamorgan,
Automatic Building Extrusion from a TIN model Using LiDAR and Ordnance Survey Landline Data Rebecca O.C. Tse, Maciej Dakowicz, Christopher Gold and Dave Kidner University of Glamorgan, Treforest, Mid Glamorgan,
Lecture 9. Raster Data Analysis. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lecture 9 Raster Data Analysis Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Raster Data Model The GIS raster data model represents datasets in which square
Lecture 9 Raster Data Analysis Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Raster Data Model The GIS raster data model represents datasets in which square
Representing Geography
 Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATION. Lecture 6
 COORDINATE TRANSFORMATION Lecture 6 SGU 1053 SURVEY COMPUTATION 1 Introduction Geomatic professional are mostly confronted in their work with transformations from one two/three-dimensional coordinate system
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATION Lecture 6 SGU 1053 SURVEY COMPUTATION 1 Introduction Geomatic professional are mostly confronted in their work with transformations from one two/three-dimensional coordinate system
Progressive Surface Modeling Based On 3D Motion Sketch
 Progressive Surface Modeling Based On 3D Motion Sketch SHENGFENG IN, and DAVID K WRIGHT School of Engineering and Design Brunel University Uxbridge, Middlesex UB8 3PH UK Abstract: - This paper presents
Progressive Surface Modeling Based On 3D Motion Sketch SHENGFENG IN, and DAVID K WRIGHT School of Engineering and Design Brunel University Uxbridge, Middlesex UB8 3PH UK Abstract: - This paper presents
Surface Analysis. Data for Surface Analysis. What are Surfaces 4/22/2010
 Surface Analysis Cornell University Data for Surface Analysis Vector Triangulated Irregular Networks (TIN) a surface layer where space is partitioned into a set of non-overlapping triangles Attribute and
Surface Analysis Cornell University Data for Surface Analysis Vector Triangulated Irregular Networks (TIN) a surface layer where space is partitioned into a set of non-overlapping triangles Attribute and
Overview. Image Geometric Correction. LA502 Special Studies Remote Sensing. Why Geometric Correction?
 LA502 Special Studies Remote Sensing Image Geometric Correction Department of Landscape Architecture Faculty of Environmental Design King AbdulAziz University Room 103 Overview Image rectification Geometric
LA502 Special Studies Remote Sensing Image Geometric Correction Department of Landscape Architecture Faculty of Environmental Design King AbdulAziz University Room 103 Overview Image rectification Geometric
Study on Delaunay Triangulation with the Islets Constraints
 Intelligent Information Management, 2010, 2, 375-379 doi:10.4236/iim.2010.26045 Published Online June 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/iim) Study on Delaunay Triangulation with the Islets Constraints
Intelligent Information Management, 2010, 2, 375-379 doi:10.4236/iim.2010.26045 Published Online June 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/iim) Study on Delaunay Triangulation with the Islets Constraints
Raster GIS. Raster GIS 11/1/2015. The early years of GIS involved much debate on raster versus vector - advantages and disadvantages
 Raster GIS Google Earth image (raster) with roads overlain (vector) Raster GIS The early years of GIS involved much debate on raster versus vector - advantages and disadvantages 1 Feb 21, 2010 MODIS satellite
Raster GIS Google Earth image (raster) with roads overlain (vector) Raster GIS The early years of GIS involved much debate on raster versus vector - advantages and disadvantages 1 Feb 21, 2010 MODIS satellite
COMPONENTS. The web interface includes user administration tools, which allow companies to efficiently distribute data to internal or external users.
