CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 8 Case Study
|
|
|
- Pierce Leonard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
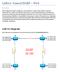
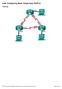
1 Objectives: Consolidate routing table reading skills. Introduce the idea of more than 1 routing protocol running into the same router. Explain the use of routes to Null0 interface. Intro: Connex Inc. is having trouble on their network and needs help. Part of their network has no connectivity. Topology:
2 Scenario: According to the report, network 1 is not able to reach network 2. As shown on Connex Network Topology above, Connex Inc. has 2 routing protocols running due transition issues. The goal is to have only one protocol running within the network but for now the older protocol must be kept. Step 1 Checking the routers You connect to R4 via console port to check its configuration. R4 is a RIPv2 speaker and a quick look at its configuration does not show anything unexpected: RIPv2 is correctly configured at R4, R4 has valid routes learnt via RIPv2, and all interfaces are up. R4 also has a default route, learnt via RIPv2 and pointing to R3 s serial 0/0. Still from R4, you issue pings to a few PCs under network 2, to R3 s interfaces, to R2 s interfaces, to R1 s interfaces and watch them flow successfully. You also issue a few pings from a few PCs under network 2 towards a few PCs under network 1 but all of such pings fail. You switch the console cable to R3 and check its configuration. Once more, the configuration looks good: all R3 s interfaces are up, RIPv2 is correctly configured and R3 has RIPv2 routes installed into its routing table. R3 also has a default route pointing to R2 s serial 0/1 which was learnt via RIPv2. You issue a few pings from R3 to different points of Connex network. All pings are successful. Since the configuration are correct so far, you suspect R1 has wrong routes to network 2. You move the console cable once more and connect it to R1. R1 speaks EIGRP to R2. You confirm EIGRP is configured correctly in R1, all R1 interfaces are up and R1 s routing table has all expected EIGRP routes. R1 also has a static default route pointing to R2 s serial 0/0. A few pings from R1 to different points of Connex network are successful but all pings to network 2 fail. R1 s configuration seems to be correct. You take a moment to analyze Connex network. Its structure keeps the RIPv2 section and the EIGRP section completely unaware of each other or formally speaking, no route redistribution is being performed. If a packet is to be sent from one section to another, default routes are used. Because of this, R1 uses its default route when it has packets to network 2. As mentioned before, R1 has a static default route. You connect the console cable to R2 and check its configuration. Because R2 is the junction point of both routing protocols (RIPV2 and EIGRP), R2 speaks both protocols at the same time.
3 Question 1: R2 speaks 2 routing protocols simultaneously. How many routing tables R2 keeps? Answer: Only 1 routing table. Despites the number of routing protocols running into a router, only one routing table is kept and only the best route is installed into the routing table. Many parameters are considered when selecting the best route. The most common are administrative distance, metric, and subnet mask length. EIGRP and RIPv2 were correctly configured into R2. All R2 s interfaces are up and it has RIPv2 and EIGRP routes installed into its routing table. R2 also have an interface connecting Connex Inc. to the outside world and Internet. R2 s default route uses this link to reach the world and any network outside Connex network address range. You decide to take a closer look at R2 s routing table. It is listed below: R2#sh ip route *Jan 31 21:37:04.091: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is to network C* /24 is directly connected, Loopback /27 is subnetted, 3 subnets R [120/1] via , 00:00:07, Serial0/0/1 C is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 S /24 is directly connected, Null0 S [1/0] via /27 is subnetted, 2 subnets D [90/ ] via , 00:50:41, Serial0/0/0 C is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 S /24 is directly connected, Null0 R2# R2 s routing table shows a few interesting things: 1. It shows a direct connected route to /24. The * right after the C means it is a candidate to default-route. This route is being used as the link to outside and Internet. 2. It shows a RIPv2 route to /27 via This route has metric 1 and administrative distance 120 which is the default administrative distance to RIP routes. 3. It shows a direct connected route to /27 representing R2 s serial interface 0/1 4. It shows a static route to /27 point to R1. This is the route used by R2 to reach network 2 but it points to R1 instead of R3. 5. An EIGRP route to /27 via with administrative distance 90 (AD=90) which is the default AD to internal EIGRP routes. This route is used by R2 to reach network 1 and it is correct
