Physiological Motion Compensation in Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery Part I
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Hoover
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physiological Motion Compensation in Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery Part I Tobias Ortmaier Laboratoire de Robotique de Paris 18, route du Panorama - BP Fontenay-aux-Roses Cedex France Tobias.Ortmaier@alumni.tum.de
2 Overview Introduction - Minimally invasive surgery - Minimally invasive robotic surgery Motion compensation in beating heart surgery - Manual manipulation limitations - Motion measurement with artificial markers - Motion measurement with natural landmarks Predicting the heart motion - Local prediction - Global prediction - Sensor fusion Conclusion and Outlook 2
3 What is Minimally Invasive Surgery? Surgeon works with long instruments through small incisions and uses laparoscope for visual feedback. 3
4 What is Minimally Invasive Surgery? Schematic overview - pecularities Reverse hand motion Scaling of velocity Loss of degrees of freedom 4
5 What is Minimally Invasive Surgery? Properties Advantages - Less trauma - Shorter hospital stay - Cosmetical advantages Disadvantages - Reduced sight - Trocar kinematics - Reduced haptic feedback - Long training period 5
6 Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery Telepresence System Instruments are not manipulated directly by the surgeon but by specialized robotic arms 6
7 Existing MIRS Systems No haptic feedback No full manipulability inside patient Scaling of motion Optical magnification Modular system Computer Motion Inc. - Zeus 7
8 Existing MIRS Systems No haptic feedback Full manipulability inside patient Scaling of motion Optical magnification Monolithic system Intuitive Surgery Inc. - davinci 8
9 Existing MIRS Systems 7 Degrees of Freedom Small Size Robot University of Tokyo Small 7 degrees of freedom surgical robot Sterilizable instruments Passive system to position the surgical robot Prof. Nakamura, Univ. Tokyo 9
10 Overview Introduction - Minimally invasive surgery - Minimally invasive robotic surgery Motion compensation in beating heart surgery - Manual manipulation limitations - Motion measurement with artificial markers - Motion measurement with natural landmarks Predicting the heart motion - Local prediction - Global prediction - Sensor fusion Conclusion and Outlook 10
11 Fields of Application Radiosurgery - Tumor motion is measured with stereo X-ray cameras - Companies: BrainLab (Novalis) and Cyberknife Liver biopsy - Needles are guided towards the moving lesions - Carnegie Mellon University (Riviere et al) and University of Tokyo (Hong et al) Heart valve repair - Moving valve is automatically grasped - GABIE project in the French ROBEA program Bypass grafts - Motion of beating heart is compensated - German Aerospace Center, LSIIT Strasbourg, Univ. of Tokyo 11
12 Fitt s Law Describes the difficulty to touch a (non-moving) goal Index ID [bit] for movement difficulty: ID = log 2 (2 A / W) with A: amplitude of intended movement W: target width Time needed to complete task: T m = k m + c m ID with k m : constant, being approx s c m : measure of information handling capacity, being approx. 0.1 s / bit With increasing distance the necessary time increases 12
13 Modified Fitt s Law Modification of Fitt s law for moving targets, proposed by Jagacinski et al Time needed to complete task: with T m = c + d A + e (V + 1) [(1 / W ) - 1] c, d, e: constant coefficients A: amplitude of intended movement W: target width V: target velocity With increasing velocity the necessary time increases 13
14 Manual Control and Tracking Studies of manual tracking performance indicate a bandwidth estimation of about 1 Hz. Therefore, a heart rate of 1 Hz (i.e. 60 beats / min) lies at natural limit. Manual position accuracy is limited to 0.1 mm to 0.2 mm. Wait and see or locking strategy not applicable due to irregular motion. Manual tracking experiments were carried out at Heartcenter Leipzig to further investigate influence of motion. Falk, MD, PhD., Leipzig 14
15 Manual Control and Tracking Experimental set-up Falk, MD, PhD., Leipzig 15
16 Manual Control and Tracking Time to touch two targets in a horizontal line Distances A1 < A2 < A3 Frequencies 35 and 50 / min Amplitudes: st = stabilized nst = nonstabilized Experimental Results Error rates for complex pattern touch task With higher frequency and larger amplitude error rate increases Falk, MD, PhD., Leipzig 16
17 Minimally Invasive Beating Heart Surgery Gentle form of surgery No heart-lung machine Heart Motion Mechanical stabilizer Remaining motion (motion 1.5 mm 2.0 mm; frequencies up to 2 Hz) Long operation duration Additional training does not improve quality of surgery Solution: Motion compensation in minimally invasive beating heart surgery 17
18 Minimally Invasive Beating Heart Surgery 18
19 Overview of Research in Motion Compensation in Beating Heart Surgery Motion compensation with - artificial landmarks (i.e. markers), Hz highspeed camera, - and adaptive filtering. - Performed at LSIIT Strasbourg, by M. de Mathelin - Detailed in next presentation Virtual stillness - Performed at University of Tokyo, by Y. Nakamura - Detailed in this presentation Motion compensation with natural landmarks - German Aerospace Centre - Detailed in this presentation 19
20 Virtual Stillness Nakamura, Univ. Tokyo Experimental setup - Overview Artificial markers to track heart motion High speed camera (955 frames per second) Visual stabilization Small 7 degrees of freedom surgical robot Sterilizable instruments Passive system to position the surgical robot Motion compensation 20
21 Visual Stabilization Stabilization of point of interest by cutting out, moving, and zooming area of interest Prof. Nakamura, Univ. Tokyo 21
22 Motion Compensation In vivo experiment on a beating pig heart Prof. Nakamura, Univ. Tokyo 22
23 Motion Estimation with Natural Landmarks Properties - Limited space - Strongly nonlinear motion of tissue - No motion model available Natural landmarks - Prominent image features - Intensity based approach - Local motion model - Image preprocessing is necessary (illumination and specularities) 23
24 Motion Tracking Scheme Heart Motion 24
25 Specular Reflections - Detection Arise on heart surface from directed light source Irregular occurrence disrupts tracking Distinctive intensity allows Detection by thresholding Fast and robust approach 25
26 Specular Reflections - Detection Thresholding I = I offset TH + Dilation twice S = I(image) 26
27 27 Specular Reflections - Structure Detection Structure Tensor ( ) = = 2 2 ) ( ) ( * * x f y f x f y f x f x f g f f g J σ σ σ σ σ σ ρ σ σ ρ ρ with Gradient of Gaussian smoothed image Tensor product Integration scale Noise scale f σ ρ σ
28 Specular Reflections - Reconstruction Algorithm Calculate eigenvalues of structure matrix : J λ1 λ2 Eigenvector corresponding to smaller eigenvalue ( λ 2 ) gives structure orientation Determine boundary of specularity in structure direction Linear interpolation boundary points Final Gaussian smoothing ρ 28
29 Specular Reflections - Reconstruction Algorithm Principle Example 29
30 Tracking Results Original sequence with specularities Reduced affine motion model with sum of squared (SSD) differences as similarity measure applied 30
