Elementary Data Structures 2
|
|
|
- Hannah Garrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Elementary Data Structures Priority Queues, & Dictionaries Priority Queues Sell 00 IBM $ Sell 300 IBM $0 Buy 00 IBM $9 Buy 400 IBM $8
2 Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of items An item is a pair (key, element) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insertitem(k, o) inserts an item with key k and element o removemin() removes the item with smallest key and returns its element Additional methods minkey() returns, but does not remove, the smallest key of an item minelement() returns, but does not remove, the element of an item with smallest key size(), isempty() Applications: Auctions Stock market Elementary Data Structures 3 Total Order Relation Keys in a priority queue can be arbitrary objects on which an order is defined Two distinct items in a priority queue can have the same key Mathematical concept of total order relation Reflexive property: x x Antisymmetric property: x y y x x = y Transitive property: x y y z x z Elementary Data Structures 4
3 Comparator ADT A comparator encapsulates the action of comparing two objects according to a given total order relation A generic priority queue uses an auxiliary comparator The comparator is external to the keys being compared When the priority queue needs to compare two keys, it uses its comparator Methods of the Comparator ADT, all with Boolean return type islessthan(x, y) islessthanorequalto(x,y) isequalto(x,y) isgreaterthan(x, y) isgreaterthanorequalto(x,y) iscomparable(x) Elementary Data Structures What is a heap (.4.3) A heap is a binary tree storing keys at its internal nodes and satisfying the following properties: Heap-Order: for every internal node v other than the root, key(v) key(parent(v)) Complete Binary Tree: let h be the height of the heap for i = 0,, h, there are i nodes of depth i at depth h, the internal nodes are to the left of the external nodes The last node of a heap is the rightmost internal node of depth h 9 7 last node Elementary Data Structures
4 Heaps and Priority Queues We can use a heap to implement a priority queue We store a (key, element) item at each internal node We keep track of the position of the last node (, Sue) (, Pat) (, Mark) (9, Jeff) (7, Anna) Elementary Data Structures 7 Insertion into a Heap (.4.3) Method insertitem of the priority queue ADT corresponds to the insertion of a key k to the heap The insertion algorithm consists of three steps Find the insertion node z (the new last node) Store k at z and expand z into an internal node Restore the heap-order property (discussed next) z insertion node z Elementary Data Structures 8
5 Upheap After the insertion of a new key k, the heap-order property may be violated Algorithm upheap restores the heap-order property by swapping k along an upward path from the insertion node Upheap terminates when the key k reaches the root or a node whose parent has a key smaller than or equal to k 9 7 z 9 7 z Elementary Data Structures 9 Removal from a Heap (.4.3) Method removemin of the priority queue ADT corresponds to the removal of the root key from the heap The removal algorithm consists of three steps Replace the root key with the key of the last node w Compress w and its children into a leaf Restore the heap-order property (discussed next) w w 7 last node Elementary Data Structures 0
6 Downheap After replacing the root key with the key k of the last node, the heap-order property may be violated Algorithm downheap restores the heap-order property by swapping key k along a downward path from the root Upheap terminates when key k reaches a leaf or a node whose children have keys greater than or equal to k 7 9 w 9 7 w Elementary Data Structures Dictionaries and Hash Tables
7 Dictionary ADT (..) The dictionary ADT models a searchable collection of keyelement items The main operations of a dictionary are searching, inserting, and deleting items Multiple items with the same key are allowed Applications: address book credit card authorization mapping host names (e.g., cs.net) to internet addresses (e.g., ) Dictionary ADT methods: findelement(k): if the dictionary has an item with key k, returns its element, else, returns the special element NO_SUCH_KEY insertitem(k, o): inserts item (k, o) into the dictionary removeelement(k): if the dictionary has an item with key k, removes it from the dictionary and returns its element, else returns the special element NO_SUCH_KEY size(), isempty() keys(), Elements() Elementary Data Structures 3 Hash Functions and Hash Tables (..) A hash function h maps keys of a given type to integers in a fixed interval [0, N ] Example: h(x) = x mod N is a hash function for integer keys The integer h(x) is called the hash value of key x A hash table for a given key type consists of Hash function h Array (called table) of size N When implementing a dictionary with a hash table, the goal is to store item (k, o) at index i = h(k) Elementary Data Structures 4
8 Example We design a hash table for a dictionary storing items (SSN, Name), where SSN (social security number) is a nine-digit positive integer Our hash table uses an array of size N = 0,000 and the hash function h(x) = last four digits of x Elementary Data Structures Hash Functions (..3) A hash function is usually specified as the composition of two functions: Hash code map: h :keys integers Compression map: h : integers [0, N ] The hash code map is applied first, and the compression map is applied next on the result, i.e., h(x) = h (h (x)) The goal of the hash function is to disperse the keys in an apparently random way Elementary Data Structures
