Routing Fundamentals. What Is Routing? Routing Information. Routing Requirements. Most of the necessary information is contained in the routing table
|
|
|
- Monica York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Routing Fundamentals What Is Routing? Routing is the process of forwarding an item from one location to another Routers forward traffic to a logical destination in a computer network Routers perform two major functions: Routing Learning the logical topology of the network Switching Forwarding packets from an inbound interface to an outbound interface SN v Routing Requirements Routing Information Is the protocol suite active on this device? Is the destination network known to this device? Is there an entry in the routing table? Is the route currently available? Which outbound interface represents the best path? Lowest metric path is preferred Equal lowest metric paths are shared Most of the necessary information is contained in the routing table I [100/118654] via , 00:00:23, Serial0 I -- How the route was learned (IGRP) Destination logical network or subnet [ dministrative distance (trustworthiness factor) /118654] -- Metric value (reachability) via Next-hop logical address (next router) 00:00:23-- ge of entry (in hours:minutes:seconds) Serial0 -- Interface through which the route was learned and through which the packet will leave SN v SN v
2 SN v dministrative Distance dministrative distance is a selection method for IP routing protocols The lower the administrative distance, the more trusted the learning mechanism Manually entered routes are preferred to dynamically learned routes Routing protocols with sophisticated metrics are preferred over protocols with simple metric structures dministrative Distance omparison hart Route Source Default Distance onnected interface 0 Static route out an interface 0 Static route to a next hop 1 EIGRP summary route 5 External GP 20 Internal EIGRP 90 IGRP 100 OSPF 110 IS-IS 115 RIP v1, v2 120 EGP 140 External EIGRP 170 Internal GP 200 Unknown 255 SN v Routing Decisions RIP Routing Metrics Routing protocols maintain a loop-free, single path to each destination network Routes are advertised with a reachability factor referred as a metric The path to the destination network is represented by the sum of the metrics associated with all intermediate links The routing process uses the metric value to select a preferred path to each destination Multiple paths can be used if metric values are equal SN v dir conn Eth0 4.0 dir conn Ser0 R 10.0 [120/4] via 5.2, Eth0 R 10.0 [120/4] via 5.3, Eth0 R 10.0 [120/4] via 5.4, Eth0 Routing metric used by RIP is hop count Using a neighboring router interface is a hop Routing process arbitrarily selects a path from several possible equal metric paths IP load balancing is enabled by default TR FDDI These addresses are all part of the network 10.0 SN v
3 SN v IGRP Routing Metrics lassful Routing Overview These addresses are all part of the network TR FDDI 5.0 dir conn Eth0 4.0 dir conn Ser0 I 10.0 [100/327684] via 5.4, Eth0 Routing metric used by IGRP is composite andwidth, delay, reliability, load, MTU Routing process selects the fastest path IP load balancing is enabled by default lassful routing protocols are a consequence of the distance vector method of route calculation RIPv1 IGRP Routing masks are not carried within the periodic routing updates Within a network, consistency of masks is assumed SN v lassful Routes lassless Routing Overview Subnetwork routes are shared by devices within the same network Summary routes are exchanged between foreign networks Summary routes are automatically created at lass,, and network boundaries lassless routing protocols include the routing mask with the route advertisement OSPF EIGRP RIPv2 IS-IS GP Summary routes can be manually controlled within the network SN v SN v
4 SN v lassless Subnetting Requirements Distance Vector Routing Update Traffic requirement for only two host addresses VLSM support accommodates this S1 E / /30 ll Routes S / /27 E0 E /27 Router interfaces within the same network can have different subnet masks Variable-length subnet masking (VLSM) is supported This approach maximizes allocation of available host addresses In a distance vector environment, routing updates are propagated only to directly connected neighbors SN v Link-State Routing Update Traffic One Route In a link-state environment, link-state announcements are propagated to all devices in the routing domain Hierarchical design can limit the requirement to notify all devices SN v onvergence onvergence time is the time it takes for all routers to agree on the network topology after a change such as: New routes being added Existing routes changing state onvergence time is affected by: Update mechanism (hold-down timers) Size of the topology table Route calculation algorithm Media type SN v
5 SN v Routing Updates Different ways to send route information Updates RIPv1 network Routing Table Distance Vector pproach Full Table /24 Routing Table Link-State pproach Single Entry SN v Updates RIPv1 network Updates RIPv1 network / /24 Routing table /16 / /24 Routing table /16 OSPF network /24 /24 SN v SN v
