AP-468 APPLICATION BRIEF. Serial Port Mode 0 RICHARD N EVANS APPLICATIONS ENGINEER. February Order Number
|
|
|
- Damon McKenzie
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AP-468 APPLICATION BRIEF Serial Port Mode 0 8X9XBH KB KC KD RICHARD N EVANS APPLICATIONS ENGINEER February 1995 Order Number
2 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products Intel assumes no liability whatsoever including infringement of any patent or copyright for sale and use of Intel products except as provided in Intel s Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products Intel retains the right to make changes to these specifications at any time without notice Microcomputer Products may have minor variations to this specification known as errata Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners Since publication of documents referenced in this document registration of the Pentium OverDrive and icomp trademarks has been issued to Intel Corporation Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications before placing your product order Copies of documents which have an ordering number and are referenced in this document or other Intel literature may be obtained from Intel Corporation P O Box 7641 Mt Prospect IL or call COPYRIGHT INTEL CORPORATION 1996
3 CONTENTS Serial Port Mode 0 8X9XBH KB KC KD PAGE CONTENTS PAGE ABSTRACT 1 METHOD OF OPERATION 1 Timing Considerations 1 Baud Rate 1 SETTING UP THE CONTROL REGISTERS 2 RECEIVE 3 TRANSMIT 3 EXAMPLE USING MODE 0 3 HARDWARE 3 Inverter 3 OR Gate 3 DIP Switch 3 SOFTWARE 5
4
5 ABSTRACT This application brief explains how to program the MCS -96 device to operate the serial port in synchronous mode A 4-bit multiplier which utilizes mode 0 with a port expansion circuit is presented METHOD OF OPERATION The serial port can be operated in a synchronous mode This mode was intended for port expansion using shift registers For example the TXD pin is used to clock both input and output data on RXD The data is always one byte in length Whenever a write to the serial port buffer (SBUF) is performed a train of eight pulses is sent out TXD to clock the outgoing byte Likewise whenever SBUF is read a train of eight pulses is sent out TXD to clock in the byte being read See the synchronous serial mode timing diagram shown in Figure 1 Timing Considerations All timings associated with the serial port are relative to T OSC Therefore the timings are fixed whether XTAL1 or T2CLK clocks the baud rate generator T DVXH Input Data Setup to Clock (TXD) Rising Edge In other words the data has to be valid at T DVXH before the next TXD pulse rises T QVXH Output Data Setup to Clock (TXD) Rising Edge The output bit will be valid before the rising edge of the next TXD pulse for T QVXH T XLXH Serial Port Clock Falling Edge to Rising Edge The low period for the TXD clock cannot be changed For the 8X9X T XLXH e 4 T OSC g50 For KB KC and KD T XLXH e 4T OSC g50 or 2 T OSC g50 depending on the baud rate register value NOTE See the A C Characteristics in the datasheets for the timing specifications Baud Rate Baud rate is a misused term Baud rate is often used interchangeably with bits per second (BPS) This substitution is not always true though Baud rate is the speed at which packets of information are passed per second It just so happens that with the MCS-96 family the length of the information packet is 1 bit Hence the baud rate measurement is the same as the bits per second (BPS) for the MCS-96 serial port The MCS-96 has a 15-bit baud rate generator The most significant bit (bit 15) determines the clock source (XTAL1 or T2CLK) There is a baud rate register (location 0EH) This register is a byte wide When loading the baud rate register it must be written twice first the least significant byte must be written to location 0EH then the most significant byte See equation 1 for the baud rate register formula F BAUD VALUE e OSC BAUD RATE c 2 b 1 OR e T2CLK BAUD RATE Equation 1 Serial Port Synchronous Mode 0 Baud Rate Register Equations Setting up the baud rate generator is easy The example code (code 1) shows how to configure the baud rate generator to run at 9600 baud with a 16 MHz crystal Figure 1 Important Timings for Serial Port Mode 0 1
6 BAUD VALUE EQU OEH BAUD RATE REGISTER CSEG AT 2080H LDB BAUD VALUE 40H LDB BAUD VALUE 83H SET UP BAUD RATE GENERATOR FOR FOR 9600 BAUD AT A 16MHz CRYSTAL FREQUENCY Code 1 Setting up Baud Rate Generator in Mode 0 SETTING UP THE CONTROL REGISTERS (09H) INT MASK (16H) IOC (200CH) SERIAL PORT interrupt vector location There are a few control registers that need to be utilized for mode 0 operation First since TXD is shared on the same pin as P2 0 we need to select the TXD function of that pin This is accomplished by setting bit 5 in IOC1 (16H) (11H) SP CON In order to set the serial port to operate in mode 0 the serial port control register (SP CON 11H) needs to be initialized Bits 0 to 1 set the mode Hence setting them to zero enables mode 0 Also in the SP CON is the receiver enable bit Setting this bit (bit 3) enables the receiver (see RECEIVE) NOTE This interrupt is available on the 8X9X KB KC and KD There are two ways to monitor the status of the receiver and or the transmitter One is by polling the SP STAT register (specifically RI and TI) the other is by using interrupts RI is set whenever the receiver is done receiving one byte in mode 0 Likewise TI is set whenever the transmitter has sent out one byte in mode 0 If the SERIAL PORT interrupt is masked in then a rising edge on RI or TI causes the SERIAL PORT interrupt to be taken The SERIAL PORT interrupt bit in INT MASK (09H) is the inclusive OR of RI and TI Hence either RI or TI can cause a SERIAL PORT interrupt Therefore once the interrupt routine is entered SP STAT has to be tested to determine which interrupt (RI or TI) occurred (12H) INT MASK1 (11H) SP STAT (2030H) TI vector location (2032H) RI vector location The serial port status register (SP STAT 11H) is located at the same address as SP CON Writing to address 11H loads the serial port control register Reading from 11H will read from the serial port status register (SP STAT) Two status bits of importance are RI and TI When set they indicate a receive completion or a transmit completion respectively The RI and TI bits are cleared by reading SP STAT NOTE These interrupts are available on the KB KC and KD not on the 8X9X Additional interrupt vectors exist on the KB KC and KD which make it easier to write code for the serial port To interrupt on just the receive completion the RI interrupt vector can be masked in Similarly the TI interrupt has a separate vector for transmit completion 2
7 RECEIVE Reading the SP STAT register always clears the RI bit and TI bit If the RI bit is cleared while the RECEIVER ENABLE bit (bit 3 in SP CON) is high then another reception is started Hence it is possible to start another reception and overwrite the previous one Therefore don t poll SP STAT to monitor the receiver Use the serial port interrupt the receive interrupt vector or INT PEND1 (KB KC and KD) to test the RI bit for receive completion It is a good programming practice to use the serial port interrupt or the RI interrupt for testing the RI bit First load the interrupt vector location with the appropriate ISR routine address Next enable the interrupt using either INT MASK or INT MASK1 depending on which interrupt is chosen Now enable interrupts using the EI instruction Then disable the receiver by clearing bit 3 in SP CON Now the receiver is in a known state To start a reception initiate a rising edge on the receiver enable bit (set bit 3 in SP CON) When the service routine is entered disable interrupts (i e PUSHF or PUSHA) and read SBUF (07H) to obtain the received byte To start another reception clear the RI bit by reading SP STAT Then enable interrupts (i e POPF or POPA) and return from the interrupt service routine Clearing the RI bit while the receiver is enabled starts a reception and allows another serial port or receive interrupt to occur To disable the receiver simply clear the RECEIVER ENABLE bit in SP CON See the programming example in the following pages TRANSMIT Transmitting a byte is much more straightforward First load SBUF (07H) with the byte to be transmitted Two methods can be used to detect when transmit completion occurs polling TI in SP STAT or using the serial port interrupt or TI interrupt (KB KC and KD) Once again using an interrupt to detect transmit complete is good programming practice To set up the transmit interrupt service routine load the address of the ISR into either the serial port interrupt vector (200CH) or the TI interrupt vector (2030H) As with receive mask in the appropriate interrupt using either INT MASK or INT MASK1 Enable interrupts with EI and load SBUF with the byte to transmit When the interrupt service routine is entered disable interrupts (i e PUSHF or PUSHA) After the routine is executed another transmit can be started by loading SBUF again Clear the TI bit in SP STAT by reading SP STAT This action allows another transmit or serial interrupt to occur Enable interrupts before returning from the service routine (i e POPF or POPA) When the next transmit is done another interrupt occurs (serial or transmit) EXAMPLE