Planning Guide: Verizon LTE Split Data Routing, for Cisco ISR 4000, 8x9, 1900/2900/3900 Series
|
|
|
- Alice Heath
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Guide Planning Guide: Verizon LTE Split Data Routing, for Cisco ISR 4000, 8x9, 1900/2900/3900 Series Overview Verizon has offered four 3G/4G data services for enterprises to connect remote sites through Verizon Wireless Long Term Evolution (LTE): Machine-to-Machine (M2M) with Internet access and dynamic IP: This service enables a router to connect devices to the Internet or an enterprise network (via a customer premises equipment (CPE)-based VPN. M2M plan with Internet access with static IP: This service offers the same services as the previous one, except the 3G or 4G interface of each router receives a consistent predetermined IP address. Mobile Private Network (MPN): This service enables a router to connect users to an organization s private network. Traffic does not traverse the Internet. It generally requires a customer premises-based VPN for the LTE router such as Cisco IWAN. MPN with Dynamic Mobile Network Routing (DMNR): This service enables a router to connect users to an organization s private network without the need for customer premises-based VPN. Traffic does not traverse the Internet. Dynamic routing allows changing of local and remote IP addresses without coordination with Verizon. It can be used with any Cisco VPN option, including Group Encrypted Transport VPN. Verizon now offers a 5 th LTE data service for enterprises that combines Internet access and private network access. The new offering, Verizon LTE Split Data Routing, allows a remote LTE-connected site to directly access the Internet while also directly accessing the organization s private network. Features include: A single SIM and rate plan. The service does not require multiple SIMs nor multiple LTE modems/modules. Direct Internet access without having to traverse the private network, providing a higher performing more efficient route (does not use private network links nor datacenter Internet gateway/security resources). Combined with a Cisco ISR, the Verizon Split Data Routing Service: Allows for strong security via firewall, IPS, DNS and VRF options Can provide upstream quality of service (QoS) on both connections, and service level objectives on the private network connection via Verizon Private Network Traffic Management offering (PNTM) Combines the power of direct Internet access and Verizon s DMNR service for the highest flexibility and design, with dynamic routing whenever an organization makes changes 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 33
2 This planning guide outlines the process to plan for Verizon Split Data Routing LTE service. Relevant documents are also referenced. 1. No special service is needed outside of an approved plan and a provisioned SIM (Subscriber Identity Module. However, the LTE enhanced high-speed WAN interface card (ehwic) must be used with a Cisco Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 (ISR G2) router (Cisco 1900, 2900, or 3900 Series Integrated Services Router) whether provided by a Verizon/Cisco demonstration loan program or by your organization. For the CGR-2010 the LTE GRWIC is required. For the ISR 4K the LTE NIM is required. For the 819, 829, 899, the LTE interface is integrated. 2. Ensure you have a subscriber identity module (SIM/USIM/Mini-SIM or Micro SIM that is appropriate for the ISR and module being used: a. Verizon SKU "DIRECTSIM4G-D" for LTE NIM/eHWIC/GRWIC/CGM, 819, 899, 809, 829 b. Verizon SKU DFILLSIM3FF-A for NIM-LTEA-EA 3. Ensure the SIM is properly provisioned: a. The SIM (its phone number, e.g. MDN/MSISDN) must be provisioned and associated with the international mobility equipment identity (IMEI) of the ISR LTE modem before activation on an approved plan. i. The IMEI information is available via Cisco Commerce Workspace shipment details or via sh cell x hardware command on the ISR. ii. If this ISR is a demonstration unit provided by Verizon Wireless, an appropriately provisioned SIM should be included as part of the package sent to you. b. The APNs will need to be set manually. OTA-DM will not automatically set the APNs. Your Verizon Wireless representative can provide the APN information. No username or password is set for the APNs 4. Insert the SIM using the instructions found at The GRWIC on CGR is similar. The 819 has a small SIM panel underneath. The 809/829 have external slots. 5. Install the ehwic/nim/grwic/cmg module into the ISR/CGR (modular platforms only). a. The instructions to physically install the LTE ehwic or NIM into the ISR are at The CGR-2010 is similar. The 8x9 ISRs have the LTE already integrated. b. Install the LTE ehwic/nim into the right-most ehwic slot (looking at the rear of the ISR, slot 0/0). Figure 1. LTE ehwic 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 2 of 33
3 6. Power up the ISR and ensure that the antennas are positioned appropriately. a. With terminal or console access to the ISR (logging the terminal console is recommended): di. Hit Enter, and log in if the ISR has already been configured. If the unit is new, no ID or password may be set. If a new unit prompts for userid/password, try cisco/cisco. If there is, follow the instructions to reset the password at: ii. iii. At the console prompt type enable. Position antennas for the best RSSI signal > -80 dbm and RSRP signal > dbm, with the show cell 0/0/0 radio command (show cell 0 radio for 819). Type sh cell 0/x/0 hardware (cell 0 for 819) and show version, and ensure that the recommended Cisco IOS Software version is running. The generally recommended Cisco IOS software release depends on the LTE modem firmware level (seen via show cell 0/x/0 0 hardware command). The SKUs below are approved or will be tested for operation with Verizon Split Data Routing. ISR LTE SKU LTE Modem Recommended firmware Recommended IOS Release EHWIC-4G-LTE-VZ MC M2 C819G-4G-VZ-K9 MC M2 C899G-LTE-VZ-K9 MC M2 C819G-LTE-MNA-K9 MC M2 C819GW-LTE-MNA-K9 MC M2 NIM-LTEA-EA ISR4 EMM NIM-4G-LTE-VZ ISR4K MC TBD NIM-LTEA-EA on ENCS EMM NFVIS IOS IR809G-LTE-VZ-K9 MC M2 IR829GW-LTE-VZ-AK9 MC M2 IR829-2LTE-EA-BK9 MC (3)M2 C1111-8PLTEEA C1111-4PLTEEA EMM A iv. Type show run to see if the configuration matches the configuration guide on the following pages. v. If the configuration does not match the provided configuration, add or change the appropriate lines..through the command-line interface (CLI) config t, etc. Note: The cell interface s IP address is always..defined as ip address negotiated as the network always assigns it (even with persistent addressing) Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 3 of 33
4 7. Set the APNs appropriately for both public and private networks a. Verizon Split Data Routing allows for 2 active data connections, 1 public Internet, 1 private network, via connection to 2 separate Packet Data Networks (PDNs). These connections are defined by the appropriate LTE modem profiles. There is a separate ISR interface associated with each connection (cell 0 and 1 for 8xx, cell 0/x/0 and 0/x/1 for modular ISRs). b. If a new deployment, the Internet APN (profile 3) will already be set. The private APN is defined via IOS enable-mode command. The profile number is different for ISR 4K vs ISR 8xx. For 8xx: cell 0 lte profile create 6 <theapnvalue> <enter> <enter> <enter> For 4K: cell 0/x/0 lte profile create 4 <theapnvalue> <enter> <enter> <enter> c. If this ISR is an existing deployment, profile 3 is in use for the private network. Both the Internet profile and private network profile are defined via IOS enable-mode command. For both: cell 0 lte profile create 3 VZWINTERNET none ipv4v6 <enter> <enter> <enter> For 8xx: cell 0 lte profile create 6 <theapnvalue> <enter> <enter> <enter> For 4K: cell 0/x/0 lte profile create 4 <theapnvalue> <enter> <enter> <enter> d. The Cisco IOS Software command show cellular 0/x/0 profile displays the APN (show cellular 0 profile for the 8x9). 8. Connect both antennas (at least one with an antenna extension cable) to the LTE ehwic/nim/grwic/8x9. The antennas should be at least 2 feet apart. Instructions can be found in the section Additional Information. 9. If the LTE connection becomes active but then begins to flap (repeats going down and up periodically, usually every 5 to 60 seconds), a configuration problem must be resolved. a. This behavior can be caused by a network disconnect due to IP source address violations. It is resolved by reconfiguring the traffic to be tunneled, NAT, or access control lists (ACLs) so that no traffic is routed without being tunneled or subjected to NAT. If you cannot determine which IP address is causing the IP source violation, contact the Verizon Wireless Enterprise Help Desk ( ) and ask them to trace the call and report the IP address that is causing the problem. Then correct or add NAT, ACL, or VPN to stop any packets with a source address other than the LTE ehwic IP address from leaking out. 10. See the configurations and display output in the sections below. Note that these configurations are for LTE only, and do not include security. As the ISR is connected to both the Internet and private network, strong security should be enabled on the ISR. The following page reviews available ISR security features (under Branch Threat Defense ): Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 4 of 33
