DS0141 Datasheet. PolarFire. Preliminary
|
|
|
- Delilah Blake
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DS0141 Datasheet PolarFire Preliminary
2 Contents 1 Revision History Revision Revision Revision Overview References Device Offering Silicon Status DC Characteristics Absolute Maximum Rating Recommended Operating Conditions DC Characteristics over Recommended Operating Conditions Maximum Allowed Overshoot and Undershoot Input and Output DC Input and Output Levels Differential DC Input and Output Levels Complementary Differential DC Input and Output Levels HSIO On-Die Termination GPIO On-Die Termination AC Switching Characteristics I/O Standards Specifications Input Delay Measurement Methodology Maximum PHY Rate for Memory Interface IP Output Delay Measurement Methodology Input Buffer Speed Output Buffer Speed Maximum PHY Rate for Memory Interface IP User I/O Switching Characteristics Clocking Specifications Clocking PLL DLL RC Oscillators Fabric Specifications Math Blocks SRAM Blocks Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2
3 7.4 Transceiver Switching Characteristics Transceiver Performance Transceiver Reference Clock Performance Transceiver Reference Clock I/O Standards Transceiver Interface Performance Transmitter Performance Receiver Performance Transceiver Protocol Characteristics PCI Express Interlaken GbE (10GBASE-R, and 10GBASE-KR) GbE (1000BASE-T) SGMII and QSGMII SDI CPRI JESD204B Non-Volatile Characteristics FPGA Programming Cycle and Retention FPGA Programming Time FPGA Bitstream Sizes Digest Cycles Digest Time Zeroization Time Verify Time Authentication Time Secure NVM Performance Secure NVM Programming Cycles System Services System Services Throughput Characteristics Fabric Macros UJTAG Switching Characteristics UJTAG_SEC Switching Characteristics USPI Switching Characteristics Tamper Detectors System Controller Suspend Switching Characteristics Dynamic Reconfiguration Interface Power-Up to Functional Timing Power-On (Cold) Reset Initialization Sequence Warm Reset Initialization Sequence Power-On Reset Voltages Design Dependence of T PUFT and T WRFT Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2
4 7.9.5 Cold Reset to Fabric and I/Os (Low Speed) Functional Warm Reset to Fabric and I/Os (Low Speed) Functional Miscellaneous Initialization Parameters I/O Calibration Dedicated Pins JTAG Switching Characteristics SPI Switching Characteristics SmartDebug Probe Switching Characteristics DEVRST_N Switching Characteristics FF_EXIT Switching Characteristics User Crypto TeraFire 5200B Switching Characteristics TeraFire 5200B Throughput Characteristics Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2
5 1 Revision History The revision history describes the changes that were implemented in the document. The changes are listed by revision, starting with the most current publication. 1 Revision 2 Revision 2 was published in June The following is a summary of changes. The datasheet has moved to preliminary status. Every table has been updated. 2 Revision 1 Revision 1 was published in August The following is a summary of changes. LVDS specifications changed to 25G. For more information, see HSIO Maximum Input Buffer Speed and HSIO Maximum Output Buffer Speed. LVDS18, LVDS25/LVDS33, and LVDS25 specifications changed to 800 Mbps. For more information, see I/O Standards Specifications. A note was added indicting a zeroization cycle counts as a programming cycle. For more information, see Non-Volatile Characteristics. A note was added defining power down conditions for programming recovery conditions. For more information, see Power-Supply Ramp Times. 3 Revision 0 Revision 0 was the first publication of this document. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 1
6 2 Overview This datasheet describes PolarFire FPGA device characteristics with industrial temperature range ( 40 C to 100 C T J) and extended commercial temperature range (0 C to 100 C T J). The devices are provided with a standard speed grade (STD) and a 1 speed grade with higher performance. The FPGA core supply V DD can operate at 0 V for lower-power or 05 V for higher performance. Similarly, the transceiver core supply V can also operate at 0 V or 05 V. Users select the core operating voltage DDA while creating the Libero project. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 2
7 3 References The following documents are recommended references. For more information about PolarFire static and dynamic power data, see the PolarFire Power Estimator Spreadsheet. PO0137: PolarFire FPGA Product Overview New Errata: PolarFire FPGA Pre-Production Device Errata UG0722: PolarFire FPGA Packaging and Pin Descriptions Users Guide UG0726: PolarFire FPGA Board Design User Guide UG0686: PolarFire FPGA User I/O User Guide UG0680: PolarFire FPGA Fabric User Guide UG0714: PolarFire FPGA Programming User Guide UG0684: PolarFire FPGA Clocking Resources User Guide UG0687: PolarFire FPGA 1G Ethernet Solutions User Guide UG0727: PolarFire FPGA 10G Ethernet Solutions User Guide UG0748: PolarFire FPGA Low Power User Guide UG0676: PolarFire FPGA DDR Memory Controller User Guide UG0743: PolarFire FPGA Debugging User Guide UG0725: PolarFire FPGA Device Power-Up and Resets User Guide UG0677: PolarFire FPGA Transceiver User Guide UG0685: PolarFire FPGA PCI Express User Guide UG0753: PolarFire FPGA Security User Guide UG0752: PolarFire FPGA Power Estimator User Guide Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 3
8 4 Device Offering The following table lists the PolarFire FPGA device options using the MPF300T as an example. The MPF100T, MPF200T, and MPF500T device densities have identical offerings. Device Options Table 1 PolarFire FPGA Device Options Extended Commercial 0 C 100 C Industrial 40 C 100 C STD 1 Transceivers T MPF300T Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes MPF300TL Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Lower Static Power L MPF300TS Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes MPF300TLS Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Data Security S Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 4
9 5 Silicon Status There are three silicon status levels: Advanced initial estimated information based on simulations Preliminary information based on simulation and/or initial characterization Production final production silicon data The following table shows the status of the PolarFire FPGA device. Table 2 PolarFire FPGA Silicon Status Device MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS Silicon Status Preliminary Preliminary Preliminary Preliminary Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 5
10 6 DC Characteristics This section lists the DC characteristics of the PolarFire FPGA device. 6.1 Absolute Maximum Rating The following table lists the absolute maximum ratings for PolarFire devices. Table 3 Absolute Maximum Rating Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit FPGA core power supply VDD V Transceiver Tx and Rx lanes supply VDDA V Programming and HSIO receiver supply VDD V FPGA core and FPGA PLL high-voltage supply VDD V Transceiver PLL high-voltage supply VDDA V Transceiver reference clock supply VDD_XCVR_CLK V Global V REF for transceiver reference clocks XCVRVREF V HSIO DC I/O supply 2 x V GPIO DC I/O supply 2 x V Dedicated I/O DC supply for JTAG and SPI V GPIO auxiliary power supply for I/O bank x 2 VDDAUXx V Maximum DC input voltage on GPIO VIN V Maximum DC input voltage on HSIO VIN V Transceiver Receiver absolute input voltage Transceiver VIN V Transceiver Reference clock absolute input voltage Transceiver REFCLK VIN V Storage temperature (ambient) 1 TSTG C Junction temperature 1 TJ C Maximum soldering temperature RoHS TSOLROHS 260 C Maximum soldering temperature leaded TSOLPB 220 C See FPGA Programming Cycles vs Retention Characteristics for retention time vs. temperature. The total time used in calculating the device retention includes storage time and the device stored temperature. 2. The power supplies for a given I/O bank x are shown as x and VDDAUXx. 6.2 Recommended Operating Conditions The following table lists the recommended operating conditions. Table 4 Recommended Operating Conditions Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit FPGA core supply at 0 V mode 1 VDD V FPGA core supply at 05 V mode 1 VDD V Transceiver TX and RX lanes supply at 0 V mode VDDA V (when all lane rates are Gbps or less) 1 Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 6
11 Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Transceiver TX and RX lanes supply at 05 V mode VDDA V (when any lane rate is greater than Gbps) 1 Programming and HSIO receiver supply VDD V FPGA core and FPGA PLL high-voltage supply VDD V Transceiver PLL high-voltage supply VDDA V Transceiver reference clock supply 3.3 V nominal VDD_XCVR_CLK V Transceiver reference clock supply 2.5 V nominal VDD_XCVR_CLK V Global V REF for transceiver reference clocks3 XCVRVREF Ground VDD_XCVR_ CLK V HSIO DC I/O supply. Allowed nominal options: 2 V, x 14 Various 89 V 35 V, 5 V, and 8 V 4 GPIO DC I/O supply. Allowed nominal options: 2 V, x 14 Various V 5 V, 8 V, 2.5 V, and 3.3 V 2,4 Dedicated I/O DC supply for JTAG and SPI (GPIO Bank 3). Allowed nominal options: 8 V, 2.5 V, and 3.3 V 3 71 Various V GPIO auxiliary supply for I/O bank x with V DDIx = 3.3 V VDDAUXx V nominal 2,4 GPIO auxiliary supply for I/O bank x with V DDIx = 2.5 V VDDAUXx V nominal or lower 2,4 Extended commercial temperature range TJ C Industrial temperature range C Extended commercial programming temperature range TPRG C Industrial programming temperature range C V DD and V DDA can independently operate at 0 V or 05 V nominal. These supplies are not dynamically adjustable. For GPIO buffers where I/O bank is designated as bank number, if V DDIx is 2.5 V nominal or 3.3 V nominal, V DDAUXx must be connected to the V DDIx supply for that bank. If V DDIx for a given GPIO bank is <2.5 V nominal, V DDAUXx per I/O bank must be powered at 2.5 V nominal. XCVR VREF globally sets the reference voltage of the transceiver's single-ended reference clock input buffers. It is typically near V _ /2 V but is allowed in the specified range. DD XCVR_CLK The power supplies for a given I/O bank x are shown as x and VDDAUXx. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 7
12 6.2.1 DC Characteristics over Recommended Operating Conditions The following table lists the DC characteristics over recommended operating conditions. Table 5 DC Characteristics over Recommended Operating Conditions Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit Condition Input pin capacitance 1 Input or output leakage current per pin C IN (dedicated GPIO) 5.6 pf C IN (GPIO) 5.6 pf C IN (HSIO) 2.8 pf I L (GPIO) 10 µa I/O disabled, high Z I L (HSIO) 10 µa I/O disabled, high Z Input rise time (10% 90% of V DDIx) 2, 3, 4 TRISE ns V DDIx = 3.3 V Input rise time (10% 90% of V DDIx) 2, 3, ns V DDIx = 2.5 V Input rise time (10% 90% of V DDIx) 2, 3, ns V DDIx = 8 V Input rise time (10% 90% of V DDIx) 2, 3, ns V DDIx = 5 V Input rise time (10% 90% of V DDIx) 2, 3, ns V DDIx = 2 V Input fall time (90% 10% of V DDIx) 2, 3, 4 TFALL ns V DDIx = 3.3 V Input fall time (90% 10% of V DDIx) 2, 3, ns V DDIx = 2.5 V Input fall time (90% 10% of V DDIx) 2, 3, ns V DDIx = 8 V Input fall time (90% 10% of V DDIx) 2, 3, ns V DDIx = 5 V Input fall time (90% 10% of V DDIx) 2, 3, ns V DDIx = 2 V Pad pull-up when V IN = 05 IPU µa V DDIx = 3.3 V Pad pull-up when V IN = µa V DDIx = 2.5 V Pad pull-up when V IN = µa V DDIx = 8 V Pad pull-up when V IN = µa V DDIx = 5 V Pad pull-up when V IN = µa V DDIx = 35 V Pad pull-up when V IN = µa V DDIx = 2 V Pad pull-down when V IN = 3.3 V5 IPD µa V DDIx = 3.3 V Pad pull-down when V IN = 2.5 V µa V DDIx = 2.5 V Pad pull-down when V IN = 8 V µa V DDIx = 8 V Pad pull-down when V IN = 5 V µa V DDIx = 5 V Pad pull-down when V IN = 35 V µa V DDIx = 35 V Pad pull-down when V IN = 2 V µa V DDIx = 2 V Represents the die input capacitance at the pad not the package. Voltage ramp must be monotonic. Numbers based on rail-to-rail input signal swing and minimum 1 V/ns and maximum 4 V/ns. These are to be used for input delay measurement consistency. I/O signal standards with smaller than rail-to-rail input swings can use a nominal value of 200 ps 20% 80% of swing and maximum value of 500 ps 20% 80% of swing. GPIO only Maximum Allowed Overshoot and Undershoot During transitions, input signals may overshoot and undershoot the voltage shown in the following table. Input currents must be limited to less than 100 ma per latch-up specifications. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 8
13 The maximum overshoot duration is specified as a high-time percentage over the lifetime of the device. A DC signal is equivalent to 100% of the duty-cycle. The following table shows the maximum AC input voltage (V IN) overshoot duration for HSIO. Table 6 Maximum Overshoot During Transitions for HSIO AC (V IN) Overshoot Duration as % at TJ = 100 C Condition (V) Note: Overshoot level is for at 8 V. The following table shows the maximum AC input voltage (V IN) undershoot duration for HSIO. Table 7 Maximum Undershoot During Transitions for HSIO AC (V IN ) Undershoot Duration as % at TJ = 100 C Condition (V) The following table shows the maximum AC input voltage (V IN) overshoot duration for GPIO. Table 8 Maximum Overshoot During Transitions for GPIO AC (V IN) Overshoot Duration as % at TJ = 100 C Condition (V) Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 9
14 AC (V IN) Overshoot Duration as % at TJ = 100 C Condition (V) Note: Overshoot level is for V DDI at 3.3 V. The following table shows the maximum AC input voltage (V IN) undershoot duration for GPIO. Table 9 Maximum Undershoot During Transitions for GPIO AC (V IN) Undershoot Duration as % at TJ = 100 C Condition (V) Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 10
15 Power-Supply Ramp Times The following table shows the allowable power-up ramp times. Times shown correspond to the ramp of the supply from 0 V to the minimum recommended voltage as specified in the section Recommended Operating Conditions (see page 6). All supplies must rise and fall monotonically. Table 10 Power-Supply Ramp Times Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit FPGA core supply VDD ms Transceiver core supply VDDA ms Must connect to 8 V supply VDD ms Must connect to 2.5 V supply VDD ms Must connect to 2.5 V supply VDDA ms HSIO bank I/O power supplies [0,1,6,7] ms GPIO bank I/O power supplies [2,4,5] ms Bank 3 dedicated I/O buffers (GPIO) ms GPIO bank auxiliary power supplies VDDAUX[2,4,5] ms Transceiver reference clock supply VDD_XCVR_CLK ms Global V REF for transceiver reference clocks XCVRVREF ms Note: For proper operation of programming recovery mode, if a VDD supply brownout occurs during programming, a minimum supply ramp down time for only the VDD supply is recommended to be 10 ms or longer by using a programmable regulator or on-board capacitors Hot Socketing The following table lists the hot-socketing DC characteristics over recommended operating conditions. Table 11 Hot Socketing DC Characteristics over Recommended Operating Conditions Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Condition Current per transceiver Rx input pin (P or N single-ended) 1, 2 Current per transceiver Tx output pin (P or N single-ended) 3 Current per transceiver reference clock input pin (P or N single-ended) 4 XCVRRX_HS ±4 ma V DDA = 0 V XCVRTX_HS ±10 ma V DDA = 0 V XCVRREF_HS ±1 ma V DD_XCVR_CLK = 0 V Current per GPIO pin IGPIO_HS ±1 ma V DDIx = 0 V (P or N single-ended) 5 Current per HSIO pin (P or N single-ended) Hot socketing not supported in HSIO Assumes that the device is powered-down, all supplies are grounded, AC-coupled interface, and input pin pairs are driven by a CML driver at the maximum amplitude (1 V pk pk) that is toggling at any rate with PRBS 27 data. Each P and N transceiver input has less than the specified maximum input current. Each P and N transceiver output is connected to a 40 Ω resistor (50 Ω CML termination 20% tolerance) to the maximum allowed output voltage (V DDAmax V = 4 V) through an AC-coupling capacitor with all PolarFire device supplies grounded. This shows the current for a worst-case DC coupled interface. As an AC-coupled interface, the output signal will settle at ground and no hot socket current will be seen. V DD_XCVR_CLK is powered down and the device is driven to 0.3 V < V IN < V DD_XCVR_CLK. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 11
16 5. V DDIx is powered down and the device is driven to 0.3 V < V IN < GPIO V DDImax. Note: The following dedicated pins do not support hot socketing: TMS, TDI, TRSTB, DEVRST_N, and FF_EXIT_N. Weak pull up (as specified in GPIO) is always enabled. 6.3 Input and Output The following section describes: DC I/O levels Differential and complementary differential DC I/O levels HSIO and GPIO on-die termination specifications LVDS specifications DC Input and Output Levels The following tables list the DC I/O levels. Table 12 DC Input Levels I/O Standard Min (V) Typ (V) Max (V) VIL Min (V) PCI VIL Max (V) VIH Min (V) 0.5 VIH 1 Max (V) 3.45 LVTTL LVCMOS LVCMOS LVCMOS LVCMOS LVCMOS SSTL25I VREF 0.15 SSTL25II VREF 0.15 SSTL18I VREF 0 SSTL18II VREF 0 SSTL15I VREF VREF VREF VREF + 0 VREF + 0 VREF Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 12
