Block & Row Decoder ...
|
|
|
- Daniela Carson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
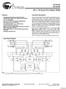
1 2-Mbit (128 K 16) F-RAM Memory 2-Mbit (128 K 16) F-RAM Memory Features 2-Mbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 128 K 16 Configurable as 256 K 8 using UB and LB High-endurance 100 trillion (10 14 ) read/writes 151-year data retention (see the Data Retention and Endurance table) NoDelay writes Page mode operation to 30-ns cycle time Advanced high-reliability ferroelectric process SRAM compatible Industry-standard 128 K 16 SRAM pinout 60-ns access time, 110-ns cycle time Advanced features Software-programmable block write-protect Superior to battery-backed SRAM modules No battery concerns Monolithic reliability True surface mount solution, no rework steps Superior for moisture, shock, and vibration Low power consumption Active current 8 ma (typ) Standby current 90 A (typ) Sleep mode current 5 A (max) Low-voltage operation: V DD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V Industrial temperature: 40 C to +85 C Logic Block Diagram A 16-0 Address Latch & Write Protect A 16-2 A 1-0 Block & Row Decoder pin thin small outline package (TSOP) Type II Restriction of hazardous substances (RoHS) compliant Functional Overview The FM21L16 is a 128 K 16 nonvolatile memory that reads and writes similar to a standard SRAM. A ferroelectric random access memory or F-RAM is nonvolatile, which means that data is retained after power is removed. It provides data retention for over 151 years while eliminating the reliability concerns, functional disadvantages, and system design complexities of battery-backed SRAM (BBSRAM). Fast write timing and high write endurance make the F-RAM superior to other types of memory. The FM21L16 operation is similar to that of other RAM devices and therefore, it can be used as a drop-in replacement for a standard SRAM in a system. Read and write cycles may be triggered by or simply by changing the address. The F-RAM memory is nonvolatile due to its unique ferroelectric memory process. These features make the FM21L16 ideal for nonvolatile memory applications requiring frequent or rapid writes. The FM21L16 includes a low voltage monitor that blocks access to the memory array when V DD drops below V DD min. The memory is protected against an inadvertent access and data corruption under this condition. The device also features software-controlled write protection. The memory array is divided into 8 uniform blocks, each of which can be individually write protected. The device is available in a 400-mil, 44-pin TSOP-II surface mount package. Device specifications are guaranteed over the industrial temperature range 40 C to +85 C. For a complete list of related documentation, click here. 16 K x 16 block 16 K x 16 block 16 K x 16 block 16 K x 16 block 16 K x 16 block 16 K x 16 block 16 K x 16 block 16 K x 16 block UB, LB OE Control Logic... Column Decoder I/O Latch & Bus Driver DQ15-0 ZZ Cypress Semiconductor Corporation 198 Champion Court San Jose, CA Document Number: Rev. *C Revised November 19, 2014
2 Contents Pinout... 3 Pin Definitions... 3 Device Operation... 4 Memory Operation... 4 Read Operation... 4 Write Operation... 4 Page Mode Operation... 4 Pre-charge Operation... 4 Sleep Mode... 4 Software Write Protect... 5 Software Write-Protect Timing... 7 SRAM Drop-In Replacement... 8 Maximum Ratings... 9 Operating Range... 9 DC Electrical Characteristics... 9 Data Retention and Endurance Capacitance Thermal Resistance AC Test Conditions AC Switching Characteristics SRAM Read Cycle SRAM Write Cycle Power Cycle and Sleep Mode Timing Functional Truth Table Byte Select Truth Table Ordering Information Ordering Code Definitions Package Diagram Acronyms Document Conventions Units of Measure Document History Page Sales, Solutions, and Legal Information Worldwide Sales and Design Support Products PSoC Solutions Cypress Developer Community Technical Support Document Number: Rev. *C Page 2 of 22
3 Pinout Figure pin TSOP II pinout Pin Definitions A 4 A 3 A 2 A 1 A 0 DQ 0 DQ 1 DQ 2 DQ 3 V DD V SS DQ 4 DQ 5 DQ 6 DQ 7 A 16 A 15 A 14 A 13 A 12 Pin Name I/O Type Description A 16 A 0 Input Address inputs: The 17 address lines select one of 128K words in the F-RAM array. The lowest two address lines A 1 A 0 may be used for page mode read and write operations. DQ 15 DQ 0 Input/Output Data I/O Lines: 16-bit bidirectional data bus for accessing the F-RAM array. Input Write Enable: A write cycle begins when is asserted. The rising edge causes the FM21L16 to write the data on the DQ bus to the F-RAM array. The falling edge of latches a new column address for page mode write cycles. Input Chip Enable: The device is selected and a new memory access begins on the falling edge of. The entire address is latched internally at this point. Subsequent changes to the A 1 A 0 address inputs allow page mode operation. OE Input Output Enable: When OE is LOW, the FM21L16 drives the data bus when the valid read data is available. Deasserting OE HIGH tristates the DQ pins. UB Input Upper Byte Select: Enables DQ 15 DQ 8 pins during reads and writes. These pins are HI-Z if UB is HIGH. If the user does not perform byte writes and the device is not configured as a 256 K 8, the UB and LB pins may be tied to ground. LB Input Lower Byte Select: Enables DQ 7 DQ 0 pins during reads and writes. These pins are HI-Z if LB is HIGH. If the user does not perform byte writes and the device is not configured as a 256 K 8, the UB and LB pins may be tied to ground. ZZ Input Sleep: When ZZ is LOW, the device enters a low-power sleep mode for the lowest supply current condition. ZZ must be HIGH for a normal read/write operation. If unused, tie ZZ pin to V DD. V SS Ground Ground for the device. Must be connected to the ground of the system. V DD Power supply Power supply input to the device. NC No connect No connect. This pin is not connected to the die pin TSOP II ( 16) Top View (not to scale) A 5 A 6 A 7 OE UB LB DQ 15 DQ 14 DQ 13 DQ 12 V SS V DD DQ 11 DQ 10 DQ 9 DQ 8 ZZ A 8 A 9 A 10 A11 NC Document Number: Rev. *C Page 3 of 22
4 Device Operation The FM21L16 is a word wide F-RAM memory logically organized as 131, and accessed using an industry-standard parallel interface. All data written to the part is immediately nonvolatile with no delay. The device offers page mode operation, which provides high-speed access to addresses within a page (row). Access to a different page requires that either transitions LOW or the upper address (A 16 A 2 ) changes. See the Functional Truth Table on page 17 for a complete description of read and write modes. Memory Operation Users access 131,072 memory locations, each with 16 data bits through a parallel interface. The F-RAM array is organized as eight blocks, each having 4096 rows. Each row has four column locations, which allow fast access in page mode operation. When an initial address is latched by the falling edge of, subsequent column locations may be accessed without the need to toggle. When is deasserted HIGH, a pre-charge operation begins. Writes occur immediately at the end of the access with no delay. The pin must be toggled for each write operation. The write data is stored in the nonvolatile memory array immediately, which is a feature unique to F-RAM called NoDelay writes. Read Operation A read operation begins on the falling edge of. The falling edge of causes the address to be latched and starts a memory read cycle if is HIGH. Data becomes available on the bus after the access time is met. When the address is latched and the access completed, a new access to a random location (different row) may begin while is still LOW. The minimum cycle time for random addresses is t RC. Note that unlike SRAMs, the FM21L16's -initiated access time is faster than the address access time. The FM21L16 will drive the data bus when OE and at least one of the byte enables (UB, LB) is asserted LOW. The upper data byte is driven when UB is LOW, and the lower data byte is driven when LB is LOW. If OE is asserted after the memory access time is met, the data bus will be driven with valid data. If OE is asserted before completing the memory access, the data bus will not be driven until valid data is available. This feature minimizes supply current in the system by eliminating transients caused by invalid data being driven to the bus. When OE is deasserted HIGH, the data bus will remain in a HI-Z state. Write Operation In the FM21L16, writes occur in the same interval as reads. The FM21L16 supports both and controlled write cycles. In both cases, the address A 16 A 2 is latched on the falling edge of. In a -controlled write, the signal is asserted before beginning the memory cycle. That is, is LOW when falls. In this case, the device begins the memory cycle as a write. The FM21L16 will not drive the data bus regardless of the state of OE as long as is LOW. Input data must be valid when is deasserted HIGH. In a -controlled write, the memory cycle begins on the falling edge of. The signal falls some time later. Therefore, the memory cycle begins as a read. The data bus will be driven if OE is LOW; however, it will be HI-Z when is asserted LOW. The - and -controlled write timing cases are shown in the page 14. Write access to the array begins on the falling edge of after the memory cycle is initiated. The write access terminates on the rising edge of or, whichever comes first. A valid write operation requires the user to meet the access time specification before deasserting or. The data setup time indicates the interval during which data cannot change before the end of the write access (rising edge of or ). Unlike other nonvolatile memory technologies, there is no write delay with F-RAM. Because the read and write access times of the underlying memory are the same, the user experiences no delay through the bus. The entire memory operation occurs in a single bus cycle. Data polling, a technique used with EEPROMs to determine if a write is complete, is unnecessary. Page Mode Operation The F-RAM array is organized as eight blocks, each having 4096 rows. Each row has four column-address locations. Address inputs A 1 A 0 define the column address to be accessed. An access can start on any column address, and other column locations may be accessed without the need to toggle the pin. For fast access reads, after the first data byte is driven to the bus, the column address inputs A 1 A 0 may be changed to a new value. A new data byte is then driven to the DQ pins no later than t AAP, which is less than half the initial read access time. For fast access writes, the first write pulse defines the first write access. While is LOW, a subsequent write pulse along with a new column address provides a page mode write access. Pre-charge Operation The pre-charge operation is an internal condition in which the memory state is prepared for a new access. Pre-charge is user-initiated by driving the signal HIGH. It must remain HIGH for at least the minimum pre-charge time, t PC. Pre-charge is also activated by changing the upper addresses, A 16 A 2. The current row is first closed before accessing the new row. The device automatically detects an upper order address change, which starts a pre-charge operation. The new address is latched and the new read data is valid within the t AA address access time; see Figure 9 on page 13. A similar sequence occurs for write cycles; see Figure 14 on page 14. The rate at which random addresses can be issued is t RC and t WC, respectively. Sleep Mode The device incorporates a sleep mode of operation, which allows the user to achieve the lowest power supply current condition. It enters a low-power sleep mode by asserting the ZZ pin LOW. Read and write operations must complete before the ZZ pin going LOW. When ZZ is LOW, all pins are ignored except the ZZ pin. When ZZ is deasserted HIGH, there is some time delay (t ZZEX ) before the user can access the device. If sleep mode is not used, the ZZ pin should be tied to V DD. Document Number: Rev. *C Page 4 of 22