5 Additional Information Cisco LTE Portal: Verizon planning/configuration documents: LTE ehwic hardware overview, SIM install, antenna connection, and module install: LTE NIM hardware overview, SIM install, antenna connection, and module install: LTE ehwic Cisco IOS Software configuration (use the Verizon planning/configuration documents): LTE NIM Cisco IOS Software configuration (use the Verizon planning/configuration documents): LTE ehwic antenna, cabling, and lightning arrestor instructions: Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 5 of 33
6 Configuration Guide: Verizon Internet Access, Static IP, and LTE ehwic High-Level Network Diagram The traffic to/from the public network is logically separate from the traffic to/from the private network, between the ISR cellular interface and destination. Behind the ISR cellular interfaces, traffic can be logically separated using VRFs, policy-based routing, access control lists, and zone-based firewall SR functions. Both LTE interfaces will send and receive traffic based on the ISR routing configuration. This is no different than wireline ISR interfaces. All ISR techniques are available to be used with cellular interfaces; however their use depends on configuration: - Private Network APN: o NeMo (Verizon DMNR service). Provides a default route, marked as an M (mobile) route. The organization s private LTE network peers with LTE ISRs and advertises the appropriate networks behind each LTE ISR to the organization s private wireline network. The configuration examples shown are for Verizon DMNR service with the private network APN. o IGP (interior gateway routing protocols such as EIGRP and OSPF) can be used only if tunneled (i.e. DMVPN, FlexVPN, GRE) between each LTE ISR and the organization s VPN head end. o Policy-Based Routing (PBR) in conjunction with one of the two methods above - Public Internet APN: o Static routes with NAT (Network Address Translation) o Policy-Based Routing (PBR) with NAT Recommendations for Split Data Routing with MPN and CPE-based VPN Tunnels (DMVPN, FlexVPN, etc.) - Use an IGP (OSPF, EIGRP, etc.) within the Tunnel over the cellular interface to the LTE private network to receive specific route advertisements from the wireline VPN head end. This provides for routing to the private network without receiving a default route from the private network. - Use a static default route pointing to the LTE interface to the public Internet. Thus any traffic not destined to the private network will be forwarded to the Internet via a single configuration line o Example: ip route cell 0 for 8x9, ip route cell 0/x/0 for ISR 4K Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 6 of 33
7 Recommendations for Split Data Routing with MPN and DMNR (NeMo) - Verizon Dynamic Network Mobile Routing (DMNR) offers organizations LTE network routing/advertising that is simple, cost effective (no VPN tunnel head end equipment to acquire, maintain, manage), highly scalable (from ten to tens of thousands of LTE routers) and dynamic (add a subnet to the remote router, it is automatically advertised and reachable across the private wireline network). - However, the LTE router receives a default route from the private network. There are 2 ways to direct traffic to public cloud services on the Internet 1. Override the dynamically assigned default route to the private network with a static default route to the public network (cell 0 or cell 0/x/0); define static routes pointing to the private network (cell 0 or cell 0/x/1). a. Example: ip route cell 0 for 8x9, ip route cell 0/0/0 for ISR 4K b. Example: ip route cell 1 8x9, ip route cell 0/0/1 ISR 4K 2. Leave in place the static default route for interface cell 1 (8x9) or 0/x/1 (modular ISR) to the private network. Define static routes to cover the publicly routable IP space via cell 0 (8x9) or 0/x/0 (modular ISR). a. A set of static routes accomplishing this is included in each configuration example and the display output in this guide. NAT is always required for the Public Internet APN. Verizon provides one IP address (actually one IPv4 and one IPv6) to the ISR cell interface representing the public Internet connection. The NAT technique NPAT or PAT is used so that multiple users/devices can access the Internet via the single LTE IP address. This is also a common configuration for many broadband Internet connections. The show running-config is provided for an ISR 4000 and 819. Other platforms will be similar (1900/2900/3900, 899). Only the configuration commands pertinent to LTE and IP routing are shown. Full configurations for various LTE scenarios can be found in the guides here: Display output (show command results) is subsequently provided for both platforms Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 7 of 33
8 ISR 4000 Series NIM-LTEA-EA Split Data Routing/Dual APN Configuration ### command allowing for LTE test cellular enable mode commands ### service internal hostname c4321-4g ### load appropriate IOS image ### boot system bootflash:isr4300-universalk spa.bin interface Loopback1234 description ### NEMO Router Home Address ip address ### The maximum TCP MSS is set to 1390 bytes to allow for GRE, IPsec and other network overhead. The route-map clears DF bits in the IP headers. ### interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address ip nat inside ip tcp adjust-mss 1390 ip policy route-map clear-df load-interval 30 media-type rj45 negotiation auto interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address ip nat inside ip tcp adjust-mss 1390 ip policy route-map clear-df load-interval 30 negotiation auto ### Interface Cellular 0/x/0 x depends on ISR slot. This interface is for the Internet PDN. Connection is activated using dialer watch list 1. ### interface Cellular0/1/0 ip address negotiated no ip unreachables ip nat outside ip tcp adjust-mss 1390 load-interval 30 dialer in-band dialer idle-timeout 0 dialer enable-timeout 2 dialer watch-group 1 pulse-time 1 ### Interface Cellular 0/x/1 x depends on ISR slot. This interface is for the private network PDN. Connection activated via dialer watch list 2. NAT not needed as all traffic sent in the NeMo (IP Mobile Router) tunnel. ### 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 8 of 33
9 interface Cellular0/1/1 ip address negotiated no ip unreachables ip mobile router-service roam ip mobile router-service collocated ccoa-only ip tcp adjust-mss 1390 load-interval 30 dialer in-band dialer idle-timeout 0 dialer enable-timeout 2 dialer watch-group 2 pulse-time 1 ### This stanza enables NEMO Routing. Admin distance can be adjusted ### router mobile distance 33 ### This NAT statement ensures all traffic leaving the ISR is sourced with the IP address of the LTE cellular interface, to avoid auto-disconnection by the network. All traffic appears to come from the LTE IP address. ### ip nat inside source list 100 interface Cellular0/1/0 overload ### This ACL enables NATing of traffic leaving the cell interface. Permit ip any any is no longer supported. This example will NAT any packet with the source address s 1 st octet having an even number (including 10.x.x.x 172.x.x.x and 192.x.x.x, a superset of RFC1918 addresses). ### access-list 100 permit ip any ### These static routes send all traffic destined to Internet routable destinations via the LTE Internet connection/interface. This is the 2 nd option mentioned earlier, leaving the M/Mobile IP default route in place ### ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/ Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 9 of 33
10 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ip route Cellular0/1/0 ### This command configures NEMO Authentication with EXGW. Use the appropriate EXGW IP address based on the geographic location (page 3). Note that SPI and KEY must match to what is set on the EXGW under the NEMO service. Note that the algorithm must be set to hmac-md5. ### ip mobile secure home-agent XXX.XXX spi decimal 256 key ascii VzWNeMo algorithm hmac-md5 ### This section configures the NEMO Mobile Router parameters and defines what router interfaces and their subnets to be included into the NEMO registration with EXGW. Use the appropriate EXGW IP address as above. ### ip mobile router address collocated single-tunnel home-agent XXX.XXX mobile-network GigabitEthernet0/0/1 mobile-network GigabitEthernet0/0/0 non-connected-network register extend expire 10 retry 3 interval 5 reverse-tunnel tunnel mode gre ### This route-map clears the DF-bit in IP packets that come into the ISR from the Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. ### route-map clear-df permit 10 set ip df 0 ### This section defines the LTE call activation triggers and timers. ### ### The LTE connection for cell 0/x/0 will be triggered by this statement. The address is a dummy route. Any dummy value can be used. ### dialer watch-list 1 ip ### The ISR will wait 60 sec. before activating LTE after initial boot. ### dialer watch-list 1 delay route-check initial 60 ### The ISR will wait 1 sec. before activating the call. ### dialer watch-list 1 delay connect 1 ### These watch-list commands are for interface cell 0/x/1 dialer watch-list 2 ip dialer watch-list 2 delay route-check initial 60 dialer watch-list 2 delay connect 1 end 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 10 of 33
