Medical Robotics. Control Modalities
|
|
|
- Louisa Floyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Università di Roma La Sapienza Medical Robotics Control Modalities Marilena Vendittelli
2 differ for the the way human input is mapped to the motions of surgical instruments strictly related to the degree of autonomy of surgical robots can be combined in mixed control schemes the choice is affected by the function and, hence, by the domain of use domain of use function control modality (strictly related to the degree of autonomy) kinematic architecture sensors and actuators orthopedics machining of rigid surface cooperative or handson MIS constrained manipulation neurosurgery, intervantional radiology, radiotherapy constrained targeting microsurgery micromanipulation shared/cooperative control M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Università di Roma La Sapienza ) Control Modalities 2
3 semiautonomous motion the motion of the surgical instrument is interactively specified by the surgeon, usually on the basis of medical images the computer fills in the details and motion starts with surgeon concurrence allows the execution of complex paths starting from simple task description examples: selection of tool cutter paths for orthopaedic bone machining and needle target and insertion points for percutaneous therapy teleoperated systems the surgeon manipulates the input device called master and a device slave, on the patient side, follows the input allow filtering and scaling of position and force, remote tool control other human interfaces are also used (e.g., voice control) examples: common telesurgery systems such as the davinci M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Università di Roma La Sapienza ) Control Modalities 3
4 cooperative or handson systems both the robot and the surgeon interact directly with a surgical instrument a force sensor detects the direction toward which the surgeon wishes to move the tool and the controller makes the robot move to comply surgeons find this form of control to be very convenient and natural for surgical tasks combines the precision, strength, and tremorfree motion of robotic devices with some of the immediacy of freehand surgical manipulation less expensive than telesurgical systems (less hardware) and easier to introduce into existing surgical settings force scaling is allowed but position scaling is inherently not permitted incompatible with any degree of remoteness between the surgeon and the surgical tool it is not practical to provide handson control of instruments with distal dexterity examples: orthopedic surgery, microsurgery M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Università di Roma La Sapienza ) Control Modalities 4
5 cooperative systems peculiarities typically nonbackdrivable and velocitycontrolled actuators the velocity of such admittancetype systems is typically controlled with a highbandwidth servo controller to be proportional to the operatorapplied force forcetomotion scaling linear admittancetype device control is generally modeled by V (s) = Y (s)f (s) with F (s): measured command force externally applied by the surgeon; Y (s): device admittance; V (s): device desired velocity nonbackdrivability and natural stiffness of the robot are assumed to be sufficient to reject applied external forces from the operator and the environment not used by the controller the selection of Y determines the responsiveness of the system to human inputs, allowing significant scaling between humanapplied force and robot velocity, which improves accuracy smoothness can be enhanced by thresholding and filtering the measured command force and by reducing unintentional motions and tremor the admittance value is limited by stability considerations admittance control can also be modified to provide haptic feedback and virtual fixtures ( ) M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Università di Roma La Sapienza ) Control Modalities 5
6 The HandsOn Acrobot (Active Constraint Robot) handson robotic system for bone machining in knee replacement surgery preoperative phase CT scan of the knee an interactive software allows elaboration of the CT images to build 3d views of the knee the surgeon decides size and position of the prosthesis on the basis of the 3D models built from CT images once positioned the prosthesis in the model, the software generates the constraints for the motion of the surgical tool M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Universita di Roma La Sapienza ) Acrobot 6
7 System description spherical manipulator with three orthogonal axes of motion: yaw, pitch (within [ 30 o, 30 o ]), and extension (within cm) kinematic design: mechanical impedance of the axes is low and similar for all axes allowing the robot to be moved by the surgeon with low force; force generated during hard bone cutting can be detected without the need for force sensors in the robot cutter the surgeon moves the robot by pushing the handle near the tip of the robot the handle incorporates a sixaxes force sensor, which measures the guiding forces and torques a highspeed orthopaedic cutter motor (removable for autoclave sterilization) is mounted at the tip the Acrobot is placed on a sixaxes gross positioning device to increase its small working envelope M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Università di Roma La Sapienza ) Acrobot 7
8 Control idea: gradually increase the robot stiffness when approaching a boundary defined in the intervention planning phase the robot is free to move inside the safe region (RI) due to the low mechanical impedance of the robot at the boundary of the safe region, the robot becomes very stiff, thus preventing further motion over the boundary (RIII) the portion of the guiding force normal to the boundary is directly compensated, which substantially reduces the overboundary error (this error is inevitable due to the limited motor power) to avoid instabilities at the boundary, the stiffness increases gradually over a small region (with width D 1 ) close to the boundary (RII) only the stiffness in a direction toward the boundary is adjusted, to allow motion along or away from the boundary with a very low guiding force M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Università di Roma La Sapienza ) Acrobot 8
9 Control cont inner pos/vel control loop, 2 ms (550Hz) th X d, e co inn Ẋ d mpe IK J 1 ( d d KP KD gravity + friction J T C robot J T, joi ) F C external forces (organs, patient) law F G, outer control loop implementing the active constraints 1015 ms (100Hz) M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Università di Roma La Sapienza ) Acrobot 9
10 Control cont two control loops: an inner joint position/velocity control loop (2 ms) with friction, gravity and surgeon s guiding force : τ = K P (Θ d Θ) + K D ( Θ d Θ) + τ C + f (Θ, Θ) + g (Θ) τ torque output from the controller to the robot motors, K P, K D proportional/derivative gains, Θ d, Θ d (Θ, Θ) desired (measured) joint position and velocity, τ C of the surgeon s guiding force F G, f (Θ, Θ), g (Θ) respectively friction and gravity the outer control loop is slower (1015 ms) and implements the idea of active constraint cartesian control provides the gains of the inner loop K P and K D, the desired position and velocity (in operative space) X d, Ẋ d ( Θ d, Θ d are obtained by kinematic inversion) and the amount of force F C ( τ C = J T F C, quasistatic operational conditions) the controller parameters are adapted on the basis of the endeffector position X and of the force F G determined the point on the boundary X np closest to X, define N np : normal to the boundary at X np d = X X np = (X X np ) N np M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Università di Roma La Sapienza ) Acrobot 10
11 Control cont RI (d > D 1 ) the PD gains are small to allow the surgeon to feel the cutting forces X d = X Ẋ d = AF G admittance is the same in all directions F C = 0 the surgeon s guiding force is not compensated in this region th X d, e co inn Ẋ d mpe admittance A IK J 1 ( d d K P K D gravity + friction robot J T external forces (organs, patient), joi ) F G Ẋ d X RI D 1 RII N np : X np RIII F G, M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Università di Roma La Sapienza ) Acrobot 11