31 Tracking Results Structure tensor based reconstruction Reduced affine motion model with sum of squared (SSD) differences as similarity measure applied 31
32 Tracking Results Landmark trajectories 32
33 Tracking Results Amplitude spectrum Dominant peaks Respiration frequency (f 1 =14.5 1/min) Heart rate (f 2 =70.9 1/min) 33
34 Overview Introduction - Minimally invasive surgery - Minimally invasive robotic surgery Motion compensation in beating heart surgery - Manual manipulation limitations - Motion measurement with artificial markers - Motion measurement with natural landmarks Predicting the heart motion - Local prediction - Global prediction - Sensor fusion Conclusion and Outlook 34
35 Motivation What happens in case of occlusions? Tracking fails! Solution: Motion prediction 35
36 Motion Prediction Scheme Prediction of heart motion based on Quasi-periodicity of trajectories Additional signals (ECG and RPS) Model for heart motion difficult Patient specific Dependent on mechanical stabilizer position Unknown model parameters Solution: Model free prediction scheme 36
37 Local Prediction Exploitation of quasi-periodicity of trajectories Prerequisites Smooth trajectories No transient inner states 37
38 Motion Prediction Scheme Takens Theorem: Taking a sufficiently long vector built of past values of a time series enables the reconstruction of the underlying structure of the system dynamics which produced the sequence. Consequence: Two ways to describe a dynamic system: explicit model appropriate embedding vectors 38
39 Local Prediction + Dynamic positioning of tracking search area + Compensation of outliers - Only short disturbances 39
40 Five-Step Prediction + More step prediction is possible - Prediction accuracy deteriorates 40
41 One-step prediction Local Prediction - Summary Application of Takens Theorem Detection and compensation of outliers Positioning of search window More-step prediction With increasing prediction interval prediction accuracy deteriorates 41
42 Global Prediction Not all LMs are simultaneously occluded Use visible LMs for prediction of occluded LMs Prerequisite: functional relationship between trajectories Result: Global prediction scheme 42
43 Global Prediction Simultaneous exploitation of several landmarks Prerequisite: functional relationship between trajectories 43
44 Global Prediction Position of landmarks 44
45 Global Prediction + Longer disturbances + More robust than local scheme - Estimation depends on visual information only 45
46 Global Prediction - Summary Application of Takens Theorem Robust long-term prediction Combination of local and global prediction scheme possible Compensation for long occlusions What happens if vision fails? 46
47 ECG and RPS Based Prediction Correlation of signals ECG, RPS, t x, t y Correlation 47
48 Algorithm and Landmarks Similar to global prediction ECG and RPS as additional LM 48
49 Global Prediction - Results Predicted trajectory Prediction error 49
50 Overview Introduction - Minimally invasive surgery - Minimally invasive robotic surgery Motion compensation in beating heart surgery - Manual manipulation limitations - Motion measurement with artificial markers - Motion measurement with natural landmarks Predicting the heart motion - Local prediction - Global prediction - Sensor fusion Conclusion and Outlook 50
51 Conclusion Minimally invasive surgery offers significant benefits for the patient Physiological organ motion deteriorates surgeon s performance In MIRS systems organ motion can be compensated Then, surgeon works on a virtually stabilized organ Robust organ motion measurement in a clinical environment is crucial Overall system reliability is increased by - Motion prediction - Additional sensor signals 51
52 Outlook System Overview I 52
53 Outlook System Overview II 53
Robot Control for Medical Applications and Hair Transplantation
 Dr. John Tenney Director of Research Restoration Robotics, Inc. Robot Control for Medical Applications and Hair Transplantation Presented to the IEEE Control Systems Society, Santa Clara Valley 18 November
Dr. John Tenney Director of Research Restoration Robotics, Inc. Robot Control for Medical Applications and Hair Transplantation Presented to the IEEE Control Systems Society, Santa Clara Valley 18 November
Prof. Fanny Ficuciello Robotics for Bioengineering Visual Servoing
 Visual servoing vision allows a robotic system to obtain geometrical and qualitative information on the surrounding environment high level control motion planning (look-and-move visual grasping) low level
Visual servoing vision allows a robotic system to obtain geometrical and qualitative information on the surrounding environment high level control motion planning (look-and-move visual grasping) low level
Automatic Tracking of an Organ Section with an Ultrasound Probe: Compensation of Respiratory Motion
 Automatic Tracking of an Organ Section with an Ultrasound Probe: Compensation of Respiratory Motion Caroline Nadeau 1, Alexandre Krupa 2, and Jacques Gangloff 3 1 Université de Rennes I, IRISA, 342 Rennes,
Automatic Tracking of an Organ Section with an Ultrasound Probe: Compensation of Respiratory Motion Caroline Nadeau 1, Alexandre Krupa 2, and Jacques Gangloff 3 1 Université de Rennes I, IRISA, 342 Rennes,
Edge and corner detection
 Edge and corner detection Prof. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking Goals Where is the information in an image? How is an object characterized? How can I find measurements
Edge and corner detection Prof. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking Goals Where is the information in an image? How is an object characterized? How can I find measurements
Computer Vision 2. SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung. Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier
 Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Tightly-Integrated Visual and Inertial Navigation for Pinpoint Landing on Rugged Terrains
 Tightly-Integrated Visual and Inertial Navigation for Pinpoint Landing on Rugged Terrains PhD student: Jeff DELAUNE ONERA Director: Guy LE BESNERAIS ONERA Advisors: Jean-Loup FARGES Clément BOURDARIAS
Tightly-Integrated Visual and Inertial Navigation for Pinpoint Landing on Rugged Terrains PhD student: Jeff DELAUNE ONERA Director: Guy LE BESNERAIS ONERA Advisors: Jean-Loup FARGES Clément BOURDARIAS
Volumetric Deformable Models for Simulation of Laparoscopic Surgery
 Volumetric Deformable Models for Simulation of Laparoscopic Surgery S. Cotin y, H. Delingette y, J.M. Clément z V. Tassetti z, J. Marescaux z, N. Ayache y y INRIA, Epidaure Project 2004, route des Lucioles,
Volumetric Deformable Models for Simulation of Laparoscopic Surgery S. Cotin y, H. Delingette y, J.M. Clément z V. Tassetti z, J. Marescaux z, N. Ayache y y INRIA, Epidaure Project 2004, route des Lucioles,
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 14 130307 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Stereo Dense Motion Estimation Translational
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 14 130307 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Stereo Dense Motion Estimation Translational
Range Imaging Through Triangulation. Range Imaging Through Triangulation. Range Imaging Through Triangulation. Range Imaging Through Triangulation
