Advanced Security and Mobile Networks
|
|
|
- Roberta Todd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advanced Security and Mobile Networks W.Buchanan (1)
2 9. GSM/3G Unit 7: Mobile Networks. Wireless. Security. Mobile IP. Mobile Agents. Spread spectrum. Military/Emergency Networks 8. Ad-hoc 7. Mobile Networks Security Elements W.Buchanan (2)
3 Mobile phone technology. This integrates with the GSM network. Wireless (IEEE ). This normally integrated with a fixed network. Bluetooth. This normally allows networking between noncomputer-type devices, such as mobile phones, hi-fi s, and so on. Infra-red. This technology is too slow and has a limited range for most applications. Line-of-sight optics. This allows for easy connections between buildings, and involves a laser directing it beam to a receiver. It is typically used around cities and gives speeds of several Gbps. Wireless connections which technology? W.Buchanan (3)
4 IEEE a a deals with communications available in the 5GHz frequency, and has a maximum data rate of 54 Mbps. IEEE b b, or Wi-Fi, is the standard that is most commonly used in wireless LAN communications. It has a maximum bandwidth of 11Mbps, at a frequency of 2.4GHz. IEEE c c is a group set up to deal with bridging operations when developing access points. IEEE f f is concerned with standardising access point roaming.which is involved in making sure that interoperability between access points is guaranteed. IEEE g (Proposed) g is a proposed standard that hopes to provide 54Mbps maximum bandwidth over a 2.4GHz connection, the same frequency as the popular b standard. IEEE Wireless W.Buchanan (4)
5 Operating Channels: 11 for N. America, 14 Japan, 13 Europe (ETSI), 2 Spain, 4 France Operating Frequency: GHz (North America), GHz (Japan), GHz (Europe ETSI), GHz (Spain), GHz (France) Data Rate: 1, 2, 5.5 or 11Mbps Media Access Protocol: CSMA/CA, Compliant Range: 11Mbps: 140m (460 feet) 5.5Mbps: 200m (656 feet) 2Mbps: 270m (885 feet) 1Mbps: 400m (1311 feet) RF Technology: Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Modulation: CCK (11Mps, 5.5Mbps), DQPSK (2Mbps), DBPSK (1Mbps) IEEE b W.Buchanan (5)
6 A wireless access point (AP) allow several wireless clients to connect to a single device. Wireless access point W.Buchanan (6)
7 Wireless (IEEE b) Connection. And possibly a Bluetooth connection Wireless adaptor W.Buchanan (7)
8 IEEE b settings W.Buchanan (8)
9 Server Ethernet backbone Access point Access point LAN01 LAN02 Infrastructure network W.Buchanan (9)
10 SSID = group 1 SSID = group 1 SSID = group 1 SSID = group 1 Access point Ethernet SSID W.Buchanan (10)
11 Ad-hoc wireless LAN 1 Ad-hoc wireless LAN 2 Channel is identical such as channel = 3 Channel = 5 Ad-hoc network W.Buchanan (11)
12 Ad-hoc Radius of coverage =2L L L Access point Infrastructure L Span of network W.Buchanan (12)
13 Military and rescue operations Battlefield Evacuation of a building on fire Terrorism & Rescue Operations Hospitals Retrieve patient s information from hospital s database while in surgery Conference meetings Share information quickly Schedule meetings Networking while on the road Inter-vehicle communication Applications of Ad-hoc networks W.Buchanan (13)
14 Authentication algorithm. This sets whether the adapter uses an open system (where other nodes can listen to the communications), or uses encryption (using either a WEP key, or a shared key). Channel. If an ad-hoc network is used, then the nodes which communicate must use the same channel. Fragmentation threshold. This can be used to split large data frames into smaller fragments. The value can range from 64 to 1500 bytes. This is used to improve the efficiency when there is a high amount of traffic on the wireless network, as smaller frames make more efficient usage of the network. Network type. This can either be set to an infrastructure network (which use access points, or wireless hubs) or Ad-hoc, which allows nodes to interconnect without the need for an access point. Network settings W.Buchanan (14)
15 Preamble mode. This can either be set to Long (which is the default) or short. A long preamble allows for interoperatively with 1Mbps and 2Mbps DSSS specifications. The shorter allows for faster operations (as the preamble is kept to a minimum) and can be used where the transmission parameters must be maximized, and that there are no interoperatablity problems. RTS/CTS threshold. The RTS Threshold prevents the Hidden Node problem, where two wireless nodes are within range of the same access point, but are not within range of each other. As they do not know that they both exist on the network, they may try to communicate with the access point at the same time. When they do, their data frames may collide when arriving simultaneously at the Access Point, which causes a loss of data frames from the nodes. The RTS threshold tries to overcome this by enabling the handshaking signals of Ready To Send (RTS) and Clear To Send (CTS). When a node wishes to communicate with the access point it sends a RTS signal to the access point. Once the access point defines that it can then communicate, the access point sends a CTS message. The node can then send its data. Network settings (cont.) W.Buchanan (15)
16 Multipath radio wave propagation. Radio wave propagate outwards in all directions, and will thus hit obstacles, which causes multiple paths for the radio wave. These waves thus add/subtract to signal, and can cause distortion on the wave. Radio data frames collide. Two or more radio devices can be transmitting a data frame at the same time using the same radio frequency. The data frames may thus collide and cause errors in the data frames. Out-of-range threshold. Wireless devices which are at the boundary of the wireless domain can suffer from problems with signal strength as the data frames is being transmitted. This will typically occur when a device is moving around the threshold of the domain, as weak signal strengths are more affected by noise than strong ones. Noisy environment. Many types of electrical equipment can generate high-frequency radio waves, which might interfere with the transmitted data frame. Problems with wireless environments W.Buchanan (16)
17 Multiple paths for the wireless signal W.Buchanan (17)
18 IEEE can use two mechanisms for shared access: CSMA/CA. CSMA/CA is, like standard Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) a contention-based protocol, but uses collision avoidance rather than collision detection. It would be impossible to use collision detection as a radio wave is always either sending or receiving and can never do both at the same time. The nodes will thus not be able to listen on the channel while they are transmitting. Point Coordination Function (PCF). This is an optional priority-based protocol, which provides contention-free frame transfer for transmission of time-critical data, such as real-time video or audio. With this, the point coordinator (PC) operates in the wireless access point and identifies the devices which are allowed to transmit at any given time. Each PC then, with the contention-free (CF) period, the PC polls each of the enabled PCF to determine if they wish to transmit data frames. No other device is allowed to transmit while a another node is being polled. Thus, PCF will be contention-free and enables devices to transmit data frames synchronously, with defined time delays between data frame transmissions. CSMA/CA and PCF W.Buchanan (18)
