Operation Overloading.
|
|
|
- Mary Watts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Operation Overloading
2 Operation Overloading Operation overloading means, same operation has different response to different objects We have seen function overloading distance(int, int); distance(point); //from origin distance(point, Point); Below are examples of operator overloading x + y; //where x and y are double object s1 + s2; //where s1 and s2 are string objects c1 + c2; //where c1 and c2 are complex objects
3 Operator Overloading Operator based expressions are much easier to read; compare a + b * c with plus(a, times(b, c)) Operator Overloading is a powerful tool in C++, but at the same time could be quiet error prone, and confusing C++ allows programmers to give different meaning to operator; and this, providing a new meaning to an operator is called operator overloading
4 Suppose, you want to have a class Complex such that following client executes as expected What operations you need to define for this? Four operator: >>, +, <<, = You don t have to overload =, as default copying in C++ suffices for this class; Others we need to. We have not learned so far how to write such class
5 Another Client program, doing same functionality, but uses different class interface This Complex class probably you can write? However, users of the class would probably appreciate previous interface; that uses operators rather than functions To have operator based interface you need to overload appropriate operator
6 Exercise Given this (side by) definition of class Implement following function A global function: Complex add(const Complex&, const Complex&); A member function to class Complex: Complex add(const Complex&);
7 add as global function Here is how you would use this function to add two Complex numbers Complex c1, c2, c3; c1.read( cin ); c2.read( cin ); c3 = add(c1, c2);
8 add as member function Here is how you would use this function to add two Complex numbers Complex c1, c2, c3; c1.read( cin ); c2.read( cin ); c3 = c1.add( c2 );
9 Two solution for adding two complex numbers Both are doing job. How does that matter to you; Global function can not access private data members of the class; while member function can
10 Operator Overloading Operators, however can not be defined new meaning for primitive data types; When we define overloading, one of the operator has to be of user defined types Operators in C++ can be overloaded in two ways- They can be defined as global functions, or can be defined as member functions.
11 Operator Overloading as global functions For this, you define a global function whose name is operator followed by the operator symbol, and operands are parameters to it; left operand as first parameter while right operand as second parameter; as shown below -
12 When you have this function defined, you can write following expression: c1 + c2 Compiler interprets this expression as function call operator+(c1, c2) The function Implementation defines actions that needs to be performed when such expression encounters
13 Overload the operator to add objects of two different types Suppose, you want to write an expression c ; for this you may have to write another function, which takes, second parameter of other type, say double in this case -
14 Operator Member function When define operator+ as member function, and write expression: c1 + c2 Then, the compiler would interprets it as function call c1.operator+(c2)
15 Defines operator+ such that a double can be added to a Complex object: c Then, the compiler would interprets it as function call c1.operator+(5.6)
16 Operator Overloading When your write expression: a + b where a, b are objects of some class; suppose classes A and B respectively A and B could be same class or two different classes; normally are from same class though Compiler attempts to translate this expression to a function call and binds it to appropriate function definition, if finds, otherwise raises compilation error Note that, right now, we are talking about binary operator only
17 Operator Overloading When compiler finds this expression, first it looks for a member function operator+ in class A, if finds, then translates above expression to a.operator+(b) If not then looks for a global function operator+, having two parameters of type A and B respectively, if finds then translates expression a+b to operator+(a,b) If still does not find; compiler raises error: no match for 'operator+' in a + b'
18 Thanks
Operation Overloading.
 Operation Overloading pm_jat@daiict.ac.in Recap: Why do we need Operator Overloading? Operator based expressions are more readable: Compare a + b * c with plus(a, times(b, c)) Recap: What is Operator Overloading?
Operation Overloading pm_jat@daiict.ac.in Recap: Why do we need Operator Overloading? Operator based expressions are more readable: Compare a + b * c with plus(a, times(b, c)) Recap: What is Operator Overloading?
Instantiation of Template class
 Class Templates Templates are like advanced macros. They are useful for building new classes that depend on already existing user defined classes or built-in types. Example: stack of int or stack of double
Class Templates Templates are like advanced macros. They are useful for building new classes that depend on already existing user defined classes or built-in types. Example: stack of int or stack of double
Operators & Expressions
 Operators & Expressions Operator An operator is a symbol used to indicate a specific operation on variables in a program. Example : symbol + is an add operator that adds two data items called operands.
Operators & Expressions Operator An operator is a symbol used to indicate a specific operation on variables in a program. Example : symbol + is an add operator that adds two data items called operands.
