Example Networks on chip Freescale: MPC Telematics chip
|
|
|
- Cleopatra Daniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
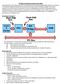
1 Lecture 22: Interconnects & I/O Administration Take QUIZ 16 over P&H , before 11:59pm Project: Cache Simulator, Due April 29, 2010 NEW OFFICE HOUR TIME: Tuesday 1-2, McKinley Exams in ACES with Gem Naivar Last Time Reliable and Available Storage Memory technology, Disk, RAID, Flash Today How are chips connected to Memory, Disk, & other devices? How does the system perform I/O operations? UTCS 352, Lecture 22 1 Example Networks on chip Freescale: MPC Telematics chip Telematics Domain Embedded processor for cars Combines wireless, graphics, audio, & GPS for integrated applications Embedded Linux OS freescale_mpc5200_diagram.gif (GIF Image, 438x399 pixels) UTCS 352, Lecture
2 Interconnecting Components Need interconnections between CPU, memory, I/O controllers Bus: shared communication channel Parallel set of wires for data transfer and synchronization Becomes a bottleneck On chip does best with known latencies Performance limited by physical factors Wire length, number of connections Modern alternative high-speed serial connections with switches On Chip Networks UTCS 352, Lecture 22 3 Bus Types Processor-Memory buses Short, high speed Design is matched to memory organization I/O buses Longer, allowing multiple connections Specified by standards for interoperability Connect to processor-memory bus through a bridge UTCS 352, Lecture
3 Bus Signals and Synchronization Data lines Carry address and data Multiplexed or separate Control lines Indicate data type, synchronize transactions Synchronous Uses a bus clock Asynchronous Uses request/acknowledge control lines for handshaking UTCS 352, Lecture 22 5 I/O Bus Examples Firewire USB 2.0 PCI Express Serial ATA Serial Attached SCSI Intended use External External Internal Internal External Devices per channel Data width 4 2 2/lane 4 4 Peak bandwidth Hot pluggable 50MB/s or 100MB/s 0.2MB/s, 1.5MB/s, or 60MB/s 250MB/s/lane 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, MB/s Yes Yes Depends Yes Yes Max length 4.5m 5m 0.5m 1m 8m Standard IEEE 1394 USB Implementers Forum 300MB/s PCI-SIG SATA-IO INCITS TC T10 UTCS 352, Lecture
4 Typical x86 PC I/O System UTCS 352, Lecture 22 7 I/O Management I/O is mediated by the OS Multiple programs share I/O resources Need protection and scheduling I/O causes asynchronous interrupts Same mechanism as exceptions OS provides I/O abstractions directly to programs Synchronous I/O programming model: Request I/O (e.g., read file from disk, mouse movement, etc.) Kernel issues I/O device specific commands on application s behalf Kernel then returns control to application UTCS 352, Lecture
5 I/O Commands at OS level I/O devices are managed by I/O controller hardware Transfers data to/from device OS synchronizes operations with software OS sets command registers Cause device to do something OS queries reserved status registers Indicate what the device is doing and any errors OS queries reserved data registers Write: transfer data to a device Read: transfer data from a device UTCS 352, Lecture 22 9 I/O Register Mapping Memory mapped I/O Reserve a special part of memory for I/O OS read/writes registers and special memory addresses Hardware address decoder distinguishes between application vs I/O memory commands OS uses address translation mechanism to make them only accessible to OS I/O instructions Separate instructions to access I/O registers Can only be executed in kernel mode Example: x86 UTCS 352, Lecture
6 Polling Hardware periodically checks I/O status register For example, at the beginning of every instruction issue If device ready, do operation If error, take action Common in small or low-performance real-time embedded systems Predictable timing Low hardware cost In other systems, wastes CPU time UTCS 352, Lecture Interrupts When a device is ready or error occurs Controller interrupts CPU Interrupt is like an exception But not synchronized to instruction execution stops the current program Invokes OS software handler between instructions Cause identifies the interrupting device restarts the program or a different one Priority interrupts Devices needing more urgent attention get higher priority Can interrupt handler for a lower priority interrupt UTCS 352, Lecture
7 I/O Data Transfer OS sets status and cause registers status register cause register 15 8 interrupt mask pending interrupts Exception code 4 user mode 1 exception level 0 interrupt enable Polling and interrupt-driven I/O CPU transfers data between memory and I/O data registers Time consuming for high-speed devices Direct memory access (DMA) OS provides starting address in memory I/O controller transfers to/from memory autonomously Controller interrupts CPU on completion or error UTCS 352, Lecture DMA/Cache Interaction If DMA writes to a memory block that is cached Cached copy becomes stale If write-back cache has dirty block, and DMA reads memory block Reads stale data Need to ensure cache coherence Flush blocks from cache if they will be used for DMA Or use non-cacheable memory locations for I/O UTCS 352, Lecture
8 DMA/VM Interaction OS uses virtual addresses for memory DMA blocks may not be contiguous in physical memory Should DMA use virtual addresses? requires controller to do translation If DMA uses physical addresses Must break big transfers into page-sized chunks Or allocate contiguous physical pages for DMA UTCS 352, Lecture Measuring I/O Performance I/O performance depends on Hardware: CPU, memory, controllers, buses Software: operating system, database management system, application Workload: request rates and patterns I/O system design can trade-off between response time and throughput Measurements of throughput often done with constrained response-time UTCS 352, Lecture
9 Transaction Processing Benchmarks Transactions Small data accesses to a DBMS Interested in I/O rate, not data rate Measure throughput Subject to response time limits and failure handling ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) Overall cost per transaction Transaction Processing Council (TPC) benchmarks ( TPC-APP: B2B application server and web services TCP-C: on-line order entry environment TCP-E: on-line transaction processing for brokerage firm TPC-H: decision support business oriented ad-hoc queries UTCS 352, Lecture File System & Web Benchmarks SPEC System File System (SFS) Synthetic workload for NFS server, based on monitoring real systems Results Throughput (operations/sec) Response time (average ms/operation) SPEC Web Server benchmark Measures simultaneous user sessions, subject to required throughput/session Three workloads: Banking, Ecommerce, and Support UTCS 352, Lecture
10 I/O vs. CPU Performance Amdahl s Law Don t neglect I/O performance as parallelism increases Example Benchmark takes 90s CPU time, 10s I/O time Double the number of CPUs/2 years I/O unchanged Year CPU time I/O time Elapsed time % I/O time now 90s 10s 100s 10% +2 45s 10s 55s 18% +4 23s 10s 33s 31% +6 11s 10s 21s 47% UTCS 352, Lecture Summary Interconnects & I/O Buses based on I/O device Future networks on chip OS handles I/O with hardware support for interrupts Next Time Coarse grain parallelism Parallel programs Shared memory parallel architectures Hardware multithreading Reading: P&H UTCS 352, Lecture
Chapter 6. Storage and Other I/O Topics
 Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behaviour: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections
Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behaviour: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections
Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 I/O System Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Introduction (1) I/O devices can be characterized by Behavior: input, output, storage
I/O System Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Introduction (1) I/O devices can be characterized by Behavior: input, output, storage
Computer Architecture Computer Science & Engineering. Chapter 6. Storage and Other I/O Topics BK TP.HCM