USING MODE 0 A programming example is included to demonstrate most of the above procedures for implementing mode 0 An evaluation board was used in conjunction with an I O port expansion circuit to test out the following code The program reads in one byte from an external shift register Then it multiplies the lower nibble by the upper nibble The product is transmitted to another external shift register and is displayed on LEDs The largest product is 0E1H which is 0FH x 0FH HARDWARE The schematic for this example is pictured in Figure 2 The data-in byte is generated by a DIP switch attached to a parallel-in serial-out shift register (74LS165) The output display is simply eight LEDs The clock (TXD) is used to clock the parallel-in serial-out shift register (74LS165) This (74LS165) register has two modes a shift mode and a load mode When the transmit part of the circuit is activated the 74LS165 is put into LOAD mode so the transmit shift register is not interfered with To enable the transmit circuit the TXD clock is gated to the 74LS164 (serial-in parallel-out) The transmit circuit is enabled by the active low signal ENABLE The RXD line is used for receiving and transmitting Inverter The inverter (74LS05) has an open-collector output A weak (15K) pull-up is used at the output The purpose of the weak pull-up is so the RXD (when used as an output) can drive the data on RXD high or low If a regular inverter were used then contention would exist between RXD (when used as an output) and the inverter output Notice that the input to the inverter is QH hence the output of the inverter is the actual data QH OR Gate The OR gate is a switch for the TXD clock TXD is at one input The other input is the ENABLE line (from P2 6) When the ENABLE line is low TXD passes freely through the OR gate However when ENABLE is high the output of the OR gate is always high As a result there are no transistions at the output of the OR gate and the 74LS164 is not clocked DIP Switch The DIP switch is weakly pulled high (switch off) and strongly driven low (switch on) 3
8 Figure 2 I O Port Expansion and Example Schematic 4
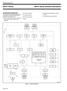
9 SOFTWARE See the program listing for the software part of this example Only the serial port interrupt is used in this example Hence this program is compatible with 8X9XBH KB KC and KD The flow chart in Figure 3 illustrates the algorithm register to shift mode Port 2 is used to output control signals to the shift register and the transmit enable gate Clearing P2 7 loads the shift register Setting P2 7 puts the register in shift mode Furthermore to allow TXD to clock the transmit shift register P2 6 must be cleared Setting P2 6 disables the TXD clock to the transmit shift register Port 2 is diagrammed below (10H) PORT The next step in starting a receive in this example is to disable the clock to the transmit circuit (see above) P2 6 is set by performing a logical OR Next mode 0 is selected and the receiver is disabled by clearing all bits in SP CON Now a rising edge on the REN bit is initiated by setting bit 3 in SP CON Finally SP STAT is cleared by reading it Note that a special procedure was used to clear SP STAT This routine only needs to be called for the 8X9XBH (see techbit MC3391) The KB KC and KD can simply do a LDB temp SP STAT The foreground loop is entered until an interrupt occurs There is only one interrupt routine the serial port interrupt service routine The first step in an interrupt routine is to disable other interrupts and save the flags Next the receiver is disabled by clearing SP CON Then the TXD clock to the transmit circuitry is disabled by setting P2 6 The completion bits RI and TI are cleared (call SP STAT rd) to allow for the next interrupt SP IMAGE is returned from the SP STAT rd procedure SP IMAGE contains the status of the serial port upon entry into the service routine The RI bit is tested in SP IMAGE for receive completion Figure 3 Flowchart of Example Mode 0 Program During the initialize procedure the control registers are set to a known state The serial port interrupt is masked in Then the TXD function is enabled on its respective pin Next the baud rate is set The baud rate generator can be clocked by either XTAL1 or T2CLK Now the first receive is started The shift register must be loaded with the DIP switch byte Hence a procedure is called to load the shift register and to set the If a receive just finished then a transmit is initiated First the received byte is read in Then the nibbles are multiplied The TXD clock to the transmit circuitry is enabled and the transmit is initiated Now if a transmit caused the interrupt then a receive is started First the external shift register is loaded by calling load shift reg Then the receiver is enabled A rising edge on REN starts another reception The RI bit has already been cleared because SP STAT rd was called Hence when the interrupt service routine is exited the POPF enables interrupts and allows for the receive interrupt to occur Once again the foreground loop is entered to await another interrupt 5
10
11
12
Software Serial Port Implemented with the PCA
 APPLICATION BRIEF Software Serial Port Implemented with the PCA BETSY JONES ECO APPLICATIONS ENGINEER August 1988 Order Number 270531-002 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel
APPLICATION BRIEF Software Serial Port Implemented with the PCA BETSY JONES ECO APPLICATIONS ENGINEER August 1988 Order Number 270531-002 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel
Memory Expansion for the 8096
 APPLICATION BRIEF Memory Expansion for the 8096 DOUG YODER ECO APPLICATIONS ENGINEER April 1989 Order Number 270522-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products Intel
APPLICATION BRIEF Memory Expansion for the 8096 DOUG YODER ECO APPLICATIONS ENGINEER April 1989 Order Number 270522-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products Intel
How to Implement I 2 C Serial Communication Using Intel MCS-51 Microcontrollers
 APPLICATION NOTE How to Implement I 2 C Serial Communication Using Intel MCS-51 Microcontrollers SABRINA D QUARLES APPLICATIONS ENGINEER April 1993 Order Number 272319-001 Information in this document
APPLICATION NOTE How to Implement I 2 C Serial Communication Using Intel MCS-51 Microcontrollers SABRINA D QUARLES APPLICATIONS ENGINEER April 1993 Order Number 272319-001 Information in this document
Interfacing an Intel386 TM EX Microprocessor to an CAN Controller
 APPLICATION NOTE Interfacing an Intel386 TM EX Microprocessor to an 82527 CAN Controller GREG SCOTT TECHNICAL MARKETING ENGINEER January 1996 Order Number 272790-001 COPYRIGHT INTEL CORPORATION 1995 1
APPLICATION NOTE Interfacing an Intel386 TM EX Microprocessor to an 82527 CAN Controller GREG SCOTT TECHNICAL MARKETING ENGINEER January 1996 Order Number 272790-001 COPYRIGHT INTEL CORPORATION 1995 1
DMA Latency
 AB-36 APPLICATION BRIEF 80186 80188 DMA Latency STEVE FARRER APPLICATIONS ENGINEER April 1989 Order Number 270525-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products Intel assumes
AB-36 APPLICATION BRIEF 80186 80188 DMA Latency STEVE FARRER APPLICATIONS ENGINEER April 1989 Order Number 270525-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products Intel assumes
Interfacing the Graphics Coprocessor to the 8051
 APPLICATION BRIEF Interfacing the 82786 Graphics Coprocessor to the 8051 RICK SCHUE REGIONAL APPLICATIONS SPECIALIST INDIANAPOLIS INDIANA February 1996 Order Number 270528-003 Information in this document
APPLICATION BRIEF Interfacing the 82786 Graphics Coprocessor to the 8051 RICK SCHUE REGIONAL APPLICATIONS SPECIALIST INDIANAPOLIS INDIANA February 1996 Order Number 270528-003 Information in this document
Migrating from the 8XC251Sx to the 8XC251Tx
 Migrating from the 8XC251Sx to the 8XC251Tx Application Note May 1999 Order Number: 273252-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products. No license, express or implied,
Migrating from the 8XC251Sx to the 8XC251Tx Application Note May 1999 Order Number: 273252-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products. No license, express or implied,
DRAM Refresh Control with the
 APPLICATION BRIEF DRAM Refresh Control with the 80186 80188 STEVE FARRER APPLICATIONS ENGINEER August 1990 Order Number 270524-002 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products
APPLICATION BRIEF DRAM Refresh Control with the 80186 80188 STEVE FARRER APPLICATIONS ENGINEER August 1990 Order Number 270524-002 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products
8051 Serial Communication
 8051 Serial Communication Basics of serial communication Parallel: transfers eight bits of data simultaneously over eight data lines expensive - short distance fast Serial : one bit at a time is transferred
8051 Serial Communication Basics of serial communication Parallel: transfers eight bits of data simultaneously over eight data lines expensive - short distance fast Serial : one bit at a time is transferred
MCS-51 Serial Port A T 8 9 C 5 2 1
 MCS-51 Serial Port AT89C52 1 Introduction to Serial Communications Serial vs. Parallel transfer of data Simplex, Duplex and half-duplex modes Synchronous, Asynchronous UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter.
