Lab - Mapping the Internet
|
|
|
- Trevor Willis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Objectives Part 1: Test Network Connectivity Using Ping Part 2: Trace a Route to a Remote Server Using Windows Tracert Part 3: Trace a Route to a Remote Server Using Web-Based and Software Tools Part 4: Compare Traceroute Results Background Route tracing computer software is a utility that lists the networks data has to traverse from the user's originating end device to a distant destination network. This network tool is typically executed at the command line as: or tracert <destination network name or end device address> (Microsoft Windows systems) traceroute <destination network name or end device address> (Unix and similar systems) Route tracing utilities allow a user to determine the path or routes as well as the delay across an IP network. Several tools exist to perform this function. The traceroute (or tracert) tool is often used for network troubleshooting. By showing a list of routers traversed, it allows the user to identify the path taken to reach a particular destination on the network or across internetworks. Each router represents a point where one network connects to another network and through which the data packet was forwarded. The number of routers is known as the number of "hops" the data traveled from source to destination. The displayed list can help identify data flow problems when trying to access a service such as a website. It can also be useful when performing tasks such as downloading data. If there are multiple websites (mirrors) available for the same data file, one can trace each mirror to get a good idea of which mirror would be the fastest to use. Two trace routes between the same source and destination conducted some time apart may produce different results. This is due to the "meshed" nature of the interconnected networks that comprise the Internet and the Internet Protocols ability to select different pathways over which to send packets. Command-line-based route tracing tools are usually embedded with the operating system of the end device. Other tools, such as VisualRoute, are proprietary programs that provide extra information. VisualRoute uses available online information to graphically display the route. This lab assumes the installation of VisualRoute. If the computer you are using does not have VisualRoute installed, you can download the program using the following link: If you have any trouble downloading or installing VisualRoute, ask your instructor for assistance. Ensure that you download the Lite Edition Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 11
2 Scenario Using an Internet connection, you will use three route tracing utilities to examine the Internet pathway to destination networks. This activity should be performed on a computer that has Internet access and access to the command line. First, you will use the Windows embedded tracert utility. Second, you will use a web-based traceroute tool ( Finally, you will use the VisualRoute traceroute program. Required Resources 1 PC (Windows 7, Vista, or XP with Internet access) Part 1: Test Network Connectivity Using Ping Step 1: Determine whether the remote server is reachable. To trace the route to a distant network, the PC used must have a working connection to the Internet. a. The first tool we will use is ping. Ping is a tool used to test whether a host is reachable. Packets of information are sent to the remote host with instructions to reply. Your local PC measures whether a response is received to each packet, and how long it takes for those packets to cross the network. The name ping comes from active sonar technology in which a pulse of sound is sent underwater and bounced off of terrain or other ships. b. From your PC, click the Windows Start icon, type cmd in the Search programs and files box, and then press Enter. c. At the command-line prompt, type ping Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 2 of 11
3 d. The first output line displays the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) e144.dscb.akamaiedge.net. This is followed by the IP address Cisco hosts the same web content on different servers throughout the world (known as mirrors). Therefore, depending upon where you are geographically, the FQDN and the IP address will be different. e. From this portion of the output: Four pings were sent and a reply was received from each ping. Because each ping was responded to, there was 0% packet loss. On average, it took 54 ms (54 milliseconds) for the packets to cross the network. A millisecond is 1/1,000 th of a second. Streaming video and online games are two applications that suffer when there is packet loss, or a slow network connection. A more accurate determination of an Internet connection speed can be determined by sending 100 pings, instead of the default 4. Here is how to do that: And here is what the output from that looks like: f. Now ping Regional Internet Registry (RIR) websites located in different parts of the world: For Africa: C:\> ping For Australia: C:\> ping Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 3 of 11
4 For Europe: C:\> ping For South America: C:\> ping lacnic.net All these pings were run from a computer located in the U.S. What happens to the average ping time in milliseconds when data is traveling within the same continent (North America) as compared to data from North America traveling to different continents? What is interesting about the pings that were sent to the European website? 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 4 of 11
5 Part 2: Trace a Route to a Remote Server Using Tracert Step 1: Determine what route across the Internet traffic takes to the remote server. Now that basic reachability has been verified by using the ping tool, it is helpful to look more closely at each network segment that is crossed. To do this, the tracert tool will be used. a. At the command-line prompt, type tracert b. Save the tracert output in a text file as follows: 1) Right-click the title bar of the Command Prompt window and choose Edit > Select All. 2) Right-click the title bar of the Command Prompt window again and choose Edit > Copy. 3) Open the Windows Notepad program: Windows Start icon > All Programs > Accessories > Notepad. 4) To paste the output into Notepad, choose Edit > Paste. 5) Choose File > Save As and save the Notepad file to your desktop as tracert1.txt. c. Run tracert for each destination website and save the output in sequentially numbered files. C:\> tracert C:\> tracert d. Interpreting tracert outputs. Routes traced can go through many hops and a number of different Internet Service Providers (ISPs), depending on the size of your ISP and the location of the source and destination hosts. Each hop represents a router. A router is a specialized type of computer used to direct traffic across the Internet. Imagine taking an automobile trip across several countries using many highways. At different points in the trip you come to a fork in the road in which you have the option to select from several different highways. Now further imagine that there is a device at each fork in the road that directs you to take the correct highway to your final destination. That is what a router does for packets on a network Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 5 of 11