6 SN v Routing Updates RIPv1 Network / /24 OSPF Network / /24 /24 /24 /16 /24 s Entries are listed in an efficient search order Simplifies the search mechanism Multiple paths to a common destination can be listed Load balancing is enabled by default for IP Displayed by the show ip route command Entries can be refreshed by the clear ip route command To specify a single entry, use network number To specify all entries, use wildcard character (*) SN v Sample ackbone_r1#show ip route odes: - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, - GP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O- OSPF, I - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSS external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSS external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, * - candidate default Gateway of last resort is to network /24 is subnetted, 2 subnets is directly connected, Loopback is directly connected, Loopback101 O E /16 [110/20] via , 01:03:01, Serial1/2 [110/20] via , 01:03:01, Serial1/3 [110/20] via , 01:03:01, Serial1/4 O E /24 [110/20] via , 01:03:01, Serial1/3 O E /24 [110/20] via , 01:03:01, Serial1/ /24 is subnetted, 4 subnets is directly connected, Serial1/ is directly connected, Serial1/ is directly connected, Serial1/ is directly connected, Serial1/0 O E /24 [110/20] via , 01:03:02, Serial1/2 S* /0 [1/0] via SN v
shortcut Tap into learning NOW! Visit for a complete list of Short Cuts. Your Short Cut to Knowledge
 shortcut Your Short Cut to Knowledge The following is an excerpt from a Short Cut published by one of the Pearson Education imprints. Short Cuts are short, concise, PDF documents designed specifically
shortcut Your Short Cut to Knowledge The following is an excerpt from a Short Cut published by one of the Pearson Education imprints. Short Cuts are short, concise, PDF documents designed specifically
Chapter 3. Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols. CCNA2-1 Chapter 3
 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols CCNA2-1 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols CCNA2-2 Chapter 3 Perspective and Background Dynamic
Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols CCNA2-1 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols CCNA2-2 Chapter 3 Perspective and Background Dynamic
INTERNET TEACHING LAB: Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) LAB
 INTERNET TEACHING LAB: Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) LAB Overview In this lab, we will explore some common interior gateway protocols - RIP version 1 (Routing Information Protocol) - OSPF (Open Shortest
INTERNET TEACHING LAB: Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) LAB Overview In this lab, we will explore some common interior gateway protocols - RIP version 1 (Routing Information Protocol) - OSPF (Open Shortest
Configuration and Management of Networks
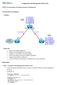 EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-7-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-7-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers
Network Layer Week 5. Module : Computer Networks Lecturer: Lucy White Office : 324
 Network Layer Week 5 Module : Computer Networks Lecturer: Lucy White lbwhite@wit.ie Office : 324 1 Network Layer Network Layer Protocols Common Network Layer Protocols Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4)
Network Layer Week 5 Module : Computer Networks Lecturer: Lucy White lbwhite@wit.ie Office : 324 1 Network Layer Network Layer Protocols Common Network Layer Protocols Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4)
Planning for Information Network
 Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols 1 Objectives Describe the role of dynamic routing protocols and place these protocols in the context of modern network design. Identify several ways to classify
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols 1 Objectives Describe the role of dynamic routing protocols and place these protocols in the context of modern network design. Identify several ways to classify
Routing Protocols and
 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocol Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 3 1 Objectives Describe the role of dynamic routing protocols and place these protocols in the context of modern network
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocol Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 3 1 Objectives Describe the role of dynamic routing protocols and place these protocols in the context of modern network
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols V 4.0
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols V 4.0 3.1.1 What are the four routing RIP, RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPFv2 protocols that are the focus of this course? 3.1.1.2 What are routing protocols?
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols V 4.0 3.1.1 What are the four routing RIP, RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPFv2 protocols that are the focus of this course? 3.1.1.2 What are routing protocols?
Why we need to divide network?
 Content Introduction Layer 3 IP Protocol IP-Header: www.ietf.org and RFC-760 Addressing Schemes Subnetting Routing Layer 3 Solution in Trains Communication Matrix (Information Based Communication) 53 Why
Content Introduction Layer 3 IP Protocol IP-Header: www.ietf.org and RFC-760 Addressing Schemes Subnetting Routing Layer 3 Solution in Trains Communication Matrix (Information Based Communication) 53 Why
Two types of routing protocols are used in internetworks: interior gateway protocols (IGPs) and exterior gateway protocols (EGPs).
