Session 4.2. Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session Subscriber zones / subscriber grid model = >
|
|
|
- Ruth Andrews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ITU Seminar Bangkok, Thailand, November 2002 Session 4.2 Switching/Routing and Transmission planning Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session Location problem Subscriber zones / subscriber grid model = > Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session 4.2-2
2 Location problem Theoretically for the set of optimal location (X,Y ) the partial derivatives of the total network X = 0 cost function, C, with regard to for =1,2, K NX Y = 0 X and Y are equal to zero : Different methods for solving this 2* equation system could be employed depending upon the methods of measuring the distances in the network In the most complicated case we get a system of 2*NX non-linear equations If X and Y are expanded into Taylor-series this leads to a system of 2*NX linear equations in X F and Y F, which can easily be solved by standard methods Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session Location problem - distance measurement methods Mean distance from exchange to grid element : (x, y) (x 2, y2 ) The mean distance from to the rectangle can then be found from: (X,Y ) Ly D( X (x1, y1 ) L x along the cathetie :, Y, x, y) = X x + Y y (X, Y ) x2 y2 1 D = d ( X,Y, x, y ) dx dy area x y 1 1 along the hypotenuse : D( X,Y, x, y ) = ( X x) Lx + ( Y y ) Ly Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session 4.2-4
3 Simplified method for location optimization Based on the access network cost S j only : S j = sub ( i, j ) Cs ( D ) for ( i, j ) i For optimal locations (X,Y ) the partial derivatives of the cost function C= S j with regard to X and Y are equal to zero : X Y = 0 = 0 for = 1,2, KNX For a case with one location only for X we get: X = [ Cc ( D) D X ] ( i, j ) the partial derivative depends only on the distance Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session Simplified method for location optimization With simplified distance method along the cathetie : D( X, Y, = X j + Y i We get : Thus : X = 1 if j X C ( D ) if X j c ( i, j ) 1 C ( D ).( + 1) + c ( < X ( > X C ( D c ).( 1) = 0 Or : C ( D c ( i, j ) < X ( i, j ) > X Finally if disregard the tr. media cost (same everywhere) we get: ) = C ( D ) c ( < X ( j ) = > X Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session 4.2-6
4 Location problem Graph model(subscribers in nodes) = > Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session Location problem - graph model Graph model presents network nodes and links connecting these nodes - cost function, C, is a discrete function over all node locations, i.e. it is not possible to use partial derivatives of C Obvious solution is to calculate the total network cost, C, for all combinations (solutions) and find the smallest C = Cmin Distances calculation as distances on graph shortest path problem and corresponding algorithms For n nodes and N equipment items n! cost combinations (n-n)! N! Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session 4.2-8
5 Location problem - graph model Check all combinations - for very small networks - pointless to investigate many of the combinations Heuristic methods - eliminate the obvious senseless combinations and investigate only some of the combinations Probabilistic methods for location optimization - simulated annealing / simulated allocation Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session Boundaries problem grid model graph model Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session
6 Boundaries problem Boundary optimization is finding service/exchange area boundaries in such a way that total network costs is minimized The cost of connecting one subscriber at location (x,y), belonging to traffic zone K, to an exchange/node at ( X,Y ) can thus be expressed as : C( ) = C ( K, ) + C ( ) + D C ( D ) + C j b s f It depends of the cost of connecting the subscriber, the average exchange cost per subscriber, the backbone network cost of any subscriber The decision for the boundary can be made simply by comparison for every grid/node element ( the value C() is calculated for every exchange /node and the lowest C() then determines Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session Routing planning transiting of traffic Direct routing 5 hierarchical network High-usage route part of the traffic is carried on the direct route and the rest of the traffic overflows through a tandem 3 4 high-usage routes final routes Optimum 1 2 Dual homing (load sharing) C(N) alternative routes Primary routes with Poisson-type offered traffic N Circuits N OPT N D Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session
7 Routing planning Dual homing (load sharing) - overflowing traffic is divided with predefined coefficient a SF-A VT VN Combinatorial optimization Disjoint Routing Problem of Virtual Private Networks (VPN) demands must be routed through a network so that their paths do not share common nodes or links SZ methods for non-hierarchical routing optimize routing and simultaneously optimally dimension link capacities disjoint routing Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session Transmission planning Based on circuit/bandwidth matrix and transmission node/link data Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session
8 Transmission planning Optimization of ring/mesh protected transport networks Two types of nodes could be distinguished in the network : traffic access nodes represent the abstract traffic entry points (e.g. local exchange) transmission nodes represent the actual network nodes (e.g. ADMs or DXCs ) Requirements to the topology for protection - ring or mesh topologies, multi-ring structures, hybrid ring-mesh topologies different protection schemes: path protection, link protection, path diversity In the optimization methods are solved combinatorial problems usually with heuristic algorithms and based on the shortest path approach Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session Transmission planning Shortest path problem B 5 D 6 G to determine the shortest path between any two nodes as minimum distance A H 5 J to determine the minimum cost path between two nodes C F I Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session
9 Transmission planning examine the adjacent nodes and label each one with its distance from the source node examine nodes adjacent to those already labeled; when a node has links to two or more labeled nodes, its distance from each node is added to the label of that node; the smallest sum is chosen and used as the label for the new node repeat above until either the destination node is reached (if the shortest route to only one node is required) or until all nodes have been labeled (if the shortest routes to all nodes are required) Shortest path problem algorithm of Dantzig Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session Transmission planning Shortest path problem shortest path from A to J all partial paths contained in the path from A to J-(ABHJ): (AB), (AB), (ABH), (B), (BH), (BHJ), (H), (HJ), (HJ) are optimal paths, e.g. from B to J, the optimal path is (BHJ) every optimal path consists of partially optimal paths Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session