6 Because computers talk in numbers, rather than words, routers are uniquely identified using IP addresses (numbers with the format x.x.x.x). The tracert tool shows you what path through the network a packet of information takes to reach its final destination. The tracert tool also gives you an idea of how fast traffic is going on each segment of the network. Three packets are sent to each router in the path, and the return time is measured in milliseconds. Now use this information to analyze the tracert results to Below is the entire traceroute: Below is the breakdown: In the example output shown above, the tracert packets travel from the source PC to the local router default gateway (hop 1: ) to the ISPs Point of Presence (POP) router (hop 2: ). Every ISP has numerous POP routers. These POP routers are at the edge of the ISP s network and are the means by which customers connect to the Internet. The packets travel along the Verizon network for two hops and then jump to a router that belongs to alter.net. This could mean that the packets have traveled to another ISP. This is significant because sometimes there is packet loss in the transition between ISPs, or sometimes one ISP is slower than another. How could we determine if alter.net is another ISP or the same ISP? 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 6 of 11
7 e. There is an Internet tool known as whois. The whois tool allows us to determine who owns a domain name. A web-based whois tool is found at This domain is also owned by Verizon according to the web-based whois tool. To summarize, Internet traffic starts at a home PC and travels through the home router (hop 1). It then connects to the ISP and travels through its network (hops 2-7) until it arrives at the remote server (hop 8). This is a relatively unusual example in which there is only one ISP involved from start to finish. It is typical to have two or more ISP involved as displayed in the following examples Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 7 of 11
8 f. Now examine an example that involves Internet traffic crossing multiple ISPs. Below is the tracert for What happens at hop 7? Is level3.net the same ISP as hops 2-6, or a different ISP? Use the whois tool to answer this question. What happens in hop 10 to the amount of time it takes for a packet to travel between Washington D.C. and Paris, as compared with the earlier hops 1-9? What happens in hop 18? Do a whois lookup on using the whois tool. Who owns this network? 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 8 of 11
9 g. Type tracert What happens in hop 7? Part 3: Trace a Route to a Remote Server Using Web-Based and SoftwareTools Step 1: Use a web-based traceroute tool. a. Using to trace the route to the following websites: Capture and save the output in Notepad. How is the traceroute different when going to from the command prompt (see Part 1) rather than from the online website? (Your results may vary depending upon where you are located geographically, and which ISP is providing connectivity to your school.) 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 9 of 11
10 Compare the tracert from Part 1 that goes to Africa with the tracert that goes to Africa from the web interface. What difference do you notice? Some of the traceroutes have the abbreviation asymm in them. Any guesses as to what this means? What is its significance? Step 2: Use VisualRoute Lite Edition VisualRoute is a proprietary traceroute program that can display the tracing path results graphically. a. Please download the VisualRoute Lite Edition from the following link if it is not already installed: If you have any trouble downloading or installing VisualRoute, ask your instructor for assistance. Ensure that you download the Lite Edition. b. Using VisualRoute 2010 Lite Edition, trace the routes to c. Record the IP addresses in the path in Notepad Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 10 of 11
11 Part 4: Compare Traceroute Results Compare the traceroute results to from Parts 2 and 3. Step 1: List the path to using tracert. Step 2: List the path to using the web-based tool on subnetonline.com. Step 3: List the path to using VisualRoute Lite edition. Did all the traceroute utilities use the same paths to Why or Why not? Reflection Having now viewed traceroute through three different tools (tracert, web interface, and VisualRoute), are there any insights that using VisualRoute provided that the other two tools did not? 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 11 of 11
Lab - Mapping the Internet
 Objectives Part 1: Test Network Connectivity Using Ping Part 2: Trace a Route to a Remote Server Using Windows Tracert Background Route tracing computer software is a utility that lists the networks data
Objectives Part 1: Test Network Connectivity Using Ping Part 2: Trace a Route to a Remote Server Using Windows Tracert Background Route tracing computer software is a utility that lists the networks data
GAME100 Lab 5. Before beginning the lab, please download and install Cisco Packet Trace
 GAME100 Lab 5 Name: Part 1: Learn to Use Packet Tracer Objectives Develop an understanding of the basic functions of Packet Tracer. Create/model a simple Ethernet network using two hosts and a switch.
GAME100 Lab 5 Name: Part 1: Learn to Use Packet Tracer Objectives Develop an understanding of the basic functions of Packet Tracer. Create/model a simple Ethernet network using two hosts and a switch.
Lab 6.7.1: Ping and Traceroute
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1-ISP R2-Central Eagle Server S0/0/0 10.10.10.6 255.255.255.252 N/A Fa0/0 192.168.254.253 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1-ISP R2-Central Eagle Server S0/0/0 10.10.10.6 255.255.255.252 N/A Fa0/0 192.168.254.253 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0
Lab Using Wireshark to Examine Ethernet Frames
 Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture and Analyze Ethernet Frames Background / Scenario When upper layer protocols communicate with
Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture and Analyze Ethernet Frames Background / Scenario When upper layer protocols communicate with
Table of Contents 1 System Maintenance and Debugging Commands 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 System Maintenance and Debugging Commands 1-1 System Maintenance Commands 1-1 ping 1-1 ping ipv6 1-5 tracert 1-6 tracert ipv6 1-7 System Debugging Commands 1-8 debugging 1-8 display
Table of Contents 1 System Maintenance and Debugging Commands 1-1 System Maintenance Commands 1-1 ping 1-1 ping ipv6 1-5 tracert 1-6 tracert ipv6 1-7 System Debugging Commands 1-8 debugging 1-8 display
ICMP messages generating by the Ping program; ICMP messages generated by the Traceroute program; the format and contents of an ICMP message.