Operators. Lecture 12 Section Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Fri, Feb 9, 2018
 Operators Lecture 12 Section 14.5 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Feb 9, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Operators Fri, Feb 9, 2018 1 / 21 Outline 1 Operators as Functions 2 Operator
Operators Lecture 12 Section 14.5 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Feb 9, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Operators Fri, Feb 9, 2018 1 / 21 Outline 1 Operators as Functions 2 Operator
OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING USING C++ CSCI Object Oriented Analysis and Design By Manali Torpe
 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING USING C++ CSCI 5448- Object Oriented Analysis and Design By Manali Torpe Fundamentals of OOP Class Object Encapsulation Abstraction Inheritance Polymorphism Reusability C++
OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING USING C++ CSCI 5448- Object Oriented Analysis and Design By Manali Torpe Fundamentals of OOP Class Object Encapsulation Abstraction Inheritance Polymorphism Reusability C++
Ch. 12: Operator Overloading
 Ch. 12: Operator Overloading Operator overloading is just syntactic sugar, i.e. another way to make a function call: shift_left(42, 3); 42
Ch. 12: Operator Overloading Operator overloading is just syntactic sugar, i.e. another way to make a function call: shift_left(42, 3); 42
Computer Organization & Assembly Language Programming
 Computer Organization & Assembly Language Programming CSE 2312 Lecture 11 Introduction of Assembly Language 1 Assembly Language Translation The Assembly Language layer is implemented by translation rather
Computer Organization & Assembly Language Programming CSE 2312 Lecture 11 Introduction of Assembly Language 1 Assembly Language Translation The Assembly Language layer is implemented by translation rather
CS11 Intro C++ Spring 2018 Lecture 5
 CS11 Intro C++ Spring 2018 Lecture 5 C++ Abstractions C++ provides rich capabilities for creating abstractions class Complex { double re, im; public: Complex(double re, double im);... ; Would be nice if
CS11 Intro C++ Spring 2018 Lecture 5 C++ Abstractions C++ provides rich capabilities for creating abstractions class Complex { double re, im; public: Complex(double re, double im);... ; Would be nice if
More Advanced Class Concepts
 More Advanced Class Concepts Operator overloading Inheritance Templates PH (RH) (Roger.Henriksson@cs.lth.se) C++ Programming 2016/17 146 / 281 Operator Overloading In most programming languages some operators
More Advanced Class Concepts Operator overloading Inheritance Templates PH (RH) (Roger.Henriksson@cs.lth.se) C++ Programming 2016/17 146 / 281 Operator Overloading In most programming languages some operators
Friend Functions and Friend Classes
 Friend Functions and Friend Classes C++ allows you to declare another class to be a friend of the current class to make it easier to access variables. OOP purists have criticized this feature as weakening
Friend Functions and Friend Classes C++ allows you to declare another class to be a friend of the current class to make it easier to access variables. OOP purists have criticized this feature as weakening
Review: C++ Basic Concepts. Dr. Yingwu Zhu
 Review: C++ Basic Concepts Dr. Yingwu Zhu Outline C++ class declaration Constructor Overloading functions Overloading operators Destructor Redundant declaration A Real-World Example Question #1: How to
Review: C++ Basic Concepts Dr. Yingwu Zhu Outline C++ class declaration Constructor Overloading functions Overloading operators Destructor Redundant declaration A Real-World Example Question #1: How to
KOM3191 Object Oriented Programming Dr Muharrem Mercimek OPERATOR OVERLOADING. KOM3191 Object-Oriented Programming
 KOM3191 Object Oriented Programming Dr Muharrem Mercimek 1 OPERATOR OVERLOADING KOM3191 Object-Oriented Programming KOM3191 Object Oriented Programming Dr Muharrem Mercimek 2 Dynamic Memory Management
KOM3191 Object Oriented Programming Dr Muharrem Mercimek 1 OPERATOR OVERLOADING KOM3191 Object-Oriented Programming KOM3191 Object Oriented Programming Dr Muharrem Mercimek 2 Dynamic Memory Management
Reference Parameters A reference parameter is an alias for its corresponding argument in the function call. Use the ampersand (&) to indicate that
 Reference Parameters There are two ways to pass arguments to functions: pass-by-value and pass-by-reference. pass-by-value A copy of the argument s value is made and passed to the called function. Changes
Reference Parameters There are two ways to pass arguments to functions: pass-by-value and pass-by-reference. pass-by-value A copy of the argument s value is made and passed to the called function. Changes
Launchpad Lecture -10
 Saturday, 24 September Launchpad Lecture -10 Dynamic Allocation, Object Oriented Programming-1 Prateek Narang 2 Recap 1. How to define pointers? 2. Address of Operator? 3. Dereference operator? 4. Arithmetic
Saturday, 24 September Launchpad Lecture -10 Dynamic Allocation, Object Oriented Programming-1 Prateek Narang 2 Recap 1. How to define pointers? 2. Address of Operator? 3. Dereference operator? 4. Arithmetic
Program construction in C++ for Scientific Computing
 1 (26) School of Engineering Sciences Program construction in C++ for Scientific Computing 2 (26) Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 3 (26) Our Point class is a model for the vector space R 2. In this space, operations
1 (26) School of Engineering Sciences Program construction in C++ for Scientific Computing 2 (26) Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 3 (26) Our Point class is a model for the vector space R 2. In this space, operations
11.2. Overloading Operators
 11.2 Overloading Operators Overloading Operators In the Money class, function add was used to add two objects of type Money In this section we see how to use the '+' operator to make the following code
11.2 Overloading Operators Overloading Operators In the Money class, function add was used to add two objects of type Money In this section we see how to use the '+' operator to make the following code
(5 2) Introduction to Classes in C++ Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 7, 2018) Washington State University
 (5 2) Introduction to Classes in C++ Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 7, 2018) Washington State University Key Concepts Function templates Defining classes with member functions The Rule
(5 2) Introduction to Classes in C++ Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 7, 2018) Washington State University Key Concepts Function templates Defining classes with member functions The Rule
QUIZ Friends class Y;
 QUIZ Friends class Y; Is a forward declaration neeed here? QUIZ Friends QUIZ Friends - CONCLUSION Forward (a.k.a. incomplete) declarations are needed only when we declare member functions as friends. They
QUIZ Friends class Y; Is a forward declaration neeed here? QUIZ Friends QUIZ Friends - CONCLUSION Forward (a.k.a. incomplete) declarations are needed only when we declare member functions as friends. They
[CS302-Data Structures] Homework 2: Stacks
![[CS302-Data Structures] Homework 2: Stacks [CS302-Data Structures] Homework 2: Stacks](/thumbs/89/99620872.jpg) [CS302-Data Structures] Homework 2: Stacks Instructor: Kostas Alexis Teaching Assistants: Shehryar Khattak, Mustafa Solmaz, Bishal Sainju Fall 2018 Semester Section 1. Stack ADT Overview wrt Provided Code
[CS302-Data Structures] Homework 2: Stacks Instructor: Kostas Alexis Teaching Assistants: Shehryar Khattak, Mustafa Solmaz, Bishal Sainju Fall 2018 Semester Section 1. Stack ADT Overview wrt Provided Code
 https://lambda.mines.edu Evaluating programming languages based on: Writability: How easy is it to write good code? Readability: How easy is it to read well written code? Is the language easy enough to
https://lambda.mines.edu Evaluating programming languages based on: Writability: How easy is it to write good code? Readability: How easy is it to read well written code? Is the language easy enough to