12 Control cont RII (D 1 d > 0) the control gains increase as the distance to the boundary d decreases if F G N np 0 X d, Ẋ d and F C as in RI otherwise F G is decomposed into a normal and a tangential component F GN = (F G N np )N np Ẋ d = AF GT + A N F GN, A N = d D 1 A F GT = F G F GN F G is compensated in a region with width D 2 < D 1 if d > D 2 F C = 0, otherwise F C = D 2 d D 2 F GN th X d, e co inn Ẋ d mpe admittance A (AN) IK J 1 ( d d K P K D F C JT gravity + friction C robot J T external forces (organs, patient), joi ) RI RII Ẋ d F G N np : X np RIII RI F G Ẋ d RII N np : X np RIII F G, of F GN M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Università di Roma La Sapienza ) Acrobot 12
13 Control cont RIII (d 0) the PD gains are high X d = X np if the direction of F G points away from the boundary, Ẋ d and F C are set as in RI otherwise Ẋ d = AF GT, F C = F GN th X d, e co inn Ẋ d mpe admittance A IK J 1 ( d d K P KD F C JT gravity + friction C robot J T external forces (organs, patient), joi ) RI RII N np : X d = X np if the dire RIII RI RII RIII Ẋ d F G N np : X np F G Ẋ d F G, of F GN M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Università di Roma La Sapienza ) Acrobot 13
14 the used prosthesis requires a number of flat planes to be cut; a 2.5D constraint is defined: the plane part allows cutting a flat plane into the bone, the 2D outline part provides protection for the surrounding tissue the two parts of the boundary are orthogonal X d, Ẋ d, F c can be computed separately for each part, following the above rules, and then combined before being passed on to the inner loop K P and K D are determined by the nearest point on the whole boundary 1999 the Acrobot Company was set up after 8 years of research at Imperial College London 2010 the Acrobot Company was acquired by the Stanmore Implants Worldwide Ltd (SIW) 2013 SIW sold the Acrobot system to the American company MAKO M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Università di Roma La Sapienza ) Acrobot 14
15 Acrobot today Bibliography M. Jakopec, F. Rodriguez y Baena, S. j. Harris, P. Gomes, J. Cobb, B. L. Davies, The handson orthopaedic robot acrobot : Early clinical trials of total knee replacement surgery, IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, Special Issue on Medical Robotics, vol. 19, no. 5, pp , G.D. Hager, A.M. Okamura, P. Kazanzides, L.L. Whitcomb, G. Fichtinger, R. H. Taylor, Surgical and interventional robotics: Part III, IEEE Robotics and Automation Magazine, vol. 15, no. 4, pp , M. Vendittelli Medical Robotics (Università di Roma La Sapienza ) Acrobot 15
Development of a Master Slave System with Force Sensing Using Pneumatic Servo System for Laparoscopic Surgery
 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Roma, Italy, 10-14 April 2007 WeC8.3 Development of a Master Slave System with Force Sensing Using Pneumatic Servo System for Laparoscopic
2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Roma, Italy, 10-14 April 2007 WeC8.3 Development of a Master Slave System with Force Sensing Using Pneumatic Servo System for Laparoscopic
Spatial Motion Constraints: Theory and Demonstrations for Robot Guidance Using Virtual Fixtures
 Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation Taipei, Taiwan, September 14-19, 2003 Spatial Motion Constraints: Theory and Demonstrations for Robot Guidance Using Virtual
Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation Taipei, Taiwan, September 14-19, 2003 Spatial Motion Constraints: Theory and Demonstrations for Robot Guidance Using Virtual
A Constrained Optimization Approach to Virtual Fixtures
 A Constrained Optimization Approach to Virtual Fixtures Ming Li, Ankur Kapoor and Russell H. Taylor Department of Computer Science NSF Engineering Research Center for Computer-Integrated Surgical Systems
A Constrained Optimization Approach to Virtual Fixtures Ming Li, Ankur Kapoor and Russell H. Taylor Department of Computer Science NSF Engineering Research Center for Computer-Integrated Surgical Systems
Telemanipulation of Snake-Like Robots for Minimally Invasive Surgery of the Upper Airway
 Telemanipulation of Snake-Like Robots for Minimally Invasive Surgery of the Upper Airway Ankur Kapoor 1, Kai Xu 2, Wei Wei 2 Nabil Simaan 2 and Russell H. Taylor 1 1 ERC-CISST Department of Computer Science
Telemanipulation of Snake-Like Robots for Minimally Invasive Surgery of the Upper Airway Ankur Kapoor 1, Kai Xu 2, Wei Wei 2 Nabil Simaan 2 and Russell H. Taylor 1 1 ERC-CISST Department of Computer Science
A Control Technique for a 6-DOF Master-Slave Robot Manipulator System for Miniature Tasks
 A Control Technique for a 6-DOF Master-Slave Robot Manipulator System for Miniature Tasks Sangveraphunsiri V., Malithong K. and Vongbunyong S. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,
A Control Technique for a 6-DOF Master-Slave Robot Manipulator System for Miniature Tasks Sangveraphunsiri V., Malithong K. and Vongbunyong S. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,
Robot Control for Medical Applications and Hair Transplantation
 Dr. John Tenney Director of Research Restoration Robotics, Inc. Robot Control for Medical Applications and Hair Transplantation Presented to the IEEE Control Systems Society, Santa Clara Valley 18 November
Dr. John Tenney Director of Research Restoration Robotics, Inc. Robot Control for Medical Applications and Hair Transplantation Presented to the IEEE Control Systems Society, Santa Clara Valley 18 November
Study Report - Neuro-Endoscopic Manipulator
 Study Report - Neuro-Endoscopic Manipulator Draft: 1. - 14th April 1998 Author: Stephen J Starkie Contents Introduction Design Specification Manipulator Architecture Force Control Strategy Manipulator
Study Report - Neuro-Endoscopic Manipulator Draft: 1. - 14th April 1998 Author: Stephen J Starkie Contents Introduction Design Specification Manipulator Architecture Force Control Strategy Manipulator
Sensor-aided Milling with a Surgical Robot System
 1 Sensor-aided Milling with a Surgical Robot System Dirk Engel, Joerg Raczkowsky, Heinz Woern Institute for Process Control and Robotics (IPR), Universität Karlsruhe (TH) Engler-Bunte-Ring 8, 76131 Karlsruhe
1 Sensor-aided Milling with a Surgical Robot System Dirk Engel, Joerg Raczkowsky, Heinz Woern Institute for Process Control and Robotics (IPR), Universität Karlsruhe (TH) Engler-Bunte-Ring 8, 76131 Karlsruhe
Suture knot manipulation with a robot
 Suture knot manipulation with a robot Tian Xia Ph.D Advisor: Peter Kazanzides Project Advisor: Russell Taylor, Rajesh Kumar Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, Maryland, USA 9/16/09 1 Knot Tying Video
Suture knot manipulation with a robot Tian Xia Ph.D Advisor: Peter Kazanzides Project Advisor: Russell Taylor, Rajesh Kumar Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, Maryland, USA 9/16/09 1 Knot Tying Video
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW. Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino
 ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Control Part 4 Other control strategies These slides are devoted to two advanced control approaches, namely Operational space control Interaction
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Control Part 4 Other control strategies These slides are devoted to two advanced control approaches, namely Operational space control Interaction
Table of Contents Introduction Historical Review of Robotic Orienting Devices Kinematic Position Analysis Instantaneous Kinematic Analysis
 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Background in Robotics 1 1.2 Robot Mechanics 1 1.2.1 Manipulator Kinematics and Dynamics 2 1.3 Robot Architecture 4 1.4 Robotic Wrists 4 1.5 Origins of the Carpal
Table of Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Background in Robotics 1 1.2 Robot Mechanics 1 1.2.1 Manipulator Kinematics and Dynamics 2 1.3 Robot Architecture 4 1.4 Robotic Wrists 4 1.5 Origins of the Carpal
A Miniature Instrument Tip Force Sensor for Robot/Human Cooperative Microsurgical Manipulation with Enhanced Force Feedback
 A Miniature Instrument Tip Force Sensor for Robot/Human Cooperative Microsurgical Manipulation with Enhanced Force Feedback Peter J. Berkelman, Louis L. Whitcomb, Russell H. Taylor, and Patrick Jensen
A Miniature Instrument Tip Force Sensor for Robot/Human Cooperative Microsurgical Manipulation with Enhanced Force Feedback Peter J. Berkelman, Louis L. Whitcomb, Russell H. Taylor, and Patrick Jensen
Keehoon Kim, Wan Kyun Chung, and M. Cenk Çavuşoğlu. 1 Jacobian of the master device, J m : q m R m ẋ m R r, and
 1 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Anchorage Convention District May 3-8, 1, Anchorage, Alaska, USA Restriction Space Projection Method for Position Sensor Based Force Reflection