 Ethereal Lab: ICMP Version: 1.0 2005 J.F. Kurose, K.W. Ross. All Rights Reserved Computer Networking: A Topdown Approach Featuring the Internet, 3 rd edition. In this lab, we ll explore several aspects
Ethereal Lab: ICMP Version: 1.0 2005 J.F. Kurose, K.W. Ross. All Rights Reserved Computer Networking: A Topdown Approach Featuring the Internet, 3 rd edition. In this lab, we ll explore several aspects
Ping, tracert and system debugging commands
 Contents Ping, tracert and system debugging commands 1 Ping and tracert commands 1 ping 1 ping ipv6 5 tracert 7 tracert ipv6 9 System debugging commands 10 debugging 10 display debugging 11 i Ping, tracert
Contents Ping, tracert and system debugging commands 1 Ping and tracert commands 1 ping 1 ping ipv6 5 tracert 7 tracert ipv6 9 System debugging commands 10 debugging 10 display debugging 11 i Ping, tracert
Lesson 12 Lab Key Lab Exercises
 Lab 1 Doing a Ping Test Lesson 12 Lab Key Lab Exercises The purpose of this lab is to familiarize the student with running a ping test. This lab will also help the student correctly interpret the results
Lab 1 Doing a Ping Test Lesson 12 Lab Key Lab Exercises The purpose of this lab is to familiarize the student with running a ping test. This lab will also help the student correctly interpret the results
CCNA Routing and Switching: Routing and Switching Essentials 6.0. Instructor Lab Manual
 CCNA Routing and Switching: Routing and Switching Essentials 6.0 Instructor Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for
CCNA Routing and Switching: Routing and Switching Essentials 6.0 Instructor Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for
Fig (1) client and Server network
 2.2 How Does the Internet Work? The international network known as the internet consists of hundreds of thousands of smaller networks linking educational, commercial, nonprofit, and military organizations,
2.2 How Does the Internet Work? The international network known as the internet consists of hundreds of thousands of smaller networks linking educational, commercial, nonprofit, and military organizations,
Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging Commands 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging Commands 1-1 System Maintaining Commands 1-1 ping 1-1 tracert 1-4 System Debugging Commands 1-6 debugging 1-6 display debugging 1-7 i 1 System Maintaining
Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging Commands 1-1 System Maintaining Commands 1-1 ping 1-1 tracert 1-4 System Debugging Commands 1-6 debugging 1-6 display debugging 1-7 i 1 System Maintaining
1/18/13. Network+ Guide to Networks 5 th Edition. Objectives. Chapter 10 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking
 Network+ Guide to Networks 5 th Edition Chapter 10 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking Objectives Understand methods of network design unique to TCP/IP networks, including subnetting, CIDR, and address translation
Network+ Guide to Networks 5 th Edition Chapter 10 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking Objectives Understand methods of network design unique to TCP/IP networks, including subnetting, CIDR, and address translation
ICMP Computer Networks Lab Lab Course Number: Lab Course Name: Computer Networks (A) 3. Lab Name: ICMP
 112039 Computer Networks Lab - 3 ICMP 1. Lab Course Number: 112039 2. Lab Course Name: Computer Networks (A) 3. Lab Name: ICMP 4. Lab Overview: In this lab, we ll investigate the ICMP protocol; examine
112039 Computer Networks Lab - 3 ICMP 1. Lab Course Number: 112039 2. Lab Course Name: Computer Networks (A) 3. Lab Name: ICMP 4. Lab Overview: In this lab, we ll investigate the ICMP protocol; examine
Lab Using Wireshark to Examine Ethernet Frames
 Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture and Analyze Ethernet Frames Background / Scenario When upper layer protocols communicate with
Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture and Analyze Ethernet Frames Background / Scenario When upper layer protocols communicate with
Lab : Challenge OSPF Configuration Lab. Topology Diagram. Addressing Table. Default Gateway. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
CS356 Lab NIL (Lam) In this lab you will learn: Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 20 min Access Control Lists PartC 30 min Explore!
 CS356 Lab NIL (Lam) In this lab you will learn: PartA Time: 2 hrs 40 min Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 20 min Access Control Lists PartC 30 min Explore! Components used: 2 computers
CS356 Lab NIL (Lam) In this lab you will learn: PartA Time: 2 hrs 40 min Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 20 min Access Control Lists PartC 30 min Explore! Components used: 2 computers
Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1 Ping 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Configuring Ping 1-1 Ping Configuration Example 1-2 Tracert 1-4 Introduction 1-4
Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1 Ping 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Configuring Ping 1-1 Ping Configuration Example 1-2 Tracert 1-4 Introduction 1-4
Lab Assignment 4 ECE374 Spring Posted: 03/22/18 Due: 03/29/18. In this lab, we ll take a quick look at the ICMP and IP protocols.
