Parallel Computing Prehistory
|
|
|
- Liliana Webster
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 John Information Technology Department Virginia Tech... FDI Summer Track V: Using Virginia Tech High Performance Computing jburkardt/presentations/fdi 2009 history.pdf May 2009
2 How Did We Get Here? [date uncertain] I don t know where I am, but I m making record time! Last transmission from a Navy pilot, somewhere in the Pacific...
3 What Happens if You Don t Know Where You Are In 1707, Admiral Sir Cloudesly Shovell sank his fleet by sailing directly into the Scilly Islands, which weren t where he thought they were...because he didn t know where he was.
4 Fine Clockwork Can Tell You Where You Are The British Admiralty put out an RFP, seeking a reliable means of determining longitude. John Harrison s superclock solved the problem...though of course he had much trouble getting reimbursed!
5 Babbage Shows Calculation is Like Clockwork The Navy still had plenty of navigational problems in the 19th century, and (partially) funded Charles Babbage s Difference Engine and his Analytical Engine.
6 Hollerith Automates Data Processing Hermann Hollerith, inspired by an automatic weaving device, developed a machine to tabulate the 1890 census - later a big seller for the International Business Machine Corporation, aka IBM.
7 Numerical Calculations Were Done by Computers Computing was done by computers, that is, people. This is the computer lab for the Harvard Astronomical Observatory in 1890.
8 Richardson Forecasts the Weather Lewis Richardson attempted the first weather forecast in (It was for 20 May 1910; it was wrong.)
9 The Atanasoff Computer John Atanasoff, of Iowa State University, took a midnight drive to the Mississippi and worked out the final details for the ABC machine. It could only solve linear systems, up to order 29, by entering two equations at a time by hand, and eliminating one variable and outputing the revised pair of equations. As the result of a lawsuit settled in 1973, the ABC machine was declared the first working computer. (Though it never worked)
10 The Atanasoff Computer The Atanasoff-Berry Computer or ABC
11 The COLOSSUS Computer Early computers were hardwired for very specific tasks and could not be reprogrammed. The Colossus computer, built in World War II, read a paper tape punched with a ciphered message, and compared it to another tape containing output from a cipher machine, looking for matches. (As the tapes were spun back and forth, they tended to stretch, causing errors and delays!)
12 The COLOSSUS Computer The Colossus Computer, with which Alan Turing was associated.
13 The Password was SLOW Everything about early computers was so slow that there was no obvious reason to speed anything up. The data was punched onto cards or paper tape, and read, one at a time, as needed. The program might be literally hardwired (the computer could do one thing.) More advanced computers might have plugs (like old telephone switches) that allowed the operator to modify the computation. Everything was so slow that there were no obvious inefficiencies!
14 ENIAC Arrives World War II showed the power of computing. ENIAC was the first general purpose electronic computer. Initially intended to compute artillery firing tables, it could be reprogrammed to solve a wide range of mathematical problems. ENIAC could do about 5000 additions or 400 multiplications per second.
15 ENIAC Could Store Data Internally ENIAC could store 20 numbers of 10 decimal digits. Each decimal digit was stored as a voltage level in a vacuum tube and the set of tubes was known as an accumulator. One number could be added to another by rearranging plugs on a board; this caused the voltage levels in one set of vacuum tubes to be sent to the other, in such a way that the corresponding digits were incremented. Since each accumulator essentially could perform arithmetic independently of the others, it is sometimes claimed that this was a beginning of parallel processing!
16 ENIAC Weighed 30 Tons
17 Some Parts of ENIAC Were Not Slow Enough The ENIAC processor was so fast that most of the time it was doing nothing, while waiting for new instructions. The computer s designers realized that the computer would be even faster if the program itself was also stored in memory, along with the data. EDVAC, the second version of the machine, was one of the first stored program computers. It also, thank goodness, switched to binary arithmetic! Here was an early example where speeding up one part of a computer meant changes in other parts.
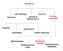
18 ENIAC inspires the von Neumann Architecture ENIAC was actually useful (!) so it required a user manual. Princeton mathematician John von Neumann studied the machine and wrote up instructions and a description, now known as the von Neumann architecture. The main feature was the division of the computer into main memory and the central processing unit or CPU. A controller unit fetched data and instructions from memory.
19 The von Neumann Architecture
20 The von Neumannn Architecture The von Neumann architecture is the standard model of a computer. New advances required adjusting these blueprints. Memories got enormous, so it took more time to find data. Processors got faster, so they needed data faster. Result: the von Neumann bottleneck
21 The von Neumann Bottleneck Faster CPU s + huge memories => starvation. The von Neumann bottleneck showed that there was a third important problem in computation: memory processing power communication!
22 Supercomputers The power of computers created an insatiable demand for bigger and faster computations. With unlimited money available, very fast (and very expensive) new hardware was developed. Supercomputers in the late 70s and 80s were able to achieve faster computation by faster communication: increasing the connections between memory and CPU using faster connections moving the data closer to the memory
23 Supercomputers - Vectorization Supercomputers also began to find new ways to improve performance by dealing with the von Neumann bottleneck. When a computation involved carrying out the same operations on many elements of a vector, the computer could achieve far greater speeds than seemed possible. the CPU had two input connections to memory, and one output, all of which could be operating independently the CPU included several functional units, which could all do useful work independently (computing addresses, doing arithmetic the arithmetic functional units had a sort of internal assembly line ; even though an arithmetic operation might take 5 or 6 clock cycles, the unit could produce a new result every clock cycle.
24 Light Speed Not Fast Enough As processor clock cycles speeded up, an interesting problem was discovered: c = speed of light = 186,282 miles / second = 983,568,960 feet / second = 983,568 feet / millisecond (1 kilohz) = 983 feet / microsecond (1 megahz) = feet / nanosecond (1 GigaHz)
25 Light Goes 1000 Feet A MicroSecond Grace Hopper illustrates how far light can go in a microsecond. She handed out rulers for nanoseconds, and packets of pepper for picoseconds!
26 Light Goes 1000 Feet A MicroSecond Today s fast computer chips have clock cycles of about 4 GigaHertz. That means that in a single clock cycle, a beam of light can travel at most 3 inches (optimistic!). Faster clocks require chip components too small to manufacture, and more heat in smaller spaces. So the computer chips of tomorrow and the forseeable future will also have clock cycles of about 4 GigaHertz.