17 I/O Standard Min (V) Typ (V) Max (V) VIL Min (V) SSTL15II VREF 0.1 VIL Max (V) SSTL135I VREF 0.09 SSTL135II VREF 0.09 HSTL15I VREF 0.1 HSTL15II VREF 0.1 HSTL135I VREF 0.09 HSTL135II VREF 0.09 HSTL12I VREF 0.1 HSTL12II VREF 0.1 HSUL18I HSUL18II HSUL12I VREF 0.1 POD12I VREF 0.08 POD12II VREF 0.08 VIH Min (V) VREF VREF VREF VREF VREF VREF VREF VREF VREF VREF VREF VREF VIH 1 Max (V) GPIO V IH max is 3.45 V with PCI clamp diode turned off regardless of mode, that is, over-voltage tolerant. 2. For external stub-series resistance. This resistance is on-die for GPIO. Note: 3.3 V and 2.5 V are only supported in GPIO banks. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 13
18 Table 13 DC Output Levels I/O Standard Min (V) Typ (V) Max (V) VOL Min (V) VOL Max (V) VOH Min (V) VOH Max (V) IOL 2,6 ma IOH 2,6 ma PCI LVTTL LVCMOS LVCMOS LVCMOS LVCMOS LVCMOS SSTL25I VTT SSTL25II VTT SSTL18I VTT SSTL18II VTT SSTL15I SSTL15II SSTL135I SSTL135II VTT VTT VTT VTT V OL /40 (V DDI V OH) /40 V OL /34 (V DDI V OH) /34 V OL /40 (V DDI V OH) /40 V OL /34 (V DDI V OH) /34 HSTL15I HSTL15II Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 14
19 I/O Standard Min (V) Typ (V) Max (V) VOL Min (V) VOL Max (V) VOH Min (V) VOH Max (V) IOL 2,6 ma IOH 2,6 ma HSTL135I V OL /50 (V DDI V OH) /50 HSTL135II V OL /25 (V DDI V OH) /25 HSTL12I V OL /50 (V DDI V OH) /50 HSTL12II V OL /25 (V DDI V OH) /25 HSUL18I V OL /55 (V DDI V OH) /55 HSUL18II V OL /25 (V DDI V OH) /25 HSUL12I V OL /40 (V DDI V OH) /40 POD12I 4, V OL /48 (V DDI V OH) /48 POD12II 4, V OL /34 (V DDI V OH) /34 Drive strengths per PCI specification V/I curves. 2. Refer to UG0686: PolarFire FPGA User I/O User Guide for details on supported drive strengths. 3. For external stub-series resistance. This resistance is on-die for GPIO. 4. I OL/I OH units for impedance standards in amps (not ma). 5. VOH_MAX based on external pull-up termination (pseudo-open drain). 6. The total DC sink/source current of all IOs within a lane is limited as follows: a. HSIO lane: 120 ma per 12 IO buffers. b. GPIO lane: 160 ma per 12 IO buffers. Note: 3.3 V and 2.5 V are only supported in GPIO banks Differential DC Input and Output Levels The follow tables list the differential DC I/O levels. I/O Standard Table 14 Differential DC Input Levels Bank Type VICM_Range Libero Setting VICM 1,3 Min (V) VICM 1,3 Typ (V) VICM 1,3 Max (V) VID 2 Min (V) VID Typ (V) LVDS33 GPIO Mid (default) Low LVDS25 GPIO Mid (default) Low LVDS18 4 GPIO Mid (default) VID Max (V) Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 15
20 I/O Standard Bank Type VICM_Range Libero Setting VICM 1,3 Min (V) VICM 1,3 Typ (V) VICM 1,3 Max (V) VID 2 Min (V) VID Typ (V) Low LVDS18 HSIO Mid (default) Low LCMDS33 GPIO Mid (default) Low LCMDS18 HSIO Mid (default) Low LCMDS25 GPIO Mid (default) Low RSDS33 GPIO Mid (default) Low RSDS25 GPIO Mid (default) Low RSDS18 5 HSIO Mid (default) Low MINILVDS33 GPIO Mid (default) Low MINILVDS25 GPIO Mid (default) Low MINILVDS18 5 HSIO Mid (default) Low SUBLVDS33 GPIO Mid (default) Low SUBLVDS25 GPIO Mid (default) Low SUBLVDS18 5 HSIO Mid (default) Low PPDS33 GPIO Mid (default) Low PPDS25 GPIO Mid (default) Low PPDS18 5 HSIO Mid (default) Low SLVS33 6 GPIO Mid (default) Low SLVS25 6 GPIO Mid (default) Low SLVS18 5 HSIO Mid (default) Low HCSL33 6 GPIO Mid (default) Low VID Max (V) Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 16
21 I/O Standard a. b. c. d. Bank Type VICM_Range Libero Setting VICM 1,3 Min (V) VICM 1,3 Typ (V) VICM 1,3 Max (V) VID 2 Min (V) VID Typ (V) HCSL25 6 GPIO Mid (default) Low HCSL18 5 HSIO Mid (default) Low BUSLVDSE25 GPIO Mid (default) n Low n MLVDSE25 GPIO Mid (default) Low LVPECL33 GPIO Mid (default) Low LVPECLE33 GPIO Mid (default) Low MIPI25 GPIO Mid (default) I/O Standard Low V ICM is the input common mode. V ID is the input differential voltage. V ICM rules are as follows: V ICM must be less than V DDI 0.4 V; V ID/2 must be <V DDI V; V ICM V ID/2 must be >VSS 0.3 V; Any differential input with VICM 0.6 V requires the low common mode setting in Libero (VICM_Range=LOW). = 8 V, VDDAUX = 2.5 V. HSIO receiver only. GPIO receiver only. Table 15 Differential DC Output Levels Bank Type VOCM 1 Min (V) VOCM Typ (V) VOCM Max (V) VOD 2 Min (V) VOD 2 Typ (V) LVDS33 GPIO LVDS25 GPIO LCMDS33 GPIO LCMDS25 GPIO RSDS33 GPIO RSDS25 GPIO MINILVDS33 GPIO MINILVDS25 GPIO SUBLVDS33 GPIO SUBLVDS25 GPIO PPDS33 GPIO PPDS25 GPIO SLVSE15 3 GPIO, HSIO VID Max (V) VOD 2 Max (V) BUSLVDSE25 3 GPIO Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 17
22 I/O Standard Bank Type VOCM 1 Min (V) VOCM Typ (V) VOCM Max (V) VOD 2 Min (V) VOD 2 Typ (V) MLVDSE25 3 GPIO LVPECLE33 3 GPIO MIPIE25 3 GPIO V OCM is the output common mode voltage. V OD is the output differential voltage. Emulated output only Complementary Differential DC Input and Output Levels The following tables list the complementary differential DC I/O levels. VOD 2 Max (V) Table 16 Complementary Differential DC Input Levels I/O Standard Min (V) Typ (V) Max (V) VICM 1,3 Min (V) VICM 1,3 Typ (V) VICM 1,3 Max (V) SSTL25I SSTL25II SSTL18I SSTL18II SSTL15I SSTL15II SSTL135I SSTL135II HSTL15I HSTL15II HSTL135I HSTL135II HSTL12I HSUL18I HSUL18II HSUL12I POD12I POD12II VID 2 Min (V) VID Max (V) I/O Standard V ICM is the input common mode voltage. V ID is the input differential voltage. V ICM rules are as follows: a. b. c. V ICM must be less than V DDI -0.4V; V ID/2 must be <V DDI V; V ICM V ID/2 must be >VSS 0.3 V. Table 17 Complementary Differential DC Output Levels Min (V) Typ (V) Max (V) VOL Min (V) VOL Max (V) SSTL25I V TT VOH 1,3 Min (V) V TT IOL 2 Min (ma) IOH 2 Min (ma) Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 18
23 I/O Standard Min (V) Typ (V) Max (V) VOL Min (V) VOL Max (V) SSTL25II V TT SSTL18I V TT SSTL18II V TT VOH 1,3 Min (V) V TT V TT V TT IOL 2 Min (ma) IOH 2 Min (ma) SSTL15I V OL /40 (V DDI V OH)/40 SSTL15II V OL /34 (V DDI V OH)/34 SSTL135I V OL /40 (V DDI V OH)/40 SSTL135II V OL /34 (V DDI V OH)/34 HSTL15I V DDI HSTL15II V DDI HSTL135I V OL /50 (V DDI V OH)/50 HSTL135II V OL /25 (V DDI V OH)/25 HSTL12I V OL /50 (V DDI V OH)/50 HSUL18I V OL /55 (V DDI V OH)/55 HSUL18II V OL /25 (V DDI V OH)/25 HSUL12I V OL /40 (V DDI V OH)/40 POD12I 3, V OL /48 (V DDI V OH)/48 POD12II 3, V OL /34 (V DDI V OH)/34 V OH is the single-ended high-output voltage. The total DC sink/source current of all IOs within a lane is limited as follows: a. HSIO lane: 120 ma per 12 IO buffers. b. GPIO lane: 160 ma per 12 IO buffers V OH_MAX based on external pull-up termination (pseudo-open drain). I OL/I OH units for impedance standards in amps (not ma) HSIO On-Die Termination The following tables lists the on-die termination calibration accuracy specifications for HSIO bank. Table 18 Single-Ended Thevenin Termination (Internal Parallel Thevenin Termination) Min (%) Typ Max (%) Unit Condition Ω V DDI = 8 V/5 V/35 V/2 V Ω V DDI = 8 V Ω V DDI = 8 V Ω V DDI = 5 V/35 V Ω V DDI = 5 V/35 V Ω V DDI = 5 V/35 V Ω V DDI = 5 V/35 V Ω V DDI = 5 V/35 V Ω V DDI = 2 V Ω V DDI = 2 V Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 19
24 Note: Thevenin impedance is calculated based on independent P and N as measured at 50% of V 50 Ω/75 Ω/150 Ω cases, nearest supported values of 40 Ω/60 Ω/120 Ω are used. DDI. For Table 19 Single-Ended Termination to (Internal Parallel Termination to ) Min (%) Typ Max (%) Unit Condition Ω V DDI = 2 V Ω V DDI = 2 V Ω V DDI = 2 V Ω V DDI = 2 V Ω V DDI = 2 V Ω V DDI = 2 V Ω V DDI = 2 V Note: Measured at 80% of V DDI. Table 20 Single-Ended Termination to VSS (Internal Parallel Termination to VSS) Min (%) Typ Max (%) Unit Condition Ω V DDI = 8 V/5 V Ω V DDI = 8 V/5 V Ω V DDI = 2 V Ω V DDI = 2 V Note: Measured at 50% of V DDI GPIO On-Die Termination The following table lists the on-die termination calibration accuracy specifications for GPIO bank. Table 21 On-Die Termination Calibration Accuracy Specifications for GPIO Bank Parameter Description Min (%) Typ Max (%) Unit Condition Differential termination 1 Single-ended thevenin termination 2, 3 Single-ended termination to VSS 4, 5 Internal differential termination Internal parallel thevenin termination Internal parallel Ω V CM < 0.8 V, common mode selection PC_REG_VSEL = "11" Ω 0.6 V < V CM < 65 V, common mode selection PC_REG_VSEL ="00" Ω 4 V < VCM, common mode selection PC_REG_VSEL = "00" Ω V DDI = 8 V/5 V Ω V DDI = 8 V Ω V DDI = 8 V Ω V DDI = 5 V Ω V DDI = 5 V Ω V DDI = 5 V Ω V DDI = 5 V Ω V DDI = 5 V Ω V DDI = 2.5 V/8 V/5 V/2 V Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 20
25 Parameter Description Min (%) Typ Max (%) Unit Condition termination to VSS Ω V DDI = 2.5 V/8 V/5 V/2 V Measured across P to N with 400 mv bias. Thevenin impedance is calculated based on independent P and N as measured at 50% of V DDI. For 50 Ω/75 Ω/150 Ω cases, nearest supported values of 40 Ω/60 Ω/120 Ω are used. Measured at 50% of V DDI. Supported terminations vary with the IO type regardless of V nominal voltage. Refer to Libero for DDI available combinations. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 21
26 7 AC Switching Characteristics This section contains the AC switching characteristics of the PolarFire FPGA device. 7.1 I/O Standards Specifications This section describes I/O delay measurement methodology, buffer speed, switching characteristics, digital latency, gearing training calibration, and maximum physical interface (PHY) rate for memory interface IP. 7.1 Input Delay Measurement Methodology Maximum PHY Rate for Memory Interface IP The following table provides information about the methodology for input delay measurement. Table 22 Input Delay Measurement Methodology Standard Description VL 1 VH 1 VID 2 VICM 2 VMEAS 3, 4 VREF 1, 5 Unit PCI PCIE 3.3 V 0 /2 V LVTTL33 LVTTL 3.3 V 0 /2 V LVCMOS33 LVCMOS 3.3 V 0 /2 V LVCMOS25 LVCMOS 2.5 V 0 /2 V LVCMOS18 LVCMOS 8 V 0 /2 V LVCMOS15 LVCMOS 5 V 0 /2 V LVCMOS12 LVCMOS 2 V 0 /2 V SSTL25I SSTL25II SSTL18I SSTL18II SSTL15I SSTL15II SSTL135I SSTL135II HSTL15I HSTL15II HSTL135I HSTL135II SSTL 2.5 V Class I SSTL 2.5 V Class II SSTL 8 V Class I SSTL 8 V Class II SSTL 5 V Class I SSTL 5 V Class II SSTL 35 V Class I SSTL 35 V Class II HSTL 5 V Class I HSTL 5 V Class II HSTL 35 V Class I HSTL 35 V Class II V REF 0.5 V REF 0.5 V REF 0.5 V REF 0.5 V REF.175 V REF.175 V REF.16 V REF.16 V REF.5 V REF.5 V REF 0.45 V REF.45 HSTL12 HSTL 2 V V REF.4 V REF V REF V REF V REF V REF V REF V REF +.16 V REF +.16 V REF +.5 V REF +.5 V REF V REF +.45 V REF +.4 VREF 25 V VREF 25 V VREF 0.90 V VREF 0.90 V VREF 0.75 V VREF 0.75 V VREF V VREF V VREF 0.75 V VREF 0.75 V VREF V VREF V VREF 0.60 V Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 22
27 Standard Description VL 1 VH 1 VID 2 VICM 2 VMEAS 3, 4 VREF 1, 5 Unit HSUL18I HSUL18II HSUL 8 V Class I HSUL 8 V Class II V REF 0.54 V REF 0.54 HSUL12 HSUL 2 V V REF.22 POD12I POD12II LVDS33 Pseudo open drain (POD) logic 2 V Class I POD 2 V Class II Low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) 3.3 V V REF.15 V REF.15 V ICM LVDS25 LVDS 2.5 V V ICM LVDS18 LVDS 8 V V ICM RSDS33 RSDS 3.3 V V ICM RSDS25 RSDS 2.5 V V ICM RSDS18 RSDS 8 V V ICM MINILVDS33 MINILVDS25 MINILVDS18 SUBLVDS33 SUBLVDS25 SUBLVDS18 PPDS33 Mini-LVDS 3.3 V Mini-LVDS 2.5 V Mini-LVDS 8 V Sub-LVDS 3.3 V Sub-LVDS 2.5 V Sub-LVDS 8 V Point-to-point differential signaling 3.3 V V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM PPDS25 PPDS 2.5 V V ICM PPDS18 PPDS 8 V V ICM SLVS33 Scalable lowvoltage signaling 3.3 V V ICM V REF V REF V REF +.22 V REF +.15 V REF +.15 VREF 0.90 V VREF 0.90 V VREF 0.60 V VREF 0.84 V VREF 0.84 V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 23
28 Standard Description VL 1 VH 1 VID 2 VICM 2 VMEAS 3, 4 VREF 1, 5 Unit SLVS25 SLVS 2.5 V V ICM SLVS18 SLVS 8 V V ICM HCSL33 High-speed current steering logic (HCSL) 3.3 V V ICM HCSL25 HCSL 2.5 V V ICM HCSL18 HCSL 8 V V ICM BLVDSE25 6 MLVDSE25 6 LVPECL33 LVPECLE33 6 SSTL25I SSTL25II SSTL18I SSTL18II SSTL15 SSTL135 HSTL15I HSTL15II HSTL135I Bus LVDS 2.5 V Multipoint LVDS 2.5 V Low-voltage positive emitter coupled logic Low-voltage positive emitter coupled logic Differential SSTL 2.5 V Class I Differential SSTL 2.5 V Class II Differential SSTL 8 V Class I Differential SSTL 8 V Class II Differential SSTL 5 V Class I Differential SSTL 5 V Class II Differential HSTL 5 V Class I Differential HSTL 5 V Class II Differential HSTL 35 V Class I V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM V ICM V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 24
29 Standard Description VL 1 VH 1 VID 2 VICM 2 VMEAS 3, 4 VREF 1, 5 Unit HSTL135II Differential HSTL 35 V Class II V ICM V HSTL12 Differential HSTL 2 V V ICM V HSUL18I Differential HSUL 8 V Class I V ICM V HSUL18II Differential HSUL 8 V Class II V ICM V HSUL12 Differential HSUL 2 V V ICM V POD12I Differential POD 2 V Class I V ICM V POD12II Differential POD 2 V Class II V ICM V MIPI25 Mobile Industry Processor Interface V ICM V Measurements are made at typical, minimum, and maximum V REF values. Reported delays reflect worst-case of these measurements. V REF values listed are typical. Input waveform switches between V L and V H. All rise and fall times must be 1 V/ns. Differential receiver standards all use 250 mv V ID for timing. V CM is different between different standards. Input voltage level from which measurement starts. The value given is the differential input voltage. This is an input voltage reference that bears no relation to the V REF/V MEAS parameters found in IBIS models or shown in Output Delay Measurement Single-Ended Test Setup (see page 27). Emulated bi-directional interface. 7.2 Output Delay Measurement Methodology The following section provides information about the methodology for output delay measurement. Table 23 Output Delay Measurement Methodology Standard Description R REF (Ω) C REF (pf) V MEAS (V) V REF (V) PCI PCIE 3.3 V LVTTL33 LVTTL 3.3 V 1M 0 65 LVCMOS33 LVCMOS 3.3 V 1M 0 65 LVCMOS25 LVCMOS 2.5 V 1M 0 25 LVCMOS18 LVCMOS 8 V 1M LVCMOS15 LVCMOS 5 V 1M LVCMOS12 LVCMOS 2 V 1M SSTL25I Stub-series terminated logic 2.5 V Class I 50 0 VREF 25 SSTL25II SSTL 2.5 V Class II 50 0 VREF 25 Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 25
30 Standard Description R REF (Ω) C REF (pf) V MEAS (V) V REF (V) SSTL18I SSTL 8 V Class I 50 0 VREF 0.9 SSTL18II SSTL 8 V Class II 50 0 VREF 0.9 SSTL15I SSTL 5 V Class I 50 0 VREF 0.75 SSTL15II SSTL 5 V Class II 50 0 VREF 0.75 SSTL135I SSTL 35 V Class I 50 0 VREF SSTL135II SSTL 35 V Class II 50 0 VREF HSTL15I High-speed transceiver logic (HSTL) 5 V Class I The value given is the differential output voltage VREF 0.75 HSTL15II HSTL 5 V Class II 50 0 VREF 0.75 HSTL135I HSTL 35 V Class I 50 0 VREF HSTL135II HSTL 35 V Class II 50 0 VREF HSTL12 HSTL 2 V 50 0 VREF 0.6 HSUL18I High-speed unterminated logic 8 V Class I 50 0 VREF 0.9 HSUL18II HSUL 8 V Class II 50 0 VREF 0.9 HSUL12 HSUL 2 V 50 0 VREF 0.6 POD12I Pseudo open drain (POD) logic 2 V Class I 50 0 VREF 0.84 POD12II POD 2 V Class II 50 0 VREF 0.84 LVDS33 LVDS 3.3 V LVDS25 LVDS 2.5 V LVDS18 LVDS 8 V RSDS33 Reduced swing differential signaling 3.3 V RSDS25 RSDS 2.5 V RSDS18 RSDS 8 V MINILVDS33 Mini-LVDS 3.3 V MINILVDS25 Mini-LVDS 2.5 V SUBLVDS33 Sub-LVDS 3.3 V SUBLVDS25 Sub-LVDS 2.5 V PPDS33 Point-to-point differential signaling 3.3 V PPDS25 PPDS 2.5 V BUSLVDSE25 Bus LVDS MLVDSE25 Multipoint LVDS 2.5 V LVPECLE33 Low-voltage positive emitter-coupled logic MIPIE25 Mobile industry processor interface 2.5 V Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 26
31 Figure 1 Output Delay Measurement Single-Ended Test Setup Figure 2 Output Delay Measurement Differential Test Setup 7.3 Input Buffer Speed The following tables provide information about input buffer speed. Table 24 HSIO Maximum Input Buffer Speed Standard STD 1 Unit LVDS Mbps RSDS Mbps MINILVDS Mbps SUBLVDS Mbps PPDS Mbps SLVS Mbps SSTL18I Mbps SSTL18II Mbps SSTL15I Mbps SSTL15II Mbps SSTL135I Mbps SSTL135II Mbps Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 27
32 Standard STD 1 Unit HSTL15I Mbps HSTL15II Mbps HSTL135I Mbps HSTL135II Mbps HSUL18I Mbps HSUL18II Mbps HSUL Mbps HSTL Mbps POD12I Mbps POD12II Mbps LVCMOS18 (12 ma) Mbps LVCMOS15 (10 ma) Mbps LVCMOS12 (8 ma) Mbps Performance is achieved with VID 200 mv. Table 25 GPIO Maximum Input Buffer Speed Standard STD 1 Unit LVDS25/LVDS33/LCMDS25/LCMDS Mbps RSDS25/RSDS Mbps MINILVDS25/MINILVDS Mbps SUBLVDS25/SUBLVDS Mbps PPDS25/PPDS Mbps SLVS25/SLVS Mbps SLVSE Mbps HCSL25/HCSL Mbps BUSLVDSE Mbps MLVDSE Mbps LVPECL Mbps SSTL25I Mbps SSTL25II Mbps SSTL18I Mbps SSTL18II Mbps SSTL15I Mbps SSTL15II Mbps HSTL15I Mbps HSTL15II Mbps HSUL18I Mbps HSUL18II Mbps PCI Mbps LVTTL33 (20 ma) Mbps LVCMOS33 (20 ma) Mbps LVCMOS25 (16 ma) Mbps Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 28
