Oblique Factor Rotation Explained
|
|
|
- Julian Turner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Oblique Factor Rotation Explained Grant B. Morgan Baylor University September 6, 2014 A Step-by-Step Look at Promax Factor Rotation For this post, I will continue my attempt to demistify factor rotation to the extent that I can. To keep things easier to visualize, I will only use two factors so we ll be rotating the solution in two-dimensional space. Let s get started by generating some data from a true two-factor model. library(lavaan) oblique.model <- ' f1 =~.7*x *x2 +.7*x3 +.7*x4 +.7*x5 f2 =~.7*x6 +.7*x7 +.7*x8 +.7*x9 +.7*x10 f1 ~ 1 f2 ~ 1 f2 ~~.4*f1 ' oblique.data <- simulatedata(oblique.model, sample.nobs=500l, seed=0110, std.lv=true) Perform EFA without rotation First, let s extract two factors but keep the solution unrotated to see how it looks. library(psych) fa.norotate <- factanal(factors = 2, covmat=cov(oblique.data), rotation="none") factor.plot(fa.norotate, xlim=c(-1,1), ylim=c(-1,1), title="unrotated Two Factor Solution") 1
2 View each axis as a factor. Clearly, without rotating the solution, these clusters of items will be difficult to interpret because they are not close to either factor (i.e., axis). Rotation is clearly needed again. With orthogonal rotation, we kept both axes perpendicular to each other because we could get reasonably close the item clusters despite leaving the axes perpendicular. That isn t the case here. As we have discussed, simple structure is always preferred in factor solutions to aid in interpreting the model. As rotation methods go, orthogonal rotations provide solutions that are easier to interpret. Varimax rotation, an orthogonal rotation procedure, was specifically designed to maximize simple structure. You might think of Varimax rotation as a best case scenario...so why don t we start with a Varimax solution and see if we can force (i.e., transform) the data to fit the Varimax solution? If you enjoy Greek mythology as much I do, this sounds very Procrustean, right? These procedures are actually classified as a variant of Procrustes analysis (seriously, look it up). 2
3 Step 1 - Perform EFA with Varimax Rotation Let s use Varimax rotation and see what we come up with. library(gparotation) fa.varimax <- factanal(factors = 2, covmat=cov(oblique.data), rotation="varimax") factor.plot(fa.varimax, xlim=c(-1,1), ylim=c(-1,1), title="varimax Rotated-Two Factor Solution" The items are still in limbo between the axes, which is evidence that we need to break the orthogonality of the axes to better account for the data structure. Step 2 - Create a Target Matrix from the Varimax-rotated Solution Let s look at the loadings in the Varimax solution. 3
4 print(fa.varimax$loadings, cutoff=.01) Loadings: x x x x x x x x x x SS loadings Proportion Var Cumulative Var It looks like items 1 to 5 load most strongly on Factor 2, and items 6 to 10 load most strongly onto Factor 1. If we wanted to strengthen simple structure, we would therefore want to loadings for items 1 to 5 to be closer to zero for Factor 1 and for items 6 to 10 for Factor 2. We would also want to do this without moving the primary loadings to zero. Can you think of way of transforming the loadings to make this happen? What if we squared all of the loadings? Let s try and take a look. print((fa.varimax$loadings)**2, cutoff=.01) Loadings: x x x x x x x x x x SS loadings Proportion Var Cumulative Var
5 That looks better, right? Let s see if we can get the nonprimary loadings to be zero out to two decimal places. Let s try raising the loadings to the 4 th power. print((fa.varimax$loadings)**4, cutoff=.01) Loadings: x x x x x x x x x x SS loadings Proportion Var Cumulative Var That does it! We know this because we used the cutoff command to suppress any loading less than.01. So this becomes the loading matrix that we want to target. Therefore, let s call it the target matrix and denote it as Λ T. Step 3 - Find the Initial Transformation Matrix Using the target matrix (Λ T ) and the unrotated loading matrix (Λ 0 ), we can find a initial transformation matrix using ordinary least squares. That would look like this: ) 1 T i = (Λ 0 Λ 0 Λ 0Λ T Don t let that scare you though...it s actually the same matrix operation as when we perform multiple regression. Remember that regression coefficients are estimated: ( ) ˆB = X 1 X X y Using R we can compute the initial transformation matrix. Ti <- solve(t(fa.norotate$loadings) %*% fa.norotate$loadings) %*% (t(fa.norotate$loadings) %*% (fa.varimax$loadings)^4) Ti Factor Factor
6 Step 4 - Find the Final Transformation Matrix We can t stop here though. In promax rotation, the factor correlation matrix (Φ) is computed using ((T T) 1 = Φ). A correlation matrix must have 1s on the diagonal so if we stopped here, we wouldn t get 1s on the diagonal (see below). solve(t(ti)%*%ti) Factor Factor The diagonal of the matrix does not have 1s so we need to further transform the transformation matrix and hope it doesn t cause a black hole. First, we need to take the inverse of T T. Second, we need to take the square root of the diagonal elements. Third, we ll create a new matrix that contains those roots on the diagonal and 0s off the diagonal. Let s do it. Ti_inv<-solve(t(Ti)%*%Ti) D<-matrix(0,nrow=nrow(Ti_inv), ncol=ncol(ti_inv)) D[1,1]<-sqrt(Ti_inv[1,1]) D[2,2]<-sqrt(Ti_inv[2,2]) Ti_inv Factor Factor D [,1] [,2] [1,] [2,] Multiplying our intial transformation matrix by this new matrix, D, will give us the final transformation matrix (T). Thus: T = T i D Let s take a look at T. T<-Ti%*%D T [,1] [,2] Factor Factor Step 4a - Compute the Factor Correlation Matrix We went through all of this to get a factor correlation matrix that has 1s on the diagonal and factor correlations off the diagonal. Let s see if T T now has 1s on the diagonal. 6
7 solve(t(t)%*%t) [,1] [,2] [1,] [2,] Yes! We successfully computed the factor correlation matrix. Not only do we see that the matrix has 1s on the diagonal, but we also see the correlation between the factors - φ 2,1 =.39 (Remember that we generated the data from a population where the factor correction was.4). The factor correlation matrix, Φ, is: [ ] Φ = Step 5 - Rotate the Factor Loadings All that s left is to postmultiply the unrotated loading matrix (Λ 0 ) by the final transformation matrix (T) to get the rotated loading (i.e., pattern) matrix (Λ ). That is: Λ 0 T = Λ fa.norotate$loadings%*%t [,1] [,2] x x x x x x x x x x That s it! Now just for fun, let s see what we would get if we used the built-in promax rotation function. Verifying Using Built-in Promax Rotation Procedure fa(r = cor(oblique.data), fm = "ml", rotate="promax", nfactors=2)$loadings Loading required package: MASS Loading required package: parallel Loadings: ML1 ML2 7
8 x x x x x x x x x x ML1 ML2 SS loadings Proportion Var Cumulative Var fa(r = cor(oblique.data), fm = "ml", rotate="promax", nfactors=2)$phi [,1] [,2] [1,] [2,] Thankfully, it looks familiar! Promax rotation = Done! 8
Statistical Models for Management. Instituto Superior de Ciências do Trabalho e da Empresa (ISCTE) Lisbon. February 24 26, 2010
 Statistical Models for Management Instituto Superior de Ciências do Trabalho e da Empresa (ISCTE) Lisbon February 24 26, 2010 Graeme Hutcheson, University of Manchester Principal Component and Factor Analysis