MCS-51 Serial Port AT89C52 1 Introduction to Serial Communications Serial vs. Parallel transfer of data Simplex, Duplex and half-duplex modes Synchronous, Asynchronous UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter.
The 80C186XL 80C188XL Integrated Refresh Control Unit
 APPLICATION BRIEF The 80C186XL 80C188XL Integrated Refresh Control Unit GARRY MION ECO SENIOR APPLICATIONS ENGINEER November 1994 Order Number 270520-003 Information in this document is provided in connection
APPLICATION BRIEF The 80C186XL 80C188XL Integrated Refresh Control Unit GARRY MION ECO SENIOR APPLICATIONS ENGINEER November 1994 Order Number 270520-003 Information in this document is provided in connection
Experiment# 8: Photo-Interrupter Control
 Experiment# 8: Photo-Interrupter Control I. Objective 1. Study the schematic diagram of photo interrupter (PH1, and PH2) and the pulse generator circuit. 2. To demonstrate the control applications of photo-interrupter,
Experiment# 8: Photo-Interrupter Control I. Objective 1. Study the schematic diagram of photo interrupter (PH1, and PH2) and the pulse generator circuit. 2. To demonstrate the control applications of photo-interrupter,
80C51GB, 83C51GB, 87C51GB SPECIFICATION UPDATE
 80C51GB, 83C51GB, 87C51GB SPECIFICATION UPDATE Release Date: December, 1996 Order Number: 272880-003 The 80C51GB, 83C51GB, 87C51GB may contain design defects or errors known as errata. Characterized errata
80C51GB, 83C51GB, 87C51GB SPECIFICATION UPDATE Release Date: December, 1996 Order Number: 272880-003 The 80C51GB, 83C51GB, 87C51GB may contain design defects or errors known as errata. Characterized errata
TECHNICAL PAPER Interfacing the Byte- Wide SmartVoltage FlashFile Memory Family to the Intel486 Microprocessor Family
 E TECHNICAL PAPER Interfacing the Byte- Wide SmartVoltage FlashFile Memory Family to the Intel486 Microprocessor Family October 1996 Order Number: 297805-001 Information in this document is provided in
E TECHNICAL PAPER Interfacing the Byte- Wide SmartVoltage FlashFile Memory Family to the Intel486 Microprocessor Family October 1996 Order Number: 297805-001 Information in this document is provided in
8051 Timers and Serial Port
 8051 Timers and Serial Port EE4380 Fall 2001 Class 10 Pari vallal Kannan Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas Timer: Mode 1 Operation (recap) 16 bit counter. Load the
8051 Timers and Serial Port EE4380 Fall 2001 Class 10 Pari vallal Kannan Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas Timer: Mode 1 Operation (recap) 16 bit counter. Load the
CoE3DJ4 Digital Systems Design. Chapter 5: Serial Port Operation
 CoE3DJ4 Digital Systems Design Chapter 5: Serial Port Operation Serial port 8051 includes an on-chip serial port Hardware access to the port is through TXD and RXD (Port 3 bits 1 and 0) Serial port is
CoE3DJ4 Digital Systems Design Chapter 5: Serial Port Operation Serial port 8051 includes an on-chip serial port Hardware access to the port is through TXD and RXD (Port 3 bits 1 and 0) Serial port is
80C31BH, 80C51BH, 80C51BHP, 87C51 SPECIFICATION UPDATE
 80C31BH, 80C51BH, 80C51BHP, 87C51 SPECIFICATION UPDATE Release Date: December, 1996 Order Number: 272878-003 The 80C31BH, 80C51BH, 80C51BHP, 87C51 may contain design defects or errors known as errata.
80C31BH, 80C51BH, 80C51BHP, 87C51 SPECIFICATION UPDATE Release Date: December, 1996 Order Number: 272878-003 The 80C31BH, 80C51BH, 80C51BHP, 87C51 may contain design defects or errors known as errata.
8-bit Microcontroller with 8K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash AT89S52
 Features Compatible with MCS -51 Products 8K Bytes of In-System Programmable (ISP) Flash Memory Endurance: 10,000 Write/Erase Cycles 4.0V to 5.5V Operating Range Fully Static Operation: 0 Hz to 33 MHz
Features Compatible with MCS -51 Products 8K Bytes of In-System Programmable (ISP) Flash Memory Endurance: 10,000 Write/Erase Cycles 4.0V to 5.5V Operating Range Fully Static Operation: 0 Hz to 33 MHz
Understanding the basic building blocks of a microcontroller device in general. Knows the terminologies like embedded and external memory devices,
 Understanding the basic building blocks of a microcontroller device in general. Knows the terminologies like embedded and external memory devices, CISC and RISC processors etc. Knows the architecture and
Understanding the basic building blocks of a microcontroller device in general. Knows the terminologies like embedded and external memory devices, CISC and RISC processors etc. Knows the architecture and
8051 Microcontroller
 8051 Microcontroller The 8051, Motorola and PIC families are the 3 leading sellers in the microcontroller market. The 8051 microcontroller was originally developed by Intel in the late 1970 s. Today many
8051 Microcontroller The 8051, Motorola and PIC families are the 3 leading sellers in the microcontroller market. The 8051 microcontroller was originally developed by Intel in the late 1970 s. Today many
Serial I-O for Dinesh K. Sharma Electrical Engineering Department I.I.T. Bombay Mumbai (version 14/10/07)
 Serial I-O for 8051 Dinesh K. Sharma Electrical Engineering Department I.I.T. Bombay Mumbai 400 076 (version 14/10/07) 1 Motivation Serial communications means sending data a single bit at a time. But
Serial I-O for 8051 Dinesh K. Sharma Electrical Engineering Department I.I.T. Bombay Mumbai 400 076 (version 14/10/07) 1 Motivation Serial communications means sending data a single bit at a time. But
Control Unit: The control unit provides the necessary timing and control Microprocessor resembles a CPU exactly.
