MULTIMEDIA BROADBAND NETWORKS
|
|
|
- Sharlene Norman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 52, NO. 9-10, 2001, REVIEWS - LETTERS - REPORTS MULTIMEDIA BROADBAND NETWORKS Ivan Baroňák Peter Poliak This article gives a short view of possible implementation of technology to higher level of existing PSTN network. This evolution goes to the model of one level universal access network with one type of switches and different node services with transport layer. Universal telecommunication network includes PSTN/ and other special networks for data services and multimedia applications. K e y w o r d s: technology, PSTN network 1 NETWORK ASPECTS The most common strategy to introduce a new technology is the bottom-top approach. This means that the technology is first implemented at some local areas, and afterwards these local islands are interconnected. Normally this can be a very useful strategy, because of advantage that there is no big, over-full equipment necessary at the beginning. In the case of introducing, things might be a little different. This is due to the facts that is not a technically dedicated to a special service but a universal medium to transport very different data, ranging from voice over video to high-speed LANinterconnection, Even the smallest -hubs have a throughput of more than 1 Gbit/s, which is quite a lot for only local use. 2 TOP DOWN APPROACH FOR INTRODUCING In the top-down approach, big cities or highly-industrialised areas are interconnected in a first step with network. From the beginning on, this -network could not be used for dedicated broadband-services via transmission, leased lines or existing data-networks. There are two main advantages of this strategy. is available all across the country from the beginning on. In local areas, where a big amount of customers exist, a local access-network can be connected easily, There is no big capital spending necessary or even cost saving possible because the -network can take over, at low costs, the growth in existing traffic and can be used instead of replacing obsolete conventional switches. Furthermore, there is another potential for cost saving because there is no more need for expensive transmission equipment like multiplexors and SDH-cross connects. Last but not least, the merging of different existing networks into one will result absolutely in lower running costs. To implement an -network as universal, the network has to have at its disposal some inter-working units and connectionless servers. At this point it is important to notice that there is no inter-working between different services. The IWUs and servers are only necessary to fit the different kinds of traffic to the requests resulting from using. Another function of that IWU is the mapping of the different signalling systems used in N- and. In this way the top-down approach could easily gather a lot of traffic, so that the starting capital investment should be redeemed very fast. 3 ATTRIBUTES OF THE EXISTING NETWORK STRUCTURE The present networks were constructed on the base of the previous electromechanical switching technology and analogue transmission system. The environment was not enough adaptable to meet the customer requirements. Depending on the previous technological possibilities we have telephone network for mass communication with small areas and three or four network levels, small and high specialized data networks, leased lines and autonomous distributing networks for audio- and TVprograms. The required special technical solutions make it impossible to combine different services in common networks. First steps were done with common data networks before there were digital sources and switching and transmission methods. The next step is the present process of service integration, eg in the. The experience shows, that service integration with a consequent transposition can increase the network efficiency. Department of Telecommunications, Slovak University of Technology, Ilkovičova 3, Bratislava, Slovakia, baronak@ktl.elf.stuba.sk, poliak@decef.elf.stuba.sk ISSN c 2001 FEI STU
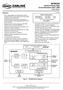
2 324 I. Baroňák P. Poliak: MULTIMEDIA BROADBAND NETWORKS LOCAL MAN IWU MAN CLS NETWORK CLS VoD B- TRIALS VIDEO ON DEMAND TV, AUDIO IWU CORE IWU Data net, FR, X.25 LONG DISTANCE NETWORK B- CONCENTRATOR ACCESS NETWORK ACCESS COMPONENTS BA PRI Legend : CLS - Connection Less Server VoD - Video on Demand IWU - Inter Working Unit PRI RSU BA Fig. 1. First application PSTN / ACCESS NARROW BAND IWU BROAD BAND ACCESS LEX ACCESS B - access BA Fig. 2. Doubled Access Network 4 SELECTED NETWORK MODEL Taking into account the existing influential magnitudes, there is developed a network model for the transport platform, which is based very closely on the optimised network concept for the telephone network/. It is to be used in the first application of the switching unit. New routes will be operated as high-usage routes with overflow to the 2 nd link to the long distance exchange. In the descending network section of the switching unit, high-usage routes are only to be installed to the larger node exchanges of the long-distance exchange area. An internal bundle must be connected to a long-distance exchange switching unit of the same location for traffic to smaller node exchanges. The smaller node exchanges can then be reached via the outlet network of the longdistance trunk switching units. The network model initially provides connection of only node exchanges with the currently running traffic to the switching units via the high-usage routes, and to channel only some % of the traffic through it. If positive results are achieved, the network will be able to take on new sections of traffic, namely:
3 Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 52, NO. 9-10, IN TMN Transit network Access network UTN UTN UTN SUBS LAN N- B- VoD Service Server Fig. 3. Implementation of Universal Telecommunication Node TRANSIT NETWORK Switch N- Switch Regional network RSU access Fig. 4. Creation of regional overlapped networks Higher quality traffic (traffic to network gates, to IN facilities... ), Larger traffic parts (switching additional routes including from smaller node exchanges to the high-usage trunk exchanges to the switching unit). From this point in time onwards, the transport platform will be introduced to cover demand in the telephone service/. 5 EVOLUTION STEPS The described target network is not to realize it in one step. Carefully planned transition steps are necessary. The steps with their characteristic attempts are: Step 1 : At the locations of long distance exchanges new switches are added to generate universal telecommunication node. The -switches have interfaces for broadband accesses from 2 Mbit/s to 155 Mbit/s and for SDHlinks from 155 Mbit/s upwards. The connecting element to the existing telephone network is the special interworking unit (IWU). So the -switch includes both functions: The function as a local switch for broadband services, The function as a transit switch for the PSTN/. In this phase there is no change in the existing PSTN/. The -switches are connected by SDH links not necessarily fully meshed, using the routing capabilities. The access network is doubled in this phase.
