Performance Analysis on the Target Detection of Linear Camera of CCD Vertical Target Coordinate Measurement System
|
|
|
- Ethan Lester
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 17, Issue 7, July 21, pp Sensors & Transducers 21 y IFSA Pulishing, S. L. Performance Analysis on the Target Detection of Linear Camera of CCD Vertical Target Coordinate Measurement System Li Jing, Lei Zhiyong, Liu Juan Department of Electronic Information Engineering, Xi an Technological University, Xi an, Shaanxi 7121, China gem99li@163.com Received: 5 May 21 /Accepted: 3 June 21 /Pulished: 31 July 21 Astract: Based on the principle of CCD vertical target measurement system, this article researched the factors of the CCD camera that affects the target detection performance, including CCD sensitivity and exposure, ackground illumination and target illumination, CCD distinguish aility, contrast etween ackground and ojectives and gave the relevant calculation methods. Through theoretical analysis, the article got the relationship among the target length, scan time, image distance, oject distance and the detection speed, the detection distance. What s more, the simulation result shows the effectiveness of the analytic conclusions. Copyright 21 IFSA Pulishing, S. L. Keywords: Linear camera, Illumination, Contras, Detection capaility. 1. Introduction CCD vertical target coordinate measurement system is on the asis of CCD (Charge Coupled Device image sensors and it gets ojective spatial coordinates of the target over time ased on the intersection measurement principle. The CCD vertical target coordinate measurement system is mainly used in the ullet location test, intensive analysis, allistics analysis and so on. It is one of the important means of testing in modern shooting range and it has important significance to improve the level of shooting range weapons identification test [1-3]. But, there are a few studies on CCD linear camera detection performance oth at home and aroad, and there is not a much more completed approach which is systematic and practical. For example, in the case of that the target which has small size and has no light itself is on high-speed flight, the signal-to-noise ratio of the target is quite low, then it is difficult to achieve etter detect results. As one of the important test equipment of shooting range, the target detection capaility of CCD linear array camera has ecame a key factor to evaluate the entire test system. On the asis of the analysis of works principle of CCD vertical target coordinate measuring system, the essay will research on the main factors that affect target detection performance of camera. Through the analysis of linear CCD camera optical performance, the characteristics of the target s ackground and surface and the target s characteristics, we can estalish linear CCD camera velocity models and detection range models for target detection. According to different light, ackground rightness and target size, we can analyze the maximum speed of targets and the most distant of targets that the linear array camera can capture within its aility. The 285
2 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 17, Issue 7, July 21, pp essay will study the linear CCD camera s detection performance through simulation, hoping to analyze and summarize the camera detection capaility in theory and improve the system from some practice. 2. The Basic Principle of the System Vertical target measurement system consists of two linear CCD cameras which are laying on the same aseline and looking up into the sky relatively with a certain angle. The two linear CCD cameras form a virtual target surface in the air. When a target P crosses the target surface, it is captured y the two linear CCD cameras. The coordinates of the target through the target surface can e otained through the intersection of computing, as is shown in Fig. 1. O 1 is CCD1 camera s lens optical center. O 2 is CCD2 camera s lens optical center. Estalish a coordinate system with CCD1 s lens optical center as the origin of coordinates. Horizontal line is the x-axis and perpendicular to the horizontal is the y-axis. The two cameras lens focal length is oth f. Distance etween the optical centers of the lens is L. The inclination angles of the two optical axis are α and β. A target point P which is in the target surface gets the corresponding image point coordinates in the image plane of CCD1 and CCD2 and then the measured target s coordinates through the target can e otained. CCD1 Y Lens f α O P(x,y β O 1 L O 2 X 1 Y 2 Fig. 1. CCD vertical target asic principle of the measurement system. Y 1 X CCD2 3. Camera Detection Capaility Analysis Linear CCD with high sensitivity, wide dynamic range, fast work, high precision measurement has many advantages []. When the target gets through the detection area of the linear array camera, whether the line scan camera can capture the goals and ojectives and extract the target from the ackground X 2 depends on the camera s features, ackground illumination, target characteristics and detection distance [5, 6] Effects of CCD Camera Features In a certain ackground light, selecting the appropriate CCD camera must e considered to make the iggest difference etween the target signal and the ackground signal Time to go Through the Target and CCD Pixel Size The integration time is the time which the CCD image sensor of an optical signal spends on charge accumulation. In the dynamic test target, as the target signal strength is weak, the integration time should e longer. Extending the integration time can cause lurred image and people can not see the image information. Thus, to increase the light intensity of the ackground and contrast enhancement and to control the effective integration time can improve the ratio of the useful signal. Since the charge accumulation and transfer of CCD has a time limit, generally, CCD line camera has a scan rate range of normal use. The phenomenon of that goal goes through the target has two situations: one situation, the time that the target spends on going through the target is less than two times the integration time; another situation, the time that the goal uses to go through the target is more than or equal two times the integration time. In the second case, target within once integration time is under full exposure, the target s signal in the case of that other conditions have no change can reach maximum. In the first case, Target within once integration time may e exposed in a part-time. That is, in the integration oth the target energy and the ackground energy are involved in integration. Then it leads to the difference etween the target signal and the ackground signal to e reduced, and the signal to noise ratio gets lower, thus it is not good to the capture of the target. So High-speed Camera should e used to catch high-speed target to make the time that the goal spends on going through the target and camera integration time match. According to the CCD camera the integral time, we can determine the line scan cycle of cameras and get the est SNR. For a target whose target time is very short, its target time is far less than the integral time, line scan cycle and integration time should e made as close as possile to reduce the non-integral time gap etween two scans, avoiding the case of targets eing undetected. Pixel size of the CCD camera determines the amount of light energy that can e received y the camera [7]. In the case that the goal spends a much long time (longer than 2 times the integration time to go over the target and the target image size is much larger, The camera with large pixel size conducive to 286