Statistical Models for Management Instituto Superior de Ciências do Trabalho e da Empresa (ISCTE) Lisbon February 24 26, 2010 Graeme Hutcheson, University of Manchester Principal Component and Factor Analysis
Chapter 1 Section 1 Lesson: Solving Linear Equations
 Introduction Linear equations are the simplest types of equations to solve. In a linear equation, all variables are to the first power only. All linear equations in one variable can be reduced to the form
Introduction Linear equations are the simplest types of equations to solve. In a linear equation, all variables are to the first power only. All linear equations in one variable can be reduced to the form
Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross Product
 University of Babylon College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. Subject : Mathematics III Class : 2 nd year - first semester Date: / 10 / 2016 2016 \ 2017 Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross
University of Babylon College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. Subject : Mathematics III Class : 2 nd year - first semester Date: / 10 / 2016 2016 \ 2017 Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross
Performing Matrix Operations on the TI-83/84
 Page1 Performing Matrix Operations on the TI-83/84 While the layout of most TI-83/84 models are basically the same, of the things that can be different, one of those is the location of the Matrix key.
Page1 Performing Matrix Operations on the TI-83/84 While the layout of most TI-83/84 models are basically the same, of the things that can be different, one of those is the location of the Matrix key.
Introduction to Factor Analysis for Marketing
 Introduction to Factor Analysis for Marketing SKIM/Sawtooth Software Conference 2016, Rome Chris Chapman, Google. April 2016. Special thanks to Josh Lewandowski at Google for helpful feedback (errors are
Introduction to Factor Analysis for Marketing SKIM/Sawtooth Software Conference 2016, Rome Chris Chapman, Google. April 2016. Special thanks to Josh Lewandowski at Google for helpful feedback (errors are
Scaling Techniques in Political Science
 Scaling Techniques in Political Science Eric Guntermann March 14th, 2014 Eric Guntermann Scaling Techniques in Political Science March 14th, 2014 1 / 19 What you need R RStudio R code file Datasets You
Scaling Techniques in Political Science Eric Guntermann March 14th, 2014 Eric Guntermann Scaling Techniques in Political Science March 14th, 2014 1 / 19 What you need R RStudio R code file Datasets You
CS251 Spring 2014 Lecture 7
 CS251 Spring 2014 Lecture 7 Stephanie R Taylor Feb 19, 2014 1 Moving on to 3D Today, we move on to 3D coordinates. But first, let s recap of what we did in 2D: 1. We represented a data point in 2D data
CS251 Spring 2014 Lecture 7 Stephanie R Taylor Feb 19, 2014 1 Moving on to 3D Today, we move on to 3D coordinates. But first, let s recap of what we did in 2D: 1. We represented a data point in 2D data
A GENTLE INTRODUCTION TO THE BASIC CONCEPTS OF SHAPE SPACE AND SHAPE STATISTICS
 A GENTLE INTRODUCTION TO THE BASIC CONCEPTS OF SHAPE SPACE AND SHAPE STATISTICS HEMANT D. TAGARE. Introduction. Shape is a prominent visual feature in many images. Unfortunately, the mathematical theory
A GENTLE INTRODUCTION TO THE BASIC CONCEPTS OF SHAPE SPACE AND SHAPE STATISTICS HEMANT D. TAGARE. Introduction. Shape is a prominent visual feature in many images. Unfortunately, the mathematical theory
Equations of planes in
 Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 6: Lines, planes and other straight objects Section Equations of planes in What you need to know already: What vectors and vector operations are. What linear systems
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 6: Lines, planes and other straight objects Section Equations of planes in What you need to know already: What vectors and vector operations are. What linear systems
AH Matrices.notebook November 28, 2016
 Matrices Numbers are put into arrays to help with multiplication, division etc. A Matrix (matrices pl.) is a rectangular array of numbers arranged in rows and columns. Matrices If there are m rows and
Matrices Numbers are put into arrays to help with multiplication, division etc. A Matrix (matrices pl.) is a rectangular array of numbers arranged in rows and columns. Matrices If there are m rows and
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Three-dimensional transformation geometry and perspective
 COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Three-dimensional transformation geometry and perspective Department of Computing and Information Systems The Lecture outline Introduction Rotation about artibrary axis
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Three-dimensional transformation geometry and perspective Department of Computing and Information Systems The Lecture outline Introduction Rotation about artibrary axis
8. MINITAB COMMANDS WEEK-BY-WEEK
 8. MINITAB COMMANDS WEEK-BY-WEEK In this section of the Study Guide, we give brief information about the Minitab commands that are needed to apply the statistical methods in each week s study. They are
8. MINITAB COMMANDS WEEK-BY-WEEK In this section of the Study Guide, we give brief information about the Minitab commands that are needed to apply the statistical methods in each week s study. They are
Study Guide. Module 1. Key Terms
 Study Guide Module 1 Key Terms general linear model dummy variable multiple regression model ANOVA model ANCOVA model confounding variable squared multiple correlation adjusted squared multiple correlation
Study Guide Module 1 Key Terms general linear model dummy variable multiple regression model ANOVA model ANCOVA model confounding variable squared multiple correlation adjusted squared multiple correlation
Level 4 means that I can
 Level 4 means that I can Describe number patterns Find multiples Find factors Work out the square numbers Use word formulae Use co-ordinates in the first quadrant Multiply and divide whole numbers by 10
Level 4 means that I can Describe number patterns Find multiples Find factors Work out the square numbers Use word formulae Use co-ordinates in the first quadrant Multiply and divide whole numbers by 10
STA 570 Spring Lecture 5 Tuesday, Feb 1
 STA 570 Spring 2011 Lecture 5 Tuesday, Feb 1 Descriptive Statistics Summarizing Univariate Data o Standard Deviation, Empirical Rule, IQR o Boxplots Summarizing Bivariate Data o Contingency Tables o Row
STA 570 Spring 2011 Lecture 5 Tuesday, Feb 1 Descriptive Statistics Summarizing Univariate Data o Standard Deviation, Empirical Rule, IQR o Boxplots Summarizing Bivariate Data o Contingency Tables o Row
APPM 2360 Project 2 Due Nov. 3 at 5:00 PM in D2L
 APPM 2360 Project 2 Due Nov. 3 at 5:00 PM in D2L 1 Introduction Digital images are stored as matrices of pixels. For color images, the matrix contains an ordered triple giving the RGB color values at each
APPM 2360 Project 2 Due Nov. 3 at 5:00 PM in D2L 1 Introduction Digital images are stored as matrices of pixels. For color images, the matrix contains an ordered triple giving the RGB color values at each
Image Manipulation in MATLAB Due Monday, July 17 at 5:00 PM
 Image Manipulation in MATLAB Due Monday, July 17 at 5:00 PM 1 Instructions Labs may be done in groups of 2 or 3 (i.e., not alone). You may use any programming language you wish but MATLAB is highly suggested.