5 Figure 2. Sleep/Standby State Diagram Power Applied HIGH, ZZ HIGH Standby ZZ LOW Initialize LOW, ZZ HIGH HIGH, ZZ HIGH Sleep LOW, ZZ HIGH Normal Operation ZZ LOW ZZ HIGH Software Write Protect The 128 K 16 address space is divided into eight sectors (blocks) of 16 K 16 each. Each sector can be individually software write-protected and the settings are nonvolatile. A unique address and command sequence invokes the write-protect mode. To modify write protection, the system host must issue six read commands, three write commands, and a final read command. The specific sequence of read addresses must be provided to access the write-protect mode. Following the read address sequence, the host must write a data byte that specifies the desired protection state of each sector. For confirmation, the system must then write the complement of the protection byte immediately after the protection byte. Any error that occurs including read addresses in the wrong order, issuing a seventh read address, or failing to complement the protection value will leave the write protection unchanged. The write-protect state machine monitors all addresses, taking no action until this particular read/write sequence occurs. During the address sequence, each read will occur as a valid operation and data from the corresponding addresses will be driven to the data bus. Any address that occurs out of sequence will cause the software protection state machine to start over. After the address sequence is completed, the next operation must be a write cycle. The lower data byte contains the write-protect settings. This value will not be written to the memory array, so the address is a don't-care. Rather it will be held pending the next cycle, which must be a write of the data complement to the protection settings. If the complement is correct, the write-protect settings will be adjusted. Otherwise, the process is aborted and the address sequence starts over. The data value written after the correct six addresses will not be entered into the memory. The protection data byte consists of eight bits, each associated with the write-protect state of a sector. The data byte must be driven to the lower eight bits of the data bus, DQ 7 - DQ 0. Setting a bit to 1 write-protects the corresponding sector; a 0 enables writes for that sector. The following table shows the write-protect sectors with the corresponding bit that controls the write-protect setting. Table 1. Write Protect Sectors - 16 K 16 Blocks Sectors Sector 7 Sector 6 Sector 5 Sector 4 Sector 3 Sector 2 Sector 1 Sector 0 Blocks 1FFFFh 1C000h 1BFFFh 18000h 17FFFh 14000h 13FFFh 10000h 0FFFFh 0C000h 0BFFFh 08000h 07FFFh 04000h 03FFFh 00000h The write-protect address sequence follows: 1. Read address 12555h 2. Read address 1DAAAh 3. Read address 01333h 4. Read address 0ECCCh 5. Read address 000FFh 6. Read address 1FF00h 7. Write address 1DAAAh 8. Write address 0ECCCh 9. Write address 0FF00h 10.Read address 00000h Note If is LOw entering the sequence, then an address of 00000h must precede 12555h. The address sequence provides a secure way of modifying the protection. The write-protect sequence has a one in chance of randomly accessing exactly the first six addresses. The odds are further reduced by requiring three more write cycles, one that requires an exact inversion of the data byte. Figure 3 on page 6 shows a flow chart of the entire write-protect operation. The write-protect settings are nonvolatile. The factory default: all blocks are unprotected. For example, the following sequence write-protects addresses from 0C000h to 13FFFh (sectors 3 and 4): Address Data Read 12555h Read 1DAAAh Read 01333h Read 0ECCCh Read 000FFh Read 1FF00h Write 1DAAAh 18h; bits 3 and 4 = 1 Write 0ECCCh E7h; complement of 18h Write 0FF00h Don t care Read 00000h Document Number: Rev. *C Page 5 of 22
6 Figure 3. Write-Protect State Machine Normal Memory Operation Any other operation Write 1DAAAh? n Write 0ECCCh? n Read 12555h? y Read 1DAAAh? y Read 01333h? y Read 0ECCCh? y Read 000FFh? y n n n n n n n n y Hold Data Byte Write 0ECCCh? y Data Complement? y Write 0FF00h? Read 00000h To enter new y write protect settings y Read 1AAAAh to drive write protect settings Read 00000h Read 1FF00h? n y Sequence Detector Change Write Protect Settings Read Write Protect Settings Document Number: Rev. *C Page 6 of 22
7 Software Write-Protect Timing Figure 4. Sequence to Set Write-Protect Blocks [1] A DAAA ECCC 000FF 1FF00 1DAAA 0ECCC 0FF OE DQ 15-0 A 16-0 OE DQ Data Data Figure 5. Sequence to Read Write-Protect Settings [1] 1DAAA ECCC 000FF 1FF00 0ECCC 1AAAA t (read access time) X Data Note 1. This sequence requires t AS > 10 ns and address must be stable while is LOW. Document Number: Rev. *C Page 7 of 22
8 SRAM Drop-In Replacement The FM21L16 is designed to be a drop-in replacement for standard asynchronous SRAMs. The device does not require to toggle for each new address. may remain LOW for as long as 10 µs. While is LOW, the device automatically detects address changes and a new access begins. It also allows page mode operation at speeds up to 33 MHz. Figure 6 shows a pull-up resistor on, which will keep the pin HIGH during power cycles, assuming the MCU / MPU pin tristates during the reset condition. The pull-up resistor value should be chosen to ensure the pin tracks V DD to a high enough value, so that the current drawn when is LOW is not an issue. A 10-k resistor draws 330 µa when is LOW and V DD = 3.3 V Figure 6. Use of Pull-up Resistor on MCU / MPU V DD Note that if is tied to ground, the user must be sure is not LOW at power-up or power-down events. If and are both LOW during power cycles, data will be corrupted. Figure 7 shows a pull-up resistor on, which will keep the pin HIGH during power cycles, assuming the MCU / MPU pin tristates during the reset condition.the pull-up resistor value should be chosen to ensure the pin tracks V DD to a high enough value, so that OE FM21L16 A 16-0 DQ 15-0 the current drawn when is LOW is not an issue. A 10-k resistor draws 330 µa when is LOW and V DD = 3.3 V. Figure 7. Use of Pull-up Resistor on MCU / MPU Note If is tied to ground, the user gives up the ability to perform the software write-protect sequence. For applications that require the lowest power consumption, the signal should be active (LOW) only during memory accesses. The FM21L16 draws supply current while is LOW, even if addresses and control signals are static. While is HIGH, the device draws no more than the maximum standby current, I SB. toggling LOW on every address access is perfectly acceptable in FM21L16. The UB and LB byte select pins are active for both read and write cycles. They may be used to allow the device to be wired as a 256 K 8 memory. The upper and lower data bytes can be tied together and controlled with the byte selects. Individual byte enables or the next higher address line A 17 may be available from the system processor. Figure 8. FM21L16 Wired as 256 K 8 A 17 A 16-0 OE UB LB A 16-0 V DD 2-Mbit F-RAM FM21L16 OE FM21L16 A 16-0 DQ 15-8 DQ 15-0 ZZ DQ 7-0 D 7-0 Document Number: Rev. *C Page 8 of 22
9 Maximum Ratings Exceeding maximum ratings may shorten the useful life of the device. These user guidelines are not tested. Storage temperature C to +125 C Maximum junction temperature C Supply voltage on V DD relative to V SS V to V Voltage applied to outputs in High Z state V to V DD V Input voltage V to V and V IN < V DD V Transient voltage (< 20 ns) on any pin to ground potential V to V CC V Package power dissipation capability (T A = 25 C) W DC Electrical Characteristics Over the Operating Range Surface mount Pb soldering temperature (3 seconds) C DC output current (1 output at a time, 1s duration) ma Static discharge voltage Human Body Model (JEDEC Std JESD22-A114-F) kv Charged Device Model (JEDEC Std JESD22-C101-D) V Machine Model (JEDEC Std JESD22-A115-A) V Latch-up current... > 140 ma Operating Range Range Ambient Temperature (T A ) V DD Industrial 40 C to +85 C 2.7 V to 3.6 V Parameter Description Test Conditions Min Typ [2] Max Unit V DD Power supply voltage V I DD V DD supply current V DD = 3.6 V, cycling at min. cycle time. All inputs toggling at CMOS levels (0.2 V or V DD 0.2 V), all DQ pins unloaded ma I SB Standby current V DD = 3.6 V, at V DD, T A = 25 C µa All other pins are static and at CMOS levels T A = 85 C 270 µa (0.2 V or V DD 0.2 V), ZZ is HIGH I ZZ Sleep mode current V DD = 3.6 V, ZZ is LOW, all other inputs at CMOS levels (0.2 V or V DD 0.2 V). T A = 25 C 5 µa T A = 85 C 8 µa I LI Input leakage current V IN between V DD and V SS +1 µa I LO Output leakage current V OUT between V DD and V SS +1 µa V IH Input HIGH voltage 2.2 V DD V V IL Input LOW voltage V V OH1 Output HIGH voltage I OH = 1.0 ma 2.4 V V OH2 Output HIGH voltage I OH = 100 µa V DD 0.2 V V OL1 Output LOW voltage I OL = 2.1 ma 0.4 V V OL2 Output LOW voltage I OL = 100 µa 0.2 V Note 2. Typical values are at 25 C, V DD = V DD (typ). Not 100% tested. Document Number: Rev. *C Page 9 of 22
10 Data Retention and Endurance Parameter Description Test condition Min Max Unit T DR Data retention T A = 85 C 10 Years T A = 75 C 38 T A = 65 C 151 NV C Endurance Over operating temperature Cycles Capacitance Parameter Description Test Conditions Max Unit C I/O Input/Output capacitance (DQ) T A = 25 C, f = 1 MHz, V DD = V DD (Typ) 8 pf C IN Input capacitance 6 pf C ZZ Input capacitance of ZZ pin 8 pf Thermal Resistance Parameter Description Test Conditions 44-pin TSOP II Unit JA Thermal resistance 102 C/W (junction to ambient) JC Thermal resistance (junction to case) AC Test Conditions Input pulse levels...0 V to 3 V Input rise and fall times (10% 90%)... < 3 ns Input and output timing reference levels V Output load capacitance pf Test conditions follow standard test methods and procedures for measuring thermal impedance, in accordance with EIA/JESD C/W Document Number: Rev. *C Page 10 of 22