33 Standard STD 1 Unit LVCMOS18 (12 ma) Mbps LVCMOS15 (10 ma) Mbps LVCMOS12 (8 ma) Mbps MIPI25/MIPI Mbps 2. All SSTLD/HSTLD/HSULD/LVSTLD/POD type receivers use the LVDS differential receiver. Performance is achieved with VID 200 mv. 7.4 Output Buffer Speed Table 26 HSIO Maximum Output Buffer Speed Standard STD 1 Unit SSTL18I Mbps SSTL18II Mbps SSTL18I (differential) Mbps SSTL18II (differential) Mbps SSTL15I Mbps SSTL15II Mbps SSTL15I (differential) Mbps SSTL15II (differential) Mbps SSTL135I Mbps SSTL135II Mbps SSTL135I (differential) Mbps SSTL135II (differential) Mbps HSTL15I Mbps HSTL15II Mbps HSTL15I (differential) Mbps HSTL15II (differential) Mbps HSTL135I Mbps HSTL135II Mbps HSTL135I (differential) Mbps HSTL135II (differential) Mbps HSUL18I Mbps HSUL18II Mbps HSUL18II (differential) Mbps HSUL Mbps HSUL12I (differential) Mbps HSTL Mbps HSTL12I (differential) Mbps POD12I Mbps POD12II Mbps LVCMOS18 (12 ma) Mbps LVCMOS15 (10 ma) Mbps Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 29
34 Standard STD 1 Unit LVCMOS12 (8 ma) Mbps Table 27 GPIO Maximum Output Buffer Speed Standard STD 1 Unit LVDS25/LCMDS Mbps LVDS33/LCMDS Mbps RSDS Mbps MINILVDS Mbps SUBLVDS Mbps PPDS Mbps SLVSE Mbps BUSLVDSE Mbps MLVDSE Mbps LVPECLE Mbps SSTL25I Mbps SSTL25II Mbps SSTL25I (differential) Mbps SSTL25II (differential) Mbps SSTL18I Mbps SSTL18II Mbps SSTL18I (differential) Mbps SSTL18II (differential) Mbps SSTL15I Mbps SSTL15II Mbps SSTL15I (differential) Mbps SSTL15II (differential) Mbps HSTL15I Mbps HSTL15II Mbps HSTL15I (differential) Mbps HSTL15II (differential) Mbps HSUL18I Mbps HSUL18II Mbps HSUL18I (differential) Mbps HSUL18II (differential) Mbps PCI Mbps LVTTL33 (20 ma) Mbps LVCMOS33 (20 ma) Mbps LVCMOS25 (16 ma) Mbps LVCMOS18 (12 ma) Mbps LVCMOS15 (10 ma) Mbps LVCMOS12 (8 ma) Mbps MIPIE Mbps Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 30
35 7.5 Maximum PHY Rate for Memory Interface IP The following tables provide information about the maximum PHY rate for memory interface IP. Table 28 Maximum PHY Rate for Memory Interfaces IP for HSIO Banks Memory Standard 2. Gearing Ratio VDDAUX STD (Mbps) 1 (Mbps) Fabric STD (MHz) DDR4 1 8:1 8 V 2 V DDR3 8:1 8 V 5 V DDR3L 8:1 8 V 35 V LPDDR3 8:1 8 V 2 V Fabric 1 (MHz) QDRII+ 8:1 8 V 5 V RLDRAM3 2 8:1 8 V 35 V RLDRAM3 2 4:1 8 V 35 V RLDRAM3 2 2:1 8 V 35 V RLDRAM2 2 8:1 8 V 8 V RLDRAM2 2 4:1 8 V 8 V RLDRAM2 2 2:1 8 V 8 V Table represents DDR4 in the FC1152 package for all data widths without ECC and CRC enabled. DDR4 in the FCG484 and FCVG484 packages are limited to 16-bit interfaces for 1600 Mbps support. RLDRAM2 and RLDRAM3 are not supported with a soft IP controller currently. Table 29 Maximum PHY Rate for Memory Interfaces IP for GPIO Banks Memory Standard Gearing Ratio VDDAUX STD (Mbps) 1 (Mbps) Fabric STD (MHz) DDR3 8:1 2.5 V 5 V QDRII+ 8:1 2.5 V 5 V RLDRAM2 1 4:1 2.5 V 8 V RLDRAM2 1 2:1 2.5 V 8 V Fabric 1 (MHz) RLDRAM2 is currently not supported with a soft IP controller. 7.6 User I/O Switching Characteristics The following section describes characteristics for user I/O switching. For more information about user I/O timing, see the I/O Digital The following tables provide information about I/O digital. PolarFire I/O Timing Spreadsheet (to be released). Table 30 I/O Digital Receive Single-Data Rate Switching Characteristics Parameter Interface Name Topology STD Min STD Typ STD Max 1 Min 1 Typ 1 Max Unit Clock-to-Data Condition FMAX RX_SDR_G_A Rx SDR MHz From a global clock source, aligned Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 31
36 Parameter Interface Name Topology STD Min STD Typ STD Max 1 Min 1 Typ 1 Max Unit Clock-to-Data Condition FMAX RX_SDR_L_A Rx SDR MHz From a lane clock source, aligned FMAX RX_SDR_G_C Rx SDR MHz From a global clock source, centered FMAX RX_SDR_L_C Rx SDR MHz From a lane clock source, centered Table 31 I/O Digital Receive Double-Data Rate Switching Characteristics Parameter Interface Name Topology STD Min STD Typ STD Max 1 Min 1 Typ 1 Max Unit Clock-to- Data Condition FMAX RX_DDR_G_A Rx DDR MHz MHz From a global clock source, aligned FMAX RX_DDR_L_A Rx DDR MHz From a lane clock source, aligned FMAX RX_DDR_G_C Rx DDR MHz From a global clock source, centered FMAX RX_DDR_L_C Rx DDR MHz From a lane clock source, centered F MAX 2:1 RX_DDRX_B_A Rx DDR digital mode F MAX 4:1 RX_DDRX_B_A Rx DDR digital mode F MAX 8:1 RX_DDRX_B_A Rx DDR digital mode F MAX 2:1 RX_DDRX_B_C Rx DDR digital mode MHz MHz MHz MHz From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, aligned From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, aligned From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, aligned From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, centered Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 32
37 Parameter Interface Name Topology STD Min STD Typ STD Max 1 Min 1 Typ 1 Max Unit Clock-to- Data Condition F MAX 4:1 RX_DDRX_B_C Rx DDR digital mode MHz From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, centered F MAX 8:1 RX_DDRX_B_C Rx DDR digital mode MHz From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, centered F MAX 2:1 RX_DDRX_BL_A Rx DDR digital mode MHz From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, aligned F MAX 4:1 RX_DDRX_BL_A Rx DDR digital mode MHz From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, aligned F MAX 8:1 RX_DDRX_BL_A Rx DDR digital mode MHz From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, aligned F MAX 2:1 RX_DDRX_BL_C Rx DDR digital mode MHz From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, centered F MAX 4:1 RX_DDRX_BL_C Rx DDR digital mode MHz From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, centered F MAX 8:1 RX_DDRX_BL_C Rx DDR digital mode MHz From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, centered Table 32 I/O Digital Transmit Single-Data Rate Switching Characteristics Parameter Output FMAX Interface Name Topology STD Min STD Typ STD Max 1 Min 1 Typ 1 Max Unit Forwarded Clock-to-Data Skew TX_SDR_G_A Tx SDR MHz From a global clock source, aligned 1 TX_SDR_G_C Tx SDR MHz From a global clock source, centered 1 Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 33
38 A centered clock-to-data interface can be created with a negedge launch of the data. Table 33 I/O Digital Transmit Double-Data Rate Switching Characteristics Parameter Output F MAX Output F MAX 2:1 Output F MAX 4:1 Output F MAX 8:1 Output F MAX 2:1 Output F MAX 4:1 Output F MAX 8:1 In delay, out delay, DLL delay step sizes Interface Name Topology STD Min STD Typ STD Max 1 Min 1 Typ 1 Max Unit Forwarded Clock-to- Data Skew TX_DDR_G_A Tx DDR MHz From a global clock source, aligned TX_DDR_G_C Tx DDR MHz From a global clock source, centered TX_DDR_L_A Tx DDR MHz From a lane clock source, aligned TX_DDR_L_C Tx DDR MHz From a lane clock source, centered TX_DDRX_B_A TX_DDRX_B_A TX_DDRX_B_A TX_DDRX_B_C TX_DDRX_B_C TX_DDRX_B_C Tx DDR digital mode Tx DDR digital mode Tx DDR digital mode Tx DDR digital mode Tx DDR digital mode Tx DDR digital mode ps MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, aligned From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, aligned From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, aligned From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, centered with PLL From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, centered with PLL From a HS_IO_CLK clock source, centered with PLL Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 34
39 Table 34 I/O CDR Switching Characteristics Parameter Min Max Unit Data rate Mbps Receiver Sinusoidal jitter tolerance UI Jitter values based on bit error ratio (BER) of 10 12, 80 MHz sinusoidal jitter injected to Rx data. Note: See the LVDS output buffer specifications for transmit characteristics. 7.2 Clocking Specifications This section describes the PLL and DLL clocking and oscillator specifications Clocking The following table provides clocking specifications. Table 35 Global and Regional Clock Characteristics ( 40 C to 100 C) Parameter Symbol Global clock FMAX V DD = 0 V STD V DD = 0 V 1 V DD = 05 V STD V DD = 05 V 1 FMAXG MHz Unit Condition Regional clock FMAX Global clock duty cycle distortion Regional clock duty cycle distortion FMAXR MHz Transceiver interfaces only FMAXR MHz All other interfaces TDCDG ps At 500 MHz TDCDR ps At 250 MHz Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 35
40 The following table provides clocking specifications from 40 C to 100 C. Table 36 High-Speed I/O Clock Characteristics ( 40 C to 100 C) Parameter Symbol V DD = 0 V STD High-speed I/O clock FMAX V DD = 0 V 1 V DD = 05 V STD V DD = 05 V 1 Unit Condition FMAXB MHz HSIO and GPIO High-speed I/O clock skew 1 FSKEWB ps HSIO without bridging FSKEWB ps HSIO with bridging FSKEWB ps GPIO without bridging FSKEWB ps GPIO with bridging High-speed I/O clock duty cycle distortion 2 TDCB ps HSIO without bridging TDCB ps HSIO with bridging TDCB ps GPIO without bridging TDCB ps GPIO with bridging 2. F SKEWB is the worst-case clock-tree skew observable between sequential I/O elements. Clock-tree skew is significantly smaller at I/O registers close to each other and fed by the same or adjacent clock-tree branches. Use the Microsemi Timing Analyzer tool to evaluate clock skew specific to the design. Parameters listed in this table correspond to the worst-case duty cycle distortion observable at the I/O flip flops. IBIS should be used to calculate any additional duty cycle distortion that might be caused by asymmetrical rise/fall times for any I/O standard PLL The following table provides information about PLL. Table 37 PLL Electrical Characteristics Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Input clock frequency (integer mode) Input clock frequency (fractional mode) FINI MHz FINF MHz Minimum reference or FINPULSE 200 ps feedback pulse width 1 Frequency at the Frequency Phase Detector (PFD) (integer mode) Frequency at the PFD (fractional mode) FPHDETI MHz FPHDETF MHz Allowable input duty cycle FINDUTY % Maximum input period clock jitter (reference and feedback clocks) 2 FMAXINJ ps PLL VCO frequency FVCO MHz Loop bandwidth (Int) 3 FBW F PHDET/55 F PHDET/44 F PHDET/30 Loop bandwidth (FRAC) 3 FBW F PHDET/91 F PHDET/77 F PHDET/56 MHz MHz Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 36
41 Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Static phase offset of the TSPO Max (±60 ps, PLL outputs 4 ±0.5 degrees) ps TOUTJITTER ps PLL output duty cycle precision TOUTDUTY % PLL lock time 5 TLOCK Max (6.0 μs, 625 PFD cycles) μs PLL unlock time 6 TUNLOCK 2 8 PFD cycles PLL output frequency FOUT MHz Minimum reset pulse width TMRPW μs Maximum delay in the FMAXDFB 5 PFD feedback path 7 cycles Spread spectrum Mod_Spread % modulation spread 8 Spread spectrum Mod_Freq F PHDETF/(128x63) 32 F PHDETF/(128) modulation frequency 9 KHz Minimum time for high or low pulse width. Maximum jitter the PLL can tolerate without losing lock. Default bandwidth setting of BW_PROP_CTRL = "01" for Integer and Fraction modes leads to the typical estimated bandwidth. This bandwidth can be lowered by setting BW_PROP_CTRL = "00" and can be increased if BW_PROP_CTRL = "10" and will be at the highest value if BW_PROP_CTRL = "11". Maximum (±3-Sigma) phase error between any two outputs with nominally aligned phases. Input clock cycle is REFDIV/F REF. For example, F REF = 25 MHz, REFDIV = 1, lock time = 10.0 (assumes LOCKCOUNTSEL setting = 4'd8 (256 cycles)). Unlock occurs if two cycle slip within LOCKCOUNT/4 PFD cycles. Maximum propagation delay of external feedback path in deskew mode. Programmable capability for depth of down spread or center spread modulation. Programmable modulation rate based on the modulation divider setting (1 to 63). Note: In order to meet all data sheet specifications, the PLL must be programmed such that the PLL Loop Bandwidth < ( * VCO Frequency) MHz. The Libero PLL configuration tool will enforce this rule when creating PLL configurations DLL The following table provides information about DLL. Table 38 DLL Electrical Characteristics Parameter 1 Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Input reference clock frequency FINF MHz Input feedback clock frequency FINFDBF MHz Primary output clock frequency FOUTPF MHz Secondary output clock frequency 2 FOUTSF MHz Input clock cycle-to-cycle jitter FINJ 200 ps Output clock period cycle-to-cycle jitter (w/clean input) Output clock-to-clock skew between two outputs with the same phase settings TOUTJITTERP 300 ps TSKEW ±200 ps Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 37
42 Parameter 1 Symbol Min Typ Max Unit DLL lock time TLOCK 16 16K Reference clock cycles Minimum reset pulse width TMRPW 3 ns Minimum input pulse width 3 TMIPW 20 ns Minimum input clock pulse width high TMPWH 400 ps Minimum input clock pulse width low TMPWL 400 ps Delay step size TDEL ps Maximum delay block delay 4 TDELMAX ns Output clock duty cycle (with 50% duty cycle input) 5 TDUTY % Output clock duty cycle (in phase reference mode) 5 TDUTY % For all DLL modes. Secondary output clock divided by four option. On load, direction, move, hold, and update input signals. 128 delay taps in one delay block. Without duty cycle correction enabled RC Oscillators The following tables provide internal RC clock resources for user designs and additional information about designing systems with RF front end information about emitters generated on-chip to support programming operations. Table 39 2 MHz RC Oscillator Electrical Characteristics Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Operating frequency RC2FREQ 2 MHz Accuracy RC2FACC 4 4 % Duty cycle RC2DC % Peak-to-peak output period jitter RC2PJIT 5 10 ns Peak-to-peak output cycle-to-cycle jitter RC2CJIT 5 10 ns Operating current (V DD25) RC2IVPPA 60 µa Operating current (V DD) RC2IVDD 2.6 µa Table MHz RC Oscillator Electrical Characteristics Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Operating frequency RCSCFREQ 160 MHz Accuracy RCSCFACC 4 4 % Duty cycle RCSCDC % Peak-to-peak output period jitter RCSCPJIT 600 ps Peak-to-peak output cycle-to-cycle jitter RCSCCJIT 172 ps Operating current (V DD25) RCSCVPPA 599 µa Operating current (V DD18) RCSCVPP 0.1 µa Operating current (V DD) RCSCVDD 60.7 µa Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 38
43 7.3 Fabric Specifications The following section describes specifications for the fabric Math Blocks The following tables describe math block performance. Table 41 Math Block Performance Extended Commercial Range (0 C to 100 C) Parameter Symbol Modes V DD = 0 V STD Maximum operating frequency FMAX multiplication multiplication summed with 48-bit input multiplier pre-adder ROM mode Two 9 9 multiplication 9 9 dot product (DOTP) Complex multiplication V DD = 0 V 1 V DD = 05 V STD V DD = 05 V 1 Unit MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz Table 42 Math Block Performance Industrial Range ( 40 C to 100 C) Parameter Symbol Modes V DD = 0 V STD Maximum operating frequency FMAX multiplication multiplication summed with 48-bit input multiplier pre-adder ROM mode Two 9 9 multiplication V DD = 0 V 1 V DD = 05 V STD V DD = 05 V 1 Unit MHz MHz MHz MHz 9 9 DOTP MHz Complex multiplication MHz Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 39
44 7.3.2 SRAM Blocks The following tables describe the LSRAM blocks' performance. Table 43 LSRAM Performance Industrial Temperature Range ( 40 C to 100 C) Parameter VDD = 0 V STD Operating frequency VDD = 0 V 1 VDD = 05 V STD VDD = 05 V 1 Unit Condition MHz Two-port, all supported widths, pipelined, simple-write, and writefeed-through MHz Two-port, all supported widths, non-pipelined, simple-write, and write-feed-through MHz Dual-port, all supported widths, pipelined, simple-write, and writefeed-through MHz Dual-port, all supported widths, non-pipelined, simple-write, and write-feed-through MHz Two-port pipelined ECC mode, pipelined, simple-write, and writefeed-through MHz Two-port non-pipelined ECC mode, pipelined, simple-write, and write-feed-through MHz Two-port pipelined ECC mode, non-pipelined, simple-write, and write-feed-through MHz Two-port non-pipelined ECC mode, non-pipelined, simplewrite, and write-feed-through MHz Two-port, all supported widths, pipelined, and read-before-write MHz Two-port, all supported widths, non-pipelined, and read-beforewrite MHz Dual-port, all supported widths, pipelined, and read-before-write MHz Dual-port, all supported widths, non-pipelined, and read-beforewrite MHz Two-port pipelined ECC mode, pipelined, and read-before-write MHz Two-port non-pipelined ECC mode, pipelined, and read-beforewrite MHz Two-port pipelined ECC mode, non-pipelined, and read-beforewrite MHz Two-port non-pipelined ECC mode, non-pipelined, and readbefore-write Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 40