27 Powerful Chips + Crowded Memories = BIG HEAT Shrinking the memory and using superfast processors leads to a new computational problem: cooling!
28 Powerful Laptops Burn Up Too Supercomputers weren t the only victims of overheating. Laptop design meant that hot chips were crowded together.
29 Physics Calls a Timeout Two physics problems: the speed of light (processor-memory distance) heat transfer (tiny chips get too hot) Two software/hardware solutions: moderately fast communication between separate chips multiple processors on one chip
30 Distributed Memory Computing Instead of very fast, very expensive specialized architecture, try linking massive numbers of cheap processors. 1994: Cluster of 16 personal computers connected by Ethernet.
31 Distributed Memory Computing A cluster of 8 Playstation2 s or 32 Linux boxes could actually cooperate to solve certain problems. These problems tended to be embarassingly parallel perhaps many copies of the same program, each with a different subset of the data. The computation was only efficient if communication between computers was very low, as the communication links were quite inefficient.
32 Distributed Memory Computing - Communication Systems Results from these early distributed memory systems were so interesting that people began to figure out how to connect processors so they could communicate more quickly. Distributed memory computing became competitive. Communication networks include: EtherNet Infiniband Myrinet NUMAlink (SGI) QSnet
33 Distributed Memory Computing: Servers+Communication Orange cables connect servers to Myrinet switch.
34 Distributed Memory Computing - Communication Issues Communication Network Issues: bandwidth - how much can you send at one time? speed - how fast can you send it? latency - delay before message can be sent scalability - can same configuration be used for bigger systems?
35 Distributed Memory Computing - MPI Standard The MPI standard defines how a computation can be carried out on a distributed memory system. Each computer gets a copy of the same program. The program begins on all computers simultaneously; Each computer knows its own ID, and how many others there are. Computers are free to send results to each other.
36 Shared Memory Computing The second variation of the von Neumann architecture was to place multiple processors on a single chip. This kept the processors close to the memory, enabled chip designers to get more theoretical output using less power. Software issue: Who s in charge? Can cores cooperate on a task? How does the user talk to the chip? Each processor maintains a private cache of some of the common data. When a common data item is changed, what mechanism guarantees that cached copies are updated?
37 Shared Memory Computing A strong consistent push for multicore architecture began with the graphics and visualization groups, particularly at SGI. Rendering 2D graphics involved a simple repetitive sequence of operations, easily divided up among a set of stripped-down cores.
38 Shared Memory Computing The initial efforts showed that simple tasks could run twice as fast with two cores, four times as fast with four. And cores were getting cheaper. Soon 3D graphics could be handled in real time, and money from game companies was paying for more research. The graphical processor units (GPU), originally inflexible and highly specialized, were soon competitive with traditional architectures. The success of multicore chips in graphics programming showed a way for general purpose programming to develop.
39 Shared Memory Computing Manufacturers are rapidly developing multicore architecture. They are already designing processors with tens and hundreds of cores! Parallel programs that take advantage of this multicore architecture are called shared memory systems.
40 Shared Memory Computing - the OpenMP Standard The OpenMP interface is a shared memory standard. OpenMP allows users to write programs in C or Fortran that access the underlying parallel abilities of multicore chips. OpenMP standard emphasizes: ease of use (hide details from user) ability to convert programs one step at a time ability to run in sequential mode ability to adapt to any number of processors
41 Parallel MATLAB Computing Virginia Tech has always had a large and devoted group of MATLAB programmers. But MATLAB has not been available as a parallel programming language. Recently, the MathWorks has begun adding parallel features to MATLAB, making it possible to run on shared memory systems. A copy of this parallel MATLAB has been running on an experimental cluster at Virginia Tech. (We will have access to this cluster during the workshop). In June or July, Virginia Tech will install a substantial new cluster that will enable parallel MATLAB to run with up to 64 processors at a time.
42 That Was How We Got Here! This is Where We re Going! In this workshop, we will present some ideas on parallel programming, using parallel MATLAB, and the OpenMP and MPI interfaces. Some of what we do can be tested out as well on your laptop or desktop (particularly parallel MATLAB and OpenMP). To use MPI requires access to a cluster of computers such as System X. Access to both good software and good hardware is crucial for users of the supercomputing facilities offered by the VT Advanced Research Computing facility.
