Chapter 2: Basic Data Structures
|
|
|
- Clarissa Shepherd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2: Basic Data Structures
2 Basic Data Structures Stacks Queues Vectors, Linked Lists Trees (Including Balanced Trees) Priority Queues and Heaps Dictionaries and Hash Tables Spring 2014 CS 315 2
3 Two Definitions Depth of a node v in a tree is: n n 0 if v is root, else 1 + depth of parent of v Height of a node v is: n n 0 if external node 1 + max height of child of v Height of a tree is the maximum depth of an external node of the tree + 1 n Equivalently, maximum depth among all nodes + 1 n If we don t add the one, then tree with height h has h+1 levels! Spring 2014 CS 315 3
4 Heaps ( 2.4.3) A heap is a binary tree storing keys at its internal nodes and satisfying the following properties: n n Heap-Order: for every internal node v other than the root, key(v) key(parent(v)) Complete Binary Tree: let h be the height of the heap w for i = 0,, h 2, there are 2 i nodes of depth i w at depth h-1, the internal nodes are to the left of the external nodes The last node of a heap is the rightmost internal node of depth h last node Spring 2014 CS 315 4
5 Height of a Heap ( 2.4.3) Theorem: A heap storing n keys has height O(log n) Proof: (we apply the complete binary tree property) n Let h be the height of a heap storing n keys n Since there are 2 i keys at depth i = 0,, h 2 and at least one key at depth h 1, we have n h = 2 h = 2 h-1 n Thus, n 2 h-1, i.e., h (log n) + 1 depth 0 1 h 2 h 1 keys h 2 1 Spring 2014 CS 315 5
6 Insertion into a Heap ( 2.4.3) The insertion algorithm consists of three steps n Find the insertion node z (the new last node) n Store k at z and expand z into an internal node n Restore the heap-order property (discussed next) z insertion node 5 z Spring 2014 CS 315
7 Upheap After the insertion of a new key k, the heap-order property may be violated Algorithm upheap restores the heap-order property by swapping k along an upward path from the insertion node Upheap terminates when the key k reaches the root or a node whose parent has a key smaller than or equal to k Since a heap has height O(log n), upheap runs in O(log n) time z 1 5 z Spring 2014 CS 315 7
8 Removal from a Heap ( 2.4.3) Method removemin of the priority queue (?) ADT corresponds to the removal of the root key from the heap The removal algorithm consists of three steps n n n Replace the root key with the key of the last node w Compress w and its children into a leaf Restore the heap-order property (discussed next) w w 7 2 last node Spring 2014 CS 315 8
9 Downheap After replacing the root key with the key k of the last node, the heap-order property may be violated Algorithm downheap restores the heap-order property by swapping key k along a downward path from the root Downheap terminates when key k reaches a leaf or a node whose children have keys greater than or equal to k Since a heap has height O(log n), downheap runs in O(log n) time w 7 w 9 9 Spring 2014 CS 315 9
10 Heap-Sort ( 2.4.4) Consider a priority queue with n items implemented by means of a heap n n n the space used is O(n) methods insertitem and removemin take O(log n) time methods size, isempty, minkey, and minelement take time O(1) time Using a heap-based priority queue, we can sort a sequence of n elements in O(n log n) time The resulting algorithm is called heap-sort Heap-sort is much faster than quadratic sorting algorithms, such as insertion-sort and selection-sort Spring 2014 CS
11 Vector-based Heap Implementation ( 2.4.3) We can represent a heap with n keys by means of a vector of length n + 1 For the node at rank (index) i n the left child is at rank 2i n the right child is at rank 2i + 1 Links between nodes are not explicitly stored The leaves are not represented The cell of at rank 0 is not used Operation insertitem corresponds to inserting at rank n + 1 Operation removemin corresponds to removing at rank n (and placing in position 1) Yields in-place heap-sort Spring 2014 CS
12 Building a Heap with n nodes Just perform n insertions: O(n log n) If you know the values of all keys beforehand, can be done in O(n) time (see next few slides) Spring 2014 CS
13 Merging Two Heaps We are given two two heaps and a key k We create a new heap with the root node storing k and with the two heaps as subtrees We perform downheap to restore the heap-order property Spring 2014 CS
14 Bottom-up Heap Construction ( 2.4.3) We can construct in O(n) time a heap storing n given keys by using a bottom-up construction with log n phases In phase i, pairs of heaps with 2 i 1 keys are merged into heaps with 2 i +1 1 keys 2 i 1 2 i 1 2 i +1 1 Spring 2014 CS
15 Example Spring 2014 CS
16 Example (contd.) Spring 2014 CS 315 1
17 Example (contd.) Spring 2014 CS
18 Example (end) Spring 2014 CS
19 Analysis Consider an internal node v in the completed heap, and in particular the subtree (in the heap) rooted at v. The time to build this subtree (given the completed subtrees rooted at each child of v) is proportional to the height of the subtree. Now consider the path that starts at v, and then goes first through the right child of v, then repeatedly goes through left children until the bottom of the heap (this path may differ from the actual downheap path) (This goes from v to its inorder external successor). The length of this path equals the height of the subtree rooted at T Thus the time cost of constructing the heap is equal to the sum of the lengths of these paths (one path for each v) Spring 2014 CS