1 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Anchorage Convention District May 3-8, 1, Anchorage, Alaska, USA Restriction Space Projection Method for Position Sensor Based Force Reflection
Cecilia Laschi The BioRobotics Institute Scuola Superiore Sant Anna, Pisa
 University of Pisa Master of Science in Computer Science Course of Robotics (ROB) A.Y. 2016/17 cecilia.laschi@santannapisa.it http://didawiki.cli.di.unipi.it/doku.php/magistraleinformatica/rob/start Robot
University of Pisa Master of Science in Computer Science Course of Robotics (ROB) A.Y. 2016/17 cecilia.laschi@santannapisa.it http://didawiki.cli.di.unipi.it/doku.php/magistraleinformatica/rob/start Robot
DARPA Investments in GEO Robotics
 DARPA Investments in GEO Robotics Carl Glen Henshaw, Ph.D. Signe Redfield, Ph.D. Naval Center for Space Technology U.S. Naval Research Laboratory Washington, DC 20375 May 22, 2015 Introduction Program
DARPA Investments in GEO Robotics Carl Glen Henshaw, Ph.D. Signe Redfield, Ph.D. Naval Center for Space Technology U.S. Naval Research Laboratory Washington, DC 20375 May 22, 2015 Introduction Program
Combined Collision Avoidance and Prevention of Soft Tissue Damage Control Method for Surgical Robots
 The Fourth IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics Roma, Italy. June 4-7, Combined Collision Avoidance and Prevention of Soft Tissue Damage Control Method for
The Fourth IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics Roma, Italy. June 4-7, Combined Collision Avoidance and Prevention of Soft Tissue Damage Control Method for
Basilio Bona ROBOTICA 03CFIOR 1
 Kinematic chains 1 Readings & prerequisites Chapter 2 (prerequisites) Reference systems Vectors Matrices Rotations, translations, roto-translations Homogeneous representation of vectors and matrices Chapter
Kinematic chains 1 Readings & prerequisites Chapter 2 (prerequisites) Reference systems Vectors Matrices Rotations, translations, roto-translations Homogeneous representation of vectors and matrices Chapter
Optimum Robot Control for 3D Virtual Fixture in Constrained ENT Surgery
 Optimum Robot Control for 3D Virtual Fixture in Constrained EN Surgery Ming Li and Russell H. aylor Department of Computer Science Department NSF Engineering Research Center for Computer Integrated Surgical
Optimum Robot Control for 3D Virtual Fixture in Constrained EN Surgery Ming Li and Russell H. aylor Department of Computer Science Department NSF Engineering Research Center for Computer Integrated Surgical
Assignment 3: Robot Design and Dynamics ME 328: Medical Robotics Stanford University w Autumn 2016
 Assignment 3: Robot Design and Dynamics ME 328: Medical Robotics Stanford University w Autumn 2016 Due to submission box outside Okamura s office by :00 pm on Monday, October 2 (revised) Note: You can
Assignment 3: Robot Design and Dynamics ME 328: Medical Robotics Stanford University w Autumn 2016 Due to submission box outside Okamura s office by :00 pm on Monday, October 2 (revised) Note: You can
ANALYTICAL MODEL OF THE CUTTING PROCESS WITH SCISSORS-ROBOT FOR HAPTIC SIMULATION
 Bulletin of the ransilvania University of Braşov Series I: Engineering Sciences Vol. 4 (53) No. 1-2011 ANALYICAL MODEL OF HE CUING PROCESS WIH SCISSORS-ROBO FOR HAPIC SIMULAION A. FRAU 1 M. FRAU 2 Abstract:
Bulletin of the ransilvania University of Braşov Series I: Engineering Sciences Vol. 4 (53) No. 1-2011 ANALYICAL MODEL OF HE CUING PROCESS WIH SCISSORS-ROBO FOR HAPIC SIMULAION A. FRAU 1 M. FRAU 2 Abstract:
Suturing in Confined Spaces: Constrained Motion Control of a Hybrid 8-DoF Robot
 Suturing in Confined Spaces: Constrained Motion Control of a Hybrid 8-DoF Robot Ankur Kapoor 1, Nabil Simaan 2, Russell H. Taylor 1 1 ERC-CISST Department of Computer Science Johns Hopkins University 2
Suturing in Confined Spaces: Constrained Motion Control of a Hybrid 8-DoF Robot Ankur Kapoor 1, Nabil Simaan 2, Russell H. Taylor 1 1 ERC-CISST Department of Computer Science Johns Hopkins University 2
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW. Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino
 ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Kinematic chains Readings & prerequisites From the MSMS course one shall already be familiar with Reference systems and transformations Vectors
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Kinematic chains Readings & prerequisites From the MSMS course one shall already be familiar with Reference systems and transformations Vectors
Kinematics, position and force control issue in minimally invasive surgery. LRP, Paris, France. LIRMM, Montpellier, France
 Kinematics, position and force control issue in minimally invasive surgery G. Morel * and P. Poignet ** * LRP, Paris, France ** LIRMM, Montpellier, France morel@robot.jussieu.fr poignet@lirmm.fr Introduction
Kinematics, position and force control issue in minimally invasive surgery G. Morel * and P. Poignet ** * LRP, Paris, France ** LIRMM, Montpellier, France morel@robot.jussieu.fr poignet@lirmm.fr Introduction
Control of a Robot Manipulator for Aerospace Applications
 Control of a Robot Manipulator for Aerospace Applications Antonella Ferrara a, Riccardo Scattolini b a Dipartimento di Informatica e Sistemistica - Università di Pavia, Italy b Dipartimento di Elettronica
Control of a Robot Manipulator for Aerospace Applications Antonella Ferrara a, Riccardo Scattolini b a Dipartimento di Informatica e Sistemistica - Università di Pavia, Italy b Dipartimento di Elettronica
Robotics. SAAST Robotics Robot Arms
 SAAST Robotics 008 Robot Arms Vijay Kumar Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics and Professor of Computer and Information Science University of Pennsylvania Topics Types of robot arms
SAAST Robotics 008 Robot Arms Vijay Kumar Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics and Professor of Computer and Information Science University of Pennsylvania Topics Types of robot arms
Lecture 2: Kinesthetic haptic devices: design, kinematics and dynamics
 ME 327: Design and Control of Haptic Systems Winter 2018 Lecture 2: Kinesthetic haptic devices: design, kinematics and dynamics Allison M. Okamura Stanford University kinematics transmission 2 Capstan
ME 327: Design and Control of Haptic Systems Winter 2018 Lecture 2: Kinesthetic haptic devices: design, kinematics and dynamics Allison M. Okamura Stanford University kinematics transmission 2 Capstan
Manipulator Performance Constraints in Cartesian Admittance Control for Human-Robot Cooperation
 216 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA Stockholm, Sweden, May 16-21, 216 Manipulator Performance Constraints in Cartesian Admittance Control for Human-Robot Cooperation Fotios
216 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA Stockholm, Sweden, May 16-21, 216 Manipulator Performance Constraints in Cartesian Admittance Control for Human-Robot Cooperation Fotios
Robotics kinematics and Dynamics
 Robotics kinematics and Dynamics C. Sivakumar Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BSA Crescent Institute of Science and Technology 1 Robot kinematics KINEMATICS the analytical study
Robotics kinematics and Dynamics C. Sivakumar Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BSA Crescent Institute of Science and Technology 1 Robot kinematics KINEMATICS the analytical study
Torque-Position Transformer for Task Control of Position Controlled Robots
 28 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Pasadena, CA, USA, May 19-23, 28 Torque-Position Transformer for Task Control of Position Controlled Robots Oussama Khatib, 1 Peter Thaulad,
28 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Pasadena, CA, USA, May 19-23, 28 Torque-Position Transformer for Task Control of Position Controlled Robots Oussama Khatib, 1 Peter Thaulad,
Robotics 2 Iterative Learning for Gravity Compensation
 Robotics 2 Iterative Learning for Gravity Compensation Prof. Alessandro De Luca Control goal! regulation of arbitrary equilibium configurations in the presence of gravity! without explicit knowledge of
Robotics 2 Iterative Learning for Gravity Compensation Prof. Alessandro De Luca Control goal! regulation of arbitrary equilibium configurations in the presence of gravity! without explicit knowledge of
Kinematics and dynamics analysis of micro-robot for surgical applications
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (2009) No. 1, pp. 22-29 Kinematics and dynamics analysis of micro-robot for surgical applications Khaled Tawfik 1, Atef A.