9 Hash Code Maps (..3) Memory address: We reinterpret the memory address of the key object as an integer (default hash code of all Java objects) Good in general, except for numeric and string keys Integer cast: We reinterpret the bits of the key as an integer Suitable for keys of length less than or equal to the number of bits of the integer type (e.g., byte, short, int and float in Java) Component sum: We partition the bits of the key into components of fixed length (e.g., or 3 bits) and we sum the components (ignoring overflows) Suitable for numeric keys of fixed length greater than or equal to the number of bits of the integer type (e.g., long and double in Java) Elementary Data Structures 7 Hash Code Maps (cont.) Polynomial accumulation: We partition the bits of the key into a sequence of components of fixed length (e.g., 8, or 3 bits) a 0 a a n We evaluate the polynomial p(z) = a 0 + a z + a z + + a n z n at a fixed value z, ignoring overflows Especially suitable for strings (e.g., the choice z = 33 gives at most collisions on a set of 0,000 English words) Elementary Data Structures 8
10 Compression Maps (..4) Division: h (y) = y mod N The size N of the hash table is usually chosen to be a prime The reason has to do with number theory and is beyond the scope of this course Multiply, Add and Divide (MAD): h (y) = (ay + b) modn a and b are nonnegative integers such that a mod N 0 Otherwise, every integer would map to the same value b Elementary Data Structures 9 Collision Handling (..) Collisions occur when different elements are mapped to the same cell Chaining: let each cell in the table point to a linked list of elements that map there Chaining is simple, but requires additional memory outside the table Elementary Data Structures 0
11 Linear Probing (..) Open addressing: the colliding item is placed in a different cell of the table Linear probing handles collisions by placing the colliding item in the next (circularly) available table cell Each table cell inspected is referred to as a probe Colliding items lump together, causing future collisions to cause a longer sequence of probes Example: h(x) = x mod 3 Insert keys 8, 4,, 44, 9, 3, 3, 73, in this order Elementary Data Structures Search with Linear Probing Consider a hash table A that uses linear probing findelement(k) We start at cell h(k) We probe consecutive locations until one of the following occurs An item with key k is found, or An empty cell is found, or N cells have been unsuccessfully probed Algorithm findelement(k) i h(k) p 0 repeat c A[i] if c = return NO_SUCH_KEY else if c.key () = k return c.element() else i (i + ) mod N p p + until p = N return NO_SUCH_KEY Elementary Data Structures
12 Updates with Linear Probing To handle insertions and deletions, we introduce a special object, called AVAILABLE, which replaces deleted elements removeelement(k) We search for an item with key k If such an item (k, o) is found, we replace it with the special item AVAILABLE and we return element o Else, we return NO_SUCH_KEY insert Item(k, o) We throw an exception if the table is full We start at cell h(k) We probe consecutive cells until one of the following occurs A cell i is found that is either empty or stores AVAILABLE, or N cells have been unsuccessfully probed We store item (k, o) in cell i Elementary Data Structures 3 Double Hashing Double hashing uses a secondary hash function d(k) and handles collisions by placing an item in the first available cell of the series (i + jd(k)) mod N for j = 0,,, N The secondary hash function d(k) cannot have zero values The table size N must be a prime to allow probing of all the cells Common choice of compression map for the secondary hash function: d (k) = q k mod q where q < N q is a prime The possible values for d (k) are,,, q Elementary Data Structures 4
13 Example of Double Hashing Consider a hash table storing integer keys that handles collision with double hashing N = 3 h(k) = k mod 3 d(k) = 7 k mod 7 Insert keys 8, 4,, 44, 9, 3, 3, 73, in this order k h(k ) d (k ) Probes Elementary Data Structures Euler Tour Traversal Generic traversal of a binary tree Includes a special cases the preorder, postorder and inorder traversals Walk around the tree and visit each node three times: on the left (preorder) from below (inorder) on the right (postorder) + L B R 3 Elementary Data Structures
14 Properties of Binary Trees Notation n number of nodes e number of external nodes i number of internal nodes h height Properties: e = i + n = e h i h (n )/ e h h log e h log (n + ) Elementary Data Structures 7 Height of a Heap (.4.3) Theorem: A heap storing n keys has height O(log n) Proof: (we apply the complete binary tree property) Let h be the height of a heap storing n keys Since there are i keys at depth i = 0,, h and at least one key at depth h, we have n h + Thus, n h, i.e., h log n + depth 0 h h keys h Elementary Data Structures 8
15 Updating the Last Node The insertion node can be found by traversing a path of O(log n) nodes Go up until a left child or the root is reached If a left child is reached, go to the right child Go down left until a leaf is reached Similar algorithm for updating the last node after a removal Elementary Data Structures 9 Log File (..) A log file is a dictionary implemented by means of an unsorted sequence We store the items of the dictionary in a sequence (based on a doubly-linked lists or a circular array), in arbitrary order Performance: insertitem takes O() time since we can insert the new item at the beginning or at the end of the sequence findelement and removeelement take O(n) time since in the worst case (the item is not found) we traverse the entire sequence to look for an item with the given key The log file is effective only for dictionaries of small size or for dictionaries on which insertions are the most common operations, while searches and removals are rarely performed (e.g., historical record of logins to a workstation) Elementary Data Structures 30
Priority Queues and Heaps. More Data Structures. Priority Queue ADT ( 2.4.1) Total Order Relation. Sorting with a Priority Queue ( 2.4.