4 326 I. Baroňák P. Poliak: MULTIMEDIA BROADBAND NETWORKS REGIONAL NETWORK REGIONAL NETWORK Concentrator High usage routes User switch Universal Telecommunication Node Fig. 5. One level universal network The existing part for the PSTN connects telephone and accesses via copper cable to the concentrators or directly to telephone exchanges. Access with a bandwidth demand of 2 Mbit/s and more is connected by optical fibres to the -switch. In the case of connecting some fibre accesses an optimal step in the access network by introduction optical fibre technology as an universal platform is possible. Optimizing the transit network relating to structuring and dimensioning the logical routes and the transmission links. In all phases reliability aspects have to be watched. So it may be advantageous to have additional routes from a source exchange to more than one exchange in the next network level. Overlapped regional networks will be the result. Step 2 : The next phase is identified by the integrated interworking between low bitrate applications up to 64 kbit/s and high bitrate applications from 2 Mbit/s upwards in the TM-switch. With this step the vision of a universal telecommunications node, realised in a single switching unit, is perfect. Such a universal switching unit is able to replace the existing digital switches for the PSTN/. Additional access networks are developed to a universal platform by introduction of universal collective points with - interfaces to the universal telecommunication node. The introduction of -switches is not limited to the locations of long distance exchanges. So like in the telephone network regional networks are built, connected to long distance exchanges with transit function (Cross-Connectors). The structure of this network direct high usage links or only last choice routes is a result of a further optimalization process. Step 3 : The essential of this step is the transition to the really universal network by: Surrounding access networks to a universal access platform for all services, Placement of -switches in all access areas, Step 4 : In a consequent development of the described network approach and using the advanced -routing principles a single level network can be the final result. The main components in such a visionary network are universal access networks, powerful universal telecommunications nodes, a high capacity transmission network and the best network management equipment. 6 TOP DOWN APPROACH SAMPLE CIRCUIT EMULATIONS Migrating from a TDM-based network to an backbone very often creates the issue of how to carry traffic from existing networks over the new infrastructure. In particular, how it is possible to successfully convey data (TDM) circuits, or voice traffic from PBXs end-toend through the network. Circuit Emulation addresses this issue. Circuit Emulation allows for a traditional point-to-point connection, such as a T1 or E1 circuit between TDM nodes, to be realized over an backbone. This is accomplished by the adaptation of the digital bit stream into a Constant Bit Rate cell stream for transmission through the network, followed by the reassembly of the cell stream into the original data for transmission out of the network to a terminating device. As far as the end nodes in the circuit are concerned,
5 Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 52, NO. 9-10, TDM NODE NODE AAL1 NODE CIRCUIT EMULATIONS SERVICE (CES) Fig. 6. Circuit Emulations Service TDM NODE the fact that the intermediate physical circuit is passed through an network is transparent. The method by which the digital bit stream is divided up into cells and passed across an network is defined in a number of specifications from standard bodies such as the ITU and ANSI, and other organizations such as the Forum. In general, ITU-T I.363 and ANSI T1.630 provide the specification for Adaptation Layer 1 (AAL1) which is the Adaptation Layer defined for carrying Constant Bit Rate traffic in the network. The Forum Circuit Emulation Services specification defines the method by which various types of Circuit Emulation Services are supported in the network (for example, how physical layer alarms at an interface are propagated). Issues in circuit emulation Three critical issues may be identified for the support of a Circuit Emulation Service in a broadband network: These are: maintaining timing synchronization of the Circuit to be supported over the network; controlling the deviation in the arrival of cells at the end-point (Cell Delay Variation); minimizing the latency or propagation delay of the circuit through each switching node. Circuit emulation controller The Circuit Emulation (CE) Controller is an AAL1 ( Adaptation Layer 1) interface to switch providing a Constant Bit Rate service to interconnect legacy equipment over the broadband network. The ability to pass serial bitstreams unmodified end-to-end across the network (or Unstructured Data Transfer) is suitable for applications where simplicity of configuration is required, or the bitstream in question is proprietary and cannot be interpreted at a standard physical interface. A comprehensive series of clock recovery techniques are available on the Circuit Emulation controller. These include Adaptive Clock Recovery, Synchronous Residual Time Stamp, Network Provided Timing and Loop Timing. Between them, these techniques cover virtually all the options available to synchronize devices attached to the asynchronous network. Further options are presented when this controller is used in conjunction with the Node Timing Module. In general a serial bit stream is received by the CE Controller and packaged into cells using AAL1. Each of these cells has a one byte header followed by a 47 byte payload field. This means that each cell carries 376 bits of user data. In order to calculate the cell rate to support circuit emulation at a particular line speed, use the following equation: cells per second = (link speed in bits per second)/376. For example, a Mbit/s circuit emulation generates cells per second. It is important to know this in order to configure traffic policing information for the PVCs involved in the circuit emulation. Due to the overhead, the actual bandwidth used by a Mbit/s circuit emulation is 2.3 Mbit/s. The receiving end unpacks the cells and inserts the bits into the serial data transmit FIFO. Unstructured data transfer The UDT service describes where the entire T1 or E1 bit stream, regardless of format or content, is adapted into cells and passed across the broadband network where it is reassembled into a T1 or E1 circuit. UDT may be used when there is a non-standard framing in use by the end-user equipment, where end-to-end communication of alarm states or Facility Data Link information is important, where timing is supplied by the end user equipment and carried through the network, or where simple configuration of a service with no regard to the bandwidth used is of overriding concern. Applications Connecting Legacy Time Division Multiplexer Networks, Video Networking using external Video Codecs, Derive and transmit video streams from a Video Server device, Transport of Proprietary DataLinks, Establishment of meshed PBX Voice Network, Provisioning of Nx64 Kbps Services over Network. Typical applications include the connection of existing Voice and Data TDM networks over the infrastructure, or to directly interconnect PBX systems for Voice Interworking over the backbone. Structured data transfer The N 64 service is intended to emulate a point-topoint Fractional DS1 or T1 circuit. The service is typically accessed via either Mbit/s DSX-1 interfaces, or Mbit/s G.703 interfaces. For DS1, N of the 24 timeslots available at the DSX-1 interface, where N can be as small as 1 or as large as 24, are carried across the network and reproduced at the output edge. For E1, N can be as small as 1, or as large as 31. Because the N 64 Service can be configured to use a fraction of the timeslots or channels available on the Service Interface, it
6 328 I. Baroňák P. Poliak: MULTIMEDIA BROADBAND NETWORKS is possible to allow several independent emulated circuits to share one Service Interface. The capability of allowing several AAL1 Entities to share one Service Interface, where each AAL1 Entity is associated with a different Virtual Channel Connection (VCC), allows for functional emulation of a DS1/DS0 of E1/DS0 Digital Cross connect Switch. The SDT service describes the case where a fractional (N 64 kbit/s) T1 or E1 circuit is transmitted across the network. An arbitrary number of channels from a T1/E1 interface may be transported across the network, leading to considerable bandwidth savings compared to passing the whole T1/E1 stream. For the T1 case, up to 24 channels may be passed (24 64 kbit/s), whereas for the E1 case up to 31 channels may be passed (in E1, timeslot 0 contains local physical layer management information at each end of the circuit). SDT is particularly useful where it is necessary to minimize the bandwidth used in the network by sending only some timeslots rather than the whole T1/E1 circuit, and where the alarm states and Facility Data Link are terminated at each end of the connection, leading to more accurate physical layer fault diagnosis. SDT does, however, require that timing is provided by the network, and is not passed through from one end station to another. Applications The essential function for switches is to emulate existing Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) circuits. Since many voice and data services are currently provided by TDM circuits, seamless inter-networking between TDM and has become a system requirement. The inter-networking function that satisfies this requirement is the Circuit Emulation Service (CES). Secondly, an access multiplexor allows voice circuits to be made across a single service interface. The SCE card supports concurrent connection to a Private Branch Exchange (PBX). CAS signalling is needed to support a wide variety of legacy PBXs. Many networks look for a framing structure and octet alignment to transport data streams. Installed fractional T1 and Digital Data Service (DDS) leased line services must still be supported when the backbone is changed to. Generally, the backbone is either or circuit switched, but not both. For those backbones which are, all existing switched circuits must be migrated onto the backbone through circuit emulation. Because of its extensive support of Digital Signal Level 0s (DS0), the SCE is an ideal vehicle for constructing -based DACS and other circuit emulation devices. Structured data format is suited for these types of networks and underlying services. References [1] ANDRZEJ, J. : Broadband Switching Systems, [2] Bernd, G. : A Concept for the Network Evolution with Technology, [3] LUKE, K. : Technological Challenges for Future Brand Band Switching Systems, [4] HAAG, J. : Network evolution with implementation aspects, [5] PLATTNER, B. : Broadband Communications Networks, Applications, Future Directions, Received 31 May 2001 Ivan Baroňák (Doc, Ing, PhD), graduated from EF SVŠT in In 1992 he submitted PhD work in the field of terminal telephone equipment. In 1995 he became an Associate Professor in applied informatics. Nowadays he works at the Department of Telecommunications of Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology, Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava. Scientifically, professionally and pedagogically he focuses on problems of terminal telecommunication equipment, digital switching systems,, Telecommunication management (TMN), NB a BB, problem of optimal modelling of private telecommunication networks and services. Peter Poliak is a student at the Department of Telecommunications Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology, Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava. Since 1998 he has been interested in problems of, B-, FR, Data networks. SLOVART G.T.G. s.r.o. GmbH E X P O R T - I M P O R T E X P O R T - I M P O R T of periodical s and of non-periodic ally printed matters, book s and CD - ROM s Krupinská 4 PO BOX 152, Bratislava 5,Slovakia tel.: , fax.: gtg@internet.sk, SLOVART G.T.G. s.r.o. GmbH E X P O R T - I M P O R T