4 Question 2: EIGRP routes have administrative distance 90 while RIPv2 routes have administrative distance 120. Why is this difference important? Answer: Different routing protocols calculate route metrics using different ways. Because of this, the administrative distance is necessary to let the router know which protocol is more accurate than the other, no matter the metric value. Because EIGRP has smaller AD than RIPv2, the router knows EIGRP routes are always better than RIPv2 routes, no matter the metric. After a look at R2 s routing table, you find the problem: R2 has a route to /27 (network 2) but it points to R1 when it should point to R3. Because R1 itself has no route to network 2, it forwards the packet according to its default route, this is R2. Since R2 s route to /27 points to R1, the packet is sent back to R1 creating a routing loop and keeping network 1 from reaching network 2. Caution is highly recommended when working with static routing. Question 3: If R4, R3 and R2 have their RIPv2 process correctly configured, why is R2 learning and installing a wrong route into its routing table? Answer: R2 is not learning this wrong route via RIPv2. R2 s routing table shows the wrong route is a static route which means it was manually configured. Since static routes have AD=1, by default, they override any routes learnt via any routing protocol. In this specific case, the static route (AD=1) overrides the route learned via RIPv2 (default AD=120). You connect to R2, remove the static route from its configuration and allow a few seconds to RIPv2 update the neighbors. You check R2 s routing table again and notice a correct route to network 2 is now installed. You issue a few pings to confirm and conclude the problem is solved. Question 4 (Challenge Question): There are 2 odd static routes installed into R2 s routing table: /24 and /24, both pointing to the null0 interface. a. Is there a Null0 interface on Cisco routers? b. Since those are static routes, it is correct to assume they were manually configured. Why such routes were manually installed into R2 s routing table? Answers: a. Not exactly. Null0 interface are logical interfaces which behave a lot like Loopback interfaces. They are generally used by IOS as an elegant way to discard packets. b. Because Connex Inc addressing scheme is not contiguous (there are subnets not assigned to links), it could happen an internal device tried to send a packet to an inexistent subnet range.
5 Since the address space used internally by Connex Inc is private (belongs to RFC 1918) and all Connex internal routers have default routes pointing to R2, such packet would eventually hit R2 requiring to be routed. But since the destination address belongs to an inexistent subnet range, R2 would not have a specific route to it and would wrongly forward it, via its default network, to the outside world. To avoid this situation, a route to the major classful network, pointing to Null0 is installed into the routing table. Cisco IOS s longest match rule guarantees the Null0 route will only be used when no other more specific route is found. Below is an example based on this case study: PC1 (under network 1) sends a packet to /27 which belongs to the inexistent network /27. R4 has no specific route to /27 simply because it does not exist and forward the packet to R3 based on its own default route. R3, by its turn, has no route to /27 either and forward the packet to R2 based on R3 s default route. Since /27 does not exist, R2 has no route to it as well and ends up forwarding the packet, based on its own default route, out to ISP in a try to find the destination of the packet. Because this is a RFC 1918 ip address, if the address is not within Connex network, it isn t anywhere else and forward it to ISP is unnecessary. To avoid this situation a route to the major classful network is manually installed into R2 s routing table. If R2 has no better route (longer mask than the major classful mask) the packet is discarded.
CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 11 Case Study
 bjectives: Consolidate SPF knowledge. Describe the operation of SPF multi-area. Introduce the concept of route summarization with SPF. Introduce the concept of SPF optimization. Intro: Trevni Inc. needed
bjectives: Consolidate SPF knowledge. Describe the operation of SPF multi-area. Introduce the concept of route summarization with SPF. Introduce the concept of SPF optimization. Intro: Trevni Inc. needed
Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example
 Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113153 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113153 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 10 Case Study
 Objectives: Use OSPF single area to illustrate basic Link State components and operation. Migrate from EIGRP to OSPF single area. Intro: Trevni Inc. decided to upgrade their routing protocol from EIGRP
Objectives: Use OSPF single area to illustrate basic Link State components and operation. Migrate from EIGRP to OSPF single area. Intro: Trevni Inc. decided to upgrade their routing protocol from EIGRP
LAB8: Named EIGRP IPv4
 Page1 AB8: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB8: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
LAB11: EIGRP IPv4. EIGRP: Stub. Disclaimer
 Page1 AB11: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB11: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Network Layer Week 5. Module : Computer Networks Lecturer: Lucy White Office : 324
 Network Layer Week 5 Module : Computer Networks Lecturer: Lucy White lbwhite@wit.ie Office : 324 1 Network Layer Network Layer Protocols Common Network Layer Protocols Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4)
Network Layer Week 5 Module : Computer Networks Lecturer: Lucy White lbwhite@wit.ie Office : 324 1 Network Layer Network Layer Protocols Common Network Layer Protocols Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4)
DMVPN Topology. Page1
 DMVPN DMVPN Topology Page1 LAB 2: Configure EIGRP over DMVPN: Task 1: Configure EIGRP over DMVPN Process Step 1 In the configuration mode of router configure EIGRP over DMVPN by following command: R1:
DMVPN DMVPN Topology Page1 LAB 2: Configure EIGRP over DMVPN: Task 1: Configure EIGRP over DMVPN Process Step 1 In the configuration mode of router configure EIGRP over DMVPN by following command: R1:
LAB15: EIGRP IPv4. LAB 15: Diagram. Disclaimer
 AB15: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as
AB15: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as
Lab Configuring Static NAT
 Lab 10.5.1 Configuring Static NAT Objective Configure Network Address Translation (NAT) static translation to provide reliable outside access to three shared company servers. Scenario Step 1 The International
Lab 10.5.1 Configuring Static NAT Objective Configure Network Address Translation (NAT) static translation to provide reliable outside access to three shared company servers. Scenario Step 1 The International
LAB16: Named EIGRP IPv4
 AB16: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
AB16: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
LAB5: OSPF IPv4. OSPF: Stub. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB5: SPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB5: SPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
INTERNET TEACHING LAB: Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) LAB
 INTERNET TEACHING LAB: Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) LAB Overview In this lab, we will explore some common interior gateway protocols - RIP version 1 (Routing Information Protocol) - OSPF (Open Shortest
INTERNET TEACHING LAB: Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) LAB Overview In this lab, we will explore some common interior gateway protocols - RIP version 1 (Routing Information Protocol) - OSPF (Open Shortest
LAB1: BGP IPv4. BGP: Initial Config. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF
 hapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review configuration and verification of RIP and OSPF. onfigure passive interfaces in both RIP and OSPF. Filter routing updates
hapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review configuration and verification of RIP and OSPF. onfigure passive interfaces in both RIP and OSPF. Filter routing updates
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator
 Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuration and Management of Networks
 Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0
 Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Adapted from the Synchronization example in g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html
 Adapted from the Synchronization example in http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/internetworkin g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html When an AS provides transit service to other ASs when there are non-bgp routers in
Adapted from the Synchronization example in http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/internetworkin g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html When an AS provides transit service to other ASs when there are non-bgp routers in
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks
 Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
LAB8: OSPF IPv4. OSPF: Virtual Link. Disclaimer
 Page1 AB8: OSPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB8: OSPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
RIP. Table of Contents. General Information. Summary. Specifications
 RIP Document revision 1 (Wed Mar 24 12:32:12 GMT 2004) This document applies to V2.8 Table of Contents Table of Contents General Information Summary Specifications Related Documents Additional Documents
RIP Document revision 1 (Wed Mar 24 12:32:12 GMT 2004) This document applies to V2.8 Table of Contents Table of Contents General Information Summary Specifications Related Documents Additional Documents
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