 Obviously, this is a very slow process and not suitable for dynamic scenes. To speed things up, we can use a laser that projects a vertical line of light onto the scene. This laser rotates around its vertical
Obviously, this is a very slow process and not suitable for dynamic scenes. To speed things up, we can use a laser that projects a vertical line of light onto the scene. This laser rotates around its vertical
BSB663 Image Processing Pinar Duygulu. Slides are adapted from Selim Aksoy
 BSB663 Image Processing Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Selim Aksoy Image matching Image matching is a fundamental aspect of many problems in computer vision. Object or scene recognition Solving
BSB663 Image Processing Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Selim Aksoy Image matching Image matching is a fundamental aspect of many problems in computer vision. Object or scene recognition Solving
Sensor Modalities. Sensor modality: Different modalities:
 Sensor Modalities Sensor modality: Sensors which measure same form of energy and process it in similar ways Modality refers to the raw input used by the sensors Different modalities: Sound Pressure Temperature
Sensor Modalities Sensor modality: Sensors which measure same form of energy and process it in similar ways Modality refers to the raw input used by the sensors Different modalities: Sound Pressure Temperature
Local Feature Detectors
 Local Feature Detectors Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Slides adapted from Cordelia Schmid and David Lowe, CVPR 2003 Tutorial, Matthew Brown,
Local Feature Detectors Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Slides adapted from Cordelia Schmid and David Lowe, CVPR 2003 Tutorial, Matthew Brown,
An Endoscope With 2 DOFs Steering of Coaxial Nd:YAG Laser Beam for Fetal Surgery [Yamanaka et al. 2010, IEEE trans on Mechatronics]
![An Endoscope With 2 DOFs Steering of Coaxial Nd:YAG Laser Beam for Fetal Surgery [Yamanaka et al. 2010, IEEE trans on Mechatronics] An Endoscope With 2 DOFs Steering of Coaxial Nd:YAG Laser Beam for Fetal Surgery [Yamanaka et al. 2010, IEEE trans on Mechatronics]](/thumbs/82/86433295.jpg) An Endoscope With 2 DOFs Steering of Coaxial Nd:YAG Laser Beam for Fetal Surgery [Yamanaka et al. 2010, IEEE trans on Mechatronics] GEORGE DWYER Automatic Tracking Algorithm in Coaxial Near-infrared Laser
An Endoscope With 2 DOFs Steering of Coaxial Nd:YAG Laser Beam for Fetal Surgery [Yamanaka et al. 2010, IEEE trans on Mechatronics] GEORGE DWYER Automatic Tracking Algorithm in Coaxial Near-infrared Laser
LUMS Mine Detector Project
 LUMS Mine Detector Project Using visual information to control a robot (Hutchinson et al. 1996). Vision may or may not be used in the feedback loop. Visual (image based) features such as points, lines
LUMS Mine Detector Project Using visual information to control a robot (Hutchinson et al. 1996). Vision may or may not be used in the feedback loop. Visual (image based) features such as points, lines
WEIGHTED L1 AND L2 NORMS FOR IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION: FIRST CLINICAL RESULTS OF EIT LUNG VENTILATION DATA
 WEIGHTED L1 AND L2 NORMS FOR IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION: FIRST CLINICAL RESULTS OF EIT LUNG VENTILATION DATA PRESENTER: PEYMAN RAHMATI, PHD CANDIDATE, Biomedical Eng., Dept. of Systems and Computer Eng., Carleton
WEIGHTED L1 AND L2 NORMS FOR IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION: FIRST CLINICAL RESULTS OF EIT LUNG VENTILATION DATA PRESENTER: PEYMAN RAHMATI, PHD CANDIDATE, Biomedical Eng., Dept. of Systems and Computer Eng., Carleton
Capturing, Modeling, Rendering 3D Structures
 Computer Vision Approach Capturing, Modeling, Rendering 3D Structures Calculate pixel correspondences and extract geometry Not robust Difficult to acquire illumination effects, e.g. specular highlights
Computer Vision Approach Capturing, Modeling, Rendering 3D Structures Calculate pixel correspondences and extract geometry Not robust Difficult to acquire illumination effects, e.g. specular highlights
Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking
 Image Matching Image Retrieval Object Recognition Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking Example: Mosiacing (Panorama) M. Brown and D. G. Lowe. Recognising Panoramas. ICCV 2003 Example 3D Reconstruction
Image Matching Image Retrieval Object Recognition Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking Example: Mosiacing (Panorama) M. Brown and D. G. Lowe. Recognising Panoramas. ICCV 2003 Example 3D Reconstruction
Feature Tracking and Optical Flow
 Feature Tracking and Optical Flow Prof. D. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Many slides adapted from James Hays, Derek Hoeim, Lana Lazebnik, Silvio Saverse, who 1 in turn adapted slides from Steve Seitz, Rick Szeliski,
Feature Tracking and Optical Flow Prof. D. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Many slides adapted from James Hays, Derek Hoeim, Lana Lazebnik, Silvio Saverse, who 1 in turn adapted slides from Steve Seitz, Rick Szeliski,
Motion Estimation. There are three main types (or applications) of motion estimation:
 Members: D91922016 朱威達 R93922010 林聖凱 R93922044 謝俊瑋 Motion Estimation There are three main types (or applications) of motion estimation: Parametric motion (image alignment) The main idea of parametric motion
Members: D91922016 朱威達 R93922010 林聖凱 R93922044 謝俊瑋 Motion Estimation There are three main types (or applications) of motion estimation: Parametric motion (image alignment) The main idea of parametric motion
SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014
 SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014 SIFT SIFT: Scale Invariant Feature Transform; transform image
SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014 SIFT SIFT: Scale Invariant Feature Transform; transform image
Marcel Worring Intelligent Sensory Information Systems
 Marcel Worring worring@science.uva.nl Intelligent Sensory Information Systems University of Amsterdam Information and Communication Technology archives of documentaries, film, or training material, video
Marcel Worring worring@science.uva.nl Intelligent Sensory Information Systems University of Amsterdam Information and Communication Technology archives of documentaries, film, or training material, video
SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS
 SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS Cognitive Robotics Original: David G. Lowe, 004 Summary: Coen van Leeuwen, s1460919 Abstract: This article presents a method to extract
SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS Cognitive Robotics Original: David G. Lowe, 004 Summary: Coen van Leeuwen, s1460919 Abstract: This article presents a method to extract
Towards Projector-based Visualization for Computer-assisted CABG at the Open Heart
 Towards Projector-based Visualization for Computer-assisted CABG at the Open Heart Christine Hartung 1, Claudia Gnahm 1, Stefan Sailer 1, Marcel Schenderlein 1, Reinhard Friedl 2, Martin Hoffmann 3, Klaus
Towards Projector-based Visualization for Computer-assisted CABG at the Open Heart Christine Hartung 1, Claudia Gnahm 1, Stefan Sailer 1, Marcel Schenderlein 1, Reinhard Friedl 2, Martin Hoffmann 3, Klaus
