|
|
|
- Jerome Davis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 اصول ميکروکامپيوترها استاد درس: دکتر ا درس و Website برای تکاليف و... : ١ هجدهم فصل ا شنايی با تايمرهای 8051 و کاربرد ا ن ها ٢ ١
2 رجيسترهای مخصوص تايمرهای داخلی 8051/2 (Timer special function registers) TIMER-SFR PURPOSE ADDRESS BIT-ADDRESSABLE TCON Control 88H Yes TMOD Mode 89H No TL0 Timer0 low-byte 8AH No TL1 Timer1 low-by1e 8BH No TH0 Timer0 high-by1e 8CH No TH1 Timer1 high-byte 8DH No T2CON* Timer2 control C8H Yes RCAP2L* Timer2 low-byte capture CAH No RCAP2H* Timer2 high-byte capture CBH No TL2* Timer2 low-byte CCH No TH2* Timer 2 high-by1e CDH No ٣ رجيستر کنترل کننده تايمرها( Register (TCON TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0 TF1: Timer 1 overflow flag. TR1: Timer 1 run control bit.(tr1=1 Timer1 runs) TF0: Timer 0 overflow flag. TR0: Timer 0 run control bit..(tr0=1 Timer0 runs) IE1: External interrupt 1 edge flag. (IE-Flags are used by CPU) IT1: External interrupt 1 type flag.(it1=1 Edge-triggered) IE0: External interrupt 0 edge flag. IT0: External interrupt 0 type flag. ٤ ٢
3 TF1 TCON.7 Timer1 overflow flag. Set by hardware when timer/counter1 overflows. Cleared by hardware as the processor vectors to the interrupt service routine. TR1 TCON.6 Timer1 run control bit. Set/cleared by software to turn timer/counter1 on/off. TF0 TCON.5 Timer 0 overflow flag. Set by hardware when timer/counter0 overflows. Cleared by hardware as the processor vectors to the service routine. TR0 TCON.4 Timer 0 run control bit. Set/cleared by software to turn timer/counter0 on/off. ٥ le1 TCON.3 External interrupt1 edge flag. Set by CPU when the external interrupt edge (H-to-L transition) detected. Cleared by CPU when the interrupt is processed. Note: This flag does not latch low-level triggered interrupts. IT1 TCON.2 Interrupt1 type control bit, Set/cleared by software to specify falling edge/low-level triggered external interrupt. IE0 TCON.1 External interrupt0 edge flag. Set by CPU when external interrupt (H-to-L transition) edge detected. Cleared by CPU when interrupt is processed. Note: This flag does not latch low-level triggered interrupts. IT0 TCON.0 Interrupt0 type control bit. Set/cleared by software to specify falling edge/low-level triggered external interrupt. IT0 TCON.0 Interrupt 0 type control bit, ٦ ٣
4 رجيستر تعيين کننده مود تايمرها Register) (TMOD Gate C/T M1 M0 Gate C/T M1 M0 Timer1 Timer0 Gate : When set, timer only runs while INT0 (or 1) is high. ٧ C/T : Counter/Timer select bit. M1 : Mode bit 1. M0 : Mode bit 0. M1 M Mode 13 bit Timer Mode 16 bit Timer Mode 8 bit auto-reload Mode Split Mode Timer : ٨ ٤
5 Mode های مختلف تايمرها XTAL Oscillator f/12 C/ T= 0 TR=1 TLX THX (8bits) (8bits) TF is set when FFFF 0000 TFX Overflow Flag Mode1 XTAL Oscillator f/12 C/ T= 0 TR=1 TLX THX (5bits) (8bits) TF is set when FFFF 0000 TFX Overflow Flag Mode0 Mode2 ٩ XTAL Oscillator f/12 C/ T= 0 TR=1 TLX (8bits) THX (8bits) Reload TFX Overflow Flag Mode 3 Timer1: Timer Clock TL1 (8bits) TH1 (8bits) Timer0: Timer Clock TL0 (8bits) TF0 Overflow Flag ١٠ 12 f Osci TL0 (8bits) TF1 Overflow Flag ٥
6 عملکرد تايمر ۱ در Mode1 ١١ Example 9-12 Assuming XTAL = MHz, write a program to generate a square wave of 50 Hz frequency on pin P2.3. Look at the following steps. (a) T = 1 /50 Hz = 20 ms, the period of the square wave. (b) 1/2 of it for the high and low portion of the pulse = 10 ms (c ) 10ms / μs = 9216 and = in decimal, and in hex it is DC00H. (d) TL = 00 and TH = DC (hex) ١٢ ٦
7 The program: MOV TMOD,#10H ;timer 1, mode 1 (16-bit) AGAIN: MOV TL1,#00 ;TL1=00,low byte of timer MOV TH1,#0DCH ;TH1=DC, Hi byte SETB TR1 ;start the timer 1 BACK: JNB TF1,BACK ;stay until timer rolls over CLR TR1 ;stop timer 1 CPL P2.3 ;comp. p2.3 to get hi, 10 CLR TF1 ;clear timer flag 1 SJMP AGAIN ;reload timer since mode 1 ١٣ ;is not auto-reload Example Examine the following program and find the time delay in seconds. Exclude the over-head due to the instructions in the loop. MOV TMOD,#10H ;Timer1,mode 1 (16-bit) MOV R3,#200 ;counter for multiple delay AGAIN: MOV TLl,.#O8 ;TLl=08,low byte of timer MOV THl,#01 ;THl=01,Hi byte SETB TR1 ;start the timer 1 BACK: JNB TF1,BACK ;stay until timer rolls over CLR TR1 ;stop timer 1 CLR TF1 ;clear timer flag 1 DJNZ R3,AGAIN ;if R3 not zero then reload timer TH -TL = 0108H = 264 in decimal and = Now x us = ms, and for 200 of them we have 200 x ms = sec ١٤ ٧
8 Example 9-14 Assuming that XTAL = MHz, find (a) the frequency of the square wave generated on pin P 1.0 in the following program, and (b) the smallest frequency achievable in this program, and the TH value to do that. (a) MOV TMOD,#20H ;T1/mode 2/8-bit/auto reload MOV TH1,#5 ;TH1=5 SETB TR1 ;start the timer 1 BACK: JNB TF1,BACK ;stay till timer rolls over CPL P1.0 ;comp. P1.0 to get hi., lo CLR TF1 ;clear timer flag 1 SJMP BACK ;mode 2 is auto-reload ١٥ (a) First notice the target address of SJMP. In mode 2 we do not need to reload TH since it is auto-reload. Now (256-05) x us = 251 x µs = µs is the high portion of the pulse. Since it is a 50% duty cycle square wave, the period T is twice that; as a result T = 2 x µs = µs and the frequency = khz. (b) To get the smallest frequency, we need the largest T and that is achieved when TH = 00. In that case, we have T = 2 x 256 x µs = us and the frequency = 1.8 khz. ١٦ ٨
9 Example 9-15 Find the frequency of a square wave generated on pin P1.0. if the clock freq. is MHz. MOV TMOD,#2H ;Timer 0,mode 2 (8-bit,auto reload) MOV TH0,#0 ;TH0=0 AGAIN: MOV R5,#250 ;count for multiple delay ACALL DELAY CPL P1.0 SJMP AGAIN DELAY: SETB TR0 ;start the timer 0 BACK: JNB TF0,BACK ;stay until timer rolls over CLR TR0 ;stop timer 0 CLR TF0 ;clear TF for next round DJNZ R5,DELAY RET T = 2 (250 x 256 x I-1s) = ms, and frequency = 72 Hz. ١٧ Example 9-16 Assuming that we are programming the timers for mode 2, find the value (in hex) loaded into TH for each of the following cases. (a) MOV TH1, # -200 (b) MOV THO, # -60 (c) MOV TH1, # -3 (d) MOV TH1, # -12 (e) MOV THO, # -48 You can use the Windows scientific calculator to verify the results provided by the assembler. In Windows calculator, select decimal and enter 200. Then select hex, then +/- to get the TH value. Remember that we only use the right two digits and ignore the rest since our data is an 8-bit data. The following is what we get. Decimal 2's complement (TH value) H -60 C4H -3 FDH -12 F4H ١٨-48 D0H ٩
10 Example 9-18 Assuming that clock pulses are fed into pin T1, write a program for counter1 in mode 2 to count the pulses and display the state of the TL1 count on P2. MOV TMOD,# B ;counter 1,mode 2,C/T=1 ;external. pulses MOV TH1,#0 ;clear TH1 SETB P3.5 ;make T1 input AGAIN: SETB TR1 ;start the counter BACK: MOV A,TL1 ;get copy of count TL1 MOV P2,A ;display it on port 2 JNB IF1,Back ;keep doing it if TF=0 CLR TR1 ;stop the counter 1 CLR TF1 ;make TF=0 SJMP AGAIN ;keep doing it ١٩ Notice in the above program the role of the instruction SETB P3.5 Since ports are set up for output when the 8051 is powered up, we make P3.5 an input port by making it high. In other words, we must configure (set high) the T1 pin (pin P3.5) to allow pulses to be fed into it. P2 is connected to 8 LEDs and input T0 to pulse. ٢٠ ١٠