45 Table 44 µsram Performance Parameter Symbol VDD = 0 V STD Operating frequency Read access time VDD = 0 V 1 VDD = 05 V STD VDD = 05 V 1 Unit Condition FMAX MHz Write-port Tac 2 2 ns Read-port Table 45 µprom Performance Parameter Symbol VDD = 0 V STD VDD = 0 V 1 VDD = 05 V STD VDD = 05 V 1 Read access time Tac ns Unit 7.4 Transceiver Switching Characteristics This section describes transceiver switching characteristics Transceiver Performance The following table describes transceiver performance. Table 46 PolarFire Transceiver and TXPLL Performance Parameter Symbol STD Min Tx data rate 1,2 FTXRate Gbps Tx OOB (serializer bypass) data rate FTXRateOOB DC 5 DC 5 Gbps Rx data rate when AC coupled 2 FRxRateAC Gbps Rx data rate when DC coupled FRxRateDC Gbps Rx OOB (deserializer bypass) data rate FTXRateOOB DC 25 DC 25 Gbps TXPLL output frequency 3 FTXPLL GHz Rx CDR mode FRXCDR Gbps Rx DFE mode 2 FRXDFE Gbps Rx Eye Monitor mode 2 FRXEyeMon Gbps The reference clock is required to be a minimum of 75 MHz for data rates of 10 Gbps and above. For data rates greater than Gbps, VDDA must be set to 05 V mode. See supply tolerance in the section Recommended Operating Conditions (see page 6). The Tx PLL rate is between 0.5x to 5.5x the Tx data rate. The Tx data rate depends on per XCVR lane Tx post-divider settings Transceiver Reference Clock Performance The following table describes performance of the transceiver reference clock. STD Typ STD Max 1 Min 1 Typ 1 Max Unit Table 47 PolarFire Transceiver Reference Clock AC Requirements Parameter Symbol STD Min STD Typ Reference clock input FTXREFCLK MHz rate 1, 2 STD Max 1 Min 1 Typ 1 Max Unit Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 41
46 Parameter Symbol Reference clock input FXCVRREFCLKMAX rate1, 2, CASCADE STD Min STD Typ STD Max 1 Min 1 Typ 1 Max Unit MHz Reference clock rate at FTXREFCLKPFD MHz the PFD 4 Reference clock rate recommended at the PFD for Tx rates 10 Gbps and above 4 Tx reference clock phase noise requirements to meet jitter specifications (156 MHz clock at reference clock input) 5 FTXREFCLKPFD10G MHz FTXREFPN dbc /Hz Phase noise at 1 KHz FTXREFPN dbc /Hz Phase noise at 10 KHz FTXREFPN dbc /Hz Phase noise at 100 KHz FTXREFPN dbc /Hz Phase noise at 1 MHz FTXREFPN dbc /Hz Reference clock input rise time (10% 90%) Reference clock input fall time (90% 10%) Reference clock duty cycle TREFRISE ps TREFFALL ps TREFDUTY % Spread spectrum Mod_Spread % modulation spread 6 Spread spectrum Mod_Freq TxREF modulation frequency 7 CLKPFD/ (128) 32 TxREF CLKPFD/ (128*63) TxREF CLKPFD/ (128) 32 TxREF CLKPFD/ (128*63) See the maximum reference clock rate allowed per input buffer standard. The minimum value applies to this clock when used as an XCVR reference clock. It does not apply when used as a non-xcvr input buffer (DC input allowed). Cascaded reference clock. After reference clock input divider. Required maximum phase noise is scaled based on actual F TxRefClkPFD value by 20 log10 (TxRefClkPFD /156 MHz). It is assumed that the reference clock divider of 4 is used for these calculations to always meet the maximum PFD frequency specification. Programmable capability for depth of down-spread or center-spread modulation. Programmable modulation rate based on the modulation divider setting (1 to 63) Transceiver Reference Clock I/O Standards The following table describes the differential I/O standards supported as transceiver reference clocks. KHz Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 42
47 Table 48 Transceiver Differential Reference Clock I/O Standards I/O Standard Comment LVDS25 For DC input levels, se e table Differential DC Input and Output Levels. HCSL25 (for PCIe) Note: The transceiver reference clock differential receiver supports V CM common mode Transceiver Interface Performance The following table describes the single-ended I/O standards supported as transceiver reference clocks. Table 49 Transceiver Single-Ended Reference Clock I/O Standards I/O Standard Comment LVCMOS25 For DC input levels, see table DC Input and Output Levels Transmitter Performance The following tables describe performance of the transmitter. Table 50 Transceiver Reference Clock Input Termination Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Single-ended termination RefTerm 50 Ω Single-ended termination RefTerm 75 Ω Single-ended termination RefTerm 150 Ω Differential termination RefDiffTerm Ω Power-up termination >50K Ω Measured at VCM= 2 V and VID= 350 mv. Note: All pull-ups are disabled at power-up to allow hot plug capability. Table 51 PolarFire Transceiver User Interface Clocks Parameter Modes 1 STD Min Transceiver TX_CLK range (nondeterministic PCS mode with global or regional fabric clocks) STD Max 1 Min 1 Max 8-bit, max data rate = 6 Gbps MHz 10-bit, max data rate = 6 Gbps MHz 16-bit, max data rate = 4.8 Gbps MHz 20-bit, max data rate = 6.0 Gbps MHz 32-bit, max data rate = MHz Gbps ( STD) / 12.7 Gbps ( 1) 1 40-bit, max data rate = MHz Gbps ( STD) / 12.7 Gbps ( 1) 1 64-bit, max data rate = MHz Gbps ( STD) / 12.7 Gbps ( 1) 1 80-bit, max data rate = MHz Gbps( STD) / 12.7 Gbps ( 1) 1 Fabric pipe mode 32-bit, max data rate = 6.0 Gbps MHz 8-bit, max data rate = 6 Gbps MHz Unit Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 43
48 Parameter Modes 1 STD Min Transceiver RX_CLK range (nondeterministic PCS mode with global or regional fabric clocks) Transceiver TX_CLK range (deterministic PCS mode with regional fabric clocks) Transceiver RX_CLK range (deterministic PCS mode with regional fabric clocks) STD Max 1 Min 1 Max 10-bit, max data rate = 6 Gbps MHz 16-bit, max data rate = 4.8 Gbps MHz 20-bit, max data rate = 6.0 Gbps MHz 32-bit, max data rate = Gbps MHz 40-bit, max data rate = MHz Gbps ( STD) / 12.7 Gbps ( 1) 1 64-bit, max data rate = MHz Gbps ( STD) / 12.7 Gbps ( 1) 1 80-bit, max data rate = MHz Gbps ( STD) / 12.7 Gbps ( 1) 1 Fabric pipe mode 32-bit, max data rate = 6.0 Gbps MHz 8-bit, max data rate = 6 Gbps MHz 10-bit, max data rate = 6 Gbps MHz 16-bit, max data rate = 3.6 Gbps ( STD) / 4.25 Gbps ( 1) 20-bit, max data rate = 4.5 Gbps ( STD) / 5.32 Gbps ( 1) 32-bit, max data rate = 7.2 Gbps ( STD) / 8.5 Gbps ( 1) Unit MHz MHz MHz 40-bit, max data rate = Mhz 9.0 Gbps ( STD) / 10.6 Gbps ( 1) 1 64-bit, max data rate = MHz Gbps ( STD) / 12.7 Gbps ( 1) 1 80-bit, max data rate = MHz Gbps ( STD) / 12.7 Gbps ( 1) 1 8-bit, max data rate = 6 Gbps MHz 10-bit, max data rate = 6 Gbps MHz 16-bit, max data rate = 3.6 Gbps ( STD) / 4.25 Gbps ( 1) 20-bit, max data rate = 4.5 Gbps ( STD) / 5.32 Gbps ( 1) 32-bit, max data rate = 7.2 Gbps ( STD) / 8.5 Gbps ( 1) MHz MHz MHz 40-bit, max data rate = MHz 9.0 Gbps ( STD) / 10.6 Gbps ( 1) 1 64-bit, max data rate = MHz Gbps ( STD) / 12.7 Gbps ( 1) 1 80-bit, max data rate = MHz Gbps ( STD) / 12.7 Gbps ( 1) 1 For data rates greater than Gbps, VDDA must be set to 05 V mode. See supply tolerance in the section Recommended Operating Conditions (see page 6). Note: Until specified, all modes are non-deterministic. For more information, see UG0677: PolarFire FPGA Transceiver User Guide. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 44
49 Table 52 PolarFire Transceiver Transmitter Characteristics Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Condition Differential termination VOTERM 85 Ω VOTERM 100 Ω VOTERM 150 Ω Common mode VOCM 0.44 VDDA VDDA 0.59 VDDA V DC coupled 50% setting voltage 1 VOCM 0.52 VDDA 0.6 VDDA 0.66 VDDA V DC coupled 60% setting VOCM 0.61 VDDA 0.7 VDDA 0.75 VDDA V DC coupled 70% setting VOCM 0.63 VDDA 0.8 VDDA 0.83 VDDA V DC coupled 80% setting Rise time 2 TTxRF ps 20% to 80% Fall time ps 80% to 20% Differential peak-topeak amplitude VODPP 1040 mv 1000 mv setting VODPP 840 mv 800 mv setting VODPP 630 mv 600 mv setting VODPP 620 mv 500 mv setting VODPP 530 mv 400 mv setting VODPP 360 mv 300 mv setting VODPP 240 mv 200 mv setting VODPP 160 mv 100 mv setting Transmit lane P to N TOSKEW 8 15 ps skew 3 Lane to lane transmit TLLSKEW 75 ps Single PLL skew 4 Electrical idle transition entry time 7 Electrical idle transition exit time 7 Electrical idle amplitude TTxEITrE ntry TTxEITrE xit VTxEIpp mv TXPLL lock time TTXLock 1600 PFD cycles Digital PLL lock time 8 TDPLLLock REFCLK UIs Total jitter 5,6 Deterministic jitter 5,6 Total jitter 5,6 Deterministic jitter 5,6 Total jitter 5,6 Deterministic jitter 5,6 Total jitter 5,6 Deterministic jitter 5,6 Total jitter 5,6 Deterministic jitter 5,6 T J TDJ TJ TDJ TJ TDJ TJ TDJ TJ TDJ ps ns ns UI UI UI UI UI UI UI UI UI UI Multiple PLL Data rate 8.5 Gbps to 12.7 Gbps 9 (Tx V CO rate 4.25 GHz to 6.35 GHz) Data rate 3.2 Gbps to 8.5 Gbps (Tx V CO rate 2.5 GHz to 5.0 GHz) Data rate 6 Gbps to 3.2 Gbps (Tx V CO rate 2.5 GHz to 5.0 GHz) Data rate 800 Mbps to 6 Gbps (Tx V CO rate 2.5 GHz to 5.0 GHz) Data rate = 250 Mbps to 800 Mbps (Tx V CO rate 2.5 GHz to 5.0 GHz) Increased DC common mode settings above 50% reduce allowed V output swing capabilities. OD Adjustable through transmit emphasis. With estimated package differences. Single PLL applies to all four lanes in the same quad location with the same TxPLL. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 45
50 Improved jitter characteristics for a specific industry standard are possible in many cases due to improved reference clock or higher V CO rate used. Tx jitter is specified with all transmitters on the device enabled, a bit error rate (BER) and Tx data pattern of PRBS7. From the PMA mode, the TX_ELEC_IDLE port to the XVCR TXP/N pins. FTxRefClk = 75 MHz with typical settings. For data rates greater than Gbps, VDDA must be set to 05 V mode. See supply tolerance in the section Recommended Operating Conditions (see page 6). (see page 6) Receiver Performance The following table describes performance of the receiver. Table 53 PolarFire Transceiver Receiver Characteristics Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Condition Input voltage range VIN 0 V DDA V Differential peak-to-peak amplitude VIDPP mv Differential termination VITERM 85 Ω VITERM 100 Ω VITERM 150 Ω Common mode voltage V ICMDC VDDA 0.9 VDDA V DC coupled Exit electrical idle detection time TEIDET ns Run length of consecutive identical digits (CID) CID 200 UI CDR PPM tolerance 2 CDRPPM 15 % UI CDR lock-to-data time TLTD CDRREFCLK UI CDR lock-to-ref time TLTF CDRREFCLK UI Loss-of-signal detect (Peak VDETLHIGH mv Setting = 1 Detect Range setting = high) 9 VDETLHIGH mv Setting = 2 VDETLHIGH mv Setting = 3 VDETLHIGH mv Setting = 4 VDETLHIGH mv Setting = 5 VDETLHIGH mv Setting = 6 VDETLHIGH mv Setting = 7 Loss-of-signal detect (Peak VDETLOW mv Setting = PCIe 3,7 Detect Range setting = low) 9 VDETLOW mv Setting = SATA 4,8 VDETLOW mv Setting = 1 VDETLOW mv Setting = 2 VDETLOW mv Setting = 3 VDETLOW mv Setting = 4 VDETLOW mv Setting = 5 VDETLOW mv Setting = 6 VDETLOW mv Setting = 7 Sinusoidal jitter tolerance TSJTOL UI >8.5 Gbps 12.7 Gbps 5, 10 Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 46
51 Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Condition 0.41 UI > Gbps UI >6 to 3.2 Gbps UI >0.8 to 6 Gbps UI 250 to 800 Mpbs 5 Total jitter tolerance with stressed eye TTJTOLSE 0.65 UI 3 Gbps UI 6.25 Gbps UI Gbps 6 UI 12.7 Gbps6, 10 Sinusoidal jitter tolerance with stressed eye TSJTOLSE 0.1 UI 3 Gbps UI 6.25 Gbps UI Gbps 6 UI 12.7 Gbps6, 10 CTLE DC gain (all stages, max settings) CTLE AC gain (all stages, max settings) DFE AC gain (per 5 stages, max settings) 10 db 16 db 7.5 db Valid at 3.2 Gbps and below. Data vs. Rx reference clock frequency. Achieves compliance with PCIe electrical idle detection. Achieves compliance with SATA OOB specification. Rx jitter values based on bit error ratio (BER) of 10 12, AC coupled input with 400 mv V ID, all stages of Rx CTLE enabled, DFE disabled, 80 MHz sinusoidal jitter injected to Rx data. Rx jitter values based on bit error ratio (BER) of 10 12, AC coupled input with 400 mv V ID, all stages of Rx CTLE enabled, DFE enabled, 80 MHz sinusoidal jitter injected to Rx data. For PCIe: Low Threshold Setting = 1, High Threshold Setting = 2. For SATA: Low Threshold Setting = 2, High Threshold Setting = 3. Loss of signal detection is valid for input signals that transition at a density 1 Gbps for PRBS7 data or 6 Gbps for PRBS31 data. For data rates greater than Gbps, VDDA must be set to 05 V mode. See supply tolerance in the section Recommended Operating Conditions (see page 6). 7.5 Transceiver Protocol Characteristics The following section describes transceiver protocol characteristics PCI Express The following tables describe the PCI express. Table 54 PCI Express Gen1 Parameter Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter 2.5 Gbps 0.25 UI Receiver jitter tolerance 2.5 Gbps 0.4 UI Note: With add-in card, as specified in PCI Express CEM Rev 2.0. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 47
52 Table 55 PCI Express Gen2 Parameter Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter 5.0 Gbps 0.35 UI Receiver jitter tolerance 5.0 Gbps 0.4 UI Note: With add-in card as specified in PCI Express CEM Rev Interlaken The following table describes Interlaken. Table 56 Interlaken Parameter Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter Gbps 0.3 UI Gbps 0.3 UI 12.7 Gbps 1 UI Receiver jitter tolerance Gbps 0.6 UI Gbps 0.65 UI 12.7 Gbps 1 UI For data rates greater than Gbps, VDDA must be set to 05 V mode. See supply tolerance in the section Recommended Operating Conditions (see page 6) GbE (10GBASE-R, and 10GBASE-KR) The following table describes 10GbE (10GBASE-R). Table 57 10GbE (10GBASE-R) Parameter Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter Gbps 0.28 UI Receiver jitter tolerance Gbps 0.7 UI The following table describes 10GbE (10GBASE-KR). Table 58 10GbE (10GBASE-KR) Parameter Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter Gbps UI Receiver jitter tolerance Gbps UI The following table describes 10GbE (XAUI). Table 59 10GbE (XAUI) Parameter Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter (near end) 3 Gbps 0.35 UI Total transmit jitter (far end) 0.55 UI Receiver jitter tolerance 3 Gbps 0.65 UI The following table describes 10GbE (RXAUI). Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 48
53 Table 60 10GbE (RXAUI) Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter 6.25 Gbps UI Receiver jitter tolerance 6.25 Gbps UI GbE (1000BASE-T) The following table describes 1GbE (1000BASE-T). Table 61 1GbE (1000BASE-T) Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter 25 Gbps UI Receiver jitter tolerance 25 Gbps UI The following table describes 1GbE (1000BASE-X). Table 62 1GbE (1000BASE-X) Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter 25 Gbps UI Receiver jitter tolerance 25 Gbps UI SGMII and QSGMII The following table describes SGMII. Table 63 SGMII Parameter Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter 25 Gbps 0.24 UI Receiver jitter tolerance 25 Gbps UI The following table describes QSGMII. Table 64 QSGMII Parameter Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter 5.0 Gbps 0.3 UI Receiver jitter tolerance 5.0 Gbps 0.65 UI SDI The following table describes SDI. Table 65 SDI Parameter Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter UI Receiver jitter tolerance UI Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 49
54 7.5.7 CPRI The following table describes CPRI. Table 66 CPRI Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter Gbps UI 2288 Gbps UI Gbps UI Gbps UI Gbps UI Gbps UI Gbps UI Gbps UI Gbps 1 UI Receive jitter tolerance Gbps UI 2288 Gbps UI Gbps UI Gbps UI Gbps UI Gbps UI Gbps UI Gbps UI Gbps 1 UI For data rates greater than Gbps, VDDA must be set to 05 V mode. See supply tolerance in the section Recommended Operating Conditions (see page 6) JESD204B The following table describes JESD204B. Table 67 JESD204B Parameter Data Rate Min Max Unit Total transmit jitter 3 Gbps 0.35 UI 6.25 Gbps 0.3 UI 12.5 Gbps 1 UI Receive jitter tolerance 3 Gbps 0.56 UI 6.25 Gbps 0.6 UI 12.5 Gbps 1 UI For data rates greater than Gbps, VDDA must be set to 05V mode. See supply tolerance in the section Recommended Operating Conditions (see page 6). 7.6 Non-Volatile Characteristics The following section describes non-volatile characteristics. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 50
55 7.6.1 FPGA Programming Cycle and Retention The following table describes FPGA programming cycle and retention. Table 68 FPGA Programming Cycles vs Retention Characteristics Programming T J Programming Cycles, Max Retention Years Retention Years at T J 0 C to 85 C C 0 C to 100 C C 20 C to 100 C C 40 C to 100 C C 40 C to 85 C C 40 C to 55 C C Note: Power supplied to the device must be valid during programming operations such as programming and verify. Programming recovery mode is available only for in-application programming mode and requires an external SPI flash FPGA Programming Time The following tables describe FPGA programming time. Table 69 Master SPI Programming Time (IAP) Parameter Symbol Devices Typ Max Unit Programming time TPROG MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS s Table 70 Slave SPI Programming Time Parameter Symbol Devices Typ Max Unit Programming time TPROG MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS s SmartFusion2 with MSS running at 100 MHz, MSS_SPI_0 port running at 7 MHz. DirectC version 4. Table 71 JTAG Programming Time Parameter Symbol Devices Typ Max Unit Programming time TPROG MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS 56 s MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS 1 95 s MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS s Programmer: FlashPro5 with TCK 10 MHz. PC Configuration: Intel i7 at 3.6 GHz, 32 GB RAM, Windows 10. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 51