11 ISR 819/899 Split Data Routing/Dual APN Configuration ### command allowing for LTE test cellular enable mode commands ### service internal hostname 819-XL ### load appropriate IOS image ### boot system flash:c800-universalk9-mz.spa m2.bin ip cef ### CHAT Script to make a data call ### chat-script lte "" "ATCALL1" TIMEOUT 20 "OK" ### This Loopback address used to source pings for testing purposes. ### interface Loopback1 description ### always-on interface ### ip address ip nat inside ### The maximum TCP MSS is set to 1390 bytes to allow for GRE, IPsec and other network overhead. The route-map clears DF bits in the IP headers. ### interface VLAN1 ip address ip nat inside ip tcp adjust-mss 1390 ip policy route-map clear-df ### Interface Cell 0 is the interface is for the Internet PDN. Connection is activated using dialer watch list 1. ### interface Cellular0 ip address negotiated no ip unreachables ip nat outside encapsulation slip ip tcp adjust-mss 1390 load-interval 30 dialer in-band dialer idle-timeout 0 dialer string lte dialer watch-group 1 no peer default ip address async mode interactive pulse-time 0 routing dynamic ### Interface Cellular 0/x/1 x depends on ISR slot. This interface is for the private network PDN. Connection activated via dialer watch list 2. NAT not needed as all traffic sent in the NeMo (IP Mobile Router) tunnel. ### 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 11 of 33
12 interface Cellular1 ip address negotiated no ip unreachables ip mobile router-service roam ip mobile router-service collocated ccoa-only ip virtual-reassembly in encapsulation slip ip tcp adjust-mss 1390 load-interval 30 dialer in-band dialer idle-timeout 0 dialer string lte dialer watch-group 2 no peer default ip address async mode interactive pulse-time 0 routing dynamic ### This stanza enables NEMO Routing. Admin distance can be adjusted ### ### This command configures NEMO Authentication with EXGW. Use the appropriate EXGW IP address based on the geographic location (page 3). Note that SPI and KEY must match to what is set on the EXGW under the NEMO service. Note that the algorithm must be set to hmac-md5. ### router mobile distance 111 ### This NAT statement ensures all traffic leaving the ISR is sourced with the IP address of the LTE cellular interface, to avoid auto-disconnection by the network. All traffic appears to come from the LTE IP address. ### ip nat inside source list 100 interface Cellular0 overload ### This ACL enables NATing of traffic leaving the cell interface. Permit ip any any is no longer supported. This example will NAT any packet with the source address s 1 st octet having an even number (including 10.x.x.x 172.x.x.x and 192.x.x.x, a superset of RFC1918 addresses). ### access-list 100 permit ip any ### These static routes send all traffic destined to Internet routable destinations via the LTE Internet connection/interface. This is the 2 nd option mentioned earlier, leaving the M/Mobile IP default route in place ### ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 12 of 33
13 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ip route Cellular0 ### This section configures the NEMO Mobile Router parameters and defines what router interfaces and their subnets to be included into the NEMO registration with EXGW. Use the appropriate EXGW IP address as above. ### ip mobile secure home-agent XXX.XXX spi decimal 256 key ascii VzWNeMo algorithm hmac-md5 ip mobile router address collocated single-tunnel home-agent XXX.XXX mobile-network Loopback100 mobile-network Vlan1 non-connected-network register extend expire 10 retry 3 interval 5 reverse-tunnel tunnel mode gre ### Route-map clears DF-bit in packets to exit via the LTE interface. ### route-map clear-df permit 10 set ip df 0 ### This section defines the LTE call activation triggers and timers. ### 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 13 of 33
14 ### The LTE connection for cell 0 will be triggered by this statement. The address is a dummy route. Any dummy value can be used. ### dialer watch-list 1 ip ### Wait for 60 sec. before activating the call after the initial boot. ### dialer watch-list 1 delay route-check initial 60 ### The ISR will wait 1 sec. before activating the call. ### dialer watch-list 1 delay connect 1 ### These watch-list commands are for interface cell 1 dialer watch-list 2 ip dialer watch-list 2 delay route-check initial 60 dialer watch-list 2 delay connect 1 ### chat script lte is also called by the line interface line 3 script dialer lte modem InOut no exec transport input ssh end 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 14 of 33
15 Operation and Show Commands for ISR 4000 Series and LTE-A NIM C4321-4G#### Some public addresses have been hidden via XXXX C4321-4G#### Existing Deployment Example C4321-4G#sh cell 0/1/0 profile Profile 1 = INACTIVE ** PDP Type = IPv4v6 Access Point Name (APN) = vzwims Authentication = None Profile 2 = INACTIVE PDP Type = IPv4v6 Access Point Name (APN) = vzwadmin Authentication = None Profile 3 = ACTIVE* PDP Type = IPv4 PDP address = Access Point Name (APN) = CISCO.GW4.VZWENTP Authentication = None Primary DNS address = XXX Secondary DNS address = XXX Primary DNS IPV6 address = 0 Secondary DNS IPV6 address = 0 Profile 4 = INACTIVE PDP Type = IPv4v6 Access Point Name (APN) = vzwapp Authentication = None Profile 5 = INACTIVE PDP Type = IPv4v6 Access Point Name (APN) = vzw800 Authentication = None * - Default profile ** - LTE attach profile 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 15 of 33
16 C4321-4G#cell 0/1/0 lte profile create 3 VZWINTERNET? chap CHAP authentication only none No authentication pap PAP authentication only pap_chap PAP or CHAP authentication <cr> C4321-4G#cell 0/1/0 lte profile create 3 VZWINTERNET none? ipv4 IPv4 type Bearer ipv4v6 IPV4V6 type Bearer ipv6 IPV6 type Bearer <cr> C4321-4G#cell 0/1/0 lte profile create 3 VZWINTERNET none ipv4v6? <cr> C4321-4G#cell 0/1/0 lte profile create 3 VZWINTERNET none ipv4v6 Warning: You are attempting to modify a currently ACTIVE data profile. This is not recommended and may affect the connection state PDP Type = IPv4 Access Point Name (APN) = CISCO.GW4.VZWENTP Authentication = NONE Profile 3 already exists with above parameters. Do you want to overwrite? [confirm] Profile 3 will be overwritten with the following values: PDP type = IPV4V6 APN = VZWINTERNET Authentication = NONE Are you sure? [confirm]y Profile 3 written to modem C4321-4G# C4321-4G# C4321-4G#cellu 0/1/0 lte profile create 4 cisco.gw4.vzwentp none ipv4 PDP Type = IPv4v6 Access Point Name (APN) = vzwapp Authentication = NONE Profile 4 already exists with above parameters. Do you want to overwrite? [confirm] 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 16 of 33
17 Profile 4 will be overwritten with the following values: PDP type = IPv4 APN = cisco.gw4.vzwentp Authentication = NONE Are you sure? [confirm]n Profile 4 written to modem C4321-4G# C4321-4G#sh cell 0/1/0 all Hardware Information ==================== Modem Firmware Version = SWI9X30C_ Modem Firmware built = 2016/10/11 16:03:14 Hardware Version = 1.0 Device Model ID: EM7455 International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) = International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) = Integrated Circuit Card ID (ICCID) = Mobile Subscriber Integrated Services Digital Network-Number (MSISDN) = XXXX Modem Status = Modem Online Current Modem Temperature = 36 deg C PRI SKU ID = , PRI version = _000, Carrier = Verizon OEM PRI version = 006 Profile Information ==================== Profile 1 = INACTIVE ** PDP Type = IPv4v6 Access Point Name (APN) = vzwims Authentication = None Profile 2 = INACTIVE PDP Type = IPv4v6 Access Point Name (APN) = vzwadmin Authentication = None Profile 3 = ACTIVE* PDP Type = IPv4v6 PDP address = XXX 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 17 of 33
18 PDP IPV6 address = 2600:1002:B02D:XXXX:CC49:42FF:FE46:908/64 Scope: Global PDP IPV6 address = FE80:0:0:0:CC49:42FF:FE46:908/64 Scope: Link Access Point Name (APN) = VZWINTERNET Authentication = None Primary DNS address = XXX Secondary DNS address = XXX Primary DNS IPV6 address = 2001:4888:15:XXXX:194:D:0:0 Secondary DNS IPV6 address = 2001:4888:14:XXXX:196:D:0:0 Profile 4 = ACTIVE PDP Type = IPv4 PDP address = Access Point Name (APN) = cisco.gw4.vzwentp Authentication = None Primary DNS address = XXX Secondary DNS address = XXX Primary DNS IPV6 address = 0 Secondary DNS IPV6 address = 0 Profile 5 = INACTIVE PDP Type = IPv4v6 Access Point Name (APN) = vzw800 Authentication = None Configured default profile for active SIM 0 is profile 3. Data Connection Information =========================== Profile 1, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 2, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 3, Packet Session Status = ACTIVE Cellular0/1/0: Data Transmitted = 1440 bytes, Received = 1539 bytes IP address = XXX IPV6 address = 2600:1002:B02D:XXXX:CC49:42FF:FE46:908/64 Scope: Global IPV6 address = FE80:0:0:0:CC49:42FF:FE46:908/64 Scope: Link Primary DNS address = XXX Secondary DNS address = XXX Primary DNS IPV6 address = 2001:4888:15:XXXX:194:D:0:0 Secondary DNS IPV6 address = 2001:4888:14:XXXX:196:D:0:0 Profile 4, Packet Session Status = ACTIVE Cellular0/1/1: 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 18 of 33