11 AC Switching Characteristics Over the Operating Range Cypress Parameter Parameters [3] Description Min Max Unit SRAM Read Cycle Alt Parameter t t A Chip enable access time 60 ns t RC Read cycle time 110 ns t AA Address access time 110 ns t OH t OHA Output hold time 20 ns t AAP Page mode address access time 25 ns t OHP Page mode output hold time 5 ns t CA Chip enable active time 60 10,000 ns t PC Pre-charge time 50 ns t BA t BW UB, LB access time 20 ns t AS t SA Address setup time (to LOW) 0 ns t AH t HA Address hold time ( Controlled) 60 ns t OE t DOE Output enable access time 15 ns t HZ [4, 5] t HZ Chip Enable to output HI-Z 10 ns t OHZ [4, 5] t HZOE Output enable HIGH to output HI-Z 10 ns t BHZ [4, 5] t HZBE UB, LB HIGHHIGH to output HI-Z 10 ns Notes 3. Test conditions assume a signal transition time of 3 ns or less, timing reference levels of 0.5 V DD, input pulse levels of 0 to 3 V, output loading of the specified I OL /I OH and load capacitance shown in AC Test Conditions on page t HZ, t OHZ and t BHZ are specified with a load capacitance of 5 pf. Transition is measured when the outputs enter a high impedance state. 5. This parameter is characterized but not 100% tested. Document Number: Rev. *C Page 11 of 22
12 AC Switching Characteristics (continued) Over the Operating Range Cypress Parameter SRAM Write Cycle t WC t WC Write cycle time 110 ns t CA Chip enable active time 60 10,000 ns t CW t S Chip enable to write enable HIGH 60 ns t PC Pre-charge time 50 ns t PWC Page mode write enable cycle time 25 ns t WP t P Write enable pulse width 16 ns t AS t SA Address setup time (to LOW) 0 ns t ASP Page mode address setup time (to LOW) 8 ns t AHP Page mode address hold time (to LOW) 15 ns t WLC t P Write enable LOW to chip disabled 25 ns t BLC t BW UB, LB LOW to chip disabled 25 ns t WLA Write enable LOW to A 16-2 change 25 ns t AWH A 16-2 change to write enable HIGH 110 ns t DS t SD Data input setup time 14 ns t DH t HD Data input hold time 0 ns t WZ [6, 7] t HZ Write enable LOW to output HI-Z 10 ns t WX [7] Write enable HIGH to output driven 10 ns t WS [8] t WH [8] Parameters [3] Description Min Max Unit Alt Parameter Write enable to LOW setup time 0 ns Write enable to HIGH hold time 0 ns Notes 6. t WZ is specified with a load capacitance of 5 pf. Transition is measured when the outputs enter a high impedance state. 7. This parameter is characterized but not 100% tested. 8. The relationship between and determines if a - or -controlled write occurs. The parameters t WS and t WH are not tested. Document Number: Rev. *C Page 12 of 22
13 Figure 9. Read Cycle Timing 1 ( LOW, OE LOW) t RC t RC A 16-0 t AA t AA DQ 15-0 A 16-0 OE DQ 15-0 UB / LB A 16-2 t OH Previous Data Valid Data Figure 10. Read Cycle Timing 2 ( Controlled) t CA t t AH AS t OE t t OH t BA t OH Figure 11. Page Mode Read Cycle Timing [9] t CA t AS t PC t HZ t OHZ t BHZ t PC Valid Data A 1-0 Col 0 Col 1 Col 2 OE t OE t AAP t HZ DQ 15-0 t t OHP Data 0 Data 1 Data 2 t OHZ Note 9. Although sequential column addressing is shown, it is not required Document Number: Rev. *C Page 13 of 22
14 Figure 12. Write Cycle Timing 1 ( Controlled) [10] t CA t PC t CW t AS t WLC A16-0 DQ 15-0 A 16-0 A 16-0 DQ 15-0 UB/LB t WP t WZ t DS t DH t WX t HZ D out D in D out Figure 13. Write Cycle Timing 2 ( Controlled) t CA t PC t AS t BLC t WS t WH t DH tds D in Figure 14. Write Cycle Timing 3 ( LOW) [10] t WC t AWH t WLA t WZ t WX t DH t DS DQ 15-0 D out D in D out D in Note 10. OE (not shown) is LOW only to show the effect of on DQ pins. Document Number: Rev. *C Page 14 of 22
15 Figure 15. Page Mode Write Cycle Timing t CA t PC t CW t AS t WLC A 16-2 A 1-0 OE DQ 15-0 t AHP Col 0 Col 1 t PWC t WP t DH t DS Data 0 Data 1 t ASP Col 2 Data 2 Note 11. UB and LB to show byte enable and byte masking cases. Document Number: Rev. *C Page 15 of 22
16 Power Cycle and Sleep Mode Timing Over the Operating Range Parameter Description Min Max Unit t PU Power-up (after V DD min. is reached) to first access time 450 µs t PD Last write ( HIGH) to power down time 0 µs t VR [12, 13] V DD power-up ramp rate 50 µs/v t VF [12, 13] V DD power-down ramp rate 100 µs/v t ZZH ZZ active to DQ HI-Z time 20 ns t ZZ Last write to sleep mode entry time 0 µs t ZZL ZZ active LOW time 1 µs t ZZEN Sleep mode entry time (ZZ LOW to don t care) 0 µs t ZZEX Sleep mode exit time (ZZ HIGH to 1 st access after wakeup) 450 µs V DD ZZ DQ t VR t PU V DD min. R/W Allowed Figure 16. Power Cycle and Sleep Mode Timing t ZZEN D out t ZZL t ZZH t ZZEX R/W Allowed t ZZ D in t ZZEX V DD min. R/W Allowed t PD t VF Note 12. Slope measured at any point on the V DD waveform. 13. Cypress cannot test or characterize all V DD power ramp profiles. The behavior of the internal circuits is difficult to predict when V DD is below the level of a transistor threshold voltage. Cypress strongly recommends that V DD power up faster than 100 ms through the range of 0.4 V to 1.0 V. Document Number: Rev. *C Page 16 of 22
17 Functional Truth Table [14, 15] A 16-2 A 1-0 ZZ Operation X X X X L Sleep Mode H X X X H Standby/Idle L H H V V V V H H Read L H No Change Change H Page Mode Read L H Change V H Random Read L L L V V V V H H -Controlled Write [15] L V V H -Controlled Write L No Change V H Page Mode Write [17] L X X X X Byte Select Truth Table X X H H Starts pre-charge [15, 16] OE LB UB Operation [18] H H X X Read; Outputs disabled X H H H L H L Read upper byte; HI-Z lower byte L H Read lower byte; HI-Z upper byte L L Read both bytes L X H L Write upper byte; Mask lower byte L H Write lower byte; Mask upper byte L L Write both bytes Notes 14. H = Logic HIGH, L = Logic LOW, V = Valid Data, X = Don't Care, = toggle LOW, = toggle HIGH. 15. For write cycles, data-in is latched on the rising edge of or, whichever comes first controlled write cycle begins as a Read cycle and then A 16-2 is latched. 17. Addresses A 1-0 must remain stable for at least 10 ns during page mode operation. 18. Assumes is LOW and ZZ is HIGH for all cases.the UB and LB pins may be grounded if 1) the system does not perform byte writes and 2) the device is not configured as a 256 K x 8. Document Number: Rev. *C Page 17 of 22
18 Ordering Information Access time (ns) Ordering Code Package Diagram Package Type Operating Range 60 FM21L16-60-TG pin TSOP II Industrial FM21L16-60-TGTR All the above parts are Pb-free. Ordering Code Definitions FM 21 L TG TR Option: blank = Standard; TR = Tape and Reel Package Type: TG = 44-pin TSOP II Access Time: 60 ns I/O Width: 16 Voltage: 2.7 V to 3.6 V 2-Mbit Parallel F-RAM Cypress Document Number: Rev. *C Page 18 of 22
19 Package Diagram Figure pin TSOP Package Outline, *E Document Number: Rev. *C Page 19 of 22
20 Acronyms Acronym Description CPU Central Processing Unit CMOS Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor EIA Electronic Industries Alliance F-RAM Ferroelectric Random Access Memory I/O Input/Output MCU Microcontroller Unit MPU Microprocesser Unit RoHS Restriction of Hazardous Substances R/W Read and Write SRAM Static Random Access Memory TSOP Thin Small Outline Package Document Conventions Units of Measure Symbol Unit of Measure C degree Celsius Hz hertz khz kilohertz k kilohm MHz megahertz A microampere F microfarad s microsecond ma milliampere ms millisecond M megaohm ns nanosecond ohm % percent pf picofarad V volt W watt Document Number: Rev. *C Page 20 of 22
21 Document History Page Document Title: FM21L16, 2-Mbit (128 K 16) F-RAM Memory Document Number: Rev. ECN No. Orig. of Change Submission Date Description of Change ** GVCH 02/25/2013 New spec *A GVCH 11/14/2013 Added watermark as Not recommended for new designs. *B GVCH 03/11/2014 Typo fixed: Changed datasheet status from Preliminary to Final Converted to Cypress standard format Updated Maximum Ratings table - Removed Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) - Added junction temperature and latch up current Updated Data Retention and Endurance table Added Thermal Resistance table Typo error fixed: Updated Address range from A 17 -A 0 to A 16 -A 0 for Figure 12 and Figure 13 Removed Package Marking Scheme (top mark) *C GVCH 11/19/2014 Added related documentation hyperlink in page 1. Document Number: Rev. *C Page 21 of 22
22 Sales, Solutions, and Legal Information Worldwide Sales and Design Support Cypress maintains a worldwide network of offices, solution centers, manufacturer s representatives, and distributors. To find the office closest to you, visit us at Cypress Locations. Products Automotive Clocks & Buffers Interface Lighting & Power Control Memory PSoC Touch Sensing USB Controllers Wireless/RF cypress.com/go/automotive cypress.com/go/clocks cypress.com/go/interface cypress.com/go/powerpsoc cypress.com/go/plc cypress.com/go/memory cypress.com/go/psoc cypress.com/go/touch cypress.com/go/usb cypress.com/go/wireless PSoC Solutions psoc.cypress.com/solutions PSoC 1 PSoC 3 PSoC 4 PSoC 5LP Cypress Developer Community Community Forums Blogs Video Training Technical Support cypress.com/go/support Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. Cypress Semiconductor Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under patent or other rights. Cypress products are not warranted nor intended to be used for medical, life support, life saving, critical control or safety applications, unless pursuant to an express written agreement with Cypress. Furthermore, Cypress does not authorize its products for use as critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress products in life-support systems application implies that the manufacturer assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress against all charges. Any Source Code (software and/or firmware) is owned by Cypress Semiconductor Corporation (Cypress) and is protected by and subject to worldwide patent protection (United States and foreign), United States copyright laws and international treaty provisions. Cypress hereby grants to licensee a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to copy, use, modify, create derivative works of, and compile the Cypress Source Code and derivative works for the sole purpose of creating custom software and or firmware in support of licensee product to be used only in conjunction with a Cypress integrated circuit as specified in the applicable agreement. Any reproduction, modification, translation, compilation, or representation of this Source Code except as specified above is prohibited without the express written permission of Cypress. Disclaimer: CYPRESS MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH REGARD TO THIS MATERIAL, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Cypress reserves the right to make changes without further notice to the materials described herein. Cypress does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit described herein. Cypress does not authorize its products for use as critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress product in a life-support systems application implies that the manufacturer assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress against all charges. Use may be limited by and subject to the applicable Cypress software license agreement. Document Number: Rev. *C Revised November 19, 2014 Page 22 of 22 All products and company names mentioned in this document may be the trademarks of their respective holders.