20 Analysis For any distinct internal nodes, these proxy paths share no edges (though they may share nodes). Thus the sum of the lengths of the paths is no more than the number of edges in the heap, which is clearly less than 2n. Thus, bottom-up heap construction runs in O(n) time Bottom-up heap construction is thus faster than n successive insertions, provided we have all of the key values prior to building the heap. Spring 2014 CS
21 Binary Search
22 Dictionary ADT A dictionary is simply a data structure that stores key value pairs (like a paper dictionary). n Ex. hashtable Spring 2014 CS
23 Binary Search Binary search performs operation findelement(k) on a dictionary implemented by means of an array-based sequence, sorted by key n n n similar to looking through a phone book for a name at each step, the number of candidate items is halved terminates after O(log n) steps Example: findelement(7) 0 l 0 l m h m h l m h l=m =h Spring 2014 CS
24 Lookup Table A lookup table is a dictionary implemented by means of a sorted sequence n We store the items of the dictionary in an array-based sequence, sorted by key n We use an external comparator for the keys Performance: n findelement takes O(log n) time, using binary search n insertitem takes O(n) time since in the worst case we have to shift n items to make room for the new item n removeelement take O(n) time since in the worst case we have to shift n items to compact the items after the removal The lookup table is effective only for dictionaries of small size or for dictionaries on which searches are the most common operations, while insertions and removals are rarely performed (e.g., credit card authorizations) Spring 2014 CS
25 Now for the Data Structures Pretty much all variations on the binary search tree theme
26 Binary Search Tree A binary search tree is a binary tree storing keys (or key-element pairs) at its internal nodes and satisfying the following property: n Let u, v, and w be three nodes such that u is in the left subtree of v and w is in the right subtree of v. We have key(u) key(v) key(w) External nodes do not store items An inorder traversal of a binary search trees visits the keys in increasing order Spring 2014 CS 315 2
27 Search To search for a key k, we trace a downward path starting at the root The next node visited depends on the outcome of the comparison of k with the key of the current node If we reach a leaf, the key is not found and we return NO_SUCH_KEY Example: findelement(4) Algorithm findelement(k, v) if T.isExternal (v) return NO_SUCH_KEY if k < key(v) return findelement(k, T.leftChild(v)) else if k = key(v) return element(v) else { k > key(v) } return findelement(k, T.rightChild(v)) < 2 > 1 4 = 8 9 Spring 2014 CS
28 Performance Consider a dictionary with n items implemented by means of a binary search tree of height h n the space used is O(n) n methods findelement, insertitem and removeelement take O(h) time The height h is O(n) in the worst case and O(log n) in the best case Spring 2014 CS
29 AVL Trees v z
30 AVL Tree Definition AVL trees are balanced. An AVL Tree is a binary search tree such that for every internal node v of T, the heights of the children of v can differ by at most 1. An example of an AVL tree where the heights are shown next to the nodes: Spring 2014 CS
31 n(2) 3 Height of an AVL Tree 4 n(1) Fact: The height of an AVL tree storing n keys is O(log n). Proof: First, we re trying to bound the height of a tree with n keys. Let s come at this the reverse way, and find the lower bound on the minimum number of internal nodes, n (h), that a tree with height h must have. n Claim that n(h) grows exponentially. From this it will be easy to show that height of tree with n nodes is O(log n). So, formally, let n(h) be the minimum number of internal nodes of an AVL tree of height h. We easily see that n(1) = 1 and n(2) = 2 Spring 2014 CS
32 n(2) 3 Height of an AVL Tree 4 n(1) For h > 2, an AVL tree of height h with minimal number of nodes contains the root node, one AVL subtree of height h-1 and another of height h-2. That is, n(h) = 1 + n(h-1) + n(h-2) Knowing n(h-1) > n(h-2), we get n(h) > 2n(h-2). This indicates that n(h) at least doubles every time we increase h by two, which intuitively says that n(h) grows at least exponentially. Let s show this By induction, n(h) > 2n(h-2), n(h) > 4n(h-4), n(h) > 8n(n-),, which implies that n(h) > 2 i n(h-2i) n This holds for any positive integer i such that h-2i is positive. So, choose i so that we get a base case. That is, we want i such that either h-2i = 1 or h-2i = 2. I.e. i = (h/2)-1 or i=(h/2)-(1/2). Spring 2014 CS
33 n(2) 3 Height of an AVL Tree 4 n(1) Taking logarithms: h < 2log n(h) +2 But n(h) is the minimum number of internal nodes of an AVL tree with height h. So if an AVL tree has height h and n nodes, we have n(h) n, so that: h < 2 log n + 2 Thus the height of an AVL tree is O(log n) Spring 2014 CS
34 Where Are We? Ok, so the height of an AVL tree is O(log n). This is nice n We can search in time O(log n). But n Can we insert and delete nodes from tree in time O(log n)? Remember, we need to preserve the AVL height balancing property! Spring 2014 CS