 Introduction Dynamic routing is when protocols are used to find networks and update routing tables on routers. True, this is easier than using static or default routing, but it ll cost you in terms of
Introduction Dynamic routing is when protocols are used to find networks and update routing tables on routers. True, this is easier than using static or default routing, but it ll cost you in terms of
CHAPTER 4: ROUTING DYNAMIC. Routing & Switching
 CHAPTER 4: ROUTING DYNAMIC Routing & Switching CHAPTER4 4.1 Dynamic Routing Protocols 4.2 Distance Vector Dynamic Routing 4.3 RIP and RIPng Routing 4.4 Link-State Dynamic Routing 4.5 The Routing Table
CHAPTER 4: ROUTING DYNAMIC Routing & Switching CHAPTER4 4.1 Dynamic Routing Protocols 4.2 Distance Vector Dynamic Routing 4.3 RIP and RIPng Routing 4.4 Link-State Dynamic Routing 4.5 The Routing Table
2008 NDP Lectures 7 th Semester
 2008 NDP Lectures 7 th Semester Neeli R. Prasad, Associate Professor Head of Wireless Security and Sensor Networks Group Networking and Security Aalborg University Niels Jernes Vej 12, 9220 Aalborg East,
2008 NDP Lectures 7 th Semester Neeli R. Prasad, Associate Professor Head of Wireless Security and Sensor Networks Group Networking and Security Aalborg University Niels Jernes Vej 12, 9220 Aalborg East,
Part II. Chapter 3. Determining IP Routes
 Part II Chapter 3 Routers perform two main functions: switching and routing. The switching function is the process of moving packets from an inbound interface to an outbound interface. The switching function
Part II Chapter 3 Routers perform two main functions: switching and routing. The switching function is the process of moving packets from an inbound interface to an outbound interface. The switching function
Top-Down Network Design, Ch. 7: Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols. Top-Down Network Design. Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
Basic IP Routing. Finding Feature Information. Information About Basic IP Routing. Variable-Length Subnet Masks
 This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
Chapter 5 RIP version 1
 Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 5 RIP version 1 João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts RIPv1: A Distance Vector,
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 5 RIP version 1 João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts RIPv1: A Distance Vector,
Basic IP Routing. Finding Feature Information. Information About Basic IP Routing. Variable-Length Subnet Masks
 This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
Routing Overview. Information About Routing CHAPTER
 21 CHAPTER This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the ASA, and the routing protocols that are supported. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About
21 CHAPTER This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the ASA, and the routing protocols that are supported. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About
Antonio Cianfrani. Routing Protocols
 Antonio Cianfrani Routing Protocols Routing protocols A routing protocol provides a communication channel among routers to exchange reachability information about networks Routing tables are properly configured
Antonio Cianfrani Routing Protocols Routing protocols A routing protocol provides a communication channel among routers to exchange reachability information about networks Routing tables are properly configured
Deployment of IGRP/EIGRP
 1 eployment of IGRP/EIGRP Session 2 Presentation_I.scr 1 Understanding EIGRP Understanding and deploying EIGRP is like driving a car 3 genda Fundamentals of EIGRP UL Summarization and Load alancing EIGRP/IGRP
1 eployment of IGRP/EIGRP Session 2 Presentation_I.scr 1 Understanding EIGRP Understanding and deploying EIGRP is like driving a car 3 genda Fundamentals of EIGRP UL Summarization and Load alancing EIGRP/IGRP
Why dynamic route? (1)
 Routing Why dynamic route? (1) Static route is ok only when Network is small There is a single connection point to other network No redundant route 2 Why dynamic route? (2) Dynamic Routing Routers update
Routing Why dynamic route? (1) Static route is ok only when Network is small There is a single connection point to other network No redundant route 2 Why dynamic route? (2) Dynamic Routing Routers update
BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma
 BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Unit 9 Computer Network Routing and Routing Protocols BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Introduction to Routing Routing is the process that a router uses to forward packets toward
BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Unit 9 Computer Network Routing and Routing Protocols BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Introduction to Routing Routing is the process that a router uses to forward packets toward
Chapter 7: Routing Dynamically. Routing & Switching
 Chapter 7: Routing Dynamically Routing & Switching The Evolution of Dynamic Routing Protocols Dynamic routing protocols used in networks since the late 1980s Newer versions support the communication based
Chapter 7: Routing Dynamically Routing & Switching The Evolution of Dynamic Routing Protocols Dynamic routing protocols used in networks since the late 1980s Newer versions support the communication based
RIP. Table of Contents. General Information. Summary. Specifications
 RIP Document revision 1 (Wed Mar 24 12:32:12 GMT 2004) This document applies to V2.8 Table of Contents Table of Contents General Information Summary Specifications Related Documents Additional Documents