11 Example 9-18 Assuming that clock pulses are fed into pin T1, write a program for counter1 in mode 2 to count the pulses and display the state of the TL1 count on P2. ٢١ MOV TMOD,# B ;counter 1,mode 2,C/T=1 ;external. pulses MOV TH1,#0 ;clear TH1 SETB P3.5 ;make T1 input AGAIN: SETB TR1 ;start the counter BACK: MOV A,TL1 ;get copy of count TL1 MOV P2,A ; display it on port 2 JNB TF1,Back ;keep doing it if TF1=0 CLR TR1 ;stop the counter 1 CLR TF1 ;make TF1=0 SJMP AGAIN ;keep doing it ٢٢ ١١
12 Notice in the above program the role of the instruction SETB P3.5 Since ports are set up for output when the 8051 is powered up, we make P3.5 an input port by making it high. In other words, we must configure (set high) the T1 pin (pin P3.5) to allow pulses to be fed into it. P2 is connected to 8 LEDs and input T0 to pulse. ٢٣ Interrupt : ٢٤ ١٢
13 Interrupt Enable (IE) Register EA - ET2 ES ET1 EX1 ET0 EX0 EA : Global enable/disable. --- : Undefined. ET2 :Enable Timer 2 interrupt. ES :Enable Serial port interrupt. ET1 :Enable Timer 1 interrupt. EX1 :Enable External 1 interrupt. ET0 : Enable Timer 0 interrupt. EX0 : Enable External 0 interrupt. ٢٥ Interrupt Vector Table for the 8051 Interrupt Reset Ext. Int. (INT0) Timer 0 (TF0) Ext. Int. (INT1) Timer 1 (TF1) Serial COM (RI and TI) Location (Hex) B B 0023 pin 9 P3.2 (12) P3.3 (13) ٢٦ ١٣
14 Example 11-2 Write a program that continuously gets 8-bit data from P0 and sends it to P1 while simultaneously creating a square wave of 200 μs period on pin P2.1. Use timer 0 to create the square wave. Assume that XTAL = MHz. We will use timer 0 in mode 2 (auto reload). TH0 = 100/1.085 μ S =92. Upon wake-up the processor should go to MAIN to avoid using memory space allocated to Interrupt Vector Table. ٢٧ ORG 0000H LJMP MAIN ;by-pass interrupt vector table ;--ISR for Timer 0 to generate square wave ORG 000BH ; Timer 0 interrupt vector table CPL P2.1 ;toggle P2.1 pin RETI ;return from ISR ;--The main program for initialization ORG 0030H ;after vector table space MAIN: MOV TMOD,#02H ;Timer 0,mode 2(auto reload) MOV P0,#0FFH ;make P0 as input port MOV TH0,#-92 ;TH0=A4H for -92 MOV IE,#82H ;IE= B enable Timer 0 SETB TR0 ;Start Timer 0 BACK: MOV A,P0 ;get data from P0 MOV P1,A ;issue it to P1 SJMP BACK ;keep doing it ٢٨ ;loop unless interrupted by TF0 END ١٤
15 Example 11-3 Rewrite Example 11-2 to create a square wave that has a high portion of 1085μs and a low portion of 15 μs. Assume XTAL = MHz. Use Timer 1. Since μ S is 1000 x we need to use mode 1 of timer 1. Upon wake up go to main, avoid using memory space allocated to Interrupt Vector Table ٢٩ ORG 0000H LJMP MAIN ;by-pass interrupt vector table ;--ISR for Timer 1 to generate square wave ORG 001BH ;timer 1. interrupt vector table LJMP ISR_T1 ;jump to ISR ;--The main program for initialization ORG 0030H ;after vector table MAIN: MOV TMOD,#10H ;timer 1, mode 1 MOV P0,#0FFH ;make P0 an input port MOV TL1,#018H ;TL1=18 the low byte of MOV TH1,#OFCH ;TH1=FC the high byte of MOV IE,#88H ;IE= enable timer 1 int. SETB TR1 ;start timer 1 BACK: MOV A,P0 ;get data from P0 MOV P1,A ;issue it to P1 ٣٠ SJMP BACK ;keep doing it ١٥
16 ;-Timer 1 ISR. Must be reloaded since not auto-reload ISR_T1: CLR TRI ;stop Timer 1 CLR P2.1 ;P2.1=0, start of low portion MOV R2,#4 ; 2 MC HERE: DJNZ R2,HERE ; 4x2 machine cycle(mc)8 MC MOV TL1,#18H ;load T1 low byte value 2 MC MOV TH1,#OFCH ;load T1 high byte value 2 MC SETB TR1 ;starts timer 1 1 MC SETB P2.1 ;P2.1=1, back to high 1 MC RETI ;return to main END ٣١ Example 11-4 Write a program to generate a square wave of 50 Hz frequency on pin P1.2. This is similar to Example 9-12 except that it uses an interrupt for timer 0. Assume that XTAL = MHz. ٣٢ ١٦
17 ORG 0 LJMP MAIN ORG 00BH ;ISR for Timer 0 CPL Pl.2 MOV TL0,#00 MOV TH0,#0DCH RETI ORG 30H ; main program for initialization MAIN: MOV TMOD,#01 ;Timer 0, Mode 1 MOV TL0,#00 MOV TH0,0DCH MOV IE,#82H ;enable Timer 0 interrupt SETB TR0 HERE: SJMP HERE ٣٣ END Programming external Interrupt ٣٤ ١٧
18 Example 11-5 Assume that the INT1 pin is connected to a switch that is normally high. Whenever it goes low, it should turn on an LED. The LED is connected to P1.3 and is normally off. When it is turned on it should stay on for a fraction of a second. As long as the switch is pressed low, the LED should stay on. ٣٥ ORG 0000H LJMP MAIN ;by-pass interrupt vector table ;--ISR for hardware interrupt INT1 to turn on the LED ORG 0013H ;INT1 ISR SETB P1.3 ;turn on LED MOV R3,#255 BACK: DJNZ R3,BACK ;keep LED on for a while CLR P1.3 ;turn off the LED RETI ;return from ISR ;-- MAIN program for initialization ORG 30H MAIN: MOV IE,# B ;enable external INT 1 HERE: SJMP HERE ; stay here until get interrupt~" END Pressing the switch will cause the LED to be turned on. If it is kept ٣٦ activated, the LED stays on. ١٨
19 Example 11-6 Assuming that pin 3.3 (INT1) is connected to a pulse generator, write a program in which the tailing edge of the pulse will send a high to P1.3, which is connected to an LED (or buzzer). In other words, the LED is turned on and off at the same rate as the pulses are applied to the INT1 pin. This is an edge-triggered version of Example ٣٧ ORG 0000H LJMP MAIN ;--ISR for hardware interrupt INT1 to turn on the LED ORG 0013H ;INT1 ISR SETB P1.3 ;turn on the LED MOV R3 #255 BACK: DJNZ R3,HERE ;keep the buzzer on for a whlle CLR P1.3 ;turn off the buzzer RETI ;return from Buzzer ;--MAIN Program for initialization ORG 30H MAIN: SETB TCON.2 ;make INT1 edge-trigger interrupt MOV IE,# B ;enable External INT1 HERE: SJMP HERE ;stay here until get interrupted END ٣٨ ١٩
20 پايان ٣٩ ٢٠
INTERRUPTS PROGRAMMING
 INTERRUPTS PROGRAMMING The 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: Using Assembly and C Mazidi, Mazidi and McKinlay Chung-Ping Young 楊中平 Home Automation, Networking, and Entertainment Lab Dept. of Computer
INTERRUPTS PROGRAMMING The 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: Using Assembly and C Mazidi, Mazidi and McKinlay Chung-Ping Young 楊中平 Home Automation, Networking, and Entertainment Lab Dept. of Computer
CPEG300 Embedded System Design. Lecture 8 Timer
 CPEG300 Embedded System Design Lecture 8 Timer Hamad Bin Khalifa University, Spring 2018 Review 8051 port and port schematic Internal read/write data path Serial communication vs. parallel communication
CPEG300 Embedded System Design Lecture 8 Timer Hamad Bin Khalifa University, Spring 2018 Review 8051 port and port schematic Internal read/write data path Serial communication vs. parallel communication
The 8051 microcontroller has two 16-bit timers/counters called T0 and T1.