19 Data Transmitted = 1496 bytes, Received = 264 bytes IP address = Primary DNS address = XXX Secondary DNS address = XXX Profile 5, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 6, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 7, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 8, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 9, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 10, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 11, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 12, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 13, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 14, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 15, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 16, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Network Information =================== Current System Time = Tue May 30 17:0: Current Service Status = Normal Current Service = Packet switched Current Roaming Status = Home Network Selection Mode = Automatic Network = VzW Mobile Country Code (MCC) = 311 Mobile Network Code (MNC) = 480 Packet switch domain(ps) state = Attached LTE Carrier Aggregation state = Deconfigured Registration state(emm) = Registered EMM Sub State = Normal Service Tracking Area Code (TAC) = Cell ID = Radio Information ================= Radio power mode = online LTE Rx Channel Number = 1000 LTE Tx Channel Number = LTE Band = 2 LTE Bandwidth = 10 MHz Current RSSI = -76 dbm Current RSRP = -98 dbm Current RSRQ = -11 db Current SNR = 14.4 db 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 19 of 33
20 Physical Cell Id = 227 Number of nearby cells = 1 Idx PCI (Physical Cell Id) Radio Access Technology(RAT) Preference = AUTO Radio Access Technology(RAT) Selected = LTE Modem Security Information ========================== Active SIM = 0 SIM switchover attempts = 0 Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Disabled SIM Status = OK SIM User Operation Required = None Number of CHV1 Retries remaining = 3 Cellular Firmware List ========================== Idx Carrier FwVersion PriVersion Status 1 ATT _000 Inactive 2 GENERIC _000 Inactive 3 SPRINT _000 Inactive 4 VERIZON _000 Active Firmware Activation mode : AUTO GPS Information ========================== GPS Info GPS Feature: enabled GPS Mode Configured: not configured GPS Status: NMEA Disabled SMS Information =============== Incoming Message Information SMS stored in modem = 0 SMS archived since booting up = 0 Total SMS deleted since booting up = 0 Storage records allocated = 25 Storage records used = Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 20 of 33
21 Number of callbacks triggered by SMS = 0 Number of successful archive since booting up = 0 Number of failed archive since booting up = 0 Outgoing Message Information Total SMS sent successfully = 0 Total SMS send failure = 0 Number of outgoing SMS pending = 0 Number of successful archive since booting up = 0 Number of failed archive since booting up = 0 Last Outgoing SMS Status = SUCCESS Copy-to-SIM Status = 0x0 Send-to-Network Status = 0x0 Report-Outgoing-Message-Number: Reference Number = 0 Result Code = 0x0 Diag Code = 0x0 0x0 0x0 0x0 0x0 SMS Archive URL = Error Information ================= This command is not supported on 4G modems. Modem Crashdump Information =========================== Modem crashdump logging: off =========================== Dying Gasp Information =========================== Dying Gasp Detach: Enabled SMS: Enabled SMS Message = 4321LTEA in Horsham lab lost power Destination Number = XXXX C4321-4G#ping Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 38/68/160 ms C4321-4G#ping Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 21 of 33
22 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms sh ver i IOS Cisco IOS XE Software, Version Cisco IOS Software [Denali], ISR Software (X86_64_LINUX_IOSD-UNIVERSALK9-M), Version , RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc3) Cisco IOS-XE software, Copyright (c) by cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Certain components of Cisco IOS-XE software are documentation or "License Notice" file accompanying the IOS-XE software, or the applicable URL provided on the flyer accompanying the IOS-XE ROM: IOS-XE ROMMON C4321-4G# C4321-4G#sh ip int brie i Ce Cellular0/1/ XXX YES IPCP up up Cellular0/1/ YES IPCP up up C4321-4G# C4321-4G#sh ip rou Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP a - application route + - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR Gateway of last resort is to network M* /0 is directly connected, Tunnel0 S /5 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/ /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C is directly connected, Loopback1234 S /7 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/ /8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks S /8 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/1 C /32 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/1 S /8 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /7 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /7 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /4 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 Printed in USA C / Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 22 of 33
23 S /3 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /2 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/ /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets M XXX.XXX [33/1], 01:05:09, Cellular0/1/ /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /3 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /4 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /5 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /12 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /16 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /15 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /15 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /15 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /13 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /13 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /10 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /9 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /8 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /7 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /12 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /9 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /11 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /13 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /16 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /15 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /14 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /13 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /10 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /11 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /8 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /7 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /6 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /5 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /5 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 S /5 is directly connected, Cellular0/1/0 C4321-4G# C4321-4G#sh ip mob rou Mobile Router Enabled 06/01/17 13:21:41 Last redundancy state transition NEVER Configuration: Home Address Mask Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 23 of 33
24 Home Agent XXX.XXX Priority 100 (best) (current) Registration lifetime sec Retransmit Init 1000, Max 5000 msec, Limit 3 Extend Expire 10, Retry 3, Interval 5 Reverse tunnel required Request GRE tunnel Multi-path denied by HA, Requested metric: bandwidth Mobile Networks: GigabitEthernet0/0/1 (Down) GigabitEthernet0/0/0 (Down) non connected subnet ( / ) Monitor: Status -Registered- Using collocated care-of address On interface Cellular0/1/1 Tunnel0 mode GRE/IP C4321-4G# 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 24 of 33
25 819-XL#### Example of display output. This LTE SIM/subscription also has LTE QoS (PNTM) 819-XL#### Some public addresses have been hidden via XXXX *May 31 23:45:06.451: %CELLWAN-2-BEARER_UP: Instance id=1, Default bearer (bearer_id=7) in Cellular1 is now UP *May 31 23:45:06.551: %CELLWAN-2-BEARER_UP: Instance id=1, Dedicated bearer (bearer_id=8) QCI=7 in Cellular1 is now UP *May 31 23:45:08.555: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Cellular1, changed state to up *May 31 23:45:09.555: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Cellular1, changed state to up 819-XL# 819-XL#sh ip int brie Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Cellular X.X YES IPCP up up Cellular YES IPCP up up CellNM5 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet1 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet2 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet3 unassigned YES unset down down GigabitEthernet YES NVRAM down down Loopback99 unassigned YES unset up up Loopback YES NVRAM up up Loopback YES NVRAM up up Mobile0 unassigned YES unset up up NVI YES unset up up Serial0 unassigned YES unset down down Tunnel YES unset up up Tunnel YES TFTP up down Vlan YES NVRAM down down 819-XL#sh ip rou Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP a - application route + - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR Gateway of last resort is to network Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 25 of 33