 More Data Structures Priority Queues and Heaps Priority Queues, Comparators, Locators, Dictionaries More Data Structures v. More Data Structures v. Priority Queue ADT (.4.) Total Order Relation A priority
More Data Structures Priority Queues and Heaps Priority Queues, Comparators, Locators, Dictionaries More Data Structures v. More Data Structures v. Priority Queue ADT (.4.) Total Order Relation A priority
Hash Tables Hash Tables Goodrich, Tamassia
 Hash Tables 0 1 2 3 4 025-612-0001 981-101-0002 451-229-0004 Hash Tables 1 Hash Functions and Hash Tables A hash function h maps keys of a given type to integers in a fixed interval [0, N 1] Example: h(x)
Hash Tables 0 1 2 3 4 025-612-0001 981-101-0002 451-229-0004 Hash Tables 1 Hash Functions and Hash Tables A hash function h maps keys of a given type to integers in a fixed interval [0, N 1] Example: h(x)
Dictionaries and Hash Tables
 Dictionaries and Hash Tables 0 1 2 3 025-612-0001 981-101-0002 4 451-229-0004 Dictionaries and Hash Tables 1 Dictionary ADT The dictionary ADT models a searchable collection of keyelement items The main
Dictionaries and Hash Tables 0 1 2 3 025-612-0001 981-101-0002 4 451-229-0004 Dictionaries and Hash Tables 1 Dictionary ADT The dictionary ADT models a searchable collection of keyelement items The main
This lecture. Iterators ( 5.4) Maps. Maps. The Map ADT ( 8.1) Comparison to java.util.map
 This lecture Iterators Hash tables Formal coursework Iterators ( 5.4) An iterator abstracts the process of scanning through a collection of elements Methods of the ObjectIterator ADT: object object() boolean
This lecture Iterators Hash tables Formal coursework Iterators ( 5.4) An iterator abstracts the process of scanning through a collection of elements Methods of the ObjectIterator ADT: object object() boolean
Heaps. 2/13/2006 Heaps 1
 Heaps /13/00 Heaps 1 Outline and Reading What is a heap ( 8.3.1) Height of a heap ( 8.3.) Insertion ( 8.3.3) Removal ( 8.3.3) Heap-sort ( 8.3.) Arraylist-based implementation ( 8.3.) Bottom-up construction
Heaps /13/00 Heaps 1 Outline and Reading What is a heap ( 8.3.1) Height of a heap ( 8.3.) Insertion ( 8.3.3) Removal ( 8.3.3) Heap-sort ( 8.3.) Arraylist-based implementation ( 8.3.) Bottom-up construction
Priority Queues and Heaps. Heaps and Priority Queues 1
 Priority Queues and Heaps 2 5 6 9 7 Heaps and Priority Queues 1 Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of items An item is a pair (key, element) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT
Priority Queues and Heaps 2 5 6 9 7 Heaps and Priority Queues 1 Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of items An item is a pair (key, element) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT
Dictionaries-Hashing. Textbook: Dictionaries ( 8.1) Hash Tables ( 8.2)
 Dictionaries-Hashing Textbook: Dictionaries ( 8.1) Hash Tables ( 8.2) Dictionary The dictionary ADT models a searchable collection of key-element entries The main operations of a dictionary are searching,
Dictionaries-Hashing Textbook: Dictionaries ( 8.1) Hash Tables ( 8.2) Dictionary The dictionary ADT models a searchable collection of key-element entries The main operations of a dictionary are searching,
Heaps Goodrich, Tamassia. Heaps 1
 Heaps Heaps 1 Recall Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insert(k, x) inserts an entry with key k
Heaps Heaps 1 Recall Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insert(k, x) inserts an entry with key k
Priority Queues. Reading: 7.1, 7.2
 Priority Queues Reading: 7.1, 7.2 Generalized sorting Sometimes we need to sort but The data type is not easily mapped onto data we can compare (numbers, strings, etc) The sorting criteria changes depending
Priority Queues Reading: 7.1, 7.2 Generalized sorting Sometimes we need to sort but The data type is not easily mapped onto data we can compare (numbers, strings, etc) The sorting criteria changes depending
Priority Queue Sorting
 Priority Queue Sorting We can use a priority queue to sort a list of comparable elements 1. Insert the elements one by one with a series of insert operations 2. Remove the elements in sorted order with
Priority Queue Sorting We can use a priority queue to sort a list of comparable elements 1. Insert the elements one by one with a series of insert operations 2. Remove the elements in sorted order with
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Berner Fachhochschule - Technik und Informatik Data Structures and Algorithms Heaps and Priority Queues Philipp Locher FS 2018 Heaps and Priority Queues Page 1 Outline Heaps Heap-Sort Priority Queues Heaps
Berner Fachhochschule - Technik und Informatik Data Structures and Algorithms Heaps and Priority Queues Philipp Locher FS 2018 Heaps and Priority Queues Page 1 Outline Heaps Heap-Sort Priority Queues Heaps
Sorting. Outline. Sorting with a priority queue Selection-sort Insertion-sort Heap Sort Quick Sort
 Sorting Hiroaki Kobayashi 1 Outline Sorting with a priority queue Selection-sort Insertion-sort Heap Sort Quick Sort Merge Sort Lower Bound on Comparison-Based Sorting Bucket Sort and Radix Sort Hiroaki
Sorting Hiroaki Kobayashi 1 Outline Sorting with a priority queue Selection-sort Insertion-sort Heap Sort Quick Sort Merge Sort Lower Bound on Comparison-Based Sorting Bucket Sort and Radix Sort Hiroaki
1/27/2005 2:03 AM Priority Queues 1. Outline and Reading
 Priority Queues Sell 100 $122 Sell 300 $120 Buy 500 $119 Buy 400 $118 Priority Queues 1 Outline and Reading PriorityQueue ADT ( 2.4.1) Total order relation ( 2.4.1) Comparator ADT ( 2.4.1) Sorting with
Priority Queues Sell 100 $122 Sell 300 $120 Buy 500 $119 Buy 400 $118 Priority Queues 1 Outline and Reading PriorityQueue ADT ( 2.4.1) Total order relation ( 2.4.1) Comparator ADT ( 2.4.1) Sorting with
Heaps 2. Recall Priority Queue ADT. Heaps 3/19/14
 Heaps 3// Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 Heaps Heaps Recall Priority Queue ADT
Heaps 3// Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 Heaps Heaps Recall Priority Queue ADT
Priority Queue ADT ( 7.1) Heaps and Priority Queues 2. Comparator ADT ( 7.1.4) Total Order Relation. Using Comparators in C++