 Counters and Timers: The 8051 microcontroller has two 16-bit timers/counters called T0 and T1. As their names suggest, timer counts internal clock pulse i.e. machine cycle to provide delay. Counter counts
Counters and Timers: The 8051 microcontroller has two 16-bit timers/counters called T0 and T1. As their names suggest, timer counts internal clock pulse i.e. machine cycle to provide delay. Counter counts
Interrupts. EE4380 Fall 2001 Class 9. Pari vallal Kannan. Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas
 8051 - Interrupts EE4380 Fall 2001 Class 9 Pari vallal Kannan Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas Polling Vs Interrupts Polling: MCU monitors all served devices continuously,
8051 - Interrupts EE4380 Fall 2001 Class 9 Pari vallal Kannan Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas Polling Vs Interrupts Polling: MCU monitors all served devices continuously,
Mod-3: Interrupts,Timer operation,serial communication 1
 Mod-3: Interrupts,Timer operation,serial communication 1 Module-3 Contents: Interrupts - interrupt sources - interrupt handling programming examples. Timers operation different modes waveform generation-
Mod-3: Interrupts,Timer operation,serial communication 1 Module-3 Contents: Interrupts - interrupt sources - interrupt handling programming examples. Timers operation different modes waveform generation-
8051 Timers. Class 7 EE4380 Fall Pari vallal Kannan. Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas
 8051 Timers Class 7 EE4380 Fall 2002 Pari vallal Kannan Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas Introduction Timers Timing devices - Generate specific time delay Event
8051 Timers Class 7 EE4380 Fall 2002 Pari vallal Kannan Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas Introduction Timers Timing devices - Generate specific time delay Event
Chapter 6 Interrupts. (I. Scott Mackenzie) By: Masud-ul-Hasan
 Chapter 6 Interrupts (I. Scott Mackenzie) 1 Interrupts An interrupt is the occurrence of an event that causes a temporary suspension of a program while the condition is serviced by another program. It
Chapter 6 Interrupts (I. Scott Mackenzie) 1 Interrupts An interrupt is the occurrence of an event that causes a temporary suspension of a program while the condition is serviced by another program. It
Timers and interrupts
 Timers and interrupts CSCI 255: Introduction to Embedded Systems Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 Timers Overview Creating fixed pauses Calculate length of events Counts events Generate baud rate for serial
Timers and interrupts CSCI 255: Introduction to Embedded Systems Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 Timers Overview Creating fixed pauses Calculate length of events Counts events Generate baud rate for serial
ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.9 Timer Programming
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.9 Timer Programming Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Programming 8051 Timers Counter programming Timer programming
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.9 Timer Programming Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Programming 8051 Timers Counter programming Timer programming
Interrupt Programming: Interrupts vs. Polling Method:
 UNIT 4: INTERRUPT PROGRAMMING & SERIAL COMMUNICATION WITH 8051: Definition of an interrupt, types of interrupts, Timers and Counter programming with interrupts in assembly. 8051 Serial Communication: Data
UNIT 4: INTERRUPT PROGRAMMING & SERIAL COMMUNICATION WITH 8051: Definition of an interrupt, types of interrupts, Timers and Counter programming with interrupts in assembly. 8051 Serial Communication: Data
Department of EIE / Pondicherry Engineering College. Timer/Counters. Department of EIE / Pondicherry Engineering College 1
 Timer/Counters Department of EIE / Pondicherry Engineering College 1 The 8051 has two internal sixteen bit hardware Timer/Counters. Each Timer/Counter can be configured in various modes, typically based
Timer/Counters Department of EIE / Pondicherry Engineering College 1 The 8051 has two internal sixteen bit hardware Timer/Counters. Each Timer/Counter can be configured in various modes, typically based
Chapter 09. Programming in Assembly
 Chapter 09 Programming in Assembly Lesson 05 Programming Examples for Timers Programming TMOD Register 3 Write instructions to run T0 in Mode 0, external count inputs, internal start/stop control ANL TMOD,
Chapter 09 Programming in Assembly Lesson 05 Programming Examples for Timers Programming TMOD Register 3 Write instructions to run T0 in Mode 0, external count inputs, internal start/stop control ANL TMOD,
CoE3DJ4 Digital Systems Design. Chapter 6: Interrupts
 CoE3DJ4 Digital Systems Design Chapter 6: Interrupts Interrupts An interrupt is the occurrence of an event that causes a temporary suspension of a program while the condition is serviced by another program.
CoE3DJ4 Digital Systems Design Chapter 6: Interrupts Interrupts An interrupt is the occurrence of an event that causes a temporary suspension of a program while the condition is serviced by another program.