56 7.6.3 FPGA Bitstream Sizes The following table describes FPGA bitstream sizes. Table 72 Initialization Client Sizes Device Plaintext Ciphertext MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS 2916 KB 3006 KB MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS 4265 KB 4403 KB MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS Note: Worst case initializing all fabric LSRAM, USRAM, and UPROM. Table 73 Bitstream Sizes File Devices FPGA Security SNVM (all pages) SPI MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS DAT MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS FPGA+ SNVM FPGA+ Sec SNVM+ Sec FPGA+ SNVM+ Sec SPI MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS 5.9 MB 3.4 KB 59.7 KB 5.9 MB 5.9 MB 62.2 KB 6.0 MB DAT MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS 5.9 MB 7.3 KB 62 KB 6.0 MB 5.9 MB 66.3 KB 6.0 MB SPI MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS 9.3 MB 3.5 KB 59.7 KB 9.6 MB 9.5 MB 62.2 KB 9.6 MB DAT MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS 9.3 MB 7.6 KB 62 KB 9.6 MB 9.5 MB 66.3 KB 9.6 MB SPI MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS DAT MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS Digest Cycles Digests verify the integrity of the programmed non-volatile data. Digests are a cryptographic hash of various data areas. Any digest that reports back an error raises the digest tamper flag. Table 74 Maximum Number of Digest Cycles Retention Since Programmed (N = Number Digests During that Time) 1 Digest TJ Storage and Operating TJ N 300 N = 500 N = 1000 N = 1500 N = 2000 N = 4000 N = 6000 Unit Retention 40 to to LF 17 LF 12 LF 10 LF 8 LF 4 LF 2 LF C Years 40 to to LF 17 LF 12 LF 10 LF 8 LF 4 LF 2 LF C Years 40 to to LF 20 LF 20 LF 20 LF 16 LF 8 LF 4 LF C Years 40 to to LF 20 LF 20 LF 20 LF 20 LF 20 LF 20 LF C Years LF = Lifetime factor as defined by the number of programming cycles the device has seen under the conditions listed in the following table. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 52
57 Table 75 FPGA Programming Cycles Lifetime Factor Programming T J Programming Cycles LF 40 C to 100 C C to 85 C C to 55 C Notes: The maximum number of device digest cycles is 100K. Digests are operational only over the 40 C to 100 C temperature range. After a program cycle, an additional N digests cycles are allowed with the resultant retention characteristics for the total operating and storage temperature shown. Retention is specified for total device storage and operating temperature. All temperatures are junction temperatures (T J). Example digests cycles are performed between programming cycles. N = 500. The operating conditions are 40 C to 85 C T J. 501 programming cycles have occurred. The retention under these operating conditions is 20 LF = 20.8 = 16 years. Example 2 one programming cycle has occurred, N = 1500 digest cycles have occurred. Temperature range is 40 C to 100 C. The resultant retention is 10 LF or 10 years over the industrial temperature range Digest Time The following table describes digest time. Table 76 Digest Times Parameter Devices Typ Max Unit Setup time All 2 μs Fabric digest run time MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS ms MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS ms MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS ms MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS ms UFS CC digest run time MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS μs snvm digest run time 1 MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS ms MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS ms MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS ms MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS ms UFS UL digest run time MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS μs User key digest run time 2 MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS μs Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 53
58 Parameter Devices Typ Max Unit UFS UPERM digest run time MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS μs Factory digest run time MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS μs MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS μs The entire snvm is used as ROM. 2. Valid for user key 0 through 6. Note: These times do not include the power-up to functional timing overhead when using digest checks on power-up Zeroization Time The following tables describe zeroization time. A zeroization operation is counted as one programming cycle. Table 77 Zeroization Times for MPF100T, TL, TS, and TLS Devices Parameter Typ Max Unit Conditions Time to enter zeroization ms Zip flag set Time to destroy the fabric data 1 ms Data erased Time to destroy data in non-volatile memory (like new) 1, 2 ms One iteration of scrubbing Time to destroy data in non-volatile memory (recoverable) 1, 3 ms One iteration of scrubbing Time to destroy data in non-volatile memory (non-recoverable) 1, 4 ms One iteration of scrubbing Time to scrub the fabric data 1 s Full scrubbing Time to scrub the pnvm data (like new) 1, 2 s Full scrubbing Time to scrub the pnvm data (recoverable) 1, 3 s Full scrubbing Time to scrub the fabric data pnvm data (non-recoverable) 1, 4 s Full scrubbing Time to verify 5 s Total completion time after entering zeroization. Like new mode zeroizes user design security setting and snvm content. Recoverable mode zeroizes user design security setting, snvm and factory keys. Non-recoverable mode zeroizes user design security setting, snvm and factory keys, and factory data required for programming. Time to verify after scrubbing completes. Table 78 Zeroization Times for MPF200T, TL, TS, and TLS Devices Parameter Typ Max Unit Conditions Time to enter zeroization ms Zip flag set Time to destroy the fabric data 1 ms Data erased Time to destroy data in non-volatile memory (like new) 1, 2 ms One iteration of scrubbing Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 54
59 Parameter Typ Max Unit Conditions Time to destroy data in non-volatile memory (recoverable) 1, 3 ms One iteration of scrubbing Time to destroy data in non-volatile memory (non-recoverable) 1, 4 ms One iteration of scrubbing Time to scrub the fabric data 1 s Full scrubbing Time to scrub the pnvm data (like new) 1, 2 s Full scrubbing Time to scrub the pnvm data (recoverable) 1, 3 s Full scrubbing Time to scrub the fabric data PNVM data (non-recoverable) 1, 4 s Full scrubbing Time to verify 5 s Total completion time after interning zeroization. Like new mode zeroizes user design security setting and snvm content. Recoverable mode zeroizes user design security setting, snvm and factory keys. Non-recoverable mode zeroizes user design security setting, snvm and factory keys, and factory data required for programming. Time to verify after scrubbing completes. Table 79 Zeroization Times for MPF300T, TL, TS, and TLS Devices Parameter Typ Max Unit Conditions Time to enter zeroization ms Zip flag set Time to destroy the fabric data 1 ms Data erased Time to destroy data in non-volatile memory (like new) 1, 2 ms One iteration of scrubbing Time to destroy data in non-volatile memory (recoverable) 1, 3 ms One iteration of scrubbing Time to destroy data in non-volatile memory (non- recoverable) 1, 4 ms One iteration of scrubbing Time to scrub the fabric data 1 s Full scrubbing Time to scrub the pnvm data (like new) 1, 2 s Full scrubbing Time to scrub the pnvm data (recoverable) 1, 3 s Full scrubbing Time to scrub the fabric data pnvm data (non-recoverable) 1, 4 s Full scrubbing Time to verify 5 s Total completion time after interning zeroization. Like new mode zeroizes user design security setting and snvm content. Recoverable mode zeroizes user design security setting, snvm and factory keys. Non-recoverable mode zeroizes user design security setting, snvm and factory keys, and factory data required for programming. Time to verify after scrubbing completes. Table 80 Zeroization Times for MPF500T, TL, TS, and TLS Devices Parameter Typ Max Unit Conditions Time to enter zeroization ms Zip flag set Time to destroy the fabric data 1 ms Data erased Time to destroy data in non-volatile memory (like new) 1, 2 ms One iteration of scrubbing Time to destroy data in non-volatile memory (recoverable) 1, 3 ms One iteration of scrubbing Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 55
60 Parameter Typ Max Unit Conditions Time to destroy data in non-volatile memory (non-recoverable) 1, 4 ms One iteration of scrubbing Time to scrub the fabric data 1 s Full scrubbing Time to scrub the pnvm data (like new) 1, 2 s Full scrubbing Time to scrub the pnvm data (recoverable) 1, 3 s Full scrubbing Time to scrub the fabric data pnvm data (non-recoverable) 1 s Full scrubbing Time to verify 5 s Total completion time after entering zeroization. Like new mode zeroizes user design security setting and snvm content. Recoverable mode zeroizes user design security setting, snvm and factory keys. Non-recoverable mode zeroizes user design security setting, snvm and factory keys, and factory data required for programming. Time to verify after scrubbing completes Verify Time The following tables describe verify time. Table 81 Standalone Fabric Verify Times Parameter Devices Max Unit Standalone verification over JTAG MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS 53 1 s MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS 90 1 s MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS s Standalone verification over SPI MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS 55 2 s MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS s Programmer: FlashPro5, TCK 10 MHz; PC configuration: Intel i7 at 3.6 GHz, 32 GB RAM, Windows S martfusion2 with MSS running at 100 MHz, MSS_SPI_0 port running at 7 MHz. DirectC version 4. Notes: Standalone verify is limited to 2000 total device hours ove r the industrial 40 C to 100 C temperature. Use the digest system service, for verify device time more than 2000 hours. Standalone verify checks the programming margin on both the P and N gates of the push-pull cell. Digest checks only the P side of the push-pull gate. However, the push-pull gates work in tandem. Digest check is recommended if users believe they will exceed the 2000 hour verify time specification. s Table 82 Verify Time by Programming Hardware Devices IAP FlashPro4 FlashPro5 BP Silicon Sculptor Units MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 56
61 Notes: FlashPro4 4 MHz TCK. FlashPro5 10 MHz TCK. PC configuration: Intel i7 at 3.6 GHz, 32 GB RAM, Windows 10. Table 83 Verify System Services Parameter Symbol ServiceID Devices Typ Max Unit In application verify by index TIAP_Ver_Index 44H MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS In application verify by SPI address TIAP_Ver_Addr 45H MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS s s Authentication Time The following tables describe authentication system service time. Table 84 Authentication Services Parameter Symbol ServiceID Devices Typ Max Unit Bitstream Authentication TBIT_AUTH 22H MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS s IAP Image Authentication TIAP_AUTH 23H MPF100T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF200T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF300T, TL, TS, TLS s MPF500T, TL, TS, TLS Secure NVM Performance The following table describes secure NVM performance. Table 85 snvm Read/Write Characteristics Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Conditions Plain text programming ms Authenticated text programming ms Authenticated and encrypted text programming ms Authentication R/W 1st access from power-up overhead TPUF_OVHD ms From TFAB_READY Plain text read μs Authenticated text read μs Authenticated and decrypted text read μs Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 57
62 Notes: Page size= 252 bytes (non-authenticated), 236 bytes (authenticated). Only page reads and writes allowed. T PUF_OVHD is an additional time that occurs on the first R/W, after cold or warm boot, to snvm using authenticated or authenticated and encrypted text Secure NVM Programming Cycles The following table describes secure NVM programming cycles. Table 86 snvm Programming Cycles vs. Retention Characteristics Programming Temperature Programming Cycles Per Page, Max Programming Cycles Per Block, Max 40 C to 100 C 10, , C to 85 C 10, , C to 55 C 10, , Note: Page size = 128 bytes. Block size = 56 KBytes. Retention Years 7.7 System Services This section describes system switching and throughput characteristics System Services Throughput Characteristics The following table describes system services throughput characteristics. Table 87 System Services Throughput Characteristics Parameter Symbol Service ID Typ Max Unit Conditions Serial number TSerial 00H μs User code TUser 01H μs Design information TDesign 02H μs Device certificate TCert 03H ms Read digests Tdigest_read 04H μs Query security locks Tsec_Query 05H μs Read debug information TRd_debug 06H μs Reserved 07H 0FH Secure NVM write plain text TSNVM_Wr_Plain 10H Note 1 Secure NVM write authenticated plain text Secure NVM write authenticated cipher text TSNVM_Wr_Auth 11H Note 1 TSNVM_Wr_Cipher 12H Note 1 Reserved 13H 17H Secure NVM read TSNVM_Rd 18H Note 1 Digital signature service raw TSIG_RAW 19H ms Digital signature service DER TSIG_DER 1AH ms Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 58
63 Parameter Symbol Service ID Typ Max Unit Conditions Reserved 1BH 1FH PUF emulation TChallenge 20H ms Nonce service TNonce 21H 2 4 ms Bitstream authentication TBIT_AUTH 22H Note 4 IAP Image authentication TIAP_AUTH 23H Note 4 Reserved 26H 3FH In application programming by index TIAP_Prg_Index 42H Note 2 In application programming by SPI address TIAP_Prg_Addr 43H Note 2 In application verify by index TIAP_Ver_Index 44H Note 5 In application verify by SPI address TIAP_Ver_Addr 45H Note 5 Auto update TAutoUpdate 46H Note 2 Digest check Tdigest_chk 47H Note See snvm Read/Write Characteristics (see page 57). See SPI Master Programming Time (see page 51). See Digest Times (see page 53). See Authentication Services Time (see page 57). See Verify Services Time (see page 57). Throughputs described are measured from SS_REQ assertion to BUSY de-assertion. 7.8 Fabric Macros This section describes switching characteristics of UJTAG, UJTAG_SEC, USPI, system controller, and temper detectors and dynamic reconfiguration details UJTAG Switching Characteristics The following section describes characteristics of UJTAG switching. Table 88 UJTAG Performance Characteristics Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Condition TCK frequency FTCK 25 MHz Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 59
64 Figure 3 UJTAG Timing Diagram UJTAG_SEC Switching Characteristics The following table describes characteristics of UJTAG_SEC switching. Table 89 UJTAG Security Performance Characteristics Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Condition TCK frequency FTCK MHz USPI Switching Characteristics The following section describes characteristics of USPI switching. Table 90 SPI Macro Interface Timing Characteristics Parameter Symbol V DDI = 3.3 V Max Propagation delay from the fabric to pins 1 V DDI = 2.5 V Max V DDI = 8 V Max V DDI = 5 V Max V DDI = 2 V Max TPD_MOSI ns TPD_MISO ns TPD_SS ns TPD_SCK ns TPD_MOSI_OE ns TPD_SS_OE ns TPD_SCK_OE ns Assumes CL of the relevant I/O standard as described in the input and output delay measurement tables. Unit Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 60
65 Figure 4 USPI Switching Characteristics Tamper Detectors The following section describes tamper detectors. Table 91 ADC Conversion Rate Parameter Description Min Typ 1 Max TCONV1 Time from enable changing from zero to non-zero value to first conversion completes. Minimum value applies when POWEROFF = μs 470 μs TCONVN Time between subsequent channel conversions. 480 μs TSETUP Data channel and output to valid asserted. Data is held until next conversion completes, that is >480 μs. 0 ns TVALID 2 Width of the valid pulse. 625 μs 2 μs TRATE Time from start of first set of conversions to the start of the next set. Can be considered as the conversion rate. Is set by the conversion rate parameter. 480 μs Rate 32 μs 8128 μs Min, typ, and max refer to variation due to functional configuration and the raw TVS value. The actual internal correction time will vary based on the raw TVS value. 2. The pulse width varies depending on the time taken to complete the internal calibration multiplication, this can be up to 375 ns. Note: Once the TVS block is active, the enable signal is sampled 25 ns before the falling edge of valid. The next enabled channel in the sequence is started; that is, if channel 0 has just completed and only channels 0 and 3 are enabled; the next channel will be 3. When all the enabled channels in the sequence are completed, the TVS waits for the conversion rate timer to expire. The enable signal may be changed at any time if it changes to 4 b0000 while valid is asserted (and 25 ns before valid is deasserted), then no further conversions will be started. Table 92 Temperature and Voltage Sensor Electrical Characteristics Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Condition Temperature sensing range C Temperature sensing accuracy C Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 61