35 Yes, we can! And you re welcome to read about it in the text and the next few slides.
36 Yes, we can! And you re welcome to read about it in the text and the next few slides.or not.
37 Insertion in an AVL Tree Insertion is as in a binary search tree (may violate AVL property!) Always done by expanding an external node. Example: a=y c=z b=x Note that only nodes on path from w to root can now be unbalanced before insertion of 54 Spring 2014 CS w 54 after insertion
38 Restoring Balance We use a search and repair strategy Let z be first unbalanced node encountered on path from w up toward root Let y be child of z with higher height (not y must be an ancestor of w), and x be child of y with higher height (in case of tie, go with child that is ancestor of w) Spring 2014 CS
39 Trinode Restructuring let (a,b,c) be an inorder listing of x, y, z perform the rotations needed to make b the topmost node of the three a=z b=y (other two cases are symmetrical) a=z c=y case 2: double rotation (a right rotation about c, then a left rotation about a) T 0 c=x T 0 b=x T 1 b=y T 3 b=x T 2 T 3 a=z c=x T 1 T 2 a=z c=y case 1: single rotation (a left rotation about a) T 0 T 1 T 2 T 3 T 0 T 1 T 2 T 3 Spring 2014 CS
40 Insertion Example, continued unbalanced... T 1...balanced y x z 88 1 T 2 T 0 T 1 T 3 Spring 2014 CS
41 Restructuring (as Single Rotations) Single Rotations: Spring 2014 CS
42 Restructuring (as Double double rotations: Spring 2014 CS
43 Removal in an AVL Tree Removal begins as in a binary search tree, which means the node removed will become an empty external node. Its parent, w, may cause an imbalance. Example: before deletion of 32 after deletion Spring 2014 CS
44 Rebalancing after a Removal Let z be the first unbalanced node encountered while travelling up the tree from w. Also, let y be the child of z with the larger height, and let x be the child of y with the larger height. We perform restructure(x) to restore balance at z. As this restructuring may upset the balance of another node higher in the tree, we must continue checking for balance until the root of T is reached a=z 44 2 w 17 2 b=y c=x Spring 2014 CS
45 Running Times for a single restructure is O(1) n using a linked-structure binary tree find is O(log n) n height of tree is O(log n), no restructures needed insert is O(log n) n initial find is O(log n) n Restructuring up the tree, maintaining heights is O(log n) remove is O(log n) n initial find is O(log n) n Restructuring up the tree, maintaining heights is O(log n) Spring 2014 CS
Search Trees (Ch. 9) > = Binary Search Trees 1
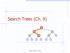 Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
Chapter 10: Search Trees
 < 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 Chapter 10: Search Trees Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++,
< 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 Chapter 10: Search Trees Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++,
Heaps. 2/13/2006 Heaps 1
 Heaps /13/00 Heaps 1 Outline and Reading What is a heap ( 8.3.1) Height of a heap ( 8.3.) Insertion ( 8.3.3) Removal ( 8.3.3) Heap-sort ( 8.3.) Arraylist-based implementation ( 8.3.) Bottom-up construction
Heaps /13/00 Heaps 1 Outline and Reading What is a heap ( 8.3.1) Height of a heap ( 8.3.) Insertion ( 8.3.3) Removal ( 8.3.3) Heap-sort ( 8.3.) Arraylist-based implementation ( 8.3.) Bottom-up construction
Priority Queues and Heaps. More Data Structures. Priority Queue ADT ( 2.4.1) Total Order Relation. Sorting with a Priority Queue ( 2.4.
 More Data Structures Priority Queues and Heaps Priority Queues, Comparators, Locators, Dictionaries More Data Structures v. More Data Structures v. Priority Queue ADT (.4.) Total Order Relation A priority
More Data Structures Priority Queues and Heaps Priority Queues, Comparators, Locators, Dictionaries More Data Structures v. More Data Structures v. Priority Queue ADT (.4.) Total Order Relation A priority
Heaps Goodrich, Tamassia. Heaps 1
 Heaps Heaps 1 Recall Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insert(k, x) inserts an entry with key k
Heaps Heaps 1 Recall Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insert(k, x) inserts an entry with key k
Heaps 2. Recall Priority Queue ADT. Heaps 3/19/14
 Heaps 3// Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 Heaps Heaps Recall Priority Queue ADT
Heaps 3// Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 Heaps Heaps Recall Priority Queue ADT
CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES. 3 8 z 4
 CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES v 6 3 8 z 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES v 6 3 8 z 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
Priority Queues and Heaps. Heaps and Priority Queues 1
 Priority Queues and Heaps 2 5 6 9 7 Heaps and Priority Queues 1 Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of items An item is a pair (key, element) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT
Priority Queues and Heaps 2 5 6 9 7 Heaps and Priority Queues 1 Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of items An item is a pair (key, element) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT
HEAPS: IMPLEMENTING EFFICIENT PRIORITY QUEUES
 HEAPS: IMPLEMENTING EFFICIENT PRIORITY QUEUES 2 5 6 9 7 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H., Wiley, 2014
HEAPS: IMPLEMENTING EFFICIENT PRIORITY QUEUES 2 5 6 9 7 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H., Wiley, 2014
AVL Trees (10.2) AVL Trees
 AVL Trees (0.) CSE 0 Winter 0 8 February 0 AVL Trees AVL trees are balanced. An AVL Tree is a binary search tree such that for every internal node v of T, the heights of the children of v can differ by
AVL Trees (0.) CSE 0 Winter 0 8 February 0 AVL Trees AVL trees are balanced. An AVL Tree is a binary search tree such that for every internal node v of T, the heights of the children of v can differ by
Dictionaries. 2/17/2006 Dictionaries 1
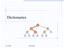 Dictionaries < 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 /17/006 Dictionaries 1 Outline and Reading Dictionary ADT ( 9.3) Log file ( 9.3.1) Binary search ( 9.3.3) Lookup table ( 9.3.3) Binary search tree ( 10.1) Search ( 10.1.1)
Dictionaries < 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 /17/006 Dictionaries 1 Outline and Reading Dictionary ADT ( 9.3) Log file ( 9.3.1) Binary search ( 9.3.3) Lookup table ( 9.3.3) Binary search tree ( 10.1) Search ( 10.1.1)