2-Mbit (128 K 16) F-RAM Memory
 2-Mbit (128 K 16) F-RAM Memory 2-Mbit (128 K 16) F-RAM Memory Features 2-Mbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 128 K 16 Configurable as 256 K 8 using UB and LB High-endurance
2-Mbit (128 K 16) F-RAM Memory 2-Mbit (128 K 16) F-RAM Memory Features 2-Mbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 128 K 16 Configurable as 256 K 8 using UB and LB High-endurance
FM16W08 64Kb Wide Voltage Bytewide F-RAM
 Pre-Production FM16W08 64Kb Wide Voltage Bytewide F-RAM Features 64Kbit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 8,192 x 8 bits High Endurance 100 Trillion (10 14 ) Read/Writes 38 year Data Retention
Pre-Production FM16W08 64Kb Wide Voltage Bytewide F-RAM Features 64Kbit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 8,192 x 8 bits High Endurance 100 Trillion (10 14 ) Read/Writes 38 year Data Retention
12-Mbit (512 K 24) Static RAM
 12-Mbit (512 K 24) Static RAM Features High speed t AA = 10 ns Low active power I CC = 175 ma at 10 ns Low CMOS standby power I SB2 = 25 ma Operating voltages of 3.3 ± 0.3V 2.0V data retention Automatic
12-Mbit (512 K 24) Static RAM Features High speed t AA = 10 ns Low active power I CC = 175 ma at 10 ns Low CMOS standby power I SB2 = 25 ma Operating voltages of 3.3 ± 0.3V 2.0V data retention Automatic
FM1608B 64Kb Bytewide 5V F-RAM Memory
 Pre-Production FM1608B 64Kb Bytewide 5V F-RAM Memory Features 64Kbit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 8,192 x 8 bits High Endurance 1 Trillion (10 12 ) Read/Writes 38 year Data Retention (@ +75
Pre-Production FM1608B 64Kb Bytewide 5V F-RAM Memory Features 64Kbit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 8,192 x 8 bits High Endurance 1 Trillion (10 12 ) Read/Writes 38 year Data Retention (@ +75
2-Mbit (128K x 16) Static RAM
 2-Mbit (128K x 16) Static RAM Features Temperature Ranges Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-A: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-E: 40 C to 125 C High speed: 55 ns Wide voltage range: 2.7V 3.6V Ultra-low active,
2-Mbit (128K x 16) Static RAM Features Temperature Ranges Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-A: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-E: 40 C to 125 C High speed: 55 ns Wide voltage range: 2.7V 3.6V Ultra-low active,
FM18L08 256Kb Bytewide FRAM Memory
 256Kb Bytewide FRAM Memory Features 256K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 32,768 x 8 bits 45 year Data Retention Unlimited Read/Write Cycles NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric
256Kb Bytewide FRAM Memory Features 256K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 32,768 x 8 bits 45 year Data Retention Unlimited Read/Write Cycles NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric
256-Kbit (32 K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM
 256-Kbit (32 K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM 64-Kbit (8 K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM Features 256-Kbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 32K 8 High-endurance 100 trillion (10 14 ) read/writes
256-Kbit (32 K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM 64-Kbit (8 K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM Features 256-Kbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 32K 8 High-endurance 100 trillion (10 14 ) read/writes
1-Mbit (64K x 16) Static RAM
 1-Mbit (64K x 16) Static RAM Features Temperature ranges Commercial: 0 C to 70 C Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-A: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-E: 40 C to 125 C Pin and function compatible with CY7C1021BV33
1-Mbit (64K x 16) Static RAM Features Temperature ranges Commercial: 0 C to 70 C Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-A: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-E: 40 C to 125 C Pin and function compatible with CY7C1021BV33
4-Mbit (512K x 8) Static RAM
 4-Mbit (512K x 8) Static RAM Features Temperature Ranges Commercial: 0 C to 70 C Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive: 40 C to 125 C High speed t AA = 10 ns Low active power 324 mw (max.) 2.0V data retention
4-Mbit (512K x 8) Static RAM Features Temperature Ranges Commercial: 0 C to 70 C Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive: 40 C to 125 C High speed t AA = 10 ns Low active power 324 mw (max.) 2.0V data retention
4-Mbit (256K x 16) Static RAM
 4-Mbit (256K x 16) Static RAM Features Temperature ranges Commercial: 0 C to 70 C Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-A: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-E: 40 C to 125 C Pin and function compatible with CY7C1041BV33
4-Mbit (256K x 16) Static RAM Features Temperature ranges Commercial: 0 C to 70 C Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-A: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-E: 40 C to 125 C Pin and function compatible with CY7C1041BV33
1-Mbit (64K x 16) Static RAM
 1-Mbit (64K x 16) Static RAM Features Temperature Ranges Commercial: 0 C to 70 C Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive: 40 C to 125 C High speed t AA = 12 ns (Commercial & Industrial) t AA = 15 ns (Automotive)
1-Mbit (64K x 16) Static RAM Features Temperature Ranges Commercial: 0 C to 70 C Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive: 40 C to 125 C High speed t AA = 12 ns (Commercial & Industrial) t AA = 15 ns (Automotive)
4K x 8 Dual-Port Static RAM and 4K x 8 Dual-Port SRAM with Semaphores
 4K x 8 Dual-Port Static RAM and 4K x 8 Dual-Port SRAM with Semaphores Features True dual-ported memory cells, which allow simultaneous reads of the same memory location 4K x 8 organization 0.65 micron
4K x 8 Dual-Port Static RAM and 4K x 8 Dual-Port SRAM with Semaphores Features True dual-ported memory cells, which allow simultaneous reads of the same memory location 4K x 8 organization 0.65 micron
100 MHz LVDS Clock Generator
 100 MHz LVDS Clock Generator 100 MHz LVDS Clock Generator Features One low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) output pair Output frequency: 100 MHz External crystal frequency: 25 MHz Low RMS phase jitter
100 MHz LVDS Clock Generator 100 MHz LVDS Clock Generator Features One low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) output pair Output frequency: 100 MHz External crystal frequency: 25 MHz Low RMS phase jitter
LVDS Crystal Oscillator (XO)
 LVDS Crystal Oscillator (XO) Features Low jitter crystal oscillator (XO) Less than 1 ps typical root mean square (RMS) phase jitter Low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) output Output frequency from
LVDS Crystal Oscillator (XO) Features Low jitter crystal oscillator (XO) Less than 1 ps typical root mean square (RMS) phase jitter Low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) output Output frequency from
16-Mbit (1 M words 16 bit / 2 M words 8 bit) Static RAM with Error-Correcting Code (ECC)
 16-Mbit (1 M words 16 bit / 2 M words 8 bit) Static RAM with Error-Correcting Code (ECC) 16-Mbit (1 M words 16 bit / 2 M words 8 bit) Static RAM with Error-Correcting Code (ECC) Features Ultra-low standby
16-Mbit (1 M words 16 bit / 2 M words 8 bit) Static RAM with Error-Correcting Code (ECC) 16-Mbit (1 M words 16 bit / 2 M words 8 bit) Static RAM with Error-Correcting Code (ECC) Features Ultra-low standby
CE PSoC 4: Time-Stamped ADC Data Transfer Using DMA
 CE97091- PSoC 4: Time-Stamped ADC Data Transfer Using DMA Objective This code example uses a DMA channel with two descriptors to implement a time-stamped ADC data transfer. It uses the Watch Dog Timer
CE97091- PSoC 4: Time-Stamped ADC Data Transfer Using DMA Objective This code example uses a DMA channel with two descriptors to implement a time-stamped ADC data transfer. It uses the Watch Dog Timer
AN1090. NoBL : The Fast SRAM Architecture. Introduction. NoBL SRAM Description. Abstract. NoBL SRAM Operation
 AN1090 NoBL : The Fast SRAM Architecture Associated Project: No Associated Part Family: All NoBL SRAMs Software Version: None Related Application Notes: None Abstract AN1090 describes the operation of
AN1090 NoBL : The Fast SRAM Architecture Associated Project: No Associated Part Family: All NoBL SRAMs Software Version: None Related Application Notes: None Abstract AN1090 describes the operation of
16-Mbit (1024 K 16) nvsram
 16-Mbit (1024 K 16) nvsram Features 16-Mbit nonvolatile static random access memory (nvsram) 30-ns and 45-ns access times Logically organized as 1024 K 16 Hands-off automatic STORE on power-down with only
16-Mbit (1024 K 16) nvsram Features 16-Mbit nonvolatile static random access memory (nvsram) 30-ns and 45-ns access times Logically organized as 1024 K 16 Hands-off automatic STORE on power-down with only
CAT28C K-Bit Parallel EEPROM
 256K-Bit Parallel EEPROM HALOGENFREE LEAD TM FREE FEATURES Fast read access times: 120/150ns Low power CMOS dissipation: Active: 25 ma max Standby: 150 µa max Simple write operation: On-chip address and
256K-Bit Parallel EEPROM HALOGENFREE LEAD TM FREE FEATURES Fast read access times: 120/150ns Low power CMOS dissipation: Active: 25 ma max Standby: 150 µa max Simple write operation: On-chip address and
I/O 0 I/O 7 WE CE 2 OE CE 1 A17 A18
 2M x 8 Static RAM Features High speed t AA = 8, 10, 12 ns Low active power 1080 mw (max.) Operating voltages of 3.3 ± 0.3V 2.0V data retention Automatic power-down when deselected TTL-compatible inputs
2M x 8 Static RAM Features High speed t AA = 8, 10, 12 ns Low active power 1080 mw (max.) Operating voltages of 3.3 ± 0.3V 2.0V data retention Automatic power-down when deselected TTL-compatible inputs
16-Mbit (512 K words 32 bits) Static RAM with Error-Correcting Code (ECC)
 16-Mbit (512 K words 32 bits) Static RAM with Error-Correcting Code (ECC) 16-Mbit (512 K words 32 bits) Static RAM with Error-Correcting Code (ECC) Features High speed t AA = 10 ns/15 ns Embedded error-correcting
16-Mbit (512 K words 32 bits) Static RAM with Error-Correcting Code (ECC) 16-Mbit (512 K words 32 bits) Static RAM with Error-Correcting Code (ECC) Features High speed t AA = 10 ns/15 ns Embedded error-correcting
A 4 A 3 A 2 ROW DECODER 64K x 16 RAM Array I/O 1 I/O X 2048 I/O 9 I/O 16
 64K x 16 Static RAM Features Pin- and function-compatible with CY7C1021BV33 High speed t AA = 8, 10, 12, and 15 ns CMOS for optimum speed/power Low active power 360 mw (max.) Data retention at 2.0V Automatic
64K x 16 Static RAM Features Pin- and function-compatible with CY7C1021BV33 High speed t AA = 8, 10, 12, and 15 ns CMOS for optimum speed/power Low active power 360 mw (max.) Data retention at 2.0V Automatic
FM18L08 256Kb Bytewide 3V FRAM Memory
 Product Preview FM18L08 256Kb Bytewide 3V FRAM Memory Features 256K bit Ferroelectric NonVolatile RAM Organized as 32,768 x 8 bits 10 year Data Retention Unlimited Read/Write Cycles NoDelay Writes Advanced
Product Preview FM18L08 256Kb Bytewide 3V FRAM Memory Features 256K bit Ferroelectric NonVolatile RAM Organized as 32,768 x 8 bits 10 year Data Retention Unlimited Read/Write Cycles NoDelay Writes Advanced
FM24C16C-GTR. 16Kb Serial 5V F-RAM Memory. Features. Description. Pin Configuration NC NC NC VSS VDD WP SCL SDA. Ordering Information.