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (2009) No. 1, pp. 22-29 Kinematics and dynamics analysis of micro-robot for surgical applications Khaled Tawfik 1, Atef A.
An Accuracy Approach to Robotic Microsurgery in the Ear
 An Accuracy Approach to Robotic Microsurgery in the Ear B. Bell¹,J.Salzmann 1, E.Nielsen 3, N.Gerber 1, G.Zheng 1, L.Nolte 1, C.Stieger 4, M.Caversaccio², S. Weber 1 ¹ Institute for Surgical Technologies
An Accuracy Approach to Robotic Microsurgery in the Ear B. Bell¹,J.Salzmann 1, E.Nielsen 3, N.Gerber 1, G.Zheng 1, L.Nolte 1, C.Stieger 4, M.Caversaccio², S. Weber 1 ¹ Institute for Surgical Technologies
Motion Capture & Simulation
 Motion Capture & Simulation Motion Capture Character Reconstructions Joint Angles Need 3 points to compute a rigid body coordinate frame 1 st point gives 3D translation, 2 nd point gives 2 angles, 3 rd
Motion Capture & Simulation Motion Capture Character Reconstructions Joint Angles Need 3 points to compute a rigid body coordinate frame 1 st point gives 3D translation, 2 nd point gives 2 angles, 3 rd
Physiological Motion Compensation in Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery Part I
 Physiological Motion Compensation in Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery Part I Tobias Ortmaier Laboratoire de Robotique de Paris 18, route du Panorama - BP 61 92265 Fontenay-aux-Roses Cedex France Tobias.Ortmaier@alumni.tum.de
Physiological Motion Compensation in Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery Part I Tobias Ortmaier Laboratoire de Robotique de Paris 18, route du Panorama - BP 61 92265 Fontenay-aux-Roses Cedex France Tobias.Ortmaier@alumni.tum.de
Stable Grasp and Manipulation in 3D Space with 2-Soft-Fingered Robot Hand
 Stable Grasp and Manipulation in 3D Space with 2-Soft-Fingered Robot Hand Tsuneo Yoshikawa 1, Masanao Koeda 1, Haruki Fukuchi 1, and Atsushi Hirakawa 2 1 Ritsumeikan University, College of Information
Stable Grasp and Manipulation in 3D Space with 2-Soft-Fingered Robot Hand Tsuneo Yoshikawa 1, Masanao Koeda 1, Haruki Fukuchi 1, and Atsushi Hirakawa 2 1 Ritsumeikan University, College of Information
Introduction To Robotics (Kinematics, Dynamics, and Design)
 Introduction To Robotics (Kinematics, Dynamics, and Design) SESSION # 5: Concepts & Defenitions Ali Meghdari, Professor School of Mechanical Engineering Sharif University of Technology Tehran, IRAN 11365-9567
Introduction To Robotics (Kinematics, Dynamics, and Design) SESSION # 5: Concepts & Defenitions Ali Meghdari, Professor School of Mechanical Engineering Sharif University of Technology Tehran, IRAN 11365-9567
Prof. Fanny Ficuciello Robotics for Bioengineering Visual Servoing
 Visual servoing vision allows a robotic system to obtain geometrical and qualitative information on the surrounding environment high level control motion planning (look-and-move visual grasping) low level
Visual servoing vision allows a robotic system to obtain geometrical and qualitative information on the surrounding environment high level control motion planning (look-and-move visual grasping) low level
Simulation. x i. x i+1. degrees of freedom equations of motion. Newtonian laws gravity. ground contact forces
 Dynamic Controllers Simulation x i Newtonian laws gravity ground contact forces x i+1. x degrees of freedom equations of motion Simulation + Control x i Newtonian laws gravity ground contact forces internal
Dynamic Controllers Simulation x i Newtonian laws gravity ground contact forces x i+1. x degrees of freedom equations of motion Simulation + Control x i Newtonian laws gravity ground contact forces internal
What is an industrial robot?
 What is an industrial robot? A robot is CFIDV 02CFIC CY A kinematic chain A multi-body dynamical system A system with motors and drives A system with digital and analogic sensors An electronic system A
What is an industrial robot? A robot is CFIDV 02CFIC CY A kinematic chain A multi-body dynamical system A system with motors and drives A system with digital and analogic sensors An electronic system A
Advanced Robotic - MAE 263D - Introduction
 Advanced Robotic - MAE 263D - Introduction Office: Engineering IV Rm. 37-146 Lab: Bionics Lab - Engineering IV, Rm. 18-111 E-mail: rosen@seas.ucla.edu Office Hrs: Wed 2:00-4:00 TA: Sepehr Ghassemi TA Room:
Advanced Robotic - MAE 263D - Introduction Office: Engineering IV Rm. 37-146 Lab: Bionics Lab - Engineering IV, Rm. 18-111 E-mail: rosen@seas.ucla.edu Office Hrs: Wed 2:00-4:00 TA: Sepehr Ghassemi TA Room:
Robot Calibration for Precise Ultrasound Image Acquisition
 Abstract Robot Calibration for Precise Ultrasound Image Acquisition Pedro M. B. Torres 1,2, Paulo J. S. Gonçalves 1,2, Jorge M. M. Martins 2 1 Polytechnic Institute of CasteloBranco, School of Technology,
Abstract Robot Calibration for Precise Ultrasound Image Acquisition Pedro M. B. Torres 1,2, Paulo J. S. Gonçalves 1,2, Jorge M. M. Martins 2 1 Polytechnic Institute of CasteloBranco, School of Technology,
2008 International ANSYS Conference
 2008 International ANSYS Conference Patient-Specific Orthopedics Simulation Using ANSYS Technologies N. Hraiech, E. Malvesin and M. Rochette ANSYS France M. Viceconti and F. Taddei Istituti Ortopedici
2008 International ANSYS Conference Patient-Specific Orthopedics Simulation Using ANSYS Technologies N. Hraiech, E. Malvesin and M. Rochette ANSYS France M. Viceconti and F. Taddei Istituti Ortopedici
VIBRATION ISOLATION USING A MULTI-AXIS ROBOTIC PLATFORM G.