10 xample boundaries Grid element with 271 subscribers on a distance of 10 steps to upper exch. and 11 lo lower exch. attach to service area of upper exch. Grid element with 86 subscribers on a distance of 11 steps to upper exch. and 10 lo lower exch. attach to service area of lower exch. Boundary between grid elements 271 and 86 Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session xample locations Optimum location according to the simplified method is the median of the accumulated subscribers sum 4033 is within row 5 (Y=R5) Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session
Session 3.4. Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session Network optimization. Cost components of telecom network
 ITU Seminar Bangkok, Thailand, 11-1515 November 2002 Session 3.4 and costing Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session 3.4-1 Cost components of telecom network Costs Optimum
ITU Seminar Bangkok, Thailand, 11-1515 November 2002 Session 3.4 and costing Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session 3.4-1 Cost components of telecom network Costs Optimum
Features, Inputs/outputs for most frequent tools: Exel, PLANITU
 ITU / BDT- COE workshop Nairobi, Kenya, 7 11 October 2002 Network Planning Lecture NP-5.2 Features, Inputs/outputs for most frequent tools: Exel, PLANITU ITU COE Network Planning Workshop, Nairobi, Kenya,
ITU / BDT- COE workshop Nairobi, Kenya, 7 11 October 2002 Network Planning Lecture NP-5.2 Features, Inputs/outputs for most frequent tools: Exel, PLANITU ITU COE Network Planning Workshop, Nairobi, Kenya,
Features, Inputs/outputs for most frequent tools: Exel, PLANITU
 Regional Seminar for the EUR and CIS Region on Network Planning Strategy for Evolving Network Architectures Session 5.2 Features, Inputs/outputs for most frequent tools: Exel, PLANITU Live demo: Exel,
Regional Seminar for the EUR and CIS Region on Network Planning Strategy for Evolving Network Architectures Session 5.2 Features, Inputs/outputs for most frequent tools: Exel, PLANITU Live demo: Exel,
Session 4.2. Switching planning. Switching/Routing planning
 ITU Semnar Warsaw Poland 6-0 Otober 2003 Sesson 4.2 Swthng/Routng plannng Network Plannng Strategy for evolvng Network Arhtetures Sesson 4.2- Swthng plannng Loaton problem : Optmal plaement of exhanges
ITU Semnar Warsaw Poland 6-0 Otober 2003 Sesson 4.2 Swthng/Routng plannng Network Plannng Strategy for evolvng Network Arhtetures Sesson 4.2- Swthng plannng Loaton problem : Optmal plaement of exhanges
Public Switched TelephoneNetwork (PSTN) By Iqtidar Ali
 Public Switched TelephoneNetwork (PSTN) By Iqtidar Ali Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) The term PSTN describes the various equipment and interconnecting facilities that provide phone service to
Public Switched TelephoneNetwork (PSTN) By Iqtidar Ali Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) The term PSTN describes the various equipment and interconnecting facilities that provide phone service to
TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS By Syed Bakhtawar Shah Abid Lecturer in Computer Science 1 Public Switched Telephone Network Structure The Local Loop Trunks and Multiplexing Switching 2 Network Structure Minimize
TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS By Syed Bakhtawar Shah Abid Lecturer in Computer Science 1 Public Switched Telephone Network Structure The Local Loop Trunks and Multiplexing Switching 2 Network Structure Minimize
For internal circulation of BSNL only
 E3-E4 E4 (CFA) Overview of SDH AGENDA SDH & PDH Hierarchy SDH Network Survivability Synchronous All elements are synchronized with one master clock. DIGITAL Information is in binary. SDH OVERVIEW HIERARCHY
E3-E4 E4 (CFA) Overview of SDH AGENDA SDH & PDH Hierarchy SDH Network Survivability Synchronous All elements are synchronized with one master clock. DIGITAL Information is in binary. SDH OVERVIEW HIERARCHY
ITU Regional Seminar. Belgrade, Serbia and Montenegro, June Session 5.2. Service and applications matrix forecasting
 ITU Regional Seminar Belgrade, Serbia and Montenegro, 20-24 24 June 2005 Session 5.2 Service and applications matrix forecasting Evolving infrastructures to NGN and related Planning Strategies and Tools
ITU Regional Seminar Belgrade, Serbia and Montenegro, 20-24 24 June 2005 Session 5.2 Service and applications matrix forecasting Evolving infrastructures to NGN and related Planning Strategies and Tools
Analysys STEM case studies
 Analysys STEM case studies Migrating separate voice and data services to an NGN platform Robin Bailey Head of Decision Systems Group 17 March 2007 Bangkok Convergence is inevitable Voice and data services
Analysys STEM case studies Migrating separate voice and data services to an NGN platform Robin Bailey Head of Decision Systems Group 17 March 2007 Bangkok Convergence is inevitable Voice and data services
How Routing Algorithms Work
 How Routing Algorithms Work A router is used to manage network traffic and find the best route for sending packets. But have you ever thought about how routers do this? Routers need to have some information
How Routing Algorithms Work A router is used to manage network traffic and find the best route for sending packets. But have you ever thought about how routers do this? Routers need to have some information
SONET Topologies and Upgrades
 CHAPTER 9 Note The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring
CHAPTER 9 Note The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring
Solutions for Operations Research Final Exam
 Solutions for Operations Research Final Exam. (a) The buffer stock is B = i a i = a + a + a + a + a + a 6 + a 7 = + + + + + + =. And the transportation tableau corresponding to the transshipment problem
Solutions for Operations Research Final Exam. (a) The buffer stock is B = i a i = a + a + a + a + a + a 6 + a 7 = + + + + + + =. And the transportation tableau corresponding to the transshipment problem
Sycamore Networks Implementation of the ITU-T G.ASON Control Plane
 Technical Brief Sycamore Networks Implementation of the ITU-T G.SON Control Plane bstract This document provides a detailed overview of the control plane behavior of Sycamore Networks SN 16000 Intelligent
Technical Brief Sycamore Networks Implementation of the ITU-T G.SON Control Plane bstract This document provides a detailed overview of the control plane behavior of Sycamore Networks SN 16000 Intelligent
SONET Topologies and Upgrades
 8 CHAPTER Note The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring
8 CHAPTER Note The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring
Advanced routing topics. Tuomas Launiainen