 Unit I 8085 and 8086 PROCESSOR Introduction to microprocessor A microprocessor is a clock-driven semiconductor device consisting of electronic logic circuits manufactured by using either a large-scale
Unit I 8085 and 8086 PROCESSOR Introduction to microprocessor A microprocessor is a clock-driven semiconductor device consisting of electronic logic circuits manufactured by using either a large-scale
8051 Microcontroller
 8051 Microcontroller 1 Salient Features (1). 8 bit microcontroller originally developed by Intel in 1980. (2). High-performance CMOS Technology. (3). Contains Total 40 pins. (4). Address bus is of 16 bit
8051 Microcontroller 1 Salient Features (1). 8 bit microcontroller originally developed by Intel in 1980. (2). High-performance CMOS Technology. (3). Contains Total 40 pins. (4). Address bus is of 16 bit
Understanding the Interrupt Control Unit of the 80C186EC/80C188EC Processor
 A AP-731 APPLICATION NOTE Understanding the Interrupt Control Unit of the 80C186EC/80C188EC Processor Sean Kohler Application Engineer Intel Corporation 5000 West Chandler Boulevard Chandler, AZ 85226
A AP-731 APPLICATION NOTE Understanding the Interrupt Control Unit of the 80C186EC/80C188EC Processor Sean Kohler Application Engineer Intel Corporation 5000 West Chandler Boulevard Chandler, AZ 85226
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. 8051 8052 and 80C51 Hardware Description December 1992 Order Number 270252-006
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. 8051 8052 and 80C51 Hardware Description December 1992 Order Number 270252-006
EEE3410 Microcontroller Applications Department of Electrical Engineering Lecture 4 The 8051 Architecture
 Department of Electrical Engineering Lecture 4 The 8051 Architecture 1 In this Lecture Overview General physical & operational features Block diagram Pin assignments Logic symbol Hardware description Pin
Department of Electrical Engineering Lecture 4 The 8051 Architecture 1 In this Lecture Overview General physical & operational features Block diagram Pin assignments Logic symbol Hardware description Pin
CS 320. Computer Architecture Core Architecture
 CS 320 Computer Architecture 8051 Core Architecture Evan Hallam 19 April 2006 Abstract The 8051 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed originally in the 1980 s by the Intel Corporation. This inexpensive and
CS 320 Computer Architecture 8051 Core Architecture Evan Hallam 19 April 2006 Abstract The 8051 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed originally in the 1980 s by the Intel Corporation. This inexpensive and
Interfacing an I 2 C Serial EEPROM to an MCS 96 Microcontroller
 APPLICATION NOTE Interfacing an I 2 C Serial EEPROM to an MCS 96 Microcontroller ROBIN MANELIS Technical Marketing Engineer Intel Automotive Operations CHRIS BANYAI Technical Marketing Engineer Intel Automotive
APPLICATION NOTE Interfacing an I 2 C Serial EEPROM to an MCS 96 Microcontroller ROBIN MANELIS Technical Marketing Engineer Intel Automotive Operations CHRIS BANYAI Technical Marketing Engineer Intel Automotive
80C186 AND 80C188 EMBEDDED MICROPROCESSORS SPECIFICATION UPDATE
 80C186 AND 80C188 EMBEDDED MICROPROCESSORS SPECIFICATION UPDATE Release Date: July, 1996 Order Number 272894-001 The 80C186 and 80C188 Embedded Microprocessors may contain design defects or errors known
80C186 AND 80C188 EMBEDDED MICROPROCESSORS SPECIFICATION UPDATE Release Date: July, 1996 Order Number 272894-001 The 80C186 and 80C188 Embedded Microprocessors may contain design defects or errors known
80C51FA/83C51FA EVENT-CONTROL CHMOS SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER Automotive
 80C51FA/83C51FA EVENT-CONTROL CHMOS SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER Automotive Y Extended Automotive Temperature Range (b40 C to a125 C Ambient) Y High Performance CHMOS Process Y Three 16-Bit Timer/Counters
80C51FA/83C51FA EVENT-CONTROL CHMOS SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER Automotive Y Extended Automotive Temperature Range (b40 C to a125 C Ambient) Y High Performance CHMOS Process Y Three 16-Bit Timer/Counters
Introducing The MCS 251 Microcontroller -- 8XC251SB
 E AP- 708 APPLICATION NOTE Introducing The MCS 251 Microcontroller -- 8XC251SB YONG-YAP SOH TECHNICAL MARKETING EIGHT-BIT MICROCONTROLLERS February 1995 Order Number: 272670-001 Intel Corporation makes
E AP- 708 APPLICATION NOTE Introducing The MCS 251 Microcontroller -- 8XC251SB YONG-YAP SOH TECHNICAL MARKETING EIGHT-BIT MICROCONTROLLERS February 1995 Order Number: 272670-001 Intel Corporation makes
8-bit RISC Microcontroller. Application Note. AVR 305: Half Duplex Compact Software UART
 AVR 305: Half Duplex Compact Software UART Features 32 Words of Code, Only Handles Baud Rates of up to 38.4 kbps with a 1 MHz XTAL Runs on Any AVR Device Only Two Port Pins Required Does Not Use Any Timer
AVR 305: Half Duplex Compact Software UART Features 32 Words of Code, Only Handles Baud Rates of up to 38.4 kbps with a 1 MHz XTAL Runs on Any AVR Device Only Two Port Pins Required Does Not Use Any Timer
Parallel-to-Serial and Serial-to-Parallel Converters
 Session 1532 Parallel-to-Serial and Serial-to-Parallel Converters Max Rabiee, Ph.D., P.E. University of Cincinnati Abstract: Microprocessors (MPUs) on a computer motherboard communicate in a parallel format
Session 1532 Parallel-to-Serial and Serial-to-Parallel Converters Max Rabiee, Ph.D., P.E. University of Cincinnati Abstract: Microprocessors (MPUs) on a computer motherboard communicate in a parallel format
80C186XL/80C188XL EMBEDDED MICROPROCESSORS SPECIFICATION UPDATE
 80C186XL/80C188XL EMBEDDED MICROPROCESSORS SPECIFICATION UPDATE Release Date: January, 2002 Order Number: 272895.003 The 80C186XL/80C188XL embedded microprocessors may contain design defects or errors
80C186XL/80C188XL EMBEDDED MICROPROCESSORS SPECIFICATION UPDATE Release Date: January, 2002 Order Number: 272895.003 The 80C186XL/80C188XL embedded microprocessors may contain design defects or errors
8051 Serial Port. EE4380 Fall02 Class 10. Pari vallal Kannan. Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas
 8051 Serial Port EE4380 Fall02 Class 10 Pari vallal Kannan Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas Serial Comm. - Introduction Serial Vs Parallel Transfer of data Simplex,
8051 Serial Port EE4380 Fall02 Class 10 Pari vallal Kannan Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas Serial Comm. - Introduction Serial Vs Parallel Transfer of data Simplex,
AP16050 SAB C161V/K/O. Emulating an asynchronous serial interface (ASC) via software routines. Microcontrollers. Application Note, V 1.0, Feb.