43 This is How We Got Here! This is Where We re Going! A satisfied user of Virginia Tech s System X.
Part (01) Introduction to Computer
 Part (01) Introduction to Computer Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee 1 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Summer 2014, Introduction to CS 1 TURING MODEL The idea of a universal computational device was first described by Alan
Part (01) Introduction to Computer Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee 1 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Summer 2014, Introduction to CS 1 TURING MODEL The idea of a universal computational device was first described by Alan
Welcome to COS151! 1.1
 Welcome to COS151! Title: Introduction to Computer Science Course website: https://cs.up.ac.za/admin/courses/cos151 Find the study guide there Announcements Assignments (download & upload) Brief overview
Welcome to COS151! Title: Introduction to Computer Science Course website: https://cs.up.ac.za/admin/courses/cos151 Find the study guide there Announcements Assignments (download & upload) Brief overview
Computers in Engineering COMP 208. A Brief History. Mechanical Calculators. A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker
 Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Computers in Engineering COMP 208
 Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Early Calculating Tools
 Early Calculating Tools Abacus At least 5,000 years old Memory aid for making calculations Cannot perform actual computations Eventually replaced by pencil and paper Early Calculating Tools Pascalene Invented
Early Calculating Tools Abacus At least 5,000 years old Memory aid for making calculations Cannot perform actual computations Eventually replaced by pencil and paper Early Calculating Tools Pascalene Invented
1: History, Generation & Classification. Shobhanjana Kalita, Dept. of CSE, Tezpur University
 1: History, Generation & Classification Shobhanjana Kalita, Dept. of CSE, Tezpur University History Computer originally (17 th century) meant someone who computes Only in the 20 th century it was associated
1: History, Generation & Classification Shobhanjana Kalita, Dept. of CSE, Tezpur University History Computer originally (17 th century) meant someone who computes Only in the 20 th century it was associated
History of Computing. Slides from NYU and Georgia Tech
 History of Computing Slides from NYU and Georgia Tech Early Computational Devices (Chinese) Abacus 2700 2300 BC Used for performing arithmetic operations Early Computational Devices Napier s Bones, 1617
History of Computing Slides from NYU and Georgia Tech Early Computational Devices (Chinese) Abacus 2700 2300 BC Used for performing arithmetic operations Early Computational Devices Napier s Bones, 1617
CHAPTER1 : Part 2 INTRODUCTION & HISTORY OF COMPUTERS. UNIVERSITI TENAGA NASIONAL Generates Professionals
 CHAPTER1 : Part 2 INTRODUCTION & HISTORY OF COMPUTERS Module Objectives At the end of the module, students should be able to: appreciate and understand the history of computers. describe the generations
CHAPTER1 : Part 2 INTRODUCTION & HISTORY OF COMPUTERS Module Objectives At the end of the module, students should be able to: appreciate and understand the history of computers. describe the generations
Chronological History of the Pre-Computer Developments
 500 B. C. Abacus 1621 Slide Rule 1623 Schickard s Adding Machine (Germany) 1642 Pascal s Adding Machine (France) 1673 Leibniz Calculator (Germany) 1804 Jacquard Loom and Punch Cards 1822 Babbage s Difference
500 B. C. Abacus 1621 Slide Rule 1623 Schickard s Adding Machine (Germany) 1642 Pascal s Adding Machine (France) 1673 Leibniz Calculator (Germany) 1804 Jacquard Loom and Punch Cards 1822 Babbage s Difference
The History of Computers
 The History of Computers First Generation Computers The first electronic computer was designed at Iowa State between 1939-1942 The Atanasoff-Berry Computer used the binary system (1 s and 0 s) Contained
The History of Computers First Generation Computers The first electronic computer was designed at Iowa State between 1939-1942 The Atanasoff-Berry Computer used the binary system (1 s and 0 s) Contained
Introduction to Computer Science. What is Computer Science?
 Introduction to Computer Science CS A101 What is Computer Science? First, some misconceptions. Misconception 1: I can put together my own PC, am good with Windows, and can surf the net with ease, so I
Introduction to Computer Science CS A101 What is Computer Science? First, some misconceptions. Misconception 1: I can put together my own PC, am good with Windows, and can surf the net with ease, so I
Great Inventions written by Bob Barton
 COMPUTER Great Inventions written by Bob Barton Computers Computers help society function in many vital ways, often without our being aware of them. Computers control traffic lights and factory operations.
COMPUTER Great Inventions written by Bob Barton Computers Computers help society function in many vital ways, often without our being aware of them. Computers control traffic lights and factory operations.
History of Modern Computing Lesson 1
 History of Modern Computing Lesson 1 www.soe.ucsc.edu/classes/cmpe080h/fall05 David Pease Computer Engineering Department Jack Baskin School of Engineering Lesson Outline Definition of a computer Types
History of Modern Computing Lesson 1 www.soe.ucsc.edu/classes/cmpe080h/fall05 David Pease Computer Engineering Department Jack Baskin School of Engineering Lesson Outline Definition of a computer Types
Let s begin with the very beginning...
 Let s begin with the very beginning... As we learned in the fourth grade science course, back in 1801, a French man, Joseph Marie Jacquard, invented a power loom that could weave textiles, which had been
Let s begin with the very beginning... As we learned in the fourth grade science course, back in 1801, a French man, Joseph Marie Jacquard, invented a power loom that could weave textiles, which had been
CHAPTER 1 Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 The Main Components of a Computer 3 1.3 An Example System: Wading through the Jargon 4 1.4 Standards Organizations 15 1.5 Historical Development 16 1.5.1 Generation
CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 The Main Components of a Computer 3 1.3 An Example System: Wading through the Jargon 4 1.4 Standards Organizations 15 1.5 Historical Development 16 1.5.1 Generation
The Generations of Computers
 The Generations of Computers The development of computers started with mechanical and electromechanical devices (17 th through 19 th century) and has progressed through four generations of computers. Mechanical
The Generations of Computers The development of computers started with mechanical and electromechanical devices (17 th through 19 th century) and has progressed through four generations of computers. Mechanical
Computer History CSCE 101
 Computer History CSCE 101 Computer History In 40 years computers went from being giant expensive machines that only corporations could own to the personal computer we see today. Early Calculating Devices
Computer History CSCE 101 Computer History In 40 years computers went from being giant expensive machines that only corporations could own to the personal computer we see today. Early Calculating Devices
Fundamentals of Python: First Programs. Chapter 1: Introduction Modifications by Mr. Dave Clausen
 Fundamentals of Python: First Programs Chapter 1: Introduction Modifications by Mr. Dave Clausen Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the basic features of an algorithm
Fundamentals of Python: First Programs Chapter 1: Introduction Modifications by Mr. Dave Clausen Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the basic features of an algorithm
COMP 102: Computers and Computing Lecture 1: Introduction!
 COMP 102: Computers and Computing Lecture 1: Introduction! Instructor: Kaleem Siddiqi (siddiqi@cim.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cim.mcgill.ca/~siddiqi/102.html Outline for today What are computers? What
COMP 102: Computers and Computing Lecture 1: Introduction! Instructor: Kaleem Siddiqi (siddiqi@cim.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cim.mcgill.ca/~siddiqi/102.html Outline for today What are computers? What
A Brief History of Computer Science. David Greenstein Monta Vista High School, Cupertino, CA
 A Brief History of Computer Science David Greenstein Monta Vista High School, Cupertino, CA History of Computing Machines Definition of Computer A programmable machine A machine that manipulates data according
A Brief History of Computer Science David Greenstein Monta Vista High School, Cupertino, CA History of Computing Machines Definition of Computer A programmable machine A machine that manipulates data according
4. History of computers and applications
 In this lesson you will learn: 4. History of computers and applications Savani and Ali have brought things like abacus, some pictures of old computers, a slide rule that was made by hand, a cloth with
In this lesson you will learn: 4. History of computers and applications Savani and Ali have brought things like abacus, some pictures of old computers, a slide rule that was made by hand, a cloth with
HISTORY OF COMPUTERS HISTORY OF COMPUTERS. Mesleki İngilizce - Technical English. Punch Card. Digital Data. II Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN.