 Heaps and Priority Queues Priority Queue ADT (.) A priority queue stores a collection of items An item is a pair (key, element) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insertitem(k, o) inserts an item ith
Heaps and Priority Queues Priority Queue ADT (.) A priority queue stores a collection of items An item is a pair (key, element) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insertitem(k, o) inserts an item ith
Data Structures Lecture 12
 Fall 2017 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Management Information Systems, National Chengchi University Data Structures Lecture 12 Advance ADTs Maps and Hash Tables Maps A map models a searchable collection
Fall 2017 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Management Information Systems, National Chengchi University Data Structures Lecture 12 Advance ADTs Maps and Hash Tables Maps A map models a searchable collection
Chapter 2: Basic Data Structures
 Chapter 2: Basic Data Structures Basic Data Structures Stacks Queues Vectors, Linked Lists Trees (Including Balanced Trees) Priority Queues and Heaps Dictionaries and Hash Tables Spring 2014 CS 315 2 Two
Chapter 2: Basic Data Structures Basic Data Structures Stacks Queues Vectors, Linked Lists Trees (Including Balanced Trees) Priority Queues and Heaps Dictionaries and Hash Tables Spring 2014 CS 315 2 Two
Chapter 9: Maps, Dictionaries, Hashing
 Chapter 9: 0 1 025-612-0001 2 981-101-0002 3 4 451-229-0004 Maps, Dictionaries, Hashing Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided
Chapter 9: 0 1 025-612-0001 2 981-101-0002 3 4 451-229-0004 Maps, Dictionaries, Hashing Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided
Maps, Hash Tables and Dictionaries. Chapter 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.5
 Maps, Hash Tables and Dictionaries Chapter 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.5 Outline Maps Hashing Dictionaries Ordered Maps & Dictionaries Outline Maps Hashing Dictionaries Ordered Maps & Dictionaries Maps A map
Maps, Hash Tables and Dictionaries Chapter 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.5 Outline Maps Hashing Dictionaries Ordered Maps & Dictionaries Outline Maps Hashing Dictionaries Ordered Maps & Dictionaries Maps A map
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Priority Queues and Heaps Page 1 BFH-TI: Softwareschule Schweiz Priority Queues and Heaps Dr. CAS SD01 Priority Queues and Heaps Page 2 Outline Priority Queues Heaps Heap-Based Priority Queues Priority
Priority Queues and Heaps Page 1 BFH-TI: Softwareschule Schweiz Priority Queues and Heaps Dr. CAS SD01 Priority Queues and Heaps Page 2 Outline Priority Queues Heaps Heap-Based Priority Queues Priority
Stores a collection of elements each with an associated key value
 CH9. PRIORITY QUEUES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 201) PRIORITY QUEUES Stores a collection
CH9. PRIORITY QUEUES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 201) PRIORITY QUEUES Stores a collection
HEAPS: IMPLEMENTING EFFICIENT PRIORITY QUEUES
 HEAPS: IMPLEMENTING EFFICIENT PRIORITY QUEUES 2 5 6 9 7 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H., Wiley, 2014
HEAPS: IMPLEMENTING EFFICIENT PRIORITY QUEUES 2 5 6 9 7 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H., Wiley, 2014
HASH TABLES. Goal is to store elements k,v at index i = h k
 CH 9.2 : HASH TABLES 1 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM JORY DENNY AND
CH 9.2 : HASH TABLES 1 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM JORY DENNY AND
CH 8. HEAPS AND PRIORITY QUEUES
 CH 8. HEAPS AND PRIORITY QUEUES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
CH 8. HEAPS AND PRIORITY QUEUES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
Heaps and Priority Queues
 Heaps and Priority Queues Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce Priority Queue ADT To discuss and illustrate Priority Queues for sorting
Heaps and Priority Queues Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce Priority Queue ADT To discuss and illustrate Priority Queues for sorting
CSED233: Data Structures (2017F) Lecture10:Hash Tables, Maps, and Skip Lists
 (2017F) Lecture10:Hash Tables, Maps, and Skip Lists Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Maps A map models a searchable collection of key-value entries The main operations of a map are for searching,
(2017F) Lecture10:Hash Tables, Maps, and Skip Lists Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Maps A map models a searchable collection of key-value entries The main operations of a map are for searching,
CH. 8 PRIORITY QUEUES AND HEAPS
 CH. 8 PRIORITY QUEUES AND HEAPS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
CH. 8 PRIORITY QUEUES AND HEAPS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
Describe how to implement deque ADT using two stacks as the only instance variables. What are the running times of the methods
 Describe how to implement deque ADT using two stacks as the only instance variables. What are the running times of the methods 1 2 Given : Stack A, Stack B 3 // based on requirement b will be reverse of
Describe how to implement deque ADT using two stacks as the only instance variables. What are the running times of the methods 1 2 Given : Stack A, Stack B 3 // based on requirement b will be reverse of
Priority Queues. Outline. COMP9024: Data Structures and Algorithms. Priority Queue ADT. Total Order Relations. Entry ADT
 COMP0: Data Structures and Algorithms Week Seven: Priority Queues Hui Wu Outline Priority Queues Heaps Adaptable Priority Queues Session, 0 http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs0 Priority Queue ADT Priority Queues
COMP0: Data Structures and Algorithms Week Seven: Priority Queues Hui Wu Outline Priority Queues Heaps Adaptable Priority Queues Session, 0 http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs0 Priority Queue ADT Priority Queues
CHAPTER 9 HASH TABLES, MAPS, AND SKIP LISTS
 0 1 2 025-612-0001 981-101-0002 3 4 451-229-0004 CHAPTER 9 HASH TABLES, MAPS, AND SKIP LISTS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH,
0 1 2 025-612-0001 981-101-0002 3 4 451-229-0004 CHAPTER 9 HASH TABLES, MAPS, AND SKIP LISTS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH,
Data Structures and Algorithms " Priority Queues!