 Advanced routing topics Tuomas Launiainen Suboptimal routing Routing trees Measurement of routing trees Adaptive routing Problems Fault-tolerant tables Point-of-failure rerouting Point-of-failure shortest
Advanced routing topics Tuomas Launiainen Suboptimal routing Routing trees Measurement of routing trees Adaptive routing Problems Fault-tolerant tables Point-of-failure rerouting Point-of-failure shortest
MODERN RECOVERY MECHANISMS FOR DATA TRANSPORT NETWORKS
 MODERN RECOVERY MECHANISMS FOR DATA TRANSPORT NETWORKS IT Specialist Dorina LuminiŃa Copaci Gorj Court IT Expert Constantin Alin Copaci ANRCTI Bucharest Abstract: A large number of recovery mechanisms
MODERN RECOVERY MECHANISMS FOR DATA TRANSPORT NETWORKS IT Specialist Dorina LuminiŃa Copaci Gorj Court IT Expert Constantin Alin Copaci ANRCTI Bucharest Abstract: A large number of recovery mechanisms
Data Communication and Parallel Computing on Twisted Hypercubes
 Data Communication and Parallel Computing on Twisted Hypercubes E. Abuelrub, Department of Computer Science, Zarqa Private University, Jordan Abstract- Massively parallel distributed-memory architectures
Data Communication and Parallel Computing on Twisted Hypercubes E. Abuelrub, Department of Computer Science, Zarqa Private University, Jordan Abstract- Massively parallel distributed-memory architectures
Automatic Service and Protection Path Computation - A Multiplexing Approach
 Automatic Service and Protection Path Computation - A Multiplexing Approach Loay Alzubaidi 1, Ammar El Hassan 2, Jaafar Al Ghazo 3 1 Department of Computer Engineering & Science, Prince Muhammad bin Fahd
Automatic Service and Protection Path Computation - A Multiplexing Approach Loay Alzubaidi 1, Ammar El Hassan 2, Jaafar Al Ghazo 3 1 Department of Computer Engineering & Science, Prince Muhammad bin Fahd
OPTICAL NETWORKS. Optical Metro Networks. A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005
 OPTICAL NETWORKS Optical Metro Networks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction Telecommunications networks are normally segmented in a three-tier hierarchy: Access, metropolitan,
OPTICAL NETWORKS Optical Metro Networks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction Telecommunications networks are normally segmented in a three-tier hierarchy: Access, metropolitan,
In this edition of HowStuffWorks, we'll find out precisely what information is used by routers in determining where to send a packet.
 How Routing Algorithms Work by Roozbeh Razavi If you have read the HowStuffWorks article How Routers Work, then you know that a router is used to manage network traffic and find the best route for sending
How Routing Algorithms Work by Roozbeh Razavi If you have read the HowStuffWorks article How Routers Work, then you know that a router is used to manage network traffic and find the best route for sending
IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 21, NO. 7, SEPTEMBER
 IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 21, NO. 7, SEPTEMBER 2003 1173 A Comprehensive Study on Next-Generation Optical Grooming Switches Keyao Zhu, Student Member, IEEE, Hui Zang, Member,
IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 21, NO. 7, SEPTEMBER 2003 1173 A Comprehensive Study on Next-Generation Optical Grooming Switches Keyao Zhu, Student Member, IEEE, Hui Zang, Member,
Tutorial 2 : Networking
 Lund University ETSN01 Advanced Telecommunication Tutorial 2 : Networking Author: Emma Fitzgerald Tutor: Farnaz Moradi November 26, 2015 Contents I Before you start 3 II Whole Class Exercise: Networking
Lund University ETSN01 Advanced Telecommunication Tutorial 2 : Networking Author: Emma Fitzgerald Tutor: Farnaz Moradi November 26, 2015 Contents I Before you start 3 II Whole Class Exercise: Networking
Code_Aster. SSNV209 Interface in contact rubbing with X-FEM
 Titre : SSNV209 - Interface en contact frottant avec X-FEM Date : 21/07/2015 Page : 1/34 SSNV209 Interface in contact rubbing with X-FEM Summary: This problem corresponds to a quasi-static analysis of
Titre : SSNV209 - Interface en contact frottant avec X-FEM Date : 21/07/2015 Page : 1/34 SSNV209 Interface in contact rubbing with X-FEM Summary: This problem corresponds to a quasi-static analysis of
The Reliability, Efficiency and Treatment Quality of Centralized versus Decentralized Water Infrastructure 1
 The Reliability, Efficiency and Treatment Quality of Centralized versus Decentralized Water Infrastructure 1 Dr Qilin Li, Associate Professor, Civil & Environmental Engineering, Rice University Dr. Leonardo
The Reliability, Efficiency and Treatment Quality of Centralized versus Decentralized Water Infrastructure 1 Dr Qilin Li, Associate Professor, Civil & Environmental Engineering, Rice University Dr. Leonardo
Backbone network technologies. T Jouni Karvo, Timo Kiravuo
 Backbone network technologies T-110.300 Jouni Karvo, Timo Kiravuo Backbone network technologies This lecture tells about backbone networks After this lecture, you should know WDM, PDH, SDH and ATM understand
Backbone network technologies T-110.300 Jouni Karvo, Timo Kiravuo Backbone network technologies This lecture tells about backbone networks After this lecture, you should know WDM, PDH, SDH and ATM understand
Diversity Coded 5G Fronthaul Wireless Networks
 IEEE Wireless Telecommunication Symposium (WTS) 2017 Diversity Coded 5G Fronthaul Wireless Networks Nabeel Sulieman, Kemal Davaslioglu, and Richard D. Gitlin Department of Electrical Engineering University
IEEE Wireless Telecommunication Symposium (WTS) 2017 Diversity Coded 5G Fronthaul Wireless Networks Nabeel Sulieman, Kemal Davaslioglu, and Richard D. Gitlin Department of Electrical Engineering University
f xx + f yy = F (x, y)
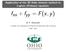 Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
On Routing Performance of MENTOR Algorithm
 1769 On Routing Performance of MENTOR Algorithm KAIRAT JAROENRAT, PISIT CHARNKEITKONG Faculty of Information Technology Rangsit University 52/347 Muang-Ake, Phaholyothin Rd., Lak-Hok, Pathumtani, THAILAND
1769 On Routing Performance of MENTOR Algorithm KAIRAT JAROENRAT, PISIT CHARNKEITKONG Faculty of Information Technology Rangsit University 52/347 Muang-Ake, Phaholyothin Rd., Lak-Hok, Pathumtani, THAILAND
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks. Routing, Zigbee, and RPL
 http://www.ee.kth.se/~carlofi/teaching/pwsn-2011/wsn_course.shtml Lecture 8 Stockholm, November 11, 2011 Routing, Zigbee, and RPL Royal Institute of Technology - KTH Stockholm, Sweden e-mail: carlofi@kth.se
http://www.ee.kth.se/~carlofi/teaching/pwsn-2011/wsn_course.shtml Lecture 8 Stockholm, November 11, 2011 Routing, Zigbee, and RPL Royal Institute of Technology - KTH Stockholm, Sweden e-mail: carlofi@kth.se
Face Detection CUDA Accelerating
 Face Detection CUDA Accelerating Jaromír Krpec Department of Computer Science VŠB Technical University Ostrava Ostrava, Czech Republic krpec.jaromir@seznam.cz Martin Němec Department of Computer Science
