Welcome to COSC Introduction to Computer Science
|
|
|
- Godwin Hines
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Welcome to COSC 1302 Introduction to Computer Science
2 (Syllabus)
3 Chapter 1 The Big Picture
4 1.1 Computing Systems Hardware The physical elements of a computing system (printer, circuit boards, wires, keyboard ) Software The programs that provide the instructions for a computer to execute 4 3
5 Layers of a Computing System 5 4
6 Abstraction Abstraction = mental model that removes complex details 6 5
7 Internal View (lots of details) 7
8 Abstract View (few details) 8
9 Abstraction Abstraction is a key concept. It will reappear throughout this class (and the rest of your life!) Make sure you grok it! Grok - Wikipedia 9 5
10 QUIZ Explain the abstractions we normally apply when using the following systems: DVD player Registering for classes on DuckTrax Walking In each case, explain what is the internal view and what is the abstract view. 10 5
11 1.2 History of computing 11
12 Early History of Computing Abacus (about 1600 BC, or even BC) = early device to record numeric values and perform addition and subtraction manually Blaise Pascal 1642 The Pascaline = mechanical device to add and subtract automatically. Gottfried Leibniz 1672 The Stepped Reckoner = mechanical device to add, subtract, divide & multiply. Leibniz anticipated many of the hardware and software concepts developed later by Babbage & Lovelace. He invented binary notation! Joseph Jacquard 1801 The Jacquard Loom. He invented punched cards! 12 6
13 Early History of Computing Charles Babbage 1822: Difference Engine : Analytical Engine Ada Lovelace, the "Enchantress of numbers" 1843: Invented the loop (to calculate Bernoulli numbers). She s considered the first programmer! William Gibson & Bruce Sterling: The Difference Engine Doron Swade: The Difference Engine, Cogwheel Brain 13 7
14 Early History of Computing Herman Hollerith Tabulating machine used for 1890 U.S. Census. This is the official birthday of the data processing industry. The term Super Computing was first used by the New York World newspaper in 1931 to refer to a large custombuilt tabulator that IBM made for Columbia University [Source: Wikipedia: Tabulating_machine] 14 7
15 What to do for next class? (a.k.a. Individual work) Read pages 2-11 of our text and write in your notebook three facts not mentioned in class. Answer end-of-chapter Exercises 1-7, and 9 in the notebook. Answer end-of-chapter Thought Question 1 in the notebook: Identify 5 abstractions in our school environment. For each, indicate some of the details hidden by the abstraction, and how the abstraction helps manage complexity. 15
16 QUIZ 1. True or False? Computer software is the collection of programs that provide the instructions that a computer carries out. 2. True or False? An abstraction is a mental model that removes or hides complex details. 3. True or False? The abacus was the world's first electronic digital computer. 4. True or False? Ada Augusta, Countess of Lovelace, is credited with being the first programmer. 16 5
17 QUIZ What is hardware? What is software? What is an abstraction and why do we need abstractions in CS? What is the internal/physical view? What is the external/abstract view? 17 5
18 Match each inventor with his/her invention(s): Pascal Leibniz s Loom Programming Loop Jacquard Punched Cards Babbage Difference Engine Lovelace Stepped Reckoner (+-*/) Binary Code Mechanical + and Analytical Engine 18 5
19 Alan Turing and WWII computers Bletchley Park German Enigma machine and British Bombe computers German Lorentz machine and British Colossus computers (Mark I, Mark II) first electronic, digital, programmable computers Alan Turing 1936: Turing Machine, Artificial Intelligence Testing (the Turing test) "On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem" (decision problem) Neil Stephenson: Cryptonomicon 19 7
20 Rejewski
21 Colossus Mark I 21 7
22 Computers after WWII Late 40s and 50s John von Neumann 1945: Stored-program computer, a.k.a. the von Neumann architecture ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC I Univac I was delivered to the US Bureau of the Census At the end of WWII, these early computers launched a new era in mathematics, physics, engineering and economics! 22 7
23 A (very) brief history of the hardware
24 First Generation Hardware ( ) Vacuum Tubes Large, not very reliable, generate a lot of heat Magnetic Drum Memory device that rotated under a read/write head Card Readers Magnetic Tape Drives Sequential auxiliary storage devices 24 8
25 Second Generation Hardware ( ) Transistor Replaced vacuum tube, fast, small, durable, cheap Magnetic Cores Replaced magnetic drums, information available instantly Magnetic Disks Replaced magnetic tape, data can be accessed directly 25 9
26 Third Generation Hardware ( ) Integrated Circuits (ICs) Replaced circuit boards, smaller cheaper, faster, more reliable Transistors Now used for memory construction Terminal An input/output device with a keyboard and screen 26 10
27 Fourth Generation Hardware ( ) Large- and Very Large Scale Integration (LSI, VLSI) Great advances in chip technology PCs, the Commercial Market, Workstations Personal Computers and Workstations emerge New companies emerge: Apple, Sun, Dell Laptops Everyone has his/her own portable computer 27 11
28 Fifth Generation Hardware (2001-today) Multi-core processors IBM Power4, released in 2001, had 2 cores in the same chip
29 QUIZ Connect each generation of computer hardware with its defining technology: 1 st Gen. ICs (SSI, MSI) 2 nd Gen. Multi-core processors 3 rd Gen. LSI, VLSI 4 th Gen. Vacuum tubes 5 th Gen. Transistors 29
30 Beyond the isolated computer Parallel Computing Computers rely on interconnected central processing and/or memory units that increase processing speed Computer Networks WAN technology started in 1969 with the ARPANET LAN technology started in 1973 with the Ethernet WANs and LANs Internet Wide-Area Network Local-Area Network 30 12
31 A (very) brief history of the software
32 First Generation Software ( ) Machine Languages Computer programs written in binary (1s and 0s) Assembly Languages and Assemblers Programs written using mnemonics, which were translated into machine language a.k.a. low-level languages (Ch.6) 32 13
33 Second Generation Software ( ) High-level Languages English-like statements (print, for, while, if then else, etc.) made programming easier Examples: Fortran, COBOL, Lisp 33 14
34 Systems Software Third Generation Software ( ) Operating system (OS), which decides: Which programs to run and when What resources to allocate to each program What utility programs to call (e.g. loaders, linkers) Programs are created to be used by nonprogrammers, e.g. SPSS
35 Fourth Generation Software ( ) New high-level languages for structured programming Pascal, C, C++, Lots of New Applications for Users Spreadsheets Word processors Database management systems (DBMS) 35 17
36 36 16
37 Fifth Generation Software (1990- present) Object-Oriented Programming Based on a hierarchy of data objects (e.g. Java, Python) World Wide Web Allows easy global communication through the Internet Single-handedly invented by a physicist, along with the HTML and the first browser!! Microsoft and the OFFICE SUITE 37 18