 Mesleki İngilizce - Technical English II Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr Notes: In the slides, texts enclosed by curly parenthesis, { }, are examples. texts enclosed by square parenthesis,
Mesleki İngilizce - Technical English II Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr Notes: In the slides, texts enclosed by curly parenthesis, { }, are examples. texts enclosed by square parenthesis,
Processor: Faster and Faster
 Chapter 4 Processor: Faster and Faster Most of the computers, no matter how it looks, can be cut into five parts: Input/Output brings things in and, once done, sends out the result; a memory remembers
Chapter 4 Processor: Faster and Faster Most of the computers, no matter how it looks, can be cut into five parts: Input/Output brings things in and, once done, sends out the result; a memory remembers
1-1 Computer Structure
 1-1 Computer Structure Computer: A computer is a programmable, multiuse machine that accepts data-raw, fact and figures; processes, or manipulates it into information we can use, such as summaries, totals,
1-1 Computer Structure Computer: A computer is a programmable, multiuse machine that accepts data-raw, fact and figures; processes, or manipulates it into information we can use, such as summaries, totals,
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers
 Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations Characteristic
Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations Characteristic
Babbage Analytical Machine
 Von Neumann Machine Babbage Analytical Machine The basis of modern computers is proposed by a professor of mathematics at Cambridge University named Charles Babbage (1972-1871). He has invented a mechanical
Von Neumann Machine Babbage Analytical Machine The basis of modern computers is proposed by a professor of mathematics at Cambridge University named Charles Babbage (1972-1871). He has invented a mechanical
Learning Objectives. In this chapter you will learn about:
 Ref Page Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations
Ref Page Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers. In this chapter you will learn about:
 Ref Page Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations
Ref Page Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations
Corso di Biblioteche Digitali
 Corso di Biblioteche Digitali Vittore Casarosa casarosa@isti.cnr.it tel. 050-621 3115 cell. 348-397 2168 Skype vittore1201 Ricevimento dopo la lezione o per appuntamento Valutazione finale 70% esame orale
Corso di Biblioteche Digitali Vittore Casarosa casarosa@isti.cnr.it tel. 050-621 3115 cell. 348-397 2168 Skype vittore1201 Ricevimento dopo la lezione o per appuntamento Valutazione finale 70% esame orale
I1100 Introduction to Computer Science Semester: 1 Academic Year: 2018/2019 Credits: 3 (30 hours) Dr. Antoun Yaacoub
 Lebanese University Faculty of Science Computer Science BS Degree I1100 Introduction to Computer Science Semester: 1 Academic Year: 2018/2019 Credits: 3 (30 hours) Dr. Antoun Yaacoub 2 Faculty of Science
Lebanese University Faculty of Science Computer Science BS Degree I1100 Introduction to Computer Science Semester: 1 Academic Year: 2018/2019 Credits: 3 (30 hours) Dr. Antoun Yaacoub 2 Faculty of Science
Computer System architectures
 CSC 203 1.5 Computer System Architecture Budditha Hettige Department of Statistics and Computer Science University of Sri Jayewardenepura 1 Historical Developments 2 Computer Generation 1. Zeroth generation-
CSC 203 1.5 Computer System Architecture Budditha Hettige Department of Statistics and Computer Science University of Sri Jayewardenepura 1 Historical Developments 2 Computer Generation 1. Zeroth generation-
Chapter 1. The Big Picture
 Chapter 1 The Big Picture 1.1 Computing Systems Hardware The physical elements of a computing system (printer, circuit boards, wires, keyboard ) Software The programs that provide the instructions for
Chapter 1 The Big Picture 1.1 Computing Systems Hardware The physical elements of a computing system (printer, circuit boards, wires, keyboard ) Software The programs that provide the instructions for
Welcome to COSC Introduction to Computer Science
 Welcome to COSC 1302 Introduction to Computer Science (Syllabus) Chapter 1 The Big Picture 1.1 Computing Systems Hardware The physical elements of a computing system (printer, circuit boards, wires, keyboard
Welcome to COSC 1302 Introduction to Computer Science (Syllabus) Chapter 1 The Big Picture 1.1 Computing Systems Hardware The physical elements of a computing system (printer, circuit boards, wires, keyboard
Chapter 1 History & Hardware
 Chapter 1 History & Hardware 1-1 Mechanical Machines History & Generations of Computing The first computers (some in the 17th century) were mechanical devices not electronic devices. While the technology
Chapter 1 History & Hardware 1-1 Mechanical Machines History & Generations of Computing The first computers (some in the 17th century) were mechanical devices not electronic devices. While the technology
Overview of a computer
 Overview of a computer One marks 1. What is von Neumann concept also called as? Stored memory or stored program concept. 2. Who is the father of computer Charles Babbage 3. What is a computer? It is an
Overview of a computer One marks 1. What is von Neumann concept also called as? Stored memory or stored program concept. 2. Who is the father of computer Charles Babbage 3. What is a computer? It is an
Chapter 1 Basic Computer Organization
 Chapter 1 Basic Computer Organization Course Outcome (CO) CO1 Explain the basic principles of modern computer systems organization Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering
Chapter 1 Basic Computer Organization Course Outcome (CO) CO1 Explain the basic principles of modern computer systems organization Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering
Algorithm: Program: Programming: Software: Hardware:
 0-1 0-2 Terminology Algorithm: A set of steps that defines how a task is performed Program: A representation of an algorithm Programming: The process of developing a program Software: Programs and algorithms
0-1 0-2 Terminology Algorithm: A set of steps that defines how a task is performed Program: A representation of an algorithm Programming: The process of developing a program Software: Programs and algorithms
HIGHER SECONDARY FIRST YEAR 2 MARK & 5 MARK NOTES CHAPTER 1 1. INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER
 1. What is computer? CHAPTER 1 1. INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER A computer is an electronic machine, capable of performing basic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, etc. The computer
1. What is computer? CHAPTER 1 1. INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER A computer is an electronic machine, capable of performing basic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, etc. The computer
ENIAC: The first electronic computer
 Chapter 3 ENIAC: The first electronic computer In 1941, a key inventor of the ENIAC machine, John Mauchly, was teaching physics in Ursinus College in Philadelphia. One day, he received an invitation from
Chapter 3 ENIAC: The first electronic computer In 1941, a key inventor of the ENIAC machine, John Mauchly, was teaching physics in Ursinus College in Philadelphia. One day, he received an invitation from
CHAPTER 1 Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 The Main Components of a Computer 3 1.3 An Example System: Wading through the Jargon 4 1.4 Standards Organizations 13 1.5 Historical Development 14 1.5.1 Generation
CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 The Main Components of a Computer 3 1.3 An Example System: Wading through the Jargon 4 1.4 Standards Organizations 13 1.5 Historical Development 14 1.5.1 Generation
Computer Evolution. Budditha Hettige. Department of Computer Science
 Computer Evolution Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science Computer Generation 1. Zeroth generation- Mechanical Computers (1642-1940) 2. First generation - Vacuum Tubes (1940-1955) 3. Second Generation
Computer Evolution Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science Computer Generation 1. Zeroth generation- Mechanical Computers (1642-1940) 2. First generation - Vacuum Tubes (1940-1955) 3. Second Generation
