Internet Overview. Internet. Copyright tutorialspoint.
|
|
|
- Brooke Lee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Internet Overview Copyright tutorialspoint.com Internet Internet is defined as an Information super Highway, to access information over the web. However, It can be defined in many ways as follows: Internet is a world-wide global system of interconnected computer networks. Internet uses the standard Internet Protocol TCP/IPTCP/IP. Every computer in internet is identified by a unique IP address. IP Address is a unique set of numbers suchas suchas which identifies a computer location. A special computer DNS DomainNameServerDomainNameServer is used to give name to the IP Address so that user can locate a computer by a name. For example, a DNS server will resolve a name to a particular IP address to uniquely identify the computer on which this website is hosted. Internet is accessible to every user all over the world.
2 Evolution The concept of Internet was originated in 1969 and has undergone several technological & Infrastructural changes as discussed below: The origin of Internet devised from the concept of Advanced Research Project Agency Network ARPANETARPANET. ARPANET was developed by United States Department of Defense. Basic purpose of ARPANET was to provide communication among the various bodies of government. Initially, there were only four nodes, formally called Hosts. In 1972, the ARPANET spread over the globe with 23 nodes located at different countries and thus became known as Internet. By the time, with invention of new technologies such as TCP/IP protocols, DNS, WWW, browsers, scripting languages etc.,internet provided a medium to publish and access information over the web. Advantages Internet covers almost every aspect of life, one can think of. Here, we will discuss some of the advantages of Internet:
3 Internet allows us to communicate with the people sitting at remote locations. There are various apps available on the wed that uses Internet as a medium for communication. One can find various social networking sites such as: o Facebook o Twitter o Yahoo o Google+ o Flickr o Orkut One can surf for any kind of information over the internet. Information regarding various topics such as Technology, Health & Science, Social Studies, Geographical Information, Information Technology, Products etc can be surfed with help of a search engine. Apart from communication and source of information, internet also serves a medium for entertainment. Following are the various modes for entertainment over internet. o Online Television o Online Games o Songs
4 o Videos o Social Networking Apps Internet allows us to use many services like: o Internet Banking o Matrimonial Services o Online Shopping o Online Ticket Booking o Online Bill Payment o Data Sharing o Internet provides concept of electronic commerce, that allows the business deals to be conducted on electronic systems Disadvantages However, Internet has prooved to be a powerful source of information in almost every field, yet there exists many disadvanatges discussed below: There are always chances to loose personal information such as name, address, credit card number. Therefore, one should be very careful while
5 sharing such information. One should use credit cards only through authenticated sites. Another disadvantage is the Spamming.Spamming corresponds to the unwanted s in bulk. These s serve no purpose and lead to obstruction of entire system. Virus can easily be spread to the computers connected to internet. Such virus attacks may cause your system to crash or your important data may get deleted. Also a biggest threat on internet is pornography. There are many pornographic sites that can be found, letting your children to use internet which indirectly affects the children healthy mental life. There are various websites that do not provide the authenticated information. This leads to misconception among many people.
6 INTERNET CONNECTIVITY Copyright tutorialspoint.com Here in this tutorial, we will discuss how to connect to internet i.e. internet service providers, software and hardware requirements, configuring internet connection etc. Internet Service Providers ISP Internet Service Provider ISP is a company offering access to internet. They offer various services: Internet Access Domain name registration Dial-up access Leased line access ISP Types ISPs can broadly be classified into six categories as shown in the following diagram: Access providers They provide access to internet through telephone lines, cable wi-fi or fiber optics. Mailbox Provider Such providers offer mailbox hosting services. Hosting ISPs Hosting ISPs offers , and other web hosting services such as virtual machines, clouds etc. Virtual ISPs Such ISPs offer internet access via other ISP services. Free ISPs
7 Free ISPs do not charge for internet services. Connection Types There exist several ways to connect to the internet. Following are these connection types available: 1. Dial-up Connection 2. ISDN 3. DSL 4. Cable TV Internet connections 5. Satellite Internet connections 6. Wireless Internet Connections Dial-up Connection Dial-up connection uses telephone line to connect PC to the internet. It requires a modem to setup dial-up connection. This modem works as an interface between PC and the telephone line. There is also a communication program that instructs the modem to make a call to specific number provided by an ISP. Dial-up connection uses either of the following protocols: 1. Serial Line Internet Protocol SLIP 2. Point to Point Protocol PPP The following diagram shows the accessing internet using modem: ISDN ISDN is acronym of Integrated Services Digital Network. It establishes the connection using the phone lines which carry digital signals instead of analog signals. There are two techniques to deliver ISDN services: 1. Basic Rate Interface BRI 2. Primary Rate Interface PRI Key points: The BRI ISDN consists of three distinct channels on a single ISDN line: t1o 64kbps B Bearer channel and one 16kbps D DeltaorData channels.
8 The PRI ISDN consists of 23 B channels and one D channels with both have operating capacity of 64kbps individually making a total transmission rate of 1.54Mbps. The following diagram shows accessing internet using ISDN connection: DSL DSL is acronym of Digital Subscriber Line. It is a form of broadband connection as it provides connection over ordinary telephone lines. Following are the several versions of DSL technique available today: 1. Asymmetric DSL ADSL 2. Symmetric DSL SDSL 3. High bit-rate DSL HDSL 4. Rate adaptive DSL RDSL 5. Very high bit-rate DSL VDSL 6. ISDN DSL IDSL All of the above mentioned technologies differ in their upload and download speed, bit transfer rate and level of service. The following diagram shows that how we can connect to internet using DSL technology:
9 Cable TV Internet Connection Cable TV Internet connection is provided through Cable TV lines. It uses coaxial cable which is capable of transferring data at much higher speed than common telephone line. Key Points: A cable modem is used to access this service, provided by the cable operator. The Cable modem comprises of two connections: one for internet service and other for Cable TV signals. Since Cable TV internet connections share a set amount of bandwidth with a group of customers, therefore, data transfer rate also depends on number of customers using the internet at the same time. The following diagram shows that how internet is accessed using Cable TV connection: Satellite Internet Connection Satellite Internet connection offers high speed connection to the internet. There are two types of satellite internet connection: one way connection or two way connection. In one way connection, we can only download data but if we want to upload, we need a dialup access through ISP over telephone line. In two way connection, we can download and upload the data by the satellite. It does not require any dialup connection. The following diagram shows how internet is accessed using satellite internet connection:
10 Wireless Internet Connection Wireless Internet Connection makes use of radio frequency bands to connect to the internet and offers a very high speed. The wireless internet connection can be obtained by either WiFi or Bluetooth. Key Points: Wi Fi wireless technology is based on IEEE standards which allow the electronic device to connect to the internet. Bluetooth wireless technology makes use of short-wavelength radio waves and helps to create personal area network PAN. Loading [MathJax]/jax/output/HTML-CSS/fonts/TeX/fontdata.js
11 INTERNET DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM Copyright tutorialspoint.com Overview When DNS was not into existence, one had to download a Host file containing host names and their corresponding IP address. But with increase in number of hosts of internet, the size of host file also increased. This resulted in increased traffic on downloading this file. To solve this problem the DNS system was introduced. Domain Name System helps to resolve the host name to an address. It uses a hierarchical naming scheme and distributed database of IP addresses and associated names IP Address IP address is a unique logical address assigned to a machine over the network. An IP address exhibits the following properties: IP address is the unique address assigned to each host present on Internet. IP address is 32 bits 4bytes long. IP address consists of two components: network component and host component. Each of the 4 bytes is represented by a number from 0 to 255, separated with dots. For example IP address is 32-bit number while on the other hand domain names are easy to remember names. For example, when we enter an address we always enter a symbolic string such as webmaster@tutorialspoint.com. Uniform Resource Locator URL Uniform Resource Locator URL refers to a web address which uniquely identifies a document over the internet. This document can be a web page, image, audio, video or anything else present on the web. For example, is an URL to the index.html which is stored on tutorialspoint web server under internet_technology directory. URL Types There are two forms of URL as listed below: 1. Absolute URL 2. Relative URL Absolute URL Absolute URL is a complete address of a resource on the web. This completed address comprises of protocol used, server name, path name and file name. For example / internet_technology /index.htm. where:
12 http is the protocol. tutorialspoint.com is the server name. index.htm is the file name. The protocol part tells the web browser how to handle the file. Similarly we have some other protocols also that can be used to create URL are: FTP https Gopher mailto news Relative URL Relative URL is a partial address of a webpage. Unlike absolute URL, the protocol and server part are omitted from relative URL. Relative URLs are used for internal links i.e. to create links to file that are part of same website as the WebPages on which you are placing the link. For example, to link an image on tutorialspoint.com/internet_technology/internet_referemce_models, we can use the relative URL which can take the form like /internet_technologies/internet-osi_model.jpg. Difference between Absolute and Relative URL Absolute URL Used to link web pages on different websites Difficult to manage. Changes when the server name or directory name changes Take time to access Relative URL Used to link web pages within the same website. Easy to Manage Remains same even of we change the server name or directory name. Comparatively faster to access. Domain Name System Architecture The Domain name system comprises of Domain Names, Domain Name Space, Name Server that have been described below: Domain Names Domain Name is a symbolic string associated with an IP address. There are several domain names available; some of them are generic such as com, edu, gov, net etc, while some country level domain names such as au, in, za, us etc. The following table shows the Generic Top-Level Domain names:
13 Domain Name Com Edu Gov Int Mil Net Org Meaning Commercial business Education U.S. government agency International entity U.S. military Networking organization Non profit organization The following table shows the Country top-level domain names: Domain Name au in cl fr us za uk jp es de ca ee hk Meaning Australia India Chile France United States South Africa United Kingdom Japan Spain Germany Canada Estonia Hong Kong Domain Name Space The domain name space refers a hierarchy in the internet naming structure. This hierarchy has multiple levels from0to127, with a root at the top. The following diagram shows the domain name space hierarchy:
14 In the above diagram each subtree represents a domain. Each domain can be partitioned into sub domains and these can be further partitioned and so on. Name Server Name server contains the DNS database. This database comprises of various names and their corresponding IP addresses. Since it is not possible for a single server to maintain entire DNS database, therefore, the information is distributed among many DNS servers. Hierarchy of server is same as hierarchy of names. The entire name space is divided into the zones Zones Zone is collection of nodes subdomains under the main domain. The server maintains a database called zone file for every zone. If the domain is not further divided into sub domains then domain and zone refers to the same thing. The information about the nodes in the sub domain is stored in the servers at the lower levels however; the original server keeps reference to these lower levels of servers. Types of Name Servers Following are the three categories of Name Servers that manages the entire Domain Name
15 System: 1. Root Server 2. Primary Server 3. Secondary Server Root Server Root Server is the top level server which consists of the entire DNS tree. It does not contain the information about domains but delegates the authority to the other server Primary Servers Primary Server stores a file about its zone. It has authority to create, maintain, and update the zone file. Secondary Server Secondary Server transfers complete information about a zone from another server which may be primary or secondary server. The secondary server does not have authority to create or update a zone file. DNS Working DNS translates the domain name into IP address automatically. Following steps will take you through the steps included in domain resolution process: When we type into the browser, it asks the local DNS Server for its IP address. Here the local DNS is at ISP end. When the local DNS does not find the IP address of requested domain name, it forwards the request to the root DNS server and again enquires about IP address of it. The root DNS server replies with delegation that I do not know the IP address of but know the IP address of DNS Server. The local DNS server then asks the com DNS Server the same question. The com DNS Server replies the same that it does not know the IP address of but knows the address of tutorialspoint.com. Then the local DNS asks the tutorialspoint.com DNS server the same question. Then tutorialspoint.com DNS server replies with IP address of Now, the local DNS sends the IP address of to the computer that sends the request. Loading [MathJax]/jax/output/HTML-CSS/jax.js
16 INTERNET SERVICES Copyright tutorialspoint.com Internet Services allows us to access huge amount of information such as text, graphics, sound and software over the internet. Following diagram shows the four different categories of Internet Services. Communication Services There are various Communication Services available that offer exchange of information with individuals or groups. The following table gives a brief introduction to these services: S.N. Service Description 1 Electronic Mail Used to send electronic message over the internet. 2 Telnet Used to log on to a remote computer that is attached to internet. 3 Newsgroup Offers a forum for people to discuss topics of common interests. 4 Internet Relay Chat IRC Allows the people from all over the world to communicate in real time. 5 Mailing Lists Used to organize group of internet users to share common information through . 6 Internet Telephony VoIP Allows the internet users to talk across internet to any PC equipped to receive the call. 7 Instant Messaging Offers real time chat between individuals and group of people. Eg. Yahoo messenger, MSN messenger. Information Retrieval Services There exist several Information retrieval services offering easy access to information present on the internet. The following table gives a brief introduction to these services: S.N. Service Description 1 File Transfer Protocol FTP Enable the users to transfer files.
17 2 Archie It s updated database of public FTP sites and their content. It helps to search a file by its name. 3 Gopher Used to search, retrieve, and display documents on remote sites. 4 Very Easy Rodent Oriented Netwide Index to Computer Achieved VERONICA VERONICA is gopher based resource. It allows access to the information resource stored on gopher s servers. Web Services Web services allow exchange of information between applications on the web. Using web services, applications can easily interact with each other. The web services are offered using concept of Utility Computing. World Wide Web WWW WWW is also known as W3. It offers a way to access documents spread over the several servers over the internet. These documents may contain texts, graphics, audio, video, hyperlinks. The hyperlinks allow the users to navigate between the documents. Video Conferencing Video conferencing or Video teleconferencing is a method of communicating by two-way video and audio transmission with help of telecommunication technologies. Modes of Video Conferencing Point-to-Point This mode of conferencing connects two locations only. Multi-point This mode of conferencing connects more than two locations through Multi-point Control Unit MCU.
18 Loading [MathJax]/jax/output/HTML-CSS/jax.js
19 WWW OVERVIEW Copyright tutorialspoint.com Overview WWW stands for World Wide Web. A technical definition of the World Wide Web is : all the resources and users on the Internet that are using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol HTTP. A broader definition comes from the organization that Web inventor Tim Berners-Lee helped found, the World Wide Web Consortium W3C. The World Wide Web is the universe of network-accessible information, an embodiment of human knowledge. In simple terms, The World Wide Web is a way of exchanging information between computers on the Internet, tying them together into a vast collection of interactive multimedia resources. Internet and Web is not the same thing: Web uses internet to pass over the information. Evolution World Wide Web was created by Timothy Berners Lee in 1989 at CERN in Geneva. World Wide Web came into existence as a proposal by him, to allow researchers to work together effectively and efficiently at CERN. Eventually it became World Wide Web. The following diagram briefly defines evolution of World Wide Web:
20 WWW Architecture WWW architecture is divided into several layers as shown in the following diagram: Identifiers and Character Set Uniform Resource Identifier URI is used to uniquely identify resources on the web and UNICODE makes it possible to built web pages that can be read and write in human languages. Syntax XML ExtensibleMarkupLanguage helps to define common syntax in semantic web.