 VIBRATION ISOLATION USING A MULTI-AXIS ROBOTIC PLATFORM G. Satheesh Kumar, Y. G. Srinivasa and T. Nagarajan Precision Engineering and Instrumentation Laboratory Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian
VIBRATION ISOLATION USING A MULTI-AXIS ROBOTIC PLATFORM G. Satheesh Kumar, Y. G. Srinivasa and T. Nagarajan Precision Engineering and Instrumentation Laboratory Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian
Overview. Animation is a big topic We will concentrate on character animation as is used in many games today. humans, animals, monsters, robots, etc.
 ANIMATION Overview Animation is a big topic We will concentrate on character animation as is used in many games today humans, animals, monsters, robots, etc. Character Representation A character is represented
ANIMATION Overview Animation is a big topic We will concentrate on character animation as is used in many games today humans, animals, monsters, robots, etc. Character Representation A character is represented
FULLY autonomous robotic systems are currently used in
 138 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ROBOTICS, VOL. 30, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2014 Active Constraints/Virtual Fixtures: A Survey Stuart A. Bowyer, Student Member, IEEE, Brian L. Davies, and Ferdinando Rodriguez y Baena,
138 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ROBOTICS, VOL. 30, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2014 Active Constraints/Virtual Fixtures: A Survey Stuart A. Bowyer, Student Member, IEEE, Brian L. Davies, and Ferdinando Rodriguez y Baena,
Dr. Pierre-Frédéric Villard Research Associate
 Advanced Computer Graphics and Visualization Lecture 15 Dr. Pierre-Frédéric Villard Research Associate email: p.villard@ @ imperial. ac. uk,, St Mary s s campus Division of Surgery, Oncology, Reproductive
Advanced Computer Graphics and Visualization Lecture 15 Dr. Pierre-Frédéric Villard Research Associate email: p.villard@ @ imperial. ac. uk,, St Mary s s campus Division of Surgery, Oncology, Reproductive
Serial Manipulator Statics. Robotics. Serial Manipulator Statics. Vladimír Smutný
 Serial Manipulator Statics Robotics Serial Manipulator Statics Vladimír Smutný Center for Machine Perception Czech Institute for Informatics, Robotics, and Cybernetics (CIIRC) Czech Technical University
Serial Manipulator Statics Robotics Serial Manipulator Statics Vladimír Smutný Center for Machine Perception Czech Institute for Informatics, Robotics, and Cybernetics (CIIRC) Czech Technical University
Simple noninterference mechanism between the pitch and yaw axes for a wrist mechanism to be employed in robot assisted laparoscopic surgery
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40648-019-0129-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Simple noninterference mechanism between the pitch and yaw axes for a wrist mechanism to be employed in robot assisted laparoscopic
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40648-019-0129-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Simple noninterference mechanism between the pitch and yaw axes for a wrist mechanism to be employed in robot assisted laparoscopic
Cobots
 Cobots http://cobot.com Michael Peshkin J. Edward Colgate Witaya Wannasuphoprasit ( Wit ) Intelligent Assist Devices IADs use computer control of motion to create functionality greater than that of conventional
Cobots http://cobot.com Michael Peshkin J. Edward Colgate Witaya Wannasuphoprasit ( Wit ) Intelligent Assist Devices IADs use computer control of motion to create functionality greater than that of conventional
FORCE CONTROL OF LINK SYSTEMS USING THE PARALLEL SOLUTION SCHEME
 FORCE CONTROL OF LIN SYSTEMS USING THE PARALLEL SOLUTION SCHEME Daigoro Isobe Graduate School of Systems and Information Engineering, University of Tsukuba 1-1-1 Tennodai Tsukuba-shi, Ibaraki 35-8573,
FORCE CONTROL OF LIN SYSTEMS USING THE PARALLEL SOLUTION SCHEME Daigoro Isobe Graduate School of Systems and Information Engineering, University of Tsukuba 1-1-1 Tennodai Tsukuba-shi, Ibaraki 35-8573,
Surgical Assist Robot for the Active Navigation in the Intraoperative MRI: Hardware Design Issues
 Surgical Assist Robot for the Active Navigation in the Intraoperative MRI: Hardware Design Issues K. Chinzei N. Hata F.A. Jolesz R. Kikinis Biomechanics Div. Surgical Planning Lab. Mechanical Engineering
Surgical Assist Robot for the Active Navigation in the Intraoperative MRI: Hardware Design Issues K. Chinzei N. Hata F.A. Jolesz R. Kikinis Biomechanics Div. Surgical Planning Lab. Mechanical Engineering
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO. Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences
 Page 1 UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam in INF3480 Introduction to Robotics Day of exam: May 31 st 2010 Exam hours: 3 hours This examination paper consists of 5 page(s).
Page 1 UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam in INF3480 Introduction to Robotics Day of exam: May 31 st 2010 Exam hours: 3 hours This examination paper consists of 5 page(s).
Biomedical Paper A Six-Degree-of-Freedom Passive Arm with Dynamic Constraints (PADyC) for Cardiac Surgery Application: Preliminary Experiments
 Computer Aided Surgery 6:340 351 (2001) Biomedical Paper A Six-Degree-of-Freedom Passive Arm with Dynamic Constraints (PADyC) for Cardiac Surgery Application: Preliminary Experiments Olivier Schneider,
Computer Aided Surgery 6:340 351 (2001) Biomedical Paper A Six-Degree-of-Freedom Passive Arm with Dynamic Constraints (PADyC) for Cardiac Surgery Application: Preliminary Experiments Olivier Schneider,
Kinematics. Kinematics analyzes the geometry of a manipulator, robot or machine motion. The essential concept is a position.