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) 1. Legal Values. Client Code for Rational ADT. ADT Design. CS 247: Software Engineering Principles
 Abstract Data Types (ADTs) CS 247: Software Engineering Principles ADT Design An abstract data type (ADT) is a user-defined type that bundles together: the range of values that variables of that type can
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) CS 247: Software Engineering Principles ADT Design An abstract data type (ADT) is a user-defined type that bundles together: the range of values that variables of that type can
CS 31: Intro to Systems Binary Arithmetic. Martin Gagné Swarthmore College January 24, 2016
 CS 31: Intro to Systems Binary Arithmetic Martin Gagné Swarthmore College January 24, 2016 Unsigned Integers Suppose we had one byte Can represent 2 8 (256) values If unsigned (strictly non-negative):
CS 31: Intro to Systems Binary Arithmetic Martin Gagné Swarthmore College January 24, 2016 Unsigned Integers Suppose we had one byte Can represent 2 8 (256) values If unsigned (strictly non-negative):
61A Lecture 2. Friday, August 28, 2015
 61A Lecture 2 Friday, August 28, 2015 Names, Assignment, and User-Defined Functions (Demo) Types of Expressions Primitive expressions: 2 add 'hello' Number or Numeral Name String Call expressions: max
61A Lecture 2 Friday, August 28, 2015 Names, Assignment, and User-Defined Functions (Demo) Types of Expressions Primitive expressions: 2 add 'hello' Number or Numeral Name String Call expressions: max
Overloading Operators in C++
 Overloading Operators in C++ C++ allows the programmer to redefine the function of most built-in operators on a class-by-class basis the operator keyword is used to declare a function that specifies what
Overloading Operators in C++ C++ allows the programmer to redefine the function of most built-in operators on a class-by-class basis the operator keyword is used to declare a function that specifies what
Operator Overloading
 C++ Programming: Operator Overloading 2018 년도 2 학기 Instructor: Young-guk Ha Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Contents Operator overloading Basics on operator overloading Overloading operators as
C++ Programming: Operator Overloading 2018 년도 2 학기 Instructor: Young-guk Ha Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Contents Operator overloading Basics on operator overloading Overloading operators as
structure syntax different levels of abstraction
 This and the next lectures are about Verilog HDL, which, together with another language VHDL, are the most popular hardware languages used in industry. Verilog is only a tool; this course is about digital
This and the next lectures are about Verilog HDL, which, together with another language VHDL, are the most popular hardware languages used in industry. Verilog is only a tool; this course is about digital
Here is a list of lecture objectives. They are provided for you to reflect on what you are supposed to learn, rather than an introduction to this
 This and the next lectures are about Verilog HDL, which, together with another language VHDL, are the most popular hardware languages used in industry. Verilog is only a tool; this course is about digital
This and the next lectures are about Verilog HDL, which, together with another language VHDL, are the most popular hardware languages used in industry. Verilog is only a tool; this course is about digital
CS 247: Software Engineering Principles. ADT Design
 CS 247: Software Engineering Principles ADT Design Readings: Eckel, Vol. 1 Ch. 7 Function Overloading & Default Arguments Ch. 12 Operator Overloading U Waterloo CS247 (Spring 2017) p.1/17 Abstract Data
CS 247: Software Engineering Principles ADT Design Readings: Eckel, Vol. 1 Ch. 7 Function Overloading & Default Arguments Ch. 12 Operator Overloading U Waterloo CS247 (Spring 2017) p.1/17 Abstract Data
Classes Ch
 Classes Ch 10.1-10.3 Highlights - public/private - constructor - friend functions - operator overloading class vs array Arrays group together similar data types (any amount you want) Classes (and structs)
Classes Ch 10.1-10.3 Highlights - public/private - constructor - friend functions - operator overloading class vs array Arrays group together similar data types (any amount you want) Classes (and structs)
CS31 Discussion 1E. Jie(Jay) Wang Week3 Oct.12
 CS31 Discussion 1E Jie(Jay) Wang Week3 Oct.12 Outline Problems from Project 1 Review of lecture String, char, stream If-else statements Switch statements loops Programming challenge Problems from Project
CS31 Discussion 1E Jie(Jay) Wang Week3 Oct.12 Outline Problems from Project 1 Review of lecture String, char, stream If-else statements Switch statements loops Programming challenge Problems from Project
EXPRESSIONS, STATEMENTS, AND FUNCTIONS 1
 EXPRESSIONS, STATEMENTS, AND FUNCTIONS 1 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A September 4, 2013 0.1 Warmup What Would Python Do? >>> x = 6 >>> def square(x):... return x * x >>> square(x) >>> max(pow(2, 3), square(-5))
EXPRESSIONS, STATEMENTS, AND FUNCTIONS 1 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A September 4, 2013 0.1 Warmup What Would Python Do? >>> x = 6 >>> def square(x):... return x * x >>> square(x) >>> max(pow(2, 3), square(-5))
61A Lecture 2. Wednesday, September 4, 2013
 61A Lecture 2 Wednesday, September 4, 2013 Names, Assignment, and User-Defined Functions (Demo) Types of Expressions Primitive expressions: 2 add 'hello' Number or Numeral Name String Call expressions:
61A Lecture 2 Wednesday, September 4, 2013 Names, Assignment, and User-Defined Functions (Demo) Types of Expressions Primitive expressions: 2 add 'hello' Number or Numeral Name String Call expressions:
Introduction to Programming EC-105. Lecture 2
 Introduction to Programming EC-105 Lecture 2 Input and Output A data stream is a sequence of data - Typically in the form of characters or numbers An input stream is data for the program to use - Typically
Introduction to Programming EC-105 Lecture 2 Input and Output A data stream is a sequence of data - Typically in the form of characters or numbers An input stream is data for the program to use - Typically
LECTURE NOTES ON PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTAL USING C++ LANGUAGE
 Department of Software The University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES ON PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTAL USING C++ LANGUAGE By Dr. Samaher Hussein Ali Collage of Information Technology, University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher_hussein@yahoo.com
Department of Software The University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES ON PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTAL USING C++ LANGUAGE By Dr. Samaher Hussein Ali Collage of Information Technology, University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher_hussein@yahoo.com
Roxana Dumitrescu. C++ in Financial Mathematics
 Roxana Dumitrescu C++ in Financial Mathematics What have we learnt? Arrays; relation between arrays and pointers.. Returning arrays from functions Passing arrays to functions Intoduction to classes Plan
Roxana Dumitrescu C++ in Financial Mathematics What have we learnt? Arrays; relation between arrays and pointers.. Returning arrays from functions Passing arrays to functions Intoduction to classes Plan
Distributed Real- Time Control Systems 13/14
 Distributed Real- Time Control Systems 13/14 Lecture 10 C++ Programming Operators and more A. Bernardino, C. Silvestre, IST- ACSDC 1 References From C programming we know that int i =3; int *p; p = &i;
Distributed Real- Time Control Systems 13/14 Lecture 10 C++ Programming Operators and more A. Bernardino, C. Silvestre, IST- ACSDC 1 References From C programming we know that int i =3; int *p; p = &i;
(3) Some memory that holds a value of a given type. (8) The basic unit of addressing in most computers.