Search Trees - 1 Venkatanatha Sarma Y
 Search Trees - 1 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Search Trees - 1 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Priority Queue ADT ( 7.1) Heaps and Priority Queues 2. Comparator ADT ( 7.1.4) Total Order Relation. Using Comparators in C++
 Heaps and Priority Queues Priority Queue ADT (.) A priority queue stores a collection of items An item is a pair (key, element) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insertitem(k, o) inserts an item ith
Heaps and Priority Queues Priority Queue ADT (.) A priority queue stores a collection of items An item is a pair (key, element) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insertitem(k, o) inserts an item ith
Elementary Data Structures 2
 Elementary Data Structures Priority Queues, & Dictionaries Priority Queues Sell 00 IBM $ Sell 300 IBM $0 Buy 00 IBM $9 Buy 400 IBM $8 Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of items An
Elementary Data Structures Priority Queues, & Dictionaries Priority Queues Sell 00 IBM $ Sell 300 IBM $0 Buy 00 IBM $9 Buy 400 IBM $8 Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of items An
AVL Trees Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees 1
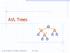 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 20 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees AVL Tree Definition Adelson-Velsky and Landis binary search tree balanced each internal node v the heights of the children of v can 2 3 7
AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 20 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees AVL Tree Definition Adelson-Velsky and Landis binary search tree balanced each internal node v the heights of the children of v can 2 3 7
Heaps and Priority Queues
 Heaps and Priority Queues Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce Priority Queue ADT To discuss and illustrate Priority Queues for sorting
Heaps and Priority Queues Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce Priority Queue ADT To discuss and illustrate Priority Queues for sorting
CH 8. HEAPS AND PRIORITY QUEUES
 CH 8. HEAPS AND PRIORITY QUEUES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
CH 8. HEAPS AND PRIORITY QUEUES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
Stores a collection of elements each with an associated key value
 CH9. PRIORITY QUEUES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 201) PRIORITY QUEUES Stores a collection
CH9. PRIORITY QUEUES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 201) PRIORITY QUEUES Stores a collection
CH. 8 PRIORITY QUEUES AND HEAPS
 CH. 8 PRIORITY QUEUES AND HEAPS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
CH. 8 PRIORITY QUEUES AND HEAPS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
AVL Tree Definition. An example of an AVL tree where the heights are shown next to the nodes. Adelson-Velsky and Landis
 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 0 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser
Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 0 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser
Describe how to implement deque ADT using two stacks as the only instance variables. What are the running times of the methods
 Describe how to implement deque ADT using two stacks as the only instance variables. What are the running times of the methods 1 2 Given : Stack A, Stack B 3 // based on requirement b will be reverse of
Describe how to implement deque ADT using two stacks as the only instance variables. What are the running times of the methods 1 2 Given : Stack A, Stack B 3 // based on requirement b will be reverse of
Sorting. Outline. Sorting with a priority queue Selection-sort Insertion-sort Heap Sort Quick Sort
 Sorting Hiroaki Kobayashi 1 Outline Sorting with a priority queue Selection-sort Insertion-sort Heap Sort Quick Sort Merge Sort Lower Bound on Comparison-Based Sorting Bucket Sort and Radix Sort Hiroaki
Sorting Hiroaki Kobayashi 1 Outline Sorting with a priority queue Selection-sort Insertion-sort Heap Sort Quick Sort Merge Sort Lower Bound on Comparison-Based Sorting Bucket Sort and Radix Sort Hiroaki
Heaps Outline and Required Reading: Heaps ( 7.3) COSC 2011, Fall 2003, Section A Instructor: N. Vlajic
 1 Heaps Outline and Required Reading: Heaps (.3) COSC 2011, Fall 2003, Section A Instructor: N. Vlajic Heap ADT 2 Heap binary tree (T) that stores a collection of keys at its internal nodes and satisfies
1 Heaps Outline and Required Reading: Heaps (.3) COSC 2011, Fall 2003, Section A Instructor: N. Vlajic Heap ADT 2 Heap binary tree (T) that stores a collection of keys at its internal nodes and satisfies
Binary Search Trees > = 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser. Binary Search Trees 1
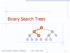 Binary Search Trees < > = Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionary (Map) ADT get (k): record with key k put (k,data): add record (k,data) remove (k): delete record with key k smallest(): record with smallest
Binary Search Trees < > = Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionary (Map) ADT get (k): record with key k put (k,data): add record (k,data) remove (k): delete record with key k smallest(): record with smallest
Priority Queues. Reading: 7.1, 7.2
 Priority Queues Reading: 7.1, 7.2 Generalized sorting Sometimes we need to sort but The data type is not easily mapped onto data we can compare (numbers, strings, etc) The sorting criteria changes depending
Priority Queues Reading: 7.1, 7.2 Generalized sorting Sometimes we need to sort but The data type is not easily mapped onto data we can compare (numbers, strings, etc) The sorting criteria changes depending
Priority Queues. Outline. COMP9024: Data Structures and Algorithms. Priority Queue ADT. Total Order Relations. Entry ADT
 COMP0: Data Structures and Algorithms Week Seven: Priority Queues Hui Wu Outline Priority Queues Heaps Adaptable Priority Queues Session, 0 http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs0 Priority Queue ADT Priority Queues
COMP0: Data Structures and Algorithms Week Seven: Priority Queues Hui Wu Outline Priority Queues Heaps Adaptable Priority Queues Session, 0 http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs0 Priority Queue ADT Priority Queues
Data Structures and Algorithms " Priority Queues!