Face Detection CUDA Accelerating Jaromír Krpec Department of Computer Science VŠB Technical University Ostrava Ostrava, Czech Republic krpec.jaromir@seznam.cz Martin Němec Department of Computer Science
Basic Communication Operations Ananth Grama, Anshul Gupta, George Karypis, and Vipin Kumar
 Basic Communication Operations Ananth Grama, Anshul Gupta, George Karypis, and Vipin Kumar To accompany the text ``Introduction to Parallel Computing'', Addison Wesley, 2003 Topic Overview One-to-All Broadcast
Basic Communication Operations Ananth Grama, Anshul Gupta, George Karypis, and Vipin Kumar To accompany the text ``Introduction to Parallel Computing'', Addison Wesley, 2003 Topic Overview One-to-All Broadcast
Optimal Detector Locations for OD Matrix Estimation
 Optimal Detector Locations for OD Matrix Estimation Ying Liu 1, Xiaorong Lai, Gang-len Chang 3 Abstract This paper has investigated critical issues associated with Optimal Detector Locations for OD matrix
Optimal Detector Locations for OD Matrix Estimation Ying Liu 1, Xiaorong Lai, Gang-len Chang 3 Abstract This paper has investigated critical issues associated with Optimal Detector Locations for OD matrix
Dynamic service Allocation with Protection Path
 www.ijcsi.org 115 Dynamic service Allocation with Protection Path Loay Alzubaidi Department of Computer Engineering & Science, Prince Muhammad bin Fahd University AL-Khobar, Saudi Arabia Abstract Path
www.ijcsi.org 115 Dynamic service Allocation with Protection Path Loay Alzubaidi Department of Computer Engineering & Science, Prince Muhammad bin Fahd University AL-Khobar, Saudi Arabia Abstract Path
Dynamic Routing and Resource Allocation in WDM Transport Networks
 Dynamic Routing and Resource Allocation in WDM Transport Networks Jan Späth University of Stuttgart, Institute of Communication Networks and Computer Engineering (IND), Germany Email: spaeth@ind.uni-stuttgart.de
Dynamic Routing and Resource Allocation in WDM Transport Networks Jan Späth University of Stuttgart, Institute of Communication Networks and Computer Engineering (IND), Germany Email: spaeth@ind.uni-stuttgart.de
Social-Network Graphs
 Social-Network Graphs Mining Social Networks Facebook, Google+, Twitter Email Networks, Collaboration Networks Identify communities Similar to clustering Communities usually overlap Identify similarities
Social-Network Graphs Mining Social Networks Facebook, Google+, Twitter Email Networks, Collaboration Networks Identify communities Similar to clustering Communities usually overlap Identify similarities
Add and Remove Nodes
 CHAPTER 12 The terms Unidirectional Path Switched Ring and UPSR may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration.
CHAPTER 12 The terms Unidirectional Path Switched Ring and UPSR may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration.
OPTICAL NETWORKS. Virtual Topology Design. A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005
 OPTICAL NETWORKS Virtual Topology Design A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Virtual Topology A lightpath provides single-hop communication between any two nodes, which could be far apart in
OPTICAL NETWORKS Virtual Topology Design A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Virtual Topology A lightpath provides single-hop communication between any two nodes, which could be far apart in
BGP. Daniel Zappala. CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University
 Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/20 Scaling Routing for the Internet scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes in routing tables
Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/20 Scaling Routing for the Internet scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes in routing tables
Topology basics. Constraints and measures. Butterfly networks.
 EE48: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture # Interconnection Networks Architecture and Design Stanford University Topology basics. Constraints and measures. Butterfly networks. Lecture #: Monday, 7 April
EE48: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture # Interconnection Networks Architecture and Design Stanford University Topology basics. Constraints and measures. Butterfly networks. Lecture #: Monday, 7 April
Basic Idea. The routing problem is typically solved using a twostep
 Global Routing Basic Idea The routing problem is typically solved using a twostep approach: Global Routing Define the routing regions. Generate a tentative route for each net. Each net is assigned to a
Global Routing Basic Idea The routing problem is typically solved using a twostep approach: Global Routing Define the routing regions. Generate a tentative route for each net. Each net is assigned to a
Unit 3: Dynamic Routing
 Unit 3: Dynamic Routing Basic Routing The term routing refers to taking a packet from one device and sending it through the network to another device on a different network. Routers don t really care about
Unit 3: Dynamic Routing Basic Routing The term routing refers to taking a packet from one device and sending it through the network to another device on a different network. Routers don t really care about
Where have all the cars gone? A model for determining traffic flow throughout a road network
 A model for determining traffic flow throughout a road network Harvey Mudd College Presentation Days 7 May 2008 Traffic monitoring Important Equations Lots of Traffic + Small Roads = Congestion Congestion
A model for determining traffic flow throughout a road network Harvey Mudd College Presentation Days 7 May 2008 Traffic monitoring Important Equations Lots of Traffic + Small Roads = Congestion Congestion
Routing Resiliency Latest Enhancements
 Routing Resiliency Latest Enhancements Clarence Filsfils cf@cisco.com Agenda Per-Prefix LFA Remote LFA Segment Routing Topology-Independent LFA 3 Acknowledgement Stephane Litkowski and Bruno Decraene,
Routing Resiliency Latest Enhancements Clarence Filsfils cf@cisco.com Agenda Per-Prefix LFA Remote LFA Segment Routing Topology-Independent LFA 3 Acknowledgement Stephane Litkowski and Bruno Decraene,
Network-on-chip (NOC) Topologies
 Network-on-chip (NOC) Topologies 1 Network Topology Static arrangement of channels and nodes in an interconnection network The roads over which packets travel Topology chosen based on cost and performance
Network-on-chip (NOC) Topologies 1 Network Topology Static arrangement of channels and nodes in an interconnection network The roads over which packets travel Topology chosen based on cost and performance
Helsinki University of Technology Telecommunications Laboratory. OSPF Routing Protocol Licenciate course seminar paper
 Helsinki University of Technology Telecommunications Laboratory OSPF Routing Protocol Licenciate course seminar paper Shkumbin I. Hamiti, 08.10.1996 Communications Laboratory, TKK-HUT email: bini#tiltu.hut.fi
Helsinki University of Technology Telecommunications Laboratory OSPF Routing Protocol Licenciate course seminar paper Shkumbin I. Hamiti, 08.10.1996 Communications Laboratory, TKK-HUT email: bini#tiltu.hut.fi