Computer Systems. Hardware, Software and Layers of Abstraction
 Computer Systems Hardware, Software and Layers of Abstraction 1 Automation & Computers Fundamental question of computer science: What can be automated? Computers automate processing of information Computer
Computer Systems Hardware, Software and Layers of Abstraction 1 Automation & Computers Fundamental question of computer science: What can be automated? Computers automate processing of information Computer
Computer Evolution. Computer Generation. The Zero Generation (3) Charles Babbage. First Generation- Time Line
 Computer Generation Computer Evolution Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science 1. Zeroth generation- Mechanical Computers (1642-1940) 2. First generation - Vacuum Tubes (1940-1955) 3. Second Generation
Computer Generation Computer Evolution Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science 1. Zeroth generation- Mechanical Computers (1642-1940) 2. First generation - Vacuum Tubes (1940-1955) 3. Second Generation
Von Neumann architecture. The first computers used a single fixed program (like a numeric calculator).
 Microprocessors Von Neumann architecture The first computers used a single fixed program (like a numeric calculator). To change the program, one has to re-wire, re-structure, or re-design the computer.
Microprocessors Von Neumann architecture The first computers used a single fixed program (like a numeric calculator). To change the program, one has to re-wire, re-structure, or re-design the computer.
Chapter 1: An Introduction to Computer Science. Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, 6-th Edition
 Chapter 1: An Introduction to Computer Science Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, 6-th Edition Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about The definition of computer science Algorithms A
Chapter 1: An Introduction to Computer Science Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, 6-th Edition Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about The definition of computer science Algorithms A
Mechanization. A little bit of history. Mechanization. The old dream of mechanical computing. Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science
 Mechanization A little bit of history Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science Mechanization 2 The old dream of mechanical computing Roman Abacus Calculating-Table by Gregor Reisch: Margarita Philosophica,
Mechanization A little bit of history Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science Mechanization 2 The old dream of mechanical computing Roman Abacus Calculating-Table by Gregor Reisch: Margarita Philosophica,
COMS 1003 Fall Introduction to Computer Programming in C. History & Computer Organization. September 15 th
 COMS 1003 Fall 2005 Introduction to Computer Programming in C History & Computer Organization September 15 th What's Ahead Some computer history Introduction to major players in the development of hardware
COMS 1003 Fall 2005 Introduction to Computer Programming in C History & Computer Organization September 15 th What's Ahead Some computer history Introduction to major players in the development of hardware
A little bit of history. Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science
 A little bit of history Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science Mechanization Introduction to Programming Dept. CS, UPC 2 Mechanization Introduction to Programming Dept. CS, UPC 3 The old dream
A little bit of history Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science Mechanization Introduction to Programming Dept. CS, UPC 2 Mechanization Introduction to Programming Dept. CS, UPC 3 The old dream
INFS 214: Introduction to Computing
 INFS 214: Introduction to Computing Session 1 History of Computing Lecturer: Dr. Ebenezer Ankrah, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eankrah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
INFS 214: Introduction to Computing Session 1 History of Computing Lecturer: Dr. Ebenezer Ankrah, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eankrah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
ENIAC - background. ENIAC - details. Structure of von Nuemann machine. von Neumann/Turing Computer Architecture
 168 420 Computer Architecture Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania Trajectory tables
168 420 Computer Architecture Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania Trajectory tables
what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored?
 Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition. Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance Analytical Engine ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance Analytical Engine ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert
1.2.1 Electronic computers based on digital switching
 1.2.1 Electronic computers based on digital switching The first true digital electronic computer was created by John V Atanasoff during 1937-1942. The Atanasoff-Berry Computer (called ABC figure 2.8) was
1.2.1 Electronic computers based on digital switching The first true digital electronic computer was created by John V Atanasoff during 1937-1942. The Atanasoff-Berry Computer (called ABC figure 2.8) was
HST250 (section 740) Exam #1 Wednesday, February 10, 2010
 HST250 (section 740) Exam #1 Wednesday, February 10, 2010 NAME: PID: Instructions Make sure you enter your name & PID on the exam sheet Select the best answer from those provided You may not leave the
HST250 (section 740) Exam #1 Wednesday, February 10, 2010 NAME: PID: Instructions Make sure you enter your name & PID on the exam sheet Select the best answer from those provided You may not leave the
HISTORY OF CALCULATION. Evolution of Computation
 HISTORY OF CALCULATION Evolution of Computation Mechanical Era Slide Rule is the first mechanical device for numeric calculation Slide Rule can do Multiplication, Division, Power, Root and Trigonometry
HISTORY OF CALCULATION Evolution of Computation Mechanical Era Slide Rule is the first mechanical device for numeric calculation Slide Rule can do Multiplication, Division, Power, Root and Trigonometry
Introduction to Computer Systems and Operating Systems
 Introduction to Computer Systems and Operating Systems Minsoo Ryu Real-Time Computing and Communications Lab. Hanyang University msryu@hanyang.ac.kr Topics Covered 1. Computer History 2. Computer System
Introduction to Computer Systems and Operating Systems Minsoo Ryu Real-Time Computing and Communications Lab. Hanyang University msryu@hanyang.ac.kr Topics Covered 1. Computer History 2. Computer System
In this chapter, you will learn about: The definition of computer science. Algorithms. Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Third Edition
 Objectives Chapter 1: An Introduction to Com puter S cience Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Third Edition In this chapter, you will learn about: The definition of computer science Algorithms
Objectives Chapter 1: An Introduction to Com puter S cience Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Third Edition In this chapter, you will learn about: The definition of computer science Algorithms
Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 1 Technology in Action Technology in Focus: The History of the PC 2 The first personal computer Sold as a kit Switches for input Lights for output Altair 8800 Bill Gates and Paul Allen created a compiler
1 Technology in Action Technology in Focus: The History of the PC 2 The first personal computer Sold as a kit Switches for input Lights for output Altair 8800 Bill Gates and Paul Allen created a compiler
An Introduction to Computer Science CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science Lecture #2
 An Introduction to Computer Science CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science Lecture #2 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB A Word About Registration for CS8 FOR THOSE OF YOU NOT YET REGISTERED: This
An Introduction to Computer Science CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science Lecture #2 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB A Word About Registration for CS8 FOR THOSE OF YOU NOT YET REGISTERED: This
You Will Need Floppy Disks for your labs!