 Data Structures and Algorithms " Priority Queues! Outline" Priority Queues! Heaps! Adaptable Priority Queues! Priority Queues" Priority Queue ADT" A priority queue stores a collection of entries! Each
Data Structures and Algorithms " Priority Queues! Outline" Priority Queues! Heaps! Adaptable Priority Queues! Priority Queues" Priority Queue ADT" A priority queue stores a collection of entries! Each
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Page 1 BFH-TI: Softwareschule Schweiz Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Dr. CAS SD01 Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Page Outline Ordered
Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Page 1 BFH-TI: Softwareschule Schweiz Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Dr. CAS SD01 Ordered Dictionaries and Binary Search Trees Page Outline Ordered
SEARCHING. the dictionary ADT. binary search. binary search trees. Searching
 the dictionary ADT binary search binary search trees SEARCHING 44 17 78 32 50 88 48 62 1 The Dictionary ADT a dictionary is an abstract model of a database like a priority queue, a dictionary stores key-element
the dictionary ADT binary search binary search trees SEARCHING 44 17 78 32 50 88 48 62 1 The Dictionary ADT a dictionary is an abstract model of a database like a priority queue, a dictionary stores key-element
Advanced Set Representation Methods
 Advanced Set Representation Methods AVL trees. 2-3(-4) Trees. Union-Find Set ADT DSA - lecture 4 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1 Advanced Set Representation. AVL Trees Problem with BSTs: worst case operation
Advanced Set Representation Methods AVL trees. 2-3(-4) Trees. Union-Find Set ADT DSA - lecture 4 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1 Advanced Set Representation. AVL Trees Problem with BSTs: worst case operation
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Berner Fachhochschule - Technik und Informatik Data Structures and Algorithms Heaps and Priority Queues Philipp Locher FS 2018 Heaps and Priority Queues Page 1 Outline Heaps Heap-Sort Priority Queues Heaps
Berner Fachhochschule - Technik und Informatik Data Structures and Algorithms Heaps and Priority Queues Philipp Locher FS 2018 Heaps and Priority Queues Page 1 Outline Heaps Heap-Sort Priority Queues Heaps
Data Structures Lecture 7
 Fall 2017 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Management Information Systems, National Chengchi University Data Structures Lecture 7 Recap We have talked about object oriented programing Chapter 1, 2,
Fall 2017 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Management Information Systems, National Chengchi University Data Structures Lecture 7 Recap We have talked about object oriented programing Chapter 1, 2,
In a postorder traversal, a node is visited after its descendants Application: compute space used by files in a directory and its subdirectories 9 1
 What is a Tree Trees Stock Fraud Make Money Fast! Winning Lotto / Bank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes ith a parent-child relation
What is a Tree Trees Stock Fraud Make Money Fast! Winning Lotto / Bank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes ith a parent-child relation
Algorithms. AVL Tree
 Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Height of a Heap. Heaps. 1. Insertion into a Heap. Heaps and Priority Queues. The insertion algorithm consists of three steps
 Heaps A heap is a binary tree storing keys at its nodes and satisfying the folloing properties:! Heap-Order: " for every internal node v other than the root, key(v)! key(parent(v))! Complete Binary Tree:
Heaps A heap is a binary tree storing keys at its nodes and satisfying the folloing properties:! Heap-Order: " for every internal node v other than the root, key(v)! key(parent(v))! Complete Binary Tree:
Priority Queues & Heaps. Chapter 9
 Priority Queues & Heaps Chapter 9 The Java Collections Framework (Ordered Data Types) Interface Abstract Class Class Iterable Collection Queue Abstract Collection List Abstract Queue Abstract List Priority
Priority Queues & Heaps Chapter 9 The Java Collections Framework (Ordered Data Types) Interface Abstract Class Class Iterable Collection Queue Abstract Collection List Abstract Queue Abstract List Priority
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Priority Queues and Heaps Page 1 BFH-TI: Softwareschule Schweiz Priority Queues and Heaps Dr. CAS SD01 Priority Queues and Heaps Page 2 Outline Priority Queues Heaps Heap-Based Priority Queues Priority
Priority Queues and Heaps Page 1 BFH-TI: Softwareschule Schweiz Priority Queues and Heaps Dr. CAS SD01 Priority Queues and Heaps Page 2 Outline Priority Queues Heaps Heap-Based Priority Queues Priority
CSED233: Data Structures (2017F) Lecture9: Priority Queues and Heaps
 (2017F) Lecture9: Priority Queues and Heaps Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a coll ection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods
(2017F) Lecture9: Priority Queues and Heaps Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a coll ection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods
10.2 AVL Trees. Definition of an AVL Tree. 438 Chapter 10. Search Trees
 438 Chapter 10. Search Trees 10. AVL Trees In theprevioussection,wediscussedwhatshouldbeanefficientmapdatastructure, but the worst-case performance it achieves for the various operations is linear time,
438 Chapter 10. Search Trees 10. AVL Trees In theprevioussection,wediscussedwhatshouldbeanefficientmapdatastructure, but the worst-case performance it achieves for the various operations is linear time,
Priority Queues & Heaps. CS16: Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms Spring 2019
 Priority Queues & Heaps CS16: Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms Spring 2019 Outline Priority Queues Motivation ADT Implementation Heaps insert( ) and upheap( ) removemin( ) and downheap( ) Motivation
Priority Queues & Heaps CS16: Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms Spring 2019 Outline Priority Queues Motivation ADT Implementation Heaps insert( ) and upheap( ) removemin( ) and downheap( ) Motivation
Priority queues. Priority queues. Priority queue operations
 Priority queues March 30, 018 1 Priority queues The ADT priority queue stores arbitrary objects with priorities. An object with the highest priority gets served first. Objects with priorities are defined
Priority queues March 30, 018 1 Priority queues The ADT priority queue stores arbitrary objects with priorities. An object with the highest priority gets served first. Objects with priorities are defined
Binary Search Trees (10.1) Dictionary ADT (9.5.1)
 Binary Search Trees (10.1) CSE 011 Winter 011 4 March 011 1 Dictionary ADT (..1) The dictionary ADT models a searchable collection of keyelement items The main operations of a dictionary are searching,
Binary Search Trees (10.1) CSE 011 Winter 011 4 March 011 1 Dictionary ADT (..1) The dictionary ADT models a searchable collection of keyelement items The main operations of a dictionary are searching,
Binary Search Trees Treesort
 Treesort CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Friday, November 13, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005 2009
Treesort CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Friday, November 13, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005 2009
(2,4) Trees. 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
Self-Balancing Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
CS 240 Fall Mike Lam, Professor. Priority Queues and Heaps