19 Listen for no activity 1 ACK ACK time-out 2 2 Node has gone. Data frame has collided with another Data frame corrupted with noise. CSMA/CD W.Buchanan (19)
20 Frame control Duration/ ID Address 1 Address 2 Address 3 Sequence control Address 4 Frame body FCS 2 Bytes Frame control. This contains control information. Duration/ID. This contains information on how long the data frame will last. Address fields. This contains different types of address, such as an individual address of group addresses. The two main types of group addresses are broadcast and multicast. Sequence control. This identifies the sequence number of the data frames, and allows the recipient to check for missing or duplicate data frames. Frame body. This part contains the actual data. The maximum amount is 2312 bytes, but most implementations use up to 1500 bytes. FCS (Frame Check Sequence). This is a strong error detection code. IEEE data frame W.Buchanan (20)
21 To avoid interference in the band, radio LANs (RLANs) use either Frequency Hopping or Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum techniques (FHSS & DSSS). These two methods avoid or lower the potential for interference within the band as shown in the next slide. Spread spectrum technologies work by spreading the actual signal over a wider bandwidth for transmission. Using these methods provides resilience from narrow band interference and also reduces interference to other sources using the ISM band. Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum technology works by splitting the ISM band into 79 1MHz channels. Data is transmitted in a sequence over the available channels, spreading the signal across the band according to a hopping pattern, which has been determined between the wireless devices. Each channel can only be occupied for a limited period of time before the system has to hop. Spread Spectrum and Frequency Hopping W.Buchanan (21)
22 Military systems have been using Spread Spectrum and Frequency Hopping for many years. This is to: Avoid jamming on a certain channel. Avoid noise on a certain channel. Confuse the enemy as the transmitting frequency moves in a way that only the sender and receiver known. Imagine having to move the dial of your radio receiver, each minute to a certain frequency in a give way. Such as Radio 1 is broadcast on 909MHz from 12:00, then 915MHz until 12:01, then 900MHz unit 12:02, and so on. Spread Spectrum and Frequency Hopping W.Buchanan (22)
23 W.Buchanan (23) FHSS Ch01 Ch02 Ch03 Ch74 Ch75 DSSS Non overlapping channels 1MHz CH1-22MHz CH7-22MHz CH13-22MHz 2400MHz CH2-22MHz MHz
24 IEEE Security Access Control W.Buchanan (24)
25 2.4GHz 2.48GHz Not recommended for battlefield conditions Wireless networks can be easily jammed by transmitting jamming signals on frequencies around the 2.4GHz. Interference and Jamming W.Buchanan (25)
26 F De-Militarized Zone (DMZ) Public FTP server External device gets behind the firewall N F F Wireless Intrusion F W.Buchanan (26)
27 F De-Militarized Zone (DMZ) Public FTP server All wireless connections are untrusted N F F Wireless Access is Untrusted F W.Buchanan (27)
28 Download Connect? Deprivation of service attack DoS attack DoS and Deprivation of Service Attack W.Buchanan (28)
29 Correct device Spoof device The client spoofs its MAC addresses to gain an IP address. MAC addresses cannot be used to authenticate nodes, as MAC addresses can be setup in some network cards Devices connect to the spoof device. Spoofing W.Buchanan (29)
30 Wireless Security IPSec standards for VPN s Wireless Security Standards Encryption Authentication - Limited to IP - Required for public access systems. WEP - Wireless Encryption Protocol WPA - Wireless Protected Access IEEE i Disaster area for wireless access EAPS - Extensible Authentication Protocol LEAP - Lightweight EAP EAP-TLS -EAP - Transport Layer Security EAP-TTLS - Tunnelled TLS PEAP - Protected EAP Wireless Security W.Buchanan (30)
31 WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy Aka Weak Encryption Protocol Access Control W.Buchanan (31)
32 WEP encryption key reduces eavesdropping It stops unauthorized access to a Wireless Access Point (along with the SSID, of course) napier01 40-bit Keys (24 bits for IV) 104-bit Keys (24 bits for IV) Generate key No standard exists to define how the WEP key is created Generating the WEP key W.Buchanan (32)
33 W.Buchanan (33) Same key is used for all nodes. Thus an eavesdropper can eventually gain the key Initialization Vector Encryption Key 24 bits 40 bits This key is used for encryption of all the data in the domain
34 W.Buchanan (34) WEP uses a stream cipher based on the RC4 algorithm. - Expands a short key into an infinite pseudo-random key. Sender Short-key Short-key Same shared key is used Receiver Short-key Short-key Infinite Infinite pseudo-random pseudo-random key key Infinite Infinite pseudo-random pseudo-random key key Data stream: X-OR X-OR
35 Short-key Short-key Infinite Infinite pseudo-random pseudo-random key key A B X-OR C D X-OR Eavesdropper can detect the key if it can read to streams encoded with the same key Eavesdropper Eavesdropper WEP - Possible Problem? Statistical Analysis W.Buchanan (35)
36 Short-key Short-key Short-key Short-key Infinite Infinite pseudo-random pseudo-random key key Infinite Infinite pseudo-random pseudo-random key key A B X-OR A C X-OR Man-in-the-middle can flip a few bits and change the text. Letters can thus be changed. Man-inthe-middle Man-inthe-middle WEP - Possible Problem? Man-in-the-Middle W.Buchanan (36)
37 WEP guards against these attacks with: An Initialization Vector (IV). This is a secret key which varies the key for every data packet. An Integrity Checker (IC). This is a 32-bit CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check). If bits are flipped, it will not give the same CRC value. Thus an error is caused. Unfortunately both methods have not been implemented properly!!! Which leads to lots of problems. IV and IC W.Buchanan (37)
38 Bits are flipped over consecutive bit positions, so that the overall CRC stays the same. Weakness of the Integrity Checker W.Buchanan (38)
39 W.Buchanan (39) The IV is a 24-bit value, which is sent as cleartext. There can only be 2 24 vectors (16,777,216) If we use 1500 byte packets, the time to send each packet is /11e6 = 1.1ms Thus, if the device is continually sending the same vector will repeat after: 1.1ms 16,777,216 = 18,302.4 seconds which is 5 hours The attacker then takes the two cipertexts which have been encrypted with the same key, and performs a statistical analysis on it.