26 M* /0 is directly connected, Tunnel0 S /5 is directly connected, Cellular /32 is subnetted, 2 subnets C is directly connected, Loopback1234 C is directly connected, Loopback100 S /7 is directly connected, Cellular /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C is directly connected, Cellular1 S /8 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /7 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /7 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /4 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /3 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /2 is directly connected, Cellular /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets M XXX.XXX [111/1], 00:10:24, Cellular /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C is directly connected, Cellular /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets M [111/1], 00:29:29, Cellular0 S /3 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /4 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /5 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /12 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /16 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /15 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /15 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /15 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /13 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /13 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /10 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /9 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /8 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /7 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /12 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /9 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /11 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /13 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /16 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /15 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /14 is directly connected, Cellular Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 26 of 33
27 S /13 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /10 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /11 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /8 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /7 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /6 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /5 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /5 is directly connected, Cellular0 S /5 is directly connected, Cellular0 819-XL#sh ip mob rou Mobile Router Enabled 05/31/17 21:36:10 Last redundancy state transition NEVER Configuration: Home Address Mask Home Agent XXX.XXX Priority 100 (best) (current) Registration lifetime sec Retransmit Init 1000, Max 5000 msec, Limit 3 Extend Expire 10, Retry 3, Interval 5 Reverse tunnel required Request GRE tunnel Multi-path denied by HA, Requested metric: bandwidth Mobile Networks: Loopback100 ( / ) Vlan1 (Down) non connected subnet ( / ) Monitor: Status -Registered- Using collocated care-of address On interface Cellular1 Tunnel0 mode GRE/IP 819-XL# 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 27 of 33
28 819-XL#sh cell 0 all Hardware Information ==================== Modem Firmware Version = SWI9X15C_ Modem Firmware built = 2015/03/05 00:02:40 Hardware Version = 1.0 Device Model ID: MC7350 Package Identifier ID: _ _MC7350_ _00_Cisco_ _000 International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) = International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) = Integrated Circuit Card ID (ICCID) = Mobile Subscriber Integrated Services Digital Network-Number (MSISDN) = XXXX Modem Status = Online Current Modem Temperature = 37 deg C PRI SKU ID = , PRI version = _000, Carrier = Verizon OEM PRI version = Profile Information ==================== Profile 1 = INACTIVE ** PDP Type = IPv4v6 Access Point Name (APN) = vzwims Authentication = None Profile 2 = INACTIVE PDP Type = IPv4v6 Access Point Name (APN) = vzwadmin Authentication = None Profile 3 = ACTIVE* PDP Type = IPv4 PDP address = XXX Access Point Name (APN) = VZWINTERNET Authentication = None Primary DNS address = XXX.XXX Secondary DNS address = XXX.XXX 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 28 of 33
29 Profile 4 = INACTIVE PDP Type = IPv4v6 Access Point Name (APN) = vzwapp Authentication = None Profile 5 = INACTIVE PDP Type = IPv4v6 Access Point Name (APN) = vzw800 Authentication = None Profile 6 = ACTIVE PDP Type = IPv4 PDP address = Access Point Name (APN) = cisco.gw4.vzwentp Authentication = None Primary DNS address = XXX.XXX Secondary DNS address = XXX.XXX * - Default profile ** - LTE attach profile Data Connection Information =========================== Profile 1, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 2, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 3, Packet Session Status = ACTIVE Cellular0: Data Transmitted = bytes, Received = bytes IP address = XXX Primary DNS address = XXX.XXX Secondary DNS address = XXX.XXX Profile 4, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 5, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE Profile 6, Packet Session Status = ACTIVE Cellular1: Data Transmitted = 952 bytes, Received = 616 bytes 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 29 of 33
30 IP address = Primary DNS address = XXX.XXX Secondary DNS address = XXX.XXX Network Information =================== Current System Time = Thu Jun 1 17:50: Current Service Status = Normal Current Service = Packet switched Current Roaming Status = Home Network Selection Mode = Automatic Network = VzW Mobile Country Code (MCC) = 311 Mobile Network Code (MNC) = 480 Packet switch domain(ps) state = Attached Registration state(emm) = Registered EMM Sub State = Normal Service Tracking Area Code (TAC) = Cell ID = Negotiated network MTU is 1428 Radio Information ================= Radio power mode = online LTE Rx Channel Number = 2125 LTE Tx Channel Number = LTE Band = 4 LTE Bandwidth = 15 MHz Current RSSI = -66 dbm Current RSRP = -95 dbm Current RSRQ = -10 db Current SNR = 19.0 db Physical Cell Id = 0xE3 Number of nearby cells = 3 Idx PCI (Physical Cell Id) Radio Access Technology(RAT) Preference = AUTO Radio Access Technology(RAT) Selected = LTE 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 30 of 33
31 Modem Security Information ========================== Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Disabled SIM Status = OK SIM User Operation Required = None Number of CHV1 Retries remaining = 3 GPS Information ========================== GPS Info GPS Feature: enabled GPS Port Selected: Dedicated GPS port GPS Status: GPS acquiring GPS auto tracking status: active GPS auto tracking config: enabled GPS Mode Configured: standalone Last Location Fix Error: Not Available [0x0] Latitude: 0 Deg 0 Min 0 Sec North Longitude: 0 Deg 0 Min 0 Sec North Timestamp (GMT): Sun Jan 6 00:00: Fix type index: 0, Height: 0 m HDOP:, GPS Mode Used: not configured/unknown Satellite Info Satellite #16, elevation 0, azimuth 0, SNR 25 SMS Information =============== Incoming Message Information SMS stored in modem = 0 SMS archived since booting up = 0 Total SMS deleted since booting up = 0 Storage records allocated = 25 Storage records used = 0 Number of callbacks triggered by SMS = Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 31 of 33
32 Number of successful archive since booting up = 0 Number of failed archive since booting up = 0 Outgoing Message Information Total SMS sent successfully = 0 Total SMS send failure = 0 Number of outgoing SMS pending = 0 Number of successful archive since booting up = 0 Number of failed archive since booting up = 0 Last Outgoing SMS Status = SUCCESS Copy-to-SIM Status = 0x0 Send-to-Network Status = 0x0 Report-Outgoing-Message-Number: Reference Number = 0 Result Code = 0x0 Diag Code = 0x0 0x0 0x0 0x0 0x0 SMS Archive URL = Error Information ================= This command is not supported on this platform. Modem Crashdump Information =========================== Chassis Model Name is C819G-4G-VZ-K9 Platform is MC73xx based Modem crashdump logging: off 819-XL#sh ip mob rou Mobile Router Enabled 05/31/17 21:36:10 Last redundancy state transition NEVER Configuration: Home Address Mask Home Agent XXX.XXX Priority 100 (best) (current) Registration lifetime sec 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 32 of 33
33 Retransmit Init 1000, Max 5000 msec, Limit 3 Extend Expire 10, Retry 3, Interval 5 Reverse tunnel required Request GRE tunnel Multi-path denied by HA, Requested metric: bandwidth Mobile Networks: Loopback100 ( / ) Vlan1 (Down) Monitor: Status -Registered- Using collocated care-of address On interface Cellular1 Tunnel0 mode GRE/IP 819-XL# David Mindel 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 33 of 33
Planning Guide: Verizon Internet Access, Static IP, for Cisco LTE ehwic/nim/grwic/8x9
 Guide Planning Guide: Verizon Internet Access, Static IP, for Cisco LTE ehwic/nim/grwic/8x9 Overview Verizon Wireless offers four 3G/4G data services for enterprises to connect remote sites through Verizon
Guide Planning Guide: Verizon Internet Access, Static IP, for Cisco LTE ehwic/nim/grwic/8x9 Overview Verizon Wireless offers four 3G/4G data services for enterprises to connect remote sites through Verizon
Configuration Guide for Verizon LTE MPN/DMNR LTE Primary Access (LTE ehwic)/grwic/819)
 Guide Configuration Guide for Verizon LTE MPN/DMNR LTE Primary Access (LTE ehwic)/grwic/819) Mobile Router Configuration Guide for Primary Wireless Access Revision 3.3 June 2013 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates.