 Preliminary FM24C16C 16Kb Serial 5V F-RAM Memory Features 16K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 2,048 x 8 bits High Endurance (10 12 ) Read/Write Cycles 36 year Data Retention at +75 C NoDelay
Preliminary FM24C16C 16Kb Serial 5V F-RAM Memory Features 16K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 2,048 x 8 bits High Endurance (10 12 ) Read/Write Cycles 36 year Data Retention at +75 C NoDelay
1-Megabit (128K x 8) Low Voltage Paged Parallel EEPROMs AT28LV010
 BDTIC www.bdtic.com/atmel Features Single 3.3V ± 10% Supply Fast Read Access Time 200 ns Automatic Page Write Operation Internal Address and Data Latches for 128 Bytes Internal Control Timer Fast Write
BDTIC www.bdtic.com/atmel Features Single 3.3V ± 10% Supply Fast Read Access Time 200 ns Automatic Page Write Operation Internal Address and Data Latches for 128 Bytes Internal Control Timer Fast Write
CAT28C17A 16K-Bit CMOS PARALLEL EEPROM
 16K-Bit CMOS PARALLEL EEPROM HALOGENFREE LEAD TM FREE FEATURES Fast Read Access Times: 200 ns Low Power CMOS Dissipation: Active: 25 ma Max. Standby: 100 µa Max. Simple Write Operation: On-Chip Address
16K-Bit CMOS PARALLEL EEPROM HALOGENFREE LEAD TM FREE FEATURES Fast Read Access Times: 200 ns Low Power CMOS Dissipation: Active: 25 ma Max. Standby: 100 µa Max. Simple Write Operation: On-Chip Address
Nine-Output 3.3 V Buffer
 Nine-Output 3.3 V Buffer Nine-Output 3.3 V Buffer Features One-input to nine-output buffer/driver Supports two DIMMs or four SO-DIMMs with one additional output for feedback to an external or chipset phase-locked
Nine-Output 3.3 V Buffer Nine-Output 3.3 V Buffer Features One-input to nine-output buffer/driver Supports two DIMMs or four SO-DIMMs with one additional output for feedback to an external or chipset phase-locked
FM24C64C-GTR. 64Kb Serial 5V F-RAM Memory Features. Pin Configuration. Description A0 A1 A2 VSS VDD SCL SDA. Ordering Information.
 Preliminary FM24C64C 64Kb Serial 5V F-RAM Memory Features 64K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 8,192 x 8 bits High Endurance 1 Trillion (10 12 ) Read/Writes 36 Year Data Retention at +75
Preliminary FM24C64C 64Kb Serial 5V F-RAM Memory Features 64K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 8,192 x 8 bits High Endurance 1 Trillion (10 12 ) Read/Writes 36 Year Data Retention at +75
16-Mbit (1M words 16 bit) Static RAM
 16-Mbit (1M words 16 bit) Static RAM 16-Mbit (1M words 16 bit) Static RAM Features High speed t AA = 10 ns/15 ns Low active power I CC = 90 ma at 100 MHz Low CMOS standby current I SB2 = 20 ma (typ) Operating
16-Mbit (1M words 16 bit) Static RAM 16-Mbit (1M words 16 bit) Static RAM Features High speed t AA = 10 ns/15 ns Low active power I CC = 90 ma at 100 MHz Low CMOS standby current I SB2 = 20 ma (typ) Operating
FM24C Kb FRAM Serial Memory Features
 Preliminary FM24C512 512Kb FRAM Serial Memory Features 512Kbit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 65,536 x 8 bits High Endurance 10 Billion (10 10 ) Read/Writes 45 year Data Retention NoDelay Writes
Preliminary FM24C512 512Kb FRAM Serial Memory Features 512Kbit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 65,536 x 8 bits High Endurance 10 Billion (10 10 ) Read/Writes 45 year Data Retention NoDelay Writes
2K x 16 Dual-Port Static RAM
 2K x 16 Dual-Port Static RAM Features True dual-ported memory cells which allow simultaneous reads of the same memory location 2K x 16 organization 0.65-micron CMOS for optimum speed/power High-speed access:
2K x 16 Dual-Port Static RAM Features True dual-ported memory cells which allow simultaneous reads of the same memory location 2K x 16 organization 0.65-micron CMOS for optimum speed/power High-speed access:
FM24C16B-GTR. 16Kb Serial 5V F-RAM Memory. Features. Pin Configuration. Description. Ordering Information NC NC NC VSS VDD WP SCL SDA.
 Preliminary FM24C16B 16Kb Serial 5V F-RAM Memory Features 16K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 2,048 x 8 bits High Endurance (10 12 ) Read/Write Cycles 38 year Data Retention NoDelay Writes
Preliminary FM24C16B 16Kb Serial 5V F-RAM Memory Features 16K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 2,048 x 8 bits High Endurance (10 12 ) Read/Write Cycles 38 year Data Retention NoDelay Writes
16-Kbit (2 K 8) Serial (I 2 C) F-RAM
 16-Kbit (2 K 8) erial (I 2 C) F-RAM 256-Kbit (32 K 8) erial (I 2 C) nvram Features 16-Kbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 2 K 8 High-endurance 100 trillion (10 14 ) read/writes
16-Kbit (2 K 8) erial (I 2 C) F-RAM 256-Kbit (32 K 8) erial (I 2 C) nvram Features 16-Kbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 2 K 8 High-endurance 100 trillion (10 14 ) read/writes
512-Kbit (64 K 8) Serial (I 2 C) F-RAM
 512-Kbit (64 K 8) erial (I 2 C) F-RAM 256-Kbit (32 K 8) erial (I 2 C) nvram Features 512-Kbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 64 K 8 High-endurance 100 trillion (10 14
512-Kbit (64 K 8) erial (I 2 C) F-RAM 256-Kbit (32 K 8) erial (I 2 C) nvram Features 512-Kbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 64 K 8 High-endurance 100 trillion (10 14
4-Mbit (256K words 16 bit) Static RAM
 4-Mbit (256K words 16 bit) Static RAM 4-Mbit (256K words 16 bit) Static RAM Features High speed t AA = 10 ns / 15 ns Low active and standby currents Active current: I CC = 38-mA typical Standby current:
4-Mbit (256K words 16 bit) Static RAM 4-Mbit (256K words 16 bit) Static RAM Features High speed t AA = 10 ns / 15 ns Low active and standby currents Active current: I CC = 38-mA typical Standby current:
FM24CL04 4Kb FRAM Serial Memory
 4Kb FRAM Serial Memory Features 4K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 512 x 8 bits Unlimited Read/Writes 45 Year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric Process
4Kb FRAM Serial Memory Features 4K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 512 x 8 bits Unlimited Read/Writes 45 Year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric Process
Pm39F010 / Pm39F020 / Pm39F040
 1 Mbit / 2 Mbit / 4 Mbit 5 Volt-only CMOS Flash Memory FEATURES Single Power Supply Operation - Low voltage range: 4.5 V - 5.5 V Memory Organization - Pm39F010: 128K x 8 (1 Mbit) - Pm39F020: 256K x 8 (2
1 Mbit / 2 Mbit / 4 Mbit 5 Volt-only CMOS Flash Memory FEATURES Single Power Supply Operation - Low voltage range: 4.5 V - 5.5 V Memory Organization - Pm39F010: 128K x 8 (1 Mbit) - Pm39F020: 256K x 8 (2
64-Kbit (8K 8) SPI nvsram
 64-Kbit (8K 8) SPI nvsram 64-Kbit (8K 8) SPI nvsram Features 64-Kbit nonvolatile static random access memory (nvsram) internally organized as 8K 8 STORE to QuantumTrap nonvolatile elements initiated automatically
64-Kbit (8K 8) SPI nvsram 64-Kbit (8K 8) SPI nvsram Features 64-Kbit nonvolatile static random access memory (nvsram) internally organized as 8K 8 STORE to QuantumTrap nonvolatile elements initiated automatically
THIS SPEC IS OBSOLETE
 THIS SPEC IS OBSOLETE Spec No: 001-17581 Spec Title: WIRELESSUSB(TM) LP RDK JAPANESE RADIO LAW TESTING AND VERIFICATION - AN17581 Replaced by: NONE AN17581 WirelessUSB LP RDK Japanese Radio Law Testing
THIS SPEC IS OBSOLETE Spec No: 001-17581 Spec Title: WIRELESSUSB(TM) LP RDK JAPANESE RADIO LAW TESTING AND VERIFICATION - AN17581 Replaced by: NONE AN17581 WirelessUSB LP RDK Japanese Radio Law Testing
Clock Programming Kit
 Clock Programming Kit Clock Programming Kit Features Supports these field-programmable clock generators: CY2077FS, CY2077FZ, CY22050KF, CY22150KF, CY22381F, CY22392F, CY22393F, CY22394F, CY22395F, CY23FP12,
Clock Programming Kit Clock Programming Kit Features Supports these field-programmable clock generators: CY2077FS, CY2077FZ, CY22050KF, CY22150KF, CY22381F, CY22392F, CY22393F, CY22394F, CY22395F, CY23FP12,
8-Mbit (512K words 16 bit) Static RAM with Error Correcting Code (ECC)
 8-Mbit (512K words 16 bit) Static RAM with Error Correcting Code (ECC) 8-Mbit (512K words 16 bit) Static RAM with Error Correcting Code (ECC) Features Ultra-low standby current Typical standby current:
8-Mbit (512K words 16 bit) Static RAM with Error Correcting Code (ECC) 8-Mbit (512K words 16 bit) Static RAM with Error Correcting Code (ECC) Features Ultra-low standby current Typical standby current:
64K x 32 Static RAM Module
 31 CYM1831 Features High-density 2-Mbit SRAM module 32-bit standard footprint supports densities from 16K x 32 through 1M x 32 High-speed CMOS SRAMs Access time of 15 ns Low active power 5.3W (max.) SMD
31 CYM1831 Features High-density 2-Mbit SRAM module 32-bit standard footprint supports densities from 16K x 32 through 1M x 32 High-speed CMOS SRAMs Access time of 15 ns Low active power 5.3W (max.) SMD
8-Mbit (1024 K 8/512 K 16) nvsram
 8-Mbit (1024 K 8/512 K 16) nvsram 8-Mbit (1024 K 8/512 K 16) nvsram Features 20 ns, 25 ns, and 45 ns access times Internally organized as 1024 K 8 (CY14B108L) or 512 K 16 () Hands off automatic STORE on