RIP Document revision 1 (Wed Mar 24 12:32:12 GMT 2004) This document applies to V2.8 Table of Contents Table of Contents General Information Summary Specifications Related Documents Additional Documents
LAB15: EIGRP IPv4. LAB 15: Diagram. Disclaimer
 AB15: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as
AB15: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as
Chapter 7 Routing Protocols
 Chapter 7 Routing Protocols Nonroutable Protocols In the early days of networking, networks were small collections of computers linked together For the purposes of sharing information and expensive peripherals
Chapter 7 Routing Protocols Nonroutable Protocols In the early days of networking, networks were small collections of computers linked together For the purposes of sharing information and expensive peripherals
Final exam study Guide
 Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
Lab 2-3 Summarization and Default Network Advertisement
 Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs
 TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
RIP Version 2. The Classless Brother
 RIP Version 2 The Classless Brother (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 1 Why RIPv2 Need for subnet information and VLSM Need for Next Hop addresses for each route entry Need for external route tags Need for multicast
RIP Version 2 The Classless Brother (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 1 Why RIPv2 Need for subnet information and VLSM Need for Next Hop addresses for each route entry Need for external route tags Need for multicast
Top-Down Network Design
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Original slides by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Selection Criteria for Switching and Routing Protocols Network traffic
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Original slides by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Selection Criteria for Switching and Routing Protocols Network traffic
Chapter 4: Manipulating Routing
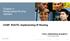 : Manipulating Routing Updates CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe network performance issues and ways to control routing updates and traffic (3). Describe the purpose of
: Manipulating Routing Updates CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe network performance issues and ways to control routing updates and traffic (3). Describe the purpose of
EIGRP Lab / lo1. .1 lo / /30
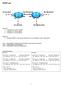 EIGRP Lab 172,16,1.0/24.1 lo1 192.168.20.0/30.2.1 Merida fa0 fa0 Vargas lo2.1 lo2.5.1 lo1 192.168.30.0/24 172.16.2.0/24 192.168.20.4.0/30 Scenario: Loopback0 is used for RouterID Loopback1 is a virtual
EIGRP Lab 172,16,1.0/24.1 lo1 192.168.20.0/30.2.1 Merida fa0 fa0 Vargas lo2.1 lo2.5.1 lo1 192.168.30.0/24 172.16.2.0/24 192.168.20.4.0/30 Scenario: Loopback0 is used for RouterID Loopback1 is a virtual
Distance vector Routing protocols. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9-1
 Distance vector Routing protocols 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9-1 IP Routing Configuration Tasks Router configuration Select routing protocols Specify networks or interfaces RIP Network 172.16.0.0 IGRP,
Distance vector Routing protocols 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9-1 IP Routing Configuration Tasks Router configuration Select routing protocols Specify networks or interfaces RIP Network 172.16.0.0 IGRP,
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 4 Distance Vector Routing Protocols V 4.0 RIP, IGRP, EIGRP
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 4 Distance Vector Routing Protocols V 4.0 4.1.1 What are the three distance vector routing protocols? What are the key characteristics of RIP? What are the key characteristics of IGRP?
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 4 Distance Vector Routing Protocols V 4.0 4.1.1 What are the three distance vector routing protocols? What are the key characteristics of RIP? What are the key characteristics of IGRP?
LAB11: EIGRP IPv4. EIGRP: Stub. Disclaimer
 Page1 AB11: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB11: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS
 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS S.Kokila, Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science, A.V.P College of Arts and Science, Tiruppur, Tamilnadu, India. G.Pramela, Assistant Professor, Department
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS S.Kokila, Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science, A.V.P College of Arts and Science, Tiruppur, Tamilnadu, India. G.Pramela, Assistant Professor, Department
Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops
 Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 Internet uses IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long range from 1.0.0.0 to
Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 Internet uses IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long range from 1.0.0.0 to
Draft Manuscript Draft M. Manuscript Draft Ma. t Manuscript Draft Manu. ipt Draft Manuscript Dra. anuscript Draft Manuscri
 M aft Ma CHAPTER 5 ript Dra RIP Version 1 Objectives aft Ma Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to answer the following questions: What are the functions, characteristics, and operation
M aft Ma CHAPTER 5 ript Dra RIP Version 1 Objectives aft Ma Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to answer the following questions: What are the functions, characteristics, and operation
Chapter 4 Lab 4-3, Manipulating Administrative Distances
 hapter 4 Lab 4-3, Manipulating Administrative Distances Topology bjectives Background onfigure RIP on a router. onfigure SPF on a router. Manipulate administrative distances. ompare routing protocol behavior.