21 Data Interchange Resource Description Framework RDF framework helps in defining core representation of data for web. RDF represents data about resource in graph form. Taxonomies RDF Schema RDFS allows more standardized description of taxonomies and other ontological constructs. Ontologies Web Ontology Language OWL offers more constructs over RDFS. It comes in following three versions: Rules OWL Lite for taxonomies and simple constraints. OWL DL for full description logic support. OWL for more syntactic freedom of RDF RIF and SWRL offers rules beyond the constructs that are available from RDFs and OWL. Simple Protocol and RDF Query Language SPARQL is SQL like language used for querying RDF data and OWL Ontologies. Proof All semantic and rules that are executed at layers below Proof and their result will be used to prove deductions. Cryptography Cryptography means such as digital signature for verification of the origin of sources is used. User Interface and Applications On the top of layer User interface and Applications layer is built for user interaction. WWW Operation WWW works on client- server approach. Following steps explains how the web works: 1. User enters the URL (say, of the web page in the address bar of web browser. 2. Then browser requests the Domain Name Server for the IP address corresponding to 3. After receiving IP address, browser sends the request for web page to the web server using HTTP protocol which specifies the way the browser and web server communicates. 4. Then web server receives request using HTTP protocol and checks its search for the requested web page. If found it returns it back to the web browser and close the HTTP connection. 5. Now the web browser receives the web page, It interprets it and display the contents of web page in web browser s window.
22 Future There had been a rapid development in field of web. It has its impact in almost every area such as education, research, technology, commerce, marketing etc. So the future of web is almost unpredictable. Apart from huge development in field of WWW, there are also some technical issues that W3 consortium has to cope up with. User Interface Work on higher quality presentation of 3-D information is under deveopment. The W3 Consortium is also looking forward to enhance the web to full fill requirements of global communities which would include all regional languages and writing systems. Technology Work on privacy and security is under way. This would include hiding information, accounting, access control, integrity and risk management. Architecture There has been huge growth in field of web which may lead to overload the internet and degrade its performance. Hence more better protocol are required to be developed. Loading [MathJax]/jax/output/HTML-CSS/jax.js
23 WEB - BASIC CONCEPTS Copyright tutorialspoint.com What is Internet? The Internet is essentially a global network of computing resources. You can think of the Internet as a physical collection of routers and circuits as a set of shared resources. Some common definitions given in the past include A network of networks based on the TCP/IP communications protocol. A community of people who use and develop those networks. A community of people who use and develop those networks. Internet-Based Services Some of the basic services available to Internet users are A fast, easy, and inexpensive way to communicate with other Internet users around the world. Telnet Allows a user to log into a remote computer as though it were a local system. FTP Allows a user to transfer virtually every kind of file that can be stored on a computer from one Internet-connected computer to another. UseNet news A distributed bulletin board that offers a combination news and discussion service on thousands of topics. World Wide Web WWW A hypertext interface to Internet information resources. What is WWW? WWW stands for World Wide Web. A technical definition of the World Wide Web is All the resources and users on the Internet that are using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol HTTP. A broader definition comes from the organization that Web inventor Tim Berners-Lee helped found, the World Wide Web Consortium W3C: The World Wide Web is the universe of networkaccessible information, an embodiment of human knowledge. In simple terms, The World Wide Web is a way of exchanging information between computers on the Internet, tying them together into a vast collection of interactive multimedia resources. What is HTTP? HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. This is the protocol being used to transfer hypertext documents that makes the World Wide Web possible. A standard web address such as Yahoo.com is called a URL and here the prefix http indicates its protocol What is URL? URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator, and is used to specify addresses on the World Wide Web. A URL is the fundamental network identification for any resource connected to the web e. g., hypertextpages, images, andsoundfiles. A URL will have the following format protocol://hostname/other_information The protocol specifies how information is transferred from a link. The protocol used for web
24 resources is HyperText Transfer Protocol HTTP. Other protocols compatible with most web browsers include FTP, telnet, newsgroups, and Gopher. The protocol is followed by a colon, two slashes, and then the domain name. The domain name is the computer on which the resource is located. Links to particular files or subdirectories may be further specified after the domain name. The directory names are separated by single forward slashes. What is Website? Currently you are on our website Tutorialspoint.com which is a collection of various pages written in HTML markup language. This is a location on the web where people can find tutorials on latest technologies. Similarly, there are millions of websites available on the web. Each page available on the website is called a web page and first page of any website is called home page for that site. What is Web Server? Every Website sits on a computer known as a Web server. This server is always connected to the internet. Every Web server that is connected to the Internet is given a unique address made up of a series of four numbers between 0 and 256 separated by periods. For example, or When you register a Web address, also known as a domain name, such as tutorialspoint.com you have to specify the IP address of the Web server that will host the site. We will see different type of Web servers in a separate chapter. What is Web Browser? Web Browsers are software installed on your PC. To access the Web you need a web browsers, such as Netscape Navigator, Microsoft Internet Explorer or Mozilla Firefox. Currently you must be using any sort of Web browser while you are navigating through my site tutorialspoint.com. On the Web, when you navigate through pages of information this is commonly known as browsing or surfing. We will see different type of Web browsers in a separate chapter. What is SMTP Server? SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Server. This server takes care of delivering s from one server to another server. When you send an to an address, it is delivered to its recipient by a SMTP Server. What is ISP? ISP stands for Internet Service Provider. They are the companies who provide you service in terms of internet connection to connect to the internet. You will buy space on a Web Server from any Internet Service Provider. This space will be used to host your Website. What is HTML? HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language. This is the language in which we write web pages for any Website. Even the page you are reading right now is written in HTML. This is a subset of Standard Generalized Mark-Up Language SGML for electronic publishing, the specific standard used for the World Wide Web. What is Hyperlink? A hyperlink or simply a link is a selectable element in an electronic document that serves as an
25 access point to other electronic resources. Typically, you click the hyperlink to access the linked resource. Familiar hyperlinks include buttons, icons, image maps, and clickable text links. What is DNS? DNS stands for Domain Name System. When someone types in your domain name, your browser will ask the Domain Name System to find the IP that hosts your site. When you register your domain name, your IP address should be put in a DNS along with your domain name. Without doing it your domain name will not be functioning properly. What is W3C? W3C stands for World Wide Web Consortium which is an international consortium of companies involved with the Internet and the Web. The W3C was founded in 1994 by Tim Berners-Lee, the original architect of the World Wide Web. The organization's purpose is to develop open standards so that the Web evolves in a single direction rather than being splintered among competing factions. The W3C is the chief standards body for HTTP and HTML. Loading [MathJax]/jax/output/HTML-CSS/jax.js
PIC 40A. Lecture 1: The Internet. Copyright 2011 Jukka Virtanen UCLA 1 03/31/14
 PIC 40A Lecture 1: The Internet 03/31/14 Copyright 2011 Jukka Virtanen UCLA 1 What is the Internet? For this class we use the following definition: The Internet is a network of networks. Ok. What is a
PIC 40A Lecture 1: The Internet 03/31/14 Copyright 2011 Jukka Virtanen UCLA 1 What is the Internet? For this class we use the following definition: The Internet is a network of networks. Ok. What is a
Local area network (LAN) Wide area networks (WANs) Circuit. Circuit switching. Packets. Based on Chapter 2 of Gary Schneider.
 Local area network (LAN) Network of computers located close together Wide area networks (WANs) Networks of computers connected over greater distances Based on Chapter 2 of Gary Schneider. (2009). E-Business.
Local area network (LAN) Network of computers located close together Wide area networks (WANs) Networks of computers connected over greater distances Based on Chapter 2 of Gary Schneider. (2009). E-Business.
Internet. Class-In charge: S.Sasirekha
 Internet Class-In charge: S.Sasirekha COMPUTER NETWORK A computer network is a collection of two or more computers, which are connected together to share information and resources. Network Operating Systems
Internet Class-In charge: S.Sasirekha COMPUTER NETWORK A computer network is a collection of two or more computers, which are connected together to share information and resources. Network Operating Systems
Outline. Internet and World Wide Web. History of the Internet. What is the Internet? How Does Data Travel Through the Internet?