 Application Note, V 1.0, Feb. 2004 SAB C161V/K/O Emulating an asynchronous serial interface (ASC) via software routines. AP16050 Microcontrollers Never stop thinking. TriCore Revision History: 2004-02
Application Note, V 1.0, Feb. 2004 SAB C161V/K/O Emulating an asynchronous serial interface (ASC) via software routines. AP16050 Microcontrollers Never stop thinking. TriCore Revision History: 2004-02
Emulating an asynchronous serial interface (ASC0) via software routines
 Microcontrollers ApNote AP165001 or æ additional file AP165001.EXE available Emulating an asynchronous serial interface (ASC0) via software routines Abstract: The solution presented in this paper and in
Microcontrollers ApNote AP165001 or æ additional file AP165001.EXE available Emulating an asynchronous serial interface (ASC0) via software routines Abstract: The solution presented in this paper and in
Emulating an asynchronous serial interface (USART) via software routines
 Microcontrollers ApNote AP083101 or æ additional file AP083101.EXE available Emulating an asynchronous serial interface (USART) via software routines Abstract: The solution presented in this paper and
Microcontrollers ApNote AP083101 or æ additional file AP083101.EXE available Emulating an asynchronous serial interface (USART) via software routines Abstract: The solution presented in this paper and
Rev. No. History Issue Date Remark
 Preliminary Bar Code Reader Document Title Bar Code Reader Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date Remark 0.0 Initial issue June 5, 2000 Preliminary 0.1 Change document title from Bar Code Reader
Preliminary Bar Code Reader Document Title Bar Code Reader Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date Remark 0.0 Initial issue June 5, 2000 Preliminary 0.1 Change document title from Bar Code Reader
b. List different system buses of 8085 microprocessor and give function of each bus. (8) Answer:
 Q.2 a. Discuss and differentiate between a Microprocessor and a Microcontroller. Microprocessor is an IC which has only the CPU inside them i.e. only the processing powers such as Intel s Pentium 1,2,3,4,
Q.2 a. Discuss and differentiate between a Microprocessor and a Microcontroller. Microprocessor is an IC which has only the CPU inside them i.e. only the processing powers such as Intel s Pentium 1,2,3,4,
8XC196KB AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATION SPECIFICATION UPDATE
 8XC196KB AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATION SPECIFICATION UPDATE Release Date: November, 1996 Order Number: 272970-001 The 8XC196KB may contain design defects or errors known as errata. Characterized errata that may
8XC196KB AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATION SPECIFICATION UPDATE Release Date: November, 1996 Order Number: 272970-001 The 8XC196KB may contain design defects or errors known as errata. Characterized errata that may
UNIT - II PERIPHERAL INTERFACING WITH 8085
 UNIT - II PERIPHERAL INTERFACING WITH 8085 Peripheral Interfacing is considered to be a main part of Microprocessor, as it is the only way to interact with the external world. The interfacing happens with
UNIT - II PERIPHERAL INTERFACING WITH 8085 Peripheral Interfacing is considered to be a main part of Microprocessor, as it is the only way to interact with the external world. The interfacing happens with
Preliminary. PACKAGE - 28-pin MLP (5mm X 5mm) Example Circuit Diagram CP V. 48MHz Oscillator. USB Function Controller 512B EEPROM
 Preliminary Single-Chip USB to UART Bridge SINGLE-CHIP USB to UART DATA TRANSFER - Integrated USB Transceiver; No External Resistors Required - Integrated Clock; No External Crystal Required - Integrated
Preliminary Single-Chip USB to UART Bridge SINGLE-CHIP USB to UART DATA TRANSFER - Integrated USB Transceiver; No External Resistors Required - Integrated Clock; No External Crystal Required - Integrated
SANKALCHAND PATEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, VISNAGAR. ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION DEPARTMENT Question Bank- 1
 SANKALCHAND PATEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, VISNAGAR ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION DEPARTMENT Question Bank- 1 Subject: Microcontroller and Interfacing (151001) Class: B.E.Sem V (EC-I & II) Q-1 Explain RISC
SANKALCHAND PATEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, VISNAGAR ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION DEPARTMENT Question Bank- 1 Subject: Microcontroller and Interfacing (151001) Class: B.E.Sem V (EC-I & II) Q-1 Explain RISC
8051 Microcontrollers
 8051 Microcontrollers Richa Upadhyay Prabhu NMIMS s MPSTME richa.upadhyay@nmims.edu March 8, 2016 Controller vs Processor Controller vs Processor Introduction to 8051 Micro-controller In 1981,Intel corporation
8051 Microcontrollers Richa Upadhyay Prabhu NMIMS s MPSTME richa.upadhyay@nmims.edu March 8, 2016 Controller vs Processor Controller vs Processor Introduction to 8051 Micro-controller In 1981,Intel corporation
MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS MATERIAL. Features of 8051:
 DEPARTMENT OF ECE MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS MATERIAL UNIT V 8051 MICROCONTROLLERS To make a complete microcomputer system, only microprocessor is not sufficient. It is necessary to add other
DEPARTMENT OF ECE MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS MATERIAL UNIT V 8051 MICROCONTROLLERS To make a complete microcomputer system, only microprocessor is not sufficient. It is necessary to add other
Intel386 TM DX MICROPROCESSOR 32-BIT CHMOS MICROPROCESSOR WITH INTEGRATED MEMORY MANAGEMENT (PQFP SUPPLEMENT)
 Intel386 TM DX MICROPROCESSOR 32-BIT CHMOS MICROPROCESSOR WITH INTEGRATED MEMORY MANAGEMENT (PQFP SUPPLEMENT) Y Flexible 32-Bit Microprocessor 8 16 32-Bit Data Types 8 General Purpose 32-Bit Registers
Intel386 TM DX MICROPROCESSOR 32-BIT CHMOS MICROPROCESSOR WITH INTEGRATED MEMORY MANAGEMENT (PQFP SUPPLEMENT) Y Flexible 32-Bit Microprocessor 8 16 32-Bit Data Types 8 General Purpose 32-Bit Registers
ISSI. IS89C51 CMOS SINGLE CHIP 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER with 4-Kbytes of FLASH ISSI IS89C51 NOVEMBER 1998 FEATURES GENERAL DESCRIPTION
 IS89C51 CMOS SINGLE CHIP 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER with 4-Kbytes of FLASH NOVEMBER 1998 FEATURES 80C51 based architecture 4-Kbytes of on-chip Reprogrammable Flash Memory 128 x 8 RAM Two 16-bit Timer/Counters
IS89C51 CMOS SINGLE CHIP 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER with 4-Kbytes of FLASH NOVEMBER 1998 FEATURES 80C51 based architecture 4-Kbytes of on-chip Reprogrammable Flash Memory 128 x 8 RAM Two 16-bit Timer/Counters
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Microcontrollers > APP 4465
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Microcontrollers > APP 4465 Keywords: MAXQ, MAXQ610, UART, USART, serial, serial port APPLICATION NOTE 4465 Using the Serial Port on the
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Microcontrollers > APP 4465 Keywords: MAXQ, MAXQ610, UART, USART, serial, serial port APPLICATION NOTE 4465 Using the Serial Port on the
SRL0 Serial Port Unit
 Summary The serial communications port peripheral devices can be configured for communications between a microprocessor and peripheral devices, or for multiprocessor communications. This document provides
Summary The serial communications port peripheral devices can be configured for communications between a microprocessor and peripheral devices, or for multiprocessor communications. This document provides
Mod-3: Interrupts,Timer operation,serial communication 1
 Mod-3: Interrupts,Timer operation,serial communication 1 Module-3 Contents: Interrupts - interrupt sources - interrupt handling programming examples. Timers operation different modes waveform generation-
Mod-3: Interrupts,Timer operation,serial communication 1 Module-3 Contents: Interrupts - interrupt sources - interrupt handling programming examples. Timers operation different modes waveform generation-
M16C R8C FoUSB/UART Debugger. User s Manual REJ10J
 REJ10J1217-0100 M16C R8C FoUSB/UART Debugger User s Manual RENESAS MICROCOMPUTER Development Environment System M16C Family R8C/Tiny Series Precautions on Connecting R8C/20, R8C/21, R8C/22, R8C/23 Rev.1.00
REJ10J1217-0100 M16C R8C FoUSB/UART Debugger User s Manual RENESAS MICROCOMPUTER Development Environment System M16C Family R8C/Tiny Series Precautions on Connecting R8C/20, R8C/21, R8C/22, R8C/23 Rev.1.00
Hardware UART for the TMS320C3x
 TMS320 DSP DESIGNER S NOTEBOOK Hardware UART for the TMS320C3x APPLICATION BRIEF: SPRA223 Contributed by Lawrence Wong Digital Signal Processing Products Semiconductor Group Texas Instruments June 1993
TMS320 DSP DESIGNER S NOTEBOOK Hardware UART for the TMS320C3x APPLICATION BRIEF: SPRA223 Contributed by Lawrence Wong Digital Signal Processing Products Semiconductor Group Texas Instruments June 1993
8XC196KC SPECIFICATION UPDATE
 8XC196KC SPECIFICATION UPDATE Release Date: May, 1997 Order Number: 272834-004 The 8XC196KC may contain design defects or errors known as errata. Characterized errata that may cause the 8XC196KC s behavior
8XC196KC SPECIFICATION UPDATE Release Date: May, 1997 Order Number: 272834-004 The 8XC196KC may contain design defects or errors known as errata. Characterized errata that may cause the 8XC196KC s behavior
Module I. Microcontroller can be classified on the basis of their bits processed like 8bit MC, 16bit MC.