UTILIZATION OF 1st ERLANG FORMULA IN ASYNCHRONOUS NETWORKS
 Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 58, NO. 6, 2007, 342 346 COMMUNICATIONS UTILIZATION OF 1st ERLANG FORMULA IN ASYNCHRONOUS NETWORKS Erik Chromý Ivan aroňák This paper emphasizes a possibility for
Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 58, NO. 6, 2007, 342 346 COMMUNICATIONS UTILIZATION OF 1st ERLANG FORMULA IN ASYNCHRONOUS NETWORKS Erik Chromý Ivan aroňák This paper emphasizes a possibility for
ITU-APT Workshop on NGN Planning March 2007, Bangkok, Thailand
 ITU-APT Workshop on NGN Planning 16 17 March 2007, Bangkok, Thailand 1/2 Riccardo Passerini, ITU-BDT 1 Question 19-1/2: Strategy for migration from existing to next-generation networks (NGN) for developing
ITU-APT Workshop on NGN Planning 16 17 March 2007, Bangkok, Thailand 1/2 Riccardo Passerini, ITU-BDT 1 Question 19-1/2: Strategy for migration from existing to next-generation networks (NGN) for developing
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION. SERIES I: INTEGRATED SERVICES DIGITAL NETWORK (ISDN) Overall network aspects and functions, ISDN usernetwork
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION CCITT I.324 THE INTERNATIONAL TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CONSULTATIVE COMMITTEE (11/1988) SERIES I: INTEGRATED SERVICES DIGITAL NETWORK (ISDN) Overall network aspects
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION CCITT I.324 THE INTERNATIONAL TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CONSULTATIVE COMMITTEE (11/1988) SERIES I: INTEGRATED SERVICES DIGITAL NETWORK (ISDN) Overall network aspects
Circuit Emulation Service
 Best in class Network Modernization Approach Circuit Emulation enables telecom operators to translate legacy systems using TDM signals such as E1/, E3/DS3, STM-n/OC-n to appropriate packet formats and
Best in class Network Modernization Approach Circuit Emulation enables telecom operators to translate legacy systems using TDM signals such as E1/, E3/DS3, STM-n/OC-n to appropriate packet formats and
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS
 BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS INTRODUCTION ATM stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode ATM is a flexible high bandwidth, low delay network technology that is: Capable of handling voice, video and data
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS INTRODUCTION ATM stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode ATM is a flexible high bandwidth, low delay network technology that is: Capable of handling voice, video and data
Communication Networks
 Communication Networks Chapter 3 Multiplexing Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Useful bandwidth of medium exceeds required bandwidth of channel Each signal is modulated to a different carrier frequency
Communication Networks Chapter 3 Multiplexing Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Useful bandwidth of medium exceeds required bandwidth of channel Each signal is modulated to a different carrier frequency
voice-enabling.book Page 72 Friday, August 23, :19 AM
 voice-enabling.book Page 72 Friday, August 23, 2002 11:19 AM voice-enabling.book Page 73 Friday, August 23, 2002 11:19 AM C H A P T E R 4 Offering Bundled and Data Services Chapter 2, VoIP Network Architectures:
voice-enabling.book Page 72 Friday, August 23, 2002 11:19 AM voice-enabling.book Page 73 Friday, August 23, 2002 11:19 AM C H A P T E R 4 Offering Bundled and Data Services Chapter 2, VoIP Network Architectures:
Development of Transport Systems for Dedicated Service Provision Using Packet Transport Technologies
 Development of Transport Systems for Dedicated Service Provision Using Transport Technologies Hidetoshi Onda, Masaki Shinkai, Takaaki Hisashima, Sachio Suda, Takeru Sakairi, Hidenori Iwashita, Masaya Ogawa,
Development of Transport Systems for Dedicated Service Provision Using Transport Technologies Hidetoshi Onda, Masaki Shinkai, Takaaki Hisashima, Sachio Suda, Takeru Sakairi, Hidenori Iwashita, Masaya Ogawa,
Wireless Networks. Communication Networks
 Wireless Networks Communication Networks Types of Communication Networks Traditional Traditional local area network (LAN) Traditional wide area network (WAN) Higher-speed High-speed local area network
Wireless Networks Communication Networks Types of Communication Networks Traditional Traditional local area network (LAN) Traditional wide area network (WAN) Higher-speed High-speed local area network
An optically transparent ultra high speed LAN-ring employing OTDM
 An optically transparent ultra high speed LAN-ring employing OTDM K. Bengi, G. Remsak, H.R. van As Vienna University of Technology, Institute of Communication Networks Gusshausstrasse 25/388, A-1040 Vienna,
An optically transparent ultra high speed LAN-ring employing OTDM K. Bengi, G. Remsak, H.R. van As Vienna University of Technology, Institute of Communication Networks Gusshausstrasse 25/388, A-1040 Vienna,
Master Course Computer Networks IN2097
 Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department of Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Stephan Günther
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department of Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Stephan Günther
Technical Committee. Circuit Emulation Service Interoperability Specification Version 2.0. af-vtoa
 Technical Committee Circuit Emulation Service Interoperability Specification Version 2.0 af-vtoa-0078.000 January 1997 af-vtoa-0078.000 CES-IS V2.0 Circuit Emulation Service Interoperability Specification
Technical Committee Circuit Emulation Service Interoperability Specification Version 2.0 af-vtoa-0078.000 January 1997 af-vtoa-0078.000 CES-IS V2.0 Circuit Emulation Service Interoperability Specification
learntelecoms interactive e-learning suite of courses: SyncNet v6 SDH-based broadband networks SyncNet
 Tel: 0845 0949 120 Email: info@ptt.co.uk Web site: www.ptt.co.uk SyncNet SyncNet v6 SDH-based broadband networks SyncNet is a suite of interactive, multimedia e-learning courses. provides training in the
Tel: 0845 0949 120 Email: info@ptt.co.uk Web site: www.ptt.co.uk SyncNet SyncNet v6 SDH-based broadband networks SyncNet is a suite of interactive, multimedia e-learning courses. provides training in the
WAN technology which are to be discussed:
 WAN Technology Operates at 3 layer OSI model as below: 1. PHY 2. Data Link 3. Network Most of WAN technology are packetswitched network categorized as Switched Virtual circuit Network ( 3-phase, connection
WAN Technology Operates at 3 layer OSI model as below: 1. PHY 2. Data Link 3. Network Most of WAN technology are packetswitched network categorized as Switched Virtual circuit Network ( 3-phase, connection
Network management and QoS provisioning - revise. When someone have to share the same resources is possible to consider two particular problems:
 Revise notes Multiplexing & Multiple Access When someone have to share the same resources is possible to consider two particular problems:. multiplexing;. multiple access. The first one is a centralized
Revise notes Multiplexing & Multiple Access When someone have to share the same resources is possible to consider two particular problems:. multiplexing;. multiple access. The first one is a centralized
WAN Technologies CCNA 4
 WAN Technologies CCNA 4 Overview Note: Most of this will be described in more detail in later chapters. Differentiate between a LAN and WAN Identify the devices used in a WAN List WAN standards Describe
WAN Technologies CCNA 4 Overview Note: Most of this will be described in more detail in later chapters. Differentiate between a LAN and WAN Identify the devices used in a WAN List WAN standards Describe
Integrating Euro-ISDN with ATM Technology : Interworking Mechanisms and Services Support
 Integrating Euro-ISDN with ATM Technology : Interworking Mechanisms and Services Support L. Mandalos [1], K. Leonidou [2], C. Andreopoulos [3], J. Drakos [4], S. Koubias [5], G. Papadopoulos [6] [1] Research
Integrating Euro-ISDN with ATM Technology : Interworking Mechanisms and Services Support L. Mandalos [1], K. Leonidou [2], C. Andreopoulos [3], J. Drakos [4], S. Koubias [5], G. Papadopoulos [6] [1] Research
CWDM CASE STUDY DESIGN GUIDE. Line Systems, Inc. uses iconverter CWDM Multiplexers to overlay Ethernet onto SONET rings
 DESIGN GUIDE CWDM CASE STUDY Line Systems, Inc. uses iconverter CWDM Multiplexers to overlay Ethernet onto SONET rings 140 Technology Drive, Irvine, CA 92618 USA 800-675-8410 +1 949-250-6510 www.omnitron-systems.com
DESIGN GUIDE CWDM CASE STUDY Line Systems, Inc. uses iconverter CWDM Multiplexers to overlay Ethernet onto SONET rings 140 Technology Drive, Irvine, CA 92618 USA 800-675-8410 +1 949-250-6510 www.omnitron-systems.com
Alcatel 7515 Media Gateway. A Compact and Cost-effective NGN Component
 Alcatel 7515 Media Gateway A Compact and Cost-effective NGN Component As a key component of Alcatel s next generation network (NGN) solution, the Alcatel 7515 Media Gateway (MG) provides seamless interworking
Alcatel 7515 Media Gateway A Compact and Cost-effective NGN Component As a key component of Alcatel s next generation network (NGN) solution, the Alcatel 7515 Media Gateway (MG) provides seamless interworking
R 155. ZyFLEX. A Fiber Optical Multiplexer For Future-Proof Telecom Solutions.