3 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 17, Issue 7, July 21, pp the expansion of the difference etween the target and ackground and it is easier to do the target detection. Pixel size corresponds with spatial resolution. The smaller the pixel size is, the higher the spatial resolution is. But the small size makes the area of light surface reduced, which will reduce the capaility of CCD camera for target detection. Therefore, we must make the resolution of the system and the amount of exposure of the camera match, or it would e difficult to meet the requirements of weak target detection CCD s Sensitivity and Exposure The higher sensitivity of CCD camera means smaller minimum light energy that can e detected y the camera. High sensitivity is conducive to detection of small-sized and high-speed targets. Spectral response range of the CCD camera especially the peak spectral response range should coincide with the target detection s reflectance spectra to make sure that CCD camera can otain the maximum signal response while the target reflected light intensity is determined in certain circumstances. Also, the system in use should adjust the camera s aperture size to make sure that the target signal and the ackground signal are always in the camera linear amplification region, avoiding the case that too weak energy causes a loss of signal or too strong energy causes signal saturation. General sensitivity of CCD camera uses CCDworking minimum power density E m (target imaging minimum illumination on the CCD, unit: Lx to represent. H E P m =, (1 DR T where Hp is the CCD saturated exposure; DR is the CCD availale dynamic range (saturation exposure / noise equivalent exposure; T is the frame integration time. CCD image plane target minimum illumination shall e not less than the minimum illumination of CCD target surface. Namely: E E m. Hi of CCD exposure amount calculated y the formula. H i = E i T i, (2 where E i is the incident light intensity to the CCD; T i is the integration time Background Illumination and Target Illumination That whether CCD vertical target coordinate measurement system can get target image mainly depends on the contrast size etween the sky ackground rightness and target s rightness. The scattering light irradiating on the target is mainly caused y reflection of sunlight from target and ground Background Brightness at the Surface of the CCD Image Irradiance Through the analysis on the optical properties of linear array camera imaging system, the ackground center illuminance formula which shows the sky ackground rightness on the CCD as the irradiance of E is [2, ]: D 2 β 2 E = B ( τ (, (3 β Relations etween the illumination axis illumination point and as the center point E = Ecos, That is to say, the light axis of the ackground image of the point is: D 2 β 2 E = B ( τ ( cos, ( β Target image point on the axis of the formula indicates the illuminance: D 2 τ K ( ( Kt = E 1 A S + E 2 ka P, (5 H ( NmA Target illumination on the axis image point: D 2 ( EA 1 S + EkA 2 P ( τk K t (cos E H m =, (6 ( NmA Among them, B is the ackground rightness, f is the image distance of the optical system, D is the effective aperture of the optical system, τ is the rate of transmission system, β is the vertical axis at a magnification of pupil (Common target canopy structure that is doule Gauss lens are doule symmetrical structure β = 1, β is the vertical axis magnification images, H is oject distance of the optical system, is field angle, is the target reflectance of sunlight as a target effective reflection, A S is the effective area of sunlight on the target illumination, E 1 is the illumination light on the target surface, and 2 E is the oservation target in the direction of the projection area, k is the face of 287
4 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 17, Issue 7, July 21, pp sunlight reflectance, A is the single pixel area, N is the imaging target system as the numer per m share, A P is the projection area of the target in the oservation direction. K is the system point spread due to attenuation, K t is attenuation due to the moving target. l K t = vt + l, (7 where L is the length of the target; V is the target speed; and T is the frame integration time Resolution and the Contrast of Target and Background In linear camera work zone, the igger the difference etween the target signals and the ackground is, the easier it is to detect the target. That is, the higher signal-to-noise ratio, the higher proaility of target detection [6]. To maximize this difference, it should make the difference etween ojective s ackground rightness and itself s rightness difference largest from the angle of the light energy. The CCD resolution is related to optical system, the detecting distance, the size of target and other factors. To the Linear CCD camera, detection aility emodies on CCD imaging width than one pixel when passing the optical system. But in practice, in order to ensure a high capture rate, general requirements on CCD target through the optical system imaging is much igger than the width of 2 pixels [8]. The definition of the contrast and illumination of the target to ackground illumination is C. E C = (8 E After the target passing the CCD field of view, in order to extract the target signal from the ackground, the target and ackground contrast should reach a certain level C (general C =.2 [9]. If C >C, the target can e extracted from the ackground; if C <C, the target will e sumerged in the ackground noise Impact on the Detection Capaility of the Target Speed According to the definition of the contrast aove, we can see contrast is related to the ackground illumination and target illumination and from the relationship etween the target illumination and ackground illumination, it can e divided into the following two cases. luminance is less than that of ackground, that is < E, using the formulas (, (6, (7 in the formula (8: D 2 τ K cos l [ ( EA 1 S + EkA 2 P ( ] H ( vt+ l ( NmA D 2 β 2 B ( τ ( cos, (9 D 2 β 2 B ( τ ( cos + > C D β B ( τ ( cos f 2 2 β After finishing we get: l M v > [ 1] T H f 2 (1 C B ( f, (1 Among them M = ( EA 1 S + EkA 2 P /( N m A. luminance is greater than that of ackground, that is > E, using formulas (, (6, (7 in the formula (8: D 2 τ K cos l [ ( EA 1 S + EkA 2 P ( ] H ( vt+ l( Nm A D 2 β 2 B ( τ ( cos, (11 D 2 β 2 B ( τ ( cos > C D 2 β 2 B ( τ ( cos After finishing we get: l M v < [ 1] T H f 2, ( C + 1 B ( f (12 Among them M = ( EA 1 S + EkA 2 P /( N m A. 288
5 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 17, Issue 7, July 21, pp Down from aove we get the two equations of (1 and (12. When the ackground illumination is less than the target illuminance, we get equation (1. Equation (1 means the target maximum speed that a camera can capture. When the ackground illumination is larger than the target illuminance, we get equation (12. Equation (12 means the target minimum speed that a camera can capture. time, image distance, oject distance in oth cases and the result is shown in the Fig. 2, Fig. 3, and Fig Target Detection Distance Analysis According to the analysis of the target detection limit velocity model, we know that the limit of detection range model is related to the oject distance. Deeper analysis is as follows: luminance is less than that of ackground, that is < E, a new formula was deduced from formula (1: Qw H > f (1 + 2( vt + l (1 C B, f Qw 2 Qw + [ ] + 2 ( vt + l (1 C B ( vt + l (1 C B (13 Fig. 2. In different of target length, limit speed followed oject distance changes. where Q = ( E 1 A S + E 2 ka P / A. luminance is greater than that of ackground, that is > E, a new formula was deduced from formula (12: Qw H < f (1 + 2( vt + l (1 + C B, f Qw 2 Qw + [ ] + 2 ( vt + l (1 + C B ( vt + l (1 + C B (1 Down from aove, we get the two equations (13 and (1. When the ackground illumination is less than the target illuminance, we get equation (13. Equation (13 is a camera can capture the target minimum distance. When the ackground illumination is more than the target illuminance, we get equation (1. Equation (1 is a camera can capture the target maximum distance. Fig. 3. In different of scan rate, limit speed followed oject distance changes.. Theoretical Simulation and Analysis When the target reflectivity =.8, the numer lf of pixels in the target is N m = [1, 11], pixel Hw 2 size w= 1 μm, single pixel area is A = w, this essay will analyze the relationship among the limit detection speed and the target length, frame integral Fig.. In different of image distance, limit speed followed oject distance changes. 289
6 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 17, Issue 7, July 21, pp As shown in Fig. 2, in the target length is 3.5 cm, 5.5 cm, 7 cm, 8 cm and 12. cm, the limit speed of target decreases with the increase of oject distance; when the oject distance is certain, the target length is greater, the faster of the target limit speed is. As is shown in Fig. 3, when the scan rate respectively is 1/ s, 1/3 s, 1/2 s, 1/15 s and 1/1 s, the limit speed of target decreases with the increase of oject distance; when the oject distance is certain, as target length is greater, the slower of the target limit speed is. As shown in Fig., when the image distance respectively is 15 mm, 2 mm, 35 mm, 5 mm, the limit speed of target decreases with the increase of oject distance; when the oject distance is certain, as image distance is greater, the target limit speed is greater. The target reflectivity at =.8, the numer of lf pixels in the target is N m =, the pixel size Hw 2 is w= 1μm, single pixel areas is A = w. In oth cases, the relationship among the limit of detection range and the target length, frame integral time, image distance, speed is shown in the Fig. 5, Fig. 6 and Fig. 7. From the Fig. 5, when the target length respectively are 3.5 cm, 5.5 cm, 7 cm, 8 cm, 12. cm, the target distance will e all decreased with the increase of the target speed, when the target speed is constant, the larger the target length is, the larger the maximum distance to the target is. the target speed, when the target speed is constant, the larger the image distance is, the larger the target limit speed is. Fig. 6. The change of different scan rate s limit distance with the thange of the target speed. Fig. 7. The change of different image distance s limit distance with the change of target speed. 