Image Manipulation in MATLAB Due Monday, July 17 at 5:00 PM 1 Instructions Labs may be done in groups of 2 or 3 (i.e., not alone). You may use any programming language you wish but MATLAB is highly suggested.
Solving Equations with Inverse Operations
 Solving Equations with Inverse Operations Math 97 Supplement LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Solve equations by using inverse operations, including squares, square roots, cubes, and cube roots. The Definition of
Solving Equations with Inverse Operations Math 97 Supplement LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Solve equations by using inverse operations, including squares, square roots, cubes, and cube roots. The Definition of
HMC CS 158, Fall 2017 Problem Set 3 Programming: Regularized Polynomial Regression
 HMC CS 158, Fall 2017 Problem Set 3 Programming: Regularized Polynomial Regression Goals: To open up the black-box of scikit-learn and implement regression models. To investigate how adding polynomial
HMC CS 158, Fall 2017 Problem Set 3 Programming: Regularized Polynomial Regression Goals: To open up the black-box of scikit-learn and implement regression models. To investigate how adding polynomial
Cluster Analysis for Microarray Data
 Cluster Analysis for Microarray Data Seventh International Long Oligonucleotide Microarray Workshop Tucson, Arizona January 7-12, 2007 Dan Nettleton IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY 1 Clustering Group objects that
Cluster Analysis for Microarray Data Seventh International Long Oligonucleotide Microarray Workshop Tucson, Arizona January 7-12, 2007 Dan Nettleton IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY 1 Clustering Group objects that
Modern Multidimensional Scaling
 Ingwer Borg Patrick Groenen Modern Multidimensional Scaling Theory and Applications With 116 Figures Springer Contents Preface vii I Fundamentals of MDS 1 1 The Four Purposes of Multidimensional Scaling
Ingwer Borg Patrick Groenen Modern Multidimensional Scaling Theory and Applications With 116 Figures Springer Contents Preface vii I Fundamentals of MDS 1 1 The Four Purposes of Multidimensional Scaling
Answers to practice questions for Midterm 1
 Answers to practice questions for Midterm Paul Hacking /5/9 (a The RREF (reduced row echelon form of the augmented matrix is So the system of linear equations has exactly one solution given by x =, y =,
Answers to practice questions for Midterm Paul Hacking /5/9 (a The RREF (reduced row echelon form of the augmented matrix is So the system of linear equations has exactly one solution given by x =, y =,
Number Systems Using and Converting Between Decimal, Binary, Octal and Hexadecimal Number Systems
 Number Systems Using and Converting Between Decimal, Binary, Octal and Hexadecimal Number Systems In everyday life, we humans most often count using decimal or base-10 numbers. In computer science, it
Number Systems Using and Converting Between Decimal, Binary, Octal and Hexadecimal Number Systems In everyday life, we humans most often count using decimal or base-10 numbers. In computer science, it
QUESTIONS 1 10 MAY BE DONE WITH A CALCULATOR QUESTIONS ARE TO BE DONE WITHOUT A CALCULATOR. Name
 QUESTIONS 1 10 MAY BE DONE WITH A CALCULATOR QUESTIONS 11 5 ARE TO BE DONE WITHOUT A CALCULATOR Name 2 CALCULATOR MAY BE USED FOR 1-10 ONLY Use the table to find the following. x -2 2 5-0 7 2 y 12 15 18
QUESTIONS 1 10 MAY BE DONE WITH A CALCULATOR QUESTIONS 11 5 ARE TO BE DONE WITHOUT A CALCULATOR Name 2 CALCULATOR MAY BE USED FOR 1-10 ONLY Use the table to find the following. x -2 2 5-0 7 2 y 12 15 18
D-Optimal Designs. Chapter 888. Introduction. D-Optimal Design Overview
 Chapter 888 Introduction This procedure generates D-optimal designs for multi-factor experiments with both quantitative and qualitative factors. The factors can have a mixed number of levels. For example,
Chapter 888 Introduction This procedure generates D-optimal designs for multi-factor experiments with both quantitative and qualitative factors. The factors can have a mixed number of levels. For example,
Section Graphs and Lines
 Section 1.1 - Graphs and Lines The first chapter of this text is a review of College Algebra skills that you will need as you move through the course. This is a review, so you should have some familiarity
Section 1.1 - Graphs and Lines The first chapter of this text is a review of College Algebra skills that you will need as you move through the course. This is a review, so you should have some familiarity
Path Analysis using lm and lavaan
 Path Analysis using lm and lavaan Grant B. Morgan Baylor University September 10, 2014 First of all, this post is going to mirror a page on the Institute for Digital Research and Education (IDRE) site
Path Analysis using lm and lavaan Grant B. Morgan Baylor University September 10, 2014 First of all, this post is going to mirror a page on the Institute for Digital Research and Education (IDRE) site
Interlude: Solving systems of Equations
 Interlude: Solving systems of Equations Solving Ax = b What happens to x under Ax? The singular value decomposition Rotation matrices Singular matrices Condition number Null space Solving Ax = 0 under
Interlude: Solving systems of Equations Solving Ax = b What happens to x under Ax? The singular value decomposition Rotation matrices Singular matrices Condition number Null space Solving Ax = 0 under
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining. Kernel Trick Fall 2017
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Kernel Trick Fall 2017 Admin Assignment 3: Due Friday. Midterm: Can view your exam during instructor office hours or after class this week. Digression: the other
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Kernel Trick Fall 2017 Admin Assignment 3: Due Friday. Midterm: Can view your exam during instructor office hours or after class this week. Digression: the other
MODERN FACTOR ANALYSIS
 MODERN FACTOR ANALYSIS Harry H. Harman «ö THE pigj UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO PRESS Contents LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS GUIDE TO NOTATION xv xvi Parti Foundations of Factor Analysis 1. INTRODUCTION 3 1.1. Brief