Visual Tracking (1) Tracking of Feature Points and Planar Rigid Objects
 Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Tracking of Feature Points and Planar Rigid Objects Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Tracking of Feature Points and Planar Rigid Objects Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
Visual Tracking (1) Feature Point Tracking and Block Matching
 Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Feature Point Tracking and Block Matching Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Feature Point Tracking and Block Matching Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
Image processing and features
 Image processing and features Gabriele Bleser gabriele.bleser@dfki.de Thanks to Harald Wuest, Folker Wientapper and Marc Pollefeys Introduction Previous lectures: geometry Pose estimation Epipolar geometry
Image processing and features Gabriele Bleser gabriele.bleser@dfki.de Thanks to Harald Wuest, Folker Wientapper and Marc Pollefeys Introduction Previous lectures: geometry Pose estimation Epipolar geometry
Simultaneous Stereoscope Localization and Soft-Tissue Mapping for Minimal Invasive Surgery
 Simultaneous Stereoscope Localization and Soft-Tissue Mapping for Minimal Invasive Surgery Peter Mountney 1, Danail Stoyanov 1, Andrew Davison 1, and Guang-Zhong Yang 1,2 1 Royal Society/Wolfson Foundation
Simultaneous Stereoscope Localization and Soft-Tissue Mapping for Minimal Invasive Surgery Peter Mountney 1, Danail Stoyanov 1, Andrew Davison 1, and Guang-Zhong Yang 1,2 1 Royal Society/Wolfson Foundation
Nonrigid Registration using Free-Form Deformations
 Nonrigid Registration using Free-Form Deformations Hongchang Peng April 20th Paper Presented: Rueckert et al., TMI 1999: Nonrigid registration using freeform deformations: Application to breast MR images
Nonrigid Registration using Free-Form Deformations Hongchang Peng April 20th Paper Presented: Rueckert et al., TMI 1999: Nonrigid registration using freeform deformations: Application to breast MR images
Development of an optomechanical measurement system for dynamic stability analysis
 Development of an optomechanical measurement system for dynamic stability analysis Simone Pasinetti Dept. of Information Engineering (DII) University of Brescia Brescia, Italy simone.pasinetti@unibs.it
Development of an optomechanical measurement system for dynamic stability analysis Simone Pasinetti Dept. of Information Engineering (DII) University of Brescia Brescia, Italy simone.pasinetti@unibs.it
A novel approach to motion tracking with wearable sensors based on Probabilistic Graphical Models
 A novel approach to motion tracking with wearable sensors based on Probabilistic Graphical Models Emanuele Ruffaldi Lorenzo Peppoloni Alessandro Filippeschi Carlo Alberto Avizzano 2014 IEEE International
A novel approach to motion tracking with wearable sensors based on Probabilistic Graphical Models Emanuele Ruffaldi Lorenzo Peppoloni Alessandro Filippeschi Carlo Alberto Avizzano 2014 IEEE International
EXAM SOLUTIONS. Image Processing and Computer Vision Course 2D1421 Monday, 13 th of March 2006,
 School of Computer Science and Communication, KTH Danica Kragic EXAM SOLUTIONS Image Processing and Computer Vision Course 2D1421 Monday, 13 th of March 2006, 14.00 19.00 Grade table 0-25 U 26-35 3 36-45
School of Computer Science and Communication, KTH Danica Kragic EXAM SOLUTIONS Image Processing and Computer Vision Course 2D1421 Monday, 13 th of March 2006, 14.00 19.00 Grade table 0-25 U 26-35 3 36-45
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators. Preprocessing
 SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators. Preprocessing. fmri Preprocessing
 SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
Resolution of spherical parallel Manipulator (SPM) forward kinematic model (FKM) near the singularities
 Resolution of spherical parallel Manipulator (SPM) forward kinematic model (FKM) near the singularities H. Saafi a, M. A. Laribi a, S. Zeghloul a a. Dept. GMSC, Pprime Institute, CNRS - University of Poitiers
Resolution of spherical parallel Manipulator (SPM) forward kinematic model (FKM) near the singularities H. Saafi a, M. A. Laribi a, S. Zeghloul a a. Dept. GMSC, Pprime Institute, CNRS - University of Poitiers
ФУНДАМЕНТАЛЬНЫЕ НАУКИ. Информатика 9 ИНФОРМАТИКА MOTION DETECTION IN VIDEO STREAM BASED ON BACKGROUND SUBTRACTION AND TARGET TRACKING
 ФУНДАМЕНТАЛЬНЫЕ НАУКИ Информатика 9 ИНФОРМАТИКА UDC 6813 OTION DETECTION IN VIDEO STREA BASED ON BACKGROUND SUBTRACTION AND TARGET TRACKING R BOGUSH, S ALTSEV, N BROVKO, E IHAILOV (Polotsk State University
ФУНДАМЕНТАЛЬНЫЕ НАУКИ Информатика 9 ИНФОРМАТИКА UDC 6813 OTION DETECTION IN VIDEO STREA BASED ON BACKGROUND SUBTRACTION AND TARGET TRACKING R BOGUSH, S ALTSEV, N BROVKO, E IHAILOV (Polotsk State University
Multi-view Surface Inspection Using a Rotating Table
 https://doi.org/10.2352/issn.2470-1173.2018.09.iriacv-278 2018, Society for Imaging Science and Technology Multi-view Surface Inspection Using a Rotating Table Tomoya Kaichi, Shohei Mori, Hideo Saito,
https://doi.org/10.2352/issn.2470-1173.2018.09.iriacv-278 2018, Society for Imaging Science and Technology Multi-view Surface Inspection Using a Rotating Table Tomoya Kaichi, Shohei Mori, Hideo Saito,
EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Industrially Focused Mathematical Modelling
 EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Industrially Focused Mathematical Modelling More Accurate Optical Measurements of the Cornea Raquel González Fariña Contents 1. Introduction... 2 Background... 2 2.
EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Industrially Focused Mathematical Modelling More Accurate Optical Measurements of the Cornea Raquel González Fariña Contents 1. Introduction... 2 Background... 2 2.
Using Geometric Blur for Point Correspondence
 1 Using Geometric Blur for Point Correspondence Nisarg Vyas Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA Abstract In computer vision applications, point correspondence
1 Using Geometric Blur for Point Correspondence Nisarg Vyas Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA Abstract In computer vision applications, point correspondence
Matching. Compare region of image to region of image. Today, simplest kind of matching. Intensities similar.
 Matching Compare region of image to region of image. We talked about this for stereo. Important for motion. Epipolar constraint unknown. But motion small. Recognition Find object in image. Recognize object.
Matching Compare region of image to region of image. We talked about this for stereo. Important for motion. Epipolar constraint unknown. But motion small. Recognition Find object in image. Recognize object.
Local features: detection and description. Local invariant features
 Local features: detection and description Local invariant features Detection of interest points Harris corner detection Scale invariant blob detection: LoG Description of local patches SIFT : Histograms
Local features: detection and description Local invariant features Detection of interest points Harris corner detection Scale invariant blob detection: LoG Description of local patches SIFT : Histograms
Overview. Video. Overview 4/7/2008. Optical flow. Why estimate motion? Motion estimation: Optical flow. Motion Magnification Colorization.