 MICROCONTROLLERS AND APPLICATIONS 1 Module 1 Module I Introduction to Microcontrollers: Comparison with Microprocessors Harvard and Von Neumann Architectures - 80C51 microcontroller features - internal
MICROCONTROLLERS AND APPLICATIONS 1 Module 1 Module I Introduction to Microcontrollers: Comparison with Microprocessors Harvard and Von Neumann Architectures - 80C51 microcontroller features - internal
Serial communication
 Serial communication CSCI 255: Introduction to Embedded Systems Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 Serial communication Terminology RS-232 protocol Baud rates Flow control Example Overview Develop functions
Serial communication CSCI 255: Introduction to Embedded Systems Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 Serial communication Terminology RS-232 protocol Baud rates Flow control Example Overview Develop functions
2. List the five interrupt pins available in INTR, TRAP, RST 7.5, RST 6.5, RST 5.5.
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6502- MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS UNIT I: 8085 PROCESSOR PART A 1. What is the need for ALE signal in
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6502- MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS UNIT I: 8085 PROCESSOR PART A 1. What is the need for ALE signal in
8XC51RA RB RC Hardware Description
 8XC51RA RB RC Hardware Description February 1995 Order Number 272668-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products Intel assumes no liability whatsoever including infringement
8XC51RA RB RC Hardware Description February 1995 Order Number 272668-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products Intel assumes no liability whatsoever including infringement
M16C R8C FoUSB/UART Debugger. User Manual REJ10J
 REJ10J1725-0100 M16C R8C FoUSB/UART Debugger User Manual Renesas Microcomputer Development Environment System R8C Family R8C/2x Series Notes on Connecting R8C/2A, R8C/2B, R8C/2C, R8C/2D Rev.1.00 Issued
REJ10J1725-0100 M16C R8C FoUSB/UART Debugger User Manual Renesas Microcomputer Development Environment System R8C Family R8C/2x Series Notes on Connecting R8C/2A, R8C/2B, R8C/2C, R8C/2D Rev.1.00 Issued
PIC-I/O Multifunction I/O Controller
 J R KERR AUTOMATION ENGINEERING PIC-I/O Multifunction I/O Controller The PIC-I/O multifunction I/O controller is compatible with the PIC-SERVO and PIC-STEP motor control modules and provides the following
J R KERR AUTOMATION ENGINEERING PIC-I/O Multifunction I/O Controller The PIC-I/O multifunction I/O controller is compatible with the PIC-SERVO and PIC-STEP motor control modules and provides the following
DATA SHEET. P80CL31; P80CL51 Low voltage 8-bit microcontrollers with UART INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Apr 15
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET Low voltage 8-bit microcontrollers with Supersedes data of January 1995 File under Integrated circuits, IC20 1997 Apr 15 CONTENTS 1 FEATURES 2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 2.1 Versions:
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET Low voltage 8-bit microcontrollers with Supersedes data of January 1995 File under Integrated circuits, IC20 1997 Apr 15 CONTENTS 1 FEATURES 2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 2.1 Versions:
8051 Microcontroller memory Organization and its Applications
 8051 Microcontroller memory Organization and its Applications Memory mapping in 8051 ROM memory map in 8051 family 0000H 4k 0000H 8k 0000H 32k 0FFFH DS5000-32 8051 1FFFH 8752 7FFFH from Atmel Corporation
8051 Microcontroller memory Organization and its Applications Memory mapping in 8051 ROM memory map in 8051 family 0000H 4k 0000H 8k 0000H 32k 0FFFH DS5000-32 8051 1FFFH 8752 7FFFH from Atmel Corporation
3 Volt Intel StrataFlash Memory to Motorola MC68060 CPU Design Guide
 3 Volt Intel StrataFlash Memory to Motorola MC68060 CPU Design Guide Application Note 703 April 2000 Document Number: 292251-002 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products.
3 Volt Intel StrataFlash Memory to Motorola MC68060 CPU Design Guide Application Note 703 April 2000 Document Number: 292251-002 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products.