 Computer Architecture Computer Science & Engineering Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behaviour: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine
Computer Architecture Computer Science & Engineering Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behaviour: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine
Storage. Hwansoo Han
 Storage Hwansoo Han I/O Devices I/O devices can be characterized by Behavior: input, out, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections 2 I/O System Characteristics
Storage Hwansoo Han I/O Devices I/O devices can be characterized by Behavior: input, out, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections 2 I/O System Characteristics
Computer Organization and Structure. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Storage and Other I/O Topics I/O Performance Measures Types and Characteristics of I/O Devices Buses Interfacing I/O Devices
Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Storage and Other I/O Topics I/O Performance Measures Types and Characteristics of I/O Devices Buses Interfacing I/O Devices
Chapter 6. Storage and Other I/O Topics. ICE3003: Computer Architecture Fall 2012 Euiseong Seo
 Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics 1 Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behaviour: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections
Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics 1 Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behaviour: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections
Introduction I/O 1. I/O devices can be characterized by Behavior: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec
 Introduction I/O 1 I/O devices can be characterized by Behavior: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections I/O Device Summary I/O 2 I/O System
Introduction I/O 1 I/O devices can be characterized by Behavior: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections I/O Device Summary I/O 2 I/O System
Chapter 6. Storage and Other I/O Topics
 Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behavior: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections
Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behavior: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections
Interconnecting Components
 Interconnecting Components Need interconnections between CPU, memory, controllers Bus: shared communication channel Parallel set of wires for data and synchronization of data transfer Can become a bottleneck
Interconnecting Components Need interconnections between CPU, memory, controllers Bus: shared communication channel Parallel set of wires for data and synchronization of data transfer Can become a bottleneck
Chapter 6. Storage and Other I/O Topics. ICE3003: Computer Architecture Spring 2014 Euiseong Seo
 Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics 1 Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behaviour: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections
Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics 1 Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behaviour: input, output, storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections
Chapter 6. Storage & Other I/O
 Chapter 6 Storage & Other I/O 5 components of a Computer Computer Processor (active) Control ( brain ) Datapath ( brawn ) Memory (passive) (where programs, data live when running) Devices Input Output
Chapter 6 Storage & Other I/O 5 components of a Computer Computer Processor (active) Control ( brain ) Datapath ( brawn ) Memory (passive) (where programs, data live when running) Devices Input Output
Chapter 6. Storage and Other I/O Topics. Jiang Jiang
 Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics Jiang Jiang jiangjiang@ic.sjtu.edu.cn [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson & Hennessy, 2008, MK] Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O
Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics Jiang Jiang jiangjiang@ic.sjtu.edu.cn [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson & Hennessy, 2008, MK] Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O
Chapter 6. Storage and Other I/O Topics
 Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behavior: input, output, t storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections
Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics Introduction I/O devices can be characterized by Behavior: input, output, t storage Partner: human or machine Data rate: bytes/sec, transfers/sec I/O bus connections
Replacement Policy: Which block to replace from the set?
 Replacement Policy: Which block to replace from the set? Direct mapped: no choice Associative: evict least recently used (LRU) difficult/costly with increasing associativity Alternative: random replacement
Replacement Policy: Which block to replace from the set? Direct mapped: no choice Associative: evict least recently used (LRU) difficult/costly with increasing associativity Alternative: random replacement
Thomas Polzer Institut für Technische Informatik
 Thomas Polzer tpolzer@ecs.tuwien.ac.at Institut für Technische Informatik Processor Interrupts Cache Memory I/O bus Main memory I/O controller I/O controller I/O controller Disk Disk Graphics output Network
Thomas Polzer tpolzer@ecs.tuwien.ac.at Institut für Technische Informatik Processor Interrupts Cache Memory I/O bus Main memory I/O controller I/O controller I/O controller Disk Disk Graphics output Network
EN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 07: I/O
 EN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 07: I/O Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring 2017 [ material
EN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 07: I/O Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring 2017 [ material
Systems Architecture II
 Systems Architecture II Topics Interfacing I/O Devices to Memory, Processor, and Operating System * Memory-mapped IO and Interrupts in SPIM** *This lecture was derived from material in the text (Chapter
Systems Architecture II Topics Interfacing I/O Devices to Memory, Processor, and Operating System * Memory-mapped IO and Interrupts in SPIM** *This lecture was derived from material in the text (Chapter
EE108B Lecture 17 I/O Buses and Interfacing to CPU. Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University
 EE108B Lecture 17 I/O Buses and Interfacing to CPU Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements Remaining deliverables PA2.2. today HW4 on 3/13 Lab4 on 3/19
EE108B Lecture 17 I/O Buses and Interfacing to CPU Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements Remaining deliverables PA2.2. today HW4 on 3/13 Lab4 on 3/19
Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics
 Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Feng-Chia Unive ersity Outline 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Dependability,
Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 6 Storage and Other I/O Topics 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Feng-Chia Unive ersity Outline 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Dependability,
Module 6: INPUT - OUTPUT (I/O)
 Module 6: INPUT - OUTPUT (I/O) Introduction Computers communicate with the outside world via I/O devices Input devices supply computers with data to operate on E.g: Keyboard, Mouse, Voice recognition hardware,
Module 6: INPUT - OUTPUT (I/O) Introduction Computers communicate with the outside world via I/O devices Input devices supply computers with data to operate on E.g: Keyboard, Mouse, Voice recognition hardware,
Computer Architecture CS 355 Busses & I/O System
 Computer Architecture CS 355 Busses & I/O System Text: Computer Organization & Design, Patterson & Hennessy Chapter 6.5-6.6 Objectives: During this class the student shall learn to: Describe the two basic
Computer Architecture CS 355 Busses & I/O System Text: Computer Organization & Design, Patterson & Hennessy Chapter 6.5-6.6 Objectives: During this class the student shall learn to: Describe the two basic
Chapter 8. A Typical collection of I/O devices. Interrupts. Processor. Cache. Memory I/O bus. I/O controller I/O I/O. Main memory.