 Lab Assignment 4 ECE374 Spring 2018 Posted: 03/22/18 Due: 03/29/18 In this lab, we ll take a quick look at the ICMP and IP protocols. Whenever possible you should hand in Wireshark screenshots that you
Lab Assignment 4 ECE374 Spring 2018 Posted: 03/22/18 Due: 03/29/18 In this lab, we ll take a quick look at the ICMP and IP protocols. Whenever possible you should hand in Wireshark screenshots that you
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Network+ Guide to Networks 5 th Edition. Chapter 10 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking
 Network+ Guide to Networks 5 th Edition Chapter 10 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking Objectives Understand methods of network design unique to TCP/IP networks, including subnetting, CIDR, and address translation
Network+ Guide to Networks 5 th Edition Chapter 10 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking Objectives Understand methods of network design unique to TCP/IP networks, including subnetting, CIDR, and address translation
Chapter 7: IP Addressing CCENT Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0
 Chapter 7: IP Addressing CCENT Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0 CCNET v6 13 Chapter 7 - Sections & Objectives 7.1 IPv4 Network Addresses Convert between binary and decimal numbering
Chapter 7: IP Addressing CCENT Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0 CCNET v6 13 Chapter 7 - Sections & Objectives 7.1 IPv4 Network Addresses Convert between binary and decimal numbering
Troubleshooting Your Network
 Troubleshooting Your Network Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 9 Copyleft 2012 Vincenzo Bruno (www.vincenzobruno.it) Released under Crative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and
Troubleshooting Your Network Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 9 Copyleft 2012 Vincenzo Bruno (www.vincenzobruno.it) Released under Crative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and
Implement Inter-VLAN Routing. LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 6 Modified by Tony Chen 11/01/2008
 Implement Inter-VLAN Routing LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 6 Modified by Tony Chen 11/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you see any mistake
Implement Inter-VLAN Routing LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 6 Modified by Tony Chen 11/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you see any mistake
CS 326e Lab 2, Edmondson-Yurkanan, Spring 2004 Router Configuration, Routing and Access Lists
 CS 326e Lab 2, Edmondson-Yurkanan, Spring 2004 Router Configuration, Routing and Access Lists Name: In this lab you will learn: PartA Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 20 min Dynamic
CS 326e Lab 2, Edmondson-Yurkanan, Spring 2004 Router Configuration, Routing and Access Lists Name: In this lab you will learn: PartA Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 20 min Dynamic
PreLab for CS356 Lab NIL (Lam) (To be submitted when you come for the lab)
 PreLab for CS356 Lab NIL (Lam) (To be submitted when you come for the lab) Name: UT EID: 1. Differentiate between Routers, Switches, and Hubs. 2. Explain subnet masks. 3. For this lab, where is subnet
PreLab for CS356 Lab NIL (Lam) (To be submitted when you come for the lab) Name: UT EID: 1. Differentiate between Routers, Switches, and Hubs. 2. Explain subnet masks. 3. For this lab, where is subnet
Lab Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE3080F tutor to get assigned to your routers.
 EEE00F Lab Basics of the Network Lab Student Lab Manual Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE00F tutor to get assigned to your routers. Contents. Resources used in the labs...
EEE00F Lab Basics of the Network Lab Student Lab Manual Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE00F tutor to get assigned to your routers. Contents. Resources used in the labs...
15-441: Computer Networks Spring 2010 Homework #2
 15-441: Computer Networks Spring 2010 Homework #2 Due: Feb 23 rd 2010, in class Lead TA: Rui Meireles (firstname@cmu.edu) Ethernet 1. Five prisoners are locked up in adjacent cells in a prison. They would
15-441: Computer Networks Spring 2010 Homework #2 Due: Feb 23 rd 2010, in class Lead TA: Rui Meireles (firstname@cmu.edu) Ethernet 1. Five prisoners are locked up in adjacent cells in a prison. They would
General Network Troubleshooting
 Overview Contents This document outlines some basic network troubleshooting techniques that can be used to test network connectivity. They are useful when troubleshooting issues with Crystal Enterprise
Overview Contents This document outlines some basic network troubleshooting techniques that can be used to test network connectivity. They are useful when troubleshooting issues with Crystal Enterprise
PoP Level Mapping And Peering Deals
 PoP Level Mapping And Peering Deals Mapping Internet Methodology Data Collection IP Classification to PoP PoP Geolocation PoP locations on Peering estimations Outline Internet Service Providers ISPs are
PoP Level Mapping And Peering Deals Mapping Internet Methodology Data Collection IP Classification to PoP PoP Geolocation PoP locations on Peering estimations Outline Internet Service Providers ISPs are
Lab - Observing DNS Resolution
 Objectives Part 1: Observe the DNS Conversion of a URL to an IP Address Part 2: Observe DNS Lookup Using the Nslookup Command on a Web Site Part 3: Observe DNS Lookup Using the Nslookup Command on Mail
Objectives Part 1: Observe the DNS Conversion of a URL to an IP Address Part 2: Observe DNS Lookup Using the Nslookup Command on a Web Site Part 3: Observe DNS Lookup Using the Nslookup Command on Mail
Overview of IPM. What Is IPM? CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 1 Overview of IPM This chapter provides an overview of Cisco s Internetwork Performance Monitor (IPM) application. It contains the following sections: What Is IPM? Key Terms and Concepts How Does
CHAPTER 1 Overview of IPM This chapter provides an overview of Cisco s Internetwork Performance Monitor (IPM) application. It contains the following sections: What Is IPM? Key Terms and Concepts How Does
15-441: Computer Networks Spring 2017 Homework 3
 15-441: Computer Networks Spring 2017 Homework 3 Assigned: Feb 15, 2018 Due: Mar 19, 2018 Lead TA: M.Ahmed Shah 1. Chapter 3: Exercise 41, page 294 2. Chapter 3: Exercise 43, page
15-441: Computer Networks Spring 2017 Homework 3 Assigned: Feb 15, 2018 Due: Mar 19, 2018 Lead TA: M.Ahmed Shah 1. Chapter 3: Exercise 41, page 294 2. Chapter 3: Exercise 43, page
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
Packet Tracer - Using Traceroute to Discover the Network (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Scenario The company you work for has acquired a new branch location.
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Scenario The company you work for has acquired a new branch location.