38 Sixth Generation Software (?) (2000- present) Component-Oriented Programming Aims to enhance code reusability (80% of software development is maintenance of old code!) The component model specifies how interfaces should be defined and the elements that should be included in an interface definition. Examples of component models: Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) Component Object Model (COM).NET Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) 38 18
39 QUIZ Connect each generation of computer software with its defining technology: 1 st Gen. OOP 2 nd Gen. Structured progr. 3 rd Gen. Systems software (OS) 4 th Gen. Component-oriented progr. 5 th Gen. Machine and assembly progr. 6 th Gen. High-level programs 39
40 SKIP: Computing as a Discipline Computing as a Tool Areas of Computer Science
41 Who am I? Read Ada s bio on pp
42 Ethical Issues What is The Tenth Strand? Read pp in our text. For more info, follow link on our webpage! 42
43 Chapter review questions Describe the layers of a computer system Describe the concept of abstraction and its relationship to computing Describe the history of computer hardware and software (only the material covered) Why is Ada Lovelace important to CS? Explain the tenth strand 43 25
44 Individual work To do by next class, before starting to work on homework: Read the entire Chapter 1 Read Ada Lovelace s bio Read Ethical Issues: The Tenth Strand Give brief answers to the chapter review questions Answer end-of-chapter questions 1 38 in your notebook 44
45 Homework Due next Wed, Sep.2: End-of-chapter ex End-of-chapter thought question 3 (paragraph-length answer required) The latest homework assigned is always available on the course webpage: 45
Chapter 1. The Big Picture
 Chapter 1 The Big Picture 1.1 Computing Systems Hardware The physical elements of a computing system (printer, circuit boards, wires, keyboard ) Software The programs that provide the instructions for
Chapter 1 The Big Picture 1.1 Computing Systems Hardware The physical elements of a computing system (printer, circuit boards, wires, keyboard ) Software The programs that provide the instructions for
Describe the layers of a computer system
 Chapter 1 The Big Picture Chapter Goals Describe the layers of a computer system Describe the concept of abstraction and its relationship to computing Describe the history of computer hardware and software
Chapter 1 The Big Picture Chapter Goals Describe the layers of a computer system Describe the concept of abstraction and its relationship to computing Describe the history of computer hardware and software
COURSE OVERVIEW. Introduction to Computer Engineering 2015 Spring by Euiseong Seo
 COURSE OVERVIEW Introduction to Computer Engineering 2015 Spring by Euiseong Seo Course Objectives Introduction to computer engineering For computer engineer-wannabe For students studying other fields
COURSE OVERVIEW Introduction to Computer Engineering 2015 Spring by Euiseong Seo Course Objectives Introduction to computer engineering For computer engineer-wannabe For students studying other fields
Chapter 01. Introduction 2018/9/17. Chapter Goals. Computing Systems. Computing Systems. Layers of a Computing System. Abstraction
 Chapter Goals Chapter 01 Describe the layers of a computer system Describe the concept of abstraction and its relationship to computing Describe the history of computer hardware and software Introduction
Chapter Goals Chapter 01 Describe the layers of a computer system Describe the concept of abstraction and its relationship to computing Describe the history of computer hardware and software Introduction
(History of Computers) Lecture # 03 By: M.Nadeem Akhtar. Lecturer. URL:
 INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES. (History of Computers) Lecture # 03 By: M.. Lecturer. Department of CS & IT. URL: https://sites.google.com/site/nadeemcsuoliict/home/lectures 1
INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES. (History of Computers) Lecture # 03 By: M.. Lecturer. Department of CS & IT. URL: https://sites.google.com/site/nadeemcsuoliict/home/lectures 1
Welcome to COS151! 1.1
 Welcome to COS151! Title: Introduction to Computer Science Course website: https://cs.up.ac.za/admin/courses/cos151 Find the study guide there Announcements Assignments (download & upload) Brief overview
Welcome to COS151! Title: Introduction to Computer Science Course website: https://cs.up.ac.za/admin/courses/cos151 Find the study guide there Announcements Assignments (download & upload) Brief overview
Computers in Engineering COMP 208. A Brief History. Mechanical Calculators. A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker
 Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Computers in Engineering COMP 208
 Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Overview of a computer
 Overview of a computer One marks 1. What is von Neumann concept also called as? Stored memory or stored program concept. 2. Who is the father of computer Charles Babbage 3. What is a computer? It is an
Overview of a computer One marks 1. What is von Neumann concept also called as? Stored memory or stored program concept. 2. Who is the father of computer Charles Babbage 3. What is a computer? It is an
Part (01) Introduction to Computer
 Part (01) Introduction to Computer Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee 1 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Summer 2014, Introduction to CS 1 TURING MODEL The idea of a universal computational device was first described by Alan
Part (01) Introduction to Computer Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee 1 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Summer 2014, Introduction to CS 1 TURING MODEL The idea of a universal computational device was first described by Alan
CS101 Lecture 29: Brief History of Computing
 CS101 Lecture 29: Brief History of Computing "There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home." -- Ken Olson, founder and CEO of Digital Equipment Corp., 1977 John Magee 1 August 2013 Some
CS101 Lecture 29: Brief History of Computing "There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home." -- Ken Olson, founder and CEO of Digital Equipment Corp., 1977 John Magee 1 August 2013 Some
1: History, Generation & Classification. Shobhanjana Kalita, Dept. of CSE, Tezpur University
 1: History, Generation & Classification Shobhanjana Kalita, Dept. of CSE, Tezpur University History Computer originally (17 th century) meant someone who computes Only in the 20 th century it was associated
1: History, Generation & Classification Shobhanjana Kalita, Dept. of CSE, Tezpur University History Computer originally (17 th century) meant someone who computes Only in the 20 th century it was associated
A Brief History of Computer Science. David Greenstein Monta Vista High School, Cupertino, CA
 A Brief History of Computer Science David Greenstein Monta Vista High School, Cupertino, CA History of Computing Machines Definition of Computer A programmable machine A machine that manipulates data according
A Brief History of Computer Science David Greenstein Monta Vista High School, Cupertino, CA History of Computing Machines Definition of Computer A programmable machine A machine that manipulates data according
You Will Need Floppy Disks for your labs!