 Chapter 8 1 A Typical collection of I/O devices Interrupts Cache I/O bus Main memory I/O controller I/O controller I/O controller Disk Disk Graphics output Network 2 1 Interfacing s and Peripherals I/O
Chapter 8 1 A Typical collection of I/O devices Interrupts Cache I/O bus Main memory I/O controller I/O controller I/O controller Disk Disk Graphics output Network 2 1 Interfacing s and Peripherals I/O
CS 134. Operating Systems. April 8, 2013 Lecture 20. Input/Output. Instructor: Neil Rhodes. Monday, April 7, 14
 CS 134 Operating Systems April 8, 2013 Lecture 20 Input/Output Instructor: Neil Rhodes Hardware How hardware works Operating system layer What the kernel does API What the programmer does Overview 2 kinds
CS 134 Operating Systems April 8, 2013 Lecture 20 Input/Output Instructor: Neil Rhodes Hardware How hardware works Operating system layer What the kernel does API What the programmer does Overview 2 kinds
INPUT/OUTPUT DEVICES Dr. Bill Yi Santa Clara University
 INPUT/OUTPUT DEVICES Dr. Bill Yi Santa Clara University (Based on text: David A. Patterson & John L. Hennessy, Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software Interface, 3 rd Ed., Morgan Kaufmann,
INPUT/OUTPUT DEVICES Dr. Bill Yi Santa Clara University (Based on text: David A. Patterson & John L. Hennessy, Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software Interface, 3 rd Ed., Morgan Kaufmann,
CSE 120. Overview. July 27, Day 8 Input/Output. Instructor: Neil Rhodes. Hardware. Hardware. Hardware
 CSE 120 July 27, 2006 Day 8 Input/Output Instructor: Neil Rhodes How hardware works Operating Systems Layer What the kernel does API What the programmer does Overview 2 Kinds Block devices: read/write
CSE 120 July 27, 2006 Day 8 Input/Output Instructor: Neil Rhodes How hardware works Operating Systems Layer What the kernel does API What the programmer does Overview 2 Kinds Block devices: read/write
I/O. Kevin Walsh CS 3410, Spring 2010 Computer Science Cornell University. See: P&H Chapter 6.5-6
 I/O Kevin Walsh CS 3410, Spring 2010 Computer Science Cornell University See: P&H Chapter 6.5-6 Computer System = Input + Output + Memory + Datapath + Control Video Network Keyboard USB Computer System
I/O Kevin Walsh CS 3410, Spring 2010 Computer Science Cornell University See: P&H Chapter 6.5-6 Computer System = Input + Output + Memory + Datapath + Control Video Network Keyboard USB Computer System
Lecture 13. Storage, Network and Other Peripherals
 Lecture 13 Storage, Network and Other Peripherals 1 I/O Systems Processor interrupts Cache Processor & I/O Communication Memory - I/O Bus Main Memory I/O Controller I/O Controller I/O Controller Disk Disk
Lecture 13 Storage, Network and Other Peripherals 1 I/O Systems Processor interrupts Cache Processor & I/O Communication Memory - I/O Bus Main Memory I/O Controller I/O Controller I/O Controller Disk Disk
Hardware OS & OS- Application interface
 CS 4410 Operating Systems Hardware OS & OS- Application interface Summer 2013 Cornell University 1 Today How my device becomes useful for the user? HW-OS interface Device controller Device driver Interrupts
CS 4410 Operating Systems Hardware OS & OS- Application interface Summer 2013 Cornell University 1 Today How my device becomes useful for the user? HW-OS interface Device controller Device driver Interrupts
Readings. Storage Hierarchy III: I/O System. I/O (Disk) Performance. I/O Device Characteristics. often boring, but still quite important
 Storage Hierarchy III: I/O System Readings reg I$ D$ L2 L3 memory disk (swap) often boring, but still quite important ostensibly about general I/O, mainly about disks performance: latency & throughput
Storage Hierarchy III: I/O System Readings reg I$ D$ L2 L3 memory disk (swap) often boring, but still quite important ostensibly about general I/O, mainly about disks performance: latency & throughput
Operating System: Chap13 I/O Systems. National Tsing-Hua University 2016, Fall Semester
 Operating System: Chap13 I/O Systems National Tsing-Hua University 2016, Fall Semester Outline Overview I/O Hardware I/O Methods Kernel I/O Subsystem Performance Application Interface Operating System
Operating System: Chap13 I/O Systems National Tsing-Hua University 2016, Fall Semester Outline Overview I/O Hardware I/O Methods Kernel I/O Subsystem Performance Application Interface Operating System
CS330: Operating System and Lab. (Spring 2006) I/O Systems
 CS330: Operating System and Lab. (Spring 2006) I/O Systems Today s Topics Block device vs. Character device Direct I/O vs. Memory-mapped I/O Polling vs. Interrupts Programmed I/O vs. DMA Blocking vs. Non-blocking
CS330: Operating System and Lab. (Spring 2006) I/O Systems Today s Topics Block device vs. Character device Direct I/O vs. Memory-mapped I/O Polling vs. Interrupts Programmed I/O vs. DMA Blocking vs. Non-blocking
Lecture 23: Storage Systems. Topics: disk access, bus design, evaluation metrics, RAID (Sections )
 Lecture 23: Storage Systems Topics: disk access, bus design, evaluation metrics, RAID (Sections 7.1-7.9) 1 Role of I/O Activities external to the CPU are typically orders of magnitude slower Example: while
Lecture 23: Storage Systems Topics: disk access, bus design, evaluation metrics, RAID (Sections 7.1-7.9) 1 Role of I/O Activities external to the CPU are typically orders of magnitude slower Example: while
IO System. CP-226: Computer Architecture. Lecture 25 (24 April 2013) CADSL
 IO System Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
IO System Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture. OS s Responsibilities
 ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture OS s Responsibilities ECE4680 buses.1 April 5, 2003 Recap: Summary of Bus Options: Option High performance Low cost Bus width Separate address Multiplex address
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture OS s Responsibilities ECE4680 buses.1 April 5, 2003 Recap: Summary of Bus Options: Option High performance Low cost Bus width Separate address Multiplex address
Computer Science 146. Computer Architecture