Microcontroller and Embedded Systems:
 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: Branches: 1. Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering 2. Electrical & Electronics Engineering Semester: 6 th Semester / 7 th Semester 1. Explain the differences
Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: Branches: 1. Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering 2. Electrical & Electronics Engineering Semester: 6 th Semester / 7 th Semester 1. Explain the differences
CHAPTER TIMER PROGRAMMING
 CHAPTER 9 8051 TIMER PROGRAMMING 8051 Timers The 8051 has two timers/counters, they can be used as Timers to generate a time delay Event counters to count events happening outside the microcontroller Both
CHAPTER 9 8051 TIMER PROGRAMMING 8051 Timers The 8051 has two timers/counters, they can be used as Timers to generate a time delay Event counters to count events happening outside the microcontroller Both
 اصول ميکروکامپيوترها استاد درس: دکتر http://ee.iust.ac.ir/rahmati/index.htm rahmati@iust.ac.ir ا درس Email و Website برای تکاليف و... : http://eel.iust.ac.ir/rahmati/ ١ نوزدهم فصل ا شنايی با دستورالعمل
اصول ميکروکامپيوترها استاد درس: دکتر http://ee.iust.ac.ir/rahmati/index.htm rahmati@iust.ac.ir ا درس Email و Website برای تکاليف و... : http://eel.iust.ac.ir/rahmati/ ١ نوزدهم فصل ا شنايی با دستورالعمل
2. Write an 8051 program to generate a square wave of 25 khz at pin P2.3 using XTAL = 12 MHz. Solution:
 Assignment 2 1. Assume that 5 binary data items are stored in RAM locations starting at 50h, as shown below. Write a program to find the sum of all the numbers. The calculation is in 16-bit format and
Assignment 2 1. Assume that 5 binary data items are stored in RAM locations starting at 50h, as shown below. Write a program to find the sum of all the numbers. The calculation is in 16-bit format and
Lecture 9. Timer Operations and Programming
 Lecture 9 Timer Operations and Programming Timer Operations and Programming Introduction Summary of timers Timer programming sequence Summary of timer SFRs Timer 0-1: 8-bit auto-reload mode (mode 2) Programming
Lecture 9 Timer Operations and Programming Timer Operations and Programming Introduction Summary of timers Timer programming sequence Summary of timer SFRs Timer 0-1: 8-bit auto-reload mode (mode 2) Programming
CHAPTER 11 INTERRUPTS PROGRAMMING
 CHAPTER 11 INTERRUPTS PROGRAMMING Interrupts vs. Polling An interrupt is an external or internal event that interrupts the microcontroller To inform it that a device needs its service A single microcontroller
CHAPTER 11 INTERRUPTS PROGRAMMING Interrupts vs. Polling An interrupt is an external or internal event that interrupts the microcontroller To inform it that a device needs its service A single microcontroller
e-pg Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Interrupt Programming in Embedded C Module No: CS/ES/20 Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Interrupt Programming in Embedded C Module No: CS/ES/20 Quadrant 1 e-text In this lecture embedded C program for interrupt handling
e-pg Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Interrupt Programming in Embedded C Module No: CS/ES/20 Quadrant 1 e-text In this lecture embedded C program for interrupt handling
EE6502- MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER
 . EE6502- MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER UNIT III - 8051 MICROCONTROLLER PART - A 1. What is Microcontroller? A device which contains the microprocessor with integrated peripherals like memory, serial
. EE6502- MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER UNIT III - 8051 MICROCONTROLLER PART - A 1. What is Microcontroller? A device which contains the microprocessor with integrated peripherals like memory, serial
8051 Peripherals. On-Chip Memory Timers Serial Port Interrupts. Computer Engineering Timers
 8051 Peripherals On-Chip Memory Timers Serial Port Interrupts Computer Engineering 2 2-1 8051 Timers 8051 Timers The 8051 has 2 internal 16-bit timers named Timer 0 and Timer 1 Each timer is a 16-bit counter
8051 Peripherals On-Chip Memory Timers Serial Port Interrupts Computer Engineering 2 2-1 8051 Timers 8051 Timers The 8051 has 2 internal 16-bit timers named Timer 0 and Timer 1 Each timer is a 16-bit counter
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET MICROCONTROLLER AND MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEMS ECE2216 TRIMESTER 1 (2017/2018) MP2: Construction and programming of a basic electronic piano *Note: On-the-spot evaluation may
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET MICROCONTROLLER AND MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEMS ECE2216 TRIMESTER 1 (2017/2018) MP2: Construction and programming of a basic electronic piano *Note: On-the-spot evaluation may
8051 Interrupt Organization
 Interrupt Interrupts of 8051 Introduction 8051 Interrupt organization Processing Interrupts Program Design Using Interrupts Timer Interrupts Serial Port Interrupts External Interrupts Interrupt Timings
Interrupt Interrupts of 8051 Introduction 8051 Interrupt organization Processing Interrupts Program Design Using Interrupts Timer Interrupts Serial Port Interrupts External Interrupts Interrupt Timings
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Interrupt Handling Module No: CS/ES/13 Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Interrupt Handling Module No: CS/ES/13 Quadrant 1 e-text 1. Interrupt An interrupt is the occurrence of a condition--an event --
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Interrupt Handling Module No: CS/ES/13 Quadrant 1 e-text 1. Interrupt An interrupt is the occurrence of a condition--an event --
CPEG300 Embedded System Design. Lecture 6 Interrupt System
 CPEG300 Embedded System Design Lecture 6 Interrupt System Hamad Bin Khalifa University, Spring 2018 Correction Lecture 3, page 18: Only direct addressing mode is allowed for pushing or popping the stack:
CPEG300 Embedded System Design Lecture 6 Interrupt System Hamad Bin Khalifa University, Spring 2018 Correction Lecture 3, page 18: Only direct addressing mode is allowed for pushing or popping the stack:
UNIT 2 THE 8051 INSTRUCTION SET AND PROGRAMMING
 UNIT 2 THE 8051 INSTRUCTION SET AND PROGRAMMING Instructions Alphabetical List of Instructions ACALL: Absolute Call ADD, ADDC: Add Accumulator (With Carry) AJMP: Absolute Jump ANL: Bitwise AND CJNE: Compare
UNIT 2 THE 8051 INSTRUCTION SET AND PROGRAMMING Instructions Alphabetical List of Instructions ACALL: Absolute Call ADD, ADDC: Add Accumulator (With Carry) AJMP: Absolute Jump ANL: Bitwise AND CJNE: Compare
8051 Timers and Serial Port
 8051 Timers and Serial Port EE4380 Fall 2001 Class 10 Pari vallal Kannan Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas Timer: Mode 1 Operation (recap) 16 bit counter. Load the
8051 Timers and Serial Port EE4380 Fall 2001 Class 10 Pari vallal Kannan Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas Timer: Mode 1 Operation (recap) 16 bit counter. Load the
8051 I/O and 8051 Interrupts
 8051 I/O and 8051 Interrupts Class 7 EE4380 Fall 2002 Pari vallal Kannan Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas Agenda 8051 I/O Interfacing Scanned LED displays LCD displays
8051 I/O and 8051 Interrupts Class 7 EE4380 Fall 2002 Pari vallal Kannan Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems University of Texas at Dallas Agenda 8051 I/O Interfacing Scanned LED displays LCD displays
Introduction To MCS-51
 Introduction To MCS-51 By Charoen Vongchumyen Department of Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineering KMITLadkrabang 8051 Hardware Basic Content Overview Architechture Memory map Register Interrupt Timer/Counter
Introduction To MCS-51 By Charoen Vongchumyen Department of Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineering KMITLadkrabang 8051 Hardware Basic Content Overview Architechture Memory map Register Interrupt Timer/Counter
UNIT THE 8051 INSTRUCTION SET AND PROGRAMMING
 UNIT THE 8051 INSTRUCTION SET AND PROGRAMMING Instructions Alphabetical List of Instructions ACALL: Absolute Call ADD, ADDC: Add Accumulator (With Carry) AJMP: Absolute Jump ANL: Bitwise AND CJNE: Compare
UNIT THE 8051 INSTRUCTION SET AND PROGRAMMING Instructions Alphabetical List of Instructions ACALL: Absolute Call ADD, ADDC: Add Accumulator (With Carry) AJMP: Absolute Jump ANL: Bitwise AND CJNE: Compare
Chapter 3. Bit Addressable Area. By DeccanRobots
 Chapter 3 Bit Addressable Area By DeccanRobots What is Bit Addressable Area? FFh 2Fh 20h 00h Data Memory General purpose Memory Area Bit Addressable Memory Registers Memory Area from 20H to 2FH is Bit
Chapter 3 Bit Addressable Area By DeccanRobots What is Bit Addressable Area? FFh 2Fh 20h 00h Data Memory General purpose Memory Area Bit Addressable Memory Registers Memory Area from 20H to 2FH is Bit
MCS-51 Serial Port A T 8 9 C 5 2 1
 MCS-51 Serial Port AT89C52 1 Introduction to Serial Communications Serial vs. Parallel transfer of data Simplex, Duplex and half-duplex modes Synchronous, Asynchronous UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter.
MCS-51 Serial Port AT89C52 1 Introduction to Serial Communications Serial vs. Parallel transfer of data Simplex, Duplex and half-duplex modes Synchronous, Asynchronous UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter.
MODEL ANSWER SUBJECT- MICROCONTROLLER(12187) CLASS-EJ5E CLASS TEST-02 Q1.)Attempt any THREE of the following.