 COMPONENTS LASERDATA LIS is a software suite for LiDAR data (TLS / MLS / ALS) management and analysis. The software is built on top of a GIS and supports both point and raster data. The following software
COMPONENTS LASERDATA LIS is a software suite for LiDAR data (TLS / MLS / ALS) management and analysis. The software is built on top of a GIS and supports both point and raster data. The following software
Segmentation of point clouds
 Segmentation of point clouds George Vosselman INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION Extraction of information from point clouds 1 Segmentation algorithms Extraction
Segmentation of point clouds George Vosselman INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION Extraction of information from point clouds 1 Segmentation algorithms Extraction
Session / Séance 23-D Computing and Visualizing Morphologically Sound DEMs in a Raster Environment
 Session / Séance 23-D Computing and Visualizing Morphologically Sound DEMs in a Raster Environment Juha Oksanen and Olli Jaakkola Finnish Geodetic Institute, Cartography and Geoinformatics Geodeetinrinne
Session / Séance 23-D Computing and Visualizing Morphologically Sound DEMs in a Raster Environment Juha Oksanen and Olli Jaakkola Finnish Geodetic Institute, Cartography and Geoinformatics Geodeetinrinne
View-dependent fast real-time generating algorithm for large-scale terrain
 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 1 (2009) 1147 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia The 6 th International Conference on Mining Science & Technology View-dependent
Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 1 (2009) 1147 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia The 6 th International Conference on Mining Science & Technology View-dependent
MODULE 1 BASIC LIDAR TECHNIQUES
 MODULE SCENARIO One of the first tasks a geographic information systems (GIS) department using lidar data should perform is to check the quality of the data delivered by the data provider. The department
MODULE SCENARIO One of the first tasks a geographic information systems (GIS) department using lidar data should perform is to check the quality of the data delivered by the data provider. The department
Reality Check: Processing LiDAR Data. A story of data, more data and some more data
 Reality Check: Processing LiDAR Data A story of data, more data and some more data Red River of the North Red River of the North Red River of the North Red River of the North Introduction and Background
Reality Check: Processing LiDAR Data A story of data, more data and some more data Red River of the North Red River of the North Red River of the North Red River of the North Introduction and Background
Digital Terrain Model Data Structures
 Suletin UkUr, Jld. 5, No.1, ms. 61-72,1994 a Digital Terrain Model Data Structures s i a. Alias Abdul Rahman Jabatan Geoinformatik Fakul!i Ukur Universi!i Teknologi Malaysia Abstract This paper describes
Suletin UkUr, Jld. 5, No.1, ms. 61-72,1994 a Digital Terrain Model Data Structures s i a. Alias Abdul Rahman Jabatan Geoinformatik Fakul!i Ukur Universi!i Teknologi Malaysia Abstract This paper describes
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
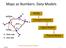 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
FOOTPRINTS EXTRACTION
 Building Footprints Extraction of Dense Residential Areas from LiDAR data KyoHyouk Kim and Jie Shan Purdue University School of Civil Engineering 550 Stadium Mall Drive West Lafayette, IN 47907, USA {kim458,
Building Footprints Extraction of Dense Residential Areas from LiDAR data KyoHyouk Kim and Jie Shan Purdue University School of Civil Engineering 550 Stadium Mall Drive West Lafayette, IN 47907, USA {kim458,
Municipal Projects in Cambridge Using a LiDAR Dataset. NEURISA Day 2012 Sturbridge, MA
 Municipal Projects in Cambridge Using a LiDAR Dataset NEURISA Day 2012 Sturbridge, MA October 15, 2012 Jeff Amero, GIS Manager, City of Cambridge Presentation Overview Background on the LiDAR dataset Solar
Municipal Projects in Cambridge Using a LiDAR Dataset NEURISA Day 2012 Sturbridge, MA October 15, 2012 Jeff Amero, GIS Manager, City of Cambridge Presentation Overview Background on the LiDAR dataset Solar
APPENDIX E2. Vernal Pool Watershed Mapping
 APPENDIX E2 Vernal Pool Watershed Mapping MEMORANDUM To: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service From: Tyler Friesen, Dudek Subject: SSHCP Vernal Pool Watershed Analysis Using LIDAR Data Date: February 6, 2014