40 IV= Dah&*43+=f Cipertext1 IV= Dah&*43+=g Cipertext 16,777,214 IV s Cipertext1 X-OR Cipertext2 IV= Dah&*43+=f Cipertext2 Some network cards actually initial at zero, and then increment by 1 each time (in fact the standard does not even specify that the IV should change, at all. Eavesdropper listens for at least five hours and waits for a recurrence of the IV Passive Attack to Decrypt Traffic W.Buchanan (40)
41 Plaintext Corresponding cipertext If eavesdropper knows part of the plaintext for a corresponding cipertext it is possible to build a correctly encrypted cipertext Modified Plaintext By performing bit flips it is possible to change the characters in the plain-text so that the CRC-32 stays the same. Encrypted text CRC-32 Active Attack to Inject Traffic W.Buchanan (41)
42 Known IP/TCP headers Corresponding cipertext Message Cipertext The eavesdropper can expand the method so that they can examine for know IP and TCP headers. Modified IP/TCP header By performing bit flips it is possible to change the characters in the plain-text so that the CRC-32 stays the same. Modified IP/TCP header Message CRC-32 By flipping bits on the IP address, the eavesdropper can send all data packets to their machine. Active Attack from Both Ends W.Buchanan (42)
43 IV=0 IV=1 IV=2 Plaintext Hello How Cipertext %4 $ 9h-= fgh== 5%6$ 79h- The eavesdropper can now decrypt all the data packets with the IV of zero. Over time others can be learnt. IV= 16,777,214 IV=16,777,215 Avbdc=+34d % $ 9h-4=+ Eavesdropper stores a table of known keys for each IV (15GB) Table-based W.Buchanan (43)
44 W.Buchanan (44) Only with this WEP also allows for authentication using a secret key (shared key) or an open system.
45 W.Buchanan (45) Open system Any node can join and there is no encryption or authentication Private-key Challenge text sent to client Request for authentication Encrypted text If correctly encrypted the device can connect
46 EAP Efficient Application Protocols Access Control W.Buchanan (46)
47 EAP provides centralized authentication and dynamic key distribution. It has been developed by the IEEE i Task Group as an end-to-end framework and uses 802.1X and EAP. This is: - Authentication. This is of both the client and the authentication server (such as a RADIUS server). - Encryption keys. These are dynamically created after authentication. They are not common to the whole network. - Centralized policy control. A session time-out generates a reauthentication and the generation of new encryption keys. A wireless client cannot gain access to the network, unless it has been authenticated by the access point or a RADIUS server, and has encryption keys. EAP - Efficient Application Protocols W.Buchanan (47)
48 W.Buchanan (48) There are many versions of EAP, including: LEAP - Lightweight EAP EAP-TLS - EAP-Transport Layer Security PEAP - Protected EAP (PEAP) EAP-TTLS - EAP-Tunnelled TLS EAP-SIM - EAP-Subscriber Identity Module
49 Device cannot access network until it has been authenticated and has encryption keys Corporate network EAPs can either be in the access point or from a RADIUS server User database RADIUS server EAPs W.Buchanan (49)
50 1. Client associates with the access point. 2. Client provides authentication details. 3. RADIUS server authenticates the user. 4. User authenticates the RADIUS server. 5. Client and RADIUS server derive unicast WEP key. 6. RADIUS server gives broadcast WEP key to access point. 7. Access point sends broadcast WEP key to client using unicast WEP key. Corporate network User database RADIUS server EAPs W.Buchanan (50)
51 Client details: User ID and password. Or User ID and digital certificate Or On-time passwords Corporate network User database RADIUS server EAPs W.Buchanan (51)
52 User Authentication: Key size: Encryption: Device Authentication: Open Standard: User differentiation: Certificate: User ID and digital certificate 128 bits RC4 Certificate Yes Group RADIUS server/wlan client Corporate network User database RADIUS server/ certificate server EAP-TLS W.Buchanan (52)
53 User Authentication: Key size: Encryption: Device Authentication: Open Standard: User differentiation: Certificate: User ID and password 128 bits RC4 Not Supported No (Cisco-derived) Group None LEAPs is open to attack from a dictionary attack. Use strong passwords!!! Corporate network User database RADIUS server LEAPs W.Buchanan (53)
54 User Authentication: Key size: Encryption: Device Authentication: Open Standard: User differentiation: Certificate: User ID and password or OTP (one-time password) 128 bits RC4 Not supported Yes Group Yes Corporate network User database RADIUS server EAP - PEAPs W.Buchanan (54)
55 User x to focus authentication of the connecting device. PEAPs W.Buchanan (55)
56 W.Buchanan (56) Along with EAPs, the new enhancements for WLAN are: TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) which are enhancements to RC4- based WEP. The IV has been increased to 48 bits (rather that 24 bits), and the Integrety Checker has been improved. AES, which is a stronger alternative to RC4. IEEE i IEEE x (Authentication of both client and access point) WPA WPA (Wi-fi (Wi-fi Protected Access)
57 Good Design Principles Access Control W.Buchanan (57)
58 10. Layer 2/3 switch 5. RADIUS or TACACS+ 9. Management traffic isolated Server for centralized authentication 4. DCHP for all IP addresses 8. No physical access to access point F 6. PKI server which provides digital certificates for users and servers. 1. No ad-hoc networks 3. Encryption enabled 2. Client supports EAPs. SNMP 7. SNMP community strong have strong names 8. Secure protocols, such as SSH using instead of Telnet (as plaintext passwords can be viewed withtelnet) Some Design Tips W.Buchanan (58)
59 W.Buchanan (59)
Unit 10. Author: W.Buchanan. Mobile Computing and A Model of the Internet (1)
 Unit 10 Author: W.Buchanan. Mobile Computing and A Model of the Internet (1) Author: W.Buchanan. Mobile Computing and A Model of the Internet (2) Mobile and the Future GG F F GG F F AA EE DD AA EE DD BB
Unit 10 Author: W.Buchanan. Mobile Computing and A Model of the Internet (1) Author: W.Buchanan. Mobile Computing and A Model of the Internet (2) Mobile and the Future GG F F GG F F AA EE DD AA EE DD BB
Author: Bill Buchanan. Wireless LAN. Unit 2: Wireless Fundamentals
 Wireless LAN Unit 2: Wireless Fundamentals Wireless connections which technology? Areas covered: Basic radio parameters. This area covers the main type of wireless communications. IEEE 802.11b issues.
Wireless LAN Unit 2: Wireless Fundamentals Wireless connections which technology? Areas covered: Basic radio parameters. This area covers the main type of wireless communications. IEEE 802.11b issues.
Aims. The aims of this unit are to:
 Aims The aims of this unit are to: Outlines the usage of mobile networks and how these may integrate into the Internet. Understand the key elements of GSM networking. Understands the key parameters used
Aims The aims of this unit are to: Outlines the usage of mobile networks and how these may integrate into the Internet. Understand the key elements of GSM networking. Understands the key parameters used
2 Wireless Networks. 2.1 Introduction. 2.2 IEEE b. Unit 2: Wireless Networks 1
 2 Wireless Networks 2.1 Introduction This unit gives an outline of the issues involved in wireless networks, and which must be considered in their design. As the world moves slowly towards a massive wireless
2 Wireless Networks 2.1 Introduction This unit gives an outline of the issues involved in wireless networks, and which must be considered in their design. As the world moves slowly towards a massive wireless
Wireless Networks. Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas. Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov.
 Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
02/21/08 TDC Branch Offices. Headquarters SOHO. Hot Spots. Home. Wireless LAN. Customer Sites. Convention Centers. Hotel
 TDC 363 Introductions to LANs Lecture 7 Wireless LAN 1 Outline WLAN Markets and Business Cases WLAN Standards WLAN Physical Layer WLAN MAC Layer WLAN Security WLAN Design and Deployment 2 The Mobile Environment
TDC 363 Introductions to LANs Lecture 7 Wireless LAN 1 Outline WLAN Markets and Business Cases WLAN Standards WLAN Physical Layer WLAN MAC Layer WLAN Security WLAN Design and Deployment 2 The Mobile Environment
Wireless technology Principles of Security
 Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Viewing Status and Statistics
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter explains how to use ADU to view the client adapter s status and its transmit and receive statistics. The following topics are covered in this chapter: Overview of ADU and Statistics
CHAPTER 7 This chapter explains how to use ADU to view the client adapter s status and its transmit and receive statistics. The following topics are covered in this chapter: Overview of ADU and Statistics
WiFi Networks: IEEE b Wireless LANs. Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018
 WiFi Networks: IEEE 802.11b Wireless LANs Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018 Background (1 of 2) In many respects, the IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN (WLAN) standard
WiFi Networks: IEEE 802.11b Wireless LANs Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018 Background (1 of 2) In many respects, the IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN (WLAN) standard
Wireless Terms. Uses a Chipping Sequence to Provide Reliable Higher Speed Data Communications Than FHSS
 How to Set Up a Secure Home Wireless Network What you don t know about setting up a home wireless network can hurt you. 2008 APCUG Convention Session Tom Jones, P.E., RCDD-NTS CQS-CWLSS AGENDA Some Terms
How to Set Up a Secure Home Wireless Network What you don t know about setting up a home wireless network can hurt you. 2008 APCUG Convention Session Tom Jones, P.E., RCDD-NTS CQS-CWLSS AGENDA Some Terms
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 8 High-Speed WLANs and WLAN Security Objectives Describe how IEEE 802.11a networks function and how they differ from 802.11 networks Outline how 802.11g
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 8 High-Speed WLANs and WLAN Security Objectives Describe how IEEE 802.11a networks function and how they differ from 802.11 networks Outline how 802.11g
Computer Networks. Wireless LANs
 Computer Networks Wireless LANs Mobile Communication Technology according to IEEE (examples) Local wireless networks WLAN 802.11 Personal wireless nw WPAN 802.15 WiFi 802.11a 802.11b 802.11h 802.11i/e/
Computer Networks Wireless LANs Mobile Communication Technology according to IEEE (examples) Local wireless networks WLAN 802.11 Personal wireless nw WPAN 802.15 WiFi 802.11a 802.11b 802.11h 802.11i/e/
Wireless Security Protocol Analysis and Design. Artoré & Bizollon : Wireless Security Protocol Analysis and Design
 Protocol Analysis and Design 1 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 2 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 1.1 WiFi 802.11 3 Networks OSI Structure 4 Networks Infrastructure Networks BSS : Basic Set Service ESS : Extended
Protocol Analysis and Design 1 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 2 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 1.1 WiFi 802.11 3 Networks OSI Structure 4 Networks Infrastructure Networks BSS : Basic Set Service ESS : Extended
U S E R M A N U A L b/g PC CARD
 U S E R M A N U A L 802.11b/g PC CARD Table of Content CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 WIRELESS LAN FEATURE FUNCTIONS... 1 1.2 REGULATORY NOTICE... 1 1.2.1 FCC Class B Statement...1 1.2.2 Canadian Regulatory
U S E R M A N U A L 802.11b/g PC CARD Table of Content CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 WIRELESS LAN FEATURE FUNCTIONS... 1 1.2 REGULATORY NOTICE... 1 1.2.1 FCC Class B Statement...1 1.2.2 Canadian Regulatory
Wireless Networking based on Chapter 15 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers
 Wireless Networking 802.11 based on Chapter 15 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers topics Standards Technical Concepts Implementation Troubleshooting 802.11 timeline source: Anandtech
Wireless Networking 802.11 based on Chapter 15 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers topics Standards Technical Concepts Implementation Troubleshooting 802.11 timeline source: Anandtech
A Configuration Protocol for Embedded Devices on Secure Wireless Networks
 A Configuration Protocol for Embedded Devices on Secure Wireless Networks Larry Sanders lsanders@ittc.ku.edu 6 May 2003 Introduction Wi-Fi Alliance Formally Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA)
A Configuration Protocol for Embedded Devices on Secure Wireless Networks Larry Sanders lsanders@ittc.ku.edu 6 May 2003 Introduction Wi-Fi Alliance Formally Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA)
Overview : Computer Networking. Spectrum Use Comments. Spectrum Allocation in US Link layer challenges and WiFi WiFi
 Overview 15-441 15-441: Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 21: Wireless Justine Sherry Peter Steenkiste Fall 2017 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f17 Link layer challenges and WiFi WiFi Basic WiFi design Some
Overview 15-441 15-441: Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 21: Wireless Justine Sherry Peter Steenkiste Fall 2017 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f17 Link layer challenges and WiFi WiFi Basic WiFi design Some
Security in IEEE Networks
 Security in IEEE 802.11 Networks Mário Nunes, Rui Silva, António Grilo March 2013 Sumário 1 Introduction to the Security Services 2 Basic security mechanisms in IEEE 802.11 2.1 Hidden SSID (Service Set
Security in IEEE 802.11 Networks Mário Nunes, Rui Silva, António Grilo March 2013 Sumário 1 Introduction to the Security Services 2 Basic security mechanisms in IEEE 802.11 2.1 Hidden SSID (Service Set
Shared Access Networks Wireless. 1/27/14 CS mywireless 1
 Shared Access Networks Wireless 1 Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected devices equals
Shared Access Networks Wireless 1 Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected devices equals
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs
 Characteristics IEEE 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming IEEE 802.11a, b, g, e HIPERLAN Bluetooth Comparisons Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 7.1 Comparison: infrastructure vs.
Characteristics IEEE 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming IEEE 802.11a, b, g, e HIPERLAN Bluetooth Comparisons Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 7.1 Comparison: infrastructure vs.
The following chart provides the breakdown of exam as to the weight of each section of the exam.