hapter 4 Lab 4-3, Manipulating Administrative Distances Topology bjectives Background onfigure RIP on a router. onfigure SPF on a router. Manipulate administrative distances. ompare routing protocol behavior.
Draft Manuscript Draft M. uscript Draft Manuscript. aft Manuscript Draft Ma. cript Draft Manuscript D. ipt Draft Manuscript Dra
 M aft Ma CHAPTER 3 ript Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols Objectives aft Ma Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able How do you determine the administrative distance of a route, and
M aft Ma CHAPTER 3 ript Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols Objectives aft Ma Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able How do you determine the administrative distance of a route, and
Objectives. Review: Classful addresses. RIPv1 Characteristics. RIP Operation. RIP version 1
 2007 isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. isco Public Objectives IP version 1 outing Protocols and oncepts hapter 5 Describe the functions, characteristics, and operation of the IPv1 protocol. onfigure
2007 isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. isco Public Objectives IP version 1 outing Protocols and oncepts hapter 5 Describe the functions, characteristics, and operation of the IPv1 protocol. onfigure
Determining IP Routes. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9-1
 Determining IP Routes, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9- Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to complete the following tasks: Distinguish the use and operation of static and dynamic routes
Determining IP Routes, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9- Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to complete the following tasks: Distinguish the use and operation of static and dynamic routes
Routing Protocols of IGP. Koji OKAMURA Kyushu University, Japan
 Routing Protocols of IGP Koji OKAMURA Kyushu University, Japan Routing Protocol AS (Autonomous System) Is operated autonomous in the organization. 6bit IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) Routing Control inside
Routing Protocols of IGP Koji OKAMURA Kyushu University, Japan Routing Protocol AS (Autonomous System) Is operated autonomous in the organization. 6bit IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) Routing Control inside
Route Redistribution 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1of 38
 1of 38 Basic Route Redistribution Presented by: Allan Johnson Cisco Academy Conference 2005 2of 38 Outline of Discussion Route Redistribution Overview Example 1: IGRP and EIGRP Automatic Redistribution
1of 38 Basic Route Redistribution Presented by: Allan Johnson Cisco Academy Conference 2005 2of 38 Outline of Discussion Route Redistribution Overview Example 1: IGRP and EIGRP Automatic Redistribution
Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops
 Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 Internet uses IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long range from 1.0.0.0 to
Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 Internet uses IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long range from 1.0.0.0 to
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Information About Routing
 19 CHAPTER This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the adaptive security appliance, and the routing protocols that are supported. The chapter includes the following sections:,
19 CHAPTER This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the adaptive security appliance, and the routing protocols that are supported. The chapter includes the following sections:,
RIP version 1. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 5. Version Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1
 RIP version 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 5 Version 4.0 1 Objectives Describe the functions, characteristics, and operation of the RIPv1 protocol. Configure a device for using RIPv1. Verify
RIP version 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 5 Version 4.0 1 Objectives Describe the functions, characteristics, and operation of the RIPv1 protocol. Configure a device for using RIPv1. Verify
Routing Basics. Routing Concepts. IPv4. IPv4 address format. A day in a life of a router. What does a router do? IPv4 Routing
 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 1 2 IPv4 IPv4 address format Internet uses IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long range
Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Routing Basics ISP/IXP Workshops Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 1 2 IPv4 IPv4 address format Internet uses IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long range
LAB16: Named EIGRP IPv4
 AB16: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
AB16: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Small additions by Dr. Enis Karaarslan, Purdue - Aaron Jarvis (Network Engineer)
 Routing Basics 1 Small additions by Dr. Enis Karaarslan, 2014 Purdue - Aaron Jarvis (Network Engineer) Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 3 IPv4
Routing Basics 1 Small additions by Dr. Enis Karaarslan, 2014 Purdue - Aaron Jarvis (Network Engineer) Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 3 IPv4
CCENT Study Guide. Chapter 9 IP Routing
 CCENT Study Guide Chapter 9 IP Routing Chapter 9 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: 3.0 Routing Technologies 3.1 Describe the routing concepts. 3.1.a Packet handling along the
CCENT Study Guide Chapter 9 IP Routing Chapter 9 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: 3.0 Routing Technologies 3.1 Describe the routing concepts. 3.1.a Packet handling along the
The most simple way to accelerate a Router is at 9.8 m/sec/sec.