 F O TA R 155 A Fiber Optical Multiplexer For Future-Proof Telecom Solutions www..com.tw FOM FORTA155 Fiber Optic Multiplexer Scaleable capacity :supports 4, 8, 12, and 16 T1/E1 channels N*64 Kbps with
F O TA R 155 A Fiber Optical Multiplexer For Future-Proof Telecom Solutions www..com.tw FOM FORTA155 Fiber Optic Multiplexer Scaleable capacity :supports 4, 8, 12, and 16 T1/E1 channels N*64 Kbps with
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2008
 Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2008 Lecture 2: Communication Networks The first major topic we will study will be WLANs. But before that, we need to consider a few basics of networking.
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2008 Lecture 2: Communication Networks The first major topic we will study will be WLANs. But before that, we need to consider a few basics of networking.
DigiPoints Volume 1. Leader Guide. Module 12 Asynchronous Transfer Mode. Summary. Outcomes. Objectives. Prerequisites
 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Page 12.i DigiPoints Volume 1 Module 12 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Summary This last module of, covers ATM, and provides an end-to-end data communications model that draws on
Asynchronous Transfer Mode Page 12.i DigiPoints Volume 1 Module 12 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Summary This last module of, covers ATM, and provides an end-to-end data communications model that draws on
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
 ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Protocol Architecture (diag) CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 2 1 Reference Model Planes User plane Provides for user information transfer Control
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Protocol Architecture (diag) CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 2 1 Reference Model Planes User plane Provides for user information transfer Control
Cisco - An Introduction to Circuit Emulation Services
 Page 1 of 14 An Introduction to Circuit Emulation Services Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used CES Concepts Types of Signaling Frame and Cell Processing Types
Page 1 of 14 An Introduction to Circuit Emulation Services Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used CES Concepts Types of Signaling Frame and Cell Processing Types
ATM-SS7 Interworking. Public Narrowband SS7 Network. Central Office. Subscriber. Copyright Hughes Software Systems Ltd., 1999
 ATM-SS7 Interworking White Paper from Hughes Software Systems Discusses the Evolution of Communication Networks and the convergence of voice and data networks Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) signaling
ATM-SS7 Interworking White Paper from Hughes Software Systems Discusses the Evolution of Communication Networks and the convergence of voice and data networks Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) signaling
ATM Logical Connections: VCC. ATM Logical Connections: VPC
 ATM Logical Connections: VCC Logical Connections in ATM are referred to as virtual channel connections (VCCs). Virtual channel (VC) is a generic term used to describe unidirectional transport of ATM cells
ATM Logical Connections: VCC Logical Connections in ATM are referred to as virtual channel connections (VCCs). Virtual channel (VC) is a generic term used to describe unidirectional transport of ATM cells
Bandwidth-on-Demand up to very high speeds. Variety of physical layers using optical fibre, copper, wireless. 3BA33 D.Lewis
 Broadband ISDN 3BA33 David Lewis 3BA33 D.Lewis 2007 1 B-ISDN Model has 3 planes User Control Management 3BA33 D.Lewis 2007 3 Broadband ISDN Was Expected to be the Universal Network of the future Takes
Broadband ISDN 3BA33 David Lewis 3BA33 D.Lewis 2007 1 B-ISDN Model has 3 planes User Control Management 3BA33 D.Lewis 2007 3 Broadband ISDN Was Expected to be the Universal Network of the future Takes
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW
 1 INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW The past few decades have seen the merging of computer and communication technologies Wide-area and local-area computer networks have been deployed to interconnect computers
1 INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW The past few decades have seen the merging of computer and communication technologies Wide-area and local-area computer networks have been deployed to interconnect computers
MetroEthernet Options
 MetroEthernet Options Customise your service features for optimum performance With VectorFibre MetroEthernet you can choose between a range of options for bandwidth, service availability, service configuration
MetroEthernet Options Customise your service features for optimum performance With VectorFibre MetroEthernet you can choose between a range of options for bandwidth, service availability, service configuration
CPEG 514. Lecture 11 Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) CPEG 514
 Lecture 11 Asynchronous Transfer Mode () Outline Introduction Virtual Circuit Setup PVC vs. SVC Quality of Service and Congestion Control IP over and Frame Relay interworking Network (integrated voice,
Lecture 11 Asynchronous Transfer Mode () Outline Introduction Virtual Circuit Setup PVC vs. SVC Quality of Service and Congestion Control IP over and Frame Relay interworking Network (integrated voice,
TC32 presentation to ECMA General Assembly, Edinburgh, 22nd June 2000
 TC32 presentation to ECMA General Assembly, Edinburgh, 22nd June 2000 John Elwell, Chairman ECMA TC32 Siemens Communications (International) Limited john.elwell@siemenscomms.co.uk ECMA/TC32/2000/103 ECMA/GA/2000/69
TC32 presentation to ECMA General Assembly, Edinburgh, 22nd June 2000 John Elwell, Chairman ECMA TC32 Siemens Communications (International) Limited john.elwell@siemenscomms.co.uk ECMA/TC32/2000/103 ECMA/GA/2000/69
CHAPTER -1. Introduction to Computer Networks
 CHAPTER -1 Introduction to Computer Networks PRELIMINARY DEFINITIONS computer network :: [Tanenbaum] a collection of autonomous computers interconnected by a single technology. communications network ::a
CHAPTER -1 Introduction to Computer Networks PRELIMINARY DEFINITIONS computer network :: [Tanenbaum] a collection of autonomous computers interconnected by a single technology. communications network ::a
CHANNELIZED DS-1/E1, DS-3, and OC-3/STM-1 CEM NETWORK MODULES
 CHANNELIZED /E1, DS-3, and OC-3/STM-1 CEM NETWORK MODULES Circuit Emulation Interfaces for ASX, TNX, BXR 400, and BXR1600 Multiservice Switches Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) networks have long been
CHANNELIZED /E1, DS-3, and OC-3/STM-1 CEM NETWORK MODULES Circuit Emulation Interfaces for ASX, TNX, BXR 400, and BXR1600 Multiservice Switches Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) networks have long been
Competitive Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) Wide- Area Network (WAN) Access Using Signaling System 7 (SS7)
 Competitive Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) Wide- Area Network (WAN) Access Using Signaling System 7 (SS7) Definition Using conventional Internet access equipment, service providers may access
Competitive Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) Wide- Area Network (WAN) Access Using Signaling System 7 (SS7) Definition Using conventional Internet access equipment, service providers may access
ACE-2002, ACE-2002E. Multiservice Access Concentrators/ ATM Network Termination Units FEATURES
 Multiservice Access Concentrators/ ATM Network Termination Units FEATURES Multiservice/ATM network demarcation device or access concentrator (ACE-2002), cellular access concentrator () Offer converged
Multiservice Access Concentrators/ ATM Network Termination Units FEATURES Multiservice/ATM network demarcation device or access concentrator (ACE-2002), cellular access concentrator () Offer converged
WAN Technologies (to interconnect IP routers) Mario Baldi