Add and Remove Nodes
 14 CHAPTER The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration.
14 CHAPTER The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration.
MSEC PLANT LAYOUT OPTIMIZATION CONSIDERING THE EFFECT OF MAINTENANCE
 Proceedings of Proceedings of the 211 ASME International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference MSEC211 June 13-17, 211, Corvallis, Oregon, USA MSEC211-233 PLANT LAYOUT OPTIMIZATION CONSIDERING
Proceedings of Proceedings of the 211 ASME International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference MSEC211 June 13-17, 211, Corvallis, Oregon, USA MSEC211-233 PLANT LAYOUT OPTIMIZATION CONSIDERING
DYN-OPT Users Manual. Cenk Caliskan Randolph W. Hall. California PATH Working Paper UCB-ITS-PWP-97-6
 CALIFORNIA PATH PROGRAM INSTITUTE OF TRANSPORTATION STUDIES UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY DYN-OPT Users Manual Cenk Caliskan Randolph W Hall California PATH Working Paper UCB-ITS-PWP-97-6 This work
CALIFORNIA PATH PROGRAM INSTITUTE OF TRANSPORTATION STUDIES UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY DYN-OPT Users Manual Cenk Caliskan Randolph W Hall California PATH Working Paper UCB-ITS-PWP-97-6 This work
Fundamentals of Networking Types of Topologies
 Fundamentals of Networking Types of Topologies Kuldeep Sonar 1 Bus Topology Bus topology is a network type in which every computer and network device is connected to single cable. When it has exactly two
Fundamentals of Networking Types of Topologies Kuldeep Sonar 1 Bus Topology Bus topology is a network type in which every computer and network device is connected to single cable. When it has exactly two
Computer Vision. Image Segmentation. 10. Segmentation. Computer Engineering, Sejong University. Dongil Han
 Computer Vision 10. Segmentation Computer Engineering, Sejong University Dongil Han Image Segmentation Image segmentation Subdivides an image into its constituent regions or objects - After an image has
Computer Vision 10. Segmentation Computer Engineering, Sejong University Dongil Han Image Segmentation Image segmentation Subdivides an image into its constituent regions or objects - After an image has
CSE 202: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4
 CSE 202: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Greedy Algorithms Direct argument - MST Exchange argument - Caching Greedy approximation algorithms Greedy Approximation
CSE 202: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Greedy Algorithms Direct argument - MST Exchange argument - Caching Greedy approximation algorithms Greedy Approximation
Add and Remove Nodes
 13 CHAPTER The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration.
13 CHAPTER The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration.
Rerouting Schemes for Wireless ATM Networks
 Communications and Network, 204, 6, 28-227 Published Online November 204 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/cn http://dx.doi.org/0.4236/cn.204.64024 Rerouting Schemes for Wireless ATM Networks Hasan
Communications and Network, 204, 6, 28-227 Published Online November 204 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/cn http://dx.doi.org/0.4236/cn.204.64024 Rerouting Schemes for Wireless ATM Networks Hasan
Announcements. Edges. Last Lecture. Gradients: Numerical Derivatives f(x) Edge Detection, Lines. Intro Computer Vision. CSE 152 Lecture 10
 Announcements Assignment 2 due Tuesday, May 4. Edge Detection, Lines Midterm: Thursday, May 6. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10 Edges Last Lecture 1. Object boundaries 2. Surface normal
Announcements Assignment 2 due Tuesday, May 4. Edge Detection, Lines Midterm: Thursday, May 6. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10 Edges Last Lecture 1. Object boundaries 2. Surface normal
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers This document describes commands for configuring and monitoring Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) functionality on Cisco routers and switches. This
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers This document describes commands for configuring and monitoring Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) functionality on Cisco routers and switches. This
Motion Detection. Final project by. Neta Sokolovsky
 Motion Detection Final project by Neta Sokolovsky Introduction The goal of this project is to recognize a motion of objects found in the two given images. This functionality is useful in the video processing
Motion Detection Final project by Neta Sokolovsky Introduction The goal of this project is to recognize a motion of objects found in the two given images. This functionality is useful in the video processing
Network Planning Strategy for Evolving Network Architectures
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION Telecommunications Development Bureau (BDT) Network Planning Strategy for Evolving Network Architectures 10 October 2003 Riccardo Passerini, ITU-BDT Signalling Network
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION Telecommunications Development Bureau (BDT) Network Planning Strategy for Evolving Network Architectures 10 October 2003 Riccardo Passerini, ITU-BDT Signalling Network
A Heuristic Algorithm for Designing Logical Topologies in Packet Networks with Wavelength Routing
 A Heuristic Algorithm for Designing Logical Topologies in Packet Networks with Wavelength Routing Mare Lole and Branko Mikac Department of Telecommunications Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing,
A Heuristic Algorithm for Designing Logical Topologies in Packet Networks with Wavelength Routing Mare Lole and Branko Mikac Department of Telecommunications Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing,
Optical Communications and Networking 朱祖勍. Nov. 27, 2017
 Optical Communications and Networking Nov. 27, 2017 1 What is a Core Network? A core network is the central part of a telecommunication network that provides services to customers who are connected by
Optical Communications and Networking Nov. 27, 2017 1 What is a Core Network? A core network is the central part of a telecommunication network that provides services to customers who are connected by
ITC-21. IGen: Generation of Router-level Internet Topologies Using Network Design Heuristics