LAB12: OSPF IPv6. OSPF: Redistribution. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB12: OSPF IPv6 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB12: OSPF IPv6 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
ASA Has High CPU Usage Due to a Traffic Loop When VPN Clients Disconnect
 ASA Has High CPU Usage Due to a Traffic Loop When VPN Clients Disconnect Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Problem: Packets Destined for a Disconnected
ASA Has High CPU Usage Due to a Traffic Loop When VPN Clients Disconnect Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Problem: Packets Destined for a Disconnected
Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE
 MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers
 OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Finding Feature Information OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Last Updated: June 24, 2011 The OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers feature provides the
OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Finding Feature Information OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Last Updated: June 24, 2011 The OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers feature provides the
RIPv2. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 7. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
 RIPv2 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 7 1 Objectives Encounter and describe the limitations of RIPv1 s limitations. Apply the basic Routing Information Protocol Version 2 (RIPv2) configuration commands
RIPv2 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 7 1 Objectives Encounter and describe the limitations of RIPv1 s limitations. Apply the basic Routing Information Protocol Version 2 (RIPv2) configuration commands
Lab Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
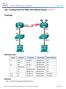 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Lab- Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
 Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
LAB1: EIGRP IPv4. EIGRP: Initial Config. Disclaimer
 Page1 AB1: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB1: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Chapter 7 Lab 7-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute
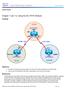 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates. Topology. Objectives. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology Objectives Filter routes using a distribute list and ACL. Filter routes using a distribute list and prefix list. Filter redistributed routes using
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology Objectives Filter routes using a distribute list and ACL. Filter routes using a distribute list and prefix list. Filter redistributed routes using
BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma
 BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Unit 9 Computer Network Routing and Routing Protocols BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Introduction to Routing Routing is the process that a router uses to forward packets toward
BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Unit 9 Computer Network Routing and Routing Protocols BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Introduction to Routing Routing is the process that a router uses to forward packets toward
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing
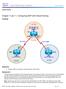 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
RR> RR> RR>en RR# RR# RR# RR# *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 RR#
 RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
MPLS VPN Half-Duplex VRF
 The feature provides scalable hub-and-spoke connectivity for subscribers of an Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service. This feature addresses the limitations of hub-and-spoke
The feature provides scalable hub-and-spoke connectivity for subscribers of an Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service. This feature addresses the limitations of hub-and-spoke
Configuration and Management of Networks
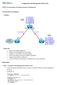 EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
Module 9, Assignment 7
 Module 9, Assignment 7 7.2.3 Control Router via Console (in Packet Tracer) 1. Prepare a Cisco 1841 Router (see figure 6-9). 2. Prepare a PC for administration. 3. Prepare a console cable and plug the serial
Module 9, Assignment 7 7.2.3 Control Router via Console (in Packet Tracer) 1. Prepare a Cisco 1841 Router (see figure 6-9). 2. Prepare a PC for administration. 3. Prepare a console cable and plug the serial
LAB2: Named EIGRP IPv4
 Page1 AB2: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB2: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Lab 2-3 Summarization and Default Network Advertisement
 Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
CCENT Study Guide. Chapter 9 IP Routing
 CCENT Study Guide Chapter 9 IP Routing Chapter 9 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: 3.0 Routing Technologies 3.1 Describe the routing concepts. 3.1.a Packet handling along the
CCENT Study Guide Chapter 9 IP Routing Chapter 9 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: 3.0 Routing Technologies 3.1 Describe the routing concepts. 3.1.a Packet handling along the
Chapter 5 RIP version 1
 Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 5 RIP version 1 João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts RIPv1: A Distance Vector,
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 5 RIP version 1 João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts RIPv1: A Distance Vector,
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 with Stub Area
 Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS
 QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
Lab 8a. OSPF. Set up OSPF in a single area so that all subnets are visible from all routers.