MODERN FACTOR ANALYSIS Harry H. Harman «ö THE pigj UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO PRESS Contents LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS GUIDE TO NOTATION xv xvi Parti Foundations of Factor Analysis 1. INTRODUCTION 3 1.1. Brief
Supervised vs unsupervised clustering
 Classification Supervised vs unsupervised clustering Cluster analysis: Classes are not known a- priori. Classification: Classes are defined a-priori Sometimes called supervised clustering Extract useful
Classification Supervised vs unsupervised clustering Cluster analysis: Classes are not known a- priori. Classification: Classes are defined a-priori Sometimes called supervised clustering Extract useful
General Instructions. Questions
 CS246: Mining Massive Data Sets Winter 2018 Problem Set 2 Due 11:59pm February 8, 2018 Only one late period is allowed for this homework (11:59pm 2/13). General Instructions Submission instructions: These
CS246: Mining Massive Data Sets Winter 2018 Problem Set 2 Due 11:59pm February 8, 2018 Only one late period is allowed for this homework (11:59pm 2/13). General Instructions Submission instructions: These
Basics of Computational Geometry
 Basics of Computational Geometry Nadeem Mohsin October 12, 2013 1 Contents This handout covers the basic concepts of computational geometry. Rather than exhaustively covering all the algorithms, it deals
Basics of Computational Geometry Nadeem Mohsin October 12, 2013 1 Contents This handout covers the basic concepts of computational geometry. Rather than exhaustively covering all the algorithms, it deals
Note that ALL of these points are Intercepts(along an axis), something you should see often in later work.
 SECTION 1.1: Plotting Coordinate Points on the X-Y Graph This should be a review subject, as it was covered in the prerequisite coursework. But as a reminder, and for practice, plot each of the following
SECTION 1.1: Plotting Coordinate Points on the X-Y Graph This should be a review subject, as it was covered in the prerequisite coursework. But as a reminder, and for practice, plot each of the following
The transition: Each student passes half his store of candies to the right. students with an odd number of candies eat one.
 Kate s problem: The students are distributed around a circular table The teacher distributes candies to all the students, so that each student has an even number of candies The transition: Each student
Kate s problem: The students are distributed around a circular table The teacher distributes candies to all the students, so that each student has an even number of candies The transition: Each student
8 th Grade Mathematics Unpacked Content For the new Common Core standards that will be effective in all North Carolina schools in the
 8 th Grade Mathematics Unpacked Content For the new Common Core standards that will be effective in all North Carolina schools in the 2012-13. This document is designed to help North Carolina educators
8 th Grade Mathematics Unpacked Content For the new Common Core standards that will be effective in all North Carolina schools in the 2012-13. This document is designed to help North Carolina educators
Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering. Some problems by Gilbert Strang
 Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering Some problems by Gilbert Strang Problems. Consider u, v, w to be non-zero vectors in R 7. These vectors span a vector space. What are the possible
Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering Some problems by Gilbert Strang Problems. Consider u, v, w to be non-zero vectors in R 7. These vectors span a vector space. What are the possible
I can solve simultaneous equations algebraically, where one is quadratic and one is linear.
 A* I can manipulate algebraic fractions. I can use the equation of a circle. simultaneous equations algebraically, where one is quadratic and one is linear. I can transform graphs, including trig graphs.
A* I can manipulate algebraic fractions. I can use the equation of a circle. simultaneous equations algebraically, where one is quadratic and one is linear. I can transform graphs, including trig graphs.
Computer Graphics Hands-on
 Computer Graphics Hands-on Two-Dimensional Transformations Objectives Visualize the fundamental 2D geometric operations translation, rotation about the origin, and scale about the origin Learn how to compose
Computer Graphics Hands-on Two-Dimensional Transformations Objectives Visualize the fundamental 2D geometric operations translation, rotation about the origin, and scale about the origin Learn how to compose
Matrix Inverse 2 ( 2) 1 = 2 1 2
 Name: Matrix Inverse For Scalars, we have what is called a multiplicative identity. This means that if we have a scalar number, call it r, then r multiplied by the multiplicative identity equals r. Without
Name: Matrix Inverse For Scalars, we have what is called a multiplicative identity. This means that if we have a scalar number, call it r, then r multiplied by the multiplicative identity equals r. Without
Lecture 25: Review I
 Lecture 25: Review I Reading: Up to chapter 5 in ISLR. STATS 202: Data mining and analysis Jonathan Taylor 1 / 18 Unsupervised learning In unsupervised learning, all the variables are on equal standing,
Lecture 25: Review I Reading: Up to chapter 5 in ISLR. STATS 202: Data mining and analysis Jonathan Taylor 1 / 18 Unsupervised learning In unsupervised learning, all the variables are on equal standing,
The Curse of Dimensionality
 The Curse of Dimensionality ACAS 2002 p1/66 Curse of Dimensionality The basic idea of the curse of dimensionality is that high dimensional data is difficult to work with for several reasons: Adding more
The Curse of Dimensionality ACAS 2002 p1/66 Curse of Dimensionality The basic idea of the curse of dimensionality is that high dimensional data is difficult to work with for several reasons: Adding more
WEEK 4 REVIEW. Graphing Systems of Linear Inequalities (3.1)
 WEEK 4 REVIEW Graphing Systems of Linear Inequalities (3.1) Linear Programming Problems (3.2) Checklist for Exam 1 Review Sample Exam 1 Graphing Linear Inequalities Graph the following system of inequalities.
WEEK 4 REVIEW Graphing Systems of Linear Inequalities (3.1) Linear Programming Problems (3.2) Checklist for Exam 1 Review Sample Exam 1 Graphing Linear Inequalities Graph the following system of inequalities.