 WAN Technologies (to interconnect IP routers) Mario Baldi www.baldi.info WAN_Technologies - 1 Copyright: see page 2 Copyright Notice This set of transparencies, hereinafter referred to as slides, is protected
WAN Technologies (to interconnect IP routers) Mario Baldi www.baldi.info WAN_Technologies - 1 Copyright: see page 2 Copyright Notice This set of transparencies, hereinafter referred to as slides, is protected
ATM. Asynchronous Transfer Mode. (and some SDH) (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy)
 ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode (and some SDH) (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) Why use ATM? Circuit switched connections: After initial setup no processing in network nodes Fixed bit rates, fixed time delay
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode (and some SDH) (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) Why use ATM? Circuit switched connections: After initial setup no processing in network nodes Fixed bit rates, fixed time delay
Switching Technology S38.165
 Switching Technology S38.165 Pertti Raatikainen VTT Information Technology pertti.raatikainen@vtt.fi L1-1 General Lecturer: Pertti Raatikainen, research professor /VTT email: pertti.raatikainen@vtt.fi
Switching Technology S38.165 Pertti Raatikainen VTT Information Technology pertti.raatikainen@vtt.fi L1-1 General Lecturer: Pertti Raatikainen, research professor /VTT email: pertti.raatikainen@vtt.fi
Telco Scalable Backbones
 Telco Scalable Backbones PDH, SONET/SDH (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 Everything that can be invented has been invented Charles H. Duell, commissioner of the US Office of Patents 1899 Agenda Basics Shannon
Telco Scalable Backbones PDH, SONET/SDH (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 Everything that can be invented has been invented Charles H. Duell, commissioner of the US Office of Patents 1899 Agenda Basics Shannon
A typical WAN structure includes the following components.
 CBCN4103 WAN is a computer network that spans a relatively large geographical area. Typically, a WAN consists of two or more LANs. A WAN is a network usually provided by a specialised company called a
CBCN4103 WAN is a computer network that spans a relatively large geographical area. Typically, a WAN consists of two or more LANs. A WAN is a network usually provided by a specialised company called a
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Emerging multimedia, high-speed data, and imaging applications are generating a demand for public networks to be able to multiplex and switch simultaneously a wide spectrum of data rates. These networks
Emerging multimedia, high-speed data, and imaging applications are generating a demand for public networks to be able to multiplex and switch simultaneously a wide spectrum of data rates. These networks
Module 2 Overview of Computer Networks
 Module 2 Overview of Computer Networks Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link:
Module 2 Overview of Computer Networks Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link:
Module 2 Overview of. Computer Networks
 Module Overview of Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link: CS454/654 - Issues How
Module Overview of Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link: CS454/654 - Issues How
Computer Communication Networks
 Contents ELL 785 Computer Communication Networks Introduction Lecture 1 Taxonomy of communication works Computer Communication Networks Building a work ed work architecture 1-1 Introduction PC server wireless
Contents ELL 785 Computer Communication Networks Introduction Lecture 1 Taxonomy of communication works Computer Communication Networks Building a work ed work architecture 1-1 Introduction PC server wireless
Application Note. Re-timing: Cost-effective Synchronization via Re-timed E1 and DS1 Signals. Precision, Stability, Innovation, Support.
 Re-timing: Cost-effective Synchronization via Re-timed E1 and DS1 Signals Application Note Number 14 TELECOM NETWORKS PROFESSIONAL MANUFACTURING POWER & UTILITIES DIGITAL BROADCASING TIME & FREQUENCY TIME
Re-timing: Cost-effective Synchronization via Re-timed E1 and DS1 Signals Application Note Number 14 TELECOM NETWORKS PROFESSIONAL MANUFACTURING POWER & UTILITIES DIGITAL BROADCASING TIME & FREQUENCY TIME
Signaling System 7 (SS7) By : Ali Mustafa
 Signaling System 7 (SS7) By : Ali Mustafa Contents Types of Signaling SS7 Signaling SS7 Protocol Architecture SS7 Network Architecture Basic Call Setup SS7 Applications SS7/IP Inter-working VoIP Network
Signaling System 7 (SS7) By : Ali Mustafa Contents Types of Signaling SS7 Signaling SS7 Protocol Architecture SS7 Network Architecture Basic Call Setup SS7 Applications SS7/IP Inter-working VoIP Network
Module 1. Introduction. Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 1 Introduction Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur Introduction In this module we shall highlight some of the basic aspects of computer networks in two lessons. In lesson 1.1 we shall start with the historical
Module 1 Introduction Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur Introduction In this module we shall highlight some of the basic aspects of computer networks in two lessons. In lesson 1.1 we shall start with the historical
E1-E2 (EB) Chapter 1 MLLN
 E1-E2 (EB) Chapter 1 MLLN MLLN Drawback Of Traditional Leased Line Circuits No Intramedia in between. Grew from 64 kbps they have to jump over to 2 Mbps only. Data Cards support only upto 64 Kbps From
E1-E2 (EB) Chapter 1 MLLN MLLN Drawback Of Traditional Leased Line Circuits No Intramedia in between. Grew from 64 kbps they have to jump over to 2 Mbps only. Data Cards support only upto 64 Kbps From
Teletraffic theory (for beginners)
 Teletraffic theory (for beginners) samuli.aalto@hut.fi teletraf.ppt S-38.8 - The Principles of Telecommunications Technology - Fall 000 Contents Purpose of Teletraffic Theory Network level: switching principles
Teletraffic theory (for beginners) samuli.aalto@hut.fi teletraf.ppt S-38.8 - The Principles of Telecommunications Technology - Fall 000 Contents Purpose of Teletraffic Theory Network level: switching principles
Multimedia Systems. Networks WS 2009/2010
 Multimedia Systems WS 2009/2010 Networks Prof. Dr. Paul Müller University of Kaiserslautern, Germany Integrated Communication Systems Lab Email: pmueller@informatik.uni-kl.de 1 Outline Network basics for
Multimedia Systems WS 2009/2010 Networks Prof. Dr. Paul Müller University of Kaiserslautern, Germany Integrated Communication Systems Lab Email: pmueller@informatik.uni-kl.de 1 Outline Network basics for
Module 3. Wide Area Networking (WAN)
 Module 3 Wide Area Networking (WAN) When many nodes or LAN s are connected together in a large scale, we have a WAN. This may be world wide. Because of the separation of the nodes, the Public Data Network
Module 3 Wide Area Networking (WAN) When many nodes or LAN s are connected together in a large scale, we have a WAN. This may be world wide. Because of the separation of the nodes, the Public Data Network
Lecture 1 Overview - Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet
 DATA AND COMPUTER COMMUNICATIONS Lecture 1 Overview - Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet Mei Yang Based on Lecture slides by William Stallings 1 OUTLINE Data Communications and Networking
DATA AND COMPUTER COMMUNICATIONS Lecture 1 Overview - Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet Mei Yang Based on Lecture slides by William Stallings 1 OUTLINE Data Communications and Networking
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) ATM concepts
 Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a switching technique for telecommunication networks. It uses asynchronous time-division multiplexing,[1][2] and it encodes data into
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a switching technique for telecommunication networks. It uses asynchronous time-division multiplexing,[1][2] and it encodes data into
Changing the Voice of