 Computer Science 46 Computer Architecture Spring 24 Harvard University Instructor: Prof dbrooks@eecsharvardedu Lecture 22: More I/O Computer Science 46 Lecture Outline HW5 and Project Questions? Storage
Computer Science 46 Computer Architecture Spring 24 Harvard University Instructor: Prof dbrooks@eecsharvardedu Lecture 22: More I/O Computer Science 46 Lecture Outline HW5 and Project Questions? Storage
Last class: Today: Course administration OS definition, some history. Background on Computer Architecture
 1 Last class: Course administration OS definition, some history Today: Background on Computer Architecture 2 Canonical System Hardware CPU: Processor to perform computations Memory: Programs and data I/O
1 Last class: Course administration OS definition, some history Today: Background on Computer Architecture 2 Canonical System Hardware CPU: Processor to perform computations Memory: Programs and data I/O
I/O Systems. Jo, Heeseung
 I/O Systems Jo, Heeseung Today's Topics Device characteristics Block device vs. Character device Direct I/O vs. Memory-mapped I/O Polling vs. Interrupts Programmed I/O vs. DMA Blocking vs. Non-blocking
I/O Systems Jo, Heeseung Today's Topics Device characteristics Block device vs. Character device Direct I/O vs. Memory-mapped I/O Polling vs. Interrupts Programmed I/O vs. DMA Blocking vs. Non-blocking
C02: Interrupts and I/O
 CISC 7310X C02: Interrupts and I/O Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 2/8/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Von Neumann Computers Process and memory connected by a bus
CISC 7310X C02: Interrupts and I/O Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 2/8/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Von Neumann Computers Process and memory connected by a bus
Computer System Overview OPERATING SYSTEM TOP-LEVEL COMPONENTS. Simplified view: Operating Systems. Slide 1. Slide /S2. Slide 2.
 BASIC ELEMENTS Simplified view: Processor Slide 1 Computer System Overview Operating Systems Slide 3 Main Memory referred to as real memory or primary memory volatile modules 2004/S2 secondary memory devices
BASIC ELEMENTS Simplified view: Processor Slide 1 Computer System Overview Operating Systems Slide 3 Main Memory referred to as real memory or primary memory volatile modules 2004/S2 secondary memory devices
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 31: Computer Input/Output Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview for today Input and output are fundamental for
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 31: Computer Input/Output Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview for today Input and output are fundamental for
Introduction to Input and Output
 Introduction to Input and Output The I/O subsystem provides the mechanism for communication between the CPU and the outside world (I/O devices). Design factors: I/O device characteristics (input, output,
Introduction to Input and Output The I/O subsystem provides the mechanism for communication between the CPU and the outside world (I/O devices). Design factors: I/O device characteristics (input, output,
Administrivia. CMSC 411 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 19 Storage Systems, cont. Disks (cont.) Disks - review
 Administrivia CMSC 411 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 19 Storage Systems, cont. Homework #4 due Thursday answers posted soon after Exam #2 on Thursday, April 24 on memory hierarchy (Unit 4) and
Administrivia CMSC 411 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 19 Storage Systems, cont. Homework #4 due Thursday answers posted soon after Exam #2 on Thursday, April 24 on memory hierarchy (Unit 4) and
CS 341l Fall 2008 Test #4 NAME: Key
 CS 341l all 2008 est #4 NAME: Key CS3411 est #4, 21 November 2008. 100 points total, number of points each question is worth is indicated in parentheses. Answer all questions. Be as concise as possible
CS 341l all 2008 est #4 NAME: Key CS3411 est #4, 21 November 2008. 100 points total, number of points each question is worth is indicated in parentheses. Answer all questions. Be as concise as possible
The control of I/O devices is a major concern for OS designers
 Lecture Overview I/O devices I/O hardware Interrupts Direct memory access Device dimensions Device drivers Kernel I/O subsystem Operating Systems - June 26, 2001 I/O Device Issues The control of I/O devices
Lecture Overview I/O devices I/O hardware Interrupts Direct memory access Device dimensions Device drivers Kernel I/O subsystem Operating Systems - June 26, 2001 I/O Device Issues The control of I/O devices
Module 11: I/O Systems
 Module 11: I/O Systems Reading: Chapter 13 Objectives Explore the structure of the operating system s I/O subsystem. Discuss the principles of I/O hardware and its complexity. Provide details on the performance
Module 11: I/O Systems Reading: Chapter 13 Objectives Explore the structure of the operating system s I/O subsystem. Discuss the principles of I/O hardware and its complexity. Provide details on the performance
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 29: Computer Input/Output Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Announcements ECE Honors Exhibition Wednesday, April
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 29: Computer Input/Output Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Announcements ECE Honors Exhibition Wednesday, April
QUIZ Ch.6. The EAT for a two-level memory is given by:
 QUIZ Ch.6 The EAT for a two-level memory is given by: EAT = H Access C + (1-H) Access MM. Derive a similar formula for three-level memory: L1, L2 and RAM. Hint: Instead of H, we now have H 1 and H 2. Source:
QUIZ Ch.6 The EAT for a two-level memory is given by: EAT = H Access C + (1-H) Access MM. Derive a similar formula for three-level memory: L1, L2 and RAM. Hint: Instead of H, we now have H 1 and H 2. Source:
Computer System Overview
 Computer System Overview Operating Systems 2005/S2 1 What are the objectives of an Operating System? 2 What are the objectives of an Operating System? convenience & abstraction the OS should facilitate