 MODEL ANSWER SUBJECT- MICROCONTROLLER(12187) CLASS-EJ5E CLASS TEST-02 Q1.)Attempt any THREE of the following. (9M) 1) Describe the instructions SWAP A and MOVX@DPTR,A with one example. (3Marks) SWAP A
MODEL ANSWER SUBJECT- MICROCONTROLLER(12187) CLASS-EJ5E CLASS TEST-02 Q1.)Attempt any THREE of the following. (9M) 1) Describe the instructions SWAP A and MOVX@DPTR,A with one example. (3Marks) SWAP A
Embedded Controller Programming
 Embedded Controller Programming Counters, Timers and I/O in Assembly Language Ken Arnold Copyright 2000-2004 Ken Arnold 1 Outline Timer/Counters Serial Port More 8051 Instructions Examples Copyright 2000-2004
Embedded Controller Programming Counters, Timers and I/O in Assembly Language Ken Arnold Copyright 2000-2004 Ken Arnold 1 Outline Timer/Counters Serial Port More 8051 Instructions Examples Copyright 2000-2004
8051 Microcontroller memory Organization and its Applications
 8051 Microcontroller memory Organization and its Applications Memory mapping in 8051 ROM memory map in 8051 family 0000H 4k 0000H 8k 0000H 32k 0FFFH DS5000-32 8051 1FFFH 8752 7FFFH from Atmel Corporation
8051 Microcontroller memory Organization and its Applications Memory mapping in 8051 ROM memory map in 8051 family 0000H 4k 0000H 8k 0000H 32k 0FFFH DS5000-32 8051 1FFFH 8752 7FFFH from Atmel Corporation
Timer Counter and Interrupt. Equation (16 bits counter, Mode 1, 16MHz):
 Equation (16 bits counter, Mode 1, 16MHz): THxTLx = 65536 - (Tt * 16.777216 e6) where: Tt: Target time x: Timer/Counter (0, 1 and 2) THx: Timer high byte TLx: Timer low byte Used Interrupts: 1 (Address,
Equation (16 bits counter, Mode 1, 16MHz): THxTLx = 65536 - (Tt * 16.777216 e6) where: Tt: Target time x: Timer/Counter (0, 1 and 2) THx: Timer high byte TLx: Timer low byte Used Interrupts: 1 (Address,
VRS540-4kB Flash, 128B RAM, 25~40MHz, 8-Bit MCU
 VRS540-4kB Flash, 28B RAM, 25~40MHz, 8-Bit MCU 34 Ste Catherine Street West, Suite 900, Montreal, Quebec, Canada H3B H4 Tel: (54) 87-2447 http://www.goalsemi.com P.3 P.2 XTAL NC P0./AD VRS540 Overview
VRS540-4kB Flash, 28B RAM, 25~40MHz, 8-Bit MCU 34 Ste Catherine Street West, Suite 900, Montreal, Quebec, Canada H3B H4 Tel: (54) 87-2447 http://www.goalsemi.com P.3 P.2 XTAL NC P0./AD VRS540 Overview
VRS550-8kB Flash, 256B RAM, 25~40MHz, 8-Bit MCU VRS560-16kB Flash, 256B RAM, 40MHz, 8-Bit MCU
 VRS550-8kB Flash, 256B RAM, 25~40MHz, 8-Bit MCU VRS560-6kB Flash, 256B RAM, 40MHz, 8-Bit MCU 34 Ste Catherine Street West, Suite 900, Montreal, Quebec, Canada H3B H4 Tel: (54) 87-2447 http://www.goalsemi.com
VRS550-8kB Flash, 256B RAM, 25~40MHz, 8-Bit MCU VRS560-6kB Flash, 256B RAM, 40MHz, 8-Bit MCU 34 Ste Catherine Street West, Suite 900, Montreal, Quebec, Canada H3B H4 Tel: (54) 87-2447 http://www.goalsemi.com
C51 Family. C51 Family Programmer s Guide and Instruction Set. Summary
 C51 Family Programmer s Guide and Instruction Set Summary 1. Memory Organization.................................................... I.3.2 1.1. Program Memory.......................................................................
C51 Family Programmer s Guide and Instruction Set Summary 1. Memory Organization.................................................... I.3.2 1.1. Program Memory.......................................................................
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. 8051 8052 and 80C51 Hardware Description December 1992 Order Number 270252-006
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. 8051 8052 and 80C51 Hardware Description December 1992 Order Number 270252-006
8051 Core Specification
 8051 Core Specification Authors: Jaka Simsic Simon Teran jakas@opencores.org simont@opencores.org Rev. 0.1 August 14, 2001 First Draft www.opencores.org Rev 0.1 First Draft 1 of 26 Revision History Rev.
8051 Core Specification Authors: Jaka Simsic Simon Teran jakas@opencores.org simont@opencores.org Rev. 0.1 August 14, 2001 First Draft www.opencores.org Rev 0.1 First Draft 1 of 26 Revision History Rev.
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION
 Subject Code: 17534 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Subject Code: 17534 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
The Timers/Counters The Serial Interface The Interrupt System Reset P0.0-P0.7 P2.0-P2.7. Port 2 Drivers. Port 2 Latch
 HARDWARE DESCRIPTION This chapter provides a detailed description of the 80C51 microcontroller (see Figure 1). Included in this description are: The port drivers and how they function both as ports and,
HARDWARE DESCRIPTION This chapter provides a detailed description of the 80C51 microcontroller (see Figure 1). Included in this description are: The port drivers and how they function both as ports and,
VRS570 32K Flash, 1kB RAM, 25~40MHz, 8-Bit MCU VRS580 64K Flash, 1kB RAM, 25~40MHz, 8-Bit MCU
 VRS570 32K Flash, 1kB RAM, 25~40MHz, 8-Bit MCU VRS580 64K Flash, 1kB RAM, 25~40MHz, 8-Bit MCU 1134 Ste Catherine Street West, Suite 900, Montreal, Quebec, Canada H3B 1H4 Tel: (514) 871-2447 http://www.goalsemi.com
VRS570 32K Flash, 1kB RAM, 25~40MHz, 8-Bit MCU VRS580 64K Flash, 1kB RAM, 25~40MHz, 8-Bit MCU 1134 Ste Catherine Street West, Suite 900, Montreal, Quebec, Canada H3B 1H4 Tel: (514) 871-2447 http://www.goalsemi.com
Chapter 09. Programming in Assembly
 Chapter 09 Programming in Assembly Lesson 03 Programming Approach for Main and Interrupt Service Routines in 8051 Program Approach for programming Main Program Instructions 3 Main program initial instructions
Chapter 09 Programming in Assembly Lesson 03 Programming Approach for Main and Interrupt Service Routines in 8051 Program Approach for programming Main Program Instructions 3 Main program initial instructions
MCS -51 Programmer s Guide and Instruction Set
 MCS -51 Programmer s Guide and Instruction Set November 1992 Order Number 270249-003 COPYRIGHT INTEL CORPORATION 1996 MCS -51 PROGRAMMER S GUIDE AND INSTRUCTION SET CONTENTS PAGE MEMORY ORGANIZATION 1
MCS -51 Programmer s Guide and Instruction Set November 1992 Order Number 270249-003 COPYRIGHT INTEL CORPORATION 1996 MCS -51 PROGRAMMER S GUIDE AND INSTRUCTION SET CONTENTS PAGE MEMORY ORGANIZATION 1
8-bit Microcontroller with 2/4-Kbyte Flash AT89LP2052 AT89LP4052
 Features Compatible with MCS 51 Products 20 MIPS Throughput at 20 MHz Clock Frequency and 2.4V, 85 C Operating Conditions Single Clock Cycle per Byte Fetch 2/4K Bytes of In-System Programmable (ISP) Flash
Features Compatible with MCS 51 Products 20 MIPS Throughput at 20 MHz Clock Frequency and 2.4V, 85 C Operating Conditions Single Clock Cycle per Byte Fetch 2/4K Bytes of In-System Programmable (ISP) Flash
8051 Microcontroller
 8051 Microcontroller 1 Salient Features (1). 8 bit microcontroller originally developed by Intel in 1980. (2). High-performance CMOS Technology. (3). Contains Total 40 pins. (4). Address bus is of 16 bit
8051 Microcontroller 1 Salient Features (1). 8 bit microcontroller originally developed by Intel in 1980. (2). High-performance CMOS Technology. (3). Contains Total 40 pins. (4). Address bus is of 16 bit
MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS MATERIAL. Features of 8051:
 DEPARTMENT OF ECE MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS MATERIAL UNIT V 8051 MICROCONTROLLERS To make a complete microcomputer system, only microprocessor is not sufficient. It is necessary to add other
DEPARTMENT OF ECE MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS MATERIAL UNIT V 8051 MICROCONTROLLERS To make a complete microcomputer system, only microprocessor is not sufficient. It is necessary to add other
8-bit Microcontroller with 8K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash AT89S52
 Features Compatible with MCS -51 Products 8K Bytes of In-System Programmable (ISP) Flash Memory Endurance: 10,000 Write/Erase Cycles 4.0V to 5.5V Operating Range Fully Static Operation: 0 Hz to 33 MHz
Features Compatible with MCS -51 Products 8K Bytes of In-System Programmable (ISP) Flash Memory Endurance: 10,000 Write/Erase Cycles 4.0V to 5.5V Operating Range Fully Static Operation: 0 Hz to 33 MHz
Vidyalankar T.E. Sem. V [ETRX] Microprocessors and Microcontrollers I Prelim Question Paper Solution
![Vidyalankar T.E. Sem. V [ETRX] Microprocessors and Microcontrollers I Prelim Question Paper Solution Vidyalankar T.E. Sem. V [ETRX] Microprocessors and Microcontrollers I Prelim Question Paper Solution](/thumbs/74/70555699.jpg) 1. (a) 1. (b) T.E. Sem. V [ETRX] Microprocessors and Microcontrollers I Prelim Question Paper Solution Priority modes. 1) Fully Nested Mode : It is a general purpose mode. IR 0 highest priority IR 1 lowest