 CS 7A Final Exam - Fall 206 - Final Exam Solutions 2/3/6. Write the number of the definition on the right next to the term it defines. () Defining two functions or operators with the same name but different
CS 7A Final Exam - Fall 206 - Final Exam Solutions 2/3/6. Write the number of the definition on the right next to the term it defines. () Defining two functions or operators with the same name but different
C++ basics Getting started with, and Data Types.
 C++ basics Getting started with, and Data Types pm_jat@daiict.ac.in Recap Last Lecture We talked about Variables - Variables, their binding to type, storage etc., Categorization based on storage binding
C++ basics Getting started with, and Data Types pm_jat@daiict.ac.in Recap Last Lecture We talked about Variables - Variables, their binding to type, storage etc., Categorization based on storage binding
Module Operator Overloading and Type Conversion. Table of Contents
 1 Module - 33 Operator Overloading and Type Conversion Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Operator Overloading 3. this pointer 4. Overloading Unary Operators 5. Overloading Binary Operators 6. Overloading
1 Module - 33 Operator Overloading and Type Conversion Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Operator Overloading 3. this pointer 4. Overloading Unary Operators 5. Overloading Binary Operators 6. Overloading
Page. No. 1/15 CS201 Introduction to Programmming Solved Subjective Questions From spring 2010 Final Term Papers By vuzs Team
 Page. No. 1/15 CS201 Introduction to Programmming Solved Subjective Questions From spring 2010 Final Term Papers By vuzs Team Question No: 1 ( Marks: 2 ) Write a declaration statement for an array of 10
Page. No. 1/15 CS201 Introduction to Programmming Solved Subjective Questions From spring 2010 Final Term Papers By vuzs Team Question No: 1 ( Marks: 2 ) Write a declaration statement for an array of 10
2. Distinguish between a unary, a binary and a ternary operator. Give examples of C++ operators for each one of them.
 1. Why do you think C++ was not named ++C? C++ is a super set of language C. All the basic features of C are used in C++ in their original form C++ can be described as C+ some additional features. Therefore,
1. Why do you think C++ was not named ++C? C++ is a super set of language C. All the basic features of C are used in C++ in their original form C++ can be described as C+ some additional features. Therefore,
(7-2) Operator Overloading D & D Chapter 10. Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 23, 2018) Washington State University
 (7-2) Operator Overloading D & D Chapter 10 Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 23, 2018) Washington State University Key Concepts Keyword operator Operator overloading 2 What is Operator
(7-2) Operator Overloading D & D Chapter 10 Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 23, 2018) Washington State University Key Concepts Keyword operator Operator overloading 2 What is Operator
Vectors of Pointers to Objects. Vectors of Objects. Vectors of unique ptrs C++11. Arrays of Objects
 Vectors of Objects As we have mentioned earlier, you should almost always use vectors instead of arrays. If you need to keep track of persons (objects of class Person), you must decide what to store in
Vectors of Objects As we have mentioned earlier, you should almost always use vectors instead of arrays. If you need to keep track of persons (objects of class Person), you must decide what to store in
Streams contd. Text: Chapter12, Big C++
 Streams contd pm_jat@daiict.ac.in Text: Chapter12, Big C++ Streams Objects are Abstracted Wrapper around input/output source/destinations Steps in reading/writing streams- Open: Establish connection between
Streams contd pm_jat@daiict.ac.in Text: Chapter12, Big C++ Streams Objects are Abstracted Wrapper around input/output source/destinations Steps in reading/writing streams- Open: Establish connection between
EXPRESSIONS, STATEMENTS, AND FUNCTIONS 1
 EXPRESSIONS, STATEMENTS, AND FUNCTIONS 1 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A June 24, 2014 0.1 Warmup What Would Python Do? >>> x = 6 >>> def square(x):... return x * x >>> square(x) >>> max(pow(2, 3), square(-5)) -
EXPRESSIONS, STATEMENTS, AND FUNCTIONS 1 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A June 24, 2014 0.1 Warmup What Would Python Do? >>> x = 6 >>> def square(x):... return x * x >>> square(x) >>> max(pow(2, 3), square(-5)) -
Let s put together a Manual Processor
 Lecture 14 Let s put together a Manual Processor Hardware Lecture 14 Slide 1 The processor Inside every computer there is at least one processor which can take an instruction, some operands and produce
Lecture 14 Let s put together a Manual Processor Hardware Lecture 14 Slide 1 The processor Inside every computer there is at least one processor which can take an instruction, some operands and produce
CS-XXX: Graduate Programming Languages. Lecture 23 Types for OOP; Static Overloading and Multimethods. Dan Grossman 2012
 CS-XXX: Graduate Programming Languages Lecture 23 Types for OOP; Static Overloading and Multimethods Dan Grossman 2012 So far... Last lecture (among other things): The difference between OOP and records
CS-XXX: Graduate Programming Languages Lecture 23 Types for OOP; Static Overloading and Multimethods Dan Grossman 2012 So far... Last lecture (among other things): The difference between OOP and records
For Teacher's Use Only Q No Total Q No Q No
 Student Info Student ID: Center: Exam Date: FINALTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 CS201- Introduction to Programming Time: 90 min Marks: 58 For Teacher's Use Only Q No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Total Marks Q No. 9