 CIS121 Instructor: Lynne Mayer VoiceMail: (847) 697-1000 x 2328 Lmayer@elgin.edu Office Hours: ICT 122 Mon.: 9:15-10:15 AM, 5:15-6:00 PM Wed.: 9:15-10:15 AM Fri.: 2:30-3:30 PM Website: faculty.elgin.edu/lmayer
CIS121 Instructor: Lynne Mayer VoiceMail: (847) 697-1000 x 2328 Lmayer@elgin.edu Office Hours: ICT 122 Mon.: 9:15-10:15 AM, 5:15-6:00 PM Wed.: 9:15-10:15 AM Fri.: 2:30-3:30 PM Website: faculty.elgin.edu/lmayer
Chapter One. Introduction to Computer System. Definition Objectives Types according to their size Internet
 Principles of Programming-I / 131101 Prepared by: Dr. Bahjat Qazzaz -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Chapter One Introduction to Computer System
Principles of Programming-I / 131101 Prepared by: Dr. Bahjat Qazzaz -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Chapter One Introduction to Computer System
Evolution of the Computer
 Evolution of the Computer Janaka Harambearachchi (Engineer/Systems Development) Zeroth Generation- Mechanical 1. Blaise Pascal -1642 Mechanical calculator only perform + - 2. Von Leibiniz -1672 Mechanical
Evolution of the Computer Janaka Harambearachchi (Engineer/Systems Development) Zeroth Generation- Mechanical 1. Blaise Pascal -1642 Mechanical calculator only perform + - 2. Von Leibiniz -1672 Mechanical
Computer Organization CS 206T
 Computer Organization CS 206T Topics Introduction Historical Background Structure & Function System Interconnection 2 1. Introduction Why study computer organization and architecture? Design better programs,
Computer Organization CS 206T Topics Introduction Historical Background Structure & Function System Interconnection 2 1. Introduction Why study computer organization and architecture? Design better programs,
CSC101 Furman University Professor Batchelor
 CSC101 Furman University Professor Batchelor The First Mechanical Calculator Blaise Pascal The Difference Engine Charles Babbage While Tomas of Colmar was developing the first successful commercial
CSC101 Furman University Professor Batchelor The First Mechanical Calculator Blaise Pascal The Difference Engine Charles Babbage While Tomas of Colmar was developing the first successful commercial
Chapter 2. Perkembangan Komputer
 Chapter 2 Perkembangan Komputer 1 ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania Trajectory tables for weapons Started 1943 Finished 1946
Chapter 2 Perkembangan Komputer 1 ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania Trajectory tables for weapons Started 1943 Finished 1946
SSRVM Content Creation Template
 SSRVM Content Creation Template Title: Evolution of Computers Contributors: Sreeja. T Std: IV Submission Date: Reviewers: Approval Date: REF No: Brief Description: Goal: Brief History which reveals a clear
SSRVM Content Creation Template Title: Evolution of Computers Contributors: Sreeja. T Std: IV Submission Date: Reviewers: Approval Date: REF No: Brief Description: Goal: Brief History which reveals a clear
Parallelism and Concurrency. COS 326 David Walker Princeton University
 Parallelism and Concurrency COS 326 David Walker Princeton University Parallelism What is it? Today's technology trends. How can we take advantage of it? Why is it so much harder to program? Some preliminary
Parallelism and Concurrency COS 326 David Walker Princeton University Parallelism What is it? Today's technology trends. How can we take advantage of it? Why is it so much harder to program? Some preliminary
An Incomplete History of Computation
 An Incomplete History of Computation Charles Babbage 1791-1871 Lucasian Professor of Mathematics, Cambridge University, 1827-1839 First computer designer Ada Lovelace 1815-1852 First computer programmer
An Incomplete History of Computation Charles Babbage 1791-1871 Lucasian Professor of Mathematics, Cambridge University, 1827-1839 First computer designer Ada Lovelace 1815-1852 First computer programmer
Describe the layers of a computer system
 Chapter 1 The Big Picture Chapter Goals Describe the layers of a computer system Describe the concept of abstraction and its relationship to computing Describe the history of computer hardware and software
Chapter 1 The Big Picture Chapter Goals Describe the layers of a computer system Describe the concept of abstraction and its relationship to computing Describe the history of computer hardware and software
CS 265. Computer Architecture. Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng.
 CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. 1 Part 2: Introduction to Computer Architecture Our goal: have a basic look at architecture of computer, its functions and structure, its history and
CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. 1 Part 2: Introduction to Computer Architecture Our goal: have a basic look at architecture of computer, its functions and structure, its history and
Monday, January 27, 2014
 Monday, January 27, 2014 Topics for today History of Computing (brief) Encoding data in binary Unsigned integers Signed integers Arithmetic operations and status bits Number conversion: binary to/from
Monday, January 27, 2014 Topics for today History of Computing (brief) Encoding data in binary Unsigned integers Signed integers Arithmetic operations and status bits Number conversion: binary to/from
Computer & Microprocessor Architecture HCA103
 Computer & Microprocessor Architecture HCA103 Computer Evolution and Performance UTM-RHH Slide Set 2 1 ENIAC - Background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania
Computer & Microprocessor Architecture HCA103 Computer Evolution and Performance UTM-RHH Slide Set 2 1 ENIAC - Background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania
Chapter 2 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF COMPUTERS
 Chapter 2 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF COMPUTERS History of Computers Outline Generations of Computers Types of Computers 2 History of Computers A computer is a machine that works with data and information
Chapter 2 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF COMPUTERS History of Computers Outline Generations of Computers Types of Computers 2 History of Computers A computer is a machine that works with data and information
Chapter 5 12/2/2013. Objectives. Computer Systems Organization. Objectives. Objectives (continued) Introduction. INVITATION TO Computer Science 1
 Chapter 5 Computer Systems Organization Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: The components of a computer system Putting all the pieces together the Von Neumann architecture The future: non-von
Chapter 5 Computer Systems Organization Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: The components of a computer system Putting all the pieces together the Von Neumann architecture The future: non-von
Part 1: Computer and Information Literacy
 What is Computer? Understand Computers Part 1: Computer and Information Literacy Computer is an electronic devices that under a program s direction and control, perform four basic operations: Input, Processing,
What is Computer? Understand Computers Part 1: Computer and Information Literacy Computer is an electronic devices that under a program s direction and control, perform four basic operations: Input, Processing,
Figure 1-1. A multilevel machine.
 1 INTRODUCTION 1 Level n Level 3 Level 2 Level 1 Virtual machine Mn, with machine language Ln Virtual machine M3, with machine language L3 Virtual machine M2, with machine language L2 Virtual machine M1,
1 INTRODUCTION 1 Level n Level 3 Level 2 Level 1 Virtual machine Mn, with machine language Ln Virtual machine M3, with machine language L3 Virtual machine M2, with machine language L2 Virtual machine M1,
A Brief History of Computer Science
 A Brief History of Computer Science 4700 Hundred years ago Sumerians invented the abacus Sand, lines, pebbles Sexagesimal Base 60 still used today Time, distance How do you count like that? Side trip Factors
A Brief History of Computer Science 4700 Hundred years ago Sumerians invented the abacus Sand, lines, pebbles Sexagesimal Base 60 still used today Time, distance How do you count like that? Side trip Factors
John Vincent Atanasoff The father of the computer (October 4, June 15, 1995)
 John Vincent Atanasoff The father of the computer (October 4, 1903 - June 15, 1995) Introduction Clifford E. Berry Iowa State College (during the 1940s) ABC (Atanasoff-Berry Computer) - the first electronic
John Vincent Atanasoff The father of the computer (October 4, 1903 - June 15, 1995) Introduction Clifford E. Berry Iowa State College (during the 1940s) ABC (Atanasoff-Berry Computer) - the first electronic
Chapter 1 : Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction A Microprocessor is a multipurpose programmable, clock driven, register based electronic device that reads binary instructions from a storage device called memory,
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction A Microprocessor is a multipurpose programmable, clock driven, register based electronic device that reads binary instructions from a storage device called memory,
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3. Annalisa Massini /2015
 Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - Von Neumann Architecture 2 Two lessons Summary of the traditional computer architecture Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - Von Neumann Architecture 2 Two lessons Summary of the traditional computer architecture Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
Introductory Visualizing Technology
 Introductory Visualizing Technology Seventh Edition Chapter 1 What Is a Computer? Learning Objectives 1.1 Explain the Functions of a Computer 1.2 Describe the Evolution of Computer Hardware 1.3 Describe
Introductory Visualizing Technology Seventh Edition Chapter 1 What Is a Computer? Learning Objectives 1.1 Explain the Functions of a Computer 1.2 Describe the Evolution of Computer Hardware 1.3 Describe
Note: Though solved with care, not responsible for the accuracy.
 Question # 1 of 10 ( Start time: 05:10:26 PM ) () The name of first commercially available PC was: UNIVAC 1 ENIAC EDVAC Altair 8800 Question # 2 of 10 ( Start time: 05:11:49 PM ) () The first Web browser
Question # 1 of 10 ( Start time: 05:10:26 PM ) () The name of first commercially available PC was: UNIVAC 1 ENIAC EDVAC Altair 8800 Question # 2 of 10 ( Start time: 05:11:49 PM ) () The first Web browser
CS 1 Notes 1 - Early Computing and 2 - Electronic Computing
 CS 1 Notes 1 - Early Computing and 2 - Electronic Computing Computer Science: The discipline that seeks to build a scientific foundation for such topics as: computer design computer programming information
CS 1 Notes 1 - Early Computing and 2 - Electronic Computing Computer Science: The discipline that seeks to build a scientific foundation for such topics as: computer design computer programming information
Fundamentals of Digital Computers The mechanical computer age began with the advent of the abacus in 500 B.C by Babylonians. The abacus, which was
 1 Fundamentals of Digital Computers The mechanical computer age began with the advent of the abacus in 500 B.C by Babylonians. The abacus, which was used extensively and is still in use today, was not
1 Fundamentals of Digital Computers The mechanical computer age began with the advent of the abacus in 500 B.C by Babylonians. The abacus, which was used extensively and is still in use today, was not
Introduction To Computers. About the Course
 Introduction To Computers Chapter No 1 Introduction About the Course Course instructor Course policies Topics to be covered Course Website and Reference material Assignments and Projects ITC - Chapter
Introduction To Computers Chapter No 1 Introduction About the Course Course instructor Course policies Topics to be covered Course Website and Reference material Assignments and Projects ITC - Chapter