1. (a) 1. (b) T.E. Sem. V [ETRX] Microprocessors and Microcontrollers I Prelim Question Paper Solution Priority modes. 1) Fully Nested Mode : It is a general purpose mode. IR 0 highest priority IR 1 lowest
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Serial Port Programming in Assembly Module No: CS/ES/12 Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Serial Port Programming in Assembly Module No: CS/ES/12 Quadrant 1 e-text In this lecture, serial communication control register
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Serial Port Programming in Assembly Module No: CS/ES/12 Quadrant 1 e-text In this lecture, serial communication control register
 اصول ميکروکامپيوترها استاد درس: دکتر http://eeiustacir/rahmati/indexhtm rahmati@iustacir ا درس Email و Website برای تکاليف و : http://eeliustacir/rahmati/ ١ /١۴ هفدهم فصل ا شنايی با دستورالعمل ها وMode
اصول ميکروکامپيوترها استاد درس: دکتر http://eeiustacir/rahmati/indexhtm rahmati@iustacir ا درس Email و Website برای تکاليف و : http://eeliustacir/rahmati/ ١ /١۴ هفدهم فصل ا شنايی با دستورالعمل ها وMode
Rev. No. History Issue Date Remark
 Preliminary Bar Code Reader Document Title Bar Code Reader Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date Remark 0.0 Initial issue June 5, 2000 Preliminary 0.1 Change document title from Bar Code Reader
Preliminary Bar Code Reader Document Title Bar Code Reader Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date Remark 0.0 Initial issue June 5, 2000 Preliminary 0.1 Change document title from Bar Code Reader
ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.4 I/O Ports
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.4 I/O Ports Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 8051 I/O programming I/O bit manipulation programming I/O PORT
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.4 I/O Ports Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 8051 I/O programming I/O bit manipulation programming I/O PORT
EEE3410 Microcontroller Applications Department of Electrical Engineering Lecture 4 The 8051 Architecture
 Department of Electrical Engineering Lecture 4 The 8051 Architecture 1 In this Lecture Overview General physical & operational features Block diagram Pin assignments Logic symbol Hardware description Pin
Department of Electrical Engineering Lecture 4 The 8051 Architecture 1 In this Lecture Overview General physical & operational features Block diagram Pin assignments Logic symbol Hardware description Pin
Three criteria in Choosing a Microcontroller
 The 8051 Microcontroller architecture Contents: Introduction Block Diagram and Pin Description of the 8051 Registers Some Simple Instructions Structure of Assembly language and Running an 8051 program
The 8051 Microcontroller architecture Contents: Introduction Block Diagram and Pin Description of the 8051 Registers Some Simple Instructions Structure of Assembly language and Running an 8051 program
Microcontroller and Applications
 S.Y. Diploma : Sem. IV [DE/EJ/ET/EN/EX/EQ/IS/IC/IE] Microcontroller and Applications Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 70 Q.1 Attempt any FIVE of the following : [10] Q.1(a) Define
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. IV [DE/EJ/ET/EN/EX/EQ/IS/IC/IE] Microcontroller and Applications Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 70 Q.1 Attempt any FIVE of the following : [10] Q.1(a) Define
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI UNIT- IV
 UNIT- IV PART A (2 MARK QUESTIONS) 1. What is the need for de-bouncing the keyboard? (AUC NOV 2012) Debouncing is any kind of hardware device or software that ensures that only a single signal will be
UNIT- IV PART A (2 MARK QUESTIONS) 1. What is the need for de-bouncing the keyboard? (AUC NOV 2012) Debouncing is any kind of hardware device or software that ensures that only a single signal will be
C H A P T E R 1 INTRODUCTION
 C H A P T E R 1 INTRODUCTION The mentioned project is based on the worlds most powerful intel controller 8051. Most of the services provided in todays world are voice interactive, you call up your bank
C H A P T E R 1 INTRODUCTION The mentioned project is based on the worlds most powerful intel controller 8051. Most of the services provided in todays world are voice interactive, you call up your bank
Principle and Interface Techniques of Microcontroller
 Principle and Interface Techniques of Microcontroller --8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems Using Assembly and C LI, Guang ( 李光 ) Prof. PhD, DIC, MIET WANG, You ( 王酉 ) PhD, MIET 杭州 浙江大学 2014 Chapter
Principle and Interface Techniques of Microcontroller --8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems Using Assembly and C LI, Guang ( 李光 ) Prof. PhD, DIC, MIET WANG, You ( 王酉 ) PhD, MIET 杭州 浙江大学 2014 Chapter
JUMP, LOOP AND CALL INSTRUCTIONS
 JUMP, LOOP AND CALL INSTRUCTIONS After you have understood the tutorial on Introduction to assembly language which includes simple instruction sets like input/output operations, now it s time to learn
JUMP, LOOP AND CALL INSTRUCTIONS After you have understood the tutorial on Introduction to assembly language which includes simple instruction sets like input/output operations, now it s time to learn
80C51 family programmer s guide and instruction set. 80C51 Family. PROGRAMMER S GUIDE AND INSTRUCTION SET Memory Organization. Philips Semiconductors
 PROGRAMMER S GUIDE AND INSTRUCTION SET Memory Organization Program Memory The 80C51 has separate address spaces for program and data memory. The Program memory can be up to 64k bytes long. The lower 4k
PROGRAMMER S GUIDE AND INSTRUCTION SET Memory Organization Program Memory The 80C51 has separate address spaces for program and data memory. The Program memory can be up to 64k bytes long. The lower 4k
Timer programming
 5.8051 Timer programming In this tutorial, we are going to discuss the Timer module of 8051. First, we will see what are timers, their working and later we will configure the 8051 timers to generate the
5.8051 Timer programming In this tutorial, we are going to discuss the Timer module of 8051. First, we will see what are timers, their working and later we will configure the 8051 timers to generate the
8051 Microcontroller. Ali Ziya Alkar 1
 8051 Microcontroller Ali Ziya Alkar 1 8051 Introduction 8051 is one of the most popular microcontrollers in use today. Many derivative microcontrollers have since been developed that are based on--and
8051 Microcontroller Ali Ziya Alkar 1 8051 Introduction 8051 is one of the most popular microcontrollers in use today. Many derivative microcontrollers have since been developed that are based on--and
T.Y. Diploma : Sem. V [EJ/EN/ET/EX/DE/IS/IC/IE/EV/MU] Micro-controller
![T.Y. Diploma : Sem. V [EJ/EN/ET/EX/DE/IS/IC/IE/EV/MU] Micro-controller T.Y. Diploma : Sem. V [EJ/EN/ET/EX/DE/IS/IC/IE/EV/MU] Micro-controller](/thumbs/84/89719419.jpg) T.Y. Diploma : Sem. V [EJ/EN/ET/EX/DE/IS/IC/IE/EV/MU] Microcontroller Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any THREE of the following: [12] Q.1(a) (i) Distinguish between
T.Y. Diploma : Sem. V [EJ/EN/ET/EX/DE/IS/IC/IE/EV/MU] Microcontroller Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any THREE of the following: [12] Q.1(a) (i) Distinguish between
 Contents 8051 Instruction Set BY D. BALAKRISHNA, Research Assistant, IIIT-H Chapter I : Control Transfer Instructions Lesson (a): Loop Lesson (b): Jump (i) Conditional Lesson (c): Lesson (d): Lesson (e):
Contents 8051 Instruction Set BY D. BALAKRISHNA, Research Assistant, IIIT-H Chapter I : Control Transfer Instructions Lesson (a): Loop Lesson (b): Jump (i) Conditional Lesson (c): Lesson (d): Lesson (e):
CoE3DJ4 Digital Systems Design. Chapter 5: Serial Port Operation
 CoE3DJ4 Digital Systems Design Chapter 5: Serial Port Operation Serial port 8051 includes an on-chip serial port Hardware access to the port is through TXD and RXD (Port 3 bits 1 and 0) Serial port is
CoE3DJ4 Digital Systems Design Chapter 5: Serial Port Operation Serial port 8051 includes an on-chip serial port Hardware access to the port is through TXD and RXD (Port 3 bits 1 and 0) Serial port is
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Microcontroller Model Answer Subject Code: 17534 I m p o r t a n t I n s t r u c t i o n s t o e x a m i n e r s : 1) The answers should be examined by key words and
WINTER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Microcontroller Model Answer Subject Code: 17534 I m p o r t a n t I n s t r u c t i o n s t o e x a m i n e r s : 1) The answers should be examined by key words and
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 2016 EXAMINATIONS.