 Changing the Voice of Telecommunications Level 3 Solutions for Voice Service Providers Competitive: It is a word you know well. As a voice services provider, you face a unique set of challenges that originate
Changing the Voice of Telecommunications Level 3 Solutions for Voice Service Providers Competitive: It is a word you know well. As a voice services provider, you face a unique set of challenges that originate
Assisting Developing Countries for developing an NGN strategy
 ITU Regional Development Forum Tashkent, 10-11 June 2008 Assisting Developing Countries for developing an NGN strategy Riccardo Passerini Telecommunication Development Bureau International Telecommunication
ITU Regional Development Forum Tashkent, 10-11 June 2008 Assisting Developing Countries for developing an NGN strategy Riccardo Passerini Telecommunication Development Bureau International Telecommunication
Overview of Networks
 CMPT765/408 08-1 Overview of Networks Qianping Gu 1 Overview of Networks This note is mainly based on Chapters 1-2 of High Performance of Communication Networks by J. Walrand and P. Pravin, 2nd ed, and
CMPT765/408 08-1 Overview of Networks Qianping Gu 1 Overview of Networks This note is mainly based on Chapters 1-2 of High Performance of Communication Networks by J. Walrand and P. Pravin, 2nd ed, and
Backbone network technologies. T Jouni Karvo, Timo Kiravuo
 Backbone network technologies T-110.300 Jouni Karvo, Timo Kiravuo Backbone network technologies This lecture tells about backbone networks After this lecture, you should know WDM, PDH, SDH and ATM understand
Backbone network technologies T-110.300 Jouni Karvo, Timo Kiravuo Backbone network technologies This lecture tells about backbone networks After this lecture, you should know WDM, PDH, SDH and ATM understand
Part 5: Link Layer Technologies. CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: Chapter 5, Kurose and Ross
 Part 5: Link Layer Technologies CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: Chapter 5, Kurose and Ross 1 Outline PPP ATM X.25 Frame Relay 2 Point to Point Data Link Control One sender, one receiver,
Part 5: Link Layer Technologies CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: Chapter 5, Kurose and Ross 1 Outline PPP ATM X.25 Frame Relay 2 Point to Point Data Link Control One sender, one receiver,
EVALUATION OF THREE CAC METHODS: GAUSSIAN APPROXIMATION METHOD, METHOD OF EFFECTIVE BANDWIDTH AND DIFFUSION APPROXIMATION METHOD
 Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 57, NO. 6, 2006, 360 364 EVALUATION OF THREE CAC METHODS: GAUSSIAN APPROXIMATION METHOD, METHOD OF EFFECTIVE BANDWIDTH AND DIFFUSION APPROXIMATION METHOD Peter Kvačkaj
Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 57, NO. 6, 2006, 360 364 EVALUATION OF THREE CAC METHODS: GAUSSIAN APPROXIMATION METHOD, METHOD OF EFFECTIVE BANDWIDTH AND DIFFUSION APPROXIMATION METHOD Peter Kvačkaj
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION. SERIES I: INTEGRATED SERVICES DIGITAL NETWORK (ISDN) Internetwork interfaces
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION CCITT I.510 THE INTERNATIONAL TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CONSULTATIVE COMMITTEE (11/1988) SERIES I: INTEGRATED SERVICES DIGITAL NETWORK (ISDN) Internetwork interfaces
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION CCITT I.510 THE INTERNATIONAL TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CONSULTATIVE COMMITTEE (11/1988) SERIES I: INTEGRATED SERVICES DIGITAL NETWORK (ISDN) Internetwork interfaces
CSIS Frequency Division Multiplexing. Basic Types of Multiplexing. Frequency Division Multiplexing. Frequency Division Multiplexing.
 Multiplexing: combining information streams from multiple sources for transmission over a shared medium Demultiplexing: separating a combination back into individual information streams CSIS 4222 Ch 11:
Multiplexing: combining information streams from multiple sources for transmission over a shared medium Demultiplexing: separating a combination back into individual information streams CSIS 4222 Ch 11:
Name of Course : E1-E2 CFA. Chapter 14. Topic : NG SDH & MSPP
 Name of Course : E1-E2 CFA Chapter 14 Topic : NG SDH & MSPP Date of Creation : 28.03.2011 NGN SDH and MSPP 1. Introduction: Innovation, the lifeline to survival in the telecommunication market, has spurred
Name of Course : E1-E2 CFA Chapter 14 Topic : NG SDH & MSPP Date of Creation : 28.03.2011 NGN SDH and MSPP 1. Introduction: Innovation, the lifeline to survival in the telecommunication market, has spurred
CES Test An Alternative Real-World Approach
 WHITE PAPER Test An Alternative Real-World Approach By Tommy Cook, CEO Calnex Solutions Upgrading the wireless backhaul network to exclusively Ethernet transport is a compelling strategy for Service Providers
WHITE PAPER Test An Alternative Real-World Approach By Tommy Cook, CEO Calnex Solutions Upgrading the wireless backhaul network to exclusively Ethernet transport is a compelling strategy for Service Providers
ATM. Asynchronous Transfer Mode. these slides are based on USP ATM slides from Tereza Carvalho. ATM Networks Outline
 ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode these slides are based on USP ATM slides from Tereza Carvalho 1 ATM Networks Outline ATM technology designed as a support for ISDN Definitions: STM and ATM Standardization
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode these slides are based on USP ATM slides from Tereza Carvalho 1 ATM Networks Outline ATM technology designed as a support for ISDN Definitions: STM and ATM Standardization
ETSI EG V2.1.1 ( )
 EG 201 730-3 V2.1.1 (2006-07) Guide Terminals' access to Public Telecommunications Networks; Application of the Directive 1999/5/EC (R&TTE), article 4.2; Guidelines for the publication of interface specifications;
EG 201 730-3 V2.1.1 (2006-07) Guide Terminals' access to Public Telecommunications Networks; Application of the Directive 1999/5/EC (R&TTE), article 4.2; Guidelines for the publication of interface specifications;
Transport Network Technologies
 Course 34310 Introduction to Communication Technology Course 34311 Introduction to Networks for Telecommunication and Data Communication Transport Network Technologies October 23, 2010 Lars Staalhagen
Course 34310 Introduction to Communication Technology Course 34311 Introduction to Networks for Telecommunication and Data Communication Transport Network Technologies October 23, 2010 Lars Staalhagen
GPON - EPON Comparison. Vestyx Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
 GPON - EPON Comparison Vestyx Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Contents Introduction 3 Protocol fundamentals 4 Framing/service adaption 4 Basic operation 5 Service hierarchy 7 Bandwidth allocation 7 Dynamic Bandwidth
GPON - EPON Comparison Vestyx Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Contents Introduction 3 Protocol fundamentals 4 Framing/service adaption 4 Basic operation 5 Service hierarchy 7 Bandwidth allocation 7 Dynamic Bandwidth
Protocol Architecture (diag) Computer Networks. ATM Connection Relationships. ATM Logical Connections
 168 430 Computer Networks Chapter 11 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Protocol Architecture Similarities between ATM and packet switching Transfer of data in discrete chunks Multiple logical connections over
168 430 Computer Networks Chapter 11 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Protocol Architecture Similarities between ATM and packet switching Transfer of data in discrete chunks Multiple logical connections over
PPP. Point-to-Point Protocol
 PPP Point-to-Point Protocol 1 Introduction One of the most common types of WAN connection is the point-to-point connection. Point-to-point connections are used to connect LANs to service provider WANs,
PPP Point-to-Point Protocol 1 Introduction One of the most common types of WAN connection is the point-to-point connection. Point-to-point connections are used to connect LANs to service provider WANs,
)454 - ).4%2.!4)/.!, 4)-% $)6)3)/. -5,4)0,%8 4$- 4%,%'2!0( 3934%-3 -!).4%.!.#% ).4%2.!4)/.!, 4%,%'2!0( 3934%-3!.$ 0(/4/4%,%'2!0( 42!.3-)33)/.