 ITC-21 IGen: Generation of Router-level Internet Topologies Using Network Design Heuristics B. Quoitin, V. Van den Schrieck, P. François and O. Bonaventure (bruno.quoitin@uclouvain.be) 1 1 Motivations
ITC-21 IGen: Generation of Router-level Internet Topologies Using Network Design Heuristics B. Quoitin, V. Van den Schrieck, P. François and O. Bonaventure (bruno.quoitin@uclouvain.be) 1 1 Motivations
Basics of Network Analysis
 Basics of Network Analysis Hiroki Sayama sayama@binghamton.edu Graph = Network G(V, E): graph (network) V: vertices (nodes), E: edges (links) 1 Nodes = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 2 3 Links = 12, 13, 15, 23,
Basics of Network Analysis Hiroki Sayama sayama@binghamton.edu Graph = Network G(V, E): graph (network) V: vertices (nodes), E: edges (links) 1 Nodes = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 2 3 Links = 12, 13, 15, 23,
Session 5. Network Planning
 ITU Regional Development Forum 2008 for CIS, CEE and the Baltic States Bridging the ICT standardization gap in developing countries Session 5 Network Planning Ignat Stanev ITC, Bulgaria ITU Regional Development
ITU Regional Development Forum 2008 for CIS, CEE and the Baltic States Bridging the ICT standardization gap in developing countries Session 5 Network Planning Ignat Stanev ITC, Bulgaria ITU Regional Development
MPLS VPN--Inter-AS Option AB
 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
Performance Analysis of Storage-Based Routing for Circuit-Switched Networks [1]
![Performance Analysis of Storage-Based Routing for Circuit-Switched Networks [1] Performance Analysis of Storage-Based Routing for Circuit-Switched Networks [1]](/thumbs/89/97802209.jpg) Performance Analysis of Storage-Based Routing for Circuit-Switched Networks [1] Presenter: Yongcheng (Jeremy) Li PhD student, School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Soochow University, China
Performance Analysis of Storage-Based Routing for Circuit-Switched Networks [1] Presenter: Yongcheng (Jeremy) Li PhD student, School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Soochow University, China
CONNECTICUT ACCESS SERVICE TARIFF. The Southern New England Original Page 22-1 Telephone Company d/b/a Frontier Communications of Connecticut
 The Southern New England Original Page 22-1 22.1 General Description OCN Point-to-Point service is designed to provide the customer with a custom point to point linear network. The Optical Point-to-Point
The Southern New England Original Page 22-1 22.1 General Description OCN Point-to-Point service is designed to provide the customer with a custom point to point linear network. The Optical Point-to-Point
Different network topologies
 Network Topology Network topology is the arrangement of the various elements of a communication network. It is the topological structure of a network and may be depicted physically or logically. Physical
Network Topology Network topology is the arrangement of the various elements of a communication network. It is the topological structure of a network and may be depicted physically or logically. Physical
Business Case Studies with STEM
 ITU-D/ ITU-T T Seminar on Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks for the Arab Region 29 April 2 May 2007, Manama, Barhain with STEM Oscar González Soto ITU Consultant Expert Strategic
ITU-D/ ITU-T T Seminar on Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks for the Arab Region 29 April 2 May 2007, Manama, Barhain with STEM Oscar González Soto ITU Consultant Expert Strategic
Adaptive Load Balancing Using MPLS
 Adaptive Load Balancing Using MPLS Riikka Susitaival, Jorma Virtamo and Samuli Aalto Networking Laboratory Helsinki University of Technology Content Introduction Objectives of research Proposed algorithms
Adaptive Load Balancing Using MPLS Riikka Susitaival, Jorma Virtamo and Samuli Aalto Networking Laboratory Helsinki University of Technology Content Introduction Objectives of research Proposed algorithms
UNIT 1. Advantages of Computer Networks
 UNIT 1 COMPUTER NETWORKS :- A Network is a set of devices or nodes connected by media links.a node can be a computer, printer,scanner,voip phone etc.computer network means an interconnected collection
UNIT 1 COMPUTER NETWORKS :- A Network is a set of devices or nodes connected by media links.a node can be a computer, printer,scanner,voip phone etc.computer network means an interconnected collection
A Cost-Effective Approach to Selective IP Paging Scheme Using Explicit Multicast 1
 A Cost-Effective Approach to Selective IP Paging Scheme Using Explicit Multicast 1 Sangheon Pack Kyoungae Kim Yanghee Choi 31-518, Seoul National University, Shilim-dong, Kwanak-gu, Seoul, Korea Abstract
A Cost-Effective Approach to Selective IP Paging Scheme Using Explicit Multicast 1 Sangheon Pack Kyoungae Kim Yanghee Choi 31-518, Seoul National University, Shilim-dong, Kwanak-gu, Seoul, Korea Abstract
Networking interview questions
 Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 17. PATH ANALYSIS AND NETWORK APPLICATIONS 17.1 Path Analysis 17.1.1 Source Raster 17.1.2 Cost Raster Box 17.1 Cost Raster for a Site Analysis of Pipelines 17.1.3 Cost Distance Measures 17.1.4
Chapter 17. PATH ANALYSIS AND NETWORK APPLICATIONS 17.1 Path Analysis 17.1.1 Source Raster 17.1.2 Cost Raster Box 17.1 Cost Raster for a Site Analysis of Pipelines 17.1.3 Cost Distance Measures 17.1.4
WDM Network Provisioning
 IO2654 Optical Networking WDM Network Provisioning Paolo Monti Optical Networks Lab (ONLab), Communication Systems Department (COS) http://web.it.kth.se/~pmonti/ Some of the material is taken from the
IO2654 Optical Networking WDM Network Provisioning Paolo Monti Optical Networks Lab (ONLab), Communication Systems Department (COS) http://web.it.kth.se/~pmonti/ Some of the material is taken from the
An iteration of Branch and Bound One iteration of Branch and Bound consists of the following four steps: Some definitions. Branch and Bound.
 ranch and ound xamples and xtensions jesla@man.dtu.dk epartment of Management ngineering Technical University of enmark ounding ow do we get ourselves a bounding function? Relaxation. Leave out some constraints.
ranch and ound xamples and xtensions jesla@man.dtu.dk epartment of Management ngineering Technical University of enmark ounding ow do we get ourselves a bounding function? Relaxation. Leave out some constraints.