Table of Laplace Transforms
 Table of Laplace Transforms 1 1 2 3 4, p > -1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Heaviside Function 27 28. Dirac Delta Function 29 30. 31 32. 1 33 34. 35 36. 37 Laplace Transforms
Table of Laplace Transforms 1 1 2 3 4, p > -1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Heaviside Function 27 28. Dirac Delta Function 29 30. 31 32. 1 33 34. 35 36. 37 Laplace Transforms
Animated Cartoons by Computer Using Ellipsoids
 Animated Cartoons by Computer Using Ellipsoids Don Herbison-Evans, donherbisonevans@yahoo.com Technical Report 94 (1974), Basser Department of Computer Science, University of Sydney, Australia ABSTRACT
Animated Cartoons by Computer Using Ellipsoids Don Herbison-Evans, donherbisonevans@yahoo.com Technical Report 94 (1974), Basser Department of Computer Science, University of Sydney, Australia ABSTRACT
CSE 547: Machine Learning for Big Data Spring Problem Set 2. Please read the homework submission policies.
 CSE 547: Machine Learning for Big Data Spring 2019 Problem Set 2 Please read the homework submission policies. 1 Principal Component Analysis and Reconstruction (25 points) Let s do PCA and reconstruct
CSE 547: Machine Learning for Big Data Spring 2019 Problem Set 2 Please read the homework submission policies. 1 Principal Component Analysis and Reconstruction (25 points) Let s do PCA and reconstruct
3.3 Optimizing Functions of Several Variables 3.4 Lagrange Multipliers
 3.3 Optimizing Functions of Several Variables 3.4 Lagrange Multipliers Prof. Tesler Math 20C Fall 2018 Prof. Tesler 3.3 3.4 Optimization Math 20C / Fall 2018 1 / 56 Optimizing y = f (x) In Math 20A, we
3.3 Optimizing Functions of Several Variables 3.4 Lagrange Multipliers Prof. Tesler Math 20C Fall 2018 Prof. Tesler 3.3 3.4 Optimization Math 20C / Fall 2018 1 / 56 Optimizing y = f (x) In Math 20A, we
Therefore, after becoming familiar with the Matrix Method, you will be able to solve a system of two linear equations in four different ways.
 Grade 9 IGCSE A1: Chapter 9 Matrices and Transformations Materials Needed: Straightedge, Graph Paper Exercise 1: Matrix Operations Matrices are used in Linear Algebra to solve systems of linear equations.
Grade 9 IGCSE A1: Chapter 9 Matrices and Transformations Materials Needed: Straightedge, Graph Paper Exercise 1: Matrix Operations Matrices are used in Linear Algebra to solve systems of linear equations.
I can solve simultaneous equations algebraically and graphically. I can solve inequalities algebraically and graphically.
 B I can factorise and expand complex expressions. I can factorise Quadratics I can recognise the Difference of Two Squares (D.O.T.S) simultaneous equations algebraically and graphically. inequalities algebraically
B I can factorise and expand complex expressions. I can factorise Quadratics I can recognise the Difference of Two Squares (D.O.T.S) simultaneous equations algebraically and graphically. inequalities algebraically
Classification. 1 o Semestre 2007/2008
 Classification Departamento de Engenharia Informática Instituto Superior Técnico 1 o Semestre 2007/2008 Slides baseados nos slides oficiais do livro Mining the Web c Soumen Chakrabarti. Outline 1 2 3 Single-Class
Classification Departamento de Engenharia Informática Instituto Superior Técnico 1 o Semestre 2007/2008 Slides baseados nos slides oficiais do livro Mining the Web c Soumen Chakrabarti. Outline 1 2 3 Single-Class
Introduction to Homogeneous coordinates
 Last class we considered smooth translations and rotations of the camera coordinate system and the resulting motions of points in the image projection plane. These two transformations were expressed mathematically
Last class we considered smooth translations and rotations of the camera coordinate system and the resulting motions of points in the image projection plane. These two transformations were expressed mathematically
MAT 003 Brian Killough s Instructor Notes Saint Leo University
 MAT 003 Brian Killough s Instructor Notes Saint Leo University Success in online courses requires self-motivation and discipline. It is anticipated that students will read the textbook and complete sample
MAT 003 Brian Killough s Instructor Notes Saint Leo University Success in online courses requires self-motivation and discipline. It is anticipated that students will read the textbook and complete sample
Stage 7 Checklists Have you reached this Standard?
 Stage 7 Checklists Have you reached this Standard? Main Criteria for the whole year. J K L Use positive integer powers and associated real roots Apply the four operations with decimal numbers Write a quantity
Stage 7 Checklists Have you reached this Standard? Main Criteria for the whole year. J K L Use positive integer powers and associated real roots Apply the four operations with decimal numbers Write a quantity
Cluster algebras and infinite associahedra
 Cluster algebras and infinite associahedra Nathan Reading NC State University CombinaTexas 2008 Coxeter groups Associahedra and cluster algebras Sortable elements/cambrian fans Infinite type Much of the
Cluster algebras and infinite associahedra Nathan Reading NC State University CombinaTexas 2008 Coxeter groups Associahedra and cluster algebras Sortable elements/cambrian fans Infinite type Much of the
Get to Know Your Calculator!