8-Mbit (1024 K 8/512 K 16) nvsram 8-Mbit (1024 K 8/512 K 16) nvsram Features 20 ns, 25 ns, and 45 ns access times Internally organized as 1024 K 8 (CY14B108L) or 512 K 16 () Hands off automatic STORE on
CAT22C Bit Nonvolatile CMOS Static RAM
 256-Bit Nonvolatile CMOS Static RAM FEATURES Single 5V Supply Fast RAM Access Times: 200ns 300ns Infinite E 2 PROM to RAM Recall CMOS and TTL Compatible I/O Power Up/Down Protection 100,000 Program/Erase
256-Bit Nonvolatile CMOS Static RAM FEATURES Single 5V Supply Fast RAM Access Times: 200ns 300ns Infinite E 2 PROM to RAM Recall CMOS and TTL Compatible I/O Power Up/Down Protection 100,000 Program/Erase
64K (8K x 8) Battery-Voltage Parallel EEPROM with Page Write and Software Data Protection AT28BV64B
 Features Single 2.7V to 3.6V Supply Hardware and Software Data Protection Low Power Dissipation 15mA Active Current 20µA CMOS Standby Current Fast Read Access Time 200ns Automatic Page Write Operation
Features Single 2.7V to 3.6V Supply Hardware and Software Data Protection Low Power Dissipation 15mA Active Current 20µA CMOS Standby Current Fast Read Access Time 200ns Automatic Page Write Operation
256K x 18 Synchronous 3.3V Cache RAM
 Features Supports 117-MHz microprocessor cache systems with zero wait states 256K by 18 common I/O Fast clock-to-output times 7.5 ns (117-MHz version) Two-bit wrap-around counter supporting either interleaved
Features Supports 117-MHz microprocessor cache systems with zero wait states 256K by 18 common I/O Fast clock-to-output times 7.5 ns (117-MHz version) Two-bit wrap-around counter supporting either interleaved
FM24C Kb FRAM Serial Memory Features
 256Kb FRAM Serial Memory Features 256Kbit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 32,768 x 8 bits High Endurance 10 Billion (10 10 ) Read/Writes 45 year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability
256Kb FRAM Serial Memory Features 256Kbit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 32,768 x 8 bits High Endurance 10 Billion (10 10 ) Read/Writes 45 year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability
DS1345W 3.3V 1024k Nonvolatile SRAM with Battery Monitor
 19-5587; Rev 10/10 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES 10 years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Power supply monitor resets processor when
19-5587; Rev 10/10 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES 10 years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Power supply monitor resets processor when
4-Megabit (512K x 8) 5-volt Only CMOS Flash Memory AT49F040 AT49F040T AT49F040/040T AT49F040/040T. Features. Description. Pin Configurations
 Features Single Voltage Operation 5V Read 5V Reprogramming Fast Read Access Time - 70 ns Internal Program Control and Timer 16K bytes Boot Block With Lockout Fast Erase Cycle Time - 10 seconds Byte By
Features Single Voltage Operation 5V Read 5V Reprogramming Fast Read Access Time - 70 ns Internal Program Control and Timer 16K bytes Boot Block With Lockout Fast Erase Cycle Time - 10 seconds Byte By
Pm39LV512 / Pm39LV010 / Pm39LV020 / Pm39LV040
 512 Kbit / 1Mbit / 2Mbit / 4Mbit 3.0 Volt-only CMOS Flash Memory FEATURES Single Power Supply Operation - Low voltage range: 2.7 V - 3.6 V Memory Organization - Pm39LV512: 64K x 8 (512 Kbit) - Pm39LV010:
512 Kbit / 1Mbit / 2Mbit / 4Mbit 3.0 Volt-only CMOS Flash Memory FEATURES Single Power Supply Operation - Low voltage range: 2.7 V - 3.6 V Memory Organization - Pm39LV512: 64K x 8 (512 Kbit) - Pm39LV010:
ESMT M24L416256SA. 4-Mbit (256K x 16) Pseudo Static RAM. Features. Functional Description. Logic Block Diagram
 PSRAM 4-Mbit (256K x 16) Pseudo Static RAM Features Wide voltage range: 2.7V 3.6V Access time: 55 ns, 60 ns and 70 ns Ultra-low active power Typical active current: 1 ma @ f = 1 MHz Typical active current:
PSRAM 4-Mbit (256K x 16) Pseudo Static RAM Features Wide voltage range: 2.7V 3.6V Access time: 55 ns, 60 ns and 70 ns Ultra-low active power Typical active current: 1 ma @ f = 1 MHz Typical active current:
Use the Status Register when the firmware needs to query the state of internal digital signals.
 1.60 Features Up to 8-bit General Description The allows the firmware to read digital signals. When to Use a Use the when the firmware needs to query the state of internal digital signals. Input/Output
1.60 Features Up to 8-bit General Description The allows the firmware to read digital signals. When to Use a Use the when the firmware needs to query the state of internal digital signals. Input/Output
256-Kbit (32K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM with Extended Temperature
 256-Kbit (32K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM with Extended Temperature 256-Kbit (32K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM with Extended Temperature Features 256-Kbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized
256-Kbit (32K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM with Extended Temperature 256-Kbit (32K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM with Extended Temperature Features 256-Kbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized
EZ-USB NX2LP USB 2.0 NAND Flash Controller
 EZ-USB NX2LP USB 2.0 NAND Flash Controller EZ-USB NX2LP USB 2.0 NAND Flash Controller Features High-Speed (480-Mbps) or Full-Speed (12-Mbps) USB support Both common NAND page sizes supported 512 bytes
EZ-USB NX2LP USB 2.0 NAND Flash Controller EZ-USB NX2LP USB 2.0 NAND Flash Controller Features High-Speed (480-Mbps) or Full-Speed (12-Mbps) USB support Both common NAND page sizes supported 512 bytes
1 Megabit Serial Flash EEPROM SST45LF010
 EEPROM FEATURES: Single.0-.V Read and Write Operations Serial Interface Architecture SPI Compatible: Mode 0 and Mode Byte Serial Read with Single Command Superior Reliability Endurance: 00,000 Cycles (typical)
EEPROM FEATURES: Single.0-.V Read and Write Operations Serial Interface Architecture SPI Compatible: Mode 0 and Mode Byte Serial Read with Single Command Superior Reliability Endurance: 00,000 Cycles (typical)
16-Mbit (2048K 8/1024K 16/512K 32) nvsram
 16-Mbit (2048K 8/1024K 16/512K 32) nvsram 16-Mbit (2048K 8/1024K 16/512K 32) nvsram Features 16-Mbit nonvolatile static random access memory (nvsram) 25-ns, 30-ns and 45-ns access times Internally organized
16-Mbit (2048K 8/1024K 16/512K 32) nvsram 16-Mbit (2048K 8/1024K 16/512K 32) nvsram Features 16-Mbit nonvolatile static random access memory (nvsram) 25-ns, 30-ns and 45-ns access times Internally organized
1-megabit (64K x 16) 5-volt Only Flash Memory AT49F1024A Features Description Pin Configurations
 BDTIC www.bdtic.com/atmel Features Single-voltage Operation 5V Read 5V Reprogramming Fast Read Access Time 45 ns Internal Program Control and Timer 8K Word Boot Block with Lockout Fast Erase Cycle Time
BDTIC www.bdtic.com/atmel Features Single-voltage Operation 5V Read 5V Reprogramming Fast Read Access Time 45 ns Internal Program Control and Timer 8K Word Boot Block with Lockout Fast Erase Cycle Time
SST 29EE V-only 1 Megabit Page Mode EEPROM
 Data Sheet SST 29EE010 July 1996 5.1 Features: Single 5.0-Volt Read and Write Operations CMOS SuperFlash EEPROM Technology Endurance: 100,000 Cycles (typical) Greater than 100 years Data Retention Low
Data Sheet SST 29EE010 July 1996 5.1 Features: Single 5.0-Volt Read and Write Operations CMOS SuperFlash EEPROM Technology Endurance: 100,000 Cycles (typical) Greater than 100 years Data Retention Low
256K-Bit PARALLEL EEPROM
 256K-Bit PARALLEL EEPROM FEATURES Fast read access times: 120/150ns Low power CMOS dissipation: Active: 25 ma max Standby: 150 µa max Simple write operation: On-chip address and data latches Self-timed
256K-Bit PARALLEL EEPROM FEATURES Fast read access times: 120/150ns Low power CMOS dissipation: Active: 25 ma max Standby: 150 µa max Simple write operation: On-chip address and data latches Self-timed
AT49BV004(T) TSOP Top View Type 1 1. AT49BV4096A(T) TSOP Top View Type 1 A16 BYTE GND I/O7 I/O14 I/O6 I/O13 I/O5 I/O12 I/O4 VCC I/O11 I/O3 I/O10 I/O2
 Features 2.7V to 3.6V Read/Write Operation Fast Read Access Time - 120 ns Internal Erase/Program Control Sector Architecture One 8K Words (16K bytes) Boot Block with Programming Lockout Two 4K Words (8K
Features 2.7V to 3.6V Read/Write Operation Fast Read Access Time - 120 ns Internal Erase/Program Control Sector Architecture One 8K Words (16K bytes) Boot Block with Programming Lockout Two 4K Words (8K
1-Megabit (128K x 8) 5-volt Only Flash Memory AT29C010A. Features. Description. Pin Configurations
 Features Fast Read Access Time - 70 ns 5-Volt Only Reprogramming Sector Program Operation Single Cycle Reprogram (Erase and Program) 1024 Sectors (128 bytes/sector) Internal Address and Data Latches for
Features Fast Read Access Time - 70 ns 5-Volt Only Reprogramming Sector Program Operation Single Cycle Reprogram (Erase and Program) 1024 Sectors (128 bytes/sector) Internal Address and Data Latches for
Use the Status Register when the firmware needs to query the state of internal digital signals.