Student Info Student ID: Center: Exam Date: FINALTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 CS201- Introduction to Programming Time: 90 min Marks: 58 For Teacher's Use Only Q No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Total Marks Q No. 9
Preprocessor Directives
 C++ By 6 EXAMPLE Preprocessor Directives As you might recall from Chapter 2, What Is a Program?, the C++ compiler routes your programs through a preprocessor before it compiles them. The preprocessor can
C++ By 6 EXAMPLE Preprocessor Directives As you might recall from Chapter 2, What Is a Program?, the C++ compiler routes your programs through a preprocessor before it compiles them. The preprocessor can
multiple variables having the same value multiple variables having the same identifier multiple uses of the same variable
 PART III : Language processing, interpretation, translation, the concept of binding, variables, name and scope, Type, l-value, r-value, reference and unnamed variables, routines, generic routines, aliasing
PART III : Language processing, interpretation, translation, the concept of binding, variables, name and scope, Type, l-value, r-value, reference and unnamed variables, routines, generic routines, aliasing
Protection Levels and Constructors The 'const' Keyword
 Protection Levels and Constructors The 'const' Keyword Review: const Keyword Generally, the keyword const is applied to an identifier (variable) by a programmer to express an intent that the identifier
Protection Levels and Constructors The 'const' Keyword Review: const Keyword Generally, the keyword const is applied to an identifier (variable) by a programmer to express an intent that the identifier
B16 Object Oriented Programming
 B16 Object Oriented Programming Michael A. Osborne mosb@robots.ox.ac.uk http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~mosb/teaching.html#b16 Hilary 2013 Topic 4: Constructors Recall our definition of the Complex class.
B16 Object Oriented Programming Michael A. Osborne mosb@robots.ox.ac.uk http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~mosb/teaching.html#b16 Hilary 2013 Topic 4: Constructors Recall our definition of the Complex class.
Fundamentals of Programming CS-110. Lecture 2
 Fundamentals of Programming CS-110 Lecture 2 Last Lab // Example program #include using namespace std; int main() { cout
Fundamentals of Programming CS-110 Lecture 2 Last Lab // Example program #include using namespace std; int main() { cout
Midterm 2. CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Fall Instructions Total 100. Name: November 11, 2015
 Name: Midterm 2 CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Fall 2015 November 11, 2015 Instructions This exam contains 8 pages, including this one. Make sure you have all the pages. Write your name on the top
Name: Midterm 2 CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Fall 2015 November 11, 2015 Instructions This exam contains 8 pages, including this one. Make sure you have all the pages. Write your name on the top
Note 12/1/ Review of Inheritance Practice: Please write down 10 most important facts you know about inheritance...
 CISC 2000 Computer Science II Fall, 2014 Note 12/1/2014 1 Review of Inheritance Practice: Please write down 10 most important facts you know about inheritance... (a) What s the purpose of inheritance?
CISC 2000 Computer Science II Fall, 2014 Note 12/1/2014 1 Review of Inheritance Practice: Please write down 10 most important facts you know about inheritance... (a) What s the purpose of inheritance?
Welcome Back. CSCI 262 Data Structures. Hello, Let s Review. Hello, Let s Review. How to Review 8/19/ Review. Here s a simple C++ program:
 Welcome Back CSCI 262 Data Structures 2 - Review What you learned in CSCI 261 (or equivalent): Variables Types Arrays Expressions Conditionals Branches & Loops Functions Recursion Classes & Objects Streams
Welcome Back CSCI 262 Data Structures 2 - Review What you learned in CSCI 261 (or equivalent): Variables Types Arrays Expressions Conditionals Branches & Loops Functions Recursion Classes & Objects Streams
Question: How can we compare two objects of a given class to see if they are the same? Is it legal to do: Rectangle r(0,0,3,3);,, Rectangle s(0,0,4,4)
 Classes and Objects in C++: Operator Overloading CSC 112 Fall 2009 Question: How can we compare two objects of a given class to see if they are the same? Is it legal to do: Rectangle r(0,0,3,3);,, Rectangle
Classes and Objects in C++: Operator Overloading CSC 112 Fall 2009 Question: How can we compare two objects of a given class to see if they are the same? Is it legal to do: Rectangle r(0,0,3,3);,, Rectangle
Lecture 7: Primitive Recursion is Turing Computable. Michael Beeson
 Lecture 7: Primitive Recursion is Turing Computable Michael Beeson Closure under composition Let f and g be Turing computable. Let h(x) = f(g(x)). Then h is Turing computable. Similarly if h(x) = f(g 1
Lecture 7: Primitive Recursion is Turing Computable Michael Beeson Closure under composition Let f and g be Turing computable. Let h(x) = f(g(x)). Then h is Turing computable. Similarly if h(x) = f(g 1
Stating the obvious, people and computers do not speak the same language.
 3.4 SYSTEM SOFTWARE 3.4.3 TRANSLATION SOFTWARE INTRODUCTION Stating the obvious, people and computers do not speak the same language. People have to write programs in order to instruct a computer what
3.4 SYSTEM SOFTWARE 3.4.3 TRANSLATION SOFTWARE INTRODUCTION Stating the obvious, people and computers do not speak the same language. People have to write programs in order to instruct a computer what
Arrays in Functions!