 Math BD Calculator Lab Name: Date: Get to Know Your Calculator! You are allowed to use a non-graphing, scientific calculator for this course. A scientific calculator is different from an ordinary hand-held
Math BD Calculator Lab Name: Date: Get to Know Your Calculator! You are allowed to use a non-graphing, scientific calculator for this course. A scientific calculator is different from an ordinary hand-held
Name: Tutor s
 Name: Tutor s Email: Bring a couple, just in case! Necessary Equipment: Black Pen Pencil Rubber Pencil Sharpener Scientific Calculator Ruler Protractor (Pair of) Compasses 018 AQA Exam Dates Paper 1 4
Name: Tutor s Email: Bring a couple, just in case! Necessary Equipment: Black Pen Pencil Rubber Pencil Sharpener Scientific Calculator Ruler Protractor (Pair of) Compasses 018 AQA Exam Dates Paper 1 4
3D Geometry and Camera Calibration
 3D Geometry and Camera Calibration 3D Coordinate Systems Right-handed vs. left-handed x x y z z y 2D Coordinate Systems 3D Geometry Basics y axis up vs. y axis down Origin at center vs. corner Will often
3D Geometry and Camera Calibration 3D Coordinate Systems Right-handed vs. left-handed x x y z z y 2D Coordinate Systems 3D Geometry Basics y axis up vs. y axis down Origin at center vs. corner Will often
GSE Algebra 1 Name Date Block. Unit 3b Remediation Ticket
 Unit 3b Remediation Ticket Question: Which function increases faster, f(x) or g(x)? f(x) = 5x + 8; two points from g(x): (-2, 4) and (3, 10) Answer: In order to compare the rate of change (roc), you must
Unit 3b Remediation Ticket Question: Which function increases faster, f(x) or g(x)? f(x) = 5x + 8; two points from g(x): (-2, 4) and (3, 10) Answer: In order to compare the rate of change (roc), you must
Orthogonal complements
 Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 9: Orthogonality Section 3 Orthogonal complements What you need to know already: What orthogonal and orthonormal bases are. What you can learn here: How we can
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 9: Orthogonality Section 3 Orthogonal complements What you need to know already: What orthogonal and orthonormal bases are. What you can learn here: How we can
Year 6 Maths Scheme of Work
 Year 6 National Curriculum The 2014 2015 Year 6 cohort will be using the old national curriculum as this is what will be used for the KS2 SATs 2015. Below are the objectives students are required to meet
Year 6 National Curriculum The 2014 2015 Year 6 cohort will be using the old national curriculum as this is what will be used for the KS2 SATs 2015. Below are the objectives students are required to meet
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining. More Linear Classifiers Fall 2017
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining More Linear Classifiers Fall 2017 Admin Assignment 3: Due Friday of next week. Midterm: Can view your exam during instructor office hours next week, or after
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining More Linear Classifiers Fall 2017 Admin Assignment 3: Due Friday of next week. Midterm: Can view your exam during instructor office hours next week, or after
Unsupervised Learning
 Unsupervised Learning Learning without Class Labels (or correct outputs) Density Estimation Learn P(X) given training data for X Clustering Partition data into clusters Dimensionality Reduction Discover
Unsupervised Learning Learning without Class Labels (or correct outputs) Density Estimation Learn P(X) given training data for X Clustering Partition data into clusters Dimensionality Reduction Discover
Mapping Common Core State Standard Clusters and. Ohio Grade Level Indicator. Grade 5 Mathematics
 Mapping Common Core State Clusters and Ohio s Grade Level Indicators: Grade 5 Mathematics Operations and Algebraic Thinking: Write and interpret numerical expressions. Operations and Algebraic Thinking:
Mapping Common Core State Clusters and Ohio s Grade Level Indicators: Grade 5 Mathematics Operations and Algebraic Thinking: Write and interpret numerical expressions. Operations and Algebraic Thinking:
The first thing we ll need is some numbers. I m going to use the set of times and drug concentration levels in a patient s bloodstream given below.
 Graphing in Excel featuring Excel 2007 1 A spreadsheet can be a powerful tool for analyzing and graphing data, but it works completely differently from the graphing calculator that you re used to. If you
Graphing in Excel featuring Excel 2007 1 A spreadsheet can be a powerful tool for analyzing and graphing data, but it works completely differently from the graphing calculator that you re used to. If you
Computer Science 336 Fall 2017 Homework 2
 Computer Science 336 Fall 2017 Homework 2 Use the following notation as pseudocode for standard 3D affine transformation matrices. You can refer to these by the names below. There is no need to write out
Computer Science 336 Fall 2017 Homework 2 Use the following notation as pseudocode for standard 3D affine transformation matrices. You can refer to these by the names below. There is no need to write out
Confidence Intervals. Dennis Sun Data 301
 Dennis Sun Data 301 Statistical Inference probability Population / Box Sample / Data statistics The goal of statistics is to infer the unknown population from the sample. We ve already seen one mode of
Dennis Sun Data 301 Statistical Inference probability Population / Box Sample / Data statistics The goal of statistics is to infer the unknown population from the sample. We ve already seen one mode of
GRETL FOR TODDLERS!! CONTENTS. 1. Access to the econometric software A new data set: An existent data set: 3
 GRETL FOR TODDLERS!! JAVIER FERNÁNDEZ-MACHO CONTENTS 1. Access to the econometric software 3 2. Loading and saving data: the File menu 3 2.1. A new data set: 3 2.2. An existent data set: 3 2.3. Importing
GRETL FOR TODDLERS!! JAVIER FERNÁNDEZ-MACHO CONTENTS 1. Access to the econometric software 3 2. Loading and saving data: the File menu 3 2.1. A new data set: 3 2.2. An existent data set: 3 2.3. Importing
Pure Math 30: Explained!
 www.puremath30.com 30 part i: stretches about other lines Stretches about other lines: Stretches about lines other than the x & y axis are frequently required. Example 1: Stretch the graph horizontally
www.puremath30.com 30 part i: stretches about other lines Stretches about other lines: Stretches about lines other than the x & y axis are frequently required. Example 1: Stretch the graph horizontally
CS354 Computer Graphics Rotations and Quaternions
 Slide Credit: Don Fussell CS354 Computer Graphics Rotations and Quaternions Qixing Huang April 4th 2018 Orientation Position and Orientation The position of an object can be represented as a translation
Slide Credit: Don Fussell CS354 Computer Graphics Rotations and Quaternions Qixing Huang April 4th 2018 Orientation Position and Orientation The position of an object can be represented as a translation
Inverse Kinematics (part 1) CSE169: Computer Animation Instructor: Steve Rotenberg UCSD, Winter 2018
 Inverse Kinematics (part 1) CSE169: Computer Animation Instructor: Steve Rotenberg UCSD, Winter 2018 Welman, 1993 Inverse Kinematics and Geometric Constraints for Articulated Figure Manipulation, Chris
Inverse Kinematics (part 1) CSE169: Computer Animation Instructor: Steve Rotenberg UCSD, Winter 2018 Welman, 1993 Inverse Kinematics and Geometric Constraints for Articulated Figure Manipulation, Chris
Vector Algebra Transformations. Lecture 4
 Vector Algebra Transformations Lecture 4 Cornell CS4620 Fall 2008 Lecture 4 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Geometry A part of mathematics concerned with questions of size, shape, and relative positions of figures
Vector Algebra Transformations Lecture 4 Cornell CS4620 Fall 2008 Lecture 4 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Geometry A part of mathematics concerned with questions of size, shape, and relative positions of figures
Tentti/Exam Midterm 2/Välikoe 2, December
 1: 2: 3: Extra: Total 1-3: / 23 4: 5: 6: Total 4-6: / 20 Aalto ME-C3100 Computer Graphics, Fall 2015 Lehtinen / Kemppinen, Ollikainen, Puomio Tentti/Exam Midterm 2/Välikoe 2, December 16 2015 Name, student
1: 2: 3: Extra: Total 1-3: / 23 4: 5: 6: Total 4-6: / 20 Aalto ME-C3100 Computer Graphics, Fall 2015 Lehtinen / Kemppinen, Ollikainen, Puomio Tentti/Exam Midterm 2/Välikoe 2, December 16 2015 Name, student
Math 2B Linear Algebra Test 2 S13 Name Write all responses on separate paper. Show your work for credit.