Computer System Overview Operating Systems 2005/S2 1 What are the objectives of an Operating System? 2 What are the objectives of an Operating System? convenience & abstraction the OS should facilitate
I/O Handling. ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Duke University, Spring Based on Operating Systems Concepts, Silberschatz Chapter 13
 I/O Handling ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Duke University, Spring 2018 Based on Operating Systems Concepts, Silberschatz Chapter 13 Input/Output (I/O) Typical application flow consists of
I/O Handling ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Duke University, Spring 2018 Based on Operating Systems Concepts, Silberschatz Chapter 13 Input/Output (I/O) Typical application flow consists of
Bus Example: Pentium II
 Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Conventional PCI, often shortened to PCI, is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer. PCI stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Conventional PCI, often shortened to PCI, is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer. PCI stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect
Organisasi Sistem Komputer
 LOGO Organisasi Sistem Komputer OSK 5 Input Output 1 1 PT. Elektronika FT UNY Input/Output Problems Wide variety of peripherals Delivering different amounts of data At different speeds In different formats
LOGO Organisasi Sistem Komputer OSK 5 Input Output 1 1 PT. Elektronika FT UNY Input/Output Problems Wide variety of peripherals Delivering different amounts of data At different speeds In different formats
Connectivity. Module 2.2. Copyright 2006 EMC Corporation. Do not Copy - All Rights Reserved. Connectivity - 1
 Connectivity Module 2.2 2006 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Connectivity - 1 Connectivity Upon completion of this module, you will be able to: Describe the physical components of a networked storage
Connectivity Module 2.2 2006 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Connectivity - 1 Connectivity Upon completion of this module, you will be able to: Describe the physical components of a networked storage
COT 4600 Operating Systems Fall Dan C. Marinescu Office: HEC 439 B Office hours: Tu-Th 3:00-4:00 PM
 COT 4600 Operating Systems Fall 2009 Dan C. Marinescu Office: HEC 439 B Office hours: Tu-Th 3:00-4:00 PM Lecture 23 Attention: project phase 4 due Tuesday November 24 Final exam Thursday December 10 4-6:50
COT 4600 Operating Systems Fall 2009 Dan C. Marinescu Office: HEC 439 B Office hours: Tu-Th 3:00-4:00 PM Lecture 23 Attention: project phase 4 due Tuesday November 24 Final exam Thursday December 10 4-6:50
 Accessing I/O Devices Interface to CPU and Memory Interface to one or more peripherals Generic Model of IO Module Interface for an IO Device: CPU checks I/O module device status I/O module returns status
Accessing I/O Devices Interface to CPU and Memory Interface to one or more peripherals Generic Model of IO Module Interface for an IO Device: CPU checks I/O module device status I/O module returns status
6.9. Communicating to the Outside World: Cluster Networking
 6.9 Communicating to the Outside World: Cluster Networking This online section describes the networking hardware and software used to connect the nodes of cluster together. As there are whole books and
6.9 Communicating to the Outside World: Cluster Networking This online section describes the networking hardware and software used to connect the nodes of cluster together. As there are whole books and
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 20: Busses and OS s Responsibilities. Recap: IO Benchmarks and I/O Devices
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 20: ses and OS s Responsibilities April 7, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http://http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 20: ses and OS s Responsibilities April 7, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http://http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
CSE 451: Operating Systems Winter I/O System. Gary Kimura
 CSE 451: Operating Systems Winter 2012 I/O System Gary Kimura What s Ahead Principles of I/O Hardware Structuring of I/O Software Layers of an I/O System Operation of an I/O System 2 Hardware Environment
CSE 451: Operating Systems Winter 2012 I/O System Gary Kimura What s Ahead Principles of I/O Hardware Structuring of I/O Software Layers of an I/O System Operation of an I/O System 2 Hardware Environment
Input/Output Problems. External Devices. Input/Output Module. I/O Steps. I/O Module Function Computer Architecture
 168 420 Computer Architecture Chapter 6 Input/Output Input/Output Problems Wide variety of peripherals Delivering different amounts of data At different speeds In different formats All slower than CPU
168 420 Computer Architecture Chapter 6 Input/Output Input/Output Problems Wide variety of peripherals Delivering different amounts of data At different speeds In different formats All slower than CPU
I/O CANNOT BE IGNORED
 LECTURE 13 I/O I/O CANNOT BE IGNORED Assume a program requires 100 seconds, 90 seconds for main memory, 10 seconds for I/O. Assume main memory access improves by ~10% per year and I/O remains the same.
LECTURE 13 I/O I/O CANNOT BE IGNORED Assume a program requires 100 seconds, 90 seconds for main memory, 10 seconds for I/O. Assume main memory access improves by ~10% per year and I/O remains the same.
Final Lecture. A few minutes to wrap up and add some perspective
 Final Lecture A few minutes to wrap up and add some perspective 1 2 Instant replay The quarter was split into roughly three parts and a coda. The 1st part covered instruction set architectures the connection
Final Lecture A few minutes to wrap up and add some perspective 1 2 Instant replay The quarter was split into roughly three parts and a coda. The 1st part covered instruction set architectures the connection
CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 18: Input-Output. Outline of Today s Lecture. The Big Picture: Where are We Now?
 CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 18: Input-Output Robert Wagner cps 104.1 RW Fall 2000 Outline of Today s Lecture The system Magnetic Disk Tape es DMA cps 104.2 RW Fall 2000 The Big
CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 18: Input-Output Robert Wagner cps 104.1 RW Fall 2000 Outline of Today s Lecture The system Magnetic Disk Tape es DMA cps 104.2 RW Fall 2000 The Big
Lecture 23. Finish-up buses Storage
 Lecture 23 Finish-up buses Storage 1 Example Bus Problems, cont. 2) Assume the following system: A CPU and memory share a 32-bit bus running at 100MHz. The memory needs 50ns to access a 64-bit value from
Lecture 23 Finish-up buses Storage 1 Example Bus Problems, cont. 2) Assume the following system: A CPU and memory share a 32-bit bus running at 100MHz. The memory needs 50ns to access a 64-bit value from
COSC121: Computer Systems. Exceptions and Interrupts
 COSC121: Computer Systems. Exceptions and Interrupts Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Constructed using materials: - Patt and Patel Introduction to Computing Systems (2nd) - Patterson and
COSC121: Computer Systems. Exceptions and Interrupts Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Constructed using materials: - Patt and Patel Introduction to Computing Systems (2nd) - Patterson and
5.b Principles of I/O Hardware CPU-I/O communication
 Three communication protocols between CPU and I/O 1. Programmed I/O (or polling or busy waiting ) the CPU must repeatedly poll the device to check if the I/O request completed 2. Interrupt-driven I/O the
Three communication protocols between CPU and I/O 1. Programmed I/O (or polling or busy waiting ) the CPU must repeatedly poll the device to check if the I/O request completed 2. Interrupt-driven I/O the
CSE 120. Operating Systems. March 27, 2014 Lecture 17. Mass Storage. Instructor: Neil Rhodes. Wednesday, March 26, 14
 CSE 120 Operating Systems March 27, 2014 Lecture 17 Mass Storage Instructor: Neil Rhodes Paging and Translation Lookaside Buffer frame dirty? no yes CPU checks TLB PTE in TLB? Free page frame? no yes OS
CSE 120 Operating Systems March 27, 2014 Lecture 17 Mass Storage Instructor: Neil Rhodes Paging and Translation Lookaside Buffer frame dirty? no yes CPU checks TLB PTE in TLB? Free page frame? no yes OS
Computer Systems Architecture I. CSE 560M Lecture 18 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James
 Computer Systems Architecture I CSE 560M Lecture 18 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James Plan for Today Announcements No class meeting on Monday, meet in project groups Project demos < 2 weeks, Nov 23 rd Questions
Computer Systems Architecture I CSE 560M Lecture 18 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James Plan for Today Announcements No class meeting on Monday, meet in project groups Project demos < 2 weeks, Nov 23 rd Questions
I/O. Fall Tore Larsen. Including slides from Pål Halvorsen, Tore Larsen, Kai Li, and Andrew S. Tanenbaum)
 I/O Fall 2011 Tore Larsen Including slides from Pål Halvorsen, Tore Larsen, Kai Li, and Andrew S. Tanenbaum) Big Picture Today we talk about I/O characteristics interconnection devices & controllers (disks
I/O Fall 2011 Tore Larsen Including slides from Pål Halvorsen, Tore Larsen, Kai Li, and Andrew S. Tanenbaum) Big Picture Today we talk about I/O characteristics interconnection devices & controllers (disks
I/O. Fall Tore Larsen. Including slides from Pål Halvorsen, Tore Larsen, Kai Li, and Andrew S. Tanenbaum)
 I/O Fall 2010 Tore Larsen Including slides from Pål Halvorsen, Tore Larsen, Kai Li, and Andrew S. Tanenbaum) Big Picture Today we talk about I/O characteristics interconnection devices & controllers (disks
I/O Fall 2010 Tore Larsen Including slides from Pål Halvorsen, Tore Larsen, Kai Li, and Andrew S. Tanenbaum) Big Picture Today we talk about I/O characteristics interconnection devices & controllers (disks
Where We Are in This Course Right Now. ECE 152 Introduction to Computer Architecture Input/Output (I/O) Copyright 2012 Daniel J. Sorin Duke University
 Introduction to Computer Architecture Input/Output () Copyright 2012 Daniel J. Sorin Duke University Slides are derived from work by Amir Roth (Penn) Spring 2012 Where We Are in This Course Right Now So
Introduction to Computer Architecture Input/Output () Copyright 2012 Daniel J. Sorin Duke University Slides are derived from work by Amir Roth (Penn) Spring 2012 Where We Are in This Course Right Now So
Department of Computer Science, Institute for System Architecture, Operating Systems Group. Real-Time Systems '08 / '09. Hardware.
 Department of Computer Science, Institute for System Architecture, Operating Systems Group Real-Time Systems '08 / '09 Hardware Marcus Völp Outlook Hardware is Source of Unpredictability Caches Pipeline
Department of Computer Science, Institute for System Architecture, Operating Systems Group Real-Time Systems '08 / '09 Hardware Marcus Völp Outlook Hardware is Source of Unpredictability Caches Pipeline
I/O Systems. Jinkyu Jeong Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 I/O Systems Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Today s Topics Device characteristics Block device vs. Character device Direct I/O vs.
I/O Systems Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Today s Topics Device characteristics Block device vs. Character device Direct I/O vs.