 Outline Internet and World Wide Web Internet World Wide Web Creating Web Pages CS 1410 Intro to Computer Tecnology Internet and World Wide Web 2 What is the Internet? The internet is a network of networks
Outline Internet and World Wide Web Internet World Wide Web Creating Web Pages CS 1410 Intro to Computer Tecnology Internet and World Wide Web 2 What is the Internet? The internet is a network of networks
Internet Basics. Basic Terms and Concepts. Connecting to the Internet
 Internet Basics In this Learning Unit, we are going to explore the fascinating and ever-changing world of the Internet. The Internet is the largest computer network in the world, connecting more than a
Internet Basics In this Learning Unit, we are going to explore the fascinating and ever-changing world of the Internet. The Internet is the largest computer network in the world, connecting more than a
The Internet and the World Wide Web
 Technology Briefing The Internet and the World Wide Web TB5-1 Learning Objectives TB5-2 Learning Objectives TB5-3 How Did the Internet Get Started? Internet derived from internetworking 1960s U.S. Defense
Technology Briefing The Internet and the World Wide Web TB5-1 Learning Objectives TB5-2 Learning Objectives TB5-3 How Did the Internet Get Started? Internet derived from internetworking 1960s U.S. Defense
The Internet Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) How the Internet Works Transport Control Protocol (TCP)
 The Internet, Intranets, and Extranets 1 The Internet The Internet is a collection of interconnected network of computers, all freely exchanging information. These computers use specialized software to
The Internet, Intranets, and Extranets 1 The Internet The Internet is a collection of interconnected network of computers, all freely exchanging information. These computers use specialized software to
3 The Internet and the electronic mail
 3 The Internet and the electronic mail The chapter concerns the following; ² Internet operation ² Internet services ² Searching information ² Uniform Resource Locator-URL ² IP addresses ² Domain name ²
3 The Internet and the electronic mail The chapter concerns the following; ² Internet operation ² Internet services ² Searching information ² Uniform Resource Locator-URL ² IP addresses ² Domain name ²
Component 4: Introduction to Information and Computer Science
 Component 4: Introduction to Information and Computer Science Unit 2: Internet and the World Wide Web Lecture 1 This material was developed by Oregon Health & Science University, funded by the Department
Component 4: Introduction to Information and Computer Science Unit 2: Internet and the World Wide Web Lecture 1 This material was developed by Oregon Health & Science University, funded by the Department
The Internet. and the World Wide Web
 The Internet and the World Wide Web Discussion What is the internet? What do you use the internet for? History Advanced Research Projects Agency created ARPANET in the late 1960s. 1970s more universities
The Internet and the World Wide Web Discussion What is the internet? What do you use the internet for? History Advanced Research Projects Agency created ARPANET in the late 1960s. 1970s more universities
1. Web Technology... 6
 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Web Technology... 6 1.1. Introduction (Hypertext, URL, Domain Name)...6 1.2. Web Browser and ISP...8 1.3. Upload and download files...10 1.4. Control of Internet...10 2. E-mail components
TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Web Technology... 6 1.1. Introduction (Hypertext, URL, Domain Name)...6 1.2. Web Browser and ISP...8 1.3. Upload and download files...10 1.4. Control of Internet...10 2. E-mail components
Chapter 3. The Basics of Networking
 Chapter 3 The Basics of Networking Learning Objectives Tell whether a communication technology (Internet, radio, LAN, etc.) is synchronous or asynchronous; broadcast or point-to-point Explain the roles
Chapter 3 The Basics of Networking Learning Objectives Tell whether a communication technology (Internet, radio, LAN, etc.) is synchronous or asynchronous; broadcast or point-to-point Explain the roles
Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web
 Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web Chapter 2 Objectives Explain how to access and connect to the Internet Explain how to view pages and search for information on the Web Describe the types of Web
Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web Chapter 2 Objectives Explain how to access and connect to the Internet Explain how to view pages and search for information on the Web Describe the types of Web
Introduction to Internet
 242 :: Data Entry Operations 10 Introduction to Internet 10.1 INTRODUCTION In the present age of information Technology, use of Internet is becoming quite popular for accessing information on any topic
242 :: Data Entry Operations 10 Introduction to Internet 10.1 INTRODUCTION In the present age of information Technology, use of Internet is becoming quite popular for accessing information on any topic
Chapter Ten. From Internet to Information Superhighway
 Chapter Ten From Internet to Information Superhighway After reading this chapter you should be able to: Describe the nature of the Internet and the variety of functions it performs Discuss several software
Chapter Ten From Internet to Information Superhighway After reading this chapter you should be able to: Describe the nature of the Internet and the variety of functions it performs Discuss several software
Özgür ZEYDAN (PhD.)
 Özgür ZEYDAN (PhD.) http://cevre.beun.edu.tr/zeydan/ Computer Network A group of computer systems and other computing hardware devices that are linked together through communication channels. Purpose:
Özgür ZEYDAN (PhD.) http://cevre.beun.edu.tr/zeydan/ Computer Network A group of computer systems and other computing hardware devices that are linked together through communication channels. Purpose:
Discovering Computers Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Discuss the evolution of the Internet Identify and briefly describe various broadband Internet connections and
Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Discuss the evolution of the Internet Identify and briefly describe various broadband Internet connections and
Scale Yourself. Lesson 3: Introduction to Internet Technology. Computer Technology 3/13/2015
 Computer Technology Lesson 3: Introduction to Internet Technology Learning Goal: Students will be able to understand the elements of a network. Scale Yourself 4 I do understand the elements of a network.
Computer Technology Lesson 3: Introduction to Internet Technology Learning Goal: Students will be able to understand the elements of a network. Scale Yourself 4 I do understand the elements of a network.