5. Conclusion Fig. 5. The change of different target length s limit distance with the change of the target speed. From the Fig. 6, when the respectively scan rates are 1/ s, 1/3 s, 1/2 s, 1/1 s, the target s limit distance will e all decreased with the increase of the target speed, when the target speed is constant, the larger the scan rate is, the smaller of the target s limit distance is. From the Fig. 7, when the image distance are 15 mm, 2 mm, 35 mm, 5 mm, limited distance of the target will e all decreased within the increase of Based on the optical properties of linear CCD camera, the article researches the ackground characteristics of the target surface, the targets own characteristics, the main factors that affect the aility of the camera to detect. Also it estalishes speed mode of linear CCD for target detection, model of linear CCD camera for target detection distance and for different lighting, different ackground luminance, target size. It also gives analysis of the target maximum speed that line scan cameras and of the target most distant line scan cameras captured. The simulation results of the effectiveness conclusions of the linear array CCD camera detection performance for goals. It has some significance for the range of tests strong ackground high speed small target detection. 29
7 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 17, Issue 7, July 21, pp References [1]. Liu Wen, Xiong Rensheng, Zhang Yunqi, et al, Research on acquirement rate of CCD vertical target coordinate measurement system, Acta Photonica Sinica, Vol. 37, Issue 2, 28, pp [2]. Wang Miao, Li Hua, Capturing of CCD vertical target measurement system, Acta Photonica Sinica, Vol. 38, Issue 6, 29, pp [3]. Li Hua, Lei Lei, Chang Hemin, et al, Research on CCD vertical target capturing of faint and high-speed flight projectile, Acta Photonica Sinica, Vol. 37, Issue 6, 28, pp []. An Ying, Study of the sensitivity of the optical and mechanical system of sky screens, Journal of Xi an Technological University, Vol., 211, pp [5]. Ma Jingran, Lei Zhiyong, Wang Zemin, Capture rate of Linear-CCD intersection measuring system for indoor environment, Electronic Design Engineering, Vol. 5, 212, pp [6]. Wang Zemin, Lei Zhiyong, Li Hanshan, et al, Research o Linear-CCD intersection measuring system for indoor environment. Journal of Xi an Technological University, Vol., 211, pp [7]. Li Hanshan, Lei Zhiyong, Wang Zemin, Analysis of two kinds of target intersection measurement system, Journal of Ballistics, Vol. 1, 21, pp [8]. Ni Jinping, Tian Hui, Target test principle of olique incidence of the projectile with target location, Optical Technique, Vol., 26, pp [9]. Li Hanshan, Gao Junchai, Lei Zhiyong, et al, Detection performance analysis of optic-electric detecting target oard, Electronics Optics & Control, Vol. 7, 28, pp [1]. Lei Zhiyong, Jiang Shousan, Linear scan CCD technology and it s application in target measurement, Journal of Xi an Technological University, Vol. 3, 22, pp. 22. [11]. Han Bingchen, Zhang Qingquan, Chen Shuyue, Research and application of linear CCD intersection measuring model, Sci/Tech Information Development & Economy, Vol. 5, 25, pp Copyright, International Frequency Sensor Association (IFSA Pulishing, S. L. All rights reserved. ( 291
result, it is very important to design a simulation system for dynamic laser scanning
 3rd International Conference on Multimedia Technology(ICMT 2013) Accurate and Fast Simulation of Laser Scanning Imaging Luyao Zhou 1 and Huimin Ma Abstract. In order to design a more accurate simulation
3rd International Conference on Multimedia Technology(ICMT 2013) Accurate and Fast Simulation of Laser Scanning Imaging Luyao Zhou 1 and Huimin Ma Abstract. In order to design a more accurate simulation
Analysis of the effect of target scattering on the operational effectiveness of seeker
 2nd International Conference on Materials Science, Machinery and Energy Engineering (MSMEE 2017) Analysis of the effect of target scattering on the operational effectiveness of seeker Jun-chao Yuan1, a,
2nd International Conference on Materials Science, Machinery and Energy Engineering (MSMEE 2017) Analysis of the effect of target scattering on the operational effectiveness of seeker Jun-chao Yuan1, a,
Sensor Modeling Realization Based on Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm
 Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Sensor Modeling Realization Based on Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm Zhongju CHEN College of Computer Science, Yangtze University, 434023,
Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Sensor Modeling Realization Based on Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm Zhongju CHEN College of Computer Science, Yangtze University, 434023,
Research on Measured Course Accuracy Based on Relative Measure between Azimuth and Relative Bearing
 nd International Conference on Education Technology, Management and Humanities Science (ETMHS 016) Research on Measured Course Accuracy Based on Relative Measure etween Azimuth and Relative Bearing Wang
nd International Conference on Education Technology, Management and Humanities Science (ETMHS 016) Research on Measured Course Accuracy Based on Relative Measure etween Azimuth and Relative Bearing Wang
NEAR-IR BROADBAND POLARIZER DESIGN BASED ON PHOTONIC CRYSTALS
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 77, Iss. 3, 2015 ISSN 1223-7027 NEAR-IR BROADBAND POLARIZER DESIGN BASED ON PHOTONIC CRYSTALS Bogdan Stefaniţă CALIN 1, Liliana PREDA 2 We have successfully designed a
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 77, Iss. 3, 2015 ISSN 1223-7027 NEAR-IR BROADBAND POLARIZER DESIGN BASED ON PHOTONIC CRYSTALS Bogdan Stefaniţă CALIN 1, Liliana PREDA 2 We have successfully designed a
Location of air-borne SAR imagery without GCPs and error analysis
 International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering (RSETE 2013) Location of air-borne SAR imagery without GCPs and error analysis FAN Ning-jun, ZHAO Ling-jun, KUANG
International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering (RSETE 2013) Location of air-borne SAR imagery without GCPs and error analysis FAN Ning-jun, ZHAO Ling-jun, KUANG
Time-of-flight basics
 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Glossary of Terms... 3 3. Recovering phase from cross-correlation... 4 4. Time-of-flight operating principle: the lock-in amplifier... 6 5. The time-of-flight sensor pixel...
Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Glossary of Terms... 3 3. Recovering phase from cross-correlation... 4 4. Time-of-flight operating principle: the lock-in amplifier... 6 5. The time-of-flight sensor pixel...
Adaptive Zoom Distance Measuring System of Camera Based on the Ranging of Binocular Vision
 Adaptive Zoom Distance Measuring System of Camera Based on the Ranging of Binocular Vision Zhiyan Zhang 1, Wei Qian 1, Lei Pan 1 & Yanjun Li 1 1 University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, China
Adaptive Zoom Distance Measuring System of Camera Based on the Ranging of Binocular Vision Zhiyan Zhang 1, Wei Qian 1, Lei Pan 1 & Yanjun Li 1 1 University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, China
Measurement of period difference in grating pair based on analysis of grating phase shift
 Measurement of period difference in grating pair based on analysis of grating phase shift Chao Guo, Lijiang Zeng State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments Department of Precision
Measurement of period difference in grating pair based on analysis of grating phase shift Chao Guo, Lijiang Zeng State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments Department of Precision
E (sensor) is given by; Object Size
 A P P L I C A T I O N N O T E S Practical Radiometry It is often necessary to estimate the response of a camera under given lighting conditions, or perhaps to estimate lighting requirements for a particular
A P P L I C A T I O N N O T E S Practical Radiometry It is often necessary to estimate the response of a camera under given lighting conditions, or perhaps to estimate lighting requirements for a particular
ISSN: [Chenglin* et al., 6(5): May, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116
![ISSN: [Chenglin* et al., 6(5): May, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116 ISSN: [Chenglin* et al., 6(5): May, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116](/thumbs/91/106575835.jpg) ISSN: 2277-9655 IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY THE USE OF DAYLIGHT FOR INTERIOR ILLUMINATION SYSTEM WITH WINDOW SHADE REFLECTOR Li Chenglin *, Mahmudul Kabir
ISSN: 2277-9655 IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY THE USE OF DAYLIGHT FOR INTERIOR ILLUMINATION SYSTEM WITH WINDOW SHADE REFLECTOR Li Chenglin *, Mahmudul Kabir
A Novel Double Triangulation 3D Camera Design
 Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Information Acquisition August 20-23, 2006, Weihai, Shandong, China A Novel Double Triangulation 3D Camera Design WANG Lei,BOMei,GAOJun, OU ChunSheng
Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Information Acquisition August 20-23, 2006, Weihai, Shandong, China A Novel Double Triangulation 3D Camera Design WANG Lei,BOMei,GAOJun, OU ChunSheng
A Kind of Wireless Sensor Network Coverage Optimization Algorithm Based on Genetic PSO
 Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com A Kind of Wireless Sensor Network Coverage Optimization Algorithm Based on Genetic PSO Yinghui HUANG School of Electronics and Information,
Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com A Kind of Wireless Sensor Network Coverage Optimization Algorithm Based on Genetic PSO Yinghui HUANG School of Electronics and Information,
A Balancing Algorithm in Wireless Sensor Network Based on the Assistance of Approaching Nodes
 Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com A Balancing Algorithm in Wireless Sensor Network Based on the Assistance of Approaching Nodes 1,* Chengpei Tang, 1 Jiao Yin, 1 Yu Dong 1
Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com A Balancing Algorithm in Wireless Sensor Network Based on the Assistance of Approaching Nodes 1,* Chengpei Tang, 1 Jiao Yin, 1 Yu Dong 1
Subpixel Corner Detection Using Spatial Moment 1)
 Vol.31, No.5 ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA September, 25 Subpixel Corner Detection Using Spatial Moment 1) WANG She-Yang SONG Shen-Min QIANG Wen-Yi CHEN Xing-Lin (Department of Control Engineering, Harbin Institute
Vol.31, No.5 ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA September, 25 Subpixel Corner Detection Using Spatial Moment 1) WANG She-Yang SONG Shen-Min QIANG Wen-Yi CHEN Xing-Lin (Department of Control Engineering, Harbin Institute
Computer Vision. The image formation process
 Computer Vision The image formation process Filippo Bergamasco (filippo.bergamasco@unive.it) http://www.dais.unive.it/~bergamasco DAIS, Ca Foscari University of Venice Academic year 2016/2017 The image
Computer Vision The image formation process Filippo Bergamasco (filippo.bergamasco@unive.it) http://www.dais.unive.it/~bergamasco DAIS, Ca Foscari University of Venice Academic year 2016/2017 The image
The research of the accurate measure of static transfer function for the TDI CCD camera
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series The research of the accurate measure of static transfer function for the TDI CCD camera To cite this article: Li Guo-ning et al 2011 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 276 012131
Journal of Physics: Conference Series The research of the accurate measure of static transfer function for the TDI CCD camera To cite this article: Li Guo-ning et al 2011 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 276 012131
Video Inter-frame Forgery Identification Based on Optical Flow Consistency
 Sensors & Transducers 24 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Video Inter-frame Forgery Identification Based on Optical Flow Consistency Qi Wang, Zhaohong Li, Zhenzhen Zhang, Qinglong
Sensors & Transducers 24 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Video Inter-frame Forgery Identification Based on Optical Flow Consistency Qi Wang, Zhaohong Li, Zhenzhen Zhang, Qinglong
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing. Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19
 Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
GEOG 4110/5100 Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture 2
 GEOG 4110/5100 Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture 2 Data Quality Radiometric Distortion Radiometric Error Correction Relevant reading: Richards, sections 2.1 2.8; 2.10.1 2.10.3 Data Quality/Resolution Spatial
GEOG 4110/5100 Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture 2 Data Quality Radiometric Distortion Radiometric Error Correction Relevant reading: Richards, sections 2.1 2.8; 2.10.1 2.10.3 Data Quality/Resolution Spatial
Simple Spectrograph. grating. slit. camera lens. collimator. primary
 Simple Spectrograph slit grating camera lens collimator primary Notes: 1) For ease of sketching, this shows a transmissive system (refracting telescope, transmission grating). Most telescopes use a reflecting
Simple Spectrograph slit grating camera lens collimator primary Notes: 1) For ease of sketching, this shows a transmissive system (refracting telescope, transmission grating). Most telescopes use a reflecting
The Lens. Refraction and The Lens. Figure 1a:
 Lenses are used in many different optical devices. They are found in telescopes, binoculars, cameras, camcorders and eyeglasses. Even your eye contains a lens that helps you see objects at different distances.
Lenses are used in many different optical devices. They are found in telescopes, binoculars, cameras, camcorders and eyeglasses. Even your eye contains a lens that helps you see objects at different distances.
4. Recommended alignment procedure:
 4. Recommended alignment procedure: 4.1 Introduction The described below procedure presents an example of alignment of beam shapers Shaper and Focal- Shaper (F- Shaper) with using the standard Shaper Mount
4. Recommended alignment procedure: 4.1 Introduction The described below procedure presents an example of alignment of beam shapers Shaper and Focal- Shaper (F- Shaper) with using the standard Shaper Mount
1. Polarization effects in optical spectra of photonic crystals
 Speech for JASS 05. April 2005. Samusev A. 1. Polarization effects in optical spectra of photonic crystals Good afternoon. I would like to introduce myself. My name is Anton Samusev. I m a student of Saint
Speech for JASS 05. April 2005. Samusev A. 1. Polarization effects in optical spectra of photonic crystals Good afternoon. I would like to introduce myself. My name is Anton Samusev. I m a student of Saint
Chapter 36. Diffraction. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 36 Diffraction Copyright 36-1 Single-Slit Diffraction Learning Objectives 36.01 Describe the diffraction of light waves by a narrow opening and an edge, and also describe the resulting interference
Chapter 36 Diffraction Copyright 36-1 Single-Slit Diffraction Learning Objectives 36.01 Describe the diffraction of light waves by a narrow opening and an edge, and also describe the resulting interference
Why use video imaging? Estimation and validation for imaging-based measurement of particle size distribution
 Why use video imaging? Estimation and validation for imaging-ased measurement of particle size distriution Paul A. Larsen and James B. Rawlings High value-added products in the chemical industry are ecoming
Why use video imaging? Estimation and validation for imaging-ased measurement of particle size distriution Paul A. Larsen and James B. Rawlings High value-added products in the chemical industry are ecoming
IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS
 2017 Imaging Science Ph.D. Qualifying Examination June 9, 2017 9:00AM to 12:00PM IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS You must complete two (2) of the three (3) questions given for each of the core graduate classes.
2017 Imaging Science Ph.D. Qualifying Examination June 9, 2017 9:00AM to 12:00PM IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS You must complete two (2) of the three (3) questions given for each of the core graduate classes.
Analysis of Crosstalk in HgCdTe based Vertical Photoconductive LWIR Detector Arrays
 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 54, ssue 7, July 203, pp. 38-42 Sensors & Transducers 203 by FSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Analysis of Crosstalk in HgCdTe based Vertical Photoconductive LWR Detector Arrays
Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 54, ssue 7, July 203, pp. 38-42 Sensors & Transducers 203 by FSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Analysis of Crosstalk in HgCdTe based Vertical Photoconductive LWR Detector Arrays
Dr. Larry J. Paxton Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Laurel, MD (301) (301) fax
 Dr. Larry J. Paxton Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Laurel, MD 20723 (301) 953-6871 (301) 953-6670 fax Understand the instrument. Be able to convert measured counts/pixel on-orbit into
Dr. Larry J. Paxton Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Laurel, MD 20723 (301) 953-6871 (301) 953-6670 fax Understand the instrument. Be able to convert measured counts/pixel on-orbit into
Renishaw invia Raman Microscope (April 2006)
 Renishaw invia Raman Microscope (April 2006) I. Starting the System 1. The main system unit is ON all the time. 2. Switch on the Leica microscope and light source for reflective bright field (BF) imaging.
Renishaw invia Raman Microscope (April 2006) I. Starting the System 1. The main system unit is ON all the time. 2. Switch on the Leica microscope and light source for reflective bright field (BF) imaging.