Chapter 3. Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection. Yonsei University
 Chapter 3 Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection Contents Computer Components Computer Function Interconnection Structures Bus Interconnection PCI 3-2 Program Concept Computer components
Chapter 3 Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection Contents Computer Components Computer Function Interconnection Structures Bus Interconnection PCI 3-2 Program Concept Computer components
I/O Buffering and Streaming
 I/O Buffering and Streaming I/O Buffering and Caching I/O accesses are reads or writes (e.g., to files) Application access is arbitary (offset, len) Convert accesses to read/write of fixed-size blocks
I/O Buffering and Streaming I/O Buffering and Caching I/O accesses are reads or writes (e.g., to files) Application access is arbitary (offset, len) Convert accesses to read/write of fixed-size blocks
Review: Hardware user/kernel boundary
 Review: Hardware user/kernel boundary applic. applic. applic. user lib lib lib kernel syscall pg fault syscall FS VM sockets disk disk NIC context switch TCP retransmits,... device interrupts Processor
Review: Hardware user/kernel boundary applic. applic. applic. user lib lib lib kernel syscall pg fault syscall FS VM sockets disk disk NIC context switch TCP retransmits,... device interrupts Processor
Input/Output Introduction
 Input/Output 1 Introduction Motivation Performance metrics Processor interface issues Buses 2 Page 1 Motivation CPU Performance: 60% per year I/O system performance limited by mechanical delays (e.g.,
Input/Output 1 Introduction Motivation Performance metrics Processor interface issues Buses 2 Page 1 Motivation CPU Performance: 60% per year I/O system performance limited by mechanical delays (e.g.,
Introduction. Motivation Performance metrics Processor interface issues Buses
 Input/Output 1 Introduction Motivation Performance metrics Processor interface issues Buses 2 Motivation CPU Performance: 60% per year I/O system performance limited by mechanical delays (e.g., disk I/O)
Input/Output 1 Introduction Motivation Performance metrics Processor interface issues Buses 2 Motivation CPU Performance: 60% per year I/O system performance limited by mechanical delays (e.g., disk I/O)
Virtual Memory Input/Output. Admin
 Virtual Memory Input/Output Computer Science 104 Lecture 21 Admin Projects Due Friday Dec 7 Homework #6 Due Next Wed Dec 5 Today VM VM + Caches, I/O Reading I/O Chapter 8 Input Output (primarily 8.4 and
Virtual Memory Input/Output Computer Science 104 Lecture 21 Admin Projects Due Friday Dec 7 Homework #6 Due Next Wed Dec 5 Today VM VM + Caches, I/O Reading I/O Chapter 8 Input Output (primarily 8.4 and
CS370 Operating Systems
 CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Spring 2018 Lecture 2 Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 2 What is an Operating System? What is
CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Spring 2018 Lecture 2 Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 2 What is an Operating System? What is
CS252 Graduate Computer Architecture Spring 2014 Lecture 17: I/O
 CS252 Graduate Computer Architecture Spring 2014 Lecture 17: Krste Asanovic krste@eecs.berkeley.edu http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs252/sp14 Last Time in Lecture 16 Virtual Machines User- Level - ABI
CS252 Graduate Computer Architecture Spring 2014 Lecture 17: Krste Asanovic krste@eecs.berkeley.edu http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs252/sp14 Last Time in Lecture 16 Virtual Machines User- Level - ABI
Virtual Memory. Reading. Sections 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.8, 5.10 (2) Lecture notes from MKP and S. Yalamanchili
 Virtual Memory Lecture notes from MKP and S. Yalamanchili Sections 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.8, 5.10 Reading (2) 1 The Memory Hierarchy ALU registers Cache Memory Memory Memory Managed by the compiler Memory Managed
Virtual Memory Lecture notes from MKP and S. Yalamanchili Sections 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.8, 5.10 Reading (2) 1 The Memory Hierarchy ALU registers Cache Memory Memory Memory Managed by the compiler Memory Managed
Prof. Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2015 Computer Science Cornell University. See: Online P&H Chapter 6.5 6
 Prof. Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2015 Computer Science Cornell University See: Online P&H Chapter 6.5 6 Project3 submit souped up bot to CMS Project3 Cache Race Games night Monday, May 4 th, 5pm
Prof. Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2015 Computer Science Cornell University See: Online P&H Chapter 6.5 6 Project3 submit souped up bot to CMS Project3 Cache Race Games night Monday, May 4 th, 5pm
I/O Systems. Amir H. Payberah. Amirkabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic)
 I/O Systems Amir H. Payberah amir@sics.se Amirkabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic) Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) I/O Systems 1393/9/15 1 / 57 Motivation Amir H. Payberah (Tehran
I/O Systems Amir H. Payberah amir@sics.se Amirkabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic) Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) I/O Systems 1393/9/15 1 / 57 Motivation Amir H. Payberah (Tehran
Storage Systems. Storage Systems
 Storage Systems Storage Systems We already know about four levels of storage: Registers Cache Memory Disk But we've been a little vague on how these devices are interconnected In this unit, we study Input/output
Storage Systems Storage Systems We already know about four levels of storage: Registers Cache Memory Disk But we've been a little vague on how these devices are interconnected In this unit, we study Input/output
I/O Devices. Nima Honarmand (Based on slides by Prof. Andrea Arpaci-Dusseau)
 I/O Devices Nima Honarmand (Based on slides by Prof. Andrea Arpaci-Dusseau) Hardware Support for I/O CPU RAM Network Card Graphics Card Memory Bus General I/O Bus (e.g., PCI) Canonical Device OS reads/writes
I/O Devices Nima Honarmand (Based on slides by Prof. Andrea Arpaci-Dusseau) Hardware Support for I/O CPU RAM Network Card Graphics Card Memory Bus General I/O Bus (e.g., PCI) Canonical Device OS reads/writes
Input/Output Systems
 CSE325 Principles of Operating Systems Input/Output Systems David P. Duggan dduggan@sandia.gov April 2, 2013 Input/Output Devices Output Device Input Device Processor 4/2/13 CSE325 - I/O Systems 2 Why
CSE325 Principles of Operating Systems Input/Output Systems David P. Duggan dduggan@sandia.gov April 2, 2013 Input/Output Devices Output Device Input Device Processor 4/2/13 CSE325 - I/O Systems 2 Why
Bus System. Bus Lines. Bus Systems. Chapter 8. Common connection between the CPU, the memory, and the peripheral devices.