APPENDIX E2 Vernal Pool Watershed Mapping MEMORANDUM To: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service From: Tyler Friesen, Dudek Subject: SSHCP Vernal Pool Watershed Analysis Using LIDAR Data Date: February 6, 2014
CONSISTENT COLOR RESAMPLE IN DIGITAL ORTHOPHOTO PRODUCTION INTRODUCTION
 CONSISTENT COLOR RESAMPLE IN DIGITAL ORTHOPHOTO PRODUCTION Yaron Katzil 1, Yerach Doytsher 2 Mapping and Geo-Information Engineering Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering Technion - Israel Institute
CONSISTENT COLOR RESAMPLE IN DIGITAL ORTHOPHOTO PRODUCTION Yaron Katzil 1, Yerach Doytsher 2 Mapping and Geo-Information Engineering Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering Technion - Israel Institute
Dijkstra's Algorithm
 Shortest Path Algorithm Dijkstra's Algorithm To find the shortest path from the origin node to the destination node No matrix calculation Floyd s Algorithm To find all the shortest paths from the nodes
Shortest Path Algorithm Dijkstra's Algorithm To find the shortest path from the origin node to the destination node No matrix calculation Floyd s Algorithm To find all the shortest paths from the nodes
DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS
 DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS 1 Digital Terrain Models Dr. Mohsen Mostafa Hassan Badawy Remote Sensing Center GENERAL: A Digital Terrain Models (DTM) is defined as the digital representation of the spatial distribution
DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS 1 Digital Terrain Models Dr. Mohsen Mostafa Hassan Badawy Remote Sensing Center GENERAL: A Digital Terrain Models (DTM) is defined as the digital representation of the spatial distribution
Lidar and GIS: Applications and Examples. Dan Hedges Clayton Crawford
 Lidar and GIS: Applications and Examples Dan Hedges Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density Creating raster DEMs and DSMs Data area
Lidar and GIS: Applications and Examples Dan Hedges Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density Creating raster DEMs and DSMs Data area
Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects. William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA
 Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA Overview 1. Some Ways to Structure Space 2. What to Put into a Grid 3. Objects and Fields 4. Hybrid Structures
Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA Overview 1. Some Ways to Structure Space 2. What to Put into a Grid 3. Objects and Fields 4. Hybrid Structures
Algorithms for GIS. Spatial data: Models and representation (part I) Laura Toma. Bowdoin College
 Algorithms for GIS Spatial data: Models and representation (part I) Laura Toma Bowdoin College Outline Spatial data in GIS applications Point data Networks Terrains Planar maps and meshes Data structures
Algorithms for GIS Spatial data: Models and representation (part I) Laura Toma Bowdoin College Outline Spatial data in GIS applications Point data Networks Terrains Planar maps and meshes Data structures
I. Project Title Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) Processing
 I. Project Title Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) Processing II. Lead Investigator Ryan P. Lanclos Research Specialist 107 Stewart Hall Department of Geography University of Missouri Columbia Columbia,
I. Project Title Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) Processing II. Lead Investigator Ryan P. Lanclos Research Specialist 107 Stewart Hall Department of Geography University of Missouri Columbia Columbia,
Server Side Generation of VRML Program by Parametric Modeling
 Server Side Generation of VRML Program by Parametric Modeling Tsuyoshi HONJO and En-Mi LIM 1 Introduction Landscape visualization has been mainly used for accurately analyzing existing landscape resources
Server Side Generation of VRML Program by Parametric Modeling Tsuyoshi HONJO and En-Mi LIM 1 Introduction Landscape visualization has been mainly used for accurately analyzing existing landscape resources
Extracting Elevation from Air Photos
 Extracting Elevation from Air Photos TUTORIAL A digital elevation model (DEM) is a digital raster surface representing the elevations of a terrain for all spatial ground positions in the image. Traditionally