Wednesday, January 28, 2018
 Wednesday, January 28, 2018 Topics for today History of Computing (brief) Encoding data in binary Unsigned integers Signed integers Arithmetic operations and status bits Number conversion: binary to/from
Wednesday, January 28, 2018 Topics for today History of Computing (brief) Encoding data in binary Unsigned integers Signed integers Arithmetic operations and status bits Number conversion: binary to/from
Ms. Minerva A. Lagarde
 Ms. Minerva A. Lagarde Introduction Objectives At the end of this module, you should be able to: 1. explain how a computer works; 2. state the functions of each basic hardware component of a computer system;
Ms. Minerva A. Lagarde Introduction Objectives At the end of this module, you should be able to: 1. explain how a computer works; 2. state the functions of each basic hardware component of a computer system;
An Introduction to Computer Science CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science, Winter 2018 Lecture #2
 An Introduction to Computer Science CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science, Winter 2018 Lecture #2 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB A Word About Registration for CS8 FOR THOSE OF YOU NOT YET
An Introduction to Computer Science CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science, Winter 2018 Lecture #2 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB A Word About Registration for CS8 FOR THOSE OF YOU NOT YET
6.823 Computer System Architecture
 6.823 Computer System Architecture http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 The emphasis in this course is on architectural mechanisms and not on quantitative performance evaluation. - Evolution of instruction
6.823 Computer System Architecture http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 The emphasis in this course is on architectural mechanisms and not on quantitative performance evaluation. - Evolution of instruction
The Modern Computer. Exploring Computer Science
 The Modern Computer Exploring Computer Science 2016-2017 Programmers at Work on ENIAC Gloria Ruth Gordon [Bolotsky] and Ester Gerston c. 1946 Source: http://ftp.arl.mil/ftp/historic-computers/ Programmers
The Modern Computer Exploring Computer Science 2016-2017 Programmers at Work on ENIAC Gloria Ruth Gordon [Bolotsky] and Ester Gerston c. 1946 Source: http://ftp.arl.mil/ftp/historic-computers/ Programmers
History. 3rd Generation- Integrated Circuits, Transistors (Integrated Circuit form) for Memory ( memory is now volatile), Terminal/Keyboard for I/O
 Early History History Know what the contributions of Charles Babbage, Ada Lovelace, and Alan Turing were Know Babbages Analytical Machine, which was limited by current technology Know that Ada Lovelace
Early History History Know what the contributions of Charles Babbage, Ada Lovelace, and Alan Turing were Know Babbages Analytical Machine, which was limited by current technology Know that Ada Lovelace
o MAC (6/18 or 33%) o WIN (17/18 or 94%) o Unix (0/18 or 0%)
 Computer OS: Feel comfortable with these operating systems o MAC (6/18 or 33%) o WIN (17/18 or 94%) o Unix (0/18 or 0%) CS120 The Information Era LECTURE 2 TOPICS:, Review, Computer Basics, Computer History,
Computer OS: Feel comfortable with these operating systems o MAC (6/18 or 33%) o WIN (17/18 or 94%) o Unix (0/18 or 0%) CS120 The Information Era LECTURE 2 TOPICS:, Review, Computer Basics, Computer History,
MATLAB Parallel Computing
 MATLAB Parallel Computing John Burkardt Information Technology Department Virginia Tech... FDI Summer Track V: Using Virginia Tech High Performance Computing http://people.sc.fsu.edu/ jburkardt/presentations/fdi
MATLAB Parallel Computing John Burkardt Information Technology Department Virginia Tech... FDI Summer Track V: Using Virginia Tech High Performance Computing http://people.sc.fsu.edu/ jburkardt/presentations/fdi
Licensed to: ichapters User
 Foundations of Computer Science, 2nd edition Behrouz Forouzan and Firouz Mosharraf Publishing Director: John Yates Manufacturing Manager: Helen Mason Production Controller: Maeve Healy Publisher: Gaynor
Foundations of Computer Science, 2nd edition Behrouz Forouzan and Firouz Mosharraf Publishing Director: John Yates Manufacturing Manager: Helen Mason Production Controller: Maeve Healy Publisher: Gaynor
Computer Architecture Review. ICS332 - Spring 2016 Operating Systems
 Computer Architecture Review ICS332 - Spring 2016 Operating Systems ENIAC (1946) Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator Stored-Program Computer (instead of Fixed-Program) Vacuum tubes, punch cards
Computer Architecture Review ICS332 - Spring 2016 Operating Systems ENIAC (1946) Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator Stored-Program Computer (instead of Fixed-Program) Vacuum tubes, punch cards
2. Computer Evolution and Performance
 2. Computer Evolution and Performance Spring 2016 Spring 2016 CS430 - Computer Architecture 1 Chapter 2: Computer Evolution and Performance Reading: pp. 16-49 Good Problems to Work: 2.1, 2.3, 2.4, 2.8,
2. Computer Evolution and Performance Spring 2016 Spring 2016 CS430 - Computer Architecture 1 Chapter 2: Computer Evolution and Performance Reading: pp. 16-49 Good Problems to Work: 2.1, 2.3, 2.4, 2.8,
COMPUTERIZED OFFICE MANAGEMENT
 COMPUTERIZED OFFICE MANAGEMENT Module 1 (COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS) COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS : INTRODUCTION : The term computer is derived from the Latin word compute which means to calculate. Computer is a fast
COMPUTERIZED OFFICE MANAGEMENT Module 1 (COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS) COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS : INTRODUCTION : The term computer is derived from the Latin word compute which means to calculate. Computer is a fast
Basic definitions and history of the Computer Systems
 Introduction to Computer Systems (1) Basic definitions and history of the Computer Systems Piotr Mielecki Ph. D. http://www.wssk.wroc.pl/~mielecki piotr.mielecki@pwr.edu.pl pmielecki@gmail.com Literature
Introduction to Computer Systems (1) Basic definitions and history of the Computer Systems Piotr Mielecki Ph. D. http://www.wssk.wroc.pl/~mielecki piotr.mielecki@pwr.edu.pl pmielecki@gmail.com Literature
Unit 4: Emerging Technologies. A History of Personal Computing by Mrs. Ogletree
 Unit 4: Emerging Technologies A History of Personal Computing by Mrs. Ogletree EVOLUTION OF TECHNOLOGY Technology has been constantly changing COMPUTER HISTORY Computers have been around for a very, very,
Unit 4: Emerging Technologies A History of Personal Computing by Mrs. Ogletree EVOLUTION OF TECHNOLOGY Technology has been constantly changing COMPUTER HISTORY Computers have been around for a very, very,
A (BRIEF) HISTORY OF COMPUTING. By Dane Paschal
 A (BRIEF) HISTORY OF COMPUTING By Dane Paschal BIASES Amero-Euro centric Computer science centric Google centric ANCIENT ORIGINS Counting is hard The Human Brain Abacus Numerals THE 1700 S AND 1800 S Computing
A (BRIEF) HISTORY OF COMPUTING By Dane Paschal BIASES Amero-Euro centric Computer science centric Google centric ANCIENT ORIGINS Counting is hard The Human Brain Abacus Numerals THE 1700 S AND 1800 S Computing