Module 2. Embedded Processors and Memory. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 11 Embedded Processors - II Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Signals of a Typical Microcontroller In this lesson the student will
Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 11 Embedded Processors - II Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Signals of a Typical Microcontroller In this lesson the student will
Fig 1. Block diagram of a microcomputer
 MICRO CONTROLLERS www.bookspar.com VTU NOTES QUESTION PAPERS UNIT - 1 Computer: A computer is a multipurpose programmable machine that reads binary instructions from its memory, accepts binary data as
MICRO CONTROLLERS www.bookspar.com VTU NOTES QUESTION PAPERS UNIT - 1 Computer: A computer is a multipurpose programmable machine that reads binary instructions from its memory, accepts binary data as
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: 8051 Architecture Module No: CS/ES/5 Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: 8051 Architecture Module No: CS/ES/5 Quadrant 1 e-text In this lecture the detailed architecture of 8051 controller, register bank,
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: 8051 Architecture Module No: CS/ES/5 Quadrant 1 e-text In this lecture the detailed architecture of 8051 controller, register bank,
Interfacing the HI7190 to a Microcontroller
 Interfacing the to a Microcontroller Application Note September 1995 AN9527 Authors: Stephen LaJeunesse and John Kornblum Introduction The Intersil is a 24-bit monolithic instrumentation sigma delta A/D
Interfacing the to a Microcontroller Application Note September 1995 AN9527 Authors: Stephen LaJeunesse and John Kornblum Introduction The Intersil is a 24-bit monolithic instrumentation sigma delta A/D
Northern India Engineering College, Delhi (GGSIP University) PAPER I
 PAPER I Q1.Explain IVT? ANS. interrupt vector table is a memory space for storing starting addresses of all the interrupt service routine. It stores CS:IP PAIR corresponding to each ISR. An interrupt vector
PAPER I Q1.Explain IVT? ANS. interrupt vector table is a memory space for storing starting addresses of all the interrupt service routine. It stores CS:IP PAIR corresponding to each ISR. An interrupt vector
8086 Interrupts and Interrupt Responses:
 UNIT-III PART -A INTERRUPTS AND PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLERS Contents at a glance: 8086 Interrupts and Interrupt Responses Introduction to DOS and BIOS interrupts 8259A Priority Interrupt Controller
UNIT-III PART -A INTERRUPTS AND PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLERS Contents at a glance: 8086 Interrupts and Interrupt Responses Introduction to DOS and BIOS interrupts 8259A Priority Interrupt Controller
DS1306. Serial Alarm Real Time Clock (RTC)
 www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Real time clock counts seconds, minutes, hours, date of the month, month, day of the week, and year with leap year compensation valid up to 2100 96-byte nonvolatile RAM for data
www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Real time clock counts seconds, minutes, hours, date of the month, month, day of the week, and year with leap year compensation valid up to 2100 96-byte nonvolatile RAM for data
Flexibility in Frame Size with the 8044
 AP-283 APPLICATION NOTE Flexibility in Frame Size with the 8044 PARVIZ KHODADADI APPLICATIONS ENGINEER November 1990 Order Number 292019-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with
AP-283 APPLICATION NOTE Flexibility in Frame Size with the 8044 PARVIZ KHODADADI APPLICATIONS ENGINEER November 1990 Order Number 292019-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with
Summer 2003 Lecture 21 07/15/03
 Summer 2003 Lecture 21 07/15/03 Simple I/O Devices Simple i/o hardware generally refers to simple input or output ports. These devices generally accept external logic signals as input and allow the CPU
Summer 2003 Lecture 21 07/15/03 Simple I/O Devices Simple i/o hardware generally refers to simple input or output ports. These devices generally accept external logic signals as input and allow the CPU
CPEG300 Embedded System Design. Lecture 6 Interrupt System
 CPEG300 Embedded System Design Lecture 6 Interrupt System Hamad Bin Khalifa University, Spring 2018 Correction Lecture 3, page 18: Only direct addressing mode is allowed for pushing or popping the stack:
CPEG300 Embedded System Design Lecture 6 Interrupt System Hamad Bin Khalifa University, Spring 2018 Correction Lecture 3, page 18: Only direct addressing mode is allowed for pushing or popping the stack:
Error Correction Control and Parity BIOS Implementation Example
 Error Correction Control and Parity BIOS Implementation Example White Paper Revision 1.2 THIS SPECIFICATION [DOCUMENT] IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITH NO WARRANTIES WHATSOEVER, INCLUDING ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY,
Error Correction Control and Parity BIOS Implementation Example White Paper Revision 1.2 THIS SPECIFICATION [DOCUMENT] IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITH NO WARRANTIES WHATSOEVER, INCLUDING ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY,
UNIT IV MICROCONTROLLER
 UNIT IV 8051- MICROCONTROLLER Prepared by R. Kavitha Page 1 Application Prepared by R. Kavitha Page 2 Pin Description of the 8051 UNIT IV- 8051 MICROCONTROLLER P1.0 P1.1 P1.2 P1.3 P1.4 P1.5 P1.6 P1.7 RST
UNIT IV 8051- MICROCONTROLLER Prepared by R. Kavitha Page 1 Application Prepared by R. Kavitha Page 2 Pin Description of the 8051 UNIT IV- 8051 MICROCONTROLLER P1.0 P1.1 P1.2 P1.3 P1.4 P1.5 P1.6 P1.7 RST
NAND32GW3F4A. 32-Gbit (4 x 8 Gbits), two Chip Enable, 4224-byte page, 3 V supply, multiplane architecture, SLC NAND flash memories.
 32-Gbit (4 x 8 Gbits), two Chip Enable, 4224-byte page, 3 V supply, multiplane architecture, SLC NAND flash memories Features High-density SLC NAND flash memory 32 Gbits of memory array 1 Gbit of spare
32-Gbit (4 x 8 Gbits), two Chip Enable, 4224-byte page, 3 V supply, multiplane architecture, SLC NAND flash memories Features High-density SLC NAND flash memory 32 Gbits of memory array 1 Gbit of spare
A. This Errata sheet represents the known bugs, anomalies and work-arounds for the ADuC812 MicroConverter.
 a MicroConverter, Multi-Channel 12-bit ADC with Embedded FLASH MCU ADuC812 A. This Errata sheet represents the known bugs, anomalies and work-arounds for the ADuC812 MicroConverter. B. The Errata listed,
a MicroConverter, Multi-Channel 12-bit ADC with Embedded FLASH MCU ADuC812 A. This Errata sheet represents the known bugs, anomalies and work-arounds for the ADuC812 MicroConverter. B. The Errata listed,
EE6502- MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER
 . EE6502- MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER UNIT III - 8051 MICROCONTROLLER PART - A 1. What is Microcontroller? A device which contains the microprocessor with integrated peripherals like memory, serial
. EE6502- MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER UNIT III - 8051 MICROCONTROLLER PART - A 1. What is Microcontroller? A device which contains the microprocessor with integrated peripherals like memory, serial
Lecture 10. Serial Communication
 Lecture 10 Serial Communication Serial Communication Introduction Serial communication buses Asynchronous and synchronous communication UART block diagram UART clock requirements Programming the UARTs
Lecture 10 Serial Communication Serial Communication Introduction Serial communication buses Asynchronous and synchronous communication UART block diagram UART clock requirements Programming the UARTs
3. The MC6802 MICROPROCESSOR
 3. The MC6802 MICROPROCESSOR This chapter provides hardware detail on the Motorola MC6802 microprocessor to enable the reader to use of this microprocessor. It is important to learn the operation and interfacing
3. The MC6802 MICROPROCESSOR This chapter provides hardware detail on the Motorola MC6802 microprocessor to enable the reader to use of this microprocessor. It is important to learn the operation and interfacing
StrongARM** SA-110/21285 Evaluation Board
 StrongARM** SA-110/21285 Evaluation Board Brief Datasheet Product Features Intel offers a StrongARM** SA-110/21285 Evaluation Board (EBSA-285) that provides a flexible hardware environment to help manufacturers
StrongARM** SA-110/21285 Evaluation Board Brief Datasheet Product Features Intel offers a StrongARM** SA-110/21285 Evaluation Board (EBSA-285) that provides a flexible hardware environment to help manufacturers
DS1305EN. Serial Alarm Real-Time Clock
 Serial Alarm Real-Time Clock www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Real-time clock (RTC) counts seconds, minutes, hours, date of the month, month, day of the week, and year with leap-year compensation valid up to
Serial Alarm Real-Time Clock www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Real-time clock (RTC) counts seconds, minutes, hours, date of the month, month, day of the week, and year with leap-year compensation valid up to
EXPERIMENT NO.1. A Microcontroller is a complete computer system built on a single chip.