 CIS121 Instructor: Lynne Mayer VoiceMail: (847) 697-1000 x 2328 Lmayer@elgin.edu Office Hours: ICT 122 Mon.: 9:15-10:15 AM, 5:15-6:00 PM Wed.: 9:15-10:15 AM Fri.: 2:30-3:30 PM Website: faculty.elgin.edu/lmayer
CIS121 Instructor: Lynne Mayer VoiceMail: (847) 697-1000 x 2328 Lmayer@elgin.edu Office Hours: ICT 122 Mon.: 9:15-10:15 AM, 5:15-6:00 PM Wed.: 9:15-10:15 AM Fri.: 2:30-3:30 PM Website: faculty.elgin.edu/lmayer
Introduction To Computers. About the Course
 Introduction To Computers Chapter No 1 Introduction About the Course Course instructor Course policies Topics to be covered Course Website and Reference material Assignments and Projects ITC - Chapter
Introduction To Computers Chapter No 1 Introduction About the Course Course instructor Course policies Topics to be covered Course Website and Reference material Assignments and Projects ITC - Chapter
A Brief History of Computer Science
 A Brief History of Computer Science 4700 Hundred years ago Sumerians invented the abacus Sand, lines, pebbles Sexagesimal Base 60 still used today Time, distance How do you count like that? Side trip Factors
A Brief History of Computer Science 4700 Hundred years ago Sumerians invented the abacus Sand, lines, pebbles Sexagesimal Base 60 still used today Time, distance How do you count like that? Side trip Factors
History of Computing. Slides from NYU and Georgia Tech
 History of Computing Slides from NYU and Georgia Tech Early Computational Devices (Chinese) Abacus 2700 2300 BC Used for performing arithmetic operations Early Computational Devices Napier s Bones, 1617
History of Computing Slides from NYU and Georgia Tech Early Computational Devices (Chinese) Abacus 2700 2300 BC Used for performing arithmetic operations Early Computational Devices Napier s Bones, 1617
EVOLUTION OF COMPUTERS. In the early years, before the computer was invented, there are several inventions of counting machines.
 EVOLUTION OF COMPUTERS In the early years, before the computer was invented, there are several inventions of counting machines. 200 BC 500 BC CHINESE ABACUS EGYPTIAN ABACUS 1620 JOHN NAPIER NAPIER'S BONES
EVOLUTION OF COMPUTERS In the early years, before the computer was invented, there are several inventions of counting machines. 200 BC 500 BC CHINESE ABACUS EGYPTIAN ABACUS 1620 JOHN NAPIER NAPIER'S BONES
Algorithm: Program: Programming: Software: Hardware:
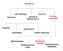 0-1 0-2 Terminology Algorithm: A set of steps that defines how a task is performed Program: A representation of an algorithm Programming: The process of developing a program Software: Programs and algorithms
0-1 0-2 Terminology Algorithm: A set of steps that defines how a task is performed Program: A representation of an algorithm Programming: The process of developing a program Software: Programs and algorithms
What You Will Learn Today
 CS101 Lecture 2: Brief History of Computing "There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home." -- Ken Olson, founder and CEO of Digital Equipment Corp., 1977 Aaron Stevens 21 January 2011
CS101 Lecture 2: Brief History of Computing "There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home." -- Ken Olson, founder and CEO of Digital Equipment Corp., 1977 Aaron Stevens 21 January 2011
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers
 Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations Characteristic
Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations Characteristic
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers. In this chapter you will learn about:
 Ref Page Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations
Ref Page Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations
Chapter 1: An Introduction to Computer Science. Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, 6-th Edition
 Chapter 1: An Introduction to Computer Science Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, 6-th Edition Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about The definition of computer science Algorithms A
Chapter 1: An Introduction to Computer Science Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, 6-th Edition Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about The definition of computer science Algorithms A
Part 1: Computer and Information Literacy
 What is Computer? Understand Computers Part 1: Computer and Information Literacy Computer is an electronic devices that under a program s direction and control, perform four basic operations: Input, Processing,
What is Computer? Understand Computers Part 1: Computer and Information Literacy Computer is an electronic devices that under a program s direction and control, perform four basic operations: Input, Processing,
Fundamentals of Python: First Programs. Chapter 1: Introduction Modifications by Mr. Dave Clausen
 Fundamentals of Python: First Programs Chapter 1: Introduction Modifications by Mr. Dave Clausen Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the basic features of an algorithm
Fundamentals of Python: First Programs Chapter 1: Introduction Modifications by Mr. Dave Clausen Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the basic features of an algorithm
Learning Objectives. In this chapter you will learn about:
 Ref Page Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations
Ref Page Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations
Introduction to Computer Systems
 Introduction to Computer Systems By Farhan Ahmad farhanahmad@uet.edu.pk Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Engineering & Technology Lahore Introducing Computer Systems Exploring computers
Introduction to Computer Systems By Farhan Ahmad farhanahmad@uet.edu.pk Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Engineering & Technology Lahore Introducing Computer Systems Exploring computers
An Introduction to Computer Science CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science Lecture #2
 An Introduction to Computer Science CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science Lecture #2 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB A Word About Registration for CS8 FOR THOSE OF YOU NOT YET REGISTERED: This