Fundamentals of Information Systems, Seventh Edition
 Fundamentals of Information Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Telecommunications, the Internet, Intranets, and Extranets Fundamentals of Information Systems, Seventh Edition 1 An Overview of Telecommunications
Fundamentals of Information Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Telecommunications, the Internet, Intranets, and Extranets Fundamentals of Information Systems, Seventh Edition 1 An Overview of Telecommunications
CHAPTER2. 1. The Internet was launched in 1969 and was originally called
 CHAPTER2 Multiple Choice 1. The Internet was launched in 1969 and was originally called a) AARPNET b) CERNET c) CERN d) ARPANET Answer: D Difficulty level: Hard Page: 30 Response: The Internet was originally
CHAPTER2 Multiple Choice 1. The Internet was launched in 1969 and was originally called a) AARPNET b) CERNET c) CERN d) ARPANET Answer: D Difficulty level: Hard Page: 30 Response: The Internet was originally
The Internet The Internet
 The Internet The Internet is a computer network made up of thousands of networks worldwide. No one knows exactly how many computers are connected to the Internet. It is certain, however, that these number
The Internet The Internet is a computer network made up of thousands of networks worldwide. No one knows exactly how many computers are connected to the Internet. It is certain, however, that these number
09-Jan-17. Objectives Overview. The Internet. Objectives Overview. Evolution of the Internet. Evolution of the Internet. Discovering Computers 2012
 Objectives Overview Discuss the evolution of the Identify and briefly describe various broadband connections and state differences between broadband connections and dialup connections Describe the types
Objectives Overview Discuss the evolution of the Identify and briefly describe various broadband connections and state differences between broadband connections and dialup connections Describe the types
INTRODUCTION TO THE INTERNET. Presented by the Benbrook Public Library
 INTRODUCTION TO THE INTERNET Presented by the Benbrook Public Library INTRODUCTION TO THE INTERNET What is the Internet? How did it come about? What is the World Wide Web? How does it work? How do I get
INTRODUCTION TO THE INTERNET Presented by the Benbrook Public Library INTRODUCTION TO THE INTERNET What is the Internet? How did it come about? What is the World Wide Web? How does it work? How do I get
Acknowledgment and Disclaimer:
 What is the Internet Acknowledgment and Disclaimer: This presentation is supported in part by the National Science Foundation under Grant 1240841. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations
What is the Internet Acknowledgment and Disclaimer: This presentation is supported in part by the National Science Foundation under Grant 1240841. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations
The Internet, the Web, and Electronic Commerce The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Discuss the origins of the Internet and the Web. Describe how to access the Web using providers and browsers. Discuss Internet communications, including e- mail, instant messaging, social networking, blogs,
Discuss the origins of the Internet and the Web. Describe how to access the Web using providers and browsers. Discuss Internet communications, including e- mail, instant messaging, social networking, blogs,
8 9 Before: Computers are categorized into three main categories from least to most powerful: microcomputers minicomputers mainframe computers Today:
 1 Computer, Internet, and Network Basics 2 Computer Basics A computer system includes a computer, peripheral devices, and software Computer refers to a device that accepts data as input, processes data,
1 Computer, Internet, and Network Basics 2 Computer Basics A computer system includes a computer, peripheral devices, and software Computer refers to a device that accepts data as input, processes data,
INTERNET PROGRAMMING INTRODUCTION
 INTERNET PROGRAMMING INTRODUCTION Software Engineering Branch / 4 th Class Computer Engineering Department University of Technology ORGANIZATION Lecture Mondays, 08:30-10:30 (Hall 4). Project 1. The project
INTERNET PROGRAMMING INTRODUCTION Software Engineering Branch / 4 th Class Computer Engineering Department University of Technology ORGANIZATION Lecture Mondays, 08:30-10:30 (Hall 4). Project 1. The project
Internet Basics. Basic Terms and Concepts. Connecting to the Internet
 Internet Basics In this Learning Unit, we are going to explore the fascinating and ever-changing world of the Internet. The Internet is the largest computer network in the world, connecting more than a
Internet Basics In this Learning Unit, we are going to explore the fascinating and ever-changing world of the Internet. The Internet is the largest computer network in the world, connecting more than a
2. Introduction to Internet Applications
 2. Introduction to Internet Applications 1. Representation and Transfer 2. Web Protocols 3. Some Other Application Layer Protocols 4. Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) 5. Uniform Resource Locators (URLs)
2. Introduction to Internet Applications 1. Representation and Transfer 2. Web Protocols 3. Some Other Application Layer Protocols 4. Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) 5. Uniform Resource Locators (URLs)
Chapter 3. E-commerce The Evolution of the Internet 1961 Present. The Internet: Technology Background. The Internet: Key Technology Concepts
 E-commerce 2015 business. technology. society. eleventh edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Chapter 3 E-commerce Infrastructure: The Internet, Web, and Mobile Platform Copyright 2015 Pearson
E-commerce 2015 business. technology. society. eleventh edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Chapter 3 E-commerce Infrastructure: The Internet, Web, and Mobile Platform Copyright 2015 Pearson
Full file at Chapter 2: Technology Infrastructure: The Internet and the World Wide Web
 Chapter 2: Technology Infrastructure: The Internet and the World Wide Web TRUE/FALSE 1. Computer networks and the Internet form the basic technology structure that underlies all electronic commerce. T
Chapter 2: Technology Infrastructure: The Internet and the World Wide Web TRUE/FALSE 1. Computer networks and the Internet form the basic technology structure that underlies all electronic commerce. T
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA MAHASAMUND
 क न द र य व द य लय मह सम द KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA MAHASAMUND MAHASAMUND (C.G.)493445 Session-2017. Unit-I Basic Of Information Technology What is Basic of IT- Information technology (IT) is the application
क न द र य व द य लय मह सम द KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA MAHASAMUND MAHASAMUND (C.G.)493445 Session-2017. Unit-I Basic Of Information Technology What is Basic of IT- Information technology (IT) is the application
AQU Information Systems Fundamentals Spring 2012 Pg. 9.1
 AQU Information Systems Fundamentals Spring 2012 Pg. 9.1 c h a p t e r 9 THE INTERNET & THE NEW INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY INFRASTRUCTURE 9.1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe features of infrastructure & connectivity
AQU Information Systems Fundamentals Spring 2012 Pg. 9.1 c h a p t e r 9 THE INTERNET & THE NEW INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY INFRASTRUCTURE 9.1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe features of infrastructure & connectivity
An internet or interconnected network is formed when two or more networks are connected.
 Computers I 3. The Internet An internet or interconnected network is formed when two or more networks are connected. The most notable internet is called the Internet and is composed of millions of these
Computers I 3. The Internet An internet or interconnected network is formed when two or more networks are connected. The most notable internet is called the Internet and is composed of millions of these
WHAT IS THE INTERNET?
 The Internet WHAT IS THE INTERNET? A world-wide network of computers allows people to share information electronically It is a BIG book with many web-pages on different topics. It Can be accessed anywhere
The Internet WHAT IS THE INTERNET? A world-wide network of computers allows people to share information electronically It is a BIG book with many web-pages on different topics. It Can be accessed anywhere
Chapter Topics. The History of the Internet. Chapter 7: Computer Networks, the Internet, and the World Wide Web
 Chapter Topics Chapter 7: Computer Networks, the Internet, and the World Wide Web CS10051: Intro. to Computer Science Kent State University History of the Internet History of the World Wide Web Internet
Chapter Topics Chapter 7: Computer Networks, the Internet, and the World Wide Web CS10051: Intro. to Computer Science Kent State University History of the Internet History of the World Wide Web Internet
Principles of Information Systems textbook: Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition. Dr.Amer Alzaidi Department of Information Systems
 + Principles of Information Systems textbook: Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition Dr.Amer Alzaidi Department of Information Systems Chapter 4 Telecommunications, the Internet, Intranets, and
+ Principles of Information Systems textbook: Principles of Information Systems, Sixth Edition Dr.Amer Alzaidi Department of Information Systems Chapter 4 Telecommunications, the Internet, Intranets, and
INFS 321 Information Sources
 INFS 321 Information Sources Session 12 The Internet Lecturer: Prof. Perpetua S. Dadzie, DIS Contact Information: pdadzie@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education 2014/2015
INFS 321 Information Sources Session 12 The Internet Lecturer: Prof. Perpetua S. Dadzie, DIS Contact Information: pdadzie@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education 2014/2015
The Basics of Networking
 c h a p t e r 3 The Basics of Networking Making the Connection lawrence snyder Times are Changing Nowhere Is Remote People are more interconnected Social interactions are changing Freedom of Seach and
c h a p t e r 3 The Basics of Networking Making the Connection lawrence snyder Times are Changing Nowhere Is Remote People are more interconnected Social interactions are changing Freedom of Seach and
Chapter 7. Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology
 Chapter 7 Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology LEARNING OBJECTIVES What are the principal components of telecommunications networks and key networking technologies? What are the different
Chapter 7 Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology LEARNING OBJECTIVES What are the principal components of telecommunications networks and key networking technologies? What are the different
ENG224 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part I 3. The Internet. 3. The Internet
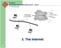 1 Reference Peter Norton, Introduction to Computers, McGraw Hill, 5 th Ed, 2003 2 What is the Internet? A global network that allows one computer to connect with other computers in the world What can be
1 Reference Peter Norton, Introduction to Computers, McGraw Hill, 5 th Ed, 2003 2 What is the Internet? A global network that allows one computer to connect with other computers in the world What can be
Chapter 2A. The Internet s History
 Chapter 2A The Internet and the World Wide Web 1 The Internet s History At about 10:30 PM on October 29th, 1969, a connection was established over a 50 kbps line provided by the AT&T telephone company,
Chapter 2A The Internet and the World Wide Web 1 The Internet s History At about 10:30 PM on October 29th, 1969, a connection was established over a 50 kbps line provided by the AT&T telephone company,
Internetwork - B. What are. Example. Domain (Top-level domains) Other countries domain names. UserName HostName Subdomain Domain
 What are UserName? HostName? Internetwork - B Subdomain? Domain? CSIT100 2 UserName, HostName, Subdomain, Domain Example My e-mail is: UserName HostName Subdomain Domain kousoulism@mail.montclair.edu =
What are UserName? HostName? Internetwork - B Subdomain? Domain? CSIT100 2 UserName, HostName, Subdomain, Domain Example My e-mail is: UserName HostName Subdomain Domain kousoulism@mail.montclair.edu =
Typical Network Uses
 Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Overview of the Internet
 Overview of the Internet IVPR 1 Outline Goals and Objectives Topics headlines Introduction Internet and WWW Client/Server Model Diagnostic commands Evolution of Internet Transmission IP Addresses and Domain
Overview of the Internet IVPR 1 Outline Goals and Objectives Topics headlines Introduction Internet and WWW Client/Server Model Diagnostic commands Evolution of Internet Transmission IP Addresses and Domain
Computers: Information Technology in Perspective, 11e
 Computers: Information Technology in Perspective, 11e Larry Long and Nancy Long Chapter 3 Going Online Copyright Prentice Hall, Inc. 1 Objectives Once you have read and studied this chapter, you will have
Computers: Information Technology in Perspective, 11e Larry Long and Nancy Long Chapter 3 Going Online Copyright Prentice Hall, Inc. 1 Objectives Once you have read and studied this chapter, you will have
The Internet and How It Works 12 11/21/2016. Define what a computer network is, and how networks are conceptually structured.