Lab Configuring HSRP and GLBP Topology
 Topology 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Lab 2.8.2: Challenge Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 Web Server Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 209.165.200.225
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 Web Server Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 209.165.200.225
Using Diagnostic Tools
 Using Diagnostic Tools The Tools System Diagnostics page on the INVESTIGATE view provides several diagnostic tools that help troubleshoot various kinds of network problems and process monitors. Tech Support
Using Diagnostic Tools The Tools System Diagnostics page on the INVESTIGATE view provides several diagnostic tools that help troubleshoot various kinds of network problems and process monitors. Tech Support
Lab - Configuring IPv6 Addresses on Network Devices
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address Prefix Length Default Gateway Objectives R1 G0/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1 64 N/A G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 64 N/A S1 VLAN 1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::B 64 N/A PC-A
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address Prefix Length Default Gateway Objectives R1 G0/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1 64 N/A G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 64 N/A S1 VLAN 1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::B 64 N/A PC-A
3/10/2011. Copyright Link Technologies, Inc.
 Mikrotik Certified Trainer / Engineer MikroTik Certified Dude Consultant Consulting Since 1997 Enterprise Class Networks WAN Connectivity Certifications Cisco, Microsoft, MikroTik BGP/OSPF Experience Deployed
Mikrotik Certified Trainer / Engineer MikroTik Certified Dude Consultant Consulting Since 1997 Enterprise Class Networks WAN Connectivity Certifications Cisco, Microsoft, MikroTik BGP/OSPF Experience Deployed
Static Routing. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine directly
Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine directly
Firewall Stateful Inspection of ICMP
 Firewall Stateful Inspection of ICMP Last Updated: March 26, 2012 The Firewall Stateful Inspection of ICMP feature addresses the limitation of qualifying Internet Control Management Protocol (ICMP) messages
Firewall Stateful Inspection of ICMP Last Updated: March 26, 2012 The Firewall Stateful Inspection of ICMP feature addresses the limitation of qualifying Internet Control Management Protocol (ICMP) messages
Chapter 5: Trouble shooting of a network
 5 Troubleshooting TCP/IP Fig 5 show trouble shooting a TCP/IP Chapter 5: Trouble shooting of a network Steps 1 First, determines whether your local host is properly configured. Step 2 Next, uses the ping
5 Troubleshooting TCP/IP Fig 5 show trouble shooting a TCP/IP Chapter 5: Trouble shooting of a network Steps 1 First, determines whether your local host is properly configured. Step 2 Next, uses the ping
Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks
 Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks Lecturers Amnach Khawne Jirasak Sittigorn Chapter 1 1 Network Fundamentals Chapter 5 : OSI Network Layer Chapter 6 : Addressing the Network IPv4 Chapter 11
Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks Lecturers Amnach Khawne Jirasak Sittigorn Chapter 1 1 Network Fundamentals Chapter 5 : OSI Network Layer Chapter 6 : Addressing the Network IPv4 Chapter 11
Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs DNS Operations
 Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs DNS Operations First Published: August 14, 2006 Last Updated: January 6, 2011 This module describes how to configure the Cisco IOS IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) Domain
Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs DNS Operations First Published: August 14, 2006 Last Updated: January 6, 2011 This module describes how to configure the Cisco IOS IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) Domain
ITEC310 Computer Networks II
 ITEC310 Computer Networks II Chapter 22 Network Layer:, and Routing Department of Information Technology Eastern Mediterranean University Objectives 2/131 After completing this chapter you should be able
ITEC310 Computer Networks II Chapter 22 Network Layer:, and Routing Department of Information Technology Eastern Mediterranean University Objectives 2/131 After completing this chapter you should be able
BSc Year 2 Data Communications Lab - Using Wireshark to View Network Traffic. Topology. Objectives. Background / Scenario
 BSc Year 2 Data Communications Lab - Using Wireshark to View Network Traffic Topology Objectives Part 1: (Optional) Download and Install Wireshark Part 2: Capture and Analyze Local ICMP Data in Wireshark
BSc Year 2 Data Communications Lab - Using Wireshark to View Network Traffic Topology Objectives Part 1: (Optional) Download and Install Wireshark Part 2: Capture and Analyze Local ICMP Data in Wireshark
KillTest ᦝ䬺 䬽䭶䭱䮱䮍䭪䎃䎃䎃ᦝ䬺 䬽䭼䯃䮚䮀 㗴 㓸 NZZV ]]] QORRZKYZ PV ٶ瀂䐘މ悹伥濴瀦濮瀃瀆ݕ 濴瀦
![KillTest ᦝ䬺 䬽䭶䭱䮱䮍䭪䎃䎃䎃ᦝ䬺 䬽䭼䯃䮚䮀 㗴 㓸 NZZV ]]] QORRZKYZ PV ٶ瀂䐘މ悹伥濴瀦濮瀃瀆ݕ 濴瀦 KillTest ᦝ䬺 䬽䭶䭱䮱䮍䭪䎃䎃䎃ᦝ䬺 䬽䭼䯃䮚䮀 㗴 㓸 NZZV ]]] QORRZKYZ PV ٶ瀂䐘މ悹伥濴瀦濮瀃瀆ݕ 濴瀦](/thumbs/90/102664913.jpg) KillTest Exam : 100-101 Title : CCNA Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices 1 (ICND1) Version : Demo 1 / 15 1.Which three statements are true about the operation of a full-duplex Ethernet network? (Choose
KillTest Exam : 100-101 Title : CCNA Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices 1 (ICND1) Version : Demo 1 / 15 1.Which three statements are true about the operation of a full-duplex Ethernet network? (Choose
Introduction to Networking. Topologies and Definitions. Network Topology and Definitions. Some Icons. Network Topologies. Network Topologies
 Network Topology and Definitions Definitions and icons Network topologies PoP topologies Introduction to Networking Interconnections and s ISP/ IP Addressing Gluing it all together 1 2 Some Icons Router
Network Topology and Definitions Definitions and icons Network topologies PoP topologies Introduction to Networking Interconnections and s ISP/ IP Addressing Gluing it all together 1 2 Some Icons Router
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing
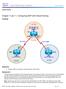 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Lab IP Addresses and Network Communication
 Lab 3.5.2 IP Addresses and Network Communication Objectives Build a simple peer-to-peer network and verify physical connectivity. Assign various IP addresses to hosts and observe the effects on network
Lab 3.5.2 IP Addresses and Network Communication Objectives Build a simple peer-to-peer network and verify physical connectivity. Assign various IP addresses to hosts and observe the effects on network
Avaya ExpertNet Lite Assessment Tool
 IP Telephony Contact Centers Mobility Services WHITE PAPER Avaya ExpertNet Lite Assessment Tool April 2005 avaya.com Table of Contents Overview... 1 Network Impact... 2 Network Paths... 2 Path Generation...