An Introduction to Computer Science CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science Lecture #2 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB A Word About Registration for CS8 FOR THOSE OF YOU NOT YET REGISTERED: This
Chapter 2 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF COMPUTERS
 Chapter 2 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF COMPUTERS History of Computers Outline Generations of Computers Types of Computers 2 History of Computers A computer is a machine that works with data and information
Chapter 2 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF COMPUTERS History of Computers Outline Generations of Computers Types of Computers 2 History of Computers A computer is a machine that works with data and information
CS 1 Notes 1 - Early Computing and 2 - Electronic Computing
 CS 1 Notes 1 - Early Computing and 2 - Electronic Computing Computer Science: The discipline that seeks to build a scientific foundation for such topics as: computer design computer programming information
CS 1 Notes 1 - Early Computing and 2 - Electronic Computing Computer Science: The discipline that seeks to build a scientific foundation for such topics as: computer design computer programming information
Early Calculating Tools
 Early Calculating Tools Abacus At least 5,000 years old Memory aid for making calculations Cannot perform actual computations Eventually replaced by pencil and paper Early Calculating Tools Pascalene Invented
Early Calculating Tools Abacus At least 5,000 years old Memory aid for making calculations Cannot perform actual computations Eventually replaced by pencil and paper Early Calculating Tools Pascalene Invented
Fundamentals of Digital Computers The mechanical computer age began with the advent of the abacus in 500 B.C by Babylonians. The abacus, which was
 1 Fundamentals of Digital Computers The mechanical computer age began with the advent of the abacus in 500 B.C by Babylonians. The abacus, which was used extensively and is still in use today, was not
1 Fundamentals of Digital Computers The mechanical computer age began with the advent of the abacus in 500 B.C by Babylonians. The abacus, which was used extensively and is still in use today, was not
Computer History CSCE 101
 Computer History CSCE 101 Computer History In 40 years computers went from being giant expensive machines that only corporations could own to the personal computer we see today. Early Calculating Devices
Computer History CSCE 101 Computer History In 40 years computers went from being giant expensive machines that only corporations could own to the personal computer we see today. Early Calculating Devices
HISTORY OF COMPUTING
 NAME: DATE: PERIOD: 01) Definition of computers: HISTORICAL DEVICES 02) How is the term Analog used when representing data? 03) Answer the questions for the two devices used prior to the invention of the
NAME: DATE: PERIOD: 01) Definition of computers: HISTORICAL DEVICES 02) How is the term Analog used when representing data? 03) Answer the questions for the two devices used prior to the invention of the
The Generations of Computers
 The Generations of Computers The development of computers started with mechanical and electromechanical devices (17 th through 19 th century) and has progressed through four generations of computers. Mechanical
The Generations of Computers The development of computers started with mechanical and electromechanical devices (17 th through 19 th century) and has progressed through four generations of computers. Mechanical
Maninder Kaur.
 1 Maninder Kaur professormaninder@gmail.com What is a Computer? System Unit A computer is an electronic machine that can be programmed to accept data (input), process it into useful information (output),
1 Maninder Kaur professormaninder@gmail.com What is a Computer? System Unit A computer is an electronic machine that can be programmed to accept data (input), process it into useful information (output),
A (BRIEF) HISTORY OF COMPUTING. By Dane Paschal
 A (BRIEF) HISTORY OF COMPUTING By Dane Paschal BIASES Amero-Euro centric Computer science centric Google centric ANCIENT ORIGINS Counting is hard The Human Brain Abacus Numerals THE 1700 S AND 1800 S Computing
A (BRIEF) HISTORY OF COMPUTING By Dane Paschal BIASES Amero-Euro centric Computer science centric Google centric ANCIENT ORIGINS Counting is hard The Human Brain Abacus Numerals THE 1700 S AND 1800 S Computing
In this chapter, you will learn about: The definition of computer science. Algorithms. Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Third Edition
 Objectives Chapter 1: An Introduction to Com puter S cience Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Third Edition In this chapter, you will learn about: The definition of computer science Algorithms
Objectives Chapter 1: An Introduction to Com puter S cience Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Third Edition In this chapter, you will learn about: The definition of computer science Algorithms
Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 1 Technology in Action Technology in Focus: The History of the PC 2 The first personal computer Sold as a kit Switches for input Lights for output Altair 8800 Bill Gates and Paul Allen created a compiler
1 Technology in Action Technology in Focus: The History of the PC 2 The first personal computer Sold as a kit Switches for input Lights for output Altair 8800 Bill Gates and Paul Allen created a compiler
HISTORY OF CALCULATION. Evolution of Computation
 HISTORY OF CALCULATION Evolution of Computation Mechanical Era Slide Rule is the first mechanical device for numeric calculation Slide Rule can do Multiplication, Division, Power, Root and Trigonometry
HISTORY OF CALCULATION Evolution of Computation Mechanical Era Slide Rule is the first mechanical device for numeric calculation Slide Rule can do Multiplication, Division, Power, Root and Trigonometry
Great Inventions written by Bob Barton
 COMPUTER Great Inventions written by Bob Barton Computers Computers help society function in many vital ways, often without our being aware of them. Computers control traffic lights and factory operations.
COMPUTER Great Inventions written by Bob Barton Computers Computers help society function in many vital ways, often without our being aware of them. Computers control traffic lights and factory operations.