 Summer 2016 EXAMINATIONS Subject Code: 17534 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the answer scheme. 2) The
Summer 2016 EXAMINATIONS Subject Code: 17534 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the answer scheme. 2) The
Interrupts, timers and counters
 Interrupts, timers and counters Posted on May 10, 2008, by Ibrahim KAMAL, in Micro-controllers, tagged Most microcontrollers come with a set of ADD-ONs called peripherals, to enhance the functioning of
Interrupts, timers and counters Posted on May 10, 2008, by Ibrahim KAMAL, in Micro-controllers, tagged Most microcontrollers come with a set of ADD-ONs called peripherals, to enhance the functioning of
MASSEY UNIVERSITY PALMERSTON NORTH CAMPUS
 MASSEY UNIVERSITY PALMERSTON NORTH CAMPUS EXAMINATION FOR 159.233 COMPUTER SYSTEMS Semester One June 2008 Time allowed: THREE (3) hours This exam contains THREE (3) questions ANSWER ALL THREE (3) QUESTIONS
MASSEY UNIVERSITY PALMERSTON NORTH CAMPUS EXAMINATION FOR 159.233 COMPUTER SYSTEMS Semester One June 2008 Time allowed: THREE (3) hours This exam contains THREE (3) questions ANSWER ALL THREE (3) QUESTIONS
~: Simple Programs in 8051 assembly language :~
 ~: Simple Programs in 8051 assembly language :~ Here some simple programs of 8051 are given to understand the operation of different instructions and to understand the logic behind particular program.
~: Simple Programs in 8051 assembly language :~ Here some simple programs of 8051 are given to understand the operation of different instructions and to understand the logic behind particular program.
Q 1 a) Attempt any THREE of the following: 12 TMOD.7 TMOD.6 TMOD.5 TMOD.4 TMOD.3 TMOD.2 TMOD.1 TMOD.0 GATE C/T M1 M0 GATE C/T M1 M0
 Page 1 of 33 Q 1 a) Attempt any THREE of the following: 12 Q 1 a i) Describe Timer modes of 8051. Ans: Timer 0 and Timer 1 can both be used as either Counters or Timers. There are 4 different operating
Page 1 of 33 Q 1 a) Attempt any THREE of the following: 12 Q 1 a i) Describe Timer modes of 8051. Ans: Timer 0 and Timer 1 can both be used as either Counters or Timers. There are 4 different operating
8051 Microcontroller Interrupts
 8051 Microcontroller Interrupts There are five interrupt sources for the 8051, which means that they can recognize 5 different events that can interrupt regular program execution. Each interrupt can be
8051 Microcontroller Interrupts There are five interrupt sources for the 8051, which means that they can recognize 5 different events that can interrupt regular program execution. Each interrupt can be
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET. P89C738; P89C739 8-bit microcontrollers Dec 15. Product specification File under Integrated Circuits, IC20
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC20 1997 Dec 15 CONTENTS 1 FEATURES 2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 3 ORDERING INFORMATION 4 BLOCK DIAGRAM 5 FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM 6 PINNING INFORMATION
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC20 1997 Dec 15 CONTENTS 1 FEATURES 2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 3 ORDERING INFORMATION 4 BLOCK DIAGRAM 5 FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM 6 PINNING INFORMATION
CS 320. Computer Architecture Core Architecture
 CS 320 Computer Architecture 8051 Core Architecture Evan Hallam 19 April 2006 Abstract The 8051 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed originally in the 1980 s by the Intel Corporation. This inexpensive and
CS 320 Computer Architecture 8051 Core Architecture Evan Hallam 19 April 2006 Abstract The 8051 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed originally in the 1980 s by the Intel Corporation. This inexpensive and
SUMMER 13 EXAMINATION
 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC - 27001-2005 Certified) Subject Code: 12187 SUMMER 13 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC - 27001-2005 Certified) Subject Code: 12187 SUMMER 13 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should
Module I. Microcontroller can be classified on the basis of their bits processed like 8bit MC, 16bit MC.
 MICROCONTROLLERS AND APPLICATIONS 1 Module 1 Module I Introduction to Microcontrollers: Comparison with Microprocessors Harvard and Von Neumann Architectures - 80C51 microcontroller features - internal
MICROCONTROLLERS AND APPLICATIONS 1 Module 1 Module I Introduction to Microcontrollers: Comparison with Microprocessors Harvard and Von Neumann Architectures - 80C51 microcontroller features - internal
SANKALCHAND PATEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, VISNAGAR. ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION DEPARTMENT Question Bank- 1
 SANKALCHAND PATEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, VISNAGAR ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION DEPARTMENT Question Bank- 1 Subject: Microcontroller and Interfacing (151001) Class: B.E.Sem V (EC-I & II) Q-1 Explain RISC
SANKALCHAND PATEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, VISNAGAR ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION DEPARTMENT Question Bank- 1 Subject: Microcontroller and Interfacing (151001) Class: B.E.Sem V (EC-I & II) Q-1 Explain RISC
MICROCONTROLLER BASED WATER LEVEL CONTROL SYSTEM
 MICROCONTROLLER BASED WATER LEVEL CONTROL SYSTEM The present concept implements controlling of pump which pumps water from the sump (underground tank) to the overhead tank, using 8951 microcontroller.
MICROCONTROLLER BASED WATER LEVEL CONTROL SYSTEM The present concept implements controlling of pump which pumps water from the sump (underground tank) to the overhead tank, using 8951 microcontroller.