 CS 240 Fall 2015 Mike Lam, Professor Priority Queues and Heaps Priority Queues FIFO abstract data structure w/ priorities Always remove item with highest priority Store key (priority) with value Store
CS 240 Fall 2015 Mike Lam, Professor Priority Queues and Heaps Priority Queues FIFO abstract data structure w/ priorities Always remove item with highest priority Store key (priority) with value Store
(2,4) Trees Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
Inf 2B: AVL Trees. Lecture 5 of ADS thread. Kyriakos Kalorkoti. School of Informatics University of Edinburgh
 Inf 2B: AVL Trees Lecture 5 of ADS thread Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Dictionaries A Dictionary stores key element pairs, called items. Several elements might have
Inf 2B: AVL Trees Lecture 5 of ADS thread Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Dictionaries A Dictionary stores key element pairs, called items. Several elements might have
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Priority Queues Outline Priority Queues 1 Priority Queues Jumping the Queue Priority Queues In normal queue, the mode of selection is first in,
Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Priority Queues Outline Priority Queues 1 Priority Queues Jumping the Queue Priority Queues In normal queue, the mode of selection is first in,
Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
Multiway Search Trees. Multiway-Search Trees (cont d)
 Multiway Search Trees Each internal node v of a multi-way search tree T has at least two children contains d-1 items, where d is the number of children of v an item is of the form (k i,x i ) for 1 i d-1,
Multiway Search Trees Each internal node v of a multi-way search tree T has at least two children contains d-1 items, where d is the number of children of v an item is of the form (k i,x i ) for 1 i d-1,
Trees. A tree is a directed graph with the property
 2: Trees Trees A tree is a directed graph with the property There is one node (the root) from which all other nodes can be reached by exactly one path. Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees
2: Trees Trees A tree is a directed graph with the property There is one node (the root) from which all other nodes can be reached by exactly one path. Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees
Stacks, Queues, and Priority Queues. Inf 2B: Heaps and Priority Queues. The PriorityQueue ADT
 Stacks, Queues, and Priority Queues Inf 2B: Heaps and Priority Queues Lecture 6 of ADS thread Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Stacks, queues, and priority queues are all
Stacks, Queues, and Priority Queues Inf 2B: Heaps and Priority Queues Lecture 6 of ADS thread Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Stacks, queues, and priority queues are all
CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6
 CS Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6 Priority Queues and Heaps In this lecture, we will discuss priority queues, another important ADT. As stacks and queues, priority queues store arbitrary collections
CS Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6 Priority Queues and Heaps In this lecture, we will discuss priority queues, another important ADT. As stacks and queues, priority queues store arbitrary collections
Splay Trees. Splay Trees 1
 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
CS 234. Module 8. November 15, CS 234 Module 8 ADT Priority Queue 1 / 22
 CS 234 Module 8 November 15, 2018 CS 234 Module 8 ADT Priority Queue 1 / 22 ADT Priority Queue Data: (key, element pairs) where keys are orderable but not necessarily distinct, and elements are any data.
CS 234 Module 8 November 15, 2018 CS 234 Module 8 ADT Priority Queue 1 / 22 ADT Priority Queue Data: (key, element pairs) where keys are orderable but not necessarily distinct, and elements are any data.
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 12: Heaps and Priority Queues MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 Heaps and Priority Queues 2 Priority Queues Heaps Priority Queue 3 QueueADT Objects are added and
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 12: Heaps and Priority Queues MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 Heaps and Priority Queues 2 Priority Queues Heaps Priority Queue 3 QueueADT Objects are added and
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 10: Search and Heaps MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Spring 2018 Search and Heaps 2 Linear Search Binary Search Introduction to trees Priority Queues Heaps Linear Search
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 10: Search and Heaps MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Spring 2018 Search and Heaps 2 Linear Search Binary Search Introduction to trees Priority Queues Heaps Linear Search
Analysis of Algorithms
 Analysis of Algorithms Trees-I Prof. Muhammad Saeed Tree Representation.. Analysis Of Algorithms 2 .. Tree Representation Analysis Of Algorithms 3 Nomenclature Nodes (13) Size (13) Degree of a node Depth
Analysis of Algorithms Trees-I Prof. Muhammad Saeed Tree Representation.. Analysis Of Algorithms 2 .. Tree Representation Analysis Of Algorithms 3 Nomenclature Nodes (13) Size (13) Degree of a node Depth
Search Trees - 2. Venkatanatha Sarma Y. Lecture delivered by: Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore. M.S Ramaiah School of Advanced Studies - Bangalore
 Search Trees - 2 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Search Trees - 2 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees. Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler
 Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Multiway Seach Tree: a new type of search trees: for ordered d dictionary
Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Multiway Seach Tree: a new type of search trees: for ordered d dictionary
CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6
 CS Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6 Priority Queues and Heaps In this lecture, we will discuss another important ADT: PriorityQueue. Like stacks and queues, priority queues store arbitrary collections
CS Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6 Priority Queues and Heaps In this lecture, we will discuss another important ADT: PriorityQueue. Like stacks and queues, priority queues store arbitrary collections
Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015
 Presentation for use ith the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Ch.03 Binary Search Trees Binary Search Binary search can perform nearest neighbor queries
Presentation for use ith the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Ch.03 Binary Search Trees Binary Search Binary search can perform nearest neighbor queries
/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Priority Queues / Heaps Date: 9/27/17
 01.433/33 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Priority Queues / Heaps Date: 9/2/1.1 Introduction In this lecture we ll talk about a useful abstraction, priority queues, which are
01.433/33 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Priority Queues / Heaps Date: 9/2/1.1 Introduction In this lecture we ll talk about a useful abstraction, priority queues, which are
AVL Trees. (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 17
 AVL Trees (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 17 Balanced Binary Tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time
AVL Trees (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 17 Balanced Binary Tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time
Priority Queues Heaps Heapsort