 Kinematics Kinematics analyzes the geometry of a manipulator, robot or machine motion. The essential concept is a position. 1/31 Statics deals with the forces and moments which are aplied on the mechanism
Kinematics Kinematics analyzes the geometry of a manipulator, robot or machine motion. The essential concept is a position. 1/31 Statics deals with the forces and moments which are aplied on the mechanism
Inverse Kinematics Software Design and Trajectory Control Programming of SCARA Manipulator robot
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 11, Number 11 (2018), pp. 1759-1779 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Inverse Kinematics
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 11, Number 11 (2018), pp. 1759-1779 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Inverse Kinematics
EEE 187: Robotics Summary 2
 1 EEE 187: Robotics Summary 2 09/05/2017 Robotic system components A robotic system has three major components: Actuators: the muscles of the robot Sensors: provide information about the environment and
1 EEE 187: Robotics Summary 2 09/05/2017 Robotic system components A robotic system has three major components: Actuators: the muscles of the robot Sensors: provide information about the environment and
Hand. Desk 4. Panda research 5. Franka Control Interface (FCI) Robot Model Library. ROS support. 1 technical data is subject to change
 TECHNICAL DATA 1, 2 Arm degrees of freedom 7 DOF payload 3 kg sensitivity joint torque sensors in all 7 axes maximum reach 855 mm joint position limits A1: -170/170, A2: -105/105, [ ] A3: -170/170, A4:
TECHNICAL DATA 1, 2 Arm degrees of freedom 7 DOF payload 3 kg sensitivity joint torque sensors in all 7 axes maximum reach 855 mm joint position limits A1: -170/170, A2: -105/105, [ ] A3: -170/170, A4:
Unit 2: Locomotion Kinematics of Wheeled Robots: Part 3
 Unit 2: Locomotion Kinematics of Wheeled Robots: Part 3 Computer Science 4766/6778 Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland January 28, 2014 COMP 4766/6778 (MUN) Kinematics of
Unit 2: Locomotion Kinematics of Wheeled Robots: Part 3 Computer Science 4766/6778 Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland January 28, 2014 COMP 4766/6778 (MUN) Kinematics of
Dual-loop Control for Backlash Correction in Trajectory-tracking of a Planar 3-RRR Manipulator
 Dual-loop Control for Backlash Correction in Trajectory-tracking of a Planar -RRR Manipulator Abhishek Agarwal, Chaman Nasa, Sandipan Bandyopadhyay Abstract The presence of backlash in the gearheads is
Dual-loop Control for Backlash Correction in Trajectory-tracking of a Planar -RRR Manipulator Abhishek Agarwal, Chaman Nasa, Sandipan Bandyopadhyay Abstract The presence of backlash in the gearheads is
Incorporating Target Registration Error Into Robotic Bone Milling
 Incorporating Target Registration Error Into Robotic Bone Milling Michael A. Siebold *a, Neal P. Dillon b, Robert J. Webster III a,b, and J. Michael Fitzpatrick a a Electrical Engineering and Computer
Incorporating Target Registration Error Into Robotic Bone Milling Michael A. Siebold *a, Neal P. Dillon b, Robert J. Webster III a,b, and J. Michael Fitzpatrick a a Electrical Engineering and Computer
Task Control with Remote Center of Motion Constraint for Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery
 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) Karlsruhe, Germany, May 6-10, 2013 Task Control with Remote Center of Motion Constraint for Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery Nastaran
2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) Karlsruhe, Germany, May 6-10, 2013 Task Control with Remote Center of Motion Constraint for Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery Nastaran
Real-time Tissue Tracking with B-Mode Ultrasound Using Speckle and Visual Servoing
 Real-time Tissue Tracking with B-Mode Ultrasound Using Speckle and Visual Servoing Alexandre Krupa, Gabor Fichtinger, and Gregory D. Hager IRISA - INRIA Rennes, France, alexandre.krupa@irisa.fr Engineering
Real-time Tissue Tracking with B-Mode Ultrasound Using Speckle and Visual Servoing Alexandre Krupa, Gabor Fichtinger, and Gregory D. Hager IRISA - INRIA Rennes, France, alexandre.krupa@irisa.fr Engineering
Design of a Three-Axis Rotary Platform
 Design of a Three-Axis Rotary Platform William Mendez, Yuniesky Rodriguez, Lee Brady, Sabri Tosunoglu Mechanics and Materials Engineering, Florida International University 10555 W Flagler Street, Miami,
Design of a Three-Axis Rotary Platform William Mendez, Yuniesky Rodriguez, Lee Brady, Sabri Tosunoglu Mechanics and Materials Engineering, Florida International University 10555 W Flagler Street, Miami,
Virtual Remote Center of Motion Control for Needle Placement Robots
 Virtual Remote Center of Motion Control for Needle Placement Robots Emad M. Boctor, Robert J. Webster, Herve Mathieu, Allison M. Okamura, and Gabor Fichtinger Engineering Research Center for Computer Integrated
Virtual Remote Center of Motion Control for Needle Placement Robots Emad M. Boctor, Robert J. Webster, Herve Mathieu, Allison M. Okamura, and Gabor Fichtinger Engineering Research Center for Computer Integrated
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introduction This dissertation will describe the mathematical modeling and development of an innovative, three degree-of-freedom robotic manipulator. The new device, which has been named the
Chapter 1: Introduction This dissertation will describe the mathematical modeling and development of an innovative, three degree-of-freedom robotic manipulator. The new device, which has been named the
Robotics 2 Information
 Robotics 2 Information Prof. Alessandro De Luca Robotics 2! 2017/18! Second semester! Monday, February 26 Wednesday, May 30, 2018! Courses of study (code)! Master in Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
Robotics 2 Information Prof. Alessandro De Luca Robotics 2! 2017/18! Second semester! Monday, February 26 Wednesday, May 30, 2018! Courses of study (code)! Master in Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
Robot programming by demonstration
 Robot programming by demonstration Denasi, A.; Verhaar, B.T.; Kostic, D.; Bruijnen, D.J.H.; Nijmeijer, H.; Warmerdam, T.P.H. Published in: Proceedings of the 1th Philips Conference on Applications of Control
Robot programming by demonstration Denasi, A.; Verhaar, B.T.; Kostic, D.; Bruijnen, D.J.H.; Nijmeijer, H.; Warmerdam, T.P.H. Published in: Proceedings of the 1th Philips Conference on Applications of Control
Weakly supervised segmentation and
 Weakly supervised segmentation and Firma convenzione Politecnico recognition di Milano of surgical e Veneranda gestures Fabbrica del Duomo di Milano Tutor: Elena De Momi, PhD Co-tutor: Danail Stoyanov,
Weakly supervised segmentation and Firma convenzione Politecnico recognition di Milano of surgical e Veneranda gestures Fabbrica del Duomo di Milano Tutor: Elena De Momi, PhD Co-tutor: Danail Stoyanov,
drilling carriage for stereotactic neurosurgery
 Authors: Tzung-Cheng Tsai, Yeh-Liang Hsu (2004-06-29); recommended: Yeh-Liang Hsu (2004-06-29). Note: This paper is presented at IEEE SMC 2004, International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics,
Authors: Tzung-Cheng Tsai, Yeh-Liang Hsu (2004-06-29); recommended: Yeh-Liang Hsu (2004-06-29). Note: This paper is presented at IEEE SMC 2004, International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics,
Flexible Modeling and Simulation Architecture for Haptic Control of Maritime Cranes and Robotic Arms
 Flexible Modeling and Simulation Architecture for Haptic Control of Maritime Cranes and Robotic Arms F. Sanfilippo, H. P. Hildre, V. Æsøy and H.X. Zhang Department of Maritime Technology and Operation
Flexible Modeling and Simulation Architecture for Haptic Control of Maritime Cranes and Robotic Arms F. Sanfilippo, H. P. Hildre, V. Æsøy and H.X. Zhang Department of Maritime Technology and Operation