High Resolution BSI Scientific CMOS
 CMOS, EMCCD AND CCD CAMERAS FOR LIFE SCIENCES High Resolution BSI Scientific CMOS Prime BSI delivers the perfect balance between high resolution imaging and sensitivity with an optimized pixel design and
CMOS, EMCCD AND CCD CAMERAS FOR LIFE SCIENCES High Resolution BSI Scientific CMOS Prime BSI delivers the perfect balance between high resolution imaging and sensitivity with an optimized pixel design and
WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
 WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Optical Metrology and NDT ME-593L, C 2018 Introduction: Wave Optics January 2018 Wave optics: coherence Temporal coherence Review interference
WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Optical Metrology and NDT ME-593L, C 2018 Introduction: Wave Optics January 2018 Wave optics: coherence Temporal coherence Review interference
Lab2: Single Photon Interference
 Lab2: Single Photon Interference Xiaoshu Chen* Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Rochester, NY, 14623 ABSTRACT The wave-particle duality of light was verified by multi and single photon
Lab2: Single Photon Interference Xiaoshu Chen* Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Rochester, NY, 14623 ABSTRACT The wave-particle duality of light was verified by multi and single photon
Secondary grating formation by readout at Bragg-null incidence
 Secondary grating formation by readout at Bragg-null incidence Ali Adibi, Jose Mumbru, Kelvin Wagner, and Demetri Psaltis We show that when a dynamic hologram is read out by illumination at the Bragg nulls
Secondary grating formation by readout at Bragg-null incidence Ali Adibi, Jose Mumbru, Kelvin Wagner, and Demetri Psaltis We show that when a dynamic hologram is read out by illumination at the Bragg nulls
Measurements using three-dimensional product imaging
 ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 10 Special Issue 3/2010 41 46 7/3 Measurements using
ARCHIVES of FOUNDRY ENGINEERING Published quarterly as the organ of the Foundry Commission of the Polish Academy of Sciences ISSN (1897-3310) Volume 10 Special Issue 3/2010 41 46 7/3 Measurements using
SiPM and SPAD Arrays for Next Generation LiDAR
 SiPM and SPAD Arrays for Next Generation LiDAR Salvatore Gnecchi, PhD Senior LiDAR Engineer International SPAD-Sensor Workshop 26 February 2018 SensL All Rights Reserved -- ISSW 2018 1 SensL Quick Facts
SiPM and SPAD Arrays for Next Generation LiDAR Salvatore Gnecchi, PhD Senior LiDAR Engineer International SPAD-Sensor Workshop 26 February 2018 SensL All Rights Reserved -- ISSW 2018 1 SensL Quick Facts
Laser sensors. Transmitter. Receiver. Basilio Bona ROBOTICA 03CFIOR
 Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 3 Laser sensors Rays are transmitted and received coaxially The target is illuminated by collimated rays The receiver measures the time of flight (back and
Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 3 Laser sensors Rays are transmitted and received coaxially The target is illuminated by collimated rays The receiver measures the time of flight (back and
Laser Trianglation Displacement Measurement Method Using Prism-Based Optical Structure
 Laser Trianglation Displacement Measurement Method Using Prism-Based Optical Structure bstract This paper presented a novel method using prismbased optical structure to correct the nonlinear problem of
Laser Trianglation Displacement Measurement Method Using Prism-Based Optical Structure bstract This paper presented a novel method using prismbased optical structure to correct the nonlinear problem of
Improvement of SURF Feature Image Registration Algorithm Based on Cluster Analysis
 Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Improvement of SURF Feature Image Registration Algorithm Based on Cluster Analysis 1 Xulin LONG, 1,* Qiang CHEN, 2 Xiaoya
Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Improvement of SURF Feature Image Registration Algorithm Based on Cluster Analysis 1 Xulin LONG, 1,* Qiang CHEN, 2 Xiaoya
An optical multiplier setup with dual digital micromirror
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS An optical multiplier setup with dual digital micromirror array devices To cite this article: Liu Hui-feng et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 679 012044
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS An optical multiplier setup with dual digital micromirror array devices To cite this article: Liu Hui-feng et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 679 012044
Phase Reversed Image Reconstruction Method of. Industrial Ultrasonic CT
 17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China Phase Reversed Image Reconstruction Method of Industrial Ultrasonic CT Yi-Fang CHEN 1, Wen-Ai SONG 1, Ke-Yi YUAN 1 1 Department
17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China Phase Reversed Image Reconstruction Method of Industrial Ultrasonic CT Yi-Fang CHEN 1, Wen-Ai SONG 1, Ke-Yi YUAN 1 1 Department
A. K. Srivastava, K.C. Sati, Satyander Kumar alaser Science and Technology Center, Metcalfe House, Civil Lines, Delhi , INDIA
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 8, Issue 7, July-2017 1752 Optical method for measurement of radius of curvature of large diameter mirrors A. K. Srivastava, K.C. Sati,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 8, Issue 7, July-2017 1752 Optical method for measurement of radius of curvature of large diameter mirrors A. K. Srivastava, K.C. Sati,
Available online at Procedia Engineering 7 (2010) Procedia Engineering 00 (2010)
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 7 (2010) 290 296 Procedia Engineering 00 (2010) 000 000 Procedia Engineering www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 7 (2010) 290 296 Procedia Engineering 00 (2010) 000 000 Procedia Engineering www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia
Dynamics Response of Spatial Parallel Coordinate Measuring Machine with Clearances
 Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Dynamics Response of Spatial Parallel Coordinate Measuring Machine with Clearances Yu DENG, Xiulong CHEN, Suyu WANG Department of mechanical
Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Dynamics Response of Spatial Parallel Coordinate Measuring Machine with Clearances Yu DENG, Xiulong CHEN, Suyu WANG Department of mechanical
FRESNEL EQUATION RECIPROCAL POLARIZATION METHOD
 FRESNEL EQUATION RECIPROCAL POLARIZATION METHOD BY DAVID MAKER, PH.D. PHOTON RESEARCH ASSOCIATES, INC. SEPTEMBER 006 Abstract The Hyperspectral H V Polarization Inverse Correlation technique incorporates
FRESNEL EQUATION RECIPROCAL POLARIZATION METHOD BY DAVID MAKER, PH.D. PHOTON RESEARCH ASSOCIATES, INC. SEPTEMBER 006 Abstract The Hyperspectral H V Polarization Inverse Correlation technique incorporates
Back Illuminated Scientific CMOS
 Prime 95B Scientific CMOS Camera Datasheet CMOS, EMCCD AND CCD CAMERAS FOR LIFE SCIENCES Back Illuminated Scientific CMOS Discovery depends on every photon Primary applications: Super-Resolution Microscopy
Prime 95B Scientific CMOS Camera Datasheet CMOS, EMCCD AND CCD CAMERAS FOR LIFE SCIENCES Back Illuminated Scientific CMOS Discovery depends on every photon Primary applications: Super-Resolution Microscopy
Target User TARGET USER:
 High level 8x optical Mega Zoom 36 290 mm* 3.3 Megapixel 1/2.5-type CCD with primary colour filter Rapid AF with Predictive Focus Control Low power consumption more than 500 frames using 4 AA alkaline
High level 8x optical Mega Zoom 36 290 mm* 3.3 Megapixel 1/2.5-type CCD with primary colour filter Rapid AF with Predictive Focus Control Low power consumption more than 500 frames using 4 AA alkaline
STUDY ON LASER SPECKLE CORRELATION METHOD APPLIED IN TRIANGULATION DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT
 STUDY ON LASER SPECKLE CORRELATION METHOD APPLIED IN TRIANGULATION DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT 2013 г. L. Shen*, D. G. Li*, F. Luo** * Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, PR China ** China
STUDY ON LASER SPECKLE CORRELATION METHOD APPLIED IN TRIANGULATION DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT 2013 г. L. Shen*, D. G. Li*, F. Luo** * Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, PR China ** China
ratio of the volume under the 2D MTF of a lens to the volume under the 2D MTF of a diffraction limited