 Introduction The CWSP-205 exam, covering the 2015 objectives, will certify that the successful candidate understands the security weaknesses inherent in WLANs, the solutions available to address those
Introduction The CWSP-205 exam, covering the 2015 objectives, will certify that the successful candidate understands the security weaknesses inherent in WLANs, the solutions available to address those
Wireless LAN -Architecture
 Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security. Spring 2007 Lecture 8
 CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2007 Lecture 8 Announcements Reminder: Project 1 is due on tonight by midnight. Midterm 1 will be held next Thursday, Feb. 8th. Example midterms
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2007 Lecture 8 Announcements Reminder: Project 1 is due on tonight by midnight. Midterm 1 will be held next Thursday, Feb. 8th. Example midterms
ICE 1332/0715 Mobile Computing (Summer, 2008)
 ICE 1332/0715 Mobile Computing (Summer, 2008) IEEE 802.11 Prof. Chansu Yu http://academic.csuohio.edu/yuc/ Contents Overview of IEEE 802.11 Frame formats MAC frame PHY frame IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802.11b IEEE
ICE 1332/0715 Mobile Computing (Summer, 2008) IEEE 802.11 Prof. Chansu Yu http://academic.csuohio.edu/yuc/ Contents Overview of IEEE 802.11 Frame formats MAC frame PHY frame IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802.11b IEEE
Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-2
 Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment:
 Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
Wireless LAN Security. Gabriel Clothier
 Wireless LAN Security Gabriel Clothier Timeline 1997: 802.11 standard released 1999: 802.11b released, WEP proposed [1] 2003: WiFi alliance certifies for WPA 2004: 802.11i released 2005: 802.11w task group
Wireless LAN Security Gabriel Clothier Timeline 1997: 802.11 standard released 1999: 802.11b released, WEP proposed [1] 2003: WiFi alliance certifies for WPA 2004: 802.11i released 2005: 802.11w task group
CS-435 spring semester Network Technology & Programming Laboratory. Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis
 CS-435 spring semester 2016 Network Technology & Programming Laboratory University of Crete Computer Science Department Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis CS-435 Lecture preview 802.11 Security IEEE
CS-435 spring semester 2016 Network Technology & Programming Laboratory University of Crete Computer Science Department Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis CS-435 Lecture preview 802.11 Security IEEE
CWNP PW Certified Wireless Network Expert. Download Full Version :
 CWNP PW0-300 Certified Wireless Network Expert Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pw0-300 Answer: B, E QUESTION: 130 Which parameters accurately describe the Beacon Interval
CWNP PW0-300 Certified Wireless Network Expert Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pw0-300 Answer: B, E QUESTION: 130 Which parameters accurately describe the Beacon Interval
4.3 IEEE Physical Layer IEEE IEEE b IEEE a IEEE g IEEE n IEEE 802.
 4.3 IEEE 802.11 Physical Layer 4.3.1 IEEE 802.11 4.3.2 IEEE 802.11b 4.3.3 IEEE 802.11a 4.3.4 IEEE 802.11g 4.3.5 IEEE 802.11n 4.3.6 IEEE 802.11ac,ad Andreas Könsgen Summer Term 2012 4.3.3 IEEE 802.11a Data
4.3 IEEE 802.11 Physical Layer 4.3.1 IEEE 802.11 4.3.2 IEEE 802.11b 4.3.3 IEEE 802.11a 4.3.4 IEEE 802.11g 4.3.5 IEEE 802.11n 4.3.6 IEEE 802.11ac,ad Andreas Könsgen Summer Term 2012 4.3.3 IEEE 802.11a Data
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
IEEE Technical Tutorial. Introduction. IEEE Architecture
 IEEE 802.11 Technical Tutorial Introduction The purpose of this document is to give technical readers a basic overview of the new 802.11 Standard, enabling them to understand the basic concepts, principle
IEEE 802.11 Technical Tutorial Introduction The purpose of this document is to give technical readers a basic overview of the new 802.11 Standard, enabling them to understand the basic concepts, principle
Product Brief: SDC-EC25N n ExpressCard Card with Integrated Antenna
 Product Brief: SDC-EC25N 802.11n ExpressCard Card with Integrated Antenna The SDC-EC25N ExpressCard radio card from Summit Data Communications combines a high-performance, dual-band 802.11n radio with
Product Brief: SDC-EC25N 802.11n ExpressCard Card with Integrated Antenna The SDC-EC25N ExpressCard radio card from Summit Data Communications combines a high-performance, dual-band 802.11n radio with
Appendix E Wireless Networking Basics
 Appendix E Wireless Networking Basics This chapter provides an overview of Wireless networking. Wireless Networking Overview The FWG114P v2 Wireless Firewall/Print Server conforms to the Institute of Electrical
Appendix E Wireless Networking Basics This chapter provides an overview of Wireless networking. Wireless Networking Overview The FWG114P v2 Wireless Firewall/Print Server conforms to the Institute of Electrical
WLAN Security. Dr. Siwaruk Siwamogsatham. ThaiCERT, NECTEC
 WLAN Security Dr. Siwaruk Siwamogsatham ThaiCERT, NECTEC Agenda Wireless Technology Overview IEEE 802.11 WLAN Technology WLAN Security Issues How to secure WLAN? WLAN Security Technologies Wireless Technologies
WLAN Security Dr. Siwaruk Siwamogsatham ThaiCERT, NECTEC Agenda Wireless Technology Overview IEEE 802.11 WLAN Technology WLAN Security Issues How to secure WLAN? WLAN Security Technologies Wireless Technologies
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
I N D E X Numerics 100 Mbps WLANs, WLANs, 88
 I N D E X Numerics 100 Mbps WLANs, 233 234 802.11 WLANs, 88 control frames, 54 ACK frames, 57 CF-End frames, 57 58 CTS frames, 56 PS-Poll frames, 54 55 RTS frames, 55 56 DSSS, 93-95 data frames, 76-78
I N D E X Numerics 100 Mbps WLANs, 233 234 802.11 WLANs, 88 control frames, 54 ACK frames, 57 CF-End frames, 57 58 CTS frames, 56 PS-Poll frames, 54 55 RTS frames, 55 56 DSSS, 93-95 data frames, 76-78
Expected Outcomes Able to design the network security for the entire network Able to develop and suggest the security plan and policy
 CHAPTER 9 DEVELOPING NETWORK SECURITY STRATEGIES Expected Outcomes Able to design the network security for the entire network Able to develop and suggest the security plan and policy Network Security Design
CHAPTER 9 DEVELOPING NETWORK SECURITY STRATEGIES Expected Outcomes Able to design the network security for the entire network Able to develop and suggest the security plan and policy Network Security Design
Vendor: HP. Exam Code: HP2-Z32. Exam Name: Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks. Version: Demo
 Vendor: HP Exam Code: HP2-Z32 Exam Name: Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks Version: Demo QUESTION 1 A network administrator deploys several HP MSM APs and an HP MSM Controller. The APs discover the
Vendor: HP Exam Code: HP2-Z32 Exam Name: Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks Version: Demo QUESTION 1 A network administrator deploys several HP MSM APs and an HP MSM Controller. The APs discover the
Wireless Local Area Networks. Networks: Wireless LANs 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Multi-Function Gigabit Wireless-N Client Bridge 2.4GHz 300Mbps Client Bridge/AP/ WDS/Repeater
 Multi-Function Gigabit Wireless-N Client Bridge 2.4GHz 300Mbps Client Bridge/AP/ WDS/Repeater ECB-9750 ECB-9750 is a powerful and multi-functioned 11n product with 7 major multi-functions, is designed
Multi-Function Gigabit Wireless-N Client Bridge 2.4GHz 300Mbps Client Bridge/AP/ WDS/Repeater ECB-9750 ECB-9750 is a powerful and multi-functioned 11n product with 7 major multi-functions, is designed
Wireless Networks. CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: , Kurose and Ross
 Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Princess Nora Bint Abdulrahman University College of computer and information sciences Networks department Networks Security (NET 536)
 Princess Nora Bint Abdulrahman University College of computer and information sciences Networks department Networks Security (NET 536) Prepared by Dr. Samia Chelloug E-mail: samia_chelloug@yahoo.fr Content
Princess Nora Bint Abdulrahman University College of computer and information sciences Networks department Networks Security (NET 536) Prepared by Dr. Samia Chelloug E-mail: samia_chelloug@yahoo.fr Content
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371
 Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
CSMC 417. Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala Ashok Agrawala. Fall 2018 CMSC417 Set 1 1
 CSMC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2018 Ashok Agrawala Fall 2018 CMSC417 Set 1 1 The Medium Access Control Sublayer November 18 Nov 6, 2018 2 Wireless Networking Technologies November 18
CSMC 417 Computer Networks Prof. Ashok K Agrawala 2018 Ashok Agrawala Fall 2018 CMSC417 Set 1 1 The Medium Access Control Sublayer November 18 Nov 6, 2018 2 Wireless Networking Technologies November 18
Wireless Networking Basics. Ed Crowley
 Wireless Networking Basics Ed Crowley 2014 Today s Topics Wireless Networking Economic drivers and Vulnerabilities IEEE 802.11 Family WLAN Operational Modes Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) WPA and WPA2
Wireless Networking Basics Ed Crowley 2014 Today s Topics Wireless Networking Economic drivers and Vulnerabilities IEEE 802.11 Family WLAN Operational Modes Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) WPA and WPA2
Outline : Wireless Networks Lecture 10: Management. Management and Control Services : Infrastructure Reminder.