IP Telephony Contact Centers Mobility Services WHITE PAPER Avaya ExpertNet Lite Assessment Tool April 2005 avaya.com Table of Contents Overview... 1 Network Impact... 2 Network Paths... 2 Path Generation...
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition. Chapter 9 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking
 Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 9 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking Objectives Describe methods of network design unique to TCP/IP networks, including subnetting, CIDR, and address translation
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 9 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking Objectives Describe methods of network design unique to TCP/IP networks, including subnetting, CIDR, and address translation
Configuring and Testing Your Network
 Configuring and Testing Your Network Network Fundamentals Chapter 11 1 Role of Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Identify several classes of devices that have IOS embedded 2 Role of Internetwork Operating
Configuring and Testing Your Network Network Fundamentals Chapter 11 1 Role of Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Identify several classes of devices that have IOS embedded 2 Role of Internetwork Operating
Smart Serial. Show interfaces. Shut down. logging synchronous
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
Homework 2 TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management
 Homework 2 TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management Hw 2 Assigned on 2015/9/1, Due 2015/9/15 Hand-In Requirement Prepare a activity/laboratory report (name it Hw4-WebSys-YourName.docx) using the ECET Lab
Homework 2 TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management Hw 2 Assigned on 2015/9/1, Due 2015/9/15 Hand-In Requirement Prepare a activity/laboratory report (name it Hw4-WebSys-YourName.docx) using the ECET Lab
Contents. Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands 1 debugging 1 display debugging 2 ping 2 ping ipv6 5 tracert 7 tracert ipv6 9
 Contents Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands 1 debugging 1 display debugging 2 ping 2 ping ipv6 5 tracert 7 tracert ipv6 9 i Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands debugging Syntax Default
Contents Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands 1 debugging 1 display debugging 2 ping 2 ping ipv6 5 tracert 7 tracert ipv6 9 i Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands debugging Syntax Default
Routing Concepts. 1.0 Routing Concepts. Chapter Introduction Class Activity - Do We Really Need a Map?
 Chapter 1 Routing Concepts 1.0 Routing Concepts 1.0.1.1 Introduction Networks allow people to communicate, collaborate, and interact in many ways. Networks are used to access web pages, talk using IP telephones,
Chapter 1 Routing Concepts 1.0 Routing Concepts 1.0.1.1 Introduction Networks allow people to communicate, collaborate, and interact in many ways. Networks are used to access web pages, talk using IP telephones,
Introduction to Computer
 PDHonline Course E175 (8 PDH) Introduction to Computer Instructor: Dale W. Callahan, Ph.D., P.E. and Lea B. Callahan, P.E. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone
PDHonline Course E175 (8 PDH) Introduction to Computer Instructor: Dale W. Callahan, Ph.D., P.E. and Lea B. Callahan, P.E. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone
Chapter 6. The Protocol TCP/IP. Introduction to Protocols
 Chapter 6 The Protocol TCP/IP 1 Introduction to Protocols A protocol is a set of rules that governs the communications between computers on a network. These rules include guidelines that regulate the following
Chapter 6 The Protocol TCP/IP 1 Introduction to Protocols A protocol is a set of rules that governs the communications between computers on a network. These rules include guidelines that regulate the following
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLs Topology
 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Which of the following are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.) - packet switching - path selection
 Which three statements are true regarding the encapsulation and de-encapsulation of packets when traveling through a router? (Choose three.) - The router modifies the TTL field, decrementing it by one.
Which three statements are true regarding the encapsulation and de-encapsulation of packets when traveling through a router? (Choose three.) - The router modifies the TTL field, decrementing it by one.