CS610- Computer Network Solved Subjective From Midterm Papers
 Solved Subjective From Midterm Papers May 08,2012 MC100401285 Moaaz.pk@gmail.com Mc100401285@gmail.com PSMD01 CS610- Computer Network Midterm Examination - Fall 2011 1. Where are destination and source
Solved Subjective From Midterm Papers May 08,2012 MC100401285 Moaaz.pk@gmail.com Mc100401285@gmail.com PSMD01 CS610- Computer Network Midterm Examination - Fall 2011 1. Where are destination and source
Some previous important concepts
 Almustansorya University College of Education Computer Science Department Communication and Computer Networks Class 4 (A/B) Lesson 6... Network Topology Abstract This lesson will mainly focus on the network
Almustansorya University College of Education Computer Science Department Communication and Computer Networks Class 4 (A/B) Lesson 6... Network Topology Abstract This lesson will mainly focus on the network
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers Feature History Release 11.1CT 12.1(3)T 12.1(5)T 12.0(14)ST 12.0(21)ST 12.0(22)S Modification The document introduced MPLS and was titled Tag Switching
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers Feature History Release 11.1CT 12.1(3)T 12.1(5)T 12.0(14)ST 12.0(21)ST 12.0(22)S Modification The document introduced MPLS and was titled Tag Switching
Creating a Dynamic Serial Edge For Integrated Industrial Networks
 Creating a Dynamic Serial Edge For Integrated Industrial Networks Technical Brief GarrettCom, Inc. As industrial networks evolve, is becoming the standard technology for new system interfaces and for new
Creating a Dynamic Serial Edge For Integrated Industrial Networks Technical Brief GarrettCom, Inc. As industrial networks evolve, is becoming the standard technology for new system interfaces and for new
CS6702 GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATIONS 2 MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 CS6702 GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATIONS 2 MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1 UNIT I INTRODUCTION CS6702 GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATIONS 2 MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1. Define Graph. A graph G = (V, E) consists
CS6702 GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATIONS 2 MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1 UNIT I INTRODUCTION CS6702 GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATIONS 2 MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1. Define Graph. A graph G = (V, E) consists
Local Area Networks and the Network Protocol Stack
 Local Area Networks and the CSC362, Information Security Introduction problems inherent in transmitting packets network topologies network protocol stack Packet Switching Problems packet switching can
Local Area Networks and the CSC362, Information Security Introduction problems inherent in transmitting packets network topologies network protocol stack Packet Switching Problems packet switching can
ITU / BDT regional seminar Network Planning for the CEE, CIS and Baltic
 ITU / BDT regional seminar Network Planning for the CEE, CIS and Baltic Belgrade, Serbia and Montenegro, 20 24 June 2005 Network Design and Dimensioning Oscar González Soto ITU Consultant Expert Strategic
ITU / BDT regional seminar Network Planning for the CEE, CIS and Baltic Belgrade, Serbia and Montenegro, 20 24 June 2005 Network Design and Dimensioning Oscar González Soto ITU Consultant Expert Strategic
Chapter 5 Network Layer
 Chapter Network Layer Network layer Physical layer: moe bit seqence between two adjacent nodes Data link: reliable transmission between two adjacent nodes Network: gides packets from the sorce to destination,
Chapter Network Layer Network layer Physical layer: moe bit seqence between two adjacent nodes Data link: reliable transmission between two adjacent nodes Network: gides packets from the sorce to destination,
MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB
 First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
Uncovering the Lagrangian of a system from discrete observations
 Uncovering the Lagrangian of a system from discrete observations Yakov Berchenko-Kogan Massachusetts Institute of Technology 7 January, 2012 Yakov Berchenko-Kogan (MIT) Uncovering the Lagrangian 7 January,
Uncovering the Lagrangian of a system from discrete observations Yakov Berchenko-Kogan Massachusetts Institute of Technology 7 January, 2012 Yakov Berchenko-Kogan (MIT) Uncovering the Lagrangian 7 January,
David Tipper Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh. Motivation
 Survivable Network Design David Tipper Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2110 Slides 12 Motivation Communications networks need to be survivable? Communication
Survivable Network Design David Tipper Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2110 Slides 12 Motivation Communications networks need to be survivable? Communication
Resilient Networks. 3.1 Resilient Network Design - Intro. Mathias Fischer
 Mathias Fischer Resilient Networks. Resilient Network Design - Intro Prepared along: Michal Pioro and Deepankar Medhi - Routing, Flow, and Capacity Design in Communication and Computer Networks, The Morgan
Mathias Fischer Resilient Networks. Resilient Network Design - Intro Prepared along: Michal Pioro and Deepankar Medhi - Routing, Flow, and Capacity Design in Communication and Computer Networks, The Morgan
Analysis and Algorithms for Partial Protection in Mesh Networks
 Technical Report, April 2011 Analysis and Algorithms for Partial Protection in Mesh Networks Greg uperman MIT LIDS Cambridge, MA 02139 gregk@mit.edu Eytan Modiano MIT LIDS Cambridge, MA 02139 modiano@mit.edu
Technical Report, April 2011 Analysis and Algorithms for Partial Protection in Mesh Networks Greg uperman MIT LIDS Cambridge, MA 02139 gregk@mit.edu Eytan Modiano MIT LIDS Cambridge, MA 02139 modiano@mit.edu
Juniper JN Security, Specialist (JNCIS-SEC)
 Juniper JN0-333 Security, Specialist (JNCIS-SEC) http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/jn0-333 QUESTION: 231 Which statement is true about a logical interface? A. A logical interface can belong to