 Overview Video Optical flow Motion Magnification Colorization Lecture 9 Optical flow Motion Magnification Colorization Overview Optical flow Combination of slides from Rick Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Alyosha
Overview Video Optical flow Motion Magnification Colorization Lecture 9 Optical flow Motion Magnification Colorization Overview Optical flow Combination of slides from Rick Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Alyosha
Augmented Reality VU. Computer Vision 3D Registration (2) Prof. Vincent Lepetit
 Augmented Reality VU Computer Vision 3D Registration (2) Prof. Vincent Lepetit Feature Point-Based 3D Tracking Feature Points for 3D Tracking Much less ambiguous than edges; Point-to-point reprojection
Augmented Reality VU Computer Vision 3D Registration (2) Prof. Vincent Lepetit Feature Point-Based 3D Tracking Feature Points for 3D Tracking Much less ambiguous than edges; Point-to-point reprojection
2D and 3d In-Vivo Imaging for Robotic Surgery. Peter K. Allen Department of Computer Science Columbia University
 2D and 3d In-Vivo Imaging for Robotic Surgery Peter K. Allen Department of Computer Science Columbia University CU Robotics Medical Devices 1. In-vivo imaging device (mono) 2. In-vivo imaging device (stereo)
2D and 3d In-Vivo Imaging for Robotic Surgery Peter K. Allen Department of Computer Science Columbia University CU Robotics Medical Devices 1. In-vivo imaging device (mono) 2. In-vivo imaging device (stereo)
Lecture 16: Computer Vision
 CS4442/9542b: Artificial Intelligence II Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 16: Computer Vision Motion Slides are from Steve Seitz (UW), David Jacobs (UMD) Outline Motion Estimation Motion Field Optical Flow Field
CS4442/9542b: Artificial Intelligence II Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 16: Computer Vision Motion Slides are from Steve Seitz (UW), David Jacobs (UMD) Outline Motion Estimation Motion Field Optical Flow Field
Motion Tracking and Event Understanding in Video Sequences
 Motion Tracking and Event Understanding in Video Sequences Isaac Cohen Elaine Kang, Jinman Kang Institute for Robotics and Intelligent Systems University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA Objectives!
Motion Tracking and Event Understanding in Video Sequences Isaac Cohen Elaine Kang, Jinman Kang Institute for Robotics and Intelligent Systems University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA Objectives!
ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies"
 ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies" lhm@jpl.nasa.gov, 818-354-3722" Announcements" First homework grading is done! Second homework is due
ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies" lhm@jpl.nasa.gov, 818-354-3722" Announcements" First homework grading is done! Second homework is due
Building a Panorama. Matching features. Matching with Features. How do we build a panorama? Computational Photography, 6.882
 Matching features Building a Panorama Computational Photography, 6.88 Prof. Bill Freeman April 11, 006 Image and shape descriptors: Harris corner detectors and SIFT features. Suggested readings: Mikolajczyk
Matching features Building a Panorama Computational Photography, 6.88 Prof. Bill Freeman April 11, 006 Image and shape descriptors: Harris corner detectors and SIFT features. Suggested readings: Mikolajczyk
State Estimation for Continuous-Time Systems with Perspective Outputs from Discrete Noisy Time-Delayed Measurements
 State Estimation for Continuous-Time Systems with Perspective Outputs from Discrete Noisy Time-Delayed Measurements António Pedro Aguiar aguiar@ece.ucsb.edu João Pedro Hespanha hespanha@ece.ucsb.edu Dept.
State Estimation for Continuous-Time Systems with Perspective Outputs from Discrete Noisy Time-Delayed Measurements António Pedro Aguiar aguiar@ece.ucsb.edu João Pedro Hespanha hespanha@ece.ucsb.edu Dept.
Ground Plane Motion Parameter Estimation For Non Circular Paths
 Ground Plane Motion Parameter Estimation For Non Circular Paths G.J.Ellwood Y.Zheng S.A.Billings Department of Automatic Control and Systems Engineering University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK J.E.W.Mayhew
Ground Plane Motion Parameter Estimation For Non Circular Paths G.J.Ellwood Y.Zheng S.A.Billings Department of Automatic Control and Systems Engineering University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK J.E.W.Mayhew
Perceptual Grouping from Motion Cues Using Tensor Voting
 Perceptual Grouping from Motion Cues Using Tensor Voting 1. Research Team Project Leader: Graduate Students: Prof. Gérard Medioni, Computer Science Mircea Nicolescu, Changki Min 2. Statement of Project
Perceptual Grouping from Motion Cues Using Tensor Voting 1. Research Team Project Leader: Graduate Students: Prof. Gérard Medioni, Computer Science Mircea Nicolescu, Changki Min 2. Statement of Project
Active motion compensation for cardiac surgery
 Active motion compensation for cardiac surgery Prof. Dr. Ing. Philippe POIGNET LIRMM UMR 5506 CNRS - University of Montpellier RoboDcs Department, France poignet@lirmm.fr BioDev 14 LIRMM / Robo)cs Dpt
Active motion compensation for cardiac surgery Prof. Dr. Ing. Philippe POIGNET LIRMM UMR 5506 CNRS - University of Montpellier RoboDcs Department, France poignet@lirmm.fr BioDev 14 LIRMM / Robo)cs Dpt
CS 4495 Computer Vision A. Bobick. CS 4495 Computer Vision. Features 2 SIFT descriptor. Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing
 CS 4495 Computer Vision Features 2 SIFT descriptor Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia PS 3: Out due Oct 6 th. Features recap: Goal is to find corresponding locations in two images.
CS 4495 Computer Vision Features 2 SIFT descriptor Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia PS 3: Out due Oct 6 th. Features recap: Goal is to find corresponding locations in two images.
The SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature
 The SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) Detector and Descriptor developed by David Lowe University of British Columbia Initial paper ICCV 1999 Newer journal paper IJCV 2004 Review: Matt Brown s Canonical
The SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) Detector and Descriptor developed by David Lowe University of British Columbia Initial paper ICCV 1999 Newer journal paper IJCV 2004 Review: Matt Brown s Canonical
Functional MRI in Clinical Research and Practice Preprocessing
 Functional MRI in Clinical Research and Practice Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization
Functional MRI in Clinical Research and Practice Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization
Dense Image-based Motion Estimation Algorithms & Optical Flow
 Dense mage-based Motion Estimation Algorithms & Optical Flow Video A video is a sequence of frames captured at different times The video data is a function of v time (t) v space (x,y) ntroduction to motion
Dense mage-based Motion Estimation Algorithms & Optical Flow Video A video is a sequence of frames captured at different times The video data is a function of v time (t) v space (x,y) ntroduction to motion
Fingertips Tracking based on Gradient Vector
 Int. J. Advance Soft Compu. Appl, Vol. 7, No. 3, November 2015 ISSN 2074-8523 Fingertips Tracking based on Gradient Vector Ahmad Yahya Dawod 1, Md Jan Nordin 1, and Junaidi Abdullah 2 1 Pattern Recognition
Int. J. Advance Soft Compu. Appl, Vol. 7, No. 3, November 2015 ISSN 2074-8523 Fingertips Tracking based on Gradient Vector Ahmad Yahya Dawod 1, Md Jan Nordin 1, and Junaidi Abdullah 2 1 Pattern Recognition
Aircraft Tracking Based on KLT Feature Tracker and Image Modeling
 Aircraft Tracking Based on KLT Feature Tracker and Image Modeling Khawar Ali, Shoab A. Khan, and Usman Akram Computer Engineering Department, College of Electrical & Mechanical Engineering, National University
Aircraft Tracking Based on KLT Feature Tracker and Image Modeling Khawar Ali, Shoab A. Khan, and Usman Akram Computer Engineering Department, College of Electrical & Mechanical Engineering, National University
Robotics 2 Iterative Learning for Gravity Compensation
 Robotics 2 Iterative Learning for Gravity Compensation Prof. Alessandro De Luca Control goal! regulation of arbitrary equilibium configurations in the presence of gravity! without explicit knowledge of
Robotics 2 Iterative Learning for Gravity Compensation Prof. Alessandro De Luca Control goal! regulation of arbitrary equilibium configurations in the presence of gravity! without explicit knowledge of
Motion Estimation for Video Coding Standards
 Motion Estimation for Video Coding Standards Prof. Ja-Ling Wu Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taiwan University Introduction of Motion Estimation The goal of video compression
Motion Estimation for Video Coding Standards Prof. Ja-Ling Wu Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taiwan University Introduction of Motion Estimation The goal of video compression
Vision-based endoscope tracking for 3D ultrasound image-guided surgical navigation [Yang et al. 2014, Comp Med Imaging and Graphics]
![Vision-based endoscope tracking for 3D ultrasound image-guided surgical navigation [Yang et al. 2014, Comp Med Imaging and Graphics] Vision-based endoscope tracking for 3D ultrasound image-guided surgical navigation [Yang et al. 2014, Comp Med Imaging and Graphics]](/thumbs/85/91497264.jpg) Vision-based endoscope tracking for 3D ultrasound image-guided surgical navigation [Yang et al. 2014, Comp Med Imaging and Graphics] Gustavo Sato dos Santos IGI Journal Club 23.10.2014 Motivation Goal:
Vision-based endoscope tracking for 3D ultrasound image-guided surgical navigation [Yang et al. 2014, Comp Med Imaging and Graphics] Gustavo Sato dos Santos IGI Journal Club 23.10.2014 Motivation Goal:
Prediction of Heartbeat Motion with a Generalized Adaptive Filter
 28 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Pasadena, CA, USA, May 19-23, 28 Prediction of Heartbeat Motion with a Generalized Adaptive Filter Timothy J. Franke, Ozkan Bebek, M. Cenk Cavusoglu
28 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Pasadena, CA, USA, May 19-23, 28 Prediction of Heartbeat Motion with a Generalized Adaptive Filter Timothy J. Franke, Ozkan Bebek, M. Cenk Cavusoglu
Subpixel accurate refinement of disparity maps using stereo correspondences
 Subpixel accurate refinement of disparity maps using stereo correspondences Matthias Demant Lehrstuhl für Mustererkennung, Universität Freiburg Outline 1 Introduction and Overview 2 Refining the Cost Volume
Subpixel accurate refinement of disparity maps using stereo correspondences Matthias Demant Lehrstuhl für Mustererkennung, Universität Freiburg Outline 1 Introduction and Overview 2 Refining the Cost Volume
FOREWORD TO THE SPECIAL ISSUE ON MOTION DETECTION AND COMPENSATION
 Philips J. Res. 51 (1998) 197-201 FOREWORD TO THE SPECIAL ISSUE ON MOTION DETECTION AND COMPENSATION This special issue of Philips Journalof Research includes a number of papers presented at a Philips
Philips J. Res. 51 (1998) 197-201 FOREWORD TO THE SPECIAL ISSUE ON MOTION DETECTION AND COMPENSATION This special issue of Philips Journalof Research includes a number of papers presented at a Philips
Dense 3-D Reconstruction of an Outdoor Scene by Hundreds-baseline Stereo Using a Hand-held Video Camera
 Dense 3-D Reconstruction of an Outdoor Scene by Hundreds-baseline Stereo Using a Hand-held Video Camera Tomokazu Satoy, Masayuki Kanbaray, Naokazu Yokoyay and Haruo Takemuraz ygraduate School of Information
Dense 3-D Reconstruction of an Outdoor Scene by Hundreds-baseline Stereo Using a Hand-held Video Camera Tomokazu Satoy, Masayuki Kanbaray, Naokazu Yokoyay and Haruo Takemuraz ygraduate School of Information
Medical Robotics. Control Modalities
 Università di Roma La Sapienza Medical Robotics Control Modalities Marilena Vendittelli differ for the the way human input is mapped to the motions of surgical instruments strictly related to the degree
Università di Roma La Sapienza Medical Robotics Control Modalities Marilena Vendittelli differ for the the way human input is mapped to the motions of surgical instruments strictly related to the degree
Object Recognition with Invariant Features
 Object Recognition with Invariant Features Definition: Identify objects or scenes and determine their pose and model parameters Applications Industrial automation and inspection Mobile robots, toys, user
Object Recognition with Invariant Features Definition: Identify objects or scenes and determine their pose and model parameters Applications Industrial automation and inspection Mobile robots, toys, user
Correspondence and Stereopsis. Original notes by W. Correa. Figures from [Forsyth & Ponce] and [Trucco & Verri]
![Correspondence and Stereopsis. Original notes by W. Correa. Figures from [Forsyth & Ponce] and [Trucco & Verri] Correspondence and Stereopsis. Original notes by W. Correa. Figures from [Forsyth & Ponce] and [Trucco & Verri]](/thumbs/80/81283374.jpg) Correspondence and Stereopsis Original notes by W. Correa. Figures from [Forsyth & Ponce] and [Trucco & Verri] Introduction Disparity: Informally: difference between two pictures Allows us to gain a strong
Correspondence and Stereopsis Original notes by W. Correa. Figures from [Forsyth & Ponce] and [Trucco & Verri] Introduction Disparity: Informally: difference between two pictures Allows us to gain a strong
Lecture 16: Computer Vision
 CS442/542b: Artificial ntelligence Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 16: Computer Vision Motion Slides are from Steve Seitz (UW), David Jacobs (UMD) Outline Motion Estimation Motion Field Optical Flow Field Methods
CS442/542b: Artificial ntelligence Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 16: Computer Vision Motion Slides are from Steve Seitz (UW), David Jacobs (UMD) Outline Motion Estimation Motion Field Optical Flow Field Methods
Thin Plate Spline Feature Point Matching for Organ Surfaces in Minimally Invasive Surgery Imaging
 Thin Plate Spline Feature Point Matching for Organ Surfaces in Minimally Invasive Surgery Imaging Bingxiong Lin, Yu Sun and Xiaoning Qian University of South Florida, Tampa, FL., U.S.A. ABSTRACT Robust
Thin Plate Spline Feature Point Matching for Organ Surfaces in Minimally Invasive Surgery Imaging Bingxiong Lin, Yu Sun and Xiaoning Qian University of South Florida, Tampa, FL., U.S.A. ABSTRACT Robust
Visual Tracking. Image Processing Laboratory Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica Università degli studi di Catania.