66 Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Condition Voltage sensing range V Voltage sensing accuracy 5 5 % Table 93 Tamper Macro Timing Characteristics Flags and Clearing Parameter Symbol Typ Max Unit From event detection to flag generation TJTAG_ACTIVE 1, 2 5 ns TMESH_ERR μs TCLK_GLITCH 1, 2 50 ns TCLK_FREQ 1, 2 4 μs TLOW_1P μs THIGH_1P μs THIGH_2P μs TGLITCH_1P ns TSECDEC 1, 2 5 ns TDRI_ERR 2 50 ns TWDOG 1, 2 5 ns TLOCK_ERR 2 5 ns Time from system controller instruction execution to flag generation TINST_BUF_ACCESS 2, 3 TINST_DEBUG 2, 3 TINST_CHK_DIGEST 2, 3 TINST_EC_SETUP 2, 3 TINST_FACT_PRIV 2, 3 TINST_KEY_VAL 2, 3 TINST_MISC 2, 3 TINST_PASSCODE_MATCH 2, 3 TINST_PASSCODE_SETUP 2, 3 TINST_PROG 2, 3 TINST_PUB_INFO 2, 3 TINST_ZERO_RECO 2, 3 TINST_PASSCODE_FAIL 2, 3 TINST_KEY_VAL_FAIL 2, 3 TINST_UNUSED 2, 3 Time from sending the CLEAR to deassertion on FLAG TCLEAR_FLAG 3 ns Not available during Flash*Freeze. The timing does not impact the user design, however it is useful for security analysis. System service requests from the fabric will interrupt the system controller delaying the generation of the flag. Table 94 Tamper Macro Response Timing Characteristics Parameter Symbol Typ Max Unit Time from triggering the response to all I/Os disabled TIO_DISABLE 150 ns Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 62
67 Parameter Symbol Typ Max Unit Time from negation of RESPONSE to all I/Os re-enabled TCLR_IO_DISABLE 10 us Time from triggering the response to security locked TLOCKDOWN 20 ns Time from negation of RESPONSE to earlier security unlock condition TCLR_LOCKDOWN 20 ns Time from triggering the response to device enters RESET Ttr_RESET Time from triggering the response to start of zeroization Ttr_ZEROLISE System Controller Suspend Switching Characteristics The following table describes the characteristics of system controller suspend switching. Table 95 System Controller Suspend Entry and Exit Characteristics Parameter Symbol Definition Typ Max Unit Time from TRSTb falling edge to SUSPEND_EN signal assertion Tsuspend_Tr 1, 2 Suspend entry time from TRST_N assertion ns Time from TRSTb rising edge to ACTIVE signal assertion Tsuspend_exit Suspend exit time from TRST_N negation ns 2. ACTIVE indicates that the system controller is inactive or active regardless of the state of SUSPEND_EN. ACTIVE signal must never be asserted with SUSPEND_EN is asserted Dynamic Reconfiguration Interface The following table provides interface timing information for the DRI, which is an embedded APB slave interface within the FPGA fabric that does not use FPGA resources. Table 96 Dynamic Reconfiguration Interface Timing Characteristics Parameter Symbol Max Unit PCLK frequency FPD _PCLK 200 MHz 7.9 Power-Up to Functional Timing Microsemi non-volatile FPGA technology offers the fastest boot-time of any mid-range FPGA in the market. The following tables describes both cold-boot (from power-on) and warm-boot (assertion of DEVRST_N pin or assertion of reset from the tamper macro) timing. The power-up diagrams assume all power supplies to the device are stable Power-On (Cold) Reset Initialization Sequence The following cold reset timing diagram shows the initialization sequencing of the device. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 63
68 Figure 5 Cold Reset Timing Notes: The previous diagram showsthe case where /VDDAUX of I/O banks are powered either before or sufficiently soon after VDD/VDD18/VDD25 that the I/O bank enable time is measured from the assertion time of VDD/VDD18/VDD25 (that is, the PUFT specification). If /VDDAUX of I/O banks are powered sufficiently after VDD/VDD18/VDD25, then the I/O bank enable time is measured from the assertion of /VDDAUX and is not specified by the PUFT specification. In this case, I/O operation is indicated by the assertion of BANK_i STATUS, rather than being measured relative to FABRIC_POR_N negation. AUTOCALIB_DONE assertion indicates the completion of calibration for any I/O banks specified by the user for auto-calibration. AUTOCALIB_DONE asserts independently of DEVICE_INIT_DONE. It may assert before or after DEVICE_INIT_DONE and is determined by the following: How long after VDD/VDD18/VDD25 that /VDDAUX are powered on. Note that if any of the user-specified I/O banks are not powered on within the auto-calibration timeout window, then AUTOCALIB_DONE doesn't assert until after this timeout. The specified ramp times of of each I/O bank designated for auto-calibration. How much auto-initialization is to be performed for the PCIe, SERDES transceivers, and fabric LSRAMs. If any of the I/O banks specified for auto-calibration do not have their /VDDAUX powered on within the auto-calibration timeout window, then it will be approximately auto-calibrated whenever /VDDAUX is subsequently powered on. To obtain an accurate calibration however, on such IO banks, it is necessary to initiate a re-calibration (using CALIB_START from fabric). AVM_ACTIVE only asserts if avionics mode is being used. It is asserted when the later of DEVICE_INIT_DONE or AUTOCALIB_DONE assert Warm Reset Initialization Sequence The following warm reset timing diagram shows the initialization sequencing of the device when either DEVRST_N or TAMPER_RESET_DEVICE signals are asserted. Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 64
69 Figure 6 Warm Reset Timing Power-On Reset Voltages Main Supplies The start of power-up to functional time (T PUFT) is defined as the point at which the latest of the main supplies (VDD, VDD18, VDD25) reach the reference voltage levels specified in the following table. This starts the process of releasing the reset of the device and powering on the FPGA fabric and IOs. Table 97 POR Ref Voltages Supply Power-On Reset Start Point (V) Note VDD 0.95 Applies to both 0 V and 05 V operation. VDD18 71 VDD I/O-Related Supplies For the I/Os to become functional (for low speed, sub 400 MHz operation), the (per-bank) I/O supplies (, VDDAUX) must reach the trip point voltage levels specified in the following table and the main supplies above must also be powered on. Table 98 I/O-Related Supplies Supply 0.85 VDDAUX 6 I/O Power-Up Start Point (V) There are no sequencing requirements for the power supplies. However, 3 and must be valid at same time as the main supplies. The other IO supplies (, VDDAUX) have no effect on power-up of FPGA fabric (that is, the fabric still powers up even if the IO supplies of some IO banks remain powered off). Microsemi Proprietary and Confidential. DS0141 Datasheet Revision 2 65
ER0207 Errata. PolarFire FPGAs: Engineering Samples (ES) Devices
 ER0207 Errata PolarFire FPGAs: Engineering Samples () Devices PolarFire FPGAs: Engineering Samples () Devices Contents 1 Revision History... 1 1.1 Revision 2.1... 1 1.2 Revision 2.0... 1 1.3 Revision 1.0...
ER0207 Errata PolarFire FPGAs: Engineering Samples () Devices PolarFire FPGAs: Engineering Samples () Devices Contents 1 Revision History... 1 1.1 Revision 2.1... 1 1.2 Revision 2.0... 1 1.3 Revision 1.0...
Intel MAX 10 General Purpose I/O User Guide
 Intel MAX 10 General Purpose I/O User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel MAX 10 I/O Overview...3
Intel MAX 10 General Purpose I/O User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel MAX 10 I/O Overview...3
MAX 10 General Purpose I/O User Guide
 MAX 10 General Purpose I/O User Guide Subscribe UG-M10GPIO 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents MAX 10 I/O Overview... 1-1 MAX 10 Devices I/O Resources Per Package...1-1
MAX 10 General Purpose I/O User Guide Subscribe UG-M10GPIO 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents MAX 10 I/O Overview... 1-1 MAX 10 Devices I/O Resources Per Package...1-1
MAX 10 FPGA Signal Integrity Design Guidelines
 2014.12.15 M10-SIDG Subscribe Today s complex FPGA system design is incomplete without addressing the integrity of signals coming in to and out of the FPGA. Simultaneous switching noise (SSN) often leads
2014.12.15 M10-SIDG Subscribe Today s complex FPGA system design is incomplete without addressing the integrity of signals coming in to and out of the FPGA. Simultaneous switching noise (SSN) often leads
8. Selectable I/O Standards in Arria GX Devices
 8. Selectable I/O Standards in Arria GX Devices AGX52008-1.2 Introduction This chapter provides guidelines for using industry I/O standards in Arria GX devices, including: I/O features I/O standards External
8. Selectable I/O Standards in Arria GX Devices AGX52008-1.2 Introduction This chapter provides guidelines for using industry I/O standards in Arria GX devices, including: I/O features I/O standards External
Intel Stratix 10 General Purpose I/O User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 General Purpose I/O User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Stratix 10 I/O
Intel Stratix 10 General Purpose I/O User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 18.0 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1. Intel Stratix 10 I/O
UG0725 User Guide PolarFire FPGA Device Power-Up and Resets
 UG0725 User Guide PolarFire FPGA Device Power-Up and Resets Microsemi Corporate Headquarters One Enterprise, Aliso Viejo, CA 92656 USA Within the USA: +1 (800) 713-4113 Outside the USA: +1 (949) 380-6100
UG0725 User Guide PolarFire FPGA Device Power-Up and Resets Microsemi Corporate Headquarters One Enterprise, Aliso Viejo, CA 92656 USA Within the USA: +1 (800) 713-4113 Outside the USA: +1 (949) 380-6100
Intel Stratix 10 General Purpose I/O User Guide
 Intel Stratix 10 General Purpose I/O User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel Stratix 10 I/O
Intel Stratix 10 General Purpose I/O User Guide Updated for Intel Quartus Prime Design Suite: 17.1 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel Stratix 10 I/O
6. I/O Features in Stratix IV Devices
 6. I/O Features in Stratix IV Devices September 2012 SIV51006-3.4 SIV51006-3.4 This chapter describes how Stratix IV devices provide I/O capabilities that allow you to work in compliance with current and
6. I/O Features in Stratix IV Devices September 2012 SIV51006-3.4 SIV51006-3.4 This chapter describes how Stratix IV devices provide I/O capabilities that allow you to work in compliance with current and
PO0137 Product Overview. PolarFire FPGA
 PO0137 Product Overview PolarFire FPGA Contents 1 Revision History... 1 1.1 Revision 1.2... 1 1.2 Revision 1.1... 1 1.3 Revision 1.0... 1 2 Overview... 2 2.1 Summary of Features... 2 2.1.1 Low-Power Features...
PO0137 Product Overview PolarFire FPGA Contents 1 Revision History... 1 1.1 Revision 1.2... 1 1.2 Revision 1.1... 1 1.3 Revision 1.0... 1 2 Overview... 2 2.1 Summary of Features... 2 2.1.1 Low-Power Features...
6. I/O Features in Arria II Devices
 6. I/O Features in Arria II Devices December 2011 AIIGX51006-4.2 AIIGX51006-4.2 This chapter describes how Arria II devices provide I/O capabilities that allow you to work in compliance with current and
6. I/O Features in Arria II Devices December 2011 AIIGX51006-4.2 AIIGX51006-4.2 This chapter describes how Arria II devices provide I/O capabilities that allow you to work in compliance with current and
MAX 10 FPGA Device Datasheet
 2015.05.04 M10-DATASHEET Subscribe This datasheet describes the electrical characteristics, switching characteristics, configuration specifications, and timing for MAX 10 devices. Table 1: MAX 10 Device
2015.05.04 M10-DATASHEET Subscribe This datasheet describes the electrical characteristics, switching characteristics, configuration specifications, and timing for MAX 10 devices. Table 1: MAX 10 Device
Intel MAX 10 FPGA Device Datasheet
 M10-DATASHEET 2017.06.16 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents Intel MAX 10 FPGA Device Datasheet... 3 Electrical Characteristics... 3 Operating Conditions...4 Switching Characteristics...25 Core Performance
M10-DATASHEET 2017.06.16 Subscribe Send Feedback Contents Contents Intel MAX 10 FPGA Device Datasheet... 3 Electrical Characteristics... 3 Operating Conditions...4 Switching Characteristics...25 Core Performance
6. I/O Features for HardCopy IV Devices
 6. I/O Features for HardCopy IV Devices March 2012 HIV51006-2.3 HIV51006-2.3 This chapter describes the I/O standards, features, termination schemes, and performance supported in HardCopy IV devices. All
6. I/O Features for HardCopy IV Devices March 2012 HIV51006-2.3 HIV51006-2.3 This chapter describes the I/O standards, features, termination schemes, and performance supported in HardCopy IV devices. All
AN 754: MIPI D-PHY Solution with Passive Resistor Networks in Intel Low-Cost FPGAs
 AN 754: MIPI D-PHY Solution with Passive Resistor Networks in Intel Low-Cost FPGAs Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents AN 754: MIPI D-PHY Solution with Passive
AN 754: MIPI D-PHY Solution with Passive Resistor Networks in Intel Low-Cost FPGAs Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents AN 754: MIPI D-PHY Solution with Passive
MIPI D-PHY Solution with Passive Resistor Networks in Altera Low Cost FPGA
 2015.12.23 MIPI D-PHY Solution with Passive Resistor Networks in Altera Low Cost FPGA AN-754 Subscribe Introduction to MIPI D-PHY The Mobile Industry Processor Interface (MIPI) is an industry consortium
2015.12.23 MIPI D-PHY Solution with Passive Resistor Networks in Altera Low Cost FPGA AN-754 Subscribe Introduction to MIPI D-PHY The Mobile Industry Processor Interface (MIPI) is an industry consortium
Frequency Generator for Pentium Based Systems
 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ICS969C-23 Frequency Generator for Pentium Based Systems General Description The ICS969C-23 is a low-cost frequency generator designed specifically for Pentium-based chip
Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ICS969C-23 Frequency Generator for Pentium Based Systems General Description The ICS969C-23 is a low-cost frequency generator designed specifically for Pentium-based chip
ZL40218 Precision 1:8 LVDS Fanout Buffer
 Precision 1:8 LVDS Fanout Buffer Data Sheet Features Inputs/Outputs Accepts differential or single-ended input LVPECL, LVDS, CML, HCSL, LVCMOS Eight precision LVDS outputs Operating frequency up to 750
Precision 1:8 LVDS Fanout Buffer Data Sheet Features Inputs/Outputs Accepts differential or single-ended input LVPECL, LVDS, CML, HCSL, LVCMOS Eight precision LVDS outputs Operating frequency up to 750
PI6C557-01BQ. PCIe 3.0 Clock Generator with 1 HCSL Outputs. Features. Description. Pin Configuration (16-Pin TQFN) Block Diagram
 s Features ÎÎPCIe 3.0 compliant à à Phase jitter - 0.45ps RMS (High Freq. Typ.) ÎÎLVDS compatible output ÎÎSupply voltage of 3.3V ±10% ÎÎ25MHz crystal or clock input frequency ÎÎHCSL outputs, 0.8V Current
s Features ÎÎPCIe 3.0 compliant à à Phase jitter - 0.45ps RMS (High Freq. Typ.) ÎÎLVDS compatible output ÎÎSupply voltage of 3.3V ±10% ÎÎ25MHz crystal or clock input frequency ÎÎHCSL outputs, 0.8V Current
3.3V ZERO DELAY CLOCK BUFFER
 3.3V ZERO DELAY CLOCK BUFFER IDT2309A FEATURES: Phase-Lock Loop Clock Distribution 10MHz to 133MHz operating frequency Distributes one clock input to one bank of five and one bank of four outputs Separate
3.3V ZERO DELAY CLOCK BUFFER IDT2309A FEATURES: Phase-Lock Loop Clock Distribution 10MHz to 133MHz operating frequency Distributes one clock input to one bank of five and one bank of four outputs Separate
6. I/O Features for HardCopy III Devices
 6. I/O Features or HardCopy III Devices January 2011 HIII51006-3.1 HIII51006-3.1 This chapter describes the I/O standards, eatures, termination schemes, and perormance supported in HardCopy III devices.
6. I/O Features or HardCopy III Devices January 2011 HIII51006-3.1 HIII51006-3.1 This chapter describes the I/O standards, eatures, termination schemes, and perormance supported in HardCopy III devices.
4. Selectable I/O Standards in Stratix II and Stratix II GX Devices
 4. Selectable I/O Standards in Stratix II and Stratix II GX Devices SII52004-4.6 Introduction This chapter provides guidelines for using industry I/O standards in Stratix II and Stratix II GX devices,
4. Selectable I/O Standards in Stratix II and Stratix II GX Devices SII52004-4.6 Introduction This chapter provides guidelines for using industry I/O standards in Stratix II and Stratix II GX devices,
Cyclone III Device Handbook Volume 2
 Cyclone III Device Handbook Cyclone III Device Handbook 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com CIII5V2-4.1 Document last updated for Altera Complete Design Suite version: Document publication
Cyclone III Device Handbook Cyclone III Device Handbook 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com CIII5V2-4.1 Document last updated for Altera Complete Design Suite version: Document publication
MC Channel FPGA Bridge IC. for. MIPI D-PHY Systems and SLVS to LVDS Conversion PRELIMINARY DATASHEET. Version August 2014.