 Rev. 08.09 Lab 8a. OSPF c cnac o okbook.com G O A L Set up OSPF in a single area so that all subnets are visible from all routers. Gi 0/0 Gi 0/0 Lo 0. 0..0.0 /0. 0..0. / Topology You'll need routers of
Rev. 08.09 Lab 8a. OSPF c cnac o okbook.com G O A L Set up OSPF in a single area so that all subnets are visible from all routers. Gi 0/0 Gi 0/0 Lo 0. 0..0.0 /0. 0..0. / Topology You'll need routers of
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
เฉลยแล ป Packet Activity
 เฉลยแล ป Packet Activity CCNA LAB 4-4: IP Routing - EIGRP [ต งค าท Ranet HQ (คล กท เคร อง console)] : (ไปย งแท บ Desktop > คล ก Terminal > กด OK) Ranet-HQ>en Ranet-HQ#conf t Enter configuration commands,
เฉลยแล ป Packet Activity CCNA LAB 4-4: IP Routing - EIGRP [ต งค าท Ranet HQ (คล กท เคร อง console)] : (ไปย งแท บ Desktop > คล ก Terminal > กด OK) Ranet-HQ>en Ranet-HQ#conf t Enter configuration commands,
IP NAT Troubleshooting. Solutions. Luke Bibby, CCIE #45527
 IP NAT Troubleshooting Solutions Luke Bibby, CCIE #45527 Quick Overview of Scenario Solutions Scenario #1 R2 s E0/0 should be NAT inside not NAT outside ACL 100 is configured incorrectly NAT policy missing
IP NAT Troubleshooting Solutions Luke Bibby, CCIE #45527 Quick Overview of Scenario Solutions Scenario #1 R2 s E0/0 should be NAT inside not NAT outside ACL 100 is configured incorrectly NAT policy missing
6.5.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge Activity Topology Diagram
 6.5.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge Activity Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page
6.5.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge Activity Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page
LAB20: EIGRP IPv6. EIGRP: Summarization. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB20: EIGRP IPv6 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB20: EIGRP IPv6 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Route Redistribution 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1of 38
 1of 38 Basic Route Redistribution Presented by: Allan Johnson Cisco Academy Conference 2005 2of 38 Outline of Discussion Route Redistribution Overview Example 1: IGRP and EIGRP Automatic Redistribution
1of 38 Basic Route Redistribution Presented by: Allan Johnson Cisco Academy Conference 2005 2of 38 Outline of Discussion Route Redistribution Overview Example 1: IGRP and EIGRP Automatic Redistribution
Distance vector Routing protocols. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9-1
 Distance vector Routing protocols 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9-1 IP Routing Configuration Tasks Router configuration Select routing protocols Specify networks or interfaces RIP Network 172.16.0.0 IGRP,
Distance vector Routing protocols 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9-1 IP Routing Configuration Tasks Router configuration Select routing protocols Specify networks or interfaces RIP Network 172.16.0.0 IGRP,
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4
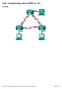 Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Antonio Cianfrani. Routing Protocols
 Antonio Cianfrani Routing Protocols Routing protocols A routing protocol provides a communication channel among routers to exchange reachability information about networks Routing tables are properly configured
Antonio Cianfrani Routing Protocols Routing protocols A routing protocol provides a communication channel among routers to exchange reachability information about networks Routing tables are properly configured
Routing Overview. Path Determination
 This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the Cisco ASA, and the routing protocols that are supported. Routing is the act of moving information across a network from a source
This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the Cisco ASA, and the routing protocols that are supported. Routing is the act of moving information across a network from a source
FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example
 FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example Document ID: 118888 Contributed by Piotr Kupisiewicz, Wen Zhang, and Frederic Detienne, Cisco TAC Engineers. Apr 08, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example Document ID: 118888 Contributed by Piotr Kupisiewicz, Wen Zhang, and Frederic Detienne, Cisco TAC Engineers. Apr 08, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
Sybex CCENT Chapter 8: IP Routing. Instructor & Todd Lammle
 Sybex CCENT 100-101 Chapter 8: IP Routing Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 8 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: IP Routing Technologies Describe basic routing concepts CEF Packet
Sybex CCENT 100-101 Chapter 8: IP Routing Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 8 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: IP Routing Technologies Describe basic routing concepts CEF Packet