CHAPTER1 : Part 2 INTRODUCTION & HISTORY OF COMPUTERS. UNIVERSITI TENAGA NASIONAL Generates Professionals
 CHAPTER1 : Part 2 INTRODUCTION & HISTORY OF COMPUTERS Module Objectives At the end of the module, students should be able to: appreciate and understand the history of computers. describe the generations
CHAPTER1 : Part 2 INTRODUCTION & HISTORY OF COMPUTERS Module Objectives At the end of the module, students should be able to: appreciate and understand the history of computers. describe the generations
COMPUTER - GENERATIONS
 COMPUTER - GENERATIONS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_fundamentals/computer_generations.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Generation in computer terminology is a change in technology a computer
COMPUTER - GENERATIONS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_fundamentals/computer_generations.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Generation in computer terminology is a change in technology a computer
Chronological History of the Pre-Computer Developments
 500 B. C. Abacus 1621 Slide Rule 1623 Schickard s Adding Machine (Germany) 1642 Pascal s Adding Machine (France) 1673 Leibniz Calculator (Germany) 1804 Jacquard Loom and Punch Cards 1822 Babbage s Difference
500 B. C. Abacus 1621 Slide Rule 1623 Schickard s Adding Machine (Germany) 1642 Pascal s Adding Machine (France) 1673 Leibniz Calculator (Germany) 1804 Jacquard Loom and Punch Cards 1822 Babbage s Difference
An Introduction to Computer Science CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science, Winter 2018 Lecture #2
 An Introduction to Computer Science CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science, Winter 2018 Lecture #2 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB A Word About Registration for CS8 FOR THOSE OF YOU NOT YET
An Introduction to Computer Science CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science, Winter 2018 Lecture #2 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB A Word About Registration for CS8 FOR THOSE OF YOU NOT YET
Evolution of the Computer
 Evolution of the Computer Janaka Harambearachchi (Engineer/Systems Development) Zeroth Generation- Mechanical 1. Blaise Pascal -1642 Mechanical calculator only perform + - 2. Von Leibiniz -1672 Mechanical
Evolution of the Computer Janaka Harambearachchi (Engineer/Systems Development) Zeroth Generation- Mechanical 1. Blaise Pascal -1642 Mechanical calculator only perform + - 2. Von Leibiniz -1672 Mechanical
1-1 Computer Structure
 1-1 Computer Structure Computer: A computer is a programmable, multiuse machine that accepts data-raw, fact and figures; processes, or manipulates it into information we can use, such as summaries, totals,
1-1 Computer Structure Computer: A computer is a programmable, multiuse machine that accepts data-raw, fact and figures; processes, or manipulates it into information we can use, such as summaries, totals,
SSRVM Content Creation Template
 SSRVM Content Creation Template Title: Evolution of Computers Contributors: Sreeja. T Std: IV Submission Date: Reviewers: Approval Date: REF No: Brief Description: Goal: Brief History which reveals a clear
SSRVM Content Creation Template Title: Evolution of Computers Contributors: Sreeja. T Std: IV Submission Date: Reviewers: Approval Date: REF No: Brief Description: Goal: Brief History which reveals a clear
Fundamental concepts of Information Technology
 Fundamental concepts of Information Technology A brief history, the Neumann architecture, the language of computers Csernyi Gábor Department of English Linguistics University of Debrecen Csernyi Gábor
Fundamental concepts of Information Technology A brief history, the Neumann architecture, the language of computers Csernyi Gábor Department of English Linguistics University of Debrecen Csernyi Gábor
1.The First Instrument known in the history of computers was. a) Pascal s adding machine b) Napier s bones c) Abacus d) Analytical Engine
 Quiz Questions 1.The First Instrument known in the history of computers was. a) Pascal s adding machine b) Napier s bones c) Abacus d) Analytical Engine 5/1/2006 Computer Programming TA 103 BE I year 2
Quiz Questions 1.The First Instrument known in the history of computers was. a) Pascal s adding machine b) Napier s bones c) Abacus d) Analytical Engine 5/1/2006 Computer Programming TA 103 BE I year 2
Notes By: Shailesh Bdr. Pandey, TA, Computer Engineering Department, Nepal Engineering College
 HISTORY AND GENERATIONS OF COMPUTING Modified by: Shailesh Bdr. Pandey, TA, Computer Engineering, Nepal Engineering College Copyright Remains with the Original Creators Original Source: http://www.tcf.ua.edu/az/ithistoryoutline.htm
HISTORY AND GENERATIONS OF COMPUTING Modified by: Shailesh Bdr. Pandey, TA, Computer Engineering, Nepal Engineering College Copyright Remains with the Original Creators Original Source: http://www.tcf.ua.edu/az/ithistoryoutline.htm
UNIT 1. Variables Binary Math
 UNIT 1 Variables Binary Math DAY 1 History of Computers Variables and Assignment I can.. Identify important inventions and people in the history of computers. Explain the purpose of a variable in computer
UNIT 1 Variables Binary Math DAY 1 History of Computers Variables and Assignment I can.. Identify important inventions and people in the history of computers. Explain the purpose of a variable in computer
CS140 Lecture 09a: Brief History of Computing
 CS140 Lecture 09a: Brief History of Computing "There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home." -- Ken Olson, founder and CEO of Digital Equipment Corp., 1977 John Magee 17 February 2017
CS140 Lecture 09a: Brief History of Computing "There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home." -- Ken Olson, founder and CEO of Digital Equipment Corp., 1977 John Magee 17 February 2017
The trusted, student-friendly online reference tool. Name: Date:
 World Book Online: The trusted, student-friendly online reference tool. World Book Advanced Database* Name: Date: History of Computers Computers! Virtually no other form of technology has become so powerful
World Book Online: The trusted, student-friendly online reference tool. World Book Advanced Database* Name: Date: History of Computers Computers! Virtually no other form of technology has become so powerful
4. History of computers and applications
 In this lesson you will learn: 4. History of computers and applications Savani and Ali have brought things like abacus, some pictures of old computers, a slide rule that was made by hand, a cloth with
In this lesson you will learn: 4. History of computers and applications Savani and Ali have brought things like abacus, some pictures of old computers, a slide rule that was made by hand, a cloth with
Computer science First Class Lecture 1
 Historical Brief 1- The First Computer Man's need to handle data & information increases with the evaluation of society& with industrial development it was Blaise Pascal in 1647 who designed an adding
Historical Brief 1- The First Computer Man's need to handle data & information increases with the evaluation of society& with industrial development it was Blaise Pascal in 1647 who designed an adding
HIGHER SECONDARY FIRST YEAR 2 MARK & 5 MARK NOTES CHAPTER 1 1. INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER
 1. What is computer? CHAPTER 1 1. INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER A computer is an electronic machine, capable of performing basic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, etc. The computer
1. What is computer? CHAPTER 1 1. INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER A computer is an electronic machine, capable of performing basic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, etc. The computer
MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEM DESIGN
 MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEM DESIGN COURSE INTRODUCTION 1 MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEM DESIGN ET011G History of Computer Micro-controllers Introduction Course Aims? Course contents? Invisible computing 2 History EARLY
MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEM DESIGN COURSE INTRODUCTION 1 MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEM DESIGN ET011G History of Computer Micro-controllers Introduction Course Aims? Course contents? Invisible computing 2 History EARLY
I1100 Introduction to Computer Science Semester: 1 Academic Year: 2018/2019 Credits: 3 (30 hours) Dr. Antoun Yaacoub
 Lebanese University Faculty of Science Computer Science BS Degree I1100 Introduction to Computer Science Semester: 1 Academic Year: 2018/2019 Credits: 3 (30 hours) Dr. Antoun Yaacoub 2 Faculty of Science
Lebanese University Faculty of Science Computer Science BS Degree I1100 Introduction to Computer Science Semester: 1 Academic Year: 2018/2019 Credits: 3 (30 hours) Dr. Antoun Yaacoub 2 Faculty of Science
A little bit of history. Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science
 A little bit of history Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science Mechanization Introduction to Programming Dept. CS, UPC 2 Mechanization Introduction to Programming Dept. CS, UPC 3 The old dream
A little bit of history Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science Mechanization Introduction to Programming Dept. CS, UPC 2 Mechanization Introduction to Programming Dept. CS, UPC 3 The old dream
PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE PARADIGMS & THE MAIN PRINCIPLES OF OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
 PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE PARADIGMS & THE MAIN PRINCIPLES OF OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING JAN BARTONÍČEK This paper's goal is to briefly explain the basic theory behind programming languages and their history
PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE PARADIGMS & THE MAIN PRINCIPLES OF OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING JAN BARTONÍČEK This paper's goal is to briefly explain the basic theory behind programming languages and their history
Downloaded from
 Learning Objectives : After learning the Unit the students will be able to: learn about the various inventions in computers understand the technological changes occurs in computer in terms of hardware
Learning Objectives : After learning the Unit the students will be able to: learn about the various inventions in computers understand the technological changes occurs in computer in terms of hardware
Mechanization. A little bit of history. Mechanization. The old dream of mechanical computing. Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science
 Mechanization A little bit of history Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science Mechanization 2 The old dream of mechanical computing Roman Abacus Calculating-Table by Gregor Reisch: Margarita Philosophica,
Mechanization A little bit of history Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science Mechanization 2 The old dream of mechanical computing Roman Abacus Calculating-Table by Gregor Reisch: Margarita Philosophica,
CS 101 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING
 CS 101 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING WHAT IS THE COMPUTER An electronic device that manipulate information or "data". It has the ability to store, retrieve and process the data. WHAT IS T USED FOR TODAY Text
CS 101 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING WHAT IS THE COMPUTER An electronic device that manipulate information or "data". It has the ability to store, retrieve and process the data. WHAT IS T USED FOR TODAY Text
INFS 214: Introduction to Computing
 INFS 214: Introduction to Computing Session 1 History of Computing Lecturer: Dr. Ebenezer Ankrah, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eankrah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
INFS 214: Introduction to Computing Session 1 History of Computing Lecturer: Dr. Ebenezer Ankrah, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eankrah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
Computer Systems. Hardware, Software and Layers of Abstraction
 Computer Systems Hardware, Software and Layers of Abstraction 1 Automation & Computers Fundamental question of computer science: What can be automated? Computers automate processing of information Computer
Computer Systems Hardware, Software and Layers of Abstraction 1 Automation & Computers Fundamental question of computer science: What can be automated? Computers automate processing of information Computer
HISTORY OF COMPUTERS HISTORY OF COMPUTERS. Mesleki İngilizce - Technical English. Punch Card. Digital Data. II Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN.
 Mesleki İngilizce - Technical English II Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr Notes: In the slides, texts enclosed by curly parenthesis, { }, are examples. texts enclosed by square parenthesis,
Mesleki İngilizce - Technical English II Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr Notes: In the slides, texts enclosed by curly parenthesis, { }, are examples. texts enclosed by square parenthesis,
Computer Organization CS 206T
 Computer Organization CS 206T Topics Introduction Historical Background Structure & Function System Interconnection 2 1. Introduction Why study computer organization and architecture? Design better programs,
Computer Organization CS 206T Topics Introduction Historical Background Structure & Function System Interconnection 2 1. Introduction Why study computer organization and architecture? Design better programs,
HST250 (section 740) Exam #1 Wednesday, February 10, 2010
 HST250 (section 740) Exam #1 Wednesday, February 10, 2010 NAME: PID: Instructions Make sure you enter your name & PID on the exam sheet Select the best answer from those provided You may not leave the
HST250 (section 740) Exam #1 Wednesday, February 10, 2010 NAME: PID: Instructions Make sure you enter your name & PID on the exam sheet Select the best answer from those provided You may not leave the
Babbage s computer 1830s Boolean logic 1850s. Hollerith s electric tabulator Analog computer 1927 EDVAC 1946 ENIAC
 Abacus 1100 BC Slide rule - 1617 Mechanical calculator - 1642 Automatic loom (punched cards) - 1804 Babbage s computer 1830s Boolean logic 1850s Hollerith s electric tabulator - 1880 Analog computer 1927
Abacus 1100 BC Slide rule - 1617 Mechanical calculator - 1642 Automatic loom (punched cards) - 1804 Babbage s computer 1830s Boolean logic 1850s Hollerith s electric tabulator - 1880 Analog computer 1927
Introduction to Computer Science. What is Computer Science?