Guide Configuration Guide for Verizon LTE MPN/DMNR LTE Primary Access (LTE ehwic)/grwic/819) Mobile Router Configuration Guide for Primary Wireless Access Revision 3.3 June 2013 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates.
Cisco Fourth-Generation LTE Network Interface Module Software Configuration Guide
 Cisco Fourth-Generation LTE Network Interface Module Software Configuration Guide First Published: 2015-05-26 Last Modified: -- Cisco Fourth-Generation LTE Network Interface Module Software Configuration
Cisco Fourth-Generation LTE Network Interface Module Software Configuration Guide First Published: 2015-05-26 Last Modified: -- Cisco Fourth-Generation LTE Network Interface Module Software Configuration
Cisco 4G LTE-Advanced Configuration
 This section contains the following topics: Cisco Fourth-Generation LTE Advanced on the Cisco IR1101 Series Integrated Services Router, on page 1 Cisco Fourth-Generation LTE Advanced on the Cisco IR1101
This section contains the following topics: Cisco Fourth-Generation LTE Advanced on the Cisco IR1101 Series Integrated Services Router, on page 1 Cisco Fourth-Generation LTE Advanced on the Cisco IR1101
Chapter 6: Network Layer
 Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks Intro to Networks v5 Network Layer Intro to Networks v5 2 The Network Layer End to End Transport processes Addressing end devices Encapsulation of Packets
Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks Intro to Networks v5 Network Layer Intro to Networks v5 2 The Network Layer End to End Transport processes Addressing end devices Encapsulation of Packets
Configuring Network Access to the GGSN
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure access from the gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) to a serving GPRS support node (SGSN), public data network (PDN), and optionally to a Virtual Private
CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure access from the gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) to a serving GPRS support node (SGSN), public data network (PDN), and optionally to a Virtual Private
Configure Initial Router Settings on Cisco 4000 Series ISRs
 Configure Initial Router Settings on Cisco 4000 Series ISRs This chapter describes how to perform the initial configuration on Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs). It contains the following
Configure Initial Router Settings on Cisco 4000 Series ISRs This chapter describes how to perform the initial configuration on Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs). It contains the following
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example
 Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example
 FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example Document ID: 118888 Contributed by Piotr Kupisiewicz, Wen Zhang, and Frederic Detienne, Cisco TAC Engineers. Apr 08, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example Document ID: 118888 Contributed by Piotr Kupisiewicz, Wen Zhang, and Frederic Detienne, Cisco TAC Engineers. Apr 08, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
 Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing
 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Troubleshooting Guide for 3G Module for CGR 1000 Series Router (Cisco CG-OS)
 Troubleshooting Guide for 3G Module for CGR 1000 Series Router (Cisco CG-OS) Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Troubleshoot Verify that CGR can Recognize the 3G Module Check
Troubleshooting Guide for 3G Module for CGR 1000 Series Router (Cisco CG-OS) Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Troubleshoot Verify that CGR can Recognize the 3G Module Check
Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Inheritence with EIGRP Named mode Route Replication with EIGRP name mode Routing Context
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Inheritence with EIGRP Named mode Route Replication with EIGRP name mode Routing Context
RR> RR> RR>en RR# RR# RR# RR# *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 RR#
 RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
Lab Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Chapter 7 Lab 7-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute
 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM
 Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks
 Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
Intelligent WAN Remote Site 4G LTE Deployment Guide
 Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Remote Site 4G LTE Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deployment Details...1 Deploying Remote
Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Remote Site 4G LTE Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deployment Details...1 Deploying Remote
MRD-310 MRD G Cellular Modem / Router Web configuration reference guide. Web configuration reference guide
 Web configuration reference guide 6623-3201 MRD-310 MRD-330 Westermo Teleindustri AB 2008 3G Cellular Modem / Router Web configuration reference guide www.westermo.com Table of Contents 1 Basic Configuration...
Web configuration reference guide 6623-3201 MRD-310 MRD-330 Westermo Teleindustri AB 2008 3G Cellular Modem / Router Web configuration reference guide www.westermo.com Table of Contents 1 Basic Configuration...
Configuring Dynamic Addressing on the GGSN
 CHAPTER 13 This chapter describes how to configure dynamic IP addressing on the gateway GRPS support node (GGSN). Note Dynamic IP addressing is not supported for IPv6 and PPP PDP types. Therefore, the
CHAPTER 13 This chapter describes how to configure dynamic IP addressing on the gateway GRPS support node (GGSN). Note Dynamic IP addressing is not supported for IPv6 and PPP PDP types. Therefore, the
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator
 Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4
 Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
GRE and DM VPNs. Understanding the GRE Modes Page CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 23 You can configure Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) and Dynamic Multipoint (DM) VPNs that include GRE mode configurations. You can configure IPsec GRE VPNs for hub-and-spoke, point-to-point,
CHAPTER 23 You can configure Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) and Dynamic Multipoint (DM) VPNs that include GRE mode configurations. You can configure IPsec GRE VPNs for hub-and-spoke, point-to-point,
LAB8: OSPF IPv4. OSPF: Virtual Link. Disclaimer
 Page1 AB8: OSPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB8: OSPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
IP NAT Troubleshooting. Solutions. Luke Bibby, CCIE #45527
 IP NAT Troubleshooting Solutions Luke Bibby, CCIE #45527 Quick Overview of Scenario Solutions Scenario #1 R2 s E0/0 should be NAT inside not NAT outside ACL 100 is configured incorrectly NAT policy missing
IP NAT Troubleshooting Solutions Luke Bibby, CCIE #45527 Quick Overview of Scenario Solutions Scenario #1 R2 s E0/0 should be NAT inside not NAT outside ACL 100 is configured incorrectly NAT policy missing
Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE
 MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
DMVPN to Group Encrypted Transport VPN Migration
 DMVPN to Group Encrypted Transport VPN Migration This document provides the steps for Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) to Group Encrypted Transport VPN migration. DMVPN to Group Encrypted Transport VPN Migration
DMVPN to Group Encrypted Transport VPN Migration This document provides the steps for Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) to Group Encrypted Transport VPN migration. DMVPN to Group Encrypted Transport VPN Migration
Configuring Security on the GGSN
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure security features on the gateway GPRS support node (GGSN), including Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA), and RADIUS. IPSec on the Cisco
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure security features on the gateway GPRS support node (GGSN), including Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA), and RADIUS. IPSec on the Cisco
LAB5: OSPF IPv4. OSPF: Stub. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB5: SPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB5: SPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
Access Server Dial In IP/PPP Configuration With Dedicated V.120 PPP
 Access Server Dial In IP/PPP Configuration With Dedicated V.120 PPP Document ID: 6306 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information How V.120 Affects
Access Server Dial In IP/PPP Configuration With Dedicated V.120 PPP Document ID: 6306 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information How V.120 Affects
Configuration and Management of Networks
 Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration
 Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration Topology Objectives Configure IPv6 addressing. Configure and verify RIPng on R1 and R2. Configure IPv6 static routes between R2 and R3.