Extracting Elevation from Air Photos TUTORIAL A digital elevation model (DEM) is a digital raster surface representing the elevations of a terrain for all spatial ground positions in the image. Traditionally
REFINEMENT OF FILTERED LIDAR DATA USING LOCAL SURFACE PROPERTIES INTRODUCTION
 REFINEMENT OF FILTERED LIDAR DATA USING LOCAL SURFACE PROPERTIES Suyoung Seo, Senior Research Associate Charles G. O Hara, Associate Research Professor GeoResources Institute Mississippi State University
REFINEMENT OF FILTERED LIDAR DATA USING LOCAL SURFACE PROPERTIES Suyoung Seo, Senior Research Associate Charles G. O Hara, Associate Research Professor GeoResources Institute Mississippi State University
Contour Simplification with Defined Spatial Accuracy
 Contour Simplification with Defined Spatial Accuracy Bulent Cetinkaya, Serdar Aslan, Yavuz Selim Sengun, O. Nuri Cobankaya, Dursun Er Ilgin General Command of Mapping, 06100 Cebeci, Ankara, Turkey bulent.cetinkaya@hgk.mil.tr
Contour Simplification with Defined Spatial Accuracy Bulent Cetinkaya, Serdar Aslan, Yavuz Selim Sengun, O. Nuri Cobankaya, Dursun Er Ilgin General Command of Mapping, 06100 Cebeci, Ankara, Turkey bulent.cetinkaya@hgk.mil.tr
PRODUCTION SYSTEM FOR AUTONOMOUS 3-DIMENSIONAL MODELING WITH LIDAR, IFSAR, AND PHOTOGRAMMETRIC DSM DATA INTRODUCTION
 PRODUCTION SYSTEM FOR AUTONOMOUS 3-DIMENSIONAL MODELING WITH LIDAR, IFSAR, AND PHOTOGRAMMETRIC DSM DATA Mark Rahmes, Software Engineer Josef DeVaughn Allen, Software Engineer J. Harlan Yates, System Engineer
PRODUCTION SYSTEM FOR AUTONOMOUS 3-DIMENSIONAL MODELING WITH LIDAR, IFSAR, AND PHOTOGRAMMETRIC DSM DATA Mark Rahmes, Software Engineer Josef DeVaughn Allen, Software Engineer J. Harlan Yates, System Engineer
National Science Foundation Engineering Research Center. Bingcai Zhang BAE Systems San Diego, CA
 Bingcai Zhang BAE Systems San Diego, CA 92127 Bingcai.zhang@BAESystems.com Introduction It is a trivial task for a five-year-old child to recognize and name an object such as a car, house or building.
Bingcai Zhang BAE Systems San Diego, CA 92127 Bingcai.zhang@BAESystems.com Introduction It is a trivial task for a five-year-old child to recognize and name an object such as a car, house or building.
Creating raster DEMs and DSMs from large lidar point collections. Summary. Coming up with a plan. Using the Point To Raster geoprocessing tool
 Page 1 of 5 Creating raster DEMs and DSMs from large lidar point collections ArcGIS 10 Summary Raster, or gridded, elevation models are one of the most common GIS data types. They can be used in many ways
Page 1 of 5 Creating raster DEMs and DSMs from large lidar point collections ArcGIS 10 Summary Raster, or gridded, elevation models are one of the most common GIS data types. They can be used in many ways
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015
 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
8 Geographers Tools: Automated Mapping. Digitizing a Map IMPORTANT 2/19/19. v Tues., Feb. 26, 2019.
 Next Class: FIRST EXAM v Tues., Feb. 26, 2019. Combination of multiple choice questions and map interpretation. Bring a #2 pencil with eraser. Based on class lectures supplementing Chapter 1. Review lectures
Next Class: FIRST EXAM v Tues., Feb. 26, 2019. Combination of multiple choice questions and map interpretation. Bring a #2 pencil with eraser. Based on class lectures supplementing Chapter 1. Review lectures
Construction of Complex City Landscape with the Support of CAD Model
 Construction of Complex City Landscape with the Support of CAD Model MinSun 1 JunChen 2 AinaiMa 1 1.Institute of RS & GIS, Peking University, Beijing, China, 100871 2.National Geomatics Center of China,
Construction of Complex City Landscape with the Support of CAD Model MinSun 1 JunChen 2 AinaiMa 1 1.Institute of RS & GIS, Peking University, Beijing, China, 100871 2.National Geomatics Center of China,
AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF LARGE COMPLEX BUILDINGS USING LIDAR DATA AND DIGITAL MAPS
 AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF LARGE COMPLEX BUILDINGS USING LIDAR DATA AND DIGITAL MAPS Jihye Park a, Impyeong Lee a, *, Yunsoo Choi a, Young Jin Lee b a Dept. of Geoinformatics, The University of Seoul, 90
AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF LARGE COMPLEX BUILDINGS USING LIDAR DATA AND DIGITAL MAPS Jihye Park a, Impyeong Lee a, *, Yunsoo Choi a, Young Jin Lee b a Dept. of Geoinformatics, The University of Seoul, 90