 Outline 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 10: 802.11 Management Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2016 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss16/
Outline 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 10: 802.11 Management Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2016 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss16/
CITS3002 Networks and Security. The IEEE Wireless LAN protocol. 1 next CITS3002 help3002 CITS3002 schedule
 1 next CITS3002 help3002 CITS3002 schedule The IEEE-802.11 Wireless LAN protocol We'll next examine devices implementing the IEEE-802.11 family of wireless networking protocols, and get an appreciation
1 next CITS3002 help3002 CITS3002 schedule The IEEE-802.11 Wireless LAN protocol We'll next examine devices implementing the IEEE-802.11 family of wireless networking protocols, and get an appreciation
Topic 2b Wireless MAC. Chapter 7. Wireless and Mobile Networks. Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach
 Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
11n Wireless USB Adapter
 User Manual 11n Wireless USB Adapter Model No.: SP907NS Table of Content 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 1.1 Features... 2 1.2 Specifications... 2 1.3 Package Contents... 3 2. INSTALLATION PROCEDURE... 4 2.1 Install
User Manual 11n Wireless USB Adapter Model No.: SP907NS Table of Content 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 1.1 Features... 2 1.2 Specifications... 2 1.3 Package Contents... 3 2. INSTALLATION PROCEDURE... 4 2.1 Install
Configuring the Wireless Parameters (CPE and WBS)
 Configuring the Wireless Parameters (CPE and WBS) CHAPTERS 1. Configure Basic Wireless Parameters 2. Configure Wireless Client Parameters 3. Configure Wireless AP Parameters 4. Configure Multi-SSID 5.
Configuring the Wireless Parameters (CPE and WBS) CHAPTERS 1. Configure Basic Wireless Parameters 2. Configure Wireless Client Parameters 3. Configure Wireless AP Parameters 4. Configure Multi-SSID 5.
Multiple Access in Cellular and Systems
 Multiple Access in Cellular and 802.11 Systems 1 GSM The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels. (200 khz in GSM) Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel (8 users) A channel
Multiple Access in Cellular and 802.11 Systems 1 GSM The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels. (200 khz in GSM) Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel (8 users) A channel
Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 7: Wireless LAN
 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 7: Wireless LAN [Schiller, Section 7.3] [Reader, Part 6] [Optional: "IEEE 802.11n Development: History, Process, and Technology", Perahia, IEEE Communications
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 7: Wireless LAN [Schiller, Section 7.3] [Reader, Part 6] [Optional: "IEEE 802.11n Development: History, Process, and Technology", Perahia, IEEE Communications
Data and Computer Communications. Chapter 13 Wireless LANs
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures
 Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures Wireless Network Technology Wireless network refers to any type of computer network which is wireless, and is commonly associated with a network whose interconnections
Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures Wireless Network Technology Wireless network refers to any type of computer network which is wireless, and is commonly associated with a network whose interconnections
Wireless LANs. ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications
 Wireless LANs ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Aim: Aim and Contents Understand how IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs work Understand what influences the performance of wireless LANs Contents: IEEE
Wireless LANs ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Aim: Aim and Contents Understand how IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs work Understand what influences the performance of wireless LANs Contents: IEEE
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer. Computer Networks: Wireless LANs
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
Product Brief: SDC-PE15N n PCIe Module with Antenna Connectors
 Product Brief: SDC-PE15N 802.11n PCIe Module with Antenna Connectors The SDC-PE15N PCI Express Mini Card (PCIe) radio module from Summit Data Communications combines a high-performance, dual-band 802.11n
Product Brief: SDC-PE15N 802.11n PCIe Module with Antenna Connectors The SDC-PE15N PCI Express Mini Card (PCIe) radio module from Summit Data Communications combines a high-performance, dual-band 802.11n
Lecture 23 Overview. Last Lecture. This Lecture. Next Lecture ADSL, ATM. Wireless Technologies (1) Source: chapters 6.2, 15
 Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
M a/b/g Outdoor Layer-2 MESH AP
 802.11a/b/g Outdoor Layer-2 MESH AP 2.4GHz / 5GHz 802.11 a/b/g MESH PRODUCT DESCRIPTION EnGenius Mesh AP is designed with IEEE802.11a/b/g standards and addressed on providing high performance mesh network.
802.11a/b/g Outdoor Layer-2 MESH AP 2.4GHz / 5GHz 802.11 a/b/g MESH PRODUCT DESCRIPTION EnGenius Mesh AP is designed with IEEE802.11a/b/g standards and addressed on providing high performance mesh network.