User-defined Download Application Note
 User-defined Download 1. Applied Products: SM59XX Series, SM59DXX Series, SM59RXX Series. 2. Object: User can define command as entry ISP password through ISAP software to run programming. 3. Operation
User-defined Download 1. Applied Products: SM59XX Series, SM59DXX Series, SM59RXX Series. 2. Object: User can define command as entry ISP password through ISAP software to run programming. 3. Operation
How to use the PSoC based 16C450 Replacement
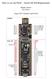 How to use the PSoC based 16C450 Replacement Matthew Burns Eric Ponce August 2017 (Updated April 2018) 1 Overview The PSoC based 16C450 Replacement is intended to replace the 16C450 serial communication
How to use the PSoC based 16C450 Replacement Matthew Burns Eric Ponce August 2017 (Updated April 2018) 1 Overview The PSoC based 16C450 Replacement is intended to replace the 16C450 serial communication
The Final Word on 8051 Microcontroller
 The Final Word on 8051 Microcontroller This is a book about the Intel 8051 microcontroller and its large family of descendants. It is intended to give you, the reader, some new techniques for optimizing
The Final Word on 8051 Microcontroller This is a book about the Intel 8051 microcontroller and its large family of descendants. It is intended to give you, the reader, some new techniques for optimizing
Serial I-O for Dinesh K. Sharma Electrical Engineering Department I.I.T. Bombay Mumbai (version 14/10/07)
 Serial I-O for 8051 Dinesh K. Sharma Electrical Engineering Department I.I.T. Bombay Mumbai 400 076 (version 14/10/07) 1 Motivation Serial communications means sending data a single bit at a time. But
Serial I-O for 8051 Dinesh K. Sharma Electrical Engineering Department I.I.T. Bombay Mumbai 400 076 (version 14/10/07) 1 Motivation Serial communications means sending data a single bit at a time. But
Timer-1 can be run using the internal clock, fosc/12 (timer mode) or from any external source via pin T1 (P3.5) (Counter mode).
 EC 6504 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER Electronics and Communication Engineering Fifth Semester UNIT-V Part A 1. List the modes of Timer in 8051. [N/D16] The timers available in 8051 are Timer 0 (T0)
EC 6504 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER Electronics and Communication Engineering Fifth Semester UNIT-V Part A 1. List the modes of Timer in 8051. [N/D16] The timers available in 8051 are Timer 0 (T0)
80C451 operation of port 6
 INTRODUCTION The features of the are shared with the 80C5 or are conventional except for the operation of port 6. The flexibility of this port facilitates high-speed parallel data communications. This
INTRODUCTION The features of the are shared with the 80C5 or are conventional except for the operation of port 6. The flexibility of this port facilitates high-speed parallel data communications. This
ISSI. IS89C51 CMOS SINGLE CHIP 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER with 4-Kbytes of FLASH ISSI IS89C51 NOVEMBER 1998 FEATURES GENERAL DESCRIPTION
 IS89C51 CMOS SINGLE CHIP 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER with 4-Kbytes of FLASH NOVEMBER 1998 FEATURES 80C51 based architecture 4-Kbytes of on-chip Reprogrammable Flash Memory 128 x 8 RAM Two 16-bit Timer/Counters
IS89C51 CMOS SINGLE CHIP 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER with 4-Kbytes of FLASH NOVEMBER 1998 FEATURES 80C51 based architecture 4-Kbytes of on-chip Reprogrammable Flash Memory 128 x 8 RAM Two 16-bit Timer/Counters
Question Bank Microprocessor and Microcontroller
 QUESTION BANK - 2 PART A 1. What is cycle stealing? (K1-CO3) During any given bus cycle, one of the system components connected to the system bus is given control of the bus. This component is said to
QUESTION BANK - 2 PART A 1. What is cycle stealing? (K1-CO3) During any given bus cycle, one of the system components connected to the system bus is given control of the bus. This component is said to
A Facilitated Learning Environment for Mentally Disabled Children
 A Facilitated Learning Environment for Mentally Disabled Children Jeanette Chan Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.115 Microprocessor Lab May 14, 2002 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Overview... 2 1.2
A Facilitated Learning Environment for Mentally Disabled Children Jeanette Chan Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.115 Microprocessor Lab May 14, 2002 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Overview... 2 1.2
80C51 Block Diagram. CSE Overview 1
 80C51 Block Diagram CSE 477 8051 Overview 1 80C51 Memory CSE 477 8051 Overview 3 8051 Memory The data width is 8 bits Registers are 8 bits Addresses are 8 bits i.e. addresses for only 256 bytes! PC is
80C51 Block Diagram CSE 477 8051 Overview 1 80C51 Memory CSE 477 8051 Overview 3 8051 Memory The data width is 8 bits Registers are 8 bits Addresses are 8 bits i.e. addresses for only 256 bytes! PC is
Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Question Bank
 www.examquestionpaper.in Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Question Bank SUBJECT CODE / NAME: ET7102 / MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEM DESIGN BRANCH : M.E. (C&I) YEAR / SEM : I / I
www.examquestionpaper.in Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Question Bank SUBJECT CODE / NAME: ET7102 / MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEM DESIGN BRANCH : M.E. (C&I) YEAR / SEM : I / I
ET2640 Microprocessors
 ET2640 Microprocessors Unit -2 Processor Programming Concepts Basic Control Instructor : Stan Kong Email : skong@itt-tech.edu Figure 2 4 Bits of the PSW Register 8051 REGISTER BANKS AND STACK 80 BYTES
ET2640 Microprocessors Unit -2 Processor Programming Concepts Basic Control Instructor : Stan Kong Email : skong@itt-tech.edu Figure 2 4 Bits of the PSW Register 8051 REGISTER BANKS AND STACK 80 BYTES
Control Transfer Instructions Jump, Loop, and Call. ECE473/573 Microprocessor System Design, Dr. Shiue
 Control Transfer Instructions Jump, Loop, and Call 1 Jump Instructions JZ label ; Jump if A=0 JNZ label ; Jump if A!=0 DJNZ reg, label ; Decrement and Jump if A (or reg.)!=0 CJNE A, byte ; Compare and
Control Transfer Instructions Jump, Loop, and Call 1 Jump Instructions JZ label ; Jump if A=0 JNZ label ; Jump if A!=0 DJNZ reg, label ; Decrement and Jump if A (or reg.)!=0 CJNE A, byte ; Compare and
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER Table of Contents- 1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 4 2 FEATURES... 5 3 PARTS INFORMATION LIST... 6 3.1 Lead Free (RoHS) Parts information list... 6 4 PIN CONFIGURATIONS... 7 5 PIN DESCRIPTIONS...
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER Table of Contents- 1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 4 2 FEATURES... 5 3 PARTS INFORMATION LIST... 6 3.1 Lead Free (RoHS) Parts information list... 6 4 PIN CONFIGURATIONS... 7 5 PIN DESCRIPTIONS...
Chapter Family Microcontrollers Instruction Set
 Chapter 4 8051 Family Microcontrollers Instruction Set Lesson 5 Program Flow Control and Interrupt Flow Control Instructions 2 Branch instructions- Jump to new value of Program Counter (PC) LJMP address16
Chapter 4 8051 Family Microcontrollers Instruction Set Lesson 5 Program Flow Control and Interrupt Flow Control Instructions 2 Branch instructions- Jump to new value of Program Counter (PC) LJMP address16
8XC51RA RB RC Hardware Description
 8XC51RA RB RC Hardware Description February 1995 Order Number 272668-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products Intel assumes no liability whatsoever including infringement
8XC51RA RB RC Hardware Description February 1995 Order Number 272668-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products Intel assumes no liability whatsoever including infringement
MODULE-1. Short Answer Questions
 MODULE-1 Short Answer Questions 1. Give the comparison between microprocessor and microcontroller. It is very clear from figure that in microprocessor we have to interface additional circuitry for providing
MODULE-1 Short Answer Questions 1. Give the comparison between microprocessor and microcontroller. It is very clear from figure that in microprocessor we have to interface additional circuitry for providing
8XC151SA and 8XC151SB Hardware Description
 8XC151SA and 8XC151SB Hardware Description June 1996 Order Number 272832-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products Intel assumes no liability whatsoever including infringement
8XC151SA and 8XC151SB Hardware Description June 1996 Order Number 272832-001 Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products Intel assumes no liability whatsoever including infringement