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES.9 Strehl ratio (a.u.).5 Singlet Doublet 2 Incident angle (degree) 3 Supplementary Figure. Strehl ratio of the singlet and doublet metasurface lenses. Strehl ratio is the ratio of
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES.9 Strehl ratio (a.u.).5 Singlet Doublet 2 Incident angle (degree) 3 Supplementary Figure. Strehl ratio of the singlet and doublet metasurface lenses. Strehl ratio is the ratio of
SVD-4120A SSNR Low Light, WDR, Day & Night Vandal-Proof Color Dome Camera
 Low Light, WDR, Day & Night Vandal-Proof Color Dome Camera SVD-4120A www.samsungcctv.com Built-in chip Originally Developed by Samsung Techwin Crisp and clear images in any light Samsung Techwin's new
Low Light, WDR, Day & Night Vandal-Proof Color Dome Camera SVD-4120A www.samsungcctv.com Built-in chip Originally Developed by Samsung Techwin Crisp and clear images in any light Samsung Techwin's new
Dynamic Balance Design of the Rotating Arc Sensor Based on PSO Algorithm
 016 International Conference on Advanced Manufacture Technology and Industrial Application (AMTIA 016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-387-8 Dynamic Balance Design of the Rotating Arc Sensor Based on PSO Algorithm Ji-zhong
016 International Conference on Advanced Manufacture Technology and Industrial Application (AMTIA 016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-387-8 Dynamic Balance Design of the Rotating Arc Sensor Based on PSO Algorithm Ji-zhong
An algorithm of lips secondary positioning and feature extraction based on YCbCr color space SHEN Xian-geng 1, WU Wei 2
 International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics (AMEII 015) An algorithm of lips secondary positioning and feature extraction based on YCbCr color space SHEN Xian-geng
International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics (AMEII 015) An algorithm of lips secondary positioning and feature extraction based on YCbCr color space SHEN Xian-geng
Security Monitoring around a Video Surveillance Car with a Pair of Two-camera Omnidirectional
 Security Monitoring around a Video Surveillance Car with a Pair of Two-camera Omnidirectional Imaging Devices Pei-Hsuan Yuan Institute of Multimedia Engineering National Chiao Tung University Hsinchu,
Security Monitoring around a Video Surveillance Car with a Pair of Two-camera Omnidirectional Imaging Devices Pei-Hsuan Yuan Institute of Multimedia Engineering National Chiao Tung University Hsinchu,
International Conference on Information Sciences, Machinery, Materials and Energy (ICISMME 2015)
 International Conference on Information Sciences, Machinery, Materials and Energy (ICISMME 2015) Study on Obtaining High-precision Velocity Parameters of Visual Autonomous Navigation Method Considering
International Conference on Information Sciences, Machinery, Materials and Energy (ICISMME 2015) Study on Obtaining High-precision Velocity Parameters of Visual Autonomous Navigation Method Considering
Influence of the Optical Multi-Film Thickness on the Saturation of the Structural Color Displayed 1
 Advances in Natural Science Vol. 3, No. 2,, pp.317-323 www.cscanada.net ISSN 1715-7862 [PRINT] ISSN 1715-787 [ONLINE] www.cscanada.org *The 3rd International Conference of Bionic Engineering* Influence
Advances in Natural Science Vol. 3, No. 2,, pp.317-323 www.cscanada.net ISSN 1715-7862 [PRINT] ISSN 1715-787 [ONLINE] www.cscanada.org *The 3rd International Conference of Bionic Engineering* Influence
Research and Design of Laser Accurate Displacement Measurement System Xiaogang Wang 1, a, Yuewei Bai 1,b and Kai Liu 1,c
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 2011-07-27 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 301-303, pp 1289-1292 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.301-303.1289 2011 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Research and Design
Advanced Materials Research Online: 2011-07-27 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 301-303, pp 1289-1292 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.301-303.1289 2011 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Research and Design
RASNIK Image Processing with a Steepest Ascent Algorithm
 ATLAS Internal Note MUON-No-092 RASNIK Image Processing with a Steepest Ascent Algorithm Kevan S. Hashemi and James R. Bensinger Brandeis University August 1995 Introduction The RASNIK alignment instrument
ATLAS Internal Note MUON-No-092 RASNIK Image Processing with a Steepest Ascent Algorithm Kevan S. Hashemi and James R. Bensinger Brandeis University August 1995 Introduction The RASNIK alignment instrument
ACTA TECHNICA CORVINIENSIS Bulletin of Engineering Tome X [2017] Fascicule 2 [April June] ISSN:
![ACTA TECHNICA CORVINIENSIS Bulletin of Engineering Tome X [2017] Fascicule 2 [April June] ISSN: ACTA TECHNICA CORVINIENSIS Bulletin of Engineering Tome X [2017] Fascicule 2 [April June] ISSN:](/thumbs/88/117280512.jpg) Tome X [2017] Fascicule 2 [April June] ISSN: 2067 3809 1. Yung-Cheng WANG, 2. Bean-Yin LEE, 1. Chih-Hao HUANG, 3. Chi-Hsiang CHEN DEVELOPMENT OF THE AXIAL PRECISION INSPECTION SYSTEM FOR SPINDLES IN TOOL
Tome X [2017] Fascicule 2 [April June] ISSN: 2067 3809 1. Yung-Cheng WANG, 2. Bean-Yin LEE, 1. Chih-Hao HUANG, 3. Chi-Hsiang CHEN DEVELOPMENT OF THE AXIAL PRECISION INSPECTION SYSTEM FOR SPINDLES IN TOOL
METRIC PLANE RECTIFICATION USING SYMMETRIC VANISHING POINTS
 METRIC PLANE RECTIFICATION USING SYMMETRIC VANISHING POINTS M. Lefler, H. Hel-Or Dept. of CS, University of Haifa, Israel Y. Hel-Or School of CS, IDC, Herzliya, Israel ABSTRACT Video analysis often requires
METRIC PLANE RECTIFICATION USING SYMMETRIC VANISHING POINTS M. Lefler, H. Hel-Or Dept. of CS, University of Haifa, Israel Y. Hel-Or School of CS, IDC, Herzliya, Israel ABSTRACT Video analysis often requires
Performance Improvement of a 3D Stereo Measurement Video Endoscope by Means of a Tunable Monochromator In the Illumination System
 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=22672 Performance Improvement of a 3D Stereo Measurement Video Endoscope by Means of a Tunable Monochromator In the Illumination System Alexander S.
More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=22672 Performance Improvement of a 3D Stereo Measurement Video Endoscope by Means of a Tunable Monochromator In the Illumination System Alexander S.
SIMULATION AND VISUALIZATION IN THE EDUCATION OF COHERENT OPTICS
 SIMULATION AND VISUALIZATION IN THE EDUCATION OF COHERENT OPTICS J. KORNIS, P. PACHER Department of Physics Technical University of Budapest H-1111 Budafoki út 8., Hungary e-mail: kornis@phy.bme.hu, pacher@phy.bme.hu
SIMULATION AND VISUALIZATION IN THE EDUCATION OF COHERENT OPTICS J. KORNIS, P. PACHER Department of Physics Technical University of Budapest H-1111 Budafoki út 8., Hungary e-mail: kornis@phy.bme.hu, pacher@phy.bme.hu
Research on Measuring and Optimization Method of Dynamic Accuracy of CNC Machine Tools
 Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Research on Measuring and Optimization Method of Dynamic Accuracy of CNC Machine Tools 1, 2 Zhiming FENG, 2 Guofu YIN,
Sensors & Transducers 2014 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Research on Measuring and Optimization Method of Dynamic Accuracy of CNC Machine Tools 1, 2 Zhiming FENG, 2 Guofu YIN,
Agus Harjoko Lab. Elektronika dan Instrumentasi, FMIPA, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
 A Comparison Study of the Performance of the Fourier Transform Based Algorithm and the Artificial Neural Network Based Algorithm in Detecting Faric Texture Defect Agus Harjoko La. Elektronika dan Instrumentasi,
A Comparison Study of the Performance of the Fourier Transform Based Algorithm and the Artificial Neural Network Based Algorithm in Detecting Faric Texture Defect Agus Harjoko La. Elektronika dan Instrumentasi,
CIS 580, Machine Perception, Spring 2015 Homework 1 Due: :59AM
 CIS 580, Machine Perception, Spring 2015 Homework 1 Due: 2015.02.09. 11:59AM Instructions. Submit your answers in PDF form to Canvas. This is an individual assignment. 1 Camera Model, Focal Length and
CIS 580, Machine Perception, Spring 2015 Homework 1 Due: 2015.02.09. 11:59AM Instructions. Submit your answers in PDF form to Canvas. This is an individual assignment. 1 Camera Model, Focal Length and
Spectrographs. C. A. Griffith, Class Notes, PTYS 521, 2016 Not for distribution.