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration Topology Objectives Configure IPv6 addressing. Configure and verify RIPng on R1 and R2. Configure IPv6 static routes between R2 and R3.
Configuring FlexVPN Spoke to Spoke
 Last Published Date: March 28, 2014 The FlexVPN Spoke to Spoke feature enables a FlexVPN client to establish a direct crypto tunnel with another FlexVPN client leveraging virtual tunnel interfaces (VTI),
Last Published Date: March 28, 2014 The FlexVPN Spoke to Spoke feature enables a FlexVPN client to establish a direct crypto tunnel with another FlexVPN client leveraging virtual tunnel interfaces (VTI),
Intelligent WAN Multiple VRFs Deployment Guide
 Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Multiple VRFs Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deploying the Cisco IWAN Multiple VRFs...
Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Multiple VRFs Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deploying the Cisco IWAN Multiple VRFs...
Configuring NAT for IP Address Conservation
 This module describes how to configure Network Address Translation (NAT) for IP address conservation and how to configure inside and outside source addresses. This module also provides information about
This module describes how to configure Network Address Translation (NAT) for IP address conservation and how to configure inside and outside source addresses. This module also provides information about
Finding Feature Information
 The feature provides PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) client support on routers. PPPoE is a commonly used application in the deployment of digital subscriber lines (DSLs). The PPP over Ethernet Client feature
The feature provides PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) client support on routers. PPPoE is a commonly used application in the deployment of digital subscriber lines (DSLs). The PPP over Ethernet Client feature
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 with Stub Area
 Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Finding Feature Information
 This module describes how to configure Network Address Translation (NAT) for IP address conservation and how to configure inside and outside source addresses. This module also provides information about
This module describes how to configure Network Address Translation (NAT) for IP address conservation and how to configure inside and outside source addresses. This module also provides information about
Configuring a GSM (3G) modem on a GW2040 Series Router
 Configuring a GSM (3G) modem on a GW2040 Series Router Issue 1.5 Date 10 May 2012 Table of contents 1 About this document... 3 1.1 Scope... 3 1.2 Readership... 3 1.3 More information... 3 1.3.1 Assigned
Configuring a GSM (3G) modem on a GW2040 Series Router Issue 1.5 Date 10 May 2012 Table of contents 1 About this document... 3 1.1 Scope... 3 1.2 Readership... 3 1.3 More information... 3 1.3.1 Assigned
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
ipv6 mobile home-agent (global configuration)
 ipv6 mobile home-agent (global configuration) ipv6 mobile home-agent (global configuration) To enter home agent configuration mode, use the ipv6 mobile home-agent command in global configuration mode.
ipv6 mobile home-agent (global configuration) ipv6 mobile home-agent (global configuration) To enter home agent configuration mode, use the ipv6 mobile home-agent command in global configuration mode.
GE MDS, LLC. 175 Science Parkway, Rochester, NY USA Phone +1 (585) , FAX +1 (585) Web:
 APPLICATION BULLETIN NUMBER: AB14005_A June 2014 MDS Orbit MCR Series GE MDS, LLC. 175 Science Parkway, Rochester, NY 14620 USA Phone +1 (585) 242-9600, FAX +1 (585) 242-9620 Web: www.gemds.com Orbit MCR
APPLICATION BULLETIN NUMBER: AB14005_A June 2014 MDS Orbit MCR Series GE MDS, LLC. 175 Science Parkway, Rochester, NY 14620 USA Phone +1 (585) 242-9600, FAX +1 (585) 242-9620 Web: www.gemds.com Orbit MCR
examcollection.premium.exam.68q. Exam code: Exam name: Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks (TSHOOT) Version 15.
 300-135.examcollection.premium.exam.68q Number: 300-135 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 / Exam code: 300-135 Exam name: Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks (TSHOOT)
300-135.examcollection.premium.exam.68q Number: 300-135 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 / Exam code: 300-135 Exam name: Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks (TSHOOT)
Initial Configuration for the Switch
 Options for Initial Configuration, page 1 Configuring the Switch Using the Web User Interface, page 1 Configuring the Switch Using the CLI, page 4 Configuring the Switch in the ROMMON Mode, page 12 Options
Options for Initial Configuration, page 1 Configuring the Switch Using the Web User Interface, page 1 Configuring the Switch Using the CLI, page 4 Configuring the Switch in the ROMMON Mode, page 12 Options
MPLS VPN Half-Duplex VRF
 The feature provides scalable hub-and-spoke connectivity for subscribers of an Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service. This feature addresses the limitations of hub-and-spoke
The feature provides scalable hub-and-spoke connectivity for subscribers of an Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service. This feature addresses the limitations of hub-and-spoke
Lab- Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
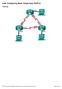 Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Cisco Virtual Office High-Scalability Design
 Solution Overview Cisco Virtual Office High-Scalability Design Contents Scope of Document... 2 Introduction... 2 Platforms and Images... 2 Design A... 3 1. Configure the ACE Module... 3 2. Configure the
Solution Overview Cisco Virtual Office High-Scalability Design Contents Scope of Document... 2 Introduction... 2 Platforms and Images... 2 Design A... 3 1. Configure the ACE Module... 3 2. Configure the
SD-WAN Deployment Guide (CVD)
 SD-WAN Deployment Guide (CVD) All Cisco Meraki security appliances are equipped with SD-WAN capabilities that enable administrators to maximize network resiliency and bandwidth efficiency. This guide introduces
SD-WAN Deployment Guide (CVD) All Cisco Meraki security appliances are equipped with SD-WAN capabilities that enable administrators to maximize network resiliency and bandwidth efficiency. This guide introduces
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11 8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 8.3.3.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv3 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard
CCNA Semester 2 labs Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11 8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 8.3.3.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv3 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard
Configuring PPP over Ethernet with NAT
 CHAPTER 3 The Cisco Secure Router 520 Ethernet-to-Ethernet routers support Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) clients and network address translation (NAT). Multiple PCs can be connected to
CHAPTER 3 The Cisco Secure Router 520 Ethernet-to-Ethernet routers support Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) clients and network address translation (NAT). Multiple PCs can be connected to
Configuring and Troubleshooting Frame Relay
 Configuring and Troubleshooting Frame Relay Document ID: 16563 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device. Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites
Configuring and Troubleshooting Frame Relay Document ID: 16563 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device. Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites
Lab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interfaces
 IPsec virtual tunnel interfaces (VTIs) provide a routable interface type for terminating IPsec tunnels and an easy way to define protection between sites to form an overlay network IPsec VTIs simplify
IPsec virtual tunnel interfaces (VTIs) provide a routable interface type for terminating IPsec tunnels and an easy way to define protection between sites to form an overlay network IPsec VTIs simplify
Configuring PPP over Ethernet with NAT
 This chapter provides an overview of Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) clients and network address translation (NAT) that can be configured on the Cisco 819, Cisco 860, Cisco 880, and Cisco
This chapter provides an overview of Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) clients and network address translation (NAT) that can be configured on the Cisco 819, Cisco 860, Cisco 880, and Cisco
LAB1: BGP IPv4. BGP: Initial Config. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Lab Configuring IPv6 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A
Remote Access MPLS-VPNs
 First Published: August 12, 2002 Last Updated: May 4, 2009 The feature allows the service provider to offer a scalable end-to-end Virtual Private Network (VPN) service to remote users. This feature integrates
First Published: August 12, 2002 Last Updated: May 4, 2009 The feature allows the service provider to offer a scalable end-to-end Virtual Private Network (VPN) service to remote users. This feature integrates
Chapter 8 Lab Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS
 Chapter 8 Lab Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Chapter 8 Lab Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Segment Routing On Demand Next Hop for L3/L3VPN
 Segment Routing On Demand Next Hop for L3/L3VPN When redistributing routing information across domains, provisioning of multi-domain services (L2VPN & L3VPN) has its own complexity and scalability issues.