ALL SINGULARITIES OF THE 9-DOF DLR MEDICAL ROBOT SETUP FOR MINIMALLY INVASIVE APPLICATIONS
 ALL SINGULARITIES OF THE 9-DOF DLR MEDICAL ROBOT SETUP FOR MINIMALLY INVASIVE APPLICATIONS Rainer Konietschke, Gerd Hirzinger German Aerospace Center, Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics P.O. Box 6,
ALL SINGULARITIES OF THE 9-DOF DLR MEDICAL ROBOT SETUP FOR MINIMALLY INVASIVE APPLICATIONS Rainer Konietschke, Gerd Hirzinger German Aerospace Center, Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics P.O. Box 6,
Parallel Robots. Mechanics and Control H AMID D. TAG HI RAD. CRC Press. Taylor & Francis Group. Taylor & Francis Croup, Boca Raton London NewYoric
 Parallel Robots Mechanics and Control H AMID D TAG HI RAD CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London NewYoric CRC Press Is an Imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informs business Contents
Parallel Robots Mechanics and Control H AMID D TAG HI RAD CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London NewYoric CRC Press Is an Imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informs business Contents
Development of an optomechanical measurement system for dynamic stability analysis
 Development of an optomechanical measurement system for dynamic stability analysis Simone Pasinetti Dept. of Information Engineering (DII) University of Brescia Brescia, Italy simone.pasinetti@unibs.it
Development of an optomechanical measurement system for dynamic stability analysis Simone Pasinetti Dept. of Information Engineering (DII) University of Brescia Brescia, Italy simone.pasinetti@unibs.it
Increasing the accuracy with a rich sensor system for robotic laser osteotomy
 Increasing the accuracy with a rich sensor system for robotic laser osteotomy Holger Mönnich moennich@ira.uka.de Daniel Stein dstein@ira.uka.de Jörg Raczkowsky rkowsky@ira.uka.de Heinz Wörn woern@ira.uka.de
Increasing the accuracy with a rich sensor system for robotic laser osteotomy Holger Mönnich moennich@ira.uka.de Daniel Stein dstein@ira.uka.de Jörg Raczkowsky rkowsky@ira.uka.de Heinz Wörn woern@ira.uka.de
MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control. Lecture 1: Introduction
 MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 1: Introduction Reading: SHV Chapter 1 Robotics and Automation Handbook, Chapter 1 Assigned readings from several articles. Cleveland State University
MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 1: Introduction Reading: SHV Chapter 1 Robotics and Automation Handbook, Chapter 1 Assigned readings from several articles. Cleveland State University
Motion Control of a Master-Slave Minimally Invasive Surgical Robot Based on the Hand-Eye-Coordination
 Motion Control of a Master-Slave Minimally Invasive Surgical Robot Based on the Hand-Eye-Coordination Aolin Tang, Qixin Cao, Hongbing Tan, Masakatsu G. Fujie 2, Tiewen Pan 3, State Key Lab of Mechanical
Motion Control of a Master-Slave Minimally Invasive Surgical Robot Based on the Hand-Eye-Coordination Aolin Tang, Qixin Cao, Hongbing Tan, Masakatsu G. Fujie 2, Tiewen Pan 3, State Key Lab of Mechanical
We recommend you cite the published version. The publisher s URL is:
 Dagnino, G., Georgilas, I., Tarasolli, P., Atkins, R. and Dogramadzi, S. (2016) Vision-based real-time position control of a semi-automated system for robot-assisted joint fracture surgery. International
Dagnino, G., Georgilas, I., Tarasolli, P., Atkins, R. and Dogramadzi, S. (2016) Vision-based real-time position control of a semi-automated system for robot-assisted joint fracture surgery. International
Lecture VI: Constraints and Controllers
 Lecture VI: Constraints and Controllers Motion Constraints In practice, no rigid body is free to move around on its own. Movement is constrained: wheels on a chair human body parts trigger of a gun opening
Lecture VI: Constraints and Controllers Motion Constraints In practice, no rigid body is free to move around on its own. Movement is constrained: wheels on a chair human body parts trigger of a gun opening
Automatic Control Industrial robotics
 Automatic Control Industrial robotics Prof. Luca Bascetta (luca.bascetta@polimi.it) Politecnico di Milano Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Prof. Luca Bascetta Industrial robots
Automatic Control Industrial robotics Prof. Luca Bascetta (luca.bascetta@polimi.it) Politecnico di Milano Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Prof. Luca Bascetta Industrial robots
ACE Project Report. December 10, Reid Simmons, Sanjiv Singh Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University
 ACE Project Report December 10, 2007 Reid Simmons, Sanjiv Singh Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University 1. Introduction This report covers the period from September 20, 2007 through December 10,
ACE Project Report December 10, 2007 Reid Simmons, Sanjiv Singh Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University 1. Introduction This report covers the period from September 20, 2007 through December 10,
Kinematic design considerations for minimally invasive surgical robots: an overview
 THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL ROBOTICS AND COMPUTER ASSISTED SURGERY Int J Med Robotics Comput Assist Surg 2012; 8: 127 145. Published online 9 January 2012 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).453
THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL ROBOTICS AND COMPUTER ASSISTED SURGERY Int J Med Robotics Comput Assist Surg 2012; 8: 127 145. Published online 9 January 2012 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).453
Dipartimento di Elettronica Informazione e Bioingegneria Robotics
 Dipartimento di Elettronica Informazione e Bioingegneria Robotics properties and performance measures @ 25 Redundancy first definition McKerrow When a manipulator can reach a specified position with more
Dipartimento di Elettronica Informazione e Bioingegneria Robotics properties and performance measures @ 25 Redundancy first definition McKerrow When a manipulator can reach a specified position with more
Spherical wrist dimensional synthesis adapted for tool-guidance medical robots
 Spherical wrist dimensional synthesis adapted for tool-guidance medical robots T. ESSOMBA a-b, L. NOUAILLE a, M.A. LARIBI b, C.A. NELSON c, S. ZEGHLOUL b, G. POISSON a a. University of Orléans, PRISME
Spherical wrist dimensional synthesis adapted for tool-guidance medical robots T. ESSOMBA a-b, L. NOUAILLE a, M.A. LARIBI b, C.A. NELSON c, S. ZEGHLOUL b, G. POISSON a a. University of Orléans, PRISME
THÈSE / UNIVERSITÉ DE RENNES 1 sous le sceau de l Université Européenne de Bretagne
 N o d ordre : 48 ANNÉE 21 THÈSE / UNIVERSITÉ DE RENNES 1 sous le sceau de l Université Européenne de Bretagne pour le grade de DOCTEUR DE L UNIVERSITÉ DE RENNES 1 Mention : Traitement du Signal Ecole doctorale
N o d ordre : 48 ANNÉE 21 THÈSE / UNIVERSITÉ DE RENNES 1 sous le sceau de l Université Européenne de Bretagne pour le grade de DOCTEUR DE L UNIVERSITÉ DE RENNES 1 Mention : Traitement du Signal Ecole doctorale
Real-time FEM based control of soft surgical robots
 Real-time FEM based control of soft surgical robots Frederick Largilliere, Eulalie Coevoet, Laurent Grisoni, Christian Duriez To cite this version: Frederick Largilliere, Eulalie Coevoet, Laurent Grisoni,
Real-time FEM based control of soft surgical robots Frederick Largilliere, Eulalie Coevoet, Laurent Grisoni, Christian Duriez To cite this version: Frederick Largilliere, Eulalie Coevoet, Laurent Grisoni,
A Novel Remote Center-of Motion Parallel manipulator for Minimally Invasive Celiac Surgery
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volume 3 Issue 8 ǁ August. 2015 ǁ PP.15-19 A Novel Remote Center-of Motion Parallel
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volume 3 Issue 8 ǁ August. 2015 ǁ PP.15-19 A Novel Remote Center-of Motion Parallel