 Spectrographs C A Griffith, Class Notes, PTYS 521, 2016 Not for distribution 1 Spectrographs and their characteristics A spectrograph is an instrument that disperses light into a frequency spectrum, which
Spectrographs C A Griffith, Class Notes, PTYS 521, 2016 Not for distribution 1 Spectrographs and their characteristics A spectrograph is an instrument that disperses light into a frequency spectrum, which
Doppler Global Velocimetry: A Potential Velocity Measurement Method for General Aviation Applications
 Doppler Global Velocimetry: A Potential Velocity Measurement Method for General Aviation Applications L. Scott Miller The Wichita State University Wichita, Kansas and James F. Meyers, and Jimmy W. Usry
Doppler Global Velocimetry: A Potential Velocity Measurement Method for General Aviation Applications L. Scott Miller The Wichita State University Wichita, Kansas and James F. Meyers, and Jimmy W. Usry
An Adaptive Histogram Equalization Algorithm on the Image Gray Level Mapping *
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 25 (2012 ) 601 608 2012 International Conference on Solid State Devices and Materials Science An Adaptive Histogram Equalization Algorithm on
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 25 (2012 ) 601 608 2012 International Conference on Solid State Devices and Materials Science An Adaptive Histogram Equalization Algorithm on
Rectangle Positioning Algorithm Simulation Based on Edge Detection and Hough Transform
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 58 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2014, 8, 58-62 Open Access Rectangle Positioning Algorithm Simulation Based on Edge Detection and Hough
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 58 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2014, 8, 58-62 Open Access Rectangle Positioning Algorithm Simulation Based on Edge Detection and Hough
Real-Time Median Filtering for Embedded Smart Cameras
 Real-Time Median Filtering for Emedded Smart Cameras Yong Zhao Brown University Yong Zhao@rown.edu Gariel Tauin Brown University tauin@rown.edu Figure 1: System architecture of our proof-of-concept Visual
Real-Time Median Filtering for Emedded Smart Cameras Yong Zhao Brown University Yong Zhao@rown.edu Gariel Tauin Brown University tauin@rown.edu Figure 1: System architecture of our proof-of-concept Visual
The Parameters Optimization of Fusion Winglet Based on Orthogonal Experiment Yue LUO 1, *, Qi WANG 1, Qi DU 1 and Hou-An DING 1
 2016 International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-329-8 The Parameters Optimization of Fusion Winglet Based on Orthogonal Experiment Yue LUO 1, *, Qi WANG 1, Qi DU 1
2016 International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-329-8 The Parameters Optimization of Fusion Winglet Based on Orthogonal Experiment Yue LUO 1, *, Qi WANG 1, Qi DU 1
Measuring Light: Radiometry and Cameras
 Lecture 11: Measuring Light: Radiometry and Cameras Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2015 Slides credit: a majority of these slides were created by Matt Pharr and Pat Hanrahan Simulating a pinhole
Lecture 11: Measuring Light: Radiometry and Cameras Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2015 Slides credit: a majority of these slides were created by Matt Pharr and Pat Hanrahan Simulating a pinhole
Mag.x system 125 A new high end modular microscope. Dr. Ralf Großkloß QIOPTIQ
 Mag.x system 125 A new high end modular microscope Dr. Ralf Großkloß QIOPTIQ Mag.x system 125 A new high end modular microscope Dr. Ralf Großkloß QIOPTIQ Resolution Speed Sensitivity Qioptiq 2011 3 Optical
Mag.x system 125 A new high end modular microscope Dr. Ralf Großkloß QIOPTIQ Mag.x system 125 A new high end modular microscope Dr. Ralf Großkloß QIOPTIQ Resolution Speed Sensitivity Qioptiq 2011 3 Optical
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Interferometric scattering microscopy with polarization-selective dual detection scheme: Capturing the orientational information of anisotropic nanometric objects Il-Buem Lee
Supplementary Information Interferometric scattering microscopy with polarization-selective dual detection scheme: Capturing the orientational information of anisotropic nanometric objects Il-Buem Lee
Chapter 5 Example and Supplementary Problems
 Chapter 5 Example and Supplementary Problems Single-Slit Diffraction: 1) A beam of monochromatic light (550 nm) is incident on a single slit. On a screen 3.0 meters away the distance from the central and
Chapter 5 Example and Supplementary Problems Single-Slit Diffraction: 1) A beam of monochromatic light (550 nm) is incident on a single slit. On a screen 3.0 meters away the distance from the central and
4. Refraction. glass, air, Perspex and water.
 Mr. C. Grima 11 1. Rays and Beams A ray of light is a narrow beam of parallel light, which can be represented by a line with an arrow on it, in diagrams. A group of rays makes up a beam of light. In laboratory
Mr. C. Grima 11 1. Rays and Beams A ray of light is a narrow beam of parallel light, which can be represented by a line with an arrow on it, in diagrams. A group of rays makes up a beam of light. In laboratory
2012 Imaging Science Ph.D. Comprehensive Examination June 15, :00AM to 1:00PM IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS
 2012 Imaging Science Ph.D. Comprehensive Examination June 15, 2012 9:00AM to 1:00PM IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS You must complete two (2) of the three (3) questions given for each of the core graduate classes.
2012 Imaging Science Ph.D. Comprehensive Examination June 15, 2012 9:00AM to 1:00PM IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS You must complete two (2) of the three (3) questions given for each of the core graduate classes.