 Routing Introduction Direct vs. Indirect Delivery Static vs. Dynamic Routing Distance Vector vs. Link State (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 The most simple way to accelerate a Router is at 9.8 m/sec/sec. Seen
Routing Introduction Direct vs. Indirect Delivery Static vs. Dynamic Routing Distance Vector vs. Link State (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 The most simple way to accelerate a Router is at 9.8 m/sec/sec. Seen
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0
 Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Chapter 6 Reading Organizer
 Name Date Chapter 6 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and plan a network using OSPF Design and configure a network using single-area OSPF Work with multi-protocol
Name Date Chapter 6 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and plan a network using OSPF Design and configure a network using single-area OSPF Work with multi-protocol
EIGRP. About EIGRP. CLI Book 1: Cisco ASA Series General Operations CLI Configuration Guide, 9.7 1
 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (). About, page 1
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (). About, page 1
Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two)
 ICND1 OSPF Questions Question 1 Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C.
ICND1 OSPF Questions Question 1 Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C.
Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example
 Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113153 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113153 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Chapter 5. RIP Version 1 (RIPv1) CCNA2-1 Chapter 5
 Chapter 5 RIP Version 1 (RIPv1) CCNA2-1 Chapter 5 RIP Version 1 RIPv1: Distance Vector, Classful Routing Protocol CCNA2-2 Chapter 5 Background and Perspective RIP evolved from the Xerox Network System
Chapter 5 RIP Version 1 (RIPv1) CCNA2-1 Chapter 5 RIP Version 1 RIPv1: Distance Vector, Classful Routing Protocol CCNA2-2 Chapter 5 Background and Perspective RIP evolved from the Xerox Network System
Routing Information Protocol
 Routing Information Protocol A simple distance vector scheme dr. C. P. J. Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam February 24, 2008 dr. C. P. J. Koymans (UvA) Routing Information Protocol
Routing Information Protocol A simple distance vector scheme dr. C. P. J. Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam February 24, 2008 dr. C. P. J. Koymans (UvA) Routing Information Protocol
Interplay Between Routing, Forwarding
 Internet Routing 1 Interplay Between Routing, Forwarding routing algorithm local forwarding table header value output link 0100 0101 0111 1001 3 1 value in arriving packet s header 0111 3 1 Graph Abstraction
Internet Routing 1 Interplay Between Routing, Forwarding routing algorithm local forwarding table header value output link 0100 0101 0111 1001 3 1 value in arriving packet s header 0111 3 1 Graph Abstraction
Al-Mustansiriyah University Fourth Year ( )
 What subnet and broadcast address is IP address 172.16.10.33, 255.255.255.224 (/27) a member of? Answer: The interesting octet is the fourth octet. 256-224=32 block size. Because 32+32=64 and 33 is between
What subnet and broadcast address is IP address 172.16.10.33, 255.255.255.224 (/27) a member of? Answer: The interesting octet is the fourth octet. 256-224=32 block size. Because 32+32=64 and 33 is between
Back to basics J. Addressing is the key! Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Transport. Transport (TCP/UDP) Internet (IPv4/IPv6)
 Routing Basics Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E connectivity (app-to-app) Port numbers
Routing Basics Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E connectivity (app-to-app) Port numbers
Distance Vector Routing Protocols
 Distance Vector Routing Protocols Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 4 Version 4.0 1 Objectives Identify the characteristics of distance vector routing protocols. Describe the network discovery process
Distance Vector Routing Protocols Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 4 Version 4.0 1 Objectives Identify the characteristics of distance vector routing protocols. Describe the network discovery process
Routing Protocol comparison
 Routing Protocol comparison Introduction to routing Networks allow people to communicate, collaborate, and interact in many ways. Networks are used to access web pages, talk using IP telephones, participate
Routing Protocol comparison Introduction to routing Networks allow people to communicate, collaborate, and interact in many ways. Networks are used to access web pages, talk using IP telephones, participate
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
ASA Has High CPU Usage Due to a Traffic Loop When VPN Clients Disconnect
 ASA Has High CPU Usage Due to a Traffic Loop When VPN Clients Disconnect Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Problem: Packets Destined for a Disconnected