 Bus System Chapter 8 CSc 314 T W Bennet Mississippi College 1 CSc 314 T W Bennet Mississippi College 3 Bus Systems Common connection between the CPU, the memory, and the peripheral devices. One device
Bus System Chapter 8 CSc 314 T W Bennet Mississippi College 1 CSc 314 T W Bennet Mississippi College 3 Bus Systems Common connection between the CPU, the memory, and the peripheral devices. One device
Generic Model of I/O Module Interface to CPU and Memory Interface to one or more peripherals
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 th Edition Chapter 7 Input/Output Input/Output Problems Wide variety of peripherals Delivering different amounts of data At different speeds In
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 th Edition Chapter 7 Input/Output Input/Output Problems Wide variety of peripherals Delivering different amounts of data At different speeds In
Announcement. Computer Architecture (CSC-3501) Lecture 23 (17 April 2008) Chapter 7 Objectives. 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 I/O and Performance
 Computer Architecture (CSC-3501) Lecture 23 (17 April 2008) Announcement Homework #8 and #9 are uploaded at class website Seung-Jong Park (Jay) http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~sjpark 1 2 Chapter 7 Objectives 7.1
Computer Architecture (CSC-3501) Lecture 23 (17 April 2008) Announcement Homework #8 and #9 are uploaded at class website Seung-Jong Park (Jay) http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~sjpark 1 2 Chapter 7 Objectives 7.1
CMSC 313 Lecture 26 DigSim Assignment 3 Cache Memory Virtual Memory + Cache Memory I/O Architecture
 CMSC 313 Lecture 26 DigSim Assignment 3 Cache Memory Virtual Memory + Cache Memory I/O Architecture UMBC, CMSC313, Richard Chang CMSC 313, Computer Organization & Assembly Language Programming
CMSC 313 Lecture 26 DigSim Assignment 3 Cache Memory Virtual Memory + Cache Memory I/O Architecture UMBC, CMSC313, Richard Chang CMSC 313, Computer Organization & Assembly Language Programming
Anne Bracy CS 3410 Computer Science Cornell University
 Anne Bracy CS 3410 Computer Science Cornell University The slides were originally created by Deniz ALTINBUKEN. P&H Chapter 4.9, pages 445 452, appendix A.7 Manages all of the software and hardware on the
Anne Bracy CS 3410 Computer Science Cornell University The slides were originally created by Deniz ALTINBUKEN. P&H Chapter 4.9, pages 445 452, appendix A.7 Manages all of the software and hardware on the
Virtual Machines Disco and Xen (Lecture 10, cs262a) Ion Stoica & Ali Ghodsi UC Berkeley February 26, 2018
 Virtual Machines Disco and Xen (Lecture 10, cs262a) Ion Stoica & Ali Ghodsi UC Berkeley February 26, 2018 Today s Papers Disco: Running Commodity Operating Systems on Scalable Multiprocessors, Edouard
Virtual Machines Disco and Xen (Lecture 10, cs262a) Ion Stoica & Ali Ghodsi UC Berkeley February 26, 2018 Today s Papers Disco: Running Commodity Operating Systems on Scalable Multiprocessors, Edouard
EE282H: Computer Architecture and Organization. EE282H: Computer Architecture and Organization -- Course Overview
 : Computer Architecture and Organization Kunle Olukotun Gates 302 kunle@ogun.stanford.edu http://www-leland.stanford.edu/class/ee282h/ : Computer Architecture and Organization -- Course Overview Goals»
: Computer Architecture and Organization Kunle Olukotun Gates 302 kunle@ogun.stanford.edu http://www-leland.stanford.edu/class/ee282h/ : Computer Architecture and Organization -- Course Overview Goals»
Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Operating Systems Group REAL-TIME MICHAEL ROITZSCH OVERVIEW
 Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Operating Systems Group REAL-TIME MICHAEL ROITZSCH OVERVIEW 2 SO FAR talked about in-kernel building blocks: threads memory IPC drivers
Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Operating Systems Group REAL-TIME MICHAEL ROITZSCH OVERVIEW 2 SO FAR talked about in-kernel building blocks: threads memory IPC drivers
Input / Output. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College April 12, 2018
 Input / Output Kevin Webb Swarthmore College April 12, 2018 xkcd #927 Fortunately, the charging one has been solved now that we've all standardized on mini-usb. Or is it micro-usb? Today s Goals Characterize
Input / Output Kevin Webb Swarthmore College April 12, 2018 xkcd #927 Fortunately, the charging one has been solved now that we've all standardized on mini-usb. Or is it micro-usb? Today s Goals Characterize
Lecture 13 Input/Output (I/O) Systems (chapter 13)
 Bilkent University Department of Computer Engineering CS342 Operating Systems Lecture 13 Input/Output (I/O) Systems (chapter 13) Dr. İbrahim Körpeoğlu http://www.cs.bilkent.edu.tr/~korpe 1 References The
Bilkent University Department of Computer Engineering CS342 Operating Systems Lecture 13 Input/Output (I/O) Systems (chapter 13) Dr. İbrahim Körpeoğlu http://www.cs.bilkent.edu.tr/~korpe 1 References The
Where We Are in This Course Right Now. ECE 152 Introduction to Computer Architecture Input/Output (I/O) Copyright 2011 Daniel J. Sorin Duke University
 Introduction to Computer Architecture Input/Output (I/O) Copyright 2011 Daniel J. Sorin Duke University Slides are derived from work by Amir Roth (Penn) Spring 2011 Where We Are in This Course Right Now
Introduction to Computer Architecture Input/Output (I/O) Copyright 2011 Daniel J. Sorin Duke University Slides are derived from work by Amir Roth (Penn) Spring 2011 Where We Are in This Course Right Now
PC I/O. May 7, Howard Huang 1
 PC I/O Today wraps up the I/O material with a little bit about PC I/O systems. Internal buses like PCI and ISA are critical. External buses like USB and Firewire are becoming more important. Today also
PC I/O Today wraps up the I/O material with a little bit about PC I/O systems. Internal buses like PCI and ISA are critical. External buses like USB and Firewire are becoming more important. Today also
ECE 250 / CPS 250 Computer Architecture. Input/Output
 ECE 250 / CPS 250 Computer Architecture Input/Output Benjamin Lee Slides based on those from Andrew Hilton (Duke), Alvy Lebeck (Duke) Benjamin Lee (Duke), and Amir Roth (Penn) Where We Are in This Course
ECE 250 / CPS 250 Computer Architecture Input/Output Benjamin Lee Slides based on those from Andrew Hilton (Duke), Alvy Lebeck (Duke) Benjamin Lee (Duke), and Amir Roth (Penn) Where We Are in This Course
OPERATING SYSTEMS CS136
 OPERATING SYSTEMS CS136 Jialiang LU Jialiang.lu@sjtu.edu.cn Based on Lecture Notes of Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, 1 Chapter 5 INPUT/OUTPUT 2 Overview o OS controls I/O devices => o Issue commands,
OPERATING SYSTEMS CS136 Jialiang LU Jialiang.lu@sjtu.edu.cn Based on Lecture Notes of Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, 1 Chapter 5 INPUT/OUTPUT 2 Overview o OS controls I/O devices => o Issue commands,
Lecture 10: Simple Data Path
 Lecture 10: Simple Data Path Course so far Performance comparisons Amdahl s law ISA function & principles What do bits mean? Computer math Today Take QUIZ 6 over P&H.1-, before 11:59pm today How do computers
Lecture 10: Simple Data Path Course so far Performance comparisons Amdahl s law ISA function & principles What do bits mean? Computer math Today Take QUIZ 6 over P&H.1-, before 11:59pm today How do computers