 Math 2B Linear Algebra Test 2 S3 Name Write all responses on separate paper. Show your work for credit.. Construct a matrix whose a. null space consists of all combinations of (,3,3,) and (,2,,). b. Left
Math 2B Linear Algebra Test 2 S3 Name Write all responses on separate paper. Show your work for credit.. Construct a matrix whose a. null space consists of all combinations of (,3,3,) and (,2,,). b. Left
Here is the data collected.
 Introduction to Scientific Analysis of Data Using Spreadsheets. Computer spreadsheets are very powerful tools that are widely used in Business, Science, and Engineering to perform calculations and record,
Introduction to Scientific Analysis of Data Using Spreadsheets. Computer spreadsheets are very powerful tools that are widely used in Business, Science, and Engineering to perform calculations and record,
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS. Date: Lesson: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers
 Chapter 3: Portions and Integers CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
Chapter 3: Portions and Integers CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
CMP Book: Investigation Number Objective: PASS: 1.1 Describe data distributions and display in line and bar graphs
 Data About Us (6th Grade) (Statistics) 1.1 Describe data distributions and display in line and bar graphs. 6.5.1 1.2, 1.3, 1.4 Analyze data using range, mode, and median. 6.5.3 Display data in tables,
Data About Us (6th Grade) (Statistics) 1.1 Describe data distributions and display in line and bar graphs. 6.5.1 1.2, 1.3, 1.4 Analyze data using range, mode, and median. 6.5.3 Display data in tables,
Data Analysis and Solver Plugins for KSpread USER S MANUAL. Tomasz Maliszewski
 Data Analysis and Solver Plugins for KSpread USER S MANUAL Tomasz Maliszewski tmaliszewski@wp.pl Table of Content CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1. ABOUT DATA ANALYSIS PLUGIN... 3 1.3. ABOUT SOLVER PLUGIN...
Data Analysis and Solver Plugins for KSpread USER S MANUAL Tomasz Maliszewski tmaliszewski@wp.pl Table of Content CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1. ABOUT DATA ANALYSIS PLUGIN... 3 1.3. ABOUT SOLVER PLUGIN...
Spatializing GIS Commands with Self-Organizing Maps. Jochen Wendel Barbara P. Buttenfield Roland J. Viger Jeremy M. Smith
 Spatializing GIS Commands with Self-Organizing Maps Jochen Wendel Barbara P. Buttenfield Roland J. Viger Jeremy M. Smith Outline Introduction Characterizing GIS Commands Implementation Interpretation of
Spatializing GIS Commands with Self-Organizing Maps Jochen Wendel Barbara P. Buttenfield Roland J. Viger Jeremy M. Smith Outline Introduction Characterizing GIS Commands Implementation Interpretation of
Euclidean Space. Definition 1 (Euclidean Space) A Euclidean space is a finite-dimensional vector space over the reals R, with an inner product,.
 Definition 1 () A Euclidean space is a finite-dimensional vector space over the reals R, with an inner product,. 1 Inner Product Definition 2 (Inner Product) An inner product, on a real vector space X
Definition 1 () A Euclidean space is a finite-dimensional vector space over the reals R, with an inner product,. 1 Inner Product Definition 2 (Inner Product) An inner product, on a real vector space X
(Refer Slide Time: 00:04:20)
 Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 8 Three Dimensional Graphics Welcome back all of you to the lectures in Computer
Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 8 Three Dimensional Graphics Welcome back all of you to the lectures in Computer
Integers & Absolute Value Properties of Addition Add Integers Subtract Integers. Add & Subtract Like Fractions Add & Subtract Unlike Fractions
 Unit 1: Rational Numbers & Exponents M07.A-N & M08.A-N, M08.B-E Essential Questions Standards Content Skills Vocabulary What happens when you add, subtract, multiply and divide integers? What happens when
Unit 1: Rational Numbers & Exponents M07.A-N & M08.A-N, M08.B-E Essential Questions Standards Content Skills Vocabulary What happens when you add, subtract, multiply and divide integers? What happens when
Review for Quarter 3 Cumulative Test
 Review for Quarter 3 Cumulative Test I. Solving quadratic equations (LT 4.2, 4.3, 4.4) Key Facts To factor a polynomial, first factor out any common factors, then use the box method to factor the quadratic.
Review for Quarter 3 Cumulative Test I. Solving quadratic equations (LT 4.2, 4.3, 4.4) Key Facts To factor a polynomial, first factor out any common factors, then use the box method to factor the quadratic.
MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT COURSE OUTLINE TERM 1/2/3 YEAR 7
 MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT COURSE OUTLINE 2016-17 TERM 1/2/3 YEAR 7 Week Topic YEAR 7- Mathematics Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Learning outcomes 1/2 Numbers and the number system Recall prime numbers up to 50 Know
MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT COURSE OUTLINE 2016-17 TERM 1/2/3 YEAR 7 Week Topic YEAR 7- Mathematics Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Learning outcomes 1/2 Numbers and the number system Recall prime numbers up to 50 Know
FMA901F: Machine Learning Lecture 3: Linear Models for Regression. Cristian Sminchisescu
 FMA901F: Machine Learning Lecture 3: Linear Models for Regression Cristian Sminchisescu Machine Learning: Frequentist vs. Bayesian In the frequentist setting, we seek a fixed parameter (vector), with value(s)
FMA901F: Machine Learning Lecture 3: Linear Models for Regression Cristian Sminchisescu Machine Learning: Frequentist vs. Bayesian In the frequentist setting, we seek a fixed parameter (vector), with value(s)
Year 8 Set 2 : Unit 1 : Number 1
 Year 8 Set 2 : Unit 1 : Number 1 Learning Objectives: Level 5 I can order positive and negative numbers I know the meaning of the following words: multiple, factor, LCM, HCF, prime, square, square root,
Year 8 Set 2 : Unit 1 : Number 1 Learning Objectives: Level 5 I can order positive and negative numbers I know the meaning of the following words: multiple, factor, LCM, HCF, prime, square, square root,
Junior Circle Meeting 9 Commutativity and Inverses. May 30, We are going to examine different ways to transform the square below:
 Junior Circle Meeting 9 Commutativity and Inverses May 0, 2010 We are going to examine different ways to transform the square below: Just as with the triangle from last week, we are going to examine flips
Junior Circle Meeting 9 Commutativity and Inverses May 0, 2010 We are going to examine different ways to transform the square below: Just as with the triangle from last week, we are going to examine flips
Math 308 Autumn 2016 MIDTERM /18/2016
 Name: Math 38 Autumn 26 MIDTERM - 2 /8/26 Instructions: The exam is 9 pages long, including this title page. The number of points each problem is worth is listed after the problem number. The exam totals
Name: Math 38 Autumn 26 MIDTERM - 2 /8/26 Instructions: The exam is 9 pages long, including this title page. The number of points each problem is worth is listed after the problem number. The exam totals
Answers. Chapter 2. 1) Give the coordinates of the following points:
 Answers Chapter 2 1) Give the coordinates of the following points: a (-2.5, 3) b (1, 2) c (2.5, 2) d (-1, 1) e (0, 0) f (2, -0.5) g (-0.5, -1.5) h (0, -2) j (-3, -2) 1 2) List the 48 different possible
Answers Chapter 2 1) Give the coordinates of the following points: a (-2.5, 3) b (1, 2) c (2.5, 2) d (-1, 1) e (0, 0) f (2, -0.5) g (-0.5, -1.5) h (0, -2) j (-3, -2) 1 2) List the 48 different possible
Ingredients of Change: Nonlinear Models
 Chapter 2 Ingredients of Change: Nonlinear Models 2.1 Exponential Functions and Models As we begin to consider functions that are not linear, it is very important that you be able to draw scatter plots,
Chapter 2 Ingredients of Change: Nonlinear Models 2.1 Exponential Functions and Models As we begin to consider functions that are not linear, it is very important that you be able to draw scatter plots,
Computer Graphics Hands-on
 Computer Graphics Hands-on Two-Dimensional Transformations Objectives Visualize the fundamental 2D geometric operations translation, rotation about the origin, and scale about the origin Experimentally
Computer Graphics Hands-on Two-Dimensional Transformations Objectives Visualize the fundamental 2D geometric operations translation, rotation about the origin, and scale about the origin Experimentally
Year 9: Long term plan
 Year 9: Long term plan Year 9: Long term plan Unit Hours Powerful procedures 7 Round and round 4 How to become an expert equation solver 6 Why scatter? 6 The construction site 7 Thinking proportionally
Year 9: Long term plan Year 9: Long term plan Unit Hours Powerful procedures 7 Round and round 4 How to become an expert equation solver 6 Why scatter? 6 The construction site 7 Thinking proportionally
The Mplus modelling framework
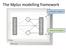 The Mplus modelling framework Continuous variables Categorical variables 1 Mplus syntax structure TITLE: a title for the analysis (not part of the syntax) DATA: (required) information about the data set
The Mplus modelling framework Continuous variables Categorical variables 1 Mplus syntax structure TITLE: a title for the analysis (not part of the syntax) DATA: (required) information about the data set
Modern Multidimensional Scaling
 Ingwer Borg Patrick J.F. Groenen Modern Multidimensional Scaling Theory and Applications Second Edition With 176 Illustrations ~ Springer Preface vii I Fundamentals of MDS 1 1 The Four Purposes of Multidimensional
Ingwer Borg Patrick J.F. Groenen Modern Multidimensional Scaling Theory and Applications Second Edition With 176 Illustrations ~ Springer Preface vii I Fundamentals of MDS 1 1 The Four Purposes of Multidimensional
Quaternion Rotations AUI Course Denbigh Starkey
 Major points of these notes: Quaternion Rotations AUI Course Denbigh Starkey. What I will and won t be doing. Definition of a quaternion and notation 3 3. Using quaternions to rotate any point around an
Major points of these notes: Quaternion Rotations AUI Course Denbigh Starkey. What I will and won t be doing. Definition of a quaternion and notation 3 3. Using quaternions to rotate any point around an
Activity Graphical Analysis with Excel and Logger Pro
 Activity Graphical Analysis with Excel and Logger Pro Purpose Vernier s Logger Pro is a graphical analysis software that will allow you to collect, graph and manipulate data. Microsoft s Excel is a spreadsheet
Activity Graphical Analysis with Excel and Logger Pro Purpose Vernier s Logger Pro is a graphical analysis software that will allow you to collect, graph and manipulate data. Microsoft s Excel is a spreadsheet
Cecil Jones Academy Mathematics Fundamental Map
 Fundamentals Year 7 (Core) Knowledge Unit 1 Unit 2 Solve problems involving prime numbers Use highest common factors to solve problems Use lowest common multiples to solve problems Explore powers and roots
Fundamentals Year 7 (Core) Knowledge Unit 1 Unit 2 Solve problems involving prime numbers Use highest common factors to solve problems Use lowest common multiples to solve problems Explore powers and roots
Linear and Affine Transformations Coordinate Systems
 Linear and Affine Transformations Coordinate Systems Recall A transformation T is linear if Recall A transformation T is linear if Every linear transformation can be represented as matrix Linear Transformation
Linear and Affine Transformations Coordinate Systems Recall A transformation T is linear if Recall A transformation T is linear if Every linear transformation can be represented as matrix Linear Transformation
The Singular Value Decomposition: Let A be any m n matrix. orthogonal matrices U, V and a diagonal matrix Σ such that A = UΣV T.
 Section 7.4 Notes (The SVD) The Singular Value Decomposition: Let A be any m n matrix. orthogonal matrices U, V and a diagonal matrix Σ such that Then there are A = UΣV T Specifically: The ordering of
Section 7.4 Notes (The SVD) The Singular Value Decomposition: Let A be any m n matrix. orthogonal matrices U, V and a diagonal matrix Σ such that Then there are A = UΣV T Specifically: The ordering of
Updated: January 11, 2016 Calculus III Section Math 232. Calculus III. Brian Veitch Fall 2015 Northern Illinois University
 Math 232 Calculus III Brian Veitch Fall 2015 Northern Illinois University 12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Definition 1: Vector Equation of a Line L Let L be a line in three-dimensional space. P (x,
Math 232 Calculus III Brian Veitch Fall 2015 Northern Illinois University 12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Definition 1: Vector Equation of a Line L Let L be a line in three-dimensional space. P (x,
Fall 09, Homework 5
 5-38 Fall 09, Homework 5 Due: Wednesday, November 8th, beginning of the class You can work in a group of up to two people. This group does not need to be the same group as for the other homeworks. You
5-38 Fall 09, Homework 5 Due: Wednesday, November 8th, beginning of the class You can work in a group of up to two people. This group does not need to be the same group as for the other homeworks. You