ASA Has High CPU Usage Due to a Traffic Loop When VPN Clients Disconnect Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Problem: Packets Destined for a Disconnected
Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ]
![Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ]](/thumbs/78/78661506.jpg) s@lm@n Cisco Exam 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Topic 1, Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements Cisco
s@lm@n Cisco Exam 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Topic 1, Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements Cisco
CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 8 Case Study
 Objectives: Consolidate routing table reading skills. Introduce the idea of more than 1 routing protocol running into the same router. Explain the use of routes to Null0 interface. Intro: Connex Inc. is
Objectives: Consolidate routing table reading skills. Introduce the idea of more than 1 routing protocol running into the same router. Explain the use of routes to Null0 interface. Intro: Connex Inc. is
Routing Information Protocol. A simple distance vector scheme
 Routing Information Protocol A simple distance vector scheme RIP version 1 RFC 1058 Charles Hedrick, Rutgers University, 1988 Based on Bellman-Ford distance vector Also used as ARPANET routing protocol
Routing Information Protocol A simple distance vector scheme RIP version 1 RFC 1058 Charles Hedrick, Rutgers University, 1988 Based on Bellman-Ford distance vector Also used as ARPANET routing protocol
Routing Information Protocol. RIP application. RIP version 1
 Routing Information Protocol A simple distance vector scheme dr. C. P. J. Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 1.1, 2010/02/19 12:38:50) Wednesday, February 24, 2010 RIP version
Routing Information Protocol A simple distance vector scheme dr. C. P. J. Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 1.1, 2010/02/19 12:38:50) Wednesday, February 24, 2010 RIP version
EXAM TOPICS COVERED IN THIS CHAPTER INCLUDE:
 4293book.fm Page 1 Tuesday, October 7, 2003 5:59 PM Chapter 1 Routing Principles EXAM TOPICS COVERED IN THIS CHAPTER INCLUDE: Understand how routers route data Know the difference between classful and
4293book.fm Page 1 Tuesday, October 7, 2003 5:59 PM Chapter 1 Routing Principles EXAM TOPICS COVERED IN THIS CHAPTER INCLUDE: Understand how routers route data Know the difference between classful and
CertifyMe. CertifyMe
 CertifyMe Number: 642-661 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CertifyMe-642-661 Exam A QUESTION 1 Exhibit: Certkiller router#show ip route Codes: C - connected,
CertifyMe Number: 642-661 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CertifyMe-642-661 Exam A QUESTION 1 Exhibit: Certkiller router#show ip route Codes: C - connected,
9.1. Routing Protocols
 9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
IP Routing Protocol-Independent Commands
 IP Routing Protocol-Independent Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the features that are routing protocol-independent. For configuration information and examples on IP routing
IP Routing Protocol-Independent Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the features that are routing protocol-independent. For configuration information and examples on IP routing
Implementing an EIGRP Solution
 Chapter 3 Implementing an EIGRP Solution This chapter contains the following sections: Dynamic Routing Review EIGRP Features and Function Troubleshooting EIGRP Implementing EIGRP for IPv6 Chapter Summary
Chapter 3 Implementing an EIGRP Solution This chapter contains the following sections: Dynamic Routing Review EIGRP Features and Function Troubleshooting EIGRP Implementing EIGRP for IPv6 Chapter Summary
Configuring IP Routing Protocols
 CHAPTER 18 Configuring IP Routing Protocols This chapter describes how to configure the various Internet Protocol (IP) routing protocols. For a complete description of the commands listed in this chapter,
CHAPTER 18 Configuring IP Routing Protocols This chapter describes how to configure the various Internet Protocol (IP) routing protocols. For a complete description of the commands listed in this chapter,
Lecture (03) RIP. By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee. Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Fall 2016, Practical App. Networks II
 Lecture (03) RIP By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Fall 2016, Practical App. Networks II Dynamic Routing Protocol Overview Routing protocols are used between routers to determine paths
Lecture (03) RIP By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Fall 2016, Practical App. Networks II Dynamic Routing Protocol Overview Routing protocols are used between routers to determine paths
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Topology...1 1.3 Configuration... 2 1.4 Validation... 3 2 Configuring RIP...5 2.1 Overview...
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Topology...1 1.3 Configuration... 2 1.4 Validation... 3 2 Configuring RIP...5 2.1 Overview...