 Priority Queues Heaps Heapsort After this lesson, you should be able to apply the binary heap insertion and deletion algorithms by hand implement the binary heap insertion and deletion algorithms explain
Priority Queues Heaps Heapsort After this lesson, you should be able to apply the binary heap insertion and deletion algorithms by hand implement the binary heap insertion and deletion algorithms explain
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Binary Search Tree - Best Time All BST operations are O(d), where d is tree depth minimum d is d = ëlog for a binary tree
CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Binary Search Tree - Best Time All BST operations are O(d), where d is tree depth minimum d is d = ëlog for a binary tree
Final Exam. EECS 2011 Prof. J. Elder - 1 -
 Final Exam Ø Wed Apr 11 2pm 5pm Aviva Tennis Centre Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps and hash tables, binary search, loop
Final Exam Ø Wed Apr 11 2pm 5pm Aviva Tennis Centre Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps and hash tables, binary search, loop
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS. Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap Summary of the previous lecture TREE is hierarchical (non linear) data structure Binary trees Definitions Full tree,
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap Summary of the previous lecture TREE is hierarchical (non linear) data structure Binary trees Definitions Full tree,
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Balanced search trees Balanced search tree: A search-tree data structure for which a height of O(lg n) is guaranteed when
CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Balanced search trees Balanced search tree: A search-tree data structure for which a height of O(lg n) is guaranteed when
Multi-Way Search Trees
 Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
We will show that the height of a RB tree on n vertices is approximately 2*log n. In class I presented a simple structural proof of this claim:
 We have seen that the insert operation on a RB takes an amount of time proportional to the number of the levels of the tree (since the additional operations required to do any rebalancing require constant
We have seen that the insert operation on a RB takes an amount of time proportional to the number of the levels of the tree (since the additional operations required to do any rebalancing require constant
COMP171. AVL-Trees (Part 1)
 COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
Priority Queues. T. M. Murali. January 23, T. M. Murali January 23, 2008 Priority Queues
 Priority Queues T. M. Murali January 23, 2008 Motivation: Sort a List of Numbers Sort INSTANCE: Nonempty list x 1, x 2,..., x n of integers. SOLUTION: A permutation y 1, y 2,..., y n of x 1, x 2,..., x
Priority Queues T. M. Murali January 23, 2008 Motivation: Sort a List of Numbers Sort INSTANCE: Nonempty list x 1, x 2,..., x n of integers. SOLUTION: A permutation y 1, y 2,..., y n of x 1, x 2,..., x
Lecture 7. Transform-and-Conquer
 Lecture 7 Transform-and-Conquer 6-1 Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a transformation to a simpler/more convenient instance of the same problem (instance simplification)
Lecture 7 Transform-and-Conquer 6-1 Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a transformation to a simpler/more convenient instance of the same problem (instance simplification)
Priority Queues. T. M. Murali. January 29, 2009
 Priority Queues T. M. Murali January 29, 2009 Motivation: Sort a List of Numbers Sort INSTANCE: Nonempty list x 1, x 2,..., x n of integers. SOLUTION: A permutation y 1, y 2,..., y n of x 1, x 2,..., x
Priority Queues T. M. Murali January 29, 2009 Motivation: Sort a List of Numbers Sort INSTANCE: Nonempty list x 1, x 2,..., x n of integers. SOLUTION: A permutation y 1, y 2,..., y n of x 1, x 2,..., x
CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By
 CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By Abstract Data Type : A set of data values and associated operations that are precisely specified independent of any particular implementation. Also known as ADT Algorithm
CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By Abstract Data Type : A set of data values and associated operations that are precisely specified independent of any particular implementation. Also known as ADT Algorithm
Ch04 Balanced Search Trees
 Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
Balanced Search Trees. CS 3110 Fall 2010
 Balanced Search Trees CS 3110 Fall 2010 Some Search Structures Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Balanced Search Trees CS 3110 Fall 2010 Some Search Structures Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Binary Search Trees, etc.
 Chapter 12 Binary Search Trees, etc. Binary Search trees are data structures that support a variety of dynamic set operations, e.g., Search, Minimum, Maximum, Predecessors, Successors, Insert, and Delete.
Chapter 12 Binary Search Trees, etc. Binary Search trees are data structures that support a variety of dynamic set operations, e.g., Search, Minimum, Maximum, Predecessors, Successors, Insert, and Delete.
10/23/2013. AVL Trees. Height of an AVL Tree. Height of an AVL Tree. AVL Trees
 // AVL Trees AVL Trees An AVL tree is a binary search tree with a balance condition. AVL is named for its inventors: Adel son-vel skii and Landis AVL tree approximates the ideal tree (completely balanced
// AVL Trees AVL Trees An AVL tree is a binary search tree with a balance condition. AVL is named for its inventors: Adel son-vel skii and Landis AVL tree approximates the ideal tree (completely balanced
CS350: Data Structures AVL Trees
 S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
Binary heaps (chapters ) Leftist heaps
 Binary heaps (chapters 20.3 20.5) Leftist heaps Binary heaps are arrays! A binary heap is really implemented using an array! 8 18 29 20 28 39 66 Possible because of completeness property 37 26 76 32 74
Binary heaps (chapters 20.3 20.5) Leftist heaps Binary heaps are arrays! A binary heap is really implemented using an array! 8 18 29 20 28 39 66 Possible because of completeness property 37 26 76 32 74
SFU CMPT Lecture: Week 9
 SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 1 Lecture: Week 9 SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 Lecture: Week 9 Ján Maňuch E-mail: jmanuch@sfu.ca Lecture on July 8, 2008, 5.30pm-8.20pm SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 2 Lecture: Week 9 Binary search trees
SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 1 Lecture: Week 9 SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 Lecture: Week 9 Ján Maňuch E-mail: jmanuch@sfu.ca Lecture on July 8, 2008, 5.30pm-8.20pm SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 2 Lecture: Week 9 Binary search trees
Multi-Way Search Trees
 Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
FINALTERM EXAMINATION Fall 2009 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one The data of the problem is of 2GB and the hard
 FINALTERM EXAMINATION Fall 2009 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 The data of the problem is of 2GB and the hard disk is of 1GB capacity, to solve this problem we should Use better data structures
FINALTERM EXAMINATION Fall 2009 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 The data of the problem is of 2GB and the hard disk is of 1GB capacity, to solve this problem we should Use better data structures
CS 3343 Fall 2007 Red-black trees Carola Wenk
 CS 3343 Fall 2007 Red-black trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with small changes by Carola Wenk CS 334 Analysis of Algorithms 1 Search Trees A binary search tree is a binary tree.