 Arrays in Functions! 1E3! Topic 12! 12 Arrays in Functions 1 Objectives! n This topic should allow students to! n Pass array elements to functions! n Pass whole arrays to functions! n Write functions that
Arrays in Functions! 1E3! Topic 12! 12 Arrays in Functions 1 Objectives! n This topic should allow students to! n Pass array elements to functions! n Pass whole arrays to functions! n Write functions that
Part X. Advanced C ++
 Part X Advanced C ++ topics Philip Blakely (LSC) Advanced C++ 158 / 217 References The following are highly regarded books. They are fairly in-depth, and I haven t read them in their entirity. However,
Part X Advanced C ++ topics Philip Blakely (LSC) Advanced C++ 158 / 217 References The following are highly regarded books. They are fairly in-depth, and I haven t read them in their entirity. However,
C expressions. (Reek, Ch. 5) 1 CS 3090: Safety Critical Programming in C
 C expressions (Reek, Ch. 5) 1 Shift operations Left shift: value > n Two definitions: logical version: discard the n
C expressions (Reek, Ch. 5) 1 Shift operations Left shift: value > n Two definitions: logical version: discard the n
Binary Search. Roland Backhouse February 5th, 2001
 1 Binary Search Roland Backhouse February 5th, 2001 Outline 2 An implementation in Java of the card-searching algorithm is presented. Issues concerning the correctness of the implementation are raised
1 Binary Search Roland Backhouse February 5th, 2001 Outline 2 An implementation in Java of the card-searching algorithm is presented. Issues concerning the correctness of the implementation are raised
STUDY NOTES UNIT 1 - INTRODUCTION TO OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING STUDY NOTES UNIT 1 - INTRODUCTION TO OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING 1. Object Oriented Programming Paradigms 2. Comparison of Programming Paradigms 3. Basic Object Oriented Programming
OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING STUDY NOTES UNIT 1 - INTRODUCTION TO OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING 1. Object Oriented Programming Paradigms 2. Comparison of Programming Paradigms 3. Basic Object Oriented Programming
ENCM 369 Winter 2019 Lab 6 for the Week of February 25
 page of ENCM 369 Winter 29 Lab 6 for the Week of February 25 Steve Norman Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Calgary February 29 Lab instructions and other documents for ENCM
page of ENCM 369 Winter 29 Lab 6 for the Week of February 25 Steve Norman Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Calgary February 29 Lab instructions and other documents for ENCM
Data type of a pointer must be same as the data type of the variable to which the pointer variable is pointing. Here are a few examples:
 Unit IV Pointers and Polymorphism in C++ Concepts of Pointer: A pointer is a variable that holds a memory address of another variable where a value lives. A pointer is declared using the * operator before
Unit IV Pointers and Polymorphism in C++ Concepts of Pointer: A pointer is a variable that holds a memory address of another variable where a value lives. A pointer is declared using the * operator before
CHAPTER 1.2 INTRODUCTION TO C++ PROGRAMMING. Dr. Shady Yehia Elmashad
 CHAPTER 1.2 INTRODUCTION TO C++ PROGRAMMING Dr. Shady Yehia Elmashad Outline 1. Introduction to C++ Programming 2. Comment 3. Variables and Constants 4. Basic C++ Data Types 5. Simple Program: Printing
CHAPTER 1.2 INTRODUCTION TO C++ PROGRAMMING Dr. Shady Yehia Elmashad Outline 1. Introduction to C++ Programming 2. Comment 3. Variables and Constants 4. Basic C++ Data Types 5. Simple Program: Printing
Compiler Design Spring 2017
 Compiler Design Spring 2017 Patterns (again) Dr. Zoltán Majó Compiler Group Java HotSpot Virtual Machine Oracle Corporation Why? Remember questionnaire (from the beginning of the semester)? Question 7:
Compiler Design Spring 2017 Patterns (again) Dr. Zoltán Majó Compiler Group Java HotSpot Virtual Machine Oracle Corporation Why? Remember questionnaire (from the beginning of the semester)? Question 7:
CSE143 Exam with answers Problem numbering may differ from the test as given. Midterm #2 February 16, 2001
 CSE143 Exam with answers Problem numbering may differ from the test as given. All multiple choice questions are equally weighted. You can generally assume that code shown in the questions is intended to
CSE143 Exam with answers Problem numbering may differ from the test as given. All multiple choice questions are equally weighted. You can generally assume that code shown in the questions is intended to
Java Object Oriented Design. CSC207 Fall 2014
 Java Object Oriented Design CSC207 Fall 2014 Design Problem Design an application where the user can draw different shapes Lines Circles Rectangles Just high level design, don t write any detailed code
Java Object Oriented Design CSC207 Fall 2014 Design Problem Design an application where the user can draw different shapes Lines Circles Rectangles Just high level design, don t write any detailed code
Encapsulation in C++
 pm_jat@daiict.ac.in In abstract sense, it is all about information hiding Informally, you can call it as packaging of data and function together in a single entity called class such that you get implementation
pm_jat@daiict.ac.in In abstract sense, it is all about information hiding Informally, you can call it as packaging of data and function together in a single entity called class such that you get implementation
Stacks. Ordered list with property: Insertions and deletions always occur at the same end. INSERT DELETE A3 A3 TOP TOP TOP
 Stacks Ordered list with property: Insertions and deletions always occur at the same end. INSERT A3 A3 TOP DELETE A2 TOP A2 A2 TOP A1 A1 A1 A0 A0 A0 Stacks Implementation Implementation with arrays: Declare
Stacks Ordered list with property: Insertions and deletions always occur at the same end. INSERT A3 A3 TOP DELETE A2 TOP A2 A2 TOP A1 A1 A1 A0 A0 A0 Stacks Implementation Implementation with arrays: Declare
QUIZ on Ch.5. Why is it sometimes not a good idea to place the private part of the interface in a header file?