 Introduction to Computer Science CS A101 What is Computer Science? First, some misconceptions. Misconception 1: I can put together my own PC, am good with Windows, and can surf the net with ease, so I
Introduction to Computer Science CS A101 What is Computer Science? First, some misconceptions. Misconception 1: I can put together my own PC, am good with Windows, and can surf the net with ease, so I
Chapter 1 History & Hardware
 Chapter 1 History & Hardware 1-1 Mechanical Machines History & Generations of Computing The first computers (some in the 17th century) were mechanical devices not electronic devices. While the technology
Chapter 1 History & Hardware 1-1 Mechanical Machines History & Generations of Computing The first computers (some in the 17th century) were mechanical devices not electronic devices. While the technology
Computer Systems. Computer Systems. Wolfgang Schreiner Research Institute for Symbolic Computation (RISC-Linz) Johannes Kepler University
 Computer Systems Wolfgang Schreiner Research Institute for Symbolic Computation (RISC-Linz) Johannes Kepler University Wolfgang.Schreiner@risc.uni-linz.ac.at http://www.risc.uni-linz.ac.at/people/schreine
Computer Systems Wolfgang Schreiner Research Institute for Symbolic Computation (RISC-Linz) Johannes Kepler University Wolfgang.Schreiner@risc.uni-linz.ac.at http://www.risc.uni-linz.ac.at/people/schreine
CSSE232 Computer Architecture. Introduc5on
 CSSE232 Computer Architecture Introduc5on Reading Be:er for you if done before class For today: Ch 1 (esp 1.1-3, 10) App. C Sec5ons 2.4, 3.1-2 Outline Introduc5ons Class details Syllabus, website, schedule
CSSE232 Computer Architecture Introduc5on Reading Be:er for you if done before class For today: Ch 1 (esp 1.1-3, 10) App. C Sec5ons 2.4, 3.1-2 Outline Introduc5ons Class details Syllabus, website, schedule
7. History of computers and applications
 In this lesson you will learn: 7. History of computers and applications Jyoti and Tejas have brought things like abacus, some pictures of old computers, a slide rule that was made by hand, a cloth with
In this lesson you will learn: 7. History of computers and applications Jyoti and Tejas have brought things like abacus, some pictures of old computers, a slide rule that was made by hand, a cloth with
Objectives. Learn why today almost everyone is a computer operator. Learn about the predecessors of modern computer hardware and software
 Objectives Learn why today almost everyone is a computer operator Learn about the predecessors of modern computer hardware and software Trace the development of computer hardware and software through several
Objectives Learn why today almost everyone is a computer operator Learn about the predecessors of modern computer hardware and software Trace the development of computer hardware and software through several
Licensed to: ichapters User
 Foundations of Computer Science, 2nd edition Behrouz Forouzan and Firouz Mosharraf Publishing Director: John Yates Manufacturing Manager: Helen Mason Production Controller: Maeve Healy Publisher: Gaynor
Foundations of Computer Science, 2nd edition Behrouz Forouzan and Firouz Mosharraf Publishing Director: John Yates Manufacturing Manager: Helen Mason Production Controller: Maeve Healy Publisher: Gaynor
Monday, January 27, 2014
 Monday, January 27, 2014 Topics for today History of Computing (brief) Encoding data in binary Unsigned integers Signed integers Arithmetic operations and status bits Number conversion: binary to/from
Monday, January 27, 2014 Topics for today History of Computing (brief) Encoding data in binary Unsigned integers Signed integers Arithmetic operations and status bits Number conversion: binary to/from
History of Modern Computing Lesson 1
 History of Modern Computing Lesson 1 www.soe.ucsc.edu/classes/cmpe080h/fall05 David Pease Computer Engineering Department Jack Baskin School of Engineering Lesson Outline Definition of a computer Types
History of Modern Computing Lesson 1 www.soe.ucsc.edu/classes/cmpe080h/fall05 David Pease Computer Engineering Department Jack Baskin School of Engineering Lesson Outline Definition of a computer Types
Basic Computer Information Technology-I
 SYLLABUS Class B.Com. V Sem. Subject Basic Computer Information Technology-I Basic Computer Information Technology-I Unit-I Unit-II Unit-III Unit-IV Unit-V INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ORGANIZATION-I : History
SYLLABUS Class B.Com. V Sem. Subject Basic Computer Information Technology-I Basic Computer Information Technology-I Unit-I Unit-II Unit-III Unit-IV Unit-V INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ORGANIZATION-I : History
CHAPTER 1 Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 The Main Components of a Computer 3 1.3 An Example System: Wading through the Jargon 4 1.4 Standards Organizations 13 1.5 Historical Development 14 1.5.1 Generation
CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 The Main Components of a Computer 3 1.3 An Example System: Wading through the Jargon 4 1.4 Standards Organizations 13 1.5 Historical Development 14 1.5.1 Generation
ALGORITHMS AND PROGRAMMING
 ALGORITHMS AND PROGRAMMING -2- CSC 2201 Dokuz Eylul University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics 2 History of Computers 2600 (BC) Abacus Simple addition and subtraction 1621 Slide Rule 3 The
ALGORITHMS AND PROGRAMMING -2- CSC 2201 Dokuz Eylul University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics 2 History of Computers 2600 (BC) Abacus Simple addition and subtraction 1621 Slide Rule 3 The
COMS 1003 Fall Introduction to Computer Programming in C. History & Computer Organization. September 15 th
 COMS 1003 Fall 2005 Introduction to Computer Programming in C History & Computer Organization September 15 th What's Ahead Some computer history Introduction to major players in the development of hardware
COMS 1003 Fall 2005 Introduction to Computer Programming in C History & Computer Organization September 15 th What's Ahead Some computer history Introduction to major players in the development of hardware
CHAPTER 1 Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 The Main Components of a Computer 3 1.3 An Example System: Wading through the Jargon 4 1.4 Standards Organizations 15 1.5 Historical Development 16 1.5.1 Generation
CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 The Main Components of a Computer 3 1.3 An Example System: Wading through the Jargon 4 1.4 Standards Organizations 15 1.5 Historical Development 16 1.5.1 Generation
Fundamentals Of Computer
 Fundamentals Of Computer Brief History Of Computers Abacus Earlier people used figures, Stones and bones for calculations. Abacus was the first calculating device, It was mainly used by merchants and traders.
Fundamentals Of Computer Brief History Of Computers Abacus Earlier people used figures, Stones and bones for calculations. Abacus was the first calculating device, It was mainly used by merchants and traders.