FAQ on Cisco Aironet Wireless Security
 FAQ on Cisco Aironet Wireless Security Document ID: 68583 Contents Introduction General FAQ Troubleshooting and Design FAQ Related Information Introduction This document provides information on the most
FAQ on Cisco Aironet Wireless Security Document ID: 68583 Contents Introduction General FAQ Troubleshooting and Design FAQ Related Information Introduction This document provides information on the most
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Wireless Router at Home
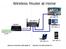 Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit. Manual
 Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit Manual Dear Customer, Thanks for choosing Hamlet. Please carefully follow the instructions for its use and maintenance and, once this item has run its life span, we kindly
Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit Manual Dear Customer, Thanks for choosing Hamlet. Please carefully follow the instructions for its use and maintenance and, once this item has run its life span, we kindly
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371
 Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
Wireless Protocols. Training materials for wireless trainers
 Wireless Protocols Training materials for wireless trainers Goals The goal of this lecture is to introduce: IEEE wireless protocols coverage 802.11 radio protocols terminology WiFi modes of operation details
Wireless Protocols Training materials for wireless trainers Goals The goal of this lecture is to introduce: IEEE wireless protocols coverage 802.11 radio protocols terminology WiFi modes of operation details
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION. Learn more about EnGenius Solutions at
 Wireless Long Range Multi-function Client Bridge 2.4 GHz EIRP up to 400mW Access point Client Bridge Repeater Client Router PRODUCT DESCRIPTION is a powerful client bridge. It supports several networking
Wireless Long Range Multi-function Client Bridge 2.4 GHz EIRP up to 400mW Access point Client Bridge Repeater Client Router PRODUCT DESCRIPTION is a powerful client bridge. It supports several networking
original standard a transmission at 5 GHz bit rate 54 Mbit/s b support for 5.5 and 11 Mbit/s e QoS
 IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
Configuring the WMIC for the First Time
 Configuring the WMIC for the First Time This document describes how to configure basic settings on a Cisco Wireless Mobile Interface Card (WMIC) for the first time. Before You Start Before you install
Configuring the WMIC for the First Time This document describes how to configure basic settings on a Cisco Wireless Mobile Interface Card (WMIC) for the first time. Before You Start Before you install
Configuring a VAP on the WAP351, WAP131, and WAP371
 Article ID: 5072 Configuring a VAP on the WAP351, WAP131, and WAP371 Objective Virtual Access Points (VAPs) segment the wireless LAN into multiple broadcast domains that are the wireless equivalent of
Article ID: 5072 Configuring a VAP on the WAP351, WAP131, and WAP371 Objective Virtual Access Points (VAPs) segment the wireless LAN into multiple broadcast domains that are the wireless equivalent of
EAP Wireless Access Point. 2.4 GHz b/g 54 Mbps
 EAP-3660 is a small form factor wireless product. It is stylish and looks like a smoke detector on the ceiling. EAP-3660 is a / Repeater / WDS that operates seamlessly in the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum
EAP-3660 is a small form factor wireless product. It is stylish and looks like a smoke detector on the ceiling. EAP-3660 is a / Repeater / WDS that operates seamlessly in the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum
Wireless High power Multi-function AP
 Wireless High power Multi-function AP EAP-3660 2.4GHz Super G 108Mbps Access Point/ WDS/Universal Repeater The EAP-3660 is a smoke detector looking Wireless Access Point / Universal Repeater / WDS that
Wireless High power Multi-function AP EAP-3660 2.4GHz Super G 108Mbps Access Point/ WDS/Universal Repeater The EAP-3660 is a smoke detector looking Wireless Access Point / Universal Repeater / WDS that
Wireless LANs. The Protocol Stack The Physical Layer The MAC Sublayer Protocol The Frame Structure Services 802.
 Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks
 CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
Physical and Link Layer Attacks
 Physical and Link Layer Attacks CMSC 414 November 1, 2017 Attenuation Physical links are subject to attenuation Copper cables have internal resistance, which degrades signal over large distances Fiber
Physical and Link Layer Attacks CMSC 414 November 1, 2017 Attenuation Physical links are subject to attenuation Copper cables have internal resistance, which degrades signal over large distances Fiber
PROTECTED EXTENSIBLE AUTHENTICATION PROTOCOL
 Q&A PROTECTED EXTENSIBLE AUTHENTICATION PROTOCOL This document answers questions about Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol. OVERVIEW Q. What is Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol? A.
Q&A PROTECTED EXTENSIBLE AUTHENTICATION PROTOCOL This document answers questions about Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol. OVERVIEW Q. What is Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol? A.
STA-MU-A0028S (MiniCard-USB version)
 STA-MU-A0028S (MiniCard-USB version) WiFi 802.11 b/g and Bluetooth v2.0 + EDR Combo Mini Card Module Approval Sheet Ver: 1.1 CONTENT 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Features & Benefits...3 1.2 Applications...4
STA-MU-A0028S (MiniCard-USB version) WiFi 802.11 b/g and Bluetooth v2.0 + EDR Combo Mini Card Module Approval Sheet Ver: 1.1 CONTENT 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Features & Benefits...3 1.2 Applications...4
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks
 Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach Featuring the Internet, 3 rd edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, July 2004. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach Featuring the Internet, 3 rd edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, July 2004. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6
Topics for Today. More on Ethernet. Wireless LANs Readings. Topology and Wiring Switched Ethernet Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet. 4.3 to 4.