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature enables you to configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature enables you to configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes
Lab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping
 Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Homework 2: Lab Activity TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management
 Homework 2: Lab Activity TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management Hw 2 Assigned on 2017/8/29, Due 2017/9/7 Hand-In Requirement Prepare a activity/laboratory report (name it Hw2-WebSys-YourName.docx) using
Homework 2: Lab Activity TCP/IP Network Monitoring and Management Hw 2 Assigned on 2017/8/29, Due 2017/9/7 Hand-In Requirement Prepare a activity/laboratory report (name it Hw2-WebSys-YourName.docx) using
COMPUTER NETWORKING LAB EXERCISES (TP) 4
 Name 1: Name 2: Group number: COMPUTER NETWORKING LAB EXERCISES (TP) 4 IPV6 December 14, 2009 Abstract In this TP you will revisit some of the basic networking tools that were introduced in TP1, only this
Name 1: Name 2: Group number: COMPUTER NETWORKING LAB EXERCISES (TP) 4 IPV6 December 14, 2009 Abstract In this TP you will revisit some of the basic networking tools that were introduced in TP1, only this
Planning for Information Network
 Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
8.9.2 Lab: Configure an Ethernet NIC to use DHCP in Windows Vista
 8.9.2 Lab: Configure an Ethernet NIC to use DHCP in Windows Vista Introduction If Vista is not available in your classroom, you may complete this lab by viewing the figures in this document. Print and
8.9.2 Lab: Configure an Ethernet NIC to use DHCP in Windows Vista Introduction If Vista is not available in your classroom, you may complete this lab by viewing the figures in this document. Print and
COMP 2000 W 2012 Lab no. 3 Page 1 of 11
 COMP 2000 W 2012 Lab no. 3 Page 1 of 11 Lab Introduction Background The Internet is based on packet-switched protocols. Information is carried in packets (it is divided into packets), which can be imagined
COMP 2000 W 2012 Lab no. 3 Page 1 of 11 Lab Introduction Background The Internet is based on packet-switched protocols. Information is carried in packets (it is divided into packets), which can be imagined
Chapter 8. The Routing Table: A Closer Look
 Chapter 8 The Routing Table: A Closer Look CCNA2-1 Chapter 8 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks
Chapter 8 The Routing Table: A Closer Look CCNA2-1 Chapter 8 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks
Firewall Stateful Inspection of ICMP
 The feature categorizes Internet Control Management Protocol Version 4 (ICMPv4) messages as either malicious or benign. The firewall uses stateful inspection to trust benign ICMPv4 messages that are generated
The feature categorizes Internet Control Management Protocol Version 4 (ICMPv4) messages as either malicious or benign. The firewall uses stateful inspection to trust benign ICMPv4 messages that are generated
Networking Basics. Networking Fundamentals Series
 Networking Basics Networking Fundamentals Series Copyright Information Copyright 2012 INE, Inc. All rights reserved. This publication,, was developed by INE, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Networking Basics Networking Fundamentals Series Copyright Information Copyright 2012 INE, Inc. All rights reserved. This publication,, was developed by INE, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Network I Lab 02. What are the major external components of the PC including the peripherals? / Characteristics
 Part 01 : PC Hardware Network I Lab 02 Objective Become familiar with the basic peripheral components of a PC computer system. Identify PC connections including network attachment. Examine the internal
Part 01 : PC Hardware Network I Lab 02 Objective Become familiar with the basic peripheral components of a PC computer system. Identify PC connections including network attachment. Examine the internal
Shortest Path First Example
 IP Exercises (Solutions in Class) 1 Shortest Path First Example Example: Received Set of Link State Update Packets (from Fig. 5-13, Computer Networks) Identity Sequence # Age List of Neighbors A 2021 60
IP Exercises (Solutions in Class) 1 Shortest Path First Example Example: Received Set of Link State Update Packets (from Fig. 5-13, Computer Networks) Identity Sequence # Age List of Neighbors A 2021 60
COMP2330 Data Communications and Networking
 COMP2330 Data Communications and Networking Dr. Chu Xiaowen (Second semester, 2009-2010 academic year) Last update : Jan-19-2010 Laboratory 2 IP techniques: ipconfig, ping, tracert and netstat Objectives:
COMP2330 Data Communications and Networking Dr. Chu Xiaowen (Second semester, 2009-2010 academic year) Last update : Jan-19-2010 Laboratory 2 IP techniques: ipconfig, ping, tracert and netstat Objectives:
What is a Network? A connection of two or more computers so that they can share resources.
 NETWORKS What is a Network? A connection of two or more computers so that they can share resources. Network Benefits Remote access Sharing files & resources Communication Cost Maintenance Communication
NETWORKS What is a Network? A connection of two or more computers so that they can share resources. Network Benefits Remote access Sharing files & resources Communication Cost Maintenance Communication
Lab Configuring IPv6 Static and Default Routes
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/0 FC00::2/64
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/0 FC00::2/64
TCP/IP Diagnostic Utilities on Windows 2008 Server
 TCP/IP Diagnostic Utilities on Windows 2008 Server June 20, 2012 Copyright 2012 by World Class CAD, LLC. All Rights Reserved. TCP/IP Utilities In this lesson, we will learn about how to use the TCP/IP
TCP/IP Diagnostic Utilities on Windows 2008 Server June 20, 2012 Copyright 2012 by World Class CAD, LLC. All Rights Reserved. TCP/IP Utilities In this lesson, we will learn about how to use the TCP/IP
The Basics of Networking
 c h a p t e r 3 The Basics of Networking Making the Connection lawrence snyder Times are Changing Nowhere Is Remote People are more interconnected Social interactions are changing Freedom of Seach and
c h a p t e r 3 The Basics of Networking Making the Connection lawrence snyder Times are Changing Nowhere Is Remote People are more interconnected Social interactions are changing Freedom of Seach and
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM
 Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals. Chapter 06 Addressing the Network IPv4
 CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals Chapter 06 Addressing the Network IPv4 Updated: 20/05/2008 1 6.0.1 Introduction Addressing is a key function of Network layer protocols that enables data communication
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals Chapter 06 Addressing the Network IPv4 Updated: 20/05/2008 1 6.0.1 Introduction Addressing is a key function of Network layer protocols that enables data communication
Access Switch VLAN Y Y.1 /24
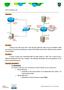 Topology: Fa 0/1 VNC Server Fa 0/0 Port B Access Router Trunk VLAN X Access Switch VLAN Y Backbone Router 141.85.Y.1 /24 28.0.0.42 OSPF X.0.0.0/8 Port A 27.45.67.89 Work Station DHCP Server The Goal: Connect
Topology: Fa 0/1 VNC Server Fa 0/0 Port B Access Router Trunk VLAN X Access Switch VLAN Y Backbone Router 141.85.Y.1 /24 28.0.0.42 OSPF X.0.0.0/8 Port A 27.45.67.89 Work Station DHCP Server The Goal: Connect
Unit A - Connecting to the Network
 Unit A - Connecting to the Network 1 What is a network? The ability to connect people and equipment no matter where they are in the world. telephone computers television How does your body work as a network?