 Data Structures and Algorithms " Priority Queues! Outline" Priority Queues! Heaps! Adaptable Priority Queues! Priority Queues" Priority Queue ADT" A priority queue stores a collection of entries! Each
Data Structures and Algorithms " Priority Queues! Outline" Priority Queues! Heaps! Adaptable Priority Queues! Priority Queues" Priority Queue ADT" A priority queue stores a collection of entries! Each
Priority Queues & Heaps. Chapter 9
 Priority Queues & Heaps Chapter 9 The Java Collections Framework (Ordered Data Types) Interface Abstract Class Class Iterable Collection Queue Abstract Collection List Abstract Queue Abstract List Priority
Priority Queues & Heaps Chapter 9 The Java Collections Framework (Ordered Data Types) Interface Abstract Class Class Iterable Collection Queue Abstract Collection List Abstract Queue Abstract List Priority
In a postorder traversal, a node is visited after its descendants Application: compute space used by files in a directory and its subdirectories 9 1
 What is a Tree Trees Stock Fraud Make Money Fast! Winning Lotto / Bank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes ith a parent-child relation
What is a Tree Trees Stock Fraud Make Money Fast! Winning Lotto / Bank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes ith a parent-child relation
Priority queues. Priority queues. Priority queue operations
 Priority queues March 30, 018 1 Priority queues The ADT priority queue stores arbitrary objects with priorities. An object with the highest priority gets served first. Objects with priorities are defined
Priority queues March 30, 018 1 Priority queues The ADT priority queue stores arbitrary objects with priorities. An object with the highest priority gets served first. Objects with priorities are defined
CSED233: Data Structures (2017F) Lecture9: Priority Queues and Heaps
 (2017F) Lecture9: Priority Queues and Heaps Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a coll ection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods
(2017F) Lecture9: Priority Queues and Heaps Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a coll ection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods
Hash Tables. Johns Hopkins Department of Computer Science Course : Data Structures, Professor: Greg Hager
 Hash Tables What is a Dictionary? Container class Stores key-element pairs Allows look-up (find) operation Allows insertion/removal of elements May be unordered or ordered Dictionary Keys Must support
Hash Tables What is a Dictionary? Container class Stores key-element pairs Allows look-up (find) operation Allows insertion/removal of elements May be unordered or ordered Dictionary Keys Must support
Priority queues. Priority queues. Priority queue operations
 Priority queues March 8, 08 Priority queues The ADT priority queue stores arbitrary objects with priorities. An object with the highest priority gets served first. Objects with priorities are defined by
Priority queues March 8, 08 Priority queues The ADT priority queue stores arbitrary objects with priorities. An object with the highest priority gets served first. Objects with priorities are defined by
Heaps Outline and Required Reading: Heaps ( 7.3) COSC 2011, Fall 2003, Section A Instructor: N. Vlajic
 1 Heaps Outline and Required Reading: Heaps (.3) COSC 2011, Fall 2003, Section A Instructor: N. Vlajic Heap ADT 2 Heap binary tree (T) that stores a collection of keys at its internal nodes and satisfies
1 Heaps Outline and Required Reading: Heaps (.3) COSC 2011, Fall 2003, Section A Instructor: N. Vlajic Heap ADT 2 Heap binary tree (T) that stores a collection of keys at its internal nodes and satisfies
Topics on the Midterm
 Midterm Review Topics on the Midterm Data Structures & Object-Oriented Design Run-Time Analysis Linear Data Structures The Java Collections Framework Recursion Trees Priority Queues & Heaps Maps, Hash
Midterm Review Topics on the Midterm Data Structures & Object-Oriented Design Run-Time Analysis Linear Data Structures The Java Collections Framework Recursion Trees Priority Queues & Heaps Maps, Hash
Dictionaries. 2/17/2006 Dictionaries 1
 Dictionaries < 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 /17/006 Dictionaries 1 Outline and Reading Dictionary ADT ( 9.3) Log file ( 9.3.1) Binary search ( 9.3.3) Lookup table ( 9.3.3) Binary search tree ( 10.1) Search ( 10.1.1)
Dictionaries < 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 /17/006 Dictionaries 1 Outline and Reading Dictionary ADT ( 9.3) Log file ( 9.3.1) Binary search ( 9.3.3) Lookup table ( 9.3.3) Binary search tree ( 10.1) Search ( 10.1.1)
CS2210 Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS2210 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 5: Hash Tables Instructor: Olga Veksler 0 1 2 3 025-612-0001 981-101-0002 4 451-229-0004 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia Outline Hash Tables Motivation Hash functions
CS2210 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 5: Hash Tables Instructor: Olga Veksler 0 1 2 3 025-612-0001 981-101-0002 4 451-229-0004 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia Outline Hash Tables Motivation Hash functions
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 12: Heaps and Priority Queues MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 Heaps and Priority Queues 2 Priority Queues Heaps Priority Queue 3 QueueADT Objects are added and
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 12: Heaps and Priority Queues MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 Heaps and Priority Queues 2 Priority Queues Heaps Priority Queue 3 QueueADT Objects are added and
Data Structures Lecture 7
 Fall 2017 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Management Information Systems, National Chengchi University Data Structures Lecture 7 Recap We have talked about object oriented programing Chapter 1, 2,
Fall 2017 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Management Information Systems, National Chengchi University Data Structures Lecture 7 Recap We have talked about object oriented programing Chapter 1, 2,
Height of a Heap. Heaps. 1. Insertion into a Heap. Heaps and Priority Queues. The insertion algorithm consists of three steps
 Heaps A heap is a binary tree storing keys at its nodes and satisfying the folloing properties:! Heap-Order: " for every internal node v other than the root, key(v)! key(parent(v))! Complete Binary Tree:
Heaps A heap is a binary tree storing keys at its nodes and satisfying the folloing properties:! Heap-Order: " for every internal node v other than the root, key(v)! key(parent(v))! Complete Binary Tree:
Priority Queues & Heaps. CS16: Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms Spring 2019
 Priority Queues & Heaps CS16: Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms Spring 2019 Outline Priority Queues Motivation ADT Implementation Heaps insert( ) and upheap( ) removemin( ) and downheap( ) Motivation
Priority Queues & Heaps CS16: Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms Spring 2019 Outline Priority Queues Motivation ADT Implementation Heaps insert( ) and upheap( ) removemin( ) and downheap( ) Motivation