 Topics for Today More on Ethernet Topology and Wiring Switched Ethernet Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet Wireless LANs Readings 4.3 to 4.4 1 Original Ethernet Wiring Heavy coaxial cable, called thicknet,
Topics for Today More on Ethernet Topology and Wiring Switched Ethernet Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet Wireless LANs Readings 4.3 to 4.4 1 Original Ethernet Wiring Heavy coaxial cable, called thicknet,
Security Setup CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes how to set up your bridge s security features. This chapter contains the following sections: Security Overview, page 8-2 Setting Up WEP, page 8-7 Enabling Additional WEP
CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes how to set up your bridge s security features. This chapter contains the following sections: Security Overview, page 8-2 Setting Up WEP, page 8-7 Enabling Additional WEP
Wireless SOHO Router/Bridge 2.4 GHz b/g 54 Mbps
 Wireless SOHO Router/Bridge ECB-1220R 2.4 GHz 802.11 b/g 54 Mbps ECB-1220R is a 2.4GHz 802.11b/g broadband Wi-Fi Router with advanced AP/Client Bridge/Repeater functions. So you could implement this crossover
Wireless SOHO Router/Bridge ECB-1220R 2.4 GHz 802.11 b/g 54 Mbps ECB-1220R is a 2.4GHz 802.11b/g broadband Wi-Fi Router with advanced AP/Client Bridge/Repeater functions. So you could implement this crossover
ECB N Multi-Function Gigabit Client Bridge
 ECB9500 is a powerful and multi-functioned 11n product with 7 major multi-functions, is designed to operate in every working environment for enterprises. ECB9500 is a Wireless Network device that delivers
ECB9500 is a powerful and multi-functioned 11n product with 7 major multi-functions, is designed to operate in every working environment for enterprises. ECB9500 is a Wireless Network device that delivers
Configuring a Wireless LAN Connection
 CHAPTER 9 The Cisco Secure Router 520 Series routers support a secure, affordable, and easy-to-use wireless LAN solution that combines mobility and flexibility with the enterprise-class features required
CHAPTER 9 The Cisco Secure Router 520 Series routers support a secure, affordable, and easy-to-use wireless LAN solution that combines mobility and flexibility with the enterprise-class features required
Data Communication & Networks G Session 5 - Main Theme Wireless Networks. Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti
 Data Communication & Networks G22.2262-001 Session 5 - Main Theme Wireless Networks Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences
Data Communication & Networks G22.2262-001 Session 5 - Main Theme Wireless Networks Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences
TestsDumps. Latest Test Dumps for IT Exam Certification
 TestsDumps http://www.testsdumps.com Latest Test Dumps for IT Exam Certification Exam : PW0-200 Title : Certified wireless security professional(cwsp) Vendors : CWNP Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid PW0-200
TestsDumps http://www.testsdumps.com Latest Test Dumps for IT Exam Certification Exam : PW0-200 Title : Certified wireless security professional(cwsp) Vendors : CWNP Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid PW0-200
Hardware Capabilities. Product Brief: SDC-PC20G g PCMCIA Card with Integrated Antenna
 Product Brief: SDC-PC20G 802.11g PCMCIA Card with Integrated Antenna The SDC-PC20G PCMCIA card from Summit Data Communications combines Summit s 802.11g radio and customized software both proven on mobile
Product Brief: SDC-PC20G 802.11g PCMCIA Card with Integrated Antenna The SDC-PC20G PCMCIA card from Summit Data Communications combines Summit s 802.11g radio and customized software both proven on mobile
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei 1393
 Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 Wireless Links, WiFi, Cellular Internet Access, and Mobility Slides derived from those available on the Web site of the book Computer Networking, by Kurose
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 Wireless Links, WiFi, Cellular Internet Access, and Mobility Slides derived from those available on the Web site of the book Computer Networking, by Kurose
CWNP PW Certified Wireless Analysis Professional. Download Full Version :
 CWNP PW0-270 Certified Wireless Analysis Professional Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pw0-270 QUESTION: 50 ABC Company is having VoWiFi latency problems on their 802.11g
CWNP PW0-270 Certified Wireless Analysis Professional Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pw0-270 QUESTION: 50 ABC Company is having VoWiFi latency problems on their 802.11g
Wireless Technologies
 Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
IP network that supports DHCP or manual assignment of IP address, gateway, and subnet mask
 Network Requirements, page 1 Wireless LAN, page 2 Wi-Fi Network Components, page 3 802.11 Standards for WLAN Communications, page 6 Security for Communications in WLANs, page 9 WLANs and Roaming, page
Network Requirements, page 1 Wireless LAN, page 2 Wi-Fi Network Components, page 3 802.11 Standards for WLAN Communications, page 6 Security for Communications in WLANs, page 9 WLANs and Roaming, page
Securing a Wireless LAN
 Securing a Wireless LAN This module describes how to apply strong wireless security mechanisms on a Cisco 800, 1800, 2800, or 3800 series integrated services router, hereafter referred to as an access
Securing a Wireless LAN This module describes how to apply strong wireless security mechanisms on a Cisco 800, 1800, 2800, or 3800 series integrated services router, hereafter referred to as an access
WNC-0300USB. 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL
 WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
Advanced Computer Networks WLAN
 Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2014 1 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Outlook Medium Access COPE Short Range Wireless Networks:
Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2014 1 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Outlook Medium Access COPE Short Range Wireless Networks:
1. INTRODUCTION. Wi-Fi 1
 Wi-Fi 1 1. INTRODUCTION Wi-Fi, or Wireless Fidelity, is freedom: it allows you to connect to the Internet from your home, a bed in a hotel room or at a conference room at work without wires. How? Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi 1 1. INTRODUCTION Wi-Fi, or Wireless Fidelity, is freedom: it allows you to connect to the Internet from your home, a bed in a hotel room or at a conference room at work without wires. How? Wi-Fi
MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8
 MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8 Michael L. Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University November 2017 The Multiple Access Problem How can multiple mobiles access (communicate with) the same
MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8 Michael L. Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University November 2017 The Multiple Access Problem How can multiple mobiles access (communicate with) the same
ECB Gon Tel: +44 (0) Fax: +44 (0) Wireless Long Range Multi-function 7+1 AP
 Wireless Long Range Multi-function 7+1 AP (Access Point/Client Bridge/Repeater/WDS AP/ WDS Bridge/ Client Router/AP Router) 2.4 GHz Super G 108Mbps EIRP up to 2000mW PRODUCT DESCRIPTION is a powerful,
Wireless Long Range Multi-function 7+1 AP (Access Point/Client Bridge/Repeater/WDS AP/ WDS Bridge/ Client Router/AP Router) 2.4 GHz Super G 108Mbps EIRP up to 2000mW PRODUCT DESCRIPTION is a powerful,
STA-UI-A003D (USB version)
 STA-UI-A003D (USB version) WiFi 802.11 b/g and Bluetooth v2.0 + EDR Combo USB Dongle Module Ver: 1.0 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. CONTENT Introduction...3 1.1Features & Benefits...3 1.2Applications...4 Product
STA-UI-A003D (USB version) WiFi 802.11 b/g and Bluetooth v2.0 + EDR Combo USB Dongle Module Ver: 1.0 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. CONTENT Introduction...3 1.1Features & Benefits...3 1.2Applications...4 Product
CUA-854 Wireless-G Long Range USB Adapter with Antenna. User s Guide
 CUA-854 Wireless-G Long Range USB Adapter with Antenna User s Guide Table of Contents Chapter 1. Introduction...5 1.1. About CUA-854...5 1.2. Key Features...5 1.3. Package Included...5 Chapter 2. Connect
CUA-854 Wireless-G Long Range USB Adapter with Antenna User s Guide Table of Contents Chapter 1. Introduction...5 1.1. About CUA-854...5 1.2. Key Features...5 1.3. Package Included...5 Chapter 2. Connect
Product Brief: SDC-PC22AG a/g PCMCIA Card with Integrated Antenna
 Product Brief: SDC-PC22AG 802.11a/g PCMCIA Card with Integrated Antenna The SDC-PC22AG PC Card (PCMCIA) radio card from Summit Data Communications combines a high-performance 802.11a/g radio with customized
Product Brief: SDC-PC22AG 802.11a/g PCMCIA Card with Integrated Antenna The SDC-PC22AG PC Card (PCMCIA) radio card from Summit Data Communications combines a high-performance 802.11a/g radio with customized
Data Communications. Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs
 Data Communications Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs Wireless Networks Several different types of communications networks are using unguided media. These networks are generally referred to as wireless
Data Communications Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs Wireless Networks Several different types of communications networks are using unguided media. These networks are generally referred to as wireless