 MC20901 5 Channel FPGA Bridge IC for MIPI D-PHY Systems and SLVS to LVDS Conversion PRELIMINARY DATASHEET Version 1.06 August 2014 Meticom GmbH Meticom GmbH Page 1 of 17 Revision History MC20901 Version
MC20901 5 Channel FPGA Bridge IC for MIPI D-PHY Systems and SLVS to LVDS Conversion PRELIMINARY DATASHEET Version 1.06 August 2014 Meticom GmbH Meticom GmbH Page 1 of 17 Revision History MC20901 Version
2 TO 4 DIFFERENTIAL CLOCK MUX ICS Features
 DATASHEET 2 TO 4 DIFFERENTIAL CLOCK MUX ICS557-06 Description The ICS557-06 is a two to four differential clock mux designed for use in PCI-Express applications. The device selects one of the two differential
DATASHEET 2 TO 4 DIFFERENTIAL CLOCK MUX ICS557-06 Description The ICS557-06 is a two to four differential clock mux designed for use in PCI-Express applications. The device selects one of the two differential
Intel Stratix 10 Device Datasheet
 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents... 3 Electrical Characteristics... 4 Operating Conditions...4 Switching Characteristics...24 L-Tile Transceiver Performance
Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents... 3 Electrical Characteristics... 4 Operating Conditions...4 Switching Characteristics...24 L-Tile Transceiver Performance
2:1 MULTIPLEXER CHIP FOR PCI-EXPRESS ICS Features
 DATASHEET 2:1 MULTIPLEXER CHIP FOR PCI-EXPRESS ICS557-08 Description The ICS557-08 is a 2:1 multiplexer chip that allows the user to select one of the two HCSL (Host Clock Signal Level) input pairs and
DATASHEET 2:1 MULTIPLEXER CHIP FOR PCI-EXPRESS ICS557-08 Description The ICS557-08 is a 2:1 multiplexer chip that allows the user to select one of the two HCSL (Host Clock Signal Level) input pairs and
Section II. HardCopy APEX Device Family Data Sheet
 Section II. HardCopy APEX Device Family Data Sheet This section provides designers with the data sheet specifications for HardCopy APEX TM devices. These chapters contain feature definitions of the internal
Section II. HardCopy APEX Device Family Data Sheet This section provides designers with the data sheet specifications for HardCopy APEX TM devices. These chapters contain feature definitions of the internal
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 8-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH
 QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V -BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS3VH244 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to VCC Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to VCC or GND
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V -BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS3VH244 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to VCC Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to VCC or GND
UG0850 User Guide PolarFire FPGA Video Solution
 UG0850 User Guide PolarFire FPGA Video Solution Microsemi Headquarters One Enterprise, Aliso Viejo, CA 92656 USA Within the USA: +1 (800) 713-4113 Outside the USA: +1 (949) 380-6100 Sales: +1 (949) 380-6136
UG0850 User Guide PolarFire FPGA Video Solution Microsemi Headquarters One Enterprise, Aliso Viejo, CA 92656 USA Within the USA: +1 (800) 713-4113 Outside the USA: +1 (949) 380-6100 Sales: +1 (949) 380-6136
ZL40223 Precision 2:8 LVDS Fanout Buffer with Glitchfree Input Reference Switching and On-Chip Input Termination Data Sheet
 Features Inputs/Outputs Accepts two differential or single-ended inputs LVPECL, LVDS, CML, HCSL, LVCMOS Glitch-free switching of references On-chip input termination and biasing for AC coupled inputs Eight
Features Inputs/Outputs Accepts two differential or single-ended inputs LVPECL, LVDS, CML, HCSL, LVCMOS Glitch-free switching of references On-chip input termination and biasing for AC coupled inputs Eight
DATA SHEET AGM AG16K FPGA. Low Cost and High Performance FPGA. Revision: 1.0. Page 1 of 17
 DATA SHEET Revision: 1.0 AGM AG16K FPGA Low Cost and High Performance FPGA Page 1 of 17 General Description AGM AG16K FPGA devices are targeted to high-volume, cost-sensitive, applications, enabling system
DATA SHEET Revision: 1.0 AGM AG16K FPGA Low Cost and High Performance FPGA Page 1 of 17 General Description AGM AG16K FPGA devices are targeted to high-volume, cost-sensitive, applications, enabling system
CKSET V CC _VCO FIL SDO+ MAX3952 SCLKO+ SCLKO- PRBSEN LOCK GND TTL
 19-2405; Rev 0; 4/02 10Gbps 16:1 Serializer General Description The 16:1 serializer is optimized for 10.3Gbps and 9.95Gbps Ethernet applications. A serial clock output is provided for retiming the data
19-2405; Rev 0; 4/02 10Gbps 16:1 Serializer General Description The 16:1 serializer is optimized for 10.3Gbps and 9.95Gbps Ethernet applications. A serial clock output is provided for retiming the data
CAP+ CAP. Loop Filter
 STS-12/STS-3 Multirate Clock and Data Recovery Unit FEATURES Performs clock and data recovery for 622.08 Mbps (STS-12/OC-12/STM-4) or 155.52 Mbps (STS-3/OC-3/STM-1) NRZ data 19.44 MHz reference frequency
STS-12/STS-3 Multirate Clock and Data Recovery Unit FEATURES Performs clock and data recovery for 622.08 Mbps (STS-12/OC-12/STM-4) or 155.52 Mbps (STS-3/OC-3/STM-1) NRZ data 19.44 MHz reference frequency
FIN1101 LVDS Single Port High Speed Repeater
 FIN1101 LVDS Single Port High Speed Repeater General Description This single port repeater is designed for high speed interconnects utilizing Low Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS) technology. It accepts
FIN1101 LVDS Single Port High Speed Repeater General Description This single port repeater is designed for high speed interconnects utilizing Low Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS) technology. It accepts
3.3 Volt CMOS Bus Interface 8-Bit Latches
 Q 3.3 Volt CMOS Bus Interface 8-Bit Latches QS74FCT3373 QS74FCT32373 FEATURES/BENEFITS Pin and function compatible to the 74F373 JEDEC spec compatible 74LVT373 and 74FCT373T IOL = 24 ma Com. Available
Q 3.3 Volt CMOS Bus Interface 8-Bit Latches QS74FCT3373 QS74FCT32373 FEATURES/BENEFITS Pin and function compatible to the 74F373 JEDEC spec compatible 74LVT373 and 74FCT373T IOL = 24 ma Com. Available
4. Selectable I/O Standards in Stratix & Stratix GX Devices
 4. Selectable I/O Standards in Stratix & Stratix GX Devices S52004-3.4 Introduction The proliferation of I/O standards and the need for higher I/O performance have made it critical that devices have flexible
4. Selectable I/O Standards in Stratix & Stratix GX Devices S52004-3.4 Introduction The proliferation of I/O standards and the need for higher I/O performance have made it critical that devices have flexible
Section II. I/O Interfaces
 Section II. I/O Interfaces January 2011 Revision History This section includes the following chapters: Chapter 6, I/O Features for HardCopy IV Devices Chapter 7,
Section II. I/O Interfaces January 2011 Revision History This section includes the following chapters: Chapter 6, I/O Features for HardCopy IV Devices Chapter 7,
8. Migrating Stratix II Device Resources to HardCopy II Devices
 8. Migrating Stratix II Device Resources to HardCopy II Devices H51024-1.3 Introduction Altera HardCopy II devices and Stratix II devices are both manufactured on a 1.2-V, 90-nm process technology and
8. Migrating Stratix II Device Resources to HardCopy II Devices H51024-1.3 Introduction Altera HardCopy II devices and Stratix II devices are both manufactured on a 1.2-V, 90-nm process technology and
FIN1102 LVDS 2 Port High Speed Repeater
 LVDS 2 Port High Speed Repeater General Description This 2 port repeater is designed for high speed interconnects utilizing Low Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS) technology. The FIN1102 accepts and
LVDS 2 Port High Speed Repeater General Description This 2 port repeater is designed for high speed interconnects utilizing Low Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS) technology. The FIN1102 accepts and
TF10CP02 / TF10CP Gbps 2x2 LVDS Crosspoint Switches. Features. Description. Applications. Function Diagram. Ordering Information.
 Features DC to 1.5 Gbps low jitter, low skew, low power operation Pin configurable, fully differential, non-blocking architecture eases system design and PCB layout On-chip 100W input termination minimizes
Features DC to 1.5 Gbps low jitter, low skew, low power operation Pin configurable, fully differential, non-blocking architecture eases system design and PCB layout On-chip 100W input termination minimizes
Low Skew, 1-to-9, Differential-to- HSTL Fanout Buffer PRODUCT DISCONTINUATION NOTICE - LAST TIME BUY EXPIRES MAY 6, 2017
 Low Skew, 1-to-9, Differential-to- PRODUCT DISCONTINUATION NOTICE - LAST TIME BUY EXPIRES MAY 6, 2017 8521 DATASHEET GENERAL DESCRIPTION The 8521 is a low skew, 1-to-9 Differential-to-HSTL Fanout Buffer.
Low Skew, 1-to-9, Differential-to- PRODUCT DISCONTINUATION NOTICE - LAST TIME BUY EXPIRES MAY 6, 2017 8521 DATASHEET GENERAL DESCRIPTION The 8521 is a low skew, 1-to-9 Differential-to-HSTL Fanout Buffer.
Features. Applications
 Ultra-Precision 1:8 CML Fanout Buffer with Internal I/O Termination General Description The is a 2.5V/3.3V precision, high-speed, fully differential CML 1:8 fanout buffer. The is optimized to provide eight
Ultra-Precision 1:8 CML Fanout Buffer with Internal I/O Termination General Description The is a 2.5V/3.3V precision, high-speed, fully differential CML 1:8 fanout buffer. The is optimized to provide eight
DATA SHEET. Low Cost and High Performance FPGA. Revision: 1.1. Release date: Page 1 of 18
 DATA SHEET Revision: 1.1 Release date: AGM FPGA Low Cost and High Performance FPGA Page 1 of 18 General Description AGM FPGA devices are targeted to high-volume, cost-sensitive, applications, enabling
DATA SHEET Revision: 1.1 Release date: AGM FPGA Low Cost and High Performance FPGA Page 1 of 18 General Description AGM FPGA devices are targeted to high-volume, cost-sensitive, applications, enabling
2:1 MULTIPLEXER CHIP FOR PCI-EXPRESS ICS Description. Features. Block Diagram DATASHEET
 DATASHEET 2:1 MULTIPLEXER CHIP FOR PCI-EXPRESS ICS557-08 Description The ICS557-08 is a 2:1 multiplexer chip that allows the user to select one of the two HCSL (Host Clock Signal Level) or LVDS input pairs
DATASHEET 2:1 MULTIPLEXER CHIP FOR PCI-EXPRESS ICS557-08 Description The ICS557-08 is a 2:1 multiplexer chip that allows the user to select one of the two HCSL (Host Clock Signal Level) or LVDS input pairs
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 16-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH
 QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 16-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS32XVH245 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to VCC Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to VCC or
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 16-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS32XVH245 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to VCC Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to VCC or
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V/3.3V 20-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH
 QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V/3.3V 20-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS32XVH34 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to VCC Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to VCC or GND
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V/3.3V 20-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS32XVH34 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to VCC Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to VCC or GND
3.3V, 2.0GHz ANY DIFF. IN-TO-LVDS PROGRAMMABLE CLOCK DIVIDER FANOUT BUFFER W/ INTERNAL TERMINATION
 3.3V, 2.0GHz ANY DIFF. -TO-LVDS PROGRAMMABLE CLOCK DIVIDER FANOUT BUFFER W/ TERNAL TERMATION FEATURES Guaranteed AC performance > 2.0GHz f MAX output toggle > 3.0GHz f MAX input < 800ps t PD (matched-delay
3.3V, 2.0GHz ANY DIFF. -TO-LVDS PROGRAMMABLE CLOCK DIVIDER FANOUT BUFFER W/ TERNAL TERMATION FEATURES Guaranteed AC performance > 2.0GHz f MAX output toggle > 3.0GHz f MAX input < 800ps t PD (matched-delay
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 20-BIT DUAL PORT, HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH
 QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 20-BIT DUAL PORT, HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS3VH1662 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to Vcc Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 20-BIT DUAL PORT, HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS3VH1662 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to Vcc Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path
PI6C GHz 1:4 LVPECL Fanout Buffer with Internal Termination GND Q0+ Q0- REF_IN+ V TH V REF-AC REF_IN- Q1+ Q1- Q2+ Q2- Q3+ Q3- VDD.
 Features ÎÎInput Clock Frequency up to 6 GHz Typical ÎÎ4 pairs of differential LVPECL outputs ÎÎLow additive jitter, < 0.05ps (max) ÎÎInput CLK accepts: LVPECL, LVDS, CML, SSTL input level ÎÎOutput to
Features ÎÎInput Clock Frequency up to 6 GHz Typical ÎÎ4 pairs of differential LVPECL outputs ÎÎLow additive jitter, < 0.05ps (max) ÎÎInput CLK accepts: LVPECL, LVDS, CML, SSTL input level ÎÎOutput to
5. Using MAX V Devices in Multi-Voltage Systems
 June 2017 MV51005-2017.06.16 5. Using MAX V Devices in Multi-Voltage Systems MV51005-2017.06.16 This chapter describes how to implement Altera devices in multi-voltage systems without damaging the device
June 2017 MV51005-2017.06.16 5. Using MAX V Devices in Multi-Voltage Systems MV51005-2017.06.16 This chapter describes how to implement Altera devices in multi-voltage systems without damaging the device
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V QUAD ACTIVE LOW, HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH
 QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V QUAD ACTIVE LOW, HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS3VH125 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to VCC Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V QUAD ACTIVE LOW, HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS3VH125 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to VCC Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to
PI6LC48L0201A 2-Output LVDS Networking Clock Generator
 Features ÎÎTwo differential LVDS output pairs ÎÎSelectable crystal oscillator interface or LVCMOS/LVTTL single-ended clock input ÎÎSupports the following output frequencies: 62.5MHz, 125MHz, 156.25MHz
Features ÎÎTwo differential LVDS output pairs ÎÎSelectable crystal oscillator interface or LVCMOS/LVTTL single-ended clock input ÎÎSupports the following output frequencies: 62.5MHz, 125MHz, 156.25MHz
Features. Applications
 2.5/3.3V 1-to-1 Differential to LVCMOS/LVTTL Translator Precision Edge General Description Micrel s is a 1-to-1, differential-to-lvcmos / LVTTL translator. The differential input is highly flexible and
2.5/3.3V 1-to-1 Differential to LVCMOS/LVTTL Translator Precision Edge General Description Micrel s is a 1-to-1, differential-to-lvcmos / LVTTL translator. The differential input is highly flexible and
MAX9210/MAX9214/ MAX9220/MAX9222. Programmable DC-Balance 21-Bit Deserializers. Features. General Description. Applications. Ordering Information
 General Description The MAX9210/MAX9214/ deserialize three LVDS serial data inputs into 21 single-ended LVCMOS/ LVTTL outputs. A parallel rate LVDS clock received with the LVDS data streams provides timing
General Description The MAX9210/MAX9214/ deserialize three LVDS serial data inputs into 21 single-ended LVCMOS/ LVTTL outputs. A parallel rate LVDS clock received with the LVDS data streams provides timing
Low-Jitter Frequency Synthesizer with Selectable Input Reference MAX3673
 19-44 ; Rev 0; 2/09 E V A L U A T I O N K I T A V A I L A B L E Low-Jitter Frequency Synthesizer General Description The is a low-jitter frequency synthesizer that accepts two reference clock inputs and
19-44 ; Rev 0; 2/09 E V A L U A T I O N K I T A V A I L A B L E Low-Jitter Frequency Synthesizer General Description The is a low-jitter frequency synthesizer that accepts two reference clock inputs and
BLOCK DIAGRAM PIN ASSIGNMENT I Data Sheet. Low Skew, 1-to-9 Differential-to-HSTL Fanout Buffer ICS852911I
 Low Skew, 1-to-9 Differential-to-HSTL Fanout Buffer 852911I Data Sheet GENERAL DESCRIPTION The 852911I is a low skew, 1-to-9 Differential-to-HSTL Fanout Buffer. The 852911I has two selectable clock inputs
Low Skew, 1-to-9 Differential-to-HSTL Fanout Buffer 852911I Data Sheet GENERAL DESCRIPTION The 852911I is a low skew, 1-to-9 Differential-to-HSTL Fanout Buffer. The 852911I has two selectable clock inputs
3.3V, 3.2Gbps DIFFERENTIAL 4:1 LVDS MULTIPLEXER with INTERNAL INPUT TERMINATION
 3.3V, 3.2Gbps DIFFERENTIAL 4:1 LVDS MULTIPLEXER with TERNAL PUT TERMATION FEATURES Selects among four differential inputs Guaranteed AC performance over temp and voltage: DC-to > 3.2Gbps data rate throughput
3.3V, 3.2Gbps DIFFERENTIAL 4:1 LVDS MULTIPLEXER with TERNAL PUT TERMATION FEATURES Selects among four differential inputs Guaranteed AC performance over temp and voltage: DC-to > 3.2Gbps data rate throughput
I/O Features in Axcelerator Family Devices
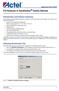 I/O Features in Axcelerator Family Devices Application Note AC249 Introduction and Feature Summary The Axcelerator family offers I/O features to support a very wide variety of user designs. An outline
I/O Features in Axcelerator Family Devices Application Note AC249 Introduction and Feature Summary The Axcelerator family offers I/O features to support a very wide variety of user designs. An outline
ILI2511. ILI2511 Single Chip Capacitive Touch Sensor Controller. Specification ILI TECHNOLOGY CORP. Version: V1.4. Date: 2018/7/5
 Single Chip Capacitive Touch Sensor Controller Specification Version: V1.4 Date: 2018/7/5 ILI TECHNOLOGY CORP. 8F., No.1, Taiyuan 2 nd St., Zhubei City, Hsinchu County 302, Taiwan (R.O.C.) Tel.886-3-5600099;
Single Chip Capacitive Touch Sensor Controller Specification Version: V1.4 Date: 2018/7/5 ILI TECHNOLOGY CORP. 8F., No.1, Taiyuan 2 nd St., Zhubei City, Hsinchu County 302, Taiwan (R.O.C.) Tel.886-3-5600099;
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 32-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH
 QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 32-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS3XVH25 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to VCC Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to VCC or 5V
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 32-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS3XVH25 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to VCC Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to VCC or 5V
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 24-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH
 QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 24-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to Vcc Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to Vcc or 5V tolerant in
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 24-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to Vcc Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to Vcc or 5V tolerant in
PI6C GND REF_IN+ V TH V REF-AC REF_IN- Q0+ Q0- Q1+ Q1- VDD. 6 GHz / 12 Gbps Clock / Data Fanout Buffer with Internal Termination.