CS 3343 Fall 2007 Red-black trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with small changes by Carola Wenk CS 334 Analysis of Algorithms 1 Search Trees A binary search tree is a binary tree.
Quiz 1 Solutions. (a) f(n) = n g(n) = log n Circle all that apply: f = O(g) f = Θ(g) f = Ω(g)
 Introduction to Algorithms March 11, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Spring 2009 Professors Sivan Toledo and Alan Edelman Quiz 1 Solutions Problem 1. Quiz 1 Solutions Asymptotic orders
Introduction to Algorithms March 11, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Spring 2009 Professors Sivan Toledo and Alan Edelman Quiz 1 Solutions Problem 1. Quiz 1 Solutions Asymptotic orders
AVL Trees. Reading: 9.2
 AVL Trees Reading: 9.2 Balance Factor of a Node The difference in height of its two subtrees (h R -h L ) Balanced Node if -1 BF 1 Unbalanced Node if BF 1 h L h R Balance Factor of a Binar Tree Corresponds
AVL Trees Reading: 9.2 Balance Factor of a Node The difference in height of its two subtrees (h R -h L ) Balanced Node if -1 BF 1 Unbalanced Node if BF 1 h L h R Balance Factor of a Binar Tree Corresponds
UNIT III BALANCED SEARCH TREES AND INDEXING
 UNIT III BALANCED SEARCH TREES AND INDEXING OBJECTIVE The implementation of hash tables is frequently called hashing. Hashing is a technique used for performing insertions, deletions and finds in constant
UNIT III BALANCED SEARCH TREES AND INDEXING OBJECTIVE The implementation of hash tables is frequently called hashing. Hashing is a technique used for performing insertions, deletions and finds in constant
Binary Search Trees. Analysis of Algorithms
 Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Lecture 13: AVL Trees and Binary Heaps
 Data Structures Brett Bernstein Lecture 13: AVL Trees and Binary Heaps Review Exercises 1. ( ) Interview question: Given an array show how to shue it randomly so that any possible reordering is equally
Data Structures Brett Bernstein Lecture 13: AVL Trees and Binary Heaps Review Exercises 1. ( ) Interview question: Given an array show how to shue it randomly so that any possible reordering is equally
Chapter. Binary Search Trees. Contents
 Chapter 4 Balanced Binary Search Trees U.S. Navy Blue Angels, performing their delta formation during the Blues on the Bay Air Show at Marine Corps Base Hawaii in 2007. U.S. government photo by Petty Officer
Chapter 4 Balanced Binary Search Trees U.S. Navy Blue Angels, performing their delta formation during the Blues on the Bay Air Show at Marine Corps Base Hawaii in 2007. U.S. government photo by Petty Officer
Suggested Study Strategy
 Final Exam Thursday, 7 August 2014,19:00 22:00 Closed Book Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (hash tables, binary search trees, sorting, graphs) Suggested Study Strategy
Final Exam Thursday, 7 August 2014,19:00 22:00 Closed Book Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (hash tables, binary search trees, sorting, graphs) Suggested Study Strategy
Course Review for Finals. Cpt S 223 Fall 2008
 Course Review for Finals Cpt S 223 Fall 2008 1 Course Overview Introduction to advanced data structures Algorithmic asymptotic analysis Programming data structures Program design based on performance i.e.,
Course Review for Finals Cpt S 223 Fall 2008 1 Course Overview Introduction to advanced data structures Algorithmic asymptotic analysis Programming data structures Program design based on performance i.e.,
CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees
 CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees Irwin King king@cse.cuhk.edu.hk http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~king Department of Computer Science & Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Introduction General Tree
CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees Irwin King king@cse.cuhk.edu.hk http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~king Department of Computer Science & Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Introduction General Tree
Balanced Binary Search Trees. Victor Gao
 Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
9. Heap : Priority Queue
 9. Heap : Priority Queue Where We Are? Array Linked list Stack Queue Tree Binary Tree Heap Binary Search Tree Priority Queue Queue Queue operation is based on the order of arrivals of elements FIFO(First-In
9. Heap : Priority Queue Where We Are? Array Linked list Stack Queue Tree Binary Tree Heap Binary Search Tree Priority Queue Queue Queue operation is based on the order of arrivals of elements FIFO(First-In
COMP : Trees. COMP20012 Trees 219
 COMP20012 3: Trees COMP20012 Trees 219 Trees Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees Search Trees Family Trees Hierarchical Structures Management Directories COMP20012 Trees 220 Trees have natural
COMP20012 3: Trees COMP20012 Trees 219 Trees Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees Search Trees Family Trees Hierarchical Structures Management Directories COMP20012 Trees 220 Trees have natural