Unit A - Connecting to the Network 1 What is a network? The ability to connect people and equipment no matter where they are in the world. telephone computers television How does your body work as a network?
Weather Direct Post-US Migration Guidelines
 Weather Direct Post-US Migration Guidelines Thank you for your patience in the last few weeks. The Weather Direct servers are now in the US, which shortens the path your data needs to travel to reach your
Weather Direct Post-US Migration Guidelines Thank you for your patience in the last few weeks. The Weather Direct servers are now in the US, which shortens the path your data needs to travel to reach your
WHITE PAPER. The Shortfalls of Traceroute in Modern Multi-Path Networks
 WHITE PAPER The Shortfalls of Traceroute in Modern Multi-Path Networks THE SHORTFALLS OF TRACEROUTE IN MODERN MULTI-PATH NETWORKS INTRODUCTION Traceroute is a fantastically popular network troubleshooting
WHITE PAPER The Shortfalls of Traceroute in Modern Multi-Path Networks THE SHORTFALLS OF TRACEROUTE IN MODERN MULTI-PATH NETWORKS INTRODUCTION Traceroute is a fantastically popular network troubleshooting
Introduction to Computer Networks
 Introduction to Computer Networks Tian Song ( 嵩天 ), Ph.D., Assoc. Prof. songtian@bit.edu.cn Introduction to Computer Networks ICMP, ARP, DHCP, OSPF, BGP Tian Song ( 嵩天 ), Ph.D., Assoc. Prof. songtian@bit.edu.cn
Introduction to Computer Networks Tian Song ( 嵩天 ), Ph.D., Assoc. Prof. songtian@bit.edu.cn Introduction to Computer Networks ICMP, ARP, DHCP, OSPF, BGP Tian Song ( 嵩天 ), Ph.D., Assoc. Prof. songtian@bit.edu.cn
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature lets you configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes and Multiprotocol
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature lets you configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes and Multiprotocol
User Guide. Sage ERP MAS 90 Online
 User Guide Sage ERP MAS 90 Online Sage ERP MAS 90 Online Page 1 Last Updated: November 18, 2011 Table of Contents OVERVIEW... 1 SUPPORT... 1 SAGE ERP MAS 90 ONLINE 24 X 7 CONNECTIVITY SUPPORT... 1 PRODUCT
User Guide Sage ERP MAS 90 Online Sage ERP MAS 90 Online Page 1 Last Updated: November 18, 2011 Table of Contents OVERVIEW... 1 SUPPORT... 1 SAGE ERP MAS 90 ONLINE 24 X 7 CONNECTIVITY SUPPORT... 1 PRODUCT
Configure IP SLA Tracking for IPv4 Static Routes on an SG550XG Switch
 Configure IP SLA Tracking for IPv4 Static Routes on an SG550XG Switch Introduction When using static routing, you may experience a situation where a static route is active, but the destination network
Configure IP SLA Tracking for IPv4 Static Routes on an SG550XG Switch Introduction When using static routing, you may experience a situation where a static route is active, but the destination network
Module 5 Policy Based Routing
 Module 5 Policy Based Routing Objective: Using interesting lab exercises, the student will implement some of the fundamental techniques of Policy Routing, as applied in Cisco IOS. Prerequisite: Module
Module 5 Policy Based Routing Objective: Using interesting lab exercises, the student will implement some of the fundamental techniques of Policy Routing, as applied in Cisco IOS. Prerequisite: Module
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs Topology
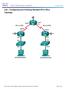 Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-2 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-2 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
Module 1b IS-IS. Prerequisites: The setup section of Module 1. The following will be the common topology used for the first series of labs.
 Module 1b IS-IS Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one IS-IS Area. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working properly. Prerequisites: The setup section
Module 1b IS-IS Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one IS-IS Area. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working properly. Prerequisites: The setup section
Basic Cisco Router Configuration: Multiple Routers
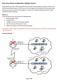 Basic Cisco Router Configuration: Multiple Routers Routers rarely exist alone. Most organizations have several to several dozens of routers. In this Lab, we will study two different ways in which routers
Basic Cisco Router Configuration: Multiple Routers Routers rarely exist alone. Most organizations have several to several dozens of routers. In this Lab, we will study two different ways in which routers
CS 386M Lab 1 Router Configuration and Routing
 CS 386M Lab 1 Router Configuration and Routing In this lab you will learn: PartA Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 30 min Dynamic Routing PartC 40 min Explore! Components used in this
CS 386M Lab 1 Router Configuration and Routing In this lab you will learn: PartA Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 30 min Dynamic Routing PartC 40 min Explore! Components used in this
Public Switched TelephoneNetwork (PSTN) By Iqtidar Ali
 Public Switched TelephoneNetwork (PSTN) By Iqtidar Ali Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) The term PSTN describes the various equipment and interconnecting facilities that provide phone service to
Public Switched TelephoneNetwork (PSTN) By Iqtidar Ali Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) The term PSTN describes the various equipment and interconnecting facilities that provide phone service to
Network Configuration
 Network Configuration Setting up your Home or Office network to allow your DVR to be accessible externally can be kind of tricky, but I will try to explain basic network concepts to allow you to configure
Network Configuration Setting up your Home or Office network to allow your DVR to be accessible externally can be kind of tricky, but I will try to explain basic network concepts to allow you to configure