 EXPERIMENT NO.1 AIM: Study of 8051 Microcontroller TOOLS: 8051 kit THEORY: Salient Features of 8051 A Microcontroller is a complete computer system built on a single chip. It contains all components like
EXPERIMENT NO.1 AIM: Study of 8051 Microcontroller TOOLS: 8051 kit THEORY: Salient Features of 8051 A Microcontroller is a complete computer system built on a single chip. It contains all components like
The Timers/Counters The Serial Interface The Interrupt System Reset P0.0-P0.7 P2.0-P2.7. Port 2 Drivers. Port 2 Latch
 HARDWARE DESCRIPTION This chapter provides a detailed description of the 80C51 microcontroller (see Figure 1). Included in this description are: The port drivers and how they function both as ports and,
HARDWARE DESCRIPTION This chapter provides a detailed description of the 80C51 microcontroller (see Figure 1). Included in this description are: The port drivers and how they function both as ports and,
Techniques for Lowering Power Consumption in Design Utilizing the Intel EP80579 Integrated Processor Product Line
 Techniques for Lowering Power Consumption in Design Utilizing the Intel Integrated Processor Product Line Order Number: 320180-003US Legal Lines and Disclaimers INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED
Techniques for Lowering Power Consumption in Design Utilizing the Intel Integrated Processor Product Line Order Number: 320180-003US Legal Lines and Disclaimers INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED
Module 3. Embedded Systems I/O. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 3 Embedded Systems I/O Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 15 Interrupts Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would learn Interrupts
Module 3 Embedded Systems I/O Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 15 Interrupts Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would learn Interrupts
Microcontroller and Embedded Systems:
 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: Branches: 1. Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering 2. Electrical & Electronics Engineering Semester: 6 th Semester / 7 th Semester 1. Explain the differences
Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: Branches: 1. Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering 2. Electrical & Electronics Engineering Semester: 6 th Semester / 7 th Semester 1. Explain the differences
DMX512 Receiver Datasheet DMX512Rx V 1.0. Features and Overview
 Datasheet DMX512Rx V 1.0 001-14404 Rev. *G DMX512 Receiver Copyright 2007-2014 Cypress Semiconductor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. Resources PSoC Blocks API Memory (Bytes) Digital Analog CT Analog
Datasheet DMX512Rx V 1.0 001-14404 Rev. *G DMX512 Receiver Copyright 2007-2014 Cypress Semiconductor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. Resources PSoC Blocks API Memory (Bytes) Digital Analog CT Analog
Pin Description, Status & Control Signals of 8085 Microprocessor
 Pin Description, Status & Control Signals of 8085 Microprocessor 1 Intel 8085 CPU Block Diagram 2 The 8085 Block Diagram Registers hold temporary data. Instruction register (IR) holds the currently executing
Pin Description, Status & Control Signals of 8085 Microprocessor 1 Intel 8085 CPU Block Diagram 2 The 8085 Block Diagram Registers hold temporary data. Instruction register (IR) holds the currently executing
Addressing scheme to address a specific devices on a multi device bus Enable unaddressed devices to automatically ignore all frames
 23. USART 23.1 Features Full-duplex operation Asynchronous or synchronous operation Synchronous clock rates up to 1/2 of the device clock frequency Asynchronous clock rates up to 1/8 of the device clock
23. USART 23.1 Features Full-duplex operation Asynchronous or synchronous operation Synchronous clock rates up to 1/2 of the device clock frequency Asynchronous clock rates up to 1/8 of the device clock
1. INTRODUCTION TO MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER ARCHITECTURE:
 1. INTRODUCTION TO MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER ARCHITECTURE: A microprocessor is a programmable electronics chip that has computing and decision making capabilities similar to central processing unit
1. INTRODUCTION TO MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER ARCHITECTURE: A microprocessor is a programmable electronics chip that has computing and decision making capabilities similar to central processing unit
Interrupt Programming: Interrupts vs. Polling Method:
 UNIT 4: INTERRUPT PROGRAMMING & SERIAL COMMUNICATION WITH 8051: Definition of an interrupt, types of interrupts, Timers and Counter programming with interrupts in assembly. 8051 Serial Communication: Data
UNIT 4: INTERRUPT PROGRAMMING & SERIAL COMMUNICATION WITH 8051: Definition of an interrupt, types of interrupts, Timers and Counter programming with interrupts in assembly. 8051 Serial Communication: Data
CE PSoC 4: Time-Stamped ADC Data Transfer Using DMA
 CE97091- PSoC 4: Time-Stamped ADC Data Transfer Using DMA Objective This code example uses a DMA channel with two descriptors to implement a time-stamped ADC data transfer. It uses the Watch Dog Timer
CE97091- PSoC 4: Time-Stamped ADC Data Transfer Using DMA Objective This code example uses a DMA channel with two descriptors to implement a time-stamped ADC data transfer. It uses the Watch Dog Timer
3 Volt Intel StrataFlash Memory to i960 H CPU Design Guide
 3 Volt Intel StrataFlash Memory to i960 H CPU Design Guide Application Note 705 April 2000 Document Number: 292253-002 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products. No license,
3 Volt Intel StrataFlash Memory to i960 H CPU Design Guide Application Note 705 April 2000 Document Number: 292253-002 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products. No license,
Three criteria in Choosing a Microcontroller
 The 8051 Microcontroller architecture Contents: Introduction Block Diagram and Pin Description of the 8051 Registers Some Simple Instructions Structure of Assembly language and Running an 8051 program
The 8051 Microcontroller architecture Contents: Introduction Block Diagram and Pin Description of the 8051 Registers Some Simple Instructions Structure of Assembly language and Running an 8051 program
PIO 8255 (cont..) M Krishna kumar MAM/M3/LU9e/V1/2004 1
 PIO 8255 (cont..) The parallel input-output port chip 8255 is also called as programmable peripheral input-output port. The Intel s 8255 is designed for use with Intel s 8-bit, 16-bit and higher capability
PIO 8255 (cont..) The parallel input-output port chip 8255 is also called as programmable peripheral input-output port. The Intel s 8255 is designed for use with Intel s 8-bit, 16-bit and higher capability
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Serial Port Programming in Assembly Module No: CS/ES/12 Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Serial Port Programming in Assembly Module No: CS/ES/12 Quadrant 1 e-text In this lecture, serial communication control register
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Serial Port Programming in Assembly Module No: CS/ES/12 Quadrant 1 e-text In this lecture, serial communication control register
ST78C34 GENERAL PURPOSE PARALLEL PRINTER PORT WITH 83 BYTE FIFO DESCRIPTION. PLCC Package FEATURES ORDERING INFORMATION
 GENERAL PURPOSE PARALLEL PRINTER PORT WITH 83 BYTE FIFO DESCRIPTION The ST78C34 is a monolithic Bidirectional Parallel port designed to operate as a general purpose I/O port. It contains all the necessary
GENERAL PURPOSE PARALLEL PRINTER PORT WITH 83 BYTE FIFO DESCRIPTION The ST78C34 is a monolithic Bidirectional Parallel port designed to operate as a general purpose I/O port. It contains all the necessary
8051SERIAL PORT PROGRAMMING
 8051SERIAL PORT PROGRAMMING Basics of Serial Communication Computers transfer data in two ways: Parallel Often 8 or more lines (wire conductors) are used to transfer data to a device that is only a few
8051SERIAL PORT PROGRAMMING Basics of Serial Communication Computers transfer data in two ways: Parallel Often 8 or more lines (wire conductors) are used to transfer data to a device that is only a few
ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.10 Serial Port Programming
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.10 Serial Port Programming Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Basics of Serial Communication Serial port programming
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.10 Serial Port Programming Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Basics of Serial Communication Serial port programming