Supporting information
 Velocity (μm/s) Z (μm) Supporting information Precise gold nanoparticles sorting in flowing system Wei Wu, Xiaoqiang Zhu, Yunfeng Zuo, Li Liang, Shunping Zhang, Xuming Zhang, Yi Yang *. School of Physics
Velocity (μm/s) Z (μm) Supporting information Precise gold nanoparticles sorting in flowing system Wei Wu, Xiaoqiang Zhu, Yunfeng Zuo, Li Liang, Shunping Zhang, Xuming Zhang, Yi Yang *. School of Physics
Lab Report: Optical Image Processing
 Lab Report: Optical Image Processing Kevin P. Chen * Advanced Labs for Special Topics in Photonics (ECE 1640H) University of Toronto March 5, 1999 Abstract This report describes the experimental principle,
Lab Report: Optical Image Processing Kevin P. Chen * Advanced Labs for Special Topics in Photonics (ECE 1640H) University of Toronto March 5, 1999 Abstract This report describes the experimental principle,
UHD 185 FAQs. Optical System
 UHD 185 FAQs System Setup How is a typical setup of the UHD 185? Is a wireless control during flight possible? How do I trigger the image acquisition? What is the power consumption? What are the specs
UHD 185 FAQs System Setup How is a typical setup of the UHD 185? Is a wireless control during flight possible? How do I trigger the image acquisition? What is the power consumption? What are the specs
Anti-Distortion Image Contrast Enhancement Algorithm Based on Fuzzy Statistical Analysis of the Histogram Equalization
 , pp.101-106 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.123.20 Anti-Distortion Image Contrast Enhancement Algorithm Based on Fuzzy Statistical Analysis of the Histogram Equalization Yao Nan 1, Wang KaiSheng
, pp.101-106 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.123.20 Anti-Distortion Image Contrast Enhancement Algorithm Based on Fuzzy Statistical Analysis of the Histogram Equalization Yao Nan 1, Wang KaiSheng
Simulation study of phase retrieval for hard X-ray in-line phase contrast imaging
 450 Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2005 Vol.48 No.4 450 458 Simulation study of phase retrieval for hard X-ray in-line phase contrast imaging YU Bin 1,2, PENG Xiang 1,2, TIAN Jindong
450 Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2005 Vol.48 No.4 450 458 Simulation study of phase retrieval for hard X-ray in-line phase contrast imaging YU Bin 1,2, PENG Xiang 1,2, TIAN Jindong
Lecture 16 Diffraction Ch. 36
 Lecture 16 Diffraction Ch. 36 Topics Newtons Rings Diffraction and the wave theory Single slit diffraction Intensity of single slit diffraction Double slit diffraction Diffraction grating Dispersion and
Lecture 16 Diffraction Ch. 36 Topics Newtons Rings Diffraction and the wave theory Single slit diffraction Intensity of single slit diffraction Double slit diffraction Diffraction grating Dispersion and
All forms of EM waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s This speed is constant in air as well
 Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Technical Basis for optical experimentation Part #4
 AerE 545 class notes #11 Technical Basis for optical experimentation Part #4 Hui Hu Department of Aerospace Engineering, Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 50011, U.S.A Light sensing and recording Lenses
AerE 545 class notes #11 Technical Basis for optical experimentation Part #4 Hui Hu Department of Aerospace Engineering, Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 50011, U.S.A Light sensing and recording Lenses
A Survey of Modelling and Rendering of the Earth s Atmosphere
 Spring Conference on Computer Graphics 00 A Survey of Modelling and Rendering of the Earth s Atmosphere Jaroslav Sloup Department of Computer Science and Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague
Spring Conference on Computer Graphics 00 A Survey of Modelling and Rendering of the Earth s Atmosphere Jaroslav Sloup Department of Computer Science and Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Apr 22, 2012 Light from distant things We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can
Chapter 36 Image Formation Apr 22, 2012 Light from distant things We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can
Algorithm research of 3D point cloud registration based on iterative closest point 1
 Acta Technica 62, No. 3B/2017, 189 196 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Algorithm research of 3D point cloud registration based on iterative closest point 1 Qian Gao 2, Yujian Wang 2,3,
Acta Technica 62, No. 3B/2017, 189 196 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Algorithm research of 3D point cloud registration based on iterative closest point 1 Qian Gao 2, Yujian Wang 2,3,
Flexible Calibration of a Portable Structured Light System through Surface Plane
 Vol. 34, No. 11 ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA November, 2008 Flexible Calibration of a Portable Structured Light System through Surface Plane GAO Wei 1 WANG Liang 1 HU Zhan-Yi 1 Abstract For a portable structured
Vol. 34, No. 11 ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA November, 2008 Flexible Calibration of a Portable Structured Light System through Surface Plane GAO Wei 1 WANG Liang 1 HU Zhan-Yi 1 Abstract For a portable structured
The Design of Electronic Color Screen Based on Proteus Visual Designer Ting-Yu HOU 1,a, Hao LIU 2,b,*
 2016 Joint International Conference on Service Science, Management and Engineering (SSME 2016) and International Conference on Information Science and Technology (IST 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-379-3 The
2016 Joint International Conference on Service Science, Management and Engineering (SSME 2016) and International Conference on Information Science and Technology (IST 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-379-3 The
Diffraction. Single-slit diffraction. Diffraction by a circular aperture. Chapter 38. In the forward direction, the intensity is maximal.
 Diffraction Chapter 38 Huygens construction may be used to find the wave observed on the downstream side of an aperture of any shape. Diffraction The interference pattern encodes the shape as a Fourier
Diffraction Chapter 38 Huygens construction may be used to find the wave observed on the downstream side of an aperture of any shape. Diffraction The interference pattern encodes the shape as a Fourier
normal angle of incidence increases special angle no light is reflected
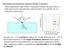 Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Chapters 1-4: Summary
 Chapters 1-4: Summary So far, we have been investigating the image acquisition process. Chapter 1: General introduction Chapter 2: Radiation source and properties Chapter 3: Radiation interaction with
Chapters 1-4: Summary So far, we have been investigating the image acquisition process. Chapter 1: General introduction Chapter 2: Radiation source and properties Chapter 3: Radiation interaction with
Single Photon Interference Christopher Marsh Jaime Vela
 Single Photon Interference Christopher Marsh Jaime Vela Abstract The purpose of this experiment was to study the dual wave-particle nature of light. Using a Mach-Zehnder and double slit interferometer,
Single Photon Interference Christopher Marsh Jaime Vela Abstract The purpose of this experiment was to study the dual wave-particle nature of light. Using a Mach-Zehnder and double slit interferometer,
34.2: Two Types of Image
 Chapter 34 Images 34.2: Two Types of Image For you to see an object, your eye intercepts some of the light rays spreading from the object and then redirect them onto the retina at the rear of the eye.
Chapter 34 Images 34.2: Two Types of Image For you to see an object, your eye intercepts some of the light rays spreading from the object and then redirect them onto the retina at the rear of the eye.
Glare Spread Function (GSF) - 12 Source Angle
 Normalized Pixel Value POWERED BY OPTEST SOFTWARE Stray Light Measurement on LensCheck Lens Measurement Systems 1 Glare Spread Function (GSF) - 12 Source Angle 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.0001 0.00001 0.000001 1
Normalized Pixel Value POWERED BY OPTEST SOFTWARE Stray Light Measurement on LensCheck Lens Measurement Systems 1 Glare Spread Function (GSF) - 12 Source Angle 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.0001 0.00001 0.000001 1
Stripe Noise Removal from Remote Sensing Images Based on Stationary Wavelet Transform
 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 78, Issue 9, September 204, pp. 76-8 Sensors & Transducers 204 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Stripe Noise Removal from Remote Sensing Images Based on
Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 78, Issue 9, September 204, pp. 76-8 Sensors & Transducers 204 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Stripe Noise Removal from Remote Sensing Images Based on
Beam Profilier - Beamage 3.0
 Profilier - age 3.0 KEY FEATURES High resolution (160x120 points) 2.2 MPixels resolution gives accurate profile measurements on very small beams Large Area The 11.3 x 6.0 mm sensor allows to measure very
Profilier - age 3.0 KEY FEATURES High resolution (160x120 points) 2.2 MPixels resolution gives accurate profile measurements on very small beams Large Area The 11.3 x 6.0 mm sensor allows to measure very
CALCULATIONS FOR ENLARGEMENTS & REDUCTIONS
 CALCULATIONS FOR ENLARGEMENTS & REDUCTIONS This handout is designed to help you learn to calculate magnification (reproduction percent) and exposure time when an original must be enlarged or reduced. Magnification
CALCULATIONS FOR ENLARGEMENTS & REDUCTIONS This handout is designed to help you learn to calculate magnification (reproduction percent) and exposure time when an original must be enlarged or reduced. Magnification
Chapter 36. Diffraction. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 36 Diffraction Dr. Armen Kocharian Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This phenomena
Chapter 36 Diffraction Dr. Armen Kocharian Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This phenomena
ULTRASONIC TESTING AND FLAW CHARACTERIZATION. Alex KARPELSON Kinectrics Inc., Toronto, Canada
 ULTRASONIC TESTING AND FLAW CHARACTERIZATION Alex KARPELSON Kinectrics Inc., Toronto, Canada 1. Introduction Ultrasonic Testing (UT) is a commonly used inspection method. Various techniques are employed
ULTRASONIC TESTING AND FLAW CHARACTERIZATION Alex KARPELSON Kinectrics Inc., Toronto, Canada 1. Introduction Ultrasonic Testing (UT) is a commonly used inspection method. Various techniques are employed