Sybex CCENT Chapter 8: IP Routing. Instructor & Todd Lammle
 Sybex CCENT 100-101 Chapter 8: IP Routing Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 8 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: IP Routing Technologies Describe basic routing concepts CEF Packet
Sybex CCENT 100-101 Chapter 8: IP Routing Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 8 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: IP Routing Technologies Describe basic routing concepts CEF Packet
CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name Score Grade Question Answer Question Answer
 CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name: Score: Grade: Question Answer Question Answer 1 A B C D E F 51 A B C D E F 2 A B C D E F 52 A B C D E F 3 A B C D E F 53 A B C D E F 4 A B C D E F 54 A B C
CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name: Score: Grade: Question Answer Question Answer 1 A B C D E F 51 A B C D E F 2 A B C D E F 52 A B C D E F 3 A B C D E F 53 A B C D E F 4 A B C D E F 54 A B C
Configuring EIGRP. Overview CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 24 This chapter describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information, using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
CHAPTER 24 This chapter describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information, using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
LAB8: Named EIGRP IPv4
 Page1 AB8: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB8: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator
 Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview... 6 1.2 Topology...6 1.3 Configuration... 7 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP...10 2.1 Overview... 10
FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview... 6 1.2 Topology...6 1.3 Configuration... 7 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP...10 2.1 Overview... 10
Which of the following are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.) - packet switching - path selection
 Which three statements are true regarding the encapsulation and de-encapsulation of packets when traveling through a router? (Choose three.) - The router modifies the TTL field, decrementing it by one.
Which three statements are true regarding the encapsulation and de-encapsulation of packets when traveling through a router? (Choose three.) - The router modifies the TTL field, decrementing it by one.
Configuring IGRP. The Cisco IGRP Implementation
 Configuring IGRP This chapter describes how to configure the Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP). For a complete description of the IGRP commands in this chapter, refer to the IGRP s chapter of the
Configuring IGRP This chapter describes how to configure the Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP). For a complete description of the IGRP commands in this chapter, refer to the IGRP s chapter of the
Claim desired outcome
 Assessment Authoring - Table of Specification (TOS) The Table of Specification (TOS) is a high-level design template for a given assessment. It identifies the claims, components skills, targeted number
Assessment Authoring - Table of Specification (TOS) The Table of Specification (TOS) is a high-level design template for a given assessment. It identifies the claims, components skills, targeted number
Exam : : Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Title. Ver :
 Exam : 642-801 Title : Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Ver : 03-22-05 QUESTION 1 A packet that needs to be forwarded arrives on an interface of a router. In order for a router to route data,
Exam : 642-801 Title : Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Ver : 03-22-05 QUESTION 1 A packet that needs to be forwarded arrives on an interface of a router. In order for a router to route data,
Routing in the Internet
 Routing in the Internet Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Scaling Routing for the Internet 2/29 scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes
Routing in the Internet Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Scaling Routing for the Internet 2/29 scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes
Chapter 4: VLSM and Classless Inter Domain Routing. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 4: VLSM and Classless Inter Domain Routing 1 What will we Learn from chapter 4? Compare and contrast classful and classless IP addressing. Review VLSM and explain the benefits of classless IP addressing.
Chapter 4: VLSM and Classless Inter Domain Routing 1 What will we Learn from chapter 4? Compare and contrast classful and classless IP addressing. Review VLSM and explain the benefits of classless IP addressing.
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Topology... 6 1.3 Configuration... 6 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP... 10 2.1 Overview...10
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Topology... 6 1.3 Configuration... 6 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP... 10 2.1 Overview...10
REDDIG II Computer Networking Training
 REDDIG II Computer Networking Training JM SANCHEZ / PH RASSAT -20/06/2012 Invierno 2011 Capacitacion en fabrica - CORPAC Dynamic Routing Dynamic Routing Function(s) of Dynamic Routing Protocols: Dynamically
REDDIG II Computer Networking Training JM SANCHEZ / PH RASSAT -20/06/2012 Invierno 2011 Capacitacion en fabrica - CORPAC Dynamic Routing Dynamic Routing Function(s) of Dynamic Routing Protocols: Dynamically
Configuration and Management of Networks
 Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
Table of Contents. Cisco Introduction to EIGRP
 Table of Contents Introduction to EIGRP...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 What is IGRP?...2 What is EIGRP?...2 How Does EIGRP Work?...2 EIGRP
Table of Contents Introduction to EIGRP...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 What is IGRP?...2 What is EIGRP?...2 How Does EIGRP Work?...2 EIGRP