 QUIZ on Ch.5 Why is it sometimes not a good idea to place the private part of the interface in a header file? Example projects where we don t want the implementation visible to the client programmer: The
QUIZ on Ch.5 Why is it sometimes not a good idea to place the private part of the interface in a header file? Example projects where we don t want the implementation visible to the client programmer: The
Data Storage. August 9, Indiana University. Geoffrey Brown, Bryce Himebaugh 2015 August 9, / 19
 Data Storage Geoffrey Brown Bryce Himebaugh Indiana University August 9, 2016 Geoffrey Brown, Bryce Himebaugh 2015 August 9, 2016 1 / 19 Outline Bits, Bytes, Words Word Size Byte Addressable Memory Byte
Data Storage Geoffrey Brown Bryce Himebaugh Indiana University August 9, 2016 Geoffrey Brown, Bryce Himebaugh 2015 August 9, 2016 1 / 19 Outline Bits, Bytes, Words Word Size Byte Addressable Memory Byte
Recap: Pointers. int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff
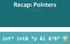 Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
Programming Abstractions
 Programming Abstractions C S 1 0 6 B Cynthia Lee Today s Topics ADTs Stack Example: Reverse-Polish Notation calculator Queue Example: Mouse Events Stacks New ADT: Stack stack.h template
Programming Abstractions C S 1 0 6 B Cynthia Lee Today s Topics ADTs Stack Example: Reverse-Polish Notation calculator Queue Example: Mouse Events Stacks New ADT: Stack stack.h template
Chapter Five: Functions. by Cay Horstmann Copyright 2018 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved
 Chapter Five: Functions by Cay Horstmann Chapter Goals To be able to implement functions To become familiar with the concept of parameter passing To appreciate the importance of function comments To develop
Chapter Five: Functions by Cay Horstmann Chapter Goals To be able to implement functions To become familiar with the concept of parameter passing To appreciate the importance of function comments To develop
CS 31: Introduction to Computer Systems. 03: Binary Arithmetic January 29
 CS 31: Introduction to Computer Systems 03: Binary Arithmetic January 29 WiCS! Swarthmore Women in Computer Science Slide 2 Today Binary Arithmetic Unsigned addition Subtraction Representation Signed magnitude
CS 31: Introduction to Computer Systems 03: Binary Arithmetic January 29 WiCS! Swarthmore Women in Computer Science Slide 2 Today Binary Arithmetic Unsigned addition Subtraction Representation Signed magnitude
Eric Roberts Handout #39 CS 106B February 20, 2015 Sets
 Eric Roberts Handout #39 S 106 February 20, 2015 Sets Sets Eric Roberts S 106 February 20, 2015 Outline 1. Midcourse correction 2. Sets in mathematics 3. Venn diagrams 4. High-level set operations 5. Implementing
Eric Roberts Handout #39 S 106 February 20, 2015 Sets Sets Eric Roberts S 106 February 20, 2015 Outline 1. Midcourse correction 2. Sets in mathematics 3. Venn diagrams 4. High-level set operations 5. Implementing
Chapter 3: Describing Syntax and Semantics. Introduction Formal methods of describing syntax (BNF)
 Chapter 3: Describing Syntax and Semantics Introduction Formal methods of describing syntax (BNF) We can analyze syntax of a computer program on two levels: 1. Lexical level 2. Syntactic level Lexical
Chapter 3: Describing Syntax and Semantics Introduction Formal methods of describing syntax (BNF) We can analyze syntax of a computer program on two levels: 1. Lexical level 2. Syntactic level Lexical
Arrays. myints = new int[15];
![Arrays. myints = new int[15]; Arrays. myints = new int[15];](/thumbs/72/66387724.jpg) Arrays As you know from COMP 202 (or equivalent), an array is a data structure that holds a set of elements that are of the same type. Each element in the array can be accessed or indexed by a unique number
Arrays As you know from COMP 202 (or equivalent), an array is a data structure that holds a set of elements that are of the same type. Each element in the array can be accessed or indexed by a unique number
Operators. Lecture 3 COP 3014 Spring January 16, 2018
 Operators Lecture 3 COP 3014 Spring 2018 January 16, 2018 Operators Special built-in symbols that have functionality, and work on operands operand an input to an operator Arity - how many operands an operator
Operators Lecture 3 COP 3014 Spring 2018 January 16, 2018 Operators Special built-in symbols that have functionality, and work on operands operand an input to an operator Arity - how many operands an operator
Distributed Real-Time Control Systems. Lecture 14 Intro to C++ Part III
 Distributed Real-Time Control Systems Lecture 14 Intro to C++ Part III 1 Class Hierarchies The human brain is very efficient in finding common properties to different entities and classify them according
Distributed Real-Time Control Systems Lecture 14 Intro to C++ Part III 1 Class Hierarchies The human brain is very efficient in finding common properties to different entities and classify them according
Fixed-Point Math and Other Optimizations
 Fixed-Point Math and Other Optimizations Embedded Systems 8-1 Fixed Point Math Why and How Floating point is too slow and integers truncate the data Floating point subroutines: slower than native, overhead
Fixed-Point Math and Other Optimizations Embedded Systems 8-1 Fixed Point Math Why and How Floating point is too slow and integers truncate the data Floating point subroutines: slower than native, overhead
CS304 Object Oriented Programming Final Term
 1. Which of the following is the way to extract common behaviour and attributes from the given classes and make a separate class of those common behaviours and attributes? Generalization (pg 29) Sub-typing
1. Which of the following is the way to extract common behaviour and attributes from the given classes and make a separate class of those common behaviours and attributes? Generalization (pg 29) Sub-typing
Programming in C++ Prof. Partha Pratim Das Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Programming in C++ Prof. Partha Pratim Das Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 08 Constants and Inline Functions Welcome to module 6 of Programming
Programming in C++ Prof. Partha Pratim Das Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 08 Constants and Inline Functions Welcome to module 6 of Programming
Boolean Algebra Boolean Algebra
 What is the result and type of the following expressions? Int x=2, y=15; float u=2.0, v=15.0; -x x+y x-y x*v y / x x/y y%x x%y u*v u/v v/u u%v x * u (x+y)*u u / (x-x) x++ u++ u = --x u = x -- u *= ++x
What is the result and type of the following expressions? Int x=2, y=15; float u=2.0, v=15.0; -x x+y x-y x*v y / x x/y y%x x%y u*v u/v v/u u%v x * u (x+y)*u u / (x-x) x++ u++ u = --x u = x -- u *= ++x
Chapter 8. Operator Overloading, Friends, and References. Copyright 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved
 Chapter 8 Operator Overloading, Friends, and References Copyright 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Learning Objectives Basic Operator Overloading Unary operators As member functions Friends
Chapter 8 Operator Overloading, Friends, and References Copyright 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Learning Objectives Basic Operator Overloading Unary operators As member functions Friends
Week 2: Console I/O and Operators Arithmetic Operators. Integer Division. Arithmetic Operators. Gaddis: Chapter 3 (2.14,3.1-6,3.9-10,5.