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 10: Search and Heaps MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Spring 2018 Search and Heaps 2 Linear Search Binary Search Introduction to trees Priority Queues Heaps Linear Search
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 10: Search and Heaps MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Spring 2018 Search and Heaps 2 Linear Search Binary Search Introduction to trees Priority Queues Heaps Linear Search
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Page 1 BFH-TI: Softwareschule Schweiz Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Dr. CAS SD01 Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Page Outline Ordered
Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Page 1 BFH-TI: Softwareschule Schweiz Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Dr. CAS SD01 Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Page Outline Ordered
Search Trees (Ch. 9) > = Binary Search Trees 1
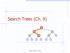 Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
Binary Search Trees (10.1) Dictionary ADT (9.5.1)
 Binary Search Trees (10.1) CSE 011 Winter 011 4 March 011 1 Dictionary ADT (..1) The dictionary ADT models a searchable collection of keyelement items The main operations of a dictionary are searching,
Binary Search Trees (10.1) CSE 011 Winter 011 4 March 011 1 Dictionary ADT (..1) The dictionary ADT models a searchable collection of keyelement items The main operations of a dictionary are searching,
SEARCHING. the dictionary ADT. binary search. binary search trees. Searching
 the dictionary ADT binary search binary search trees SEARCHING 44 17 78 32 50 88 48 62 1 The Dictionary ADT a dictionary is an abstract model of a database like a priority queue, a dictionary stores key-element
the dictionary ADT binary search binary search trees SEARCHING 44 17 78 32 50 88 48 62 1 The Dictionary ADT a dictionary is an abstract model of a database like a priority queue, a dictionary stores key-element
COSC 2007 Data Structures II Final Exam. Part 1: multiple choice (1 mark each, total 30 marks, circle the correct answer)
 COSC 2007 Data Structures II Final Exam Thursday, April 13 th, 2006 This is a closed book and closed notes exam. There are total 3 parts. Please answer the questions in the provided space and use back
COSC 2007 Data Structures II Final Exam Thursday, April 13 th, 2006 This is a closed book and closed notes exam. There are total 3 parts. Please answer the questions in the provided space and use back
Chapter 10: Search Trees
 < 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 Chapter 10: Search Trees Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++,
< 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 Chapter 10: Search Trees Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++,
Binary Search Trees > = 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser. Binary Search Trees 1
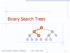 Binary Search Trees < > = Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionary (Map) ADT get (k): record with key k put (k,data): add record (k,data) remove (k): delete record with key k smallest(): record with smallest
Binary Search Trees < > = Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionary (Map) ADT get (k): record with key k put (k,data): add record (k,data) remove (k): delete record with key k smallest(): record with smallest
CPSC 331 Term Test #2 March 26, 2007
 CPSC 331 Term Test #2 March 26, 2007 Name: Please DO NOT write your ID number on this page. Instructions: Answer all questions in the space provided. Point form answers are acceptable if complete enough
CPSC 331 Term Test #2 March 26, 2007 Name: Please DO NOT write your ID number on this page. Instructions: Answer all questions in the space provided. Point form answers are acceptable if complete enough
CS251-SE1. Midterm 2. Tuesday 11/1 8:00pm 9:00pm. There are 16 multiple-choice questions and 6 essay questions.
 CS251-SE1 Midterm 2 Tuesday 11/1 8:00pm 9:00pm There are 16 multiple-choice questions and 6 essay questions. Answer the multiple choice questions on your bubble sheet. Answer the essay questions in the
CS251-SE1 Midterm 2 Tuesday 11/1 8:00pm 9:00pm There are 16 multiple-choice questions and 6 essay questions. Answer the multiple choice questions on your bubble sheet. Answer the essay questions in the
Priority Queues Goodrich, Tamassia. Priority Queues 1
 Priority Queues Priority Queues 1 Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insert(k, x) inserts an entry
Priority Queues Priority Queues 1 Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insert(k, x) inserts an entry
Priority Queues. Priority Queue. Keys and Total Order Relations. The Priority Queue ADT
 Priority Queues Priority Queue The priority queue ADT Implementing a priority queue with a Elementary sorting using a Priority Queue Issues in sorting Queue where we can insert in any order. When we remove
Priority Queues Priority Queue The priority queue ADT Implementing a priority queue with a Elementary sorting using a Priority Queue Issues in sorting Queue where we can insert in any order. When we remove
Subject : Computer Science. Paper: Data Structures. Module: Priority Queue and Applications. Module No: CS/DS/14
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Data Structures Module: Priority Queue and Applications Module No: CS/DS/14 Quadrant 1- e-text Welcome to the e-pg Pathshala Lecture Series on Data Structures.
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Data Structures Module: Priority Queue and Applications Module No: CS/DS/14 Quadrant 1- e-text Welcome to the e-pg Pathshala Lecture Series on Data Structures.
Priority Queues. Lecture15: Heaps. Priority Queue ADT. Sequence based Priority Queue
 Priority Queues (0F) Lecture: Heaps Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH bhhan@postech.ac.kr Queues Stores items (keys) in a linear list or array FIFO (First In First Out) Stored items do not have priorities. Priority
Priority Queues (0F) Lecture: Heaps Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH bhhan@postech.ac.kr Queues Stores items (keys) in a linear list or array FIFO (First In First Out) Stored items do not have priorities. Priority
FINALTERM EXAMINATION Fall 2009 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one The data of the problem is of 2GB and the hard
 FINALTERM EXAMINATION Fall 2009 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 The data of the problem is of 2GB and the hard disk is of 1GB capacity, to solve this problem we should Use better data structures
FINALTERM EXAMINATION Fall 2009 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 The data of the problem is of 2GB and the hard disk is of 1GB capacity, to solve this problem we should Use better data structures
Stacks, Queues, and Priority Queues. Inf 2B: Heaps and Priority Queues. The PriorityQueue ADT
 Stacks, Queues, and Priority Queues Inf 2B: Heaps and Priority Queues Lecture 6 of ADS thread Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Stacks, queues, and priority queues are all