Small additions by Dr. Enis Karaarslan, Purdue - Aaron Jarvis (Network Engineer)
 Routing Basics 1 Small additions by Dr. Enis Karaarslan, 2014 Purdue - Aaron Jarvis (Network Engineer) Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 3 IPv4
Routing Basics 1 Small additions by Dr. Enis Karaarslan, 2014 Purdue - Aaron Jarvis (Network Engineer) Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 3 IPv4
CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 5 Case Study
 Objectives: Enforce RIPv1 poor metric calculation (hop count). Enforce importance of smooth routing protocol migration. Introduce the concept of Load Balance. Consolidate the interface bandwidth command
Objectives: Enforce RIPv1 poor metric calculation (hop count). Enforce importance of smooth routing protocol migration. Introduce the concept of Load Balance. Consolidate the interface bandwidth command
Routing Overview. Information About Routing CHAPTER
 21 CHAPTER This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the ASA, and the routing protocols that are supported. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About
21 CHAPTER This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the ASA, and the routing protocols that are supported. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About
Routing Fundamentals. What Is Routing? Routing Information. Routing Requirements. Most of the necessary information is contained in the routing table
 Routing Fundamentals What Is Routing? Routing is the process of forwarding an item from one location to another Routers forward traffic to a logical destination in a computer network Routers perform two
Routing Fundamentals What Is Routing? Routing is the process of forwarding an item from one location to another Routers forward traffic to a logical destination in a computer network Routers perform two
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Lab VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
Draft Manuscript Draft M. Manuscript Draft Ma. t Manuscript Draft Manu. ipt Draft Manuscript Dra. anuscript Draft Manuscri
 M aft Ma CHAPTER 5 ript Dra RIP Version 1 Objectives aft Ma Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to answer the following questions: What are the functions, characteristics, and operation
M aft Ma CHAPTER 5 ript Dra RIP Version 1 Objectives aft Ma Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to answer the following questions: What are the functions, characteristics, and operation
Initial Configurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link
 Initial onfigurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link Document ID: 13687 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions OSPF over a Point to Point Link with IP Addresses
Initial onfigurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link Document ID: 13687 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions OSPF over a Point to Point Link with IP Addresses
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem
 How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
Lab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Lab 4: Routing using OSPF
 Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
CCNA Questions/Answers Routing Protocols
 Refer to the exhibit and configuration shown above. Routers R1 and R2 are properly configured with eigrp 976 protocol and are able to ping interfaces fa0/1 and fa0/2, respectively. Which commands are necessary
Refer to the exhibit and configuration shown above. Routers R1 and R2 are properly configured with eigrp 976 protocol and are able to ping interfaces fa0/1 and fa0/2, respectively. Which commands are necessary
Ch6 Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge Topology Diagram
 Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 7 Addressing Table for R1 Device Interface IP Address
Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 7 Addressing Table for R1 Device Interface IP Address
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols 1 Objectives Describe the role of dynamic routing protocols and place these protocols in the context of modern network design. Identify several ways to classify
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols 1 Objectives Describe the role of dynamic routing protocols and place these protocols in the context of modern network design. Identify several ways to classify
Configuring Scalable Hub-and-Spoke MPLS VPNs
 Configuring Scalable Hub-and-Spoke MPLS VPNs Last Updated: December 15, 2011 This module explains how to ensure that virtual private network (VPN) clients that connect to the same provider edge (PE) router
Configuring Scalable Hub-and-Spoke MPLS VPNs Last Updated: December 15, 2011 This module explains how to ensure that virtual private network (VPN) clients that connect to the same provider edge (PE) router
EIGRP Lab / lo1. .1 lo / /30