 Week 2: Console I/O and Operators Gaddis: Chapter 3 (2.14,3.1-6,3.9-10,5.1) CS 1428 Fall 2014 Jill Seaman 1 2.14 Arithmetic Operators An operator is a symbol that tells the computer to perform specific
Week 2: Console I/O and Operators Gaddis: Chapter 3 (2.14,3.1-6,3.9-10,5.1) CS 1428 Fall 2014 Jill Seaman 1 2.14 Arithmetic Operators An operator is a symbol that tells the computer to perform specific
Chapter 4. Computation. Bjarne Stroustrup.
 Chapter 4 Computation Bjarne Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programming Abstract Today, I ll present the basics of computation. In particular, we ll discuss expressions, how to iterate over a series of
Chapter 4 Computation Bjarne Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programming Abstract Today, I ll present the basics of computation. In particular, we ll discuss expressions, how to iterate over a series of
Circle all of the following which would make sense as the function prototype.
 Student ID: Lab Section: This test is closed book, closed notes. Points for each question are shown inside [ ] brackets at the beginning of each question. You should assume that, for all quoted program
Student ID: Lab Section: This test is closed book, closed notes. Points for each question are shown inside [ ] brackets at the beginning of each question. You should assume that, for all quoted program
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION
 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION A digital computer system consists of hardware and software: The hardware consists of the physical components of the system. The software is the collection of programs that a computer
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION A digital computer system consists of hardware and software: The hardware consists of the physical components of the system. The software is the collection of programs that a computer
1. a) What #include statement do you put at the top of a program that does uses cin, cout or endl?
 Exercises with solutions. 1. a) What #include statement do you put at the top of a program that does uses cin, cout or endl? #include b) What using statement do you always put at the top of
Exercises with solutions. 1. a) What #include statement do you put at the top of a program that does uses cin, cout or endl? #include b) What using statement do you always put at the top of
OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING USING C++
 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING USING C++ Overview of C++ Overloading Overloading occurs when the same operator or function name is used with different signatures Both operators and functions can be overloaded
OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING USING C++ Overview of C++ Overloading Overloading occurs when the same operator or function name is used with different signatures Both operators and functions can be overloaded
Programming in C++ Prof. Partha Pratim Das Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Programming in C++ Prof. Partha Pratim Das Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 33 Overloading Operator for User - Defined Types: Part 1 Welcome
Programming in C++ Prof. Partha Pratim Das Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 33 Overloading Operator for User - Defined Types: Part 1 Welcome
DATA STRUCTURES CHAPTER 1
 DATA STRUCTURES CHAPTER 1 FOUNDATIONAL OF DATA STRUCTURES This unit introduces some basic concepts that the student needs to be familiar with before attempting to develop any software. It describes data
DATA STRUCTURES CHAPTER 1 FOUNDATIONAL OF DATA STRUCTURES This unit introduces some basic concepts that the student needs to be familiar with before attempting to develop any software. It describes data
Side Effects (3A) Young Won Lim 1/13/18
 Side Effects (3A) Copyright (c) 2016-2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
Side Effects (3A) Copyright (c) 2016-2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
IN CHAPTER 7, SUBROUTINES AND MODULES, you learned how to organize
 8 Object-Oriented Programming IN CHAPTER 7, SUBROUTINES AND MODULES, you learned how to organize your code into subroutines, packages, and modules. In this chapter, you ll find out how to create objects
8 Object-Oriented Programming IN CHAPTER 7, SUBROUTINES AND MODULES, you learned how to organize your code into subroutines, packages, and modules. In this chapter, you ll find out how to create objects
B16 Object Oriented Programming
 B16 Object Oriented Programming Michael A Osborne mosb@robots.ox.ac.uk http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~mosb/b16.html Hilary 2014 Topic 4: Constructors Recall our definition of the Complex class. class Complex
B16 Object Oriented Programming Michael A Osborne mosb@robots.ox.ac.uk http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~mosb/b16.html Hilary 2014 Topic 4: Constructors Recall our definition of the Complex class. class Complex
Lecture 9: Parameter Passing, Generics and Polymorphism, Exceptions
 Lecture 9: Parameter Passing, Generics and Polymorphism, Exceptions COMP 524 Programming Language Concepts Stephen Olivier February 12, 2008 Based on notes by A. Block, N. Fisher, F. Hernandez-Campos,
Lecture 9: Parameter Passing, Generics and Polymorphism, Exceptions COMP 524 Programming Language Concepts Stephen Olivier February 12, 2008 Based on notes by A. Block, N. Fisher, F. Hernandez-Campos,