Stacks, Queues, and Priority Queues Inf 2B: Heaps and Priority Queues Lecture 6 of ADS thread Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Stacks, queues, and priority queues are all
Lecture 7. Transform-and-Conquer
 Lecture 7 Transform-and-Conquer 6-1 Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a transformation to a simpler/more convenient instance of the same problem (instance simplification)
Lecture 7 Transform-and-Conquer 6-1 Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a transformation to a simpler/more convenient instance of the same problem (instance simplification)
(2,4) Trees. 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
CSE Data Structures and Introduction to Algorithms... In Java! Instructor: Fei Wang. Mid-Term Exam. CSE2100 DS & Algorithms 1
 CSE 2100 Data Structures and Introduction to Algorithms...! In Java!! Instructor: Fei Wang! Mid-Term Exam CSE2100 DS & Algorithms 1 1. True or False (20%=2%x10)! (1) O(n) is O(n^2) (2) The height h of
CSE 2100 Data Structures and Introduction to Algorithms...! In Java!! Instructor: Fei Wang! Mid-Term Exam CSE2100 DS & Algorithms 1 1. True or False (20%=2%x10)! (1) O(n) is O(n^2) (2) The height h of
Summer Final Exam Review Session August 5, 2009
 15-111 Summer 2 2009 Final Exam Review Session August 5, 2009 Exam Notes The exam is from 10:30 to 1:30 PM in Wean Hall 5419A. The exam will be primarily conceptual. The major emphasis is on understanding
15-111 Summer 2 2009 Final Exam Review Session August 5, 2009 Exam Notes The exam is from 10:30 to 1:30 PM in Wean Hall 5419A. The exam will be primarily conceptual. The major emphasis is on understanding
Priority Queues 3/19/14
 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Priority Queues Priority Queues 1 Priority
Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Priority Queues Priority Queues 1 Priority
CSE 332 Autumn 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators)
 Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Autumn 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Autumn 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Final Exam. EECS 2011 Prof. J. Elder - 1 -
 Final Exam Ø Wed Apr 11 2pm 5pm Aviva Tennis Centre Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps and hash tables, binary search, loop
Final Exam Ø Wed Apr 11 2pm 5pm Aviva Tennis Centre Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps and hash tables, binary search, loop
CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By
 CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By Abstract Data Type : A set of data values and associated operations that are precisely specified independent of any particular implementation. Also known as ADT Algorithm
CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By Abstract Data Type : A set of data values and associated operations that are precisely specified independent of any particular implementation. Also known as ADT Algorithm
DataStruct 8. Heaps and Priority Queues
 2013-2 DataStruct 8. Heaps and Priority Queues Michael T. Goodrich, et. al, Data Structures and Algorithms in C++, 2 nd Ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2011. November 13, 2013 Advanced Networking Technology
2013-2 DataStruct 8. Heaps and Priority Queues Michael T. Goodrich, et. al, Data Structures and Algorithms in C++, 2 nd Ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2011. November 13, 2013 Advanced Networking Technology
(2,4) Trees Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
DATA STRUCTURE : A MCQ QUESTION SET Code : RBMCQ0305
 Q.1 If h is any hashing function and is used to hash n keys in to a table of size m, where n
Q.1 If h is any hashing function and is used to hash n keys in to a table of size m, where n
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING E&CE 250 ALGORITHMS AND DATA STRUCTURES
 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING E&CE 250 ALGORITHMS AND DATA STRUCTURES Final Examination Instructors: RESeviora and LTahvildari 3 hrs, Apr, 200 Name: Student ID:
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING E&CE 250 ALGORITHMS AND DATA STRUCTURES Final Examination Instructors: RESeviora and LTahvildari 3 hrs, Apr, 200 Name: Student ID:
Module 2: Classical Algorithm Design Techniques
 Module 2: Classical Algorithm Design Techniques Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Associate Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Module
Module 2: Classical Algorithm Design Techniques Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Associate Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Module
CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms
 CE 2 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 6: Priority Queues (Binary Heaps) Text: Read Weiss, 6.1 6.3 Izmir University of Economics 1 A kind of queue Priority Queue (Heap) Dequeue gets element with the
CE 2 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 6: Priority Queues (Binary Heaps) Text: Read Weiss, 6.1 6.3 Izmir University of Economics 1 A kind of queue Priority Queue (Heap) Dequeue gets element with the
BINARY HEAP cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015
 BINARY HEAP cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 10 is due on Thursday -midterm grades out tomorrow 3 last time 4 -a hash table is a general storage
BINARY HEAP cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 10 is due on Thursday -midterm grades out tomorrow 3 last time 4 -a hash table is a general storage
CSE 332 Winter 2015: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators)
 _ UWNetID: Lecture Section: A CSE 332 Winter 2015: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will give
_ UWNetID: Lecture Section: A CSE 332 Winter 2015: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will give
R10 SET - 1. Code No: R II B. Tech I Semester, Supplementary Examinations, May
 Code No: R21051 R10 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester, Supplementary Examinations, May - 2012 DATA STRUCTURES (Com. to CSE, IT, ECC ) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry
Code No: R21051 R10 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester, Supplementary Examinations, May - 2012 DATA STRUCTURES (Com. to CSE, IT, ECC ) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry
CSE 214 Computer Science II Searching
 CSE 214 Computer Science II Searching Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Introduction Searching in a
CSE 214 Computer Science II Searching Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Introduction Searching in a
Round 3: Trees. Tommi Junttila. Aalto University School of Science Department of Computer Science. CS-A1140 Data Structures and Algorithms Autumn 2017
 Round 3: Trees Tommi Junttila Aalto University School of Science Department of Computer Science CS-A1140 Data Structures and Algorithms Autumn 2017 Tommi Junttila (Aalto University) Round 3 CS-A1140 /
Round 3: Trees Tommi Junttila Aalto University School of Science Department of Computer Science CS-A1140 Data Structures and Algorithms Autumn 2017 Tommi Junttila (Aalto University) Round 3 CS-A1140 /
MID TERM MEGA FILE SOLVED BY VU HELPER Which one of the following statement is NOT correct.