 Chapter 12 The Internet and How It Works Learning Objectives This lesson introduces students to Internet basics. At the end of the lesson, the students will be able to: Discuss the origins of the Internet.
Chapter 12 The Internet and How It Works Learning Objectives This lesson introduces students to Internet basics. At the end of the lesson, the students will be able to: Discuss the origins of the Internet.
E-Business Tenth Edition. Chapter 2 E-Business Technology Basics
 E-Business Tenth Edition Chapter 2 E-Business Technology Basics Learning Objectives In this chapter, you will learn: About the origin, growth, and current structure of the Internet How packet-switched
E-Business Tenth Edition Chapter 2 E-Business Technology Basics Learning Objectives In this chapter, you will learn: About the origin, growth, and current structure of the Internet How packet-switched
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY 402
 NAME : CLASS/ SEC : ROLL: SESSION : QUOTE : PART 1: Working With Accessibility Options 1. Accessibility options: These are the options in Windows Operating System which makes handling of computer easy
NAME : CLASS/ SEC : ROLL: SESSION : QUOTE : PART 1: Working With Accessibility Options 1. Accessibility options: These are the options in Windows Operating System which makes handling of computer easy
Computer Networks. Computer Networks. Telecommunication Links. CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing - Spring Chapter 12: Computer Networks 1
 Computer Networks Chapter 12 Topics: Communication links LAN / WAN Internet / WWW CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson 1 Computer Networks A computer network is a set of independent computer
Computer Networks Chapter 12 Topics: Communication links LAN / WAN Internet / WWW CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson 1 Computer Networks A computer network is a set of independent computer
Introduction to Internet, Web, and TCP/IP Protocols SEEM
 Introduction to Internet, Web, and TCP/IP Protocols SEEM 3460 1 Local-Area Networks A Local-Area Network (LAN) covers a small distance and a small number of computers LAN A LAN often connects the machines
Introduction to Internet, Web, and TCP/IP Protocols SEEM 3460 1 Local-Area Networks A Local-Area Network (LAN) covers a small distance and a small number of computers LAN A LAN often connects the machines
Class X Subject : IT (Vocational) Chapter -1 Ouestion / Answer
 Class X Subject : IT (Vocational) Chapter -1 Ouestion / Answer Q1 What is a computer network? A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of computers and other hardware
Class X Subject : IT (Vocational) Chapter -1 Ouestion / Answer Q1 What is a computer network? A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of computers and other hardware
The Internet, the Web, and Electronic Commerce The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Discuss the origins of the Internet and the Web. Describe how to access the Web using providers and browsers. Discuss Internet communications, including e- mail, instant messaging, social networking, blogs,
Discuss the origins of the Internet and the Web. Describe how to access the Web using providers and browsers. Discuss Internet communications, including e- mail, instant messaging, social networking, blogs,
Basic Internet. Basic Internet
 Basic Internet Basic Internet What is the Internet? The Internet is a global network connecting millions of computers which are linked together around the world, cooperating and communication with each
Basic Internet Basic Internet What is the Internet? The Internet is a global network connecting millions of computers which are linked together around the world, cooperating and communication with each
Discovering Computers Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web
 Discovering Computers 2008 Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web Just remember It took 38 years for radio to reach 50 million users 13 years for television to reach 50 million users Less than 4 years
Discovering Computers 2008 Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web Just remember It took 38 years for radio to reach 50 million users 13 years for television to reach 50 million users Less than 4 years
Chapter 1: Into the Internet
 1. A global network of computers and mobile devices connected together to share information and other resources is the. a. web b. email network c. Internet d. IRC network REFERENCES: 2 2. A is a computer
1. A global network of computers and mobile devices connected together to share information and other resources is the. a. web b. email network c. Internet d. IRC network REFERENCES: 2 2. A is a computer
DOWNLOAD FULL TEST BANK FOR DISCOVERING THE INTERNET BRIEF 5TH EDITION BY CAMPBELL
 DOWNLOAD FULL TEST BANK FOR DISCOVERING THE INTERNET BRIEF 5TH EDITION BY CAMPBELL Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-for-discovering-the-internetbrief-5th-edition-by-campbell/
DOWNLOAD FULL TEST BANK FOR DISCOVERING THE INTERNET BRIEF 5TH EDITION BY CAMPBELL Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-for-discovering-the-internetbrief-5th-edition-by-campbell/
From administrivia to what really matters
 From administrivia to what really matters Questions about the syllabus? Logistics Daily lectures, quizzes and labs Two exams and one long project My teaching philosophy...... is informed by my passion
From administrivia to what really matters Questions about the syllabus? Logistics Daily lectures, quizzes and labs Two exams and one long project My teaching philosophy...... is informed by my passion
Chapter 002 The Internet, the Web, and Electronic Commerce
 Chapter 002 The Internet, the Web, and Electronic Commerce Multiple Choice Questions 1. Launched in 1969 as a U.S. funded project that developed a national computer network, the Internet was initially
Chapter 002 The Internet, the Web, and Electronic Commerce Multiple Choice Questions 1. Launched in 1969 as a U.S. funded project that developed a national computer network, the Internet was initially
Chapter 2: Technology Infrastructure: The Internet and the World Wide Web
 Chapter 2: Technology Infrastructure: The Internet and the World Wide Web Student: 1. Networks of computers and the Internet that connects them to each other form the basic technological structure that
Chapter 2: Technology Infrastructure: The Internet and the World Wide Web Student: 1. Networks of computers and the Internet that connects them to each other form the basic technological structure that
The Internet. Connecting to the internet. Role of the ISP. Who is online? Internet users by country 2/18/2009. The Internet More than Just WWW
 The Internet What does it mean to be connected to the internet? I.e. What does the internet do?? What do you need to connect your computer to the internet as opposed to any other network? The Internet
The Internet What does it mean to be connected to the internet? I.e. What does the internet do?? What do you need to connect your computer to the internet as opposed to any other network? The Internet
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 BMS2062 Introduction to Bioinformatics Use of information technology and telecommunications in bioinformatics Topic 1: Practical uses of Internet services Ros Gibson IT Staff Lecturer: Ros Gibson gibson@acslink.aone.net.au
BMS2062 Introduction to Bioinformatics Use of information technology and telecommunications in bioinformatics Topic 1: Practical uses of Internet services Ros Gibson IT Staff Lecturer: Ros Gibson gibson@acslink.aone.net.au
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 BMS2062 Introduction to Bioinformatics Use of information technology and telecommunications in bioinformatics Topic 1: Practical uses of Internet services Ros Gibson IT Staff Lecturer: Ros Gibson gibson@acslink.aone.net.au
BMS2062 Introduction to Bioinformatics Use of information technology and telecommunications in bioinformatics Topic 1: Practical uses of Internet services Ros Gibson IT Staff Lecturer: Ros Gibson gibson@acslink.aone.net.au
Web Programming Paper Solution (Chapter wise)
 Introduction to web technology Three tier/ n-tier architecture of web multitier architecture (often referred to as n-tier architecture) is a client server architecture in which presentation, application
Introduction to web technology Three tier/ n-tier architecture of web multitier architecture (often referred to as n-tier architecture) is a client server architecture in which presentation, application
ACE Chapter 4 review. Name: Class: Date: True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 Name: Class: Date: ACE Chapter 4 review True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Today s Internet joins together networks of over 300 million computers, or Internet hosts, to create
Name: Class: Date: ACE Chapter 4 review True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Today s Internet joins together networks of over 300 million computers, or Internet hosts, to create
Internet The full name of Internet is the International Network. Internet is the world largest computer network. It is the network of network. Interne
 Internet Basics By Bhupendra Ratha, Lecturer School of Library and Information Science Devi Ahilya University, Indore Email: bhu261@gmail.com Internet The full name of Internet is the International Network.