Segment Routing On Demand Next Hop for L3/L3VPN When redistributing routing information across domains, provisioning of multi-domain services (L2VPN & L3VPN) has its own complexity and scalability issues.
Packet Tracer - Connect a Router to a LAN (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
Interchassis Asymmetric Routing Support for Zone-Based Firewall and NAT
 Interchassis Asymmetric Routing Support for Zone-Based Firewall and NAT The Interchassis Asymmetric Routing Support for Zone-Based Firewall and NAT feature supports the forwarding of packets from a standby
Interchassis Asymmetric Routing Support for Zone-Based Firewall and NAT The Interchassis Asymmetric Routing Support for Zone-Based Firewall and NAT feature supports the forwarding of packets from a standby
show gprs access-point
 show gprs access-point show gprs access-point To display information about access points on the GGSN, use the show gprs access-point privileged EXEC command. show gprs access-point {access-point-index
show gprs access-point show gprs access-point To display information about access points on the GGSN, use the show gprs access-point privileged EXEC command. show gprs access-point {access-point-index
Configuring WAN Backhaul Redundancy
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure WAN backhaul redundancy for cellular and WiMAX interfaces on the Cisco 1000 Series Connected Grid Routers (hereafter referred to as the Cisco CG-OS router).
CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure WAN backhaul redundancy for cellular and WiMAX interfaces on the Cisco 1000 Series Connected Grid Routers (hereafter referred to as the Cisco CG-OS router).
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable
 Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable Document ID: 12084 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable Document ID: 12084 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
IPv6 over DMVPN. Finding Feature Information
 This document describes how to implement the Dynamic Multipoint VPN for IPv6 feature, which allows users to better scale large and small IPsec Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) by combining generic routing
This document describes how to implement the Dynamic Multipoint VPN for IPv6 feature, which allows users to better scale large and small IPsec Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) by combining generic routing
Understanding and Troubleshooting Idle Timeouts
 Understanding and Troubleshooting Idle Timeouts Document ID: 23423 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Common Problems and Symptoms Idle Timeouts Interesting Traffic
Understanding and Troubleshooting Idle Timeouts Document ID: 23423 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Common Problems and Symptoms Idle Timeouts Interesting Traffic
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem
 How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
DMVPN Topology. Page1
 DMVPN DMVPN Topology Page1 LAB 2: Configure EIGRP over DMVPN: Task 1: Configure EIGRP over DMVPN Process Step 1 In the configuration mode of router configure EIGRP over DMVPN by following command: R1:
DMVPN DMVPN Topology Page1 LAB 2: Configure EIGRP over DMVPN: Task 1: Configure EIGRP over DMVPN Process Step 1 In the configuration mode of router configure EIGRP over DMVPN by following command: R1:
Implementing DHCP for IPv6
 This module describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for IPv6. DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation, page 1 How to Implement DHCP for IPv6, page 6 DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation The IPv6 Access
This module describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for IPv6. DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation, page 1 How to Implement DHCP for IPv6, page 6 DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation The IPv6 Access
Proxy Mobile IPv6 Support for MAG Functionality
 The feature provides network-based IP Mobility management to a mobile node (MN) without requiring the participation of the mobile node in any IP Mobility-related signaling. The Mobile Access Gateway (MAG)
The feature provides network-based IP Mobility management to a mobile node (MN) without requiring the participation of the mobile node in any IP Mobility-related signaling. The Mobile Access Gateway (MAG)
Seattle Cisco Users Group
 Seattle Cisco Users Group CCNA Lab Project #3 Joe Rinehart MBA, CCIE #14256 CCNP/DP/VP June 10, 2011 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1. The CCNA Certification... 3 1.2. Purpose of the Lab Project...
Seattle Cisco Users Group CCNA Lab Project #3 Joe Rinehart MBA, CCIE #14256 CCNP/DP/VP June 10, 2011 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1. The CCNA Certification... 3 1.2. Purpose of the Lab Project...
Lab Securing Network Devices
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3
Pass4sures. Latest Exam Guide & Learning Materials
 Pass4sures http://www.pass4sures.top/ Latest Exam Guide & Learning Materials Exam : 200-125 Title : CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 200-125
Pass4sures http://www.pass4sures.top/ Latest Exam Guide & Learning Materials Exam : 200-125 Title : CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 200-125
Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example
 Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example Document ID: 113361 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Related Information
Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example Document ID: 113361 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Related Information
Feature-by-Feature Router Configurations
 CHAPTER 3 Feature-by-Feature Router Configurations This chapter includes feature-by-feature configuration procedures for the Cisco 806 router. This chapter is useful if you have a network in place and
CHAPTER 3 Feature-by-Feature Router Configurations This chapter includes feature-by-feature configuration procedures for the Cisco 806 router. This chapter is useful if you have a network in place and
Advanced IPv6 Training Course. Lab Manual. v1.3 Page 1
 Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
Lab Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Chapter 6: Network Layer
 Chapter 6: Network Layer CCNA Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0 Chapter 6 - Sections & Objectives 6.1 Network Layer Protocols Explain how network layer protocols and services support
Chapter 6: Network Layer CCNA Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0 Chapter 6 - Sections & Objectives 6.1 Network Layer Protocols Explain how network layer protocols and services support
Quick Note. Configure an IPSec VPN tunnel in Aggressive mode between a TransPort LR router and a Cisco router. Digi Technical Support 7 October 2016
 Quick Note Configure an IPSec VPN tunnel in Aggressive mode between a TransPort LR router and a Cisco router. Digi Technical Support 7 October 2016 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Outline... 3 1.2 Assumptions...
Quick Note Configure an IPSec VPN tunnel in Aggressive mode between a TransPort LR router and a Cisco router. Digi Technical Support 7 October 2016 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Outline... 3 1.2 Assumptions...
Managing Site-to-Site VPNs
 CHAPTER 21 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
CHAPTER 21 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
Intelligent WAN Multiple Data Center Deployment Guide
 Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Multiple Data Center Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deployment Details...1 Deploying
Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Multiple Data Center Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deployment Details...1 Deploying
Reverse Route Injection
 Reverse Route Injection Last Updated: October 15, 2012 Reverse route injection (RRI) is the ability to automatically insert static routes in the routing process for those networks and hosts protected by
Reverse Route Injection Last Updated: October 15, 2012 Reverse route injection (RRI) is the ability to automatically insert static routes in the routing process for those networks and hosts protected by
Operation Manual IPv4 Routing H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration... 1-1 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Static Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Default Route... 1-1 1.1.3 Application Environment of Static Routing...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration... 1-1 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Static Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Default Route... 1-1 1.1.3 Application Environment of Static Routing...
BGP Best External. Finding Feature Information
 The feature provides the network with a backup external route to avoid loss of connectivity of the primary external route. The feature advertises the most preferred route among those received from external
The feature provides the network with a backup external route to avoid loss of connectivity of the primary external route. The feature advertises the most preferred route among those received from external
ALEOS Release Notes
 ALEOS 4.8.0 is for AirLink RV50X, AirLink RV50, AirLink GX450, AirLink ES450, and AirLink MP70 gateways. For upgrade instructions, refer to the ALEOS 4.8.0 Software Configuration User Guide. Gateways shipped
ALEOS 4.8.0 is for AirLink RV50X, AirLink RV50, AirLink GX450, AirLink ES450, and AirLink MP70 gateways. For upgrade instructions, refer to the ALEOS 4.8.0 Software Configuration User Guide. Gateways shipped
Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Managing Site-to-Site VPNs: The Basics
 CHAPTER 21 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
CHAPTER 21 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