 1.70 Features Up to 8-bit General Description The allows the firmware to read digital signals. When to Use a Use the when the firmware needs to query the state of internal digital signals. Input/Output
1.70 Features Up to 8-bit General Description The allows the firmware to read digital signals. When to Use a Use the when the firmware needs to query the state of internal digital signals. Input/Output
4-Mbit (256K 16) Automotive nvsram
 4-Mbit (256K 16) Automotive nvsram 4-Mbit (256K 16) Automotive nvsram Features 25 ns and 45 ns access times Internally organized as 256K 16 Hands off automatic STORE on power-down with only a small capacitor
4-Mbit (256K 16) Automotive nvsram 4-Mbit (256K 16) Automotive nvsram Features 25 ns and 45 ns access times Internally organized as 256K 16 Hands off automatic STORE on power-down with only a small capacitor
4K x 16/18 and 8K x 16/18 Dual-Port Static RAM with SEM, INT, BUSY
 4K x 16/18 and 8K x 16/18 Dual-Port Static RAM with SEM, INT, BUSY Features True dual-ported memory cells that allow simultaneous reads of the same memory location 4K 16 organization (CY7C024E) 4K 18 organization
4K x 16/18 and 8K x 16/18 Dual-Port Static RAM with SEM, INT, BUSY Features True dual-ported memory cells that allow simultaneous reads of the same memory location 4K 16 organization (CY7C024E) 4K 18 organization
4-Mbit (512 K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM
 4-Mbit (512 K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM 4-Mbit (512 K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM Features 4-Mbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 512 K 8 High-endurance 100 trillion (10 14 ) read/writes
4-Mbit (512 K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM 4-Mbit (512 K 8) Serial (SPI) F-RAM Features 4-Mbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 512 K 8 High-endurance 100 trillion (10 14 ) read/writes
1-Megabit (128K x 8) Low Voltage Paged Parallel EEPROMs
 Features Single 3.3V ± 10% Supply Fast Read Access Time - 200 ns Automatic Page Write Operation Internal Address and Data Latches for 128 Bytes Internal Control Timer Fast Write Cycle Time Page Write Cycle
Features Single 3.3V ± 10% Supply Fast Read Access Time - 200 ns Automatic Page Write Operation Internal Address and Data Latches for 128 Bytes Internal Control Timer Fast Write Cycle Time Page Write Cycle
FM25L16-DG. 16Kb FRAM Serial 3V Memory. Features. Pin Configuration
 16Kb FRAM Serial 3V Memory Features 16K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 2,048 x 8 bits Unlimited Read/Write Cycles 45 Year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric
16Kb FRAM Serial 3V Memory Features 16K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 2,048 x 8 bits Unlimited Read/Write Cycles 45 Year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric
128K x 36 Synchronous-Pipelined Cache RAM
 1CY7C1347 Features Supports 100-MHz bus for Pentium and PowerPC operations with zero wait states Fully registered inputs and outputs for pipelined operation 128K by 36 common I/O architecture 3.3V core
1CY7C1347 Features Supports 100-MHz bus for Pentium and PowerPC operations with zero wait states Fully registered inputs and outputs for pipelined operation 128K by 36 common I/O architecture 3.3V core
FM25L04 4Kb FRAM Serial 3V Memory
 4Kb FRAM Serial 3V Memory Features 4K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 512 x 8 bits Unlimited Read/Write Cycles 45 Year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric
4Kb FRAM Serial 3V Memory Features 4K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 512 x 8 bits Unlimited Read/Write Cycles 45 Year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric
Voltage Reference (Vref) Features. General Description. Input/Output Connections. When to Use a Vref Voltage references and supplies
 PSoC Creator Component Datasheet Voltage Reference (Vref) 1.60 Features Voltage references and supplies Multiple options Bandgap principle to achieve temperature, and voltage stability General Description
PSoC Creator Component Datasheet Voltage Reference (Vref) 1.60 Features Voltage references and supplies Multiple options Bandgap principle to achieve temperature, and voltage stability General Description
FM24CL64 64Kb Serial 3V F-RAM Memory Features
 64Kb Serial 3V F-RAM Memory Features 64K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 8,192 x 8 bits Unlimited Read/Write Cycles 45 year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric
64Kb Serial 3V F-RAM Memory Features 64K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 8,192 x 8 bits Unlimited Read/Write Cycles 45 year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric
DS1225Y 64k Nonvolatile SRAM
 19-5603; Rev 10/10 NOT RECOMMENDED FOR NEW DESIGNS 64k Nonvolatile SRAM www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES 10 years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during
19-5603; Rev 10/10 NOT RECOMMENDED FOR NEW DESIGNS 64k Nonvolatile SRAM www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES 10 years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during
Writing to Internal Flash in PSoC 3 and PSoC 5
 Writing to Internal Flash in PSoC 3 and PSoC 5 Code Example Objective CE62384 demonstrates how to write to the internal flash to change its contents during run time. CE62384 Associated Part Families: CY8C3xxx
Writing to Internal Flash in PSoC 3 and PSoC 5 Code Example Objective CE62384 demonstrates how to write to the internal flash to change its contents during run time. CE62384 Associated Part Families: CY8C3xxx
2Mb Ultra-Low Power Asynchronous CMOS SRAM. Features. Power Supply (Vcc)
 2Mb Ultra-Low Power Asynchronous CMOS SRAM 128Kx16 bit Features Overview The is an integrated memory device containing a 2 Mbit Static Random Access Memory organized as 131,072 words by 16 bits. The device
2Mb Ultra-Low Power Asynchronous CMOS SRAM 128Kx16 bit Features Overview The is an integrated memory device containing a 2 Mbit Static Random Access Memory organized as 131,072 words by 16 bits. The device
Excelon -Auto 2-Mbit (256K 8) Automotive-E Serial (SPI) F-RAM
 Excelon -Auto 2-Mbit (256K 8) Automotive-E Serial (SPI) F-RAM 2-Mbit (256K 8) Automotive-E Serial (SPI) F-RAM Features 2-Mbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 256K 8 Virtually
Excelon -Auto 2-Mbit (256K 8) Automotive-E Serial (SPI) F-RAM 2-Mbit (256K 8) Automotive-E Serial (SPI) F-RAM Features 2-Mbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 256K 8 Virtually
3.3 Volt, Byte Alterable E 2 PROM
 1M X28LV010 128K x 8 Bit 3.3 Volt, Byte Alterable E 2 PROM FEATURES Access Time: 70, 90, 120, 150ns Simple Byte and Page Write Single 3.3V±10% supply No external high voltages or V PP control circuits
1M X28LV010 128K x 8 Bit 3.3 Volt, Byte Alterable E 2 PROM FEATURES Access Time: 70, 90, 120, 150ns Simple Byte and Page Write Single 3.3V±10% supply No external high voltages or V PP control circuits
SST 29EE V-only 512 Kilobit Page Mode EEPROM
 Data Sheet SST 29EE512 June 1997 2.1 Features: Single 5.0-Volt Read and Write Operations CMOS SuperFlash EEPROM Technology Endurance: 100,000 Cycles (typical) Greater than 100 years Data Retention Low
Data Sheet SST 29EE512 June 1997 2.1 Features: Single 5.0-Volt Read and Write Operations CMOS SuperFlash EEPROM Technology Endurance: 100,000 Cycles (typical) Greater than 100 years Data Retention Low
Programmable Threshold Comparator Data Sheet
 10. Programmable Threshold Comparator Programmable Threshold Comparator Data Sheet Copyright 2001-2009 Cypress Semiconductor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. CMPPRG Resources CY8C29/27/24/22xxx, CY8C23x33,
10. Programmable Threshold Comparator Programmable Threshold Comparator Data Sheet Copyright 2001-2009 Cypress Semiconductor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. CMPPRG Resources CY8C29/27/24/22xxx, CY8C23x33,
DS1249Y/AB 2048k Nonvolatile SRAM
 19-5631; Rev 11/10 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES 10 years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Unlimited write cycles Low-power CMOS operation
19-5631; Rev 11/10 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES 10 years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Unlimited write cycles Low-power CMOS operation
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. APPLICATION NOTE A V A I L A B L E AN61 16K X25160 2K x 8 Bit SPI Serial
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. APPLICATION NOTE A V A I L A B L E AN61 16K X25160 2K x 8 Bit SPI Serial
Battery-Voltage. 16K (2K x 8) Parallel EEPROMs AT28BV16. Features. Description. Pin Configurations
 Features 2.7 to 3.6V Supply Full Read and Write Operation Low Power Dissipation 8 ma Active Current 50 µa CMOS Standby Current Read Access Time - 250 ns Byte Write - 3 ms Direct Microprocessor Control
Features 2.7 to 3.6V Supply Full Read and Write Operation Low Power Dissipation 8 ma Active Current 50 µa CMOS Standby Current Read Access Time - 250 ns Byte Write - 3 ms Direct Microprocessor Control