1 Trajectories. Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733. Figure 1: Robot control system.
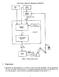 Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
Miniaturized Force-Indentation Depth Sensor for Tissue Abnormality Identification during Laparoscopic Surgery
 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Anchorage Convention District May 3-8, 2010, Anchorage, Alaska, USA Miniaturized Force-Indentation Depth Sensor for Tissue Abnormality Identification
2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Anchorage Convention District May 3-8, 2010, Anchorage, Alaska, USA Miniaturized Force-Indentation Depth Sensor for Tissue Abnormality Identification
Model-Aided Controller Evaluation for a Surgical Assistance Robot to Track Patient Movements in Real Time
 Model-Aided Controller Evaluation for a Surgical Assistance Robot to Track Patient Movements in Real Time H.-C. Schneider J. Wahrburg H. Roth Center for Sensorsystems, University of Siegen, Germany (e-mail:
Model-Aided Controller Evaluation for a Surgical Assistance Robot to Track Patient Movements in Real Time H.-C. Schneider J. Wahrburg H. Roth Center for Sensorsystems, University of Siegen, Germany (e-mail:
Dynamic State Estimation using Quadratic Programming
 214 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 214) September 14-18, 214, Chicago, IL, USA Dynamic State Estimation using Quadratic Programming X Xinjilefu, Siyuan Feng and
214 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 214) September 14-18, 214, Chicago, IL, USA Dynamic State Estimation using Quadratic Programming X Xinjilefu, Siyuan Feng and
CMPUT 412 Motion Control Wheeled robots. Csaba Szepesvári University of Alberta
 CMPUT 412 Motion Control Wheeled robots Csaba Szepesvári University of Alberta 1 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements Kinematic/dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel
CMPUT 412 Motion Control Wheeled robots Csaba Szepesvári University of Alberta 1 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements Kinematic/dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel
Spatial R-C-C-R Mechanism for a Single DOF Gripper
 NaCoMM-2009-ASMRL28 Spatial R-C-C-R Mechanism for a Single DOF Gripper Rajeev Lochana C.G * Mechanical Engineering Department Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, New Delhi, India * Email: rajeev@ar-cad.com
NaCoMM-2009-ASMRL28 Spatial R-C-C-R Mechanism for a Single DOF Gripper Rajeev Lochana C.G * Mechanical Engineering Department Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, New Delhi, India * Email: rajeev@ar-cad.com
FABRICATION OF A 5 D.O.F ROBOT ARM CONTROLLED BY HAPTIC TECHNOLOGY
 FABRICATION OF A 5 D.O.F ROBOT ARM CONTROLLED BY HAPTIC TECHNOLOGY 1 NITHIN RAJAN, 2 V.MANOJ KUMAR 1 Graduate Student, 2 Ass. Professor SRM University E-mail: Nitz.719@gmail.com, vmanojkumar19@gmail Abstract-
FABRICATION OF A 5 D.O.F ROBOT ARM CONTROLLED BY HAPTIC TECHNOLOGY 1 NITHIN RAJAN, 2 V.MANOJ KUMAR 1 Graduate Student, 2 Ass. Professor SRM University E-mail: Nitz.719@gmail.com, vmanojkumar19@gmail Abstract-
THE DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF FLEXIBILITY IN MOBILE ROBOTIC MANIPULATOR SYSTEMS
 Proc. VIII World Congress on the Theroy of Machines and Mechanisms, Prague, Czechoslavakia, July 1991- Revised 1/1/9 THE DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF FLEXIBILITY IN MOBILE ROBOTIC MANIPULATOR SYSTEMS S. Dubowsky
Proc. VIII World Congress on the Theroy of Machines and Mechanisms, Prague, Czechoslavakia, July 1991- Revised 1/1/9 THE DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF FLEXIBILITY IN MOBILE ROBOTIC MANIPULATOR SYSTEMS S. Dubowsky
Table of Contents. Chapter 1. Modeling and Identification of Serial Robots... 1 Wisama KHALIL and Etienne DOMBRE
 Chapter 1. Modeling and Identification of Serial Robots.... 1 Wisama KHALIL and Etienne DOMBRE 1.1. Introduction... 1 1.2. Geometric modeling... 2 1.2.1. Geometric description... 2 1.2.2. Direct geometric
Chapter 1. Modeling and Identification of Serial Robots.... 1 Wisama KHALIL and Etienne DOMBRE 1.1. Introduction... 1 1.2. Geometric modeling... 2 1.2.1. Geometric description... 2 1.2.2. Direct geometric
DELTA TAU Data Systems, Inc.
 DELTA TAU Data Systems, Inc. Last revision: 12/5/01 Why PMAC Controllers Are Easy To Use Delta Tau s PMAC and Turbo PMAC families of controllers justly have the reputation as being the most powerful and
DELTA TAU Data Systems, Inc. Last revision: 12/5/01 Why PMAC Controllers Are Easy To Use Delta Tau s PMAC and Turbo PMAC families of controllers justly have the reputation as being the most powerful and
Genmark Automation, Inc. - Technology Highlights
 Genmark Automation, Inc. - Technology Highlights May 6, 2011 Genmark Automation has been a leading designer and manufacturer of highperformance material handling and integrated systems, by introducing
Genmark Automation, Inc. - Technology Highlights May 6, 2011 Genmark Automation has been a leading designer and manufacturer of highperformance material handling and integrated systems, by introducing
Spatial Motion Constraints for Robot Assisted Suturing using Virtual Fixtures
 Accepted in Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Palm Springs, USA, October 26-29, 2005 Spatial Motion Constraints for Robot Assisted Suturing using Virtual Fixtures Ankur Kapoor,
Accepted in Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Palm Springs, USA, October 26-29, 2005 Spatial Motion Constraints for Robot Assisted Suturing using Virtual Fixtures Ankur Kapoor,
Design of a bilateral position/force master slave teleoperation system with nonidentical robots
 Design of a bilateral position/force master slave teleoperation system with nonidentical robots P.W.M. van Zutven DCT 28.8 Supervisors CINVESTAV (Mexico D.F.): Dr. A. Rodriguez Angeles Dr. C. A. Cruz Villar
Design of a bilateral position/force master slave teleoperation system with nonidentical robots P.W.M. van Zutven DCT 28.8 Supervisors CINVESTAV (Mexico D.F.): Dr. A. Rodriguez Angeles Dr. C. A. Cruz Villar
Modeling and kinematics simulation of freestyle skiing robot
 Acta Technica 62 No. 3A/2017, 321 334 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Modeling and kinematics simulation of freestyle skiing robot Xiaohua Wu 1,3, Jian Yi 2 Abstract. Freestyle skiing robot
Acta Technica 62 No. 3A/2017, 321 334 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Modeling and kinematics simulation of freestyle skiing robot Xiaohua Wu 1,3, Jian Yi 2 Abstract. Freestyle skiing robot