Internet Basics By Bhupendra Ratha, Lecturer School of Library and Information Science Devi Ahilya University, Indore Email: bhu261@gmail.com Internet The full name of Internet is the International Network.
Chapter 3 The Basics of Networking
 Fluency with Information Technology 7 th Edition Chapter 3 The Basics of Networking HTML Hypertext Markup Language Layout of document (Margin, font, text, image, ) Jump from point to point (non-linear)
Fluency with Information Technology 7 th Edition Chapter 3 The Basics of Networking HTML Hypertext Markup Language Layout of document (Margin, font, text, image, ) Jump from point to point (non-linear)
Using the Internet and the World Wide Web
 Using the Internet and the World Wide Web Computer Literacy BASICS: A Comprehensive Guide to IC 3, 3 rd Edition 1 Objectives Understand the difference between the Internet and the World Wide Web. Identify
Using the Internet and the World Wide Web Computer Literacy BASICS: A Comprehensive Guide to IC 3, 3 rd Edition 1 Objectives Understand the difference between the Internet and the World Wide Web. Identify
Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet
 Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet Don Mason Associate Director Copyright 2011 National Center for Justice and the Rule of Law All Rights Reserved Inside vs. Outside Inside the Box What the computer
Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet Don Mason Associate Director Copyright 2011 National Center for Justice and the Rule of Law All Rights Reserved Inside vs. Outside Inside the Box What the computer
Introduction to Networking
 Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
CSC Introduction to Computers and Their Applications. Background
 CSC 170 - Introduction to Computers and Their Applications Lecture 7 The Internet Background The history of the Internet begins in 1957. In a response to the Soviet Union launching Sputnik, the first man-made
CSC 170 - Introduction to Computers and Their Applications Lecture 7 The Internet Background The history of the Internet begins in 1957. In a response to the Soviet Union launching Sputnik, the first man-made
CPET 499/ITC 250 Web Systems. Topics
 CPET 499/ITC 250 Web Systems Week 1 Web System Infrastructure, Protocols, and Applications Paul I-Hai Lin, Professor Dept. of Computer, Electrical, and Information Technology College of Engineering, Technology,
CPET 499/ITC 250 Web Systems Week 1 Web System Infrastructure, Protocols, and Applications Paul I-Hai Lin, Professor Dept. of Computer, Electrical, and Information Technology College of Engineering, Technology,
Web Information System. Truong Thi Dieu Linh, PhD Nguyen Hong Phuong, Msc.
 Web Information System Truong Thi Dieu Linh, PhD Nguyen Hong Phuong, Msc. Objectives Provide students with theory and concept about web information system from the past to future: Basic concepts of Internet,
Web Information System Truong Thi Dieu Linh, PhD Nguyen Hong Phuong, Msc. Objectives Provide students with theory and concept about web information system from the past to future: Basic concepts of Internet,
How does the Internet Work? The Basics: Getting a Web Page. The Basics: Getting a Web Page. Client-Server model. The Internet: Basics
 How does the Internet Work? When you type a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) into a Web Browser and press Return, what do you think happens? That is, what steps do you think are required to obtain a web
How does the Internet Work? When you type a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) into a Web Browser and press Return, what do you think happens? That is, what steps do you think are required to obtain a web
Inside vs. Outside. Inside the Box What the computer owner actually has possession of 1/18/2011
 Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet Don Mason Associate Director Copyright 2011 National Center for Justice and the Rule of Law All Rights Reserved Inside vs. Outside Inside the Box What the computer
Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet Don Mason Associate Director Copyright 2011 National Center for Justice and the Rule of Law All Rights Reserved Inside vs. Outside Inside the Box What the computer
Objectives. Introduction to HTML. Objectives. Objectives
 Objectives Introduction to HTML Developing a Basic Web Page Review the history of the Web, the Internet, and HTML. Describe different HTML standards and specifications. Learn about the basic syntax of
Objectives Introduction to HTML Developing a Basic Web Page Review the history of the Web, the Internet, and HTML. Describe different HTML standards and specifications. Learn about the basic syntax of
INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY (ICT) LECTURE 1 : WEEK 1 CSC-111-T
 INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY (ICT) LECTURE 1 : WEEK 1 CSC-111-T Credit : (2 + 1) / Week 2 TEXT AND REF. BOOKS Text Book: Peter Norton (2011), Introduction to Computers, 7 /e,
INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY (ICT) LECTURE 1 : WEEK 1 CSC-111-T Credit : (2 + 1) / Week 2 TEXT AND REF. BOOKS Text Book: Peter Norton (2011), Introduction to Computers, 7 /e,
Full file at
 ch02 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Computer networks and the Internet form the basic technology structure that underlies all electronic commerce. 2. The USENET was the
ch02 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Computer networks and the Internet form the basic technology structure that underlies all electronic commerce. 2. The USENET was the
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 10 Networking Essentials
 A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
ECS 15; Lectures 17 and 18. The Internet. What is the internet, and how does it work? TA feedback
 ECS 15; Lectures 17 and 18 The Internet What is the internet, and how does it work? TA feedback Python -- Run your code!! Term paper: Start a paragraph with the point of the paragraph, not in modern times
ECS 15; Lectures 17 and 18 The Internet What is the internet, and how does it work? TA feedback Python -- Run your code!! Term paper: Start a paragraph with the point of the paragraph, not in modern times
= a hypertext system which is accessible via internet
 10. The World Wide Web (WWW) = a hypertext system which is accessible via internet (WWW is only one sort of using the internet others are e-mail, ftp, telnet, internet telephone... ) Hypertext: Pages of
10. The World Wide Web (WWW) = a hypertext system which is accessible via internet (WWW is only one sort of using the internet others are e-mail, ftp, telnet, internet telephone... ) Hypertext: Pages of
E-commerce Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver. business. technology. society. tenth edition
 E-commerce 2014 business. technology. society. tenth edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 3 E-commerce Infrastructure:
E-commerce 2014 business. technology. society. tenth edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 3 E-commerce Infrastructure:
CONTENTS. Internet Basics. Internet Explorer. Search Engines. . Advantages and Disadvantages of the Internet. Some good websites
 USING THE INTERNET CONTENTS Internet Basics Internet Explorer Search Engines E-Mail Advantages and Disadvantages of the Internet Some good websites 2 WHAT IS INTERNET? A computer network Two or more connected
USING THE INTERNET CONTENTS Internet Basics Internet Explorer Search Engines E-Mail Advantages and Disadvantages of the Internet Some good websites 2 WHAT IS INTERNET? A computer network Two or more connected
Web Design and Development ACS-1809
 Web Design and Development ACS-1809 Chapter 1 9/11/2018 1 Pre-class Housekeeping Course Outline Text book : HTML A beginner s guide, Wendy Willard, 5 th edition Work on HTML files On Windows PCs Tons of
Web Design and Development ACS-1809 Chapter 1 9/11/2018 1 Pre-class Housekeeping Course Outline Text book : HTML A beginner s guide, Wendy Willard, 5 th edition Work on HTML files On Windows PCs Tons of
E-commerce Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver. business. technology. society. tenth edition
 E-commerce 2014 business. technology. society. tenth edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall e Commerce Course : Chapter 3 E-commerce
E-commerce 2014 business. technology. society. tenth edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall e Commerce Course : Chapter 3 E-commerce
Computers Are Your Future
 Computers Are Your Future Computers Are Your Future The Internet and World Wide Web 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Slide 2 What You Will Learn... What You Will Learn... How the Internet works Methods for accessing
Computers Are Your Future Computers Are Your Future The Internet and World Wide Web 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Slide 2 What You Will Learn... What You Will Learn... How the Internet works Methods for accessing
Introduction to the Internet. Part 1. What is the Internet?