 Image Processing Laboratory Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica Università degli studi di Catania 1 What is visual tracking? estimation of the target location over time 2 applications Six main areas:
Image Processing Laboratory Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica Università degli studi di Catania 1 What is visual tracking? estimation of the target location over time 2 applications Six main areas:
Computer Vision I. Announcements. Fourier Tansform. Efficient Implementation. Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 13.
 Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Navigation System for ACL Reconstruction Using Registration between Multi-Viewpoint X-ray Images and CT Images
 Navigation System for ACL Reconstruction Using Registration between Multi-Viewpoint X-ray Images and CT Images Mamoru Kuga a*, Kazunori Yasuda b, Nobuhiko Hata a, Takeyoshi Dohi a a Graduate School of
Navigation System for ACL Reconstruction Using Registration between Multi-Viewpoint X-ray Images and CT Images Mamoru Kuga a*, Kazunori Yasuda b, Nobuhiko Hata a, Takeyoshi Dohi a a Graduate School of
Real-time FEM based control of soft surgical robots
 Real-time FEM based control of soft surgical robots Frederick Largilliere, Eulalie Coevoet, Laurent Grisoni, Christian Duriez To cite this version: Frederick Largilliere, Eulalie Coevoet, Laurent Grisoni,
Real-time FEM based control of soft surgical robots Frederick Largilliere, Eulalie Coevoet, Laurent Grisoni, Christian Duriez To cite this version: Frederick Largilliere, Eulalie Coevoet, Laurent Grisoni,
3D Modeling of Objects Using Laser Scanning
 1 3D Modeling of Objects Using Laser Scanning D. Jaya Deepu, LPU University, Punjab, India Email: Jaideepudadi@gmail.com Abstract: In the last few decades, constructing accurate three-dimensional models
1 3D Modeling of Objects Using Laser Scanning D. Jaya Deepu, LPU University, Punjab, India Email: Jaideepudadi@gmail.com Abstract: In the last few decades, constructing accurate three-dimensional models
Research Subject. Dynamics Computation and Behavior Capture of Human Figures (Nakamura Group)
 Research Subject Dynamics Computation and Behavior Capture of Human Figures (Nakamura Group) (1) Goal and summary Introduction Humanoid has less actuators than its movable degrees of freedom (DOF) which
Research Subject Dynamics Computation and Behavior Capture of Human Figures (Nakamura Group) (1) Goal and summary Introduction Humanoid has less actuators than its movable degrees of freedom (DOF) which
Motion Analysis. Motion analysis. Now we will talk about. Differential Motion Analysis. Motion analysis. Difference Pictures
 Now we will talk about Motion Analysis Motion analysis Motion analysis is dealing with three main groups of motionrelated problems: Motion detection Moving object detection and location. Derivation of
Now we will talk about Motion Analysis Motion analysis Motion analysis is dealing with three main groups of motionrelated problems: Motion detection Moving object detection and location. Derivation of
Harder case. Image matching. Even harder case. Harder still? by Diva Sian. by swashford
 Image matching Harder case by Diva Sian by Diva Sian by scgbt by swashford Even harder case Harder still? How the Afghan Girl was Identified by Her Iris Patterns Read the story NASA Mars Rover images Answer
Image matching Harder case by Diva Sian by Diva Sian by scgbt by swashford Even harder case Harder still? How the Afghan Girl was Identified by Her Iris Patterns Read the story NASA Mars Rover images Answer
Image matching. Announcements. Harder case. Even harder case. Project 1 Out today Help session at the end of class. by Diva Sian.
 Announcements Project 1 Out today Help session at the end of class Image matching by Diva Sian by swashford Harder case Even harder case How the Afghan Girl was Identified by Her Iris Patterns Read the
Announcements Project 1 Out today Help session at the end of class Image matching by Diva Sian by swashford Harder case Even harder case How the Afghan Girl was Identified by Her Iris Patterns Read the
Omni-Directional Visual Servoing for Human-Robot Interaction
 Omni-Directional Visual Servoing for Human-Robot Interaction Peng Chang and Martial Hebert [Peng, hebert]@ri.cmu.edu Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh PA 15213 Abstract In this
Omni-Directional Visual Servoing for Human-Robot Interaction Peng Chang and Martial Hebert [Peng, hebert]@ri.cmu.edu Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh PA 15213 Abstract In this
Harder case. Image matching. Even harder case. Harder still? by Diva Sian. by swashford
 Image matching Harder case by Diva Sian by Diva Sian by scgbt by swashford Even harder case Harder still? How the Afghan Girl was Identified by Her Iris Patterns Read the story NASA Mars Rover images Answer
Image matching Harder case by Diva Sian by Diva Sian by scgbt by swashford Even harder case Harder still? How the Afghan Girl was Identified by Her Iris Patterns Read the story NASA Mars Rover images Answer
Automating endoscopic camera motion for teleoperated minimally invasive surgery using inverse reinforcement learning
 Worcester Polytechnic Institute Digital WPI Masters Theses (All Theses, All Years) Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2018-12-13 Automating endoscopic camera motion for teleoperated minimally invasive
Worcester Polytechnic Institute Digital WPI Masters Theses (All Theses, All Years) Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2018-12-13 Automating endoscopic camera motion for teleoperated minimally invasive
Intercostal DC Intercostal ThorAccess MIS Retractor
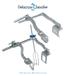 T h o r A c c e s s M I S R e t r a c t o r s Intercostal DC82100-00 Intercostal ThorAccess MIS Retractor Perfect exposure through a mini-thoracotomy, Better adaptation to patient s anatomy thanks to doublehinged
T h o r A c c e s s M I S R e t r a c t o r s Intercostal DC82100-00 Intercostal ThorAccess MIS Retractor Perfect exposure through a mini-thoracotomy, Better adaptation to patient s anatomy thanks to doublehinged
Anno accademico 2006/2007. Davide Migliore
 Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Optical Flow-Based Motion Estimation. Thanks to Steve Seitz, Simon Baker, Takeo Kanade, and anyone else who helped develop these slides.