Quantum Trap 512 X 512 STORE RECALL STATIC RAM ARRAY 512 X 512 COLUMN I/O COLUMN DEC
 Features 35 ns and 45 ns Access Times Automatic nonvolatile STORE on power loss Nonvolatile STORE under hardware or software control Automatic RECALL to SRAM on power up Unlimited Read/Write endurance
Features 35 ns and 45 ns Access Times Automatic nonvolatile STORE on power loss Nonvolatile STORE under hardware or software control Automatic RECALL to SRAM on power up Unlimited Read/Write endurance
HM628128BI Series. 131,072-word 8-bit High speed CMOS Static RAM
 131,072-word 8-bit High speed CMOS Static RAM ADE-203-363A(Z) Rev. 1.0 Apr. 28, 1995 The Hitachi HM628128BI is a CMOS static RAM organized 131,072-word 8-bit. It realizes higher density, higher performance
131,072-word 8-bit High speed CMOS Static RAM ADE-203-363A(Z) Rev. 1.0 Apr. 28, 1995 The Hitachi HM628128BI is a CMOS static RAM organized 131,072-word 8-bit. It realizes higher density, higher performance
4-Kbit (512 8) Serial (SPI) Automotive F-RAM
 4-Kbit (512 8) Serial (SPI) Automotive F-RAM 4-Kbit (512 8) Serial (SPI) Automotive F-RAM Features 4-Kbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 512 8 High-endurance 10 trillion
4-Kbit (512 8) Serial (SPI) Automotive F-RAM 4-Kbit (512 8) Serial (SPI) Automotive F-RAM Features 4-Kbit ferroelectric random access memory (F-RAM) logically organized as 512 8 High-endurance 10 trillion
S-2812A/2817A. Rev.1.1. CMOS 16K-bit PARALLEL E 2 PROM
 Rev.1.1 CMOS 16K-bit PARALLEL E 2 PROM The S-2812A and the S-2817A are low power 2K 8-bit parallel E 2 PROMs. The S-2812A features wide operating voltage range, and the S-2817A features 5-V single power
Rev.1.1 CMOS 16K-bit PARALLEL E 2 PROM The S-2812A and the S-2817A are low power 2K 8-bit parallel E 2 PROMs. The S-2812A features wide operating voltage range, and the S-2817A features 5-V single power
This optional pin is present if the Mode parameter is set to SyncMode or PulseMode. Otherwise, the clock input does not show.
 1.60 Features Up to 8-bit General Description The allows the firmware to output digital signals. When to Use a Use a when the firmware needs to interact with a digital system. You can also use the as a
1.60 Features Up to 8-bit General Description The allows the firmware to output digital signals. When to Use a Use a when the firmware needs to interact with a digital system. You can also use the as a
Battery-Voltage. 256K (32K x 8) Parallel EEPROMs AT28BV256. Features. Description. Pin Configurations
 Features Single 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Fast Read Access Time - 200 ns Automatic Page Write Operation Internal Address and Data Latches for 64 Bytes Internal Control Timer Fast Write Cycle Times Page Write
Features Single 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Fast Read Access Time - 200 ns Automatic Page Write Operation Internal Address and Data Latches for 64 Bytes Internal Control Timer Fast Write Cycle Times Page Write
AT25PE40. 4-Mbit DataFlash-L Page Erase Serial Flash Memory ADVANCE DATASHEET. Features
 4-Mbit DataFlash-L Page Erase Serial Flash Memory Features ADVANCE DATASHEET Single 1.65V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports SPI modes 0 and 3 Supports RapidS operation
4-Mbit DataFlash-L Page Erase Serial Flash Memory Features ADVANCE DATASHEET Single 1.65V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports SPI modes 0 and 3 Supports RapidS operation
DS1243Y 64K NV SRAM with Phantom Clock
 19-6076; Rev 11/11 DS1243Y 64K NV SRAM with Phantom Clock FEATURES Real-Time Clock Keeps Track of Hundredths of Seconds, Seconds, Minutes, Hours, Days, Date of the Month, Months, and Years 8K x 8 NV SRAM
19-6076; Rev 11/11 DS1243Y 64K NV SRAM with Phantom Clock FEATURES Real-Time Clock Keeps Track of Hundredths of Seconds, Seconds, Minutes, Hours, Days, Date of the Month, Months, and Years 8K x 8 NV SRAM
FM25L04 4Kb FRAM Serial 3V Memory
 4Kb FRAM Serial 3V Memory Features 4K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 512 x 8 bits Unlimited Read/Write Cycles 45 Year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric
4Kb FRAM Serial 3V Memory Features 4K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 512 x 8 bits Unlimited Read/Write Cycles 45 Year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric
CAT28LV kb CMOS Parallel EEPROM
 64 kb CMOS Parallel EEPROM Description The CAT28LV65 is a low voltage, low power, CMOS Parallel EEPROM organized as 8K x 8 bits. It requires a simple interface for in system programming. On chip address
64 kb CMOS Parallel EEPROM Description The CAT28LV65 is a low voltage, low power, CMOS Parallel EEPROM organized as 8K x 8 bits. It requires a simple interface for in system programming. On chip address
GT24C WIRE. 1024K Bits. Serial EEPROM
 GT24C1024 2-WIRE 1024K Bits Serial EEPROM Copyright 2013 Giantec Semiconductor Inc. (Giantec). All rights reserved. Giantec reserves the right to make changes to this specification and its products at
GT24C1024 2-WIRE 1024K Bits Serial EEPROM Copyright 2013 Giantec Semiconductor Inc. (Giantec). All rights reserved. Giantec reserves the right to make changes to this specification and its products at
P3C1256 HIGH SPEED 32K x 8 3.3V STATIC CMOS RAM
 HIGH SPEED 3K x 8 3.3 STATIC CMOS RAM FEATURES 3.3 Power Supply High Speed (Equal Access and Cycle Times) 1///5 (Commercial) //5 (Industrial) Low Power Single 3.3 olts ±.3olts Power Supply Easy Memory
HIGH SPEED 3K x 8 3.3 STATIC CMOS RAM FEATURES 3.3 Power Supply High Speed (Equal Access and Cycle Times) 1///5 (Commercial) //5 (Industrial) Low Power Single 3.3 olts ±.3olts Power Supply Easy Memory
AN SIO Tips and Tricks in PSoC 3 / PSoC 5. Application Note Abstract. Introduction
 SIO Tips and Tricks in PSoC 3 / PSoC 5 Application Note Abstract AN60580 Author: Pavankumar Vibhute Associated Project: Yes Associated Part Family: CY8C38xxxx Software Version: PSoC Creator Associated
SIO Tips and Tricks in PSoC 3 / PSoC 5 Application Note Abstract AN60580 Author: Pavankumar Vibhute Associated Project: Yes Associated Part Family: CY8C38xxxx Software Version: PSoC Creator Associated
DS1265Y/AB 8M Nonvolatile SRAM
 19-5616; Rev 11/10 www.maxim-ic.com 8M Nonvolatile SRAM FEATURES 10 years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Unlimited write cycles
19-5616; Rev 11/10 www.maxim-ic.com 8M Nonvolatile SRAM FEATURES 10 years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Unlimited write cycles
AT45DB021E. 2-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 64-Kbits), 1.65V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory PRELIMINARY DATASHEET. Features
 AT45DB021E 2-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 64-Kbits), 1.65V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory Features PRELIMINARY DATASHEET Single 1.65V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports
AT45DB021E 2-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 64-Kbits), 1.65V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory Features PRELIMINARY DATASHEET Single 1.65V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports
This optional pin is present if the Mode parameter is set to SyncMode or PulseMode. Otherwise, the clock input does not show.
 1.70 Features Up to 8-bit General Description The allows the firmware to output digital signals. When to Use a Use a when the firmware needs to interact with a digital system. You can also use the as a
1.70 Features Up to 8-bit General Description The allows the firmware to output digital signals. When to Use a Use a when the firmware needs to interact with a digital system. You can also use the as a
THIS SPEC IS OBSOLETE
 THIS SPEC IS OBSOLETE Spec Number: 001-84741 Spec Title: PSoC 5 to PSoC 5LP Migration Guide Sunset Owner: MKEA Replaced By: None AN84741 Author: Mark Ainsworth Associated Project: No Associated Part Family:
THIS SPEC IS OBSOLETE Spec Number: 001-84741 Spec Title: PSoC 5 to PSoC 5LP Migration Guide Sunset Owner: MKEA Replaced By: None AN84741 Author: Mark Ainsworth Associated Project: No Associated Part Family:
8 to 1 Analog Multiplexer Datasheet AMux8 V 1.1. Features and Overview
 Datasheet AMux8 V 1.1 001-13257 Rev. *J 8 to 1 Analog Multiplexer Copyright 2001-2015 Cypress Semiconductor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. Resources PSoC Blocks API Memory (Bytes) Digital Analog CT
Datasheet AMux8 V 1.1 001-13257 Rev. *J 8 to 1 Analog Multiplexer Copyright 2001-2015 Cypress Semiconductor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. Resources PSoC Blocks API Memory (Bytes) Digital Analog CT
GT34C02. 2Kb SPD EEPROM
 Advanced GT34C02 2Kb SPD EEPROM Copyright 2010 Giantec Semiconductor Inc. (Giantec). All rights reserved. Giantec reserves the right to make changes to this specification and its products at any time without
Advanced GT34C02 2Kb SPD EEPROM Copyright 2010 Giantec Semiconductor Inc. (Giantec). All rights reserved. Giantec reserves the right to make changes to this specification and its products at any time without