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION )454 - TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU -!).4%.!.#% ).4%2.!4)/.!, 4%,%'2!0( 3934%-3!.$ 0(/4/4%,%'2!0( 42!.3-)33)/. ).4%2.!4)/.!, 4)-% $)6)3)/. -5,4)0,%8
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION )454 - TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU -!).4%.!.#% ).4%2.!4)/.!, 4%,%'2!0( 3934%-3!.$ 0(/4/4%,%'2!0( 42!.3-)33)/. ).4%2.!4)/.!, 4)-% $)6)3)/. -5,4)0,%8
Mobile Systems Challenges in Next Generation Networks
 International Journal of Future Generation Communication and Networking 15 Mobile Systems Challenges in Next Generation Networks Seyed Ali Alavian, Jahangir Dadkhah Chimeh Faculty of Applied Science of
International Journal of Future Generation Communication and Networking 15 Mobile Systems Challenges in Next Generation Networks Seyed Ali Alavian, Jahangir Dadkhah Chimeh Faculty of Applied Science of
UNIT-II OVERVIEW OF PHYSICAL LAYER SWITCHING & MULTIPLEXING
 1 UNIT-II OVERVIEW OF PHYSICAL LAYER SWITCHING & MULTIPLEXING Syllabus: Physical layer and overview of PL Switching: Multiplexing: frequency division multiplexing, wave length division multiplexing, synchronous
1 UNIT-II OVERVIEW OF PHYSICAL LAYER SWITCHING & MULTIPLEXING Syllabus: Physical layer and overview of PL Switching: Multiplexing: frequency division multiplexing, wave length division multiplexing, synchronous
Evolving Telecommunications to Triple Play:
 Hands-On Evolving Telecommunications to Triple Play: IPTV, VoIP and TV Delivery Systems for System Engineers-DataCom Course Description With the introduction of Next Generation Networks to telecommunications
Hands-On Evolving Telecommunications to Triple Play: IPTV, VoIP and TV Delivery Systems for System Engineers-DataCom Course Description With the introduction of Next Generation Networks to telecommunications
Modelling a Video-on-Demand Service over an Interconnected LAN and ATM Networks
 Modelling a Video-on-Demand Service over an Interconnected LAN and ATM Networks Kok Soon Thia and Chen Khong Tham Dept of Electrical Engineering National University of Singapore Tel: (65) 874-5095 Fax:
Modelling a Video-on-Demand Service over an Interconnected LAN and ATM Networks Kok Soon Thia and Chen Khong Tham Dept of Electrical Engineering National University of Singapore Tel: (65) 874-5095 Fax:
Understanding TeleCom Networks Today II The World of Data
 Understanding The World of Data Course Description Explore the world of data 2.5/3G, Optical, Frame Relay, ATM Networks, Wireless and more... Networks are converging. No more discrete data and voice networks
Understanding The World of Data Course Description Explore the world of data 2.5/3G, Optical, Frame Relay, ATM Networks, Wireless and more... Networks are converging. No more discrete data and voice networks
Sample. Overview of WAN Connections. Objectives. Module 1
 Module 1 Objectives This module introduces the basic elements of WAN connections and describes the role each element plays in creating that connection. After completing this module, you should be able
Module 1 Objectives This module introduces the basic elements of WAN connections and describes the role each element plays in creating that connection. After completing this module, you should be able
Backbone network technologies. T Jouni Karvo, Timo Kiravuo
 Backbone network technologies T-110.300 Jouni Karvo, Timo Kiravuo Backbone network technologies This lecture tells about landline backbone networks After this lecture, you should know WDM, PDH, SDH and
Backbone network technologies T-110.300 Jouni Karvo, Timo Kiravuo Backbone network technologies This lecture tells about landline backbone networks After this lecture, you should know WDM, PDH, SDH and
Network Topologies & Error Performance Monitoring in SDH Technology
 Network Topologies & Error Performance Monitoring in SDH Technology Shiva Sharma Electronics and Communications Department Dronacharya College of Engineering Gurgaon, Haryana Shiva.92@hotmail.com Abstract
Network Topologies & Error Performance Monitoring in SDH Technology Shiva Sharma Electronics and Communications Department Dronacharya College of Engineering Gurgaon, Haryana Shiva.92@hotmail.com Abstract
Lecture 4. Data Transmission Modes and Switching. Data Transmission & Switching 1-1
 Lecture 4 Data Transmission Modes and Switching Data Transmission & Switching 1-1 Agenda Introduction to Data Transmission Modes Parallel and Serial Transmission Transmission Media Guided and unguided
Lecture 4 Data Transmission Modes and Switching Data Transmission & Switching 1-1 Agenda Introduction to Data Transmission Modes Parallel and Serial Transmission Transmission Media Guided and unguided
VC Look-Up Table. External Memory Controller. TX SAR Local Memory. Local Memory. Figure 1 - MT90528 Block Diagram
 28-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-0078.000) Supports both Unstructured and
28-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-0078.000) Supports both Unstructured and
Configuring the E1 + G.703 and T1 + DSX-1 Modules
 9 Configuring the E1 + G.703 and T1 + DSX-1 Modules Contents Using an E1- or T1-Carrier Line for Data and Voice................... 9-3 Drop-and-Insert Modules..................................... 9-3 Standards
9 Configuring the E1 + G.703 and T1 + DSX-1 Modules Contents Using an E1- or T1-Carrier Line for Data and Voice................... 9-3 Drop-and-Insert Modules..................................... 9-3 Standards
William Stallings Data and Computer Communications 7 th Edition. Chapter 11 Asynchronous Transfer Mode
 William Stallings Data and Computer Communications 7 th Edition Chapter 11 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Protocol Architecture Similarities between ATM and packet switching Transfer of data in discrete chunks
William Stallings Data and Computer Communications 7 th Edition Chapter 11 Asynchronous Transfer Mode Protocol Architecture Similarities between ATM and packet switching Transfer of data in discrete chunks
ATM Technology in Detail. Objectives. Presentation Outline
 ATM Technology in Detail Professor Richard Harris Objectives You should be able to: Discuss the ATM protocol stack Identify the different layers and their purpose Explain the ATM Adaptation Layer Discuss
ATM Technology in Detail Professor Richard Harris Objectives You should be able to: Discuss the ATM protocol stack Identify the different layers and their purpose Explain the ATM Adaptation Layer Discuss
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION SERIES Q: SWITCHING AND SIGNALLING
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU Series Q Supplement 24 (12/1999) SERIES Q: SWITCHING AND SIGNALLING Technical Report TRQ.3020: Operation of the
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU Series Q Supplement 24 (12/1999) SERIES Q: SWITCHING AND SIGNALLING Technical Report TRQ.3020: Operation of the
Synchronous Optical Networks (SONET) Advanced Computer Networks
 Synchronous Optical Networks (SONET) Advanced Computer Networks SONET Outline Brief History SONET Overview SONET Rates SONET Ring Architecture Add/Drop Multiplexor (ADM) Section, Line and Path Virtual
Synchronous Optical Networks (SONET) Advanced Computer Networks SONET Outline Brief History SONET Overview SONET Rates SONET Ring Architecture Add/Drop Multiplexor (ADM) Section, Line and Path Virtual
Real Time Implementation of Data Communication using Ipv4Telecom Network through Sdhstm-4 Digital Transmission Wan