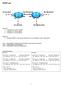 EIGRP Lab 172,16,1.0/24.1 lo1 192.168.20.0/30.2.1 Merida fa0 fa0 Vargas lo2.1 lo2.5.1 lo1 192.168.30.0/24 172.16.2.0/24 192.168.20.4.0/30 Scenario: Loopback0 is used for RouterID Loopback1 is a virtual
EIGRP Lab 172,16,1.0/24.1 lo1 192.168.20.0/30.2.1 Merida fa0 fa0 Vargas lo2.1 lo2.5.1 lo1 192.168.30.0/24 172.16.2.0/24 192.168.20.4.0/30 Scenario: Loopback0 is used for RouterID Loopback1 is a virtual
Information About Routing
 19 CHAPTER This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the adaptive security appliance, and the routing protocols that are supported. The chapter includes the following sections:,
19 CHAPTER This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the adaptive security appliance, and the routing protocols that are supported. The chapter includes the following sections:,
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS. Cisco Lab Øvelse Af Kim Donnerborg / RTS. Side 0 af 8
 KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA ( )
 STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA (640-802) Developed By, Router Infotech Career Academy LAB: 09 Static Route Configuration Objective: To configure & implement Static Route successfully on said devices and test its
STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA (640-802) Developed By, Router Infotech Career Academy LAB: 09 Static Route Configuration Objective: To configure & implement Static Route successfully on said devices and test its
Layer3 VPN with RIP protocol between CE-PE
 MPLS Layer3 VPN with IP protocol between E-PE Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to
MPLS Layer3 VPN with IP protocol between E-PE Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to
Final exam study Guide
 Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
BGP Best External. Finding Feature Information
 The feature provides the network with a backup external route to avoid loss of connectivity of the primary external route. The feature advertises the most preferred route among those received from external
The feature provides the network with a backup external route to avoid loss of connectivity of the primary external route. The feature advertises the most preferred route among those received from external
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
 Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Configuring Easy Virtual Network Shared Services
 Configuring Easy Virtual Network Shared Services This chapter describes how to use route replication and redistribution to share services in an Easy Virtual Network (EVN). Finding Feature Information,
Configuring Easy Virtual Network Shared Services This chapter describes how to use route replication and redistribution to share services in an Easy Virtual Network (EVN). Finding Feature Information,
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Topology...1 1.3 Configuration... 2 1.4 Validation... 3 2 Configuring RIP...5 2.1 Overview...
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Topology...1 1.3 Configuration... 2 1.4 Validation... 3 2 Configuring RIP...5 2.1 Overview...
Chapter 4 Lab 4-3, Manipulating Administrative Distances
 hapter 4 Lab 4-3, Manipulating Administrative Distances Topology bjectives Background onfigure RIP on a router. onfigure SPF on a router. Manipulate administrative distances. ompare routing protocol behavior.
hapter 4 Lab 4-3, Manipulating Administrative Distances Topology bjectives Background onfigure RIP on a router. onfigure SPF on a router. Manipulate administrative distances. ompare routing protocol behavior.
Lab : Challenge OSPF Configuration Lab. Topology Diagram. Addressing Table. Default Gateway. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview... 6 1.2 Topology...6 1.3 Configuration... 7 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP...10 2.1 Overview... 10
FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview... 6 1.2 Topology...6 1.3 Configuration... 7 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP...10 2.1 Overview... 10
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
Introduction. Lab Diagram
 Introduction The Troubleshooting routing protocols module provides you with the instructions and isco hardware to develop your hands on skills in troubleshooting routing protocols, specifically EIGRP.
Introduction The Troubleshooting routing protocols module provides you with the instructions and isco hardware to develop your hands on skills in troubleshooting routing protocols, specifically EIGRP.
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols V 4.0
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols V 4.0 3.1.1 What are the four routing RIP, RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPFv2 protocols that are the focus of this course? 3.1.1.2 What are routing protocols?
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols V 4.0 3.1.1 What are the four routing RIP, RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPFv2 protocols that are the focus of this course? 3.1.1.2 What are routing protocols?