 Optical Flow-Based Motion Estimation Thanks to Steve Seitz, Simon Baker, Takeo Kanade, and anyone else who helped develop these slides. 1 Why estimate motion? We live in a 4-D world Wide applications Object
Optical Flow-Based Motion Estimation Thanks to Steve Seitz, Simon Baker, Takeo Kanade, and anyone else who helped develop these slides. 1 Why estimate motion? We live in a 4-D world Wide applications Object
Ulrik Söderström 17 Jan Image Processing. Introduction
 Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 17 Jan 2017 Image Processing Introduction Image Processsing Typical goals: Improve images for human interpretation Image processing Processing of images for
Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 17 Jan 2017 Image Processing Introduction Image Processsing Typical goals: Improve images for human interpretation Image processing Processing of images for
Segmentation and Tracking of Partial Planar Templates
 Segmentation and Tracking of Partial Planar Templates Abdelsalam Masoud William Hoff Colorado School of Mines Colorado School of Mines Golden, CO 800 Golden, CO 800 amasoud@mines.edu whoff@mines.edu Abstract
Segmentation and Tracking of Partial Planar Templates Abdelsalam Masoud William Hoff Colorado School of Mines Colorado School of Mines Golden, CO 800 Golden, CO 800 amasoud@mines.edu whoff@mines.edu Abstract
Project Updates Short lecture Volumetric Modeling +2 papers
 Volumetric Modeling Schedule (tentative) Feb 20 Feb 27 Mar 5 Introduction Lecture: Geometry, Camera Model, Calibration Lecture: Features, Tracking/Matching Mar 12 Mar 19 Mar 26 Apr 2 Apr 9 Apr 16 Apr 23
Volumetric Modeling Schedule (tentative) Feb 20 Feb 27 Mar 5 Introduction Lecture: Geometry, Camera Model, Calibration Lecture: Features, Tracking/Matching Mar 12 Mar 19 Mar 26 Apr 2 Apr 9 Apr 16 Apr 23
Visual Tracking (1) Pixel-intensity-based methods
 Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Pixel-intensity-based methods Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Pixel-intensity-based methods Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
Development of a Master Slave System with Force Sensing Using Pneumatic Servo System for Laparoscopic Surgery
 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Roma, Italy, 10-14 April 2007 WeC8.3 Development of a Master Slave System with Force Sensing Using Pneumatic Servo System for Laparoscopic
2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Roma, Italy, 10-14 April 2007 WeC8.3 Development of a Master Slave System with Force Sensing Using Pneumatic Servo System for Laparoscopic
ELEC Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW
 ELEC 4622 Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW Review of Motion Modelling and Estimation Introduction to Motion Modelling & Estimation Forward Motion Backward Motion Block Motion Estimation Motion
ELEC 4622 Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW Review of Motion Modelling and Estimation Introduction to Motion Modelling & Estimation Forward Motion Backward Motion Block Motion Estimation Motion
A Video Guided Solution for Screw Insertion in Orthopedic Plate Fixation
 A Video Guided Solution for Screw Insertion in Orthopedic Plate Fixation J. Magaraggia a,b, G. Kleinszig b, R. Graumann b, E. Angelopoulou a, J. Hornegger a a Pattern Recognition Lab, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg,
A Video Guided Solution for Screw Insertion in Orthopedic Plate Fixation J. Magaraggia a,b, G. Kleinszig b, R. Graumann b, E. Angelopoulou a, J. Hornegger a a Pattern Recognition Lab, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg,
Chapter 3 Image Registration. Chapter 3 Image Registration
 Chapter 3 Image Registration Distributed Algorithms for Introduction (1) Definition: Image Registration Input: 2 images of the same scene but taken from different perspectives Goal: Identify transformation
Chapter 3 Image Registration Distributed Algorithms for Introduction (1) Definition: Image Registration Input: 2 images of the same scene but taken from different perspectives Goal: Identify transformation
Feature Based Registration - Image Alignment
 Feature Based Registration - Image Alignment Image Registration Image registration is the process of estimating an optimal transformation between two or more images. Many slides from Alexei Efros http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463/2007_fall/463.html
Feature Based Registration - Image Alignment Image Registration Image registration is the process of estimating an optimal transformation between two or more images. Many slides from Alexei Efros http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463/2007_fall/463.html
ESPCI ParisTech, Laboratoire d Électronique, Paris France AMPS LLC, New York, NY, USA Hopital Lariboisière, APHP, Paris 7 University, Paris France
 Efficient modeling of ECG waves for morphology tracking Rémi Dubois, Pierre Roussel, Martino Vaglio, Fabrice Extramiana, Fabio Badilini, Pierre Maison Blanche, Gérard Dreyfus ESPCI ParisTech, Laboratoire
Efficient modeling of ECG waves for morphology tracking Rémi Dubois, Pierre Roussel, Martino Vaglio, Fabrice Extramiana, Fabio Badilini, Pierre Maison Blanche, Gérard Dreyfus ESPCI ParisTech, Laboratoire
EPI Data Are Acquired Serially. EPI Data Are Acquired Serially 10/23/2011. Functional Connectivity Preprocessing. fmri Preprocessing
 Functional Connectivity Preprocessing Geometric distortion Head motion Geometric distortion Head motion EPI Data Are Acquired Serially EPI Data Are Acquired Serially descending 1 EPI Data Are Acquired
Functional Connectivity Preprocessing Geometric distortion Head motion Geometric distortion Head motion EPI Data Are Acquired Serially EPI Data Are Acquired Serially descending 1 EPI Data Are Acquired
Developing Algorithms for Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Developing Algorithms for Robotics and Autonomous Systems Jorik Caljouw 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Key Takeaway of this Talk Success in developing an autonomous robotics system requires: 1. Multi-domain
Developing Algorithms for Robotics and Autonomous Systems Jorik Caljouw 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Key Takeaway of this Talk Success in developing an autonomous robotics system requires: 1. Multi-domain
Colour Segmentation-based Computation of Dense Optical Flow with Application to Video Object Segmentation
 ÖGAI Journal 24/1 11 Colour Segmentation-based Computation of Dense Optical Flow with Application to Video Object Segmentation Michael Bleyer, Margrit Gelautz, Christoph Rhemann Vienna University of Technology
ÖGAI Journal 24/1 11 Colour Segmentation-based Computation of Dense Optical Flow with Application to Video Object Segmentation Michael Bleyer, Margrit Gelautz, Christoph Rhemann Vienna University of Technology
Combined Collision Avoidance and Prevention of Soft Tissue Damage Control Method for Surgical Robots
 The Fourth IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics Roma, Italy. June 4-7, Combined Collision Avoidance and Prevention of Soft Tissue Damage Control Method for
The Fourth IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics Roma, Italy. June 4-7, Combined Collision Avoidance and Prevention of Soft Tissue Damage Control Method for
Motion Planning for Dynamic Knotting of a Flexible Rope with a High-speed Robot Arm
 The 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems October 18-22, 2010, Taipei, Taiwan Motion Planning for Dynamic Knotting of a Flexible Rope with a High-speed Robot Arm Yuji
The 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems October 18-22, 2010, Taipei, Taiwan Motion Planning for Dynamic Knotting of a Flexible Rope with a High-speed Robot Arm Yuji
Robert Collins CSE598G. Intro to Template Matching and the Lucas-Kanade Method
 Intro to Template Matching and the Lucas-Kanade Method Appearance-Based Tracking current frame + previous location likelihood over object location current location appearance model (e.g. image template,
Intro to Template Matching and the Lucas-Kanade Method Appearance-Based Tracking current frame + previous location likelihood over object location current location appearance model (e.g. image template,