 Introduction to the Internet Part 1 What is the Internet? A means of connecting a computer to any other computer anywhere in the world via dedicated routers and servers. When two computers are connected
Introduction to the Internet Part 1 What is the Internet? A means of connecting a computer to any other computer anywhere in the world via dedicated routers and servers. When two computers are connected
Web Information System Design. Tatsuya Hagino
 Web Information System Design Tatsuya Hagino (hagino@sfc.keio.ac.jp) 1 Course Summary Understanding the current Web architecture Web components Web as document space Structure of Web documents Web principles
Web Information System Design Tatsuya Hagino (hagino@sfc.keio.ac.jp) 1 Course Summary Understanding the current Web architecture Web components Web as document space Structure of Web documents Web principles
Chapter 02 Technology Infrastructure The Internet and the World Wide Web
 Chapter 02 Technology Infrastructure The Internet and the World Wide Web TRUEFALSE 1. Networks of computers and the Internet that connects them to each other form the basic technological structure that
Chapter 02 Technology Infrastructure The Internet and the World Wide Web TRUEFALSE 1. Networks of computers and the Internet that connects them to each other form the basic technological structure that
Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web
 Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web Chapter 2 Objectives Discuss the history of the Internet Describe the types of Web sites Explain how to access and connect to the Internet Recognize how Web pages
Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web Chapter 2 Objectives Discuss the history of the Internet Describe the types of Web sites Explain how to access and connect to the Internet Recognize how Web pages
The Internet and World Wide Web. Chapter4
 The Internet and World Wide Web Chapter4 ITBIS105 IS-IT-UOB 2016 The Internet What is the Internet? Worldwide collection of millions of computers networks that connects ITBIS105 IS-IT-UOB 2016 2 History
The Internet and World Wide Web Chapter4 ITBIS105 IS-IT-UOB 2016 The Internet What is the Internet? Worldwide collection of millions of computers networks that connects ITBIS105 IS-IT-UOB 2016 2 History
Computer science. Assignment of. Durdana Saleem. Roll No: Submitted to. Dr. Afifa Khanam. Dated
 Assignment of Computer science Name: Class: Durdana Saleem B.Ed (hons.) Roll No: 1649 Topic: internet Submitted to Dr. Afifa Khanam Dated 9-7-2013 Lahore College For Women University, Lahore Table of Contents:
Assignment of Computer science Name: Class: Durdana Saleem B.Ed (hons.) Roll No: 1649 Topic: internet Submitted to Dr. Afifa Khanam Dated 9-7-2013 Lahore College For Women University, Lahore Table of Contents:
Computer networks 2013
 Chapter 4 EXERCISE 1 1 Describe what is meant by each of the following: a Router b Bridge c Proxy server Answers: see the Glossary. 2 Many small businesses have computer networks. a List three advantages
Chapter 4 EXERCISE 1 1 Describe what is meant by each of the following: a Router b Bridge c Proxy server Answers: see the Glossary. 2 Many small businesses have computer networks. a List three advantages
Introduction to the Internet and Web
 Introduction to the Internet and Web Internet It is the largest network in the world that connects hundreds of thousands of individual networks all over the world. The popular term for the Internet is
Introduction to the Internet and Web Internet It is the largest network in the world that connects hundreds of thousands of individual networks all over the world. The popular term for the Internet is
An introduction to the Internet. Joining a connected world
 An introduction to the Internet Joining a connected world Agenda 1.! What do you already know about using the Internet? 2.! What is this thing called the World Wide Web? 3.! How the Internet works 4.!
An introduction to the Internet Joining a connected world Agenda 1.! What do you already know about using the Internet? 2.! What is this thing called the World Wide Web? 3.! How the Internet works 4.!
Impact. Course Content. Objectives of Lecture 2 Internet and WWW. CMPUT 499: Internet and WWW Dr. Osmar R. Zaïane. University of Alberta 4
 Web Technologies and Applications Winter 2001 CMPUT 499: Internet and WWW Dr. Osmar R. Zaïane University of Alberta Impact Babyboomer after the WWII, generation X late 60s. I have the incline to call the
Web Technologies and Applications Winter 2001 CMPUT 499: Internet and WWW Dr. Osmar R. Zaïane University of Alberta Impact Babyboomer after the WWII, generation X late 60s. I have the incline to call the
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Internet. Solutions
 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Internet Solutions Summative Assessment Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) 1. A search engine can be defined as a software program that provides the required information in
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Internet Solutions Summative Assessment Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) 1. A search engine can be defined as a software program that provides the required information in
Session 2. Background. Lecture Objectives
 Session 2 Background 1 Lecture Objectives Understand how an Internet resource is accessed Understand the high level structure of the Internet cloud Understand the high level structure of the TCP/IP protocols
Session 2 Background 1 Lecture Objectives Understand how an Internet resource is accessed Understand the high level structure of the Internet cloud Understand the high level structure of the TCP/IP protocols
WWW and Web Browser. 6.1 Objectives In this chapter we will learn about:
 WWW and Web Browser 6.0 Introduction WWW stands for World Wide Web. WWW is a collection of interlinked hypertext pages on the Internet. Hypertext is text that references some other information that can
WWW and Web Browser 6.0 Introduction WWW stands for World Wide Web. WWW is a collection of interlinked hypertext pages on the Internet. Hypertext is text that references some other information that can
An electronic transmission of information that has been encoded digitally for storage and processing by computers.
 An electronic transmission of information that has been encoded digitally for storage and processing by computers. Transmission of electronic data over some media. The media used to transmit may be guided
An electronic transmission of information that has been encoded digitally for storage and processing by computers. Transmission of electronic data over some media. The media used to transmit may be guided