History. 3rd Generation- Integrated Circuits, Transistors (Integrated Circuit form) for Memory ( memory is now volatile), Terminal/Keyboard for I/O
 Early History History Know what the contributions of Charles Babbage, Ada Lovelace, and Alan Turing were Know Babbages Analytical Machine, which was limited by current technology Know that Ada Lovelace
Early History History Know what the contributions of Charles Babbage, Ada Lovelace, and Alan Turing were Know Babbages Analytical Machine, which was limited by current technology Know that Ada Lovelace
A Short History of Computing. Tim Bergin Computing History Museum American University
 A Short History of Computing Tim Bergin Computing History Museum American University Ancient History Abacus 3000 BCE, early form of beads on wires, used in China From semitic abaq, meaning dust. Table
A Short History of Computing Tim Bergin Computing History Museum American University Ancient History Abacus 3000 BCE, early form of beads on wires, used in China From semitic abaq, meaning dust. Table
Chapter 2. The History and Development of Computers
 Chapter 2 The History and Development of Computers Ancient Computing Devices Fingers Tally bones Sticks Stones cal Abacus- 5000 years ago John Napier 1617 Scotland Napier s Bones Square sticks with numbers
Chapter 2 The History and Development of Computers Ancient Computing Devices Fingers Tally bones Sticks Stones cal Abacus- 5000 years ago John Napier 1617 Scotland Napier s Bones Square sticks with numbers
History of computing. Until future. Computers: Information Technology in Perspective By Long and Long
 History of computing Until future Computers: Information Technology in Perspective By Long and Long Copyright 2002 Prentice Hall, Inc. & 2011 J. Holvikivi Evolution of Computing 1.2 First Computers 1960s
History of computing Until future Computers: Information Technology in Perspective By Long and Long Copyright 2002 Prentice Hall, Inc. & 2011 J. Holvikivi Evolution of Computing 1.2 First Computers 1960s
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 ICT
 Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 ICT I. Underline the correct answer. Duration: 2 Hours Index No:- 1) Components of a computer CPU are (a) ALU, CU (b)
Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 ICT I. Underline the correct answer. Duration: 2 Hours Index No:- 1) Components of a computer CPU are (a) ALU, CU (b)
Computer Architecture. Prologue. Topics Computer Architecture. Computer Organization. Organization vs. Architecture. History of Computers
 Computer Architecture Prologue 1 Topics Computer Architecture Computer Organization Organization vs. Architecture History of Computers Generations of Computers Moore s Law 2 Computer Architecture (1) Definition?
Computer Architecture Prologue 1 Topics Computer Architecture Computer Organization Organization vs. Architecture History of Computers Generations of Computers Moore s Law 2 Computer Architecture (1) Definition?
Corso di Biblioteche Digitali
 Corso di Biblioteche Digitali Vittore Casarosa casarosa@isti.cnr.it tel. 050-621 3115 cell. 348-397 2168 Skype vittore1201 Ricevimento dopo la lezione o per appuntamento Valutazione finale 70% esame orale
Corso di Biblioteche Digitali Vittore Casarosa casarosa@isti.cnr.it tel. 050-621 3115 cell. 348-397 2168 Skype vittore1201 Ricevimento dopo la lezione o per appuntamento Valutazione finale 70% esame orale
Introduction to Computer World Fall 2016
 Introduction to Computer World Fall 2016 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies CSD 102 Email: mehwish.fatima@ciitlahore.edu.pk Website: https://sites.google.com/a/ciitlahore.edu.pk/ict/
Introduction to Computer World Fall 2016 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies CSD 102 Email: mehwish.fatima@ciitlahore.edu.pk Website: https://sites.google.com/a/ciitlahore.edu.pk/ict/
CS1100 Introduction to Programming
 Course Outline Introduction to Computing CS00 Introduction to Programming Introduction to Computing Programming (in C) Exercises and examples from the mathematical area of Numerical Methods Madhu Mutyam
Course Outline Introduction to Computing CS00 Introduction to Programming Introduction to Computing Programming (in C) Exercises and examples from the mathematical area of Numerical Methods Madhu Mutyam
The History of Computers. How did this all get started?
 The History of Computers How did this all get started? Learning Goals By the end of this unit, you should be able to... Recognize and state the trends that led to current day computers Be able to list
The History of Computers How did this all get started? Learning Goals By the end of this unit, you should be able to... Recognize and state the trends that led to current day computers Be able to list
Chapter 1. Computer System Organization
 Chapter 1 Computer System Organization Prepared By: Manish Kumar Prajapati PGT (Comp.Sc.) (First Shift) Kendriya Vidyalaya Bailey Road Patna-14 What is Computer? A computer is an electronic device that
Chapter 1 Computer System Organization Prepared By: Manish Kumar Prajapati PGT (Comp.Sc.) (First Shift) Kendriya Vidyalaya Bailey Road Patna-14 What is Computer? A computer is an electronic device that
Characteristics of Computers
 The word computer comes from word compute, which means to calculate. A computer is a programmable machine (or more precisely, a programmable sequential state machine) that operates on data and is used
The word computer comes from word compute, which means to calculate. A computer is a programmable machine (or more precisely, a programmable sequential state machine) that operates on data and is used
History of Computers. What Is A Computer? Egyptian Numbers. Ancient Tools for Computation. Introduction to Computers
 What Is A Computer? History of Computers Introduction to Computers Adapted from slides by Prof. Polly Huang and Prof. KM Chao (National Taiwan University) com put er Pronunciation: kâm-'pyü-ter Function:
What Is A Computer? History of Computers Introduction to Computers Adapted from slides by Prof. Polly Huang and Prof. KM Chao (National Taiwan University) com put er Pronunciation: kâm-'pyü-ter Function:
Why am I taking Computer Science? What doors does this open up for me?
 Computer Science Induction Document Why am I taking Computer Science? What doors does this open up for me? We are living in a digital age which has a growing need for computer scientists because computer
Computer Science Induction Document Why am I taking Computer Science? What doors does this open up for me? We are living in a digital age which has a growing need for computer scientists because computer
CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER OVERVIEW
 CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER OVERVIEW WHAT IS A COMPUTER? Def: A computer is an electronic device that can perform a variety of operations in accordance with set of instructions called program. DATA Data. Data in
CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER OVERVIEW WHAT IS A COMPUTER? Def: A computer is an electronic device that can perform a variety of operations in accordance with set of instructions called program. DATA Data. Data in