 MID TERM MEGA FILE SOLVED BY VU HELPER Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the elements may locate at far positions
MID TERM MEGA FILE SOLVED BY VU HELPER Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the elements may locate at far positions
COMP250: Priority queue ADT, Heaps. Lecture 23 Jérôme Waldispühl School of Computer Science McGill University
 COMP250: Priority queue ADT, Heaps Lecture 23 Jérôme Waldispühl School of Computer Science McGill University Priority queue ADT Like a dictionary, a priority queue stores a set of pairs (key, info) The
COMP250: Priority queue ADT, Heaps Lecture 23 Jérôme Waldispühl School of Computer Science McGill University Priority queue ADT Like a dictionary, a priority queue stores a set of pairs (key, info) The
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
ASSIGNMENTS. Progra m Outcom e. Chapter Q. No. Outcom e (CO) I 1 If f(n) = Θ(g(n)) and g(n)= Θ(h(n)), then proof that h(n) = Θ(f(n))
 ASSIGNMENTS Chapter Q. No. Questions Course Outcom e (CO) Progra m Outcom e I 1 If f(n) = Θ(g(n)) and g(n)= Θ(h(n)), then proof that h(n) = Θ(f(n)) 2 3. What is the time complexity of the algorithm? 4
ASSIGNMENTS Chapter Q. No. Questions Course Outcom e (CO) Progra m Outcom e I 1 If f(n) = Θ(g(n)) and g(n)= Θ(h(n)), then proof that h(n) = Θ(f(n)) 2 3. What is the time complexity of the algorithm? 4
Definition of a Heap. Heaps. Priority Queues. Example. Implementation using a heap. Heap ADT
 Heaps Definition of a heap What are they for: priority queues Insertion and deletion into heaps Implementation of heaps Heap sort Not to be confused with: heap as the portion of computer memory available
Heaps Definition of a heap What are they for: priority queues Insertion and deletion into heaps Implementation of heaps Heap sort Not to be confused with: heap as the portion of computer memory available
CSE 332 Spring 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators)
 Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Spring 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Spring 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Computer Science E-22 Practice Final Exam
 name Computer Science E-22 This exam consists of three parts. Part I has 10 multiple-choice questions that you must complete. Part II consists of 4 multi-part problems, of which you must complete 3, and
name Computer Science E-22 This exam consists of three parts. Part I has 10 multiple-choice questions that you must complete. Part II consists of 4 multi-part problems, of which you must complete 3, and
Priority Queues and Binary Heaps
 Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland In this lecture, we will learn our first tree data structure called the binary heap which serves as an implementation of the priority queue. Priority Queue A priority
Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland In this lecture, we will learn our first tree data structure called the binary heap which serves as an implementation of the priority queue. Priority Queue A priority
University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Midterm Examination. ECE 345 Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 2012
 1 University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Examination ECE 345 Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 2012 Print your name and ID number neatly in the space provided
1 University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Examination ECE 345 Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 2012 Print your name and ID number neatly in the space provided
CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6
 CS Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6 Priority Queues and Heaps In this lecture, we will discuss priority queues, another important ADT. As stacks and queues, priority queues store arbitrary collections
CS Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6 Priority Queues and Heaps In this lecture, we will discuss priority queues, another important ADT. As stacks and queues, priority queues store arbitrary collections
CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 4
 CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 4 Hash Tables In this lecture, we will introduce a particularly efficient data structure for the Dictionary ADT. 4.1 Dictionaries A Dictionary stores key element
CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 4 Hash Tables In this lecture, we will introduce a particularly efficient data structure for the Dictionary ADT. 4.1 Dictionaries A Dictionary stores key element
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
COMP : Trees. COMP20012 Trees 219
 COMP20012 3: Trees COMP20012 Trees 219 Trees Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees Search Trees Family Trees Hierarchical Structures Management Directories COMP20012 Trees 220 Trees have natural
COMP20012 3: Trees COMP20012 Trees 219 Trees Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees Search Trees Family Trees Hierarchical Structures Management Directories COMP20012 Trees 220 Trees have natural
Priority Queues. INFO0902 Data Structures and Algorithms. Priority Queues (files à priorités) Keys. Priority Queues
 Priority Queues INFO0902 Data Structures and Algorithms Priority Queues Justus H. Piater Priority Queues (files à priorités) Keys Extract the top-priority element at any time. No notion of order, positions,
Priority Queues INFO0902 Data Structures and Algorithms Priority Queues Justus H. Piater Priority Queues (files à priorités) Keys Extract the top-priority element at any time. No notion of order, positions,
Final Exam. CSE 2011 Prof. J. Elder Last Updated: :41 PM
 Final Exam Ø Tue, 17 Apr 2012 19:00 22:00 LAS B Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps, hashing, binary search trees, sorting,
Final Exam Ø Tue, 17 Apr 2012 19:00 22:00 LAS B Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps, hashing, binary search trees, sorting,
! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges. ! Parent: source node of directed edge. ! Child: terminal node of directed edge
 Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
Priority Queues. Outline and Required Reading: The Priority Queue ADT ( 7.1) Implementing a Priority Queue with a Sequence ( 7.2)
 1 Priority Queues Outline and Required Reading: The Priority Queue ADT (.1) Implementing a Priority Queue with a Sequence (.2) COSC 20, Fall 200, Section A Instructor: N. Vlajic Keys 2 Key object / attribute
1 Priority Queues Outline and Required Reading: The Priority Queue ADT (.1) Implementing a Priority Queue with a Sequence (.2) COSC 20, Fall 200, Section A Instructor: N. Vlajic Keys 2 Key object / attribute
UNIT III BALANCED SEARCH TREES AND INDEXING
 UNIT III BALANCED SEARCH TREES AND INDEXING OBJECTIVE The implementation of hash tables is frequently called hashing. Hashing is a technique used for performing insertions, deletions and finds in constant
UNIT III BALANCED SEARCH TREES AND INDEXING OBJECTIVE The implementation of hash tables is frequently called hashing. Hashing is a technique used for performing insertions, deletions and finds in constant
Tree: non-recursive definition. Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps. Tree: recursive definition. Tree: example.
 Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI KUALA LUMPUR
 STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION PSD2023 ALGORITHM & DATA STRUCTURE DSEW-E-F-2/13 25 MAY 2015 9.00 AM
STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION PSD2023 ALGORITHM & DATA STRUCTURE DSEW-E-F-2/13 25 MAY 2015 9.00 AM