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Real Time Implementation of Data Communication using Ipv4Telecom Network through Sdhstm-4 Digital Transmission Wan SharadaOhatkar*, Sanjay Thakare**, RachnaChavan*, Mugdha Kulkarni *,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Real Time Implementation of Data Communication using Ipv4Telecom Network through Sdhstm-4 Digital Transmission Wan SharadaOhatkar*, Sanjay Thakare**, RachnaChavan*, Mugdha Kulkarni *,
Chapter 5. Voice Network Concepts. Voice Network Concepts. Voice Communication Concepts and Technology
 Chapter 5 Voice Communication Concepts and Technology Voice Network Concepts Telephone switchboard - Circa 1898 Voice Network Concepts Telephone calls are connected from source via circuit switching. Circuit
Chapter 5 Voice Communication Concepts and Technology Voice Network Concepts Telephone switchboard - Circa 1898 Voice Network Concepts Telephone calls are connected from source via circuit switching. Circuit
I Voice Trunking Format over MPLS Implementation Agreement. MPLS /Frame Relay Alliance 5.0.0
 I.366.2 Voice Trunking Format over MPLS Implementation Agreement MPLS /Frame Relay Alliance 5.0.0 MPLS /Frame Relay Alliance Technical Committee August 2003 I.366.2 Voice Trunking Format over MPLS Implementation
I.366.2 Voice Trunking Format over MPLS Implementation Agreement MPLS /Frame Relay Alliance 5.0.0 MPLS /Frame Relay Alliance Technical Committee August 2003 I.366.2 Voice Trunking Format over MPLS Implementation
Introduction...1 Timing in TDM Services...2 Timing in NGN Services...3 Traditional Synchronization...5. Evolution...6 Conclusion...
 APPLICATION BRIEF NGN SERIES Table of Contents Introduction................1 in TDM Services......2 in NGN Services......3 Traditional Synchronization...5 and Synchronization Evolution..................6
APPLICATION BRIEF NGN SERIES Table of Contents Introduction................1 in TDM Services......2 in NGN Services......3 Traditional Synchronization...5 and Synchronization Evolution..................6
ITU-T I.150. B-ISDN asynchronous transfer mode functional characteristics
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T I.150 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (02/99) SERIES I: INTEGRATED SERVICES DIGITAL NETWORK General structure General description of asynchronous
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T I.150 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (02/99) SERIES I: INTEGRATED SERVICES DIGITAL NETWORK General structure General description of asynchronous
What is SDH? Telecommunications Standards Primer. Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy (PDH) Limitations of PDH Network
 Página 1 de 7 Telecommunications Standards Primer What is SDH? This document is intended as an introductory guide to the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) standard. The following is a representative
Página 1 de 7 Telecommunications Standards Primer What is SDH? This document is intended as an introductory guide to the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) standard. The following is a representative
Information Systems Infrastructure. Learning Objectives. Telecommunications Deregulation
 Information Systems Infrastructure APPA-Institute for Facilities Management J. Craig Klimczak, D.V.M., M.S. Vice-chancellor for Technology St. Louis Community College 300 South Broadway St. Louis, MO 63102
Information Systems Infrastructure APPA-Institute for Facilities Management J. Craig Klimczak, D.V.M., M.S. Vice-chancellor for Technology St. Louis Community College 300 South Broadway St. Louis, MO 63102
Information and Communication Networks. Communication
 Information Technology Communication Information and Communication Networks Integrating IP and : Delivering QoS in an IP Environment Multiservice Platforms G One infrastructure supporting voice, video
Information Technology Communication Information and Communication Networks Integrating IP and : Delivering QoS in an IP Environment Multiservice Platforms G One infrastructure supporting voice, video
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS
 BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS INTRODUCTION TO DATA COMMUNICATION NETWORKS Data communications are the exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as a wire cable.
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS INTRODUCTION TO DATA COMMUNICATION NETWORKS Data communications are the exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as a wire cable.
Migration to Next Generation IP Network Amir Ahmed Omer Yousif, Dr. Hamid Abbas Ali, UofK, Prof. Sami M. Sharif, UofK
 www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 4 Issue 1 January 2015, Page No. 9916-9928 Migration to Next Generation IP Network Amir Ahmed Omer Yousif, Dr.
www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 4 Issue 1 January 2015, Page No. 9916-9928 Migration to Next Generation IP Network Amir Ahmed Omer Yousif, Dr.
TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS By Syed Bakhtawar Shah Abid Lecturer in Computer Science 1 Public Switched Telephone Network Structure The Local Loop Trunks and Multiplexing Switching 2 Network Structure Minimize
TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS By Syed Bakhtawar Shah Abid Lecturer in Computer Science 1 Public Switched Telephone Network Structure The Local Loop Trunks and Multiplexing Switching 2 Network Structure Minimize
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS
 BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS SWITCHING A switch is a mechanism that allows us to interconnect links to form a larger network. A switch is a multi-input, multi-output device, which transfers packets
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS SWITCHING A switch is a mechanism that allows us to interconnect links to form a larger network. A switch is a multi-input, multi-output device, which transfers packets
ITSF 2007 overview of future sync applications and architecture challenges
 ITSF 2007 overview of future sync applications and architecture challenges Orange Labs Sébastien JOBERT, Research & Development 14/11/2007, presentation to ITSF 2007, London agenda section 1 section 2
ITSF 2007 overview of future sync applications and architecture challenges Orange Labs Sébastien JOBERT, Research & Development 14/11/2007, presentation to ITSF 2007, London agenda section 1 section 2
Chapter 4 Transmission Systems and the Telephone Network. School of Info. Sci. & Eng. Shandong Univ.
 Chapter 4 Transmission Systems and the Telephone Network School of Info. Sci. & Eng. Shandong Univ. Skip in Chapter 3 Articles 3.8.7, 3.8.8 (polynomial math for CRC codes) Skip in Chapter 4 4.2.2 (SONET
Chapter 4 Transmission Systems and the Telephone Network School of Info. Sci. & Eng. Shandong Univ. Skip in Chapter 3 Articles 3.8.7, 3.8.8 (polynomial math for CRC codes) Skip in Chapter 4 4.2.2 (SONET
NGN Migration scenarios and strategies: A vision from ITU Specifications
 ITU Regional Development Forum 2008: Bridging the standardization Gap in Developing Countries Damascus, 20-22 July 2008 NGN Migration scenarios and strategies: A vision from ITU Specifications Souheil
ITU Regional Development Forum 2008: Bridging the standardization Gap in Developing Countries Damascus, 20-22 July 2008 NGN Migration scenarios and strategies: A vision from ITU Specifications Souheil