 Features ÎÎInput Clock Frequency up to 6 GHz Typical ÎÎMaximum Input Data Rate up to 12 Gbps Typical ÎÎ2 pairs of differential CML outputs ÎÎLow additive jitter, < 0.05ps (max) ÎÎInput accepts: CML, LVDS,
Features ÎÎInput Clock Frequency up to 6 GHz Typical ÎÎMaximum Input Data Rate up to 12 Gbps Typical ÎÎ2 pairs of differential CML outputs ÎÎLow additive jitter, < 0.05ps (max) ÎÎInput accepts: CML, LVDS,
MC FPGA Bridge IC. for. MIPI D-PHY Systems and SLVS to LVDS Conversion DATASHEET. Version August Meticom GmbH
 FPGA Bridge IC for MIPI D-PHY Systems and SLVS to LVDS Conversion DATASHEET Version 1.09 August 2016 Meticom GmbH Meticom GmbH Page 1 of 14 Revision History Version Date of Issue Change 1.01 April 25,
FPGA Bridge IC for MIPI D-PHY Systems and SLVS to LVDS Conversion DATASHEET Version 1.09 August 2016 Meticom GmbH Meticom GmbH Page 1 of 14 Revision History Version Date of Issue Change 1.01 April 25,
MIPI D-PHY REFERENCE TERMINATION BOARD (RTB) OVERVIEW AND DATASHEET
 The InterOperability Laboratory MIPI D-PHY REFERENCE TERMINATION BOARD (RTB) OVERVIEW AND DATASHEET Abstract: This document serves as the primary documentation for the MIPI D-PHY Reference Termination
The InterOperability Laboratory MIPI D-PHY REFERENCE TERMINATION BOARD (RTB) OVERVIEW AND DATASHEET Abstract: This document serves as the primary documentation for the MIPI D-PHY Reference Termination
DSC Q0093. General Description. Features. Applications. Block Diagram. Crystal-less Configurable Clock Generator
 Crystal-less Configurable Clock Generator General Description The is a four output crystal-less clock generator. It utilizes Microchip's proven PureSilicon MEMS technology to provide excellent jitter and
Crystal-less Configurable Clock Generator General Description The is a four output crystal-less clock generator. It utilizes Microchip's proven PureSilicon MEMS technology to provide excellent jitter and
Features. Applications
 6GHz, 1:4 CML Fanout Buffer/Translator with Internal I/O Termination General Description The is a 2.5V/3.3V precision, high-speed, fully differential 1:4 CML fanout buffer. Optimized to provide four identical
6GHz, 1:4 CML Fanout Buffer/Translator with Internal I/O Termination General Description The is a 2.5V/3.3V precision, high-speed, fully differential 1:4 CML fanout buffer. Optimized to provide four identical
Features. Applications
 3.3V Ultra-Precision 1:4 LVDS Fanout Buffer/Translator with Internal Termination General Description The is a 3.3V, high-speed 2GHz differential low voltage differential swing (LVDS) 1:4 fanout buffer
3.3V Ultra-Precision 1:4 LVDS Fanout Buffer/Translator with Internal Termination General Description The is a 3.3V, high-speed 2GHz differential low voltage differential swing (LVDS) 1:4 fanout buffer
PI6C20400A. 1:4 Clock Driver for Intel PCIe Chipsets. Features. Description. Pin Configuration. Block Diagram
 Features Phase jitter filter for PCIe 2.0 application Four Pairs of Differential Clocks Low skew < 50ps Low jitter < 50ps cycle-to-cycle < 1 ps additive RMS phase jitter Output Enable for all outputs Outputs
Features Phase jitter filter for PCIe 2.0 application Four Pairs of Differential Clocks Low skew < 50ps Low jitter < 50ps cycle-to-cycle < 1 ps additive RMS phase jitter Output Enable for all outputs Outputs
AMT-2 & 3 (ATLAS Muon TDC version 2 & 3) Data Sheets
 AMT-2 & 3 (ATLAS Muon TDC version 2 & 3) Data Sheets Yasuo Arai KEK, National High Energy Accelerator Research Organization 1-1 Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305, Japan yasuo.arai@kek.jp, http://atlas.kek.jp/tdc/
AMT-2 & 3 (ATLAS Muon TDC version 2 & 3) Data Sheets Yasuo Arai KEK, National High Energy Accelerator Research Organization 1-1 Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305, Japan yasuo.arai@kek.jp, http://atlas.kek.jp/tdc/
SY89645L. General Description. Features. Block Diagram. Applications. Markets. Precision Low Skew, 1-to-4 LVCMOS/LVTTL-to-LVDS Fanout Buffer
 Precision Low Skew, 1-to-4 LVCMOS/LVTTL-to-LVDS Fanout Buffer General Description The is a 3.3V, fully differential, low skew, 1:4 LVDS fanout buffer that accepts LVTTL or LVCMOS inputs. It is capable
Precision Low Skew, 1-to-4 LVCMOS/LVTTL-to-LVDS Fanout Buffer General Description The is a 3.3V, fully differential, low skew, 1:4 LVDS fanout buffer that accepts LVTTL or LVCMOS inputs. It is capable
3.3V CMOS 1-TO-5 CLOCK DRIVER
 3. CMOS 1-TO-5 CLOCK DRIVER 3. CMOS 1-TO-5 CLOCK DRIVER IDT74FCT38075 FEATURES: Advanced CMOS Technology Guaranteed low skew < 100ps (max.) Very low duty cycle distortion< 250ps (max.) High speed propagation
3. CMOS 1-TO-5 CLOCK DRIVER 3. CMOS 1-TO-5 CLOCK DRIVER IDT74FCT38075 FEATURES: Advanced CMOS Technology Guaranteed low skew < 100ps (max.) Very low duty cycle distortion< 250ps (max.) High speed propagation
CARDINAL COMPONENTS, INC.
 SERIES CJTDAE CJTDAL The Cardinal Cappuccino Crystal Oscillator LVDS/ LVPECL TCXO Features 3.3V supply voltage- configurable 10MHz to 250MHz LVDS and LVPECL outputs- configurable Better than 2Hz tuning
SERIES CJTDAE CJTDAL The Cardinal Cappuccino Crystal Oscillator LVDS/ LVPECL TCXO Features 3.3V supply voltage- configurable 10MHz to 250MHz LVDS and LVPECL outputs- configurable Better than 2Hz tuning
PI6C20800B. PCI Express 3.0 1:8 HCSL Clock Buffer. Features. Description. Pin Configuration (48-Pin TSSOP)
 PCI Express 3.0 1:8 HCSL Clock Buffer Features Î ÎPhase jitter filter for PCIe 3.0 application Î ÎEight Pairs of Differential Clocks Î ÎLow skew < 50ps (PI6C20800B),
PCI Express 3.0 1:8 HCSL Clock Buffer Features Î ÎPhase jitter filter for PCIe 3.0 application Î ÎEight Pairs of Differential Clocks Î ÎLow skew < 50ps (PI6C20800B),
CARDINAL COMPONENTS, INC.
 SERIES CJAL CJAE The Cardinal Cappuccino Crystal Oscillator LVDS/ LVPECL Features 2.5V or 3.3V supply voltageconfigurable 10MHz to 250MHz LVDS and LVPECL outputs- configurable Better than 2Hz tuning resolution
SERIES CJAL CJAE The Cardinal Cappuccino Crystal Oscillator LVDS/ LVPECL Features 2.5V or 3.3V supply voltageconfigurable 10MHz to 250MHz LVDS and LVPECL outputs- configurable Better than 2Hz tuning resolution
Pentium Processor Compatible Clock Synthesizer/Driver for ALI Aladdin Chipset
 1CY 225 7 fax id: 3517 Features Multiple clock outputs to meet requirements of ALI Aladdin chipset Six CPU clocks @ 66.66 MHz, 60 MHz, and 50 MHz, pin selectable Six PCI clocks (CPUCLK/2) Two Ref. clocks
1CY 225 7 fax id: 3517 Features Multiple clock outputs to meet requirements of ALI Aladdin chipset Six CPU clocks @ 66.66 MHz, 60 MHz, and 50 MHz, pin selectable Six PCI clocks (CPUCLK/2) Two Ref. clocks
Rambutan (-I) Data sheet. Rambutan is a dual-band (2.4 or 5 GHz) module with a fast 720 MHz CPU and 128 MB of RAM and Flash
 (-I) is a dual-band (2.4 or 5 GHz) module with a fast 720 MHz CPU and 128 MB of RAM and Flash is based on QCA 9557 or 9550 SoC and comes in two temperature ranges: commercial* () and industrial** (-I).
(-I) is a dual-band (2.4 or 5 GHz) module with a fast 720 MHz CPU and 128 MB of RAM and Flash is based on QCA 9557 or 9550 SoC and comes in two temperature ranges: commercial* () and industrial** (-I).
RW CH Segment Driver
 Functions: Dot matrix LCD driver with two 40 channel outputs Bias voltage (V1 ~ V4) Input/output signals Input : Serial display data and control pulse from controller IC Output : 40 X 2 channels waveform
Functions: Dot matrix LCD driver with two 40 channel outputs Bias voltage (V1 ~ V4) Input/output signals Input : Serial display data and control pulse from controller IC Output : 40 X 2 channels waveform
CrossLink Hardware Checklist Technical Note
 FPGA-TN-02013 Version 1.1 August 2017 Contents Acronyms in This Document... 3 Introduction... 4 Power Supplies... 5 CrossLink MIPI D-PHY and PLL Power Supplies... 5 Power Estimation... 6 Configuration
FPGA-TN-02013 Version 1.1 August 2017 Contents Acronyms in This Document... 3 Introduction... 4 Power Supplies... 5 CrossLink MIPI D-PHY and PLL Power Supplies... 5 Power Estimation... 6 Configuration
Interfacing Cyclone III Devices with 3.3/3.0/2.5-V LVTTL/LVCMOS I/O Systems
 Interfacing Devices with 3.3/3.0/2.5-V LVTTL/LVCMOS I/O Systems April 2008 AN-447-1.1 Introduction Altera Cyclone III devices are compatible and support 3.3/3.0/2.5-V LVTTL/LVCMOS I/O standards. This application
Interfacing Devices with 3.3/3.0/2.5-V LVTTL/LVCMOS I/O Systems April 2008 AN-447-1.1 Introduction Altera Cyclone III devices are compatible and support 3.3/3.0/2.5-V LVTTL/LVCMOS I/O standards. This application
1.8 V, 12-LVDS/24-CMOS Output, Low Power Clock Fanout Buffer ADCLK854
 .8 V, 2-LVDS/24-CMOS Output, Low Power Clock Fanout Buffer AD854 FEATURES 2 selectable differential inputs Selectable LVDS/CMOS outputs Up to 2 LVDS (.2 GHz) or 24 CMOS (250 MHz) outputs
.8 V, 2-LVDS/24-CMOS Output, Low Power Clock Fanout Buffer AD854 FEATURES 2 selectable differential inputs Selectable LVDS/CMOS outputs Up to 2 LVDS (.2 GHz) or 24 CMOS (250 MHz) outputs
Programmable CMOS LVDS Transmitter/Receiver
 SPECIFICATION 1. FEATURES Technology TSMC 0.13um CMOS 3.3 V analog power supply 1.2 V digital power supply 1.2V CMOS input and output logic signals 8-step (3-bit) adjustable transmitter output current
SPECIFICATION 1. FEATURES Technology TSMC 0.13um CMOS 3.3 V analog power supply 1.2 V digital power supply 1.2V CMOS input and output logic signals 8-step (3-bit) adjustable transmitter output current
TF90LVDS047-6CG. Quad LVDS Line Driver with Flow-Through Pinout. Description. Features. Applications. Function Diagram. Ordering Information
 Features Companion driver to Quad Extended Common Mode LVDS Receiver TF0LVDS048 DC to 400 Mbps / 200 MHz low noise, low skew, low power operation t 350 ps (max) channel-to-channel skew t 250 ps (max) pulse
Features Companion driver to Quad Extended Common Mode LVDS Receiver TF0LVDS048 DC to 400 Mbps / 200 MHz low noise, low skew, low power operation t 350 ps (max) channel-to-channel skew t 250 ps (max) pulse
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 8:1 MUX / DEMUX HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH
 QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 8:1 MUX / DEMUX HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS3VH251 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to VCC Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V / 3.3V 8:1 MUX / DEMUX HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS SWITCH IDTQS3VH251 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to VCC Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to
NAND32GW3F4A. 32-Gbit (4 x 8 Gbits), two Chip Enable, 4224-byte page, 3 V supply, multiplane architecture, SLC NAND flash memories.
 32-Gbit (4 x 8 Gbits), two Chip Enable, 4224-byte page, 3 V supply, multiplane architecture, SLC NAND flash memories Features High-density SLC NAND flash memory 32 Gbits of memory array 1 Gbit of spare
32-Gbit (4 x 8 Gbits), two Chip Enable, 4224-byte page, 3 V supply, multiplane architecture, SLC NAND flash memories Features High-density SLC NAND flash memory 32 Gbits of memory array 1 Gbit of spare
ILI2303. ILI2303 Capacitive Touch Sensor Controller. Specification
 Capacitive Touch Sensor Controller Specification Version: V1.03 Date: 2014/9/17 ILI TECHNOLOGY CORP. 8F, No.38, Taiyuan St., Jhubei City, Hsinchu County 302, Taiwan, R.O.C. Tel.886-3-5600099; Fax.886-3-5600055
Capacitive Touch Sensor Controller Specification Version: V1.03 Date: 2014/9/17 ILI TECHNOLOGY CORP. 8F, No.38, Taiyuan St., Jhubei City, Hsinchu County 302, Taiwan, R.O.C. Tel.886-3-5600099; Fax.886-3-5600055
PI6C49S1510 Rev J
 High Performance Differential Fanout Buffer Features ÎÎ10 differential outputs with 2 banks ÎÎUser configurable output signaling standard for each bank: LVDS or LVPECL or HCSL ÎÎLVCMOS reference output
High Performance Differential Fanout Buffer Features ÎÎ10 differential outputs with 2 banks ÎÎUser configurable output signaling standard for each bank: LVDS or LVPECL or HCSL ÎÎLVCMOS reference output
PI3PCIE V, PCI Express 1-lane, 2:1 Mux/DeMux Switch. Features. Description. Application. Pin Description (Top-side view) Truth Table
 3.3V, PCI Express 1-lane, Features 2 Differential Channel, 2:1 Mux/DeMux PCI Express 2.0 Performance, 5.0Gbps Pinout optimized for placement between two PCIe slots Bi-directional operation Low Bit-to-Bit
3.3V, PCI Express 1-lane, Features 2 Differential Channel, 2:1 Mux/DeMux PCI Express 2.0 Performance, 5.0Gbps Pinout optimized for placement between two PCIe slots Bi-directional operation Low Bit-to-Bit
PAL22V10 Family, AmPAL22V10/A
 FINAL COM L: -7//5 PAL22V Family, AmPAL22V/A 24-Pin TTL Versatile PAL Device Advanced Micro Devices DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS As fast as 7.5-ns propagation delay and 9 MHz fmax (external) Macrocells
FINAL COM L: -7//5 PAL22V Family, AmPAL22V/A 24-Pin TTL Versatile PAL Device Advanced Micro Devices DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS As fast as 7.5-ns propagation delay and 9 MHz fmax (external) Macrocells
SY89610L. General Description. Features. Applications MHz to 694MHz Jitter Attenuator and Low Phase Noise Frequency Synthesizer
 77.75MHz to 694MHz Jitter Attenuator and Low Phase Noise Frequency Synthesizer General Description The is a 3.3V, fully differential jitter attenuator and frequency synthesizer that accepts a noise clock
77.75MHz to 694MHz Jitter Attenuator and Low Phase Noise Frequency Synthesizer General Description The is a 3.3V, fully differential jitter attenuator and frequency synthesizer that accepts a noise clock
IDTQS3VH383 QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V/3.3V 8-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS EXCHANGE BUS SWITCH
 QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V/3.3V 8-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS EXCHANGE BUS SWITCH IDTQS3VH383 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to Vcc Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to
QUICKSWITCH PRODUCTS 2.5V/3.3V 8-BIT HIGH BANDWIDTH BUS EXCHANGE BUS SWITCH IDTQS3VH383 FEATURES: N channel FET switches with no parasitic diode to Vcc Isolation under power-off conditions No DC path to
Intel Cyclone 10 GX Device Datasheet
 Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents...3 Electrical Characteristics... 3 Operating Conditions...3 Switching Characteristics...21 Transceiver Performance Specifications...
Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents...3 Electrical Characteristics... 3 Operating Conditions...3 Switching Characteristics...21 Transceiver Performance Specifications...
Pin Configuration and Selector Guide appear at end of data sheet. Typical Operating Circuits
 Rev 2; 4/08 106.25MHz/212.5MHz/425MHz General Description The DS4106, DS4212, and DS4425 ceramic surfacemount crystal oscillators are part of Maxim s DS4-XO series of crystal oscillators. These devices
Rev 2; 4/08 106.25MHz/212.5MHz/425MHz General Description The DS4106, DS4212, and DS4425 ceramic surfacemount crystal oscillators are part of Maxim s DS4-XO series of crystal oscillators. These devices
Features. Applications
 HCSL-Compatible Clock Generator for PCI Express General Description The is the smallest, high performance, lowest power, 2 differential output clock IC available for HCSL timing applications. offers -130dBc
HCSL-Compatible Clock Generator for PCI Express General Description The is the smallest, high performance, lowest power, 2 differential output clock IC available for HCSL timing applications. offers -130dBc
AN 523: Cyclone III Devices Configuration Interface Guidelines with EPCS Devices
 AN 523: Devices Configuration Interface Guidelines with Devices February 2014 AN-523-1.3 Introduction This application note provides the guidelines to Cyclone III family devices ( and LS devices) interfacing
AN 523: Devices Configuration Interface Guidelines with Devices February 2014 AN-523-1.3 Introduction This application note provides the guidelines to Cyclone III family devices ( and LS devices) interfacing
250 Mbps Transceiver in LC FB2M5LVR
 250 Mbps Transceiver in LC FB2M5LVR DATA SHEET 650 nm 250 Mbps Fiber Optic Transceiver with LC Termination LVDS I/O IEC 61754-20 Compliant FEATURES LC click lock mechanism for confident connections Compatible
250 Mbps Transceiver in LC FB2M5LVR DATA SHEET 650 nm 250 Mbps Fiber Optic Transceiver with LC Termination LVDS I/O IEC 61754-20 Compliant FEATURES LC click lock mechanism for confident connections Compatible
3.3V CMOS OCTAL BIDIRECTIONAL TRANSCEIVER
 . CMOS OCTAL IDIRECTIONAL TRANSCEIVER. CMOS OCTAL IDIRECTIONAL TRANSCEIVER IDT7FCT/A FEATURES: 0. MICRON CMOS Technology ESD > 00 per MIL-STD-, Method 0; > 0 using machine model (C = 00pF, R = 0) VCC =.
. CMOS OCTAL IDIRECTIONAL TRANSCEIVER. CMOS OCTAL IDIRECTIONAL TRANSCEIVER IDT7FCT/A FEATURES: 0. MICRON CMOS Technology ESD > 00 per MIL-STD-, Method 0; > 0 using machine model (C = 00pF, R = 0) VCC =.
PI6C :4 Clock Driver for Intel PCI Express Chipsets. Features. Description. Block Diagram. Pin Configuration
 Features Four Pairs of Differential Clocks Low skew < 50ps Low jitter < 50ps Output Enable for all outputs Outputs tristate control via SMBus Power Management Control Programmable PLL Bandwidth PLL or
Features Four Pairs of Differential Clocks Low skew < 50ps Low jitter < 50ps Output Enable for all outputs Outputs tristate control via SMBus Power Management Control Programmable PLL Bandwidth PLL or
128Kx8 CMOS MONOLITHIC EEPROM SMD
 128Kx8 CMOS MONOLITHIC EEPROM SMD 5962-96796 WME128K8-XXX FEATURES Read Access Times of 125, 140, 150, 200, 250, 300ns JEDEC Approved Packages 32 pin, Hermetic Ceramic, 0.600" DIP (Package 300) 32 lead,
128Kx8 CMOS MONOLITHIC EEPROM SMD 5962-96796 WME128K8-XXX FEATURES Read Access Times of 125, 140, 150, 200, 250, 300ns JEDEC Approved Packages 32 pin, Hermetic Ceramic, 0.600" DIP (Package 300) 32 lead,
AN 447: Interfacing Intel FPGA Devices with 3.3/3.0/2.5 V LVTTL/ LVCMOS I/O Systems
 AN 447: Interfacing Intel FPGA Devices with 3.3/3.0/2.5 V LVTTL/ LVCMOS I/O Systems Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Interfacing Intel FPGA Devices with 3.3/3.0/2.5
AN 447: Interfacing Intel FPGA Devices with 3.3/3.0/2.5 V LVTTL/ LVCMOS I/O Systems Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents Interfacing Intel FPGA Devices with 3.3/3.0/2.5