Juniper JN0-333 Security, Specialist (JNCIS-SEC) http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/jn0-333 QUESTION: 231 Which statement is true about a logical interface? A. A logical interface can belong to
Independent Submission Request for Comments: 6847 Category: Informational. Huawei January 2013
 Independent Submission Request for Comments: 6847 Category: Informational ISSN: 2070-1721 D. Melman T. Mizrahi Marvell D. Eastlake 3rd Huawei January 2013 Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) over Transparent
Independent Submission Request for Comments: 6847 Category: Informational ISSN: 2070-1721 D. Melman T. Mizrahi Marvell D. Eastlake 3rd Huawei January 2013 Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) over Transparent
Module 10 Frame Relay and ATM
 Module 10 Frame Relay and ATM Lesson 35 ATM: Virtual Path, Virtual Channel. ATM Adaptation Layer (AAL) 10.3.1 VIRTUAL PATH AND VIRTUAL CHANNEL Connection between two endpoints is accomplished through virtual
Module 10 Frame Relay and ATM Lesson 35 ATM: Virtual Path, Virtual Channel. ATM Adaptation Layer (AAL) 10.3.1 VIRTUAL PATH AND VIRTUAL CHANNEL Connection between two endpoints is accomplished through virtual
COMPUTER AIDED PLANNING AND DIMENSIONING OF THE SIGNALLING NETWORK
 COMPUTER AIDED PLANNING AND DIMENSIONING OF THE SIGNALLING NETWORK Main tasks of Signalling Network Planning: Determination/optimization of the Signalling Network Structure Determination of an optimised
COMPUTER AIDED PLANNING AND DIMENSIONING OF THE SIGNALLING NETWORK Main tasks of Signalling Network Planning: Determination/optimization of the Signalling Network Structure Determination of an optimised
Index Terms Backbone Networks Optimization, Resilience, Virtual Private Network, Traffic Demands and Traffic Flows
 International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 2, Issue 8, November 2011] 12 ISSN 2047-3338 Designing Different Models of Robust IP/MPLS over DWDM Networks Marko Rožman University
International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 2, Issue 8, November 2011] 12 ISSN 2047-3338 Designing Different Models of Robust IP/MPLS over DWDM Networks Marko Rožman University
CSE 202: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 5
 CSE 202: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 5 Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Announcements Kamalika s Office hours today moved to tomorrow, 12:15-1:15pm Homework 1 due now Midterm on Feb 14 Algorithm
CSE 202: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 5 Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Announcements Kamalika s Office hours today moved to tomorrow, 12:15-1:15pm Homework 1 due now Midterm on Feb 14 Algorithm
LECTURES 3 and 4: Flows and Matchings
 LECTURES 3 and 4: Flows and Matchings 1 Max Flow MAX FLOW (SP). Instance: Directed graph N = (V,A), two nodes s,t V, and capacities on the arcs c : A R +. A flow is a set of numbers on the arcs such that
LECTURES 3 and 4: Flows and Matchings 1 Max Flow MAX FLOW (SP). Instance: Directed graph N = (V,A), two nodes s,t V, and capacities on the arcs c : A R +. A flow is a set of numbers on the arcs such that
Sami Ilvonen Pekka Manninen. Introduction to High-Performance Computing with Fortran. September 19 20, 2016 CSC IT Center for Science Ltd, Espoo
 Sami Ilvonen Pekka Manninen Introduction to High-Performance Computing with Fortran September 19 20, 2016 CSC IT Center for Science Ltd, Espoo All material (C) 2009-2016 by CSC IT Center for Science Ltd.
Sami Ilvonen Pekka Manninen Introduction to High-Performance Computing with Fortran September 19 20, 2016 CSC IT Center for Science Ltd, Espoo All material (C) 2009-2016 by CSC IT Center for Science Ltd.
A Connection between Network Coding and. Convolutional Codes
 A Connection between Network Coding and 1 Convolutional Codes Christina Fragouli, Emina Soljanin christina.fragouli@epfl.ch, emina@lucent.com Abstract The min-cut, max-flow theorem states that a source
A Connection between Network Coding and 1 Convolutional Codes Christina Fragouli, Emina Soljanin christina.fragouli@epfl.ch, emina@lucent.com Abstract The min-cut, max-flow theorem states that a source
Mesh Decimation. Mark Pauly
 Mesh Decimation Mark Pauly Applications Oversampled 3D scan data ~150k triangles ~80k triangles Mark Pauly - ETH Zurich 280 Applications Overtessellation: E.g. iso-surface extraction Mark Pauly - ETH Zurich
Mesh Decimation Mark Pauly Applications Oversampled 3D scan data ~150k triangles ~80k triangles Mark Pauly - ETH Zurich 280 Applications Overtessellation: E.g. iso-surface extraction Mark Pauly - ETH Zurich
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Combinatorial Optimization G. Guérard Department of Nouvelles Energies Ecole Supérieur d Ingénieurs Léonard de Vinci Lecture 1 GG A.I. 1/34 Outline 1 Motivation 2 Geometric resolution
Artificial Intelligence Combinatorial Optimization G. Guérard Department of Nouvelles Energies Ecole Supérieur d Ingénieurs Léonard de Vinci Lecture 1 GG A.I. 1/34 Outline 1 Motivation 2 Geometric resolution
Pre-requisite Material for Course Heuristics and Approximation Algorithms
 Pre-requisite Material for Course Heuristics and Approximation Algorithms This document contains an overview of the basic concepts that are needed in preparation to participate in the course. In addition,
Pre-requisite Material for Course Heuristics and Approximation Algorithms This document contains an overview of the basic concepts that are needed in preparation to participate in the course. In addition,
Optical Channel Circuits and Virtual Patchcords Reference
 CHAPTER 11 Optical Channel Circuits and Virtual Patchcords Reference This chapter explains the Cisco ONS 15454 dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) optical channel (OCH) circuit types and virtual
CHAPTER 11 Optical Channel Circuits and Virtual Patchcords Reference This chapter explains the Cisco ONS 15454 dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) optical channel (OCH) circuit types and virtual
